Marketing > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Chapter 2—Enhancing Brand Equity and Accountability. Correct Answers (All)
Chapter 2—Enhancing Brand Equity and Accountability. Correct Answers
Document Content and Description Below
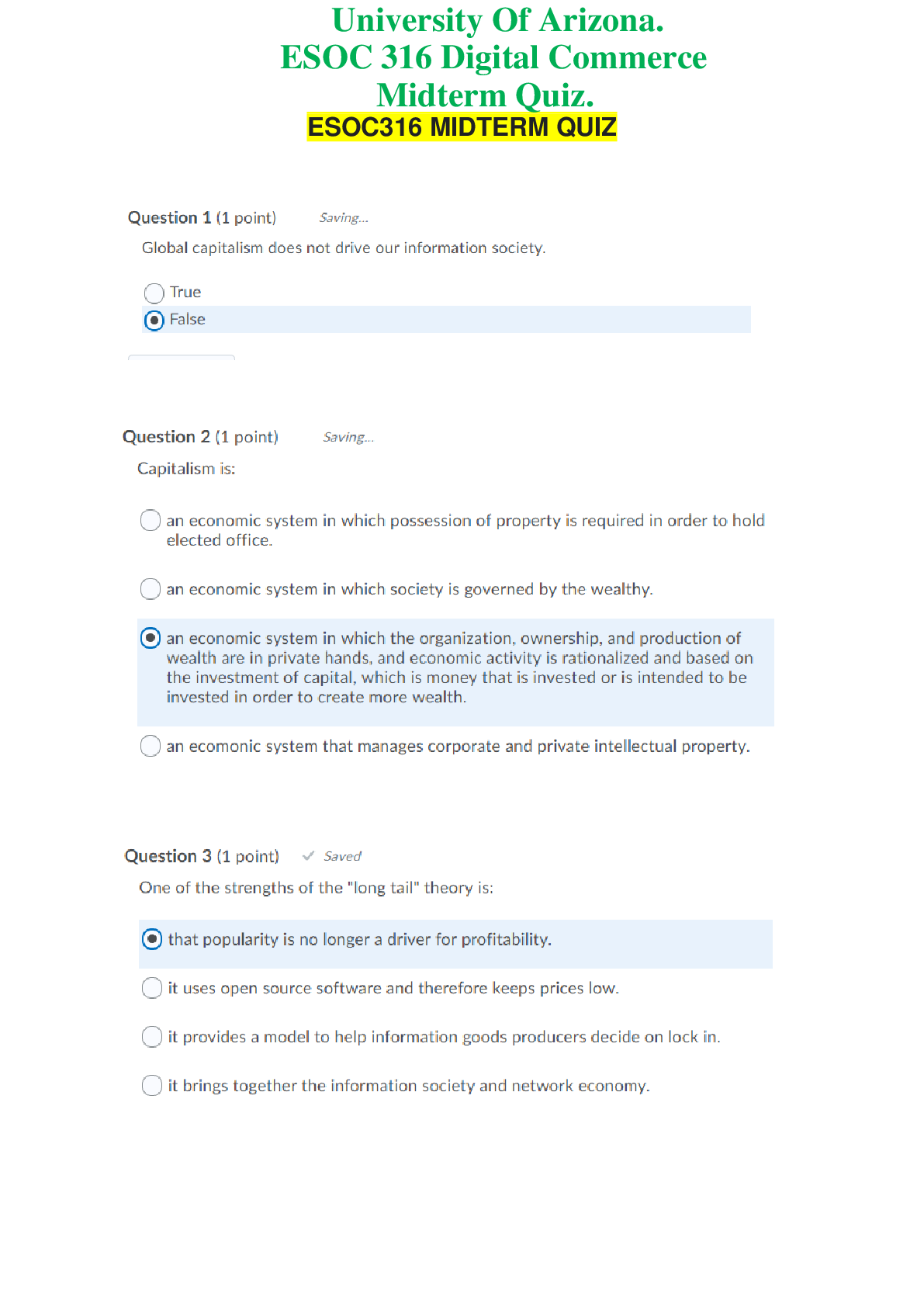
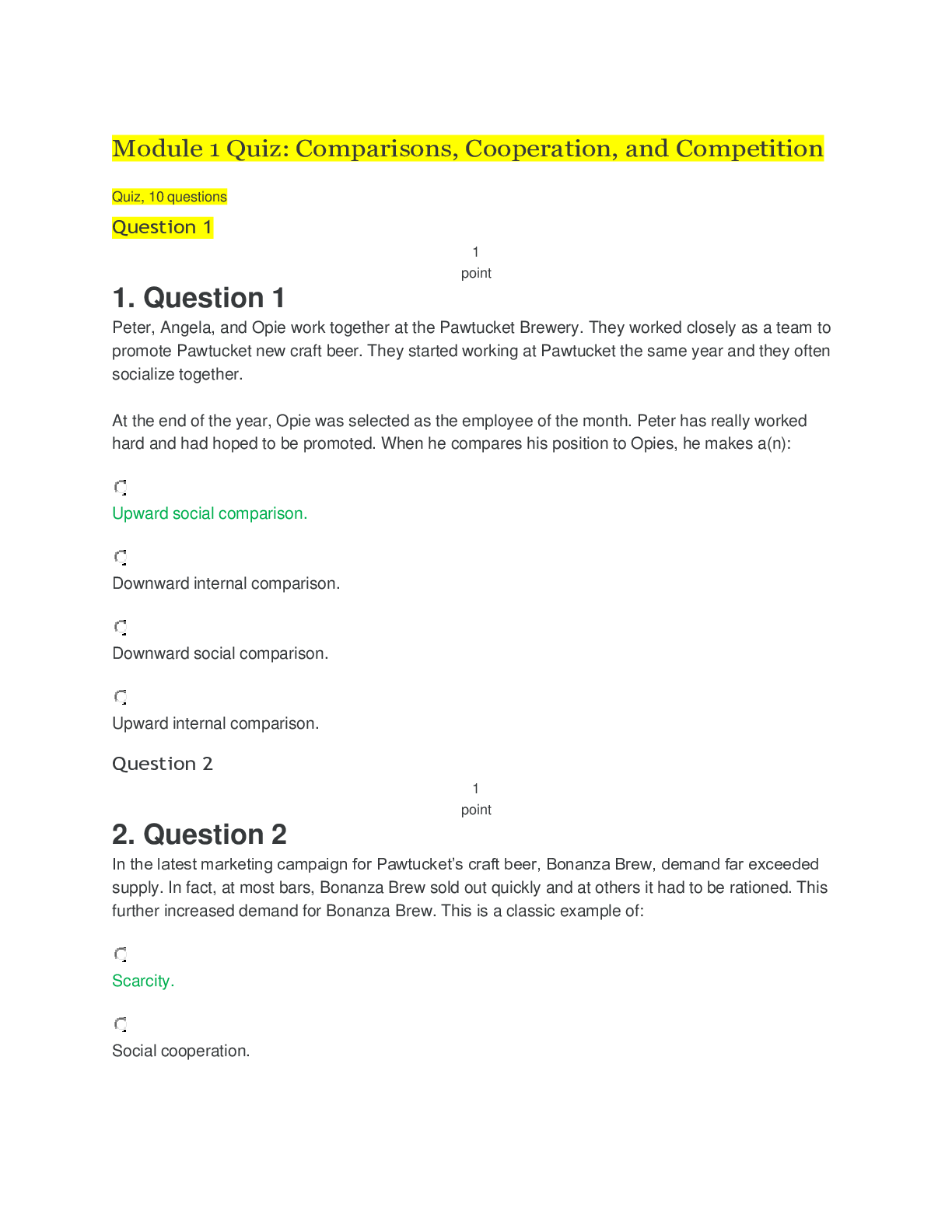
Chapter 2—Enhancing Brand Equity and Accountability TRUE/FALSE 1. A brand is a name, term, sign, symbol, or design, or a combination of them, intended to identify the goods and services of on... e seller or groups of sellers and to differentiate them from those of competition. : T PTS: 1 2. All organizations and their products can be considered brands. : T PTS: 1 3. The concept of brand equity is considered only from the perspective of the customer. : F PTS: 1 4. Brand equity occurs when the consumer considers two competing brands to be similar. : F PTS: 1 5. A firm-based viewpoint of brand equity focuses on outcomes extending from efforts to enhance a brand’s value to is various stakeholders. : T PTS: 1 6. Revenue premium is defined as the revenue differential between a branded item and a corresponding private labeled brand. : T PTS: 1 7. Many private-label products possess levels of quality that are equivalent to manufacturers’ national brands. : T PTS: 1 8. From the perspective of the customer, brand preference is the basic dimension of brand equity. : F PTS: 1 9. Brand equity from the customer’s perspective consists of two forms of brand-related knowledge: brand awareness and brand image. : T PTS: 1 10. Brand image is an issue of whether a brand name comes to mind when consumers think about a particular product category and the ease with which the name is evoked. : F PTS: 1 11. A brand has no equity if consumers are unfamiliar with it. : T PTS: 1 12. Brand recall reflects a relatively superficial level of awareness, whereas brand recognition indicates a deeper form of awareness. : F PTS: 1 13. The marcom imperative is to move brands from a state of unawareness, to recognition, on to recall, and ultimately to top-of-mind awareness (TOMA). : T PTS: 1 14. Brand image can be thought of in terms of the types of associations that come to the customer’s or consumer’s mind when contemplating a particular brand. : T PTS: 1 15. Brand associations can be conceptualized in terms of type, favorability, strength, and uniqueness. : T PTS: 1 16. Research has identified ten personality dimensions that describe most brands. : F PTS: 1 17. Brands scoring high on the sincerity dimension are considered reliable, intelligent, and successful. : F PTS: 1 18. The objective of marketing communication is to deemphasize brand equity. : F PTS: 1 19. By trying and using brands, consumers learn how good (or bad) they are and what benefits they are (in)capable of delivering, which is known as the leveraging approach to enhancing brand equity. : F PTS: 1 20. Marketing communicators draw meaning from the culturally constituted world and trfer that meaning to consumer goods. : T PTS: 1 21. A brand can leverage associations by connecting itself with other brands, places, things, and people. : T PTS: 1 22. Co-branding occurs when two or more brands enter into a partnership that potentially serves to enhance both brands’ equity and profitability. : T PTS: 1 23. A potential downside for the host brand with respect to ingredient branding is that the equity of the ingredient brand might be so great that it overshadows the host brand. : T PTS: 1 24. One major by-product of efforts to increase a brand’s equity is that consumer brand loyalty might also increase, which in turn, could positively influence long-term growth and profitability. : T PTS: 1 25. The EquiTrend survey asks respondents to rate a number of brands in terms of two dimensions: quality and salience. : T PTS: 1 26. Successful brands employ just one or two marcom tools in order to satisfy the brand’s positioning strategy. : F PTS: 1 27. One trait shared by the world’s strongest brands is that the company monitors sources of brand equity through ongoing brand audits or tracking studies. : T PTS: 1 28. Enhancing brand equity is a me of moving customers to favorable action toward the brand. : T PTS: 1 29. The vast majority of marketing executives and marketing academics are against gauging the effect of marcom efforts in terms of the return on marketing investment, or ROMI, because it is almost impossible to measure. : F PTS: 1 30. Measuring marcom effectiveness is relatively simple, and most organizations are currently doing a sophisticated job of doing so. : F PTS: 1 31. One difficulty with measuring marcom effectiveness is the identification of an appropriate measure, or metric, of effectiveness. : T PTS: 1 32. Whatever the measure chosen, any effort to meaningfully assess marcom performance requires having data that are reliable and valid. : T PTS: 1 33. A technique called promotion-mix modeling is increasingly being used to determine the relative effect each marcom program element has on sales volume compared to the effects of other elements. : F PTS: 1 34. Marketing-mix modeling employs multivariate regression analysis to estimate the effects that the various advertising and promotion elements have in driving sales volume. : T PTS: 1 35. To employ marketing-mix modeling, a relatively long series of longitudinal data (i.e., two-year period) is required. : T PTS: 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. A _____ is a name, term, sign, symbol, or design, or a combination of them intended to identify the goods and services of one seller or group of sellers to differentiate them from those of competition. a. trademark b. market c. tradename d. brand e. guarantee : D PTS: 1 2. A _____ is everything that one company’s particular offering stands for in comparison to competitors’ offerings. a. trademark b. logo c. symbol d. brand e. sign : D PTS: 1 3. The concept of brand equity is considered from which perspective? a. from the perspective of the organization that owns the brand b. from the vantage point of the customer c. from the perspective of the other brands in the product category d. a and b only e. a, b, and c : D PTS: 1 4. From the perspective of the firm that owns the brand, which of the following is a positive outcome of increased brand equity? a. higher market share b. increased brand loyalty c. ability to charge premium prices d. earning a revenue premium e. All of these are correct. : E PTS: 1 5. As a brand’s equity increases, its elasticity of demand _____. a. becomes less elastic b. becomes more elastic c. becomes less inelastic d. remains constant e. increases : A PTS: 1 6. The revenue differential between a branded item and a corresponding private labeled item is known as _____. a. market premium b. price premium c. revenue premium d. profit premium e. equity premium : C PTS: 1 7. Tide laundry detergent is a well known brand that sells for approximately $8.00 for a 64 ounce bottle, and Procter & Gamble usually sells 2 million of these sizes each year. An average private label store brand costs $6.00 for the same size, and typically 1 million are sold each year. What is Tide’s revenue premium? a. $2.00 b. $1 million c. $6 million d. $10 million e. $16 million : D PTS: 1 8. A research study involving McDonald’s products discovered a new form of firm-based brand equity that has been labeled _____ brand equity. a. name-recognition b. taste-premium c. market-share d. revenue-premium e. price-premium : B PTS: 1 9. From the perspective of the customer or consumer, _____ is the extent to which they are familiar with the brand and have stored in their memory favorable, strong, and unique brand associations. a. brand awareness b. brand image c. brand preference d. brand equity e. brand effectiveness : D PTS: 1 10. Brand equity from the customer’s perspective consists of _____. a. brand awareness and brand image b. brand awareness and brand preference c. brand image and brand insistence d. brand image and brand tolerance e. brand awareness and brand tolerance : A PTS: 1 11. _____ refers to the extent to which a brand name comes to mind when consumers think about a particular product category and the ease with which the name is evoked. a. Brand image b. Brand awareness c. Brand loyalty d. Brand preference e. Brand knowledge : B PTS: 1 12. The basic dimension of brand equity is _____. a. brand image b. brand preference c. brand tolerance d. brand insistence e. brand awareness : E PTS: 1 13. What is the initial challenge for new brands? a. achieving brand awareness b. enhancing brand image c. achieving brand preference d. achieving brand insistence e. building revenue premium : A PTS: 1 14. Brand _____ reflects a relatively superficial level of awareness, whereas brand _____ indicates a deeper form of awareness. a. image; equity b. equity; image c. recognition; recall d. recall; recognition e. associations; image : C PTS: 1 15. Bill is given a list of brands of shaving products by a researcher and is asked to mark all those that he is aware of. Which level of awareness is this assessing? a. recall b. recognition c. aided recall d. unaided recall e. positive awareness : B PTS: 1 16. Maria is asked by a market researcher to list all the brands of toothpaste she can think of. Which type of awareness is this assessing? a. recall b. recognition c. positive awareness d. free-association awareness e. aided recognition : A PTS: 1 17. The pinnacle of brand-name awareness that exists when your company’s brand is the first brand that consumers recall when thinking about brands in a particular product category is known as _____. a. top-of-category awareness (TOCA) b. recognition c. tip-of-the-tongue awareness (TOTA) d. top-of-mind awareness (TOMA) e. top-of-class awareness (TOCA) : D PTS: 1 18. Which of the following statements is true regarding brand awareness? a. Only consumer-oriented (B2C) firms must be concerned with building brand awareness. b. Most consumers are able to retrieve a brand name from memory without any reminders. c. There are two levels of brand awareness: primary and secondary. d. Brand recall reflects a relatively superficial level of awareness, whereas brand recognition indicates a deeper form of awareness. e. Although building brand awareness is a necessary step toward brand equity enhancement, it is insufficient. : E PTS: 1 19. The types of associations that come to the consumer’s mind when contemplating a particular brand is known as _____. a. brand image b. brand equity c. brand awareness d. brand cognitions e. brand parity : A PTS: 1 20. Maria is asked by a market researcher to tell him the particular thoughts and feelings she has about Starbuck’s coffee. A particular thought or feeling that comes to Maria’s mind is known as a(n) _____. a. brand dimension b. cognition c. brand link d. association e. think-feel linkage : D PTS: 1 21. Brand associations can be conceptualized in terms of _____. a. type b. favorability c. strength d. uniqueness e. All of these are correct. : E PTS: 1 22. Research has identified _____ dimensions that seem to capture the personalities of a variety of consumer brands. a. four b. five c. six d. seven e. eight : B PTS: 1 23. Which of the following is NOT a personality dimension that describes most brands? a. sincerity b. excitement c. competence d. innocence e. ruggedness : B PTS: 1 24. This dimension includes brands that are down-to-earth, honest, wholesome, and cheerful. a. excitement b. sophistication c. competence d. sincerity e. ruggedness : D PTS: 1 25. Toyota automobiles are regarded by consumers as reliable, intelligent, and successful. The levels of satisfaction of Toyota owners is at or near the top of satisfaction ratings. Which brand-related personality dimension best describes Toyota? a. excitement b. competence c. sophistication d. ruggedness e. innocence : B PTS: 1 26. Luxury items, such as Rolex watches, generally score high on which brand-related personality dimension? a. Sincerity b. Excitement c. Competence d. Sophistication e. Ruggedness : D PTS: 1 27. Which personality dimension has General Motors attempted to create for its repair services through its hypothetical “Mr. Goodwrench,” who represents the name and “face” of the trained technici who work in thousands of GM dealerships? a. sincerity b. excitement c. competence d. sophistication e. ruggedness : A PTS: 1 28. What is necessary to create favorable, strong, and unique associations about a brand? a. heavy mass media advertising b. co-branding c. sustained marketing communications d. ingredient-branding e. brand preference : C PTS: 1 29. Which of the following is NOT an approach by which brand equity is enhanced? a. brand awareness approach b. speak-for-itself approach c. message-driven approach d. leveraging approach e. All of these are approaches. : A PTS: 1 30. Consumers learn how good (or bad) a brand is and what benefits it is (in)capable to delivering by trying and using a brand. Which approach to enhancing brand equity is this known as? a. message-driven approach b. leveraging approach c. trial-and-error approach d. speak-for-itself approach e. initial approach : D PTS: 1 31. In which approach to enhancing brand equity do marcom practitioners attempt to build advantageous associations through creative, attention getting, and believable messages? a. speak-for-itself approach b. message-driven approach c. leveraging approach d. shotgun approach e. cast-a-wide-net approach : B PTS: 1 32. Brand associations can be shaped and equity enhanced through marketing communications that associate the brand with people, places, and “things” that are available to consumers. This approach is known as the _____. a. speak-for-itself approach b. message-driven approach c. leveraging approach d. culturally constituted approach e. meaning trfer approach : C PTS: 1 33. People learn cultural values, form beliefs, and become familiar with the physical manifestations, or artifacts, of these values and beliefs through _____. a. marcom b. media exposure c. socialization d. brand awareness e. active synthesis : C PTS: 1 34. When a marketing communicator connects a consumer good with a representation of the culturally constituted world, s/he is engaging in _____. a. lifestyle marketing b. sales promotion c. socialization d. point-of-purchase advertising e. meaning trfer : E PTS: 1 35. Marketing communicators _____ meaning and create associations for their brands by connecting them with other objects that already possess well-known meaning. a. promote b. locate c. leverage d. advertise e. obtain : C PTS: 1 36. Which marcom tool is an especially important instrument of meaning trfer? a. sales promotion b. personal selling c. advertising d. public relations e. frequency programs : C PTS: 1 37. Lee Michaels is a national chain jewelry store found in many malls across the U.S. Laurie went in to look at the watches, but she was unfamiliar with some of the brands. The salesperson told her that they were all Swiss-made, meaning they were made in Switzerland, which is known worldwide for the quality of the timepieces produced there. From which source are these brands leveraging their brand meaning? a. other brands b. people c. places d. things e. names : C PTS: 1 38. Which of the following is a source by which brand meaning can be leveraged? a. other brands b. places c. things d. people e. All of these are correct. : E PTS: 1 39. When two or more brands enter into a partnership that potentially serves to enhance both brands’ equity and profitability, _____ has occurred. a. cross-branding b. co-branding c. multi-branding d. family-branding e. house-branding : B PTS: 1 40. Kellogg’s, a cereal manufacturer, and Disney and Pixar have partnered in brands of cereal targeted to children that are named after their movies, such as Finding Nemo and The Incredibles. What is this alliance known as? a. cross-branding b. ingredient branding c. family-branding d. co-branding e. multi-branding : D PTS: 1 41. The most important requirement for co-branding is that _____. a. there is a logical fit between the two brands b. the two brands are similar in price c. the two products are not directly competing against each other d. the two products have the same target market e. the two products are manufactured by the same firm : A PTS: 1 42. An example of _____ is the sticker on a Dell computer that says “Intel Inside.” a. cross-branding b. multi-branding c. reference branding d. ingredient branding e. planned branding : D PTS: 1 43. The EquiTrend survey asks respondents to rate a number of brands in terms of which two dimensions? a. quality and personality b. awareness and image c. familiarity and quality d. image and quality e. image and preference : C PTS: 1 44. Creating and increasing brand loyalty results in a corresponding increase in the value of the _____. a. firm b. target market c. product position d. market share e. trustmark : E PTS: 1 45. Which of the following is NOT a trait shared by the world’s strongest brands? a. The brand excels at delivering the benefits customers truly desire. b. The brand stays relevant. c. The pricing system is based on consumers’ perceptions of value. d. The brand relies on mass media advertising to satisfy the brand’s positioning strategy. e. The brand portfolio and hierarchy make sense. : D PTS: 1 46. One trait shared by the world’s strongest brands is that the brand’s managers understand what the brand me to _____. a. the news media b. competitors c. customers d. them e. stock analysts : C PTS: 1 47. The objective of marketing communications is to enhance brand equity as a me of _____. a. defining the marketing mix b. moving customers to favorable action toward the brand c. increasing short-term sales d. reducing the advertising budget e. reducing the promotional budget : B PTS: 1 48. From the marketer’s standpoint, marcom’s objective is to ultimately affect _____. a. brand equity b. brand awareness c. brand image d. sales volume and revenue e. investment : D PTS: 1 49. The effect of marcom, or of its specific elements such as advertising, can be gauged in terms of whether it generates a reasonable _____. a. return on marketing investment (ROMI) b. return on customer investment (ROCI) c. return on equity investment (ROEI) d. return on brand investment (ROBI) e. return on sales investment (ROSI) : A PTS: 1 50. Which of the following is a motivation underlying the increased focus on measuring marketing performance? a. greater demands for accountability on the marketing function from the CEO, the Board, and other executives b. the imperative for the CMO to get better at what they do c. required by the IRS to report the gains from marketing investment d. a and b only e. a, b, and c : D PTS: 1 51. Which of the following is NOT a reason for the difficulty in measuring marcom effectiveness? a. lack of ability by marcom practitioners b. obstacles in identifying an appropriate measure, or metric, of effectiveness c. complications with getting people throughout the organization to agree that a particular measure is the most appropriate d. snags with gathering accurate data to assess effectiveness e. problems with determining the exact effect that specific marcom elements have on the measure that has been selected to indicate effectiveness : A PTS: 1 52. Specific measures that are used to judge marcom effectiveness are also called _____. a. variables b. metrics c. coefficients d. models e. variances : B PTS: 1 53. Harold is trying to determine the appropriate metric his company should use to gauge the effectiveness of its marcom efforts. Which of the following is a possible option? a. brand awareness b. attitudes toward the brand c. purchase intentions d. sales volume e. All of these are correct. : E PTS: 1 54. A recent study by the Association of National Advertisers found that among the most common metrics used for measuring ROMI was _____. a. change in consumer purchase behavior b. incremental sales revenue generated by marketing activities c. increases in S-O-M compared to changes in S-O-V d. changes in brand loyalty generated by advertising e. changes in brand image with increased expenditure on sales promotion : B PTS: 1 55. Why is it difficult to gain agreement on a suitable system for measuring marcom performance? a. People are uncooperative. b. People in other disciplines do not understand marketing and marketing communications c. Individuals from different backgrounds and with varied organizational interests often see the “world” differently or operate with varying ideas of what best indicates suitable performance. d. There is so little difference among the measures that it is difficult for individuals outside of marketing to understand them. e. If it isn’t in terms of dollars, others in the organization don’t even want to look at it. : C PTS: 1 56. Whatever the measure chosen, any effort to meaningfully assess marcom performance necessitates having data that are _____. a. short-term and long-term b. communication-based and sales-based c. representative and normal d. normal and bi-modal e. reliable and valid : E PTS: 1 57. What is the most complicated problem of all when assessing marcom performance? a. How much data is necessary? b. How much relative effect does each program element have compared to the effects of other elements? c. How does one assess reliability and validity? d. How can a researcher be sure that the data are appropriate for the metric being assessed? e. How does one account for sampling and measurement errors? : B PTS: 1 58. Which technique is increasingly being used to assess the relative effect each program element has compared to the effects of other elements? a. marketing-mix modeling b. structural equation modeling c. marketing optimization modeling d. multidimensional scaling e. calibration modeling : A PTS: 1 59. Marketing-mix modeling typically employs which statistical technique to estimate the effects that the various marcom elements have in driving sales volume? a. cluster analysis b. structural equation modeling c. multivariate regression analysis d. ANOVA e. MANOVA : C PTS: 1 60. Sam is tasked with employing marketing-mix modeling to determine the effectiveness of various marcom elements in affecting sales volume. What will Sam need to conduct this analysis? a. at least five observations for each element assessed along with the level of sales for those time periods b. a relatively long series of longitudinal data, such as two years, indicating the level of sales during that period along with corresponding marcom expenditures for each program element c. at least ten observations for each element assessed along with the level of sales for those time periods d. over 1,000 observations for each element assessed along with the level of sales for those time periods e. parameter estimates of the individual effects the various marcom elements have on sales : B PTS: 1 61. Which of the following statements is FALSE regarding marketing-mix modeling? a. In order to employ marketing-mix modeling, a relatively long series of longitudinal data (i.e., for a two-year period) is required. b. Marketing-mix modeling employs well known statistical techniques (e.g., multivariate regression analysis) to estimate the effects that the various marcom elements have in driving sales volume. c. Parameter estimates indicate the individual effects the various marcom elements have on sales. d. Managers learn from such analysis which elements are outperforming others and can use this information to shift budgets from program element to element. e. Once the model is estimated, results can be generalized to other situations. : E PTS: 1 62. Managers learn from the analytic aspect of marketing mix modeling which marcom elements are outperforming others and can then use this statistical information to _____. a. shift budgets from program element to element b. reposition products to better meet the needs of consumers c. develop new products and services d. construct more appropriate messages for their target market e. identify new markets for their products and/or services : A PTS: 1 63. In using marketing-mix modeling, the finer, or more disaggregated, the data the better the analysis can be in determining which specific marketing mix elements are most and least effective in _____. a. generating awareness b. creating brand loyalty c. developing new markets d. reaching the current target market e. driving sales : E PTS: 1 ESSAY 1. Discuss the benefits of brand equity from the firm’s perspective. PTS: 1 2. Name and describe the two forms of brand knowledge from a consumer perspective. PTS: 1 3. Briefly discuss the five dimensions of brand personality. The five dimensions of brand personality are: 4. Name and describe the three ways by which brand equity is enhanced. 5. Discuss the reasons accounting for the difficulty in measuring marcom effectiveness. : [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 17 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Nov 06, 2019
Number of pages
17
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Nov 06, 2019
Downloads
0
Views
74