Economics > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Clayton State University ECON 6100 Chapter 10 Strategy The Quest to Keep Profit From Eroding. 71 Que (All)
Clayton State University ECON 6100 Chapter 10 Strategy The Quest to Keep Profit From Eroding. 71 Questions and Answers
Document Content and Description Below
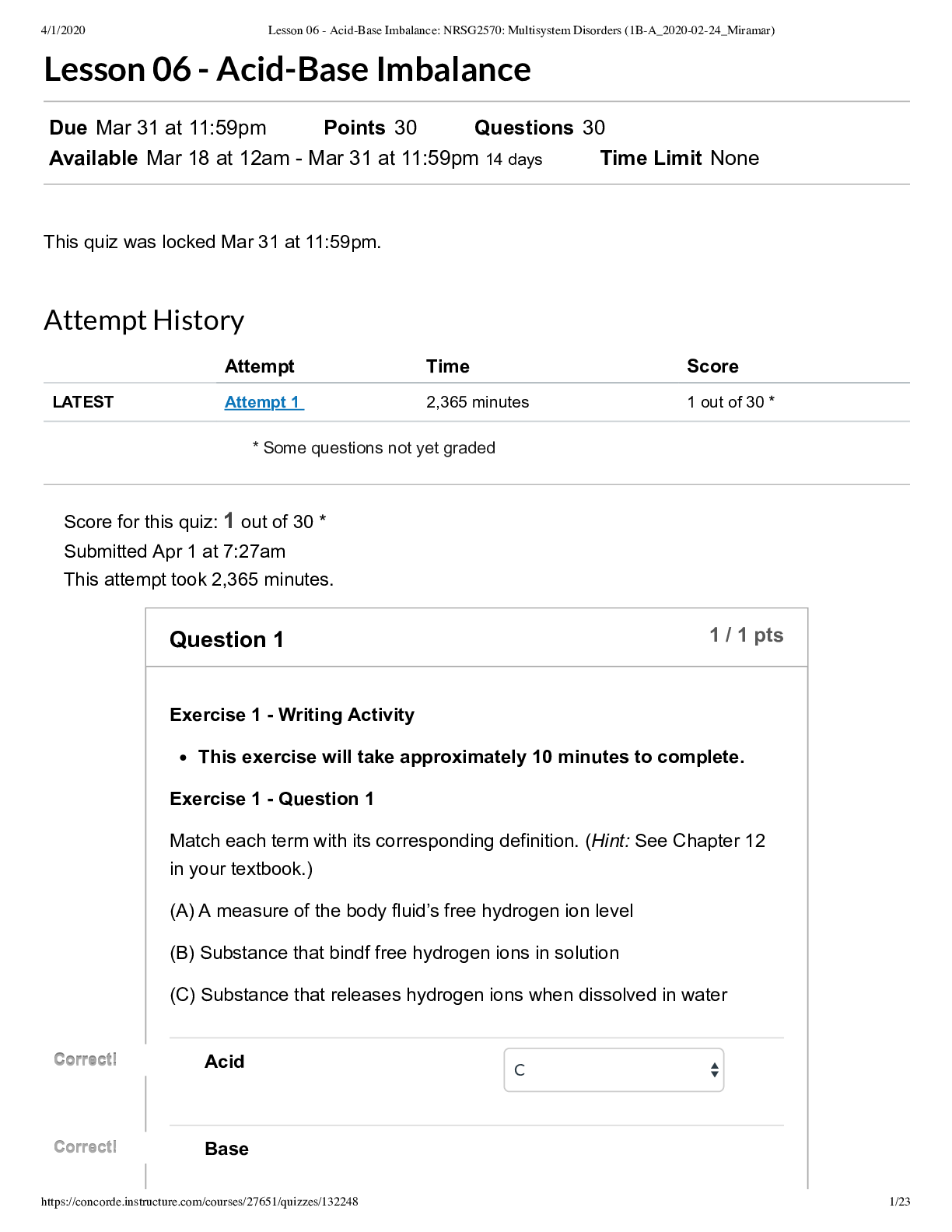
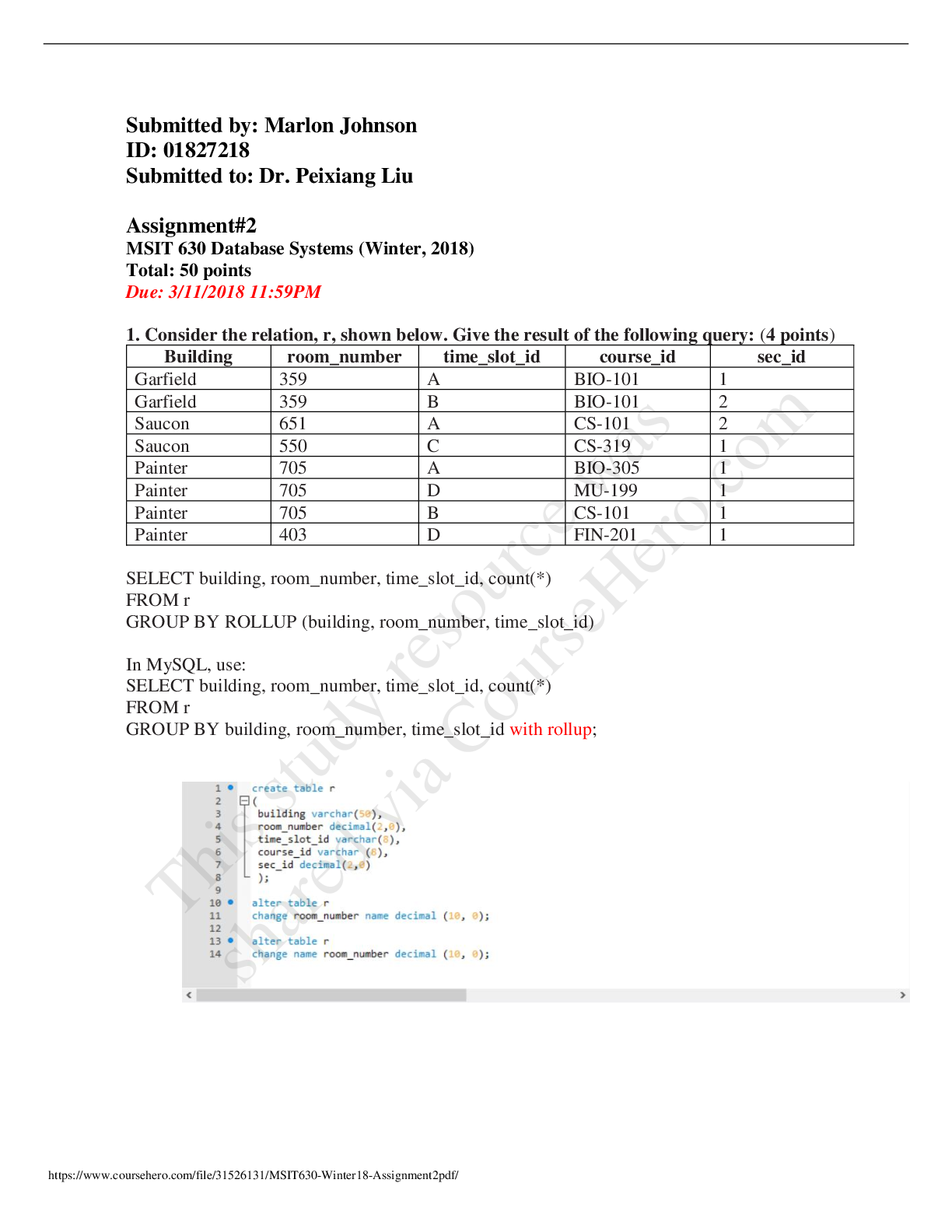
1. Firms maintain their completive edge by a. Providing a good at lower costs than their rivals b. Providing a superior product at the same cost as your rival c. Being innovative d. All the above ... TOPICS: Section 1: Strategy is Simple 2. Which of the following is the foundation for success for a company facing competition a. Create an advantage over the competition b. Protect the advantage created over the competition c. Create and protect advantages over the competition d. None of the above TOPICS: Section 1: Strategy is Simple 3. If a customer values good A at $15, and it costs the firm $10 to produce, current profit per unit is a. $10 b. $8 c. $5 d. $1 TOPICS: Section 1: Strategy is Simple 4. Strategy is a. The art of matching the resources and capabilities of a firm to the opportunities and risks in its environment b. Developing a resource for the company that is both rare and valuable to create competitive advantage c. Making sure that the resource developed is non-fungible to create a sustainable advantage d. All of the above TOPICS: Section 1: Strategy is Simple 5. Intense market competition is ________ for consumers, since it_______. a. Bad; erodes producer surplus b. Bad, increases variety in the market c. Good, increases the price level in the market d. Good; decreases the price level in the market TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 6. Intense market competition is ________ for producers, since it_______. a. Bad; erode consumer surplus b. Bad, erode producer profits c. Good, increase the price level in the market d. Good; decrease the price level in the market TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 7. It is more profitable for a firm to be_______ than ________ a. In perfect competition; monopolists b. A monopolists; in perfect competition c. Not in business; in business d. All of the above TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 8. The IO Economics perspective locates the source of competitive advantage for a firm at the a. Individual firm level b. Industry level c. Customer Level d. None of the above TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 9. The RBV perspective locates the source of competitive advantage for a firm at the a. Individual firm level b. Industry level c. Customer Level d. None of the above TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 10. In the IO perspective, it is important to enter an industry with a. High barriers to entry b. Low buyer power c. Low supplier power d. All of the above TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 11. In the IO perspective, it is important to enter an industry with a. High barriers to entry b. High buyer power c. High supplier power d. All of the above TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 12. In the IO perspective it is important to enter an industry with a. Low supplier power b. Low threat from substitutes c. Low levels of rivalry between firms d. All of the above TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 13. In the IO perspective it is important to enter an industry with a. High supplier power b. Low threat from substitutes c. Low levels of rivalry between firms d. Only B & C TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 14. In the IO perspective it is important to enter an industry with a. High barriers to entry b. Differentiated products c. Small number of competing firms of different sizes d. All of the above TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 15. Which of the following could potentially capture the value created in a market a. Suppliers b. Industry rivals c. Buyers d. All of the above TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 16. Supplier power tends to be high when a. your firm purchases critical inputs from the supplier b. your input choices are highly differentiated c. Both A&B d. None of the above TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 17. Supplier power tends to be low when a. The supplier provides critical inputs b. The supplier provides homogenous inputs c. Both A&B d. None of the above TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 18. Supplier power tends to be low when a. The supplier provides non-critical inputs b. The supplier provides homogenous inputs c. Both A&B d. None of the above TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 19. Supplier power tends to be higher when a. Suppliers are concentrated b. There are high costs to switching between suppliers c. Both A&B d. None of the above TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 20. Supplier power tends to be lower when a. Suppliers are less concentrated b. There are low costs to switching between suppliers c. Both A&B d. None of the above TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 21. Supplier power tends to be lower when a. Suppliers are concentrated b. There are high costs to switching between suppliers c. Both A&B d. None of the above TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 22. You operate a small poultry farm in east Texas. You sell most of your output through a regional distributor of poultry products in the area. In this case, you are subject to a. Low buyer power b. High buyer power c. No buyer power d. All of the above TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 23. More buyer power means a. Buyers would find it easier to capture the value created b. Buyers would find it more difficult to capture the value created c. Buyers would not be able to capture any value created d. None of the above TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 24. Even if there are significant barriers to entry, firms may not be highly profitable a. Substitute product offerings among rivals b. The ability of consumers to switch to substitute products easily c. All of the above d. None of the above TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 25. Rivalry among firms would tend to be high if a. There is a small number of firms in the market b. There is a large number of firms in the market c. There is only one firm in the market d. None of the above TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 26. Rivalry among firms would tend to be high if a. Firms are located further from each other b. Firms are located close to one another c. There is only one firm in the market d. None of the above TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 27. Rivalry among firms would tend to be high if a. Customers are locked into the competitors technology b. Customers can easily switch between competitor’s technologies c. All of the above d. None of the above TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 28. Rivalry among firms would tend to be highest if a. the industry is growing quickly b. the industry is growing slowly c. the industry is shrinking d. None of the above TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 29. To decrease supplier power, the firm can a. Increase rivalry among its suppliers b. Buy from multiple suppliers c. Both A&B d. None of the above TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 30. To decrease buyer power, the firm can a. Differentiate its product b. Decrease dependency on a single buyer c. Sell its products in locations with multiple buyers d. All of the above TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 31. Porter’s five forces portray a. A zero-sum game b. A game where your profitability comes at the expense of someone else’s c. The ability of market participants to create a larger total pie d. Only A&B TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 32. A software design company wants to pursue a platform strategy. Which of the following strategies is the firm likely to want to adopt? a. Focus on softening rivalry b. Encourage complementary innovation c. Encourage substitute innovation d. All of the above TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 33. The industrial organization or (IO) perspective predicts a. firm’s profitability differs only if they are in different industries b. firms within an industry are equally profitable c. firm’s profitability within industries varies widely d. Only A&B TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 34. The RBV perspective predicts a. firm’s profitability differs only if they are in different industries b. firms within an industry are equally profitable c. firm’s profitability within industries varies widely d. Only A&B TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 35. The RBV perspective is based on a. Resource mobility b. Resource immobility c. Resource heterogeneity d. Only A&C TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 36. Which of the following is more likely to be able to command a higher price for its products a. A specialty frozen yogurt producer, with high quality product b. A mall kiosk selling costume jewelry c. A specialty toy store that allows customers to self-design teddy bears d. Both A&C TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 37. Which firm in an industry is likely to have higher profits? a. Sellers with higher costs than their competitors b. Sellers with lower costs than their competitors c. Sellers with the same costs as their competitors d. All of the above TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 38. The resource based perspective indicates that firms exhibit different performances within the same industry because a. Some firms have better resources than others b. Some firms have organizational structures that can be duplicated c. Some firms sell goods that have a more elastic demand d. Some firms sell goods that have a perfectly elastic demand TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 39. Supplier power tends to be low when a. Suppliers are less concentrated b. Inputs provided by the supplier are not vital c. Inputs are homogenous d. All the above TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 40. Supplier power is high when a. Suppliers are concentrated b. The inputs provided are critical c. The inputs provided are unsubstitutable d. All of the above TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 41. The industrial organization economics perspective locates the source of competitive advantage at the a. Individual firm level b. Industry level c. Both a and b d. None of the above TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 42. The resource based view locates the source of competitive advantage at the a. Individual firm level b. Industry level c. Both a and b d. None of the above TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 43. Which of the following is true according to the IO perspective? a. Industry structure determines firm conduct which in turn determines firms’ performance b. Industry structure determines firm performance which in turn determines firms’ conduct c. Industry conduct determines firm structure which in turn determines firms’ performance d. Industry performance determines firm conduct which in turn determines firms’ structure TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 44. Typical structure characteristics of interest to Industrial Organization researchers include a. Barriers to entry b. Product differentiation among firms c. The number and size distribution of firms d. All of the above TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 45. Industries with high barriers to entry a. Pushes profits to normal returns b. Increases the likelihood of firms entering the industry c. Help firms sustain long term profits d. Increases the number of competitors TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 46. All of the following are examples of entry barriers, except a. Government protection through patents or licensing requirements b. Strong brands c. Low capital requirements for entry d. Lower costs driven by economies of scale TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 47. One of the limitation of Five Forces is that they a. Reduce producer surplus b. For one firm to increase profit, the profit of another participant must decrease c. Does not provide a firm with sustainable competitive advantage d. Both b and c TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 48. Assumptions that underlie the Resource-based View include a. Resource heterogeneity b. Resource immobility c. Barriers to entry d. Both a and b TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 49. The concept that explains the firm’s ability to produce output with differing bundles of resources is called a. Resource heterogeneity b. Resource immobility c. Barriers to entry d. Imitability TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 50. The five forces model is a framework a. For increasing buyer power in the market b. For improving competition in the industry c. For analyzing the attractiveness of an industry d. For increasing supplier power in the market TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 51. Attractive industries have all the following attributes, except a. High supplier power b. Low buyer power c. High entry barriers d. Low rivalry TOPICS: Section 2: Sources of Economic Profit 52. Firms have a competitive advantage when a. They can deliver the same product benefits as their competitors but at a lower cost b. They can deliver superior product at a similar cost c. Both of the above d. None of the above TOPICS: Section 3: The Three Basic Strategies 53. If a customer values good A at $15, and it costs the firm $10 to produce, the firm can increase its profits if a. Redesign the product such that it delivers $16 in customer value b. Redesign the production process so that the costs fall to $9 c. One or both of the above d. None of the above TOPICS: Section 3: The Three Basic Strategies 54. Having a competitive advantage emanates from a. Increased price b. Decreased cost c. One or both of the above d. None of the above TOPICS: Section 3: The Three Basic Strategies 55. For a resource to be able to generate temporary competitive advantage over rivals, it must be a. Valuable b. Rare c. Valuable and rare d. Not valuable but rare TOPICS: Section 3: The Three Basic Strategies 56. For a resource to be able to generate sustained competitive advantage over rivals, it must be a. Valuable b. Rare c. Difficult to imitate or substitute away from d. All of the above TOPICS: Section 3: The Three Basic Strategies 57. Which of the following makes a firm’s resources hard to imitate? a. They flow from the firm’s unique history b. The link between resources and advantage is simple c. They aren’t socially complex d. All of the above TOPICS: Section 3: The Three Basic Strategies 58. Which of the following makes a firm’s resources hard to imitate? a. They don’t flow from the firm’s unique history b. The link between resources and advantages is difficult to discern c. They aren’t socially complex d. All of the above TOPICS: Section 3: The Three Basic Strategies 59. Which of the following makes a firm’s resources hard to imitate? a. Do not use resources that flow from the firm’s unique history b. Keep the link between resources and advantage simple c. Resources emanate from a socially complex organizational structure d. All of the above TOPICS: Section 3: The Three Basic Strategies 60. Which of the following makes a firm’s resources hard to imitate? a. They flow from the firm’s unique history b. The link between resources and advantages is difficult to discern c. Resources emanate from a socially complex organizational structure d. All of the above TOPICS: Section 3: The Three Basic Strategies 61. One should be wary of consultants peddling best practices or secrets to success because a. They have different incentives than you do b. Such best practices are public knowledge and easily duplicated c. These best practices can at best only provide temporary profitability d. All of the above TOPICS: Section 3: The Three Basic Strategies 62. If the stock price of a company is higher than the discounted value of its future earnings, a. Buy the stock only if the company has a sustained competitive advantage b. Don’t buy the stock, even if the company has a sustained competitive advantage c. Always buy the stock d. None of the above TOPICS: Section 3: The Three Basic Strategies 63. Apple has continued to be innovative to ensure that the demand for its products stays or becomes a. More inelastic b. More elastic c. Unitary elastic d. None of the above TOPICS: Section 3: The Three Basic Strategies 64. All of these allow a firm to differentiate its product, except a. Product branding b. Reducing quality c. Advertising d. Limiting availability TOPICS: Section 3: The Three Basic Strategies 65. Which of the following can a firm use to reduce competition in the market? a. Locking in customers to long term contracts b. Seek an exclusive government contract c. Acquire patents d. All the above TOPICS: Section 3: The Three Basic Strategies 66. To stay one step ahead of the forces of competition, a firm can adopt any one of these strategies except a. Cost reduction b. Product differentiation c. Operating where marginal benefits equal marginal costs d. Develop non-fungible valuable resources TOPICS: Section 3: The Three Basic Strategies 67. Low cost strategies are usually found in industries where a. Products are not particularly differentiated b. Price competition tends to be fierce c. Both a and b d. None of the above TOPICS: Section 3: The Three Basic Strategies 68. Cost-reduction generates a. Increases in long-run profitability b. Increases in long-run profitability only if the cost reduction is difficult to imitate c. Decreases in long run profitability d. No change in profitability TOPICS: Section 3: The Three Basic Strategies 69. Buyer Power Nora’s Nicest Knick Knacks has sold a variety of products to hundreds of small retailers. Over time, she has added distributers who have a talent for finding more retailers for Nora. Now, over half of her sales go through just two of these distributers. Rather than making periodic orders as stock gets low, these distributers make only a few large purchases each year. How can these aspects of her buyer relationships affect how much of the value she creates that she gets to capture? 70. Supplier Power Nora’s Nicest Knick Knacks has produces a variety of products sold as souvenirs. She started out printing local sayings on tee-shirts, e.g., FDNY, and purchased plain tee-shirts from a single supplier. Since then, she has added coffee mugs, key chains, souvenirs spoons and many other items. For each of these, she has lined up one or more suppliers. How does the change in the sourcing of her inputs affect how much of the value she creates that she gets to capture? 71. Mutual Fund Products Amplitude Investments offers a variety of mutual fund products for investors with different preferences. When they develop a new product for an under-served niche, they find out that their competitors will imitate them within a few months. Is investigating and developing new products going to be profitable for Amplitude? [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 12 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 16, 2022
Number of pages
12
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 16, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
54
















.png)

.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)


.png)


.png)


.png)



