Biology > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Chapter 18—LIFE'S ORIGIN AND EARLY EVOLUTION. All Answers (All)
Chapter 18—LIFE'S ORIGIN AND EARLY EVOLUTION. All Answers
Document Content and Description Below
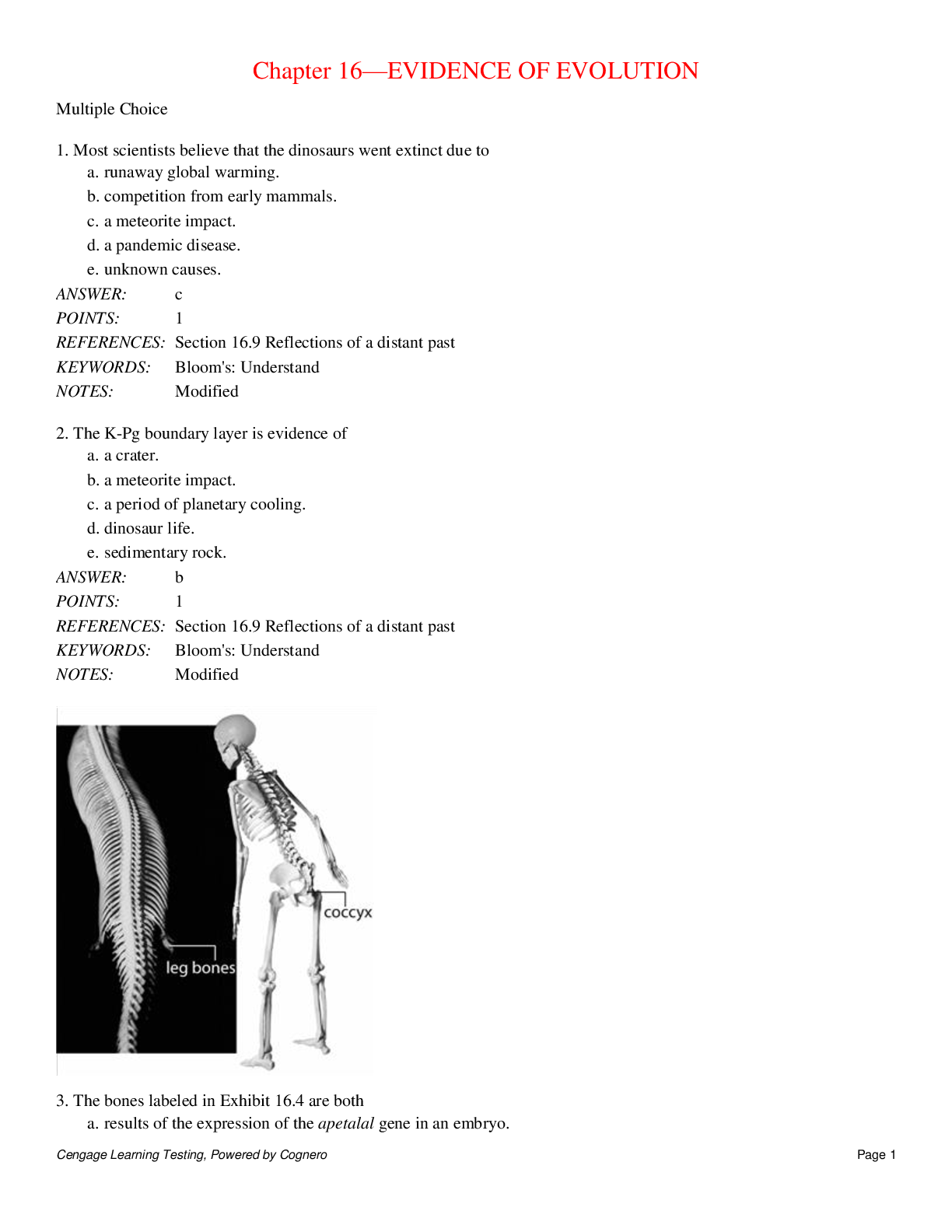
Multiple Choice 1. The metabolic reactions that occur in all cells require a certain molecule that was also believed to be present very early on Earth. What is this molecule? a. nitrogen b. ... carbon c. water d. oxygen e. hydrocarbon c POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 18.2 What steps led to the formation of the first cells? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember NOTES: New 2. The primitive Earth's atmosphere did NOT contain a. free oxygen. b. free nitrogen. c. free hydrogen. d. water vapor. e. inert gases. a POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 18.1 What was the building material for earth's first life? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember 3. Life probably never would have emerged if the ancient atmosphere had been the same as the present one because this molecule interferes with the assembly of simple organic compounds: a. nitrogen b. oxygen c. hydrogen d. silica e. carbon dioxide b POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 18.1 What was the building material for earth's first life? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember NOTES: Modified 4. Experiments like those first performed by Miller and Urey demonstrated that a. amino acids and other organic compounds could form in conditions that mimicked the earth's early atmosphere. b. a lipid-protein film will eventually be formed by thermal convection. c. DNA forms readily and reproduces itself. d. complete, functioning prokaryotic cells are formed after approximately three months. e. meteorites contained organic compounds. a POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 18.1 What was the building material for earth's first life? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember NOTES: Modified 5. Who demonstrated the possibility of producing organic compounds from gases and water if the mixture is exposed to sparks from an electrode? a. Platt b. Thompsen c. Miller and Urey d. Pauling e. Starr c POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 18.1 What was the building material for earth's first life? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember NOTES: Modified Selecting the Exception 6. Four of the five answers below were organic compounds included in the Miller and Urey experiment designed to study the early synthesis of organic compounds. Select the exception. a. hydrogen. b. methane. c. oxygen. d. ammonia. e. water. c POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 18.1 What was the building material for earth's first life? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember NOTES: Modified 7. Four of the five answers represent events that occurred when free oxygen (O2) became available in the atmosphere. Select the exception. a. aerobic respiration emerged. b. some organisms changed their metabolism. c. some species that could not detoxify free radicals became restricted to the low-oxygen environments that remained. d. oxygen was toxic to many species and some cells and forms of life became extinct. e. photosynthesis was no longer a common form of energy production. e POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 18.1 What was the building material for earth's first life? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember NOTES: Modified 8. Four of the five groups listed below are in the domain Eukarya. Select the exception. a. plants b. protists c. animals d. fungi e. bacteria e POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 18.1 What was the building material for earth's first life? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember 9. Four of the five answers listed below are components of the mixture used in Miller and Urey's experiment. Select the exception. a. ammonia b. methane c. water d. hydrogen e. oxygen e POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 18.1 What was the building material for earth's first life? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember NOTES: Modified 10. While it is very difficult to find fossils of the earliest cells, there are some probable early cell characteristics. Four of the five answers represent possible traits that the first cells may have had. Select the exception: a. prokaryotic b. autotroph c. aerobic d. anerobic e. hetrotroph c POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 18.1 What was the building material for earth's first life? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Understand OTHER: Select the exception NOTES: New 11. Four of the five answers below are traits that are signatures of a eukaryotic cell fossil. Select the exception. a. complex patterns b. small cell wall diameter c. biomarker such as steroids d. large size e. cell wall with spikes b POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 18.1 What was the building material for earth's first life? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Understand OTHER: Select the exception NOTES: New 12. What may have been a site for the synthesis of organic molecules on the early Earth with its source of hot water and metal ions from rocks? a. dried-out mud flats b. stratified mica crystals c. deep sea hydrothermal vents d. the bottoms of tidal pools e. pockets in lava beds c POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 18.1 What was the building material for earth's first life? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Understand OTHER: Select the exception NOTES: Modified 13. When scientists experimentally simulated conditions near a hydrothermal vent, _____ appeared within a week. a. cells b. nucleic acids c. hydrocarbons d. amino acids e. lipid membranes d POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 18.1 What was the building material for earth's first life? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember NOTES: Modified 14. What has been detected in meteorites that have fallen to the Earth? a. organic compounds b. organic polymers c. evidence of cells with a nucleus d. fossilized proto-cells e. oxygen molecules a POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 18.1 What was the building material for earth's first life? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember NOTES: Modified 15. In simulations of tidal flat conditions, amino acids form short chains by binding to a. clay particles. b. water molecules. c. rock chambers. d. iron sulfide. e. hyrdothermal vents. a POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 18.2 What steps led to the formation of the first cells? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember OTHER: Select the exception NOTES: Modified 16. Before DNA, ____ likely served as the genetic material. a. RNA b. protein c. carbohydrate d. lipid e. free nucleotides a POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 18.2 What steps led to the formation of the first cells? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember OTHER: Select the exception NOTES: Modified 17. What step occurred first in the evolution of life? a. formation of protein-RNA systems b. formation of lipid spheres c. formation of membrane-bound protocells d. formation of ATP e. spontaneous formation of lipids, proteins, carbohydrates, and nucleotides e POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 18.2 What steps led to the formation of the first cells? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Understand OTHER: Select the exception NOTES: Modified 18. Protein synthesis on the primordial Earth may have been catalyzed by ____ before the evolution of enzymes. a. lightning b. RNA c. carbohydrates d. amino acids e. DNA b POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 18.2 What steps led to the formation of the first cells? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Understand OTHER: Select the exception 19. All species on Earth today are descended from a cell that lived as early as: a. 4 billion years ago. b. 570 million years ago. c. more than 5 billion years ago. d. more than 10 billions years ago. e. 1.4 billion years ago. a POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 18.2 What steps led to the formation of the first cells? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember OTHER: Select the exception NOTES: Modified 20. The first organisms were most probably a. eukaryotic. b. multicellular. c. prokaryotic. d. algae. e. protozoans. c POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 18.2 What steps led to the formation of the first cells? LEARNING OBJECTIVES: BCA.SES.11 Bloom's: knowled - Bloom's: knowledge KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember OTHER: Selecting the Exception 21. Stromatolites were formed by a. heterotrophic bacteria. b. plants. c. animals. d. photosynthetic bacteria. e. red algae. d POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 18.2 What steps led to the formation of the first cells? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember NOTES: Modified 22. The first O2 producing organisms were probably a. cyanobacteria. b. Archaea. c. green algae. d. red algae. e. plants. a POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 18.2 What steps led to the formation of the first cells? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember 23. The first fossilized eukaryotes date to about how many years ago? a. 3.8 billion b. 6,000 c. 2.1 billion d. 1 million e. 1.8 billion e POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 18.2 What steps led to the formation of the first cells? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember OTHER: Critical Thinking NOTES: Modified 24. The earliest species known to reproduce sexually was a a. cyanobacterium. b. green alga. c. fungus. d. red alga. e. archaebacterium. d POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 18.2 What steps led to the formation of the first cells? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember NOTES: Modified 25. Chloroplasts a. have membrane bound nuclei containing DNA. b. evolved from cyanobacteria. c. have been found as symbionts inside mitochondria. d. evolved from photosynthetic eukaryotes. e. are the site of aerobic respiration. b POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 18.2 What steps led to the formation of the first cells? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Remember NOTES: Modified 26. Mitochondria arose from an endosymbiotic relationship between a eukaryotic cell and an aerobic bacteria. Which statement supports this theory? a. Fossilized mitochondria are older than the oldest fossilized eukaryotes. b. Mitochondria can produce ATP outside of a eukaryotic cell. c. A mitochondrion has its own DNA in the form of a single circular chromosome, like bacteria. d. A mitochondrion has a only one outer membrane. e. A mitochondrion can survive indefinitely when removed from a eukaryotic cell. c POINTS: 1 REFERENCES: Section 18.3 What do we know about early cells? KEYWORDS: Bloom's: Understand NOTES: New 27. The first major split in evolution separated a. all three lineages from each other. b. Archaea from bacteria and eukaryote ancestors. c. Bacteria from Archaea and eukaryote ancestors. d. eukaryote ancestors from Archaea and Bacteria. e. none of these. 28. Which was present first? a. mitochondria b. aerobic respiration c. chloroplasts d. fungi e. photosynthesis 29. Which of the following arose first? a. animals b. archaea c. fungi d. protists e. plants 30. The prevalance of iron-sulfide cofactors in organisms supports the hypothesis that life arose _____. a. in outer space b. on tidal flats c. in volcanic springs d. in the upper atmosphere e. near geothermal vents 31. Ribosomes can catalyze formation of peptide bonds. This supports the hypothesis that _____ . a. an RNA world preceded DNA-based genomes b. RNA can hold more information than DNA c. the first protists had RNA as their genetic material d. RNA's only role is that of an enzyme e. protocells contained DNA 32. By one hypothesis, clay _____. a. facilitated assembly of early organic polymers by concentrating monomers through it's negative charge b. was present at hydrothermal vents c. provided energy for early metabolism d. has a positive charge and repelled organic monomers e. helped physically form the plasma membrane of protocells 33. Mitochondria most resemble _____. a. anaerobic bacteria b. archaeans c. cyanobacteria d. aerobic bacteria e. early eukaryotes 34. Oxygen released by ____ accumulated in early Earth's atmosphere and produced the ozone layer. a. early eukaryotes b. cyanobacteria c. archaeans d. protocells e. aerobic bacteria 35. A rise in oxygen in Earth’s air and seas put organisms that engaged in _____ at a selective advantage. a. fermentation b. photosynthesis c. sexual reproduction d. aerobic respiration e. anaerobic respiration 36. There are several proposed mechanisms that could have produced organic monomers. What mechanism involves the formation of organic compounds in interstellar clouds? a. hydrothermic vents b. organic compounds arriving on earth via meteorites c. reactions involving hot water and metal ions from rocks d. lightening fueled-atmospheric reactions e. the aggregation of dust and rock bits that were orbiting the sun to form earth 37. What compound served to contain interacting organic molecules within a protocell? a. RNA b. DNA c. lipids d. single amino acids e. amino acid polymers 38. What structure may have acted as a boundary for a cell-like environment before protocells formed? a. acidic water from volcanic springs b. chambers in rocks c. metal ions from rocks d. clay e. lipid membrane 39. Metabolism may have begun when ________ within rocks donated electrons to dissolved carbon monoxide (CO), forming organic compounds. a. oxygen b. iron sulfide c. hydrogen gas d. carbon dioxide e. ammonia 40. Arrange the following steps into the order that correctly represents the sequence for the evolution of cells: 1. organic polymers 2. DNA based cells 3. inorganic molecules 4. organic monomers 5. protocells a. 5, 3, 1, 2, 4 b. 1, 4, 3, 2, 5 c. 1, 4, 3, 5, 2 d. 3, 1, 4, 5, 2 e. 3, 4, 1, 5, 2 41. How did the eukaryotic nucleus arise? a. through the uptake of the cell's genome by a membrane organelle already present in the cell b. through cytoplasmic diffusion c. through an endosymbiotic relationship with a bacteria d. through infoldings of the cell's plasma membrane e. through formation of a new internal membrane by the eurkaryotic cell 42. Once an endosymbiotic relationship was established between a bacteria and a eukaryotic cell, what effect did it have on their genomes? a. The eukaryotic genome lost some genes whose function could be supported by the bacteria but the bacterial genome did not change. b. Both genomes evolved so that eventually the host and the bacteria became incapable of living independently. c. The bacteria transferred all of its DNA to the eukaryotic nucleus. d. The bacteria lost its genome and relied solely on the eukaryotic cell. e. The endosymbiotic relationship did not affect either cell's genome. Subjective Short Answer 43. Place the following evolutionary advances in order starting with the earliest. a. origin of chloroplasts b. origin of mitochondria c. separation of eukaryote ancestors from Archaea d. origin of photosynthesis e. origin of animals f. origin of aerobic respiration g. origin of protocells h. origin of organic material 1. ____ 2. ____ 3. ____ 4. ____ 5. ____ 6. ____ 7. ____ 8. ____ Exhibit 18.4 depicts Miller and Urey’s apparatus designed to test the atmosphere on the early Earth. Match the letters on Exhibit 18.4 with features of the experiment. 44. Which letter indicates the location of the boiling water? 45. Which letter points to the electrodes used to mimic lightning on the early Earth? 46. Which letter shows the location of gases thought to be present on early Earth? 47. What is a ribozyme made of? 48. Which provides a more stable genome, DNA or RNA? 49. What evidence supports the theory of an early "RNA world"? 50. One source of fossils from early cells is stromatolites. What are stromatolites and how are they formed? 51. How did the formation of the ozone layer allow life to move from water to land? 52. Mitochondria likely arose from _________ and chloroplasts likely arose from _________. 53. Why were scientists excited about the possibility of life on Mars once they discovered ice on the planet? 54. If life exists on Mars, it is predicted that organisms would live underground and be anaerobic. Why? Essay 55. Researchers looking for fossils of the earliest life forms face many hurdles. For example, few sedimentary rocks date back more than 3 billion years. Review what you learned about plate tectonics. Explain why so few remaining samples of these early rocks remain. 56. Craig Venter and Claire Fraser are working to create a “minimal organism.” They are starting with Mycoplasma genitalium, a bacterium that has 517 genes. By disabling its genes one at a time, they discovered that 265–350 of them code for essential proteins. The scientists are synthesizing the essential genes and inserting them, one by one, into an engineered cell consisting only of a plasma membrane and cytoplasm. They want to see how few genes it takes to build a new life form. What properties would such a cell have to exhibit for you to conclude that it was alive? 57. Why is it very challenging to find and identify signs of early cells? 58. What scientific evidence supports the endosymbiont hypothesis? [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 17 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Nov 27, 2019
Number of pages
17
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Nov 27, 2019
Downloads
0
Views
61




















.png)


.png)


.png)


.png)

.png)

