Marketing > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Chapter 9—Overview of Advertising Management. Questions and Answers (All)
Chapter 9—Overview of Advertising Management. Questions and Answers
Document Content and Description Below
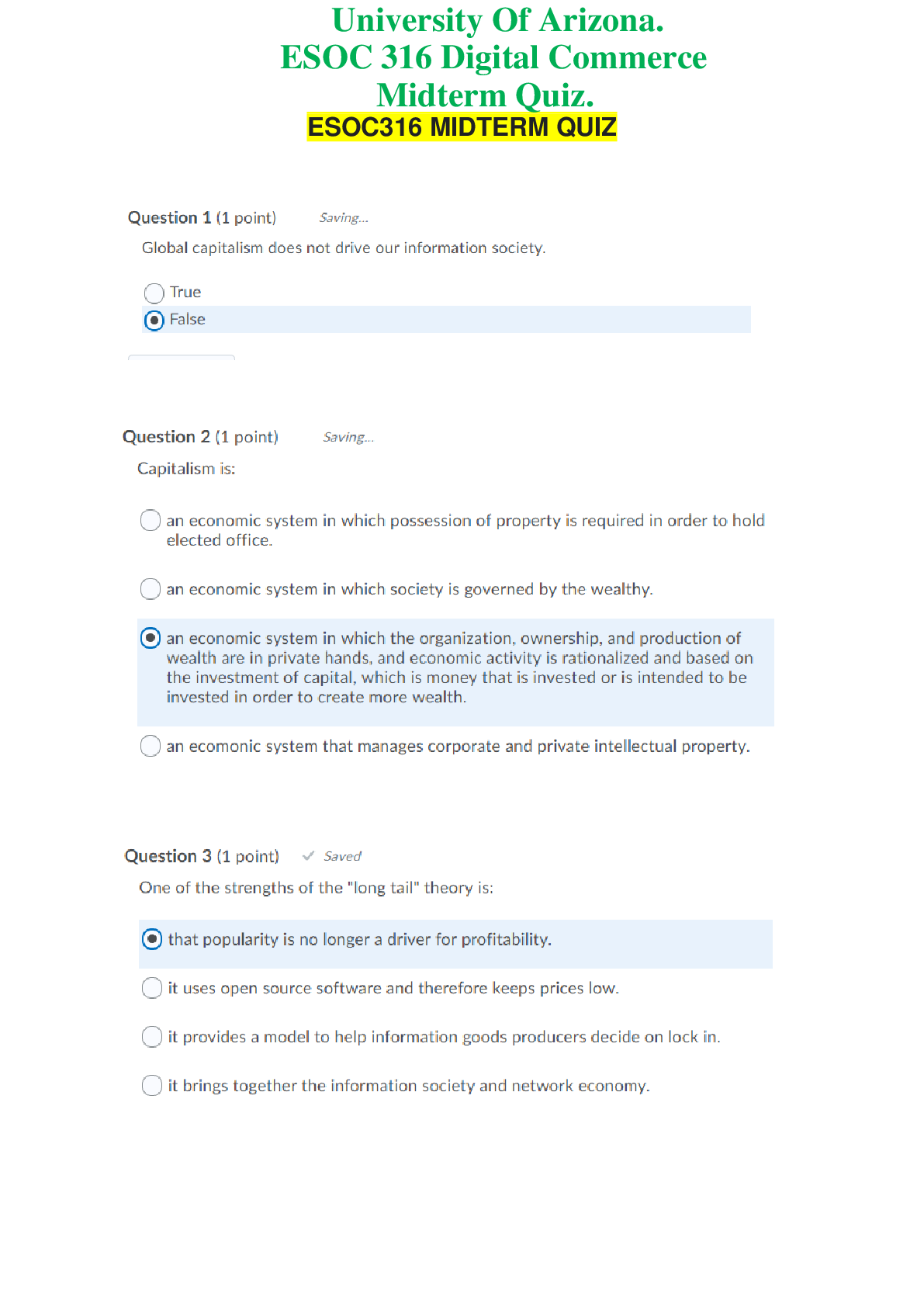
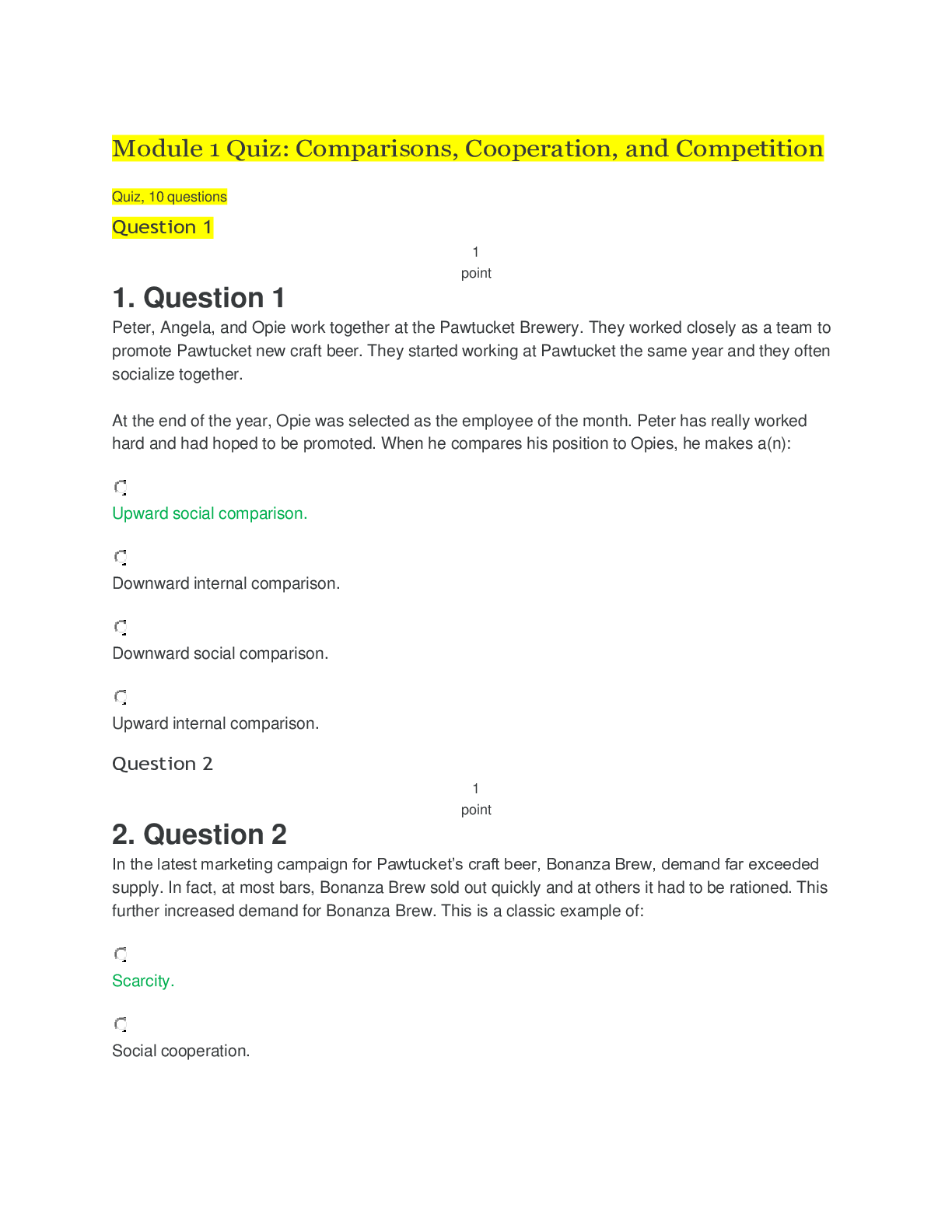
TRUE/FALSE 1. Advertising is defined as “a paid, mediated form of communication from an identifiable source, designed to persuade the receiver to take some action, now or in the future.” T... PTS: 1 2. The difference between advertising and public relations is that, for advertising, media exposure is paid for by the advertiser, and for public relations it is not. T PTS: 1 3. Most advertising is undertaken by companies that market their brands to other companies (B2B advertising). F PTS: 1 4. Over half of world-wide ad spending takes place in the United States. T PTS: 1 5. Of the product categories of automobiles, computers and software, drugs, food, personal care items, and telephone service, the category of automobiles has the highest average advertising-to-sales ratio. F PTS: 1 6. Smaller competitors in an industry typically have to invest relatively larger percentages of their sales revenues in advertising than do larger competitors. T PTS: 1 7. Even though advertising is costly, its effects are certain. F PTS: 1 8. Most successful companies are aware that consistent investment spending is the key factor underlying successful advertising. T PTS: 1 9. Advertising’s most important function is to increase sales. F PTS: 1 10. Advertising is an efficient form of communication, capable of reaching mass audiences at a relatively low cost per contact. T PTS: 1 11. Usage expansion advertising consists of teaching new uses for existing brands. T PTS: 1 12. Primary demand is creating demand for a specific company's brand. F PTS: 1 13. Secondary demand is creating demand for an entire product category. F PTS: 1 14. A commercial that creates demand for Mountain Dew is an example of secondary demand. T PTS: 1 15. One function of advertising is to increase brand salience, which means enriching the memory trace for a brand such that the brand comes to mind in relevant choice situations. T PTS: 1 16. Advertising has not been demonstrated to influence brand switching. F PTS: 1 17. There are three basic ways by which companies can add value to their offerings: innovating, altering consumer perceptions, and lowering price. F PTS: 1 18. Advertising adds value to brands by influencing perceptions. T PTS: 1 19. Advertising’s primary role is at times to facilitate other marcom efforts. T PTS: 1 20. Account executives are involved in tactical decision making and day-to-day contact with brand managers and other client personnel. T PTS: 1 21. Advertising management generally involves the organization that has a product or service to advertise and an independent agency, or agencies, responsible for creating ads, making media choices, and measuring results. T PTS: 1 22. Advertising strategy implementation involves setting objectives, devising budgets, creating messages, and developing the media strategy. F PTS: 1 23. Measuring advertising effectiveness often requires that baseline measures be taken before an advertising campaign begins and then afterward to determine whether the objective was achieved. T PTS: 1 24. Most of the major U.S. ad agencies are located in Los Angeles. F PTS: 1 25. In an in-house advertising operation, the advertiser employs an advertising staff and absorbs the overhead required to maintain the staff’s operations. T PTS: 1 26. One advantage of purchasing advertising services a la carte from specialized agencies is potential cost efficiencies. T PTS: 1 27. An advantage of using a full-service advertising agency is the ability to obtain negotiating leverage with the media. T PTS: 1 28. Media planners are responsible for developing the overall media strategy and purchasing the specific media vehicles for the advertiser. F PTS: 1 29. Account management provides the mechanism to link the agency with the client. T PTS: 1 30. Management supervisors in a full-service agency are involved in tactical decision making and day-to-day contact with brand managers and other client personnel. F PTS: 1 31. Historically, advertising agencies charged a standard commission of 20 percent of the gross amount of media billings. F PTS: 1 32. The most common advertising agency compensation method today is a labor-based fee system. T PTS: 1 33. Outcome-based programs represent the oldest approach to agency compensation. F PTS: 1 34. Outcome-based compensation programs encourages agencies to use whatever IMC programs are needed to build brand sales. T PTS: 1 35. Whether one chooses to invest or disinvest in advertising a brand depends largely on expectations about how advertising will influence a brand’s sales volume and revenue. T PTS: 1 36. In terms of profitability, investing in advertising can be justified only if the incremental revenue generated from the advertising effort exceeds the advertising expense. T PTS: 1 37. Most sophisticated companies are willing to place their bets on advertising’s ability to boost revenues and thus enhance profits from the revenue-increase side rather than from the expense-reduction side. T PTS: 1 38. Elasticity is a measure of how responsive quantity demanded is to changes in marketing variables such as price and advertising. T PTS: 1 39. An ad price elasticity coefficient of 0.15 indicates that a one percent increase in ad expenditures increases volume by 15 percent. F PTS: 1 40. Advertising elasticity is, in fact, a measure of advertising strength. T PTS: 1 41. Creating better, more creative, and stronger advertising than competitors can lead to increased market shares. T PTS: 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. _____ is a paid, mediated form of communication from an identifiable source, designed to persuade the receiver to take some action, now or in the future. a. Public relations b. Advertising c. Communications d. Marketing e. Marcom B PTS: 1 2. To distinguish advertising, which typically is conveyed via print, TV, radio, the Internet, etc., from person-to-person forms of communication, including personal selling and word of mouth, the term _____ communication is used. a. mediated b. paid-for c. commercial d. technological e. focused A PTS: 1 3. Over half of world-wide ad spending takes place in which country? a. United States b. Canada c. China d. Germany e. Japan A PTS: 1 4. Which product category has the highest average advertising-to-sales ratio? a. automobiles b. computers and software c. food d. personal care items e. drugs D PTS: 1 5. Advertising is costly and its effects are often _____. a. certain b. uncertain c. predetermined d. constant e. detrimental B PTS: 1 6. An ex-CEO at Procter & Gamble—one of the world’s largest advertisers—aptly draws an analogy between advertising and exercise in that both provide _____. a. short-term benefits b. irreversible benefits c. long-term benefits d. a learning environment e. life to its participants C PTS: 1 7. Most successful companies are aware that _____ spending is the key factor underlying successful advertising. a. increased b. decreased c. consistent investment d. maximum e. minimum C PTS: 1 8. Which of the following is an advertising function? a. informing b. influencing c. reminding d. adding value e. All of these are correct. E PTS: 1 9. Which is NOT a function performed by advertising? a. persuading b. reminding c. adding value d. assisting production e. informing D PTS: 1 10. Advertising that teaches new uses for existing brands is known as _____. a. elaboration advertising b. top-of-mind awareness advertising c. primary demand advertising d. usage expansion advertising e. alternative use advertising D PTS: 1 11. An example of usage expansion advertising is _____. a. a soft drink manufacturer who is the first to introduce a five liter plastic bottle b. a manufacturer of baking soda promoting a new use for the product c. a retailer who doubles the promotional budget d. a retailer that was only using newspaper advertising that is now expanding into radio advertising e. a gas station advertising that they are open 24 hours a day B PTS: 1 12. Creating demand for an entire product category is known as _____ demand. a. joint b. elastic c. derived d. primary e. secondary D PTS: 1 13. The Dairy Council’s campaign points out that weight-conscious consumers can buy low-fat dairy products. This message is primarily designed to _____. a. persuade b. deceive c. add value d. inform e. remind D PTS: 1 14. The Beef Council sponsored a variety of advertisements encouraging people to eat more meat. These advertisements were designed to create _____ demand. a. secondary b. derived c. elastic d. joint e. primary E PTS: 1 15. Which of the following is an example of an advertisement that was designed to create primary demand? a. "Weekends were made for Michelob." b. "Orange juice isn't just for breakfast anymore." c. "Like a good neighbor, State Farm is there." d. "You're in good hands with Allstate." e. "Gillette: the best a man can get." B PTS: 1 16. The National Dairy Council sponsored a series of commercials promoting milk and cheese as healthy foods. This advertising was designed to create _____. a. secondary demand b. horizontal demand c. vicarious demand d. primary demand e. joint demand D PTS: 1 17. Influencing people to purchase a specific brand is creating _____ demand. a. elastic b. inelastic c. joint d. secondary e. primary D PTS: 1 18. PepsiCo's commercials that encourage people to purchase Mountain Dew is an example of creating _____ demand. a. elastic b. primary c. secondary d. derived e. joint C PTS: 1 19. An advertisement that was designed to keep a company's brand fresh in the consumer's memory performs the advertising function of _____. a. informing b. persuading c. adding value d. reminding e. assisting other company efforts D PTS: 1 20. Making a brand more _____ means enriching the memory trace for a brand such that the brand comes to mind in relevant choice situations. a. primary b. secondary c. salient d. important e. valuable C PTS: 1 21. How can companies add value to their offerings? a. innovating b. improving quality c. altering consumer perceptions d. a and b only e. a, b, and c E PTS: 1 22. Advertising adds value to brands by _____. a. influencing perceptions b. innovating the offering c. improving the quality of the offering d. creating primary demand e. creating secondary demand A PTS: 1 23. A Korean brand of television was perceived as “low quality” by over 70 percent of American consumers who were surveyed. However, after an extensive advertising campaign, the percentage of American consumers who perceived this brand as low quality fell to 20 percent. In this instance, advertising has successfully altered consumers’ perceptions and performed which function? a. adding value b. informing c. persuading d. reminding e. assisting other company efforts A PTS: 1 24. An advertisement that is designed to presell a company's products and provide salespeople with valuable introductions performs the advertising function of _____. a. informing b. persuading c. adding value d. reminding e. assisting other company efforts E PTS: 1 25. An advertisement that is designed to encourage you to buy Nike shoes is attempting to stimulate _____ demand. a. inelastic b. elastic c. secondary d. primary e. joint C PTS: 1 26. Advertising that is designed to deliver coupons and sweepstakes is performing the function of _____. a. informing b. influencing c. reminding d. adding value e. assisting other company efforts E PTS: 1 27. Customers are known to be more responsive to retailers’ price deals when retailers _____. a. use rebate offers b. advertise those deals c. offer coupons d. provide additional incentives e. include in-package premiums B PTS: 1 28. _____ is the process of creating ad messages, selecting media in which to place the ads, and measuring the effects of the advertising efforts. a. Marketing management b. Advertising management c. Marcom management d. Promotion management e. Advertising B PTS: 1 29. Clara’s job responsibilities include the process of creating ad messages, selecting media in which to place the ads, and measuring the effects of the advertising efforts. Clara is involved in _____. a. marketing management b. message management c. marcom management d. communication management e. advertising management E PTS: 1 30. Advertising strategy formulation involves which activity? a. setting objectives b. devising budgets c. message creation d. media strategy e. All of these are correct. E PTS: 1 31. Rick’s job at a major consumer goods manufacturer is to oversee the process of setting advertising objectives, devising budgets, message creation, and determining media strategy. Rick is involved in _____. a. formulating advertising strategy b. implementing advertising strategy c. account management d. marketing management e. implementing marketing strategy A PTS: 1 32. _____ deals with the tactical, day-to-day activities that must be performed to carry out an advertising campaign. a. Marketing management b. Advertising management c. Advertising strategy formulation d. Advertising strategy implementation e. Measuring effectiveness D PTS: 1 33. Gwen works at a consumer-goods manufacturer and deals with the tactical, day-to-day activities that must be performed to carry out an advertising campaign. Gwen is involved in _____. a. formulating advertising strategy b. implementing advertising strategy c. account management d. marketing management e. formulating marketing strategy B PTS: 1 34. The _____ are involved in tactical decision making and day-to-day contact with brand managers and other client personnel. a. account executives b. management supervisors c. assistant supervisors d. product managers e. line managers A PTS: 1 35. Message strategies and decisions are most often the joint enterprise of the companies that advertise and their _____. a. advertising agencies b. marketing departments c. advertising departments d. promotion departments e. communication consultants A PTS: 1 36. Most of the major U.S. advertising agencies are located in _____. a. Detroit b. Chicago c. Los Angeles d. Dallas e. New York City E PTS: 1 37. Which of the following is a way advertisers can perform the advertising function? a. purchase advertising services on an as-needed basis from specialized agencies b. use a full-service advertising agency c. use an in-house advertising operation d. a and b only e. a, b, and c E PTS: 1 38. One option for an organization wishing to advertise is to recruit the services of a variety of firms with particular specialties in distinct aspects of advertising. These firms are called _____. a. specialty firms b. boutiques c. cafeteria agencies d. full-service agencies e. buffet agencies B PTS: 1 39. A full-service advertising agency _____. a. necessitates employing an advertising staff and absorbing the overhead required to maintain the staff's operations b. is unprofitable unless a company does a large and continuous amount of advertising c. has the advantage of complete control over the advertising function d. perform all the basic functions of advertising for a client e. does not perform other marcom functions, such as sales promotion and publicity D PTS: 1 40. Which of the following is a basic function performed by full-service advertising agencies? a. creative services b. media services c. research services d. account management e. All of these are correct. E PTS: 1 41. Which of the following is NOT a basic function performed by a full-service advertising agency? a. account management b. creative services c. product research and development services d. media services e. research services C PTS: 1 42. Which of the following is an advantage of employing the services of a full-service agency? a. obtaining negotiating leverage with the media b. ability to contract for services only when they are needed c. greater control over the advertising function d. greater control over competitive information e. more effective advertising A PTS: 1 43. Eric is a copywriter employed by a full-service advertising agency. Which function of a full-service agency does Eric’s job fall into? a. media services b. account management c. creative services d. research services e. production services C PTS: 1 44. Which unit of a full-service advertising agency is charged with the task of selecting the best advertising media for reaching the client’s target market, achieving ad objectives, and meeting the budget? a. creative services b. media services c. research services d. account management e. production services B PTS: 1 45. ____ are responsible for developing overall media strategy. a. Account executives b. Account planners c. Media planners d. Media buyers e. Media directors C PTS: 1 46. Addilson is responsible for developing the overall media strategy for his agency’s clients. Addilson is a(n) ____. a. media planner b. media buyer c. creative director d. account executive e. account planner A PTS: 1 47. ____ procure specific vehicles within particular media that have been selected for an agency’s clients. a. Account executives b. Account planners c. Media planners d. Media buyers e. Media directors D PTS: 1 48. Carrie works at an advertising agency, and her job is to procure specific vehicles within particular media that have been selected for the agency’s clients. Carrie is a(n) ____. a. media planner b. media buyer c. creative director d. account executive e. account planner B PTS: 1 49. Sam works for a full-service advertising agency. His job includes studying the buying habits of clients’ customers, their purchase preferences, and their responsiveness to advertising concepts and finished ads. Sam most likely works in _____. a. account management b. media services c. research services d. the creative department e. sponsorship management C PTS: 1 50. _____ act as liaisons so that the client does not need to interact directly with several different service departments and specialists in a full-service advertising agency. a. Account managers b. Account planners c. Media managers d. Account directors e. Client managers A PTS: 1 51. _____ are involved in tactical decision making and day-to-day contact with brand managers and other client personnel. a. Management supervisors b. Account executives c. Client managers d. Account planners e. Project managers B PTS: 1 52. Rebecca's position at an advertising agency has her involved in tactical decision making and day-to-day contact with brand managers and other client personnel. Rebecca is a(n) _____. a. line manager b. product manager c. assistant supervisor d. management supervisor e. account executive E PTS: 1 53. _____ are involved in getting new business for the agency and working with clients at a strategic level. a. Management supervisors b. Account executives c. Project managers d. Advertising managers e. Account planners A PTS: 1 54. Lucille's position at an advertising agency has her involved in getting new business for the agency and working with clients at a strategic level. Lucille is a(n) _____. a. line manager b. senior vice-president c. assistant supervisor d. management supervisor e. account executive D PTS: 1 55. Account executives report to _____. a. regional managers b. senior vice-presidents c. the chief executive officer d. the board of directors e. account managers E PTS: 1 56. Which of the following is a form of advertising agency compensation? a. commissions from media b. labor-based fee system c. outcome-based programs d. a and b only e. a, b, and c E PTS: 1 57. In the past, what was the standard media commission paid to advertising agencies? a. 5 percent b. 10 percent c. 15 percent d. 20 percent e. 25 percent C PTS: 1 58. Creative Advertising Agency buys $100,000 of magazine advertising space for its client. Using the historical standard media commission rate, how much will the agency be compensated for this media buy? a. $5,000 b. $10,000 c. $15,000 d. $20,000 e. $25,000 C PTS: 1 59. The most common method of compensation for advertising agencies today is _____. a. a labor-based fee system b. a standard commission of 10 percent of the gross amount of the billing c. a standard commission of 15 percent of the gross amount of the billing d. a standard commission of 20 percent of the gross amount of the billing e. outcome-based programs A PTS: 1 60. A compensation system in which agencies carefully monitor their time and bill clients a fee based on time commitment is known as a(n) _____. a. commission-based system b. input-based system c. labor-based fee system d. outcome-based program e. performance-based system C PTS: 1 61. _____ represent the newest approach to agency compensation. a. Fee-based programs b. Outcome-based programs c. Contingency-based programs d. Outsource-based programs e. Commission-based programs B PTS: 1 62. Which agency compensation method is closely aligned with the advertiser’s sales? a. Media-commission system b. Labor-based fee system c. Outcome-based programs d. Investment-based programs e. Equity-based programs C PTS: 1 63. A firm’s sales volume is obtained by which of the following equations? a. Revenue – Expenses b. Marginal Profit – Marginal Costs c. Price Production Units d. Trial + Repeat e. Marginal Revenue Production Units D PTS: 1 64. Whether one chooses to invest or disinvest in advertising a brand depends largely on expectations about how advertising will influence a brand’s sales volume and _____. a. revenue b. variable cost c. discretionary cost d. marginal cost e. price A PTS: 1 65. In terms of profitability, investing in advertising can be justified only if the incremental revenue generated from the advertising effort exceeds the _____. a. production expense b. operational expense c. discretionary expense d. advertising expense e. commission expense D PTS: 1 66. The case for investing in advertising is based on the belief that it can increase profitability and thus increase revenue beyond the incremental advertising expense by _____. a. increasing sales volume b. enabling higher selling prices c. reducing promotion costs d. a and b only e. a, b, and c D PTS: 1 67. Effective advertising should build sales volume by enhancing brand equity, both by _____ and by _____. a. building brand knowledge; increasing trial b. providing information; including a reason to buy c. including a sales promotion offer; reminding consumers d. increasing brand loyalty; using a credible endorser e. increasing brand awareness; enhancing brand image E PTS: 1 68. When firms choose to reduce advertising expenditures if a brand is performing well or during periods of economic recession, this is referred to as _____. a. disinvesting b. disintermediation c. divesting d. discharging e. harvesting A PTS: 1 69. Advertising’s long-term role has been described as “Strong advertising represents a deposit in the brand equity bank.” By “strong” is meant the advertising _____. a. is repeated at least three times b. provides sufficient product information as well as an emotional appeal c. includes convincing arguments for purchase d. is different, unique, clever, and memorable e. is credible, informative, and humorous D PTS: 1 70. _____ is a measure of how responsive the quantity demanded is to changes in marketing variables such as price and advertising. a. Profitability b. Elasticity c. Production d. Disinvesting e. Connectivity B PTS: 1 71. The _____ says that sales volume, or quantity, typically increases when prices are reduced, and vice versa. a. elasticity model b. sales-price curve c. law of inverse demand d. converse sales law e. sales demand equation C PTS: 1 72. In general, there are four combinations of advertising and price elasticities. Which of the following is NOT one of the combinations? a. grow volume via price discounting b. increase advertising and/or discount prices c. maintain the status quo d. build image via increased advertising e. decrease prices and advertising expenses E PTS: 1 73. In a situation where demand is more advertising elastic than price elastic it is advisable to _____. a. maintain the status quo b. build image via increased advertising c. grow volume via price discounting d. increase advertising and/or discount prices e. decrease advertising and discount prices B PTS: 1 74. It is possible to translate the idea of advertising “strength” into numerical values by capitalizing on the concept of _____. a. advertising elasticity b. return on investment c. share of market d. advertising variance e. competitive analysis A PTS: 1 ESSAY 1. Edwin L. Artzt, former chairman and CEO of Procter & Gamble, draws an analogy between exercising and advertising. Explain the meaning of this analogy, particularly in reference to brand equity. 2. List and describe the five functions of advertising. 3. Describe the advertising management process from the advertiser’s perspective. 4. Identify situations where an advertiser would use in-house advertising operations, full-service advertising agencies, and a la carte arrangements. Your answer should include a discussion of the advantages and disadvantages of each of the three alternatives. 5. Describe the various forms of advertising agency compensation. 6. In general, we can consider four combinations of advertising and price elasticities. Discuss the implications of each of these situations. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 19 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Nov 07, 2019
Number of pages
19
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Nov 07, 2019
Downloads
0
Views
70



















.png)
.png)
.png)

.png)


.png)
.png)
.png)




