Marketing > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Chapter 7—The Role of Persuasion in Integrated Marketing Communications. All Answers (All)
Chapter 7—The Role of Persuasion in Integrated Marketing Communications. All Answers
Document Content and Description Below
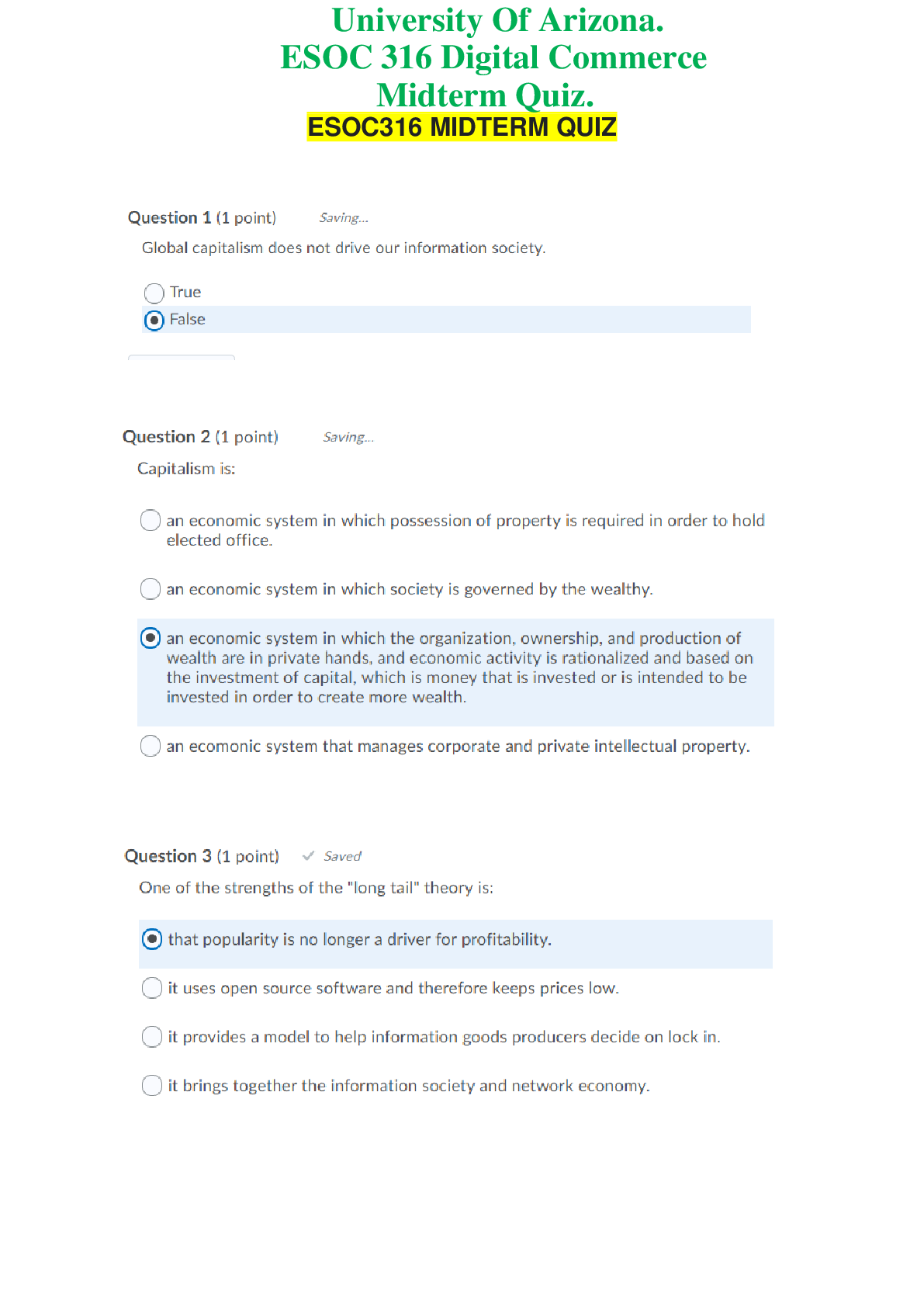
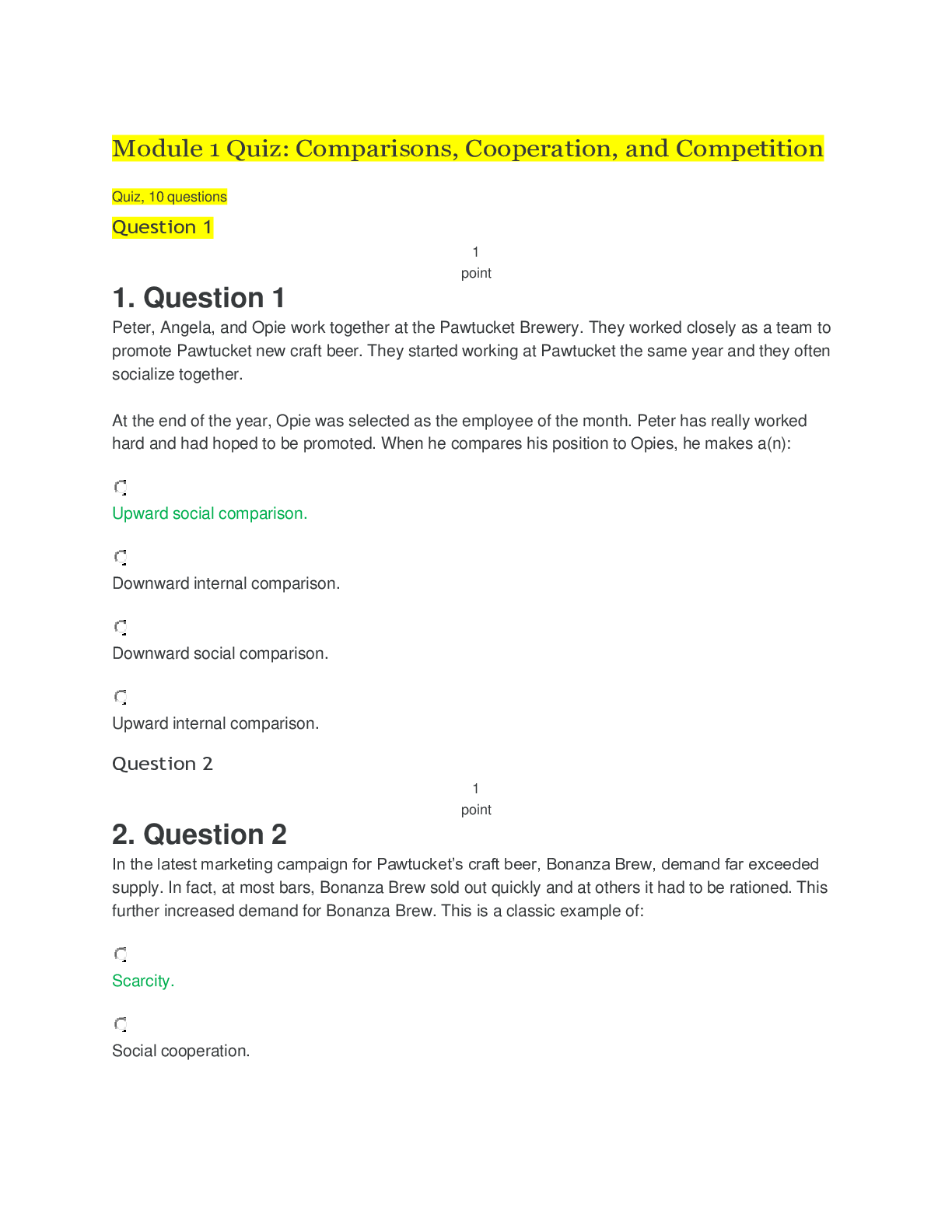
TRUE/FALSE 1. Attitudes are learned. T PTS: 1 2. The effective component of an attitude refers to the evaluative or feeling aspect of an attitude. T PTS: 1 3. The cognitive compone... nt of an attitude represents one's behavioral tendency. F PTS: 1 4. Reciprocation can happen with individual consumers, but not in business-to-business marketing interactions. F PTS: 1 5. Consumers are more likely to adopt an attitude or undertake an action when a likable person promotes that action. T PTS: 1 6. Peripheral cues may play a more important role than message arguments in determining the outcome of a persuasive effort. T PTS: 1 7. The personal relevance that a communication has for a receiver is a critical determinant of the extent and form of persuasion. T PTS: 1 8. Supportive arguments arise when the receiver challenges a message claim. F PTS: 1 9. Counterarguments occur when a receiver agrees with a message argument. F PTS: 1 10. Elaboration involves the matter of whether it is physically possible for a person to process a message. F PTS: 1 11. Motivation is high when a message relates to a person's present goals and needs. T PTS: 1 12. Motivation, opportunity, and attitude determine each person's elaboration likelihood for a particular message. F PTS: 1 13. When elaboration likelihood is high, the receiver will focus predominantly on peripheral cues rather than message arguments. F PTS: 1 14. The theory of reasoned action proposes that all forms of planned and reasoned behavior have two primary determinants: attitudes and normative influences. T PTS: 1 15. Outcomes are the consumer's subjective probability assessments, or expectations, regarding the likelihood that performing a certain act will lead to a certain result. F PTS: 1 16. Beliefs involve those aspects of product ownership that the consumer either desires to obtain or avoid. F PTS: 1 17. The three strategies for changing attitudes include influencing consumers' brand-related beliefs, influencing existing evaluations, and adding an entirely new outcome into how consumers judge brands in a product category. T PTS: 1 18. A television commercial's peripheral cues could be the background music. T PTS: 1 19. In Pavlov's experiment, the meat powder was the conditioned response. F PTS: 1 20. In Pavlov's experiment, the bell was the conditioned stimulus. T PTS: 1 21. Pavlov's experiment utilized operant conditioning. F PTS: 1 22. According to the ELM theory, people experience only temporary attitude changes when persuaded via the peripheral route. T PTS: 1 23. According to the ELM theory, the form of persuasion will depend on the characteristics of the market and the strengths of the marketing communicator's relative market position. T PTS: 1 24. Marketers can enhance consumers' motivation to process brand information by using celebrities in the advertising. F PTS: 1 25. Marketers can enhance consumers' opportunity to encode information by repeating the ad on multiple occasions. T PTS: 1 26. Marketers can enhance the consumers' ability to access knowledge structures by employing verbal framing. T PTS: 1 27. Involuntary attention requires little or no effort on the part of a receiver. T PTS: 1 28. Voluntary attention occurs when a person is attracted to a stimulus and continues to pay attention because it holds his or her interest. F PTS: 1 29. Habituation occurs when a stimulus becomes more familiar to people. T PTS: 1 30. Attitude is a physical property of the consumer. F PTS: 1 31. Persuasion is an effort by a marketing communicator to influence the consumer’s attitude and behavior in a manner that benefits the communicator. T PTS: 1 32. Attitudes are hypothetical constructs. T PTS: 1 33. Attitudes are constantly changing. F PTS: 1 34. The conative component of attitude represents one’s predisposition to act toward an object. T PTS: 1 35. Persuasion is the essence of marketing communications. T PTS: 1 36. Persuasion is the smallest component of marketing communications. F PTS: 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Attitudes _____. a. can be observed b. are inherited c. are relatively enduring d. do not influence behavior e. All of these are correct. C PTS: 1 2. Which of the following statements reflects the effective attitude component? a. Oranges are high in vitamin C. b. I like oranges. c. Oranges are expensive. d. Oranges grow in Florida. e. I often buy oranges. B PTS: 1 3. The effective component of attitudes focuses on _____. a. feelings and evaluations b. beliefs c. knowledge d. behavioral tendencies e. information A PTS: 1 4. Which of the following statements reflects the cognitive attitude component? a. I like playing tennis. b. I enjoy outdoor sports. c. I play tennis three times a week. d. Playing tennis is a form of exercise. e. I do not enjoy playing basketball. D PTS: 1 5. The _____ component of attitudes focuses on behavioral tendencies. a. effective b. instrumental c. conative d. cognitive e. behavioral C PTS: 1 6. Which of the following statements reflects the conative attitude component? a. I enjoy reading. b. Reading improves the mind. c. Everyone should try to improve their reading skills. d. Mysteries are fun to read. e. I plan to purchase three books this week. E PTS: 1 7. The employee's intention to donate or not donate to a charity is best described as the _____ attitude component. a. cognitive b. conative c. instrumental d. effective e. planned B PTS: 1 8. Which tool of influence is being used when a salesperson gives someone a gift with the hope that they will purchase something? a. reciprocation b. commitment and consistency c. social proof d. authority e. scarcity A PTS: 1 9. Which tool of influence is being used when a car salesperson gets a consumer to agree to a price and then says they have to get their sales manager's approval? a. reciprocation b. commitment and consistency c. social proof d. authority e. scarcity B PTS: 1 10. Audrey Thomas-Alexander is asked to make a contribution to United Way. She asks the amount other people are giving and ends up giving that amount. She has used the _____ tool of influence. a. reciprocation b. commitment and consistency c. social proof d. liking e. scarcity C PTS: 1 11. A salesperson is hired because he is the same age as most of the shoppers and is considered handsome. What tool of influence is being used? a. reciprocation b. commitment and consistency c. social proof d. scarcity e. liking E PTS: 1 12. The influence tactic that is based on the principle that things become more desirable when they are in great demand but short supply is known as _____. a. liking b. scarcity c. social proof d. commitment and consistency e. reciprocation B PTS: 1 13. A clothing salesperson is using the _____ tool of influence when she tells a customer that there are only a few scarves left and they are selling fast. a. liking b. scarcity c. commitment and consistency d. social proof e. reciprocation B PTS: 1 14. According to the theory of psychological reactance, _____. a. people react against any efforts to reduce their freedoms of choice b. consumer behavior is seen as emotional c. consumer behavior is seen as highly cognitive d. people satisfy primary needs before acquired needs e. the personal relevance that a communication has for a receiver is a critical determinant of the extent and form of persuasion A PTS: 1 15. Betty Franks agrees with the message in an advertisement for a political candidate. This is an example of _____. a. planned arguments b. policy arguments c. antiarguments d. supportive arguments e. counterarguments D PTS: 1 16. When the receiver challenges a message claim, _____ arise. a. planned arguments b. policy arguments c. antiarguments d. supportive arguments e. counterarguments E PTS: 1 17. Jack Joseph challenges the message claim made in an automobile commercial. This is an example of _____. a. planned arguments b. policy arguments c. antiarguments d. counterarguments e. supportive arguments D PTS: 1 18. The mental activity in response to a message such as an advertisement is known as _____. a. motivation b. opportunity c. elaboration d. ability e. perception A PTS: 1 19. The three factors that determine each individual's elaboration likelihood for a particular message are _____. a. motivation, opportunity, and ability b. motivation, objectives, and attitude c. motivation, opportunity, and attitude d. motivation, objectives, and ability e. motivation, opinions, and ability A PTS: 1 20. The theory of reasoned action proposes that all forms of planned and reasoned behavior have two primary determinants: _____ and _____. a. motivation; normative influences b. attitudes; normative influences c. attitudes; value-expressive influences d. attitudes; informational influences e. motivation; informational influences B PTS: 1 21. An example of a peripheral cue would be _____. a. background music in a television commercial b. scenery in a television commercial c. a salesperson's accent d. a salesperson's physical appearance e. All of these are correct. E PTS: 1 22. In Pavlov's experiment, the meat powder was the _____. a. conditioned stimulus b. preconditioned stimulus c. conditioned response d. preconditioned response e. None of these are correct. E PTS: 1 23. In Pavlov's experiment, the bell was the _____. a. conditioned stimulus b. unconditioned stimulus c. conditioned response d. unconditioned response e. None of these are correct. A PTS: 1 24. In Pavlov's experiment, the _____ was the unconditioned stimulus. a. dog salivating b. bell c. meat powder d. trainer e. None of these are correct. C PTS: 1 25. Pavlov's experiment is an application of _____. a. operant conditioning b. classical conditioning c. reasoning d. cognitive dissonance e. stimulus generalization B PTS: 1 26. Marketers can enhance consumers' motivation to attend to a message by _____. a. increasing curiosity about the brand b. repeating the ad on multiple occasions c. employing verbal framing d. appealing to hedonistic needs e. using concretizations D PTS: 1 27. A marketer who is using colorful ads is enhancing the consumers' _____. a. motivation to attend to the message b. motivation to process brand information c. opportunity to encode information d. opportunity to reduce processing time e. ability to access knowledge structures A PTS: 1 28. Marketers can enhance the consumers' opportunity to encode information by _____. a. using loud music b. using colorful ads c. repeating brand information d. employing verbal framing e. increasing curiosity about the brand C PTS: 1 29. Evelyn Rivers is the advertising director of a chain of health clubs. She is putting together an advertisement. She wants to enhance the consumers' opportunity to encode information. The best way to accomplish this objective would be to _____. a. repeat the ad on multiple occasions b. use loud music c. use celebrities d. use colorful ads e. employ verbal framing A PTS: 1 30. Marketers can enhance the consumers' opportunity to reduce processing time by _____. a. appealing to hedonistic needs b. heightening ad complexity c. repeating brand information d. creating gestalt processing e. employing verbal framing D PTS: 1 31. Marketers can enhance the consumers' ability to access knowledge structures by _____. a. using loud music b. using colorful ads c. employing verbal framing d. repeating brand information e. increasing curiosity about the brand C PTS: 1 32. Marketers can enhance the consumers' ability to access knowledge structures by _____. a. appealing to hedonistic needs b. using large pictures c. using celebrities d. repeating key scenes e. None of these are correct. E PTS: 1 33. A(n) _____ is a specimen or model of a particular concept or idea. a. frame b. exemplar c. symbol d. sign e. reference B PTS: 1 34. Margaret Stephens notices the television commercial because of the loud sounds. This is an example of _____. a. exposure b. involuntary attention c. nonvoluntary attention d. voluntary attention e. interpretation B PTS: 1 35. _____ attention requires very little effort on the part of the receiver. a. Involuntary b. Voluntary c. Selective d. All of these are correct. e. None of these are correct. A PTS: 1 36. When a person is attracted to a stimulus and continues to pay attention because it holds his or her interest, _____ has occurred. a. exposure b. comprehension c. voluntary attention d. nonvoluntary attention e. persuasion D PTS: 1 37. When a person willfully notices a stimulus, _____ has occurred. a. exposure b. comprehension c. voluntary attention d. nonvoluntary attention e. persuasion C PTS: 1 38. Attitudes are _____. a. physical constructs b. constantly changing c. hypothetical constructs d. feelings e. All of these are correct. C PTS: 1 39. A clear progression is implied from initial cognition, to affection, to _____. a. assimilation b. conation c. decoding d. acquisition e. None of these are correct. B PTS: 1 40. According to the ELM theory, people experience _____ attitude changes when persuaded via the peripheral route. a. temporary b. permanent c. semi-permanent d. exceptional e. None of these are correct. A PTS: 1 41. The central and peripheral paths represent endpoints on a continuum of persuasion strategies and are intended to imply that persuasion is a(n) _____. a. either-or proposition b. combination of the two c. unrelated activity d. unnecessary activity e. None of these are correct. E PTS: 1 42. Attitudes toward a brand result from a combination of _____ attitude-formation processes. a. primary and secondary b. linear and non-linear c. associative and non-associative d. central- and peripheral-route e. None of these are correct. D PTS: 1 43. In recognizing alternative paths to attitude formation and thus to persuasion, the ELM points out that the form of persuasion will depend both on consumer _____ (their motivation, opportunity, and ability to process marketing messages) and the relative strengths of the brand. a. aptitudes b. characteristics c. decoding strategies d. encoding strategies e. feelings B PTS: 1 44. When consumers are attracted to stimuli that supply relevant facts and figures, they are interested in meeting their _____. a. heuristic needs b. emotional needs c. hedonic needs d. informational needs e. symbolic needs D PTS: 1 45. In general, novel messages are _____. a. unusual b. distinctive c. unpredictable d. All of these are correct. e. None of these are correct. D PTS: 1 46. The secret to facilitating encoding is _____. a. repetition b. heuristics c. hedonism d. motivation e. opportunity A PTS: 1 47. As part of the socialization process in all cultures, people acquire a _____. a. norm of engagement b. norm of reciprocity c. norm of awareness d. norm of cognition e. norm of complacency B PTS: 1 48. Gina went to a drugstore for a bottle of shampoo. She walked past a point-of-purchase display for Jhirmack shampoos and conditioners, ignored a price-off coupon for Prell, and went directly to the shelf display for the brand she always purchases—Johnson & Johnson’s Baby Shampoo. Chances are, Gina’s decision is driven most by which attitude component? a. cognitions b. affect c. message arguments d. peripheral cues e. opportunity B PTS: 1 49. A university fraternity sponsored a blood drive in cooperation with the Red Cross, but students weren’t eager to donate. Red Cross volunteers took an impromptu survey and discovered that students erroneously believed they could contract AIDS in the process of giving blood. The erroneous belief that AIDS can be contracted while donating blood is best described as the _____ component of the student body’s attitude. a. affective b. cognitive c. constructive d. emotive e. evaluative B PTS: 1 50. The students’ intentions to give or not to give blood in a drive sponsored by the Red Cross is best described as the _____ attitude component. a. affective b. cognitive c. constructive d. conative e. evaluative D PTS: 1 51. Calvin refuses to eat his spinach. His father says, “Eat your spinach, Calvin, and you can stay up one hour longer than your normal bedtime.” What influence tool is the father using? a. commitment and consistency b. social proof c. reciprocation d. liking e. authority C PTS: 1 52. Calvin refuses to eat his spinach. His father asks, “Calvin, do you want to grow up to be big and strong?” Calvin says, “Yes.” The father says, “Popeye eats spinach and he’s strong, don’t you agree Calvin?” Calvin again says, “Yes.” The father then says, “Then why don’t you eat your spinach?” What influence tool is the father using? a. commitment and consistency b. social proof c. reciprocation d. liking e. authority A PTS: 1 53. You are asked to donate money to a charity drive conducted by a university sorority. Not knowing how much to donate, you ask, “How much are other students giving?” The fund raiser repliers, “Anywhere between $3 to $5.” Which influence tool best characterizes this situation? a. commitment and consistency b. social proof c. reciprocation d. liking e. authority B PTS: 1 54. Suppose a salesperson made the following statement in attempting to sell you stereo speakers. “The head of the music department at the University bought these exact speakers just last week.” What influence tool is the salesperson using? a. commitment and consistency b. social proof c. reciprocation d. authority e. liking D PTS: 1 55. Suppose a stereo salesperson was hired by the store owner because he is about the same age as most shoppers in the store and is considered handsome. What influence tool did the owner have in mind when hiring this salesperson? a. commitment and consistency b. social proof c. reciprocation d. liking e. authority D PTS: 1 56. Suppose Gina, who has always purchased Johnson & Johnson Baby Shampoo in the past, decides to switch to Paul Mitchell shampoo and conditioner (a line sold only in hair salons). Her switch occurs because she has been convinced that gentleness is not as important as she previously thought. In attitude-change-strategy terms, what has happened? a. A new attribute has been added to Gina’s cognitive structure. b. An attribute has been removed. c. An existing evaluation has been changed. d. A belief has been changed. e. A new outcome has been added. C PTS: 1 57. Based on the attitude formation equation, , the bij term refers to a _____. a. belief regarding outcome i b. behavior regarding outcome i c. behavioral intention d. behavior regarding outcome j e. belief regarding outcome j A PTS: 1 58. Based on the attitude formation equation, , the ei term refers to an _____. a. elaboration toward outcome i b. estimation of outcome i c. evaluation of outcome i d. enduring attitude change e. evaluation of brand i C PTS: 1 59. Based on the attitude formation equation, , the n term refers to _____. a. normative influence b. normative beliefs c. the number of normative beliefs d. the number of outcomes or attributes considered e. the number of brands considered D PTS: 1 60. Consider the attitude formation equation, . According to the theory of reason action (TORA), if all outcomes were equally important to consumers in a particular situation, what term could be removed without any loss in explanation? a. ABj b. bij c. ei d. n e. None of the terms could be removed. C PTS: 1 ESSAY 1. Explain your cognitive, affective, and conative components for a food category such as oranges or pork. Explain how marketers could change the components. Attitudes are made up of these three components. The affective component refers to a person’s liking of the object. The cognitive component refers to what a person thinks about an object and the conative component is how a person will intend to behave. Applied to pork, it might look like this: (1) I do not like pork, (2) I believe pork is an unhealthy food option, and (3) I will not eat pork. PTS: 1 2. Identify and explain the six tools of influence that were identified by Robert Cialdini. 3. Explain the significance of the theory of psychological reactance. 4. Write a description of the elaboration likelihood model and discuss the implications of this model on marketing communications. 5. Explain how the concept of click-whirr behavior applies to consumers. 6. Explain why physical attractiveness and similarity are important. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 16 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Nov 06, 2019
Number of pages
16
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Nov 06, 2019
Downloads
0
Views
237