Chemistry > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Questions and Answers > University of Illinois, Urbana Champaign - MCB 450 Exam 3 SP14 Key. From Spr (All)
Questions and Answers > University of Illinois, Urbana Champaign - MCB 450 Exam 3 SP14 Key. From Spring 2014. Best For quick exam Prep. 100%.
Document Content and Description Below
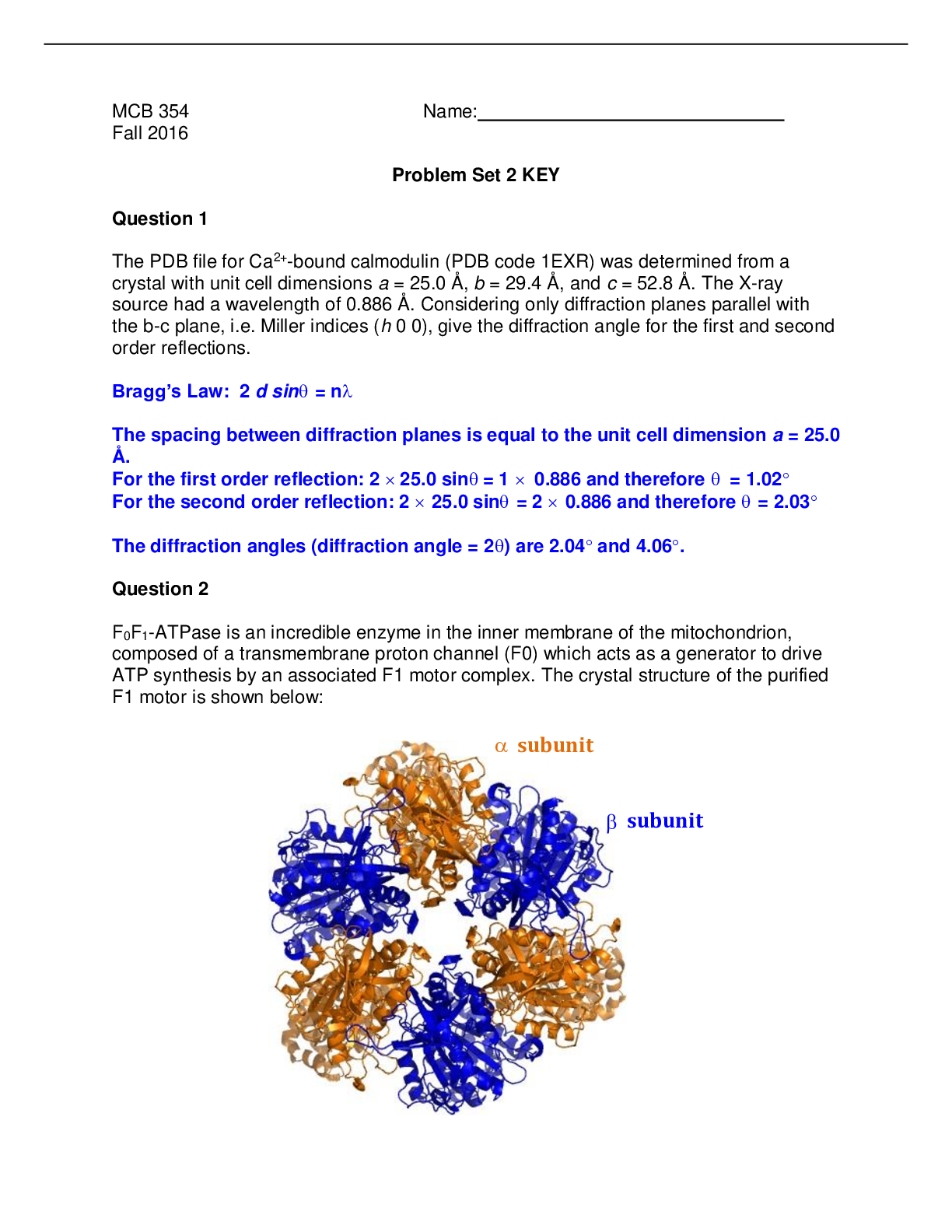
NAME:______________________________ NETWORK ID:___________________ MCB 450 – Spring 2014 Exam III April 10th, 2014 Form A Choose the BEST answer fro... m the available choices. Only non-‐graphing calculators are permitted for use on this exam. Section 1-‐ 34 Multiple-‐choice Questions. Each question is worth 4 points. 1. A metabolic reaction that best serves as a control point for regulation ________. a. is a near equilibrium reaction b. is endergonic c. is thermodynamically irreversible d. follows Michaelis-Menten kinetics e. must be covalently modified 2. Which of the following statements about activated carriers is FALSE: a. Almost all activated carriers are derived from vitamins. b. All activated carriers are covalently associated with an enzyme. c. Many of the steps in metabolism rely on a relatively small number of activated carriers. d. The activated carrier coenzyme A carries acyl groups. e. Activated carriers are kinetically quite stable in the absence of a catalyst. 3. The ultimate product of complete oxidation of carbohydrates is ________.NAME:______________________________ NETWORK ID:___________________ a. carbon dioxide b. acetyl CoA c. pyruvate d. lactate e. oxaloacetate 4. Energy charge is an index that reflects the energy status of the cell. Which of the following statements about energy charge is FALSE? a. It can have a value between 0 and 1 b. It can be assessed by the following formula: [ATP]+½[ADP] [ATP] + [ADP] + [AMP] c. The rates of reactions in energy-consuming pathways are decreased in response to a larger energy charge value. d. It regulates the rates of catabolic pathways. e. It is buffered in the sense that its value is maintained within narrow limits. 5. ATP is thermodynamically suited as a carrier of phosphoryl groups in animal cells because _________. a. it is kinetically unstable under cell conditions b. it is has a small activation energy c. it is intermediate in group-transfer potential d. it is thermodynamically stable under cell conditions e. it can be stored in large quantities 6. What is substrate-level phosphorylation? a. Phosphorylation of AMP by ATP. b. ATP synthesis when the phosphate donor is a substrate with highphosphoryl-transfer potential. c. Phosphorylation of glycolytic intermediates by ATP. d. Phosphorylation of ATP coupled to an ion gradient. e. ATP and AMP synthesis from two molecules of ADP.NAME:______________________________ NETWORK ID:___________________ 7. All of the following decrease the activity of pyruvate kinase EXCEPT: a. High alanine b. cAMP-dependent phosphorylation c. High acetyl-CoA d. High fructose-1,6-bisphosphate e. Glucagon 8. Patients in shock often suffer from lactic acidosis owing to a deficiency of O2. Why does this lack of O2 lead to lactate accumulation? a. A decrease in O2 will necessitate an increase in anaerobic glycolysis to generate sufficient ATP. b. A decrease in O2 will increase the concentration of NAD+, which stimulates the conversion of pyruvate to lactate. c. A decrease in O2 will cause an increase in NAD+, which can act as a positive effector for the lactate dehydrogenase enzyme. d. A decrease in O2 will cause increased ATP levels that will inhibit gluconeogenesis in muscles. e. A decrease in O2 will inhibit glycolysis in liver. 9. Phosphofructokinase I (PFK/PFK-1) deficiency results in: a. Fructose 6-phosphate deficiency b. Overproduction of Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate c. Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate deficiency d. Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate deficiency e. Choices b and d are both correct. 10. The conversion of pyruvate to ethanol also causes the ________. a. reduction of NAD+NAME:______________________________ NETWORK ID:___________________ b. production of ATP c. consumption of O2 d. generation of an ion gradient across mitochondrial membranes e. release of CO2 11. There are four isozymes that can catalyze the first step of glycolysis. They are hexokinases I, II and III and glucokinase (hexokinase IV). Hexokinases I, II and III have Km values near 0.1 mM. Glucokinase has a Km range of 6-8 mM. If after a heavy meal the blood glucose level rises to 8 mM which statement will be true? a. At this high blood glucose level all four hexokinases are saturated with substrate. b. Hexokinases I, II and III are catalyzing at their maximum rate, but glucokinase can still respond to increases in blood glucose levels. c. None of the enzymes are saturated. All of them help to increase the rate of glycolysis. d. The rate of glucokinase will be extremely low. The only significant catalysis is done by hexokinases I, II and III. e. Glucokinsase is catalyzing at its maximum rate, but Hexokinases I, II and III can still respond to increases in blood glucose levels. 12. All of the following choices are true regarding the allosteric regulation of phosphofructokinase (PFK/PFK-1) EXCEPT: a. Glucose-6-phosphate acts as an allosteric inhibitor in the muscles. b. Citrate acts as an allosteric inhibitor in the liver. c. Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate acts as an allosteric stimulator in the liver. d. High AMP acts as an allosteric stimulator in muscles. e. Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate alleviates the heterotropic effects of ATP in the liver. 13. The glycolytic pathway oxidizes glucose to two molecules of pyruvate and also produces a net of two molecules of ATP. ATP allosterically inhibits the enzyme, phosphofructokinase (PFK-1), that catalyzes the third step of glycolysis. This is anNAME:______________________________ NETWORK ID:___________________ example of ________. a. feed-forward activation b. feedback inhibition c. negative cooperativity d. competitive inhibition e. homotropic effect 14. High blood sugar level will do all of the following EXCEPT: a. Inhibits gluconeogenesis b. Stimulates glycolysis c. Causes phosphorylation of phosphofructokinase 2 (PFK2) d. Increase the levels of fructose-2,6-bisphosphate (F-2,6-2BP) e. Decrease the binding of cAMP to protein kinase A 15. Glucagon works by activating cAMP-dependent protein kinase (protein kinase A; PKA), which will phosphorylate the glycolytic enzyme ______________and thus ____________this enzyme. a. hexokinase; inhibit b. pyruvate carboxylase; activate c. fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (F-1,6-Bpase); inhibit d. phosphofructokinase (PFK/PFK1); activate e. pyruvate kinase; inhibit 16. Which of the following reactions represents the gluconeogenic reversal of the glycolytic enzyme phosphofructokinase (PFK/PFK1) reaction? a. fructose-6-P + ADP → fructose + ATP b. fructose-6-P + H2O → fructose + Pi c. fructose-1,6-bisphosphate + ADP → fructose-6-P + ATPNAME:______________________________ NETWORK ID:___________________ d. fructose-1,6-bisphosphate + H2O → fructose-6-P + Pi e. fructose-2,6-biphosphate + ADP → fructose-6-P + ATP 17. Which of the following reactions is catalyzed by the enzyme transaldolase as part of the pentose phosphate pathway? a. C5 + C5 ßà C3 + C7 b. C4 + C3 ßà C3 + C5 c. C3 + C7 ßà C6 + C4 d. C5 + C5 ßà C4 + C6 e. C3 + C5 ßà C4 + C4 18. What is the key regulatory enzyme in the pentose phosphate pathway and what is its most prominent regulatory signal? a. transketolase; acetyl CoA b. glutathione reductase; NAD+ c. phosphopentose epimerase; NADH d. 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase; ATP e. glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase; NADPH 19. All of the following are substrates for gluconeogenesis EXCEPT: a. Fatty acids b. Glycerol c. Oxalacetate d. Lactic acid e. AlanineNAME:______________________________ NETWORK ID:___________________ 20. For every molecule of pyruvate dehydrogenase processing one molecule of pyruvate which of the following are true regarding stoichiometric coenzymes? a. One molecule of AcetylCoA and one molecule of FAD are used. b. One molecule of lipoic acid and one molecule TPP are used. c. Two molecules of thiamine and 2 ATPs are used. d. One molecule of HS-CoA and one molecule of NAD+ are used. e. One molecule of AcetylCoA and one molecule of NAD+ are used. 21. An example of an anaplerotic reaction for the citric acid cycle is: a. The condensation of oxacloacetate with acetyl CoA. b. The replenishment of pyruvate from lipid breakdown. c. The replenishment of oxalacetate from lipid breakdown. d. The conversion of pyruvate to oxaloacetate. e. The conversion of oxalacetate to PEP. 22. Which of the following inhibits pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase? a. Pyruvate b. NADH c. Acetyl CoA. d. ATP e. Glucagon 23. Which 5-carbon intermediate of the citric acid cycle is converted to a 4-carbon molecule with the release of carbon dioxide? a. Fumarase b. α-Ketoglutarate c. Succinate d. Isocitrate e. CitrateNAME:______________________________ NETWORK ID:___________________ 24. What are the steps in chronological order involved in the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA? a. Decarboxylation, oxidation, thioester bond formation, transfer to CoA b. Decarboxylation, phosphorylation, transfer to CoA, oxidation c. Thioester bond formation, oxidation, decarboxylation, transfer to CoA d. Oxidation, transfer to CoA, decarboxylation e. Thioester bond formation, decarboxylation, oxidation, transfer to CoA 25. In which reaction is ATP/GTP directly formed in the citric acid cycle? a. Conversion of succinyl CoA to succinate b. Decarboxylation of α-ketoglutarate c. Conversion of isocitrate to α-ketoglutarate d. Reduction of succinate to fumarate e. Oxidation of malate to oxaloacetate 26. Compounds with a large _________ reduction potential have a strong tendency to undergo oxidation, and as such, NADH is a strong ___________ agent. a. positive; oxidizing b. negative; reducing c. negative; oxidizing d. positive; reducing e. cannot be determined from the information given Table to accompany question 27NAME:______________________________ NETWORK ID:___________________ oxidant reductant n E’o(V) α-ketoglutarate isocitrate 2 - 0.380 NAD+ NADH 2 - 0.32 27. The Δξ°′ for the oxidation of isocitrate to α-ketoglutarate catalyzed by the enzyme isocitrate dehydrogenase that uses NAD+ as the coenzyme is: (Refer to table above for half equations and corresponding ξ°′ values) a. –12.8 V b. – 0.06 V c. + 0.06 V d. + 12.8 V e. – 0.7 V 28. Which of the following has the most negative reduction potential? a. NADH b. Complex I c. Complex II d. O2 e. FADH2 29. To reduce one molecule of O2, ________ electron(s) must be passed through the electron transport chain and ________ molecule(s) of NADH is (are) oxidized. a. 4; 2 b. 2; 1 c. 1; 1 d. 1; 2 e. 4; 4NAME:______________________________ NETWORK ID:___________________ 30. Which complex in the electron transport chain does not contribute directly to the proton gradient? a. I b. II c. III d. IV e. Neither, all four complexes contribute to proton gradient 31. Gluconeogenesis takes place during exercise, which seems counterintuitive. Why would an organism synthesize glucose and, at the same time, use glucose to generate energy? a. The increased glycolysis in response to exercise generates ATP, which stimulates gluconeogenesis in muscles. b. The increased glycolysis in muscles generates lactate, which stimulates gluconeogenesis in liver. c. Epinephrine released during exercise stimulates gluconeogenesis in muscle. d. Ca2+ released by contracting muscles stimulates pyruvate carboxylate. e. The increased glycolysis in muscle generates high levels of alanine, which stimulate gluconeogenesis. 32. How many protons need to be translocated across the inner mitochondrial membrane for the synthesis of one molecule of ATP from ADP? a. one proton b. three protons c. hundreds of protons d. 1 mole of protons e. The number of protons required depends on the number of c subunits of the ATP synthaseNAME:______________________________ NETWORK ID:___________________ 33. Heat is generated in brown adipose tissue of hibernating mammals due to ________. a. increased ATP production by ATP synthase b. uncoupling by thermogenin c. upregulation of the malate-shuttle d. insufficient NADH production as a result of a less active pyruvate translocase e. inability of the TCA cycle t to convert the energy released by decarboxylation into NADH 34. In the glycerol phosphate shuttle, reducing equivalents from NADH enter the electron transport system by reactions carrying electrons to ________. a. complex III b. complex IV c. complex II d. complex I e. alpha-ketoglutarate Section 2-‐ 7 Multiple-‐choice Questions. Each questions is worth 2 points. 35. What important high-energy functional group is shown in molecule below? a. Methyl b. KetoneNAME:______________________________ NETWORK ID:___________________ c. Thioester d. Thioanhydride e. Thiosulfate bond 36. Transfer of a high-energy phosphoryl group to ADP, resulting in ATP occurs when ______. a. 2-phosphoglycerate → phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) b. phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) → pyruvate c. 3-phosphoglycerate → 2-phosphoglycerate d. Fructose-6-phosphate → Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate e. Glucose-6-phosphate → Glucose 37. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase converts glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate into 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate. Where does the second phosphate in the product come from? a. NADH b. Pi c. ATP d. ADP e. GTP 38. Which of the following reactions only takes place in the mitochondria? a. The conversion of oxaloacetate to PEP b. The conversion of pyruvate to oxaloacetate c. The conversion of pyruvate to PEP d. The conversion of glucose to pyruvate e. The conversion of malate to oxaloacetate 39. An intermediate found in gluconeogenesis and not glycolysis is? a. 2-phosphoglycerate b. oxaloacetateNAME:______________________________ NETWORK ID:___________________ c. phosphoenolpyruvate d. fructose 1,6-bisphosphate e. 1,3 bisphosphoglycerate 40. What type of reaction is the conversion of succinate to fumarate? a. Oxidative decarboxylation b. Hydration c. Isomerization d. Condensation e. Oxidation-reduction 41. The reduction of H2O2 to H2O generates oxidized glutathione (GS-SG). Which of the following compounds is required for the subsequent reduction of glutathione? a. NADH b. FADH2 c. ATP d. NADP e. Biotin -‐-‐-‐-‐End of Exam -‐-‐-‐-‐ [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 13 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 16, 2021
Number of pages
13
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 16, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
28






















 (2).png)
.png)