Business > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > BUSINESS 1007 (All)
BUSINESS 1007
Document Content and Description Below
BUSINESS 1007 07 Key 1. (p. 178) Managers utilize organizational resources such as employees, information, and equipment to accomplish goals. 2. (p. 178) The main job of managers today is to w... atch over people to be sure they do what the manager asks of them. 3. (p. 178) The best way to get people to do what a manager wants is for the manager to reprimand those who don't do things correctly. 4. (p. 178) Managers in progressive firms of all kinds tend to be friendly, and treat employees as partners. 5. (p. 179) Managers must earn the trust of their employees. 6. (p. 179) Because of their importance and skills, few managers lost their jobs in the economic crisis of 2008-2009. 7. (p. 179) Management is the art of getting things done through organizational resources. 8. (p. 179) A modern manager's main job is to issue orders, then follow up to make sure employees do as they were told. 9. (p. 179) Managers in progressive organizations tend to emphasize teamwork and cooperation rather than discipline and giving orders. 10. (p. 178) Managers in many of today's high-tech firms realize that workers often know much more about technology than they do. 11. (p. 179) In today's business environment, the general trend is to develop long-term relationships between workers and their employers. 12. (p. 179) Despite all of the changes in the business environment, the basic way a manager performs his or her job has remained remarkably constant. 13. (p. 179) Managers focus on making efficient use of their organization's human resources, but leave decisions about the efficient use of other resources such as buildings, machinery, and supplies to engineers and accountants. Managers must practice the art of getting things done through organizational resources including people, financial resources, information and all types of equipment and assets. 14. (p. 179) Given the lack of discipline and short attention spans of today's workers, modern managers must watch their workers closely, set strict rules, and vigorously enforce policies. Today's managers emphasize teamwork and cooperation rather than discipline and order giving. Managers now guide, train, support, motivate and coach employees. 15. (p. 178) In most high tech industries, the best way to respond quickly to rapid technological changes is to keep most authority and responsibility in the hands of a few key managers who provide precise, detailed directions to the workers. Managers of high-tech firms realize that workers often know much more about technology than they do. Thus, most progressive managers emphasize teamwork and cooperation rather than discipline and order giving. 16. (p. 178) Due to the fact that employees today often know much more about technology and the technical aspects of their jobs than their managers do, progressive managers emphasize team work and cooperation as a strategy for getting work done. Managers of high-tech firms realize that workers often know much more about technology than they do. Thus, most modern managers emphasize teamwork and cooperation rather than discipline and order giving. 17. (p. 179) Because of advancements in technology, managers now have an easier time obtaining long-term commitments from workers. Today, many companies find employees don't hesitate to leave a job if their needs are not being met. 18. (p. 179) Because of advancements in technology, it is likely that you will work for the same company for most of your career. Today, many companies' findees and employees don't hesitate to leave a job if their needs are not being met. 19. (p. 179) Managers make decisions about how to use organizational resources to accomplish goals. 20. (p. 179) Financing is one of the four key functions of management. 21. (p. 179) The four key management functions are planning, organizing, leading, and controlling. 22. (p. 180) One trend of the "leading" management function is to empower employees, giving them as much freedom as possible to become self-directed and self-motivated. 23. (p. 180) Leading is the management function of designing the structure of the organization so that everyone can function together. 24. (p. 181) As a management function, the main focus of controlling is to keep complete and up-to-date records of the organization's financial transactions for tax and regulatory purposes. 25. (p. 180) The management function that involves guiding, training, and motivating others to work toward the achievement of an organization's goals is called leading. 26. (p. 180) In many smaller firms the manager's role is to direct the employees, telling them exactly what to do. 27. (p. 179) Planning is the function of management that includes anticipating future trends and determining the best strategies and tactics to achieve an organization's goals and objectives. 28. (p. 179) Planning is a key management function because other management functions depend on having a good plan. 29. (p. 180) Today's progressive organizations are designed around the needs of the customer. The idea is to organize systems to be responsive to customer needs. Organizing includes designing the structure of the organization and creating conditions and systems in which everyone and everything work together to achieve the organization's goals and objectives. 30. (p. 181) Beth has spent the last two hours going over some consumer surveys to see how well her company is achieving its goal of improving customer satisfaction. Beth's efforts are an example of the controlling function of management. Controlling is the function concerned with determining whether or not an organization is progressing toward achieving its goals and objectives. 31. (p. 179) Jack, a manager with Tiny Tots Toy Company, has just participated in a meeting that looked at future trends in the toy industry, and identified new challenges and opportunities for Tiny Tots. Jack's participation in this meeting was part of the organizing function of management. Jack's activities are part of the planning function. Planning involves anticipating future trends and identifying business opportunities and challenges. 32. (p. 180) Harold is a no-nonsense boss who believes that the best way for an organization to achieve its goals is for workers to follow their boss's orders. Thus, he tells workers exactly what to do and how to do it. Harold's approach is an example of directing. Directing involves telling workers exactly what to do. This approach is still common among managers in small companies, but managers in larger firms tend to rely more on leading rather than directing. 33. (p. 180) Rita is a manager of a medium-sized service company. She is currently involved in redesigning her department to ensure that employees and other resources can respond more quickly and efficiently to the needs of its customers. Rita's efforts are part of the organizing function of management. Organizing involves designing the structure of the organization so that resources can efficiently achieve the organization's objectives. One of the key objectives today is to find ways to organize businesses so that they please the customer. 34. (p. 180) According to the "Reaching Beyond Our Borders" box in Chapter 7, a key problem in expanding in global markets is a lack of professional managers to run operations. Jack Welch, former CEO of General Electric, cites the lack of professional managers as a reason many companies are not growing their business globally. 35. (p. 181) Planning involves setting the organizational vision, goals and objectives. 36. (p. 181) Progressive managers consider planning to be of little importance in today's rapidly changing business environment. 37. (p. 181) Goals tend to be broad and focus on the long-term while objectives tend to be specific and more short-term in their focus. 38. (p. 181) A vision is a detailed set of specific steps that a firm must take to achieve its short-run objectives. 39. (p. 181) A statement about why an organization exists and what it is trying to achieve is called the organization's directive. 40. (p. 181) A vision is the overall explanation of why an organization exists and where it is trying to head. 41. (p. 181) A vision gives the organization a sense of purpose and a set of values that unite employees toward a common destiny. 42. (p. 181) A mission statement outlines the fundamental purposes of an organization. 43. (p. 181) Today, a mission statement should also address social responsibility. 44. (p. 181) Goals are broad, long-term accomplishments an organization wants to achieve. 45. (p. 181) While goals are measurable, objectives are not. 46. (p. 181) Goals are developed and agreed to by management so that the workers can follow them. 47. (p. 181) Objectives should be expressed as broad, general principles rather than as specific short-term results. 48. (p. 182) Continuous planning is not necessary, because plans that worked well in the past are likely to continue to work well in the future. 49. (p. 182) Planning is a continuous process. 50. (p. 182) The SWOT analysis helps firms identify competitive threats and market opportunities. 51. (p. 182) An analysis of the business environment helps managers identify threats and opportunities that face their firm. 52. (p. 184) Strategic planning is now much easier than it used to be because managers have access to very reliable computerized forecasting tools. 53. (p. 184) Tactical planning deals with setting long-range goals, while strategic planning develops the specific strategies needed to achieve the organization's operational goals. 54. (p. 183) Strategic planning determines the major goals of the organization. 55. (p. 184) Today's business environment changes so rapidly that strategic planning is becoming more difficult and subject to change. 56. (p. 184) Managers or teams of managers at the lower levels of an organization normally develop strategic plans, but top managers do most of the tactical planning. 57. (p. 184) Contingency planning involves developing alternative courses of action to be used if the primary plans do not achieve the desired results. 58. (p. 184) Operational planning looks at the organization as a whole, while strategic planning focuses on specific departmental actions. 59. (p. 184) One example of tactical planning is setting annual budgets and deciding on other details and activities necessary to meet the strategic objectives. 60. (p. 185) Many cities and businesses are now developing contingency plans to respond to potential terrorist attacks. 61. (p. 184) Instead of creating detailed strategic plans, the leaders of market-based companies (companies that respond quickly to environmental changes) set flexible directions so as to allow for change and seize opportunities when they come. 62. (p. 185) Decision-making occurs in all management functions. 63. (p. 186) The first step in the rational decision-making model is to identify alternative solutions. 64. (p. 186) The last step in the rational decision-making model is to determine whether the decision was a good one and follow up. 65. (p. 186) One step in the rational decision-making model is to develop alternatives. 66. (p. 185) Crisis planning develops responses to sudden changes in the environment. 67. (p. 186) Brainstorming is coming up with as many solutions as possible in a short period of time with a focus toward not censoring anyone's ideas. 68. (p. 186) Problem-solving is more formal than using the rational decision-making model. 69. (p. 186) PMI is a problem solving technique that involves listing pluses, minuses and implications. 70. (p. 182) A mission statement should provide a detailed explanation of how a company will achieve its objectives. A mission statement is an outline of the organization's fundamental purposes, not a detailed explanation of what is to be done and who is to do it. Figure 7.2 shows an actual mission statement for Starbucks that clearly illustrates this. 71. (p. 182) The SWOT analysis focuses only on the internal activities of the firm, while a PERT analysis is used to review the external environment in which the firm operates. SWOT stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. While the strengths and weaknesses part of SWOT analysis focuses on internal aspects of the organization, the opportunities and threats part of SWOT looks at the external environment in which the organization operates. 72. (p. 184) Tactical planning involves making decisions about which customers to serve, what products or services to sell, and the geographic areas in which the firm will compete. The fundamental nature of the topics described in this question would be considered in the strategic planning process. 73. (p. 185) Contingency planning is most important in markets where conditions are relatively stable and market growth is predictable. Contingency planning is the process of preparing alternative courses of action that may be used if the primary plans don't achieve the organization's objectives. The need to implement contingency plans is more likely to arise in markets where there is a great deal of rapid change and uncertainty. 74. (p. 181) The top managers at the Sax Department Store find that their employees do not really share a common sense of purpose or have a common set of values. This suggests that top management has not provided a clear vision for the firm. A vision is a broad statement of why an organization exists and what it seeks to accomplish. It is intended to give the organization a sense of purpose and provide workers with a set of values and a sense of direction. 75. (p. 184) In order to ensure effective implementation, managers should make only one set of plans and carefully follow them to ensure that the organization's objectives are achieved. Economic and competitive conditions change so rapidly that it is wise to have alternative plans available in the event the primary plan does not achieve its objectives. This is the idea behind contingency planning. 76. (p. 183) Lucy is part of the top management team at Cloudy Daze Rain Gear, a company that produces umbrellas, raincoats, hats and all-weather shoes. As a member of top management, Lucy is more likely to be involved in strategic planning than in tactical planning. Top management normally carries out strategic planning, while lower-level managers are usually responsible for tactical planning. 77. (p. 184) Jamika is a manager at a well-known retail store. Each morning she determines the order in which store projects are performed; she sets work schedules for employees and standards that must be met. These activities suggest that Jamika is involved in operational planning. Operational planning is the process of setting work standards and schedules that are necessary to carry out tactical plans. 78. (p. 186) Sharon needed to solve a problem quickly, so she called together the work team in her department and asked them to list as many possible solutions as they could come up with in a short period of time. During the process she encouraged responses and avoided censoring what her workers said. Sharon is utilizing a problem solving technique known as brainstorming. Brainstorming is a problem solving technique that encourages a group of people to come up with as many suggestions for solving the problem as possible in a short period of time, and with no censoring of ideas. 79. (p. 186) After management has created a plan of action, the focus turns to the controlling function to recheck and often redo the plan. 80. (p. 186) Organizing involves allocating resources, assigning tasks, and establishing procedures for accomplishing the organizational objectives. 81. (p. 187) The visual illustration of the relationships among the people within an organization that shows who is accountable for the work and who reports to whom is called a Gantt Chart. 82. (p. 187) An organizational chart shows who is accountable for the completion of specific work and who reports to whom. 83. (p. 187) Branch and plant managers and division heads are classified as first-line managers. 84. (p. 187) A CEO is often the president of the firm and is responsible for developing the strategic plans. 85. (p. 187) The recession of 2008-2009 eliminated many middle managers giving the remaining managers more employees to supervise. 86. (p. 188) Supervisory managers are those who directly oversee the activities of workers and evaluate their daily performance. 87. (p. 187) Middle managers usually are responsible for tactical planning and controlling. 88. (p. 187) The CIO, COO, and CFO are classified as top management positions. 89. (p. 188) In this day of rapidly changing technology, technical skills are the most important skills for all levels of management. 90. (p. 188) Conceptual skills refer to the ability of a manager to perform the tasks associated with a specific discipline or department. 91. (p. 188) First-line managers typically spend less time on conceptual tasks and more time on technical skills. 92. (p. 188) Most of a top manager's time is devoted to conceptual and human relations activities. 93. (p. 188) The ability to plan, coordinate, and delegate are among a manager's most basic technical skills. 94. (p. 188) A person who is a good first-line manager is automatically likely to be a good middle or top manager. 95. (p. 188) Human relations skills include those associated with leadership, coaching, morale building and supportiveness. 96. (p. 187) The question of how to implement change within an organization is the responsibility of the firm's CEO. 97. (p. 189) Staffing involves recruiting, hiring, motivating, and retaining the best people available for the organization. 98. (p. 189) Due to the growth of the Internet, recruiting is less important today than in the past. 99. (p. 189) Staffing is a less important management function today than in the past. 100. (p. 187) Organizing involves developing a structure or framework that relates all workers, tasks and resources to each other. Operationally, organizing means allocating resources, assigning tasks, and establishing procedures for accomplishing the organizational objectives. 101. (p. 187) Top management is also known as first-line management because it deals with key managerial decisions on a priority basis. Top management consists of the president and other key company executives. On the other hand, first-line managers are immediately above an organization's workers. 102. (p. 188) Supervisory managers usually work more with ideas than with people. Supervisory managers are responsible for assigning specific jobs to workers and evaluating their daily performance. Their jobs often bring them into direct contact with the workers they supervise. Figure 7.6 illustrates this by showing that first-line managers rely more on human relations skills than on conceptual skills. 103. (p. 188) Because of the complex nature of their jobs, top managers spend most of their time developing and using technical skills. Top managers spend most of their time on tasks requiring conceptual and human relations skills. 104. (p. 188) The experience gained by first-line managers as they perform their jobs enables them to acquire all the skills they will need when promoted to higher levels of management. Different skill sets are needed at different levels of management. First-line managers tend to use technical skills extensively, but spend much less time using conceptual skills. On the other hand top managers use very few technical skills, but often perform tasks requiring exceptional conceptual skills. Thus, the skills learned by a first-line manager may not be very useful at higher levels of management. 105. (p. 188) Mark is a manager for Cable Connection. He spends most of his time scheduling the specific service calls that each employee performs during the day, verifying job completion, and evaluating employee performance on each call. These responsibilities suggest that Mark is a middle manager. First-line managers typically carry out the tasks that Mark is performing. Middle managers generally are more involved in tactical planning and controlling. 106. (p. 188) Chris was recently promoted to a position as a first-line manager. At this level of management, he will use human relations and conceptual skills as well as technical skills. Though they rely on technical skills more than managers at other levels, first-line managers must also use human and conceptual skills to a certain degree. In fact, as Figure 7.6 on page 188 shows, all three levels of management, to varying degrees, must use all three types of skills. 107. (p. 188) Liz is a first-line manager at her company, which is very traditional in its approach to management. In her position, Liz probably spends a lot of time giving employees detailed and specific instructions. First-line managers are directly responsible for supervising workers and evaluating their performance. 108. (p. 188) Fatma wants to become a manager. However, she is shy and avoids conversation with strangers. She is very comfortable with computers and information technology and has great technical skills in these areas. Fatma's personal traits make her a good candidate for a top management position. Top managers typically use few technical skills. Instead, almost all of their time is devoted to human relations and conceptual tasks. 109. (p. 188) Staffing is less important at Sony, IBM and other high-tech firms because these firms sell technology. At most high-tech companies, like IBM and Sony, the primary capital equipment is brainpower, so staffing is essential to obtain the best people available to accomplish these companies' objectives. 110. (p. 189) People who are good leaders also are almost always good managers. 111. (p. 189) Leadership is the management function of checking to determine whether or not an organization is progressing toward its objectives, and taking corrective action if it is not. 112. (p. 189) One difference between managers and leaders is that managers strive to achieve stability while leaders embrace change. 113. (p. 189) Management carries out of the vision created by leadership. 114. (p. 189) Effective leadership includes both the ability to welcome change and to promote ethical behavior. 115. (p. 189) Good leaders motivate workers and create the environment for workers to motivate themselves. 116. (p. 189) Because of the threat of terrorism, the workplace is changing from an environment in which all employees work together to accomplish common goals to an environment in which a leader dictates the rules to others. 117. (p. 190) Managers must lead by doing, not just by saying. 118. (p. 190) A leader's most important job may be to transform the way the company does business so that it's more effective and efficient. 119. (p. 190) Researchers have determined that all effective leaders have similar traits. 120. (p. 190) There is no single leadership style that works best in all situations. 121. (p. 191) Research has shown that the democratic style of leadership is the most effective style of leadership. 122. (p. 192) Research on leadership supports the idea that the best leadership style depends on several factors, including the people being led and the situation. 123. (p. 191) The autocratic style of leadership can be very effective in emergency situations. 124. (p. 191) The traits used by autocratic leaders include warmth, friendliness, and understanding. 125. (p. 191) The traits that characterize participative leaders include flexibility, good listening skills, and empathy. 126. (p. 191) Autocratic leadership is most effective with workers who like to work independently and make their own decisions. 127. (p. 191) Research has shown that employee participation in decision-making improves job satisfaction. 128. (p. 191) Free-rein leaders tend to carefully monitor their subordinates to make sure they are doing the job in the correct way. 129. (p. 192) Managers are most effective when they consistently use the same leadership style with every employee assigned to their work group. 130. (p. 192) In traditional organizations, directing includes both giving assignments to workers and providing feedback on their performance. 131. (p. 192) When businesses empower their employees, the role of a manager becomes less that of a "boss" and more that of a coach, counselor, or team player. 132. (p. 192) Empowerment means that more authority and responsibility is given to top management. 133. (p. 192) Enabling is the term used to describe the process by which employees recognize and respect the authority of managers to issue orders. 134. (p. 192) Knowledge management involves finding the right information, keeping the information accessible, and making the information known to everyone in the firm. 135. (p. 193) The focus of knowledge management is to make sure top managers have all of the information they need to run the company. 136. (p. 192) The first step to developing a knowledge management system is to develop the technology to keep information secure. 137. (p. 189) A comparison of leadership and management suggests that leadership is about creating a vision, while management is about carrying out that vision. Leadership is creating a vision, while management is the carrying out of the leadership's vision. 138. (p. 189) Heather has a strong desire to maintain and preserve order and stability. She is very good at developing tactical plans to achieve her company's goals and objectives. These characteristics suggest that Heather has characteristics of an exceptional leader. One of the characteristics of leaders is that, rather than striving for order and stability, they create and embrace change. The fact that Heather strives to produce order and stability suggests she might be a good manager, and her planning skills reinforce this conclusion. However, not all good managers make good leaders. 139. (p. 191) Brett heads a department in a major manufacturing corporation. He strives to maintain a free-rein approach to leadership in most situations. Recently, Brett's company lost a major contract that it needs to continue the current level of operation. The company needs to take quick action to adjust, including slashing expenses. Under these conditions, Brett should maintain his free-rein style of leadership. No single leadership style is always effective. The best style will depend on the people being led, the organization, and the situation. Good managers often vary their leadership styles as conditions change. In crisis situations, the autocratic approach is sometimes more effective than a free-rein approach. 140. (p. 191) Lamont is quick and decisive. He makes most decisions by himself, issues orders, and expects his subordinates to follow them without question. Lamont's behavior is an example of the free rein style of leadership. A free rein manager is one who gives his or her subordinates a substantial amount of freedom. Lamont's approach, with its emphasis on issuing orders without consultation, is more consistent with the autocratic style of leadership. 141. (p. 192) A recent customer survey has convinced top managers at Akwip Corporation that their firm is doing a poor job of responding quickly to the needs of customers. The managers are very concerned about this problem. Empowerment might be an approach that would help Akwip improve its responsiveness. Empowerment means giving employees the authority and responsibility to respond quickly to consumer requests. 142. (p. 191) Juanita is a project manager for a group of experienced and creative programmers at Idle Time Gaming, a publisher of popular computer games. Since the programmers are bright, creative, and highly motivated, Juanita brainstorms basic ideas with her group, then allows the programmers a great deal of freedom to do what it takes to reach the agreed upon objectives. Juanita is using a free-rein leadership style. A free-rein leader gives subordinates a great deal of freedom to do whatever it takes to accomplish the organization's objectives. 143. (p. 192) Bryce has worked for Carolina Hotel for 10 years. Greg is a new employee at the hotel. Rachel, who oversees both of these employees, may find that she should use a different leadership styles with Greg than with Bryce. An effective manager may use different leadership styles for different people or situations. A new worker may require more direction, while a more experienced employee may be more responsive to empowerment and a free-rein style of leadership. More experienced workers may respond better to a more democratic style. 144. (p. 191) Joseph, a department chair at a major university always gives department faculty members a chance to express their opinions and encourages them to participate in decision-making. Employees who work with Joseph are likely to have a high level of job satisfaction. Joseph is using the democratic leadership style. Research has found that this style usually increases the job satisfaction of employees. 145. (p. 192) Zoe is a middle manager at Watta-Deihl Incorporated. The company's top management has just announced that they are going to initiate a policy of empowerment. In order for this policy to succeed, Zoe and other managers will need to adopt a more autocratic style of leadership. Empowerment means giving employees more authority and responsibility to make their own decisions. Autocratic leadership, which relies on issuing orders and expecting people to follow them, is not consistent with empowerment. Managers in firms where empowerment is practiced typically give fewer detailed instructions and spend more time coaching, assisting and counseling workers. 146. (p. 192) As a manager, Bob believes in empowerment and strives to provide all workers with easy access to the information they need to make good decisions. Bob's views suggest that he would place a great deal of emphasis on knowledge management. Knowledge management is all about finding the right information, keeping it in a readily accessible place, and making the information known to everyone within the organization. Effective knowledge management is a key to successful empowerment 147. (p. 193) The steps of the controlling function include assigning tasks and establishing procedures to accomplish organizational goals. 148. (p. 193) Controlling provides managers and workers with feedback that helps them adjust to deviations from plans. 149. (p. 193) If managers do a good job planning and organizing, there shouldn't be a need for them to be involved with controlling. 150. (p. 193) Two of the key components of the control process are setting clear performance standards and communicating results and deviations to the employees involved. 151. (p. 193) The first step in the controlling process is to monitor and record the actual results. 152. (p. 193) Without clear standards, the control process is impossible to implement. 153. (p. 194) In the control process, performance standards should be stated in general terms in order to give management as much flexibility as possible. 154. (p. 194) In order to be effective, performance standards must be specific, attainable, and measurable. 155. (p. 194) Accounting and finance are important for control systems because they provide the numbers management needs to evaluate progress. 156. (p. 194) External customers are those individuals or units that receive services from other units within the same organization. 157. (p. 194) A customer-oriented firm should focus exclusively on satisfying its internal customers. 158. (p. 194) When all is said and done, financial standards such as profit and return on investment are the only relevant measures of how well a firm is meeting its goals. 159. (p. 194) When controlling, it is advisable to set performance standards that exceed what workers can actually achieve, because setting lofty goals encourages workers to put forth a maximum effort. Performance standards in the controlling process should be specific, attainable, and measurable. 160. (p. 194) When setting standards used in controlling, it is better to simply state general goals such as "better quality" or "higher levels of consumer satisfaction" than it is to spend a lot of time and effort developing more specific standards. If standards are stated in very general terms, it becomes difficult to determine whether the goals are being met. General and vague goals do not clearly identify what the firm is trying to achieve. 161. (p. 193) Chase is a manager for World Graphic Design, Inc., a firm that designs and manufactures greeting cards, invitations, announcements, and other event material. Chase spends a lot of time trying to find the right people for various positions at his company. These efforts are part of the controlling function of management. Controlling is concerned with checking to see whether the organization is meeting its goals by setting standards, measuring actual performance, comparing actual results with the desired standards, providing feedback, and taking corrective action if necessary. Staffing, which is the process of finding the right people for various positions within an organization, is part of the organizing function of management. 162. (p. 194) Rebecca is concerned about the number of customers complaining about the poor service provided by the department she manages for a hardware store. She is convinced that her employees can provide better service and cut complaints significantly. Rebecca has set a goal for her department to reduce customer complaints by 15% within six months. This goal is an example of the type of performance standard needed for effective controlling. An effective standard for the controlling process should be specific, attainable, and measurable. It is also important to establish a time period for the achievement of the goal. Assuming that she is correct about the ability to reduce complaints significantly, Rebecca's standard satisfies these criteria. 163. (p. 194) Pro Fit, Inc., a maker of men's sportswear, has just reported a record profit. This proves that the firm is successfully achieving its goals. Although measures of financial success (such as profit) are very important indicators of business performance, they are not the only measures. The purpose of a firm today is to satisfy a broad group of stakeholders, including employees, customers, and the people living in the local communities where the business has operations. The success of the firm at satisfying the diverse interests of these groups cannot be measured by focusing on financial criteria alone. 164. (p. 179) __________ is the art of utilizing organizational resources to accomplish goals at work. A. Socialization B. Justification C. Preparation D. Management 165. (p. 178) Management is more progressive today. There is more emphasis on: A. individual work that can be successfully measured. B. working in teams. C. striving to eliminate the control function of management. D. placing greater reliance on the government for financing. 166. (p. 178) One of the challenges facing today's managers is to: A. deal with a workforce that is less educated and less self-directed than in the past. B. find ways to encourage conformity instead of diversity. C. work with a more educated workforce. D. cope with the sudden and unexpected slowdown in the pace of innovation and change. 167. (p. 178) Today's progressive managers: A. prefer to use the autocratic style of leadership. B. emphasize teamwork and cooperation rather than discipline and order-giving. C. face fewer challenges and problems than managers in the past. D. can rely on a much higher level of worker loyalty to the organization than in the past. 168. (p. 178) Which of the following statements comparing today's workers with those from earlier eras is most accurate? Compared to earlier workers, today's employees are: A. more loyal to the firm. B. less educated and less self-directed. C. more willing to leave the firm to seek better opportunities. D. more likely to need direct guidance and direction from their managers. In the past, a worker would expect to work for the same company for many years, maybe even a lifetime. Today, many employees don't hesitate to leave if their needs are not being met. 169. (p. 178) The revolution in management that is currently underway suggests that the most effective managers of the future will: A. be very strict in their treatment of workers. B. emphasize individual initiative rather than teamwork. C. specialize in performing one of the four management functions. D. emphasize team work. Management is experiencing a revolution. The manager of the future will likely be working in teams and assuming completely new roles in the firm. 170. (p. 178) How are managers today different from managers in the past? A. Managers today are more likely to reprimand workers B. Managers in the past would use praise and gentle suggestions C. Managers in the past were less loyal to their employer D. Managers today emphasize teamwork Employees today are more educated and demand more self-direction. As a result, today's managers are educated to guide, train, support, motivate, and coach employees rather than to tell them what to do. These managers are likely to emphasize teamwork and communication rather than discipline and order giving. 171. (p. 180) Which of the following statements has resulted in changes in the role of management? A. Most workers today show little initiative or creativity, so managers must spend more time directing their efforts B. The marketplace is becoming global, which increases both competition and opportunities for cooperation and integration C. Firms are recognizing that their workforces are too diverse, so managers must find ways to reduce diversity without violating federal laws against discrimination D. The desire to encourage teamwork has resulted in larger, more cumbersome organizations with too many workers The marketplace is now global, and the advent of the Internet means that competition from global competitors is only a mouse click away. But the global marketplace also offers opportunities for expansion, collaboration and integration but as the Reaching Beyond Our Borders box notes, more capable managers are needed to work in the global environment. 172. (p. 179) One of the four primary functions of management is: A. controlling. B. marketing. C. financing. D. designing. 173. (p. 179) The management function concerned with anticipating future trends and determining the best strategies to achieve an organization's goals and objectives is known as: A. directing. B. leadership. C. planning. D. forecasting. 174. (p. 180) According to the "Reaching Beyond Our Borders" box in Chapter 7, Jack Welch, former CEO of General Electric, said the key problem companies face in addressing opportunities for in the global market is: A. the lack of engineer and scientists in the global market. B. the lack of support from the U.S. government for global expansion. C. the lack of professional managers at all levels to run operations. D. the lack of production capability to keep up with global demand. 175. (p. 180) When managers work on creating conditions and systems to ensure that everything and everyone works together to achieve the organization's goals, they are involved in the __________ function of management. A. controlling B. leading C. planning D. organizing 176. (p. 181) __________ is the management function that involves determining whether an organization is progressing toward its goals, rewarding employees for doing a good job, and taking corrective action when they are not. A. Organizing B. Controlling C. Leading D. Officiating 177. (p. 179) ___________ is the management function that involves setting goals, strategies, and tactics for achieving the organization's goals and objectives. A. Forecasting B. Planning C. Conceptualizing D. Controlling 178. (p. 180) ___________ is the management function of creating a vision for the organization and guiding, training, coaching, and motivating employees to help achieve the goals and objectives of the organization. A. Organizing B. Controlling C. Leading D. Officiating 179. (p. 180) Which of the following goals best describes today's view of the organizing function? Organizing today focuses on: A. achieving unified opinions from a diversified workforce. B. designing the organization around the customer. C. simplifying the process of measuring outcomes related to performance standards. D. developing the most efficient strategic plans for the firm. Today's organizations are being designed to focus on customer needs. Managers want to organize the firm so that everybody in the organization is working to please the customer, while keeping in mind that the firm must be profitable. 180. (p. 181) When managers determine that an organization is not making sufficient progress toward achieving its goals and objectives and they develop corrective measures, they are involved in: A. controlling. B. planning. C. directing. D. accounting. Controlling is the management function that involves checking to see whether or not an organization is progressing toward its goals and objectives, and taking corrective action if it is not. 181. (p. 179) When managers identify a market trend that suggests a new opportunity and then devise a strategy to go after this new opportunity, they are involved in the function of: A. controlling. B. planning. C. leading. D. organizing. Planning is the management function that includes anticipating trends and determining the best strategies and tactics to achieve organizational goals and objectives. 182. (p. 180) Which of the following activities would be a part of the leading function of management? A. Devising a new strategic plan to enter a new foreign market currently dominated by a competing firm B. Recruiting qualified workers to join the organization and assigning them to their proper position C. Examining a financial report to see whether the firm's profits are improving and taking corrective action if they are not D. Training and coaching workers to help them understand their job and perform it effectively Leading involves creating a vision for an organization and guiding, training, coaching and motivating workers so that they can work effectively within the organization. 183. (p. 179) Which of the following activities is part of the planning function of management? A. Assigning a particular worker to do a specific task B. Looking at market forecasts to identify future business opportunities and challenges C. Praising a sales representative who has far exceeded her monthly sales objectives D. Conducting a job interview with a potential new employee Planning involves anticipating trends, identifying opportunities and challenges, and devising strategies and tactics that will help the firm achieve its goals and objectives. 184. (p. 180) Which of the following activities is part of the organizing function of management? A. Going over a spreadsheet to analyze some financial data B. Teaching a new employee how to use a piece of office equipment C. Giving front-line workers additional resources needed to provide faster and better service to customers D. Developing a broad general strategy to help the organization meet its long-term growth objectives Organizing includes creating the conditions and systems in which everyone and everything works together to achieve an organization's objectives. Many of today's organizations attempt to organize in ways that enable them to please their customers at a profit. 185. (p. 180) As a manager, two of Sylvia's strengths are her ability to communicate goals clearly, and her ability to guide, coach, and motivate workers. Based on these strengths, __________ is a management function that Sylvia is likely to be good at performing. A. Controlling B. Planning C. Leading D. Organizing Leading involves communicating, guiding, training, coaching, and motivating others to work effectively toward achieving an organization's goals. 186. (p. 181) Amanda, a regional manager for Flairol Cosmetics, has just seen a report showing that sales in her region are trending lower than anticipated for the third quarter. Her next task is to determine the reason for the disappointing results and find a way to get sales up to their desired level. Amanda's efforts are part of the ____________ function of management. A. controlling B. directing C. organizing D. planning Controlling involves checking to determine whether goals and objectives are being met, and taking corrective action if they are not. 187. (p. 181) A __________ is an overall explanation of why an organization exists and where it is trying to head. A. tactical plan B. prime directive C. corporate charter D. vision 188. (p. 181) A vision for a company is: A. an explanation of why the company exists and where it wants to go. B. the same thing as an objective. C. a detailed plan that outlines the major organizational structure of the firm. D. very relevant for the short-term, but less useful for the long-term. 189. (p. 181) A meaningful mission statement should address topics such as the organization's: A. form of ownership and methods of financing. B. self-concept and company philosophy. C. advertising strategy and distribution plan. D. tactical plans and contingency plans. 190. (p. 181) Employees often work with managers to develop a(n) __________ that outlines the fundamental purposes of their organization. A. organization chart B. value statement C. mission statement D. PERT diagram 191. (p. 181) __________ involves setting the organization's vision, goals, and objectives. A. Organizing B. Planning C. Controlling D. Directing 192. (p. 181) ___________ are broad, long-term accomplishments an organization wants to achieve. A. Goals B. Objectives C. Directives D. Agendas 193. (p. 181) __________ are specific, short-term, measurable results an organization wants to achieve in order to fulfill its long term goals. A. Directives B. Opportunity targets C. Objectives D. Mission complements 194. (p. 182) A __________ analysis is used to help companies evaluate their internal strengths and weaknesses, and develop an awareness of external threats and opportunities. A. WISH B. SWAMP C. ASSET D. SWOT 195. (p. 183) __________ planning determines the major goals of an organization and lays the foundation for obtaining and using resources to achieve those goals. A. Strategic B. Contingency C. Central D. Tactical 196. (p. 184) The type of planning that is concerned with developing detailed short-term actions about what is to be done, who is to do it, and how it is to be done is known as __________ planning. A. strategic B. contingency C. first-line D. tactical 197. (p. 184) __________ planning prepares alternative courses of action that may be used if the primary plans are not achieving objectives. A. Strategic B. Contingency C. Tactical D. Alternative 198. (p. 184) Tactical planning is concerned with: A. determining the best way to cope with an emergency situation. B. developing detailed strategies about what is to be done, who is to do it, and how it is to be done. C. devising temporary courses of action to be used if the primary plans do not achieve the desired results. D. setting long run goals that will govern the general course of the organization for years. 199. (p. 184) Which of the following is involved in setting work standards and schedules needed to implement the firm's tactical objectives? A. Mission statement B. Tactical planning C. Operational planning D. Contingency planning 200. (p. 184) A(n) __________ would be used by a department manager as a tool for making daily and weekly assignments: A. operational plan B. vision statement C. mission statement D. tactical plan 201. (p. 184) Strategic planning looks at the organization as a whole, while ________ planning focuses on daily tasks and decisions. A. tactical B. strategic C. mission D. operational 202. (p. 185) _________ planning is a part of contingency planning that is used to deal with sudden and unexpected changes in the business environment. A. Crisis B. Tactical C. Operational D. SWOT 203. (p. 185) __________ is choosing among two or more alternatives. A. Contingency planning B. Decision-making C. Organizational selection D. Utility analysis 204. (p. 186) The first step in the rational decision-making model is to: A. recruit team members to work on the problem. B. gather data. C. develop alternative responses. D. define the situation. 205. (p. 186) __________ is a problem solving technique that attempts to come up with as many solutions as possible in a short time without censoring the ideas. A. Brainstorming B. Game theory C. CAD/CAM D. PMI 206. (p. 186) PMI is a: A. computer program used to help managers write mission statements. B. statistical technique used in the controlling process. C. problem solving technique used to evaluate possible solutions to a problem. D. rule of thumb used to determine how many employees should be managed by any single manager. 207. (p. 181) In a company in which a effective vision has been provided: A. there is no need for tactical planning. B. the economic and competitive environments tend to be much more predictable. C. employees are likely to have a sense of purpose and a common set of values. D. goals and objectives are no longer needed. A vision communicates why an organization exists and where it is going. A clear vision gives employees a sense of purpose and a set of values. 208. (p. 181) A basic difference between goals and objectives is that goals are: A. precise, while objectives are vague. B. set by tactical plans, while objectives are set by strategic plans. C. set by middle management, while objectives are set by first-line managers. D. concerned with broad, long-term accomplishments, while objectives focus on specific short-term details. Goals are broad, long-term accomplishments an organization wishes to attain. Objectives are specific, short-term statements detailing how to achieve the goals. 209. (p. 183) Which of the following would be a concern addressed in a strategic plan? A. Should the firm make a long-term commitment to expand into new markets? B. Which specific jobs should be assigned to each employee? C. How much output should be produced this week in a given production facility? D. Which computer software package should the firm's human resources office use to manage the payroll? In strategic planning, an organization answers basic questions such as which customers to serve, what products to produce, and which geographic areas to select as markets. 210. (p. 185) According to the "Spotlight on Small Business" box in Chapter 7, the Blue Man Group knew that if they wanted to expand their product planning and organization were critical. Therefore, the three partners spent considerable time writing a: A. strategic plan B. performance plan C. crisis plan D. responsive plan Strategic planning is a must for any business that intends to expand or improve its operations. The Blue Man Group is no different which is why the three partners spent days writing the 132 page Blue Man operating manual 211. (p. 184) Because economic and competitive environments frequently change, organizations should: A. set a long-term plan and stick to it. B. develop contingency plans. C. save time and money by cutting back on planning. D. eliminate any long-term strategic plans, but devise short-term tactical plans and update them once a year. Contingency planning identifies alternative courses of action for use if the primary plans do not achieve the objectives of the organization. This type of planning is necessary in today's environment where economic and competitive conditions change frequently. 212. (p. 186) Which of the following techniques would a team of workers be most likely to use if they wanted to evaluate several possible solutions to a specific problem their company needs to solve? A. PERT B. Regression analysis C. PMI D. MBO PMI is a problem solving technique that evaluates possible solutions by identifying their pluses, minuses, and implications. 213. (p. 181) Jenna Raiter, the president and CEO of AutoMotion Auto Service Centers, has asked several managers and employees to help establish a statement to outline the fundamental purposes of their company. The result of this effort is likely to be a document known as a(n): A. payoff matrix. B. mission statement. C. tactical plan. D. organization chart. Employees and managers often work together to design a mission statement that reflects the organization's fundamental purposes. 214. (p. 183) Jamal is part of a management group that is examining whether his company, State Engineering, should offer some important new services that would broaden its business by appealing to a different group of potential clients. Jamal's group is involved with: A. contingency planning. B. operational planning. C. strategic planning. D. tactical planning. Strategic planning involves setting the major goals of the organization and the policies and strategies for obtaining and using resources to achieve those goals. This type of planning looks at which customers to serve, what products or services to offer, and the geographic areas where the firm will operate. 215. (p. 181) Monica was hired by the Misty Mount Corporation to take over as the new chief executive officer. Her initial impression is that the company is in disarray, primarily because the employees do not have a sense of purpose or a common set of values. Monica's observations suggest that she needs to provide a(n) _________ for Misty Mount: A. vision B. contingency plan C. objective function D. corporate logo A vision explains why an organization exists and where it is trying to go. The purpose of a vision is to provide a sense of purpose and a common set of values to unite the workers and give them a sense of direction. 216. (p. 181) Customers who visit any Good As New Appliance Repair Center see a framed statement prominently displayed near the front door. The plaque describes the company's fundamental purposes. In part, it states that "All Good As New Centers operate under the belief that every customer deserves good quality parts, fast and dependable service, and a fair price." The words on this plaque reflect the ____________ of Good As New. A. strategic plan B. mission statement C. corporate agenda D. corporate charter A mission statement is an attempt to reflect the organization's fundamental values. It identifies the guiding principles of the organization. 217. (p. 184) Setting contingency plans in an organization is considered very important today mainly because: A. managers have historically been poor tactical planners. B. the government can charge firms with unfair business practices if they do not have such plans. C. conditions change rapidly in today's economic and competitive environments. D. most employees and staff don't understand strategic planning, so they tend to rely more on contingency plans. Contingency planning involves developing alternative plans that can be used if the primary plan proves unsatisfactory. This type of planning helps firms cope with changes in the economic and competitive environment that might render the primary plan ineffective. 218. (p. 182) When a firm makes use of the SWOT analysis, one of its objectives is to: A. identify the best employees to fill each position within the organization. B. set specific short-term performance standards for each department. C. evaluate the desirability of issuing stocks or bonds in the current financial climate. D. identify the things it does well as an organization and the things it needs to improve. SWOT analysis identifies an organization's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. In the context of SWOT, strengths and weaknesses are internal to the firm. In other words, strengths refer to what the firm currently does well, and weaknesses refer to the areas where the company needs to improve. 219. (p. 184) Jermaine is a manager with Drevil Industries. Part of his job is to make specific short-term decisions about what his department must do to achieve Drevil's long-term success. Jermaine is involved in: A. strategic planning. B. contingency planning. C. tactical planning. D. complimentary planning. Tactical planning is concerned with developing specific short run decisions about what is to be done, who is to do it, and how it is to be done. 220. (p. 185) According to the "Spotlight on Small Business" box in Chapter 7, one of the keys to the success of the Blue Man Group has been: A. keeping the price for their show as low as possible. B. focusing on the small markets where the competition for entertainment is less intense. C. the decision to keep the organization small and not risk losing control through expansion. D. the development of a strategic plan to manage the product's growth and everyday operations. The three partners in the Blue Man Group spent days writing a 132-page manual that addressed how the organization would operate. Today they have over 500 employees, 70 of whom appear as Blue Men in 12 cities around the world. 221. (p. 184) Kayla is a supervisor who manages a production line. She spends several hours each week developing specific employee work assignments and production schedules for the coming week so that the production department can meet its short-term production objectives. This suggests that a significant component of Kayla's job involves: A. strategic planning. B. contingency planning. C. tactical planning. D. operational planning. Operational planning is the process of setting work standards and schedules necessary to implement tactical objectives. Lower level managers such as supervisors and department managers usually carry out this type of planning. 222. (p. 184) Flavio, CEO of Fabulous Frozen Custard believes that alternate plans are almost as important as the primary operational plans because external circumstances such as the weather, competitor moves, and even economic conditions make it important to have a Plan B. Flavio endorses: A. tactical planning. B. retroactive planning. C. concurrent planning. D. contingency planning. Contingency plans provide alternative courses of action for use if the organization's primary plans fail to achieve their intended results. 223. (p. 186) Carlos had been thinking of setting up a graphic design service business for quite some time. He knew that he wanted to work at home and he now had several leads for prospective customers. He also knew how much money he needed to make to cover his expenses. He had several ways to approach his new business including working by himself or taking on a partner. Both ways needed more thought to determine what each would involve. In terms of the rational decision-making model, Carlos is in which of the following steps? A. Defining the situation B. Describing and collect needed information C. Develop alternatives D. Develop agreement among those involved Carlos has already defined the situation—that of opening a graphic design service business. He has described that he would like to locate the business in his home and who some of the customers might be. Further he has collected information about how much money he must earn. He is just beginning to consider whether he should work alone or with a partner so he is in the "develop alternatives" step. 224. (p. 186) __________ is the management function that involves allocating resources, assigning tasks, and establishing procedures for accomplishing the organizational objectives. A. Controlling B. Outsourcing C. Organizing D. Coordinating 225. (p. 187) A(n) __________ is used by an organization to show who is accountable for the completion of specific work and who reports to whom. A. balance sheet B. Venn diagram C. stakeholder outline D. organization chart 226. (p. 187) A(n) ________________ is a visual device which shows relationships among people and divides the organization's work. A. organization chart B. Venn diagram C. corporate tree D. Gantt chart Learning Goal: 07-4 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms Nickels - Chapter 07 #226 Topic: Organizing: Creating a Unified System 227. (p. 188) The level of management that is directly responsible for assigning specific jobs to workers and evaluating their daily performance is called: A. primary management. B. middle management. C. supervisory management. D. secondary management. 228. (p. 189) Middle managers are responsible for: A. establishing the vision for the organization. B. assigning specific jobs and evaluating the daily performance of workers. C. devising the organization's strategic plan. D. developing tactical plans and controlling. 229. (p. 187) General and divisional managers, plant managers, and deans and department heads at colleges are classified as: A. middle management. B. supervisory management. C. top management. D. nominal management. 230. (p. 188) Supervisory managers spend most of their time on: A. conceptual and financial skills. B. technical and human relations skills. C. strategic planning. D. external efforts such as meeting with stockholders and other stakeholders. 231. (p. 188) ___________ skills involve a manager's ability to picture the organization as a whole and the relationship among its various parts. A. Creative B. Technical C. Conceptual D. Autonomic 232. (p. 188) ____________ skills include the ability to perform tasks of a specific department or job, such as selling (marketing) or bookkeeping (accounting). A. Conceptual B. Departmental C. Technical D. Tactical 233. (p. 188) Leadership, coaching, and morale building are all part of a manager's _________ skills. A. technical B. theoretical C. empirical D. human relations 234. (p. 188) Although top managers most often possess these skills, they usually make less use of __________ skills than supervisory managers. A. technical B. conceptual C. human relations D. empirical 235. (p. 187) The downsizing that has occurred in recent years has __________ middle managers in many organizations. A. increased the number of B. eliminated the jobs of some C. strengthened the control of D. increased the importance of Learning Goal: 07-4 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms Nickels - Chapter 07 #235 Topic: Organizing: Creating a Unified System 236. (p. 187) Which of the following management positions is responsible for getting the right information to other managers to enable them to make better decisions? A. Chief executive officer (CEO) B. Chief financial officer (CFO) C. Chief planning officer (CPO) D. Chief information officer (CIO) 237. (p. 188) The further up the managerial ladder a person moves, the __________ his or her original job skills become. A. more important B. less important C. stronger D. more tactical Learning Goal: 07-4 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms Nickels - Chapter 07 #237 Topic: Tasks and Skills at Different Levels of Management 238. (p. 187) A chief operating officer (COO) would be classified as part of a firm's: A. primary management. B. middle management. C. top management. D. first-line management. Learning Goal: 07-4 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms Nickels - Chapter 07 #238 Topic: Organizing: Creating a Unified System 239. (p. 189) ___________ involves recruiting, hiring, motivating, and retaining the best people available to accomplish the company's objectives. A. Directing B. Planning C. Leading D. Staffing Learning Goal: 07-4 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms Nickels - Chapter 07 #239 Topic: Staffing: Getting and Keeping the Right People 240. (p. 188) In comparing the types of skills used by managers at different levels within an organization, which of the following is ? A. Top managers use mainly technical skills and middle and first-line managers use mostly conceptual skills B. First-line managers use mainly technical and human relations skills, while top managers devote most of their time to activities involving human relations and conceptual skills C. The types of skills used by managers do not change much from one level of management to another D. The specific skills used at different levels of management do vary, but conceptual skills are the most important at all levels First-line managers spend most of their time explaining procedures, assigning jobs, and evaluating the performance of employees within their own areas. These activities require human relations and technical skills. Top managers are more concerned with creating a vision, strategic planning, and overseeing the operations of the organization as a whole. This requires them to use conceptual and human relations skills. Blooms: Comprehension Learning Goal: 07-4 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles Nickels - Chapter 07 #240 Topic: Tasks and Skills at Different Levels of Management 241. (p. 189) Gabriella is responsible for hiring, motivating, and retaining the best employees for her organization. Gabriella is in charge of: A. staffing. B. orienting. C. directing. D. facilitating. Staffing is the function of hiring, motivating, and retaining the best people available to accomplish the company's objectives. Learning Goal: 07-4 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles Nickels - Chapter 07 #241 Topic: Staffing: Getting and Keeping the Right People 242. (p. 188) After thirteen years as a laborer for Hendrix Construction, Jimmy was promoted to the position of foreman. He is directly responsible for assigning various jobs to his work crew and evaluating their performance on a daily basis. Jimmy is now a member of: A. top management. B. middle management. C. supervisory management. D. forward management. Supervisory (or first-line) managers are concerned with assigning workers to specific jobs and evaluating the daily performance of those workers. Learning Goal: 07-4 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles Nickels - Chapter 07 #242 Topic: Organizing: Creating a Unified System 243. (p. 188) By completing the courses needed to obtain a college major in accounting, marketing, or some other field, a student can go a long way toward acquiring the _________ skills managers need to rise through the ranks of their area of specialization. A. autocratic B. technical C. human relations D. secondary Technical skills involve the knowledge and ability to perform a specific task. A portion of the course work in these technical areas is intended to enable the student to perform specific activities. Learning Goal: 07-4 Nickels - Chapter 07 #243 Topic: Tasks and Skills at Different Levels of Management 244. (p. 187) Which of the following persons is most likely to be involved in strategic planning? A. Chief executive officer B. Electrical shop supervisor C. Budget analyst D. Advertising manager Top managers, such as the chief executive officer of a firm normally develop strategic plans. Learning Goal: 07-4 Nickels - Chapter 07 #244 Topic: Organizing: Creating a Unified System 245. (p. 188) Axel is in a new position, serving as a first-line manager. Axel's position will require him to spend a lot of time: A. developing strategic plans. B. evaluating the daily performance of workers. C. creating a vision for the company. D. providing information to stakeholders. First-line managers are responsible for assigning specific jobs to workers and evaluating the performance of employees on a daily basis. Learning Goal: 07-4 Nickels - Chapter 07 #245 Topic: Organizing: Creating a Unified System 246. (p. 187) Anita is employed as plant manager for Mojo Industries, Incorporated. Though she spends some time performing all management functions, she is particularly concerned with tactical planning and controlling. Anita's position would be classified as part of Mojo's: A. top management. B. lateral management. C. supervisory management. D. middle management. Tactical planning and controlling are primarily the responsibility of middle managers. Examples of middle managers include plant managers, branch managers, deans and department heads. Learning Goal: 07-4 Nickels - Chapter 07 #246 Topic: Organizing: Creating a Unified System 247. (p. 188) After working for eleven years as a production line worker, Hollis recently was made a foreman. In his new position, Hollis will rely on: A. conceptual skills more than human relations skills. B. technical skills and human relations skills more than conceptual skills. C. technical skills and conceptual skills, but he won't really need any human relations skills. D. accounting and financial skills. As a first-line manager, Hollis will work with employees in ways that will require him to use technical and human relations skills extensively. First-line managers spend little time on activities requiring conceptual skills. Learning Goal: 07-4 Nickels - Chapter 07 #247 Topic: Tasks and Skills at Different Levels of Management 248. (p. 188) Ricardo works as a department head at Barnes Hospital. His job requires Ricardo to spend most of his time training and coaching employees to perform their jobs more effectively and teaching other managers to be better leaders. Ricardo's job requires him to make full use of his: A. technical skills. B. conceptual skills. C. orientation skills. D. human relations skills. Human relations skills include the ability to train, coach, and motivate employees so that they become more productive. Learning Goal: 07-4 Nickels - Chapter 07 #248 Topic: Tasks and Skills at Different Levels of Management 249. (p. 188) As CEO of Google, Eric Schmidt performs strategic planning for the organization as well as putting structure in place to monitor company progress. These activities make use of Eric's: A. conceptual skills. B. technical skills. C. concurrent skills. D. human relations skills. Conceptual skills refer to a manager's ability to see the organization as a whole and the relationships of various parts of the organization to each other. These types of skills are important to managers as they perform such tasks as strategic planning and controlling. Learning Goal: 07-4 Nickels - Chapter 07 #249 Topic: Tasks and Skills at Different Levels of Management 250. (p. 188) Vinnie wants to become a manager in his company, but he has always been a bit shy and has a hard time interacting with co-workers. In order for Vinnie to succeed as a manager, he will need to work on his: A. technical skills. B. human relations skills. C. control skills. D. integration skills. Working with people effectively requires managers to develop their human relations skills. Virtually all managers, regardless of level, need human relations skills to perform their jobs successfully. Learning Goal: 07-4 Nickels - Chapter 07 #250 Topic: Tasks and Skills at Different Levels of Management 251. (p. 188) Rob intends to major in accounting because he is confident that an ability to read and interpret financial and accounting data is the way to get to the top in business. Rob seems to be concerned with developing his: A. technical skills. B. verbal skills. C. qualitative skills. D. conceptual skills. Technical skills are the skills that provide a manager proficiency in a particular area, such as accounting, finance, or marketing. Learning Goal: 07-4 Nickels - Chapter 07 #251 Topic: Tasks and Skills at Different Levels of Management 252. (p. 189) _____________ involves creating a vision for others to follow, establishing corporate values and ethics, and transforming the way an organization does business so that it is more effective and efficient. A. Organizing B. Production management C. Tactical planning D. Leadership Learning Goal: 07-5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms Nickels - Chapter 07 #252 Topic: Leading: providing Continuous Vision and Values 253. (p. 189) Leaders: A. embrace change. B. are mainly concerned with tactical issues as opposed to change issues. C. tend to do the work themselves rather than delegate it to others. D. strive to maintain order and stability. Learning Goal: 07-5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms Nickels - Chapter 07 #253 Topic: Leading: providing Continuous Vision and Values 254. (p. 191) The __________ style of leadership is characterized by making managerial decisions without consulting others. A. autocratic B. bureaucratic C. free rein D. democratic Learning Goal: 07-5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms Nickels - Chapter 07 #254 Topic: Leading: providing Continuous Vision and Values 255. (p. 191) Managers who listen to their subordinates and allow them to participate in decision-making are using the ____________ style of leadership. A. autocratic B. free-rein C. participative D. bureaucratic Learning Goal: 07-5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms Nickels - Chapter 07 #255 Topic: Leadership Styles 256. (p. 191) A(n) __________ leader would set objectives and give employees a great deal of freedom to decide for themselves how to accomplish those objectives. A. free-rein B. autocratic C. Type A D. aristocratic Learning Goal: 07-5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms Nickels - Chapter 07 #256 Topic: Leadership Styles 257. (p. 189) A key to effective leadership is the ability to: A. maintain order, stability, and control. B. communicate a vision and rally others around that vision. C. master the technical details of the jobs performed by subordinates. D. maintain an autocratic approach to dealing with others. Learning Goal: 07-5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms Nickels - Chapter 07 #257 Topic: Leading: providing Continuous Vision and Values 258. (p. 192) __________ is the term used to describe giving workers the education and tools they need to assume additional decision-making powers. A. Energizing B. Provisioning C. Upgrading D. Enabling Learning Goal: 07-5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms Nickels - Chapter 07 #258 Topic: Empowering Workers 259. (p. 192) _____________ means giving employees the authority and responsibility to respond quickly to customer requests. A. Restructuring B. Delineating C. Empowerment D. Intrapreneuring Learning Goal: 07-5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms Nickels - Chapter 07 #259 Topic: Empowering Workers 260. (p. 192) In traditional organizations, ____________ involves giving explicit instructions to workers, telling them what to do to meet the goals and objectives of the organization. A. directing B. organizing C. budgeting D. controlling Learning Goal: 07-5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms Nickels - Chapter 07 #260 Topic: Empowering Workers 261. (p. 192) ____________ is concerned with finding the right information and making that information accessible and understood by everyone in an organization. A. Mission management B. Data management C. Knowledge management D. Auditing Learning Goal: 07-5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms Nickels - Chapter 07 #261 Topic: Managing Knowledge 262. (p. 192) The first step in developing a knowledge management system is to: A. empower employees to make their own decisions and accept the consequences. B. obtain the necessary information system technologies. C. recognize that perfect information is readily available in all organizations. D. determine what knowledge is most important to the organization. Learning Goal: 07-5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms Nickels - Chapter 07 #262 Topic: Managing Knowledge 263. (p. 189) One difference between managers and leaders is that: A. managers are found in businesses while leaders operate in nonprofit organizations. B. mangers work to achieve stability while leaders embrace change. C. managers use an autocratic approach while leaders embrace a democratic style. D. all employees can manage, but only top managers can lead. Business literature often notes that leaders and managers do not always share the same traits. For example, although managers typically strive for order and stability, leaders frequently embrace change. Blooms: Comprehension Learning Goal: 07-5 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles Nickels - Chapter 07 #263 Topic: Leading: providing Continuous Vision and Values 264. (p. 192) Which of the following statements about effective leadership is the most accurate? A. Effective leaders have the same personality traits B. The most effective leadership style depends on who is being led and in what situation C. The democratic style of leadership will almost always improve the effectiveness of the organization D. One trait of effective managers is that they consistently maintain the same style of leadership No single style of leadership always works best. The style that is most effective depends on the situation and the people who are being led. Blooms: Comprehension Learning Goal: 07-5 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles Nickels - Chapter 07 #264 Topic: Leading: providing Continuous Vision and Values 265. (p. 191) Autocratic leadership is likely to be effective when: A. subordinates are highly trained professionals. B. the organization faces an emergency situation. C. workers enjoy expressing their opinions and having a say in what is done. D. the manager is uncertain about the best strategy to pursue. Autocratic leadership consists of making decisions without consulting others, issuing orders, and expecting subordinates to follow orders without question. This style of leadership may be effective, and even necessary, when an organization faces a crisis in which someone must take charge and make decisions quickly. Blooms: Comprehension Learning Goal: 07-5 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles Nickels - Chapter 07 #265 Topic: Leadership Styles 266. (p. 192) Which of the following statements about leadership styles is most accurate? A. A manager should choose one style and use it consistently B. Managers have no control over the leadership style they use C. Effective managers often use a variety of leadership styles D. Managers should always start with an autocratic style, but can gradually switch to a more democratic approach if workers earn their trust Since the most effective leadership style depends on who is being led and the situation, managers may find that they need to use different styles when they deal with different employees, or when conditions change. Blooms: Comprehension Learning Goal: 07-5 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles Nickels - Chapter 07 #266 Topic: Leadership Styles 267. (p. 192) As firms make greater use of empowerment and teams, managers will find that they: A. should use the same techniques for directing employees that were used in the past. B. will need to closely supervise the teams to make sure they remain focused on the goals of the organization. C. will need to provide the teams with detailed instructions to give them a clear sense of direction. D. must become more like coaches and counselors than bosses. Empowerment means giving workers the authority and responsibility to respond quickly to customer requests. For empowerment to work, employees must be given the knowledge, tools, and freedom to make decisions without waiting for approval from their manager. Thus, a manager in an organization that relies on empowerment must be more like a coach and counselor than a boss or director who tells the workers exactly what to do. Blooms: Comprehension Learning Goal: 07-5 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles Nickels - Chapter 07 #267 Topic: Empowering Workers 268. (p. 189) Which of the following best summarizes the type of leader future organizations are likely to need? In the future, organizations will need leaders who: A. supply both a vision and a moral and ethical foundation for growth. B. provide the sense of stability and orderliness the organization needs to withstand the challenges posed by a changing environment. C. have a strong track record of focusing on the accomplishment of financial objectives. D. are effective at using autocratic techniques. Leaders provide vision. In the future, they will also be called upon to provide the organization with its moral compass by stressing corporate values and corporate ethics. Learning Goal: 07-5 Nickels - Chapter 07 #268 Topic: Leading: providing Continuous Vision and Values 269. (p. 191) The CEO of peripheral company QuickDrive uses a leadership style that encourages employees to discuss management issues with the CEO and to work together to resolve those issues in a democratic manner. Which of the following statements would the CEO of QuickDrive most likely make? A. The key to QuickDrive staying on top in a high-tech industry is not wasting time checking out what other firms do, but to act immediately on my directives B. In a high-tech business, it is more important to invest in technology than to invest in people C. The key to keeping talented employees loyal to QuickDrive is to use a participative management style and treat them with respect, value their ideas, give them the resources they need, and expect great things from them D. Spending a lot of money to buy out competitors for their technology is likely to backfire, because QuickDrive is a leader in technology development The CEO of QuickDrive uses a participative management style, one that consists of managers and employees working together to make decisions. At meetings employees discuss management issues and resolve those issues together in a democratic manner, another attribute of the participative leadership style. Learning Goal: 07-5 Nickels - Chapter 07 #269 Topic: Leadership Styles 270. (p. 191) Well-known retired basketball coach, Bob Knight, was known for his emotional antics at Indiana University and Texas Tech. If you talk with Bob, he believes in total dedication from his team and total compliance to his style of coaching. It's "his way or the highway." Bob typifies the _____________ style of leader. A. bureaucratic B. free-rein C. remanded D. autocratic Autocratic leaders make decisions without consulting others. Learning Goal: 07-5 Nickels - Chapter 07 #270 Topic: Leadership Styles 271. (p. 191) At Holyfield Chemicals, department heads usually make decisions after meeting with employees and seeking their ideas and suggestions. Department heads at Holyfield Chemicals make extensive use of the ___________ style of leadership. A. autocratic B. diplomatic C. democratic (participative) D. open shop Democratic managers seek out the opinions and ideas of their subordinates and allow them to participate in decision making. Learning Goal: 07-5 Nickels - Chapter 07 #271 Topic: Leadership Styles 272. (p. 191) At Lifeline Pharmaceuticals, highly regarded research personnel rely on top management to provide strategic direction. Beyond that, researchers work on their own to develop new drugs to satisfy customer needs and company profit objectives. Middle management at Lifeline practice _____________. A. free-rein leadership B. consultative leadership C. projectory leadership D. autocratic leadership Free-rein leadership consists of managers setting objectives, and then giving subordinates a significant degree of freedom to do what it takes to accomplish those objectives. Learning Goal: 07-5 Nickels - Chapter 07 #272 Topic: Leadership Styles 273. (p. 192) Adam is a first-line manager for Idle Time Gaming, Inc., a company whose values and focus is innovation. Having recently transferred in from a traditional retail (top/down) company, which of the following changes will the new company expect Adam to embrace? A. He must continue to issue detailed instructions to give the teams a sense of direction B. He will no longer have a management position in the firm, since the purpose of teams is to eliminate the need for first-line managers C. He will need to act less like a "boss" and more like a coach, advisor, counselor, and team player D. He will isolate himself from his subordinates Empowerment allows employees to participate more directly in decision making and gives them more flexibility to respond quickly to customer requests. The result should be better work, and better motivation. However, empowerment will require a change in the role performed by managers, who must behave less like bosses, and more like coaches, counselors, assistants, and team players. Learning Goal: 07-5 Nickels - Chapter 07 #273 Topic: Empowering Workers 274. (p. 193) The first step in controlling consists of: A. issuing orders and explaining routines. B. setting clear performance standards. C. establishing a clear chain of command. D. assigning workers to perform specific tasks. Learning Goal: 07-6 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms Nickels - Chapter 07 #274 Topic: Controlling: Making Sure it Works 275. (p. 193) In the control process the first step is to: A. communicate results and deviations to employees. B. compare results to plans and standards. C. set clear and appropriate standards. D. monitor and record performance. Learning Goal: 07-6 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms Nickels - Chapter 07 #275 Topic: Controlling: Making Sure it Works 276. (p. 194) In order for standards to be useful in the controlling process, they must have certain characteristics. One of these characteristics is that they must be: A. nonspecific. B. redundant. C. included the mission statement. D. attainable. Learning Goal: 07-6 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms Nickels - Chapter 07 #276 Topic: Controlling: Making Sure it Works 277. (p. 194) Which of the following should form the foundation of a firm's control system? A. Accounting and finance B. Marketing and production C. Human resources and finance D. Computing and production Learning Goal: 07-6 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms Nickels - Chapter 07 #277 Topic: Controlling: Making Sure it Works 278. (p. 194) __________ are units within an organization that receive services from other units within the organization. A. End-users B. Internal customers C. Third-party distribution centers D. Profit centers Learning Goal: 07-6 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms Nickels - Chapter 07 #278 Topic: Controlling: Making Sure it Works 279. (p. 194) __________ include dealers, who buy products to sell to others, and ultimate customers who buy products for their own personal use. A. End users B. External customers C. Internal customers D. Distribution centers Learning Goal: 07-6 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms Nickels - Chapter 07 #279 Topic: A Key Criteria for Management: Customer Satisfaction 280. (p. 193) Ho Han has just spent two hours going over quality reports to determine whether his department is meeting quality standards he set for the current month. Ho's efforts are part of the ___________ function of management. A. planning B. organizing C. directing D. controlling The controlling function of management involves checking to see whether the firm is making progress toward meeting its goals and objectives, and taking corrective action if necessary. Blooms: Comprehension Learning Goal: 07-6 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles Nickels - Chapter 07 #280 Topic: Controlling: Making Sure it Works 281. (p. 194) Pam is a sales manager for Paradise Beauty Products. She has told her sales people that she expects each of them to increase their customer contacts by at least 5 percent in the next month. Pam has set a(n): A. procedural policy. B. functional objective. C. policy guide. D. performance standard. In order to determine whether a firm is making progress toward its goals and objectives, managers must establish specific, attainable, and measurable standards. This is what Pam has done. Blooms: Comprehension Learning Goal: 07-6 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles Nickels - Chapter 07 #281 Topic: Controlling: Making Sure it Works 282. (p. 194) Which of the following is a clear performance standard? A. Bring about a significant improvement in the morale of all workers. B. Decrease the number of products rejected due to manufacturing defects by 10% over the next 6 months. C. Completely eliminate all customer complaints. D. Make secretaries more efficient. A good standard must be specific, measurable, and attainable. Answer "B" has all of these characteristics. Answers "A" and "D" are not good standards because "significant improvement" and "more efficient" are too vague. Answer "C" is not a good standard because a complete elimination of all complaints in one month is unlikely to be an attainable standard. Blooms: Comprehension Learning Goal: 07-6 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles Nickels - Chapter 07 #282 Topic: Controlling: Making Sure it Works 283. (p. 193) Two years ago, Travis started his own restaurant supply company, serving the greater Chicago area. Until recently, he has never concerned himself with establishing a formal control system. Now, with a recession looming, he is experiencing cost conscious restaurant owners. He has decided that a formal control system is needed. The first step Travis should take is: A. draw up a formal organization chart. B. talk to his banker to set financial goals. C. devise a set of clear performance standards. D. design an accident report form so that he can keep accurate records of all accidents that occur. The first step in the controlling process is to set clear performance standards. Learning Goal: 07-6 Nickels - Chapter 07 #283 Topic: Controlling: Making Sure it Works 284. (p. 193) As a middle manager for her firm, Tori just finished comparing the results of a promotional campaign with the outcome expectations. The next step in the control process is: A. monitor and record actual performance. B. set up contingency plans. C. communicate results and deviations with management and employees involved. D. establish discipline committees to decide on dismissals. After comparing results to standards, the next step in the control process is to communicate results and deviations to the employees involved. Learning Goal: 07-6 Nickels - Chapter 07 #284 Topic: Controlling: Making Sure it Works 285. (p. 194) Harper is a sales rep for an eyeglass company. The company is always on the cutting edge of trendy designs. In her job, she frequently relies on the marketing department to provide her with information and materials. When using customer satisfaction to judge the success of their company, Harper's managers should: A. ignore Harper's satisfaction, since she is an employee rather than a customer. B. take Harper's satisfaction into account, because customers can be internal as well as external. C. consider Harper's satisfaction, but place less emphasis it than on the satisfaction of a stockholder, since she is an external customer. D. only consider Harper's satisfaction if she has worked in the same job for at least 2 years. The criterion for measuring success in a customer-oriented firm is customer satisfaction. However, customers are now defined broadly to include internal customers (people within the organization that receive services from others within the organization) as well as external (dealers and end users). Harper would be an example of an internal customer. Learning Goal: 07-6 Nickels - Chapter 07 #285 Topic: A Key Criteria for Management: Customer Satisfaction 286. (p. 194) When establishing criteria to measure the success of a customer-oriented business, managers should: A. limit their attention to financial measures such as profit and return on investment since these are the only objective and quantifiable measures available. B. focus most of their attention on measures of employee satisfaction, since without good employees the firm will not be competitive. C. focus primarily on financial measures, but pay some attention to non-financial concerns. D. recognize that, while financial measures are important and should be considered, the purpose of the firm is to satisfy both internal and external customers. Financial measures of success, such as profit and return on investment, are important and should not be ignored. In fact, these measures have traditionally been the measures most frequently used to judge success. Today, however, the purpose of a customer-oriented firm is to please all of its stakeholders. Thus, non-financial criteria also play an important role in measuring the success of a firm. Learning Goal: 07-6 Nickels - Chapter 07 #286 Topic: A Key Criteria for Management: Customer Satisfaction 287. (p. 191) Identify and define the four key functions of management. The four functions of management are planning, organizing, leading, and controlling. Planning includes anticipating future trends and determining the best strategies and tactics to achieve organizational goals and objectives. Organizing includes designing the structure of the organization and creating conditions and systems in which everyone and everything work together to achieve the organization's goals and objectives. Leading is the function concerned with creating a vision for the organization and communicating, guiding, training, coaching, and motivating others to achieve the goals and objectives of the organization. Leading today often involves empowering workers and giving them the freedom to become self-directed and self-motivated. Controlling refers to establishing clear standards to determine whether an organization is progressing toward its goals and objectives, rewarding people for doing a good job, and taking corrective action if they are not. Basically, it means measuring whether what actually occurs meets the organization's goals. Learning Goal: 07-5 Nickels - Chapter 07 #287 Topic: Leadership Styles 288. (p. 184) Explain the differences between strategic, tactical, operational, and contingency planning. Strategic planning is long-range planning that determines major goals of the organization. It provides the foundation for the policies, procedures, and strategies for obtaining and using resources to achieve those goals. Strategic planning deals with such fundamental questions as which customers to serve, what products and services to sell, and the geographic areas in which the firm will compete. Students may note that top managers are very involved in strategic planning. Tactical planning is short-range planning that involves the process of developing detailed, short-term statements about what is to be done, who is to do it, and how it is to be done. Tactical planning involves setting annual budgets and deciding on other details which contribute to reaching strategic objectives. Students may point out that lower level managers are more heavily involved in tactical planning. Operational planning involves setting the work standards and schedules necessary to implement the company's tactical objectives. Whereas strategic planning looks at the organization as a whole, operational planning focuses on specific supervisors, department managers, and individual employees. Contingency planning is the preparation of alternative courses of action that may be used if the primary plans do not achieve the objectives of the organization. Due to rapid changes that can occur in economic and competitive environments, it is wise to have alternative plans ready to be implemented. Crisis planning is a part of contingency planning that involves reacting to sudden changes in the environment. Learning Goal: 07-3 Nickels - Chapter 07 #288 Topic: Planning and Decision Making 289. (p. 182) What is the purpose of the SWOT analysis? What types of information does this analysis provide? SWOT analysis is an analysis of an organization's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. It is used to help managers answer several fundamental questions related to the planning function. These questions include: • What is the current situation facing the organization? • What is the state of the business environment? • What opportunities currently exist for meeting people's needs? • What products and customers are most profitable? • Why do people buy (or not buy) our products? • Who are our major competitors, and what threats do they pose for our business? SWOT begins with an analysis of the general business environment. It then identifies the strengths and weaknesses of the firm. This part of SWOT involves internal analysis, which can normally be done fairly easily. Then the analysis attempts to identify opportunities and competitive and environmental threats. Since these are based on factors that are external to the firm, they are more difficult to assess. Figure 7.3 lists several issues that SWOT analysis may examine. Learning Goal: 07-3 Nickels - Chapter 07 #289 Topic: Planning and Decision Making 290. (p. 192) What is empowerment? How has the movement toward empowerment changed the role of the manager? Empowerment means giving employees the authority and responsibility to respond quickly to consumer requests. In the past, managers often were "bosses" who issued orders and expected workers to carry them out. With the trend toward empowered workers, the manager's role is changing. The role of managers of empowered workers will be less that of "boss" and more that of coach, assistant, counselor and team member. They will work to "enable" workers to perform their tasks by giving them the education, training, and resources they need to assume their self-directed responsibilities. Learning Goal: 07-5 Nickels - Chapter 07 #290 Topic: Empowering Workers 291. (p. 188) Describe the three basic types of management skills, and relate these skills to the tasks performed by different levels of management. The three basic types of management skills are technical skills, human relations skills, and conceptual skills. Technical skills are the skills needed to perform tasks in a specific discipline (such as selling a product or developing software) or department (such as marketing or information systems). Human relations skills involve communication and motivation; they enable managers to work through and with people. Such skills also include those associated with leadership, coaching, morale building, delegating, training and development, and help and supportiveness. Conceptual skills refer to the ability to picture the organization as a whole and the relationships among its various parts. Conceptual skills are needed in planning, organizing, controlling, systems development, problem analysis, decision making, coordinating, and delegating. First-line managers, who often must explain procedures and specific techniques to employees, and evaluate the performance of those employees, make extensive use of technical skills. First-line managers seldom perform tasks requiring conceptual skills. At higher levels of management, managers tend to rely more on conceptual skills to carry out their controlling and planning functions but seldom need technical skills. Managers at all levels make use of human relations skills. Learning Goal: 07-4 Nickels - Chapter 07 #291 Topic: Tasks and Skills at Different Levels of Management 292. (p. 191) Describe three different leadership styles and give an example of a situation in which each style could be most used effectively. Students should identify the following leadership styles: Autocratic leadership involves making managerial decisions without consulting others. Such a style is effective in emergencies and when absolute followership is needed—for example, when fighting fires. Autocratic leadership is also effective sometimes with new, relatively unskilled workers who need clear direction and guidance. Democratic (or participative) leadership encourages managers and employees to work together to make decisions. Research has found that employee participation in decisions may not always increase effectiveness, but it usually increases job satisfaction. Many progressive organizations are highly successful at using a democratic style of leadership that values traits such as flexibility, good listening skills, and empathy. Companies such as Wal-Mart, FedEx, IBM, Cisco, and AT&T have used this style successfully. Free-rein leadership involves setting objectives and giving employees a significant amount of freedom to do whatever it takes to accomplish those objectives. Doctors often have this flexibility in hospitals, as do other professionals such as engineers and lawyers who often work on special projects or cases. The traits needed by managers in such organizations include warmth, friendliness, and understanding. Learning Goal: 07-5 Nickels - Chapter 07 #292 Topic: Leadership Styles Mini-Case Lauzy Fare left his position as senior vice president at Blue Skies Electronics a few weeks ago to become the new CEO of Idle Time Gaming. Before joining the new company, Lauzy spent time studying Idle Time's competitive position and talking to employees in all divisions and at all levels of the organization. Based on his findings, Lauzy believes that Idle Time has potential, but also faces some serious challenges if it expects to grow. Lauzy found that when confronted by him, most of Idle Time's professional employees seemed almost afraid to express their opinions. He learned that Otto Craddick, the previous CEO and founder of the company viewed himself as the boss, and, as such, micromanaged every aspect of the business. This discouraged employees from using their own initiatives and ideas to solve problems. For example, Otto required sales and service representatives to get his approval before they made any major commitments to customers. Otto's policy prevented the organization from responding quickly to customer requests, so sales were lost. Unlike his predecessor, Lauzy believes it is important for sales and service personnel to be able to deal with many types of customer requests without needing approval from top management. He is confident that giving employees the authority and flexibility to deal with customers, and providing them with the training and resources to help them do so, will improve morale within the company, create customer satisfaction, and grow revenues. Lauzy also wants to make workers throughout the organization feel more appreciated. He plans to continue meeting with them on a regular basis to seek their advice. He hopes his work colleagues will eventually respond to his leadership style. He has already encouraged middle managers to get employees more involved in decision-making, and has suggested some problem solving techniques the managers could try. Although he thought that changing the rigidity of the company culture would be his first challenge at the new firm, Lauzy quickly realized that there were no standards in place to measure the progress of changes in internal morale, customer satisfaction, and profitability. He has asked managers in those departments to spend more time setting performance standards and then monitoring actual performance. Lauzy is confident that in a relatively short period of time internal changes will lead to good company performance. As a member of top management, Lauzy performs a variety of important tasks. Nickels - Chapter 07 293. (p. 191) Otto, the previous CEO at Idle Time Gaming relied on a(n) ___________ style of management. A. autocratic B. iconoclastic C. democratic D. free-rein Otto made decisions without consulting others, and expected subordinates to follow orders without question. These are characteristics of the autocratic style of management. Learning Goal: 07-5 Nickels - Chapter 07 #293 Topic: Leadership Styles 294. (p. 191) Lauzy seems to prefer a(n) __________ style of leadership. A. autocratic B. democratic (or participative) C. PMI D. altruistic Lauzy likes to listen to the opinions and ideas of subordinates and get them involved in decision making. This indicates a democratic, or participative, style of leadership. Learning Goal: 07-5 Nickels - Chapter 07 #294 Topic: Leadership Styles 295. (p. 186) Lauzy favors problem-solving techniques that allow teams of workers to freely identify and discuss possible solutions to a problem without having their ideas censored. Which of the following is a problem solving technique that Lauzy is likely to suggest to his managers? A. SWOT analysis B. PERT analysis C. brainstorming D. controlling Brainstorming is a problem solving technique that encourages workers to come up with as many potential solutions to the problem as possible in a short time period without censoring the ideas. Learning Goal: 07-3 Nickels - Chapter 07 #295 Topic: Planning and Decision Making 296. (p. 193) Lauzy's decision to establish well-defined standards for monitoring performance means that he expects management to seriously engage in the _________ function of management. A. research and development B. verbalizing C. organizing D. controlling Controlling is the process of measuring performance relative to objectives and standards and taking corrective action when necessary. Learning Goal: 07-6 Nickels - Chapter 07 #296 Topic: Controlling: Making Sure it Works 297. (p. 188) Which of the following statements best describes the relative importance of the various types of skills Lauzy will use to perform these tasks? The tasks Lauzy performs will require: A. only technical skills. B. mainly conceptual skills and human relations skills. C. only human relations skills. D. mainly technical skills and human relations skills. As a top manager, Lauzy may have good technical skills, but will more often use conceptual and human relations skills in day to day activities. The strategic planning, leadership, and other activities required of a CEO, however, will require him to use conceptual and human relations skills extensively. Learning Goal: 07-4 Nickels - Chapter 07 #297 Topic: Tasks and Skills at Different Levels of Management 08 Key 1. (p. 202) Organizing the structure of the company means deciding how many jobs need to be done and who is responsible for doing them. -1 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #1 Topic: Building an Organization from the Bottom Up 2. (p. 202) One reason to reorganize is to become more competitive. -1 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #2 Topic: Everyones Organizing 3. (p. 202) In a capitalist economy, organizations seldom reorganize due to changing markets. -1 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #3 Topic: Everyones Organizing 4. (p. 202) One key to organizational success is to go back to basic principles and build the business on a sound foundation. -1 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #4 Topic: Everyones Organizing 5. (p. 202-203) Small business organizations lack the size required to reap the benefits of labor specialization. -1 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #5 Topic: Building an Organization from the Bottom Up 6. (p. 202-203) The purpose of a division of labor and specialization is to improve an employee's job performance. -1 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #6 Topic: Building an Organization from the Bottom Up 7. (p. 203) Managing a growing business often requires managers to create departments to accomplish various tasks. -1 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #7 Topic: Building an Organization from the Bottom Up 8. (p. 203) The process of creating individual departments to do specialized tasks is called departmentalization. -1 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #8 Topic: Building an Organization from the Bottom Up 9. (p. 202) Division of Labor refers to deciding how many jobs must be accomplished and then dividing them up amongst the labor force. -1 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #9 Topic: Building an Organization from the Bottom Up 10. (p. 202) The success of the firm often depends on assigning the right tasks to the right person. -1 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #10 Topic: Building an Organization from the Bottom Up 11. (p. 203) The process of setting up individual departments to do specialized tasks is called job specialization. -1 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #11 Topic: Building an Organization from the Bottom Up 12. (p. 203) Correctly structuring a business organization allows managers to avoid delegating responsibility and authority to employees. -1 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #12 Topic: Building an Organization from the Bottom Up 13. (p. 203) An organization chart shows who is accountable for the completion of specific work and who reports to whom. -1 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #13 Topic: Building an Organization from the Bottom Up 14. (p. 203) Looking at a traditional organization chart, you will view who reports to whom; you will have a sense of each person's authority and responsibility, and the type of work that they perform for the organization. An organization chart shows you who reports to whom, and who is accountable for the completion of what jobs. Blooms: Comprehension -1 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #14 Topic: Building an Organization from the Bottom Up 15. (p. 202) Division of labor is difficult to achieve in small businesses. Division of labor is a basic organizational principle in all organizations. All businesses (both large and small) should contemplate the division of labor in their organizations. Blooms: Comprehension -1 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #15 Topic: Building an Organization from the Bottom Up 16. (p. 202) Reorganizing in order to compete better may require a business to reduce its labor force. Companies reorganize in order to be more competitive and reduce costs. In order to reduce costs, the firm may reduce its labor force, and reorganize the jobs and activities to those workers who remain. Blooms: Comprehension -1 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #16 Topic: Building an Organization from the Bottom Up 17. (p. 203) Reorganizing in order to compete better may require a business to reassign tasks. Companies reorganize in order to be more competitive and reduce costs. In order to reduce costs, the firm may reduce its labor force, and reorganize the jobs and activities to those workers who remain. Blooms: Comprehension -1 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #17 Topic: Building an Organization from the Bottom Up 18. (p. 203) Reorganizing in order to compete better may require a firm to reduce its number of business units. If a firm wants to remain competitive, it has the option to reevaluate the corporate structure of its business and determine which business units and operational units are benefiting the bottom line, and which may need to be re-organized or sold. Blooms: Comprehension -1 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #18 Topic: Reaching Beyond our Borders box 19. (p. 203) Departments are functional units within the business such as sales, accounting, finance, and marketing. The basic principles of organization do not differ significantly from firm to firm. As firms grow, they usually develop a system with division of labor and specialization, and then proceed to departmentalize - create departments that produce specialized tasks for the business. Blooms: Comprehension -1 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #19 Topic: Building an Organization from the Bottom Up 20. (p. 203) As depicted in the Reaching Beyond our Borders, box, "General Electric Looks for More Profits", in order to compete globally, corporate strategy should not try to match the performance of competitors. In order to compete globally, it is often necessary to increase or reduce operational segments in order to match or exceed the performance of global competitors. Blooms: Comprehension -1 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #20 Topic: Reaching Beyond our Borders box 21. (p. 203) In its effort to reorganize its floor space, Backstreet Books decided to eliminate seating space in its stores in order to make room for bookshelves due to growing interest in books about how to "go green". This company's effort is an example of how a firm may reduce its emphasis in one product line in order to serve customer preferences and trends. If a firm wants to remain competitive, it may reevaluate which product lines are more profitable than others and organize its floor space and marketing emphasis to capture consumer attention. -1 #21 Topic: Building an Organization from the Bottom Up 22. (p. 203) To better organize his landscaping business, Frank divides each job into several parts. One part is excavation and removal of old landscaping, the next part is design, followed by purchasing, and the last part is installation of new plants. If he assigns a different employee to each part, this action would be an example of departmentalization. Departmentalization is the creation of functional units of a business. The jobs described in this question would all fall under the production department. Other departments in Frank's business may include marketing, sales, and accounting. By asking different employees to perform different tasks relating to a particular job, Frank is creating division of labor within his company, and/or specialization. -1 #22 Topic: Building an Organization from the Bottom Up 23. (p. 202) Alicia dreams of opening her own restaurant and knows that she will need to organize her business. Organizing begins with determining the work to be done. Organizing, also known as adding structure to the business begins with determining what work needs to be done and then dividing up tasks among the employees. -1 #23 Topic: Building an Organization from the Bottom Up 24. (p. 202) When Eric Schmidt joined Google™, one of the most successful companies of this decade, he tackled the organization function head-on. In speaking at a large conference with Google founders, Sergey Brinn and Larry Page, he commented that Google was running pretty well, "it just needed a little structure." Schmidt was referring to basic organization principles such as division of labor, specialization, and getting the departments up and running. Basic organization principles include division of labor, specialization of tasks, and departmentalization. -1 #24 Topic: Building an Organization from the Bottom Up 25. (p. 204) As indicated in the Making Ethical Decisions box titled, "Safety versus Profit", organization decisions that affect profits in a negative way should be avoided at all cost. As indicated in the Making Ethical Decisions story, how your organization performs the job is very important. Setting an organization culture is as important as setting an organization structure. Adhering to safety precautions when doing the job demonstrates management's commitment to their employees. -1 #25 Topic: Making Ethical Decisions box 26. (p. 204) The driving force behind the change in business organizations is the change in consumer expectations. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #26 Topic: The Changing Organization 27. (p. 204) Recent changes in the organizational structure of businesses are intended to facilitate management of the firm. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #27 Topic: The Changing Organization 28. (p. 205-207) Henri Fayol and Max Weber are best known for their contributions to accounting theory. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #28 29. (p. 205) Fayol's principle of the division of labor says that functions should be divided into areas of specialization such as production, marketing, and finance. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #29 30. (p. 205) One of Fayol's principles suggests that managers should have the right to give orders and expect others to follow. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #30 31. (p. 206) Fayol's principle of esprit de corps says that employees should be divided into small groups that can be directed efficiently by a single manager. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #31 32. (p. 205) Fayol's principles suggest that the goals of the firm are less important than the goals of individual workers. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #32 33. (p. 205) According to Fayol's principle of Authority, if you have authority you also have responsibility. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #33 34. (p. 205) Fayol believed that the amount of decision-making power vested in top management should be the same in all situations. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #34 35. (p. 206) Fayol believed that managers should treat employees and peers with respect and justice. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #35 36. (p. 206) Clear communication between workers and keeping order in materials and people are included in Fayol's principles. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #36 37. (p. 206) Max Weber's principles of organization were similar to those of Henri Fayol. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #37 38. (p. 206) Weber believed that large organizations required everyone to follow the established rules and guidelines precisely. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #38 39. (p. 206) Weber was critical of bureaucrats because he felt they undermined the efficiency of the organization. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #39 40. (p. 206) Weber had a great deal of faith in managers. He was confident that a firm would do well if employees simply did as they were told. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #40 41. (p. 206) Weber promoted the idea of the pyramid-shaped organization structure for large businesses. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #41 42. (p. 206) Max Weber's organizational theories require an educated work force to operate efficiently. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #42 43. (p. 206) Weber was a strong proponent of bureaucracy. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #43 44. (p. 206) Some business organizations still follow the 1940s organizational theory of Max Weber. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #44 45. (p. 206) Weber believed that employees should be empowered to make their own decisions. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #45 46. (p. 206) Job descriptions are an important part of Max Weber's organizational theory. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #46 47. (p. 206) Max Weber believed that promotion should be based solely on seniority. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #47 48. (p. 206) The design of a bureaucratic organization assumes a well-educated workforce. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #48 49. (p. 207) An organizational hierarchy establishes one person at the top of an organization. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #49 Topic: Turning Principles into Organization Design 50. (p. 207) A chain of command is a line of authority that moves from the lowest level of the hierarchy to the top. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #50 Topic: Turning Principles into Organization Design 51. (p. 207) A hierarchy requires many top managers, but only a few middle managers. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #51 Topic: Turning Principles into Organization Design 52. (p. 207) According to Weber, a bureaucrat is a middle manager whose job is to implement top management's orders. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #52 Topic: Turning Principles into Organization Design 53. (p. 207) A bureaucracy empowers employees to quickly respond to customers' wants and desires. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #53 Topic: Turning Principles into Organization Design 54. (p. 207) A bureaucracy is an organization with many layers of managers who set rules and regulations and oversee all decisions. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #54 Topic: Turning Principles into Organization Design 55. (p. 207) Bureaucratic organizations establish rules and regulations that everyone is expected to follow. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #55 Topic: Turning Principles into Organization Design 56. (p. 207) Bureaucratic organizations are not very responsive to customers. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #56 Topic: Turning Principles into Organization Design 57. (p. 207) A bureaucracy is designed to be customer focused. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #57 Topic: Turning Principles into Organization Design 58. (p. 207) Bureaucratic organizations are structured to empower employees and please customers. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #58 Topic: Turning Principles into Organization Design 59. (p. 207) A bureaucratic style of organization is slow when responding to change. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #59 Topic: Turning Principles into Organization Design 60. (p. 207) Empowerment works only when employees are given the proper training and resources to respond. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #60 Topic: Turning Principles into Organization Design 61. (p. 207) The basic idea behind the organization design of Fayol and Weber was that management wanted to control workers. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #61 Topic: Turning Principles into Organization Design 62. (p. 205) As organizations grew, the use of Fayol's principles led to rigid organizations that didn't always respond quickly to consumer requests. Organizations were designed according to Fayol's principles so that no person had more than one boss. These principles tended to be written down as rules, policies, and regulations as organizations grew larger. The process of rule making often led to rather rigid organizations that didn't always respond quickly to consumer requests. Blooms: Comprehension -2 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #62 63. (p. 206) In today's fast-paced business environment, Weber's bureaucratic ideas work well. These principles permit business to respond quickly to customer changes. Max Weber's ideas worked well with a less educated workforce that did not make decisions. The bureaucratic model did not allow for immediate response to changing market conditions, and changing customer needs. Blooms: Comprehension -2 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #63 64. (p. 205) When we experience economies of scale this means that as production levels rise (we make more of something), the cost of supplies and cost of labor that goes into the production, goes down. Economies of scale is when the cost of production goes down, as the level of production rises. Blooms: Comprehension -2 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #64 65. (p. 207) The purpose of Weber's and Fayol's principles was for the benefit of management, as opposed to pleasing customers. Fayol and Weber's ideas made management's life easier. Their organization principles facilitated management's needs, but did little for employees or customers. Blooms: Comprehension -2 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #65 66. (p. 206) Weber put great trust in the creativity, skills, and pride of employees and believed that managers should act more as coaches than as bosses. Weber put great trust in managers and believed that workers should simply do as they were told. Blooms: Comprehension -2 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #66 67. (p. 205) Bryce is a manager at a car seat manufacturing company. He believes that it is very important and less confusing if each worker has only one boss. Bryce's view is consistent with Fayol's unity of command principle. The unity of command principle says that each worker should report to one, and only one, boss. -2 #67 68. (p. 206) Rob is a middle manager who spends much of his time devising ways to implement the ideas of top management. Max Weber would have considered Rob a bureaucrat. Max Weber used the term bureaucrat to describe middle managers whose main function was to implement top management's orders. -2 #68 69. (p. 206) Ping believes all workers should receive the same wage rate regardless of their position within a company. Ping's views on wages illustrate Fayol's principle of equity. Fayol's principle of equity says that managers should treat employees with respect and justice. It does not, however, suggest that all workers should be paid the same wage rate. -2 #69 70. (p. 206) Kate holds a middle management position with a large corporation. She prefers to involve her subordinates in decision-making. She also favors allowing workers a fair amount of flexibility in how they do their jobs. Kitty's approach to management exemplifies the principles first popularized by Max Weber. Weber believed that the firm would do well if workers simply did as they were told. He also believed that large organizations could only function efficiently if rules and guidelines were established, and everyone followed these rules precisely. -2 #70 71. (p. 207) Most businesses adopt a bureaucratic organization in order to speed up their decision making process. In a bureaucratic organization there are typically many layers of management with rigid rules and regulations. A strict chain of command is followed which can slow down the decision making process. -2 #71 Topic: Turning Principles into Organization Design 72. (p. 205) Antonio works in the accounting department of a large firm. This is an example of Fayol's division of labor concept. Henri Fayol's division of labor suggests that efficiency can be improved if employees are assigned into an area of specialization, such as production, marketing, and finance. -2 #72 73. (p. 207) As a new employee in a bureaucratic organization, Nancy can expect a great deal of independence and authority. In a bureaucratic organization, everyone is expected to follow specific rules. One of the problems with this type of organization is that employees have little flexibility to respond to customer wants and needs. -2 #73 Topic: Turning Principles into Organization Design 74. (p. 207) Soprano Industries follows a chain of command with authority moving from the top of the hierarchy down to lower-level managers. The company is organized by department with established rules and regulations that everyone is expected to follow. All of these characteristics suggest that Soprano is an example of a bureaucratic organization. Bureaucratic organizations are characterized by top down authority, division of labor, and the presence of many rules and regulations. -2 #74 Topic: Turning Principles into Organization Design 75. (p. 207) At Dilly-Dally Sportswear Store a manager needs to be called to the front of the store and sign-off on every return that a cashier performs. The CEO continues this policy because he wants every manager to "look those customers right in the eye" and "stake their job on taking those items back." Clearly, Dilly-Daly empowers its employees to make decisions at their jobs. Bureaucratic organizations are characterized by top down authority, division of labor, and the presence of many rules and regulations. Empowerment is often missing from an organization where decisions are made top down. -2 #75 Topic: Turning Principles into Organization Design 76. (p. 206) Sam supervised a group of people in a very large organization. The refrigerator in the lunchroom stopped functioning. Although he started the paperwork on the day it died, the refrigerator request went out for bid; two middle managers needed to approve it; and, the purchasing director had final approval. The refrigerator arrived six months later. Max Weber would have approved of the detail and documentation Sam's company accumulated to back-up the purchase. Max Weber is known as the originator of bureaucracy, where decisions are followed-up with lots of paperwork and documentation. There are several layers of management, and decisions must be approved by several people, creating a significant amount of lag time from the first recognition of a problem, until the problem is finally solved. -2 #76 77. (p. 208) The degree to which an organization allows lower level managers to make decisions determines the degree of decentralization. -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #77 Topic: Choosing Centralized or Decentralized Authority 78. (p. 208) An advantage of decentralized authority is that those individuals closest to the customers and more familiar with local conditions make decisions. -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #78 Topic: Choosing Centralized or Decentralized Authority 79. (p. 208) Centralized authority provides for the delegation of authority to employees who are then better able to respond to customers' needs. -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #79 Topic: Choosing Centralized or Decentralized Authority 80. (p. 208) As a result of rapidly changing markets and global differences in consumer tastes, more firms are considering centralized authority. -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #80 Topic: Choosing Centralized or Decentralized Authority 81. (p. 209) A weakened corporate image is one of the disadvantages of a decentralized business organization. -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #81 Topic: Choosing Centralized or Decentralized Authority 82. (p. 208) In firms with centralized authority, each business unit is treated as if it is a completely separate and independent organization. -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #82 Topic: Choosing Centralized or Decentralized Authority 83. (p. 208) Span of control refers to the number of different markets a business can serve efficiently. -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #83 Topic: Choosing the Appropriate Span of Control 84. (p. 208) The optimum number of subordinates a manager should supervise is referred to as the span of control. -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #84 Topic: Choosing the Appropriate Span of Control 85. (p. 209) In today's business environment, the trend is to decrease the span of control. -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #85 Topic: Choosing the Appropriate Span of Control 86. (p. 209) The more standardized the work, the wider the span of control. -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #86 Topic: Choosing the Appropriate Span of Control 87. (p. 209) Managers near the top of an organization have the broadest span of control. -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #87 Topic: Choosing the Appropriate Span of Control 88. (p. 209) The more complex the job, the narrower the span of control. -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #88 Topic: Choosing the Appropriate Span of Control 89. (p. 209) The trend towards employee empowerment results in a wider span of control. -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #89 Topic: Choosing the Appropriate Span of Control 90. (p. 209) When employees are self-managed, a company can implement a wider span of control. -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #90 Topic: Choosing the Appropriate Span of Control 91. (p. 209) Improvements in information technology have permitted companies to increase their span of control. -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #91 Topic: Choosing the Appropriate Span of Control 92. (p. 209) A tall organization structure consists of multiple levels of management. -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #92 Topic: Choosing Between Tall and Flat Organization Structures 93. (p. 209) A flat organizational structure is designed to be more responsive to the needs of management. -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #93 Topic: Choosing Between Tall and Flat Organization Structures 94. (p. 209) Flat organizations have fewer managers. -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #94 Topic: Choosing Between Tall and Flat Organization Structures 95. (p. 209) An advantage of a tall organization is that it ensures fast and efficient communications throughout the organization. -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #95 Topic: Choosing Between Tall and Flat Organization Structures 96. (p. 210) A recent business trend is the elimination of layers of management, creating flatter organizations and subsequently, a wider span of control. -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #96 Topic: Choosing Between Tall and Flat Organization Structures 97. (p. 210) Departmentalization is the dividing of organizational functions into separate units. -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #97 98. (p. 210) The traditional way to departmentalize an organization is by geographical area served. -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #98 99. (p. 210) Departmentalization by function allows employees opportunity to further develop their skills. -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #99 100. (p. 210) Departmentalization by function typically increases the cost of doing business. -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #100 101. (p. 210) Departmentalization by function groups employees based on similar skills, expertise, or resource use. -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #101 102. (p. 211) An advantage of departmentalization is "groupthink". -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #102 103. (p. 211) Organizations that utilize functional departmentalization benefit from improved communication between departments. -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #103 104. (p. 211) Departmentalization creates an environment in which people are trained in a variety of managerial responsibilities. -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #104 105. (p. 210) Economies of scale can be achieved through departmentalization. -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #105 106. (p. 211) Some firms use a combination of departmentalization techniques. -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #106 107. (p. 211) The decision on how to departmentalize should depend on the customer and the product or service the firm is offering. -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #107 108. (p. 211) Departmentalizing by customer group has proven ineffective. -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #108 109. (p. 211) If there are several steps in getting the product to its final state, the company may choose to departmentalize by process. -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #109 110. (p. 211) Some companies have created hybrid versions of departmentalization, where they combine two or more traditional ways of departmentalizing. -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #110 111. (p. 208) When management structures the organization, it clarifies who gets to make decisions, how many people report to one manager, and how many different departments the company needs in order to operate effectively. Structuring the organization involves deciding on a centralization vs. decentralization decision-making policy; decisions with regards to span of control, meaning how many employees will report to one manager, as well as how to departmentalize. Blooms: Comprehension -3 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #111 112. (p. 208) When management structures the organization, it makes decisions about which products and services it will offer and how it is going to finance the company. Structuring the organization involves deciding on a centralization vs. decentralization decision-making policy; decisions with regards to span of control, meaning how many employees will report to one manager, as well as how to departmentalize the organization. Blooms: Comprehension -3 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #112 113. (p. 209) Because top managers supervise the firm's most talented workers, they generally have a broader span of control than middle or first line managers. At higher levels of management, the work becomes less standardized and there is a greater need for face-to-face communication. These factors tend to result in a narrow span of control for top managers. Blooms: Comprehension -3 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #113 Topic: Choosing the Appropriate Span of Control 114. (p. 209) As the span of control widens, there is usually a reduction of middle management and an emphasis on empowerment. A wider span of control lends itself to empowering lower level employees to make customer decisions. Blooms: Comprehension -3 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #114 Topic: Choosing the Appropriate Span of Control 115. (p. 209) A flat organization is less likely to respond quickly to customer needs. Flat organizations have wider spans of control. A wider span of control lends itself to empowering lower level employees to respond more quickly to customer needs, without the need to get permission from managers. Blooms: Comprehension -3 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #115 Topic: Choosing Between Tall and Flat Organizations 116. (p. 210) To avoid losing that small company feel, fast growing companies try to maintain a flat organization structure. Large companies use flat structures to try to match the friendliness of small companies. Blooms: Comprehension -3 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #116 Topic: Choosing Between Tall and Flat Organizations 117. (p. 210-211) Although a firm may experience better cost controls through departmentalization, it may not increase its responsiveness to customer needs. An advantage of departmentalization is economies of scale. A disadvantage is less responsiveness to customers. Blooms: Comprehension -3 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #117 118. (p. 211) Businesses seldom create separate departments to serve customers with different needs. Some organizations departmentalize by customer group. Blooms: Comprehension -3 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #118 119. (p. 208) Rise ‘n Shine Bakeries is a nationwide bakery that has plants located throughout the United States. Top management at Rise ‘n Shine believes that customers in different regions have different tastes. It also recognizes that its bakeries face more intense competition in some regions than in others. Therefore, Rise ‘n Shine's top management gives local managers the freedom to offer different types of breads and desserts, and to decide on a reasonable pricing strategy for its products. Rise ‘n Shine typifies a decentralized organization. A decentralized organization gives decision-making authority to managers at lower levels of the hierarchy. -3 #119 Topic: Choosing Centralized or Decentralized Authority 120. (p. 208) Management at Hottie Potatee, a nationwide potato bar chain, believes that its customers value a predictable and consistent level of service and quality. When customers stop at one of its potato bar chain restaurants anywhere in the United States, they should know what to expect in terms of menu, price and quality. In order to maintain this consistency, Hottie Potatee should adopt a decentralized organization. By giving individual managers and employees more flexibility, a decentralized organization would result in less standardization and uniformity. -3 #120 Topic: Choosing Centralized or Decentralized Authority 121. (p. 208) A study at the Slumber Inn Corporation identified poor employee morale. Employee respondents indicated frustration with their inability to deal directly with customers' concerns and complaints. These employees feel that if they were empowered with the authority to make decisions, customer satisfaction would dramatically increase. This illustrates one of the disadvantages of decentralized authority. This organization is an example of centralized authority with decision-making authority maintained at the top level of management at the company's headquarters. This usually results in less responsiveness to customers, the cause of the poor employee morale. -3 #121 Topic: Choosing Centralized or Decentralized Authority 122. (p. 209) In the Crescent City manufacturing plant of the Granite Works Corporation, a foreman supervises workers. The foreman reports to the shift supervisor who reports to the head of the production department, who then reports to the assistant plant manager, who reports to the plant manager. The plant manager, in turn, reports to a district manager, who then reports to a product group manager, who reports to an assistant vice president of operations, who keeps in close touch with an executive vice president. The layers of management indicate that Granite Works Corporation is a tall organization. A tall organization is characterized by many layers of management. -3 #122 Topic: Choosing Between Tall and Flat Organizations 123. (p. 209) Martina is an experienced manager with excellent communications skills. The workers in her area are highly skilled and capable of doing their work with very little direct supervision. Martina's span of control is likely to be quite broad. The less direct supervision required by workers, the broader the span of control. -3 #123 Topic: Choosing the Appropriate Span of Control 124. (p. 210) Rome Corporation is organized into departments such as finance, production, marketing, data processing, and accounting. Rome has chosen to departmentalize by function. Departmentalization by function means to group workers into departments based on similar skills, expertise, and resource use. -3 #124 125. (p. 211) Top management at Topdown, Inc. wants to encourage communication between different departments and prevent employees from becoming narrow specialists. The best way to accomplish these goals is to departmentalize Topdown's organization by function. Two disadvantages of functional departmentalization are that it tends to reduce communication among departments, and employees often end up becoming narrow specialists. -3 #125 126. (p. 211) Green Landscapes, Inc., a company that installs underground sprinkler systems serves several commercial customers, as well as residential customers. As the business expands, Green Landscapes management may want to consider departmentalizing by customer group and then by process. Companies that serve customers with varying needs may be able to respond quicker if their employees specialize in one customer group. Beyond that, a company like the one in this example that goes through several steps in serving each customer may specialize by process. -3 #126 127. (p. 211) Jesse started a successful telecommunications company that provided voicemail services to business clients in the Midwest. As the business grew, Jesse added functional departments including a marketing department and an accounting department. After a few years, he realized that employees who specialized in these areas no longer shared knowledge with each other in the same way they did when the operation was smaller. As one of Jesse's business consultants, you explain that as the company grows taller, it cannot avoid this pitfall, and he should focus on continued functional departmentalization, especially if he supports innovation and learning. A disadvantage of functional departmentalization is a lack of communication between and among departments. Employees may identify with their own department's goals, as opposed to the goals of the company. Blooms: Analysis -3 #127 128. (p. 211) Jackie works in the finance department, at the home office of a large retailer. Her main responsibility is to watch department expenditures and find ways to cut costs whenever possible. Tim, the marketing director for the same company shares information with Jackie only when necessary. He finds her inflexible, and not understanding of what it takes to roll-out a new product line. Jackie and Tim typify a disadvantage of departmentalization. A disadvantage of departmentalization is that department members begin to think like each other and do not understand the point of view of members of other departments. They experience a phenomenon known as groupthink. -3 #128 129. (p. 213) Traditional organizational models such as a line model or a line and staff model provide the flexibility demanded in a changing business environment. -4 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #129 Topic: Organizational Models 130. (p. 213) In a line organization, there are many specialists who serve as advisors and assistants to the managers who make decisions. -4 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #130 Topic: Line Organizations 131. (p. 213) Small businesses often use a line organization model. -4 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #131 Topic: Organizational Models 132. (p. 213) Line organizations follow Fayol's traditional management rules. -4 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #132 Topic: Line Organizations 133. (p. 213) Line managers issue orders, enforce discipline, and adjust the organization as conditions change. -4 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #133 Topic: Line Organizations 134. (p. 213) In large businesses, a line organization provides firms the ability to respond quickly to a changing environment. -4 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #134 Topic: Line Organizations 135. (p. 213) Line organizations clearly define the lines of authority and responsibility. -4 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #135 Topic: Line Organizations 136. (p. 213) Line organizations often experience the problem of employees reporting to more than one boss. -4 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #136 Topic: Line Organizations 137. (p. 213) A line organization in a large business often suffers from excessively slow lines of communication. -4 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #137 Topic: Line Organizations 138. (p. 213) Staff personnel perform functions such as production and sales that contribute directly to the primary goals of the organization. -4 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #138 Topic: Line-and-Staff Organizations 139. (p. 213) In a line-and-staff organization, staff positions are temporary jobs to train new line managers. -4 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #139 Topic: Line-and-Staff Organizations 140. (p. 214) While staff personnel have the authority to make policy decisions, line personnel have the authority to advise and make suggestions. -4 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #140 Topic: Line-and-Staff Organizations 141. (p. 214) An advantage of a line-and-staff organization is that it provides people that advise and assist line managers as they perform their jobs. -4 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #141 Topic: Line-and-Staff Organizations 142. (p. 214) Line-and-staff organizations may suffer from inflexibility. -4 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #142 Topic: Line-and-Staff Organizations 143. (p. 215) The matrix organization model brings together experts from different functional units of the firm to work on specific projects. -4 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #143 Topic: Matrix-Style Organizations 144. (p. 215) The team experts in a matrix organization remain part of the traditional line-and-staff structure. -4 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #144 Topic: Matrix-Style Organizations 145. (p. 214) A matrix organization produces an environment that discourages cooperation and teamwork. 146. (p. 215) Team participants in a matrix organization model may report to two managers. 147. (p. 215) A serious disadvantage of the matrix organization is the temporary nature of the teams. 148. (p. 215) Matrix organizations give managers flexibility in assigning people to projects. 149. (p. 215) Matrix organization structures provide for more efficient use of organizational resources. 150. (p. 216) A recent trend in organization models is the development of cross-functional, self-managed teams of employees who work together on a long-term basis. 151. (p. 216) Cross-functional self-managed teams are groups of employees empowered to work with suppliers and customers to develop new products and give great service. 152. (p. 216) Cross-functional teams serve as advisory committees offering their expertise to line decision makers. 153. (p. 216) Cross-functional teams defy the trend towards customer-driven organizations. 154. (p. 216) Cross-functional teams consist of employees from different departments who work together on a long-term basis. 155. (p. 216) Cross-functional teams avoid involving groups outside of the firm to ensure their plans are not leaked to their competitors. 156. (p. 216) Cross-functional teams work best when the "voice of the customer" is brought into organizations. 157. (p. 216) Cross-functional teams work well when leadership of the team is shared. 158. (p. 216) Including customers and suppliers on cross-functional teams violates the interests of stockholders. 159. (p. 216) By structuring the company with cross-functional teams, there is a greater chance that a business is more responsive to social trends affecting customer preferences. By going beyond company borders and including others on a cross-functional self-managed team, a firm can learn first-hand from suppliers and customers about market trends that affect its business. Blooms: Comprehension -4 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #159 160. (p. 214-215) A matrix team for an aerospace company may consist of a project manager, a finance expert, a marketing specialist, a member of production, and two design engineers. Matrix teams consist of individual experts from various functional units of a company joining together to solve a problem or work on a project. These are temporary teams that disband when the assignment is completed. Blooms: Comprehension -4 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #160 Topic: Matrix-Style Organizations 161. (p. 216) It is strategically not sensible for a firm to consider asking suppliers and customers to join a cross-functional self-managed team that is testing iterations of future products. By going beyond company borders and including others on a cross-functional self-managed team, a firm can learn first-hand from suppliers and customers about market trends that affect its business. Blooms: Comprehension -4 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #161 Topic: Going Beyond Organizational Boundaries 162. (p. 215) One disadvantage of the matrix style of organization is that it is more difficult to keep development projects on schedule. The model slows down the time from design, to production, and then to market. Matrix Style Organization was purposely designed to expedite projects from conception to market. The model eliminates the communication problems that line and line and staff models experienced when trying to develop a product and get it to market. Blooms: Comprehension -4 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #162 Topic: Matrix-Style Organizations 163. (p. 216) The cross-functional team concept has resulted in lots of unhappy employees because less than 25% of employed workers do favor working with others. According to a BusinessWeek report, over 80% of employees surveyed showed a preference for working with others. Blooms: Comprehension -4 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #163 164. (p. 216) Due to the competitive nature of companies that compete for the same customers, cross-functional teams never consist of individuals from more than one firm. Cross-functional teams often include employees who work for firms that have teamed-up together to produce a product or service. Sometimes teams are interfirm, meaning from two or more companies. Blooms: Comprehension -4 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #164 165. (p. 216) Cross-functional teams that go beyond company boundaries share production information but seldom market information. Cross-functional teams are transparent. They share as much information as necessary to succeed in building a product that is needed by the marketplace. These teams go outside of the boundaries of one company. Sometimes the team will share information with government employees and/or employees from around the globe. Blooms: Comprehension -4 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #165 166. (p. 213) Buzzoff Corporation is a medium sized organization, organized with well-defined lines of authority and responsibility. Each employee reports to only one boss. The managers at Buzzoff complain that they have no expert support staff available to offer legal advice. Lately opportunities are slipping through the cracks due to inefficient long lines of communication. These characteristics suggest that Buzzoff employs a matrix organization. A line organization is characterized by well-defined lines of authority and responsibility and provides one supervisor for each person. Line organizations also have few experts and assistants to help line managers, and are frequently plagued by long lines of communication. -4 #166 Topic: Organizational Models 167. (p. 213) Julie is an attorney that works for Worldwide Food Science, Inc. that provides legal advice and assistance to the firm's managers. Julie's job with WFS, Inc. would be classified as a staff position. Staff personnel provide advice and assistance to line managers. -4 #167 Topic: Line-and-Staff Organizations 168. (p. 213) Wizard Manufacturing makes small consumer electronics like mixers and toasters. The industry is relatively stable, having few new advances in product development. Wizard should use a line or line-and-staff organizational structure to ensure efficient operations. Both line and line-and-staff organization structures work well in organizations with a relatively unchanging environment and slow product development, such as firms selling consumer products like toasters. In such firms, clear lines of authority and relatively fixed organization structures are assets that ensure efficient operations. -4 #168 Topic: Line-and-Staff Organizations 169. (p. 215) Joel, an employee of the engineering department, was temporarily assigned to work with specialists from other departments to develop a new product. Upon completion of this project, Joel returned to his position in the engineering department. This arrangement illustrates the use of a cross-functional team. In a cross-functional team, the members work together on a long-term basis. They may work together on more than one project, and over an extended period of time. The fact that Joel views his work on the team as temporary and plans to return to his old position when the project is completed suggests that the firm is using a matrix organization. -4 #169 Topic: Matrix-Style Organizations 170. (p. 216) Alleta Publishing Company, Inc. is considering the use of cross-functional teams. In order to be most effective, Alleta should include customers as members of the teams. Cross-functional teams work best when the ideas of customers are brought into the organization. The best way to do this is to actually include customers on the teams. -4 #170 Topic: Going Beyond Organizational Boundaries 171. (p. 216) Barclay developed two interactive computer games. He didn't do it entirely alone. Last year he started a small company, hired two programmers, and a marketing graduate. He considers himself a cutting-edge kind of guy and wants to position his company the same. Soliciting your advice as to how he should structure his organization as he moves forward, you suggest that he hire a few potential customers to join his team of employees as product testers. And, maybe he should solicit globally. The structure you have described would simulate a line and staff organization. Including potential customers on a work team simulates a cross- functional self-managed team. Blooms: Analysis -4 #171 172. (p. 213) Julio is the owner of Celebration, Inc. a small party supply company. The company provides tents, tables, chairs, and related paraphernalia for wedding, Bar Mitzvah, Bot Mitzvah, graduation, birthday, and other celebratory events. As sales have increased, the organization has hired more personnel and departmentalized to more efficiently handle purchasing, sales, service, and accounting. Everyone is still responsible for achieving company goals. Upon seeing Celebration's organization chart, you agree it uses a line organization model. Many small businesses begin as line organizations. In a line organization model everyone in the organization is responsible for achieving the company goals. Blooms: Analysis -4 #172 Topic: Line Organizations 173. (p. 217) Networking uses communication technology to link organizations allowing them to work together on common objectives. -5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #173 Topic: Managing the Interactions Among Firms 174. (p. 217) The Internet makes "real time" availability of data possible. -5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #174 Topic: Transparency and Virtual Organizations 175. (p. 217) Transparency describes the relationship between a firm and its stockholders. -5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #175 Topic: Transparency and Virtual Organizations 176. (p. 217) Transparency allows two companies to work more efficiently together. -5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #176 Topic: Transparency and Virtual Organizations 177. (p. 217) Most companies are no longer self-sufficient or self-contained. -5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #177 Topic: Transparency and Virtual Organizations 178. (p. 217) Networking requires transparency to work most effectively. -5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #178 Topic: Transparency and Virtual Organizations 179. (p. 217) A virtual corporation refers to a permanent network of firms linked by high-tech communication systems. -5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #179 Topic: Transparency and Virtual Organizations 180. (p. 217) A virtual corporation is a networked organization made up of replaceable firms that join the network and leave it as needed. -5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #180 Topic: Transparency and Virtual Organizations 181. (p. 218) Benchmarking requires organizations to compare each organizational function against the best in the world. -5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #181 Topic: Benchmarking and Core Competencies 182. (p. 218) Competitive benchmarking rates an organization's products and operations against the industry average. -5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #182 Topic: Benchmarking and Core Competencies 183. (p. 218) Competitive benchmarking compares a company's practices, processes, and products against others in its industry, with the goal of doing it better than the competition. -5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #183 Topic: Benchmarking and Core Competencies 184. (p. 218) The functions that a company can perform as well as or better than anyone else in the world are known as that firm's optimized capabilities. -5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #184 Topic: Benchmarking and Core Competencies 185. (p. 218) An organization's core competencies are those functions that the firm performs as well as or better than anyone else in the world. -5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #185 Topic: Benchmarking and Core Competencies 186. (p. 219) If a particular function is one of a firm's core competencies, it typically performs this function itself rather than outsourcing it to another organization. -5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #186 Topic: Benchmarking and Core Competencies 187. (p. 219) Assigning various functions that a firm might do for itself to outside organizations is known as competitive allocation. -5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #187 Topic: Benchmarking and Core Competencies 188. (p. 219) Outsourcing involves assigning various functions to outside organizations. -5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #188 Topic: Benchmarking and Core Competencies 189. (p. 219) Restructuring involves the redesign of an organization to be more responsive to customers. -5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #189 190. (p. 219) To better serve customers, many firms are restructuring to empower front-line employees. -5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #190 191. (p. 219) New technology such as the Internet has opened up opportunities for firms to sell to new markets. -5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #191 Topic: Adapting to Change 192. (p. 219) Digital natives, those who grew-up with the Internet are an important customer group that most businesses want to reach. -5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #192 Topic: Adapting to Change 193. (p. 219) Introducing change into an organization is an easy task for a manager. -5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #193 Topic: Adapting to Change 194. (p. 220) Inverted organizations define the role of front-line employees as those workers who follow the orders of top and middle management. -5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #194 195. (p. 220) Inverted organizations empower employees by adding multiple layers of management and long lines of communication. -5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #195 196. (p. 220) In an inverted organization, the purpose of management is to assist and support the decisions of employees who work directly with customers. -5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #196 197. (p. 217) Companies have learned that working transparently through real time networks has provided competitive advantages in the marketplace. The Internet has allowed companies to send to each other real time data, which expedites the process of getting products and services to customers, many of which are digital natives, having grown-up with the Internet who expect fast and exceptional service. Blooms: Comprehension -5 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #197 Topic: Transparency and Virtual Organizations 198. (p. 218) Outsourcing has become commonplace, particularly when organizations want to focus on core competencies. Outsourcing is assigning one or more functions to another organization. Often companies will look outside the firm for accounting services, transportation services, and legal services, to name a few. They prefer to utilize their resources on core competencies, those functions that they do better than most. Blooms: Comprehension -5 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #198 Topic: Benchmarking and Core Competencies 199. (p. 219) Once a company has restructured a firm to be more competitive in today's market, it alleviates the need to scan the external environment. Adapting to change is difficult but necessary in today's business world. Companies must be careful to avoid complacency. Blooms: Comprehension -5 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #199 Topic: Adapting to Change 200. (p. 217) The virtual corporation does all its business online with partners considered a permanent part of the network. Although it is possible for firms that are connected virtually to interact online, the term refers to the fact that the functional units of this type of corporation do not have permanent ties to any one corporation. The core firms hire other companies to partner with it on an as needed basis. Blooms: Comprehension -5 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #200 Topic: Transparency and Virtual Organizations 201. (p. 217) Cardinal Foods is a wholesaler serving grocery stores. High tech communications allows Cardinal to work closely with its suppliers and customers in real time. Networking allows these organizations to operate more efficiently. Networking is using communications technology to link organizations and allow them to work together on common objectives. -5 #201 Topic: Managing the Interactions Among Firms 202. (p. 218) In order to improve services to customers, Northwest Electric, a regional monopoly recently rated their company's processes and products against the results achieved by the world's best at similar processes and products. Northwest Electric has adopted a policy of international standardization. Rating an organization's practices, processes, and products against the world's best is known as competitive benchmarking. -5 #202 Topic: Benchmarking and Core Competencies 203. (p. 218) The Nutmeg Soccer Club outsourced its accounting work. This suggests that management at Nutmeg does not believe that accounting is one of the firm's core competencies. Core competencies are those functions a firm can perform as well as, or better than, anyone else. A firm should continue carrying out its core competencies, and should outsource only functions that others can perform more efficiently. -5 #203 Topic: Benchmarking and Core Competencies 204. (p. 220) Last week at Happy Trails Financial Services Company, all financial advisors who each serve more than 150 clients received a notice from the VP of Operations that every client's investment portfolio should consist of 50% individual stock purchases, 25% bonds, and 25% property. Advisors were ordered to review all client portfolios for compliance to this directive. Clearly, Happy Trails is an inverted organization because management directives such as the one described are very common. In an inverted organization first-line employees are empowered to respond quickly to the wants and needs of customers, and to provide customers with the types of products and services that benefit them individually. -5 #204 205. (p. 220) Milton Learning Centers is a private firm specializing in helping students with learning problems. Located around the country, each center employs a manager and several tutors and counselors. The counselors and tutors have a great deal of flexibility to design programs specifically for individual students. In fact, these first-line employees are considered to be the key people in the organization, and the manager's main function is to assist these employees in matters such as scheduling and securing necessary materials. This type of arrangement suggests that Milton is an inverted organization. In an inverted organization, the key people are the first-line employees who deal directly with customers. These employees are empowered to respond to the wants and needs of customers. There are few layers of management, and the job of managers is to assist first-line employees rather than boss them around. -5 #205 206. (p. 217) Jason is a self-employed patent attorney. These days he is seldom without work. Large corporations hire him on an as-need basis to review prospective ideas and help with securing patents for a variety of inventions including surgical instruments, medicines, and high tech gadgets. Once he secures a contract, he knows approximately how many weeks or months he will work. Jason works for virtual corporations. A virtual corporation has no legal ties to the companies that perform a variety of jobs for the core firm - things such as distribution, legal work, accounting, manufacturing, and production. They hire other companies on an as needed basis. -5 #206 Topic: Transparency and Virtual Organizations 207. (p. 219) Ben was confident that sports fans would fill the seats in his brewery restaurant after major league baseball games if they just knew about the place - after all, he offered convenience, easy walking distance, great local talent for entertainment and several fresh premium brews. He decided to join social networks such as Twitter and Facebook, and offer wireless services and lunch for afternoon customers. These are worthy strategies for reaching digital natives. Introducing change is difficult for any manager. In order to attract digital natives, younger generations who grew-up with the Internet, businesses are trying to reach them by frequenting places that they frequent such as social network sites. -5 #207 Topic: Adapting to Change 208. (p. 221) Organizations with positive images for performing exceptional service to customers are usually friendly places to work, as well. -6 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #208 Topic: Creating a Change-Oriented Organizational Culture 209. (p. 221) Organizational culture can produce either a positive or negative impact on an organization. -6 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #209 Topic: Creating a Change-Oriented Organizational Culture 210. (p. 221) The very best organizations have cultures that emphasize service to others, especially customers. -6 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #210 Topic: Creating a Change-Oriented Organizational Culture 211. (p. 220) Organizational culture refers to the widely shared values within a corporation that foster unity and cooperation. -6 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #211 Topic: Creating a Change-Oriented Organizational Culture 212. (p. 221) The informal organization is created by the decisions of top management. -6 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #212 213. (p. 221) While most organizations have a formal organization structure, only poorly managed firms also have an informal organization. -6 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #213 214. (p. 221) A firm's informal organization refers to the structure that identifies the authority, responsibility, and position of people within the organization. -6 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #214 215. (p. 221) The informal organization of a business can help generate creative solutions and inspires teamwork and camaraderie. -6 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #215 216. (p. 221) The formal organization of a firm provides the lines of authority to follow in routine situations. -6 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #216 217. (p. 221) Effective employees learn the relationships of employees in the firm's informal organization. -6 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #217 218. (p. 221) The grapevine refers to the formal channel used for confidential communications between members of top management. -6 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #218 219. (p. 222) An informal organization can be a valuable asset to managers attempting to create an environment of harmony among workers and establish the corporate culture. -6 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #219 220. (p. 221) The informal organization appears as dashed lines on a firm's organizational chart. -6 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #220 221. (p. 221) The informal organization is best suited for decision making on big issues. -6 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #221 222. (p. 221) The key people in a company's grapevine typically have considerable influence in the organization. The grapevine is the informal organization's nerve center. Unofficial information flows through this system. Blooms: Comprehension -6 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #222 223. (p. 222) As indicated in the Spotlight for Small Business box titled, "Keeping that Small- Company Feeling," the giant media company formed by AOL and Time Warner proved that the informal organization is not conducive to creativity and innovation. The informal organization builds camaraderie and a team environment, the same atmosphere that you have in many small businesses. Keeping that same spirit as companies grow and become larger is a key factor, if innovation and creativity are to thrive. Blooms: Comprehension -6 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #223 Topic: Spotlight on Small Business box 224. (p. 222) Successful managers will find the balance between promoting the informal organization and maintaining a formalized structure, as well. As appealing as the informal organization may be due to its ability to create camaraderie and a spirit of cooperation, informality also can be very powerful in resisting managerial directives. These resistance movements can result in Union strikes and other disruptive occurrences. Management must find the right balance between the formal and informal organization. Blooms: Comprehension -6 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #224 225. (p. 222) As indicated in the Spotlight for Small Business box titled, "Keeping that Small- Company Feeling," water cooler talk, idea brokers, and other informal ways of collecting creative ideas are proving to be good strategies for large companies. Companies that want to maintain that small-company feeling are promoting ways within their firms to get employees to talk with each other informally. Some companies have installed programs and internal social networks to generate discussion of creative ideas. Blooms: Comprehension -6 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #225 Topic: Spotlight on Small Business box 226. (p. 221) Samad accepted a managerial position at City Bank. In order to be more effective in his new position, he should try to learn who the important people are in City's informal organization. Important people within a firm's informal organization can be very helpful at teaching new employees the "ins and outs" of how to operate effectively within the organization. -6 #226 227. (p. 221) Molly, a production line employee at Holiday Industries learned from a friend at her coffee break that one of the managers in accounting is about to be fired. She is eager to learn if other friends at Holiday know any more about the situation. This flow of information is an example of Holiday's grapevine. The grapevine is the flow of unofficial (and sometimes inaccurate) information between and among managers and employees within an organization. -6 #227 228. (p. 221) Rapid Response Security Firm, a company that provides on-site security services for malls and other retail environments needs to review current procedures used by their professional officers to make certain they are in compliance with new laws. On crucial issues such as this, it is more important to gather information through the informal organization, as opposed to the formal organization. The informal organization is not well suited to making critical decisions of long term significance. It is too unstructured and emotional to allow for careful, reasoned decision making on such important topics. -6 #228 229. (p. 221) Jack just learned that several persons in Arizona became ill from the peanut butter they ate that was produced and bottled in his plant. As he walks the back stairs at the plant, he ponders, "It's time to get the informal organization in on this. We've got to stop this in its tracks!" Jack is taking the right approach to solving this serious problem. The informal organization is often too unstructured and emotional to deal with serious emergency type situations. Critical matters need reasoned and rational decision-making that needs to happen in a more formalized approach. -6 #229 230. (p. 221) Mario kept humming that old song, "Well, I heard it through the grapevine, not much longer would you be mine" Earlier today, he heard from his coworker Jessica that by the end of today, several employees would get their hours reduced and other would lose their jobs. He decided to stop by George's office. If anyone had the scoop, it would be George. To Mario, George represented an influential person in the informal organization. There are persons who are more influential than others in a firm's informal organization. It is wise to learn quickly who is important. Key people in the grapevine of the information organization have considerable influence. -6 #230 231. (p. 221) Jessica found at a job at a bank, after losing her insurance company job when the firm went bankrupt. Although she has only been with this firm for a couple of weeks, she senses a rather austere climate where not too many people take the time to get to know one another. Several of her coworkers seem to get very nervous when managers walk by and breathe sighs of relief when the VP is away for the day. When she asked her supervisor why people seemed afraid of the VP, the supervisor quoted an old Tennyson poem, "Ours is not to reason why, ours is but to do and die." Jessica realizes the bank does not operate as an open organization. It lacks a thriving informal organization. It is unlikely that Jessica will feel an allegiance to this company. Organizations do not operate effectively without both the formal and informal organizations. Blooms: Analysis -6 #231 232. (p. 202) Contemporary businesses are: A. beginning to use Fayol's principles of organization to respond quickly to changes in the marketplace. B. reorganizing to be more competitive. C. performing the organization function to look good to prospective buyers. D. adding to their workforce as part of adaptive change. -1 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #232 Topic: Everyones Organizing 233. (p. 202) Organizing a business begins with: A. acquiring the necessary resources. B. choosing the best qualified employees. C. developing an efficient plan of action. D. determining the work to be done. -1 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #233 Topic: Building an Organization from the Bottom Up 234. (p. 202) Dividing the required work among a group of employees is called: A. departmentalization. B. delegation of responsibility. C. division of labor. D. separation of control. -1 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #234 Topic: Building an Organization from the Bottom Up 235. (p. 202-203) Dividing tasks into smaller jobs is called: A. job enrichment. B. job specialization. C. departmentalization. D. division of authority. -1 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #235 Topic: Building an Organization from the Bottom Up 236. (p. 203) The process of setting up individual functional units of the business to do specialized tasks is called: A. Departmentalization. B. Division of labor. C. Job specialization. D. Delegation of authority. -1 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #236 Topic: Building an Organization from the Bottom Up 237. (p. 202) Job specialization is known to: A. minimize delegated authority and responsibility. B. improve job performance. C. create work teams and improve resource allocation. D. establish procedures. -1 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #237 Topic: Building an Organization from the Bottom Up 238. (p. 202) Due to changes in technology and competition, managing __________ has become a critical management skill. A. consumer demand B. international markets C. change D. negative spiritual issues -1 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #238 Topic: Everyones Organizing 239. (p. 203) Which of the following is an example of a move to reorganize? A. Reducing the labor force within your business B. Revising plans by creating contingency plans C. Managing by objectives and clearing pathways for success D. Developing a way to monitor financial success Reorganizations usually involve increasing or reducing the work force within the business; adding or decreasing departments; opening or closing business units; and/or reallocating resources differently within the business. Blooms: Comprehension -1 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #239 Topic: Building an Organization from the Bottom Up 240. (p. 203) As depicted in the Reaching Beyond our Borders, box, "General Electric Looks for More Profits", in order to compete globally, corporate strategy should: A. not try to match the performance of competitors. B. study competitors and try to match or exceed their performance. C. not waste time and resources going beyond the competitor's strategy, but should move within striking distance. D. centralize all services. In order to compete globally, it is often necessary to increase or reduce operational segments in order to match or exceed the performance of global competitors. Blooms: Comprehension -1 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #240 Topic: Reaching Beyond our Borders box 241. (p. 202-203) The proven success of job specialization lies in the fact that: A. it leads to groupthink. B. it avoids the pitfalls of division of labor, where workers become removed from thinking conceptually about the business. C. it is a detractor to others who are thinking about entering your industry because it successfully creates barriers to entry. D. it adds efficiency to the business's operation by identifying tasks that some do better than others. Specialization will usually result in jobs being performed more quickly and better. Blooms: Comprehension -1 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #241 Topic: Building an Organization from the Bottom Up 242. (p. 204) In the Making Ethical Decisions box, titled, "Safety versus Profit", which of the following statements best forms the theme of this passage? A. In the beginning, company procedures that require value judgments are often too costly. As the business grows, the owner can add ethical procedures to each job. B. The principles of organization state that the only company objective is to gain profits for the owner(s) or stockholders. If your competitors are cutting corners with safety regulations, you should consider the same. C. The only way to be profitable is to avoid risk. If new safety equipment becomes available that is applicable to your business, even if it slows productivity, you should adopt it. D. The corporate culture you create as you begin your service will last a long time. Your workers will adopt your values. The corporate culture you create as you begin your service will last a long time. If you want your employees to adopt your business values, it is important to emphasize safety and environmental concern from the start. Blooms: Comprehension -1 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #242 Topic: Making Ethical Decisions box 243. (p. 202) As Bret prepares to open his new business, he has identified the tasks that need to be accomplished and has assigned employees to each task. This illustrates a: A. management departmentalization. B. division of labor. C. specialization of priorities. D. mass production economies. Division of labor refers to the process of identifying what work needs to be done and then dividing up the tasks among the employees. -1 #243 Topic: Building an Organization from the Bottom Up 244. (p. 203) When Bret started his auto mechanic shop his business plan included a(n) _______________ that showed the relationship among employees in his organization and the lines of authority and responsibility. A. business view map B. department categorization C. organization chart D. operating matrix grid An organization chart shows relationships among people who work for the business, including who is accountable for the completion of specific work and who reports to whom. -1 #244 Topic: Building an Organization from the Bottom Up 245. (p. 202-203) As your good friend ponders putting some structure to his/her graphic design business idea, which of the following do you not advise him/her to do? A. Prepare the non-changeable marketing plan for the next three years, including marketing analysis and marketing strategy B. List the work that needs to be done such as 1) computer assisted design; 2) sales generation; 3) accounting and bookkeeping; 4) purchasing and supply ordering, and more C. List who will do the various jobs, including who will perform the computer work, who will keep the books, and who will go out and create sales D. Assign responsibility and authority to certain employees Organizing or structuring the business consists of creating a division of labor, setting up teams or departments to do specific tasks, and assigning responsibility and authority to various employees. -1 #245 Topic: Building an Organization from the Bottom Up 246. (p. 203) While adding structure to his graphic design business, including the allocation of resources for getting the job done, Jack knew that he would need to initially allocate a considerable amount of funds for the sales team to have face to face meetings with other businesses who needed website design and promotional materials. Since overall funds were limited, he worried about his employees using these funds for the stated purpose and in a manner that he would use them. As his business advisor, you explain: A. it always "takes money to make money", so he needs to realize that he will have to take risks B. in order to achieve a productive business, he will have to trust those that he hires but control them carefully C. it's difficult to monitor financial resources during the first year of business. This is the wild-cat year where you pull-out all stops and let the experts do the work it takes to make the sale D. creating a corporate culture that emphasizes your values goes hand in hand with structuring your organization From the start, adding the values of the owner to the business structure is very important. You will make ethical decisions on how you will treat your employees and how you expect them to treat each other and the level of consideration they show in their handling of the resources they are provided in doing their jobs. AACSB: Ethics -1 #246 Topic: Building an Organization from the Bottom Up 247. (p. 205) The concept of ____________ suggests that as a firm produces more, the average cost of goods produced goes down. A. natural growth B. survival of the fittest C. cost enhancement D. economies of scale -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #247 248. (p. 205) Henri Fayol and Max Weber are best known for their contributions to: A. production theory. B. marketing theory. C. organization theory. D. finance theory. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #248 249. (p. 205) Organization theorists emerged during the era of mass production, meaning: A. the development of ways to produce a large quantity of product efficiently. B. the development of ways to purchase raw materials in bulk. C. the decline in the cost of production due to an increase in the cottage industry. D. the era when most companies adopted very similar methods of producing goods and services, which led to standardization of organizational design. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #249 250. (p. 205) Fayol's _____________ principle states that each worker should report to one, and only one, boss. A. division of labor B. unity of command C. esprit de corps D. comparative advantage -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #250 251. (p. 205) Fayol's ____________ principle says that tasks should be divided into areas of specialization. A. departmentalization B. comparative advantage C. division of labor D. centralization -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #251 252. (p. 206) Fayol's ____________ principle says that workers' attitudes would create an environment of pride and loyalty within an organization. A. esprit de corps B. hierarchy of loyalty C. unity of command D. equity -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #252 253. (p. 206) __________ believed that managers were trustworthy and companies would do well if employees simply did what they were told. A. John Keynes B. Adam Smith C. Peter Drucker D. Max Weber -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #253 254. (p. 206) Max Weber used the term ________ to describe middle managers whose job was to implement the orders of top management: A. management B. autocrats C. staff personnel D. bureaucrats -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #254 255. (p. 206) In Weber's view of a bureaucratic organization, the role of top management was to: A. empower workers and enable them to quickly respond to customer wants. B. make decisions. C. develop the rules and procedures needed to carry out the plans of bureaucrats. D. directly supervise front-line employees to better control operations. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #255 256. (p. 206) In Weber's view of a bureaucratic organization, the organization demanded: A. a spirit of pride and loyalty among the workers. B. cross-functional teams. C. clearly established rules and guidelines that were to be precisely followed. D. self-managed teams. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #256 257. (p. 207) The line of authority that moves from the top of a hierarchy to the lowest level is called the: A. chain of logic. B. chain of command. C. organizational design. D. delegation of contingent authority. -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #257 Topic: Turning Principles into Organization Design 258. (p. 207) A(n) __________ consists of one person at the top of the organization and many levels of managers who are responsible to that person. A. hierarchy B. oligarchy C. inverted organization D. informal organization -2 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #258 Topic: Turning Principles into Organization Design 259. (p. 207) In a bureaucratic organization: A. departments communicate with each other on a regular basis. B. employees follow strict rules and regulations. C. customer satisfaction is the number one priority. D. first-line workers are empowered to respond to the needs of customers. Max Weber believed that as organizations grew, it was necessary to define strict rules and guidelines for workers. These rules were created for the purpose of making management's job easier. The organization would realize more efficiency. Blooms: Comprehension -2 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #259 Topic: Turning Principles into Organization Design 260. (p. 207) One advantage of a bureaucratic organization is that: A. it is very responsive to the wants and needs of customers. B. there are very few layers of management. C. it encourages cooperation among different departments within the organization. D. employees know they are expected to follow the rules and regulations. Max Weber believed that as organizations grew, it was necessary to define strict rules and guidelines for workers. These rules were created for the purpose of making management's job easier. The organization would realize more efficiency. Blooms: Comprehension -2 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #260 Topic: Turning Principles into Organization Design 261. (p. 207) ______________ organizations are characteristic of many layers of management and function with well-defined rules and procedures. A. Matrix B. Inverted C. Ordered D. Bureaucratic Weber believed that organizations needed bureaucracy in order to operate efficiently and effectively. Bureaucrats were middle managers who created written rules and regulations in order to carry-out the decisions of top management. Blooms: Comprehension -2 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #261 Topic: Turning Principles into Organization Design 262. (p. 205) Economies of scale: A. are available to small firms but not to large firms due to management inefficiencies. B. are achieved when a firm reduces its average cost of production as it produces more. C. can be avoided by purchasing supplies and raw materials in large quantities. D. help explain the success of small businesses. Mass production can allow a firm to increase its efficiency. As production volume increases, the per-unit cost of production decreases. This is explained, in part, by the purchase of supplies and raw materials in large quantities and labor efficiencies. Blooms: Comprehension -2 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #262 263. (p. 206) Max Weber favored which of the following? A. Inverted organizations B. Worker participation in decision making C. Staffing and promotions based on qualifications D. Flat organizations Weber emphasized job descriptions, written rules, decision guidelines, detailed records, consistent procedures, regulations and policies, and staffing and promotion based on qualifications. Blooms: Comprehension -2 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #263 264. (p. 205) Fayol believed that decision-making authority should remain in the hands of top management: A. in small organizations, but should be delegated to middle and first-line managers in large organizations. B. in large organizations, but could be delegated to middle and first-line managers in small organizations. C. in all types and sizes of organizations. D. only in organizations subjected to significant government regulation. One of Fayol's principles of organization states that the amount of decision making power vested in top management should vary according to circumstances. Fayol believed that top management could assume all decision making power in small organizations, but that decision making power could be delegated to lower levels of management in large organizations. Blooms: Comprehension -2 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #264 Topic: Turning Principles into Organization Design 265. (p. 205) Which of the following correctly identifies the explanation behind the unity of command principle of management? A. All workers must share the same goal B. Every firm has one strong leader, and everyone should support that individual C. Workers can become frustrated and confused if they have more than one boss D. All authority should rest with top management, since only top managers carry the responsibility of bad decisions The unity of command principle says that each worker should report to one, and only one, boss. The purpose of this principle is to avoid confusing and frustrating workers. Blooms: Comprehension -2 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #265 266. (p. 206) If companies follow the theories of Fayol and Weber, which of the following scenarios is likely to result? A. Organization design will be benefit by the emergence of quick decision-making B. Organization design will eliminate systems of hierarchy and chains of command due to their hindrance of esprit de corps C. Organizations that grow will develop several layers of management and the time that it takes to make a decision will increase D. There will be a significant reduction of work force due to specialization and departmentalization The adoption of Fayol and Weber's principles will result in increased layers of management and a lengthening of the time from when an idea for change is introduced and when that change will or will not be implemented. Blooms: Comprehension -2 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #266 267. (p. 206) Which of the following statements most closely identifies the problem with adopting Fayol's principles of organization design for contemporary businesses? A. Leaving some decision-making power to middle management had the effect of minimizing the effort and results that management would put into the other historical principles of organization B. The rule making that developed from these principles created organizations that didn't respond quickly to customer needs C. The principles of Fayol and Weber hampered a firm's ability to determine if it was profitable D. Authority and responsibility quickly became unrelated The process of rule making designed by Fayol and Weber led to rather rigid organizations that didn't always respond quickly to consumer requests. Blooms: Comprehension -2 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #267 268. (p. 207) Campbell is a middle manager for a bureaucratic organization. According to Max Weber's views on bureaucratic organizations, Campbell's function within the organization is to: A. make key operating decisions. B. evaluate the daily performance of first-line employees. C. ensure the organization achieves esprit de corps. D. implement the decisions of top management. Max Weber used the word bureaucrat to describe a middle manager whose function was to implement top management's orders. -2 #268 Topic: Turning Principles into Organization Design 269. (p. 205) At Green Acres Fencing Company, eight employees each perform various aspects of the company's work. One person does sales, four perform installation; one purchases materials; one does billing; one performs after-sales inspections. This type of organization reflects Fayol's principle of: A. division of labor. B. equity. C. unity of command. D. hierarchy of authority. Fayol's principle of division of labor emphasized that jobs should be divided into areas of specialization. -2 #269 270. (p. 205) Sarah is a designer for a business that installs underground sprinkler systems for residential and commercial customers. Sarah designs and presents systems to prospective customers. Brothers Tom and Bill share the ownership responsibilities. Tom is in charge of commercial accounts and Bill is in charge of residential accounts. Sometimes Tom and Bill double book Sarah's time, creating frustration and animosity. Since they share supervisory responsibility, there is no clear way to decide whose accounts are most important. This type of situation represents a violation of Fayol's ____________ principle. A. division of labor B. clarity of objective C. priority of assignment D. unity of command Fayol's unity of command principle says that each worker should report to one, and only one, boss. -2 #270 271. (p. 206) Bill, a financial manager at Carlyle Bank and Trust always strives to treat each subordinate with respect and fairness. Bill's treatment of employees is an example of Fayol's principle of: A. unity of command. B. equity. C. empowerment. D. order. Fayol's principle of equity says that employees and peers should be treated with respect and justice. -2 #271 272. (p. 207) John recently accepted a job in the marketing department with the Burbank Bagel Boys. After just a few days on the job, John learned that the company has many layers of management, and seems to have a rule to cover almost every situation. These conditions suggest that Burbank Bagel Boys is a(n): A. cross-functional organization. B. decentralized organization. C. oligopolistic organization. D. bureaucratic organization. The presence of many layers of management and extensive reliance on formal rules and regulations are all characteristics of bureaucratic organizations. -2 #272 Topic: Turning Principles into Organization Design 273. (p. 207) Fairview Community College is a multi-district college with four campuses. Each campus has one president, two vice presidents, five deans, 12 department chairs, over 100 faculty members, and several persons in support roles. The presidents from each campus report to four vice-chancellors and the vice-chancellors report to the chancellor. It is clear that Fairview has a well-defined _____________. A. channel of academic culture B. chain of command C. responsibility environment D. bureaucratic reallocation The chain of command is the line of authority that moves from the top of the hierarchy to the lowest level. -2 #273 Topic: Turning Principles into Organization Design 274. (p. 207) Andrew's company is a bureaucratic organization. Andrew is likely to encounter which of the following conditions? A. Real time decisions B. Cross-functional teams C. Empowerment of first line employees to better serve customers D. Many layers of management In a bureaucratic organization, employees are not empowered to make decisions, but rather they follow the rules and policies of top management. There are many layers of management so it often takes weeks or months to make decisions. -2 #274 Topic: Turning Principles into Organization Design 275. (p. 205) The management at Patriot Mills works hard to ensure that no one in its organization has more than one boss and all workers are treated with fairness and respect. Additionally, the firm divides the work into areas of specialization so that everyone knows to whom they should report. The management of Patriot Mills reflects the ideas and principles of: A. John M. Keynes. B. Peter Drucker. C. Karl Marx. D. Henri Fayol. The practices of Patriot Mills reflect Henri Fayol's principles of unity of command, division of labor, hierarchy of authority, and equity. -2 #275 276. (p. 206) As a manager of a retail clothing store, Lance favors detailed job descriptions, formal rules and regulations, detailed records, and standardized procedures. He also believes that staffing and promotion decisions should be based strictly on the qualifications of the people under consideration. Lance's attitudes suggest that he is strongly influenced by the ideas of: A. Ralph Nader. B. Max Weber. C. Karl Marx. D. Adam Smith. Max Weber emphasized detailed job descriptions, written rules and guidelines, detailed records, consistent procedures, and staffing and promotions based on qualifications. -2 #276 277. (p. 206) Which of the following statements would best summarize Max Weber's views on the role of workers in an organization? A. Workers should be empowered to do whatever it takes to satisfy the needs of customers B. Workers will be promoted within the organization depending upon "who they know", rather than "what they know" C. Workers should simply follow well-defined procedures D. Although top managers must ultimately make the decisions, workers are an important creative resource for a firm, and top management should listen to their ideas Weber put a great deal of trust in management, and felt that the firm would do well if employees simply did what they were told. -2 #277 278. (p. 207) Mike prepared a paper for his class about organizational styles used in business. He found that one reason the traditional bureaucratic style is less popular than in the past is that: A. business organizations are much larger than they once were. B. restructuring has not produced the increased efficiency that was expected. C. the chain of command clearly identifies areas of responsibility. D. today's workforce is better educated and prefers a greater amount of decision-making involvement in their jobs. Bureaucratic organizations worked well when workers were relatively uneducated and managers were expected to make all the decisions. Today, the workforce is educated and looking to be involved in decision making. -2 #278 Topic: Turning Principles into Organization Design 279. (p. 208) Which of the following determines the degree of decentralization a firm might use? A. The degree to which lower level management is empowered to make decisions. B. The chain of command used to follow the flow of authority from top of the hierarchy to the lowest levels. C. The geographical area served by the firm's operations. D. The degree of product standardization desired by the marketplace. -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #279 Topic: Choosing Centralized or Decentralized Authority 280. (p. 208) In a(n) _____________ organization, decision-making authority is concentrated at the top level of management. A. bottom-up B. decentralized C. inverted D. centralized -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #280 Topic: Choosing Centralized or Decentralized Authority 281. (p. 208) _______________ means that decision-making authority is delegated to lower-level managers and employees. A. Uniformity of authority B. Decentralized authority C. Specification of authority D. Standardized authority -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #281 Topic: Choosing Centralized or Decentralized Authority 282. (p. 209) As compared to a centralized management structure, which of the following is a disadvantage of the decentralized management structure? A. Less responsive to customers B. Less empowerment C. Weakened corporate image D. Lower morale away from corporate headquarters -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #282 Topic: Choosing Centralized or Decentralized Authority 283. (p. 209) As compared to the decentralized management structure, which of the following is a disadvantage of the centralized management structure? A. Potential for inter-organizational conflict B. Less top management control C. Less efficient D. Complex distribution system -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #283 Topic: Choosing Centralized or Decentralized Authority 284. (p. 208) The optimum number of subordinates a manager can supervise is referred to as the: A. manager-subordinate ratio. B. chain of command. C. employee quota. D. span of control. -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #284 Topic: Choosing the Appropriate Span of Control 285. (p. 209) The span of control for a manager: A. should never exceed 7 subordinates. B. is no longer a relevant issue in today's computerized offices. C. depends on a number of factors, and can vary from one manager to another. D. varies somewhat from manager to manager, but most managers operate best with a span of control of about 9 employees. -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #285 Topic: Choosing the Appropriate Span of Control 286. (p. 209) Due to more emphasis on empowerment and more talented and better-educated lower level management, span of control in organizations has ___________. A. increased B. decreased C. become an obsolete term in organization design D. led to tall organizations -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #286 Topic: Choosing the Appropriate Span of Control 287. (p. 209) An organization that consists of many layers of management is referred to as a(n) ____________ organization. A. flat B. wide C. tall D. deep -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #287 Topic: Choosing Between Tall and Flat Organization Structures 288. (p. 209) The ________ an organization's structure, the ________ the span of control. A. flatter; wider B. flatter; narrower C. taller; wider D. taller; flatter -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #288 Topic: Choosing Between Tall and Flat Organization Structures 289. (p. 209) An organization with only a few layers of management is known as a(n): A. tall organization. B. flat organization. C. leveraged organization. D. coordinated organization. -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #289 Topic: Choosing Between Tall and Flat Organization Structures 290. (p. 209) In recent years, large organizations have tried to improve their efficiency in communication and decision making by: A. creating specific rules for everyone to follow. B. eliminating several layers of management. C. restructuring into a bureaucratic organization. D. reducing the span of control for managers. -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #290 Topic: Choosing Between Tall and Flat Organization Structures 291. (p. 210) ________ refers to the process of dividing organizational functions (sales, production, accounting/bookkeeping) into separate units. A. Coordination B. A chain of command C. Empowerment D. Departmentalization -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #291 292. (p. 210) The traditional technique used to departmentalize an organization is by: A. function. B. customer group. C. geographic area. D. production process. -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #292 293. (p. 211) Which of the following is considered to be a disadvantage of functional departmentalization? A. There may be a lack of communication among the different departments B. Employees must develop skills in depth C. The company must achieve economies of scale D. Top management has to direct and control department activities -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #293 294. (p. 210) Which of the following is considered to be an advantage of functional departmentalization? A. Employees begin to identify with their department and its goals rather than with the goals of the entire organization B. People in the same department tend to think very differently C. Departments are isolated from one another D. Employee skills can be developed in depth -3 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #294 295. (p. 209) Within its production department, Sooner Manufacturing has shift leaders, supervisors, assistant plant managers, plant managers, product group managers, assistant division managers, division managers, an assistant vice president for production, and a vice president in charge of production. Given its multiple layer management structure, Sooner Manufacturing is an example of a(n) ____________ organization. A. tall B. wide C. cross-functional D. decentralized An organization with many layers of management is called a tall organization. Blooms: Comprehension -3 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #295 Topic: Choosing Between Tall and Flat Organization Structures 296. (p. 208-209) Which of the following factors help determine a manager's span of control? A. The number of global competitors B. The level of standardization of the work to be done C. Method of accounting for production D. Form of business ownership At lower levels, where work is standardized, it's possible to implement a broad span of control. The number gradually narrows at higher levels as the work is less standardized. Blooms: Comprehension -3 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #296 Topic: Choosing the Appropriate Span of Control 297. (p. 208) Organizations that require consistent production standards to help create a high quality public image would tend to favor: A. centralized authority. B. an inverted organization. C. a high level of employee empowerment. D. flat organizational structures. Centralized authority allows top management more control over operations and thus results in more standardized and uniform operations. Blooms: Comprehension -3 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #297 Topic: Choosing Centralized or Decentralized Authority 298. (p. 209) Today's preference to flat vs. tall organization structures is mainly due to a flat organization's ability to: A. encourage esprit de corps among employees in various departments. B. increase the cost of labor through economies of scale. C. respond readily to customer demands. D. increase sales through multiple customer contacts by several layers of management. Flat structures respond readily to customer demands because lower-level employees have authority and responsibility for making decisions that affect customers. Blooms: Comprehension -3 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #298 Topic: Choosing Tall versus Flat Organization Structures 299. (p. 208) Greenwave Garden Centers is a national chain of discount gardening stores. The top management at Greenwave realizes that different regions of the United States have very different climates and soil conditions, so they give regional managers a great deal of freedom to decide exactly what types of plants, fertilizers, and other items to stock and how to best market these products. Greenwave is an example of a _______________ organization. A. bureaucratic B. top down C. free form D. decentralized Decentralized authority occurs when decision-making authority is delegated to lower-level managers and employees who are more familiar with local conditions than headquarters' management could be. -3 #299 Topic: Choosing Centralized or Decentralized Authority 300. (p. 210) HipHop Music Company assigns workers to departments based on similar skills. Currently, the company has a marketing department, a production department, a finance department, and a human resources department. This suggests that HipHop departmentalizes by: A. process. B. function. C. user group. D. tradition. Grouping workers into departments based on similar skills is known as functional departmentalization. -3 #300 301. (p. 211) Gangsta Industries produces a variety of anti-crime and safety products such as burglar alarms, smoke detectors, surveillance cameras, and specialty locks. Gangsta sells to households, businesses, and government agencies. They have found that each market requires a different marketing strategy. Gangsta would probably benefit from departmentalization by: A. function. B. process. C. customer type. D. market opportunities. Since each type of customer requires a different approach, Gangsta should establish a different department to serve the needs of each customer group. -3 #301 302. (p. 208) As the head of the engineering department for her company, Jody works with her team on complex and challenging projects. The level of detail in this work requires Jody to spend a significant amount of time with each team member, providing advice and support. Due to the complexity and time involvement of each project, Jody has a(n) ________ span of control. A. wide B. narrow C. unlimited D. functional Challenging and complex work, and the need to meet with subordinates on a frequent basis, both put limits on how many subordinates a manager can effectively supervise, thus contributing to a narrow span of control. -3 #302 Topic: Choosing the Appropriate Span of Control 303. (p. 210) Vaughn Studios organizes its operations by activity, such as production, marketing, accounting, and finance. Vaughn utilizes _____________ departmentalization in order to maximize their efficiency: A. product B. customer C. functional D. standardized Functional departmentalization is the division of the organization into departments based on similar skills, expertise, or resource use. Typical departments would include accounting, marketing, production, and finance. -3 #303 304. (p. 211) Springfield National Bank organizes its loan operations based on the market served, such as consumer, small business, and nonprofit organizations. Departmentalization based on ________ allows Springfield to better serve borrowers with different needs. A. function B. geography C. process D. customer group Nonprofit organizations, consumers, and small businesses are different types of customer groups seeking loans for different reasons. -3 #304 305. (p. 210) JayLo Corporation has experienced rapid growth during its five years of existence. While still relatively small, JayLo is now big enough that Jennifer, the firm's CEO, has decided to organize the firm into functional departments. Jennifer can likely expect which of the following to occur? A. Quick company response to a change in the business environment B. Excellent communications between different departments C. Increase in scope of the performance of functions D. Opportunities for employees to develop their skills in depth Functional departmentalization tends to create opportunities for employees to develop skills in depth. Employees can progress within a department as they master those skills. -3 #305 306. (p. 208) International Inns and Conference Centers [IICC], a national chain of professional event centers utilizes a centralized authority structure. Which of the following provides the most likely explanation for why management at IICC would favor centralized authority? A. Top management at IICC intends to empower its first-line employees B. Top management at IICC wants to improve customer service response time C. Top management desires to maintain a uniform image and high quality service D. IICC wants to utilize a cross-functional organization Centralized authority gives top management more direct control over all of the firm's operations. This would enable management to establish standards used throughout the organization. However, centralized authority can make the firm less responsive to the needs of customers, since it limits the decision making authority of lower-level managers and employees who interact directly with customers and are most familiar with local conditions. -3 #306 Topic: Choosing Centralized or Decentralized Authority 307. (p. 209) As a response to a rapidly changing marketplace, Idea Electronics found it necessary to reorganize, including a significant downsize of its middle management. This action will likely result in ___________. A. acquiring additional firms B. flattening the organization and empowering employees, allowing them to get closer to the customer C. increasing the size of its traditional departments to handle 24/7 operations D. centralizing its decision making to better control its total quality management program A reorganization that results in a downsizing of the firm's workforce will most often affect middle management jobs. When middle management is eliminated, organizations tend to get flatter, span of control get wider, and the remaining middle management usually empowers employees to make customer decisions. -3 #307 Topic: Choosing Between Tall and Flat Organization Structures 308. (p. 211) During the past six years, the marketing department manager at Creative Concepts International made a strong push to hire mover/shaker professionals that had superior performance records prior to joining this company. It didn't take long for these enthusiastic marketers to recognize the many talents within their department. They marveled at how much they were like each other and how they seemed to agree with each other's work styles and ideas. After a while, it became difficult for others in the organization to present to this group. If the idea did not originate within the marketing department, marketers did not give it much credence. Management counselors would describe this phenomenon as ______. A. departmentalization clique B. inter-office competition C. forward thinking friction D. groupthink A disadvantage of departmentalization is that department members may engage in groupthink (they think alike) and may need input from outside to become more creative. -3 #308 309. (p. 209) Management at Hottie Potatee, a nationwide potato bar chain, believes that its customers value a predictable and consistent level of service and quality. When customers stop at one of its potato bar chain restaurants anywhere in the United States, they should know what to expect in terms of menu, price and quality. In order to maintain this consistency, Hottie Potatee adopted a(n) ______ structure. A. centralized authority B. decentralized authority C. hybrid authority D. origination authority Centralized authority may be advantageous when the corporation is trying to achieve consistency in its operation and image. -3 #309 Topic: Choosing Centralized or Decentralized Authority 310. (p. 213) A ____________ organization is characterized by direct two-way lines of responsibility, authority, and communication running from the top to the bottom of the organization, with all people reporting to only one supervisor. A. matrix B. cross-functional C. line D. line-and-staff -4 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #310 Topic: Line Organizations 311. (p. 213) __________ are responsible for directly achieving organizational goals. A. Organizational specialists B. Line personnel C. Chain of command managers D. Staff personnel -4 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #311 Topic: Line-and-Staff Organizations 312. (p. 213) Employees who perform functions that advise and assist line personnel are known as: A. middle managers. B. empowered workers. C. secondary employees. D. staff personnel. -4 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #312 Topic: Line-and-Staff Organizations 313. (p. 213) Which of the organization models follows all of Fayol's traditional management rules? A. Line organizations B. Line-and-staff organizations C. Cross-functional teams D. Matrix -4 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #313 Topic: Line Organizations 314. (p. 213) Staff positions in an organization: A. support and assist the line positions. B. are superior to line positions. C. are less well-paid than line positions. D. are ways to employ past CEOs until they retire. -4 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #314 Topic: Line-and-Staff Organizations 315. (p. 214-215) In a _____________ organization, specialists from different parts of the organization are brought together on a temporary basis to work on specific projects. A. matrix B. line C. line-and-staff D. centralized -4 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #315 Topic: Matrix-Style Organizations 316. (p. 214) Line-and-staff organizations work well in organizations with: A. operations in high-growth industries. B. stiff competition. C. short product life cycles. D. a relatively unchanging environment. -4 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #316 Topic: Matrix-Style Organizations 317. (p. 215) Matrix organizational structures were first developed in: A. Japan. B. the aerospace industry. C. the dot com Internet industry. D. the chemicals industry. -4 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #317 Topic: Matrix-Style Organizations 318. (p. 216) Which of the following was created as a solution to the temporary nature of the matrix structure? A. Line organizations B. Cross-functional self-managed teams C. Line-and-staff organizations D. Network organizations -4 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #318 319. (p. 216) Which of the following describes a group of employees from different departments working together on a long-term basis? A. Focus group B. Mixed function groups C. Cross-functional self-managed teams D. Intrapraneurial teams -4 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #319 320. (p. 216) Cross-functional self-managed teams work best when ________________. A. leadership is shared B. there are at least two line and staff mangers on the team C. the teams consist of members of only two functional units D. The academic levels of all members are comparable -4 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #320 321. (p. 213) Which of the following is an advantage of a line organization in a large business? A. It does not require specialists to advise people along the line B. Responsibility and authority are clearly defined C. Each worker has several supervisors D. It is very flexible A line organization has direct two-way lines of responsibility, authority, and communication running from the top to the bottom of the organization, with all people reporting to only one supervisor. Blooms: Comprehension -4 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #321 Topic: Line Organizations 322. (p. 213) Which of the following positions would be classified as a staff position? A. An assembly line worker for a major auto manufacturer B. The chief executive officer of a small corporation C. A sales manager for a chain of clothing stores D. An attorney in the legal department of a manufacturing corporation The function of staff personnel is to provide advice and assistance to line personnel. Since a lawyer for a manufacturing company would provide legal advice and assistance, he or she would be serving in a staff position. Blooms: Comprehension -4 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #322 Topic: Line-and-Staff Organizations 323. (p. 215) Which of the following is an advantage of a matrix organization structure? A. It is much cheaper to staff than other organization models B. It provides for efficient use of organizational resources C. The project teams are permanent D. It is a complex organization structure Matrix organizations provide for efficient use of organizational resources. Blooms: Comprehension -4 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #323 Topic: Matrix-Style Organizations 324. (p. 216) Which of the following is of cross-functional teams? A. Cross-functional teams are required not to share information across national boundaries B. Employees on the teams are frustrated by organizational rules and regulations C. Cross-functional teams work best when the voice of the customer is brought into the organization D. Cross-functional teams are disbanded once the current project is complete Cross-functional teams work best when the voice of the customer is brought into organizations. Customer input is especially valuable to product development teams. Blooms: Comprehension -4 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #324 325. (p. 216) The main difference between a matrix-style organization model and a cross-functional team is: A. the matrix model has a limit on the number of functional units who send an expert to join the team, whereas the cross-functional team does not. B. the matrix model is a temporary arrangement, whereas the cross-functional team is a more permanent arrangement. C. the matrix model shares leadership responsibilities within the group, whereas the cross-functional team does not. D. the matrix model is a more permanent arrangement, whereas the cross-functional team is a temporary arrangement. The matrix model is a temporary arrangement where participants report back to their functional unit once the project is complete. The cross-functional team is a more permanent arrangement where the same team works on several projects. Blooms: Comprehension -4 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #325 326. (p. 216) Which of the following would be the least likely to serve on a cross-functional team for the Discovery Corporation? A. a member of the Discovery marketing department B. a production manager for a firm that is one of Discovery's major customers C. a production manager for one of Discovery's main competitors D. a representative of a firm that is one of Discovery's major suppliers Discovery's cross-functional teams certainly should include specialists from its own marketing department, but to be really effective, cross-functional teams must know what customers want. Thus, customers are valuable members of such teams. Suppliers and distributors can also be valuable team members. The only person in the list who does not belong on a cross-functional team is a competitor. -4 #326 327. (p. 213) The organizational structure of the U.S. Army's 1st Infantry Division provides for direct two-way lines of responsibility, authority, and communication running from the top to the bottom. Additionally, each person in the division reports to only one superior. The 1st Infantry Division is clearly an example of a(n): A. matrix organization. B. functional organization. C. line organization. D. service organization. A line organization is characterized by direct two-way lines of authority, responsibility, and communication running from the top to the bottom of the organization. In such an organization, each person reports to only one supervisor. -4 #327 Topic: Line Organizations 328. (p. 213) Eileen works in the human resources department of a corporation with several hundred employees. Her main function is to advise and assist managers in other departments, such as marketing and production, when they make staffing decisions. Eileen's position would be classified as a(n) ___________ position. A. staff B. line C. first-line D. secondary Staff personnel advise and assist others within the organization in achieving their goals. -4 #328 Topic: Line-and-Staff Organizations 329. (p. 216) Joe, a production engineer at Freestone Tires recently joined a team of specialists from other areas, such as marketing and finance. His long-term assignment to this team has produced several new products. Joe enjoys this work environment, in part because Freestone's management has given the team the freedom and flexibility to make decisions. A recent development is the inclusion of "outsiders" from Freestone's major distributors and suppliers on the team. It appears that Joe's team is a(n): A. interfunctional matrix organization. B. multidivisional group think-tank. C. multi-modal product development team. D. cross-functional self-managed team. A cross-functional team consists of specialists from different areas who work together on a long-term basis (as opposed to the temporary nature of teams in a matrix organization). These teams can include customers, suppliers, and distributors. When they are empowered to make decisions on their own, they are called self-managed teams. -4 #329 330. (p. 213) Julio is the owner of Celebration, Inc. a small party supply company. The company provides tents, tables, chairs, and related paraphernalia for wedding, Bar Mitzvah, Bot Mitzvah, graduation, birthday, and other celebratory events. As sales have increased, the organization has hired more personnel and departmentalized to more efficiently handle purchasing, sales, service, and accounting. Everyone is still responsible for achieving company goals. Upon seeing Celebration's organization chart, you agree it uses a _______________. A. line organization model B. line and staff organization model C. matrix organization model D. cross-functional team organization model Many small businesses begin as line organizations. In a line organization model everyone in the organization is responsible for achieving the company goals. Blooms: Analysis -4 #330 Topic: Line Organizations 331. (p. 216) Barclay developed two interactive computer games. He didn't do it entirely alone. Last year he started a small company, hired two programmers, and a marketing graduate. He considers himself a cutting-edge kind of guy and wants to position his company the same. Soliciting your advice as to how he should structure his organization as he moves forward, you suggest that he hire a few potential customers to join his team of employees as product testers. And, maybe he should solicit globally. You are suggesting to Barclay that he put together a ___________. A. line organization model B. line and staff organization model C. matrix organization model D. cross-functional team Including potential customers on a work team simulates a cross- functional Self-managed team. -4 #331 332. (p. 214-215) Chang is a project manager at Paradox Industries. He is able to borrow specialists from the organization on a regular basis to assist in major projects. After the project ends, the specialists return to their functional units to await new assignments. Paradox Industries utilizes a: A. line organization model. B. bi-functional organization model. C. lateral transfer organization model. D. matrix organization model. In a matrix organization, specialists from various departments are brought together to work on specific projects, but they remain part of the line-and-staff structure and return to their permanent positions when the project ends. -4 #332 Topic: Matrix-Style Organizations 333. (p. 217) _____________ is using communications technology and other means to link organizations and allow them to work together on common objectives. A. Networking B. Structural linking C. Functional sharing D. Strategic planning -5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #333 Topic: Managing the Interactions Among Firms 334. (p. 217) Which of the following describes an environment in which data is instantly available via the Internet to organizational partners? A. Networking B. Real time C. Virtual business D. E-commerce -5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #334 Topic: Transparency and Virtual Organizations 335. (p. 217) Which term describes a company being so open to other companies working with it that electronic information is shared as if the companies were one? A. Web-based corporations B. Webworking C. Transparency D. E-connected -5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #335 Topic: Transparency and Virtual Organizations 336. (p. 217) Which of the following describes a temporary networked organization made up of replaceable firms that join and leave as needed? A. Web-based corporation B. Benchmark outsourcing system C. Network system D. Virtual corporation -5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #336 Topic: Transparency and Virtual Organizations 337. (p. 218) The process of rating an organization's practices, processes, and products against the best of the world is known as: A. webworking. B. outsourcing. C. benchmarking. D. core competencies. -5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #337 Topic: Benchmarking and Core Competencies 338. (p. 218) Which of the following describes the activity of a firm that assigns specific functions, such as accounting or legal work, to other organizations rather than performing these functions themselves? A. Functional sharing B. Outsourcing C. Benchmarking D. Virtual distribution -5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #338 Topic: Benchmarking and Core Competencies 339. (p. 218-219) __________ refer to those functions that an organization does as well as, or better than, any other organization in the world. A. Primary functions B. Comparative strengths C. Residual functions D. Core competencies -5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #339 Topic: Benchmarking and Core Competencies 340. (p. 219) Young people today are often called __________ because they have never known life without the Internet. A. the high-tech heroes B. Social networkers C. digital natives D. electronic eggheads -5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #340 Topic: Adapting to Change 341. (p. 219) Which of the following are common responses of employees when faced with change? A. "That's the way we've always done things" B. "Perhaps I'll be able to get a promotion now" C. "I'm excited to learn something new" D. "This should be easy to accept" -5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #341 Topic: Adapting to Change 342. (p. 219) Which of the following describes the redesigning of an organization so that it can more effectively and efficiently serve its customers? A. Reinventing B. Restructuring C. Radical reorganizing D. Extroverted reorganizing -5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #342 343. (p. 220) An organization that has contact people at the top and the chief executive officer at the bottom is known as a(n): A. bureaucracy. B. oligarchy. C. improvised organization. D. inverted organization. -5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #343 344. (p. 220) Empowering employees to better serve customers requires __________ front-line employees. A. fewer B. less training for C. more support for D. uniforms for -5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #344 345. (p. 218-219) _________ is the term used to describe those functions that a firm can do as well or better than others. It agrees to perform these functions in-house, rather than outsourcing. A. Benchmarks B. Standard responsibilities C. Operational requirements D. Core competencies -5 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #345 Topic: Benchmarking and Core Competencies 346. (p. 217) In today's competitive environment, cost containment is extremely important to survival. Which of the following increases efficiency in the production and distribution of goods? A. Personal computers B. Real time data C. Assembly lines D. Self-managed teams Real time simply means the present moment or the actual time in which an event takes place. Internet data is readily available between firms to help create efficiencies in production and distribution. Blooms: Comprehension -5 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #346 Topic: Transparency and Virtual Organizations 347. (p. 217) Which of the following statements best describes the evolution of organization design? A. Companies have evolved to cross-functional teams because line models and line and staff models have become too costly to maintain. B. Most companies are finding that the stages of product development are much slower than in the past because new products are much more complicated in nature than products of several years ago. Matrix models work much better in the current environment. C. The development of new technology allows for companies to be much more self-contained and able to maintain their competitive advantage due to more privacy. D. Companies are now part of a vast network of global businesses, and part of a larger system. Companies are no longer self-sufficient or self-contained. Networking and other technological advances have permitted firms to link together in a transparent manner. A few organization charts today depict the network between and among firms. Blooms: Comprehension -5 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #347 Topic: Transparency and Virtual Organizations 348. (p. 218) Companies benefit today by inter-firm cooperation. One of the ways they cooperate is through networking. Another way is by seeking technological knowledge and learning new processes from other firms that usually fall outside of their respective industries. We call this: A. competency capturing B. technology swapping C. benchmarking D. broadening the knowledge base Companies today are sharing their best practices through learning from each other. Benchmarking compares an organization's practices, processes, and products against the world's best. Management of one company seeks out another company whose technology or process in doing a particular function rivals all others. The goal is to replicate that process in its own firm. Blooms: Comprehension -5 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #348 Topic: Benchmarking and Core Competencies 349. (p. 219) One of the most difficult management challenges today is managing change. This is because: A. change requires cooperation and an awareness of a need for change. B. change requires a lot of bail-out money from the government. C. change requires decentralization of decision-making. D. change will invariably result in an inverted organization and management does not want to relinquish its position power in order to make that happen. Change requires recognition by employees and management that it is necessary in order to stay competitive. It often requires management to pursue unpleasant actions such as layoffs. In some cases, change requires extensive retraining of employees who have worked in a comfort zones for several years. Blooms: Comprehension -5 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #349 Topic: Adapting to Change 350. (p. 220) In an inverted organization, the job of management is to: A. closely monitor employee performance. B. establish rules and regulations to guide worker behavior. C. make all of the basic decisions. D. assist and support front-line people. In an inverted organization, the most important people are the front-line personnel who are in direct contact with the customers. These employees are given the flexibility and decision making authority to meet the needs of the customers. The job of management is to assist and support these contact people, not boss them around. Blooms: Comprehension -5 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #350 351. (p. 220) For an inverted organization to be effective, it requires: A. managers with strong position power. B. managers who are both technologically savvy and conceptually savvy. C. better educated, better trained, and better paid employees. D. a focus on what is best for production. Due to the fact that the inverted organization empowers front-line employees to make important customer decisions, the workforce of such an organization is typically better educated, better trained, and better paid. -5 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #351 352. (p. 218-219) Independence Electronics prides itself as a world-class producer of components used in CD and DVD players. The outstanding performance of the production department indicates that this activity is one of the firm's: A. fiscal responsibilities. B. core competencies. C. benchmark assets. D. target competitive advantages. A company's core competencies are those functions that it performs as well as or better than anyone else in the world. -5 #352 Topic: Benchmarking and Core Competencies 353. (p. 218) Excite Enterprises, a corporation of amusement parks uses an accounting firm to handle the payroll and tax functions for the company. Using the services of another firm in this manner is an example of: A. outsourcing. B. functional reassignment. C. core competencies. D. benchmarking. Outsourcing is assigning various functions, such as accounting and legal work, to outside organizations that excel in those areas. -5 #353 Topic: Benchmarking and Core Competencies 354. (p. 218) Bull's-eye, a regional discount retailer, carefully watches and compares its operation with the operations of its closest rivals. This firm does: A. outsourcing. B. functional positioning. C. core competency ranking. D. competitive benchmarking. Competitive benchmarking is rating an organization's practices, processes, and products against the world's best. -5 #354 Topic: Benchmarking and Core Competencies 355. (p. 217) HairTrend, a cosmetology trade publication, utilizes the resources of other organizations as needed. Business relationships are temporary and flexible. HairTrend is a networked organization made up of replaceable firms that join the network and leave it as needed. This unique organization is an example of: A. competitive benchmarking. B. a virtual corporation. C. core competency ranking. D. real time transparency. A virtual corporation is a temporary networked organization, made up of replaceable firms that join the network and leave it as needed. -5 #355 Topic: Transparency and Virtual Organizations 356. (p. 218) Whirlpond, a manufacturer of home appliances, has historically produced the components for their products. However, Whirlpond now contracts with other firms to produce these components. This strategy of __________ is a current trend among U.S. manufacturers. A. outsourcing B. core positioning C. foreign competency D. competitive benchmarking Outsourcing is the assigning of various functions, such as accounting, production, security, maintenance, and legal work, to outside organizations. -5 #356 Topic: Benchmarking and Core Competencies 357. (p. 220) Heather works as a sales representative for the Westerly Company. She really enjoys working for Westerly, because the company treats her and other sales representatives as highly valued employees. Sales reps at Westerly are given freedom and flexibility in their relationships with customers. While there are only a few layers of management at Westerly, Heather has found that these managers try their best to support and assist her efforts. Based on Heather's experience, it appears that Westerly is a(n): A. bureaucratic organization. B. inverted organization. C. tall organization. D. casual organization. An inverted organization is one with few layers of management, and in which the most important employees are front-line employees who deal directly with customers. In this type of organization, the job of managers is to assist and support front-line employees, not boss them around. -5 #357 358. (p. 220) The widely shared values within an organization that provide unity and cooperation to achieve common goals is together known as the: A. normative matrix. B. predefined group values. C. ethical system. D. organizational culture. -6 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #358 Topic: Creating a Change-Oriented Organizational Culture 359. (p. 221) The ____________ of a business firm is the system that details lines of authority, responsibility, and position, similar to the structure on organization charts. A. matrix reloaded structure B. formal organization C. informal organization D. normative design -6 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #359 360. (p. 221) All organizations have two organizational systems: A. the command system and the control system. B. the formal organization and the informal organization. C. the functioning system and backup system. D. the primary organization and secondary organization. -6 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #360 361. (p. 221) The __________ is the system of relationships that develop spontaneously as employees meet and form power centers. A. informal organization B. bureaucratic structure C. secondary organization D. formal organization -6 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #361 362. (p. 221) In open organizations the informal organization can be: A. a hindrance to effective management. B. an asset that promotes harmony among workers. C. a roadblock to the corporate culture. D. part of the formal organization. -6 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #362 363. (p. 221) The ___________ is the nerve center of the informal organization. A. organizational database B. intranet C. grapevine D. company newsletter -6 Level of Learning 1: Knowledge of key terms #363 364. (p. 221) The informal organization of a business is probably best suited to: A. give workers a clear idea of where they stand in the organization. B. provide helpful guidelines about how to handle routine problems. C. provide a mechanism that generates careful reasoned decisions about critical issues. D. create a feeling of camaraderie among employees and encourage teamwork. The friendships and relationships that develop in a business firm's informal organization can generate a feeling of camaraderie and can encourage people within the firm to work together. Blooms: Comprehension -6 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #364 365. (p. 221) A firm's formal organization would be better suited than its informal organization to: A. create an atmosphere of friendship and camaraderie among workers. B. find answers to critical problems that require logical analysis. C. find creative solutions to short-term problems. D. find a way around bureaucratic rules and regulations in order to get things done quickly. Informal organizations are good at creating camaraderie, finding creative solutions to short-term problems, and finding ways around the rules and regulations that slow down the implementation of decisions. However, informal organizations are too unstructured and emotional to allow for careful, reasoned decisions dealing with critical issues. A firm's formal organization is better suited for this type of decision-making. Blooms: Comprehension -6 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #365 366. (p. 222) According to the Spotlight on Small Businesses box, titled, "Keeping that Small Company Feeling", the main idea is to: A. restore the old corporate culture. B. develop a culture of innovation in large companies. C. bring in new progressive managers. D. implement a centralized form of management. "Keeping that Small Company Feeling," explains the need for large companies to maintain creativity and innovation which are usually characteristic of smaller firms. Large companies implement idea brokers, whose job it is to promote meetings among people from different parts of the firm, programs that index ideas, and others that promote internal blogging. Blooms: Comprehension -6 Level of Learning 2: Understanding of concepts and principles #366 Topic: Spotlight on Small Business box 367. (p. 220) Zach recently got his Ph.D. in analytical chemistry and was fortunate to be asked to join the Weilman Lab at a prestigious eastern university. After a month on the job, he remarked to another graduate student at his former university that the spirit of help and cooperation at the Weilman lab was remarkable. He enjoyed going to work each day and sometimes exchanged calls with other lab partners in the evening with ideas to improve each other's experiments. Zach remarked, "Now I know why this lab is considered one of the best in the nation!" Zach is referring to: A. the formal organization. B. the inverted organization. C. the Balanced organization. D. the organizational culture. Organizational culture is the widely shared values within an organization that foster unity and cooperation to achieve common goals. -6 #367 Topic: Creating a Change-Oriented Organizational Culture 368. (p. 221) When Eric Schmidt became the CEO of Google, he reported that the company in the hands of founders Larry Page and Sergey Brinn was running well, it just needed a little structure. CEO Schmidt helped develop: A. the innovative culture. B. the informal organization. C. the formal organization. D. the grapevine. The formal organization details lines of responsibility, authority, and position. This structure is also shown on organization charts. -6 #368 369. (p. 221) Ashley experienced frustration with her new job at Walnut Securities, until she befriended a secretary from another department. Over lunch in the cafeteria, her new friend shared with Ashley the way things really work at Walnut Securities. Ashley quickly learned that: A. what she learned in her business classes didn't really help her in the real world. B. an unofficial informal organization exists that she can utilize to help her do her job. C. organizational culture can be negative. D. not all businesses have a formal organization. All organizations have two organizational systems. One is the formal organization that details each person's responsibility, authority, and position. The informal organization is the human relationship side of the organization. The informal organization will identify for Ashley the unofficial power brokers. These are the influential individuals who can help her get things done. -6 #369 370. (p. 222) The Spotlight on Small Business, titled, "Keeping that Small Company Feeling", illustrates that: A. maintaining a strong informal organization is vital in today's business environment. B. maintaining a strong informal organization is so much easier to effect in large companies because they have the money to make it happen. C. although the informal organization may provide fun and diversion in the workplace it breeds unethical behavior which only the formal organization can derail. D. getting carried away with maintaining a small company feeling can stifle innovation and growth. The very best organizations understand the importance of innovation. Companies who provide a culture of inquisitive behavior, where innovation can incubate usually grow and prosper. Innovation usually develops within the informal organization. -6 #370 Topic: Spotlight on Small Business box 371. (p. 221) Carlos is the person to see in the welding department if you are a new employee. While he is not a manager, he is the person that most of the others in the department look to for advice and assistance. Carlos is an important member of the firm's: A. supervisory management. B. participatory control. C. informal organization. D. closet cabinet. Although Carlos may have little authority in the formal organization, the respect others in the department have for him makes him an important part of the informal organization. The informal organization is the system of relationships that evolve spontaneously as employees meet and form power centers. -6 #371 372. (p. 222) One of Javier's coworkers was recently promoted to a middle management position at their company. He seems to have quickly distanced himself from Javier and their other coworker, Carlos. In fact, yesterday Carlos described the situation by saying, "He's gone to the dark side." Javier understands what Carlos means because management keeps themselves removed from other employees, and seldom seriously solicit ideas for improvements or change from those in the trenches. The disadvantage in continuing this type of organizational culture is: A. nobody takes management seriously. B. the company will have to look outside the firm for new managers. C. small, incremental improvements rather than radical change will become the norm. D. the informal organization can hinder effective management. The informal organization can be powerful in resisting management directives. Employees may form unions, go on strike, and may generally disrupt operations. 373. (p. 206) Discuss Max Weber's views on organization theory. a) Max Weber's bureaucratic structure is pyramid-shaped, a structure that became very popular with large firms. b) Weber had great faith in managers, and believed that the organization would do well if workers simply followed orders. This view was reasonable at the time of Weber's writing, since many of the workers were unskilled and uneducated. Such a view is less plausible today. c) Many of Weber's contributions to organization theory were similar to those of Henri Fayol, but in addition, he emphasized the need for job descriptions, written rules and guidelines, consistent procedures and policies, and staffing based on qualifications. 374. (p. 214-215) What is a matrix organization? What advantages and disadvantages are associated with this type of organization? a) A matrix organization is an organization in which specialists from different parts of the organization are brought together to work on specific projects but still remain part of the line-and-staff structure. b) The advantages of a matrix organization are: (1) it gives managers flexibility in assigning people to projects; (2) it encourages inter organizational cooperation and teamwork; (3) it can result in creative solutions to problems such as those associated with product development, and (4) it provides for more efficient use of organizational resources. c) The disadvantages of a matrix organization are: (1) it is complex and costly to set up; (2) it can cause confusion among employees as to where their loyalty belongs; (3) it requires a high level of interpersonal skills and cooperative employees and managers, and (4) it is a temporary solution to a long-term problem. 375. (p. 216) What is a cross-functional, self-managed team? Who would serve on such teams? Why do cross-functional, self-managed teams often lead to networking? a) A cross-functional team is a group of employees from different departments (and possibly people from outside the organization) who work together on a long-term basis (as opposed to the temporary nature of teams employed in a matrix organization). These teams are often empowered to make decisions on their own, without seeking approval of management, which is why they are called self-managed teams. b) Cross-functional teams may consist of employees from different departments. For such a team to work best, however, customers, suppliers, and distributors should also be represented. c) Because cross-functional teams may include people from other organizations and even from other countries, they serve to link those organizations into a network in which the organizations can communicate and interact in a way that enables them to work together on common objectives. These teams may share market information across national boundaries. The government may encourage the networking of teams, and government coordinators may assist such projects. 376. (p. 208) Describe two major issues that are important in organizational design. There are four issues from which the student can choose: (1) Tall versus flat organizations, (2) span of control, (3) departmentalization, and (4) centralization versus decentralization. a) A tall organization is one with many levels of management and a smaller span of control. The many levels result in a "tall" pyramidal organizational chart. A flat organization, on the other hand, has fewer levels of management and a broad span of control. Many organizations are moving to a flatter organizational structure by eliminating levels of middle management. b) Span of control refers to the optimum number of people a manager can supervise. There are many factors to consider when determining span of control. At lower levels, where work is standardized, it's possible to implement a broad span of control. The number gradually narrows at higher levels of the organization because work is less standardized and there's more need for face-to-face communication. It's possible to increase the span of control as employees become more professional, as information technology makes it possible for managers to handle more information, and as employees take on more responsibility for self-management. c) Departmentalization is the dividing of organizational functions into separate units. This can be done in a number of ways. The traditional way to departmentalize organizations is by function. Functional structure is the grouping of workers into departments based on similar skills, expertise, or resource use. Thus, a functional organization divides the organization into departments such as accounting, finance, personnel, production, and marketing. Such an approach has several advantages: (1) employees can develop skills in depth and can progress within a department as they master those skills; (2) the company can achieve economies of scale in that it can centralize all the resources it needs and locate various experts in that area; (3) there is good coordination within the function, and top management can easily direct and control various departments' activities. However, the functional approach also has its drawbacks. For example, it can result in a lack of communication and coordination among functions; result in individuals identifying more with their departments than with the overall organization; make the organization less responsive to change; result in an organization of narrow specialists, and encourage people in the same department to engage in groupthink. Thus, firms have found that other approaches to departmentalization may be better. These alternative approaches include departmentalization by customer group, by geographic region, by product, or by process. d) Centralized authority occurs when decision-making authority is maintained at the top level of management at the company's headquarters. Decentralized authority means that decision making is delegated to lower-level managers and employees who are more familiar with local conditions than headquarters' management could be. The centralized approach may enable a firm to achieve more consistency and project a uniform image, but the decentralized approach gives a firm more flexibility to respond to customers. The trend today is toward more decentralized organizations. 377. (p. 221-222) Explain the difference between a firm's formal organization and its informal organization. Why are both types of organization important to managers? a) A firm's formal organization is the structure that details lines of responsibility, authority, and position. It is the structure illustrated by the firm's organization chart. b) A firm's informal organization is the system of relationships that develop spontaneously as employees meet and form power centers. This is the human side of the organization that does not show up on an organization chart. c) Effective managers use both types of organization, but in different ways. The formal organization provides useful guidelines for routine decision making, and the framework needed for careful, reasoned decision making on critical matters. The informal organization creates camaraderie, encourages teamwork among employees, and can be used to generate creative solutions to short term problems. Effective managers make an effort to identify employees who are important members of the informal organization because their status and influence with other employees can help managers cut through red tape and get things done more quickly. Mini-Case Angelica Canizales is the CEO of Mucho Dinero Enterprises. Sales have declined for four consecutive years and the firm's accountants have reported net losses in each of the last two years. Employees appear demoralized and frustrated. Recently, Angelica met with managers from marketing, production, and finance to listen to their views regarding the company's problems. The managers unanimously agreed that the main problem was a lack of communication between the several functional areas of the business. Each manager felt that the firm could increase quality and customer satisfaction with better interdepartmental communication. Angelica also met with marketing and production employees to get their respective opinions on the problems of the firm. One employee from the production department observed that, "We have so many layers of management that it takes forever to make decisions." An employee from marketing complained that, "This place is so bogged down with rules and regulations that there is no opportunity to be creative." Several employees shared their opinions regarding their bosses. Specifically, one employee expressed "My boss never pays attention to my ideas. He just issues orders and expects me to obey them." Angelica decided, after listening to many comments from employees, suppliers, and customers, that the only way to end Mucho Dinero's slide was to completely rethink the firm's structure and to make radical changes in its organization. She presented her ideas to the board of directors, promising to voluntarily resign if her efforts to reorganize did not return the firm to profitability. 378. (p. 206) Employee complaints that there are too many layers of management and too many rules and regulations suggest that Mucho Dinero is a(n): A. flat organization. B. bureaucratic organization. C. inverted organization. D. wide organization. A bureaucratic organization is characterized by many layers of management and reliance on rules and regulations to guide behavior. 379. (p. 219) Angelica's decision to completely redesign Mucho Dinero's organization indicates that she believes the best approach to her firm's problems is: A. competitive benchmarking. B. flexible departmentalization. C. restructuring. D. organizational therapy. Restructuring is redesigning an organization so that it can more effectively and efficiently serve its customers. 380. (p. 210) Currently, Mucho Dinero is organized into specialized departments such as marketing, finance, production and personnel. These departments are designed to allow people with similar skills and expertise to work together. This approach is known as ___________ departmentalization. A. functional B. process C. interest group D. task-oriented Functional departmentalization groups workers into departments based on similar skills, expertise, or resource use. 381. (p. 216) In order to encourage more interdepartmental communication and cooperation, Angelica is thinking about setting up groups of workers from different departments to work together on a long-term basis. She is even thinking about asking people from some of Mucho Dinero's suppliers, customers and distributors to join these groups. The type of group that Angelica is considering is known as a(n): A. focus group. B. dynamic group. C. matrix team. D. cross-functional team. A cross-functional team consists of workers from different departments within an organization who work together on a semi-permanent basis. These teams can also include people representing the organization's suppliers, distributors, and customers. #381 382. (p. 221) From her discussions with employees, Angelica learned quickly that production workers put their trust in 20-year veteran Willie McClaren. Many people told her that if you wanted something done, Willie was the person to see. Willie appears to be an important part of the: A. decentralized authority. B. span of control. C. informal organization. D. functional structure. [Show More]
Last updated: 2 days ago
Preview 1 out of 217 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Recommended For You
Business> QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > CLM 031 EXAM (All)

CLM 031 EXAM
CLM 031 = 100% Question 1: 5b Select the statement that is correct concerning performance work statement (PWS) requirements: - All answers are correct. - PWS should describe requirements necessary...
By Book Worm, Certified , Uploaded: Nov 03, 2022
$5
*NURSING> QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > PHIL 347 Week 6 Checkpoint Quiz. Score 100/100 (All)

PHIL 347 Week 6 Checkpoint Quiz. Score 100/100
Question: What are the three fundamental reasoning strategies listed in the text? Question: What is comparative reasoning? On what skill is it based? Question: We learned four tests for evaluating...
By Amanda Rosales , Uploaded: Mar 24, 2021
$7
Anthropology> QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > KOR 352 FA19 101 week 8 Quiz. Already Graded A (All)

KOR 352 FA19 101 week 8 Quiz. Already Graded A
KOR 352 FA19 101: Week 8 Quiz Question 1 (0.25 points) Which of the following is not true of Kim and Finch’s observations during their field research in South Korea from 1997 to 2000? Question 1 o...
By Kirsch , Uploaded: Oct 17, 2019
$9
E-Commerce> QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > ESOC 316 Digital Commerce - University Of Arizona. Midterm Quiz. 20 Q&A. 100% Score (All)
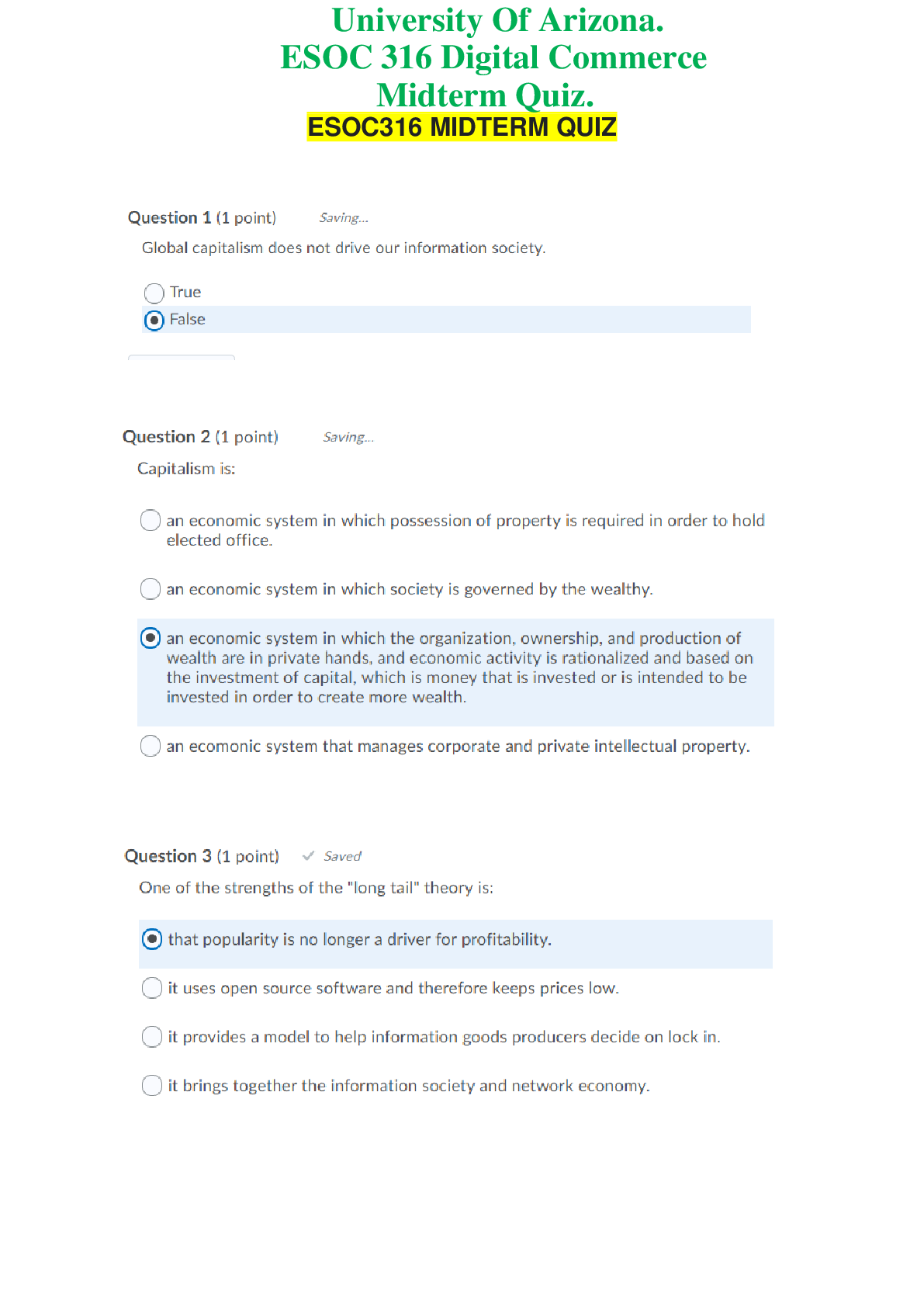
ESOC 316 Digital Commerce - University Of Arizona. Midterm Quiz. 20 Q&A. 100% Score
ESOC 316 Digital Commerce - University Of Arizona. Midterm Quiz. 20 Q&A. 100% Score ESOC316 MIDTERM QUIZQuestion 6 (1 point) Saved Information has several properties that make information goods...
By Kirsch , Uploaded: Oct 15, 2019
$9.5
Marketing> QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Marketing Management Chapter 2 to Chapter 10 Q&A (All)

Marketing Management Chapter 2 to Chapter 10 Q&A
Chapter 2 to Chapter 10 Chapter 2: Developing Marketing Strategies and Plans GENERAL CONCEPT QUESTIONS Multiple Choice 66 Chapter 1: Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships...
By Kirsch , Uploaded: Oct 14, 2019
$10
Marketing> QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > MKT 530 Customer Relationship Management. 155 Questions and Answers (All)

MKT 530 Customer Relationship Management. 155 Questions and Answers
MKT 530 All Questions and Answers MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) As the manager of an organization that is att...
By Kirsch , Uploaded: Oct 14, 2019
$10
Art> QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > MAS 337 Exam 1. Graded A (All)

MAS 337 Exam 1. Graded A
MAS 337 Exam 1 Match the son with its corresponding region. 1.Oaxaca 2.Veracruz 3.Michoacan 4.Jalisco 5.Hidalgo 1. Son istemeno 2. Son Jarocho 3. Son Abajeno 4. Son Jalisciense 5. Son Huast...
By Kirsch , Uploaded: Oct 14, 2019
$6
Art> QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > MUS 337 Final Exam Graded 100%. (All)

MUS 337 Final Exam Graded 100%.
MUS 337 Final Daisy Moreno-Cota Fri Dec 11 12:59:42 PST 2015 Tone or aural color Volume and articulation of sounds Frequency of the tone Phonic structure or relationships between the sounds Dura...
By Kirsch , Uploaded: Oct 12, 2019
$9
Art> QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > MUS 337 Final. Graded 100%. (All)

MUS 337 Final. Graded 100%.
MUS 337 Final Daisy Moreno-Cota Fri Dec 11 12:59:42 PST 2015 Tone or aural color Volume and articulation of sounds Frequency of the tone Phonic structure or relationships between the sounds Dura...
By Kirsch , Uploaded: Oct 12, 2019
$9
Art> QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > LAS MAS MUS 337 FA19 001Quiz #5. Graded A (All)

LAS MAS MUS 337 FA19 001Quiz #5. Graded A
Question 1 (4 points) Saved Match the mariachi musician to the appropriate description. Question 1 options: José Hernández Natividad "Nati" Cano Laura Sobrino Rebecca Gonzales...
By Kirsch , Uploaded: Oct 12, 2019
$9
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Oct 19, 2019
Number of pages
217
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Oct 19, 2019
Downloads
0
Views
468






