Marketing > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Chapter 1— An Overview of Integrated Marketing Communications. All Answers Correct. (All)
Chapter 1— An Overview of Integrated Marketing Communications. All Answers Correct.
Document Content and Description Below
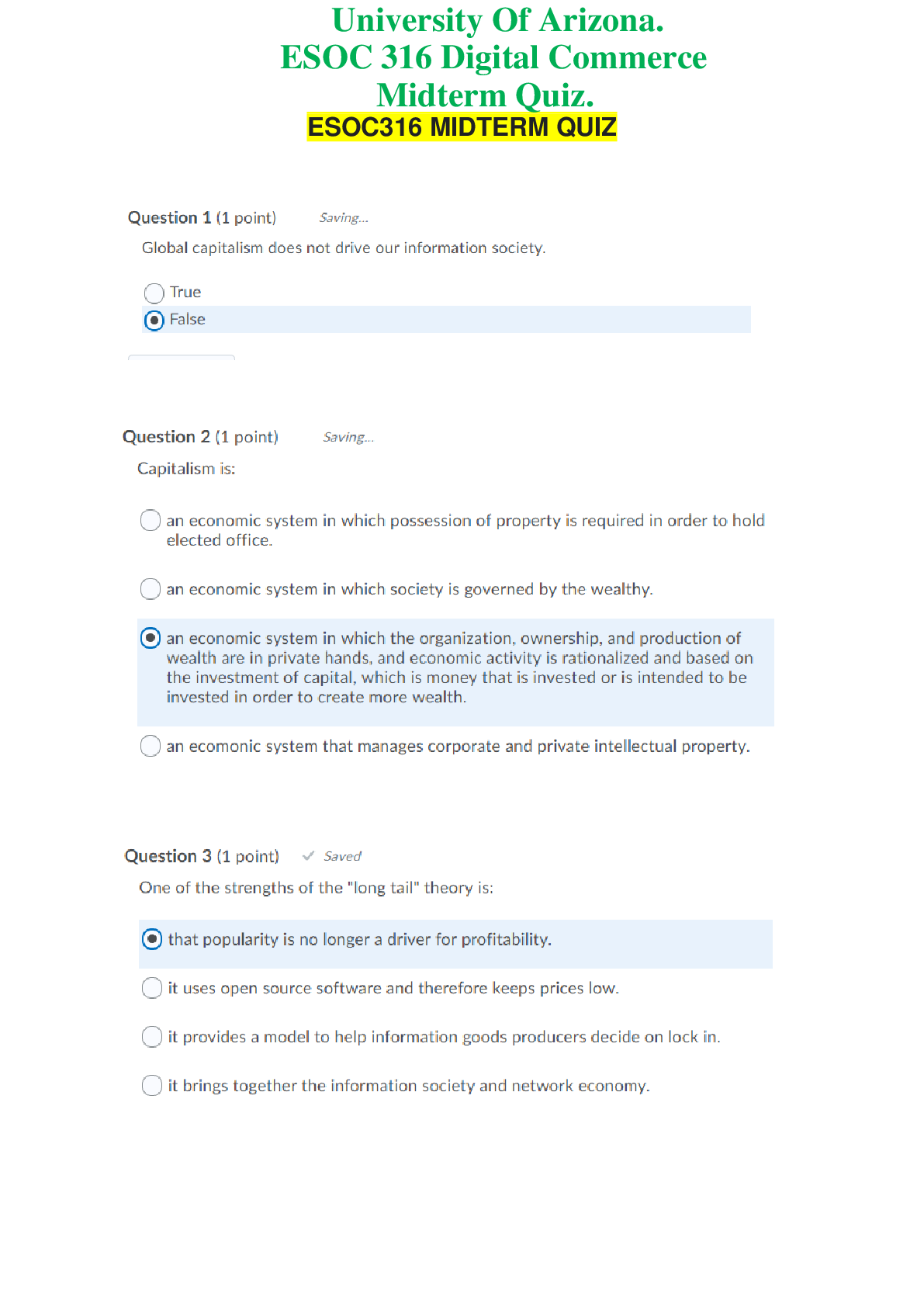
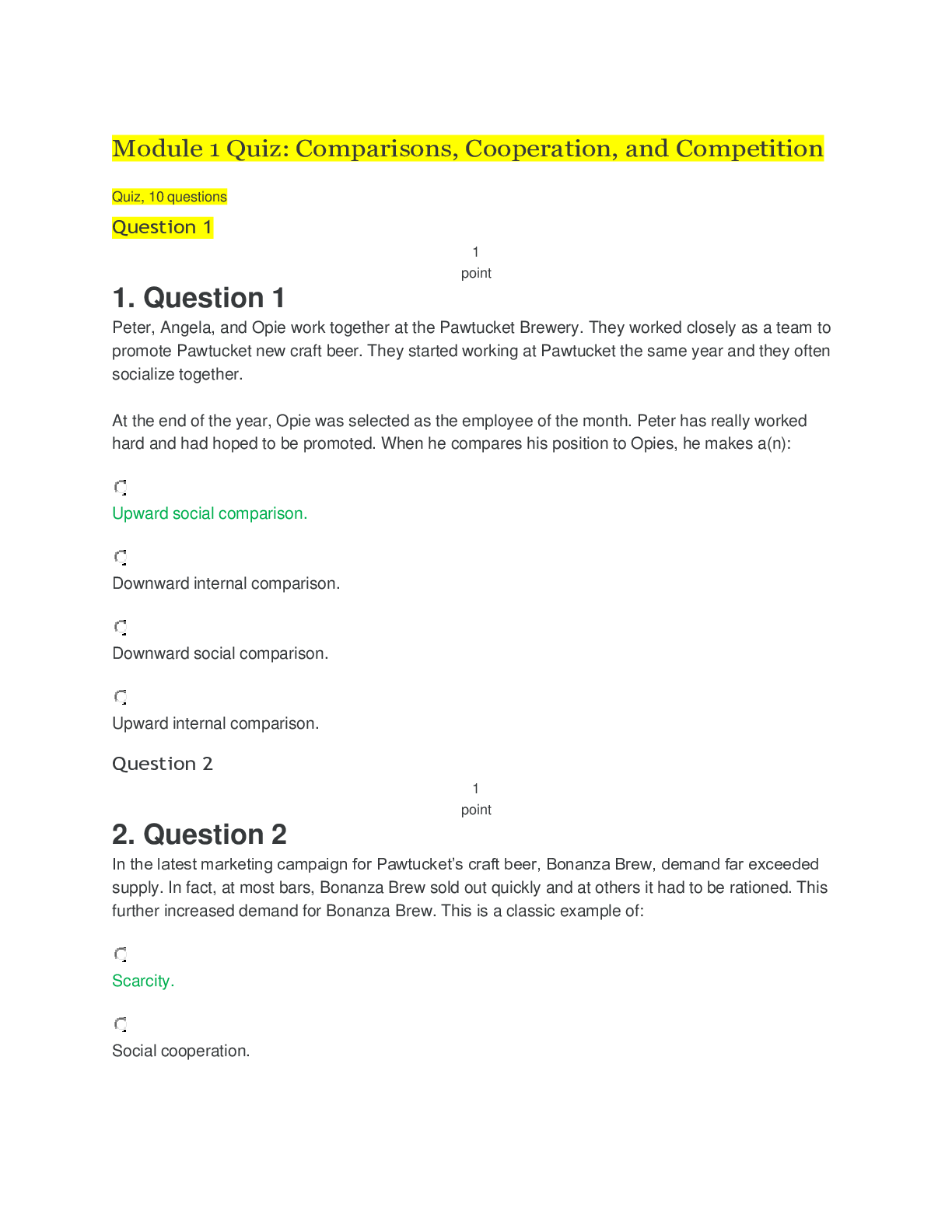
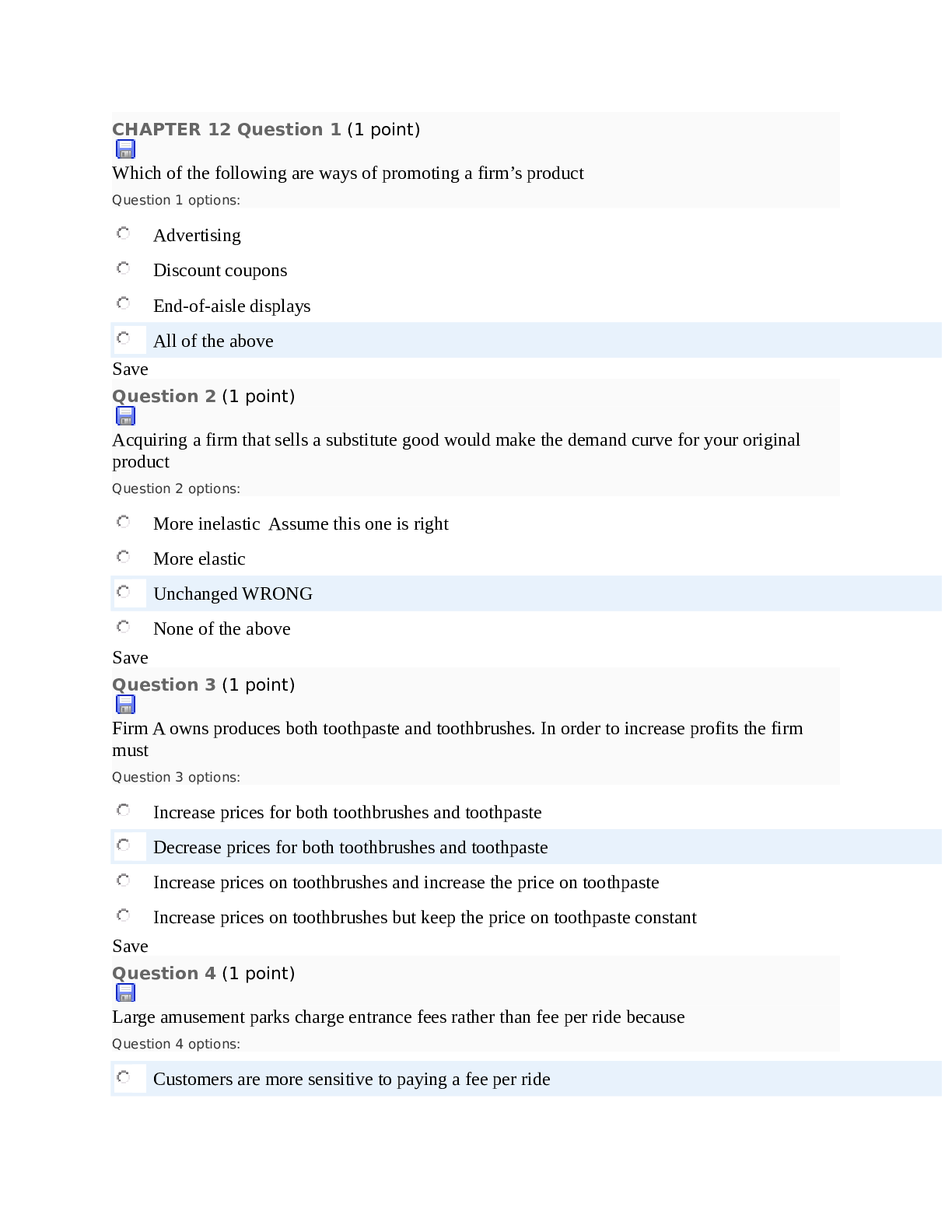
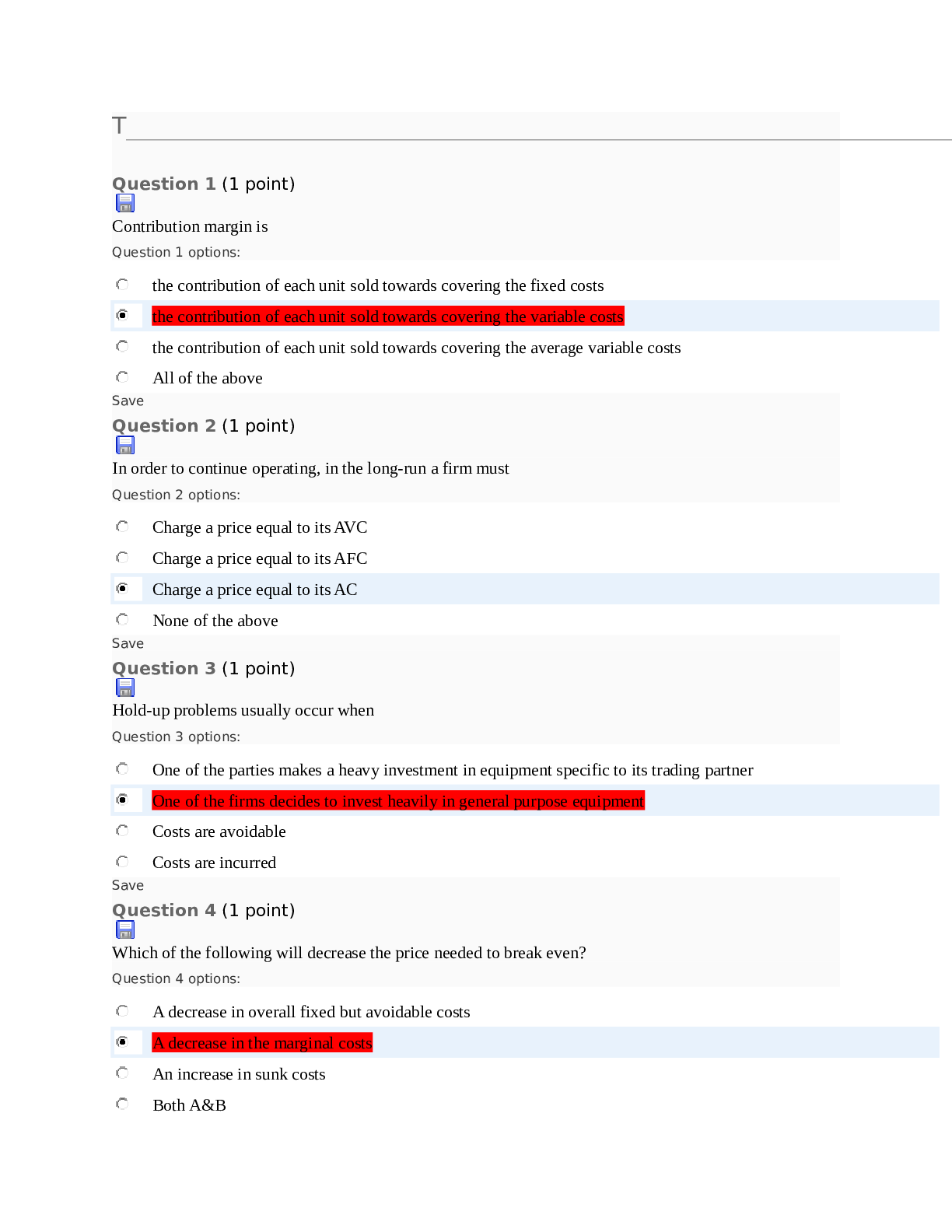
Chapter 1— An Overview of Integrated Marketing Communications TRUE/FALSE 1. Marketing communications play an important role for all companies. : T PTS: 1 2. According to a recent study... , integrated marketing communications is seldom employed by business-to-business marketers. : F PTS: 1 3. The marketing communications component of the marketing mix has decreased dramatically in importance in recent decades. : F PTS: 1 4. Marketing and communications are virtually inseparable. : T PTS: 1 5. The use of marketing communications is not appropriate for organizations delivering not-for-profit services. : F PTS: 1 6. Most marketing communications occur at the brand level. : T PTS: 1 7. The term brand is a convenient (and appropriate) label for describing any object of concerted marketing efforts. : T PTS: 1 8. Brands perform a critical strategic role by providing a key me for differentiating one company’s offering from competitive brands. : T PTS: 1 9. Many companies treat the various communication elements, such as advertising, sales promotions, public relations, and so on, as virtually separate activities rather than integrated tools that work together to achieve a common goal. : T PTS: 1 10. Interactive marketing communications, or simply IMC, is the philosophy and practice of carefully coordinating a brand’s sundry marketing communications elements. : F PTS: 1 11. One reason firms have not practiced IMC is because different units within organizations have specialized in separate aspects of marketing communications. : T PTS: 1 12. One reason firms have not practiced IMC is because outside suppliers, such as advertising, public relations, and promotion agencies, have been reluctant to broaden their function beyond the one aspect of marketing communications in which they have developed expertise and built their reputations. : T PTS: 1 13. In reality, IMC is little more than a management fad that is short lived. : F PTS: 1 14. Novice managers are more likely than experienced managers to practice IMC. : F PTS: 1 15. By closely integrating multiple communication tools and media, brand managers achieve duplicity, which me multiple methods in combination with one another yield more positive communication results than do the tools used individually. : F PTS: 1 16. The integrated marketing communication process starts by determining the strengths and weaknesses of the marketer. : F PTS: 1 17. The IMC approach uses the “inside-out” approach in identifying communication vehicles. : F PTS: 1 18. The use of integrated marketing communications is restricted to the mass media. : F PTS: 1 19. The terms touch point and contact are used interchangeably to mean any message medium capable of reaching target customers and presenting the brand in a favorable light. : T PTS: 1 20. Coordination of messages and media is absolutely critical to achieving a strong and unified brand image and moving consumers to action. : T PTS: 1 21. A positioning statement is the key idea that encapsulates what a brand is intended to stand for in its target market’s mind. : T PTS: 1 22. Successful marketing communication requires building relationships between brands and their consumers/customers. : T PTS: 1 23. One thing that has not changed in marketing communication practices is the dependence on mass media advertising. : F PTS: 1 24. The mixture of communications elements and the determination of messages, media, and momentum are all fundamental decisions in the brand-level marcom decision process. : F PTS: 1 25. The various types of brand-level marcom decisions include fundamental decisions and implementation decisions. : T PTS: 1 26. The objective of marketing communications is to enhance brand equity as a me of moving customers to favorable action toward the brand. : T PTS: 1 27. A brand has no equity if consumers are unfamiliar with it. : T PTS: 1 28. Selection of target segments is a critical step toward effective and efficient marketing communications. : T PTS: 1 29. A brand’s name is the central idea that encapsulates a brand’s meaning and distinctiveness relative to competitive brands in the product category. : F PTS: 1 30. The fundament decisions in the marcom decision process are conceptual and strategic, and the implementation decisions are practical and tactical. : T PTS: 1 31. There is an optimum mixture of expenditures between advertising and promotion that can be determined using computer models. : F PTS: 1 32. Systematic decision making requires that message content be dictated primarily by the media vehicle used to reach the target audience. : F PTS: 1 33. The concept of media is relevant to all marcom tools. : T PTS: 1 34. The ultimate objective of successful marketing communications is to cut costs. : F PTS: 1 35. Purchase intentions are not valid communication measures. : F PTS: 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The marketing mix for a brand consists of _____. a. product b. price c. promotion d. place e. All of these are correct. : E PTS: 1 2. Marketing communications is used by which type of organization? a. business-to-business organizations b. consumer marketing organizations c. not-for-profit organizations d. None of these are correct. e. All of these are correct. : E PTS: 1 3. Which of the following is NOT a form of media advertising? a. television b. radio c. magazines d. sales promotions e. newspapers : D PTS: 1 4. Coupons, trade shows, buying allowances, premiums, and price-off deals are all examples of _____. a. media advertising b. promotions c. place advertising d. point-of-purchase advertising e. public relations : B PTS: 1 5. Which term is preferred by most marketing practitioners to refer to the collection of advertising, sales promotions, public relations, event marketing, and other communication devices? a. marketing promotion b. promotion c. sales promotion d. marketing communications e. integrated marketing communications : D PTS: 1 6. Which of the following terms serves as a summary me for describing all forms of marketing focus? a. product b. brand c. communication d. promotion e. integration : B PTS: 1 7. Which of the following could be a brand? a. product b. service c. retail outlet d. person e. All of these are correct. : E PTS: 1 8. Current marketing philosophy holds that _____ is absolutely imperative for success. a. direct marketing b. e-mail c. coupons d. integration e. assessment : D PTS: 1 9. _____ is the philosophy and practice of carefully coordinating a brand’s sundry marketing communications elements. a. Interactive marketing b. Branding c. Synergistic marketing communications d. Synergistic marketing e. Integrated marketing communications : E PTS: 1 10. Which of the following has NOT been a reason for the reluctance to change from a single-function, specialist model to an IMC model? a. no way to assess the effectiveness of integration b. managerial parochialism c. fear that change might lead to possible budget cutbacks in their areas of control d. reluctance of agencies to broaden their function beyond the one aspect of marketing communications in which they have developed expertise and built their reputations e. fear of reduction in authority and power : A PTS: 1 11. Which of the following statements is true regarding the adoption of IMC? a. Novice managers are more likely than experienced managers to practice IMC. b. Firms involved in marketing services rather than products are more likely to have adopted IMC. c. Business-to-business firms are more likely to adopt IMC than business-to-consumer firms. d. Less sophisticated firms are likely adherents to IMC. e. All of these are correct. : B PTS: 1 12. Milo is employed by a manufacturer of consumer packaged goods products. His job entails the planning, creation, integration, and implementation of diverse forms of marcom, such as advertising, sales promotion, publicity releases, events, etc., that are delivered over time to a brand’s targeted customers and prospects with the ultimate goal of influencing or directly affecting their behavior. Milo is performing _____. a. integrated marketing (IM) b. marketing communications (marcom) c. integrated marketing communications (IMC) d. promotion marketing (PM) e. integrated promotion management (IPM) : C PTS: 1 13. The ultimate goal of integrated marketing communications is to _____. a. increase brand awareness b. affect the behavior of the targeted audience c. learn how to outsell the competition d. lower production costs e. All of these are correct. : B PTS: 1 14. What is achieved when multiple methods are used in combination with one another yielding more positive communication results than when the tools are used individually? a. synergy b. duplicity c. multiplicity d. redundancy e. repetition : A PTS: 1 15. Which of the following is NOT a key feature of IMC? a. The customer represents the starting point for all marketing communications activities. b. Brand managers and their agencies should be amenable to using various marketing communication tools. c. Multiple messages must speak with a single voice. d. The ultimate goal is to influence brand awareness and enhance consumer attitudes toward the brand. e. Build relationships. : D PTS: 1 16. A key feature of IMC is that the process should _____. a. use an “inside-out” approach b. be restricted to only one or a select number of communication media c. use the same media to reach all target audiences to improve efficiency d. start with the customer or prospect and then work back to the brand communicator in determining the most appropriate messages and media e. utilize the same communication media over time : D PTS: 1 17. Which approach will best serve the customers’ information needs and motivate them to purchase the brand? a. inside-out b. outside-in c. top-down d. bottom-up e. combination : B PTS: 1 18. Today, consumers are not only passive receivers of marcom messages, but are often active participants in the marcom process due to _____. a. economic advances b. technological developments c. increases in the use of sales promotion d. changes in demographics e. expion of advertising agency services : B PTS: 1 19. Brand managers should turn to alternative me of marcom as the option of first choice rather than automatically defaulting to _____. a. sales promotion b. personal selling c. point-of-purchase advertising d. event marketing e. mass media advertising : E PTS: 1 20. Which of the following terms is used to mean any message medium capable of reaching target customers and presenting the brand in a favorable light? a. touch point b. contact c. intersection d. touch point and contact e. touch point, contact, and intersection : D PTS: 1 21. The idea of surrounding the customer or prospect with a brand’s marcom messages, or that a brand’s touch points should be everywhere the target audience is, is known as _____. a. consumer-oriented marketing b. the media-neutral approach c. 360-degree branding d. the rotation principle e. event marketing : C PTS: 1 22. The marketing manager for Carver Products, Inc. asked her research staff to identify all of the points of contact that consumers are likely to have with Carver’s products. The marketing manager would most likely use this information in designing a(n) _____. a. point-of-purchase display b. board of director’s report c. integrated marketing communications program d. marketing research survey e. slice-of-life television commercial : C PTS: 1 23. The context (or medium used) influences the _____ that the message has. a. impact b. reach c. frequency d. integration e. touch points : A PTS: 1 24. The idea that “context matters,” and that not all touch points are equally effective, has been termed _____ by marcom practitioners. a. synergy b. media mix c. awareness generation d. engagement e. contact : D PTS: 1 25. What does the phrase, “speak with a single voice,” mean? a. Carefully select those tools that are most appropriate for the communications objective at hand. b. Reach the target audience efficiently and effectively using whatever touch points are most appropriate. c. Successful marketing communications requires building relationships between brands and their consumers/customers. d. All marketing communication elements should use the same endorser so that consumers do not get confused. e. Coordination of messages and media is absolutely critical to achieving a strong and unified brand image and moving consumers to action. : E PTS: 1 26. Karen is attempting to put into words the key idea that encapsulates what her company’s brand is intended to stand for in its target market’s mind. Karen is writing a _____. a. relationship statement b. creative brief c. positioning statement d. contact brief e. touch point : C PTS: 1 27. Which of the following encapsulates what a brand is intended to stand for in its target market’s mind and then consistently delivers the same idea across all media channels? a. positioning statement b. contact point c. relationship statement d. creative brief e. creative platform : A PTS: 1 28. A key characteristic of IMC is the building of relationships with customers. Which of the following is NOT a benefit of building relationships? a. repeat purchases b. loyalty toward a brand c. enduring links between a brand and its customers d. greater profitability e. huge acquisition costs : E PTS: 1 29. The fact that it costs five to 10 times more to land a new customer than to keep a current customer has been compared to a(n) _____. a. clogged drain b. leaky bucket c. sand castle d. ice sculpture e. bee hive : B PTS: 1 30. Frequency, loyalty, or ambassador programs and creating brand experiences that make positive and lasting impressions are ways to _____. a. speak with one voice b. create synergy c. build customer/brand relationships d. start with the customer/prospect e. reach consumers who cannot be reached through traditional mass media : C PTS: 1 31. One way relationships between brands and customers are nurtured is by creating brand experiences that make positive and lasting impressions. This is done by creating special events or developing exciting venues that attempt to _____. a. appeal to consumers’ demographic characteristics b. reposition products or services by connecting with consumers’ functional needs c. generate increased sales to current customers d. develop new target markets e. build the sensation that the brand is relevant to the consumer’s lifestyle : E PTS: 1 32. The ultimate objective of IMC is to _____. a. start with the customer or prospect b. move people to action c. carefully select those tools that are most appropriate for the communications objective at hand d. use as many communications outlets as possible to reach the target audience e. speak with a single voice : B PTS: 1 33. Which of the following is NOT a change in marketing communication practices? a. increased reliance on outside suppliers, or specialized services b. reduced dependence on mass media advertising c. increased reliance on highly targeted communication methods d. heightened demands on suppliers e. increased efforts to assess communications’ return on investment : A PTS: 1 34. When counseling its clients in selecting appropriate marcom tools, McCann Worldgroup uses an approach that requires that the brand marketer first identify the goal(s) a marcom program is designed to accomplish and then identify the best way to allocate the marketer’s budget. What is this approach known as? a. inside-out b. bottom-up c. media-neutral d. media-centric e. goal oriented : C PTS: 1 35. What is the greatest obstacle to implementing integrated marketing communications? a. There is a lack of interest in IMC by top management. b. The cost for implementing an IMC program is difficult to justify. c. Little can be gained by coordinating the various marketing communications elements. d. Few providers of marketing communication services have the far-ranging skills to plan and execute programs that cut across all major forms of marketing communications. e. Measuring the return on investment is nearly impossible. : D PTS: 1 36. Which of the following is a fundamental decision in the brand-level marcom decision process? a. targeting b. positioning c. setting objectives d. budgeting e. All of these are correct. : E PTS: 1 37. Which of the following is an implementation decision in the brand-level marcom decision process? a. targeting b. mixing elements c. budgeting d. positioning e. setting objectives : B PTS: 1 38. Julie and her department are responsible for making brand-level fundamental and implementation marcom decisions. What are the expected outcomes of these decisions? a. increasing sales and profits b. enhancing brand awareness and attitudes c. enhancing brand equity and affecting behavior d. increasing purchase intentions and affecting behavior e. enhancing brand equity and increasing brand awareness : C PTS: 1 39. The objective of marketing communications is to _____ as a me of moving customers to favorable action toward the brand. a. increase brand awareness b. cut costs c. increase product usage d. enhance brand equity e. increase the rate of purchase : D PTS: 1 40. _____ allows marketing communicators to deliver messages more precisely and to prevent wasted coverage to people falling outside the intended audience. a. Targeting b. Positioning c. Budgeting d. Setting objectives e. Momentum : A PTS: 1 41. Which of the following variables do companies use to identify potential target markets? a. demographic characteristics b. lifestyles c. product usage patterns d. geographic considerations e. All of these are correct. : E PTS: 1 42. A brand’s _____ represents the key feature, benefit, or image that it stands for in the target audience’s collective mind. a. equity b. image c. position d. name e. trademark : C PTS: 1 43. Which of the following is NOT a budgeting method? a. top-down budgeting (TD) b. bottom-up budgeting (BU) c. top-down/bottom-up/top-down process (TDBUTD) d. bottom-up/top-down process (BUTD) e. top-down/bottom-up process (TDBU) : C PTS: 1 44. Joan Kaufman is a senior manager of a large conglomerate. She decides how much money is allocated to each subunit. This is an example of _____ budgeting. a. top-down b. bottom-up c. bottom-up/top-down d. top-down/bottom-up e. hierarchy : A PTS: 1 45. The most frequently used budgeting method is _____. a. top-down (TD) b. bottom-up (BU) c. top-down/bottom-up/top-down (TDBUTD) d. bottom-up/top-down (BUTD) e. top-down/bottom-up (TDBU) : D PTS: 1 46. John is a subunit manager at a large consumer packaged goods manufacturer. Every year, he submits a budget request to the vice president of marketing, who coordinates the various requests and then submits an overall budget to top management for approval. This is an example of _____ budgeting. a. top-down b. bottom-up c. top-down/bottom-up d. bottom-up/top-down e. combination : D PTS: 1 47. All marketing communications should be _____. a. directed to a particular target market b. clearly positioned c. created to achieve a specific objective d. undertaken to accomplish the objective within budget constraints e. All of these are correct. : E PTS: 1 48. Fundamental decisions in the brand-level marcom decision process are _____, and implementation decisions are _____. a. tactical; strategic b. strategic; tactical c. long-term; short-term d. short-term; long-term e. practical; conceptual : B PTS: 1 49. Over the past two decades, the trend has moved toward greater expenditures on _____. a. advertising b. public relations c. personal selling d. promotions e. point-of-purchase displays : D PTS: 1 50. The decision regarding how to allocate resources between the marcom elements has been described as an “ill-structured” problem. What does this mean? a. There is no solution to the problem. b. It is difficult to define the problem. c. There is no way of determining the mathematical optimum allocation among marcom elements. d. There are solutions, but they are not acceptable. e. There is no way to measure whether the solution chosen was the correct one. : C PTS: 1 51. For a given level of expenditure, there is no way of determining the mathematical optimum allocation between advertising and promotion because _____. a. advertising and promotions are somewhat interchangeable b. advertising and promotions produce a synergistic effect c. advertising is appropriate for early stages of the product life cycle, and promotion is more appropriate during later stages d. they are somewhat interchangeable and produce a synergistic effect e. None of these are correct. : D PTS: 1 52. Allison is trying to determine how much to allocate for advertising and how much to allocate for promotions during the next year. Which implementation decision is Allison making? a. mixing elements b. creating messages c. selecting media d. establishing momentum e. targeting : A PTS: 1 53. A satisfactory mixture of advertising and promotion expenditures can be formulated by considering the different purposes of each. A key strategic consideration is whether _____. a. short- or long-term goals are more important b. the budget would allow for the relatively larger expense of advertising c. the organization has the expertise in its current staff to develop successful promotions d. the majority of the target market is price sensitive e. use of sales promotion is necessary given current economic conditions : A PTS: 1 54. The term media applies to which marcom tool? a. advertising b. public relations c. promotions d. personal selling e. All of these are correct. : E PTS: 1 55. The word _____ refers to an object’s force or speed of movement. a. drive b. push c. momentum d. force e. pull : C PTS: 1 56. Harvey is a brand manager for a national brand of soft drinks. He is making the implementation decisions in the marcom decision process, and he wants a marcom tool that is most capable of directly affecting consumer behavior. Which tool should he use? a. advertising b. sales promotion c. publicity d. events e. point-of-purchase display : B PTS: 1 57. Which of the following is an example of a communication outcome? a. increase sales to grocery stores by 10 percent b. increase total sales by 15 percent c. maintain existing sales levels in Japan d. increase brand awareness by 15 percent e. increase sales in Mexico by 15 percent : D PTS: 1 58. Which of the following is NOT a communications outcome measure? a. purchase intentions b. brand awareness c. message comprehension d. attitude toward the brand e. All of these are measures of communication outcomes. : E PTS: 1 59. Program evaluation is accomplished by _____. a. developing a budget that is based on marcom objectives and includes an optimum balance of advertising and promotion b. measuring the results of marcom efforts against the objectives that were established c. collecting data on consumers’ demographics and lifestyles d. constructing a database of information on the target market, economic conditions, and competitors’ marcom strategies e. comparing budgeted marcom expenditures against share-of-voice : B PTS: 1 60. One important factor that has led more firms to perform research and acquire data to determine whether implemented marcom decisions have accomplished the objectives they were expected to achieve is _____. a. increasing demand for accountability b. rapidly changing consumer tastes and preferences c. changing economic conditions d. increasing marcom expenses e. less reliance on outside agencies to perform the marcom function : A PTS: 1 ESSAY 1. Compare and contrast the terms promotion and marketing communications, and list the primary tools of marketing communications. 2. Describe the basic philosophy underlying integrated marketing communications (IMC), and discuss reasons why firms have not practiced IMC all along and why there is a reluctance to change. 3. Explain what the payoff is from using integrated marketing communications. 4. Explain the five key features that undergird the philosophy and practice of integrated marketing communications. 5. Discuss the changes in marketing communication practices that have been particularly prominent. 6. Debra is the brand manager for Tide laundry detergent, marketed by Procter & Gamble, and she is making the brand-level fundamental decisions in the marcom decision process. Discuss what she will be considering. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 17 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Nov 06, 2019
Number of pages
17
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Nov 06, 2019
Downloads
0
Views
51