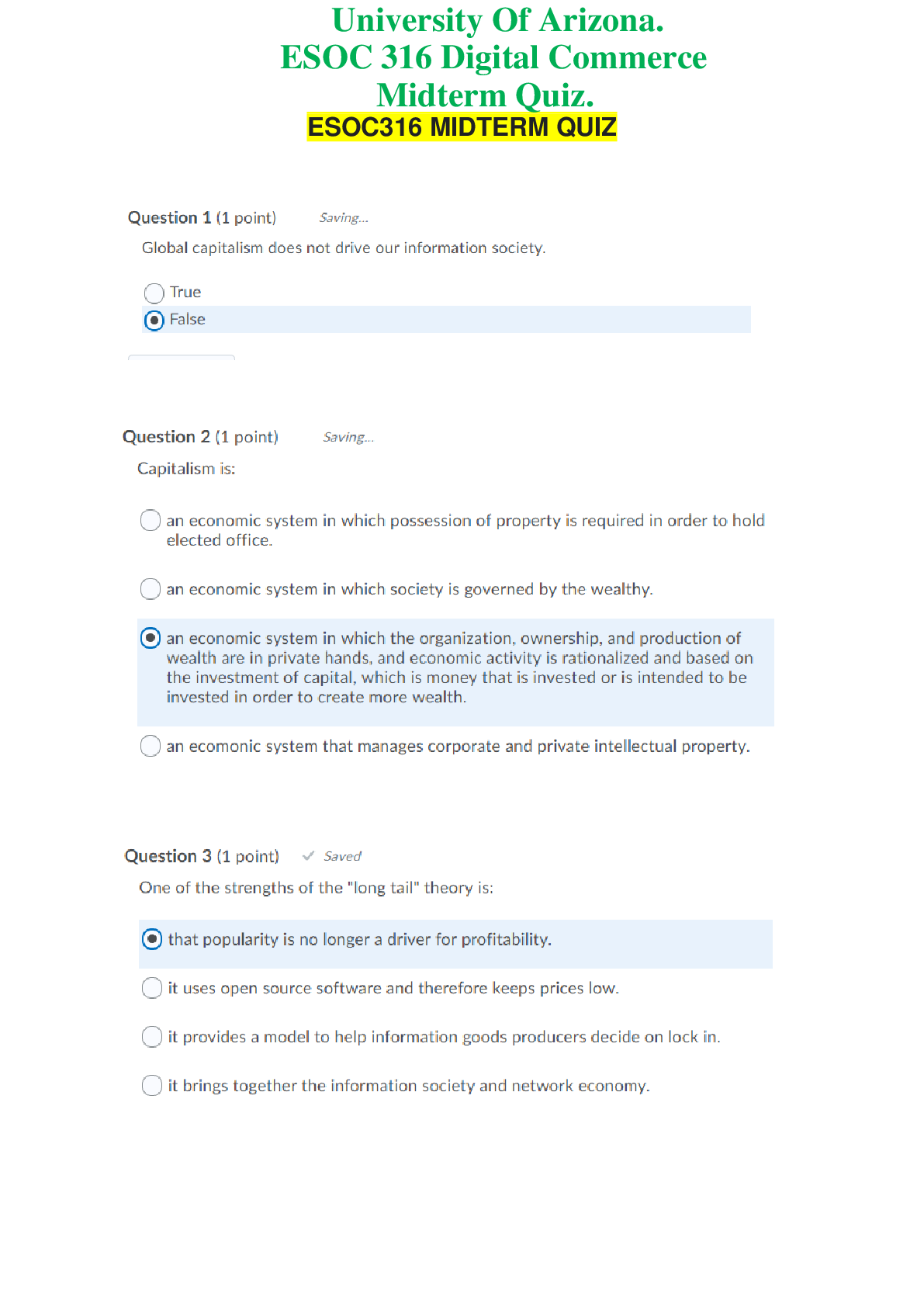
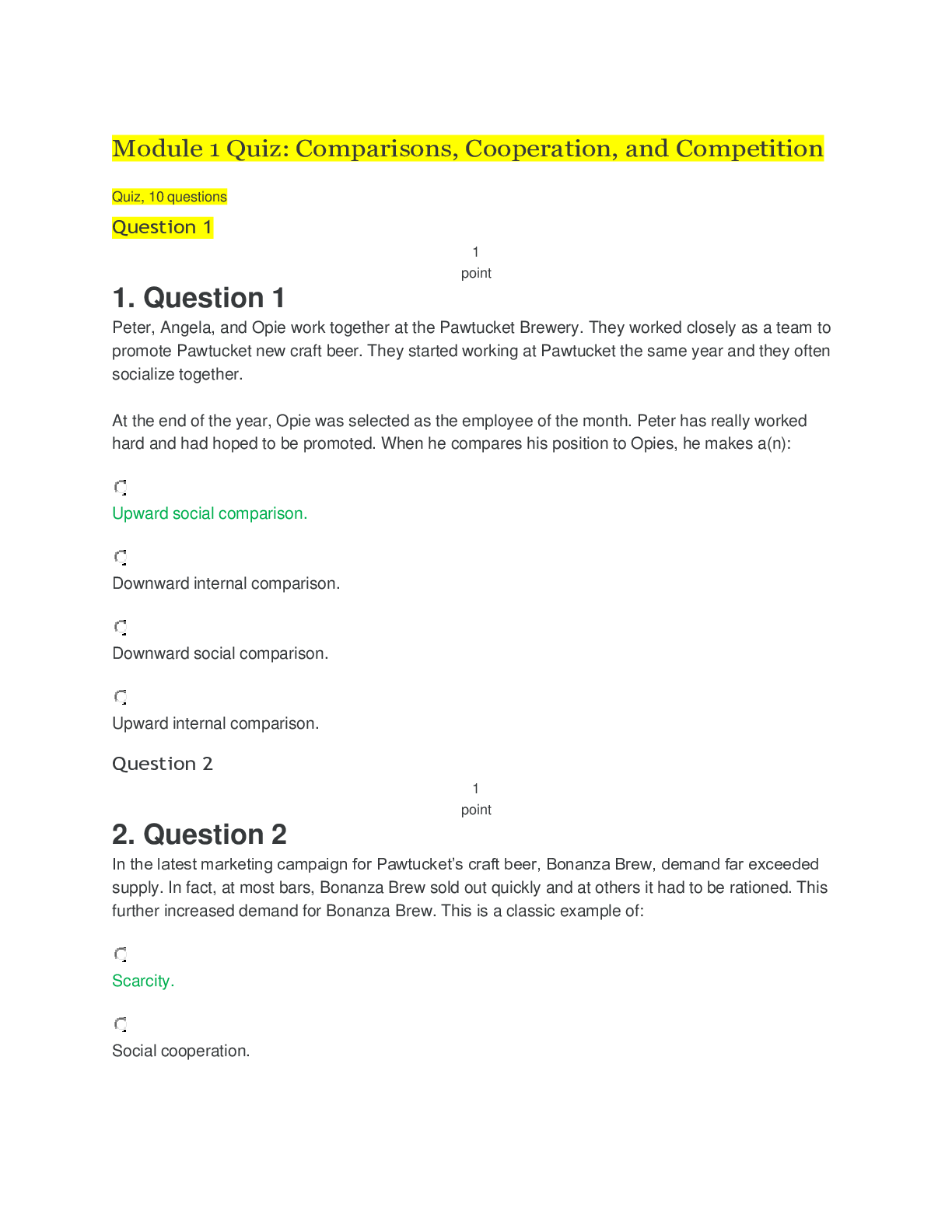
Marketing > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Marketing Management Chapter 2 to Chapter 10 Q&A (All)
Marketing Management Chapter 2 to Chapter 10 Q&A
Document Content and Description Below
Chapter 2 to Chapter 10 Chapter 2: Developing Marketing Strategies and Plans GENERAL CONCEPT QUESTIONS Multiple Choice 66 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships ... 1. A key ingredient of the marketing management process is insightful, marketing strategies and plans that can guide marketing activities. a. creative b. measurable c. macro d. micro e. niche Page: 35 2. According to a chapter story about H&M clothing stores, H&M is able to put products out quickly and inexpensively by all of the following EXCEPT . a. having few middlemen and owning no factories b. buying large volumes c. having extensive experience in the clothing industry d. having a great knowledge of which goods should be bought from which markets e. having total control of its distribution channel from the time the goods are produced until the time they are sold Page: 36 3. The task of any business is to deliver at a profit. a. customer needs b. products c. customer value d. products and services e. improved quality Page: 36 4. In a hypercompetitive economy such as ours, a company can win only by fine- tuning the value delivery process and choosing, providing, and superior value. a. communicating b. selecting target markets with c. composing d. developing e. researching Page: 36 5. The traditional view of marketing is that the firm makes something and then it. a. markets b. sells c. distributes d. prices e. services Page: 36 67 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 6. Today, the “mass-market” is actually splintering into numerous , each with its own wants, perceptions, preferences, and buying criteria. a. micromarkets b. market targets c. macromarkets d. customer cliques e. demographic units Page: 37 7. The first phase of the value creation and delivery sequence is that represents the “homework” marketing must do before any product exists. a. choosing the value b. market research c. target marketing d. service consideration e. projective thinking Page: 37 8. The last step in the value creation and delivery sequence is the value where the sales force, sales promotion, advertising, and other communication tools announce and promote the product. a. developing b. distributing c. communicating d. reversing e. researching Page: 37 9. The Japanese have refined the value delivery process to include a component that emphasizes . a. zero servicing b. zero customer feedback time c. zero promotion d. zero dependency on intermediaries e. zero marketing costs Page: 38 10. The is a tool for identifying ways to create more customer value. a. value chain b. customer survey c. brand loyalty index d. promotion channel e. supplier database Page: 38 11. The identifies nine strategically relevant activities that create value and cost in a specific business. a. value proposition b. value chain c. mission statement 68 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships d. annual report e. manager’s log Page: 38 12. The in the value chain cover the sequence of bringing materials into the business (inbound logistics), converting them into final products (operations), shipping out final products (outbound logistics), marketing them (marketing and sales), and servicing them (service). a. operations process b. manufacturing process c. primary activities d. secondary activities e. tertiary activities Page: 38 13. Procurement, technology development, human resource management, and firm infrastructure are handled in certain specialized departments and are called . a. materials handling b. support activities c. inventory activities d. primary activities e. benchmark activities Page: 38 14. The firm should estimate its competitors’ costs and performances as against which to compare its own costs and performance. a. competition b. standards c. challenges d. benchmarks e. moveable standards Page: 38 15. The firm’s success depends not only on how well each department performs its work, but also on how well the various departmental activities are coordinated to conduct . a. core strategies b. satellite businesses c. core values d. core business processes e. core technologies Page: 38 16. With respect to core business processes, all the activities involved in gathering market intelligence, disseminating it within the organization, and acting on the information is referred to as the . a. market sensing process b. market research process c. target marketing process d. market pulse process 69 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process e. deployment process Page: 38 17. With respect to the core business processes, all the activities involved in researching, developing, and launching new high-quality offerings quickly and within budget are referred to as the . a. new product process b. new offering realization process c. product development process d. product launch process e. return on investment process Page: 38 18. With respect to the core business processes, the is considered to be all the activities involved in defining target markets and prospecting for new customers. a. customer acquisition process b. customer relationship management process c. fulfillment management process d. customer prospecting process e. customer equity process Page: 38 70 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 19. A good way to describe the would be discuss all the activities involved in building deeper understanding, relationships, and offerings to individual customers. a. customer acquisition process b. customer relationship management process c. customer prospecting process d. customer fulfillment management process e. customer equity process Page: 38 20. Another way to describe a value delivery network (partnering with specific suppliers and distributors) is to call it a . a. teamwork group b. cabal c. domestic power center d. link to relationships e. supply chain Page: 39 21. The key to utilizing organizational core competencies is to that make up the essence of the business. a. make the competencies pay for themselves b. own all intermediaries who come in contact with your goods and services c. own and nurture the resources and competencies d. emphasize global promotions e. segment workforces Page: 39 22. We can say that a has three characteristics: (1) It is a source of competitive advantage in that it makes a significant contribution to perceived customer benefits, (2) it has applications in a wide variety of markets, and (3) it is difficult for competitors to imitate. a. core competency b. business strategy c. core technology d. strategic business unit e. winning strategy Page: 39 23. Core competencies tend to refer to areas of special technical and production expertise, where tend to describe excellence in broader business processes. a. process benchmarks b. distinctive capabilities c. core business values d. value statements e. mission statements Page: 40 24. George Day sees market-driven organizations as excelling in three distinctive capabilities: , customer linking, and channel bonding. 71 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process a. target marketing b. market research c. fulfilling customer needs d. market sensing e. customer service relationships Page: 40 25. Competitors find it hard to imitate companies such as Southwest Airlines, Dell, or IKEA because they are unable to copy their . a. product innovations b. distribution strategy c. pricing policies d. activity systems e. logistics system Page: 40 26. One conception of holistic marketing views it as “integrating the value exploration, , and value delivery activities with the purpose of building long-term, mutually satisfying relationships and co-prosperity among key stakeholders.” a. value creation b. value proposition c. value management d. value research e. value chain Page: 40 27. Holistic marketers achieve profitable growth by expanding customer share, , and capturing customer lifetime value. a. undermining competitive competencies b. building customer loyalty c. milking the market for product desires d. renewing a customer base e. inspecting all market share data Page: 40 28. The holistic marketing framework is designed to address three key management questions. Which of the following is one of those questions? a. Value claims—how does the company deal with value erosion? b. Value proposition—how can value propositions be made profitable? c. Value chain—are there weak links in the company’s value chain d. Value network—how can a company effectively network? e. Value exploration—how can a company identify new value opportunities? Page: 41 29. The customer’s reflects existing and latent needs and includes dimensions such as the need for participation, stability, freedom, and change. a. competence space b. resource space c. emotional space 72 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships d. relationship space e. cognitive space Page: 41 30. The company’s can be described in terms of breadth—broad versus focused scope of business; and depth—physical versus knowledge-based capabilities. a. business mission b. core strategy c. cognitive space d. competency space e. resource space Page: 41 31. The collaborator’s involves horizontal partnerships, where companies choose partners based on their ability to exploit related market opportunities, and vertical partnerships, where companies choose partners based on their ability to serve their value creation. a. resource space b. competency space c. cognitive space d. rational space e. service space Page: 41 32. Business realignment may be necessary to maximize core competencies. Which of the following would be one of the steps in this realignment process? a. Reviewing all macro relationships. b. Reviewing global outreach projections. c. Redefining the business concept (the “big idea”). d. Reviewing successes from e-commerce (if any). e. Revamping the ethics statement. Page: 41 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 33. allows the company to discover who its customers are, how they behave, and what they need or want. It also enables the company to respond appropriately, coherently, and quickly to different customer opportunities. a. Network management b. Strategic management c. Marketing management d. Customer relationship management e. Total quality management Page: 41 34. To respond effectively and provide value delivery, the company requires to integrate major business processes (e.g., order processing, general ledger, payroll, and production) within a single family of software modules. a. human resource management b. internal auditing management c. internal resource management d. strategic management e. marketing management Page: 41 35. With respect to value delivery, allows the company to handle complex relationships with its trading partners to source, process, and deliver products. a. a value matrix b. a global distribution policy c. a business development strategy d. business partnership management e. total quality management Page: 41 36. Successful marketing requires having capabilities such as understanding , creating customer value, delivering customer value, capturing customer value, and sustaining customer value. a. customer loyalty b. customer perks c. customer retention d. customer value e. customer benefits Page: 41 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 37. According to a McKinsey research study, which of the following is one of the main challenges that marketing must face in the twenty-first century? a. The threat of ethics-based lawsuits. b. Doing more with less. c. Hostile takeover attempts. d. Increasing control by big government. e. Being independent of the distribution process. Page: 42 38. Strategic planning in the twenty-first century calls for action in three key areas. Which of these key areas deals specifically with devising a long-term game plan for achieving long-run objectives? a. Creating a viable business opportunity. b. Producing a strategic fit. c. Developing an investment portfolio. d. Expanding core competencies. e. Establishing a strategy. Page: 42 39. Most large companies consist of four organizational levels: the , the division level, the business unit level, and the product level. a. board of director level b. major stakeholder level c. management team level d. corporate level e. strategic level Page: 43 40. The is the central instrument for directing and coordinating the marketing effort. a. strategic plan b. marketing plan c. tactical plan d. customer value statement e. corporate mission Page: 43 41. The lays out the target markets and the value proposition that will be offered, based on an analysis of the best market opportunities. a. organizational plan b. strategic marketing plan c. corporate tactical plan d. corporate mission e. customer value statement Page: 43 42. In which of the following plans would we most likely find directions for implementing and addressing daily challenges and opportunities in product features, promotion, merchandising, pricing, sales channels, and service areas. a. The tactical marketing plan. 75 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process b. The target marketing plan. c. The deployment plan. d. The product launch plan. e. The product development plan. Page: 43 43. If you wanted to find out more about target markets and the organization’s value proposition, which of the following types of plans would most likely contain information that might be useful to you in your quest? a. The marketing plan. b. The organizational plan. c. The strategic marketing plan. d. The tactical marketing plan. e. The marketing mix plan. Page: 43 44. The process consists of corporate, division, business, and product planning. a. implementing b. controlling c. innovation d. planning e. competitive Page: 44 45. All corporate headquarters undertake four planning activities, the first of which is . a. defining the corporate mission b. establishing strategic business units and assigning resources (SBUs) c. assigning resources to each SBU d. assessing growth opportunities e. understanding target markets Page: 44 46. A clear, thoughtful mission statement provides employees with a shared sense of purpose, direction, and . a. profitability b. target market feasibility c. opportunity d. continuous improvement e. quality products Page: 44 76 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 47. Mission statements are at their best when they reflect a . a. market b. strength c. competency d. vision e. value Page: 44 48. Which of the following terms matches to the phrase “it is a single business or collection of related businesses that can be planned separately from the rest of the company”? a. Strategic business unit. b. Diverse business unit. c. Growth business unit. d. Niche market unit. e. Specialized business unit. Page: 47 49. Market-penetration, product-development, and market-development strategies would all be examples of strategies. a. concentric b. conglomerate c. horizontal d. intensive growth e. integrative growth Page: 48 50. A(n) is when a company might seek new businesses that have no relationship to its current technology, products, or markets. a. concentric strategy b. conglomerate strategy c. horizontal strategy d. intensive growth strategy e. integrative strategy Page: 49 51. Which of the following terms most closely matches to “the shared experiences, stories, beliefs, and norms that characterize an organization”? a. Organizational dynamics. b. A business mission. c. An ethical/value statement. d. Customer relationships. e. Corporate culture. Page: 50 52. The first step in the business unit strategic-planning process deals with which of the following? a. Goal formulation. b. Business mission. c. Strategy formulation. Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process d. Program formulation. e. SWOT analysis. Page: 51 53. When a business gets to know market segments intimately and pursues either cost leadership or differentiation within the target segment it is referred to as a . a. defined strategy b. focused strategy c. value-added strategy d. competitive advantage strategy e. customer-focused strategy Page: 56 54. If a firm pursues a strategy, it must be good at engineering, purchasing, manufacturing, and physical distribution. a. differentiation b. overall cost leadership c. focus d. domestic customer relationship e. market share Page: 56 55. To keep their strategic alliances thriving, corporations have begun to develop organizational structures to support them and have come to view the ability to form and manage partnerships as core skills. This is called . a. value managed partnership b. synergistic partnership c. centralized partnership d. partner relationship management e. win-win relationship management Page: 57 56. Traditionally, most businesses focused on stockholders. Today, the focus is on what are called . a. stakeholders b. partners c. regulators d. consumer triads e. supply-chain relationships Page: 58 57. A is a written document that summarizes what the marketer has learned about the marketplace and indicates how the firm plans to reach its marketing objectives. a. strategic plan b. marketing plan c. sales plan d. target market plan e. competitive analysis plan Page: 60 78Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 58. Which of the following permits senior management to grasp the marketing plan’s major thrust? a. The situation analysis. b. The marketing strategy. c. The executive summary and table of contents. d. Financial projections. e. Implementation and controls. Page: 60 59. Most marketing plans cover . a. one year b. two years c. three years d. four years e. five years Page: 60 60. The most frequently cited shortcomings of current marketing plans, according to marketing executives, are lack of realism, insufficient competitive analysis, and a focus. a. long-term b. profit c. short-run d. product e. price Page: 60 True/False 61. The traditional view of marketing is that the firm makes something and then sells it. Page: 36 62. The traditional view of marketing begins with a first step called strategic marketing. Page: 36 63. The formula, segmentation, targeting, and positioning (STP) is the essence of strategic marketing. Page: 37 64. The Japanese have extended the value delivery process by adding the concept of zero promotions after five years. Page: 38 65. The customer relationship management process is all the activities involved in receiving and approving orders, shipping the goods on time, and collecting payment. 79Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process Page: 38 66. A principle of the value chain is that every firm is a synthesis of activities performed to design, produce, market, deliver, and support its product. Page: 38 67. Another name for a company’s value delivery network is “the intermediary team.” Page: 39 68. A core competency is usually common among competitors in a given industry. Page: 39 69. Holistic marketing focuses on the integration of value exploration, value creation, and value delivery as a means to build long-term relationships with consumers. Page: 40 70. If a manager asks “How can my company identify new value opportunities?,” he or she is examining a management question identified as being value creation. Page: 41 71. According to McKinsey research, a recommendation to managers and CEOs who are concerned about marketing performance was that marketers must test and develop programs more quickly as they enhance planning processes and research approaches. Page: 42 72. The marketing plan is the central instrument for directing and coordinating the marketing effort. Page: 43 73. A mission statement has as its primary focus the product and how to make it. Page: 44 74. One of the characteristics of a good mission statement is that it has an expansive number of goals for doing business. Page: 44 75. A good illustration of a market definition of the business a company is in would be “We sell gasoline.” Page: 46 76. If a company sought to expand the number of existing products sold to its current markets, it would use an integrative growth strategy labeled as “market- penetration strategy.” Page: 48 77. If a company sought to grow via a strategy that required the company to seek new businesses that have no relationship to its current technology, products, or markets, the company would be using a diversification strategy called a conglomerate strategy. 80 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships Page: 49 78. Scenario analysis can be used to assist companies in appraising how well their corporate culture might match (or not match) potential business partners or acquisitions. Page: 51 79. Once an organization has established a business mission in its business unit strategic-planning process, it may proceed to the second step of the planning process called goal formulation. Page: 51 80. Good illustrations of microenvironment actors in the strategic planning process would be demographics, technology, and the social-cultural arena. Page: 52 81. To evaluate opportunities, companies can use Market Opportunity Analysis (MOA) to determine the attractiveness and probability of success. Page: 53 82. An environmental threat is a challenge posed by an unfavorable trend or development that would lead, in the absence of defensive marketing action, to lower sales or profit. Page: 53 83. Once a SWOT analysis has been completed, the strategic planner is ready to proceed to the goal formulation stage of the strategic planning process model. Page: 54 84. In applying MBO (management by objectives) all objectives are treated as being equally important—objective discrimination is not allowed. Page: 54 85. For an MBO (management by objectives) system to work, one of the four criteria that the unit’s objectives must meet is that objectives must be stated quantitatively whenever possible. Page: 55 86. A strategy is a game plan for achieving what the business unit wants to achieve. Page: 56 87. Firms choosing a generic strategy centering on focus must be good at engineering, purchasing, manufacturing, and physical distribution. Page: 56 88. One of the four major categories of strategic alliance involves sharing personnel (e.g., human resource alliance) to staff alliance member marketing departments. Page: 57 81 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 89. Partner Relationship Management (PRM) can be thought of as a corporation’s development of structures that support strategic alliances and treats the formation and management of partnerships as a core skill. Page: 57 90. Companies normally measure their profit performance using ROI; however, this approach suffers because profits are arbitrarily measured and subject to manipulation. Page: 58 91. A marketing vision statement is a written document that summarizes what the marketer has learned about the marketplace and indicates how the firm plans to reach its marketing objectives. Page: 60 92. Marketing plans are becoming more production-oriented because of the high costs of doing business in today’s economy. Page: 60 93. The marketing plan should open with a situation analysis. Page: 60 94. When a manager reaches the marketing strategy section of a marketing plan, he or she will define the mission and marketing and financial objectives. Page: 60 95. One of the key questions to ask in evaluating a marketing plan is whether the plan is simple or not. Page: 61 96. Such areas as sales forecasts, expense forecasts, and breakeven analysis are usually found in the financial projections section of the marketing plan. Page: 61 97. Return on investment (ROI) shows how many units must be sold monthly to offset the monthly fixed costs and average per-unit variable costs. Page: 61 98. Most marketing plans conclude with a section that indicates how the plan will be implemented. Page: 61 99. During the marketing strategy section of the marketing plan, goals and budgets are spelled out for each month or quarter so management can review each period’s results and take corrective action as needed. Page: 61 100. A good illustration of a marketing objective would to “decrease customer acquisition costs by 1.5 percent per quarter.” Page: 64 82Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships Essay 101. There are two views of the value delivery process that may be followed by organizations seeking to gain business from consumers. Briefly, summarize each of those views. 102. The firm’s success depends not only on how well each department performs its work, but also on how well the various departmental activities are coordinated to conduct core business processes. List and briefly describe the five core business processes outlined in the text. 103. A successful company nurtures its resources and competencies. A core competency has three characteristics. Describe those characteristics. 104. A holistic marketing orientation can provide insight into the process of capturing customer value. In this vain, the holistic marketing framework is 83 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process designed to address three key management questions. Describe and illustrate each of these key management questions. Page: 41 105. Marketing faces a number of challenges in the twenty-first century. Based on an extensive 2002 research study, McKinsey (a noted consulting firm) identified three main challenges as reflected by differences in opinion between chief executive officers (CEOs) and their most senior marketing executives or chief marketing officers (CMOs). What were those challenges and which of the challenges do you think is most important? Why? 84 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships However, be sure that any answer chosen is supported by materials found in this section of the chapter. Page: 42 106. Indicate the differences and similarities between the following terms: marketing plan, strategic marketing plan, and tactical marketing plan. 107. Good mission statements are essential to being a success in business. Describe the three major characteristics that good mission statements should have. 108. Assessing growth opportunities involves planning new businesses, downsizing, or terminating older businesses. The company’s plans for existing businesses allow it to project total sales and profits. If there is a gap between future desired sales and projected sales, corporate management will have to develop or acquire new businesses to fill it. Identify and describe the three strategies that can be used to fill the strategic gap. 85 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 109. Assume that you are directed to prepare short brief explaining the steps of the Business Unit Strategic-Planning Process. Your task is to construct such a brief by carefully outlining the steps of the aforementioned process. 110. As a marketing manager for a large steel company you have been assigned the task of educating a group of new managers on how to prepare a marketing plan. Though few of these managers will actually ever have to prepare such a plan because of their functional roles in the organization, it is still very useful that each new manager know how to construct a marketing plan. Prepare a brief summary of the contents of the marketing plan for the new managers. You may keep your discussion general or make it specific to the steel industry. APPLICATION QUESTIONS Multiple Choice 111. If a manager were following the traditional view of marketing wherein the firm makes something and then sells it, all of the following would part of the “sell the product” process sequence EXCEPT . a. price b. advertise/promote c. design product d. distribute e. service Page: 36 86 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 112. As indicated in the text, critics of Nike and its shoe products often complain that . a. Nike has too many professional athletes endorsing their products b. Nike has an unfair advantage in product design c. Nike has unfair leverage with distributors d. Nike shoes cost almost nothing to make yet cost the consumer so much e. Nike does not support ecological causes Page: 37 113. According to the Japanese view of the value delivery process, the company should receive the required parts and supplies continuously through just-in- time arrangements with suppliers. This concept would be most appropriately called . a. zero customer feedback time b. zero product improvement time c. zero purchasing time d. zero setup time e. zero defect Page: 38 114. Apex Corporation is known in its industry being “best of class” in terms of costs and performance. Many companies will probably use Apex Corporation as a . a. target b. benchmark c. competitor to beat d. future supplier e. sounding board for ideas Page: 38 115. James Franks has been put in charge of gathering marketing intelligence, disseminating it within his organization, and eventually directing action on the information. Which of the following core business processes most closely matches with the task that Mr. Franks has been given? a. The market sensing process. b. The new offering realization process. c. The customer acquisition process. d. The customer relationship management process. e. The fulfillment management process. Page: 38 87Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 116. Netflix, the pioneer online DVD rental service, has what is called because they are excellent in broad business processes. a. core competency b. distinctive capabilities c. market savvy d. business touch e. intuitive synergy Page: 40 117. George Day sees organizations as excelling in three distinctive capabilities: market sensing, customer linking, and channel bonding. a. production-driven b. globally-driven c. human resource-driven d. engineering-driven e. market-driven Page: 40 118. Holistic marketers achieve profitable growth by expanding , building customer loyalty, and capturing customer lifetime value. a. design skills b. customer share c. promotion venues d. database resources e. competitive space share Page: 40 119. In the past Kodak was not necessarily known for embracing technology that did not come from Kodak engineers and designers. However, as Kodak addresses the digital revolution taking over the photographic industry, it wants customers to see it as a leader in digital photography and is moving away from its connection to print-only photography. This would be an example of which of the following value-creation steps? a. Redefining the big idea. b. Reshaping the business scope. c. Repositioning the company’s brand identity. d. Redoing its corporate logo. e. Researching its competitors. Page: 41 88 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 120. According to a McKinsey report, CEOs need and expect all areas of their organizations to be more efficient. Which of the following statements would be the best illustration of this need and expectation? a. Doing more with more. b. Doing less with less. c. Doing less with more. d. Doing more with less. e. Doing about the same with more. Page: 42 121. According to a recent McKinsey report regarding characteristics that help to position marketers as business development leaders, illustrates one of those characteristics. a. “never bite off more than you can chew” b. “if it ain’t broke, don’t fix it” c. “always pursue Internet opportunities” d. “strike while the iron is hot” e. “identify profitable unmet needs before brainstorming creative solutions” Page: 42 122. According to Collins and Porras’ Built to Last, is characterized as a visionary company—acknowledged as the industry leader and widely admired because they set ambitious goals, communicated them to their employees, and embraced a high purpose beyond making money. a. General Electric b. Delta Airlines c. Farmer’s Insurance d. Wells Fargo e. McDonald’s Page: 43 123. Juan Garcia is seen as a planner because he plans the daily promotional releases about his company’s products and services. a. strategic b. selective c. tactical d. niche e. organizational Page: 43 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 124. Sony’s former president, Akio Morita, wanted everyone to have access to “personal portable sound,” so his company created the Walkman and portable CD player. Which of the following planning aids most likely assisted Mr. Morita with his vision? a. The mission statement. b. A SWOT analysis. c. Knowledge of customers. d. A database. e. An executive summary to a formal marketing plan. Page: 44 125. Which of the following most closely matches a correct market-oriented definition of a business? a. Missouri-Pacific Railroad—we run a railroad. b. Xerox—we make copying equipment. c. Standard Oil—we sell gasoline. d. Encyclopedia Britannica—we distribute information. e. Columbia Pictures—we make movies. Page: 46 126. If you were the CEO of a company that was looking to implement strategies to fill a perceived strategic-planning gap, you would most likely explore growth first because it would be easier to improve an existing business rather than building a new one. a. intensive b. integrative c. diversification d. conglomerate e. concentric Page: 47 127. If you were the marketing manager of an organization that had chosen growth via current products sold to new markets, your organization would have chosen a strategy. a. market-penetration b. market-development c. product-development d. diversification e. concentric Page: 48 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 128. describes the way people in an organization are dressed, how they talk to one another, and the way they greet their customers. a. Strategic orientation b. Competitive positioning c. Distinctive advantage d. HR training strategy e. Corporate culture Page: 50 129. Once an organization establishes its business mission, conducts a SWOT analysis, and goes through a goal formulation process, it is ready to go through a step called to continue with a strategic-planning process. a. program formulation b. strategy formulation c. implementation d. functional analysis e. feedback and control Page: 51 130. McDonald’s has often teamed up with Disney to offer products related to current Disney films as part of its meals for children. The best description of this form of alliance would a alliance. a. product alliance b. logistics alliance c. pricing collaboration d. service e. promotional Page: 57 Short Answer 131. If you were the marketing manager for small regional toy manufacturer who embraced strategic marketing application to your value creation and delivery sequence process, you would use three processes or acts to choose the value of your offer. Name those three processes. Page: 36 132. In the example of Gymboree, we learn that they are a 530-store chain that sells children’s clothing to upscale parents. Because there are not enough parents making more than $65,000 year to support more stores, Gymboree has created Janie and Jack, a chain selling upscale baby gifts. Hot Topic, a chain that sells rock-band inspired clothes for teens, recently launched Torrid to give plus-size teens the same fashion options. Instead of emphasizing making and selling, this company sees itself as part of a value delivery process. The value delivery process consists of three parts. What are those parts and what is their function? Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process Page: 37 133. Define value chain. What does a value chain do? 134. If an organization was very strong at defining target markets and prospecting for new customers, which of the core business processes would this organization have mastered? 135. In a holistic marketing framework with respect to customer focus, what would be components that would match to value exploration, value creation, and value delivery? 136. What three spaces are discussed when a holistic marketing organization goes through a value exploration? Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 137. In the central role of strategic planning, only a handful of companies stand out as master marketers—Procter & Gamble, Southwest Airlines, Nike, Disney, Nordstrom, Wal-Mart, and McDonald’s to name a few. From a consumers perspective why do you think they stand out? Explain. 138. All corporate headquarters undertake four planning activities. What are those activities? 139. Porsche makes only expensive cars and Gerber serves primarily the baby market. Which of the major competitive spheres within which a company will operate matches most closely to the examples above? 140. Ansoft’s product-market expansion grid shows three intensive growth strategies that can be used to assist a marketing manager in finding creative ways to close a perceived strategic gap. Characterize each of the cells of Ansoft’s grid. 141. If a company decides to acquire one of its suppliers to gain more control or generate profit, it would have chosen which form of integrative growth 142. When Yahoo! began to flounder in the 2001, CEO Terry Semel imposed a more conservative, buttoned-down atmosphere on the freewheeling Internet Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process startup. At the new Yahoo!, spontaneity is out and order is in. What term is most closely applied to the organizational change phenomenon described above? Be sure to explain what the term means with respect to the example provided. 143. Describe what happens in scenario analysis and explain why firms such as Royal Dutch/Shell Group use the technique. 144. Explain what happens in a SWOT analysis during the strategic planning process. Page: 52 145. What questions would typically be asked during a market opportunity analysis (MOA)? Page: 53 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 146. For an MBO system to work, the business unit attempting to implement the process must meet four criteria. What are those criteria? 147. Which of Michael Porter’s generic strategies would be most appropriate for an organization that concentrates on achieving superior performance in an important customer benefit area valued by a large part of the market? Quality leadership would be one example of the end result of such a strategy. 148. When H&R Block and Hyatt Legal Services combined their efforts (two service businesses), they also joined marketing forces to create a strong alliance. Which of the alliance forms cited in the text most closely matches the H&R Block and Hyatt Legal Services alliance? Explain. 149. Characterize a marketing plan. Page: 60 150. During which stage of the marketing plan will the marketing manager establish the product line’s positioning? Chapter 3: Gathering Information and Scanning the Environment GENERAL CONCEPT QUESTIONS Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process Multiple Choice 1. The major responsibility for identifying significant marketplace changes falls to the . a. U.S. Department of Labor b. company’s marketers c. American Marketing Association d. industry lobby groups found in Washington, D.C. e. marketing research industry Page: 72 2. Marketers have extensive information about how consumption patterns vary across countries. On a per capita basis within Western Europe, the smoke the most cigarettes. a. Swiss b. Greeks c. Irish d. Austrians e. French Page: 72 3. All of the following questions EXCEPT , would be considered to be forms of information needs probes. a. What decisions do you regularly make? b. What information do you need to make decisions? c. What data analysis programs would you want? d. What magazines and trade reports would you like to see on a regular basis? e. What products would be most closely matched to consumer needs? Page: 73 96 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 4. consists of people, equipment, and procedures to gather, sort, analyze, evaluate, and distribute needed, timely, and accurate information to marketing decision makers. a. A marketing information system b. A marketing research system c. A marketing intelligence system d. A promotional campaign e. A marketing database Page: 73 5. The company’s marketing information system should be a cross between what managers think they need, what managers really need, and . a. what the marketing research department is able to do b. what consumers are willing to share c. what the competition is doing d. what is acceptable industry practice e. what is economically feasible Page: 73 6. Marketing managers rely on internal reports. By analyzing this information, they can spot . a. micro-markets b. opportunities and problems c. macro-markets d. competitive strategies e. consumer demographic units Page: 73 7. The heart of the internal records system is the . a. database b. asset acquisition process c. order-to-payment cycle d. service consideration e. information liquidity ratio Page: 73 8. When a marketer “mines” his or her company’s database, fresh insights can be gained into neglected customer segments, , and other useful information. a. recent customer trends b. long-term competitive trends c. possible new inventions d. possible new technologies e. new primary data possibilities Page: 74 9. The internal records system supplies results data, but the marketing intelligence system supplies data. a. concurrent b. secondary c. research 97 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process d. happenings e. premium Page: 74 10. A is a set of procedures and sources managers use to obtain everyday information about developments in the marketing environment. a. marketing research system b. marketing information system c. product management system d. marketing intelligence system e. vertical system Page: 74 11. A company can take several steps to improve the quality of its marketing intelligence. If the company purchases competitive products for study, attends open houses and trade shows, and reads competitors’ published reports and stockholder information, the company is using to improve the quality of its marketing intelligence. a. sales force surrogates b. intermediaries c. external networks d. advisory panels e. customer feedback systems Pages: 74–75 12. All of the following would be considered to be steps to improve the quality of marketing intelligence in a company EXCEPT . a. a company can train and motivate the sales force to spot and report new developments b. a company can use guerrilla tactics such as going through a competitor’s trash c. a company can motivate intermediaries to pass along important information d. a company can network externally e. a company can purchase information from outside suppliers Pages: 74–76 98 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 13. The 2000 U.S. census provides an in-depth look at the population swings, demographic groups, regional migrations, and changing family structure of 281+ million people. Which of the following steps to improve the quality of company marketing intelligence system would be most closely associated the above illustration? a. A company can purchase information from outside suppliers. b. A company can take advantage of government data sources. c. A company can use online customer feedback systems to collect data. d. A company can network externally. e. A company can use its sales force to collect and report data. Page: 76 14. There are four main ways that marketers can find relevant online information on competitors’ products and weaknesses, and summary comments and overall performance rating of a product, service, or supplier. is(are) a type of site that is concentrated in financial services and high-tech products that require professional knowledge. a. Independent customer goods and service reviews b. Distributor or sales agent feedback sites c. Combo-sites offering customer reviews and expert opinions d. Customer complaint sites e. Shopping bot service sites Page: 77 15. A is “unpredictable, short-lived, and without social, economic, and political significance.” a. fad b. fashion c. trend d. megatrend e. style Page: 77 16. A is a direction or sequence of events that has some momentum and durability; the shape of the future is revealed and many opportunities are provided. a. fad b. fashion c. trend d. megatrend e. style Page: 77 99 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 17. have been described as “large social, economic, political and technological changes [that] are slow to form, and once in place, they influence us for some time—between seven and ten years, or longer. a. Fads b. Fashions c. Trends d. Megatrends e. Styles Page: 77 18. Which of the following minority groups in the United States has been associated with one of the ten megatrends shaping the consumer landscape? a. African Americans b. Asian Americans c. European Americans d. Hispanic Americans e. Middle Eastern Americans Page: 78 19. The beginning of the new century brought a series of new challenges. All of the following would be considered to be among those challenges EXCEPT . a. a deterioration of innovative ideas b. steep decline of the stock market c. increasing unemployment d. corporate scandals e. the rise of terrorism Page: 78 20. With the rapidly changing global picture, the firm must monitor six major forces. All of the following would be among those forces EXCEPT . a. demographic b. economic c. social-cultural d. natural e. promotional Page: 78 21. The main demographic force that marketers monitor is(are) . a. suppliers b. competitors c. communication (such as advertising) d. government reports dealing with birth rates e. population Page: 79 22. The population explosion has been a source of major concern. Unchecked population growth and consumption could eventually result in all of the following EXCEPT . a. insufficient food supply b. depletion of key minerals 100 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships c. overcrowding d. restrictions on competition e. pollution Page: 79 23. One impact of explosive population growth is illustrated by the case of China. The Chinese government passed regulations limiting families to one child. One consequence of these regulations is that . a. the children are so fussed over and spoiled that they become “little emperors” b. school enrollments are dropping c. the fledgling automotive business in China will not have customers in a few years d. open rebellion is being preached e. “child-oriented businesses” have few customers Page: 80 24. A significant fact about population growth and population shifts is that in 2004 or 2005, . a. the youth market will exceed that of the adult market b. people over the age of 60 will outnumber those under five years of age c. baby boomers will be eclipsed by Gen X young adults d. most age group segments will be about equal e. Gen Y young adults will surpass the baby boomers as the largest age segment Page: 80 25. Which of the following age groups is thought to control three-quarters of the country’s wealth? a. 0–20 age segment b. 60+ age segment c. 20–30 age segment d. 30–40 age segment e. 40+ age segment Page: 81 101 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 26. At one time the United States was called a “melting pot” society because of the number of different cultures that were integrated into the U.S. culture. Today, the United States is described as a society because many ethnic groups are maintaining their ethnic differences, neighborhoods, and cultures. a. “boiling pot” b. “salad bowl” c. “banana split” d. “doubled up” e. “non-communicative” Page: 81 27. According to the 2000 census, the U.S. population of 276.2 million was 72 percent white and percent African American. The remainder consisted of Hispanic Americans and other minorities. a. 20 b. 18 c. 15 d. 13 e. 11 Page: 81 28. Diversity goes beyond ethnic and racial markets. More than million Americans have disabilities, and they constitute a market for home delivery companies (and others). a. 50 b. 40 c. 30 d. 20 e. 10 Page: 83 29. Which of the following countries is known for having 99 percent of its population literate? a. England b. Germany c. France d. United States e. Japan Page: 83 102 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 30. The household consists of a husband, wife, and children (and sometimes grandparents). a. “traditional” b. “extended” c. “diversity” d. “modern” e. “revised” Page: 83 31. Married couple households—the dominant cohort since the formulation of the United States—has slipped from nearly 80 percent in the 1950s to around percent today. a. 70 b. 60 c. 50 d. 40 e. 35 Page: 83 32. The twenty-first century saw markets grow more rapidly again due to a higher birth rate, a lower death rate, and rapid growth from foreign immigration. a. suburban b. urban c. rural d. coastal e. secondary Page: 84 33. The movement by population to the has lessened the demand for warm clothing and home heating equipment and increased demand for air conditioning. a. Grainbelt b. Pacific Northwest c. Sunbelt d. Mid-Coastal areas e. Heartland Page: 84 103 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 34. Marketers look at where consumers are gathering. Almost one in people over the age of five (120 million) moved at least one time between 1995 and 2000, according to a Census 2000 brief. a. two b. three c. four d. five e. ten Page: 85 35. In which of the following economies would we expect to find few opportunities for marketers? a. Industrializing economies. b. Land-locked economies. c. Raw-material-exporting economies. d. Industrial economies. e. Subsistence economies. Page: 86 36. According to information presented in the text, which of the following countries is surprisingly a very good market for Lamborghini automobiles (costing more than $150,000) because of the number of wealthy families that can afford expensive cars. a. Greece b. Switzerland c. Holland d. Russia e. Portugal Page: 86 37. Over the past three decades in the United States, the rich have grown richer and the middle class has . a. stayed about the same b. shrunk c. increased slightly d. matched the rich in terms of relative growth e. been ignored because of problems with the poorer classes Page: 86 38. shapes the beliefs, values, and norms that largely define the tastes and preferences. a. Marketing b. The mass media c. Government d. Production innovation and engineering e. Society Page: 87 39. If a consumer lives the lifestyle of a “pleasure seeker” or goes on a “self- realization” quest, he or she is expressing what is called . a. views of others 104 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships b. views of society c. views of themselves d. views of organizations e. views of the universe Pages: 87–88 40. According to the information found in the social-cultural environment, with respect to views of others, are considered to be things that allow people who are alone to feel they are not (e.g., television, home video games, and chat rooms on the Internet). a. social surrogates b. subliminal fantasies c. relationship avoidance d. primary products e. secondary products Page: 88 41. Today, corporations need to make sure that they are good corporate citizens and that their consumer messages are honest. Such a view would be consistent with which of the following views? a. Views of others. b. Views of organizations. c. Views of themselves. d. Views of the universe. e. Views of society. Page: 88 42. People vary in their attitudes toward their society. usually live more frugally, drive smaller cars, and wear simpler clothing. a. Makers b. Escapers c. Seekers d. Changers e. Developers Page: 88 105 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 43. People vary in their attitudes toward society and react accordingly. are a major market for movies, music, surfing, and camping. a. Makers b. Preservers c. Escapers d. Changers e. Developers Page: 88 44. All of the following have been cited by the text as being among Americans’ core values EXCEPT . a. they believe in work b. they believe in getting married c. they believe in giving to charity d. they believe in being honest e. they believe in sexual permissiveness Page: 88 45. Which of the following would be the best illustration of a secondary belief or value? a. Belief in work. b. Belief in giving to charity. c. Belief in getting married. d. Belief in getting married early. e. Belief in being honest. Page: 88 46. Which of the following is by far the most popular American leisure activity in that it is preferred by 59 percent of adults who participate in such activities? a. Gardening. b. Walking for exercise. c. Swimming. d. Photography. e. Jogging or running. Page: 89 47. Each society contains , groups with shared values emerging from their special life experiences or circumstances. a. demographic segments b. cliques c. consumer bundles d. subcultures e. behavioral niches Page: 89 106 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 48. Which of the following would be the best illustration of a subculture? a. A softball team. b. A university alumni association. c. Teenagers. d. A Boy Scout troop. e. Frequent flyers. Page: 89 49. All of the following EXCEPT have been found to influence young people today and cause a shift of secondary cores values for this group. a. U2’s Bono. b. Elvis Presley. c. The NBA’s LeBron James. d. Golf’s Tiger Woods. e. Skateboarder Tony Hawk. Page: 89 50. Although core values are fairly persistent, cultural swings do take place. caused such a swing in the 1960s. a. Ford Motor Company b. George McGovern c. G.I. Joe action characters d. The infomercial e. The Beatles Page: 89 51. Marketers need to be aware of threats and opportunities associated with four trends in the natural environment. All of the following are among those trends EXCEPT . a. the shortage of raw materials b. the increased cost of energy c. near 90 percent corporate support for “green causes” d. increased pollution levels e. the changing role of governments Page: 90 52. With respect to the shortage of raw materials, air and water are classified as resources. However, as we know, problems are beginning to plague both our air and water quality. a. infinite b. near finite c. finite renewable d. finite nonrenewable e. absolute Page: 90 107 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 53. One finite nonrenewable resource, , has created serious problems for the world economy. Because of anticipated shortages, investment and commodity markets have had wild swings. a. water b. air c. sugar d. coffee e. oil Page: 90 54. From a branding perspective, “green marketing” programs have not been entirely successful. has been cited as one of the obstacles that must be overcome for “green marketing” programs to be more successful. a. Overexposure and lack of credibility b. High cost c. Poor promotions d. Resistance by the youth segment in the marketplace e. Lack of support by governmental agencies and concerns Page: 91 55. Which of the following countries is noted for their “green movement” and support within its government for environmental quality enhancement? a. Mexico b. China c. Germany d. England e. Italy Page: 91 56. The marketer should monitor the following trends in technology, EXCEPT , if progress is to be made in business. a. the pace of change b. the difficulties found in sharing information c. the opportunities for innovation d. varying R&D budgets e. increased regulation Page: 92 57. According to some industry analysts and inventors, will eventually eclipse the PC as our most important technological device. a. iPod b. HDTV c. holographic television d. the mobile phone e. solar-powered car Page: 92 58. All of the following will most likely be among the advantages for a society that embraces telecommuting as an employment/communication alternative EXCEPT . a. reduction of auto pollution 108 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships b. bringing the family closer together c. increased bonuses and compensation perks d. creating more home-centered shopping e. entertainment centered on the home environment Page: 92 59. legislation has as its purposes to protect companies from unfair competition, to protect consumers from unfair business practices, and to protect the interests of society from unbridled business behavior. a. Business b. Consumer c. Bi-partisan d. Activist e. Global Page: 94 60. An important force affecting business is the —a movement of citizens and government organized to strengthen the rights and powers of buyers in relation to sellers. a. lobbyist movement b. consumerist movement c. environmental movement d. self-rights movement e. ethical reform movement Page: 95 True/False 61. The major responsibility for identifying significant marketplace changes falls to the company’s marketers. Page: 72 62. Today, most firms are rather sophisticated about gathering information. Page: 72 63. A marketing information system is developed from internal company records, marketing intelligence, and promotional models supplied by the marketing department. Page: 73 109 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 64. The heart of the internal records system is the bar code. Page: 73 65. According to principles found in database construction and usage, a “carpet bombing” mail out of a new offer is usually the most successful strategy. Page: 74 66. The internal records system supplies results data, but the marketing intelligence system supplies happenings data. Page: 74 67. If a company were pursuing a policy of networking externally it might collect competitors’ ads or look up news stories about competitors. Page: 75 68. One of the ways to find relevant online information on competitors’ strengths and weaknesses might be to frequent distributor or sales agent feedback sites. Page: 76 69. A style is unpredictable, short-lived, and without social, economic, and political significance. Page: 77 70. A megatrend has been described as being what follows all fads that stay on the market at least one year. Page: 77 71. One of the ten significant megatrends that will impact marketing efforts in the future is delayed retirement. Page: 78 72. Microenvironmental forces have been labeled as being “uncontrollable.” Page: 78 73. The main demographic force that marketers monitor is population. Page: 79 74. If the world were a village of 1,000 people, it would consist of 520 men and 480 women. Page: 79 75. A growing population always means a growing market. Page: 80 76. Japan has one of the world’s oldest populations. Page: 80 77. According to population studies, Gen X (numbering 72 million) is almost the same size as the huge baby boomer market. Page: 81 110 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 78. At present the largest minority in the United States is the Latinos with 13 percent of the total population. Page: 81 79. In the United States, 10 to 15 percent of the population may be functionally illiterate. Page: 83 80. Based on research done in England, a conclusion drawn about families is that “friends are the new family.” Page: 83 81. According to studies of minority markets, the disabled market is ten times more likely to be in a professional job, almost twice as likely to own a vacation home, eight times more likely to own a notebook computer, and twice as likely to own individual stocks as compared to the general population. Page: 84 82. Urban markets are once again growing because of higher birth rates, a lower death rate, and rapid growth from foreign immigration. Page: 84 83. The small office—home office segment of our society has grown to nearly 40 million; thereby, boosting the sales of electronic conveniences and ready to assemble furniture. Page: 85 84. Almost one in two people over the age of five (120 million) moved at least one time between 1995 and 2000, according to a Census 2000 brief. Page: 85 85. Available purchasing power in an economy depends on mainly one facet—supply and demand. Page: 85 86. A good illustration of a raw-material exporting economy is Egypt. Page: 86 87. Conventional retailers who offer medium-priced goods are the most vulnerable to the growing trend in the United States called a two-tier market. Page: 86 88. Through outsourcing, companies can feasibly cut between 20 to 70 percent of their labor costs. Page: 87 89. “Pleasure seekers” of the 1970s had their beliefs, values, and norms shaped by views of others. Pages: 87–88 111 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 90. If a single person has a home entertainment system that is rich in television capabilities and home video games, he or she may be using such a system as a “social surrogate.” Page: 88 91. In recent years, because of a tough job market, there has been an increasing amount of organizational loyalty among most employees. Page: 88 92. If a young college student decides to join the military to defend the principles of his or her country, the student would be classified as a “changer.” Page: 88 93. Most Americans still believe in getting married as a core belief. Page: 88 94. Teenagers would be a good example of a culture in the United States. Page: 89 95. Marketers need to be aware of the threats and opportunities associated with the trend toward increased pollution levels. Page: 90 96. Research studies have shown that consumers as a whole may not be willing to pay a premium for environmental benefits. Page: 91 97. Every new technology is a force for “creative destruction.” Page: 92 98. Virtual reality is giving consumers what they dream about. Page: 93 99. One of the major trends in the political-legal environment is the trend toward the growth of special interest groups. Page: 93 100. Today, customers are still willing to swap personal information for customized products from firms. Page: 95 Essay 101. Describe a marketing information system (MIS). From what sources is the MIS developed? Suggested marketing information system (MIS) consists of people, equipment, and procedures to gather, sort, analyze, evaluate, and distribute needed, timely, and accurate information to marketing decision makers. A 112 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships marketing information system is developed from internal company records, marketing intelligence activities, and marketing research. Page: 73 102. Describe the order-to-payment cycle and why it is important to internal records information keeping. 103. What are the various steps to improve the quality of its marketing intelligence function that can be taken by a company? 113 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 104. List and briefly describe the four main ways marketers can find relevant online information on competitors’ strengths and weaknesses, and summary comments and overall performance rating of a product, service, or supplier. Page: 77 105. What is a “megatrend”? Briefly describe five megatrends shaping the consumer landscape. Pages: 77–78 106. What is the main demographic force monitored by marketers? Why? 107. Describe the two dominant “household patterns” in the last 50 years. 114 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 108. People absorb, almost unconsciously, a worldview that defines their relationships. List and describe the “views” that assist or retard this relationship development process. 109. Describe the differences between a core belief and a secondary belief. List the primary core beliefs of Americans as revealed by the text. 110. Many marketers have tried and failed with “green sales pitches” (appeals to one’s environmental good sense) over the past decade. What obstacles (as cited by the text) did this movement encounter? Be sure to briefly explain each obstacle. 91 Level of difficulty: Medium 115 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process APPLICATION QUESTIONS Multiple Choice 111. DuPont commissioned marketing studies to uncover personal pillow behavior for its Dacron Polyester unit that supplies filling to pillow makers and sells its own Comforel brand. Which of the following was revealed by research to be the primary challenge faced by DuPont in expanding sales in the pillow industry? a. Price. b. People don’t want to give up their old pillows. c. The smell associated with polyester. d. The lack of a favorable reputation in the industry. e. Competition from China. Page: 72 112. Assume that you are a marketing information specialist for a large clothing manufacturer. Your task is to get functional managers to use the company’s MIS system on a more regular basis. All of the following questions are would be among those that might be submitted to those manager’s to pique their interest in MIS EXCEPT, ? a. What is your appraisal of the budget for your functional area this year b. What decisions do you regularly make c. What information do you need to make these decisions d. What topics would you like to be kept informed of e. What data analysis programs would you want Page: 73 113. As the manager of an organization that is attempting to build a MIS, you have been informed that a MIS is built upon three fundamental information sources. The sources are , marketing intelligence activities, and marketing research. b. external records and documents c. databases found on the Internet d. consultant reports e. internal company records f. secondary data from government sources such as the Better Business Bureau Page: 73 116 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 114. Pizza Hut has millions of customer records gleaned from point-of-sale transactions at its restaurants. Using Teradata Warehouse Miner, Pizza Hut has not only been able to , but can also target its marketing to find the best coupon offers for each household and predict the success of campaigns. a. reduce its outside research emphasis b. increase profits dramatically c. reduce television advertising d. win quality awards e. purge expensive duplicates from its direct-mail campaigns Page: 74 115. As a manager you would most likely use an internal records system to supply data, whereas, you would use your marketing intelligence system to supply happenings data. a. demand b. logistical c. psychographic d. results e. primary Page: 74 116. When McDonald’s used mystery shoppers to assess stores’ internal speed standards, McDonald’s was using which of the following steps to improve its marketing intelligence system? a. A company can train and motivate the sales force to spot and report new developments. b. A company can motivate distributors, retailers, and other intermediaries to pass along important intelligence. c. A company can network externally. d. A company can set up an advisory panel. e. A company can take advantage of government data sources. Pages: 74–76 117. Examples of that were considered to be successful for toy retailers were Beanie Babies, Furbies, and Tickle Me Elmo dolls. a. trends b. fashions c. fads d. megatrends e. styles Page: 77 117 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 118. More than half of all U.S. workers are employed in , in professional or related occupations, or in a sales or other office-based position. a. accounting b. finance c. computer information systems d. database maintenance e. management Page: 78 119. As baby boomers grow older, their impact on consumer spending can be described as being . a. substantial (without overstating) b. marginal at best c. eclipsed by the Generation X members d. only moderate e. stymied by higher taxes Page: 78 120. According to information provided in the text, is an example of a country with a very young and rapidly expanding population where products such as milk, diapers, school supplies, and toys would be important. a. Japan b. France c. Spain d. Mexico e. the United Kingdom Page: 80 121. are typically cynical about hard-sell marketing pitches that promise more than they can deliver. a. Baby boomers b. War babies c. Generation Z d. Generation X e. Net-gens Page: 81 118 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 122. A frequently noted megatrend in the United States is the increase percentage of in the total population; they made up half of all new workers in the past decade. a. Asians (excluding Chinese) b. Indians c. Chinese d. Hispanics e. Africans Page: 81 123. Because of heightened competition for top students and concerns about institutional reputations and rankings, many universities are now increasing marketing efforts with the purpose of . a. creating virtual educational processes b. creating definable “brands” c. stimulating “fun” on campus d. managing organizational resources e. delaying belt-tightening in the future Page: 83 124. What percentage of people (cohorts) in the United States are considered to be married couple households? a. 80 percent b. 70 percent c. 60 percent d. 50 percent e. 40 percent Page: 83 125. Jason has just moved in with several friends in what might commonly be called a “commune.” As a 20-something, Jason’s choice of living style is exemplified by the term . a. dropout b. pseudo-technocrat c. neo-tribe d. socialist e. fascist Page: 83 119 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 126. The outsourcing wave (computer analysis and software design) that has been experienced by India with its young technologically-proficient younger generation has had an impact on traditions as well as the economy. Young Indians (“liberation children”) are questioning . a. the tax system of the country b. the political parties of India for relevance c. the meaning of life d. their charitable responsibilities e. conservative traditions such as arranged marriages and no public kissing Page: 86 127. William rose rapidly in his organization and was the youngest CEO in the company’s history. His self-declared purpose as a leader was to make his company an integral part of the American way of life and to eventually enter into public service of his country. William would be characterized as being a . a. preserver b. maker c. taker d. seeker e. reaper Page: 88 128. How do Americans spend their leisure time—59 percent of Americans (the highest percentage) say that “walking for exercise” is their primary way of spending leisure time. What is the second most mentioned leisure activity with 45 percent? a. Swimming b. Bicycling c. Jogging or running d. Gardening e. Power boating Page: 89 129. To get around obstacles to “green marketing” and make sure environmental initiatives are implemented, some companies recommend relying on the efforts of a . a. senior ethics officer b. market maven c. Green Champion d. HR vice-president e. watch-dog committee Page: 91 130. lobby government officials and pressure business executives to pay more attention to consumers’ rights, women’s rights, senior citizens’ rights, minority rights, and gay rights. a. Political action committees (PACs) b. Universities and colleges c. The Better Business Bureau 120 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships d. The U.S. Chamber of Commerce e. Manufacturing trade associations (MTAs) Page: 95 Short Answer 131. Although every manager in an organization needs to observe the outside environment, marketers have two advantages. What are those two advantages? Page: 72 132. If you were a company’s marketing information manager, you would need to realize that your marketing information system should be a cross between three areas of concern (thoughts) for managers with respect to information. What are those three concerns (thoughts)? 133. What typically would be the function of a sales information system? Think of an example to illustrate such a function. Page: 73 134. Explain the statement that “internal records systems supply results data and marketing intelligence systems supply happenings data.” Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process sources managers use to obtain everyday information about developments in the marketing environment (happenings data). Pages: 73–74 135. One of the ways that a marketer can improve its marketing intelligence function is to network externally. What does networking externally mean? Provide an illustration to support your answer. 136. Marketers today use relevant online information to assess competitors’ product strengths and weaknesses. Additionally, summary comments and overall performance rating of products, services, and suppliers can be obtained. List the four main ways marketers can get such information online. 137. What is a trend and why is it important in marketing? 138. Assume that you are a marketing manager for a youth clothing manufacturer that has just read about the megatrend of the “rising Hispanic influence” in the United States. Explain this megatrend and indicate why it might be important to your company and industry. Page: 78 139. Characterize Generation Y or echo boomers. What implications does this generation have for marketing over the next few years? Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships Page: 81 140. The United States was originally called a “melting pot,” but there are increasing signs that the melting didn’t occur. Explain. What would be a “new” way of describing our society and how it relates to members? 141. As a marketing manager you have observed that the “traditional household” in the United States is giving way to the “nontraditional household.” Explain what this means and characterize the “nontraditional household.” Page: 83 142. What two factors have helped those businesses that cater to the growing SOHO (small office/home office) segment that is nearly 40 million strong? 143. What impact are “liberalizing children” having on India? Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 144. As indicated in the text, GAP pursues a segmented market strategy with three tiers of retail clothing stores. Explain the GAP tier system and indicate examples of the tiers. 145. Within our social-cultural environment, consumers often see themselves from different views. Assume that you were espousing the view of themselves. Characterize this view. Pages: 87–88 146. Describe the differences between a core belief and secondary belief. Provide an example to illustrate your description. 147. Assume that you were asked to write a brief paragraph indicating why a firm might wish to pursue a policy of “green marketing.” How would your paragraph read? 148. What four trends in technology should marketers monitor? Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 149. With respect to opportunities for innovation, characterize the power of virtual reality for the marketer. 150. Consumers are increasingly willing to swap personal information for customized products from firms. However, there are still consumer concerns. You know that privacy issues are still a public policy hot button. As a consumer advocate, list the consumer concerns that seem to be the most compelling and most difficult to deal with by the marketer. Chapter 4: Conducting Marketing Research and Forecasting Demand GENERAL CONCEPT QUESTIONS Multiple Choice 1. is the systematic design, collection, analysis, and reporting of data and findings relevant to a specific marketing situation facing the company. a. Marketing intelligence b. MIS (marketing information system) c. Marketing research d. Demographics e. Marketing management Page: 102 2. Marketing research is now about a billion industry globally. a. $50 b. $21.5 c. $16.5 d. $10 e. $7.5 Page: 102 125 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 3. Companies normally budget marketing research at percent of company sales. a. 1 to 2 b. 2 to 3 c. 4 d. 6.5 e. 10 to 12 Page: 103 4. Which of the following types of marketing research firms would best be described as being one that gathers consumer and trade information which they sell for a fee (e.g., Nielsen Media Research)? a. Custom marketing research firms. b. Syndicated-service research firms. c. Specialty-line marketing research firms. d. General-line marketing research firms. e. Non-profit marketing research firms. Page: 103 126 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 5. If a marketing research firm were also known as a field-service firm (e.g., it sells its field interviewing services to other firms), it would be called a . a. custom marketing research firm b. syndicated-service research firm c. specialty-line marketing research firm d. general-line marketing research firm e. systematic marketing research firm Page: 103 6. All of the following would be among the ways that small companies can conduct marketing research in creative and affordable ways EXCEPT . a. using the Internet b. engaging students to design and carry out projects c. checking out rivals d. engaging professors to design and carry out projects e. hiring syndicated-service research firms to conduct projects Page: 103 7. The first step in the marketing research process is to . a. develop a research plan b. define the problem and research objectives c. analyze the internal environment d. read marketing research journals e. contact a professional consultant Page: 103 8. Which of the following is considered to be the last step in the marketing research process? a. Present the findings. b. Analyze the information. c. Control the environment. d. Make the decision. e. Draft the report. Page: 103 9. The marketing manager needs to know the cost of the research project before approving it. During which of the following stages of the marketing research process would such a consideration most likely take place? a. Step 1—defining the problem. b. Step 1—creating decision alternatives. c. Step 1—drafting the research objectives. d. Step 2—develop the research plan. e. Step 3—information collection. Pages: 104–112 10. Designing a research plan calls for decisions on all of the following EXCEPT . a. drafting research objectives b. data sources c. research approaches 127 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process d. research instruments e. sampling plans Page: 104 11. are data that were collected for another purpose and already exist somewhere. a. Primary data b. Secondary data c. Tertiary data d. Inordinate e. Ordinate Page: 104 12. Primary data can be collected in several ways. Which of the following primary data collection methods would be exemplified by constructing see-through mirrors in a retail store whereby consumers’ actions could be recorded? a. Focus groups b. Surveys c. Observation d. Behavioral data e. Experiments Page: 105 13. A is a gathering of six to ten people who are carefully selected based on certain demographic, psychographic, or other considerations and brought together to discuss at length various topics of interest. a. market maven b. virtual research market c. consumer dyad d. focus group e. Nielsen sample family Page: 105 128 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 14. Companies undertake surveys to learn about people’s knowledge, , preferences, and satisfaction, and to measure these magnitudes in the general population. a. beliefs b. psyche c. inner id d. deepest secrets e. intelligence and literacy Page: 105 15. The most scientifically valid research is research. a. observation b. focus group c. survey d. behavioral data e. experimental Page: 106 16. All of the following would be among the “dos and don’ts” of questionnaire design EXCEPT . a. make questions as simple as possible b. make the questions specific c. ensure that fixed responses overlap d. avoid hypothetical questions e. avoid questions with a negative in them Page: 107 17. The most common instrument used to collect primary data is the . a. human eye (through observation) b. Internet c. bar code reader (behavioral data research) d. video camera (e.g., focus group research) e. questionnaire Page: 107 18. Some marketers prefer more methods for gauging consumer opinion because consumer actions do not always match their answers to survey questions. a. quantitative b. qualitative c. psychographic d. covert e. subliminal Page: 107 19. If a marketing researcher observes people using products, shopping, going to hospitals, taking the train, or using their cell phones, the researcher would most likely be using which of the following qualitative research gathering methods? a. Behavior mapping b. Consumer journals c. Shadowing 129 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process d. Extreme user interviews e. Unfocus groups Page: 107 20. If a questionnaire designer decides to use a scale that connects two bipolar words wherein the respondent selects the point that represents his or her opinion, the designer is most likely using what is called . a. a dichotomous question b. a multiple-choice question c. a Likert scale d. the semantic differential e. word association question Page: 108 21. If a marketing researcher chooses to use a word association question (e.g., “what is the first word that comes to your mind when you hear the following: airline… American…travel, et cetera), the researcher has chosen which of the following type of question for his or her research questionnaire? a. Closed-end question b. Likert scale question c. Open-end question d. Rating scale question e. Semantic differential question Page: 108 22. Which of the following types of tests matches to a question that shows a picture and respondents are asked to make up a story about what they think is happening or may happen in the picture? a. Word association b. Completely unstructured question c. Story completion d. Thematic Apperception Test (TAT) e. Holistic association Page: 108 130 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 23. is a qualitative research approach for getting inside a consumer’s mind and finding out what they are thinking or feeling (e.g., a consumer says that the John Deere brand makes them think of a rugged Midwestern male who is hard- working and trustworthy). a. Word association b. A projective technique c. Brand personification d. Laddering e. Visualization Page: 109 24. Mechanical devices are occasionally used in marketing research. For example, flashes an ad to a subject with an exposure interval that may range from one hundredth of a second to several seconds. After each exposure, the respondent describes everything he or she recalls. a. a tachistoscope b. the galvanometer c. an eye-tracking camera d. an audiometer e. a pupilometer Page: 110 25. With respect to the sampling plan, three decisions must be made. The decisions are: the sampling unit—who is to be surveyed? Sample size—how many people should be surveyed? And . a. sample cost—how much does sampling cost? b. surveyor skill—who will do the surveying? c. sample security—how to protect the sample data? d. sampling procedure—how should the respondents be chosen? e. sample supervisor—who will lead the sampling effort? Page: 110 26. If a marketing researcher selects the most accessible population members, he or she would have selected the sampling method. a. simple random b. stratified random c. cluster d. judgment e. convenience Page: 110 131 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 27. If a researcher finds and interviews a prescribed number of people in each of several categories, the researcher is using the sampling method. a. judgment b. quota c. convenience d. cluster e. simple random Page: 110 28. If a marketing researcher wished to reach people who would not give personal interviews or whose responses might be biased or distorted by the interviewers, he or she should choose the as the best way to reach people. a. mail questionnaire b. telephone interview c. online interview d. focus group interview e. cell phone interview Page: 111 29. Which of the following is considered to be the most versatile of the questioning or interviewing methods? a. Mail questionnaire b. Telephone interview c. Personal interview d. Online interview e. Cell phone interview Page: 111 30. Online research has grown significantly in the last several years. It is estimated that of all survey-based research was done online in 2004. a. 5 percent b. 10 percent c. 15 percent d. 20 percent e. 25 percent Page: 111 31. The phase of marketing research is generally the most expensive and the most prone to error. a. research objectives b. research planning c. questionnaire design d. interview design e. data collection Page: 112 32. All of the following are considered to be advantages of online research EXCEPT . a. online research is inexpensive b. online research is faster 132 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships c. online research is relatively free of technological problems and inconsistencies d. online research is more versatile e. people tend to be more honest online than in other interviewing methods Page: 113 33. When Intel commissioned research to better understand global online challenges, it found that with respect to global responses on technology the biggest obstacle to conduct international research is . a. cost b. lack of consistency c. language difficulties d. religious bias e. lack of management’s commitment in this area Page: 114 34. A has been defined as being a coordinated collection of data, systems, tools, and techniques with supporting software and hardware by which an organization gathers and interprets relevant information from business and environment and turns it into a basis for marketing action. a. marketing information system b. marketing intelligence system c. marketing decision support system d. marketing research system e. database management system Page: 115 35. All of the following are considered to be among the seven characteristics of good marketing research EXCEPT . a. the scientific method b. research creativity c. multiple methods d. ethical marketing e. independence of models and data Page: 115 133 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 36. In spite of the rapid growth of marketing research, many companies still fail to use it sufficiently or correctly. The reasons why this is true are listed below EXCEPT . a. a broad conception of the research b. uneven caliber of researchers c. poor framing of the problem d. late and occasionally erroneous findings e. personality and presentational differences Page: 116 37. In the famous case where Coca-Cola introduced the New Coke after much research, the failure of New Coke was largely due to a marketing research barrier identified as . a. a narrow conception of the research b. uneven caliber of researchers c. poor framing of the problem d. late and occasional erroneous findings e. personality and presentation differences Page: 116 38. In the 1970s, a successful research executive left General Foods for a daring gambit: Bring market research to the Hollywood film studios and give them access to the same research that spurred General Foods’ success. What famous film did he predict would be doomed because of its fantasy theme and its attention to war between nations (the film was hugely successful despite these predictions)? a. The Godfather b. Platoon c. Star Wars d. Butch Cassidy and the Sundance Kid e. The Deer Hunter Page: 116 39. Marketers are increasing being held accountable for their and must be able to justify marketing expenditures to senior management. a. product quotas b. employees c. own training d. investments e. personal character traits Page: 116 134 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 40. Two complimentary approaches to measure marketing productivity are and marketing-mix modeling to estimate casual relationships and how marketing activity affects outcomes. a. quality ratios b. salesperson satisfaction scales c. marketing metrics to assess marketing effects d. distributor satisfaction surveys e. end-user samples Page: 117 41. is(are) the set of measures that helps firms to quantify, compare, and interpret their marketing performance. a. Marketing diagnostics b. Psychographics c. Demographics d. Marketing intelligence e. Marketing metrics Page: 117 42. According to Roger Best, a strong translates into a strong customer focus, competitor orientation, and a team approach. a. product orientation b. market orientation c. innovation orientation d. productivity orientation e. global orientation Page: 117 43. All of the following would be considered to be external marketing metrics EXCEPT . a. market share b. relative price c. number of complaints d. perceived quality/esteem e. relative employee satisfaction Page: 118 44. A records how well the company is doing year after year on customer- based measures (e.g., percentage of new customers to average number of customers). a. customer-performance scorecard b. stakeholder-performance scorecard c. mission/objectives scorecard d. variance scorecard e. management scorecard Page: 118 45. If a company actively tracks the performance of its suppliers, banks, and distributors, it is using what is called a . a. customer-performance scorecard b. stakeholder-performance scorecard 135 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process c. mission/objectives scorecard d. variance scorecard e. management scorecard Page: 118 46. consists of measuring and evaluating actual sales in relation to goals. a. ROI analysis b. Demand c. Sales analysis d. Performance reviews e. Trend lines Page: 119 47. Which of the following ways to measure market share would be seen as the company’s sales expressed as a percentage of total market sales? a. Overall market share b. Served market share c. Relative market share d. Delayed market share e. Designed market share Page: 120 48. If Dell computer was seen as having a 120 percent market share and a close competitor was seen as having 90 percent market share, the market share analysis (measurement) would expressed as . a. overall market share b. served market share c. relative market share d. dual market share e. top dog market share Page: 120 49. All of the following are components of a method (formula) that can analyze market share movements EXCEPT . a. customer penetration b. competitor penetration c. customer loyalty d. customer selectivity e. price selectivity Page: 120 50. Annual-plan control requires making sure that the company is not overspending to achieve sales goals. The key ratio to watch is the . a. marketing profitability ratio b. marketing sales ratio c. share of mind ratio d. marketing expense-to-sales ratio e. marketing deliverables ratio Page: 120 136 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 51. A can be used to track period-to-period fluctuations in each ratio (e.g., marketing expense-to-sales ratio) used assist in annual-plan control. a. Gantt chart b. Likert scale c. control chart d. time chart e. profitability chart Page: 120 52. According to the financial model of return on net worth, return on assets times (X) financial leverage equals (=) . a. profit margin b. asset turnover c. sales expenses d. rate of return on net worth e. the acid test ratio Page: 121 53. Net profits divided by net sales equals (=) . a. asset turnover b. profit margin c. return on assets d. financial leverage e. rate of return on net worth Page: 121 54. If a company’s profit and loss statement showed that sales for the month were $60,000 and cost of goods sold were $39,000, what would be the gross margin? a. $99,000 b. $21,000 c. 65 percent d. 153.84 percent e. Would be unable to calculate given the problem’s figures. Page: 122 55. A manager observes that his last month’s salaries were $9,300, rent was $3,000, and supplies used by the company were $3,500. Considering that his company’s gross margin was $21,000, what would be his net profit for the period? a. $36,800 b. $60,000 c. $5,200 d. $10,400 e. Would be unable to calculate given the problem’s figures. Page: 122 56. Which of the following would be considered to be a direct cost? a. Rent. b. Corporate image expenditures. c. Public relations expenditures. d. Leasing of business space. 137 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process e. Sales commissions. Page: 124 57. A marketing manager, during an annual planning meeting, would like to have the department’s staff examine the set of consumers who have interest, income, and access to the company’s offers. The staff will need to examine information about the in order to do what it has been asked to do. a. potential market b. available market c. target market d. penetrated market e. re-positioned market Page: 126 58. for a product is the total volume that would be bought by a defined customer group in a defined geographical area in a defined time period in a defined marketing environment under a defined marketing program. a. Market share b. Market supply c. Market demand d. Market potential e. Market penetration Page: 127 138 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 59. Product penetration is the percentage of ownership or use of a product or service in a population. According to recent statistics, which of the following products has the greatest amount of penetration in the U.S. market with a staggering 98 percent? a. Health insurance. b. A car. c. A home. d. A television. e. A gun. Page: 129 60. There are several methods for assessing market potential. Which of these methods do business marketers prefer? a. Market-buildup method b. Multiple-factor index method c. Brand-development index method d. Purchase-profitability index e. Market-test index Page: 130 True/False 61. Most large companies use outside marketing research consultants rather than employ their own marketing research department. Page: 102 62. A good illustration of a syndicated-service research firm is Nielsen Media Research. Page: 103 63. The Preston Agency is a field-service firm that sells its field interviewing skills and services to other firms. In the above instance, the Preston Agency would be an example of what is called syndicated-service research firm. Page: 103 64. After developing the research plan, the marketing researcher should define the problem and research objectives. Page: 104 65. All research must begin with an exploratory research study. Page: 104 66. James conducted primary research when he distributed a survey to his dorm to discover their attitudes and opinions on campus life. Pages: 104–105 67. In general, for marketing research purposes, the larger focus groups (50 to 80) are superior to smaller focus groups (6 to 10). 139 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process Page: 105 68. A good example of collecting behavioral data would be when a store uses scanners to read bar codes on products selected by consumers. Pages: 105–106 69. The most scientifically valid research is focus group research. Page: 106 70. The most common instrument used to collect primary data is the questionnaire. Page: 107 71. An example of shadowing is keeping track of all the interactions a consumer has with a product, service, or space. Page: 107 72. If a marketing researcher decides to use a Likert scale, the researcher has chosen a technique wherein the respondent reviews a statement that shows the amount of agreement/disagreement with some product, service, or concept. Page: 108 73. “What is your opinion of the American way of life?” is an example of what might be called the semantic differential. Page: 108 74. “What does the Coca-Cola name mean to you?” would be an illustration of a question that might be used in a projective technique. Page: 109 75. A galvanometer can measure the interest or emotions aroused by exposure to a specific ad or picture. Page: 110 76. If a marketing researcher bases his or her sample on population members who are good prospects for accurate information, a judgment sample has been selected. Page: 110 77. If a marketing researcher is looking for a contact method that can gather information quickly and allow the interviewer to clarify questions if necessary, he or she will choose the telephone interview method. Page: 111 78. A good illustration of what is called the arranged interview occurs when interviewers stop people in a shopping mall or on a busy street and solicit information necessary to their research effort. Page: 111 79. The data analysis phase of the marketing research process is generally the most expensive and prone to the error phase of the process. Page: 112 140 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 80. One of the disadvantages to doing research online is that it is often more expensive than traditional means of gathering the same information. Page: 113 81. One of the characteristics of good marketing research is that it uses multiple methods. Page: 115 82. Marketing researchers should have a healthy skepticism toward glib assumptions made by managers about how a market works. Page: 115 83. In the famous case where Coca-Cola introduced the New Coke after much research, the uneven caliber of the researchers doomed the product and associated research efforts. Page: 116 84. A set of measures that helps firms to quantify, compare, and interpret their marketing performance is called marketing metrics. Page: 117 85. A stakeholder-performance scorecard tracks the satisfaction with the company and its products and services among such entities as suppliers, banks, and stockholders. Page: 118 86. Sales-variance analysis measures the relative contribution of different factors to a gap in sales performance. Page: 119 87. All the buyers who are able and willing to buy a company’s products or services are called the overall market share. Page: 120 88. The key ratio to watch in annual-plan control to make sure that the company is not overspending to achieve sales goals is the marketing expense-to-sales ratio. Page: 120 89. The return on net worth is the product of two ratios: the company’s return on assets and its asset turnover ratio. Page: 121 90. Gross margin minus (-) expenses equals (=) net profit. Page: 122 91. Direct costs are common costs whose allocation to the marketing entities is highly arbitrary. Page: 124 141 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 92. Especially popular with such companies as Procter & Gamble, marketing-mix modeling is used to allocate or reallocate expenditures. Page: 125 93. The production department is responsible for preparing sales forecasts because they have the most data about production schedules and the ability to meet orders. Page: 125 94. A target market is the set of consumers who profess a sufficient level of interest in a market offer. Page: 126 95. Market demand is not a fixed number, but rather a function of the stated conditions. Page: 127 96. A low market share penetration index indicates substantial growth potential for all the firms. Page: 128 97. With respect to product penetration percentage, gun ownership is among the highest in the United States with an 84 percent rating. Page: 129 98. A common way to estimate total market potential is to use the annual Survey of Buying Power to calculate the required estimate. Page: 130 99. The multiple-factor index method for assessing area market potential is most commonly used by those interested in consumer markets. Page: 131 100. With respect to past-sales analysis, econometric analysis consists of projecting the next period’s sales by combining an average of past sales and the most recent sales, giving more weight to the latter. Page: 134 Essay 101. What are the six steps in the marketing research process? 102. Characterize the structure and purpose of a focus group. 142 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships considerations and brought together to discuss at length various topics of interest. Page: 105 103. Explain what qualitative research is and why it might be useful to marketers. 104. Describe and illustrate the following question formats: dichotomous, Likert scale, word association, and Thematic Appreciation Test (TAT). 105. Explain what a “projective technique” is and how it might be used to assist researchers in understanding consumer actions and behavior. 106. What is the “chief” advantage (best method of usage) of using each of the following contact methods: mail questionnaire, telephone interview, and personal interview? 143 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process interview—the most versatile method because they can ask more questions and record additional observations about the respondent. Page: 111 107. According to information presented in the text, what are the seven characteristics of good marketing research? Page: 115 108. In spite of the rapid growth of marketing research, many companies still fail to use it sufficiently or correctly. List and briefly discuss five reasons why this might happen. 109. A manager has a simplified profit-and-loss statement that indicates that sales for the last quarter were $120,000, cost of goods sold was $35,000, and expenses were: salaries = $10,000, rent = $3,000, and supplies = $3,000. Calculate the net profit. 110. Describe the following terms and then construct an illustration to demonstrate the relationships involved: potential market, available market, qualified available market, target market, and penetrated market. 144 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships Page: 126 Level of difficulty: Hard APPLICATION QUESTIONS Multiple Choice 111. Procter & Gamble’s Consumer & Market Knowledge (CMK) group focuses on three kinds of work: , expert application of, and cross-business learning kinds of work, and shared services and infrastructure. a. psychographics b. database management c. proprietary research methods development d. global survey research e. brand competition research Page: 102 112. Assume that you are a marketing research director for a medium-sized manufacturing firm and you would like to engage an outside marketing research firm to conduct your field interviews. Which of the following options would be your best choice to achieve your objective? k. A syndicated-service research firm. l. A custom marketing research firm. m. A global research management firm. n. A specialty-line marketing research firm. o. A brand-management specialty research firm. Page: 103 113. As a marketing research manager you have begun calculations on the costs of a proposed marketing research project. During which stage of the marketing research process are such calculations most likely to take place? g. Stage 1—define the problem phase. h. Stage 1—develop decision alternatives phase. i. Stage 1—develop the research objectives. j. Stage 2—develop the research plan. k. Stage 3—collect the information. Page: 104 114. Before Sandra Perez opened her floral shop she read all she could on the industry. She also reviewed library data banks on growth patterns in the local area with particular interest in the location of florists throughout the city. This assisted her in deciding where to locate her store. a. primary information b. secondary information 145 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process c. guerilla marketing data d. tertiary information e. non-personal information Page: 104 115. As one marketing executive noted, are “…the most cost-effective, quickest, dirtiest way to get information in rapid time on an idea.” a. scanners b. tele-us machines c. surveys d. in-store interviews e. focus groups Page: 106 116. One of the don’ts of questionnaire construction is to ensure that fixed responses do not overlap. Which of the following is the best illustration of a problem that this “don’t” might cause? a. A question has three possible responses: yes, no, or maybe. b. An income question asks for an income designation in one of the following income categories: $0–$20,000, $20,000–$40,000, or $40,000 and above. c. A consumer is asked to describe a recent event will driving. d. A consumer must describe a cartoon about buying a car. e. A consumer is asked whether or not he or she could spy on another consumer’s shopping experience. Page: 107 146 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 117. If a questionnaire says “Small college classes are better places to learn effectively: (choose) 1 Strongly disagree, 2 Disagree, 3 Neither agree nor disagree, 4 Agree, 5 Strongly agree,” the researcher would be using which of the following to discover data. a. Likert scale b. Semantic differential c. Multiple choice d. Thematic Appreciation Test (TAT) e. Dichotomous question Page: 108 118. One set of consumers, during a focus group session, indicated that Dell computers reminded them of a surfer, Apple Computer was equated to a mad- scientist, and IBM computers to Scrooge from the Dickens’s tale. Which of the following qualitative research approaches matches to the approach described above? a. Projective techniques b. Visualization c. Brand personification d. Laddering e. Pyramiding Page: 109 119. If you decided to interview members of your class with regard to issues relating to the university and college life, you would have selected the as a means of sampling members of the total population. a. simple random sample b. stratified random sample c. cluster (area) sample d. convenience sample e. quota sample Page: 110 120. The main drawback to the is that the interviews have to be short and not too personal. a. mail questionnaire b. personal interview c. online interview d. secondary interview e. telephone interview Page: 111 147 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 121. Which of the following should be considered as a disadvantage by a marketing researcher as he or she considers whether or not to use online research as a means of gathering data? a. Online research is often slow. b. Online research is usually expensive. c. Online line research is one-dimensional. d. Online line research suffers from a poor reputation. l. Online market research is prone to technological problems and inconsistencies. Page: 113 122. If a marketing researcher were to use careful observation, hypotheses, prediction, and testing to ensure that his or her marketing research efforts were of the highest quality, the researcher would have then used characteristic of good marketing research to assist in the research effort. a. research creativity b. the scientific method c. ethical marketing d. multiple methods e. interdependence of models and data Page: 115 123. Some marketing managers view marketing research as little more than a clerical activity and treat it as such. If disappointing results occur because of this attitude, the manager has his or her negative opinion reinforced. The above is a reflection of which of the following barriers that must be overcome if successful marketing research is to occur? a. Uneven caliber of researchers. b. Poor framing of the problem. c. Erroneous findings. d. Personality differences. e. Presentation differences. Page: 116 124. According to Peter Doyle, value-based marketing in not primarily about numbers. It consists of three main elements: , a set of principles for choosing marketing strategies and making marketing decisions, and a set of processes that ensure that marketing develops, selects, and implements a strategy that is consistent with these beliefs and principles. a. a set of beliefs about consumers b. a set of beliefs about demographics c. a set of beliefs about organizational design d. a set of beliefs about the fundamental soundness of quantitative methods e. a set of beliefs about the objective of marketing Page: 117 125. A useful way to analyze market share movements is in terms of four components where overall market share equals (=) customer penetration times (X) customer loyalty times (X) customer selectivity times (X) . a. promotion sensitivity 148 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships b. price selectivity c. brand loyalty d. cultural affinity e. distribution opportunities Page: 120 126. One of the essential components of a model for calculating return on net worth is financial leverage. In this context, financial leverage is equal (=) to . a. net profits divided by net sales b. net sales divided by total assets c. total assets divided by net worth d. net profits divided by total assets e. net profits divided by net worth Page: 121 127. Sally is reviewing how to re-figure a variety of expenses and costs associated with a recent marketing effort. Her first task is to identify the direct costs associated with that effort. Which of the following would be the best example of a direct cost associated with a marketing effort? a. Rent b. Public relation’s image c. Top management salaries d. Sales commissions e. Interest on debt Page: 124 128. Jason is examining a recent breakdown of his company’s West Coast market. The terms in the report are somewhat confusing since there was no attached vocabulary key to assist the uninformed reader. Jason is looking for the set of consumers who are currently buying his company’s products. Which of the following terms will assist him in finding the right column for his data query? a. Potential market b. Bi-lateral market c. Available market d. Target market e. Penetrated market Page: 126 149 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 129. A high market penetration index suggests that . a. a substantial growth potential exists for all firms in the market b. there will be increased costs of attracting the few remaining prospects c. mistakes have been made in selecting the correct promotional alternatives d. the price of the product or service is too high with respect to competition e. it would be great time to expand distribution outlets Page: 128 130. A marketing research firm intends to ask consumers a question that reads “Do you intend to buy a automobile within the next six months?” Consumers could respond in several ways including no chance, slight possibility, fair possibility, good possibility, high possibility, and certain. Which of the following terms most accurately categorizes the type of scale that the marketing researcher will want to use in the research effort? a. Buying ratio scale b. Behavioral scale c. Attitude scale d. Purchase probability scale e. Market-test scale Page: 133 Short Answer 131. Define marketing research. 132. The text lists several creative ways that a small company can conduct marketing research without incurring the high costs often associated with a marketing research effort. List three methods that might be considered to be creative. 133. During which phase of the marketing research process will the marketing manager most likely calculate the cost of the marketing research plan? 150 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 134. If a company desires to assess the magnitude of consumers’ knowledge, beliefs, preferences, and satisfaction, the company will most likely choose which of the five research approaches outlined in the text? 135. If you needed to collect primary data and were seeking to use the research instrument that is considered to be the most common method for obtaining that type of data, what type of instrument would you select? 136. If a marketing research firm has decided to photograph people within the lobby of a movie theater over a two- to three-day period, what qualitative measure approach will most likely be used to accomplish this task? 137. The Bledsoe Marketing Research group has been hired to administer a series of “yes/no” questions to shoppers in a local mall. If questions on a survey have only two possible answers (such as “yes/no” questions), what type of questions are these? 138. A marketing manager would like to ask a few simple questions of his or her company’s target market (a population). If the manager would like to ensure that every member of that population has an equal chance of being chosen for questioning, the manager would need to select which sampling method? Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 139. Describe what might occur in an intercept interview. What are the chief disadvantages of this method of contact? 140. List the four advantages of conducting marketing research online. Page: 113 141. Describe (define) a marketing decision support system (MDSS). 142. Describe how ethical marketing assists a desire to have good marketing research. 143. Many managers see marketing research as a fact-finding operation. Is this a correct view? Explain. 152 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 144. List four external marketing metrics that will be useful for the marketing researcher. 145. Sales analysis uses two specific tools for measuring and evaluating actual sales in relation to goals. What are those two tools? Page: 119 146. Annual-plan control requires making sure that the company is not overspending to achieve sales goals. What key ratio is watched closely? How are fluctuations of this ratio tracked? 147. If a researcher is interested in the qualified available market, how would you describe this market? 148. It is often necessary for marketers to understand the nature of market demand. Define market demand. 149. What is the difference between company demand and a company sales forecast? Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process time period. The company sales forecast is the expected level of company sales based on a chosen marketing plan and an assumed marketing environment. Page: 129 150. Create a question and an associated scale that illustrate a purchase probability scale. Page: 133 Chapter 5: Creating Customer Value, Satisfaction, and Loyalty GENERAL CONCEPT QUESTIONS Multiple Choice 78. are adept at building customer relationships, not just products; they are skilled in market engineering, not just product engineering. a. Profit-centered companies b. Customer-centered companies c. Production-centered companies d. Sales-centered companies e. Promotion-centered companies Page: 139 79. The opening vignette on Washington Mutual indicates that, as the Washington Mutual experience shows, successful marketers are the ones that fully . a. understand promotional strategy b. diversify their product line c. divorce themselves from a production mentality d. satisfy their customers e. understand the sales concept Page: 140 80. In the modern customer-oriented organizational chart, which of the following is considered to be at the top of the organizational pyramid? f. Sales are at the top of the organizational pyramid. g. The president is at the top of the organizational pyramid. h. Front-line people are at the top of the organizational pyramid. 154 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships i. Customers are at the top of the organizational pyramid. j. Middle management, because of their importance, is at the top of the organizational pyramid. Page: 140 155 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 81. is the difference between the prospective customer’s evaluation of all the benefits and all the costs of an offering and the perceived alternatives. a. Perceived usefulness b. Failure avoidance rate c. Report rating d. Customer perceived value e. Competitors market share rate Page: 141 82. Total customer value is the perceived monetary value of the bundle of economic, functional, and benefits customers expect from a given market offering. a. psychological b. intangible c. realized d. fabricated e. advertised Page: 141 83. The bundle of costs customers expect to incur in evaluating, obtaining, using, and disposing of the given market offering, including monetary, time, energy, and psychic costs is called the . a. organizational expense ratio b. shopper’s fatigue c. total customer cost d. analysis paralysis e. comparison shopping to comparison buying ratio Page: 141 84. In applying a customer’s perceived value to a decision, a seller who is at a customer perceived value disadvantage has two alternatives: to increase total customer value or . a. increase a cash-back bonus b. decrease cost c. lose the sale to the competitor d. advertise more frequently e. offer an extended warranty Page: 143 85. The consists of the whole cluster of benefits the company promises to deliver; it is more than the core positioning of the offering. a. customer promise b. mission statement c. corporate pledge d. corporate perceived value e. value proposition Page: 143 86. Total customer satisfaction is measured based on the relationship of . a. anticipated and real performance b. perceived performance and expectation c. advertised outcomes and real outcomes 156 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships d. past experience and present experience e. customer attitude and salesperson’s attitude Page: 144 87. Buyers form their expectations from all of the following EXCEPT . a. past buying experience b. friends and associates advice c. marketers’ information d. competitors’ information e. governmental newsletters Page: 144 88. JetBlue is able to meet or exceed customer expectations of low price air travel in part to a few corporate commandments like: safety, caring, integrity, fun and passion. JetBlue refers to these as . a. teamwork parables b. values c. satisfaction indices d. customer focus statements e. JetBlue benefits Page: 144 89. A customer’s decision to be loyal or to defect is the sum of many small encounters with the company. Consulting firm Forum Corporation says that in order for all these small encounters to add up to customer loyalty, companies need to create . a. a reward program b. a comprehensive customer database c. a branded customer experience d. strong word-of-mouth promotions e. a top-notch advertising campaign Page: 144 90. One key to customer retention is . It would be wise for a company to measure this factor frequently. a. heavy promotion b. deep discounts for intermediaries c. to have an ethics officer d. customer satisfaction e. to have customers on the board of directors Page: 145 157 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 91. The best survey method to measure customer satisfaction directly is . a. to employ a mystery shopper b. the mailed questionnaire c. to survey former customers d. periodic surveys e. compute the customer loss rate Page: 146 92. Which of the following firms leads its industry with a number one ranking for customer satisfaction on the ACSI scale (American Consumer Satisfaction Index) with a score of 87? a. Cadillac b. Ford c. Chrysler d. Chevrolet e. Corvette Page: 146 93. is the totality of features and characteristics of a product or service that bear on its ability to satisfy stated or implied needs. a. Performance b. Value c. Quality d. Customer retention e. Customer loyalty Page: 146 94. Total quality is the key to value creation and customer satisfaction. Marketing managers have two roles to play in a quality-centered company. First, they must participate in formulating strategies and policies to help the company win through total quality excellence. Second, they must . a. participate in cross-functional team building b. deliver marketing quality alongside production quality c. define customer requirements during the innovation stage of the product life cycle d. set expectations both internally and externally e. work closely with the sales team to create a dynamic sales message Page: 147 95. is an organization-wide approach to continuously improving the quality of all the organization’s processes, products, and services. a. Total quality management b. Strategic management c. Profit-centered management d. Customer-retention management e. Total customer control management Page: 147 158 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 96. The 20-80-30 rules reflects the idea that . a. the top 20 percent of customers generate 80 percent of the company’s profits, half of which are lost serving the bottom 30 percent of unprofitable customers b. the top 20 percent of customers are highly satisfied, 80 percent of customers will recommend the company to a friend, and 30 percent are unsatisfied c. 20 percent of customers are unprofitable, 80 percent of customers make up 30 percent of a company’s profits d. 20 percent of the company’s profits are generated by 80 percent of customers, and 30 percent of customers are satisfied e. any new product offering will be accepted by 20 percent of the customers immediately, this figure will eventually rise to 30 percent, however, 80 percent of the customers will be up for grabs throughout the product life cycle for the product Page: 148 97. Most companies have learned that the are the most profitable because of service expectations and their willingness to pay almost full price for the products they purchase. a. large-size customers b. midsize customers c. small-size customers d. niche customers e. target market customers Page: 148 98. A customer is a person, household, or company that over time yields a revenue stream that exceeds by an acceptable amount the company’s cost stream of attracting, selling, and servicing that customer. a. profitable b. semi-profitable c. unprofitable d. niche e. target Page: 149 99. Customer profitability analysis (CPA) is best conducted with the tools of an accounting technique called . a. input-output analysis b. factor analysis c. Revenue-Based Costing (RBC) d. Activity-Based Costing (ABC) e. Future Date Costing (FDC) Page: 149 159 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 100. Which of the following is the best example of what is called a leverageable advantage? a. Dell avoiding selling its products in retail stores. b. Apple winning design awards and producing unique commercials. c. Microsoft’s use of its operating system to Microsoft Office as a means to supply networking applications. d. Southwest Airlines winning the J.D. Power award. e. American tobacco companies attempts to diversify their holdings after the famous tobacco case losses. Page: 150 101. Taco Bell has determined that keeping customers satisfied can be very profitable. A repeat customer in Taco Bell’s eyes can be worth as much as over the customer’s lifetime. a. $100,000 b. $61,000 c. $35,000 d. $11,000 e. $2,000 Page: 150 102. The aim of customer relationship management (CRM) is to produce high customer . a. value b. loyalty c. profitability d. satisfaction e. equity Page: 151 103. The three drivers of customer equity are: value equity, brand equity, and equity. a. relationship b. revenue c. quality d. price e. product Page: 151 104. Sub-drivers of relationship equity include all of the following EXCEPT . a. loyalty programs b. special recognition and treatment programs c. community building programs d. knowledge-building programs e. price protection programs Page: 151 105. An alternative formulation to customer equity is provided by Blattberg, Getz, and Thomas. They view customer equity as being driven by three components: acquisition, , and add-on selling. 160 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships a. satisfaction b. retention c. perceived value d. quality e. pricing Page: 151 106. is seen as the cumulative value of the firm’s network of relationships with its customers, partners, suppliers, employers, and investors. a. Responsive equity b. Market equity c. Relational equity d. Strategic equity e. Satisfaction equity Page: 152 107. The ability of a company to meet each customer’s requirements—to prepare on a mass basis individually designed products, services, programs, and communications, is referred to as . a. proactive customer service b. individualization c. mass customization d. competitive advantage e. target market customization Page: 152 108. A customer touch point in the airline industry would include an item such as . a. reservations b. mechanics ability to service the airplanes c. ease of access to the airport d. the value of air travel versus surface transportation e. competency of a travel agent Page: 152 109. All of the following would be among the Peppers and Rogers’s four-step framework for one-to-one marketing that can be adapted to CRM marketing EXCEPT . a. customizing products, services, and messages to each customer b. interacting with individual customers to learn their needs c. always offering the lowest price d. differentiating customers in terms of their needs and value to the company e. identify your prospects and customers Page: 154 110. Winning companies improve the value of their customer base by excelling at strategies listed below EXCEPT . a. eliminating low-profit customers immediately b. reducing the rate of customer defection c. increasing the longevity of the customer relationship d. making low-profit customers more profitable or terminating them 161 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process e. focusing disproportionate efforts on high-value customers Page: 154 111. Which of the following is a characteristic of one-to-one marketing? a. Mass promotion b. Standard product c. Two-way messages d. Share of market e. Customer attraction Page: 155 112. Another term for high customer is customer churn. a. retention b. defection c. value d. perception e. belief Page: 155 113. Markets can be characterized by their long-term buying dynamics and how easily and often customers can enter and leave. In , customers can leave and come back. a. permanent capture markets b. simple retention markets c. advocate markets d. simple competitive markets e. customer migration markets Page: 156 114. In marketing, the salesperson contacts the customer from time to time with suggestions about improved product uses or new products. a. accountable marketing b. proactive marketing c. reactive marketing d. partnership marketing e. basic marketing Page: 157 162 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 115. Most company’s practice only when their markets contain many customers and their unit profit margin(s) are small. a. reactive marketing b. partnership marketing c. basic marketing d. proactive marketing e. accountable marketing Page: 157 116. In markets with few customers and high profit margins, most sellers will move toward marketing. a. reactive marketing b. partnership marketing c. basic marketing d. proactive marketing e. accountable marketing Page: 157 117. The CRM (customer relationship management) imperative is characterized by five steps or factors. All of the following would be among those steps or factors EXCEPT . a. acquiring the right customer b. crafting the right value proposition c. instituting the best processes d. motivating employees e. learning to make profits through marginal customers Page: 158 118. When companies provide rewards to customers who buy frequently and in substantial amounts, this is referred to as . a. benefit programs b. frequency programs c. satisfaction programs d. loyalty programs e. quality programs Page: 159 119. Frequency marketing is an acknowledgment of the fact that 20 percent of a company’s customers might account for percent of its business. a. 50 b. 70 c. 40 d. 80 e. 90 Page: 159 120. Companies who try to increase a customer’s likelihood to repurchase a product may try to create long-term contracts, turn the product into a long-term service, and . a. send frequent surveys 163 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process b. offer coupons c. charge lower prices to customers who purchase large supplies d. request the customer join their loyalty program e. encourage customers to purchase in greater frequency Page: 162 121. An organized collection of comprehensive information about individual customers or prospects that is current, accessible, and actionable for such marketing purposes as lead generation, lead qualification, sale of a product or service, or maintenance of customer relationships is called . a. a customer database b. a customer mail list c. target market segments d. customer segments e. relationship markets Page: 162 122. The process of building, maintaining, and using customer databases and other databases for the purpose of contacting, transacting, and building customer relationships is called . a. data warehousing b. datamining c. database marketing d. custom marketing e. electronic marketing Page: 162 123. A is simply a set of names, addresses, and telephone numbers. a. customer database b. customer mailing list c. call-waiting list d. psychographic list e. demographic list Page: 163 124. A customer database should contain all of the following EXCEPT . a. a customer’s past purchases b. demographics c. psychographics d. mediagraphics e. an assessment of competitive strengths and weaknesses Page: 163 125. A would contain such items as past volumes, prices, profits, buyer team names, status of current contacts, and an assessment of competitive strengths and weaknesses. a. customer mailing list b. contact list c. customer database d. business database e. general corporate database 164 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships Page: 163 126. Savvy companies are capturing information every time a customer comes into contact with any of its departments. As a marketing manager all of the following would be available customer touch points for your consideration EXCEPT . a. a customer purchase b. an online query c. a mail-in rebate card d. an ad run on a national television network e. a customer-requested service call Page: 163 127. James Everett is a telemarketer. He can use his company’s to respond to customer inquiries more effectively because of his ability to see a total picture of the customer relationship. a. data warehouse b. call back list c. call rejection list d. corporate database e. Better Business Bureau contacts Page: 164 128. Through , marketing statisticians can extract useful information about individuals, trends, and segments from the mass of data. a. data accumulation b. target market information supplied by the government c. datamining d. data management e. data marketing Page: 164 165 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 129. involves the use of sophisticated statistical and mathematical techniques such as cluster analysis, automatic interaction detection, predictive modeling, and neural networking. a. Data management b. Data marketing c. Target market analysis d. Data accumulation e. Datamining Page: 164 130. In general, companies can use their databases in all of the following ways EXCEPT . a. to predict competitive strategies and plans b. to identify prospects c. to decide which customers should receive a particular offer d. to deepen customer loyalty e. to avoid serious customer mistakes Pages: 164–165 131. Susan Lefferts’ company advertises widely. In each magazine ad, a business reply card is attached. Ms. Lefferts uses these cards to build her company’s database. In which of the following ways would Ms. Lefferts most likely be using the newly constructed database? a. To deepen customer loyalty. b. To reactivate customer purchases. c. To avoid serious customer mistakes. d. To determine if up-selling is appropriate. e. To identify prospects. Page: 164 132. Phil Langston has just ordered a number of expensive executive gifts that he will be sending as an appreciation token to a select few customers from his client database. In which of the following ways is Mr. Langston most likely using his database? a. To identify prospects. b. To decide which customers should receive a new sales offer. c. To deepen customer loyalty. d. To avoid serious customer mistakes. e. To beat the competition to a sale. Page: 165 166 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 133. Royal Caribbean uses its to offer spur-of-the-moment cruise packages to fill all the berths on its ships. It focuses on retired people and single people because they are more able to make quick commitments. a. advertising b. database c. mail catalogs d. public relations department e. radio advertising Page: 164 134. Which of the following is considered to be one of the four problems that can deter a firm from using CRM (customer relationship marketing)? a. Competitors can often hack into CRM systems. b. Building and maintaining a customer database requires a large investment. c. It is very difficult to find and train database employees. d. Long-term results of such systems are still unproven. e. Focusing too much on databases separates a company from its customers. Page: 165 135. Building a database would not be worthwhile for a company in all of the following cases EXCEPT . a. where the product is a one-in-a-lifetime purchase b. where customers show little loyalty to a brand c. where the company already has an above average relationship with its customers d. where the unit sale is very small e. where the cost of gathering the information is too high Page: 165 136. A study estimated the average return on investment for a data warehouse over the course of three years is more than . a. 400 percent b. 200 percent c. 100 percent d. 85 percent e. 75 percent Page: 166 137. All of the following are considered to be among the main perils of CRM EXCEPT . a. implementing CRM before creating a customer strategy b. the enormous cost that might eventually drain significant profits from the organization c. rolling out CRM before changing the organization to match d. assuming more CRM technology is better e. stalking, not wooing customers Page: 167 167 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process True/False 61. Managers who believe the customer is the company’s only true “profit center” consider the traditional organization chart to be obsolete. Page: 140 62. The modern customer-oriented organization chart places top management at the top of the pyramid as long as they can think like consumers. Page: 140 63. There are two determinates of customer delivered-value: total customer value and total customer cost. Page: 141 64. Customer perceived value (CPV) is the difference between the prospective customer’s evaluation of all the benefits and all the costs of an offering and the perceived alternatives Page: 141 65. Total customer value is the perceived monetary value of all the purchases a customer makes on an annual basis. Page: 141 66. Professional buyers and purchasing agents operate under various constraints and occasionally make choices that give more weight to their personal benefit than to the company’s benefit. Page: 142 67. The value proposition is stated in the price of a product and readily recognized by the average consumer. Page: 143 68. The value-delivery system includes all the experiences the customer will have on the way to obtaining and using the offering. Page: 143 69. For a consumer to be delighted with a product or service he or she must perceive that performance exceeds expectations. Page: 144 70. The ultimate goal of the customer-centered firm is to create high customer satisfaction. Page: 144 71. The key to customer retention is customer satisfaction. Page: 145 72. At the top of the package delivery industry with a satisfaction index score of 82 is FedEx. Page: 146 168 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 73. Price-perception is the totality of features and characteristics of a product or service that bear on its ability to satisfy stated or implied needs. Page: 146 74. Conformance quality and performance quality is essentially the same thing in a marketing sense. Page: 147 75. Total quality management (TQM) is a production department approach to continuously improving the quality of all the production processes. Page: 147 76. Marketers have found that the most essential role to be played in defining and delivering high-quality goods and services to target customers is that of price (e.g., price it right and it will sell). Page: 148 77. The midsize customers for most organizations receive good service, pay nearly full price for the products and services they purchase, and are often the most profitable. Page: 148 78. A profitable customer is a person, household, or company that over time yields a revenue stream that exceeds by an acceptable amount the company’s cost stream of attracting, selling, and servicing the customer. Page: 149 79. Most companies measure customer satisfaction and individual customer profitability. Page: 149 80. Unprofitable customers who defect to a competitor should be encouraged to do so. Page: 149 81. Customer profitability analysis (CPA) is best conducted with the tools of an accounting technique called Activity-Based Costing (ABC). Page: 149 82. According to customer profitability analysis (CPA), platinum customers spend the most money with the organization thereby making them valuable. Page: 149 83. Any competitive advantage must be seen by customers as a customer advantage. Page: 150 84. Customer lifetime value (CLV) describes the net present value of the stream of future profits expected over the customer’s lifetime purchases. Page: 150 169 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 85. Carl Sewell, in Customers for Life, estimated that a customer entering his car dealership for the first time represents a potential lifetime value of over $300,000. Page: 150 86. The aim of customer relationship management is to keep the costs of meeting and tracking consumers as low as possible. Page: 151 87. Brand equity is the customer’s objective assessment of the utility of an offering based on perceptions of its benefits relative to its costs. Page: 151 88. Customer equity is driven by three components: acquisition, retention, and add on selling. Page: 151 89. A good illustration of a personal touch in the hotel business would be if the hotel employees (e.g., registration, maid service, et cetera) call a guest by his or her name. Page: 152 90. A customer touch point is the time when the customer makes a purchase. Page: 152 91. A key driver of shareholder value is the aggregate value of the customer base. Page: 154 92. One of the characteristics of mass marketing is using a one-way message in promotions. Page: 155 93. Customer churn is how rapidly a store can move customers through its checkout facility or process. Page: 155 94. Ninety-six percent of dissatisfied customers don’t complain; they just stop buying. Page: 155 95. The average company loses 25 percent of its customers each year. Page: 156 170 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 96. A good description of a permanent capture market would be “once a customer, always a customer.” Page: 156 97. In proactive marketing the salesperson simply sells the product. Page: 157 98. A customer database is simply a listing of a customer’s name, address, and phone number for credit reference. Page: 162 99. Cluster analysis is a good example of a statistical technique that might be employed in datamining. Page: 164 100. Database marketing is most frequently used by business marketers and service providers (hotels, banks, airlines, and insurance, credit card, and telephone companies) that normally and easily collect a lot of customer data. Page: 166 Essay 101. Compare and contrast the traditional organizational chart for an organization against the modern customer-oriented organization chart. 102. Provide a customer-centered definition of the term quality. 171 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 103. Describe the concept of competitive advantage. Discuss the differences between competitive advantage and leverageable advantage. Page: 150 151. Discuss the differences among customer equity, value equity, brand equity, and relationship equity. 152. Peppers and Rogers outline a four-step framework for one-to-one marketing that can be adapted to CRM marketing. What are those four steps? Pages: 153–154 153. Characterize the five levels of investment in customer relationship building that a company can follow. 172 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 154. Today, companies are increasingly concerned about customer defection. There are five main steps a company can take to reduce the defection rate. Characterize those five steps. 155. Discuss the concepts of a data warehouse and datamining. Suggested ata are collected by the company’s contact center and organized into a data warehouse. Company personnel can capture, query, and analyze the data. Inferences can be 156. Assume that a marketing manager of a small company is in the process of implementing the use of a database to assist his or her company in its marketing efforts. Considering the information found in the text, list five ways that the marketing manager might be able to use the database for marketing Pages: 164–165 157. Describe four situations or cases when building a customer database would not be worthwhile for a company. 173 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process APPLICATION QUESTIONS Multiple Choice 158. John Chambers, CEO of Cisco Systems, said “Make your customer the center of your culture.” Customer-centered companies are adept at building customer relationships, not just producing products; they are skilled in , not just product engineering. a. service engineering b. market engineering c. cultural engineering d. innovation engineering e. management engineering Page: 139 159. Next to the customers in a modern customer-oriented organization chart, we would expect to find the of an organization. a. top management b. marketing department c. middle management d. front-line people e. service department Page: 140 160. eBay sees listening, adapting, and enabling as its main roles. This is clear in one of the company’s most cherished institutions: . a. the Midnight Madness Bid b. ecological concern c. truth in advertising d. the Voice of the Customer program e. the Immediate Buyback Program Page: 141 161. If you were to write a good working definition of the term total customer value, you should write . a. the sum of value times (X) expectation b. the sum of customer perceived value and actualized value c. the perceived monetary value of the bundle of economic, functional, and psychological benefits customers expect from a given market offering d. the difference between the prospective customer’s evaluation of all the benefits and all the costs of an offering and the perceived alternatives e. the concept is simply a bundle of costs and expectations Page: 141 174 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 162. When a consumer considers a product or service, he or she will choose whichever product or service delivers the highest . a. customer perceived value b. customer perceived cost c. consumer discount d. consumer relationship e. consumer synergy Page: 141 163. Buyers do not always make logical or rational decisions. They might purchase the most expensive and least quality item for example. Which of the following would be another good example of this behavior? a. The buyer is not seen by the seller as being very intelligent. b. The buyer might be under orders to buy at the lowest price. c. The buyer might be underage. d. The buyer might be under pressure to resist sales messages. e. The buyer refuses to listen to or read any advertising. Answer: b Page: 142 164. If a company were to focus its marketing efforts on all the experiences the customer will have on the way to obtaining and using the offering, it would be focusing its marketing efforts on the customer’s . a. perception system b. cost versus benefit system c. demand d. psychological system e. value-delivery system Page: 143 165. Whether the buyer is satisfied after purchase depends on the offer’s performance in relation to the . a. buyer’s reactions b. buyer’s expectations c. seller’s delivery d. seller’s expectations e. both the buyer’s and seller’s demands Page: 144 175 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 166. All of the following are ways that a buyer forms his or her expectations EXCEPT . a. from past buying experience b. from friends’ and associates’ advice c. from marketers’ information d. from competitors’ information e. from inherited traits Page: 144 167. JetBlue Airways has significantly raised customer expectations by following what JetBlue calls the Values. All of the following would be considered to be among those Values EXCEPT . a. safety b. frugality c. caring d. integrity e. fun Page: 144 168. The Field Grocery system is considering using to pose as potential buyers and report on strong and weak points experienced in the buying the company’s and competitors’ products. a. intelligence agents b. covert operatives c. mystery shoppers d. market mavens e. opinion leaders Page: 146 169. All of the following companies have been deemed to be leaders in their respective industries because of high consumer satisfaction scores (e.g., American Satisfaction Index [ACSI]) EXCEPT . a. Dell (78) b. Cadillac (87) c. Google (82) d. Yahoo! (78) e. U.S. Post Office (75) Page: 146 176 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 170. Marketing managers have two responsibilities in a quality-centered company. First, they must participate in formulating strategies and policies to help the company win through total quality excellence. Second, . a. they must always have the lowest price in their industry b. they must deliver marketing quality alongside production quality c. they must have been approved by the J.D. Power and Associates d. they must use six-Sigma e. they must provide instant feedback from consumers Page: 147 171. Advocates of would be in favor of improving quality only on those dimensions that produce tangible customer benefits, lower costs, or increase sales. a. TQM (total quality management) b. PLC (product life cycle management) c. ROI (return on investment) d. ROQ (return on quality) e. ROP (return on promotion) Page: 148 172. According to research done by American Express, the best customers outspend those that are considered to be the best customers by significant margins. For example, in retailing the best customers outspend other customers by a ratio of . a. 16 to 1 b. 13 to 1 c. 12 to 1 d. 5 to 1 e. 3 to 1 Page: 148 173. With respect to customer profitability analysis (CPA), the customers are the most likely dropped as customers because of poor profitability. a. granite b. wood c. iron d. plastic e. lead Page: 149 177 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 174. Nike lets consumers customize athletic shoes for $10 more. A shopper with two different size feet can even get a non-matching pair. This would be an example of which of the following? a. Mass marketing. b. Environmental marketing. c. Mass customization. d. Individualization. e. Niche marketing. Page 152 175. 3M makes it easy for dialog to occur with its customers. 3M claims that over two-thirds of its product improvement ideas come from listening to . a. customer suggestions b. entrepreneurial product ideas c. customer complaints d. media feedback e. customer reactions to competitive products Page: 155 176. With respect to the CRM Imperative, “you get it” when . a. you eliminate all your strong competitors b. you have selected the most beneficial promotion channels c. you have learned how to outsource d. you develop a Web presence e. you have identified your most valuable customers Page: 158 177. The skillful use of database marketing and has made catalog house Fingerhut one of the nation’s largest direct-mail marketers. a. everyday low prices b. expanded home delivery options c. relationship building d. competitor’s mistakes e. retailer alliances Page: 164 178 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships Short Answer 178. What do managers believe is their company’s only true “profit center”? 179. Customer delivered value is based on two components. What are those components? 180. What is the definition for customer perceived value (CPV)? 181. Using European automobile giant Volvo as your illustration, create a value proposition for the company. Be sure to base your proposition on established company core positions and values. Page: 143 135. Define the term quality. 136. Sherden suggests amending the 20-80 rule to read “the 20-80-30 rule.” Interpret the meaning of “20-80-30.” 137. What are the three ways that customer profitability can be assessed? Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process Page: 149 138. What are the four classifications (tiers) of customers in customer profitability analysis using Activity-Based Costing? 139. According to Rust, Zeithaml, and Lemon, what are the three drivers of customer equity? 140. Explain the concept of mass customization. Page: 152 141. What is a customer touch point? 142. If characteristics of mass marketing were average customer, share of market, and customer attraction, what would be the associated one-to-one marketing characteristics that would match? 143. Markets can be characterized by their long-term buying dynamics and how easily and often customers can enter and leave. List and briefly characterize three such markets. 144. Explain the concept of proactive marketing. Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships Page: 157 145. Explain how a company frequency program might work. 146. Using information provided in the text, create three suggestions for creating structural ties with a customer. 147. Describe the process of database marketing. 148. According to information provided in the text, give one of the three forms of estimate with respect to increasing customer share of requirements. Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 149. Give an illustration of how a company can use a customer database to reactivate customer purchases. 150. According to information provided in the text, what are the four main perils of CRM? Chapter 6: Analyzing Consumer Markets GENERAL CONCEPT QUESTIONS Multiple Choice 138. Marketers are always looking for emerging trends that suggest new marketing opportunities. One such trend is the “metrosexual.” Which of the following items would the metrosexual most likely have some interest for? a. An IBM computer. b. Tickets to WWF wrestling. c. Saxophone lessons. d. An all-over body spray by Axe. e. Cowboy boots made from elephant hide. Page: 173 2. is the study of how individuals, groups, and organizations select, buy, use, and dispose of goods, services, ideas, or experiences to satisfy their needs and wants. a. Target marketing b. Psychographic segmentation c. Psychology d. Consumer behavior f. Product differentiation Page: 173 3. The fundamental determinant of a person’s wants and behavior is the person’s . 182 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships a. psyche b. national origin c. culture d. peer group e. family tree Page: 174 4. A child growing up in the United States is exposed to all of the following values EXCEPT . a. achievement and success b. activity c. efficiency and practicality d. the importance of the group in daily life e. freedom Page: 174 183 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 5. Which of the following would be the best illustration of a subculture? a. A religion. b. A group of close friends. c. Your university. d. A fraternity or sorority. e. Your occupation. Page: 174 6. With respect to facts about the American consumer, which of the following consumer electronics is owned by the vast majority of consuming households with a 93 percent reporting ownership? a. A personal computer. b. TiVo DVR. c. A cellular phone. d. A microwave oven. e. A VCR. Page: 175 7. is defined as being relatively homogeneous and enduring divisions in a society, which are hierarchically ordered and whose members share similar values, interests, and behavior. a. Culture b. Subculture c. Social class d. The family e. A group Page: 175 8. Social classes show distinct product and brand preferences in all the following areas EXCEPT . a. clothing b. home furnishings c. leisure activities d. automobiles e. fast food Page: 176 9. A person’s consist(s) of all the groups that have a direct (face-to-face) or indirect influence on his/her attitudes or behavior. a. culture b. subculture c. psychographics d. reference groups e. demographics Page: 177 10. A(n) group is one whose values or behavior an individual rejects. a. aspirational b. disassociative c. membership 184 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships d. primary e. procreational Page: 177 11. If a direct mail marketer wished to direct promotional efforts toward the family of , efforts need to be directed toward parents and siblings of the family members. a. orientation b. procreation c. immediacy d. intimacy e. reference Page: 177 12. Expected to account for a quarter of the U.S. population by 2050, are the fastest growing minority. a. African Americans b. Asian Americans c. Hispanic Americans d. European Americans e. Arabic Americans Page: 178 13. The dominant cohort, with respect to families, for the next fifty years may very well be the cohort. a. married-couple household b. single adults c. single seniors d. married seniors e. married-couples with parents living with them Page: 179 14. Husbands and wives display different decision-making roles in most families. The trend for dominant decision making in families is for to be responsible for most of the decisions. a. the husband b. the wife c. joint decision making (both husband and wife) d. holistic decision making e. child-oriented decision making Page: 179 15. The Disney Channel has become the company’s cash cow for its ability to reach the underserved market—8- to 14-year-olds. a. teen b. twixt c. mid- d. tween e. young adult Page: 179 185 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 16. People choose products that reflect and communicate their role and actual or desired in society. a. group b. status c. attitudes d. beliefs e. feelings Page: 180 17. Consumption may be shaped by (such as marriage, childbirth, or divorce). a. the psychological life cycle b. the product life cycle c. the life/death life cycle d. post-puberty cycles e. critical life events or transitions Page: 181 18. Product choice is greatly affected by economic circumstances. All of the following would be among those circumstances EXCEPT . a. spendable income b. savings and assets c. debts d. occupation e. borrowing power Page: 182 19. is a set of distinguishing human psychological traits that lead to relatively consistent and enduring responses to environmental stimuli. a. Image b. Personality c. Beliefs d. Heredity e. Culture Page: 182 186 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 20. When the Marlboro Man was depicted in advertising as a rugged outdoor, tough cowboy type, this was done to establish what is called a . a. trademark b. brand name c. brand personality d. psychological approach to advertising e. brand reference Page: 182 21. portrays the “whole person” interacting with his or her environment. a. Attitude b. Reference group c. Lifestyle d. Culture e. Subculture Page: 183 22. Consumers today are experiencing a time famine because of their busy lifestyles. One way to avoid the difficulties of time famine, which is of particular interest to marketers, is . a. to set fewer goals b. to multitask c. to give in to personal burdens d. to report frustration to management e. to develop a callous attitude toward marketers Page: 183 23. With respect to understanding consumer behavior, there are four key psychological processes. All of the following would be among those processes EXCEPT . a. motivation b. perception c. learning d. self-reliance e. memory Page: 184 24. A when it is aroused to a sufficient level of intensity. a. need becomes a motive b. motive becomes a need c. desire becomes a reality d. unfulfilled demand becomes a crisis e. personal demand exceeds the ability to rationally reject Page: 184 25. assumed that the psychological forces shaping people’s behavior are largely unconscious, and that a person cannot fully understand his or her own motivations. a. Abraham Maslow b. Frederick Herzberg c. Sigmund Freud 187 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process d. John Cacioppo e. Karl Marx Page: 184 26. Frederick Herzberg developed a that distinguishes dissatisfiers and satisfiers. a. trait-role theory b. psychological constraint theory c. probability scale d. leadership model e. two-factor theory Page: 185 27. At the top of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs (shown as a pyramid in the text) are needs. a. esteem b. self-actualization c. social d. safety e. physiological Page: 185 28. It has been estimated that the average person is exposed to over ads or brand communications a day. a. 1,500 b. 1,300 c. 1,000 d. 800 e. 500 Page: 186 29. is the tendency to interpret information in a way that will fit our preconceptions. a. Selective retention b. Cognitive dissonance c. Selective distortion d. Subliminal perception e. Discrimination Page: 186 30. A cigarette ad has a picture of a young man laying on his back and dreamily looking at clouds in the sky. Though not readily obvious to the casual reader, there is a message in the clouds that says “r-e-l-a-x.” This would be an example of which of the following? a. Selective distortion b. Cognitive dissonance c. Selective retention d. Subliminal perception e. Short-term memory Page: 187 188 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 31. A is a strong internal stimulus impelling action. a. cue b. drive c. reinforcement d. discrimination e. belief Page: 187 32. teaches marketers that they can build demand for a product by associating it with strong drives, using motivating cues, and providing positive reinforcement a. Demand theory b. Learning theory c. Economic theory d. Psychological theory e. Demographic theory Page: 187 33. As Rita scans the yellow pages section of her phone book looking for a florist, she sees several others products and services advertised. Though interesting on first glance, she quickly returns to her primary task of finding a florist. The items that distracted her from her search were most likely stored in which of the following types of memory? a. Short-term memory b. Long-term memory c. Middle memory d. Subconscious memory e. Subliminal memory Page: 187 189 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 34. Brand associations consist of all the brand-related thoughts, feelings, perceptions, images, experiences, beliefs, attitudes, and so on that become linked to the brand . a. stimulus b. link c. connection d. personality e. node Page: 188 35. In general, the more attention placed on the meaning of information during , the stronger the resulting associations in memory will be. a. encoding b. decoding c. classification d. retrieval e. memorization Page: 189 36. Repeated exposures to information provide greater opportunity for processing and thus the potential for . a. more profits b. more sales c. stronger associations d. increased brand personality e. more one-to-one relationships Page: 190 37. Cognitive psychologists believe that memory is , so that once information becomes stored in memory, its strength of association decays very slowly. a. very limited b. somewhat limited c. fluid d. often reflective e. extremely durable Page: 191 38. The five-stage model of the consumer buying process includes all of the following stages EXCEPT . a. problem recognition b. information search c. social interaction d. purchase decision e. influencer Page: 191 190 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 39. The buying process starts when the buyer recognizes a . a. product b. an advertisement for the product c. a salesperson from a previous visit d. problem or need e. an internal cue Page: 191 40. Which of the following is considered to be a more advanced form of information search wherein the person might phone friends or go online to secure information about a product or service? a. Heightened attention b. Short-term memory processing c. Subliminal processing of information d. Long-term memory processing e. Active information search Pages: 191–192 41. Of key interest to marketers are the major informational sources to which the consumer will turn and the relative importance of each. Which of the following would be considered to be an experiential information source? a. Consumer-rating organizations. b. The mass media. c. Acquaintances. d. Web sites. e. Using the product itself. Page: 192 42. Which of the following is considered to be biggest single source of consumer information from a commercial source (over 40 percent of car buyers use this source to gather information)? a. The U.S. Chamber of Commerce b. J.D. Power & Associates c. Consumer Reports d. The Better Business Bureau e. Underwriter’s Laboratory Page: 192 43. Brands that meet consumers’ initial buying criteria are called the . a. total set b. awareness set c. consideration set d. choice set e. decision set Page: 192 44. With respect to consumer decision making, the is the set of strong contenders from which one will be chosen as a supplier of a good or service. a. total set b. awareness set c. consideration set 191 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process d. choice set e. decision set Page: 192 45. A(n) is a descriptive thought that a person holds about something. a. attitude b. belief c. desire d. feeling e. emotion Page: 193 46. A(n) puts people into a frame of mind: liking or disliking an object, moving toward or away from it. a. attitude b. belief c. feeling d. position e. stance Page: 194 47. The expectancy-value model of attitude formation posits that consumers evaluate products and services by combining their . a. needs b. wants c. desires d. brand beliefs e. consuming attitudes Page: 194 48. All of the following would be considered to be strategies for approaching consumers who had rejected your company’s model of a product for another competitive brand EXCEPT . a. redesign your company’s product b. alter beliefs about your company’s brand c. covertly alter the qualitative data about your product d. alter beliefs about competitors’ brands e. call attention to neglected attributes Pages: 195–196 49. Customer value analysis reveals the company’s strengths and weaknesses relative to various competitors. Which of the following would be considered to be the first step in this process? a. Monitor customer values over time. b. Assess the quantitative importance of the different attributes. c. Assess the company and competitors’ performances on customer values. d. Identify the major attributes customers value. e. Examine customer ratings of the company and competitors. Page: 196 192 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 50. With respect to consumer purchase intention, all of the following would be among the sub-decisions made by consumers EXCEPT . a. emotional value b. brand c. dealer d. timing e. payment method Pages: 196–197 51. With the heuristic, the consumer sets a minimum acceptable cutoff level for each attribute and chooses the first alternative that meets the minimum standard for all attributes. a. conjunctive b. lexicographic c. elimination-by-aspects d. primary e. secondary Pages: 197 52. Even if consumers form brand evaluations, two general factors can intervene between the purchase intention and the purchase decision. One of these is unanticipated situational factors. What is the second factor? a. Amount of purchasing power. b. Attitudes of others. c. Short-term memory capabilities. d. Ability to return merchandise. e. The self-concept. Pages: 197 53. risk occurs if the product fails to perform up to expectations. a. Physical b. Financial c. Social d. Psychological e. Functional Page: 198 54. If performance meets consumer expectations, the consumer is . a. delighted b. satisfied c. disappointed d. surprised e. overwhelmed Page: 198 55. A key driver of sales frequency is the rate. a. product consumption b. disposal c. refusal d. utility e. option 193 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process Page: 199 56. The level of engagement and active processing undertaken by the consumer in responding to a marketing stimulus is called . a. elaboration likelihood b. consumer disengagement c. consumer involvement d. variety-seeking e. low-involvement Page: 200 57. If a consumer is persuaded to buy a product by a message that requires little thought and is based on an association with a brand’s positive consumption experiences from the past, the consumer used a to arrive at this purchase decision. a. central route b. peripheral route c. behavioral route d. subjective route e. objective route Page: 200 58. With the , predictions of usage are based on quickness and ease of use. a. availability heuristic b. representative heuristic c. anchoring heuristic d. adjustment heuristic e. semantic heuristic Page: 201 194 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 59. Ben always reaches for the bright blue and yellow box of Ritz crackers when he visits the snack food aisle in the grocery store. He rarely even reads the box or checks the price. Which of the following heuristics is most likely being used by Ben? a. Availability b. Representative c. Anchoring d. Adjustment e. Semantic Page: 201 60. refers to the manner by which consumers code, categorize, and evaluate financial outcomes of choices. a. Cost accounting b. Financial accounting c. Behavioral accounting d. Mental accounting e. Factual accounting Page: 202 True/False 61. Social class is the fundamental determinant of a person’s wants and behavior. Page: 174 62. An example of a subculture would be a person’s geographic region. Page: 174 63. According to facts about American consumers’ habits, Saturday is the most popular day of the week to eat out. Page: 175 64. One of the characteristics of social classes is that those within each class tend to behave more alike than persons from two different social classes. Page: 175 65. One of the demographic trends that will impact consumers in the future is “America the spacious” meaning that America’s growth potential seems to have no boundaries. Page: 176 66. Secondary groups require continuous interaction to be effective and meaningful. Page: 177 67. When Mark went to college he had a burning desire to join a social fraternity; for Mark, this would be an example of an aspirational group. Page: 177 195 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 68. The family of procreation includes one’s parents and siblings. Page: 177 69. Asian Americans tend to be more brand conscious than other minority groups, but yet are the least loyal to particular brands. Page: 178 70. A role consists of the activities a person is expected to perform. Page: 180 71. A good illustration of a critical life event or transition that might impact a consumer’s behavior is a divorce. Page: 181 72. One of the five traits of a product’s brand personality is thought to be its shape. Page: 182 73. A brand personality is the specific mix of human traits that may be attributed to a particular brand. Page: 182 74. A person’s personality portrays the “whole person” interacting with his or her environment. Page: 183 75. Psychogenic needs arise from physiological states of tension such as hunger or discomfort. Page: 184 76. Abraham Maslow assumed that the psychological forces shaping people’s behavior are largely unconscious, and that a person cannot fully understand his or her own motivations. Pages: 185 77. According to Maslow’s hierarchy of needs model, recognition, self-esteem, and status would be among a person’s social needs. Page: 185 78. According to Herzberg’s two-factor theory, satisfiers will make the major difference as to which brand the customer buys. Page: 185 79. Perception depends only on the physical stimuli experienced by the person. Page: 186 80. People are more likely to notice stimuli whose deviations are large in relation to the normal size of the stimuli. Page: 186 196 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 81. Selective attention is the tendency to interpret information in a way that will fit our preconceptions. Page: 186 82. Because of selective retention, we are likely to forget about the good points of competing products. Page: 186 83. Drives are minor stimuli that determine when, where, and how a person responds. Page: 187 84. Consistent with the elaboration memory model, consumer brand knowledge in memory can be conceptualized as consisting of a brand node in memory with a variety of linked associations. Page: 188 85. Repeated exposures to information provide greater opportunity for processing and thus the potential for stronger associations. Page: 190 86. All consumers pass through all five of the stages of buying process model when in a buying situation. Page: 191 87. The buying process starts when the buyer decides to or actually enters a store or service provider’s facility. Page: 191 88. We can distinguish between two levels of arousal—heightened attention and heightened stimulation sensation. Page: 191 89. A belief is a person’s enduring favorable or unfavorable evaluation, emotional feeling, and action tendencies toward some object or idea. Page: 194 197 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 90. The expectancy-value model of attitude formation posits that consumers evaluate products and services by combining their brand beliefs—the positives and negatives—according to importance. Page: 194 91. If a company finds that a consumer has chosen a competitive product over their company’s offering, one way to get the consumer back could be by developing a strategy wherein the company “shifts the buyer’s ideals” on one or more levels. Page: 196 92. With noncompensatory models of consumer choice, positive and negative attribute considerations usually net out. Page: 197 93. Volvo has the reputation for being one of the most “safe” cars on the road. For those that value safety, Volvo would be the logical choice. The preceding is an example of the lexicographic heuristic of consumer choice. Page: 197 94. If a product poses a threat to the physical well being of a consumer, this is called psychological risk. Page: 198 95. A key driver of sales frequency is the adoption rate. Page: 199 96. With respect to a consumer-buying situation that involves variety-seeking behavior, the market leader can encourage variety seeking by offering lower prices or deals. Page: 200 97. Many products are bought under conditions of low involvement. This means that the consumer does not touch them except from a distance. Page: 200 98. A rule of thumb is called a heuristic. Page: 201 99. In the anchoring heuristic, the consumer bases his or her predictions on the quickness and ease with which a particular example of an outcome comes to mind. Page: 201 100. Prospect theory maintains that consumers frame decision alternatives in terms of gains and losses according to a value function. Page: 203 198 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships Essay 101. Explain the differences between culture, subculture, and social class. Suggested ulture is the fundamental determinant of a person’s wants and behavior. Subcultures provide more specific identification and socialization of their members. Subcultures include nationalities, religions, racial groups, and geographic regions. Social class is a relatively homogeneous and enduring division in a society, that are hierarchically ordered and whose members share similar values, interests, and behaviors. Pages: 174–175 102. What is a reference group? Describe three different types of reference groups that can have an impact on a consumer’s purchasing behavior. . Page: 177 103. Briefly, explain Freud’s theory on human motivation and how this might be related to marketing. 104. List and briefly characterize Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs. 199 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process esteem needs—self-esteem, recognition, status; and (5) self-actualization needs—self-development and realization. Page: 185 105. People can emerge with different perceptions of the same object because of three perceptual processes. List and briefly characterize those processes. Page: 186 106. What are the five stages of the consumer buying process? 107. How is the expectancy-value model used in the evaluation of alternatives as a consumer engages in a buying process? 108. Gordon Jones is considering purchasing a computer from Best Buy. He has created a scale whereby he has rated eight different computers on three different characteristics. Gordon has decided that for a computer to make his short-list, it must score at least a seven on his scale on all three characteristics. Describe the type of choice heuristic that Mr. Jones is using as he selects a computer. 109. Heuristics can come into play when consumers forecast the likelihood of future outcomes or events. When would a consumer use an anchoring and adjustment heuristic? 200 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships Suggested onsumers will use this heuristic when the consumer arrives at an initial judgment and then makes adjustments of that first impression based on additional information. Page: 201 APPLICATION QUESTIONS Multiple Choice 110. Successful marketing requires that companies fully connect with their customers. Adopting a marketing orientation means understanding consumers—gaining a 360-degree view of both their daily lives and the changes that occur during their lifetimes. a. holistic b. customer c. segmented d. focused e. niched Page: 174 111. Americans love their leisure time. The average number of times an adult goes out to a movie annually is . a. 50 b. 15 c. 9 d. 7 e. 5 Page: 175 112. Social classes differ in media preferences, with upper-class consumers often preferring and books and lower-class consumers often preferring television. a. movies b. radio c. video or computer games d. magazines e. music downloads Page: 176 201 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 113. American Demographics predicts three trends that will impact business and marketing in the next 25 years. Which of the following is one of those predicted trends? a. More international travel. b. An increasingly diverse America with a shrinking white majority. c. The majority of all retail purchases being done online. d. Less need for a college education and more emphasis on learning a trade. e. Social class warfare that may even become violent. Page: 176 114. Jason writes a weekly column in his school’s newspaper about movies he has seen, books he has read, and concerts he has attended. His column provides information and opinions. Feedback from his fellow students is positive and appreciative of the advice that is given. Which of the following would be the most apt description of the role played by Jason? a. Silent majority b. Protestor c. Protector d. Muckraker e. Opinion leader Page: 177 115. According to information presented in the text, the cultural market segment is the most fashion conscious of all the racial groups, tend to be motivated by quality and selection, and shop more at neighborhood stores. a. African American b. Hispanic American c. Asian American d. European American e. Indian American Page: 178 116. According to recent research, which of the following market segments is characterized as valuing connections and relationships with family and friends with respect to marketing messages received? a. Men b. Women c. Seniors d. Young adults e. Single parents Page: 179 202 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 117. After being considered an unprofitable stepchild of the Disney empire, the Disney Channel has become the company’s cash cow solely from its ability to reach the underserved “ market” and leverage its success through Disney’s other divisions. a. teen b. post teen c. tween d. young adult e. toddler Page: 179 118. Bank of America is using “event-based triggers” to help its premier customers. Which of the following would be the best example of an “event-based trigger” that might catch the attention of Bank of America managers? a. A large deposit that deviates from a customer’s normal behavior. b. A championship season at a local high school. c. A child that turns 21 years of age. d. The arrival of a family member from a foreign country. e. Moving an elderly parent into one’s home. Page: 181 119. The brand personality of a new product is characterized as having the trait of if promotional messages consistently portray the product as being reliable, imaginative, and successful. a. sincerity b. excitement c. competence d. sophistication e. ruggedness Page: 182 120. Consumers often choose and use brands that have a brand personality that is matched to the consumer’s (how one would like to view oneself). a. actual self-concept b. others’ self-concept c. ideal self-concept d. dual self-concept e. perceptual self-concept Page: 183 203 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 121. Consumers who worry about the environment, want products to be produced in a sustainable way, and spend money to advance their personal development and potential have been named . a. “Green” b. “Tree Huggers” c. “LOHAS” d. “Socialists” e. “Mamas” Page: 183 122. The two factors that are most important in understanding Herzberg’s theory are . a. supply and demand b. price and quantity c. quality and performance d. satisfiers and dissatisfiers e. promotion and communication Page: 185 123. can work to the advantage of marketers with strong brands when consumers change neutral or ambiguous brand information to make it more positive. a. Selective attention b. Selective distortion c. Selective retention d. Selective choice e. Selective embellishment Page: 186 124. Maria sees her best friend driving around in her new car and decides that she needs a new car also. Which of the following forms of stimulus has activated Maria’s problem recognition process? a. External stimuli b. Internal stimuli c. Peer stimuli d. Secondary stimuli e. Marketing induced stimuli Page: 191 204 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 125. If a consumer uses Google to find comparative reports on new automobiles in preparation for deciding on whether to purchase one or not, the consumer is using which of the following information sources for assistance? a. Personal b. Public c. Experiential d. Commercial e. Under-the-radar Page: 192 126. When a consumer makes the final decision on which brand to buy, he or she selects a brand from the set. a. total b. awareness c. consideration d. choice e. belief Page: 193 127. When a marketer attempts to alter a consumer’s beliefs about the company’s brand as a means of getting the consumer to re-think his or her purchase decision, the marketer is using to accomplish this task. a. psychological repositioning b. competitive depositioning c. positioning d. repositioning e. biased positioning Page: 195 128. A consumer tells another consumer, “Every time I eat at Big Bill’s Steakhouse I get poor service.” Whether this is true or not, it is the consumer’s perception. This is an example of consumers basing future predictions on the quickness and ease with which a particular example of an outcome comes to mind. This scenario would be an illustration of the heuristic. a. discrimination b. differentiation c. availability d. screening e. representativeness Page: 201 205 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 129. When marketers interview a small number of recent purchasers, asking them to recall the events leading to their purchase, the marketers are using the method to learn more about the consumer buying process a. introspective b. retrospective c. prospective d. prescriptive e. descriptive Page: 203 Short Answer 130. In the summer of 2003, some marketing pundits proclaimed the existence of a new male market—the “metrosexual”—that was defined as straight urban men who enjoy such things as shopping and using grooming products and services. One researcher estimated that 30–35 percent of young American men exhibited metrosexual tendencies, as evidenced in part by their purchase of products such as skin-care cream and fragrances. What factors in your opinion are driving the existence of this metrosexual market? 131. Culture is the fundamental determinant of a person’s wants and behavior. The growing child acquires a set of values, perceptions, preferences, and behaviors through his or her family and other key institutions. What values are the typical American young children exposed to? 132. Explain the concept of multicultural marketing. Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships million Hispanic Americans living in the United States have not yet become big consumers of financial services. Page: 174 133. An opinion leader is the person in informal, product-related communications who offers advice or information about a specific product or product category, such as which of several brands is best or how a particular product may be used. According to the text, how do marketers try to reach opinion leaders? 134. The family is the most important consumer-buying organization in society, and family members constitute the most influential primary reference group. We can distinguish between two family categorization in the buyer’s life. Name the two families and their impact on buying behavior Page: 177 135. Explain the differences between a role and status. Page: 180 136. Explain the concept of personality. 137. Each person has personality characteristics that influence his or her buying behavior. What does personality mean in terms of buying traits? 2art 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process analyzing consumer brand choices. The idea is that brands also have personalities, and consumers are likely to choose brands whose personalities match their own. Page: 182 138. People from the same subculture, social class, and occupation may lead quite different lifestyles. A lifestyle is a person’s pattern of living in the world as expressed in activities, interests, and opinions. Lifestyle portrays the “whole person” interacting with his or her environment. Given this information, describe the LOHAS (an acronym) lifestyle described in the text and its usefulness in marketing. Page: 183 139. According to Freudian theory, how can the technique called laddering be used? 140. Abraham Maslow sought to explain why people are driven by particular needs at particular times. Describe Maslow’s hierarchy of needs. How does Maslow’s theory help marketers? 141. Frederick Herzberg developed a two-factor theory that distinguishes dissatisfiers and satisfiers. How does Herzberg’s theory affect sellers marketing strategy? Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships motivators of purchase in the market and then supply them. These satisfiers will make the major difference as to which brand the customer buys. Page: 185 142. Perception is the process by which an individual selects, organizes, and interprets information inputs to create a meaningful picture of the world. For a marketer, what is the key point of perception? 143. Explain the concept of selective retention and its association with marketing. Page: 186 144. What does the learning theory teach marketers about demand for products? Page: 187 145. Describe how the problem recognition process works in the five-stage model of the consumer buying process. 209 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process thirst, sex—rises to a threshold level and becomes a drive or a need can be aroused by an external stimuli such as an advertisement. Page: 191 146. Through gathering information, the consumer learns about competing brands and their features. The consumer will then advance through four sets with respect to brands before a decision is reached. What are those four sets? Pages: 192–193 147. Explain the differences between a belief and an attitude. Pages: 193–194 148. Describe the lexicographic heuristic used to make consumer choices. 149. How can marketers learn about the stages in the buying process for their product? List and briefly characterize four methods. Chapter 7: Analyzing Business Markets GENERAL CONCEPT QUESTIONS Multiple Choice 1. To create and capture value, sellers need to understand business organizations’ needs, resources, policies, and . 210 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships g. demands h. protocols i. strategies j. buying procedures k. personnel policies Page: 209 139. Webster and Wind define as the decision-making process by which formal organizations establish the need for purchased products and services and identify, evaluate, and choose among alternative brands and suppliers. a. marketing channels b. organizational buying c. demand-oriented buying d. purchasing e. inventory control Page: 210 140. The consists of all the organizations that acquire goods and services used in the production of other products or services that are sold, rented, or supplied to others. a. business market b. consumer market c. e-commerce market d. global market e. supplier market Page: 210 211 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 141. Business markets have several characteristics that contrast sharply with those of consumer markets. All of the following would be among those characteristics EXCEPT . a. fewer, larger buyers b. close supplier-customer relationship c. professional purchasing d. inverted demand e. multiple sales calls Pages: 210–211 142. All of the following would be among the major industries that make up the business market EXCEPT . a. agriculture, forestry, and fisheries b. manufacturing c. construction d. banking, finance, and insurance e. the Internet Page: 210 143. Trained purchasing agents, who must follow their organization’s , often purchase business goods. a. culture b. past purchasing history c. purchasing policies, constraints, and requirements d. needs e. financial budgets Page: 211 144. Ultimately, the amount of steel sold to General Motors depends on the consumer’s demand for GM cars and trucks. From the standpoint of the steel manufacturer, which of the following demand forms is most pertinent? a. Derived demand b. Inelastic demand c. Geographic demand d. Relational demand e. Static demand Page: 211 145. The demand for business goods is ultimately derived from the demand for . a. raw materials b. consumer goods c. electronics d. business solutions e. e-commerce Page: 211 146. The business buyer faces many decisions in making a purchase. The number of decisions depends on the buying situation. All of the following examples are appropriate to the preceding EXCEPT . 212 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships a. complexity of the problem being solved b. newness of the buying requirement c. number of people involved d. applicability of situation to mission statement e. time required Page: 212 147. The purchasing department buys office supplies on a routine basis. This type of purchase is classified as a . a. straight rebuy b. modified rebuy c. new task d. secondary purchase e. preordained purchase Page: 212 148. There are a series of guidelines for selling to small businesses. Which of the following should not be among those guidelines? a. Don’t waste their time. b. Do keep it simple. c. Do use the Internet. d. Don’t forget about direct contact. e. Do lump small and midsize businesses together for efficiency sake. Page: 212 149. The business buyer makes the fewest decisions in the . a. modified rebuy b. regular buy c. straight rebuy d. new rebuy e. new task buy Page: 213 150. Many business buyers prefer to buy a total solution to a problem from one seller. is the correct term for this process. a. Channel consolidation b. Systems buying c. Vertical buying d. Horizontal buying e. Supply buying Page: 213 151. Xerox offers a approach to prospective clients when it offers a complete turnkey procedure, operation, and management of the client’s information and communication need. a. supply buying b. primary buying c. systems buying d. co-op buying system e. direct buying 213 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process Page: 213 152. If Ampex Support Systems is the single supplier for a local manufacturing company’s MRO (maintenance, repair, operating) supplies and needs, Ampex Support Systems would then be considered as providing for the manufacturer. a. systems buying b. purchasing support c. turnkey logistics d. decision support e. systems contracting Page: 214 153. is a key industrial marketing strategy in bidding to build large-scale industrial products (e.g., dams, pipelines, et cetera). a. Systems contracting b. Systems buying c. Systems selling d. Solutions buying e. Turnkey logistics Page: 214 154. is composed of all those individuals and groups who participate in the purchasing decision-making process, who share some common goals and the risks arising from their decisions. a. The buying center b. The marketing sales team c. Strategic management d. Engineering support e. The logistics center Page: 214 214 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 155. In the purchasing decision process, the are those who request that something be purchased. They may be users or others in the organization. a. users b. initiators c. influencers d. deciders e. approvers Page: 214 156. In the purchasing decision process, the are those who have the power to prevent sellers or information from reaching members of the buying center. a. gatekeepers b. buyers c. initiators d. approvers e. deciders Page: 215 157. The typical buying center has a minimum of members. a. 2–3 b. 3–4 c. 4–5 d. 5–6 e. 10 Page: 215 158. Webster cautions that ultimately, make purchasing decisions. a. only senior managers b. individuals, not organizations c. organizations, not individuals d. third parties e. systems contractors Page: 215 159. Small sellers concentrate their marketing efforts on reaching . a. approvers b. initiators c. key buying influencers d. users e. the purchasing staff Page: 216 215 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 160. To the price is everything and transactional selling is used. a. solution-oriented customers b. income-oriented customers c. gold-standard customers d. strategic-value customers e. price-oriented customers Page: 216 161. The strategic-value customers want a fairly permanent sole-supplier relationship with your company. Which of the following would be the best selling format to use with the strategic-value customer? a. Transactional selling b. Consultative selling c. Quality selling d. Enterprise selling e. Indirect demand selling Page: 216 162. Some customers are willing to handle price-oriented buyers by setting a lower price, but establishing restrictive conditions. All of the following would be among those conditions EXCEPT . a. limiting the quantity that can be purchased b. no refunds c. no adjustments d. no services e. no customer advertising Page: 216 163. If a supplier signs an agreement with a customer that states $350,000 in savings will be earned by the customer over the next 18 months in an exchange for a ten-fold increase in the customer’s share of supplies ordered by the customer, the two parties will have participated in what is called . a. solution selling b. consultative selling c. risk and gain sharing d. strategic alignment e. demand shifting Page: 217 216 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 164. W.W. Grainger employees work at large customer facilities to reduce materials-management costs. Which of the following forms of solution selling is W.W. Grainger using? a. Solutions to partnerships. b. Solutions to alter corporate culture. c. Solutions to enhance customer revenues. d. Solutions to decrease customer risks. e. Solutions to reduce customer costs. Page: 217 165. In principle, business buyers seek to in relation a market offering’s costs. a. spread risks b. obtain the highest benefit package c. maintain everyday-low-prices d. outsource as much as is possible e. eliminate partners’ shares in profits as much as possible Page: 217 166. In the past, what position did purchasing departments hold in the management hierarchy of most organizations? a. A high level because of their role in managing the company’s costs. b. A moderate level because of their spotty record on controlling costs. c. A low level despite the fact that they manage more than half of the company’s costs. d. A secretive position. e. There has been no determination of this position. Page: 218 167. The new, more strategically-oriented purchasing departments have a mission. Which of the following most accurately describes that mission? a. Make the most profit possible and remain independent of entanglements. b. Approach every purchasing opportunity as means to create interdependency. c. Seek the best value from fewer and better suppliers. d. Outsource the supply function. e. Abandon all strategies except for systems selling and buying. Page: 218 168. When the purchaser’s focus is short term and tactical and they are rewarded on their ability to obtain the lowest price from suppliers for the given level of quality and availability, this is referred to as . a. procurement orientation b. supply chain management orientation c. buying orientation d. sellers orientation e. market orientation Page: 218 169. When buyers simultaneously seek quality improvements and cost reductions and they develop collaborative relationships with major suppliers and seek savings 217 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process through better management of acquisition, conversion, and disposal costs, this is referred to as . a. sellers orientation b. supply chain management orientation c. market orientation d. procurement orientation e. buying orientation Page: 218 170. When the purchasing role is further broadened to become a more strategic, value-adding operation, this is referred to as . a. supply chain management orientation b. buying orientation c. sellers orientation d. procurement orientation e. routine orientation Page: 218 171. Peter Kraljic distinguished four product-related purchasing processes. Which of the following matches to products that have high value and cost to the customer but involve little risk of supply because many companies make them? a. Strategic products b. Bottleneck products c. Leverage products d. Routine products e. Commodity products Page: 219 172. The products that have high value and cost to the customer and also involve high risk (e.g., mainframe computers) are called . a. strategic products b. bottleneck products c. leverage products d. routine products e. commodity products Page: 219 218 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 173. Most purchasing professionals describe their jobs as more , technical, team-oriented, and involving more responsibility than ever before. a. risky b. strategic c. ethically difficult d. Web-based e. human-based Page: 219 174. Robinson and Associates have identified eight stages and called them buyphases. This model is called the framework. a. buygrid b. buying/selling c. seller-centered d. commercial e. buy-analysis Page: 219 175. The first step (buyphase) in the straight rebuy buyclass is . a. problem recognition b. general need description c. product specification d. supplier search e. proposal solicitation Page: 220 176. A new task buyclass decision begins with which of the following buyphases? a. Problem recognition b. General need description c. Product specification d. Supplier search e. Proposal solicitation Page: 220 177. Business marketers can stimulate problem recognition by . a. trade directories b. direct mail, telemarketing, and calling on prospects c. encouraging the Better Business Bureau to release statistics d. consumer advertising e. requesting testimonials from existing customers Page: 221 219 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 178. When Hewlett-Packard sells such complex products as a network computer system, it is engaging in what it calls the concept because it offers information and specific solutions to unique problems. a. “product specification” b. “price de-escalation” c. “systems selling” d. “trusted advisor” e. “strategic alliance” Page: 221 179. U.S. businesses spent about on online transactions with other businesses in 2002 as compared to consumer online purchases of $71 billion during the same time period. a. $650 billion b. $500 billion c. $482 billion d. $225 billion e. $53 billion Page: 222 180. With respect to e-procurement, Web sites are organized around two types of e- hubs: . a. vertical and horizontal hubs b. vertical and functional hubs c. functional hubs and organizational hubs d. supplier and user hubs e. manufacturer and supplier hubs Page: 222 181. With respect to e-procurement, Coca-Cola, Sara Lee, Kraft, PepsiCo, Gillette, P&G, and several other companies joined forces to form a called Transora to use their combined leverage to obtain lower prices for raw materials. a. manufacturer’s co-op b. supplier’s co-op c. middleman group d. buying alliance e. cabal Page: 222 220 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 182. Business-to-business cyberbuying is flourishing on the Internet. So far, most of the products that businesses are buying electronically are , and travel and entertainment services. a. promotion services such as advertising b. HR services (e.g., employee recruitment) c. MRO materials (maintenance, repair, and operations) d. food services e. marketing research services Page: 223 183. Moving into e-procurement has many benefits. Which of the following would not be among those benefits? a. Aggregating purchasing across multiple departments gains larger volume discounts. b. Aggregating purchasing across multiple departments gains centrally negotiated volume discounts. c. There is less buying of substandard goods from outside the approved list of suppliers. d. A smaller purchasing staff is required. e. Purchasing gains a significant leverage with top management because of its management team. Page: 224 184. With respect to e-procurement commitment, in 2003 was named number one in BtoB magazine’s annual ranking of the top B-to-B Web sites because of its ability to generate sales (about 55 percent of the company’s total sales) and commitment to the process. a. Coca-Cola b. Dell Computers c. Hewlett-Packard d. Cadillac e. Boeing Page: 224 185. In the proposal solicitation process, should be marketing documents that describe value and benefits in customer terms. a. written proposals b. oral proposals c. e-proposals d. alliance proposals e. global proposals Page: 225 221 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 186. Xerox qualifies only suppliers who meet the ISO 9000 quality standards, but to win the company’s top award—certification status—a supplier must first complete . a. government certification b. an extensive ethics statement evaluation c. the Xerox Multinational Supplier Quality Survey d. a company training and indoctrination period e. a Malcolm Baldridge National Quality Award entry form and then enter Page: 225 187. All of the following are considered to be methods of assessing customer value EXCEPT . a. direct survey questions b. exit interviewing c. focus-group value assessment d. conjoint analysis e. benchmarks Page: 226 188. According to purchasing professionals, which of the following is considered to be the major responsibility of the purchasing agent in supplier negotiations? a. Forming networks for future business. b. Assuring quality conformance. c. Being fair with all parties. d. To use a team approach in negotiations. e. Negotiating price. Page: 226 189. If an industrial buyer leases heavy equipment like machinery and trucks rather than purchasing them, the lessee gains several advantages. Which of the following would NOT be among those advantages? a. Higher quality products. b. Conserving capital. c. Getting the latest products. d. Receiving better service. e. Some tax advantages. Page: 227 190. “OTIFNE” is a term that summarizes three desirable outcomes of a B-to-B transaction: OT—deliver on time; IF—in full; and, NE— . a. no error b. no emergencies c. non-experimental d. new entrepreneurs e. need equipment Page: 227 191. Corporate credibility depends on three factors: corporate expertise, corporate trustworthiness, and . a. corporate manpower b. corporate mission statement 222 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships c. corporate likeability d. corporate governance e. corporate management structure Page: 228 192. Cannon and Perreault found that buyer-suppler relationships differed according to four factors. Which of the following would NOT be among those factors? a. Importance of supply. b. Complexity of supply. c. Availability of alternatives. d. Supply market dynamism. e. Demand market conservatism. Page: 229 193. According to Cannon and Perreault, buyer-supplier relationships fall into eight different categories. Which of the following relationships is characterized as being one that has much trust and commitment leading to a true partnership? a. Mutually adaptive b. Collaborative c. Basic buying and selling d. Customer supply e. Cooperative systems Page: 229 194. In the category of Cannon and Perreault’s buyer-supplier relationship categorization, although bonded by a close, cooperative relationship, the seller adapts to meet the customer’s needs without expecting much adaptation or change on the part of the customer in exchange. a. contractual transaction b. cooperative system c. collaborative d. mutually adaptive e. customer is king Page: 229 223 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 195. Vertical coordination can facilitate stronger customer-seller ties but at the same time may increase the risk to consumer’s and supplier’s (e.g., those expenditures tailored to a particular company and value chain partner). a. logistics channel b. independent operations c. specific investments d. leverage ability e. liquidity situation Page: 230 196. The market consists of schools, hospitals, nursing homes, prisons, and other institutions that must provide goods and services to people in their care. a. vertical b. nonprofit c. spot d. secondary business e. institutional Page: 230 197. With purchases of $200 billion annually in goods and services, is the largest customer in the world. a. Wal-Mart b. Grainger c. the State of California d. the U.S. government e. Latin America Page: 232 True/False 198. Webster and Wind define organizational buying as the decision-making process by which formal organizations establish the need for purchased products and services and identify, evaluate, and choose among alternative brands and suppliers. Page: 210 199. The business market is essentially the same thing as the consumer market. Page: 210 200. The demand for business goods is ultimately derived from the demand for raw materials. Page: 211 201. The total demand for many business goods and services is inelastic—that is, not much is affected by price changes. Page: 211 202. In the straight rebuy, “out-suppliers” try to get a small order and then enlarge their purchase share over time. Page: 212 224 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 203. Over time, new-buy situations become straight rebuys and routine purchase behavior. Page: 213 204. Most business buyers, preferring to spread their risk, reject what is called systems buying from one seller. Page: 213 205. Systems selling is a key industrial marketing strategy in bidding to build large- scale industrial projects such as dams or pipelines. Page: 214 206. The buying center is where consumers go to purchase their goods and services. Page: 214 207. Initiators are those who authorize the proposed action of deciders or buyers. Page: 214 208. Users perform all seven roles in the buying center because of their direct tie to the product and what it is supposed to do. Answer: False Page: 214 209. The typical buying center has a minimum of two to three people even though large companies may have more performing this function. Page: 215 73. Webster cautions that ultimately, organizations not individuals make purchasing decisions. Page: 215 74. In the business market, small sellers concentrate on reaching as many participants as possible because their chances of success are slim. 225 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process Answer: False Page: 216 75. To gold-standard customers, a seller is wise to use what is called quality selling. Answer: True Page: 216 76. To effectively sell to price-oriented customers, a company is wise to use transactional selling. Page: 216 226 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 77. One of the forms of solution selling is to provide solutions to enhance customer revenues. Page: 217 78. Today, purchasing departments occupy a relatively low position in the management hierarchy and answer primarily to the vice-president of marketing. Page: 218 79. If a company’s purchasing department focus is short term and tactical, it is said to have a buying orientation. Page: 218 80. When business buyers work simultaneously to seek quality improvements and cost reductions, the business buyers are said to have a demand orientation. Answer: False Page: 218 81. Office supplies are good examples of what are called bottleneck products. Page: 219 82. Strategic products have high value and cost to the customer and also involve high risk. Page: 219 83. According to the buygrid framework described in the text, a performance review completes the buygrid as a last step. Page: 220 84. The buying process begins when someone places an order with a sales representative. Page: 220 227 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 85. Product value analysis (PVA) is an approach to cost reduction in which components are studied to determine if they can be redesigned or standardized or made by cheaper methods of production. Page: 222 86. A buying alliance attempts to use their combined leverage to obtain lower prices for raw materials. Page: 222 87. In the business-to-business market on the Internet, the majority of purchases fall under the category of services (e.g., advertising, financial needs, et cetera). Page: 223 88. With respect to proposal solicitation in B2B, sellers begin the process by requesting permission to make a proposal rather than waiting for the buyer to request one. Page: 225 89. In general, buyers review the product and its price rather than any other considerations about the seller as a buying decision is made. Page: 225 90. With respect to assessing customer value, in conjoint analysis customers are asked to rank their preference for alternative market offerings or concepts. Page: 226 91. The buying center has many responsibilities; however, it does not negotiate with suppliers in order to avoid a conflict of interest. Page: 226 92. “OTIFNE” is the term that summarizes three desirable outcomes of a B-to-B transaction, stands for: on time, in full, no error. Page: 227 100. Most performance reviews are conducted by outside auditing agencies to avoid bias and internal discrepancies. Answer: False Page: 227 Level of difficulty: Medium 101. Corporate credibility depends on: corporate expertise, corporate trustworthiness, and corporate likeability. Page: 228 228 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 102. One of the problems facing B2B on the Web is that many firms often impose more stringent requirements on their online business partners than they do on non- online partners. Answer: True Page: 228 Level of difficulty: Medium 103. One of the eight categories of buyer-seller relationships is the contractual transaction that generally shows low levels of trust, cooperation, and interaction; exchange is defined by formal contract. Page: 229 104. In the “customer is king” category of buyer-seller relationship, the category is characterized as being one that it relatively simple where routine exchanges with moderately high levels of cooperation and information exchange occurs. Answer: False Page: 229 Level of difficulty: Hard 105. A good illustration of a member of the institutional market would Boeing because it is a member of the aviation institution structure. Page: 230 106. The United States government is the largest customer in the world. Page: 232 100. Today, almost all companies that sell to the U.S. government use a marketing orientation because of the special relationship required. Page: 233 Essay 101. Business markets have several characteristics that contrast sharply with those of consumer markets. Name and briefly characterize five of those contrasts. Pages: 210–212 229 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 102. Illustrate the differences between a straight rebuy, modified rebuy, and a new task purchase. 103. List and briefly describe the seven roles played by members of a buying center. 104. In defining target market segments, four types of business customers can often be identified with corresponding marketing implications. List and briefly describe each of these business customers. 230 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships selling—they want a fairly permanent sole-supplier relationship with your company. Page: 216 105. Explain the concept of solution selling. Give one example of this approach. 106. The upgrading of purchasing means that business marketers must upgrade their sales personnel to match the higher caliber of the business buyers. List and briefly describe the three company purchasing orientations that buyers select from. 107. Peter Kraljic distinguished four product-related purchasing processes. List and briefly describe each of these four product groups. 108. List the stages (buyphases) of the industrial buying process. Page: 220 231 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 109. Cannon and Perreault found that buyer-supplier relationships differed according to four factors: availability of alternatives; importance of supply; complexity of supply; and supply market dynamism. Based on these four factors, they classified buyer-supplier relationships into eight different categories. What are those categories? APPLICATION QUESTIONS Multiple Choice 110. software company SAP has become a leading seller to the business market by specializing in software to automate business functions. SAP’s strategy is to focus carefully on what customers want, and shows them how SAP’s software applications can improve profits, raise revenue, or reduce costs. a. product b. service c. leadership d. concentrated e. simplistic Page: 209 232 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 111. The market consists of all the organizations that acquire goods and services used in the production of other products or services that are sold, rented, or supplied to others. a. non-profit b. business c. hardware d. software e. government Page: 210 112. IBM counts small to midsize businesses as 20 percent of its business and has launched , a line of hardware, software services, and financing, for this market. a. Impresario b. Express c. Datacount d. Smallbiz e. TaxMan Page: 210 113. More than half of U.S. business buyers are concentrated in seven states. Which of the following states WOULD NOT be among those favored by business buyers? a. Texas b. New York c. California d. Pennsylvania e. Ohio Page: 211 114. Jason Riggs’ company is considered to be an in-supplier for a lawn mower manufacturer. However, recently the lawn mower company has put out a memo to in- and out-suppliers indicating that it would like to modify product specifications and delivery schedules. Which of the following buying situations is most likely to be in operation given the data above? a. Straight rebuy b. Elastic rebuy c. Fluctuating rebuy d. Flatten rebuy e. Modified rebuy Page: 212 233 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 115. All of the following are considered to be guidelines for selling to small businesses EXCEPT . a. do not use the Internet b. do keep it simple c. don’t lump small and midsize businesses together d. don’t forget about direct contact e. do provide after the sale support Page: 212 116. Ford Motor Co. has forged supplier and manufacturing relationships around the world. Today, an accurate description of this automotive giant is one where it is characterized as being mainly a car . a. designer b. manufacturer c. assembler d. distributor e. promoter Page: 214 117. If you decided to go into the systems contracting business, which of the following categories would constitute your main area of expertise in that this area would be what service you provide for customers. a. Computer applications b. Database management c. Manufacturing d. Promotion management e. MRO (maintenance, repair, operating) supplies Page: 214 118. Think about what you have learned about a buying center. If you performed the role of the , you would be the person that has the power to prevent sellers or information from them in reaching other members of the buying center. a. initiator b. influencer c. decider d. gatekeeper e. approver Page: 215 234 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 119. According to Webster, with respect to buying center influences, senior managers should remember that people are . a. not buying products—they are buying solutions to problems b. buying products that they personally will not use c. buying surrogates that must appreciate that role d. are human shopping bots e. limited in their scope of overall business operations Page: 215 120. Consider yourself as an upper-level marketing executive a large seller of fleet trucks. Which of the following strategies would be most appropriate in reaching buying center targets? a. Concentrate on key buying influencers. b. Use multilevel in-depth selling. c. Use trade-based promotions. d. Begin all sales efforts with the secretarial support staff. e. Move all operations to the Net. Page: 216 121. Billijean Monk tells her supplier, “Price is everything! I mean if it’s not priced right, I am out of here fast.” To succeed in selling to Ms. Monk, which of the following strategies would be most appropriate? a. Consultative selling b. Quality selling c. Enterprise selling d. Transactional selling e. High pressure, high risk selling Page: 216 122. The Tuxax Company has decided that handling price-oriented buyers can be profitable under certain conditions. Conditions that would make good sense for Tuxax Company would be all of the following EXCEPT . a. limiting the quantity that can be purchased b. no services c. no adjustments d. no refunds e. no packaging or crating Page: 216 235 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 123. The new, more strategically oriented purchasing departments have a mission to . a. always make a profit b. always take the lowest bid c. seek the best value from fewer and better suppliers d. continue to seek outsourcing as their primary strategy e. use consultants whenever possible Page: 218 124. If a buyer is using the buying tactic of commoditization, he or she has a as their purchasing orientation. a. buying orientation b. procurement orientation c. supply chain management orientation d. raw materials orientation e. simultaneous orientation Page: 218 125. Spare parts are considered to be an example of a product in that they have a low value and cost to the customer but they involve some risk with respect to reliability. a. routine b. leverage c. strategic d. bottleneck e. strangle-hold Page: 219 126. Which of the following buyclasses uses the least number of buyphases (stages) in the industrial buying process? a. Straight rebuy b. Modified rebuy c. New task d. Global task e. Relational rebuy Page: 219 236 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 127. Japan has an extremely well organized organizational buying process; however, because of its strategic bottleneck position, the is critical to the success of any venture. a. marketing department b. production department c. delivery department d. accounting department e. inventory control department Page: 220 128. Which of the following methods for assessing customer value would you consider to be appropriate if you asked your customers to attach a monetary value to each of three alternative levels of a given attribute? Those values would then be added together for any offer configuration. a. Direct survey questions b. Importance ratings c. Compositional approach d. Benchmarks e. Conjoint analysis Page: 226 129. With respect to buyer-seller relationships, which of the following categories would you believe to be the most appropriate description of a situation where there was a traditional custom supply situation where competition rather than cooperation was the dominant form of governance? a. Bare bones b. Contractual transaction c. Collaborative d. Customer supply e. Customer is king Page: 229 Short Answer 130. The business market consists of all the organizations that acquire goods and services used in the production of other products or services that are sold, rented, or supplied to others. What are the major industries that make up the business market? 131. Define organizational buying. 237 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process services and identify, evaluate, and choose among alternative brands and suppliers. Page: 210 132. Explain how fluctuating demand impacts business markets differently than 133. If you were a purchasing agent facing a modified rebuy situation, how would you describe that situation? 134. In systems buying, the U.S. government often solicits bids from primary contractors. What do primary contractors do? 135. Systems selling is a key industrial marketing strategy in bidding to build large- scale industrial projects. Competition for these projects is fierce. What are the main areas of competition for these project engineering firms? 238 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 136. Webster and Wind call the decision-making unit of a buying organization the 137. Assume that you are buying center manager who has decided to pursue a market segment called the “gold-standard customers.” What would be the best strategy to reach these customers? 138. Assume that you are a purchasing manager that has adopted a “buying orientation” in making this year’s purchases. What two tactics are often used by purchasing managers with this orientation? 139. Peter Kraljic distinguished four product-related purchasing processes. Which of these processes would be most appropriate for a buyer of mainframe computers? 140. E-procurement Web sites are organized around two types of e-hubs. If you were in the advertising business and were seeking to take advantage of e- procurement, what type of e-hub should be constructed by your company? 141. Business-to-business (B2B) cyberbuying has become increasingly popular between purchasing agents and buying centers. How could “pure play” auction sites be used to conduct cyberbuying? Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 142. In 2003, Hewlett-Packard was named number one in BtoB magazine’s annual ranking of the top B-to-B Web sites. What does this Web site allow companies to do that makes it worthy of the distinction mentioned? 143. Assume that you have been given the task of assessing customer value at your organization. Further, you have been instructed to use the “compositional approach” to make this assessment. Describe what you would do if you used the compositional approach in assessing customer value. 144. In the buygrid framework model where the major stages of the industrial buying process are listed and characterized, supplier selection is an important process. What follows supplier selection and what occurs in this phase? 240 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 145. A customer tells a supplier that he or she would like “OTIFNE” as a desired outcome of upcoming purchase transaction. What has the customer indicated that he or she wants by using this acronym? 146. As a seller in the business market, you have promised your customers that you have, as a corporate goal, corporate credibility. What three factors will have some bearing on whether you will be able to meet your goal and promise? Page: 228 147. Cannon and Perreault found that buyer-supplier relationships could be classified into eight different categories. What category would be appropriate for a relationship where, although bonded by a close, cooperative relationship, the seller adapts to meet the customer’s needs without expecting much adaptation or change on the part of the customer in exchange? 148. Your organization is considering selling its products to the institutional market. What type of customers will you be making your appeals to? Give 149. As a purchasing manager, you have just completed a large contract with the U.S. government where your company sold the government several “tech- oriented” products and services. What three tips would be appropriate to pass along to those that would also like to tap into this large market? Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process sure contractors can find you, stay on top of key contracts, and work the angles), and (3) network actively. Page: 233 Chapter 8: Identifying Market Segments and Targets GENERAL CONCEPT QUESTIONS Multiple Choice 1. Instead of scattering their marketing effort (a “shotgun” approach), many companies are now embracing target marketing where the focus is on those consumers that they have the greatest chance of satisfying (a approach) with their products and services. a. “rifle” b. “focused” c. “niche” d. “macro” e. “micro” Page: 240 210. In marketing, the seller engages in the mass production, mass distribution, and mass promotion of one product for all buyers. a. group b. mass c. general d. segmented e. differentiated Page: 240 211. The argument for marketing is that it creates the largest potential market, which leads to the lowest costs, which in turn can lead to lower prices or higher margins. a. niche b. micro c. macro d. differentiated e. mass Page: 240 242 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 212. A consists of a group of customers who share a similar set of needs and wants. a. market target b. market group c. market slice d. market segment e. market level Page: 240 213. A consists of two parts: a naked solution and discretionary options. a. differentiated market offering b. flexible market offering c. rigid market offering d. vertical market offering e. horizontal market offering Page: 241 214. If a marketing manager observes that his or her market shows no natural segments and consumers seem to have roughly the same preferences, the marketing manager will most likely be faced with a preferences pattern. a. homogeneous b. heterogeneous c. diffused d. clustered e. scattered Page: 241 215. Procter & Gamble has many soap brands. One reason for this is that soap users tend to group together in terms of preferences such as bleaching action, softness, stain-removal, et cetera. Which of the following preferences pattern would most likely apply to P&G’s method of response to market needs? a. Homogeneous preferences. b. Diffused preferences. c. Clustered preferences. d. Psychological preferences. e. Cultural preferences. Page: 242 216. Marketers usually identify niches by . a. dividing a segment into subsegments b. conducting VALS tests c. allowing consumers to gravitate toward product brands d. examining the demographics section of The Handbook of Marketing e. producing products that can be used in a variety of ways Page: 242 217. A niche is characterized as being all of the following EXCEPT . a. the customers in the niche have a distinct set of needs b. the customers will pay a premium to the firm that satisfies their needs c. the niche is not likely to attract other competitors 243 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process d. the customers generally have smaller amounts of income e. the nicher gains certain economies through specialization Page: 242 218. Which of the following has greatly facilitated niche marketing? a. The Internet b. Globalization c. Industrialization d. Recession e. Excessive demand Page: 243 219. When Nike attempts to get close to its customers at the local level by sponsoring local school teams and providing shoes, equipment, and clothing to many of them, Nike is using which of the following marketing formats? a. Differentiated marketing b. Consumer marketing c. Instructional marketing d. Partner marketing e. Grassroots marketing Page: 244 220. According to thoughts expressed by Pine and Gilmore about a new economic era that is rapidly approaching, if you charge for the time customers spend with you, then and only then are you in the business. a. niche b. grassroots c. experience d. service e. goods Page: 245 221. Through customer experience management (CEM), brands can create five different types of experiences: sense, feel, think, relate, and . a. remembering b. forgetting c. simulation d. act e. bargain Page: 245 222. combines operationally driven mass customization with customized marketing in a way that empowers consumers to design the product service offering of their choice. a. Consumptionization b. Viral marketing c. Virtual marketing d. Regionalization e. Customerization Page: 246 244 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 223. Two broad groups of variables are used to segment consumer markets. One method uses descriptive characteristics such as geography. The other method is to form segments by looking at considerations. a. gender b. income c. cultural d. interest e. behavioral Page: 247 224. If a marketer decides that segmenting a market based on neighborhoods, the marketer will have chosen the method of segmentation. a. demographic b. psychographic c. geographic d. cultural e. social class Page: 247 225. According to established methods of segmenting markets, all of the following would an appropriate segment category if the family life cycle was the segmentation base ACCEPT . a. young, single b. male, female c. young, married d. older, married, no children under 18 e. young, married, youngest child 6 or over Page: 248 245 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 226. A marketing manager is considering several options to market to market segments identified as being either culture-oriented, sports-oriented, or outdoor- oriented. This manager has selected the format for segmenting markets. a. personality b. behavioral occasions c. user status d. psychographic lifestyle e. readiness stage Page: 248 227. PRIZM (Potential Rating Index by Zip Markets) identifies clusters of consumers based on a variety of characteristics such as education and affluence. Which of the following clusters would match to a consumer group that is characterized as being in their late forties and fifties, college-educated, upper- middle-class homeowners that married late and are still raising children in comfortable suburban subdivisions and are still pursuing kid-centered lifestyles. a. The cosmopolitans b. Beltway boomers c. Young digerati d. Winner’s circle e. Blue bloods Page: 249 228. Jose and Erika have just divorced. This will obviously not only have an impact on their personal lives but their consumptive lives as well. Which of the following demographic segmentation subsegment formats might be used by marketers to reach Jose or Erika? a. Life stage b. Benefits c. Age segment d. User segment e. Occasion segment Page: 250 229. Men and women tend to have different attitudinal and behavioral orientations, based partly on genetic makeup and partly on . a. income b. occupation c. socialization d. heredity e. globalization Page: 250 246 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 230. Which of the following American Generations is characterized as being great acquisitors and are value- and cause-driven despite indulgences and hedonism? a. GI generation b. Silent generation c. Baby boomers d. Generation X e. Millennials Page: 252 231. is the science of using psychology and demographics to better understand consumers. a. Psychographics b. Segmentation c. Clustering d. Demographics e. Social psychology Page: 252 232. To reach Generation Y, rock band Foo Fighters created a digital street team that sends targeted e-mail messages to members who “get the latest news, exclusive audio/video sneak previews, tons of chances to win great Foo Fighters prizes, and become part of the Foo Fighters Family. Which of the following techniques for reaching Generation Y are the Foo Fighters using? a. Student ambassadors b. Unconventional sports c. Cool events d. Computer games e. Online buzz Page: 253 233. In 2003, 4.1 million Americans turned 21. An interesting fact is that the share of college students who plan to move back home after graduation is . a. 10 percent b. 25 percent c. 50 percent d. 60 percent e. 75 percent Page: 253 247 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 234. According to the VALS 8-part typology segmentation system, are successful, sophisticated, active, “take-charge” people with high self-esteem. Their purchases often reflect cultivated tastes for relatively upscale, niche-oriented products and services. a. innovators b. thinkers c. achievers d. experiencers e. believers Page: 254 235. According to the VALS 8-part typology segmentation system, are considered to be elderly, passive people who are concerned about change. They are loyal to their favorite brands. a. believers b. strivers c. makers d. survivors e. experiencers Page: 254 236. A housewife requests a new treadmill for her birthday. With respect to consumer decision roles, which role is the housewife currently playing? a. Initiator b. Influencer c. Decider d. Buyer e. Gatekeeper Page: 255 237. With respect to occasion segmentation, Christmas, Valentine’s Day, and account for just over half of gifters’ budgets. a. Halloween b. Father’s Day c. Mother’s Day d. Thanksgiving e. Independence Day Page: 256 248 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 238. Mobil identified five different benefit segments for which products and services could be designed. (27 percent of the market) shops Mobil outlets for fast fuel, fast service, and fast food. a. Road warriors b. Generation F c. True blues d. Home bodies e. Price shoppers Page: 256 239. With respect to user status (a segmentation possibility), tend to focus on attracting potential users because they have the most to gain. a. smaller firms b. niche firms c. followers d. aggressive specialists e. market-share leaders Page: 256 240. If a market is segmented according to light, medium, and heavy product users, the marketer segmenting this market is using the as the means to segment. a. user status b. usage rate c. buyer-readiness stage d. occasion e. benefit Page: 256 241. If a buyer is loyal to two or three different brands of soap, this buyer’s loyalty status can be described as being among the . a. switchers b. shifting loyals c. split loyals d. hard-core loyals e. anti-loyals Page: 256 242. A company can learn a great deal by analyzing the degrees of brand loyalty. For example, by studying the the company can pinpoint which brands are most competitive with its own. a. hard-core loyals b. split loyals c. shifting loyals d. switchers e. anti-loyals Page: 257 243. All of the following have been designated as groups that might be found using attitude as the primary segmentation variable EXCEPT . a. synergistic 249 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process b. enthusiastic c. positive d. indifferent e. hostile Page: 257 244. A snack chip manufacturer is concerned about consumers leaving its brand and going to competitive alternatives. Which of the following groups (based on strength of commitment) would be most likely to leave the company’s offering and go somewhere else for snack products? a. Convertible b. Shallow c. Average d. Entrenched e. Hard rocks Page: 258 245. If a consumer group is designated based on their “balance of disposition,” the group can be described as one that is made up of nonusers who are as attracted to a competing brand as they are to their current brands. a. strongly unavailable b. weakly unavailable c. ambivalent d. available e. desirable Page: 258 246. If a marketer is seeking to segment a business market, which of the following variables is generally felt to be important enough by marketers to place it first among the list of other variables that can be used in segmentation process? a. Personal characteristics b. Demographic c. Situational factors d. Operating variables e. Purchasing approaches Page: 258 250 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 247. A marketer is interested in segmenting a business market based on technology and customer capabilities. Which of the following major segmentation variables would most likely be used by the marketer to assist with the task? a. Demographic b. Purchasing approaches c. Situational factors d. Personal characteristics e. Operating variables Page: 259 248. A marketer is interested in segmenting a business market on if the marketer intends to eventually segment the market based on loyalty and attitudes toward risk. a. situational factors b. purchasing approaches c. personal characteristics d. operating variables e. demographics Page: 259 249. A company can be said to have used if the company distinguished customers buying on the basis of price, service, and quality. a. macrosegmentation b. microsegmentation c. strategic segmentation d. global segmentation e. short-term segmentation Page: 260 250. Business buyers seek different bundles based on their stage in the purchase decision process. are customers who are starting their purchasing relationship and they want easy-to-read manuals, hot lines, high levels of training, and knowledgeable sales reps. a. First-time prospects b. Sophisticates c. Global partners d. Trend-setters e. Novices Page: 260 251 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 251. If your marketing department established a priority in reaching solution- oriented customers (e.g., those that want value through more benefits and advice), would be the best means for connecting with these customers. a. transaction selling b. consultative selling c. enterprise selling d. dual selling e. psychological selling Page: 261 252. During which step of the segmentation process would the marketer group customers into segments based on similar needs and benefits sought by the customer in solving a particular consumption problem? a. Step 2—segment identification b. Step 3—segment attractiveness c. Step 6—segment “acid test” d. Step 1—needs-based segmentation e. Step 7—marketing-mix strategy Page: 261 253. If an organization’s marketing department wished to create “segment storyboards” to test the attractiveness of each segment’s positioning strategy, this action would most likely occur in the step of the segmentation process. a. needs-based segmentation b. segment identification c. segment profitability d. segment “acid test” e. marketing-mix strategy Page: 261 254. To be useful, market segments must rate favorably on five key criteria. In the criterion, effective programs can be formulated for attracting and serving the segments. a. measurable b. substantial c. accessible d. differentiable e. actionable Page: 262 252 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 255. In evaluating different market segments, the firm must look at two factors: the segment’s overall attractiveness and . a. company’s objectives and resources b. the product to be sold c. the purchasing process d. competition’s strategies e. the global nature of the product Page: 262 256. Volkswagen concentrates on the small-car market and Porsche on the sports car market. These would be examples of what is called . a. single-segment concentration b. selective specialization c. product specialization d. market specialization e. full market coverage Page: 262 257. All of the following are benefits of following the approach to target market selection: a strong knowledge of the segment’s needs, a strong market presence, operating economies through specializing in production, distribution, and promotion. a. single-segment concentration b. selective specialization c. product specialization d. market specialization e. full market coverage Page: 262 258. When a symphony orchestra targets people who have broad cultural interests, rather than only those who regularly attend concerts, the orchestra is targeting what are called . a. market mavens b. strategic segments c. supersegments d. occasion segments e. psychodemographic segments Page: 262 259. Which of the following best represents the chief advantage of pursuing a multisegment strategy? a. It makes the company almost bullet proof to competitors’ actions. b. It diversifies the firm’s risk. c. It creates synergy between markets. d. It is a low cost strategy. e. It treats all buyers the same and, therefore, lowers promotion costs. Page: 262 260. The chief disadvantage to a firm that decides to follow a product specialization strategy in selecting target markets is that . a. no synergy exists 253 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process b. logistics can become a nightmare c. the product may be supplanted by an entirely new technology d. competitors can easily copy any new product introductions e. e-commerce becomes difficult for the company Page: 263 261. With as a target market strategy, the firm concentrates on serving many needs of a particular customer group. a. single-segment concentration b. selective specialization c. product specialization d. market specialization e. full market coverage Page: 263 262. The two ways that large firms can cover a whole market (e.g., full market coverage strategy) are through and differentiated marketing. a. undifferentiated b. logistical c. psychological d. niche e. macromarketing Page: 263 263. In marketing, the firm operates in several market segments and designs different products for each segment. a. segmented b. undifferentiated c. differentiated d. geodemographic e. niche Page: 263 264. The best way to manage multiple segments is to appoint with sufficient authority and responsibility for building the segment’s business. a. a product champion b. segment managers c. promotion managers d. strategic managers e. mid-level managers Page: 263 254 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 265. All of the following costs are likely to be higher if a marketer pursues a differentiated marketing approach EXCEPT . a. product modification costs b. manufacturing costs c. administrative costs d. inventory costs e. pricing costs Page: 264 266. is the strategic coordination of economic, psychological, political, and public relations skills, to gain the cooperation of a number of parties in order to enter or operate in a given market. a. Metamarketing b. Macromarketing c. Micromarketing d. Megamarketing e. Modular marketing Page: 265 267. One way to discover new market segments is to investigate the hierarchy of attributes consumers examine in choosing a brand if they use phased decision strategies. This process is called . a. market partitioning b. market positioning c. market segmentation d. strategic marketing e. brand marketing Page: 266 268. Not all attempts to target children, minorities, or other special segments draw criticism. Which of the following is the best illustration of a company (or industry) that seems to be marketing to the above in a correct and ethical way? a. McDonald’s marketing to inner-city youth. b. R. J. Reynolds marketing of the Kool brand. c. Colgate-Palmolive’s Colgate Junior toothpaste. d. The cereal industry’s approaches to children. e. G. Heileman Brewing’s approach to Colt 45 malt liquor. Page: 267 True/False 269. Markets are almost always homogeneous. Page: 239 255 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 270. To compete more effectively, many companies are now embracing target marketing. Page: 240 63. Effective target marketing requires that marketers use market segmentation, market targeting, and market positioning to achieve success in the marketplace. Page: 240 64. Henry Ford epitomized the market segmentation strategy when he offered the Model-T Ford. Page: 240 65. A market segment consists of a group of consumers who share a similar set of needs and wants. Page: 240 66. With respect to market offerings, if a marketer emphasizes a naked solution, he or she is emphasizing the product and service elements that all segment members value. Page: 241 67. A marketer glances at this month’s market-preference pattern diagram and notices that all of the customers are grouped in the middle of the diagram; therefore, customers are exhibiting clustered preferences. Page: 242 68. An attractive niche is characterized as having a distinct set of needs. Page: 242 69. Local marketing reflects a growing trend called macromarketing. Page: 244 70. Grassroots marketing done at the local level is associated with experiential marketing where experiences are more important than products or services. Page: 244 71. If you charge for the time customers spend with you, then and only then are you in the service business. Page: 245 72. When Nike and Gillette advertise and associate their products with the Boston Marathon, the two companies are engaged in a form of experiential marketing called co-branding. 256 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships Answer: True Page: 245 73. The ultimate level of segmentation leads to “segments of one,” “customized marketing,” or “one-to-one marketing.” Page: 246 74. Two broad groups of variables are used to segment consumer markets: geographic and demographic variables. Page: 247 75. Typical groupings (segments) that might be designated using the geographic method of segmentation might be density, climate, or city/metro size. Answer: True Page: 248 76. Illustrations of personality segmentation would include culture- oriented, sports- centered, or outdoor- oriented subsegments. Page: 248 257 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 77. According to a new PRIZM cluster configuration, the Cosmopolitan tends to locate in cities such as Las Vegas, Miami, or Albuquerque. Page: 249 78. A local service company has decided to segment its market based on occupation; therefore, it has chosen a form of demographic segmentation for its approach. Answer: True Page: 249 79. Life stage defines a person’s age. Page: 250 258 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 80. Men and women have different attitudinal and behavioral orientations caused mainly by their genetic makeup. Answer: False Page: 250 81. Research has shown that income is a highly accurate predictor of the “best” customers for a given product. Answer: False Page: 251 82. If you went to college in the late 1960s, you are most likely to be in a cohort shaped by the Viet Nam War. Page: 251 83. The largest American generation of the twentieth century (78 million people) is considered to be the GI Generation that fought in World War II. 259 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process Answer: False Page: 252 Level of difficulty: Medium 84. A sixty year-old man is coping with his advancing hair loss; therefore, he is dealing with what is called physiographics. Answer: True Page: 252 Level of difficulty: Hard 260 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 85. Psychographics is the science of using psychology and demographics to better understand consumers. Answer: True Page: 252 Level of difficulty: Easy 86. Generation X is considered to be a hot market because of their size, consumer savvy, and their ability to be “wired-in” to contemporary trends. Page: 253 87. Forty-seven percent of 21-year-olds own a mobile phone. Page: 253 88. In the VALS segmentation system, Thinkers are characterized as being successful, sophisticated, active, “take-charge” people with high self-esteem. Page: 254 89. According to the VALS segmentation system, the Strivers are at bottom of the typology with the lowest resources and lowest with respect to innovation. Page: 254 90. When Mobil Oil Company researched its market based on benefit expectations, it found that the largest segment (Price Shoppers) with a 27 percent share wanted fast fuel, branded products, and convenience. Answer: False Page: 256 91. An organization that could benefit from using User Status as a means for segmenting its market would be a local blood bank. Page: 256 92. Marketers would rather attract one heavy user than several light users. 261 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process Answer: True Page: 256 93. With respect to loyalty status, if a consumer is loyal to two or three brands, he or she is called shifting loyal. Answer: False Pages: 256–257 94. The most important variable in segmenting a business market is demographics. Page: 258 262 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 95. Typical categories that would appear under the heading of situational factor segmentation variables in the business marketplace would be urgency, specific application, and size of order. Answer: True Page: 259 96. The last step in the seven-step marketing segmentation process would be to develop a marketing-mix strategy reflective of segment positioning strategies. Page: 261 97. To be useful, market segments must have as one of their characteristics the ability to be measured. Answer: True Page: 262 Level of difficulty: Medium 98. As a pattern found in target market selection, market specialization means that the company offers one product to as many markets as possible. Page: 262 99. If a marketer is blocked from entering a market, the strategy of megamarketing can be used to assist in breaking into that market. Page: 265 263 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 100. Market partitioning is process of focusing on a desired position in the marketplace and then accumulating the resources to protect and defend that position. Page: 266 Essay 101. Market segments can be defined in many different ways. One way to carve up a market is to identify preference segments. List and briefly characterize three preference segments cited in the text. 102. Columbia University’s Bernd Schmitt believes that marketers can provide experiences for customers through a set of experience providers. List and briefly discuss the seven experience providers recommended by Schmitt. 103. A new trend in marketing is toward customerization. Describe what customerization is and how marketers are using it. 104. There are several major segmentation variables that might be used by a marketer to address a consumer market. If the marketer were to use social class, psychographic lifestyle, and readiness stage to segment its market, identify possible segmentation subcategories under each of the three. For example, if we were to segment based on usage rate, subcategories would be light user, medium user, and heavy user. 264 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships uppers, and upper uppers. Second, psychographic lifestyles would yield culture-oriented, sports-oriented, and outdoor-oriented. Lastly, readiness stage would yield unaware, aware, informed, interested, desirous, and intending to buy. Other sub-categories might be possible. The list above comes from Table 8.1. If you wish to deviate from this table, be sure set ground rules for the students. Page: 248 105. Briefly profile the American generations labeled as Baby boomers, Generation X, Generation Y, and Millennials. 106. Marketing to Generation Y is a challenge because of their size and characteristics. Because they are often turned off by overt branding practices and a “hard sell,” marketers have tried many different approaches to reach and persuade Gen Y. The text mentions seven methods for accomplishing this task. List and briefly discuss four of those methods. 107. The VALS segmentation system has evolved into an 8-part typology. List and briefly describe any four categories of that 8-part typology. 108. If a marketer were to segment a business market on the basis of demographics, what three subcategory segmentation variables would probably be used to 265 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process assist with this form of segmentation? What questions would be asked in each of the three categories to advance the segmentation effort? 109. To be useful, market segments must rate favorably on five key criteria. What are those criteria? 110. The text describes five possible patterns for target market selection. Describe the pattern called selective specialization. 266 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships APPLICATION QUESTIONS Multiple Choice 111. According one expert from J. Walter Thompson’s Mature Marketing Group, “everyone over 45 is lumped into a category called old.” However, the expert points out that this strategy is faulty. Seniors, particularly boomers-turned- seniors, often make buying decisions based on . a.price, not quality b. lifestyle, not age c.age perception d. what their children buy e.dreams, not realities Page: 239 112. When Coca-Cola sold only one kind of Coke in a 6.5-ounce bottle, it was practicing what is called . a. primary marketing b. micromarketing c. macromarketing d. segmented marketing e. mass marketing Page: 240 113. The marketer the segments; the marketer’s task is to identify the segments and decide which one(s) to target. a. plans b. creates c. does not create d. rarely controls e. controls Page: 240 114. Anderson and Narus have urged marketers to present flexible market offerings to all members of a segment. A flexible market offering consists of two parts. Which of those parts contains the product and service elements that all segment members’ value? a. Naked solution b. Discretionary solution c. Maximum solution d. Pseudo solution e. Virtual solution Page: 241 115. Enterprise Rent-A-Car has challenged Hertz’s supremacy in the rental car market by tailoring its marketing program to a relatively neglected target market. Which of the following would be the most accurate description of that market? 267 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process a. The singles market. b. The soccer mom market. c.The business traveler market. d. The low-budget, insurance-replacement market. e.The vacationer market. Page: 242 116. The recipe for Internet niching success is to . a. find a need and fill it b. choose a hard-to-find product that customers do not need to see and touch c. choose a low-budget product that is heavily demanded by Gen Y d. choose an exclusive product sold primarily to seniors e. find a product that has some attraction to a health-conscious market Pages: 243–244 117. One marketing commentator said, “The idea is not to sell something, but to demonstrate how a brand can enrich a customer’s life.” Which of the following forms of marketing was the commentator describing? a. Experiential marketing b. Niche marketing c. Benefit marketing d. Viral marketing e. Virtual marketing Page: 244 118. If you were a marketing manager that was considering implementing the concept of customer experience management (CEM), you would follow all of the following steps EXCEPT . a. analyzing the experiential world of the customer b. building the experiential platform c. designing the segmentation portfolio d. structuring the customer interface e. engaging in continuous innovation Page: 245 268 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 119. Home furnishing retailer Bed Bath & Beyond’s ability to cater to local tastes has fueled its phenomenal growth. Bed Bath & Beyond’s managers pick of their own merchandise, and this local focus has helped the chain evolve from one that began selling little more than bed linens to the “beyond” part—products ranging from picture frames and pot holders to imported olive oil and designer door mats. a. 40 percent b. 50 percent c. 25 percent d. 70 percent e. 90 percent Page: 248 120. If a marketing researcher saw such names (categories) Blue Blood Estates, Winner’s Circle, Hometown Retired, or Shotguns and Pickups when doing segmentation research, the marketing researcher would most likely be dealing with clusters. a. PRIZM b. geodemographic c.psychographic d. demographic e.VALS Page: 249 121. The Scion by Toyota has a hip look and feel—and an industrial strength stereo —and is sold in chrome and black showrooms tucked inside Toyota dealerships. According to Toyota, to which of the following audiences is the Scion positioned? a. Wealthy baby boomers. b. African American Generation X members. c.Hispanic American millennials. d. Generation Y. e.The silent majority. Page: 250 122. Increasingly, companies are finding that their markets are as middle-market Americans migrate toward more premium products. a. “triangle-shaped” b. “inverted” c. “hourglass-shaped” d. “circular” e. “linear” Page: 251 269 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 123. Which of the following statements accurately describes what demographers are calling the “boom-boom effect”? a. Consumers are demanding more “bang for their buck.” b. Baby boomers still rule the marketplace. c. Generation X and their taste for violence will dominate the market in the future. d. Products that appeal to 20-somethings also appeal to baby boomers. e. Companies must have success quickly or go bust. Page: 252 124. If a marketing manager employs such marketing techniques as online buzz, student ambassadors, cool events, and street teams to reach target markets, the manager is most likely appealing to the market. a.pre-school b. Generation X c.Generation Y d. Generation Z e.latent baby boomers Page: 253 125. A hardware store has decided to use the VALS segmentation system to target consumers. The store is particularly interested in reaching people who are characterized by the VALS system as being practical, down-to-earth, and self- sufficient who like to work with their hands. Which of the following VALS categories most likely matches to the hardware store’s segment of interest? a. Believers b. Strivers c. Survivors d. Experiencers e. Makers Page: 254 126. Users of a brand can be segmented into several groups based on the strength of commitment to the brand. If a brand manager is seeking to identify those users who are most likely to defect to another brand, he or she should look for users that are labeled as being . a. convertible b. shallow c. average d. entrenched e. latent Page: 258 270 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 127. A purchasing manager has decided to take a “purchasing approach” to segmenting a proposed business market. All of the following would be potential means (sub-segments) for segmenting under the “purchasing approach” EXCEPT . a.purchasing-function organization b. power structure c.specific application d. nature of existing relationships e.purchasing criteria Page: 259 128. If your assignment was (for each segment) to create a “value proposition” and product-price positioning strategy based on the segment’s unique customer needs and characteristics, you would be in which of the following steps of the segmentation process? a. Needs-based segmentation b. Segment identification c. Segment attractiveness d. Segment positioning e. Segment “acid-test” Page: 261 129. As a brand manager you have decided to use the full market coverage approach in marketing to your customers. Within the full market coverage approach, you have selected a(n) strategy whereby your firm will operate in several market segments and design different products for each segment. a. undifferentiated b. differentiated c. concentrated d. introverted e. parallel Page: 263 130. In the past, most car buyers first decided on the manufacturer and then on one of its car divisions. This type of buying strategy has been labeled as a . a. brand-dominant hierarchy b. nation-dominant hierarchy c. promotional hierarchy d. geographic hierarchy e. service-value hierarchy Page: 266 271 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process Short Answer 131. A starting point for discussing segmentation is mass marketing. Explain this concept. 132. Most companies today are turning to micromarketing at one of four levels. 133. Assume that you have decided to use a niche strategy to advance your marketing goals. Characterize an attractive niche. 134. Local marketing reflects a growing trend called grassroots marketing. Characterize grassroots marketing. 135. According to one marketing expert, “The idea is not to sell something, but to demonstrate how a brand can enrich a customer’s life.” What form of marketing is this expert referring to? 136. Pine and Gilmore have argued that we are on the brink of what might be called the “Experience Economy.” What are the four varieties of experiences that Pine and Gilmore assert will be salable in the future? 272 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 137. When a marketer attempts to segment a consumer market, two broad groups of variables may be used. What are those two broad groups of variables? Give an example of each broad group. 138. PRIZM was developed by Claritas, Inc. Explain what PRIZM is intended to do. 139. Silverstein and Fiske say that Panera bakery cafes are a good illustration of luxury good-oriented establishments that deliver three benefits that are common to new luxury good organizations. What are the three benefits listed by Silverstein and Fiske? 140. Meredith, Schewe, and Karlovich developed a framework called The Lifestage Analytic Matrix. What does this matrix do and what are the variables that might be contained in such a matrix? 141. Characterize psychographic segmentation. 142. According to the VALS Segmentation System, what four groups belong in the category that displays lower resources? 273 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 143. People play five roles in a buying decision. What are those roles? 144. Buyers can be classified according to the benefits they seek. Even car drivers who what to stop for gas may seek different benefits. Through its research, Mobil identified five different benefit segments. What are those segments and what benefits are associated with each segment? 145. Consumer attitude(s) is(are) an interesting way to segment a market. Research has shown that five attitude groups can be found in the market. What are those five attitude groups? 146. A Conversion Model is proposed in the text. What is the purpose of a conversion model in assessing behavioral segmentation? 147. Assuming you were a marketing manager that was interested in segmenting business buyers’ benefit bundles based on their stage in the purchase decision process, what three categories would be appropriate? Suggested ategories would include: (1) first-time prospects, (2) novices, and (3) sophisticates. For descriptions of each category, see chapter materials. 148. One proposed segmentation scheme classifies business buyers into three groups, each warranting a different type of selling. The groups are (1) price- 274hapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships oriented customers, (2) solution-oriented customers, and (3) strategic-value customers. What types of selling (specific selling type name) would be associated with these three groups? 149. Differentiated marketing typically creates more total sales than undifferentiated marketing. However, it also increases the costs of doing business. Assume that you are a marketing manager that is considering using differentiated marketing. What five costs that you encounter on a rather regular basis would most likely be higher because of your decision to pursue differentiated marketing? 150. As a marketing manager, you have decided to update your segmentation scheme. In the process of doing this, you have decided to use a process called market partitioning. Explain what market portioning is. Chapter 9: Creating Brand Equity GENERAL CONCEPT QUESTIONS Multiple Choice 271. At the heart of a successful brand is , backed by creatively designed and executed marketing. a. price b. promotion c. a great product or service d. a great slogan 275 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process e. a brand concept Page: 273 272. The strategic branch management process involves four main steps. Which of the following would NOT be among those steps? a. Measuring consumer brand knowledge. b. Identifying and establishing brand positioning. c. Planning and implementing brand marketing. d. Measuring and interpreting brand performance. e. Growing and sustaining brand value. Page: 274 273. The American Marketing Association defines a as “a name, term, sign, symbol, or design, or a combination of them, intended to identify the goods or services of one seller or group of sellers and to differentiate them from those of competitors.” a. holistic product concept b. product concept c. service concept d. brand e. brand image Page: 274 276 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 274. The earliest signs of branding in Europe were medieval requirement that craftspeople put trademarks on their products to protect themselves and consumers against inferior quality. a. kings’ b. churches’ c. consumers’ d. governments’ e. guilds’ Page: 274 275. Consumers learn about brands through and product marketing programs. a. the mass media b. past experiences with the product c. the sales force d. shopping bots e. independent information sources Page: 274 276. The world’s strongest brands share common attributes. Which of the following would NOT be among those common attributes? a. The brand that spends the most is the most respected and valued. b. The company monitors sources of brand equity. c. The pricing strategy is based on consumer perceptions of value. d. The brand stays relevant. e. The brand excels at delivering the benefits consumers truly desire. Page: 275 277. is endowing products and services with the power of a brand. a. Brand image b. The branding concept c. Branding d. Brand positioning e. Brand partitioning Page: 275 278. Brand is the added value endowed to products and services. a. loyalty b. equity c. preference d. satisfaction e. benefits Page: 276 277 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 279. The premise of models is that the power of a brand lies in what customers have seen, read, learned, thought, and felt about the brand over time. a. product-based brand equity b. service-based brand equity c. functional-based brand equity d. mission-driven brand equity e. consumer-based brand equity Page: 276 280. can be defined as the differential effect that brand knowledge has on consumer response to the marketing of that brand. a. Mission-driven brand equity b. Consumer-based brand equity c. Product-driven brand equity d. Service-driven brand equity e. Function-based brand equity Page: 277 281. When a consumer expresses thoughts, feelings, images, experiences, beliefs, and so on that become associated with the brand, the consumer is expressing brand . a. knowledge b. loyalty c. behavior d. preference e. equity Page: 277 282. is what drives the differences that manifest themselves in brand equity. a. Brand image b. Consumer income c. Consumer purchasing power d. Consumer knowledge e. Brand perception Page: 277 283. Strong brands possess all of the following marketing advantages EXCEPT . a. greater loyalty b. larger margins c. guaranteed profits d. improved perceptions of product performance e. more elastic consumer response to price decreases Page: 277 278 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 284. When a marketer expresses his or her vision of what the brand must be and do for consumers, they are expressing what is called . a. a brand promise b. a brand mission c. brand equity d. a brand position e. a brand concept Page: 278 285. There are four key components—or pillars—of brand equity. Which of those components or pillars measures the breadth of a brand’s appeal? a. Differentiation b. Relevance c. Esteem d. Knowledge e. Value Page: 278 286. Two pillars that point to the brand’s future value, rather than just reflecting its past, are differentiation and relevance. Differentiation and relevance combine to determine what is called brand . a. position b. image c. depth d. knowledge e. strength Page: 279 287. David Aaker views brand equity as a set of five categories of brand assets and liabilities linked to a brand that add or subtract from the value provided by a product or service to a firm and/or that firm’s customers. All of the following would be among Aaker’s five categories EXCEPT . a. brand loyalty b. brand awareness c. perceived quality d. brand price e. brand associations Page: 279 279 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 288. According to Aaker, a particularly important concept for building brand equity is —the unique set of brand associations that represent what the brand stands for and promises to consumers. a. brand knowledge b. brand preference c. brand identity d. brand vision e. brandable differences Page: 279 289. General Motors states that its is a “world class car with employees who treat customers with respect and as friends.” a. core identity b. perceived identity c. extended identity d. defensible identity e. competitive identity Pages: 280 290. According to the BRANDZ model of brand strength, brand building involves a sequential series of steps. Which of these steps would address or answer the question “Do I know about it?” a. Relevance b. Presence c. Performance d. Advantage e. Bonding Page: 280 291. The MasterCard “priceless” ad campaign is a good example of brand duality. Two advantages of the brand are demonstrated in this campaign. What are those advantages? a. Positive and negative advantages. b. Local and global advantages. c. Rational and emotional advantages. d. Segmented and differentiated advantages. e. Price and promotional advantages. Page: 280 280 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 292. All of the following are considered to be among the “six brand building blocks” EXCEPT . a. brand salience b. brand performance c. brand imagery d. brand feelings e. brand pride Page: 280 293. With respect to the “six brand building blocks,” focus on customers’ own personal opinions and evaluations. a. brand salience b. brand performance c. brand imagery d. brand judgments e. brand resonance Page: 280 294. With respect to the brand resonance pyramid, at which of the following “building block levels” would we expect the consumer to have developed an intense, active loyalty? a. Salience b. Imagery c. Feelings d. Judgments e. Resonance age: 281 295. From a marketing management perspective, there are three main sets of brand equity drivers. Which of these drivers was most applicable when McDonald’s decided to use the “golden arches” and Ronald McDonald as symbols of their brand? a. The product and all accompanying marketing activities and supporting marketing programs. b. The service and all accompanying marketing activities and supporting marketing programs. c. The initial choices for the brand elements or identities making up the brand. d. Associations indirectly transferred to the brand by linking it to some other entity. e. The profitability associated with brand development. Page: 281 281 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 296. are those trademarkable devices that serve to identify and differentiate the brand. a. Brand elements b. Brand value c. Brand perception d. Brand image e. Brand tracks Page: 281 297. Six brand elements assist in brand building. Which of the following would NOT be among those preferred brand elements? a. Adaptable b. Protectable c. Memorable d. Likeability e. Subliminal nature Page: 282 298. If a brand element can be used to introduce new products in the same or different categories, the brand element is said to be . a. memorable b. meaningful c. likeable d. transferable e. adaptable Page: 282 299. Before selecting a brand name, marketers must be assured that the brand name will be well received and understood by the consumers. In order to do this several tests may need to be performed. A(n) asks such questions as “How easily is the name pronounced?” a. association test b. learning test c. memory test d. preference test e. design test Page: 282 300. Brand names are not only important brand element. Often, , the more important it is that brand elements capture the brand’s intangible characteristics. a. the less concrete brand benefits are b. the more concrete brand benefits are c. the more varied brand perceptions are d. the less varied brand perceptions are e. the more sophisticated brand benefits are Pages: 282–283 301. With respect to powerful brand elements, a is an extremely efficient means to build brand equity. The element can function as useful “hooks” or “handles” to help consumers grasp what the brand is and what makes it special. 282 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships a. spokesperson b. product shape c. slogan d. patent e. promotional descriptor Page: 283 302. Brand elements and secondary associations can make important contributions to building brand equity; however, the primary input comes from . a. the product or service and supporting marketing activities b. marketing research c. the consumer d. the distributors e. the organizational mission statement Page: 284 303. A can be defined as any information-bearing experience a customer or prospect has with the brand, the product category, or the market that relates to the marketer’s product or service. a. brand value b. brand element c. brand trait d. brand character e. brand contact Page: 284 304. Chupa Chups has the distinction of being the world’s largest maker of and has begun to diversify its brand beyond its original market (children). Today, Chupa Chups is targeting teens and youth through “nonendorser endorsers” such as Jerry Seinfeld. a. veggie chips b. apple juice c. roller skates d. lollipops e. granola Page: 284 283 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 305. Considering holistic marketing activities, the rapid expansion of has created opportunities to personalize marketing. a. target marketing b. globalization c. the Internet d. standardization e. CD technology Page: 284 306. is about making sure that the brand and its marketing are as relevant as possible to as many customers as possible—a challenge, given that no two customers are identical. a. Personalizing marketing b. Segmenting marketing c. Brand imagery d. Emotionalizing brands e. Rationalizing brands Page: 284 307. The traditional “marketing-mix” concept and the notion of the “4 Ps” may not adequately describe modern marketing programs. is about mixing and matching marketing activities to maximize their individual and collective effects. a. Personalizing marketing b. Individualizing marketing c. Globalizing marketing d. Institutionalizing marketing e. Integrating marketing Page: 285 308. Godin identifies five specific steps to enhance effective permission marketing. Which of the following would NOT be among those steps? a. Offer the prospect an incentive to volunteer. b. Offer the interested prospect a curriculum over time that teaches the consumer about the product or service. c. Reinforce the incentive to guarantee that the prospect maintains the permission. d. Always offer a monetary incentive to demonstrate sincerity of the offer. e. Over time, leverage the permission to change consumer behavior toward profits. Page: 285 284 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 309. is the consumers’ ability to identify the brand under different conditions, as reflected by their brand recognition or recall performance. a. Brand awareness b. Brand image c. Brand alternation d. Brand perception e. Brand reflection Page: 286 310. A marketing manager has decided to study the perceptions and beliefs held by consumers, as reflected in the associations held in consumer memory. Which of the following terms is most closely associated with the marketing manager’s objective of study? a. Brand awareness b. Brand image c. Brand element d. Brand concept e. Brand trait Page: 286 311. For a brand to succeed, marketers must “walk the walk” and ensure that employees and marketing partners do the same. Marketers often must use to motivate those groups to support the brand. a. global branding b. retro-branding c. internal branding d. external branding e. dual branding Page: 286 312. Mark Thomas has observed that Shell delivers on its promises to supply the best gasoline possible to the driving public. Shell promotions, employees, and distributors send a common and consistent message about delivering on Shell promises to Mr. Thomas. A good term that describes what occurs when customers experience the company as delivering on its brand promise is the term . a. brand image b. brand enhancement c. brand belief d. brand attitude e. brand bonding Page: 286 285 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 313. The main secondary sources of brand knowledge come from all of the following EXCEPT . a. other brands b. people c. things d. local, state, and federal governments e. places Page: 287 314. Brand equity can be measured in two ways. Which of the following would be a good representation of one of those ways? a. Statistical analysis of demographics. b. Secondary evaluation of governmental statistics. c. Directly assessing the actual impact of brand knowledge on consumer response to different aspects of marketing. d. Evaluating published statistics of competitors. e. Hiring independent evaluators. Page: 288 315. A structured approach to assessing the sources and outcomes of brand equity and the manner in which marketing activities create brand value is called . a. the brand value chain b. the brand portfolio c. the brand life cycle d. brand partitioning e. brand positioning Page: 288 316. A brand manager is concerned that his organization’s brand image and physical sales are slipping in the marketplace. The manager has decided to query consumers about the health of the brand and try to discover ways to leverage the brand’s equity. Which of the following terms will most likely provide the structure and process for the manager’s investigation? a. A brand demographic matrix analysis. b. A secondary search of good brand characteristics. c. A brand audit. d. An organizational audit. e. A brand positioning study. Page: 289 286 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 317. Within a brand audit, the has as its purpose to provide a current, comprehensive profile of how all the products and services sold by a company are marketed and branded. a. cost curve calculation b. product balance sheet c. strategic plan d. brand inventory e. product assessment Page: 289 318. Many firms use to supplement traditional focus groups. They study consumers in their everyday habitats at home, at work, at play, or shopping. a. ethnography b. demography c. geodemography d. psychographics e. product profiles Page: 290 319. Irene and Dave Washburn are part of a long-term . The Washburn’s supply a national research firm with information about their brand habits, preferences, dislikes, and beliefs on a monthly basis for a period of two years. a. image study b. demographic study c. psychological profile study d. promotion management study e. tracking study Page: 290 320. has the job of estimating the total financial value of the brand. a. Brand tracking b. Brand auditing c. Brand equity d. Brand valuation e. Brand partitioning Page: 290 321. According to 2004 Brand Value estimates, was ranked number-one in the world with a brand value of $67.39 billion. a. Microsoft b. IBM c. Coca-Cola d. GE e. McDonald’s Page: 291 322. A company’s major enduring asset is . a. its leadership b. its brand c. its culture 287 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process d. its shareholders e. its workers Page: 291 323. According to Interbrand’s Brand Strength formula, the most important factor in the equation is with a 25 percent weight. a. stability b. market c. geographic spread d. trend e. leadership Page: 292 324. According to Scott Bedbury’s book, A New Brand World, all of the following are considered to be important principles for twenty-first century branding EXCEPT . a. consumers will tell you what your brand image should be b. relying on brand awareness has become marketing fool’s gold c. you have to know it before you can grow it d. great brands establish enduring customer relationships e. all brands need good parents Page: 294 325. When a firm uses an established brand to introduce a new product, it is called a(n) . a. sub-brand b. brand value c. brand extension d. brand mix e. brand posture Page: 296 326. All of the following would be examples of companies that use family branding as one of their branding strategies EXCEPT . a. Campbell Soup b. Sears c. Heinz d. General Electric e. Hunt’s Page: 297 288 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 327. According to Ries and Trout, Cadbury suffered from the when the company allowed its brand to become diluted by putting their name on such variants as mashed potatoes, powdered milk, soups, beverages, as well as chocolates and candies. a. “greed is good” trap b. “pyramid principle” c. “branding fallout” concept d. “image syndrome” e. “line-extension” trap Page: 299 328. A is the set of all brands and brand lines a particular firm offers for sale to buyers in a particular category. a. brand partition b. brand position c. brand portfolio d. brand concept e. brand image Page: 301 329. brands are positioned with respect to competitors’ brands so that more important (and more profitable) flagship brands can retain their desired positioning. a. Flanker b. Attacker c. Defender d. Blitzkrieg e. Individual Page: 302 330. The role of in the brand portfolio often may be to attract customers to the brand franchise. Trading up will often occur with this type of brand. a. the cash cow b. flanker brand c. fighting brand d. high-end prestige brand e. low-end entry-level brand Page: 303 289 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process True/False 331. At the heart of a successful brand are the successful people that run the organization. Page: 273 332. Google’s successful brand name was derived from the word googol—the number represented by a 1 followed by 100 zeroes. Page: 273 333. The American Marketing Association defines a brand as “a name, term, sign, symbol, or design, or a combination of them, intended to identify the goods or services of one seller or group of sellers and to differentiate them from those of competitors.” Page: 274 334. One of the attributes shared by the world’s strongest brands is that the brand becomes invulnerable to attack from competitors due to the support of the marketplace. Page: 275 335. The added value endowed to products and services is called brand equity. Page: 276 336. Brand knowledge is indicated when the consumer refuses to purchase competitive brands. Page: 277 337. One of the advantages of having a strong brand is the ability to have a more elastic consumer response to price decreases of the brand. Page: 277 338. The marketer’s vision of what the brand must be and do for consumers is called a brand promise. Page: 278 339. There are four key components—or pillars—of brand equity; one of these components is called knowledge. Page: 278 340. An illustration of the extended brand identity of GM’s Saturn brand is a “world-class car with employees who treat customers with respect and as friends.” 290 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships Answer: False Page: 280 341. Under the BRANDZ model of brand strength, the brand objective of bonding is translated to mean “nothing else beats it.” Page: 280 342. Brand resonance is associated with how a brand name sounds when said by spokespersons or consumers. Answer: False Page: 280 73. Brand salience relates to how often and easily the brand is evoked under various purchase or consumption situations. Page: 280 74. Brand imagery is the consumers’ emotional responses and reactions with respect to the brand. Page: 280 75. In the brand resonance pyramid, the lowest level (e.g., identity—Who are you?) is associated with what is called salience. Page: 281 76. A few good illustrations of power brand elements are Nike’s “swoosh” logo, the empowering “Just Do It” slogan, and the mythological “Nike” name based on the winged goddess of victory. Answer: True Page: 281 77. One of the selection criteria for creating a successful brand element is that it should be projectable. 291 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process Page: 282 78. If a brand element has the characteristic of being memorable, it is said to mean that the brand is credible and suggestive of its corresponding category. Answer: False Page: 282 79. One of the ways for testing a brand element is to ask consumers how well they remember the brand name; this is called a learning test. Answer: False Page: 282 Level of difficulty: Medium 80. A powerful—but sometimes overlooked—brand element is slogans. Answer: True Page: 283 81. A classic case of a company using a slogan to build brand equity is that of Avis’s 41-year-old “We Try Harder” ad campaign. 292 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships Answer: True Page: 283 Level of difficulty: Easy 82. A brand contract is defined as any information-bearing experience a customer or prospect has with a brand. Page: 284 83. Personalizing marketing is based on the fact that all customers are identical in several ways. Answer: False Page: 284 Level of difficulty: Medium 84. Gillette sent 1,000 young males a new, innovative razor product. In return, the company asked the young males to supply their e-mail addresses so future contacts could be initiated. This would be an example of what is called permission marketing. Page: 285 85. Brand awareness can be perceived as being the consumers’ ability to identify the brand under different conditions, as reflected by their brand recognition or recall performance. Page: 286 86. Internal branding is the perceptions and beliefs held by consumers, as reflected in the associations held in consumer memory. Page: 286 87. Marketers must now “walk the walk” to deliver the brand promise. Often internal branding is necessary to make sure that all employees assist in meeting the brand promise. Page: 286 293 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 88. The brand promise will not be delivered unless everyone in the company lives the brand. Page: 286 89. The indirect approach to assessing brand equity assesses the actual impact of brand knowledge on consumer response to different aspects of marketing. Page: 288 90. A brand value chain often does not exist because of an organization’s commitment to its service value chain. Page: 288 91. The brand audit can be used to set strategic direction for the brand. Page: 289 92. The purpose of brand strength (an assessment tool) is to provide a current, comprehensive profile of how all the products and services sold by a company are marketed and branded. Answer: False Page: 289 107. In order to explore more detailed information about brands, many firms are now using ethnography to supplement traditional focus groups. Page: 290 294 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 108. Tracking studies collect information from consumers on a routine basis over time. Answer: True Page: 290 95. In essence, brand equity is basically the same concept as brand valuation. Page: 290 96. At present, the most valuable brand in the world is Microsoft. Answer: False Page: 291 97. A company’s most enduring asset is its intellectual capital generated by the top officers of the organization. Page: 291 98. With respect to brand revitalization, the primary strategy for recovery is to hire a public relations firm to think of a new image for the firm and its products. Page: 294 99. When Honda expanded its brand into such areas as automobiles, motorcycles, snowblowers, lawnmowers, marine engines, and snowmobiles, it was pursuing a strategy called category extension of its brand. Page: 296 100. Brand dilution occurs when consumers no longer associate a brand with a specific product or highly similar products and start thinking less of the brand. Page: 299 Essay 101. The world’s strongest brands share a list of common attributes. List and briefly characterize five of those attributes. 295 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process Suggested ccording to information presented in the text, the world’s strongest brands possess ten common characteristics. Those characteristics appear as: (1) the brand excels at delivering the benefits consumers truly desire; (2) the brand stays relevant; (3) the pricing strategy is based on consumer perceptions of value; (4) the brand is properly positioned; (5) the brand is consistent; (6) the brand portfolio and hierarchy makes sense; (7) the brand makes use of and coordinates a full repertoire of marketing activities to build equity; (8) the brand’s managers understand what the brand means to consumers; (9) the brand is given proper, sustained support; and, (10) the company monitors sources of brand equity. The students may choose any five of the above ten for their discussion. See chapter material for addition discussion material. Page: 275 296 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 102. Explain the concept of brand equity. Suggested rand equity is the added value endowed to products and services. This value may be reflected in how consumers think, feel, and act with respect to the brand, as well as the prices, market share, and profitability that the brand commands for the firm. Brand equity is an important intangible asset that has psychological and financial value to the firm. Page: 276 103. Advertising agency Young and Rubicam (Y&R) developed a model of brand equity called Brand Asset Valuator (BAV). What is the intent of the BAV model? List and briefly characterize the four key components (pillars) of brand equity. 104. The creation of significant brand equity involves reaching the top or pinnacle of the brand pyramid. List and briefly characterize the six components of the brand resonance pyramid. 280–281 105. There are six criteria used in creating brand elements. The first three can be characterized as “brand building” in terms of how brand equity can be built through the judicious choice of a brand element. The latter three are more “defensive” and are concerned with how the brand equity contained in the brand element can be leveraged and preserved in the face of different opportunities and constraints. List and briefly characterize the six criteria. 297 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 106. Describe the similarities and differences between the concepts of brand awareness and brand image. 107. Describe the meaning and function of a brand audit. 108. According to top brand valuation firm Interbrand, brand valuation is based on an assessment of what the value is today of the earnings or cash flow the brand can be expected to generate in the future. The Interbrand Brand Strength Formula uses seven components to make this assessment. What are those seven components and their associated weights in the formula? 109. The decision as to how to brand new products is especially critical. When a firm introduces a new product, it has three main choices. What are those choices? 298 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships Page: 296 110. There are a number of specific roles brands can play as part of a brand portfolio. List and briefly describe the four roles described in the text. APPLICATION QUESTIONS Multiple Choice 111. Based on a public poll conducted in 2002, was named “Brand of the Year” by Interbrand branding consultants; in fact, the brand name has become a verb that is used to describe an online search. a. Yahoo! b. Microsoft c. Linux d. Google e. America Online Page: 273 299 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 112. Marketers of successful twenty-first-century brands must excel at — the design and implementation of marketing activities and programs to build, measure, and manage brands to maximize their value. a. promotional planning b. brand personification c. strategic brand management d. brand awareness e. competitive differential advantage Page: 274 113. All of the following are valuable functions performed by brands for firms EXCEPT . a. they simplify product handling or tracing b. helps to organize inventory and accounting records c. offers the firm legal protection through registered trademarks d. intellectual property rights can be protected e. a branded product is almost always guaranteed to be profitable Page: 274 114. If a brand has the attributes of staying relevant, is properly positioned, is consistent, and makes use of and continues a full repertoire of marketing activities to build equity, the brand is most likely to be a . a. successful brand b. domestic brand c. regional brand d. global brand e. service brand Page: 275 115. Coca-Cola, Calvin Klein, Gucci, Tommy Hilfiger, Marlboro and others have become leaders in their product categories by understanding and desires and creating relevant and appealing images around their products. a. consumer perceptions b. consumer motivations c. consumer behaviors d. consumer demographics e. consumer market segments Page: 276 300 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 116. Brands must create strong, favorable, and unique brand associations with customers, as has been the case with Volvo (safety), Hallmark ( ), and Harley-Davidson (adventure). a. caring b. love c. happiness d. giving e. humorous Page: 277 117. Apple achieves incredible brand loyalty largely by delivering on its mission as defined by CEO Steve Jobs. That mission is best described as: . a. “To dominate through technology” b. “To create great things that change people’s lives” c. “To think fast; introduce new products faster” d. “To appeal to independent thinkers” e. “To make the Mac world a reality” Page: 277 118. A marketing manager stresses to a newly hired brand manager the importance of having a strong brand. All of the following would be advantages that the marketing manager might stress to his subordinate EXCEPT . a. improved perceptions of product performance b. greater loyalty c. less vulnerability to marketing crises d. lower margins e. possible licensing opportunities Page: 277 119. Virgin, the brainchild of England’s flamboyant Richard Branson, vividly illustrates the power enjoyed and responsibility assumed by a strong brand. Which of the following most accurately describes Branson’s brand strategy? a. Compete by offering severe discounts to meet competitors’ normal pricing strategies. b. Use the credibility of the brand to challenge the dominant players in a range of industries where the perception is that consumers are not getting value for money. c. Use promotion to inspire brand loyalty and mass consumption. d. Compete by using guerrilla-marketing tactics. e. To copy, copy, copy whenever possible to save funds for promotional warfare. Page: 278 301 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 120. If a manager is looking for a “report card” on past performance of a brand, he or she should turn to an examination of the brand . a. strength b. compatibility c. stature d. image e. dominance Page: 279 121. According to Aaker, brand identity consists of twelve dimensions organized around four perspectives. Which of the four perspectives would apply to the dimensions of brand personality and brand-customer relationships? a. Brand-as-product b. Brand-as-organization c. Brand-as-person d. Brand-as-symbol e. Brand-as-competitor Page: 279 122. Any time a consumer thinks of a dependable car battery that might be needed in an emergency situation such as a snow storm, the consumer thinks first of Die Hard batteries. This would be an example of what is called brand . a. salience b. imagery c. judgments d. feelings e. scope Page: 280 123. The famous “Plop, plop, fizz, fizz! Oh, what a relief it is!” campaign is a good example of what is called a brand . a. element b. tagline c. visual d. personification e. perception Page: 281 302 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 124. One of the advantages enjoyed by Apple Computers is how aesthetically appealing its products are perceived to be. Which of the following brand element choice criteria matches to Apple’s aesthetic appeal? a. memorable b. meaningful c. likeability d. protectible e. adaptable Page: 282 125. The idea for the famous Avis slogan “We Try Harder” came from an unusual source. Which of the following would be most closely associated with that source? a. From an Avis manager during a meeting with ad agency account executives. b. From a customer during a sponsored contest. c. From a high school student during a career day. d. From factory worker during a scheduled management/union meeting. e. From a member of the National Transportation and Safety Board. Page: 283 126. According to Seth Godin, marketers can no longer use . Instead, marketers should turn to permission marketing as a way to ensure long-term customer relationships and loyalty. a. task-oriented marketing b. interruption marketing c. hard core selling d. advocacy marketing e. one-to-one marketing Page: 285 127. If the Olive Garden sends employees to special classes to teach them the value of the brand and how pasta is much more than just pasta, Olive Garden is using to accomplish this task. a. interruption marketing b. loyalty marketing c. cohort marketing d. macrobranding e. internal branding Page: 286 303 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 128. If an organization has as one of its objectives to collect information from consumers on a routine basis over time, the organization will most likely use a technique called to accomplish the desired objective. a. tracking studies b. nonmetric-multidimensional scaling c. Likert scaling d. brand visualization e. internal branding Page: 290 129. According to Interbrand, brand earnings are calculated by subtracting a number of items from brand sales. All of the following would be among those items EXCEPT . a. costs of brand sales b. marketing costs c. variable and fixed overheads d. all employee costs and benefits e. remuneration of capital charge Page: 292 130. Four general strategies can be used in branding. Which of the following strategies is the one used by Kellogg’s when it follows a sub-branding policy with Kellogg’s Rice Krispies, Kellogg’s Raisin Bran, and Kellogg’s Corn Flakes? a. Individual names. b. Blanket family names. c. Separate family names for all products. d. Global names for all products. e. Corporate name combined with individual product names. Page: 297 Short Answer 131. Assume you are a marketing manager that wishes pursue a process of strategic brand management. List the four main steps that you would most likely go through to accomplish this task. 132. How does the American Marketing Association define the term brand? 304 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships Page: 274 133. Assume that you are marketing manager attempting to explain the concept of brand equity to a new employee in your department. What would be your explanation? Page: 276 134. Your company desires to have positive customer-based brand equity. What has to occur for this to happen? 135. Volvo has a strong brand association with respect to brand knowledge when consumers perceive it as a very safe care (safety). Explain the concept of brand knowledge. 136. As a marketing manager, you have made a commitment to having a strong brand. List five advantages shared by other strong brands that you will most likely have to emulate to accomplish this objective. 137. Brand equity has four components—differentiation, relevance, esteem, and knowledge. How are these components combined to produce brand strength and brand stature? Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 138. According to Aaker, a particularly important concept for building brand equity is brand identity. Brand identity is organized around four perspectives. What are those perspectives? 139. According to the BRANDZ model of brand strength, brand building involves a series of five sequential steps. What are those five sequential steps? 140. Most strong brands employ multiple brand elements. Nike has three such powerful brand elements. According to the text, what are those brand elements? 141. As a brand manager you would like to have your brand (brand name) to be protectible. Explain what you mean by “protectible” and give an illustration. 306 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 142. Jones Soda is presented in the text as an example of a company that has succeeded in personalizing their brand. Discuss how the company has accomplished this feat. 143. Permission marketing is becoming increasingly popular with marketers. Seth Godin, a pioneer in the technique, recommends five steps in becoming an 144. Given that the power of a brand resides in the minds of consumers and how it changes their response to marketing, there are two basic approaches to measuring brand equity. Briefly, describe each of these approaches. 145. If your marketing manager asked you to design and implement a brand value chain, explain what you have been asked to do. Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process one stage transfers to the next stage. For additional insight and discussion, see chapter section. Page: 288 146. A marketing research manager has just asked you to conduct a brand exploratory. What have you been asked to do? Explain. 147. Distinguish between brand equity and brand valuation. 148. Volvo is a good illustration of a company that has been successful in defending its brand equity. However, when Volvo deviated from its brand heritage, sales slumped. What is the key concept on which the Volvo brand was built and, when reinforced, eventually revived the company’s slumping sales? 149. Scott Bedbury, author of A New Brand World, cites eight principles on which twenty-first-century branding should be built. List four of those principles. Page: 294 150. As a branding manager, you have recommended to your board of directors a corporate policy of blanket family branding. Write a brief statement outlining the advantages of blanket family branding. 308 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships strong if the manufacturer’s name is good. Campbell’s introduces new soups under its brand name with extreme simplicity and achieves instant recognition. Page: 297 Chapter 10: Crafting the Brand Positioning GENERAL CONCEPT QUESTIONS Multiple Choice 343. As part of the strategic brand management process, each company and offering must represent a distinctive in the mind of the target market. a. promotion b. cell c. big idea d. ad e. organizational concept Page: 309 344. All marketing strategy is built on STP—segmentation, targeting, and . a. positioning b. product c. planning d. promotion e. performance Page: 310 345. is the act of designing the company’s offering and image to occupy a distinctive place in the mind of the target market. a. Positioning b. Product conceptualization c. Promotion presentation d. Performance imaging e. Preproduct launching Page: 310 346. The result of positioning is the successful creation of , a cogent reason why the target market should buy the product. a. an award winning promotional campaign b. a customer-focused value proposition c. a demand channel d. every-day-low-pricing e. strategic window of opportunity Page: 310 309 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 347. A good illustration of the value position for Perdue (chicken) is . a. one price beats all b. bring chicken to the world c. ethical values, the American way, and quality chicken d. chicken any way you like it e. more tender golden chicken at a moderate premium price Page: 311 348. A starting point in defining a competitive frame of reference for a brand positioning is to determine —the products or sets of products with which a brand competes and which function as close substitutes. a. functional membership b. competitive field c. category membership d. value membership e. demand field Page: 311 349. Which of the following terms is most closely associated with the following statement: “attributes or benefits consumers strongly associate with a brand, positively evaluate, and believe that they could not find to the same extent with a competitive brand”? a. Brand image b. Points-of-difference c. Points-of-parity d. Points-of-value e. Brand concept Page: 312 350. are associations that are not necessarily unique to the brand but may in fact be shared with other brands. a. Points-of-parity b. Points-of-difference c. Brand cells d. Brand positions e. Points-of-competitive field Page: 313 351. To achieve a point-of-parity (POP) on a particular attribute or benefit, a sufficient number of consumers must believe that the brand is “ ” on that dimension. a. most excellent b. neutral c. marginal d. good enough e. service-based Page: 313 352. The preferred approach to positioning is to inform consumers of a brand’s membership before stating its . 310 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships a. point-of-parity b. point-of-difference c. point-of-conflict d. point-of-weakness e. point-of-reference Page: 314 353. There are three main ways to convey a brand’s category membership: announcing category benefits, , and relying on the product descriptor. a. overt publicity b. industry trade press c. buzz marketing d. preference positions e. comparing to exemplars Page: 315 354. To avoid confusing brand loyal customers, Ford presented the X-trainer as a “sport wagon.” With respect to ways of conveying a brand’s category membership, which of the following did Ford use with its new product? a. Announcing category benefits. b. Comparing to exemplars. c. Relying on the product descriptor. d. Using brand perception to increase profits. e. Using public relations to secure brand position. Page: 315 355. Points-of-parity are driven by the needs of category membership and . a. loyalty b. large margins c. guaranteed profits d. the necessity of negating competitors’ PODs (points-of-difference) e. the creation of PODs (points-of-difference) Page: 315 356. There are at least three key consumer desirability criteria for PODs (points-of- difference): relevance, distinctiveness, and . a. believability b. presentation style c. economy d. non-technological e. information content Page: 315 357. Which of the following desirability criteria asks a question such as “Is the positioning preemptive, defensible, and difficult to attack?” when determining a POD (point-of-difference)? a. Feasibility b. Communicability c. Sustainability 311 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process d. Knowledgeable e. Value orientation Page: 316 358. Marketers must decide at which level to anchor the brand’s points-of- differences. At the lowest level are . For example, Dove soap can talk about the fact that it is one-quarter cleansing cream. a. brand values b. brand attributes c. brand benefits d. brand specifications e. brand partitions Page: 316 359. One common difficulty in creating a strong, competitive brand positioning is that many of the attributes or benefits that make up the points-of-parity and points-of-difference are . a. negatively correlated b. positive correlated c. neither positive nor negatively correlated d. inversely correlated e. unable to be correlated Page: 316 360. All of the following would be considered to be among examples of negatively correlated attributes and benefits EXCEPT . a. low price vs. high quality b. taste vs. low calories c. supply vs. demand d. powerful vs. safe e. nutritious vs. good tasting Page: 317 312 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 361. When BMW created a straddle position with its “luxury and performance” approach, it was able to maximize . a. its core identity b. attributes c. benefits d. both attributes and benefits e. competitive parity Page: 317 362. In order to derive a fresh approach to gaining consumer insights to differentiating products and services, MacMillan and McGrath suggest in their list of questions that help in identifying new, customer-based points of differentiation. Which of the following is NOT one of those questions? a. How do consumers find your offering? b. How do consumers make their final selection? c. How is your product installed? d. How is your product stored? e. How was the product or service invented? Page: 318 363. The obvious means of differentiation, and often most compelling ones to consumers, relate to aspects of the . a. price b. distribution process c. promotions d. product and service e. sales team responsible for the product or service Page: 319 364. The Strategic Planning Institute studied the impact of higher relative product quality and found a between relative product quality and return on investment (ROI). a. positive correlation b. negative correlation c. neither a positive or negative correlation d. inverse correlation e. correlation to be infeasible Page: 319 313 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 365. Better-trained personnel exhibit six characteristics. Which of the following would NOT be among those six characteristics? a. Competence b. Courtesy c. Credibility d. Aggressiveness e. Reliability Page: 320 366. Brand image means different things to different people. Which of the following national companies is known for hiring employees based on diversity (e.g., might be tattooed or have multiple body piercing)? a. Barnes & Noble b. Borders c. J.W. Marriott d. Walt Disney e. Southwest Airline Page: 320 367. With respect to image differentiation, is the way a company aims to identify or position itself or its products. a. image b. identity c. character d. culture e. the WOW factor Page: 321 368. An effective identity does three things: it establishes the product’s character and value propositions; it conveys this character in a distinctive way; . For the identity to work, it must be conveyed through every available communication and brand contact. a. it must present everyday low price b. it must be aesthetically pleasing c. it delivers emotional power beyond a mental image d. it must have a global presence e. it must avoid all cultural taboos Page: 321 314 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 369. To say that a product has a life cycle is to assert four things. All of the following would be from that list of assertions EXCEPT . a. products have a limited life b. product sales pass through distinct stages, each posing different challenges, opportunities, and problems to the seller c. products all basically exhibit cycle-recycle growth patterns d. profits rise and fall at different stages of the product life cycle e. products require different marketing, financial, manufacturing, purchasing, and human resource strategies in each life-cycle stage Pages: 321–322 370. According to Crego and Schiffrin, if a restaurant serves a complimentary sorbet between courses and places candy on the table after the last course is served, the restaurant has a consumer value benefit that is . a. basic b. expected c. desired d. unanticipated e. meaningful Page: 322 371. The four stages of the product life cycle include all of the following EXCEPT . a. decline b. learning c. maturity d. introduction e. growth Page: 322 372. The stage of the product is characterized as being one where there is period of rapid market acceptance and substantial profit improvement. a. introduction b. growth c. maturity d. saturation e. decline Page: 322 315 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 373. According to the general bell-shaped curve used to illustrate the product life cycle, which of the following stages is generally seen when the sales curve is at its peak? a. Introduction b. Growth c. Maturity d. Decline e. Abandonment Page: 322 374. According to the illustrations describing the product life cycle, during which stage of the cycle is there a strong likelihood that negative profits will be the norm? a. Introduction b. Growth c. Maturity d. Decline e. Death Page: 322 375. Which of the following common product life-cycle patterns would be characterized as being one where sales grow rapidly when the product is first introduced and then fall to a “petrified” level that is sustained by late adopters buying the product for the first time and early adopters replacing the product? a. Cycle-recycle pattern b. Scalloped pattern c. Growth-slump-maturity pattern d. Reverse-cycle pattern e. Inverse-cycle pattern Page: 323 376. A product such as nylon (e.g., numerous uses—parachutes, hosiery, shirts, carpeting, et cetera) has been characterized as having a pattern to its product lifecycle. a. growth-slump-maturity b. scalloped c. cycle-recycle d. triangular e. fad Page: 323 316 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 377. When Mel chose his new home, he picked a Cape Cod design. Which of the following special categories of product life cycles would be most associated with the description of Mel’s home? a. Style b. Fashion c. Fad d. Ideation e. Technological Page: 323 378. do not normally survive (as a special category product life cycle) because they do not normally satisfy a strong need. a. Styles b. Fashions c. Fads d. Intra-brands e. Trends Page: 324 379. Which of the following product life-cycle stages would be appropriately described as being one where firms focus mainly on buyers from higher-income groups and prices tend to be high because costs are high? a. Introduction stage b. Growth stage c. Maturity stage d. Saturation stage e. Decline stage Page: 324 380. Most studies indicate, with respect to the product lifecycle in its introductory stage, that the gains the most advantage. a. market pioneer b. market nicher c. market reverser d. market follower e. market challenger Page: 324 381. Tellis and Golder identified five factors as underpinning long-term market leadership. Which of the following is NOT one of those factors? a. vision of mass market b. persistence c. slash-and-burn tactics d. relentless innovation e. asset leverage Page: 325 382. Which of the following product lifecycle stages is characterized as being one where a rapid climb in sales occurs, new product features are introduced by new competitors, and distribution is expanded? a. Pre-pioneering 317 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process b. Introduction c. Saturation d. Growth e. Maturity Page: 325 383. All of the following strategies have been suggested as proper for sustaining rapid market growth during the growth stage of the product life cycle EXCEPT when the firm . a. improves product quality and adds new product features and improved styling b. enters into new market segments c. lowers prices to attract the next layer of price-sensitive buyers d. shifts from product-awareness advertising to product-preference advertising e. moves to sue all new entrants into the market place Page: 325 384. Today, most products are in the of the life cycle, and most marketing managers must cope with the problems and challenges of this stage. a. pre-pioneering stage b. introduction stage c. growth stage d. maturity stage e. decline stage Page: 326 385. The maturity stage of the product life cycle can be divided into three distinct phases. If the absolute level of sales starts to decline and customers begin switching to other products, the marketing manager will most likely find that the product is in the phase of the maturity stage. a. growth b. decaying maturity c. stable d. competitive vulnerability e. abandonment Page: 326 318 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 386. A company might try to expand the market for its mature brand by working with the two factors that make up sales volume. Volume equals (=) . a. supply times (X) demand b. number of brand users times (X) amount of money spent on each purchase c. number of brand users times (X) usage rate per user d. price level of the product times (X) the number of items purchased e. price level of the product times (X) the number in the market segment selected for targeting Page: 327 387. When Campbell’s soups began advertising that soups were an excellent snack for children or adults, it was using which of the following volume-oriented brand usage strategies? a. Use the product on more occasions. b. Use more of the product on each occasion. c. Use the product in new ways. d. Use improved quality to attract new users. e. Use the product in older, more traditional ways. Page: 328 388. Managers try to stimulate sales by modifying the product’s characteristics. Which of these modifications has as its aim to increase the product’s functional performance? a. Feature improvement b. Style improvement c. Fashion improvement d. Packaging improvement e. Quality improvement Page: 328 389. When Vlasic created a cucumber 10 times larger than the traditional pickle cucumber (e.g., Hamburger Stackers), it used as a means of modifying its product so additional customers might be attracted to the brand. a. quality improvement b. feature improvement c. style improvement d. packaging improvement e. idea improvement Page: 328 319 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 390. Marketing programs can be modified to stimulate sales. Which of the following forms of marketing program modification might ask such questions as “Can the company speed up delivery?” or “Can it extend more credit?” in order to bring modification about? a. Pricing b. Distribution c. Advertising d. Personal selling e. Services Page: 329 391. In the decline phase of the product life cycle, if a firm “milks” the firm’s investment to recover cash quickly, it is using a strategy called . a. positioning b. reverse engineering c. psychological divestment d. harvesting e. abandonment Page: 330 392. If an organization chooses “harvesting” as a decline stage PLC strategy, the first step in using such a strategy would likely be to . a. rejuvenate the brand or product b. cut R&D costs and plant and equipment investment c. cut all promotional expenses d. cancel distribution contracts e. require that all distributors reduce inventory of older models of the product Page: 330 393. Which of the following is a popular criticism of product life-cycle theory? a. It is too costly to implement. b. It has few actual examples that can be benchmarked. c. It only works in the U.S. market. d. Life-cycle patterns are too variable in shape and duration. e. Stages often follow fad trends. Page: 331 394. Markets are similar to products with respect to life-cycle concepts. All of the following are considered to be stages that markets pass through in market evolution EXCEPT . a. emergence b. growth c. decline d. maturity e. destruction Page: 332 395. Which of the following stages of the product life cycle (PLC) is characterized as being one where there are low sales, high cost per customer, negative profits, and few competitors? a. Introduction 320 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships b. Growth c. Maturity d. Decline e. Abandonment Page: 332 396. During which of the following stages of the product life cycle (PLC) would we expect a marketing manager to pursue a marketing objective of maximizing market share? a. Introduction b. Growth c. Pre-pioneering d. Maturity e. Decline Page: 332 397. When sales peak, there is a low cost per customer, profits are high, and the marketing manager attempts to maximize profit while defending market share, the product is most likely in the stage of the product life cycle (PLC). a. introduction b. pre-pioneering c. growth d. maturity e. decline Page: 332 398. A manufacturer of calculators finds when examining the calculator market that there is about an even split between customers who want a small hand calculator and those that want a large one. This type of market, in which buyer preferences scatter evenly, is called a(n) market. a. emerging b. mass market c. diffused-preference d. niche e. standardized Page: 333 321 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 399. If an entrepreneur discovers that his or her firm’s market is described as being one of diffused-preferences, a (e.g., the new product can be designed to meet the preferences of one of the corners of the market) can be used to expand sales. a. mass-market strategy b. multiple-niche strategy c. bipolar design strategy d. standardized niche strategy e. single-niche strategy Page: 333 400. Eventually, competitors cover and serve all the major market segments and the market enters the maturity stage with respect to market evolution. As market growth slows down, the market splits into finer segments and high occurs. a. market ideation b. market consolidation c. market fragmentation d. market deflation e. market escalation Page: 334 401. Market fragmentation in the market evolution process is often followed by caused by the emergence of a new attribute that has strong appeal. a. a market consolidation b. a market dissolution c. a market expansion d. a market abandonment e. a market harvesting Page: 334 402. Competition produces a continuous round of new product attributes. If a new attribute succeeds, several competitors soon offer it. In an attempt to discover new attributes before competitors, a firm can use a(n) process of hunches and undertake product development without much marketing research. This approach often has difficulties as opposed to other alternatives available. a. customer-survey b. intuitive c. dialectical d. needs-hierarchy e. means-end Page: 324 322 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships True/False 403. Positioning is the act of designing the company’s offering and image to occupy a distinctive place in the mind of the target market. Page: 310 404. A good illustration of a value proposition for Domino’s Pizza would be “always the cheapest price anywhere.” Page: 311 405. Category membership is seen as the products or sets of products with which a brand competes and which function as close substitutes. Page: 311 406. Points-of-parity are attributes or benefits consumers strongly associate with a brand, positively evaluate, and believe that they could not find to the same extent with a competitive brand. Page: 312 407. Points-of-parity come in two basic forms: category and competitive. Page: 313 408. The preferred approach to positioning is to inform consumers of a brand’s membership before stating its point-of-difference. Page: 314 409. There are three consumer desirability criteria for PODs (points-of-difference): price, value, and respectability. Page: 315 410. If a product manufacturer compares its organization’s products to those of leaders in the field, the manufacturer is using what is called “comparing to exemplars” to convey a brand’s category membership. Page: 315 411. A good illustration of negatively correlated attributes or benefits is good tasting versus bad tasting. Page: 317 412. One of the most obvious means of differentiation, and often most compelling to consumers, relate aspects of the product and service. 323 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process Answer: True Page: 319 413. According to the Strategic Planning Institute, there is a significant negative correlation between relative product quality and return on investment (ROI). Page: 319 414. One of the dangers faced by firms claiming to have a high quality image is that its prestige may be lost if it goes on sale too often. Answer: True Page: 319 73. Retailers, in particular, use there top management and CEOs as a means of differentiating and positioning their brand. Page: 320 74. Companies cannot achieve differentiation by differentiating their channels as this is not the purpose of a distribution channel. Page: 320 75. Image is the way a company aims to identify or position itself or its product. Page: 321 76. Image is the way the public perceives the company or its products. Answer: True Page: 321 77. One of the assertions of saying that a product has a life cycle is to recognize that products have a limited life. 324 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships Page: 321 78. Most product life cycles are portrayed as a scalloped shaped curve. Answer: False Page: 322 79. In the product life cycle, growth is a stage of rapid market acceptance and substantial profits improvement. 325 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process Answer: True Page: 322 Level of difficulty: Medium 80. One of the shortest stages in the product life cycle is the maturity stage because of the marketing manager’s desire to keep the product in its growth stage. Answer: False Page: 322 81. The profit curve for most product life-cycles peaks during the growth stage of the life cycle. Answer: False Page: 322 Level of difficulty: Medium 82. The sales curve for most product life-cycles peaks during the maturity stage of the life cycle. 326 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships Answer: True Page: 322 Level of difficulty: Medium 83. According to information presented in the text, the pharmaceutical industry often has products that can be characterized as having cycle-recycle product life- cycle patterns. Answer: True Page: 323 Level of difficulty: Hard 84. With respect to product life cycles, a style can last for generations and go in and out of vogue. Page: 323 85. The length of a fashion cycle is usually easy to predict. Page: 323 86. In the introductory stage of a product’s life cycle, promotion expenditures are at their highest ratio to sales. Page: 324 87. Because of the pioneer advantage, virtually all market pioneers demonstrate market staying power and sustained product growth. Page: 324 88. During the growth stage of the product life cycle, prices grow along with profits. Page: 325 327 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 89. One strategy for sustaining rapid growth during the growth stage of the product life cycle is for the firm to add flanker products. Page: 325 90. Most products are in the growth stage of the life cycle, and most marketing managers cope with the problem of sustaining growth. Page: 326 91. In the maturity stage of the product life cycle, three phases appear to exist: growth, decay, and abandonment. Page: 326 92. Sales volume is made up of two factors: Volume = number of brand users times (x) usage rate per user. Answer: True Page: 327 109. An example of a volume strategy for modifying would be a situation where Tums antacid promotes usage as a calcium supplement. Page: 328 110. An example of a feature improvement product modification strategy would be one where Campbell’s soup is promoted as being a snack. Answer: False Page: 328 95. When a firm uses a “harvesting” strategy in the decline stage of the product life cycle, it maintains the firm’s investment level until the uncertainties about the industry are resolved. Page: 330 328 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 96. One of the chief advantages of using the product life cycle as a forecasting procedure is that product life-cycle patterns have proven to be stable in shape and duration. Answer: False Page: 331 97. A good pricing strategy to use in the introduction stage of the product life cycle is to charge cost-plus. Page: 332 98. A good advertising strategy to use in the maturity stage of the product life cycle would be to stress brand differences and benefits. Page: 332 99. According to ideas found in the concept of market evolution, as market growth slows down, the market splits into finer segments and high market consolidation occurs. Page: 334 100. Market fragmentation is often followed by a market consolidation caused by the emergence of a new attribute that has strong appeal. Page: 334 Essay 101. With respect to positioning, explain points-of-parity and points-of-difference. 329 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process unique to the brand but may in fact be shared with other brands. See chapter material for additional discussion material. Pages: 312–313 102. There are three main ways to convey a brand’s category membership. What are those three ways? 103. In choosing points-of-difference, one of the primary considerations is that consumers find points-of-difference desirable. There are three key consumer desirability criteria for points-of-difference. What are those three criteria? 104. Brands can be differentiated on the basis of many variables; however, four differentiation strategies are emphasized in the text. List and briefly characterize the four differentiation strategies. 105. A company’s positioning and differentiation strategy must change as the product, market, and competitors change over the product life cycle. To say that a product has a life cycle is assert four things. What are those four things? 106. The product life-cycle’s bell-shaped curve is generally depicted as being divided into four stages. Briefly, name and characterize each of the four stages. 330 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 331 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 107. Characterize the differences between style, fashion, and fad life cycles. 108. Assume that you are the marketing manager for a large appliance manufacturer. You have had five quarters of rapid sales growth and would like to prolong the eventual downturn that always follows periods of high growth for as long as possible. You also know that any one of six strategies for sustaining rapid market growth can be used to achieve your objective. What are the six generally accepted strategies for sustaining rapid growth in a market from which you will make your choice? 109. Characterize an organization’s strategies with respect to product, price, distribution, and advertising for a product in its maturity stage of the product life cycle. Use information found in the summary table on the product life cycle to construct your answer. Be sure to characterize each of the four strategic areas mentioned. 110. Like products, markets evolve through four stages. What are those four stages? Characterize each stage of a market’s evolution. 332 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships major market segments and the market enters the maturity stage; and, (4) decline—eventually, demand for the present products will begin to decrease, and the market will enter the decline stage. For additional details, see the chapter section. Pages: 331–335 APPLICATION QUESTIONS Multiple Choice 111. Which of the following statements would most closely match to Volvo’s value proposition for its station wagon line? a. The whole family will fit in comfort. b. Styling from the twenty-first century and beyond. c. The safest, most durable wagon in which your family can ride. d. Diversity of uses, diversity of users. e. Old-world styling for a new-world car. Page: 311 112. Two consultants, Michael Treacy and Fred Wiersema have proposed a positioning framework called value disciplines. Within its industry, a firm could aspire to be the product leader, the operationally excellent firm, or the firm. a. idea innovator b. customer-intimate c. globally-aware d. asset management e. competitive promotional specialist Page: 311 113. “It’s not delivery. It’s DiGiorno” This ad campaign helped DiGiorno’s Pizza become the frozen pizza leader. Which of the following terms is most associated with the company’s promotional success strategy? a. Price leader b. Value relationships c. Vertical integration d. Superior quality control e. Clever positioning Page: 312 333 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 114. may be based on virtually any type of attribute or benefit. For example, FedEx uses “guaranteed overnight delivery” and Nike uses “performance.” a. Points-of-parity b. Points-of-difference c. Points-of-conflict d. Points-of-defensibility e. Points-of-service Page: 313 115. As a marketing manager, which of the following would be the best purpose for your organization’s competitive points-of-parity? a. To point out competitive points-of-difference. b. To emphasize competitive points-of-difference. c. To rationalize competitive points-of-difference. d. To globalize competitive points-of-difference. e. To negate competitive points-of-difference. Page: 313 116. When BMW first made a strong competitive push into the U.S. market in the early 1980s, it positioned the brand as being the only automobile that offered . a. both luxury and performance b. ego enhancement c. a sexy status symbol d. a reputation in addition to outstanding performance e. value for the dollar spent Page: 314 117. There are three main ways that a brand’s category membership can be conveyed. Which of those ways is applicable in the following situation: Tums claims to have the most acid-reducing components of any antacid? a. Comparing to exemplars. b. Relying on the product descriptor. c. Announcing category benefits. d. Focusing on reliability. e. Persuasion based on believability. Page: 315 334 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 118. Assume that you are in a position to develop your organization’s points-of- difference for an upcoming promotional campaign. Which of the following sets consumer desirability criteria would best fit your promotional task? a. Value, location, service. b. Loyalty, customization, status. c. Value, reliability, dependability. d. Relevance, distinctiveness, believability. e. Licensing opportunities, promotional protection, and believability. Page: 315 119. A marketing manager asks a subordinate “Can the favorability of the new brand association we just created in our recent ad campaign be reinforced and strengthened over time?” Which of the following delivery criteria used for choosing points-of-difference would be most appropriate to the question asked? a. Relevance b. Communicability c. Sustainability d. Feasibility e. Comparisons Page: 316 120. If your task was to construct a positioning statement for a new product that your company was considering as an addition to your product portfolio, what would be the best first step for you to take? a. State the product’s cost b. State the product’s membership in a category c. State who manufactured the product d. State the image of the product e. State who would distribute the product Page: 316 121. Which of the following would be the best example of negatively correlated attributes or benefits? a. Low quality versus high quality. b. Supply versus demand. c. image versus sales. d. powerful versus safe. e. nutritious versus unhealthy. Page: 317 335 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 122. When Apple Computers launched Macintosh, its key point-of-difference was “user friendly.” Many consumers valued ease of use, especially those who bought computers for the home. One drawback with a “user-friendly” association was that consumers assumed that the computer was . a. available everywhere b. not very powerful c. not very expensive d. not compatible with any other computers e. not for university use Page: 318 123. Dallas-based Southwest Airlines carved its niche in short-haul flights. The airline knew that it could not differentiate on price alone. Which of the following is a strategy used by Southwest Airlines to create further differences? a. Selection of on board beverages. b. First-come, first-served open seating. c. New movies and communication prospects. d. Personification of employees through their dress. e. No mechanical breakdowns. Page: 318 124. According to information found in “Discovering New Points of Differentiation,” which of the following are NOT considered as customer- based points of differentiation questions? a. How do people become aware of their need for your product and service? b. How do consumers find your offering? c. What happens when your product or service is delivered? d. How is your product installed? e. How was your product invented? Page: 318 125. A company chooses that combination of tangible and intangible items, experiences, and outcomes designed to outperform competitors and with the customers’ delight and loyalty. Which of the following steps for creating a program that will exceed customer expectations would most likely be associated with the above statement? a. Defining the customer value model. b. Building the customer value hierarchy. c. Examining basic differentiation factors. d. Examining unanticipated differentiation factors. e. Deciding on the customer value package. Page: 322 336 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 126. You are somewhat shocked to learn that your product’s profit curve is in the negative. Which of the following stages of the product life cycle is your product most likely in given its position on its profit curve? a. Introduction b. Growth c. Maturity d. Saturation e. Decline Page: 322 127. While looking a series of special-case product life cycles, you observe that one of the life cycles has had a rapid growth in sales resulting in a severe peak of the sales curve followed by a rapid decline. Which of the following product life-cycle curves is most likely represented by the above illustration? a. Style life cycle b. Fashion life cycle c. Fad life cycle d. Niche life cycle e. Techno life cycle Page: 323 128. The pioneer advantage does not always ensure success in the marketplace. All of the following are reasons cited by the text that a market pioneer’s product might not be successful EXCEPT . a. the new product was too crude b. the new product was improperly positioned c. the new product appeared when there was strong demand d. the product-development costs exhausted the innovator’s resources e. managerial incompetence Page: 325 129. Markets often need modification to be able to grow and flourish. When AARP began to recruit members that were 50–55 years-of-age instead of pursuing their normal target market of 65+ seniors, it was using a market modification strategy called . a. converting nonusers b. entering new market segments c. winning competitors’ customers d. value vision e. age discounting Page: 327 337 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process 130. As an entrepreneur you have decided to launch two products simultaneously to capture two different parts of the market. Which of the following would be the best descriptive title for the strategy you are employing? a. Single-niche strategy b. Multiple-niche strategy c. Standardization strategy d. Mass-market strategy e. Adaptive strategy Page: 333 Short Answer 131. According to advertising executives Jack Trout and Al Ries, positioning is not what you do to a product. What is the proper perspective according to Trout and Ries? 132. A starting point in defining a competitive frame of reference for a brand positioning is to determine category membership. How would you define category membership? 133. With respect to points-of-parity, explain why a product does not have to be equal to a competitive product to be compared to that product. 134. As a company seeks to establish a category membership designation, how does the company approach points-of-difference? What is done first? 338 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships 135. There are three main ways to convey a brand’s category membership. Assume you were an automobile designer for Ford and wished to position a new “sports wagon.” Which of the three ways to convey the brand’s category membership would be most appropriate for your task? 136. There are three key consumer desirability criteria for creating points-of- difference. When the Westin Stamford hotel in Singapore advertised that it was the world’s tallest hotel, it attempted to create a point-of-difference. The hotel may not have been successful in its attempt to create its POD because of which consumer desirability criteria associated with PODs? 137. Delivering on promises made in points-of-difference is very important in successful marketing. There are three deliverability criteria stressed in the text with respect to PODs. What are those three criteria? 138. To communicate a company or brand positioning, marketing plans often include a positioning statement. What form should this statement follow? 139. Assume that you are a marketing manager that is trying to stimulate creative thinking on the part of your department. You would like your department to come up with a series of questions that might be used to generate new consumer-based points of differentiation. Write five questions to get your group started with their assignment. 140. Companies can achieve competitive advantage through the way they design their distribution channel. What three areas are considered in this design process? Page: 320 141. Brand managers often have to deal with the concepts of identity and image. An effective identity does three things. What are those three things? 142. Crego and Schiffrin have proposed that customer-centered organizations should study what customers value and then prepare an offering that exceeds their expectations. The best way to do this is to use a three-step process. What are those three steps? 143. As a marketing manager, you have the following facts about your product offering presented to you: (1) there is a slowdown in sales growth; (2) profits are stabilized; (3) competition has increased; and, (4) both profits and sales are likely to peak soon. Given these facts, what stage of the product life cycle is your product most likely in? 144. As a brand manager of a pharmaceutical firm you have observed that your brand is following the classic cycle-recycle pattern with respect to the product life cycle. Describe what is mostly likely happening in this pattern. 340 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships and this produces the first cycle. Later, sales start declining and the company gives the drug another promotion push, which produces the second cycle (usually of smaller magnitude and duration). Page: 323 145. The length of a fashion cycle is often hard for industry analysts to predict. Explain why this is true. 146. Most marketing managers know that most products are in the maturity stage of the life cycle. The maturity stage has been characterized as having three sub- stages or phases. What are those phases? Page: 326 147. As a marketing manager, it has become necessary for you to understand the two factors that make up sales volume so long-term planning can be accomplished. What are those two factors? volume = number of brand users times (X) usage rate per user. Page: 327 148. Experience has shown marketing managers that a product’s sales can be stimulated by modifying the product’s characteristics in one of three ways. What are those three ways of making improvement in the product’s characteristics? Pages: 328–329 149. You have been given the assignment of critiquing the product life-cycle concept by pointing out weaknesses in the concept. What are the weaknesses that should be pointed out to an aspiring marketing manager? 341 Part 1: Defining Marketing and the Marketing Process to another upsurge; and (3) the PLC pattern is the result of marketing strategies rather than an inevitable course that sales must follow. For additional information, see chapter section. Page: 331 150. Competitors often compete on the basis of product attributes. One of the problems is, however, determining what new attributes the product may have or be perceived to have. There are four approaches that a marketing manager might try to discover more information about attributes. What are those four (4) approaches? Suggested Answer: [Show More]
Last updated: 1 week ago
Preview 1 out of 273 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Oct 14, 2019
Number of pages
273
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Oct 14, 2019
Downloads
0
Views
539