Biology > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > University of Maryland, University College BIOL Quiz 2, All possible questions in 70 Pages. 100% Sco (All)
University of Maryland, University College BIOL Quiz 2, All possible questions in 70 Pages. 100% Score
Document Content and Description Below
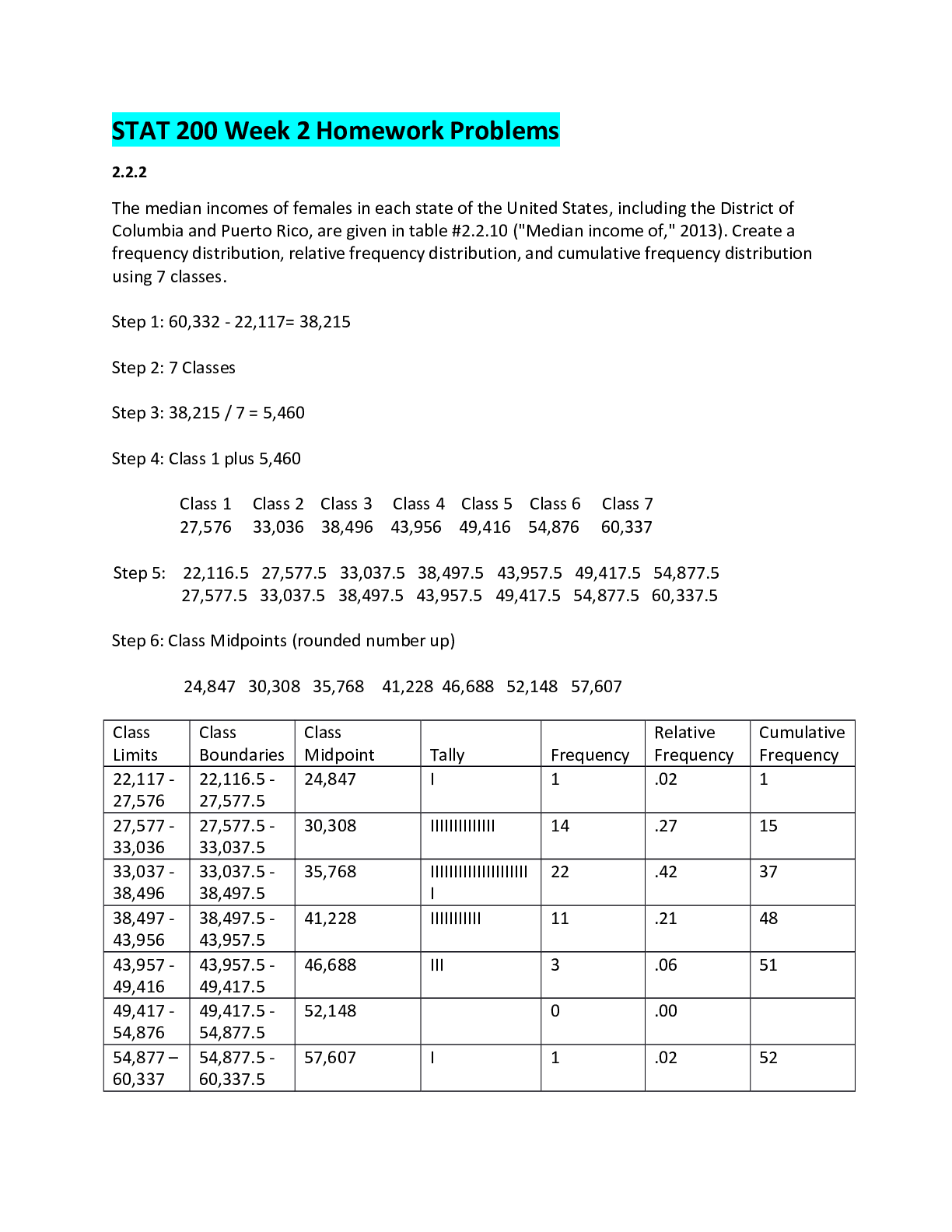
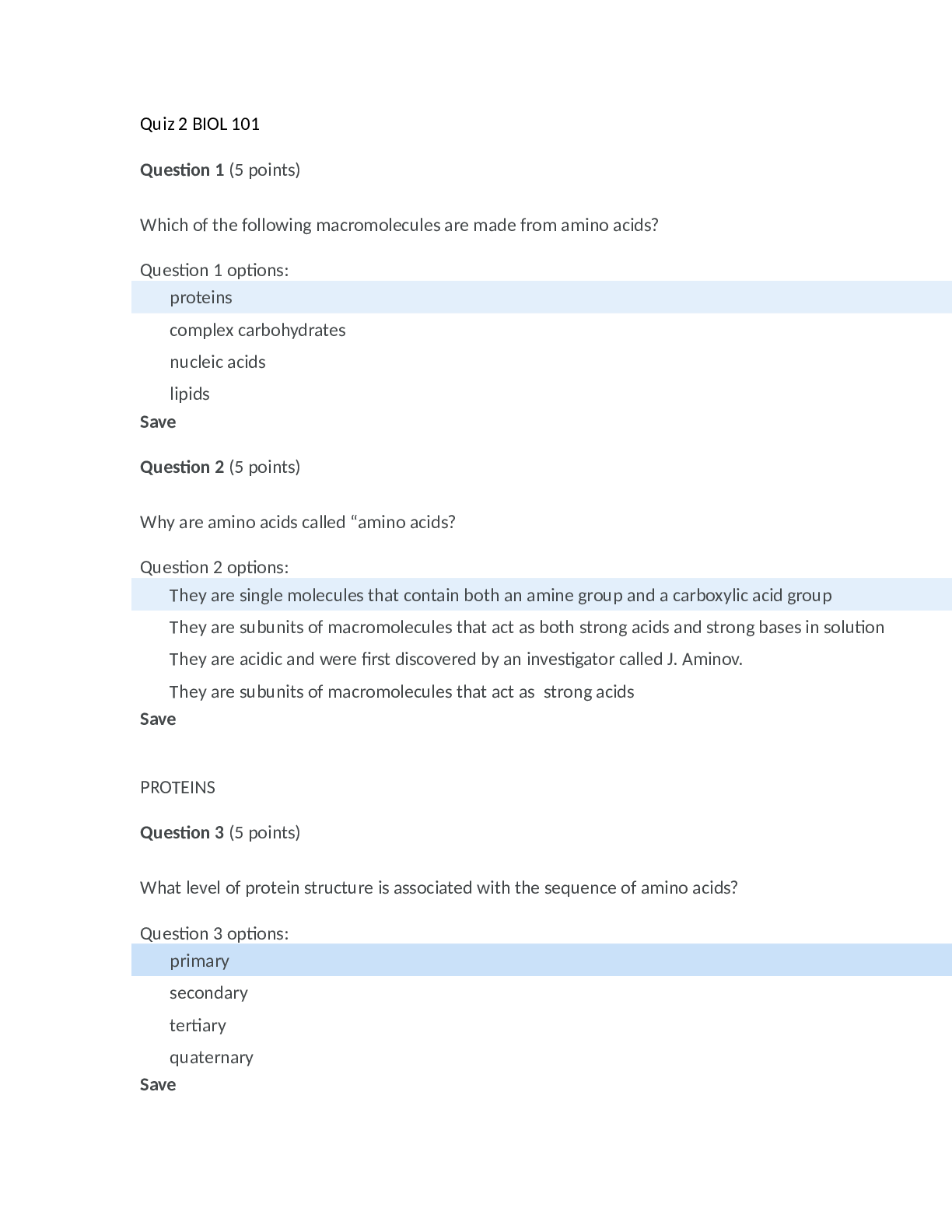
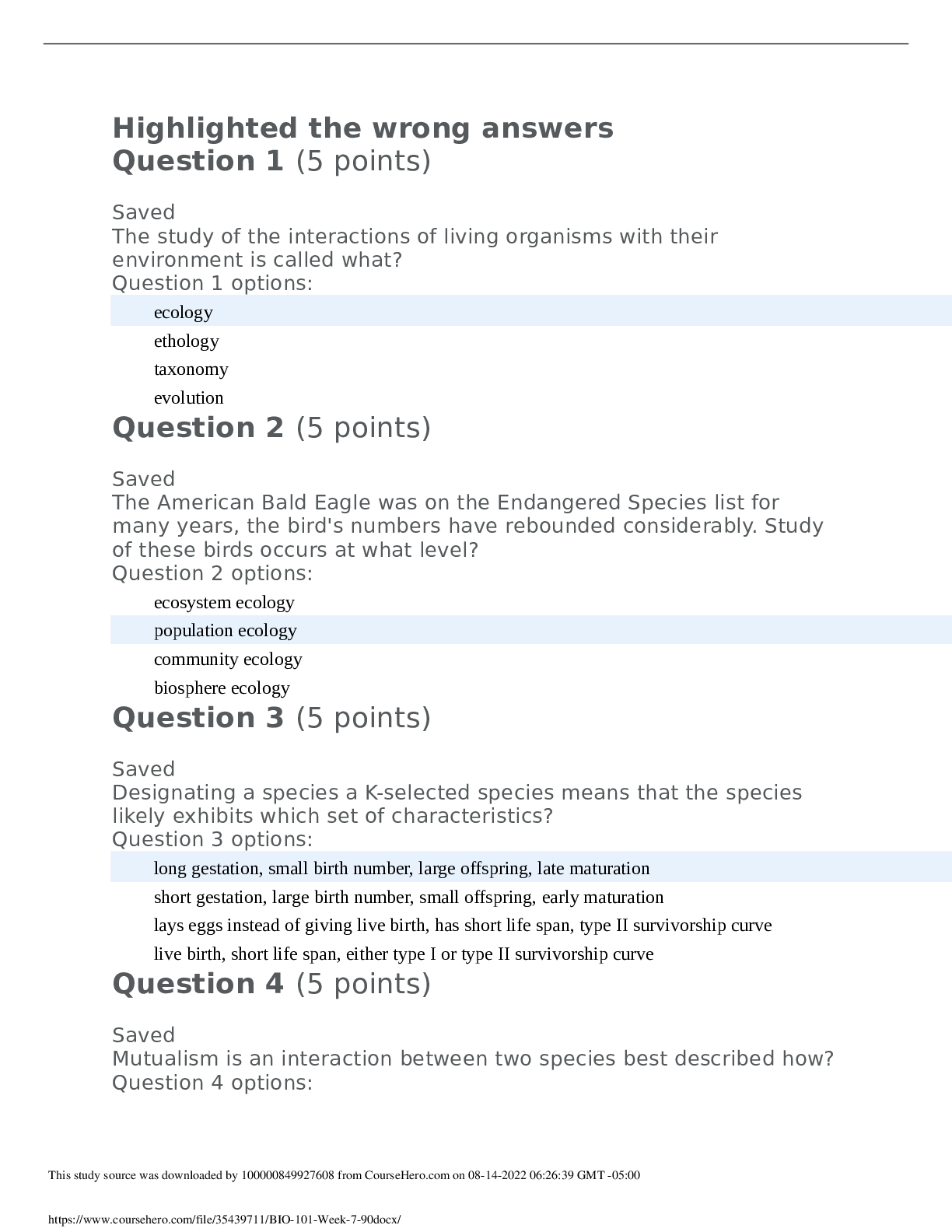
University of Maryland, University College BIOL Quiz 2, All possible questions Quiz 2 BIOL 101 Question 1 (5 points) Which of the following macromolecules are made from amino acids? Question 1 o... ptions: proteins complex carbohydrates nucleic acids lipids Save Question 2 (5 points) Why are amino acids called “amino acids? Question 2 options: They are single molecules that contain both an amine group and a carboxylic acid group They are subunits of macromolecules that act as both strong acids and strong bases in solution They are acidic and were first discovered by an investigator called J. Aminov. They are subunits of macromolecules that act as strong acids Save PROTEINS Question 3 (5 points) What level of protein structure is associated with the sequence of amino acids? Question 3 options: primary secondary tertiary quaternary Save Question 4 (5 points) How are most carbohydrates used in the human body? Question 4 options: used as building blocks for proteins used as catalysts for reactions in cells used as a source of energy used as building blocks for lipids not necessary for regular bodily functions Save Question 5 (5 points) Which of the following carbohydrates is used to store energy in animal cells? Question 5 options: cellulose glycogen starch hemi-cellulose Save LIPIDS Question 6 (5 points) Fatty acids are a component of what type of macromolecule? Question 6 options: lipids complex carbohydrates nucleic acids Proteins NUCLEIC ACIDS Question 7 (5 points) Which of the following is not part of a nucleic acid? Question 7 options: pentose sugar nitrogenous base fatty acid group phosphate group Save DENATURATION Question 8 (5 points) Why does the egg white from raw eggs go from clear to white after it is cooked? Question 8 options: because the protein is denatured in raw egg white because the protein is denatured in cooked egg white because the peptide bonds existing between amino acids break in the raw eggs because the peptide bonds existing between amino acids break in the cooked eggs Save PHOSPHOLIPIDS Question 9 (5 points) Why do phospholipids spontaneously form a bilayer when mixed with water? Question 9 options: because they have an end that is polar and another that is non-polar because the polar head groups come together in the inside of the membrane because both ends are non polar because the polar tails come together in the inside of the membrane CELL MEMBRANES Question 10 (5 points) What is a characteristic of cell membranes? Question 10 options: dynamic impermeable static symmetrical Save COMPARING EUKARYOTES & PROKARYOTES Question 11 (5 points) Describe why eukaryotic cells being compartmentalized can make their metabolism more complex? Question 11 options: same chemical reactions can occur together more frequently different chemical reactions can occur in isolation of each other different chemical reactions can occur all in the same place same chemical reactions can occur in isolation of each other Save Question 12 (5 points) Which of the following does a prokaryotic cell have that an animal cell does not? Question 12 options: DNA ribosomes cell wall Vacuole EUKARYOTES Question 13 (5 points) Select the statement that is ***incorrect*** Question 13 options: Cells contain either DNA or RNA, never both Cell are the smallest living things Most cells can divide to produce new cells All living organisms are composed of at least one cell All cells are either prokaryotic or eukaryotic Save OSMOSIS & DIFFUSION Question 14 (5 points) Incorrect answer If you place a blood cell in a beaker filled with pure water, what would likely happen? Question 14 options: Water flows into the blood cell Water flows out of the blood cell Equal amounts of water flows into and out of the blood cell Equal amounts of solutes flow into and out of the blood cell Save Question 15 (5 points) What is osmosis? Question 15 options: A process that involves the movement of water A process that requires energy A process that occurs across a cell wall The movement of any molecule from high to low concentration ACTIVE TRANSPORT Question 16 (5 points) Sodium ions are more highly concentrated outside the cell, in the extracellular fluid. Which process would be used to return any sodium ions that leaked into the cell back to the extracellular fluid? Question 16 options: osmosis active transport facilitated diffusion simple diffusion Save EUKARYOTIC ORGANELLES Question 17 (5 points) What is the function of the endoplasmic reticulum in the eukaryotic cells? Question 17 options: modifies proteins, synthesizes lipids. directs the synthesis of ribosomes and proteins organizing center of microtubules in animal cells synthesizes ATP, cellular respiration digestion of macromolecules Save Question 18 (5 points) What is the function of the peroxisome in the eukaryotic cell? Question 18 options: protein synthesis organizing center of microtubules in animal cells oxidizes and breaks down fatty acids and amino acids storage and transport ATP production ANTIBIOTICS AND PROKARYOTIC CELLS Question 19 (5 points) What is the concern with overuse of antibiotics? Question 19 options: the patient will become antibiotic resistant viruses will become antibiotic resistant. bacteria will become antibiotic resistant. the antibiotics will degrade Save Question 20 (5 points) You have a case of the common cold (which is caused by a virus). What would happen if you take antibio Question 20 options: you will get better you will get another viral infection nothing you will get worse Attempt 1 Written: Mar 11, 2018 9:11 PM - Mar 11, 2018 9:49 PM Submission View Your quiz has been submitted successfully. NO ACIDS TEINS BOHYDRATES DS CLEIC ACIDS NATURATION OSPHOLIPIDS L MEMBRANES MPARING EUKARYOTES & PROKARYOTES ARYOTES MOSIS & DIFFUSION stion 14 0 / 5 points If you place a blood cell in a beaker filled with pure water, what would likely happen? Question options: Water flows into the blood cell Water flows out of the blood cell Equal amounts of water flows into and out of the blood cell Equal amounts of solutes flow into and out of the blood cell ACTIVE TRANSPORT ARYOTIC ORGANELLES IBIOTICS AND PROKARYOTIC CELLS 95 / 100 - 95 % Overa 95 / 100 - 95 % Other references: BIOL 101 6388 Concepts of Biology (2178) Attempt Score: 95 / 100 - 95 % AMINO ACIDS Question 1 (5 points) Which of the following macromolecules are made from amino acids? Question 1 options: proteins complex carbohydrates nucleic acids lipids Question 2 (5 points) Why are amino acids called “amino acids? Question 2 options: They are single molecules that contain both an amine group and a carboxylic acid group They are subunits of macromolecules that act as both strong acids and strong bases in solution They are acidic and were first discovered by an investigator called J. Aminov. They are subunits of macromolecules that act as strong acids PROTEINS Question 3 (5 points) What is the name of the chemical bond between amino acids? Question 3 options: phosphodiester hydrogen peptide electronegative CARBOHYDRATES Question 4 (5 points) Which of the following carbohydrates is used to store long-term energy in plant cells? Question 4 options: glucose glycogen starch cellulose * incorrect Question 5 (5 points) How are most carbohydrates used in the human body? Question 5 options: used as building blocks for proteins used as catalysts for reactions in cells used as a source of energy used as building blocks for lipids not necessary for regular bodily functions Save LIPIDS Question 6 (5 points) Fatty acids are a component of what type of macromolecule? Question 6 options: lipids complex carbohydrates nucleic acids proteins NUCLEIC ACIDS Question 7 (5 points) Which of the following is not part of a nucleic acid? Question 7 options: pentose sugar nitrogenous base fatty acid group phosphate group Save DENATURATION Question 8 (5 points) Why does the egg white from raw eggs go from clear to white after it is cooked? Question 8 options: because the protein is denatured in raw egg white because the protein is denatured in cooked egg white because the peptide bonds existing between amino acids break in the raw eggs because the peptide bonds existing between amino acids break in the cooked eggs Save PHOSPHOLIPIDS Question 9 (5 points) The inside of a phospholipid bilayer is: Question 9 options: hydrophobic hydrophilic hypotonic hypertonic CELL MEMBRANES Question 10 (5 points) A set of erythrocytes is placed in a beaker of 0.9% NaCl. Nothing appears to happen to the cells. Why? Question 10 options: 0.9% NaCl is hypertonic to the cells. 0.9% NaCl is isotonic to the cells 0.9% NaCl is hypotonic to the cells Sodium blocks the movement of water Save COMPARING EUKARYOTES & PROKARYOTES Question 11 (5 points) Describe why eukaryotic cells being compartmentalized can make their metabolism more complex? Question 11 options: same chemical reactions can occur together more frequently different chemical reactions can occur all in the same place different chemical reactions can occur in isolation of each other same chemical reactions can occur in isolation of each other Save Question 12 (5 points) Which of the following does a prokaryotic cell have that an animal cell does not? Question 12 options: vacuole cell wall ribosomes DNA EUKARYOTES Question 13 (5 points) Which of the following is not a component of the endomembrane system? Question 13 options: mitochondria Golgi apparatus endoplasmic reticulum lysosome central vacuole Save OSMOSIS & DIFFUSION Question 14 (5 points) What is the diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane called? Question 14 options: pinocytosis facilitated diffusion active transport osmosis phagocytosis endocytosis Save Question 15 (5 points) If you place a blood cell in a beaker filled with a concentrated salt solution, what would likely happen? Question 15 options: Water flows into the blood cell Water flows out of the blood cell Salt flows out of the blood cell Equal amounts of water flows into and out of the blood cell ACTIVE TRANSPORT Question 16 (5 points) What is he name of the process by which a cell will uptake large molecules from the extracellular fluid? Question 16 options: endocytosis active transport facilitated diffusion exocytosis EUKARYOTIC ORGANELLES Question 17 (5 points) What is the function of the nucleus in the eukaryotic cell? Question 17 options: protein synthesis directs the synthesis of ribosomes and proteins organizing center of microtubules in animal cells digestion of macromolecules Save Question 18 (5 points) In what type of cells would you expect to find a large amount of smooth endoplasmic reticulum? Question 18 options: brain liver intestinal muscle ANTIBIOTICS AND PROKARYOTIC CELLS Question 19 (5 points) An ideal antibiotic damages only bacterial cells but not human cells. Which of the following cellular structures would be a good target for antibiotics? Question 19 options: nucleus cytoskeleton plasma membrane cell wall Save Question 20 (5 points) You have a case of the common cold (which is caused by a virus). What would happen if you take antibiotics? Question 20 options: you will get better you will get another viral infection nothing you will get worse AMINO ACIDS Question 1 (5 points) 1 What is the name of the monomer that makes up proteins? Question 1 options: nucleotides amino acids disaccharides fatty acids Question 2 (5 points) 2 Why are amino acids called “amino acids? Question 2 options: They are single molecules that contain both an amine group and a carboxylic acid group They are subunits of macromolecules that act as both strong acids and strong bases in solution They are acidic and were first discovered by an investigator called J. Aminov. They are subunits of macromolecules that act as strong acids PROTEINS Question 3 (5 points) 3 What level of protein structure is associated with the sequence of amino acids? Question 3 options: primary secondary tertiary quaternary Question 4 (5 points) Which of the following carbohydrates is used to store long-term energy in plant cells? Question 4 options: glucose starch glycogen cellulose Question 5 (5 points) Which of the following is characterized as dietary fiber? Question 5 options: sucrose glycogen cellulose starch LIPIDS Question 6 (5 points) Fatty acids are a component of what type of macromolecule? Question 6 options: WRONG lipids complex carbohydrates nucleic acids proteins NUCLEIC ACIDS Question 7 (5 points) Where is most of the DNA found in the eukaryotic cell? Question 7 options: golgi mitochondria nucleus ribosomes DENATURATION Question 8 (5 points) Why does the egg white from raw eggs go from clear to white after it is cooked? Question 8 options: because the protein is denatured in raw egg white because the protein is denatured in cooked egg white because the peptide bonds existing between amino acids break in the raw eggs because the peptide bonds existing between amino acids break in the cooked eggs PHOSPHOLIPIDS Question 9 (5 points) Why do phospholipids spontaneously form a bilayer when mixed with water? Question 9 options: because the polar tails come together in the inside of the membrane because they have an end that is polar and another that is non-polar because both ends are non polar because the polar head groups come together in the inside of the membrane CELL MEMBRANES Question 10 (5 points) A set of erythrocytes is placed in a beaker of 0.9% NaCl. Nothing appears to happen to the cells. Why? Question 10 options: 0.9% NaCl is hypertonic to the cells. 0.9% NaCl is isotonic to the cells 0.9% NaCl is hypotonic to the cells Sodium blocks the movement of water COMPARING EUKARYOTES & PROKARYOTES Question 11 (5 points) Describe why eukaryotic cells being compartmentalized can make their metabolism more complex? Question 11 options: same chemical reactions can occur together more frequently different chemical reactions can occur in isolation of each other different chemical reactions can occur all in the same place same chemical reactions can occur in isolation of each other Question 12 (5 points) Which if the following are found in eukaryotic cells but not prokaryotic cells? Question 12 options: WRONG Golgi body vacuole DNA ribosome EUKARYOTES Question 13 (5 points) Which of the following is not a component of the endomembrane system? Question 13 options: mitochondria Golgi apparatus endoplasmic reticulum lysosome central vacuole OSMOSIS & DIFFUSION Question 14 (5 points) What is the diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane called? Question 14 options: pinocytosis facilitated diffusion active transport osmosis phagocytosis endocytosis Question 15 (5 points) What is osmosis? Question 15 options: WRONG A process that involves the movement of water A process that requires energy A process that occurs across a cell wall The movement of any molecule from high to low concentration ACTIVE TRANSPORT Question 16 (5 points) What is the name of the process by which a cell will uptake large molecules from the extracellular fluid? Question 16 options: endocytosis active transport facilitated diffusion exocytosis EUKARYOTIC ORGANELLES Question 17 (5 points) What is the function of the endoplasmic reticulum in the eukaryotic cells? Question 17 options: modifies proteins, synthesizes lipids. directs the synthesis of ribosomes and proteins organizing center of microtubules in animal cells synthesizes ATP, cellular respiration digestion of macromolecules Question 18 (5 points) What is the function of the peroxisome in the eukaryotic cell? Question 18 options: protein synthesis organizing center of microtubules in animal cells oxidizes and breaks down fatty acids and amino acids storage and transport ATP production ANTIBIOTICS AND PROKARYOTIC CELLS Question 19 (5 points) Which is a plausible effect of taking oral antibiotics? Question 19 options: the antibiotics could unintentionally kill good bacteria living in your intestines, leaving you more susceptible to infection by pathogenic bacteria the antibiotics could harm your own body cells. the antibiotics could interfere with your body’s own ability to produce antibiotics, and actually end up prolonging the infection. the antibiotics could destroy viruses that have infected your body Question 20 (5 points) You have a case of the common cold (which is caused by a virus). What would happen if you take antibiotics? Question 20 options: you will get better you will get another viral infection nothing you will get worse AMINO ACIDS Question 1 (5 points) What is the name of the monomer that makes up proteins? Question 1 options: nucleotides amino acids disaccharides fatty acids Save Question 2 (5 points) Which of the following macromolecules are made from amino acids? Question 2 options: proteins complex carbohydrates nucleic acids lipids Save PROTEINS Question 3 (5 points) What is the name of the chemical bond between amino acids? Question 3 options: phosphodiester hydrogen peptide electronegative CARBOHYDRATES Question 4 (5 points) Which of the following carbohydrates is used to store energy in animal cells? Question 4 options: glycogen cellulose hemicellulose starch Save Question 5 (5 points) Which of the following is characterized as dietary fiber? Question 5 options: sucrose glycogen cellulose starch Save LIPIDS Question 6 (5 points) Fatty acids are a component of what type of macromolecule? Question 6 options: lipids complex carbohydrates nucleic acids proteins NUCLEIC ACIDS Question 7 (5 points) Which of the following is not part of a nucleic acid? Question 7 options: pentose sugar nitrogenous base fatty acid group phosphate group Save DENATURATION Question 8 (5 points) Why does the egg white from raw eggs go from clear to white after it is cooked? Question 8 options: because the protein is denatured in raw egg white because the protein is denatured in cooked egg white because the peptide bonds existing between amino acids break in the raw eggs because the peptide bonds existing between amino acids break in the cooked eggs Save PHOSPHOLIPIDS Question 9 (5 points) What property of the phospholipid bilayer allows proteins to move laterally in the membrane? Question 9 options: phospholipids and proteins are attracted to each other phospholipid molecules are not covalently bonded to each other phospholipids are attracted to each other by opposite charges proteins attract each other with opposite charges CELL MEMBRANES Question 10 (5 points) A set of erythrocytes is placed in a beaker of 0.9% NaCl. Nothing appears to happen to the cells. Why? Question 10 options: 0.9% NaCl is hypertonic to the cells. 0.9% NaCl is isotonic to the cells 0.9% NaCl is hypotonic to the cells Sodium blocks the movement of water Save COMPARING EUKARYOTES & PROKARYOTES Question 11 (5 points) What is the difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells? Question 11 options: eukaryotic cells are found in animals, while plant cells are comprised of prokaryotic cells. eukaryotic cells have a plasma membrane, which is lacking in prokaryotic cells. eukaryotic cells have a nucleoid region, which is lacking in prokaryotic cells. eukaryotic cells have membrane-enclosed organelles, which are lacking in prokaryotic cells. Save Question 12 (5 points) Which if the following are found in eukaryotic cells but not prokaryotic cells? Question 12 options: Golgi body vacuole DNA ribosome EUKARYOTES Question 13 (5 points) Select the statement that is ***incorrect*** Question 13 options: Cells contain either DNA or RNA, never both Cell are the smallest living things Most cells can divide to produce new cells All living organisms are composed of at least one cell All cells are either prokaryotic or eukaryotic Save OSMOSIS & DIFFUSION Question 14 (5 points) If you place a blood cell in a beaker filled with a concentrated salt solution, what would likely happen? Question 14 options: Water flows out of the blood cell Water flows into the blood cell Salt flows out of the blood cell Equal amounts of water flows into and out of the blood cell Save Question 15 (5 points) What is osmosis? Question 15 options: A process that involves the movement of water A process that requires energy A process that occurs across a cell wall The movement of any molecule from high to low concentration ACTIVE TRANSPORT Question 16 (5 points) What is the name of the process by which a cell will uptake large molecules from the extracellular fluid? Question 16 options: endocytosis active transport facilitated diffusion exocytosis Save EUKARYOTIC ORGANELLES Question 17 (5 points) What is the function of the endoplasmic reticulum in the eukaryotic cells? Question 17 options: modifies proteins, synthesizes lipids. directs the synthesis of ribosomes and proteins organizing center of microtubules in animal cells synthesizes ATP, cellular respiration digestion of macromolecules Save Question 18 (5 points) What is the function of the mitochondria in the eukaryotic cell? Question 18 options: protein synthesis directs the synthesis of ribosomes and proteins organizing center of microtubules in animal cells production of ATP, cellular respiration ANTIBIOTICS AND PROKARYOTIC CELLS Question 19 (5 points) What is the concern with overuse of antibiotics? Question 19 options: the patient will become antibiotic resistant viruses will become antibiotic resistant. bacteria will become antibiotic resistant. the antibiotics will degrade Save Question 20 (5 points) An ideal antibiotic damages only bacterial cells but not human cells. Which of the following cellular structures would be a good target for antibiotics? Question 20 options: nucleus cytoskeleton plasma membrane cell wall WRONG ANSWERS 0 / 5 points What property of the phospholipid bilayer allows proteins to move laterally in the membrane? Question options: holipids and proteins are attracted to each other holipid molecules are not covalently bonded to each other holipids are attracted to each other by opposite charges ns attract each other with opposite charges EMBRANES NG EUKARYOTES & PROKARYOTES TES & DIFFUSION 0 / 5 points If you place a blood cell in a beaker filled with a concentrated salt solution, what would likely happen? Question options: Water flows out of the blood cell Water flows into the blood cell Salt flows out of the blood cell Equal amounts of water flows into and out of the blood cell BIOL 101 6388 Concepts of Biology (2178) Attempt Score: 95 / 100 - 95 % AMINO ACIDS Question 1 (5 points) Which of the following macromolecules are made from amino acids? Question 1 options: proteins complex carbohydrates nucleic acids lipids Question 2 (5 points) Why are amino acids called “amino acids? Question 2 options: They are single molecules that contain both an amine group and a carboxylic acid group They are subunits of macromolecules that act as both strong acids and strong bases in solution They are acidic and were first discovered by an investigator called J. Aminov. They are subunits of macromolecules that act as strong acids PROTEINS Question 3 (5 points) What is the name of the chemical bond between amino acids? Question 3 options: phosphodiester hydrogen peptide electronegative CARBOHYDRATES Question 4 (5 points) Which of the following carbohydrates is used to store long-term energy in plant cells? Question 4 options: glucose glycogen starch cellulose * incorrect Question 5 (5 points) How are most carbohydrates used in the human body? Question 5 options: used as building blocks for proteins used as catalysts for reactions in cells used as a source of energy used as building blocks for lipids not necessary for regular bodily functions Save LIPIDS Question 6 (5 points) Fatty acids are a component of what type of macromolecule? Question 6 options: lipids complex carbohydrates nucleic acids proteins NUCLEIC ACIDS Question 7 (5 points) Which of the following is not part of a nucleic acid? Question 7 options: pentose sugar nitrogenous base fatty acid group phosphate group Save DENATURATION Question 8 (5 points) Why does the egg white from raw eggs go from clear to white after it is cooked? Question 8 options: because the protein is denatured in raw egg white because the protein is denatured in cooked egg white because the peptide bonds existing between amino acids break in the raw eggs because the peptide bonds existing between amino acids break in the cooked eggs Save PHOSPHOLIPIDS Question 9 (5 points) The inside of a phospholipid bilayer is: Question 9 options: hydrophobic hydrophilic hypotonic hypertonic CELL MEMBRANES Question 10 (5 points) A set of erythrocytes is placed in a beaker of 0.9% NaCl. Nothing appears to happen to the cells. Why? Question 10 options: 0.9% NaCl is hypertonic to the cells. 0.9% NaCl is isotonic to the cells 0.9% NaCl is hypotonic to the cells Sodium blocks the movement of water Save COMPARING EUKARYOTES & PROKARYOTES Question 11 (5 points) Describe why eukaryotic cells being compartmentalized can make their metabolism more complex? Question 11 options: same chemical reactions can occur together more frequently different chemical reactions can occur all in the same place different chemical reactions can occur in isolation of each other same chemical reactions can occur in isolation of each other Save Question 12 (5 points) Which of the following does a prokaryotic cell have that an animal cell does not? Question 12 options: vacuole cell wall ribosomes DNA EUKARYOTES Question 13 (5 points) Which of the following is not a component of the endomembrane system? Question 13 options: mitochondria Golgi apparatus endoplasmic reticulum lysosome central vacuole Save OSMOSIS & DIFFUSION Question 14 (5 points) What is the diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane called? Question 14 options: pinocytosis facilitated diffusion active transport osmosis phagocytosis endocytosis Save Question 15 (5 points) If you place a blood cell in a beaker filled with a concentrated salt solution, what would likely happen? Question 15 options: Water flows into the blood cell Water flows out of the blood cell Salt flows out of the blood cell Equal amounts of water flows into and out of the blood cell ACTIVE TRANSPORT Question 16 (5 points) What is he name of the process by which a cell will uptake large molecules from the extracellular fluid? Question 16 options: endocytosis active transport facilitated diffusion exocytosis EUKARYOTIC ORGANELLES Question 17 (5 points) What is the function of the nucleus in the eukaryotic cell? Question 17 options: protein synthesis directs the synthesis of ribosomes and proteins organizing center of microtubules in animal cells digestion of macromolecules Save Question 18 (5 points) In what type of cells would you expect to find a large amount of smooth endoplasmic reticulum? Question 18 options: brain liver intestinal muscle ANTIBIOTICS AND PROKARYOTIC CELLS Question 19 (5 points) An ideal antibiotic damages only bacterial cells but not human cells. Which of the following cellular structures would be a good target for antibiotics? Question 19 options: nucleus cytoskeleton plasma membrane cell wall Save Question 20 (5 points) You have a case of the common cold (which is caused by a virus). What would happen if you take antibiotics? Question 20 options: you will get better you will get another viral infection nothing you will get worse Quiz Submissions - Week 2 Quiz Sharmara Boston (username: SBOSTON2) Attempt 1 Written: Mar 26, 2017 10:13 PM - Mar 26, 2017 11:14 PM Submission View Your quiz has been submitted successfully. AMINO ACIDS Question 1 Why are amino acids called “amino acids? They are single molecules that contain both an amine group and a carboxylic acid group Question 2 Which of the following macromolecules are made from amino acids? proteins Question 3 What level of protein structure is associated with the sequence of amino acids? primary Question 4 How are most carbohydrates used in the human body? used as a source of energy Question 5 Which of the following carbohydrates is used to store energy in animal cells? cellulose starch hemi-cellulose glycogen LIPIDS Question 6 What type of molecule is shown here? lipid nucleic acid carbohydrate protein NUCLEIC ACIDS Question 7 Where is most of the DNA found in the eukaryotic cell? golgi mitochondria nucleus ribosomes DENATURATION Question 8 Why does heating up a protein such as an enzyme cause it to lose function? because it burns up because it loses its shape because it works best at low temperatures because it shows they are contaminated PHOSPHOLIPIDS Question 9 What property of the phospholipid bilayer allows proteins to move laterally in the membrane? phospholipids and proteins are attracted to each other phospholipid molecules are not covalently bonded to each other phospholipids are attracted to each other by opposite charges proteins attract each other with opposite charges CELL MEMBRANES Question 10 A set of erythrocytes is placed in a beaker of 0.9% NaCl. Nothing appears to happen to the cells. Why? 0.9% NaCl is hypertonic to the cells. 0.9% NaCl is isotonic to the cells 0.9% NaCl is hypotonic to the cells Sodium blocks the movement of water COMPARING EUKARYOTES & PROKARYOTES Question 11 Which if the following are found in eukaryotic cells but not prokaryotic cells? Golgi body Question 12 Which of the following does a prokaryotic cell have that an animal cell does not? cell wall ribosomes vacuole DNA EUKARYOTES Question 13 Which of the following is not a component of the endomembrane system? mitochondria Golgi apparatus endoplasmic reticulum lysosome central vacuole OSMOSIS & DIFFUSION Question 14 If you place a dialysis tubing permeable only to water filled with 30% sucrose solution into a beaker filled with a 10% solution of sucrose, what would you expect? water flows into the dialysis tubing Question 15 What is the diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane called? pinocytosis facilitated diffusion active transport osmosis phagocytosis ACTIVE TRANSPORT Question 16 Sodium ions are more highly concentrated outside the cell, in the extracellular fluid. Which process would be used to return any sodium ions that leaked into the cell back to the extracellular fluid? osmosis active transport facilitated diffusion simple diffusion EUKARYOTIC ORGANELLES Question 17 What is the function of the endoplasmic reticulum in the eukaryotic cells? modifies proteins, synthesizes lipids. Question 18 What is the function of the mitochondria in the eukaryotic cell? protein synthesis directs the synthesis of ribosomes and proteins organizing center of microtubules in animal cells production of ATP, cellular respiration ANTIBIOTICS AND PROKARYOTIC CELLS Question 19 An ideal antibiotic damages only bacterial cells but not human cells. Which of the following cellular structures would be a good target for antibiotics? cell wall Question 20 What is the concern with overuse of antibiotics? the patient will become antibiotic resistant viruses will become antibiotic resistant. bacteria will become antibiotic resistant. the antibiotics will degrade Attempt Score: Overall Grade (highest attempt): Done AMINO ACIDS Question 1 5 / 5 points Which of the following macromolecules are made from amino acids? Correct Response proteins complex carbohydrates nucleic acids lipids Question 2 5 / 5 points What is the name of the monomer that makes up proteins? nucleotides Correct Response amino acids disaccharides fatty acids PROTEINS Question 3 5 / 5 points What is the name of the chemical bond between amino acids? phosphodiester hydrogen Correct Response peptide electronegative CARBOHYDRATES Question 4 5 / 5 points Which of the following carbohydrates is used to store energy in animal cells? cellulose starch Correct Response glycogen hemi-cellulose Question 5 5 / 5 points Which of the following is characterized as dietary fiber? sucrose glycogen Correct Response cellulose starch LIPIDS Question 6 5 / 5 points Fatty acids are a component of what type of macromolecule? Correct Response lipids complex carbohydrates nucleic acids proteins NUCLEIC ACIDS Question 7 5 / 5 points Which of the following is not part of a nucleic acid? pentose sugar nitrogenous base Correct Response fatty acid group Correct Answer phosphate group DENATURATION Question 8 5 / 5 points Why does heating up a protein such as an enzyme cause it to lose function? because it burns up Correct Response because it loses its shape because it works best at low temperatures because it shows they are contaminated PHOSPHOLIPIDS Question 9 5 / 5 points The inside of a phospholipid bilayer is: Correct Response hydrophobic hydrophilic hypotonic hypertonic CELL MEMBRANES Question 10 0 / 5 points What is a characteristic of cell membranes? Correct Answer dynamic impermeable static Incorrect Response symmetrical COMPARING EUKARYOTES & PROKARYOTES Question 11 0 / 5 points What is the difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells? eukaryotic cells are found in animals, while plant cells are comprised of prokaryotic cells. eukaryotic cells have a plasma membrane, which is lacking in prokaryotic cells. Incorrect Response eukaryotic cells have a nucleoid region, which is lacking in prokaryotic cells. Correct Answer eukaryotic cells have membrane-enclosed organelles, which are lacking in prokaryotic cells. Question 12 5 / 5 points Which if the following are found in eukaryotic cells but not prokaryotic cells? Correct Response Golgi body vacuole DNA ribosome EUKARYOTES Question 13 5 / 5 points What would happen if a cell's lysosomes burst? The cell would shrivel The cell would divide into two cells Correct Response The cell would digest itself The cell would need to manufacture more lysosomes OSMOSIS & DIFFUSION Question 14 5 / 5 points If you place a dialysis tubing permeable only to water filled with 30% sucrose solution into a beaker filled with a 10% solution of sucrose, what would you expect? Correct Response water flows into the dialysis tubing water flows out of the dialysis tubing nothing happens sucrose diffuses out of the tubing sucrose diffuses into the tubing Question 15 What is osmosis? 5 / 5 points Correct Response A process that involves the movement of water A process that requires energy A process that occurs across a cell wall The movement of any molecule from high to low concentration ACTIVE TRANSPORT Question 16 5 / 5 points What is the name of the process by which a cell will uptake large molecules from the extracellular fluid? Correct Response endocytosis active transport facilitated diffusion exocytosis EUKARYOTIC ORGANELLES Question 17 5 / 5 points What is the function of the peroxisome in the eukaryotic cell? protein synthesis organizing center of microtubules in animal cells Correct Response oxidizes and breaks down fatty acids and amino acids storage and transport ATP production Question 18 5 / 5 points In what type of cells would you expect to find a large amount of smooth endoplasmic reticulum? brain Correct Response liver intestinal muscle ANTIBIOTICS AND PROKARYOTIC CELLS Question 19 5 / 5 points You have a case of the common cold (which is caused by a virus). What would happen if you take antibiotics? you will get better you will get another viral infection Correct Response nothing you will get worse Question 20 5 / 5 points Which is a plausible effect of taking oral antibiotics? Correct Response the antibiotics could unintentionally kill good bacteria living in your intestines, leaving you more susceptible to infection by pathogenic bacteria the antibiotics could harm your own body cells. the antibiotics could interfere with your body’s own ability to produce antibiotics, and actually end up prolonging the infection. the antibiotics could destroy viruses that have infected your body AMINO ACIDS Question 1 5 / 5 points Which of the following macromolecules are made from amino acids? Correct Response proteins complex carbohydrates nucleic acids lipids Question 2 5 / 5 points What is the name of the monomer that makes up proteins? nucleotides Correct Response amino acids disaccharides fatty acids PROTEINS Question 3 5 / 5 points What is the name of the chemical bond between amino acids? phosphodiester hydrogen Correct Response peptide electronegative CARBOHYDRATES Question 4 5 / 5 points Which of the following carbohydrates is used to store energy in animal cells? cellulose starch Correct Response glycogen hemi-cellulose Question 5 5 / 5 points Which of the following is characterized as dietary fiber? sucrose glycogen Correct Response cellulose starch LIPIDS Question 6 5 / 5 points Fatty acids are a component of what type of macromolecule? Correct Response lipids complex carbohydrates nucleic acids proteins NUCLEIC ACIDS Question 7 5 / 5 points Which of the following is not part of a nucleic acid? pentose sugar nitrogenous base Correct Response fatty acid group Correct Answer phosphate group DENATURATION Question 8 5 / 5 points Why does heating up a protein such as an enzyme cause it to lose function? because it burns up Correct Response because it loses its shape because it works best at low temperatures because it shows they are contaminated PHOSPHOLIPIDS Question 9 5 / 5 points The inside of a phospholipid bilayer is: Correct Response hydrophobic hydrophilic hypotonic hypertonic CELL MEMBRANES Question 10 0 / 5 points What is a characteristic of cell membranes? Correct Answer dynamic impermeable static Incorrect Response symmetrical COMPARING EUKARYOTES & PROKARYOTES Question 11 0 / 5 points What is the difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells? eukaryotic cells are found in animals, while plant cells are comprised of prokaryotic cells. eukaryotic cells have a plasma membrane, which is lacking in prokaryotic cells. Incorrect Response eukaryotic cells have a nucleoid region, which is lacking in prokaryotic cells. Correct Answer eukaryotic cells have membrane-enclosed organelles, which are lacking in prokaryotic cells. Question 12 5 / 5 points Which if the following are found in eukaryotic cells but not prokaryotic cells? Correct Response Golgi body vacuole DNA ribosome EUKARYOTES Question 13 5 / 5 points What would happen if a cell's lysosomes burst? The cell would shrivel The cell would divide into two cells Correct Response The cell would digest itself The cell would need to manufacture more lysosomes OSMOSIS & DIFFUSION Question 14 5 / 5 points If you place a dialysis tubing permeable only to water filled with 30% sucrose solution into a beaker filled with a 10% solution of sucrose, what would you expect? Correct Response water flows into the dialysis tubing water flows out of the dialysis tubing nothing happens sucrose diffuses out of the tubing sucrose diffuses into the tubing Question 15 What is osmosis? 5 / 5 points Correct Response A process that involves the movement of water A process that requires energy A process that occurs across a cell wall The movement of any molecule from high to low concentration ACTIVE TRANSPORT Question 16 5 / 5 points What is the name of the process by which a cell will uptake large molecules from the extracellular fluid? Correct Response endocytosis active transport facilitated diffusion exocytosis EUKARYOTIC ORGANELLES Question 17 5 / 5 points What is the function of the peroxisome in the eukaryotic cell? protein synthesis organizing center of microtubules in animal cells Correct Response oxidizes and breaks down fatty acids and amino acids storage and transport ATP production Question 18 5 / 5 points In what type of cells would you expect to find a large amount of smooth endoplasmic reticulum? brain Correct Response liver intestinal muscle ANTIBIOTICS AND PROKARYOTIC CELLS Question 19 5 / 5 points You have a case of the common cold (which is caused by a virus). What would happen if you take antibiotics? you will get better you will get another viral infection Correct Response nothing you will get worse Question 20 5 / 5 points Which is a plausible effect of taking oral antibiotics? Correct Response the antibiotics could unintentionally kill good bacteria living in your intestines, leaving you more susceptible to infection by pathogenic bacteria the antibiotics could harm your own body cells. the antibiotics could interfere with your body’s own ability to produce antibiotics, and actually end up prolonging the infection. the antibiotics could destroy viruses that have infected your body [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 70 pages
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Aug 12, 2022
Number of pages
70
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Aug 12, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
34












.png)






.png)



.png)