Business > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Chapter 10 Motivating Employees Questions and Answers | ALL ANSWERS CORRECT (All)
Chapter 10 Motivating Employees Questions and Answers | ALL ANSWERS CORRECT
Document Content and Description Below
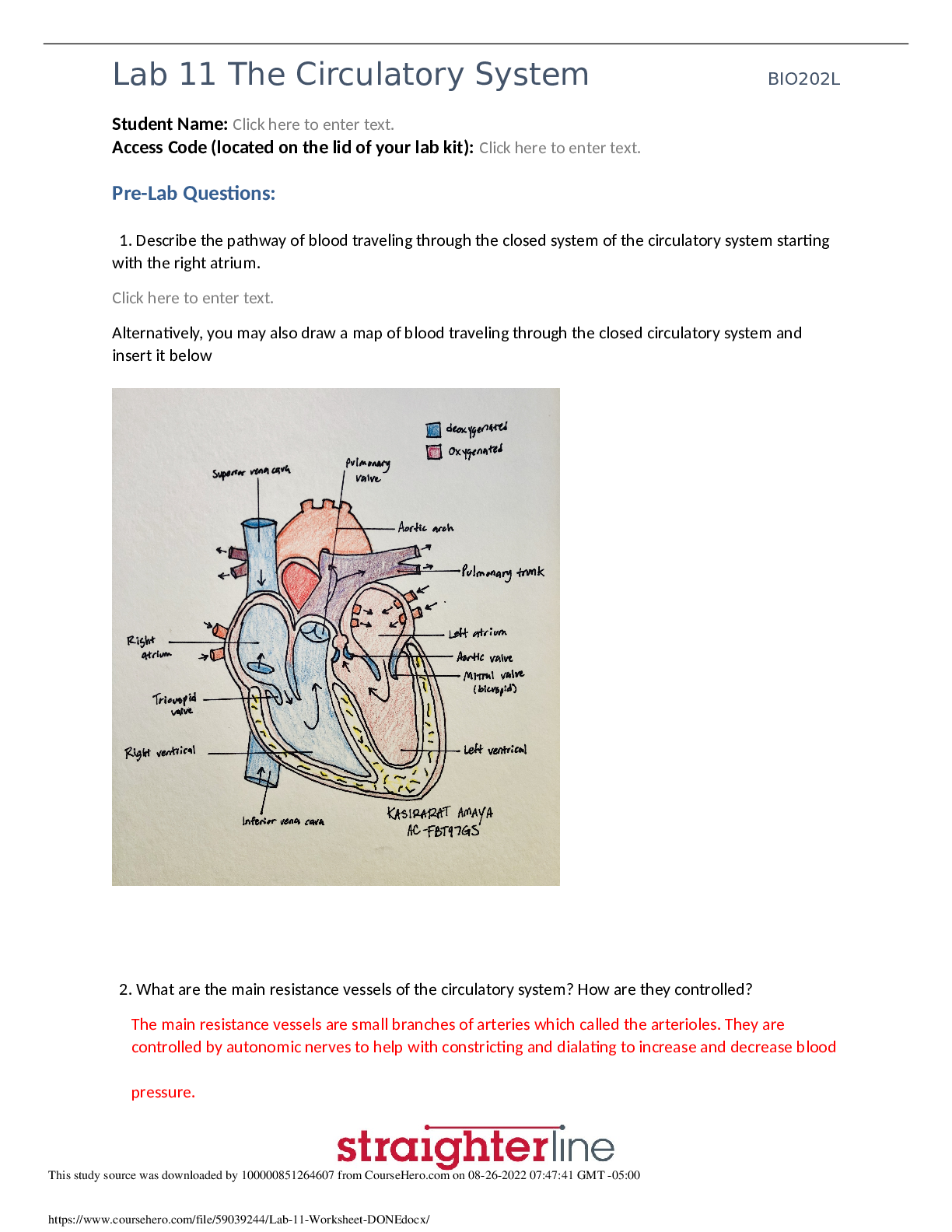
Chapter 10 Motivating Employees 1. The sense of satisfaction you get when you achieve an important goal is an intrinsic reward. True False 2. Extrinsic rewards are those that are given to a person ... by someone else. True False 3. Motivation is the drive to satisfy a need. True False 4. Since motivation comes from within an individual, there is little that managers can do to help motivate employees. True False 5. When unhappy employees leave a company, the firm normally ends up benefiting financially. True False 6. Frederick Taylor's goal was to find ways to improve worker motivation by making work more interesting and challenging. True False 7. A key element of Frederick Taylor's approach was the time-motion study, which examined the tasks performed to complete a job and the time needed to complete each task. True False 8. Frederick Taylor based his approach on the belief that each worker was an individual who should be treated as a unique asset to the firm. True False 1 9. Scientific management became the dominant strategy for improving productivity during the early 1900s. True False 10. Elton Mayo conducted studies know as the Hawthorne Studies and became known as the father of scientific management. True False 11. Frederick Taylor believed that employees would be more productive if they were allowed to decide for themselves which methods at work to use. True False 12. Three elements were basic to Taylor's approach: time, methods, and rules of work. True False 13. According to the "Legal Briefcase" box in Chapter 10, scientific management is used successfully at UPS and UPS drivers have good wages and generous benefits. True False 14. Frank and Lillian Gilbreth developed the principle of motion economy, which said that every job could be broken down into a series of elementary motions. True False 15. Frederick Taylor's ideas about improving worker productivity attracted a lot of attention at the time, but had little lasting significance. True False 16. The concept engagement is used to describe the level of passion and motivation that a person has about their work. True False 2 17. Frederick Taylor encouraged managers to make use of psychological techniques to improve worker motivation. True False 18. According to the Legal Briefcase, "Upset at UPS", companies that employ the principles of Scientific Management usually avoid costly lawsuits from unhappy employees. True False 19. According to the Legal Briefcase, "Upset at UPS", companies are still transitioning from past practices of using scientific management principles when managing employees. UPS is hiring "thinking" workers who can make a variety of workplace decisions themselves and are less tolerant of companies that place rigid rules and physical requirements on employees. In the past, occupational safety issues have cost the company millions. True False 20. Frederick Taylor believed that workers existed to make management's job easier and more efficient. He believed that workers were interested in one thing: good pay. If a business provided good pay, workers would provide the grueling labor necessary to get the job done. True False 21. Janis works for a local bakery. At one time, she loved the idea of becoming a head pastry chef, but now she is not sure that this is how she would like to spend her working career. Her current supervisor does not believe in breaks. And, lately, he stands next to her and instructs her as to how to roll out the bread dough and ice the cupcakes, as though she never learned these basic skills in culinary school. Just this morning, he commented loudly from the other side of the room, "You should be able to ice five cupcakes in a minute! Time yourself!" Frederick Taylor would have approved of Janis' supervisor. True False 22. Mark successfully completed a very challenging assignment given to him by his supervisor at work. The feeling of accomplishment and satisfaction Mark experiences is an example of an extrinsic reward. True False 3 23. The Green Velvet Lawn Care Company teaches all of its employees specific methods for fertilizing and seeding lawns. The methods are designed to ensure adequate lawn coverage with a minimum of time and effort. All employees are expected to follow these methods precisely. Green Velvet's approach to lawn care is consistent with the ideas of scientific management. True False 24. Andy is a supervisor at a web design company. Andy has observed that most employees he supervises are more productive if he lets them have some freedom and flexibility in how they go about their work. Andy's experience is consistent with the teachings of scientific management. True False 25. One of the original objectives of the Hawthorne studies was to determine the degree of lighting needed in the workplace to enable employees to achieve optimum productivity. True False 26. The original results of the Hawthorne studies proved that employees were much more productive when they worked in well-lit areas than when they worked in poorly lit areas. True False 27. A major conclusion of the Hawthorne studies was that the best way to motivate employees is with monetary incentives such as pay raises and bonuses. True False 28. The tendency of employees to behave differently when they know they are being studied is known as the Taylor effect. True False 29. The results of the Hawthorne studies encouraged researchers to begin studying human motivation and managerial styles that lead to higher productivity. True False 4 30. Elton Mayo's researchers concluded that worker motivation improved when managers listened to worker's ideas and suggestions. True False 31. The Hawthorne studies proved that the methods of scientific management were the best way to achieve maximum productivity among employees. True False 32. The Hawthorne studies conclude that intrinsic rewards are always better than extrinsic rewards. True False 33. The Hawthorne studies concluded that productivity at work seldom changed, but an employee's attitude could show significant improvement if he/she were given the opportunity to think critically at work. True False 34. Although Elton Mayo originally intended to collect data for a traditional scientific management study, his break-through research led to further research on the kinds of things that drive employees to successfully meet and exceed productivity goals at work. True False 35. Harrison is a manager at the local post office. He wants to find ways to improve worker motivation, and has read about the Hawthorne studies conducted by Elton Mayo and his colleagues. He believes these studies offer important insights into what motivates employees. Harrison is not likely to support the methods and ideas associated with scientific management. True False 36. Bianca is conducting an experiment to determine how temperatures affect the productivity of employees. She has just completed the first phase of her experiment, in which she had a group of employees perform job related tasks in a special room where the temperature was 10 degrees cooler than on the factory floor. The employees in the experimental group consistently outperformed employees in the factory. The Hawthorne effect suggests that the most likely reason for this improvement in performance is that the cooler working conditions allowed the employees in the experiment to work harder without getting tired. True False 5 37. Greg is a small business owner who wants to find a way to increase the productivity of his employees. He has just finished reading a book on worker motivation, and found the book's discussion of the Hawthorne studies particularly relevant. Based on his reading, Greg is likely to view pay increases as the best way to improve employee motivation. True False 38. Marissa works for a large pharmaceutical company in the greater Chicago area. Last week she visited with an advisor at the nearby university because her employer encourages workers to continue their education and gives them time off to go to academic related appointments, even during regularly scheduled work hours. One would assume that management at Marissa's company values the results of the Hawthorne studies, more so than traditional scientific management principles. True False 39. Abraham Maslow believed that motivation arises from the desire to satisfy unmet needs. True False 40. According to Maslow, it is impossible to rank human needs in any logical order. True False 41. According to Maslow, people will try to satisfy lower order needs before they turn their attention to higher order needs. True False 42. Safety needs are placed at the lowest level in Maslow's hierarchy of needs. True False 43. Maslow referred to the needs people had for recognition and acknowledgement from others as esteem needs. True False 44. According to Maslow, a satisfied need is no longer a motivator. True False 6 45. In Maslow's hierarchy, self-actualization needs are those needs associated with basic survival, such as the need for food and shelter. True False 46. In Maslow's view, social needs include the need to feel loved and accepted. True False 47. Maslow believed that lower-level needs may emerge at any time when they are not met and take our attention away from higher-level needs. True False 48. In order to motivate their employees, managers in less-developed nations should establish working conditions that focus on meeting their employees' self-actualization needs. True False 49. Referring to Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs Theory, one would agree that U.S. workers are more often interested in satisfying their physiological and safety needs, as opposed to their self-esteem needs. True False 50. According to Maslow, if you have a self-esteem problem, you probably will not be able to concern yourself with developing to your fullest potential. True False 51. Often times, we hear that teenagers have unmet social needs. According to Maslow, their desire to become socially accepted will consume them, at the expense of reaching for higher goals, such as developing to their fullest potential. True False 52. Jimmy is a talented musician, and has already won a number of awards. Still, he practices about two hours every day, trying to reach his highest potential. Jimmy is motivated by self-actualization needs. True False 7 53. Millie recently accepted a new job with better pay and a high degree of job security. She is now able to live in a nicer apartment and maintain a fairly comfortable life style. However, she still feels like an "outsider" at work, and does not yet perceive that her fellow employees have accepted her into their group. According to Maslow's theory, Millie is driven by a desire to satisfy her social needs. True False 54. Jon earns a decent salary and is on friendly terms with the other employees in his department. Lately, he is frustrated because his doesn't recognize or appreciate some of his accomplishments. According to Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory, Jon will have a desire to satisfy his self-esteem needs before his self-actualization needs. True False 55. The late famous broadcast journalist Walter Cronkite said that one of his regrets in life was not actively participating in the space program as an astronaut. Back in the 1980's, he was selected as a candidate to be the first journalist to fly into space, but NASA decided to take a teacher instead. In some ways, this may appear as though Cronkite was pursuing a self-esteem need; however, having already achieved celebrity status, for Cronkite, his was the pursuit of a self-actualization need. True False 56. Talk about "shell-shock"! Two nights ago, Adam was living in a tent with thirty other Marines in the hills of Afghanistan. Today he is waking up to the smell of fresh linen, in a king-sized bed, in his very own room in DeKalb, Illinois. Three days ago, his first priority was the welfare of his battle buddies. This morning, his first priority (according to his family) is not wasting anytime and getting back into College. Although he has always believed in the importance of school and the respect that comes with achieving a degree, right now he is not quite in the frame of mind. His first desire is to spend time renewing old friendships, including organizing a couple of float trips and ball game nights with the group of friends he left behind. According to Maslow's hierarchy of needs, Adam has a strong desire to satisfy his self-esteem needs. True False 57. Herzberg's research focused on determining which management style achieved the highest level of worker motivation. True False 58. Herzberg's research examined how conditions related to the job itself affected the motivation of employees. True False 8 59. Herzberg's study showed that pay was the job characteristic that ranked highest as a motivator. True False 60. Herzberg found that the factors associated with job content ranked high as employee motivators. True False 61. Herzberg found that the sense of achievement employees experienced when they performed their jobs was an important motivator. True False 62. Herzberg used the term hygiene factor to refer to an element of job content that was most important as a source of worker motivation. True False 63. According to Herzberg, when a hygiene factor is not fulfilled, employees will become dissatisfied. True False 64. Herzberg's research found that improvements in the work environment were a more effective way to motivate employees than improvements in job content. True False 65. Maslow identified and categorized basic needs that most persons would like to satisfy, while Herzberg's research identified motivators and hygiene factors that inspire employees to fulfill their needs. True False 66. Herzberg's research identified the key factors that motivate workers, including company policies and administration, wage rates, interpersonal relations with co-workers, and physical environment at work. True False 9 67. Herzberg's findings suggest that the best way for firms to increase worker motivation is to focus on improving pay and making working conditions more pleasant. True False 68. Since hygiene factors do not motivate workers toward high achievement at work, managers can safely ignore these factors when trying to develop an effective work environment. True False 69. Herzberg's findings suggest that many U.S. firms can help workers satisfy higher order needs by identifying those things that motivate (inspire) them to work at their fullest potential. True False 70. Douglas McGregor observed that all managers tend to share common assumptions about employees. True False 71. According to McGregor, Theory X managers assume that employees dislike work, and will avoid it if possible. True False 72. According to McGregor, Theory X-type managers motivate employees by giving them a great deal of freedom and responsibility. True False 73. Managers who make Theory X assumptions about employees tend to watch their subordinates very closely and provide detailed instructions to employees about how they should do their jobs. True False 74. Theory X management has essentially disappeared from the real world workplace. True False 10 75. Theory Y managers assume that most people are capable of using a relatively high degree of imagination and creativity to solve problems. True False 76. Theory Y managers assume that the main factor that motivates most employees is the desire to earn more money. True False 77. Theory Y managers are likely to use empowerment to motivate employees. True False 78. The trend in many U.S. businesses is toward a Theory Y approach to management. True False 79. Theory Y managers adhere to the principle that most people do not work to their fullest intellectual potential. True False 80. According to William Ouchi, two of the main features of the Japanese approach to management are individual decision-making and rapid promotions. True False 81. William Ouchi concluded that culture should not be a factor in one's management style. True False 82. Ouchi's Theory Z is a blend of Type A and Type J business cultures. True False 83. Theory Z calls for the creation of a sense of participation and cooperation within an organization. True False 11 84. Theory Z emphasizes reliance on individual creativity and initiative rather than collective decision-making. True False 85. Recent economic problems as well as demographic and social changes in Japan have led some Japanese firms to seek new approaches to management. True False 86. In the view of William Ouchi, managers of U.S. firms would have a smooth transition when implementing the management styles employed by Type J managers. True False 87. The best way for U.S. firms to become more competitive is to adopt the Type J approach to management. True False 88. Recent economic events and demographic trends in Japan have clearly demonstrated the superiority of a Type J approach to management. True False 89. The goal of William Ouchi was to develop a modified business culture that blends the best of Type J with the best of Type A. True False 90. Alan tries to make life easy on his employees by telling them exactly what to do and how to do it. He believes that most of his subordinates are lazy, and will goof off if he doesn't keep an eye on them, so he spends much of his time monitoring their work. When he finds an employee who is not performing up to his expectations, Alan uses threats and punishment to increase the worker's motivation. Alan is a Theory X-type manager. True False 12 91. Jerry has a great deal of faith in the abilities of his subordinates. He believes that most employees want to be productive, and will work hard if given the proper incentives. He also believes that most firms do not take full advantage of the intelligence and creativity of their employees. For these reasons Jerry favors a managerial style that allows employees to be flexible and creative in how they do their jobs, and empowers them to make and implement decisions. Jerry is a Theory Y-type manager. True False 92. Jenny is a creative and intelligent person who likes to work independently on challenging projects. Jenny would be most effective when working for a Theory X-type manager. True False 93. Marita is a very talented and ambitious person who likes to work independently and wants to move up in her company as quickly as possible. Marita may become frustrated if she worked in a firm that took a Theory Z approach to management. True False 94. Hillary enjoys working with others to solve problems and make decisions, but is also able to assume individual responsibility. She prefers working for a company that takes a holistic view of its employees. These preferences suggest that Hillary might enjoy working at a company that uses a Theory Z approach to management. True False 95. After a 3-year probationary period, career positions at Fairview Community College are fairly secure, even though the opportunity for promotion runs at a snail's pace (pretty slow). These jobs would probably appeal to people who currently work for Type A companies - similar to the way many companies operate in Silicon Valley. True False 96. Peter Drucker made an important distinction when he stated that managers do not motivate employees, but employees motivate themselves. True False 13 97. Management by Objectives (MBO) is a goal setting theory model that sets goals by getting all employees active in the goal formulation process, committing employees to meeting the goals, and then monitoring performance. True False 98. The central idea behind MBO (Management by Objectives) is that employees motivate themselves through the process toward goal achievement. True False 99. The Management by Objectives model devised by Peter Drucker works best in a dynamic, rapidly changing business environment, where management makes short-term plans. True False 100. It may be difficult to utilize the MBO (Management by Objectives) model when employees have not agreed upon the goals set by top management. True False 101. According to Victor Vroom, the effort employees exert on a specific task depends on their expectations of the outcome. True False 102. According to Victor Vroom's expectancy theory, expectations of employees can affect their motivation. True False 103. Vroom's expectancy theory contends that prior to committing maximum effort to a task, employees want to know if they can accomplish the task and if it will equally reward everyone at work, even if others were not involved in the accomplishment of the task. True False 104. According to expectancy theory, one of the things employees want to know before they commit to making a maximum effort on a task is whether the reward for accomplishing the task is worth the effort. True False 14 105. Expectancy theory says that employees will be motivated if: 1) They can actually achieve the task; 2) they will be rewarded for their achievement; 3) the reward will be worthy of their effort. True False 106. According to researchers David Nadler and Edward Lawler, managers should set performance standards that are attainable only by the most talented and dedicated employees. True False 107. According to expectancy theory, employees in a given organization tend to have very similar expectations. True False 108. Reinforcement theory suggests that employees respond to carrots (rewards) but not to sticks (punishment). True False 109. According to reinforcement theory, individuals act to receive rewards and to avoid punishment. True False 110. In reinforcement theory, reprimands and reductions in pay are examples of negative reinforcements. True False 111. The basic principle of equity theory is that employees try to maintain fairness between their efforts and their compensation compared to others in similar positions. True False 112. Equity theory tells us that when employees perceive inequitable treatment they will respond in a manner that will attempt to reestablish fairness. True False 15 113. According to equity theory, if employees perceive that their level of effort is greater than their compensation, they will work to increase their productivity. True False 114. Equity theory suggests that if employees perceive inequity in the workplace, they might respond with reduced productivity, higher absenteeism, or even voluntary resignation. True False 115. Equity judgments are precise, objective measurements of the fairness between an employee's effort and their compensation. True False 116. The best strategy to deal with a perceived inequity in the compensation of different employees is to require that salaries and other forms of compensation are kept secret. True False 117. For management by objectives to be successful, employees must be willing to accept the objectives set by top management without question and without hesitation. True False 118. A major problem with the MBO approach is that it provides no way for employees to provide input into the goal-setting process. True False 119. According to expectancy theory, worker motivation almost always increases when employees are assigned a very challenging task. True False 120. U.S. workers value being treated fairly. According to equity theory, if things seem unfair, they will either do their best to make them equitable either by withholding effort, increasing effort, or by rationalizing that they are undeserving of the same as others. True False 16 121. In reinforcement theory, extinction refers to a strategy of responding to undesirable behavior with negative reinforcements, such as verbally reprimanding an employee in front of his peers. True False 122. Elias is disappointed with the work effort of the employees in his department. According to expectancy theory, Elias could improve employee performance by setting more ambitious performance standards that exceed the ability of most employees to attain them. True False 123. Cedric works for a landscaping business. His employer has asked Cedric if he would be willing to work overtime this weekend to finish a job for an important client. According to expectancy theory, Cedric will want to compare the compensation or other rewards offered by his employer to the extra effort involved before he decides whether to agree to the job. True False 124. Ruth Eday is sorry she ever hired Helen Highwater since Helen's work is sloppy and often late. Moreover, she doesn't get along well with most of the other employees and frequently initiates arguments. According to reinforcement theory, the only effective way for Ruth to deal with Helen's behavior is to wait for Helen to do something good, and then praise and reward her for the result. True False 125. You get a lower grade in a course than your friend did even though you studied more during the semester and attended class more often. As a result, equity theory predicts that you might convince yourself that "Grades aren't all that important. After all, lots of people who succeed in the real world didn't make good grades in school." True False 126. Jill operates her own small business and is a strong advocate of equity theory. Because of her acceptance of this theory, Jill is likely to try to assure employees that they are compensated in a way that reflects their efforts and contributions relative to those of other employees. True False 17 127. As a human resources manager for your company, you are looking for ways to motivate employees to favor your company over competitors. The company cannot afford to offer a wide array of benefits, but you are confident that if you survey employees and provide them the opportunity to vote on the benefits that are most important to them, they will see this as a fair and equitable way to operate. True False 128. LivWell Biotechnology Company has four locations in the metropolitan area where you live. You work as a marketing specialist at the oldest and southern most location. Your colleagues at three other locations get ½ hour off each day to work out because there are work out facilities at each of their locations. You know that you make a little more than they do, but after measuring the cost of stopping off at the local physical fitness center on your way home each evening, you realize that your extra compensation would not cover the cost of a gym membership. You are keeping tabs on marketing positions that may open at the other locations. Although you enjoy the people that you work with at LivWell's southern location, you would agree that you are using equity theory, to bring a sense of fairness to what you perceive as an inequity. True False 129. You are a graduate student in the Biology department at Fair University. You have several graduate student friends who have graduate appointments in the business department and the English department. While everyone's compensation and employee benefits are exactly the same, your department requires you to always show-up and tutor students at least four hours each day and to serve on one university committee each semester. Graduates students at the other departments are not required by their management to follow these rules. Lately, you are doing your best to limit your daily obligation to 2 ½ to 3 hours each day. Relating your situation to one of the theories we have studied, your goal of limiting inputs is explained by expectancy theory. True False 130. As the marketing director for Chipper's Golf Resort, you are making plans for the annual golf tournament, and trying to decide on the amount for the top three prizes. In past years, you successfully raised $25,000 through registration fees and sponsorship. You know that you could easily attract some great local talent if you make the top prize $10,000; but, can you afford to announce a $10,000 top prize at the expense of losing out on a portion of the registration fee when others decide not to participate? Using expectancy theory rationale that you learned in business class, you explain to the general manager that if you set the prize too high, several better than average golfers in the area will find their chances to be "out of their league" and will be unmotivated to participate or spend the money. Your analysis of the situation is reasonable. True False 18 131. As the marketing manager for Chipper's Golf Resort, you hired interns from the local university to go out and sell your annual golf event. You provided each of three interns with their own list of past sponsors, participants, and prize contributors. You also asked each to create a marketing plan to secure five new sponsors in the next four weeks, and promised them a bonus at the end of the fourth week, if they could verify that they followed their own plan, contacted everyone on their list and also developed new sponsors. During the fourth week, you randomly contacted a few sponsors on each of the three lists and quickly learn that one of the interns had slacked-off on the job. As a motivational technique, you prefer to provide positive reinforcement. When you met with each of the three interns, you withheld the bonus from the one that did not do the job and informed him that his internship grade will reflect the fact that he was not motivated to get the job done. True False 132. Based on Herzberg's theory of motivators, job enrichment will motivate employees to satisfy higher order needs. True False 133. Job enrichment is based on Herzberg's higher motivators, such as responsibility, achievement, and recognition. True False 134. Job enlargement is about breaking down a sizeable job into smaller parts so that the employee is not overwhelmed by a large task. True False 135. Skill variety is one of the characteristics of work that lead to improved motivation and performance. True False 136. Using job enrichment strategy, management can contribute to improved motivation and worker performance by primarily increasing employee pay. True False 137. Feedback enhances worker motivation by giving employees a feeling of achievement and recognition. True False 19 138. Task identity refers to the degree to which a job has a substantial impact on the lives or work of others in the company. True False 139. Job simplification attempts to increase task efficiency by breaking the job into simple steps and assigning people to perform each of those steps. True False 140. Job simplification is an effective strategy for managers who want to achieve job enrichment. True False 141. Job enlargement is the strategy of assigning employees to different jobs within the organization on a regular basis. True False 142. Job enlargement attempts to enrich jobs by combining a series of tasks into one challenging and interesting assignment, as opposed to simplifying the job. True False 143. Job rotation attempts to make a job more interesting and motivating by moving employees from one job to another. True False 144. As part of their open communication strategy, management should reward upward communication, even if it is negative. True False 145. Open communication is a verbal strategy. It does not involve listening. True False 20 146. Open communication strategies include the removal of physical barriers such as separate offices. True False 147. As a motivational technique, open communication is enhanced when management provides several opportunities for employees to congregate and share ideas. True False 148. Special parking areas, dining rooms and rest rooms set aside for executives are barriers to open two-way communication within an organization. True False 149. By the time they graduate from high school, most people have received ample training to develop good listening skills. True False 150. At Ford Motor Company, the redesigned 2005 Mustang convertible was completed early and under budget. This can be attributed to reinventing work at Ford. True False 151. To implement self-managed teams, managers at most companies must reinvent work. True False 152. The first step in any motivational program is to establish open communication among employees in order to encourage teamwork and cooperation. True False 153. Two things many firms with highly motivated workforces have in common are open communications and self-managed teams of employees. True False 21 154. Teamwork tends to occur naturally within business organizations regardless of the plans or actions of managers. True False 155. In order to encourage teamwork between and among managers and employees, top management must create an organizational culture that allows autonomy, decentralizes authority, and rewards good work. True False 156. As a motivational technique, letting employees know they've done a good job is not as powerful as providing them with a bonus. True False 157. Progressive managers are rewarding good work in all kinds of ways including family trips, informal events at work, and just letting everyone know when someone does a good job. True False 158. When asked why they change jobs, over 80% of those surveyed said they usually leave one job for another in order to gain more job responsibility and a more senior role. True False 159. Managers who believe job enrichment can effectively improve motivation would try to give employees a significant degree of freedom and flexibility in scheduling their work and in determining the procedures they use. True False 160. The key to achieving task identity is to design jobs that demand the use of many different skills. True False 161. Job simplification is an extension of the ideas of Frederick Herzberg. True False 22 162. Feedback helps enrich a job by satisfying an employee's esteem needs. True False 163. One way for a firm to improve motivation of employees is to establish special rest rooms, dining areas, and parking areas for top executives. True False 164. If managers want to retain their employees, a good strategy may involve mentoring them for more senior roles in the organization and provide opportunities for job advancement. True False 165. As indicated in the Spotlight on Small Business box, "Big Motivators for Small Businesses", it is difficult if not impossible for small businesses to take the time to motivate their employees with open communication and or by providing jobs with broad responsibilities due to the fact that the labor force is usually small and there just isn't time for these kinds of associations. True False 166. According to the Spotlight on Small Business box titled, "Big Motivators for Small Business", small businesses can and do put thought into motivating employees to perform at high levels. The box highlights companies who provide mentoring activities for new employees and other companies who believe that stress release type activities re-energizes employees. True False 167. Fast Track Corporation moves employees from one job to another on a regular basis in order to improve motivation. Fast Track's strategy is job enlargement. True False 168. Management at the local Hottie Potatee, a potato bar with all the fixings is trying to improve task efficiency by breaking down jobs into simple steps and assigning each step to a different worker. The key benefit of this approach is that it is one of the most effective ways to achieve job enrichment. True False 23 169. Ellen supervises several employees in the accounting department of a large corporation. She makes it a priority to give her subordinates direct and clear information about their job performance. Ellen's efforts are likely to improve worker motivation. True False 170. David is the president and chief executive officer of Baxter National Bank. He wants to encourage more open two-way communication among the bank's employees and managers. One of the most important things David can do to achieve this goal is to become a good listener. True False 171. During the first year at the Millennium Company, management trainees spend two months in each of six different departments where they have the opportunity to learn skills in each functional area, but also make decisions about where they have the best match. Job rotation is a motivational strategy used by contemporary organizations. True False 172. According to the Thinking Green box titled, "Green Team Go", open communication successfully filled the company suggestion box with green ideas, but top management has not implemented any of them because they are not behind a sustainability program, claiming it is too costly. True False 173. At Blastoff.com, a web-based auction headquartered in upstate New York, when employees are at the company's main office, they do not expect to necessarily sit at the same desk everyday. They may decide to situate in a projection room; in a temporary soundproof room, or in one of several lounge areas in the building. They may locate next to someone outside of their functional area. Blastoff management believes that breaking down barriers fosters more communication and innovation, and makes jobs more interesting. True False 174. A 25-year employee at a mid-sized company remarked, "I can remember when we were small enough that we had time for water cooler talk! Sometimes I wish we could go back a few years when everyone liked being here. Now, we seem to be more excited about our next raise rather than our next product launch!" According to the Spotlight on Small Business Box, "Big Motivators for Small Business", small businesses seem to be better at motivating employees with open communication and more broad-based responsibilities, where employees exchange ideas and become generalists at what they do. True False 24 175. Brandon's manager often tells his employees "there's isn't a lot of time for chit-chat on the job. If you want to give us your opinion, as a believer in open communication, I'll gladly give you your chance to speak your mind, on your way out!" This manager is up to date on the purpose of the exit interview, as an important source of feedback for companies. Open communication always begins at this juncture. True False 176. Regardless of cultural background, most employees respond the same way to motivational approaches. True False 177. High context cultures tend to jump right in and get work done with worrying about developing close work relationships. True False 178. In a high context culture, relationship building is motivational. True False 179. In a low context culture, employees are less likely to place emphasis on relationship building. They want to jump right in and get the job done. True False 180. Even if there are cultural differences across the globe, reward preferences do not vary across cultures. True False 181. If rewards are an important part of an international firm's motivational strategy, consideration should be given to adjusting it for cultural preferences. True False 182. Most Gen X managers are likely to be flexible and good at collaboration. True False 25 183. Members of Generation X tend to be more independent and need less feedback than members of older generations. True False 184. As a group, Gen Yers tend to be impatient, skeptical and image driven. True False 185. Members of Generation Y tend to be adaptable, tech savvy, and tolerant. True False 186. Gen Xers are difficult to motivate because they lack ambition. True False 187. Gen Xers and Gen Yers will be more tolerant of change than Baby Boomers. True False 188. Motivation is largely the result of external rewards and punishments. True False 189. It is important when dealing with today's culturally diverse workforce that managers maintain a consistent motivational approach for everyone. True False 190. It is unlikely that business professionals from Saudi Arabia will be willing to start conducting business with a U.S. construction company without first trying to establish a relationship more on an interpersonal level. True False 191. When adopting a reward system as part of your international company's motivational strategy, it is not cost effective or beneficial to spend time customizing rewards for each global location. True False 26 192. It is safe to say that Gen Xers have a strong desire for balancing work life and home life due to the fact that many grew-up in environments where family time was jeopardized due to both parents working. True False 193. If you want to understand what motivates Generation X workers, it might be a good idea to study the personal experiences that this group shared - things such as stay at home moms and dads that worked very steady nine to five jobs, with hardly any fear of lay-offs. True False 194. When studying the differences in generations, it is fair to say that many ideas that each group shares resulted from common experiences during the first ten years of life. True False 195. Susan is a baby boomer. She manages an office where most of the employees are in her age group. However, she recently hired Angie, who is a member of Generation X. Susan is likely to find that Angie is more interested in work/life balance than other employees in the office. True False 196. Lisa is a Gen Xer who has just been promoted to a management position. If she is like many of her generation, one of Lisa's biggest problems is likely to be her inflexibility and difficulty at working collaboratively with other employees. True False 197. Anthony is putting together an employee group to help add new technology to his company's existing products. He is seeking employees who are comfortable with new technologies, and who are flexible, adaptable, and have a strong sense of commitment to their work. Many of his company's newest and youngest employees probably would meet these criteria. True False 198. Jennifer is an engineer for a large telecommunications company. If the company has after-hours events, Jennifer does not hesitate to take her six-month old baby along. You often hear her say, "If they don't go, I don't go." Jennifer's motivation to add or at least combine work life with family life is probably the result of growing up in an environment where adult family members worked, and work and family life were less balanced. True False 27 199. Blake was asked by his team leader to explore and evaluate the best ways to communicate with customers online. Although Blake is relatively new to the company, and is not well versed on the entire product line, he is a millennial which makes him overall well suited to knowing how people find things in common with others in an online environment. True False 200. The personal satisfaction people feel when they have done a job well is a(n) __________ reward. A. cognitive B. extrinsic C. physiological D. intrinsic 201. Rewards that come from someone else in recognition of good work are _________ rewards. A. conditional B. self-actualized C. extrinsic D. secondary 202. _________________ was the father of scientific management. A. Elton Mayo B. Frank Gilbreth C. Henry Gantt D. Frederick Tayl [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 224 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 10, 2021
Number of pages
224
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 10, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
233





.png)
.png)

















.png)

.png)




