*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Miami Dade College, Miami NUR 2212 Burns Review Questions (All)
Miami Dade College, Miami NUR 2212 Burns Review Questions
Document Content and Description Below
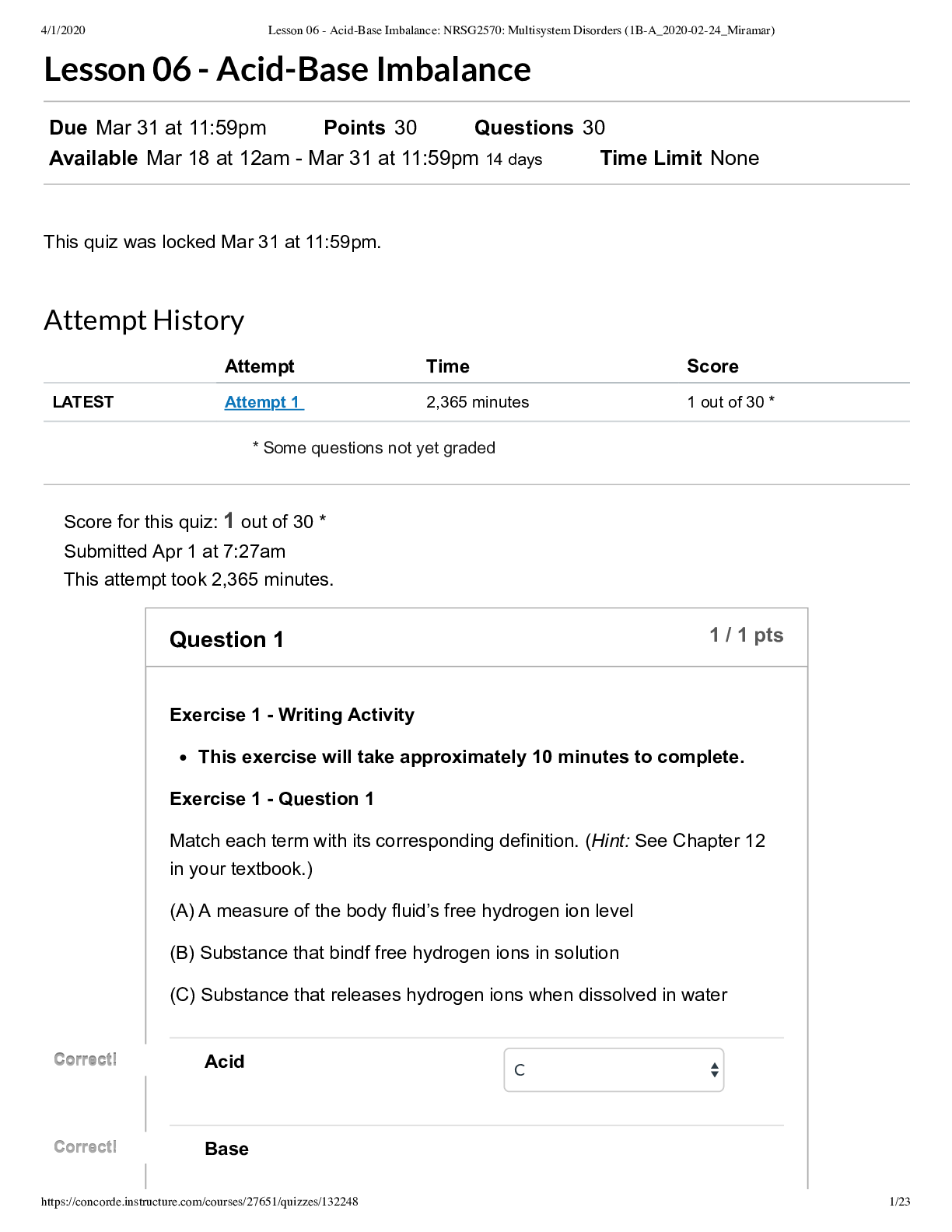
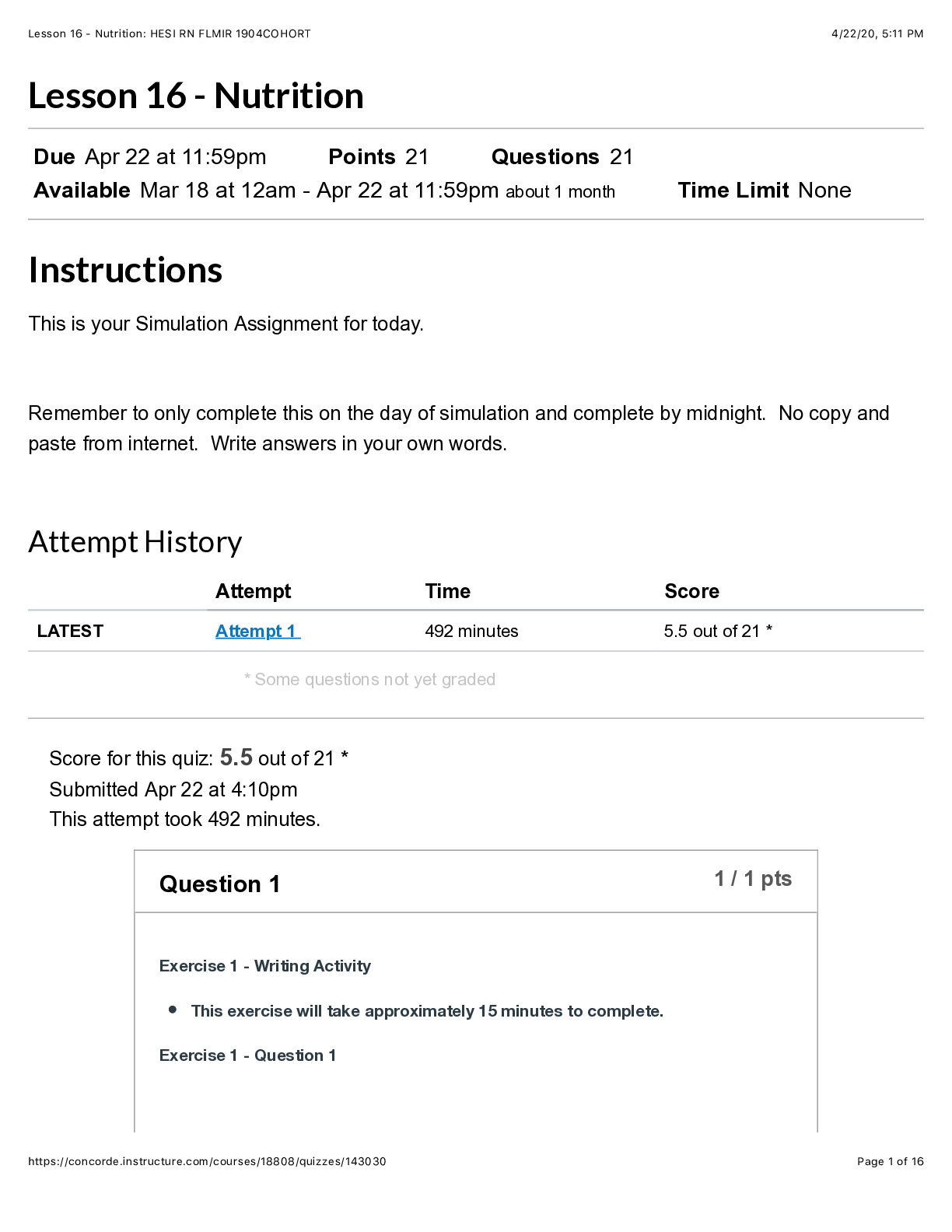
The nurse is assessing a client with severe burn wounds. What are the nursing interventions performed by the nurse in the order of priority? Correct 1. Checking for a patent airway Correct 2. Mai... ntaining effective circulation Correct 3. Performing adequate fluid replacement Correct 4. Caring for the burn wound A client is severely injured with burns and sustained major trauma from a fire incident. What is the order of assessments according to priority in this situation? Correct 1. Using a jawthrust maneuver to establish an airway Correct 2. Providing bagvalvemask (BVM) ventilation Correct 3. Palpating for the presence of a radial pulse Correct 4. Monitoring systolic blood pressure Correct 5. Assessing the score of eye opening Correct 6. Removing the clothing with scissors the eye opening, voice, and pain status. The clothes of the client are removed with scissors to prevent fabric melting into the skin. The nurse is assessing a client with burns over 15% of the body. Which priority nursing action should be taken to ensure a complete assessment? 1 Determining the level of mobility Correct2 Removing the clothes of the client 3 Placing the client in recumbent position 4 Cleaning the wounds with antiseptic solution The nurse should remove all clothing of the client with scissors to allow for thorough assessment; this A registered nurse teaches a new orienting nurse about interventions to be followed for a client with burns due to inhalation injury. Which statement made by the new orienting nurse indicates the new nurse needs more orientation? 1 "I should administer intravenous analgesia." Correct2 "I should check pulses distal to burns." 3 "I should prepare for an endotracheal intubation." 4 "I should anticipate the need for fiberoptic bronchoscopy." Inhalation injury burns occur in the nose, mouth, throat, and airway. The peripheral and central pulses are assessed, but they are not considered distal to the burn. The nurse should administer intravenousanalgesia. The nurse should anticipate both endotracheal intubation and a need for fiberoptic bronchoscopy. The nurse teaches a client about strategies to reduce burn injuries. Which statement made by the client indicates the need for further teaching? 1 "I should never smoke in bed." 2 "I should never use gasoline to start a fire." 3 "I should never leave hot oil unattended while cooking." Correct4 "I should never attend to burning candles near open curtains." The client should never leave candles unattended near open curtains. The client should never smoke in bed, use gasoline to start a fire, or leave hot oil unattended while cooking. A client is admitted to the hospital due to electrical burns. Which assessment findings does the nurse anticipate? Select all that apply. 1 Coughing Correct2 Burn odor 3 Smoky breath Correct4 Leathery skin Correct5 Cardiac arrest A client with electrical burns may have assessment findings such as burn odor, leathery skin, and cardiac arrest due to hypovolemia and electrical disturbances. Coughing and smoky breath are assessment findings associated with inhalational injuries. A client who sustained burn injuries due to a fire and explosion has a carbon monoxide level of 14%. Which pathophysiologic risk is increased in the client? 1 Stupor 2 Vertigo 3 Convulsions Correct4 Slight breathlessness Slight breathlessness may occur when the carbon monoxide level is 14%. Stupor and vertigo may result when the carbon monoxide level is in between 21% and 40%. When the level of carbon monoxide reaches between 41% and 60%, coma or convulsions may occur. The nurse is caring for a client with a burn injury and suspects atelectasis and hypoxia. Which age-related changes should the nurse associate these findings? 1 Reduced mobility 2 Reduced healing time Correct3 Reduced thoracic compliance 4 Reduced inflammatory and immune responsesThe reduction in thoracic and pulmonary compliance may increase the risk of atelectasis and hypoxia. Reduced mobility increases the risk for burn injuries. Reduced healing would have longer time with open areas, which results in greater risks for infection, metabolic derangements, and loss of function from contracture formation and scar tissue. Reduced inflammatory and immune responses would increase the risk for infection and sepsis. A client with burns is hospitalized in the emergency department and advised to get an electrocardiogram (ECG) done. Which type of burn injury has the client most likely sustained? 1 Flame burn 2 Chemical burn Correct3 Electrical burn 4 Radiation burn In an electrical burn injury, changes in the ECG may indicate damage to the heart. In flame burn injuries, the smoldering clothing and all metal objects are removed. If a client suffers from chemical burns, the dried chemicals present on skin should not be made wet but should be brushed off. If the client has radiation burn injuries, then the source should be removed using tongs or lead protective gloves. A client with burns caused by flames is hospitalized. Which specific emergency burn management would be appropriate for this client? Correct1 Removing all metal objects 2 Helping the client bathe or shower 3 Initiating cardiopulmonary resuscitation 4 Administering tetanus toxoid for prophylaxis When a client with flame burn injuries is hospitalized, the primary healthcare provider should first remove all smoldering clothing and metal objects. In case of radiation burns, the client is helped to bathe or shower. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation would be appropriate in the emergency management of an electrical burn injury. The administration of tetanus toxoid for prophylaxis would be considered as the general management for all types of burns. While caring for a client with a burn injury and in the resuscitation phase, the nurse notices that the client is hoarse and produces audible breath sound on exhalation. Which immediate action would be appropriate for the safe care of the client? Select all that apply. Correct1 Providing oxygen immediately Correct2 Notifying the rapid response team 3 Considering it a normal observation 4 Initiating an intravenous (IV) line and beginning fluid replacement 5 Obtaining an electrocardiogram (ECG) of the clientHoarseness of voice, difficulty in swallowing, or an audible breath sound on exhalation after a burn injury indicates an impaired airway. Therefore the client should be given oxygen immediately. The rapid response team should also be notified for further management. This occurrence should not be considered a normal observation. An IV line should be initiated for fluid replacement only once the client’s airway is patent. An ECG is obtained when the client suffers from electrical burns. The nurse is caring for a client with burns receiving opioid analgesics and who is sedated. Which medications should the nurse anticipate to be prescribed by the primary healthcare provider to overcome this side effect of the opioid analgesics? Select all that apply. 1 Morphine Correct2 Pregabalin 3 Lorazepam 4 Midazolam Correct5 Gabapentin Pregabalin and gabapentin are adjuvant analgesics used to overcome the side effects caused by opioid analgesics. Morphine is an opioid analgesic used in the treatment of pain that can cause sedation. Lorazepam and midazolam are anxiolytic agents used to inhibit anxiety. The registered nurse is teaching the student nurse about precautions to take when treating a client with open burn wounds. Which statement made by the student nurse indicates the need for further teaching? Correct1 I should use nonsterile gloves when applying ointments." 2 "I should use nonsterile, disposable gloves when removing old dressings." 3 "I should wear personal protective equipment before caring for the client." 4 "I should remove personal protective equipment before leaving one client to treat another." Sterile gloves are used when applying ointment to the open burn wounds. When removing contaminated dressings and washing the dirty wound, nonsterile, disposable gloves are used. When treating the client, personal protective equipment like disposable gowns and gloves are used. To prevent crosscontamination, the nurse should remove the personal protective equipment before leaving one client to treat another. Which wound care is given to a client with severe burn injuries during the acute phase? 1 Assess extent and depth of burns 2 Provide daily shower and wound care 3 Remove dead and contaminated tissue Correct4 Assess the wound daily and adjust the dressing In the acute phase, wound care is given by assessing the wound daily and adjusting the dressing if necessary according to the protocols. Assessing the extent and depth of burns is performed in the emergent phase. Providing a daily shower and removing the dead and contaminated tissue (debride) is performed in the emergent phase.The registered nurse is teaching a student nurse about the ongoing monitoring of a client with electrical burns. Which statement made by the student nurse indicates the need for further teaching? 1 "I should monitor the airway." Correct2 "I should monitor the eye pH." 3 "I should monitor vital signs." 4 "I should monitor urine output." The pH of the eye is monitored when chemical burns occur to the eye. The nurse should monitor the airway for breathing, vital signs, heart rhythm, neurovascular status of injured limbs, level of consciousness, and urine output. A client has burn injuries sustained from an electrical current. What are the interventions to follow until the client is transferred to the primary healthcare center? Select all that apply. 1 Cover the burns with ice. Correct2 Leave the adherent clothing in place. Correct3 Wrap the client in a dry clean sheet. Correct4 Remove as much burned clothing as possible. 5 Immerse the burned body part in cool water. When a client is injured due to an electrical current, the adherent clothing should be left in place until the client is transferred to a primary healthcare center. Wrapping the client in a clean dry sheet may prevent further contamination of the wound and also provide warmth. Removing as much burned clothing prevents further tissue damage. The burns should not be covered with ice, since this may cause hypothermia and vasoconstriction of blood vessels. Do not immerse the burned body part in cool water because it may cause extensive heat loss. A client was admitted with a burn injury caused by a quick heat flash. The nurse examined the skin and noticed erythema and mild swelling. What type of burn does the nurse suspect? Correct1 Firstdegree burn 2 Thirddegree burn 3 Fourthdegree burn 4 Seconddegree burn A burn injury caused by a quick heat flash is a firstdegree burn or superficial burn and is manifested as erythema and mild swelling on the skin. Thirddegree and fourthdegree burns are caused by flame, scald, chemicals, tar, and electric shock and typically involve damage to muscles, tendons, and bones; the client presents with dry, waxy white, leathery skin. Seconddegree burns include contact burns and those associated with thirdand fourthdegree burns, but they are much less severe and are characterized by fluidfilled vesicles that are red, shiny, and wet. A man who has 40% of the body surface area burned is admitted to the hospital. Fluid replacement of 7200 mL during the first 24 hours has been prescribed. Fifty percent of fluid replacement should be administered in the first 8 hours; then theremaining 50% given over the next 16 hours. What does the nurse calculate the hourly intravenous (IV) fluid to be for the first 8 hours of fluid replacement therapy? Record your answer using a whole number. ___ mL/hr Fifty percent of the total volume to be infused is 3600 mL (7200/2 = 3600). The total time of infusion for this volume is 8 hours. 3600 mL/8 hours = 450 mL/hr. A healthcare provider prescribes 2 liters of intravenous (IV) fluid to be administered over 12 hours to a client who sustained a burn injury. The drop factor of the tubing is 10 gtts/mL. The nurse should set the flow rate at how many drops per minute? Record your answer using a whole number. ___ gtts/min The total volume to be infused is 2 liters (2000 mL). The drop factor is 10 gtts/mL. Use the following formula to determine the flow rate in drops per minute. A client is admitted for treatment of partial- and full-thickness burns of the entire right lower leg extremity and the anterior portion of the right upper arm. A nurse performs an immediate appraisal of the percentage of body surface area burned using the rule of nines. What percentage of body surface area does the nurse determine is affected? Record the answer to one decimal place. _______% The entire right lower extremity is 18%; the anterior portion of the right upper extremity is 4.5%. 18 + 4.5 = 22.5. A nurse is using the rule of nines to estimate burn injury in a client. The client has burns on the front chest, front abdomen, both sides of both upper extremities, and entire head. Calculate the percentage of body surface burned. Record your answer as a whole number. ______% The chest is 9%, the front abdomen is 9%, each upper extremity is 9% (for a total of 18% for both), and the entire head and neck are 9%. 9 + 9 + 18 + 9 = 45. Following a fire, the disaster management team assesses burn injuries of the survivors. The team finds that most survivors have pink to cherry red skin with blisters. Which type of burns does the nurse identify on the survivors? 1 First degree burns 2 Third degree burns 3 Fourth degree burns Correct4 Second degree burns Blister formation and pink to cherry red skin indicates partial thickness burns that are second degree burns. In first degree burns, the client experience moderate to severe tenderness and redness of the skin.Third degree and fourth degree burns involve dry and leathery skin with impaired sensation when touched. While the nurse was caring for a client with chemical burns after a factory explosion, there was increased edema in the surrounding tissues. What might have led to increased edema? 1 Stabilizing the cervical spine Correct2 Lowering burned limbs below the heart 3 Brushing dry chemical from skin before irrigation 4 Flushing chemical from wound with saline solution The initial interventions for a client with a chemical burn include elevating the burned limbs above the heart. This helps in decreasing the edema of the localized tissue. Stabilizing the cervical spine is required as an immediate intervention for a client with chemical burns. Brushing any dry chemical from the skin before irrigation should be performed as a primary intervention. Flushing any chemicals from the wound with saline solution is done immediately and may not cause increased edema. A client who is recovering from deep partial-thickness burns develops chills, fever, flank pain, and malaise. The primary healthcare provider makes a tentative diagnosis of urinary tract infection. Which diagnostic tests should the nurse expect the primary healthcare provider to prescribe to confirm this diagnosis? 1 Cystoscopy and bilirubin level 2 Specific gravity and pH of the urine Correct3 Urinalysis and urine culture and sensitivity 4 Creatinine clearance and albumin/globulin (A/G) ratio The client’s manifestations may indicate a urinary tract infection; a culture of the urine will identify the microorganism, and sensitivity will identify the most appropriate antibiotic. A cystoscopy is too invasive as a screening procedure; altered bilirubin results indicate liver or biliary problems, not urinary signs and symptoms. Creatinine clearance reflects renal function; A/G ratio reflects liver function. Although an increased urine specific gravity may indicate red blood cells (RBCs), white blood cells (WBCs), or casts in the urine, which are associated with urinary tract infection, it will not identify the causative organism. A client who experienced extensive burns is receiving intravenous fluids to replace fluid loss. The nurse should monitor for which initial sign of fluid overload? Correct1 Crackles in the lungs 2 Decreased heart rate 3 Decreased blood pressure 4 Cyanosis Crackles, or rales, in the lungs are an early sign of pulmonary congestion and edema caused by fluid overload. Clients with fluid overload will usually demonstrate an increased heart rate and increased blood pressure. A decreased heart rate and decreased blood pressure and cyanosis in a client with fluid overload would be very late and fatal signs.The nurse is caring for a client who has been admitted with partial- and fullthickness burns over 25% of the total body surface area. Lactated Ringer solution and 5% dextrose have been prescribed. What is the purpose of these fluids? 1 Prevent fluid shifts 2 Expand the plasma 3 Maintain blood volume 4 Replace electrolytes lost Fluids during the first 48 hours are given to replace fluid lost from the intravascular compartment to interstitial spaces. Administration of fluids treats the fluid shifts but does not prevent them. Lactated Ringer solution and 5% dextrose in saline are not plasma expanders, as is albumin. Electrolytes specifically are replaced based on serial assessments of serum electrolytes and arterial blood gases. A nurse is caring for a client during the emergent phase of a severe burn injury. Which parenteral intervention prescribed by the healthcare provider should the nurse question? 1 Colloids 2 Potassium 3 Hypertonic saline 4 Lactated Ringer solution Potassium replacement generally is not indicated in the initial management of burns because hyperkalemia results from the liberation of potassium ions from the injured cells. Colloids are given to draw fluid from edematous tissue back into the bloodstream. Hypertonic saline and lactated Ringer solution are given to replace fluid and electrolytes. A client is admitted to the hospital with deep partial-thickness burns to both hands and forearms after an accident. How should the nurse apply the prescribed antimicrobial medication? 1 Place the medication directly on the dressing in a thick layer using clean gloves. Correct2 Place the medication directly on the burn wound in a thin layer using sterile gloves. 3 Put the medication in a Hubbard tank and saturate sterile dressings with it before applying the dressings to the burns. 4 Put the medication in a Hubbard tank and allow the client to soak in the tank for several minutes every day. Sterile aseptic technique is necessary for an open wound, and a thin layer of ointment is applied directly to the affected area. Surgically aseptic, not medically aseptic, technique is used. Although some medications may be placed directly in the tank, antimicrobial medications are placed directly on the affected area using surgically aseptic technique. The nurse is caring for a client with wound dressings to the burns on 55% of the body. The dressing changes are very painful, and the client rates them 7/10 on the pain scale. The client has morphine 2 mg to be administered by mouth every 2hours as needed. When planning the client's care, when does the nurse decide to administer the medication? 1 15 minutes before the dressing change Correct2 60 minutes before the dressing change 3 Along with a stool softener each time it is administered 4 Only if the client rates pain between 8 and 10 on the pain scale Oral morphine takes 30 to 90 minutes to reach peak effect and can be administered at least 60 minutes before the dressing change. Although pain medications can cause constipation, the nurse would not administer a stool softener each time the morphine is administered. If the client is experiencing pain and rates it anywhere on the pain scale, the client can receive pain medication if it is within the timeframe. It is important to premedicate a client before a painful procedure. A nurse is administering a histamine H2antagonist to a client who has extensive burns. The nurse explains to the client that this drug is given prophylactically during the first few weeks after extensive burns. What complication of burns will it prevent? 1 Colitis 2 Gastritis Correct3 Stress ulcer 4 Metabolic acidosis An ulcer of the upper gastrointestinal tract is related to excessive secretion of stressrelated hormones, which increases hydrochloric acid production. Histamine H2 antagonists decrease acid secretion. Colitis is not a complication of burns. Gastritis is not a complication of burns. Metabolic acidosis is not a complication of burns unless hypermetabolism or renal failure occurs; metabolic acidosis is not treated with H2 antagonists. A nurse is assessing the adequacy of a client's intravenous fluid replacement therapy during the first 2 to 3 days after sustaining full-thickness burns to the trunk and right thigh. What assessment will provide the nurse with the most significant data? 1 Weights every day Correct2 Urinary output every hour 3 Blood pressure every 15 minutes 4 Extent of peripheral edema every 4 hours A client with extensive burns has an indwelling urinary catheter so that urine output can be measured hourly. Urinary output reflects circulating blood volume; it is the most reliable, immediately available information to assess fluid needs. Although daily weights reflect fluid retention or loss, they are not as immediately accurate as hourly urine measurements. A blood pressure reading may indicate hypervolemia or hypovolemia, but it is not as accurate an indicator of fluid replacement as hourly urine output. Peripheral edema may have many causes; it is not an effective indicator of fluid balance. A client is rescued from a house fire and arrives at the emergency department 1 hour after the rescue. The client weighs 132 pounds (60 kilograms) and is burnedover 35% of the body. The nurse expects that the amount of lactated Ringer solution that will be prescribed to be infused in the next 8 hours is what? 1 2100 mL Correct2 4200 mL 3 6300 mL 4 8400 mL In the first 8 hours 4200 mL should be infused. According to the Parkland (Baxter) formula, one half of the total daily amount of fluid should be administered in the first 8 hours. Because the client weighs 60 kg (132 pounds ÷ 2.2 kg = 60 kg), the calculation is 60 kg × 4 mL/kg × 35% burns = 8400 mL per day; half of this amount should be infused within the first 8 hours. 2100 mL, 6300 mL, and 8400 mL are incorrect calculations. A client sustains severe burns over 40% of the surface area of the body. The nurse is assigned to care for the client during the first 48 hours after the injury. What clinical finding does the nurse anticipate if the client develops water intoxication? 1 Sootycolored sputum 2 Frothy, pinktinged sputum Correct3 Disorientation with twitching 4 Urine output of 25 mL/hr Excess extracellular fluid moves into cells (water intoxication). Intracellular fluid excess in sensitive brain cells causes altered mental status; other signs include anorexia, nausea, vomiting, twitching, sleepiness, and convulsions. Sootycolored sputum indicates inhalation of smoke or flames. Frothy, pinktinged sputum is associated with pulmonary edema. Decreased urinary output indicates insufficient fluid replacement or dehydration. A client is admitted to the burn unit with partial-thickness burns over 30% of the body surface area. Twenty-four hours later, the client, who has an intravenous (IV) line of 5% dextrose in saline running, has tremors, twitching, and signs of disorientation. During the past hour the urinary output was 110 mL. What should the nurse do next? [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 26 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 12, 2021
Number of pages
26
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 12, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
37

.png)
.png)
.png)


.png)
.png)




.png)