*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > NR566 Midterm Study Guide completed by a previous class.docx. CHAMBERLAIN UNIVERSITY COLLEGE. GRADED (All)
NR566 Midterm Study Guide completed by a previous class.docx. CHAMBERLAIN UNIVERSITY COLLEGE. GRADED A+
Document Content and Description Below
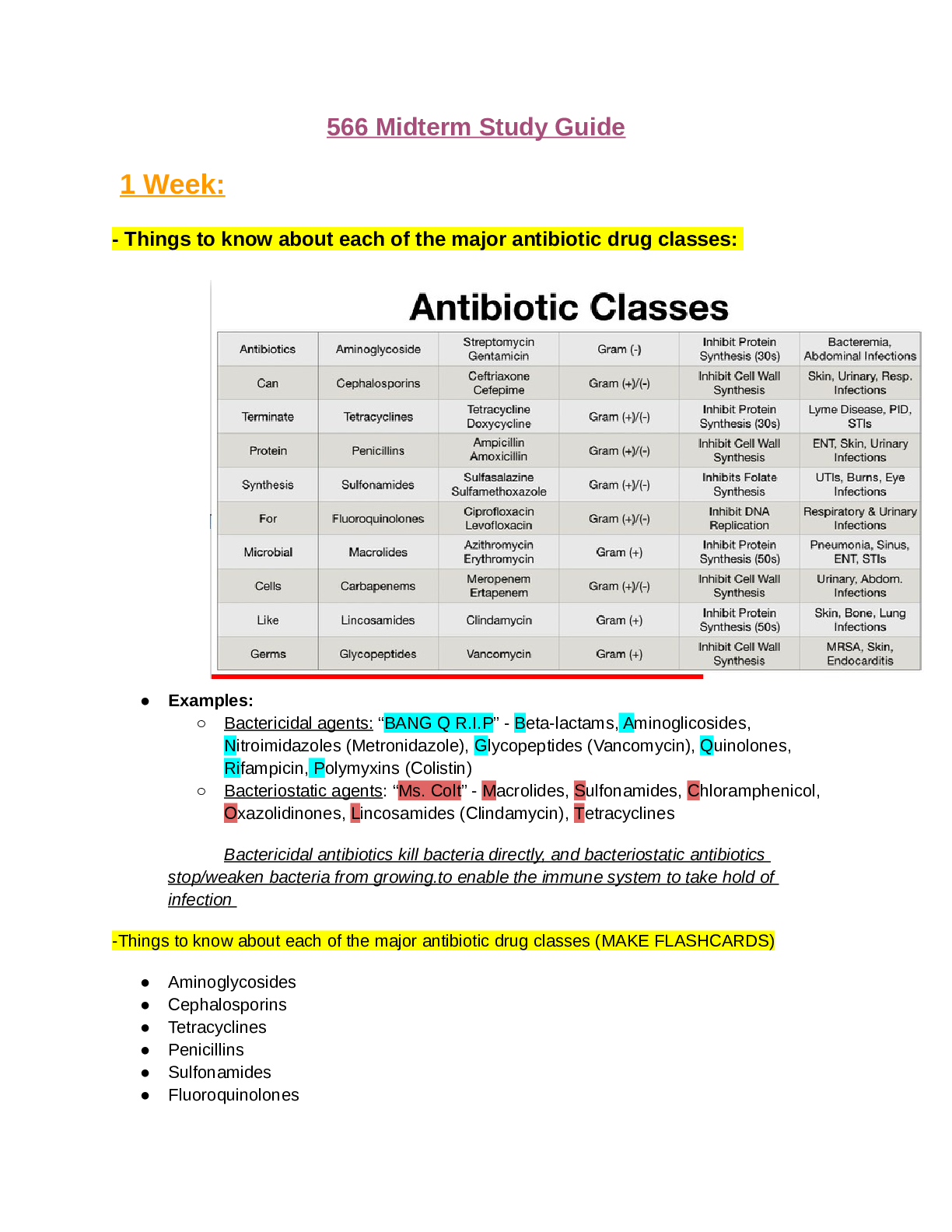
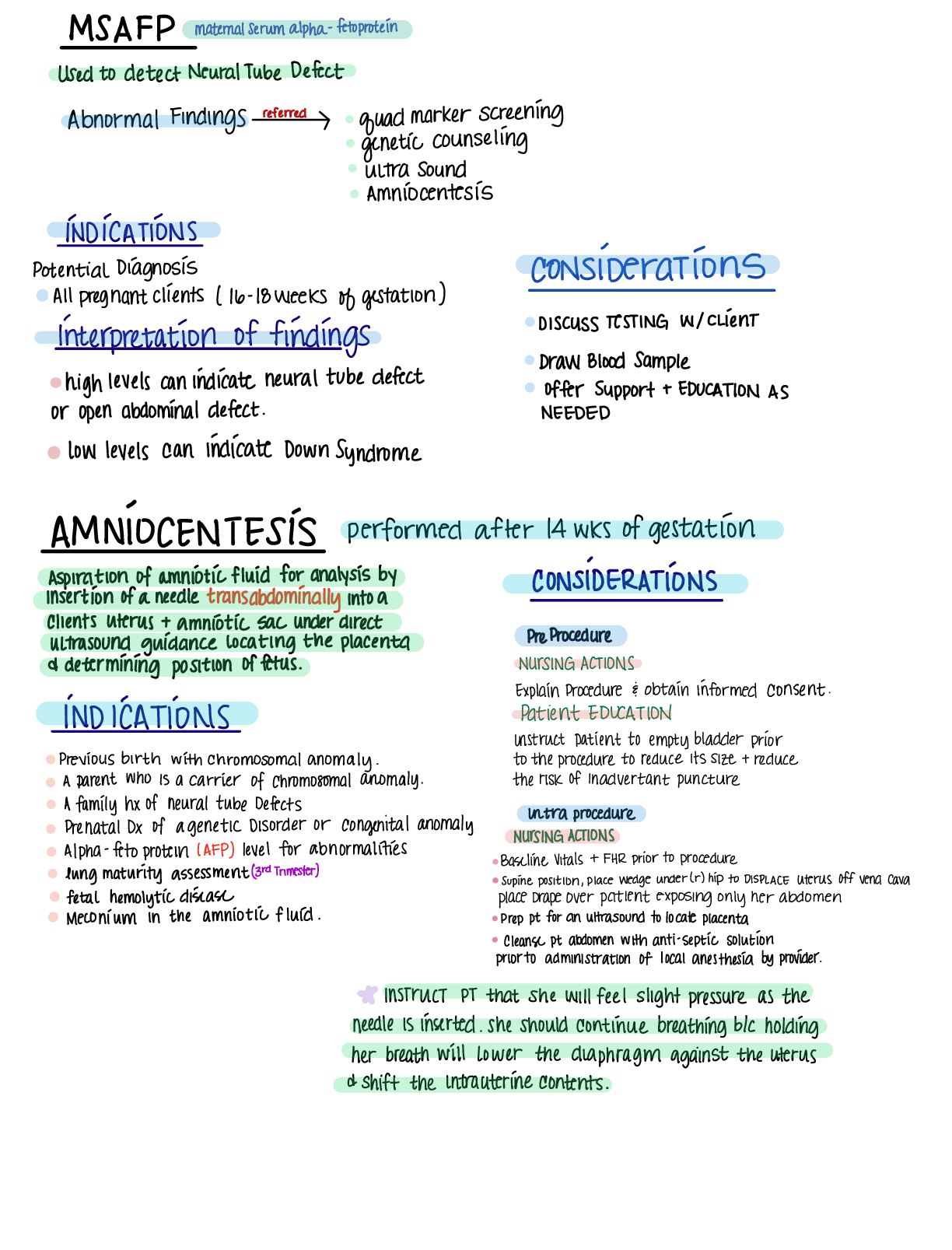
- Things to know about each of the major antibiotic drug classes: ● Examples: ○ Bactericidal agents: “BANG Q R.I.P” - Beta-lactams, Aminoglicosides, Nitroimidazoles (Metronidazole), Glycope... ptides (Vancomycin), Quinolones, Rifampicin, Polymyxins (Colistin) ○ Bacteriostatic agents: “Ms. Colt” - Macrolides, Sulfonamides, Chloramphenicol, Oxazolidinones, Lincosamides (Clindamycin), Tetracyclines Bactericidal antibiotics kill bacteria directly, and bacteriostatic antibiotics stop/weaken bacteria from growing.to enable the immune system to take hold of infection -Things to know about each of the major antibiotic drug classes (MAKE FLASHCARDS) ● Aminoglycosides ● Cephalosporins ● Tetracyclines ● Penicillins ● Sulfonamides ● Fluoroquinolones ● Macrolides ● Carbapenems ● Lincosamides ● Glycopeptides o Examples o Contraindications and high-risk patients o Know examples of each of the major antibiotic drug classes. o Monitoring needs o Which ones require renal dosing adjustments and how much (i.e., 25%, 50%, etc.) o Patient education o Lifespan considerations including pregnancy o Indications for use Considerations: ● Renal/hepatic function: doses may need to be reduced. Consider creatinine clearance. ● Age: dose adjustments may be required for pediatric and geriatric patients- weightbased may be appropriate. ● Pregnancy and lactation: Be aware of teratogenic effects of certain classes of medications ● Recent antibiotic use: Be aware of possible drug-resistant bacteria ● Exposure history: travel, congregate care settings, close contacts ● Monitoring needs ○ Next, consider the syndrome, or presenting illness. -- What system is impacted? How aggressive is the infection? Consider non-bacterial causes of symptoms (i.e. viral, fungal, or non-infections) Carefully examine the clinical presentation of illness. ● Which ones require renal dosing adjustments and how much (i.e., 25%, 50%, etc.): VII. Precautions: Antibiotics A. Antibiotics that require NO renal dose adjustment 1. Azithromycin 2. Ceftriaxone 3. Clindamycin 4. Doxycyline 5. Linezolid 6. Moxifloxacin 7. Nafcillin 8. Rifampin B. Agents to avoid in severe Chronic Kidney Disease 1. Penicillin G (Myoclonus, Seizures, coma risk) 2. Imipenem with cilastin (Seizure risk); Meropenem safe 3. Tetracycline (exacerbates Uremia); Doxycycline safe 4. Nitrofurantoin (peripheral neurotoxicity) 5. Aminoglycosides (or close level monitoring if used) C. Amoxicillin 1. Reduce to every 24 hours if GFR<10 ml/min D. Augmentin 1. Reduce to every 24 hours if GFR<10 ml/min 2. Do not use Augmentin 875/125 mg tabs if GFR<30 ml/min E. Cefazolin 1. Reduce to every 12 hours if GFR<50 ml/min 2. Reduce to 50% every 24-48 hours if GFR<10 ml/min F. Cefuroxime 1. Reduce to 250 to 500 mg every 24 hours if GFR<10 ml/min G. Cephalexin 1. Reduce to every 12-24 hours if GFR<10 ml/min H. Ciprofloxacin 1. Reduce dose to 50-75% if GFR<50 ml/min 2. Reduce dose to 50% or change to once daily dosing if GFR<10 ml/min I. Clarithromycin 1. Reduce dose to 50-100% if GFR<50 ml/min 2. Reduce dose to 50% or change to once daily dosing if GFR<10 ml/min J. Penicillin 1. Reduce to 50% if GFR <30 ml/min K. Levofloxacin 1. Reduce to every 24-48 hours if GFR<50 ml/min (or 500 mg loading dose, then 250 mg for subsequent doses) 2. Reduce to every 48 hours if GFR<20 ml/min 3. Avoid if GFR<10 ml/min L. Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMZ, Septra, Bactrim) 1. Reduce to 50% if GFR <30 ml/min 2. Avoid if GFR<15 ml/min M. Vancomycin 1. Adjust dosing intervals based on drug level and Creatinine Clearance It is important that antibiotics not be discontinued prematurely. Accordingly pts should be instructed to take their medication for the entire prescribed course, even though s/s may subside before the full course has been completed. Early discontinuation is a common cx of recurrent infection, and the organisms responsible for relapse are likely to be more drug resistant than those present when tx began. Lifespan considerations including pregnancy ● Infants: are highly vulnerable to drug toxicity. BC of poor developed kidney & liver function. Use of Sulfonamides in newborns can produce kernicterus (a severe neurological disorder cause by displacement of bilirubin from plasma proteins ● Children/adolescents: the tetracyclines provide another example of toxicity unique to the young; these antibiotics bind to the developing teeth, causing discoloration. ● Pregnant Women: Antimicrobial drugs can cross the placenta, posing a risk to the developing fetus. For example when Gentamicin is used during pg, irreversible hearing loss in the infant may result. Ax used during pg may also pose a risk to the expected mother ● Breast feeding woman: Ax can enter breast milk, possibly affecting the nursing infant. For example: Sulfonamides can reach levels in milk that are sufficient to cause kernicterus in nursing newborn. As a general guideline, ax and all other drugs should be avoided by women who are breastfeeding. If antimicrobial therapy is considered the benefits should outweigh the risk ● Older adults: In the older adult, heightened drug sensitivity is due in large part to reduced rates of drug metabolism and drug excretion, which can result in accumulation of ax to toxic levels - Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP): ● CAP Is defined as pneumonia acquired outside hospital or healthcare facilities that results in inflammatory changes and damage to the lungs. ● CAP is the type of pneumonia most often seen in primary care. ● Causative agents: ○ Most infections are caused by Streptococcus Pneumoniae (aka pneumococcus); gram positive ■ Also caused by: ● H. Influenzae (gram negative) ● Atypical bacteria - mycoplasma pneumoniae ● Viruses (e.g, influenza, respiratory syncytial virus) ○ The predominant organism in CAP depends on the age & overall health of the pt, Streptococcus Pneumoniae is the most common causative organism but other organisms should be considered when selecting tx agents. ● Diagnosed by: ○ Chest x-ray is the Gold Standard for CAP dx ● Treatment options: ○ Empiric Treatment when culture results are not available ■ If pt has NO comorbidities: ● First-line agents: Beta-lactam or doxycycline ○ Amoxicillin 1,000 mg PO TID x 5-7 days OR ○ Doxycycline 100mg PO BID x 5-7 days ● Alternative: Macrolides ○ Azithromycin (Z-pack) daily x 5 days ○ Clarithromycin BID or ER 1,000mg daily (do not use if >25% macrolide resistance ■ If patient has comorbidities (e.g. alcoholism; CHF; chronic heart, lung, liver, or kidney disease; abx in the last three months; diabetes; splenectomy/asplenia or high rates (>25%) of macrolideresistant S. pneumoniae: ● Combination therapy (beta-lactam & macrolide) ○ Amoxicillin clavulanate (Augmentin) 1,000mg/62.5mg PO BID -or- ○ Cephalosporin cefpodoxime (Vantin) or cefuroxime (Ceftin) PLUS azithromycin (Z-pack) or clarithromycin (Biaxin) 500mg BID x 5-7 days ● Alternative (respiratory fluoroquinolone; duration 5-7 days ○ Moxifloxacin (Avelox) 400 mg PO once per day ○ Gemifloxacin (Factive) 400 mg PO once per day ○ Understand the use of macrolides in pregnancy and children under the age of 8 with CAP or M. Pneumoniae (atypical pneumonia) ■ Atypical pneumonia is more commonly seen in young adults. ● Caused by: ○ 1. Mycoplasma pneumoniae ○ 2. Chlamydia pneumoniae ○ 3. Legionella pneumoniae ● Signs & Symptoms: ○ Less likely to have fever; usually c / o fatigue that is accompanied by a cough that interferes with sleep - often thought to be a cold and managed symptomatically with OTC medications unless medical care is sought ○ Referred to as walking pneumonia ● Treatment: (similar to CAP) ○ Macrolide ○ Doxycycline ■ If those therapies FAIL and a resistant organism is suspected then the use of one of the respiratory fluoroquinolones active against S. pneumoniae is warranted. ■ Macrolide antibiotics provide coverage for atypical pathogens and some coverage for S. pneumoniae, although macrolide resistance exists among both M. pneumoniae and S. pneumoniae. ■ The prototype drug to represent this class (Macrolides) is Erythromycin b/c it is 1st drug choice for CAP cx by Mycobacterium Pneumoniae, Erythromycin does penetrate the CSF but poorly, it does cross the placenta but adverse effects on the fetus have not been observed – avoid Macrolides in pts with QT prolongation, this is considered one of the safest antibiotics -- Erythromycin, azithromycin (Zithromax), clarithromycin (Biaxin) are examples of Macrolides – Avoid this class of meds with pts taking Warfarin -- Penicillins, cephalosporins, and erythromycin may be prescribed safely throughout pregnancy. ○ When to prescribe fluoroquinolones for CAP ■ Prescribe with severe CAP in combination with Beta-lactam & Macrolide -- If a resistant organism is suspected, then the use of one of the respiratory fluoroquinolones active against S. pneumoniae is warranted -- Fluoroquinolones should be avoided due to potential cartilage damage risk. TIDBIT:: **Gram (-) & (+) organisms are treated with the broad-spectrum antibiotics **Pt’s in the hospital should start Empiric IV antibiotic, broad-spectrum drug, bactericidal agent (for immunocompromised pts) after blood cultures are done **Drug selection must be based on clinical evaluation & knowledge of which MICROBES are the most likely to cause infection at a particular site. Treatment Chart from UPTODATE Age group Empiric regimen 1 to 6 months Bacterial (not Chlamydia trachomatis) Infants <3 to 6 months of age with suspected bacterial pneumonia should be hospitalized C. trachomatis Refer to UpToDate [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 42 pages
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 19, 2022
Number of pages
42
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 19, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
37








.png)
 (1).png)









.png)





