Tcfp HazMat Operations Exam 2022 with complete solutions
Document Content and Description Below
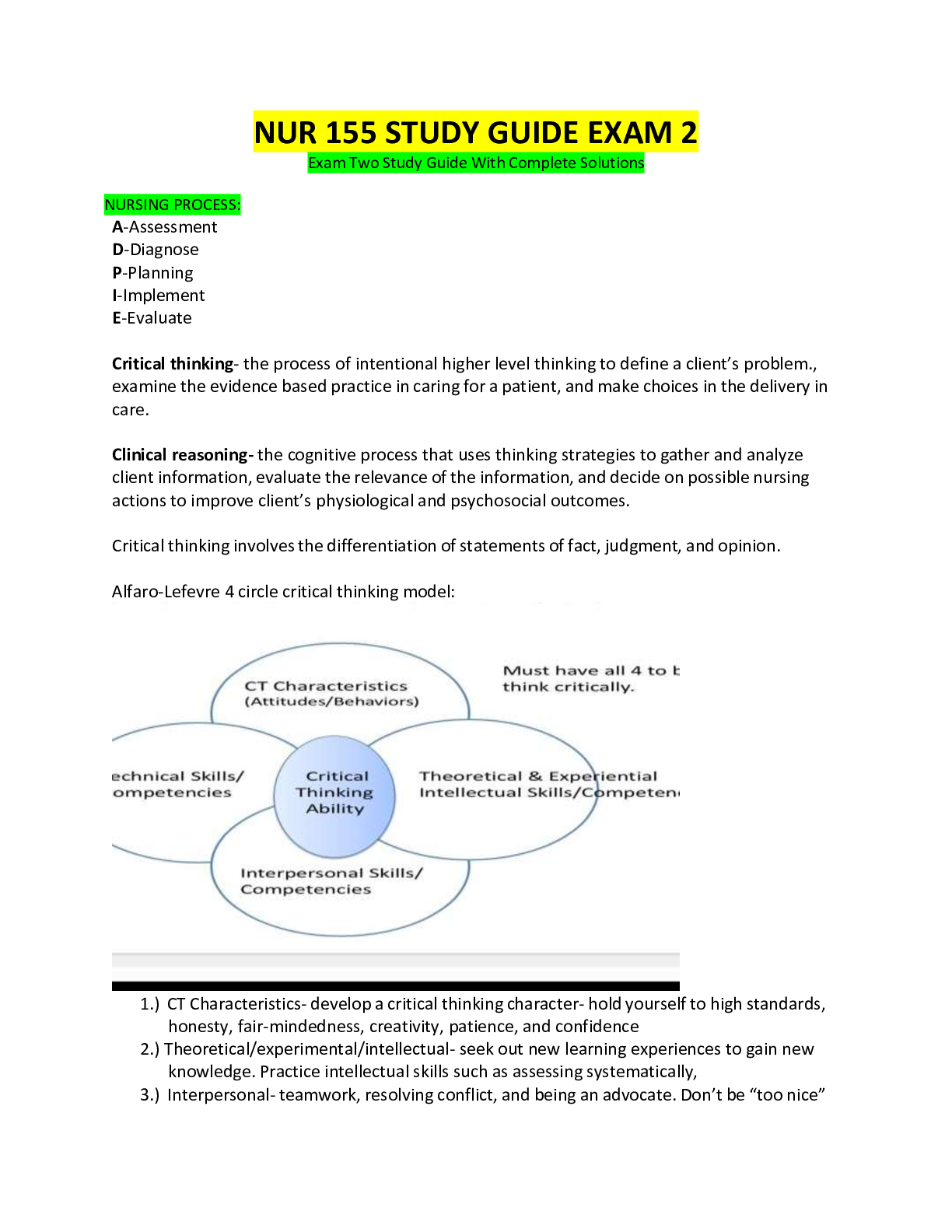
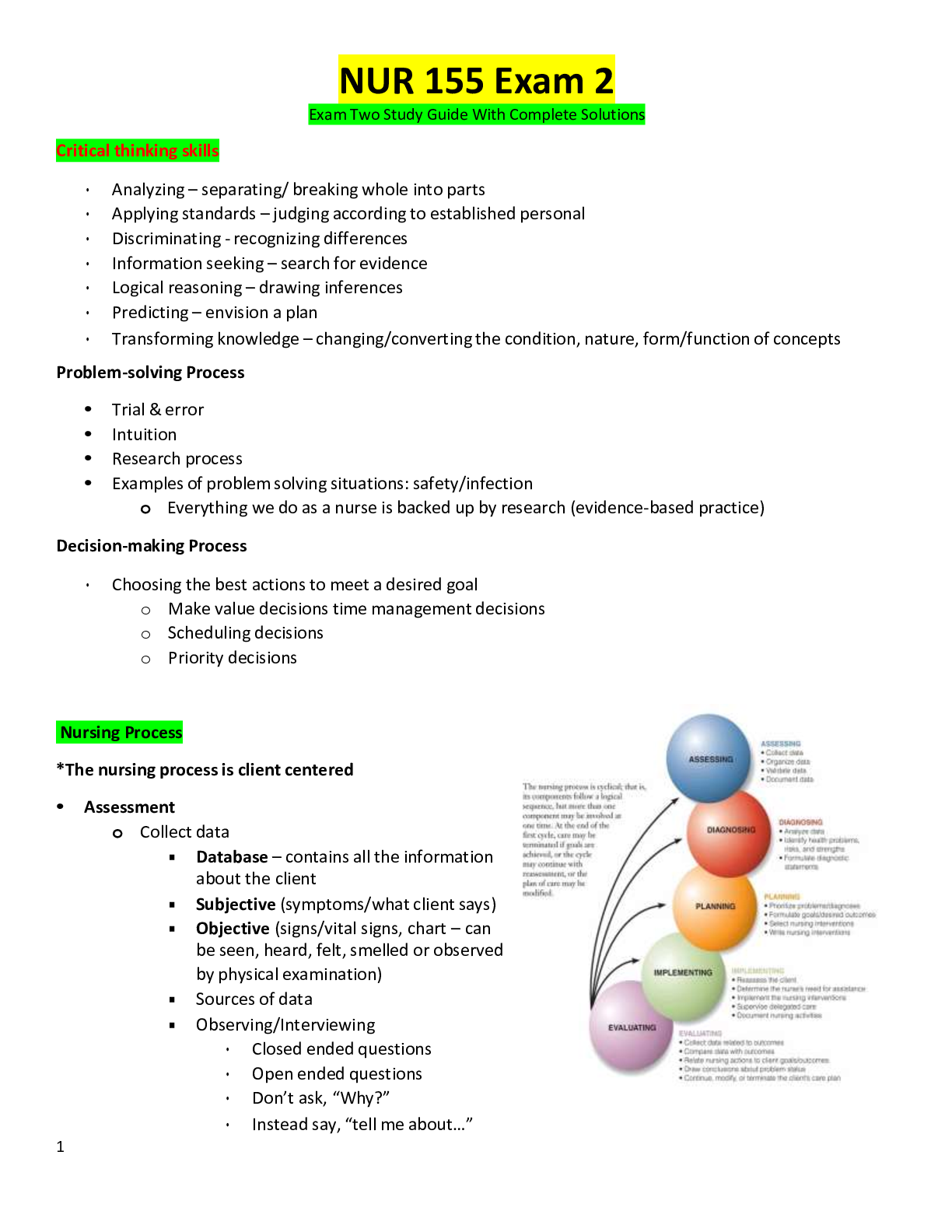
When responding to hazardous materials/WMD incidents Operations level responders shall be able to preform the following task... - ANSWER 1. Analyze a HazMat incident to determine the scope of the prob... lem 2. Plan an initial response 3. Implement a planned response 4. Evaluate the progress Analyzing a hazardous material incident to determine the scope of the problem involves... - ANSWER 1. Surveying the incident to identify containers and materials involved, determine if wether hazardous material has been released and evaluate the surrounding conditions 2. Collect hazard and response information from SDS, CHEMTREC and shipping/manufacturer contracts 3.Predict the behavior of Hazardous materials and its container 4.Estimate the potential harm through TRACE-MP What does TRACE-MP stand for? - ANSWER Types of potential harm at Hazardous Material/WMD incidents. Thermal Radiation Asphyxiation Chemical Etiological Mechanical Psychological/ Psychogenic The initial response at a HazMat incident is determined by.. - ANSWER The capabilities and competencies of available personnel and personal protective equipment The response objectives at a hazardous material/WMD incident include... - ANSWER 1.Evacuation 2. Search and Rescue 3. Exposure protection/ Isolating the Area 4. Defensive control techniques 5. Crime scene management and evidence preservation 6. Recovery and termination Describe the response options available for Evacuation - ANSWER 1. Full scale evacuation 2. Shelter-in-place 3. Combination Describe the response options available for Search and Rescue - ANSWER 1. Based on training and equipment 2. Risk-benefit analysis (risk a lot to save a lot, risk a little to save a little) Describe the response options available for Exposure protection/Isolating the Area - ANSWER 1.Establish initial isolation zone 2.Establish protective action distance 3. Establish control zones Describe the response options available for Defensive Control Techniques - ANSWER 1. Damming (Overflow or Underflow) 2. Diking 3. Retention 4. Dispersion 5. Absorption 6. Adsorption 7. Dilution 8. Dissolution 9. Diversion 10. Vapor dispersion 11. Vapor suppression 12. Ventilation 13. Remote valve shutoff What is Damming... - ANSWER Physical method of confinement by which barriers are constructed to prevent or reduce the quantity of liquid flowing into the environment. Consists of constructing a barrier across a waterway to stop/control the product flow and pick up liquid or solid contaminants What is Underflow Damming ... - ANSWER Spill control tactic used to trap floating lighter than water materials behind the dam. Dam is constructed in a manner that allows uncontaminated water to flow unobstructed under the dam while keeping the contaminant behind the dam. What is Overflow Damming... - ANSWER Spill control tactic used to trap sinking heavier than water materials behind the dam. With the product trapped, uncontaminated water is allowed to flow unobstructed over the top of the dam. What is Diking... - ANSWER Physical method of confinement by which barriers are constructed on ground used to control the movement of liquids, sludges, solids, or other materials. Prevents the passage of hazmat from entering an area where it will produce more harm. What is retention... - ANSWER Physical method of confinement by which a liquid is temporarily contained in an area where it can be absorbed, neutralized, or picked up for proper disposal What is dispersion... - ANSWER Chemical method of confinement by which certain chemical and biological agents are used to disperse or break up the material involved in liquid spills on water may result in spreading the hazardous material over a large area. What is absorption... - ANSWER Absorption occurs when one material enters the cell structure of another and is retianed within. Absorbents retain the properties of the materials they absorb and must be treated and disposed of as hazardous material What is adsorption... - ANSWER Adsorption is different from absorption in that the molecules of the hazardous materials physically adhere to the adsorbent material Adsorbents do not swell like absorbents Produces heat and can cause spontaneous combustion must be disposed of properly. Examples: activated charcoal, silica, aluminum gel, fuller's eath, POROUS clay and other clays What is dilution.. - ANSWER Dilution involves applying water to a water soluble material in order to reduce the hazard. It is a useful way to preform decontamination but it is not a practical practical spill control method as it typically requires so much water that it creates a runoff problem What is dissolution... - ANSWER Dissolution is the process of dissolving a gas in water. This tactic can only be used on water-soluble gases such as chlorine or anhydrous ammonia. What is Diversion... - ANSWER Physical method of confinement by which barriers are constructed on ground or placed in a waterway to intentionally control the movement of a hazmat into an area where it will pose less harm to the community and the environment What is Vapor Dispersion... - ANSWER Vapor dispersion is that action taken todirect or influence the course of airborne hazardous material. Pressurized streams (hoselines or unattended master streams) create turbulence which increase the rate of mixing with air and reduces the concentration of the hazardous material What is vapor suppression... - ANSWER Vapor suppression is the action taken to reduce the emission of vapors at a hazmat spill. Fire Fighting foams are effective on spills of flammable and combustible liquids. Water-miscible materials such as alcohols, esters and ketones destroy regular firefighting foams and require alcohol-resistant foams What is ventilation... - ANSWER Ventilation is any natural or mechanical means of controlling air movement. The same ventilation techniques used for smoke removal can be used for hazmat incidents What is a remote valve shutoff.. - ANSWER In some situations it may be safe and acceptable for Operations level responders to operate emergency remote shutoff valves. Activation of a remote shutoff valves varies by device but can be as simple as flipping a switch or handle or breaking a fusible device. Describe the response options available for Crime Scene management and evidence preservation - ANSWER 1. Maintain scene control 2. Limit access 3. Maintain chain of custody 4. Coordinate with AHJ What is an AHJ... - ANSWER Authority Having Jurisdiction Describe the response options available for Recovery and Termination - ANSWER 1. Short-term recovery 2. Long-term recovery 3. Termination activities a)Debriefing b) Critique c) Post incident analysis 4. Demobilization What is an EPA Level A suit and when is it used... - ANSWER Vapor protective, provides the highest level of respiratory and skin protection Used when chemical hazards are unknown, identified hazards are highly hazardous, when there is high potential for splash, immersion or exposure to vapors or when operations are conducted in a confined or poorly ventilated area What is an EPA Level B suit and when is it used... - ANSWER Liquid Splash protection, provides the highest level respiratory but lesser skin protection. Used when Atmosphere contains less than 19.5 percent oxygen or more than 23.5 percent oxygen. When there is a presence of vapors or gases indicated by a direct reading organic vapor detection instrument but vapors are not known to be harmful to skin What is an EPA Level C suit and when is it used.. - ANSWER Level B suit with an Air Purifying Respirator When the concentration and types of airborne substances are known and the criteria for using an Air Purifying Respirator are met. What is an EPA Level D suit - ANSWER Work uniforms, street clothing Used when no hazard are present, not acceptable for HazMat response beyond Awareness level What is Decontamination... - ANSWER Decontamination is performed at Hazmat incidents to remove hazardous materials from victims, PPE, Tools equipment and anything else contaminated. What are the three principles of Decon... - ANSWER 1. Get it off 2. Keep it off 3. Contain it ( Prevent cross contamination ) What is Emergency Decon.. - ANSWER Emergency decontamination is the process of removing threatening contaminants from the victim or rescuers as quickly as possible without regard for the environment or property. What are some instances where emergency decon is needed.. - ANSWER 1.Failure of protective clothing 2.Accidental contamination of first responders 3.Heat illness or other injury suffered while emergency workers were in the Hot Zone 4. When immediate medical attention is required What is Technical Decon... - ANSWER Technical Decon is using chemical or physical methods to throughly remove or neutralize contaminants. Technical decon is usually conducted within a formal decon line or corridor What is triage... - ANSWER Triage is a system used for sorting and classifying accident casualties to determine the priority for medical treatment and transportation What is Isolation and Scene control.. - ANSWER Isolation and Scene control is one of the primary strategic goals of a Hazmat incident and one of the most important means by which you can ensure the safety of yourself and others. What is an Isolation perimeter.. - ANSWER Sometimes called the outer perimeter, it is the boundary established to prevent access by the public and unauthorized persons. What are Hazard control zones.. - ANSWER Hazard control zones provide the scene control required at hazmat operations to protect responders from interference by unauthorized persons, help regulate movement across zones and minimize cross contamination What is the hot zone.. - ANSWER also called the exclusion zone, the Hot zone is potentially very dangerous. Responders need proper training and PPE to work in the hot zone. What is the warm zone.. - ANSWER The contamination reduction zone, decontamination stations are located here. PPE will normally be required here although in some circumstances the level of PPE may be a reduced level from the hot zone What is the cold zone... - ANSWER Also called the support zone. All logistical support is carried out here. PPE is not required here because it is considered safe. The multiagency command post, staging area, donning/doffing area, backup teams, research teams, logistical support, triage and transportation areas are located here as well. Describe: Cryogenic liquid tank cars (railroad) - ANSWER Fittings are in ground level cabinets at diagonal corners of the car or in the center of one end of the car. Describe: Nonpressure tank cars (railroad) - ANSWER Fittings are visible on top of these tank cars. Older Models of Nonpressure tank cars as well have an expansion dome with fittings visible on top the car. Describe: Pressure Tank cars - ANSWER Fittings are inside a protective hosing on top of the car. Describe: Nonpressure intermodal tank IM-101 - ANSWER 25.4 to 100 psi, Contents can be liquid or Solid (both hazardous and nonhazardous) Describe: Nonpressure intermodal tank IM-102 - ANSWER 14.5 to 25.4 psi, Contents can be liquid or Solid (both hazardous and nonhazardous) Describe: Pressure Intermodal tank Spec 51/IMO Type 5 - ANSWER 100 to 500 psi, Contents liquefied gas or liquids Describe: Cryogenic Intermodal tanks IMO Type 7 - ANSWER Contents: Refrigerated liquid gases, argon, oxygen, helium Describe: Tube module Intermodal Container - ANSWER 3000 or 5000 psi, Contents: Gases in high pressure cylinders mounted in the frame Describe: Compressed gas tube trailers - ANSWER Pressure at 3000 to 5000 psi Individual steel cylinders stacked and banded together Usually has overpressure device for each cylinder Valves are protected in the rear Contents: Helium, hydrogen, methane and other gases Describe: Corrosive liquid tanks - ANSWER MC 312, DOT 412, Pressure less thean 75 psi Typical capacity 7000 gallons Rubber lined or steel Small diameter round shape when viewed from the rear Splashguard serving as rollover protection around the valve fittings Contents: Corrosive liquids (usually acids) Describe: Cryogenic liquid tanks - ANSWER MC338, Pressure at less than 22 psi Well insulated steel tank Round tank with flat ends Large and bulky double shelling and heavy insulation Loading and Unloading station attached at either the rear or at the front of the rear dual wheels Contents: Liquid oxygen, liquid nitrogen, liquid carbon dioxide, and other gases that have been liquefied by lowering their temperature Describe: Dry Bulk cargo tanks - ANSWER Pressure less than 22 psi Typically not under pressure Bottom valves shape varies but has v shaped bottom unloading compartments Top manway assemblies Contents: Calcium carbide, oxidizers, corrosive solids, cement, plastic pellets and fertilizers Describe: High Pressure tanks - ANSWER MC 331, Pressure above 100 psi Typical maximum capacity of 11,500 gallons Single steel compartment Bolted manway on the front or rear Guard cage around the bottom loading and unloading piping Uninsulated tanks, single shelled vessels Contents:Pressurized gases and liquids, anhydrous ammonia, propane, butane and other gases that have been liquefied under pressure Describe: Low pressure chemical tanks - ANSWER DOT 407, MC 307 Pressure under 40psi Typical maximum capacity 7000 gallons Rubber lined or steel Typically double shell Stiffening rings may be covered or visible Circumferential roll over protection Single or multiple compartments Single outlet discharge piping at midship or rear Rounded or Horseshoe shaped ends Contents: Flammable liquids, combustible liquids, acids, caustics and poisons Describe: Non-pressure liquid tanks - ANSWER DOT 406, MC 306 Pressure less than 4 psi Typical maximum capacity 9000 gallons New tanks made out of aluminum Old tanks made out of steel Oval or Elliptical shape Multiple compartments Recessed manways Bottom valves Longitudinal rollover protection Valve assembly and unloading control box under tank Vapor recovery system on curbside and rear Contents: Gasoline, fuel oil, alcohol, other flammable/combustible liquids, other liquids and liquid fuel products Describe: Cryogenic liquid tank - ANSWER Insulated, vacuum jacketed tanks with safety release valves and rupture disk. Capacities can range from 300 to 400,000 gallons. Refrigerated storage tanks: less than 15psi High pressure cryogenic tanks: greater than 15psi What is a NFPA 704 placard.. - ANSWER Placard marking that is required at fixed facilities. The placard helps to alert responders to the health hazards, flammability and reactivity of products using a scoring system from 0 ( least ) to 4 ( severe ). There are two possible special hazards as well that can be located on the sign for Water reactive materials ( a W with line through it horizontally ) and an "OX" for oxidizers. Describe: Non- Pressure Horizontal tank - ANSWER Horizontal laying tanks sitting on legs, blocks, or similar. Typically constructed of steel with flat ends. Used typically for bulk storage in conjunction with fuel dispensing operations Contents: Flammable and combustible liquids, corrosives, poisons Cone Roof tank - ANSWER Cone-shaped or pointed roofs with weak roof-to-shell seams that will break if the container becomes overpressured -when partially full the empty space in the container contains dangers vapors Contents:flammable, combustible or corrosive liquids (Non pressured) Floating Roof tank - ANSWER The roof floats on the surface of the liquids and moves up and down depending on level of the liquids -non-pressure -minimal to no vapors -rubber/fabric seal around the edges -above ground Contents: flammable/ combustible liquids Covered Floating Roof tank - ANSWER Has a fixed cone roof with vents along the top edge, and a floating deck inside that stays on the surface of the liquids to minimize vapors -above ground -non-pressure Contents: flammable/combustible liquids Floating Roof with Geodesic Dome - ANSWER A nonpressure, floating roof with geodesic dome Contents: flammable liquids Lifter Roof tank - ANSWER The roof floats within a series of vertical guides that only allow a few feet of travel Contents: flammable/combustible liquids Vapor Dome Roof tank - ANSWER A vertical storage tank that has a geodesic dome at the top. -dome is a flexible and moves in coordination with the change in vapor pressure Contents: combustible liquids of medium volatility and other nonhazardous materials Underground Storage tank - ANSWER These tanks are made out of steel or fiberglass and have at least 10% of their surface areas underground -used at gas stations Contents: petroleum products High/Low Pressure tank examples... - ANSWER Low Pressure (0.5-15 psi) -Vertical dome roof tanks High pressure (greater than 15 psi) -Horizontal pressure vessel -Spherical pressure vessel -Noded spheroid -Underground high pressure Non-Bulk Packaging - ANSWER 1. Bags 2. Carboys and Jerricans 3. Cylinders 4. Drums 5. Dewar flask (cryogenic liquids) Different kinds of drums... - ANSWER Open head/Closed head Construction Materials Metal, Plastic, Fiberboard, Other suitable materials Fittings Bungs, Chime ring Intermediate Bulk Containers (IBC) - ANSWER Intermediate bulk containers (IBC) a. Rigid intermediate bulk containers (RIBCs) b. Flexible intermediate bulk containers (FIBCs) Ton containers a. Convex b. Concave Excepted Packaging - ANSWER Used to transport hazmats with extremely low levels of radiation Industrial Packaging - ANSWER Used to transport hazmats with low level radiation, materials may be liquid, or solidified in materials like concrete or glass Type A Packaging - ANSWER designed to contain greater amounts of radioactivity than excepted for normal transport Type B Packaging - ANSWER For highly radioactive shipments, designed to hold contents under extreme conditions Type C Packaging - ANSWER Rarely used, most hazardous amounts of radiation.. if packaging is released or shielding fails life threatening conditions could exist DOT Placarding and Labeling System - ANSWER DOT placards and labels are required on all products shipped in commerce. The DOT placard system is recognized internationally in the transportation of dangerous goods. Consists of different colors, numbers, and pictures to quickly identify hazmats. UN Numbers - ANSWER UN numbers or UN IDs are four-digit numbers that identify dangerous goods, hazardous substances and articles (such as explosives, flammable liquids, toxic substances, etc.) in the framework of international transport. They are assigned by the United Nations Committee of Experts on the Transport of Dangerous Goods. NFPA 704 System - ANSWER Red (top of diamond) Flammability Yellow (right side of diamond) Reactivity White (bottom of diamond) Special Hazards Blue (left side of diamond) Health Hazards Hazardous Materials Identification System (HMIS) - ANSWER Refers to the numbers found inside the NFPA 704 diamond. 0 being the least dangerous, 4 being the most dangerous Hazard Identification Codes (Intermodal Containers) - ANSWER Also known as "hazard identification numbers," or Kemler code, is carried on placards on tank cars and tank containers running by road under international ADR regulations. How to ID hazmats.. - ANSWER Highway Transportation vehicles you must search for... a. Company names and logos b. Vehicle identification numbers c. Manufacturer's specification plate Intermodal equipment, including tank containers you must search for a. Reporting marks b. Tank number c. Specification markings Rail transport vehicles, including tank cars you must search for a. Standard transportation commodity code (STCC) b. Commodity stencil c. Reporting marks d. Capacity stencil e. Specification markings Manufacturer's specification plate - ANSWER Will have specific instructions from the manufacturer, telling you how to deal with the hazmat What should you look for on a pipeline.. - ANSWER 1. Emergency telephone number 2. Owner 3. Product What should you look for on a pesticide label.. - ANSWER 1. Active ingredient 2. Hazard statement 3. Name of pesticide 4. EPA Registration Number 5. Precautionary statement 6. Signal word (Poison/Danger, Warning, Caution) Radioactive White-I Label - ANSWER Fissile class, white in color, low levels on surface Radioactive Yellow-II Label - ANSWER Fissile class, yellow in color, medium levels of radiation on external surface on package Radioactive Yellow-III Label - ANSWER Fissile class, yellow in color, highest level of radiation What are some surrounding conditions that will effect hazmats.. - ANSWER 1. Topography 2. Land use 3. Accessibility 4. Weather conditions 5. Bodies of water 6. Public exposure potential 7. Overhead and underground wires and pipelines 8. Storms and sewer drains 9. Possible ignition sources 10. Adjacent land use 11. Nature and extent of injuries 12. Building information 13. Ventilation ducts 14. Air returns CHEMTREC - ANSWER CHEMTREC is the acronym for the Chemical Transportation Emergency Center. It is a 24-hour emergency response service that provides assistance in the handling of incidents involving hazardous materials SDS/MSDS - ANSWER A safety data sheet, material safety data sheet, or product safety data sheet is a document provided by the manufacturer that details product hazards and spill-handling procedures. ERG - ANSWER A Guidebook for First Responders during the initial phase of a dangerous goods/hazardous materials transportation incident; is color coded yellow (UN number), blue (name), orange (on fire), and green (isolation zones). What are some additional hazards that could be associated with an incident involving terrorist/criminal activities... - ANSWER 1. Secondary events/devices intended to incapacitate or delay emergency responders 2. Armed resistance 3. Use of weapons 4. Booby traps 5. Secondary contamination from handling patients What are 4 ways to obtain the MSDS in an emergency.. - ANSWER a. Shipper b. Manufacturer c. CHEMTREC d. Websites UN/DOT Classes - ANSWER Class 1- explosives Class 2- gases Class 3- liquids Class 4- solids Class 5- oxidizers Class 6- poisons Class 7- radioactive Class 8- corrosives Class 9- misc UN/DOT Divisions - ANSWER Division 1.1 - Mass explosion hazard Division 1.2- Projection hazard Division 1.3- Fire hazard Division 1.4- Minor explosion Division 1.5- Very sensitive explosives with mass explosion hazard Division 1.6- Extremely insensitive no mass explosive hazard 1.1 is the most dangerous, 1.6 is the least What can CHEMTREC/CANUTEC/SETIQ can provide.. - ANSWER 1. Immediate advice and shipper contact information 2. Hazard information warnings and guidance Three methods of contacting the manufacturer or shipper to obtain hazard and response information.. - ANSWER a. Shipping paper contact information b. MSDS/SDS contact information c. CHEMTREC What are types of assistance provided by Federal governmental authorities with respect to criminal or terrorist activities at Hazardous Materials/WMD incidents - ANSWER DHS - Homeland Security Issues FBI - Crisis Management FEMA - Consequence Management EPA - Environmental Management US Coast Guard - Navigable Waterway Management & Port Security DOD - Explosives, Munitions, Military Shipments Technical Assistance/Response ATF - Explosives Technical Assistance What are types of assistance provided by State governmental authorities with respect to criminal or terrorist activities at Hazardous Materials/WMD incidents - ANSWER Department of Public Safety (DPS) - District Disaster Chair (DDC) TDEM - Emergency Management Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) - Environmental Management Texas General Land office (TGLO) - Water Quality Texas Railroad Commission (TRRC) - Pipelines and Propane Storage What are types of assistance provided by Local governmental authorities with respect to criminal or terrorist activities at Hazardous Materials/WMD incidents - ANSWER Local emergency management Local fire department Local police department EMS providers What are the properties of Alpha Radiation... - ANSWER Alpha particles lose energy rapidly when traveling through matter. They can be stopped by a sheet of paper or by the outer layer of human skin. Is not harmful to outside skin, but can be harmful if ingested. What are the properties of Beta Radiation.. - ANSWER These particles are more fast moving that alpha radiation, they can penetrate the outer layer of skin and cause radiation damage to the body. Can travel up to 20 feet through they air, after traveling that distance they can be stopped by a single layer of clothing What are the properties of Gamma Radiation.. - ANSWER Have no mass or electric charge but are highly penetrating. They can easily pass through the human body, inflicting severe radiation damage. Gamma radiation can be stopped by two inches of lead, two feet of concrete or several feet of dirt. What are the properties of Neutron Radiation.. - ANSWER This is normally found in research labs and nuclear power plants. These ultra-high energy particles have mass but no electrical charge and they are even more penetrating then Gamma rays. Neutron Radiation is hazardous to health because it creates secondary radiation as it passes through human tissue. Boiling Point.. - ANSWER Boiling point is the temperature at which vapor pressure is equal or greater than atmospheric pressure. When a liquid inside a container begins to boil, the increase in vapor pressure may exceed the vessel's ability to relieve excess pressure. Causing a catastrophic failure and BLEVE Chemical Reactivity is.. - ANSWER The tendency of a substance to undergo chemical changes in a system Corrosivity is.. - ANSWER Having the quality of corroding or eating away The relationship between Flammable and Explosive range - ANSWER They are interchangeable Lower Explosive Limit (LEL) is.. - ANSWER The lowest concentration of a gas or vapor in air capable of igniting, too lean to burn Upper Explosive Limit (UEL) is.. - ANSWER The highest concentration of a gas or vapor in air capable of igniting, to rich to burn Flash point is.. - ANSWER Minimum temperature at which a liquid gives off enough vapors to form an ignitable mixture with air Ignition temperature.. - ANSWER The lowest temperature at which a combustible material ignites without a spark or flame Persistence is... - ANSWER Length of time a chemical agent remains effective without dissipating ionizing radiation.. - ANSWER Radiation that causes a chemical change in atoms by removing their electrons Nonionizing radiation.. - ANSWER Energy waves composed of oscillating electric and magnetic fields traveling at the speed of light Specific gravity is.. - ANSWER The mass of a substance compared to an equal volume of water. Vapor Density.. - ANSWER weight of a given volume of pure substance compared to an equal volume of dry air Vapor Pressure - ANSWER The pressure at which a vapor in equilibrium with its liquid phase for a given temperature Water solubility.. - ANSWER Ability of a liquid or solid to mix with or dissolve in water What are three types of stress that can cause a container to release its contents.. - ANSWER 1.Thermal 2.Mechanical 3.Chemical Identify five ways in which containers can breach.. - ANSWER 1. Disintegration 2.Runaway cracking 3.Closures opening up 4.Punctures 5.Tears or spills Disintegration is.. - ANSWER To break or decompose into parts or small particles Runaway Cracking.. - ANSWER a small crack in a container that is growing rapidly Identify four ways in which containers can release their contents.. - ANSWER 1.Detonation 2. Violent rupture 3.Rapid relief 4.Spill or leak Identify at least four dispersion patterns that can be created upon release of hazardous material - ANSWER 1.Hemisphere 2.Cloud 3.Plume 4.Cone 5.Stream 6.Pool 7.Irregular Time frames for estimating the duration that hazardous materials will present an exposure risk - ANSWER Short term- Minutes and hours Medium Term- Days,Weeks or Months Long term- Years or generations Identify the Health and Physical hazards that could cause harm (TRACE-MP) - ANSWER Thermal Radiological Asphyxiation Chemical (Poisons, corrosives, etc.) Etiological Mechanical Psychological [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 20 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jul 12, 2022
Number of pages
20
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jul 12, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
192










.png)