*NURSING > Final Exam Review > NURS 6640 Walden University Final Exam Review Week 11 (76 Questions) [2021] (All)
NURS 6640 Walden University Final Exam Review Week 11 (76 Questions) [2021]
Document Content and Description Below
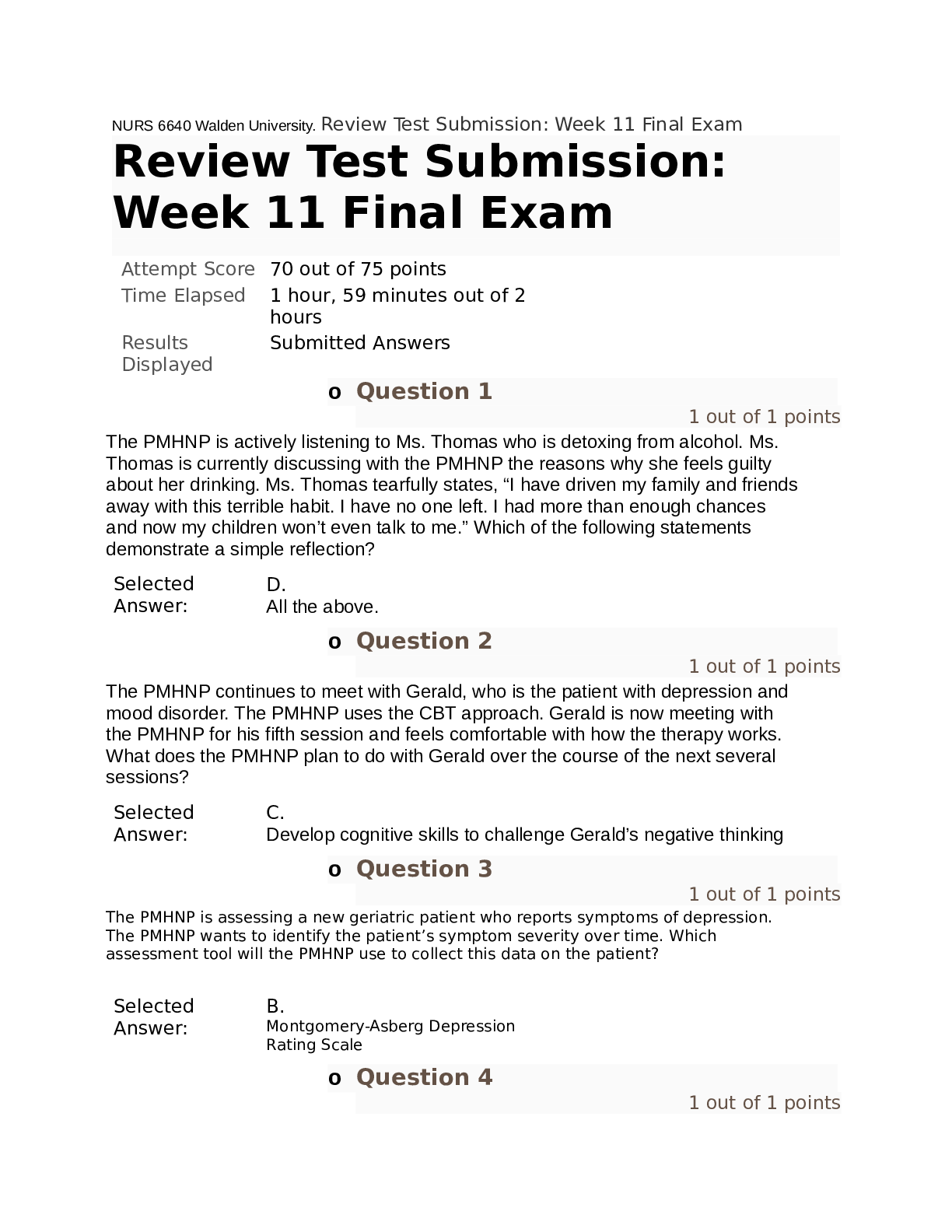
NURS 6640 Walden University. Review Test Submission: Week 11 Final Exam NURS 6640 Walden University final (76 Questions) o Question 1 1 out of 1 points The PMHNP is actively listening to Ms. Tho... mas who is detoxing from alcohol. Ms. Thomas is currently discussing with the PMHNP the reasons why she feels guilty about her drinking. Ms. Thomas tearfully states, “I have driven my family and friends away with this terrible habit. I have no one left. I had more than enough chances and now my children won’t even talk to me.” Which of the following statements demonstrate a simple reflection? Selected Answer: D. All the above. o Question 2 1 out of 1 points The PMHNP continues to meet with Gerald, who is the patient with depression and mood disorder. The PMHNP uses the CBT approach. Gerald is now meeting with the PMHNP for his fifth session and feels comfortable with how the therapy works. What does the PMHNP plan to do with Gerald over the course of the next several sessions? Selected Answer: C. Develop cognitive skills to challenge Gerald’s negative thinking o Question 3 1 out of 1 points The PMHNP is assessing a new geriatric patient who reports symptoms of depression. The PMHNP wants to identify the patient’s symptom severity over time. Which assessment tool will the PMHNP use to collect this data on the patient? Selected Answer: B. Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale o Question 4 1 out of 1 points A cocaine-addicted female patient is entering residential treatment for substance abuse. Using the 10 guiding principles of recovery, an appropriate step by the PMHNP is to ______________. Selected Answer: B. integrate services that encompass mind, body, spirit, and community o Question 5 1 out of 1 points The PMHNP uses the Adult Attachment Interview (AAI) with a male patient who reports having had a difficult time being separated from his parents during his childhood. He explains that going to school or visiting his relatives without his parents was troublesome. The PMHNP characterizes the patient as unresolved/disorganized, according to his outcomes on the AAI. What does the PMHNP anticipate from the patient? Selected Answer: A. He will have lapses in his memory of his childhood. o Question 6 1 out of 1 points A 21-year-old patient has been having trouble adjusting to college life. She tells the PMHNP that she had five alcoholic drinks at a party this past weekend. She also acknowledges that she drank the same amount of alcohol at a party the previous month. Based on this information, what would the PMHNP most likely recommend? Selected Answer: D. None of the above o Question 7 1 out of 1 points Following an attempted suicide, Mr. Durham was admitted to an acute psychiatric facility. After 4 weeks in treatment, he is preparing for discharge. He is beginning to miss individual and group therapy sessions and has refused medications twice in the past 2 days. The PMHNP demonstrates understanding in this phase by saying which of the following statements? Selected Answer: B. “Have you thought of how you will continue your treatment plans?” o Question 8 1 out of 1 points While assessing a patient using a humanistic-existential approach, a patient tells the PMHNP, “For the past few weeks, I’ve felt anxious almost every single day.” What would be an appropriate next step by the PMHNP? Selected Answer: D. Encourage the patient to clarify by asking, “You constantly feel anxious?” o Question 9 1 out of 1 points A patient’s depression is affecting her relationship with her spouse. What might the PMHNP ask during the initial sessions of interpersonal psychotherapy treatment? Selected Answer: D. All of the above. o Question 10 1 out of 1 points How does the PMHNP approach termination with the patient who has been receiving intermittent therapy? Selected Answer: D. A and C o Question 11 1 out of 1 points The PMHNP who practices motivational interviewing understands its relationship to patient behaviors and/or outcomes to mean which of the following? Selected Answer: D. There is a lower incidence of inconsistent behaviors with motivational interviewing. This is related to client engagement and better outcomes. o Question 12 1 out of 1 points The PMHNP is caring for a patient who experiences depression caused by the traumatic experience of her dog passing away. She reports not being able to eat or sleep, and sometimes doesn’t want to leave the house at all. Which statement is most appropriate for the PMHNP to maximize the patient’s adaptive coping mechanisms? Selected Answer: C. “It’s important to be mindful of how you feel and then to determine what causes those feelings.” o Question 13 1 out of 1 points A 55-year-old patient recovering from substance abuse tells the PMHNP, “It’s impossible to meet new people. I really hate being single.” Using existential psychotherapy, what might the PMHNP say next? Selected Answer: D. “What might help you to live a more meaningful life?” o Question 14 0 out of 1 points A PMHNP is using motivational interviewing (MI) with a 50-year-old patient named Dave to commit to a healthy drug-free lifestyle. By using “change talk,” the PMHNP hopes to help the patient build self-esteem and hope. True or false: If Dave is resisting change, the PMHNP should challenge his resistance in order for MI to be successful. Selected Answer: Tru e o Question 15 1 out of 1 points The PMHNP is interviewing a patient who is in the process of successfully completing a substance abuse program. During the interview, the patient states, “I wish I was strong enough to keep the same friends I had before I came here for treatment. I’m really afraid of being discharged because I’ll probably run into my old friends again.” The PMHNP offers a complex reflection when she states the following: Selected Answer: C. “You’d like to keep your old friends but know being around them may lead you to abuse substances again.” o Question 16 1 out of 1 points The PMHNP is in the process of terminating treatment with a patient who witnessed the death of her parent who used to sexually abuse her. What does the PMHNP understand about terminating this patient? Selected Answer: D. The patient may need to have follow-up sessions every few months. o Question 17 1 out of 1 points A 13-year-old patient and his parents are meeting with a PMHNP. When the PMHNP says hello, the boy just nods. His parents tell the PMHNP that he didn’t want to come to the session, but they insisted. They explain that their son has been moody and depressed at home, but is still getting good grades at school. Which of the following would be the best response by the PMHNP? Selected C. Answer: Compliment the patient on his academic achievement o Question 18 1 out of 1 points A PMHNP is using emotion-focused therapy to help a 38-year-old patient who says, “I’ve been feeling angry lately, but I’m not sure why.” The first attempt by the PMHNP is to say: Selected Answer: A. “Focus on your anger, take a deep breath, and allow an image to emerge.” o Question 19 1 out of 1 points The PMHNP is communicating with a middle-aged male patient who has a history of addiction to Percocet (acetaminophen/oxycodone). The patient suddenly yells, “I do not have a problem with pain pills! I’ve never had an overdose and no one even knows that I take them unless I tell them.” The PMHNP understands that there are phases of change and can best demonstrate “focusing” by responding with: Selected Answer: D. “I am wondering if your use of pain medication has ever prompted you to seek medical attention.” o Question 20 1 out of 1 points A 21-year-old patient is worried about starting a new job. She talks about her fears of failure and not making friends at the office. Using a person-centered approach, an appropriate response by the PMHNP is to ______________. Selected Answer: C. ask the patient to reflect on and explore what she is experiencing o Question 21 1 out of 1 points A 38-year-old patient tells the PMHNP that her father went to jail for selling drugs when she was a child. The patient is visibly upset when discussing what happened. Using a humanistic-existential approach to psychotherapy, which of the following is the most appropriate response by the PMHNP? Selected Answer: B. “What are you experiencing now as you share this story?” o Question 22 1 out of 1 points The PMHNP is caring for an adult male patient whose wife left him several months ago. He recently learned that his ex-wife is dating someone much younger. The man feels belittled, sad, and lonely. He talks about trying to meet other women, but says, “I can’t compete with the younger guys these days, with the cool clothes and the vegan diets. I’m bald and overweight, and what woman is going to want to be with me?” How does the PMHNP help raise the man’s self-esteem? Selected Answer: D. All of the above o Question 23 1 out of 1 points The PMHNP is working with a patient who describes having a painful and traumatic childhood experience, which causes her to have anxiety as an adult. When asked how she manages her anxiety, the patient dismisses it and denies that it is a problem. Using the supportive psychotherapy approach, the PMHNP will do which of the following when assessing the patient’s ego strength? Selected Answer: A. Identify the primary defenses the patient uses to ward off anxiety o Question 24 1 out of 1 points The PMHNP is assessing a 30-year-old client who reports feeling stressed out due to his current employment situation. When asked about how he manages this workrelated stress, the patient says that exercise helps him feel less anxious, so he often spends 2 or more hours at the gym each night. After completing the patient assessment, the PMHNP has determined that an existential psychotherapy approach may best benefit this client. What is the PMHNP’s goal in employing this treatment approach? Selected Answer: B. Help the patient be aware of his anxiety and embrace it o Question 25 1 out of 1 points The PMHNP is caring for a young adult patient with whom the PMHNP decides to use a dynamic supportive therapy approach in addition to pharmacological intervention. Which therapeutic action will the PMHNP take to employ the strategy of holding and containing the patient? Selected Answer: B. Asking the patient how the patient feels o Question 26 1 out of 1 points A PMHNP has been treating a 9-year-old patient who was referred by her school. Students are asked to raise their hands before speaking during group discussion, but the patient seems to blurt out what she wants to say without being called on. She also interrupts other children while they are talking instead of waiting her turn. When the patient gets frustrated, she has trouble controlling her emotions and cries often. Based on the initial information provided, the first focus by PMHNP is the child’s ____________. Selected Answer: B. selfregulation o Question 27 1 out of 1 points A PMHNP is using Gestalt therapy to communicate with a 50-year-old patient who is going through a divorce. As he is calmly sharing the details of his divorce, the PMHNP notices that Dave is tapping his fingers on his legs. What is an appropriate response by the PMHNP using the technique of focusing? Selected Answer: A. “I noticed that your fingers were tapping. Can you give a voice to your fingers?” o Question 28 1 out of 1 points The PMHNP is assessing an older adult male patient with depression and comorbidities. According to the medical chart, the patient takes medication to manage joint and bone pain. The patient reports feeling “forgetful” and complains that he has a hard time remembering where he puts things. What is the primary action by the PMHNP? Selected Answer: C. Determining if the patient’s medications can be causing memory problems o Question 29 1 out of 1 points In the planning phase of change, a 42-year-old male client who struggles with gambling discusses how he plans to abstain from gambling. He tells the PMHNP, “I am no longer going to carry cash to the casino because you can’t spend what you don’t have.” The PMHNP uses an affirming communication skill when she states: Selected Answer: A. “Not gambling is a tough habit to break; not carrying cash is a big step in the right direction.” o Question 30 0 out of 1 points A PMHNP is assessing a 40-year-old patient named Sarah who has a severe cocaine addiction and mild depression. Using the four-quadrant model, what would be the most appropriate setting to help the patient? Selected Answer: B. State psychiatric hospitals and emergency rooms o Question 31 1 out of 1 points The PMHNP has been providing supportive psychodynamic psychotherapy to a patient and is nearing the termination stage. The PMHNP will use which criteria for determining that the patient is ready for termination? Selected Answer: B. Symptoms have improved. o Question 32 1 out of 1 points The PMHNP is caring for a patient who is histrionic. Using the supportive psychodynamic therapy model, what is the best statement made by the PMHNP? Selected Answer: B. “Let’s not think too much about emotion right now. Let’s focus on what got you upset in the first place.” o Question 33 1 out of 1 points When recalling the phases of change, the PMHNP demonstrates “open questioning” in the “engagement” phase by making which statement? Selected Answer: B. “What occurred to cause you to seek treatment?” o Question 34 1 out of 1 points The PMHNP is meeting with an older, female adult patient and her daughter. The patient has early onset dementia. The daughter expresses concern, saying, “I don’t want you to just stick my mother in a home and give her medicine. I’m worried that’s what people are going to want to do.” What is the best response by the PMHNP to the daughter? Selected Answer: B. “The type of treatment depends on the stage of dementia and safety considerations.” o Question 35 0 out of 1 points The PMHNP is caring for an older adult patient who is in the acute phase of schizophrenia. Which therapeutic model will the PMHNP employ with this patient? Selected Answer: A. Individual CBT o Question 36 0 out of 0 points When completing this exam, did you comply with Walden University’s Code of Conduct including the expectations for academic integrity? Selected Answers: Ye s o Question 37 1 out of 1 points The PMHNP has been providing interpersonal psychotherapy (IPT) for a patient who the PMHNP observes implementing new ways of being, such as interacting more with peers and being less isolated in social scenarios. The PMHNP understands that the patient is approaching termination. How does the PMHNP address termination with this patient? Selected Answer: C. Embed the termination into the work of the therapeutic phase o Question 38 1 out of 1 points The PMHNP assesses a 27-year-old patient named Jeff, who was a victim of child abuse and neglect. Jeff says that he remembers a traumatic situation that he wants to share, but is having trouble talking about it. Which statement made by the PMHNP demonstrates the use of emotion-focused therapy? Selected Answer: A. “Let’s see if we can come up with some ideas for you to feel safe telling your story.” o Question 39 1 out of 1 points A PMHNP is treating a 12-year-old girl who witnessed the physical abuse of her sibling. She has been anxious and irritable since the experience. After speaking with the PMHNP, the patient says she keeps having anxiety-causing thoughts about the experience. Using the PRACTICE technique, which skill will best help the patient interrupt these negative thoughts? Selected Answer: B. Affect modulation o Question 40 1 out of 1 points A PMHNP is using interpersonal psychotherapy with a 40-year-old patient having relationship problems with his extended family. The patient shares that he has been using the strategies they identified to reduce his distress, but they have not been helping. He is frustrated and is considering stopping treatment. What would be an appropriate step by the PMHNP? Selected Answer: A. Encourage the patient to continue treatment by using alternative strategies o Question 41 1 out of 1 points The PMHNP meets with a 31-year-old woman who reports feeling as though she is “at her breaking point” with work. The PMHNP learns that the woman works 12-hour days, including one day on the weekend, because she is nervous about company layoffs. “I feel like I need to work myself to death in order to prove that I am valuable to the organization,” the woman says. Using the supportive psychodynamic therapy approach, how does the PMHNP respond? Selected Answer: D. “That must be a very tiring work schedule. How do you feel about working so much?” o Question 42 1 out of 1 points The PMHNP is assessing a patient who requires cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT). Which of the following statements made by the PMHNP approach the termination phase for this patient? Selected Answer: A. “Although it’s your first session, we will discuss how termination of your treatment will go.” o Question 43 1 out of 1 points The PMHNP is terminating treatment for a patient who has been... [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 18 pages
Reviews( 2 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 12, 2021
Number of pages
18
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 12, 2021
Downloads
2
Views
115




-converted.png)