*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > NR 511 Test Bank | AANP-FNP lightning round review-#2|Complete Solutions;Chamberlain College of Nurs (All)
NR 511 Test Bank | AANP-FNP lightning round review-#2|Complete Solutions;Chamberlain College of Nursing LATEST 2021/2022
Document Content and Description Below
AANP-FNP lightning round review-#2 1.How many sets of Kegels should be done each day to help with urinary incontinence? 2. What is the first line treatment for allergic rhinitis? -. 3. What is the ter... m used for the loss of high-pitched tones in geriatrics? 4. What type of hearing loss does cerumen impaction cause? 5. You see an older woman bending over leaving on her shopping cart at the grocery store. What is the likely diagnosis? 6. Multiple myeloma is disease of what? 7. What test in the office can you use to help diagnose sciatica? 8. I have heel pain that is worse in the morning. What is my likely diagnosis? 90. The Lachman test is used to help diagnose what? 10. Other tests for acl include 11. What is the treatment for gout and what would be the medication instructions for a flare? 12. What is a sign of colchicine toxicity? 13. What is a common cause of posterior knee pain? 14. Cotton wool spots, neovascularization and microaneurysms are all Eye exam findings in what condition? 15. And what about AV nicking and what it is? 16. What is the treatment for bacterial sinusitis? 17. I’m tired, have a sore throat and swollen posterior cervical nodes on exam. What is the likely diagnosis? - 18. Recall that swollen ANTERIOR cervical nodes are seen in 19. What is a common side effect of Pyridium, an anti-spasmodic for dysuria? 20. What would be included in your list of differentials for hematuria? 21. What is the medication treatment for MRSA? 22. What are some symptoms a patient with lupus would complain of? . 23.And what is the lab that you would order it to confirm it? 24. What is the term used to describe dry, itching skin? 25. What is the most common kind of skin cancer? 26. What medication is used to treat a cat or dog bite? 27. What do you think of when you hear a bright beefy red rash and what is the treatment? 28. How would you describe the prostate in BPH? 29. A1C> what is considered T2DM? 30. My A1C is >10, what would be the medication of choice? 31. Hypothyroidism is most common in what population? 32. Your pediatric pt has bloody discharge in his ear, what’s the likely dx? 33. Your patient presents with a burn and blisters are present. What degree burn is this? 34 What is the treatment for pertussis? 35. What bug causes the greatest mortality in community acquired pneumonia? 36. What would be seen on xray of a pt with TB? 37. Most common side effect of long-term inhaled corticosteroid use? - 38. S3 heart sound is a sign of what? - 39. What medication do use to treat a fib? 40. What is pulsus paradoxus? 41. The upcoming July 4th holiday reminds you of what diagnosis? 42. Someone with high triglyceride levels is at increased risk of what? 43. Subclinical hypothyroidism is described as what lab readings? 44. A positive Markle test is significant of what? 45. What differentials do you think of in someone with left upper quadrant pain? 46. What about left lower quadrant? 47. A positive Murphy’s sign is indicative of what? 48. What diagnostic test would you order if this were positive? 49. What is the first line treatment for GERD? 50. I was going to go over hepatitis B markers but I think it’s harder to say that out loud versus seeing it on paper so going to skip that but of course remember to review those for the exam too! 51. What diagnostic test should be done for suspicion of appendicitis? 52. What is the confirmatory test for HIV? 53. What is the treatment for syphilis? 54. And what are some presenting features of syphilis? 55. Gonorrhea treatment? 56. Cervicitis is seen in which diagnoses? - 57. I am a healthy 63-year-old patient, what is my goal BP according to JNC 8? 58. What should we keep in mind when prescribing for the elderly population? 59. A low HDL and high trig level always means what? 60. The S1 is the closure of which valves? 61. On exam you feel a weakened peripheral pulse, what diagnosis do you think of? 62. An absent red reflex is indicative of what? 63. During an eye exam you note absent venous pulsations, what is this related to? 64. The Dix Hallpike maneuver is used to test for what condition? 65. What is the most well-known medication treatment for Vertigo? 66. What medication is prescribed for essential tremors? 67. A young adult patient states that she is experiencing episodes of vision loss and abnormal limb sensations. What would be at the top of your list of differentials? 68. When assessing a patient for dementia, what is the FIRST and best thing you should do? 69. Name a difference between dementia and delirium? 70. What is the MAIN cause of delirium? 71. Cranial Nerves review (just going over the MAIN ones I’ve seen in reviews/questions for the exam) 72. UTI treatment? 73. What about UTI in a pregnant pt? 74. Anxiety…which meds to use for situational? 75. What about OCD? 76. Which population has the highest suicide rate? 77. What symptom is specific to the geriatric population when you think of UTIs? 78. PNA in Geri’s, how do they present? 79. What is the difference between sensitivity and specificity? 80. What vitamin deficiency can alcohol lead to? 81. MMSE, what score indicates dementia? 82. 10mm+ for PPD is needed for continued investigation of TB for what two populations? 83. What food is advised to try first in infants 4-6 months of age? 84. What degree of curvature in scoliosis should warrant bracing? 85. Tanner staging, anyone need a refresher on this? 86. What is the leading cause of death in children? 87. What sound during the Ortolani maneuver is a positive finding and signifies a possible hip abnormality (hip dysplasia) in infants. – 88. A newborn's mother is discovered to be HBsAg (hepatitis B surface antigen) positive. Which of the following would you recommend for this infant? 89. Which method is used to diagnose gonorrheal pharyngitis or proctitis? 90. What is the treatment for a medial tibial stress fracture (aka “shin splints”) Chapter 3. Health Promotion Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. _ 1. Which of the following is a primary prevention measure for a 76-year-old man newly diagnosed with a testosterone deficiency? a. Calcium supplementation b. Testicular self-examination c. Bone density test d. Digital rectal examination __ 2. Which of the following is an example of secondary prevention in a 50-year-old woman? a. Yearly mammogram b. Low animal fat diet c. Use of seat belt d. Daily application of sunscreen __ _ 3. Which of the following is an example of tertiary prevention in a patient with chronic renal failure? a. Fluid restriction b. Hemodialysis 4 days a week c. High-protein diet d. Maintenance of blood pressure at 120/80 __ 4. Immunizations are an example of which type of prevention? a. Primary b. Secondary c. Tertiary True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Prevalence is the number of new cases of a particular disease. __ __ 2. The number of cases of a particular disease for the past 5 years is an example of the incidence rate. 3. “There are 1,185,000 cases of HIV/AIDS in the United States” is an example of the morbidity rate. __ 4. Endemic is the term used when the presence of an event is constant. __ 5. The “bird” flu of 2005 to 2006 is considered a sporadic outbreak. _ 6. A pandemic affects many communities in a short period of time. Chapter 5. Evidence-Based Care Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ___ 1. Which of the following are parts of evidence-based practice? a. Clinician b. Patient c. Evidence d. All of the above __ 2. Which is the most important question to ask in nursing research? a. What findings constitute evidence? b. How will the findings be used? c. Is this a randomized controlled trial? d. What theory is being utilized? __ __ 3. Nursing research should be utilized by: a. Nurses at the bedside b. Advanced practice nurses c. Nurse researchers d. Nurses at all levels of practice __ 4. Applying evidence at the point of care requires: a. Readily available evidence-based resources b. Ability to review research literature c. Single articles in journals d. Current textbooks _ 5. Practice guidelines are designed to: a. Be inflexible b. Be utilized in every circumstance c. Provide a reference point for decision making d. Be created by a professional organization to guide the practice of a profession _ 6. Which of the following is a crucial element of developing a guideline? a. Creating a physician expert panel b. Reviewing the literature with ratings of available evidence c. Conducting an external review of a guideline d. Developing evidence-based tables ___ _ 7. Which of the following would be considered the research design for Level I evidence? a. Single, well-designed randomized clinical trial b. Systematic review of randomized clinical trial studies c. Well-designed controlled trials without randomization d. Systematic reviews of descriptive or qualitative studies ___ _ 8. Which of the following would be considered the research design for Level II evidence? a. Single descriptive or qualitative study b. Well-designed case control or cohort studies c. Single, well-designed, randomized clinical trial d. Systematic review of randomized clinical trial studies __ 9. Which of the following would be considered the research design for Level III evidence? a. Well-designed controlled trials without randomization b. Systematic reviews of descriptive or qualitative studies c. Systematic review of randomized clinical trial studies d. Opinion of authorities and expert committees __ __ 10. Which of the following would be considered the research design for Level IV evidence? a. Single descriptive or qualitative study b. Opinion of authorities and expert committees c. Systematic review of randomized clinical trial studies d. Well-designed controlled trials without randomization 11. Which of the following would be considered the research design for Level V evidence? a. Systematic review of randomized clinical trial studies b. Well-designed controlled trials without randomization c. Systematic reviews of descriptive or qualitative studies d. Single descriptive or qualitative study __ __ 12. Which of the following would be considered the research design for Level VI evidence? a. Systematic reviews of descriptive or qualitative studies b. Opinion of authorities and expert committees c. Well-designed case control or cohort studies d. Single descriptive or qualitative study ___ 13. Which of the following would be considered the research design for Level VII evidence? a. Well-designed controlled trials without randomization b. Opinion of authorities and expert committees c. Well-designed case control or cohort studies d. Single descriptive or qualitative study Chapter 6. Neurological Problems Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. Which statement about confusion is true? a. Confusion is a disease process. b. Confusion is always temporary. c. Age is a reliable predictor of confusion. d. Polypharmacy is a major contributor to confusion in older adults. ___ _ 2. Sondra’s peripheral vestibular disease causes dizziness and vertigo. Which of the following medications will help to decrease edema in the labyrinth of the ear? a. Meclizine b. Diphenhydramine c. Diamox d. Promethazine ___ 3. The hallmark of an absence seizure is: a. No activity at all b. A blank stare c. Urine is usually voided involuntarily d. The attack usually lasts several minutes __ __ 4. How often should drug levels be monitored when a seizure medication has controlled the seizures, and the drug level is adequate? a. Every 3 months b. Every 6 months c. Annually d. Whenever there is a problem ____ 5. Which of the following persons fits the classic description of a patient with multiple sclerosis (MS)? a. A teenage male b. A 65-year-old male c. A 25-year-old female d. A 60-year-old female ___ _ 6. Which of the following is a specific test to MS? a. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) b. Computed tomography (CT) scan c. A lumbar puncture d. There is no specific test. __ __ 7. Which drug for Alzheimer’s disease should be administered beginning at the time of diagnosis? a. Cholinesterase inhibitors b. Anxiolytics c. Antidepressants d. Atypical antipsychotics __ __ 8. Which hematoma occurs along the temporal cranial wall and results from tears in the middle meningeal artery? a. Epidural hematoma b. Subdural hematoma c. Subarachnoid hematoma d. Intraparenchymal hemorrhage __ __ 9. Which cranial nerve is affected in a patient with a cerebrovascular accident who has difficulty chewing? a. CN V b. CN VII c. CN IX d. CN X __ __ 10. Which statement best describes a carotid bruit? a. It is felt with the middle three fingers over the carotid artery. b. A bruit becomes audible when the lumen is narrowed to 1 mm or less. c. A low-pitched bruit is a medical emergency. d. The higher the pitch of the bruit, the higher the degree of stenosis. ___ _ 11. Which patient is more likely to have a cluster headache? a. A female in her reproductive years b. A 40-year-old African American male c. A 55-year-old female who drinks 10 cups of coffee daily d. A 45-year-old male awakened at night __ __ 12. Inattention and a sleep-wake cycle disturbance are the hallmark symptoms of? a. Dementia b. Alzheimer’s disease c. Parkinson’s disease d. Delirium ___ 13. Which type of meningitis is more benign, self-limiting, and caused primarily by a virus? a. Purulent meningitis b. Chronic meningitis c. Aseptic meningitis d. Herpes meningitis __ __ 14. Which is the most sensitive neuroimaging test to evaluate patients with encephalitis? a. MRI b. CT c. Electroencephalogram (EEG) d. An initial lumbar puncture ___ _ 15. What is usually the first sign or symptom that a patient would present with that would make you suspect herpes zoster? a. A stabbing pain on one small area of the body b. A vesicular skin lesion on one side of the body c. A pain that is worse upon awakening d. A lesion on the exterior ear canal __ _ 16. Gabby, aged 22, has Bell’s palsy on the right side of her face. Her mouth is distorted, and she is concerned about permanent paralysis and pain. What do you tell her? a. “Most patients have complete recovery in 3 to 6 months.” b. “Unfortunately, you’ll probably have a small amount of residual damage.” c. “Don’t worry, I’ll take care of everything.” d. “You may have a few more episodes over the course of your lifetime but no permanent damage.” ___ _ 17. Sam, aged 65, is started on L-dopa for his Parkinson’s disease (PD). He asks why this is necessary. You tell him: a. “L-dopa is neuroprotective.” b. “The primary goal of therapy is to replace depleted stores of dopamine.” c. “This is the only drug that can provide symptomatic benefit.” d. “This is the initial monotherapy drug.” ___ _ 18. Which of the following signs is seen in a patient with more advanced PD? a. Resting tremor b. Bradykinesia c. Rigidity d. Postural instability ___ 19. Which of the following is the most commonly experienced symptom of migraine? a. Light sensitivity b. Pulsatile pain c. Sound sensitivity d. Experiencing an aura ___ _ 20. Which of the following characteristics differentiates peripheral vertigo from central vertigo? a. The duration of central vertigo is shorter than that of peripheral vertigo. b. There is an auditory-associated symptom with peripheral vertigo and a visual-associated symptom with central vertigo. c. Central vertigo is positional, and peripheral vertigo is not. d. The onset of central vertigo is more sudden than that of peripheral vertigo. _ __ 21. Carotid endarterectomy should be considered only for symptomatic patients with greater than what percentage of stenosis? a. Greater than 25% b. Greater than 50% c. Greater than 75% d. Only for 100% occlusion __ _ 22. What antiplatelet agent is most widely used for secondary prevention of stroke? a. Aspirin b. Ticlopidine c. Clopidogrel d. Aspirin and clopidogrel ____ 23. Which adjunctive diagnostic test should be used in the work-up of a patient with suspected Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease or transient epileptic amnesia? a. MRI b. CT c. Cerebrospinal fluid analysis d. EEG 24. Which herbal preparation may cause delirium and should be avoided in an elderly patient? a. Sam-e b. Saint John’s Wort c. Melatonin d. Saw Palmetto ___ _ 25. Which of the following activities is part of the functional activities questionnaire? a. Asking the patient to unravel a Rubik’s cube b. Determining if the patient can drive on the highway c. Asking the patient about a news event from the current week d. Seeing if the patient can keep his or her home clean _ 26. About 90% of all headaches are? a. Tension b. Migraine c. Cluster d. Without pathological cause _ ___ 27. Which statement is true regarding driving and patients with a seizure disorder? a. Once diagnosed with a seizure disorder, patients must never drive again. b. After being seizure free for 6 months, patients may drive. c. Each state has different laws governing driving for individuals with a seizure disorder. d. These persons may drive but never alone. __ __ 28. Julie has relapsing-remitting muscular sclerosis. She has not had a good response to interferon. Which medication might help given intravenously once a month? a. Glatiramer acetate b. Natalizumab c. Fingolimod d. Glucocorticoids __ __ 29. The ‘freezing phenomenon’ is a cardinal feature of? I do not remember how the question was written a. Parkinson’s disease b. Alzheimer’s disease c. A CVA d. Bell’s palsy _ __ 30. A ratchet-like rhythmic contraction, especially in the hand, during passive stretching is known as? a. Spinothalamic dysfunction b. Ratcheting c. Cogwheeling d. Hand tremors _ __ 31. Clinical features of insidious onset, slow progression, and a lack of other findings to explain the symptoms are fairly diagnostic of which condition? a. Guillain-Barré syndrome b. Parkinson’s disease c. Alzheimer’s disease d. Huntington’s disease ___ _ 32. Which condition is characterized by the impaired ability to learn new information along with either a cognitive disturbance in language, function, or perception? a. Guillain-Barré syndrome b. Parkinson’s disease c. Alzheimer’s disease d. Delirium _ __ 33. A score of 20 to 25 on this test indicates early-stage Alzheimer’s disease: a. SLUMS b. MoCA c. FAST d. MMSE ___ _ 34. Intravenous thrombolytic therapy following an ischemic CVA should be given within how many hours of symptom onset? a. 1 hour b. 3 hours c. 6 hours d. 12 hours ___ _ 35. When administered at the beginning of an attack, oxygen therapy may help this kind of headache? a. Tension b. Migraine c. Cluster d. Stress Chapter 7. Skin Problems Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ___ 1. Simon presents with alopecia areata with well-circumscribed patches of hair loss on the crown of his head. How do you respond when he asks you the cause? a. “You must be under a lot of stress lately.” b. “It is hereditary. Did your father experience this also?” c. “The cause is unknown, but we suspect it is due to an immunologic mechanism.” d. “We’ll have to do some tests.” 2. Which of the following is “a linear crack extending from the epidermis to the dermis?” a. An ulcer b. A fissure c. Lichenification d. An excoriation ____ 3. A bulla is: a. A vesicle larger than 1 cm in diameter b. An elevated solid mass with a hard texture; the shape and borders can be regular or irregular c. A superficial elevated lesion filled with purulent fluid d. Thinning of the skin (epidermis and dermis) that appears white or translucent ____ 4. An example of ecchymosis is: a. A hematoma b. A keloid c. A bruise d. A patch ____ 5. When looking under the microscope to diagnose an intravaginal infection, you see a cluster of small and oval to round shapes. What do you suspect they are? a. Spores b. Leukocytes c. Pseudohyphae d. Epithelial cells ____ 6. Your patient is in her second trimester of pregnancy and has a yeast infection. Which of the following is a treatment that you usually recommend/order in nonpregnant patients, but is listed as a Pregnancy category D? a. Vagistat vaginal cream b. Monistat combination pack c. Terazol vaginal cream d. Diflucan, 150 mg ____ 7. Tinea unguium is also known as: a. Onychomycosis b. Tinea versicolor c. Tinea manuum d. Tinea corporis ____ 8. Sally, age 25, presents with impetigo that has been diagnosed as infected with Staphylococcus. The clinical presentation is pruritic tender, red vesicles surrounded by erythema with a rash that is ulcerating. Her recent treatment has not been adequate. Which type of impetigo is this? a. Bullous impetigo b. Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome (SSSS) c. Nonbullous impetigo d. Ecthyma ____ 9. Mark has necrotizing fasciitis of his left lower extremity. Pressure on the skin reveals crepitus due to gas production by which anaerobic bacteria? a. Staphylococcal aureus b. Clostridium perfringens c. S. pyrogenes d. Streptococcus ____ 10. When using the microscope for an intravaginal infection, you see something translucent and colorless. What do you suspect? a. A piece of hair or a thread b. Hyphae c. Leukocytes d. Spores ____ 11. Marci has a wart on her hand. She says she heard something about “silver duct tape therapy.” What do you tell her about his? a. It is an old wives’ tale. b. It is used as a last resort. c. Salicylic acid is more effective. d. It is a simple treatment that should be tried first. ____ 12. Which is the most potent and irritating dose of tretinoin? a. 0.05% liquid formulation b. 0.1% cream c. 1% foam d. 0.02% cream ____ 13. Of the following types of cellulitis, which is a streptococcal infection of the superficial layers of the skin that does not involve the subcutaneous layers? a. Necrotizing fasciitis b. Periorbital cellulitis c. Erysipelas d. “Flesh-eating” cellulitis ____ 14. Mandy presents with a cauliflower-like wart in her anogenital region. You suspect it was sexually transmitted and document this as a: a. Filiform/digitate wart b. Dysplastic cervical lesion c. Condyloma acuminata d. Koilocytosis ____ 15. Jeffrey has atopic dermatitis. You are prescribing a low-dose topical corticosteroid for him. Which would be a good choice? a. Betamethasone dipropionate 0.05% b. Hydrocortisone base 2.5% c. Halcinonide 0.1% d. Desonide 0.05% ____ 16. Harvey has a rubbery, smooth, round mass on his chest that is compressible and has a soft-to-very-firm texture. What do you diagnose this as? a. A lipoma b. A nevi c. A skin tag d. A possible adenoma ____ 17. Which of the following statements is accurate when you are removing a seborrheic keratosis lesion using liquid nitrogen? a. Do not use lidocaine as it may potentiate bleeding. b. Pinch the skin taut together. c. Use gel foam to control bleeding. d. This should be performed by a dermatologist only. ____ 18. The “B” in the ABCDEs of assessing skin cancer represents: a. Biopsy b. Best practice c. Boundary d. Border irregularity 19. The majority of HSV-1 and HSV-2 infections are asymptomatic so that only which elevated antibody titer shows evidence of previous infection? a. IgA b. IgE c. IgG d. IgM ____ 20. Eighty percent of men have noticeable hair loss by what age? a. 35 b. 50 c. 70 d. 85 ____ 21. Prevalence of psoriasis is highest in which group? a. Scandinavians b. African Americans c. Asians d. Native Americans ____ 22. The most common precancerous skin lesion found in Caucasians is: a. A skin tag b. Actinic keratosis c. A melanoma d. A basal cell lesion ____ 23. Ian, age 62, presents with a wide, diffuse area of erythematous skin on his lower left leg that is warm and tender to palpation. There is some edema involved. You suspect: a. Necrotizing fasciitis b. Kaposi’s sarcoma c. Cellulitis d. A diabetic ulcer ____ 24. Josh, aged 22, has tinea versicolor. Which description is the most likely for this condition? a. There are round, hypopigmented macules on his back. b. Josh has red papules on his face. c. There are crusted plaques in Josh’s groin area. d. There are white streaks on his neck. ____ 25. Tori is on systemic antifungals for a bad tinea infection. You are aware that the antifungals may cause: a. Renal failure b. Skin discoloration c. Breathing difficulties d. Hepatotoxicity 26. Which scalp problem can be caused by a fever and certain drugs? a. Telogen effluvium (TE) b. Trichotillomania c. Psoriasis d. Alopecia areata 27. Why do people of African descent have a lower incidence of non-melanoma skin cancer? a. They have an increased number of melanocytes. b. Their darker skin protects from ultraviolet radiation. c. Their skin is thicker. d. Their immune system is stronger. ____ 28. Which statement is true regarding chloasma, the ‘mask of pregnancy’? a. It is caused by a decrease in the melanocyte-stimulating hormone during pregnancy. b. This condition only occurs on the face. c. Exposure to sunlight will even out the discoloration. d. It is caused by increased levels of estrogen and progesterone. 29. When instructing your elderly client about treating her xerosis, what do you tell her? a. A daily hot bath may help the associated pruritus. b. Rub the skin briskly to make sure it is completely dry after bathing. c. Only take short tepid showers. d. Use a gel that is alcohol-based after bathing to soften the skin. 30. Which medication used for scabies is safe for children 2 months and older? a. Permethrin cream b. Lindane c. Crotamiton lotion and cream d. Ivermectin 31. Which of the following is an infraorbital fold skin manifestation in a patient with atopic dermatitis? a. Keratosis pilaris b. Dennie’s sign c. Keratoconus d. Pityriasis alba ____ 32. Which of the following statements about performing cryosurgery for actinic keratosis is true? a. It is better to slightly overfreeze the area, so you only have to do it once. b. Using liquid nitrogen, freeze each lesion for at least 30 seconds. c. Every lesion should be biopsied after using liquid nitrogen. d. The ‘freeze balls’ should be approximately one-and-a-half times as wide as they are deep. 33. An example of a primary skin lesion is a/an: a. Bulla b. Scale c. Excoriation d. Fissure ____ 34. Which statement regarding necrotizing fasciitis is true? a. The hallmark of this infection is its slow and steady progression. b. Once the border of the infection is “established,” it does not spread. c. Loss of life or limb is a potential complication. d. The lesion is most dangerous, because it is painless. 35. When staging a malignant melanoma using Clark’s levels, which level extends into the papillary dermis? a. Level I b. Level II c. Level III d. Level IV Chapter 8. Eyes, Ears, Nose, and Throat Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. __ _ 1. An acutely presenting, erythematous, tender lump within the eyelid is called: a. Blepharitis b. Hordeolum c. Chalazion d. Iritis ___ 2. The clinician is seeing a patient complaining of red eye. The clinician suspects conjunctivitis. The presence of mucopurulent discharge suggests which type of conjunctivitis? a. Viral conjunctivitis b. Keratoconjunctivitis c. Bacterial conjunctivitis d. Allergic conjunctivitis _ __ 3. Which subtype of cataracts is characterized by significant nearsightedness and a slow indolent course? a. Nuclear cataracts b. Cortical cataracts c. Posterior cataracts d. Immature cataracts ___ 4. Which of the following statements is true concerning the use of bilberry as a complementary therapy for cataracts? a. The body converts bilberry to vitamin A, which helps to maintain a healthy lens. b. Bilberry blocks an enzyme that leads to sorbitol accumulation that contributes to cataract formation in diabetes. c. Bilberry boosts oxygen and blood delivery to the eye. d. Bilberry is a good choice for patients with diabetes as it does not interact with antidiabetic drugs. _ __ 5. A 65-year-old man presents to the clinician with complaints of increasing bilateral peripheral vision loss, poor night vision, and frequent prescription changes that started 6 months previously. Recently, he has also been seeing halos around lights. The clinician suspects chronic open-angle glaucoma. Which of the following statements is true concerning the diagnosis of chronic open-angle glaucoma? a. The presence of increased intraocular pressure measured by tonometry is definitive for the diagnosis of open-angle glaucoma. b. The clinician can definitively diagnosis open-angle glaucoma based on the subjective complaints of the patient. c. Physical diagnosis relies on gonioscopic evaluation of the angle by an ophthalmologist. d. Early diagnosis is essential in order to reverse any damage that has occurred to the optic nerve. 6. Acute angle-closure glaucoma involves a sudden severe rise in intraocular pressure. Which of the following ranges represents normal intraocular pressure? a. 0 to 7 mm Hg b. 8 to 21 mm Hg c. 22 to 40 mm Hg d. 40 to 80 mm Hg 7. As diabetic retinopathy progresses, the presence of ‘cotton wool’ spots can be detected. Cotton wool spots refer to: a. Nerve fiber layer infarctions b. Blood vessel proliferation c. Venous beading d. Retinal hemorrhage _ 8. Which of the following is an example of sensorineural hearing loss? a. Perforation of the tympanic membrane b. Otosclerosis c. Cholesteatoma d. Presbycusis _ 9. The clinician is assessing a patient complaining of hearing loss. The clinician places a tuning fork over the patient’s mastoid process, and when the sound fades away, the fork is placed without restriking it over the external auditory meatus. The patient is asked to let the clinician know when the sound fades away. This is an example of which type of test? a. Weber test b. Schwabach test c. Rinne test d. Auditory brainstem response (ABR) test _ 10. A patient presents to the clinician complaining of ear pain. On examination, the clinician finds that the patient has tenderness on traction of the pinna as well as when applying pressure over the tragus. These findings are classic signs of which condition? a. Otitis media b. Meniere’s disease c. Tinnitus d. Otitis externa _ ___ 11. Otitis media is considered chronic when: a. Inflammation persists more than 3 months with intermittent or persistent otic discharge. b. There are more than six occurrences of otitis media in a 1-year period. c. Otitis media does not resolve after two courses of antibiotics. d. All of the above _ ___ 12. The most significant precipitating event leading to otitis media with effusion is: a. Pharyngitis b. Allergies c. Viral upper respiratory infection (URI) d. Perforation of the eardrum _ 13. Patients with acute otitis media should be referred to a specialist in which of the following situations? a. Concurrent vertigo or ataxia b. Failed closure of a ruptured tympanic membrane c. If symptoms worsen after 3 or 4 days of treatment d. All of the above _ 14. Which immunoglobulin mediates the type 1 hypersensitivity reaction involved in allergic rhinitis? a. IgA b. IgE c. IgG d. IgM _ ___ 15. Fluctuations and reductions in estrogen may be a contributing factor in which type of rhinitis? a. Vasomotor rhinitis b. Rhinitis medicamentosum c. Atrophic rhinitis d. Viral rhinitis _ 16. Sinusitis is considered chronic when there are episodes of prolonged inflammation with repeated or inadequately treated acute infection lasting greater than: a. 4 weeks b. 8 weeks c. 12 weeks d. 16 weeks _ __ 17. Which of the following antibiotics provides the best coverage in acute or chronic sinusitis when gram-negative organisms are suspected? a. Penicillin V b. Amoxicillin c. Levofloxacin d. Clindamycin _ 18. In which of the following situations would referral to a specialist be needed for sinusitis? a. Recurrent sinusitis b. Allergic sinusitis c. Sinusitis that is refractory to antibiotic therapy d. All of the above _ 19. Which type of stomatitis results in necrotic ulceration of the oral mucous membranes? a. Vincent’s stomatitis b. Allergic stomatitis c. Apthous stomatitis d. Herpetic stomatitis 20. The presence of hairy leukoplakia in a person with no other symptoms of immune suppression is strongly suggestive of which type of infection? a. HSV type 2 b. HIV c. Pneumonia d. Syphilis 21. Heart valve damage resulting from acute rheumatic fever is a long-term sequela resulting from infection with which of the following pathogens? a. Coxsackievirus b. Cytomegalovirus c. Francisella tularensis d. Group A streptococcus ___ 22. A patient presents with the following signs and symptoms: gradual onset of low-grade fever, marked fatigue, severe sore throat, and posterior cervical lymphadenopathy. Based on the signs and symptoms alone, which of the following conditions is most likely the cause? a. Gonorrhea b. Mononucleosis c. Influenza d. Herpes zoster 23. A patient presents to the clinician with a sore throat, fever of 100.7F, and tender anterior cervical lymphadenopathy. The clinician suspects strep throat and performs a rapid strep test that is negative. What would the next step be? a. The patient should be instructed to rest and increase fluid intake as the infection is most likely viral and will resolve without antibiotic treatment. b. Because the patient does not have strep throat, the clinician should start broad spectrum antibiotics in order to cover the offending pathogen. c. A throat culture should be performed to confirm the results of the rapid strep test. d. The patient should be treated with antibiotics for strep throat as the rapid strep test is not very sensitive. ___ 24. Which of the following medications used in the treatment of glaucoma works by constricting the pupils to open the angle and allow aqueous fluid to escape? a. Pilocarpine b. Timolol c. Brinzolamide d. Acetazolamide 25. You have a patient who is a positive for Strep on rapid antigen testing (rapid strep test). You order amoxicillin after checking for drug allergies (patient is negative) but he returns 3 days later, reporting that his temperature has gone up, not down (101.5 F in office). You also note significant adenopathy, most notably in the posterior and anterior cervical chains, some hepatomegaly, and a diffuse rash. You decide: a. to refer the patient. b. that he is having an allergic response and needs to be changed to a macrolide antibiotic. c. that his antibiotic dosage is not sufficient and should be changed. d. that he possibly has mononucleosis concurrent with his strep infection. 26. You are in the park playing with your children when you see that your friend is screaming for help. Her toddler has fallen and there is a stick lodged in his eye. The child is kicking and screaming and grabbing for the stick. You: a. instruct his mother to hold him securely and not allow him to touch the stick, then carefully remove the stick from the eye. b. stabilize the foreign object and accompany the mother and child to the local ER. c. find a water fountain, hold the child to the water, and flush the eye. d. call 911. True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Severe pain associated with acute otitis media signifies perforation of the tympanic membrane. Chapter 9. Respiratory Problems Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. __ __ 1. A chronic cough lasts longer than: a. 3 weeks b. 1 month c. 6 months d. 1 year 2. You are doing a cerumen extraction and touch the external meatus of your patient’s ear. He winces and starts coughing. What is the name of this reflex? a. Baker phenomenon b. Arnold reflex c. Cough reflex d. Tragus reflex 3. Julie has a postnasal drip along with her cough. You assess her for: a. Asthma b. Sinusitis c. Allergic or vasomotor rhinitis d. Influenza 4. A patient with hypertension comes in and insists that one of his new medications is causing him to cough. When looking at his list of medications, you think the cough must be from: a. Metoprolol b. Clopidogrel c. Tadalafil d. Captopril _ 5. African American patients seem to have a negative reaction to which of the following asthma medications? a. Inhaled corticosteroids b. Long-term beta-agonist bronchodilators c. Leukotriene receptor agonists d. Oral corticosteroids 6. Sam, age 78, presents to the clinic with respiratory symptoms. His pulmonary function tests are as follows: a normal total lung capacity, a decreased PaO2, and an increased PaCO2. On assessment, you auscultate coarse crackles and forced expiratory wheezes. What is your diagnosis? a. Asthma b. Emphysema c. Chronic bronchitis d. Influenza 7. You are using the CURB-65 clinical prediction tool to decide whether Mabel, whom you have diagnosed with community-acquired pneumonia (CAP), should be hospitalized or treated at home. Her score is 3. What should you do? a. Consider home treatment. b. Plan for a short inpatient hospitalization. c. Closely supervise her outpatient treatment. d. Hospitalize and consider admitting her to the intensive care unit. 8. Why do you suspect that your patient may have a decreased response to the tuberculin skin test (TBT)? a. She is on a high-protein diet. b. She is an adolescent. c. She has been on long-term corticosteroid therapy. d. She just got over a cold. 9. Marci has been started on a tuberculosis (TB) regimen. Because isoniazid (INH) may cause peripheral neuropathy, you consider ordering which of the following drugs prophylactically? a. Pyridoxine b. Thiamine c. Probiotic d. Phytonadione 10. Jolene has breast cancer that has been staged as T1, N0, M0. What might this mean? a. The tumor size cannot be evaluated; the cancer has not spread to the lymph nodes; and the distant spread cannot be evaluated. b. The cancer is in situ; it is spreading into the lymph nodes, but the spread cannot be evaluated otherwise. c. The cancer is less than 2 cm in size and has not spread to the lymph nodes or other parts of the body. d. The cancer is about 5 cm in size; nearby lymph nodes cannot be evaluated; and there is no evidence of distant spreading. 11. Nathan, a 32-year-old policeman, has a 15-pack-a-year history of smoking and continues to smoke heavily. During every visit, he gets irate when you try to talk to him about quitting. What should you do? a. Hand him literature about smoking cessation at every visit. b. Wait until he is ready to talk to you about quitting. c. Document in the record that he is not ready to quit. d. Continue to ask him at every visit if he is ready to quit. 12. Your patient has decided to try to quit smoking with Chantix. You are discussing his quit date, and he will begin taking the medicine tomorrow. When should he plan to quit smoking? a. He should stop smoking today. b. He should stop smoking tomorrow. c. His quit date should be in 1 week. d. He will be ready to quit after the first 30 days. ____ 13. Which information should be included when you are teaching your patient about the use of nicotine gum? a. The gum must be correctly chewed to a softened state and then placed in the buccal mucosa. b. Patients should not eat for 30 minutes prior to or during the use of the gum. c. Initially, one piece is chewed every 30 minutes while awake. d. Acidic foods and beverages should be encouraged during nicotine therapy. 14. Your patient states he has a strep throat infection. Which of the following symptoms makes you consider a viral etiology instead? a. Fever b. Headache c. Exudative pharyngitis d. Rhinorrhea 15. What is the first-line recommended treatment against Group A -hemolytic streptococci (GABHS), the most common cause of bacterial pharyngitis? a. Penicillin b. Quinolone c. Cephalosporin d. Macrolide ____ 16. Cydney presents with a history of asthma. She has not been treated for a while. She complains of daily but not continual symptoms, greater than 1 week and at nighttime. She has been using her rescue inhaler. Her FEV1 is 60% to 80% predicted. How would you classify her asthma severity? a. Mild intermittent b. Mild persistent c. Moderate persistent d. Severe persistent 17. Joyce is taking a long-acting beta agonist for her asthma. What additional medication should she be taking? a. Inhaled corticosteroid b. Leukotriene receptor antagonist c. Systemic corticosteroid d. Methyl xanthenes ___ 18. Your patient is on Therabid for his asthma. You want to maintain his serum levels between: a. 0 to 5 mcg/mL b. 5 to 10 mcg/mL c. 5 to 15 mcg/mL d. 10 to 20 mcg/mL ___ 19. George has chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and an 80% forced expiratory volume in 1 second. How would you classify the severity of his COPD? a. Stage 1 mild COPD b. Stage 2 moderate COPD c. Stage 3 severe COPD d. Stage 5 very severe COPD ___ 20. Most nosocomial pneumonias are caused by: a. Fungi b. Viruses c. Gram-negative bacteria d. Pneumococcal pneumonia ____ 21. Which of the following statements regarding TST is true? a. Tests should be read 48 hours after the injection. b. The size of the TST reaction has nothing to do with erythema but is based solely on induration. c. It is a type V T cell-mediated immune response. d. The diameter of the induration is measured in centimeters. ____ 22. Which obstructive lung disease is classified as reversible? a. Asthma b. Chronic bronchitis c. Emphysema d. COPD 23. You have taught Jennifer, age 15, about using a flow meter to assess how to manage her asthma exacerbations. She calls you today because her peak expiratory flow rate is 65%. What would you tell her? a. “Take your short-acting beta-2 agonist, remain quiet, and call back tomorrow.” b. “Use your rescue inhaler, begin the prescription of oral glucocorticoids you have, and call back tomorrow.” c. “Drive to the emergency room now.” d. “Call 911.” ____ 24. Which statement about adenocarcinoma of the lung is accurate? a. It is the least common type of lung cancer, representing approximately 5% to 10% of cases. b. It is the most prevalent carcinoma of the lungs in both sexes and in nonsmokers, representing 35% to 40% of all tumors. c. It is more common in men than in women and occurs almost entirely in cigarette smokers. d. It is aggressive, with rapid growth and early local and distant metastases via the lymphatic and blood vessels. 25. Jason, age 62, has obstructive sleep apnea. What do you think is one of his contributing factors? a. He is a recovering alcoholic of 6 years. b. His collar size is 17 inches. It will come as 19 inches c. He is the only person in his family who has this. d. He is extremely thin. _ ___ 26. The forced vital capacity is decreased in: a. Asthma b. Chronic bronchitis c. Emphysema d. Restrictive disease ____ 27. The most common cause of CAP is? a. Streptococcus pneumoniae b. Klebsiella pneumoniae c. Legionella pneumoniae d. Pseudomonas aeruginosa 28. Which of the following patients would you expect to have a decreased response to TST? a. Julie, a 50-year-old postal worker b. Sandy, a 40-year-old patient who recently survived a fire that left 40% of her total body surface covered in burns c. Jill, a 16-year-old cheerleader d. Mark, a 29-year-old tennis player ____ 29. Which of the following is a possible consequence of sleep apnea? a. Asthma b. Increased white blood cells c. Insulin resistance d. Hyperactivity ____ 30. Which of the following conditions is associated with cigarette smoking? a. Glaucoma b. Increased sperm quality c. Bladder cancer d. Eczema ____ 31. Marta is taking TB drugs prophylactically. How do you instruct her to take them? a. Take them on an empty stomach to facilitate absorption. b. Take them with aspirin (ASA) to prevent flushing. c. Take them with ibuprofen to prevent a headache. d. Take them with food to prevent nausea. 32. Which of the following statements regarding pulmonary function is true? a. Cigarette smoking accelerates the decline in pulmonary function tenfold. b. Smoking cessation can reverse most pathological changes. c. Cigarette smoking decreases mucus production. d. There is a normal age-related decline in pulmonary function. ____ 33. The barrel chest characteristic of emphysema is a result of: a. Chronic coughing b. Hyperinflation c. Polycythemia d. Pulmonary hypertension __ 34. Supplemental oxygen for how many hours per day has been shown to improve the mortality associated with COPD? a. 3 to 5 hours b. 6 to 10 hours c. 11 to 14 hours d. 15 to 18 hours _ ___ 35. Which ethnic group has the highest lung cancer incidence and mortality rates? a. African American men b. Scandinavian men and women c. Caucasian women d. Asian men Chapter 10. Cardiovascular Problems Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. __ 1. Which group would most benefit from statins? a. Those with a low density lipoprotein-cholesterol greater than 100 mg/dL b. Individuals with clinical arteriosclerotic cardiovascular disease c. Individuals with a 10-year risk greater than 10% d. Individuals of all ages with diabetes mellitus (DM) 2. If chest pain can be alleviated with time, analgesics, and heat applications, what might the differential diagnosis be? a. Peptic ulcer b. Hiatal hernia c. Costochondritis d. Pericarditis ___ 3. Sandra has palpitations that occur with muscle twitching, paresthesia, and fatigue. What specific diagnostic test might help determine the cause? a. Serum calcium b. Electrocardiogram (ECG) c. Thyroid-stimulating hormone test d. Complete blood cell count _ __ 4. A blood pressure (BP) of 150/90 is considered: a. Stage 2 hypertension b. Hypertensive c. Normal in healthy older adults d. Acceptable if the patient has DM _ __ 5. Lifestyle modifications to manage hypertension (HTN) include: a. Maintaining a body mass index of 17 b. Restricting dietary sodium to 2 grams per day c. Engaging in exercise or physical activity for 90 minutes a day d. Limiting beer intake to 24 ounces per day ___ 6. Mary has hypertension and previously had a stroke. Which hypertensive drug would you order for her? a. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor b. Calcium channel blocker c. Angiotensin II receptor blocker d. Beta blocker 7. Which high-density lipoprotein (HDL) level is considered cardioprotective? a. Greater than 30 b. Greater than 40 c. Greater than 50 d. Greater than 60 ____ 8. You are assessing Sigred for metabolic syndrome. Which of her parameters is indicative of this syndrome? a. Her waist is 36 inches. b. Her triglyceride level is 140 mg/dL. c. Her BP is 128/84. d. Her fasting blood sugar (BS) is 108 mg/dL. _ ___ 9. Which type of angina do you suspect in Harvey, who complains of chest pain that occurs during sleep and most often in the early morning hours? a. Stable angina b. Unstable angina c. Variant (Prinzmetal’s angina) d. Probably not angina but hiatal hernia 10. Which ECG change is typical of cardiac ischemia? a. T-wave inversion b. ST-segment elevation c. Significant Q wave d. U-wave ____ 11. In which type of arterioventricular (AV) block does the pulse rate (PR) interval lengthen until a beat is dropped? a. First-degree AV block b. Second-degree Mobitz I AV block c. Second-degree Mobitz II AV block d. Third-degree AV block _ __ 12. A Delta wave on the ECG may be present in which condition? a. Prinzmetal’s angina b. Bundle branch block c. Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome d. Aortic stenosis __ 13. Which heart sound may be heard with poorly controlled hypertension, angina, and ischemic heart disease? a. A physiologic split S2 b. A fixed split S2 c. S3 d. S4 ___ 14. Samuel is going to the dentist for some work and must take endocarditis prophylaxis because of his history of: a. Severe asthma b. A common valvular lesion c. Severe hypertension d. A prosthetic heart valve ____ 15. George, age 64, has cardiovascular disease (CVD), a total cholesterol of 280 mg/dL, and a systolic BP of 158. He is being treated for hypertension. You are doing a Framingham Risk Assessment on him. Which assessment factor would give him the highest number of points on the scale? a. His age b. His cholesterol level c. His systolic BP d. The fact that he is on antihypertensive medication ___ 16. Which pain characteristic is usually indicative of cardiac pathology? a. Fleeting b. Moving c. Diffuse d. Localized 17. What percentage of patients with angina pectoris will have simultaneous dyspnea, caused by transient increase in pulmonary venous pressures that accompany ventricular stiffening during an episode of myocardial ischemia? a. About 20% b. About 30% c. About 50% d. Almost all ___ 18. Nitroglycerine (NTG) is given for a patient having ischemic chest pain. One tablet or one spray should be used under the tongue every 5 minutes for three doses. What should be done if the pain has not been relieved after three doses? a. 911 should be called, and the patient should be transported immediately to the emergency department. b. One more dose of NTG may be tried. c. The person should be given two aspirin to chew. d. A portable defibrillator should be located to ascertain the cardiac rhythm. ____ 19. For the best therapeutic effect after a myocardial infarction (MI), thrombolytics should be administered within the first 3 hours (ideally 30 minutes) of symptom onset. Studies have shown, however, that thrombolytic therapy can be of benefit up to how many hours after the initial presentation of MI symptoms? a. 6 hours b. 8 hours c. 10 hours d. 12 hours ___ 20. When teaching post MI patients about their NTG tablets, the clinician should stress that the tablets should remain in the light-resistant bottle in which they are packaged and should not be put in another pill box or remain in areas that are or could become warm and humid. Once opened, the bottle must be dated and discarded after how many months? a. 1 month b. 3 months c. 6 months d. As long as the tablets are kept in this special bottle, they will last forever. ___ 21. There are four stages of heart failure, classified as A to D, that describe the evolution and progression of disease. In which stage are patients hospitalized or treated with specialized interventions or hospice care for refractory symptoms of heart failure despite medical therapy? a. Stage A b. Stage B c. Stage C d. Stage D ___ 22. Which of the following is abundant in the heart and rapidly rises in the bloodstream in the presence of heart failure, making it a good diagnostic test? a. B-type natriuretic peptide b. C-reactive protein c. Serum albumin d. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate 23. Which test has long been considered the gold standard for a diagnosis of venous thromboembolism? a. Ultrasound b. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) c. Ascending venogram d. D-dimer _ __ 24. Statins are approved for which age group? a. Children over the age of 2 b. Children over the age of 6 c. Children over the age of 10 d. Only adolescents and adults 25. The American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association states which of the following regarding the use of non-statin lipid-lowering agents? a. Nicotinic acid derivatives are effective for lowering LDL and triglycerides (TGs). b. Bile acid sequestrates increase HDL. c. Cholesterol absorption inhibitors decrease LDL. d. There is no sufficient evidence to use non-statin lipid-drugs. ____ 26. Which of the following medications can cause hyperlipidemia? a. Diuretics b. NSAIDs c. Opioids d. Insulin ____ 27. Jamie, age 55, has just started on a statin after having his liver function tests (LFTs) come back normal. He now asks you how often he has to have the LFTs repeated. What do you tell him? a. Initially in 6 weeks b. Every 3 months c. Every 6 months d. It’s no longer necessary for his statin regimen. ___ 28. In the CHADS2 Index for the stroke risk score for AF, the ‘A’ stands for: a. Anticoagulation b. Autoimmune disease c. Age d. Antihypertension ___ 29. Which murmurs are usually ‘watch and wait’? a. Systolic murmurs b. Diastolic murmurs c. They both are dangerous and need immediate attention. d. You can ‘watch and wait’ for both of them. ____ 30. Which of the following statements about dabigatran is true? a. It is difficult to keep the patient in therapeutic range. b. Anticoagulation cannot be immediately reversed. c. It allows for the use of tPA if the patient has a stroke despite anticoagulation. d. None of the statements are true. ____ 31. What value on the ankle-brachial index diagnoses peripheral artery disease? a. Less than 0.25 b. Less than 0.50 c. Less than 0.90 d. Greater than 1 __ 32. Your patient with permanent afib asks when he can discontinue his warfarin. You tell him: a. When your internalized normalized ratio reaches 3.0, you can stop taking your warfarin permanently. b. When you no longer feel ill c. One month after your symptoms dissipate d. You’ll probably be on it indefinitely. 33. You just started Martha on HTN therapy. The Eighth Joint National Committee recommends that if her goal BP is not reached in what length of time, you should increase the initial drug or add a second drug to it? a. 1 month b. 3 months c. 6 months d. 1 year Chapter 11. Abdominal Problems Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. __ __ 1. A 35-year-old female patient is seen in the clinic complaining of abdominal pain. Which of the following should be included in the history and physical examination? a. Digital rectal exam b. Pelvic exam c. Sexual history d. All of the above __ 2. A patient comes to the office complaining of constipation. The patient lists all of the following medications. Which drug could be responsible for the constipation? a. Multivitamin b. Magnesium hydroxide c. Pepto-Bismol® d. Ibuprofen ___ 3. A patient is seen with complaints of diarrhea. Which of the following should be included in the patient’s differential diagnosis? a. Gastroenteritis b. Inflammatory bowel disease c. Lactase deficiency d. All of the above 4. Mr. J. K., 38 years old, is 5 feet 8 inches tall and weighs 189 pounds. He reports that he has had intermittent heartburn for several months and takes Tums® with temporary relief. He has been waking during the night with a burning sensation in his chest. Which additional information would lead you to believe that gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is the cause of his pain? a. The pain seems better when he smokes to relieve his nerves. b. Coffee and fried foods don’t bother him, c. He wakes at night coughing with a bad taste in his mouth. d. All of the above ___ 5. A 29-year-old Englishman is seen in the office with complaints of pain in his chest and belly. He has been suffering the pain for 2 weeks and gets temporary relief from Alka-Seltzer®. The burning pain wakes him at night and radiates up to his chest. Which factor favors a diagnosis of gastric ulcer? a. His gender b. His age c. His use of Alka-Seltzer d. His ethnic origin ___ 6. Which of the following is most effective in diagnosing appendicitis? a. History and physical b. Sedimentation rate c. Kidney, ureter, and bladder x-ray d. Complete blood count (CBC) with differentials 7. Which of the following is associated with celiac disease (celiac sprue)? a. Malabsorption b. Constipation c. Rectal bleeding d. Esophageal ulceration 8. A 45-year-old patient presents with a chief complaint of generalized abdominal pain. Her physical examination is remarkable for left lower quadrant tenderness. At this time, which of the following should be considered in the differential diagnosis? a. Endometriosis b. Colon cancer c. Diverticulitis d. All of the above 9. A 46-year-old patient is seen in the clinic with abdominal pain. Which of the following tests is essential for this patient? a. CBC with differential b. Urine human chorionic gonadotropin c. Barium enema d. Computed tomography of the abdomen _ ___ 10. A 25-year-old accountant is seen in the clinic complaining of crampy abdominal pain after meals. She is often constipated and takes laxatives, which are followed by a couple of days of diarrhea. She temporarily feels better after a bowel movement. She states she is embarrassed by flatulence and has abdominal distension. She has had no weight loss or blood in her stool. This problem has gone on for about 6 months. What should the next step be? a. Obtain a complete history. b. Order a barium enema. c. Schedule a Bernstein’s test. d. Prescribe a trial of antispasmodics. _ 11. A 28-year-old patient is seen in the clinic with colicky abdominal pain particular with meals. She has frequent constipation, flatulence, and abdominal distension. Which of the data make a diagnosis of diverticulitis unlikely? a. Her age b. Frequent constipation c. Flatulence d. Colicky abdominal pain 12. A 28-year-old patient is seen with complaints of diarrhea. Which of the following responses to the history questions would help the primary care physician (PCP) establish the diagnosis of irritable bowel syndrome? a. Feels relief after a bowel movement b. Sometimes is constipated c. Does not defecate in the middle of the night d. All of the above __ 13. A patient is diagnosed with GERD, and his endoscopic report reveals the presence of Barrett’s epithelium. Which of the following should the PCP include in the explanation of the pathology report? a. This is a premalignant tissue. b. This tissue is resistant to gastric acid. c. This tissue supports healing of the esophagus. d. All of the above ____ 14. Which of the following dietary instructions should be given to a patient with GERD? a. Eliminate coffee. b. Drink peppermint tea to relieve stomach distress. c. Recline and rest after meals. d. Limit the amount of antacids. 15. The patient with GERD should be instructed to eliminate which of these activities? a. Swimming b. Weight lifting c. Golfing d. Walking _ 16. A patient is diagnosed with giardia after a backpacking trip in the mountains. Which of the following would be an appropriate treatment? a. Vancomycin b. Penicillin c. Metronidazole d. Bactrim ___ 17. A 22-year-old is seen complaining of vague belly pain. This type of pain is seen at what point in appendicitis? a. Very early b. 3 to 4 hours after perforation c. Late in inflammation d. Appendicitis never presents with vague pain. 18. The nurse practitioner (NP) suspects a patient has a peptic ulcer. Which of the following items on the history would lead the NP to this conclusion? a. Use of NSAIDs b. Cigarette smoker c. Ethanol consumption d. All of the above __ __ 19. A patient is seen with dark-colored urine, and the urine dipstick reveals a high level of bilirubin. Which of the following could be a cause of this problem? a. Increased breakdown of red blood cells b. Inadequate hepatocyte function c. Biliary obstruction d. All of the above ___ 20. A 21-year-old student presents with complaints of fatigue, headache, anorexia, and a runny nose, all of which began about 2 weeks ago. She started taking vitamins and over-the-counter cold preparations but feels worse. The smell of food makes her nauseated. Her boyfriend had mononucleosis about a month ago, and she wonders if she might have it also. Examination reveals cervical adenopathy and an enlarged liver and spleen. Which of the following labs would be most helpful in the differential diagnosis at this point? a. Stool culture b. Liver enzymes c. Antihepatitis D virus d. Thyroid-stimulating hormone test 21. On further questioning, the 21-year-old patient with complaints of fatigue, headache, anorexia, and a runny nose explains that she is sexually active only with her boyfriend, does not use injectable drugs, and works as an aide in a day-care center. Which of the following tests would be most helpful in confirming your diagnosis? a. Hepatitis A virus (HAV) IgM b. HAV IgG c. Anti-HAcAg d. Anti-HAsAg 22. A patient is seen in the clinic with right upper quadrant pain that is radiating to the middle of the back. The NP suspects acute cholelithiasis. The NP should expect which of the following laboratory findings? a. Decreased alanine aminotransferase and decreased aspartate aminotransferase b. Elevated alkaline phosphatase c. Elevated indirect bilirubin d. Decreased white blood cells 23. A patient has acute pancreatitis with seven of the diagnostic criteria from Ranson’s criteria. In order to plan care, the NP must understand that this criteria score has which of the following meanings? a. A high mortality rate b. An increased chance of recurrence c. A 7% chance of the disease becoming chronic d. All of the above ___ 24. A patient is seen in the office with complaints of six to seven liquid bowel movements per day. Which of the following assessment findings would lead the NP to a diagnosis of inflammatory bowel disease? a. Intermittent constipation with periods of diarrhea b. Wakens at night with diarrhea c. History of international travel d. All of the above 25. Which of the following is part of the treatment plan for the patient with irritable bowel syndrome? a. High fiber diet b. Tylenol with codeine c. Daily laxatives d. All of the above Chapter 12. Renal Problems Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A patient is seen in the clinic with a chief complaint of hematuria. To make a differential diagnosis, which of the following questions should be asked? a. “Do you have a history of liver disease?” b. “What medications are you currently taking?” c. “Have you noticed swelling in your ankles?” d. All of the above 2. The result of the patient’s 24-hour urine for protein was 4.2 g/day. The clinician should take which of the following actions? a. Repeat the test. b. Refer to a nephrologist. c. Measure the serum protein. d. Obtain a blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine. ___ 3. A patient is seen complaining of “leaking urine when I sneeze.” Which of the following actions should the clinician take first? a. Order a cystometrogram. b. Obtain a computed tomography scan. c. Instruct the patient on Kegel exercises. d. Prescribe imipramine. _ __ 4. A patient is seen in the clinic with hematuria confirmed on microscopic examination. The clinician should inquire about the ingestion of which of these substances that might be the cause of hematuria? a. NSAIDs b. Beets c. Vitamin A d. Red meat __ 5. A 27-year-old female presents with a chief complaint of burning and pain on urination. She has no previous history of urinary tract infection (UTI). What are some additional symptoms consistent with a diagnosis of lower UTI? a. Back and abdominal pain b. Fever, chills, costovertebral angle (CVA) tenderness c. Blood in urine and frequency d. Foul-smelling discharge, perineal itch ___ 6. A 30-year-old patient presents with pain on urination. The urine microscopy of unspun urine shows greater than 10 leukocytes/mL, and a dipstick is positive for nitrites. What is the probable diagnosis? a. Lower urinary tract infection b. Chlamydia infection c. Candidiasis d. Pyelonephritis ___ 7. A patient presents with CVA tenderness and a several-day history of high fever, chills, and dysuria. Which of the following diagnoses is most likely given the above information? a. Pyelonephritis b. Cystitis c. Renal calculi d. Bladder tumor ____ 8. Which of the following information is essential before prescribing Bactrim DS to a 24-year-old woman with a UTI? a. Last menstrual period b. Method of birth control c. Last unprotected sexual contact d. All of the above ___ 9. A patient is seen in the office complaining of severe flank pain. The clinician should assess this patient for which risk factor for kidney stones? a. Hypertension b. Constipation c. Tubal ligation d. Diabetes _ __ 10. A patient is diagnosed with urge incontinence. Before prescribing Detrol XL, the provider should question the patient about which of these contraindications to this medication? a. Diarrhea b. Parkinson’s disease c. Closed-angle glaucoma d. Breast cancer __B__ 11. A patient is diagnosed with overactive bladder. Which of the following instructions should be given to this woman? a. “Limit the amount of water that you drink.” b. “Eliminate caffeine from your diet.” c. “Wear panty liners.” d. All of the above 12. A 34-year-old patient was treated for a UTI and has not responded to antibiotic therapy. Which of the following actions should be taken next? a. Send a urine specimen for microscopy and evaluate for fungal colonies. b. Increase the dose of antibiotic. c. Order a cytoscopy. d. Order a different antibiotic. 13. Which of the following are predisposing factors for pyelonephritis? a. Pregnancy b. Dehydration c. Smoking d. Alkaline urine 14. A 42-year-old woman is seen in the clinic with fever, chills, vomiting, and severe dysuria. She is diagnosed with acute pyelonephritis. How should this patient be managed? a. 3-day course of oral antibiotics b. Hospitalization c. Encourage cranberry juice intake. d. 6-week course of antibiotics _ 15. A patient is seen with a sudden onset of flank pain accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and diaphoresis. In addition to nephrolithiasis, which of the following should be added to the list of differential diagnoses? a. Pancreatitis b. Peptic ulcer disease c. Diverticulitis d. All of the above _ 16. Which of the following instructions should be given to the patient with nephrolithiasis? a. Take ibuprofen, 600 mg every 8 hours. b. Take Tums for stomach upset. c. Drink more black tea. d. Increase intake of vegetables, like spinach. _ ___ 17. Which of the following patients is at risk for developing urinary tract cancer? a. The 45-year-old woman who is 100 lbs overweight b. The 78-year-old man who smokes three packs of cigarettes a day c. The 84-year-old man who worked in the asbestos mines d. All of the above 18. A patient is seen in the clinic and diagnosed with Stage I renal cancer. The provider should refer the patient to a nephrologist for which of these treatments? a. Chemotherapy b. Nephrectomy c. Palliative treatment d. Radiation ___ 19. An 86-year-old woman is seen in the clinic for recurrent hematuria. The provider suspects bladder cancer. Which of the following data from the history is considered a risk factor for this type of cancer? a. History of alcoholism b. Sedentary lifestyle c. Obesity d. 65-year smoking history ___ 20. Which of the following diagnostic tests should be ordered for a patient suspected of having bladder cancer? a. Kidneys, ureter, bladder x-ray b. Cystoscopy with biopsy c. Magnetic resonance imaging d. Urine tumor marker (NMP22) 21. A 78-year-old man is diagnosed with Stage D bladder cancer and asks the provider what that means. Which is the best response? a. “There is no such thing as Stage D cancer.” b. “You have cancer that has spread to the surrounding tissue.” c. “Your cancer has spread to other organs.” d. “Your cancer can be cured by removing your bladder.” 22. The patient is diagnosed with acute renal failure (ARF). Which of the following data obtained from the history should alert the provider that this is a case of prerenal azotemia? a. Recent heat stroke b. Nephrolithiasis c. Recent infection where gentamicin was used in treatment d. All of the above ___ 23. The patient is diagnosed with ARF. Which of the following conditions is the most common cause? a. Renal calculi b. Acute tubular necrosis c. Cardiac failure d. Acute glomerulonephritis ___ 24. An 82-year-old woman with renal failure is seen in the clinic. The provider should question the patient about the intake of which of these substances that can cause renal toxicity? a. Ibuprofen b. Captopril c. Losartan d. All of the above ___ 25. Which of the following clinical manifestations are consistent with a patient in ARF? a. Pruritis b. Glycosuria c. Irritability d. Hypotension _ __ 26. Which of the following examination findings should be expected in a patient with chronic renal failure (CRF)? a. Weak, thready pulse b. Auscultatory crackles c. Hypotension d. Pleural friction rub ____ 27. Which of the following tests is most useful in determining renal function in a patient suspected of CRF? a. BUN and creatinine b. Electrolytes c. Creatinine clearance d. Urinalysis _ 28. Which of the following foods should be limited in a patient with CRF? a. Milk b. Bananas c. Soy sauce d. All of the above True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. The urine osmolality is greater than 500 mOsm/L in patients with postrenal ARF. _ ___ 2. Cigarette smoking is a risk factor for CRF. Chapter 13. Men's Health Problems Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ A 63-year-old man is seen in the clinic with a chief complaint of nocturia. Which of the following should be included in the differential diagnosis? a. Psychogenic nocturia b. Urethral polyp c. Irritative posterior urethral lesion d. Benign prostatic hypertrophy ____ 2. A 76-year-old man is seen in the office for complaints of urinary incontinence. The clinician should explore which of these causes of incontinence in men? a. Urethral polyps b. Urinary tract infection (UTI) c. Anticholinergic medication d. All of the above ____ 3. A 14-year-old male is seen with complaints of severe testicular pain. The clinician suspects testicular torsion. Which of the following is the appropriate action? a. Refer to a urologist immediately. b. Obtain a computed tomography (CT) scan. c. Instruct the patient to elevate the scrotum. d. Prescribe ibuprofen. ____ 4. An 82-year-old man is seen in the primary care office with complaints of dribbling urine and difficulty starting his stream. Which of the following should be included in the list of differential diagnoses? a. Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) b. Parkinson’s disease c. Prostate cancer d. All of the above ____ 5. Which of the following would be an appropriate treatment for a patient with mild BPH? a. Refer to a urologist for surgery. b. Prescribe a trial of tamsulosin. c. Recommend cranberry supplements. d. Reevaluate symptoms in 1 to 3 months. ____ 6. A 30-year-old man is seen with a chief complaint of loss of libido. Which of the following laboratory tests would help establish a diagnosis? a. Testosterone level b. Prostate-specific antigen c. Nocturnal penile tumescence and rigidity d. Prolactin level _ 7. Which of the following should be considered in a patient presenting with erectile dysfunction? a. Diabetes mellitus b. Hypertension c. Atherosclerosis d. All of the above ____ 8. A 35-year-old man presents with complaints of painful erections, and he notices his penis is crooked when erect. What is the most likely diagnosis? a. Peyronie’s disease b. Damage to the pudendal artery c. Scarring of the cavernosa d. All of the above ____ 9. The patient with BPH is seen for follow-up. He has been taking finasteride (Proscar) for 6 months. The clinician should assess this patient for which of these side effects? a. Erectile dysfunction b. Glaucoma c. Hypotension d. Headache ____ 10. The clinician should prescribe an antibiotic that covers which of these organisms for a patient with acute prostatitis? a. Gram-positive cocci b. Gram-negative cocci c. Gram-positive bacillus d. Gram-negative bacillus ____ 11. The 56-year-old man with chronic prostatitis should be treated with trimethoprim 80 mg-sulfamethoxazole 400 mg (TMP-SMX, Bactrim) for how long? a. 3 to 7 days b. 14 to 21 days c. 3 to 6 weeks d. 6 to 12 weeks ____ 12. A 46-year-old man presents with urinary hesitancy and low back pain. He has no history of UTI. Digital rectal examination (DRE) reveals a normal prostate, and a diagnosis of prostatodynia is made. Which is the appropriate treatment? a. Terazosin 2 mg PO once a day b. Ice pack to the scrotal area c. Saw palmetto 320 mg per day d. All of the above ____ 13. A 23-year-old sexually active man is seen in the clinic with unilateral painful testicular swelling, and he is diagnosed with epididymitis. In order to prescribe the correct drug, the clinician must understand that which of these is the most common causative organism? a. Escherichia coli b. Staphylococcus aureus c. Chlamydia trachomatis d. Pseudomonas aeruginosa ____ 14. Which test is used to confirm a diagnosis of epididymitis? a. Urinalysis b. Gram stain of urethral discharge c. Complete blood cell count with differential d. Ultrasound of the scrotum ____ 15. Treatment for epididymitis includes which of the following? a. Warm sitz baths b. Scrotal elevation c. Masturbation d. All of the above ____ 16. Which of the following data is indicative of testicular torsion? a. Absent cremasteric reflex b. Pain relieved on testicular elevation c. Testicle very low in the scrotum d. Swollen scrotum with “red dot sign” ____ 17. A 60-year-old man presents with an enlarged scrotum. The clinician uses a penlight to transilluminate the scrotum. In a patient with a hydrocele, what would the clinician expect to find? a. The scrotum will be dark. b. The scrotum will appear light pink or yellow. c. The scrotum will appear milky white. d. The internal structures will be clearly visible. ____ 18. During a DRE on a 75-year-old man, the clinician suspects the patient has prostate cancer. What physical finding should make the clinician suspicious? a. An enlarged rubbery gland b. A hard irregular gland c. A tender gland d. A boggy gland ____ 19. A 78-year-old man is diagnosed with C2 prostate cancer, and he asks the clinician what that means. In order to answer the patient, the clinician must have which of these understandings of the Jewett rating system? a. The cancer involves the seminal vesicles. b. There is metastatic disease to regional lymph nodes. c. The cancer is confined to the capsule. d. There is metastasis to distant organs. ____ 20. A 58-year-old patient has been receiving leuprolide as treatment for prostate cancer. The clinician should instruct the patient about which of these side effects? a. Risk of osteoporosis b. May have hot flushes c. May have impotence d. All of the above ____ 21. A 22-year-old male is seen in the clinic because he found a hard lump in his testicle when performing testicular self-examination (TSE). Which of the following should be included in the list of differential diagnoses? a. Testicular cancer b. Inguinal hernia c. Varicocele d. All of the above ____ 22. What is the treatment of choice for a patient diagnosed with testicular cancer? a. Radical orchidectomy b. Lumpectomy c. Radiation implants d. All of the above ____ 23. A patient with testicular cancer is being followed after completing treatment 1 year ago. He has been symptom-free with no evidence of disease. How often should he have a CT scan? a. Every month b. Every 3 to 4 months c. Every 6 to 12 months d. Every year True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. ____ 1. Patients treated for Neisseria gonorrhoeae also should be treated for Chlamydia trachomatis. ____ 2. Hepatitis A is considered a sexually transmitted infection by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Chapter 14. Women's Health Problems Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. A 23-year-old sexually active woman presents for her first Pap smear. Her history includes nulligravida, age at first intercourse 14, and more than 10 sexual partners. Which of the following conditions should the clinician be particularly alert for during her examination? a. Human papillomavirus (HPV) b. Endometrial hyperplasia c. Vagismus d. Polycystic ovarian syndrome ____ 2. A 20-year-old woman is seen in the clinic because her boyfriend was found to have gonorrhea. Which of the following is the treatment of choice for gonorrhea? a. Ceftriaxone b. Doxycycline c. Acyclovir d. Metronidazole ____ 3. A 24-year-old woman presents to the clinic with dysuria, dyspareunia, and a mucopurulent vaginal discharge. Her boyfriend was recently treated for nongonococcal urethritis. What sexually transmitted disease has she most probably been exposed to? a. Gonorrhea b. HPV c. Chlamydia d. Trichomonas ____ 4. A 45-year-old woman is seen in the clinic with complaints of a vaginal discharge. The clinician identifies clue cells on the vaginal smear. Which of the following diagnoses is associated with this finding? a. Trichomonas b. Bacterial vaginosis c. HPV d. Herpes simplex virus ____ 5. Which of the following medications is the treatment of choice for trichomonas? a. Metronidazole b. Ceftriaxone c. Diflucan d. Doxycycline ____ 6. A 58-year-old woman presents with a breast mass. Which of the following responses by the clinician would be most appropriate? a. “It is probably just a cyst because that is the most common breast mass.” b. “We will order a mammogram and ultrasound to help establish a diagnosis.” c. “We will go ahead and schedule you for a biopsy because that is the only way to know for sure.” d. “Because your lump is painful, it is most likely not cancer.” ____ 7. A 26-year-old woman is seen with complaints of irregular vaginal bleeding. Which of the following tests should be the first priority? a. Pregnancy test b. Pelvic ultrasound c. Endometrial biopsy d. Platelet count ____ 8. A 42-year-old woman presents to the clinic with complaints of painful intercourse for the last month. Which of the following should be explored as the likely cause of her dyspareunia? a. Menopause b. Dehydration c. Excess progesterone d. Sexual trauma as a child ____ 9. A 36-year-old woman is seen with complaints of vaginal itching, burning, and discharge. On potassium hydroxide (KOH) wet mount of vaginal discharge, the clinician notices hyphae. Which of the following treatments would be appropriate? a. Fluconazole b. Estrogen vaginal cream c. Metronidazole d. Doxycycline ____ 10. A 21-year-old woman is seen in the clinic requesting birth control pills. Which of the following tests is essential before prescribing any oral contraceptive? a. Pregnancy test b. Complete blood cell count c. Thyroid-stimulating hormone d. Urine dip for protein ____ 11. A 40-year-old woman is seen for her yearly examination. She is single and not in a monogamous relationship. Her social history includes smoking cigarettes “occasionally” and drinking about two beers a day. Her body mass index (BMI) is 25. She is requesting birth control. Which of the following methods would be best for this patient? a. Intrauterine device b. Oral contraceptive c. Condom d. Vaginal contraceptive sponge ____ 12. A 44-year-old patient with breast cancer is prescribed tamoxifen by her surgeon. She is complaining about hot flashes. Which of the following responses by the clinician would be most appropriate? a. “You must be having menopause.” b. “The hot flashes are a result of the antiestrogenic effects of tamoxifen.” c. “Tamoxifen will impact your temperature regulation center.” d. “The drug destroys your ovaries.” ____ 13. A 32-year-old woman is seen in the clinic because she has been unable to get pregnant after 12 months of unprotected sex. In order to determine the cause of the infertility, the clinician should question her about which of these possible causes? a. Pelvic inflammatory disease b. Oral contraceptive use for 15 years c. Early menarche d. Diet high in soy protein ____ 14. When assessing a woman for infertility, which of the following tests should be done first? a. Analysis of partner’s sperm b. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) c. Hysterosalpingogram d. Estrogen level ____ 15. A 15-year-old girl is seen in the clinic because she has not yet had her first period. Which of the following questions would help the clinician determine the cause? a. “Are you sexually active?” b. “How long have you been underweight?” c. “Did your mother take diethylstilbestrol during her pregnancy?” d. “Have you noticed any changes in your moods lately?” ____ 16. What is the most common cause of secondary amenorrhea? a. Pregnancy b. Pituitary dysfunction c. Inadequate estrogen levels d. Genetic disorders ____ 17. A 22-year-old woman is diagnosed with premenstrual syndrome. Which of the following lifestyle changes should the clinician suggest to help minimize the patient’s symptoms? a. At least 4 cups of green tea daily b. Regular exercise c. Take vitamin A supplements d. Eat a diet high in iron ____ 18. A 25-year-old woman is seen in the clinic complaining of painful menstruation. Which of the following pelvic pathologies is the most common cause of dysmenorrhea? a. Pelvic inflammatory disease b. Endometriosis c. Sexually transmitted infections d. Ovarian cyst ____ 19. A 26-year-old woman tells the clinician that she has endometriosis, because she has frequent pelvic pain. The clinician also should consider which of these differential diagnoses? a. Diverticulitis b. Cholelithiasis c. Kidney stones d. Ovarian cysts ____ 20. Which of the following would be appropriate treatment for a woman with mild endometriosis? a. Oral contraceptives b. Leuprolide acetate injections c. Nafarelin nasal spray d. Hysterectomy ____ 21. A 45-year-old woman is seen in the clinic with abnormal uterine bleeding and pain during intercourse. The clinician should consider which of the following diagnoses? a. Leiomyoma b. Pregnancy c. Ovarian cancer d. All of the above ____ 22. A 48-year-old woman is seen in the clinic with complaints of prolonged heavy menstrual periods. She is pale and states she can no longer exercise. Pelvic exam reveals a single, very large mass. Which of the following diagnostic tests should the clinician order first? a. Transvaginal ultrasound b. Endometrial biopsy c. MRI d. Abdominal computed tomography scan ____ 23. A 45-year-old woman is seen because of irregular menstrual periods. Her follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) level is 48 mIU/mL, and her luteinizing hormone (LH) level is elevated. She asks the clinician what this means. Which would be the best response? a. “You are approaching menopause.” b. “You have a hormonal imbalance.” c. “Your FSH is normal, but your pituitary is making too much LH.” d. “There is an imbalance between your ovaries and pituitary.” ____ 24. Which of the following tests is essential for a 46-year-old woman who the clinician suspects is perimenopausal? a. Pregnancy b. Estrogen level c. Progesterone level d. LH level ____ 25. A 60-year-old woman is seen for an annual checkup. Her obstetric history reveals para 6, gravida 6. She reports that she went through menopause at age 45. Her grandmother died at age 80 of colon cancer, and her father died of lung cancer. What in her history would be a risk factor for ovarian cancer? a. Her numerous pregnancies b. Her age at menopause c. Her father’s history of lung cancer d. Her grandmother’s history of colon cancer ____ 26. A 58-year-old woman, who had a total abdominal hysterectomy at the age of 45, is diagnosed with atrophic vaginitis. Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment? a. Conjugated estrogen, 0.625 mg/day oral b. Estradiol, 7.5 mcg/24 hr vaginal ring c. Medroxyprogesterone, 10 mg/day oral d. Conjugated estrogen, 0.3 mg + medroxyprogesterone 1.5 mg/day oral True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. ____ 1. Oral contraceptive pills can cause endometrial cancer. ____ 2. A woman taking estradiol is at risk for developing endometrial cancer. ____ 3. Most breast cancer cases are in women with a family history of breast cancer. Chapter 15. Musculoskeletal Problems Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ___ 1. One of the initial steps in assessing patients with musculoskeletal complaints is to determine whether the complaint is articular or nonarticular in origin. Which of the following is an example of an articular structure? a. Bone b. Synovium c. Tendons d. Fascia ____ 2. You have detected the presence of crepitus on examination of a patient with a musculoskeletal complaint. Additionally, there is limited range of motion (ROM) with both active and passive movement. These findings suggest that the origin of the musculoskeletal complaint is: a. Articular b. Inflammatory c. Nonarticular d. A and B ____ 3. Which of the following signs or symptoms indicate an inflammatory etiology to musculoskeletal pain? a. Decreased C-reactive protein b. Hyperalbuminemia c. Morning stiffness d. Weight gain ____ 4. Which of the following statements concerning the musculoskeletal examination is true? a. The uninvolved side should be examined initially and then compared to the involved side. b. The part of the body that is causing the patient pain should be examined first. c. When possible, the patient should not be asked to perform active range-of-motion (ROM) exercises to avoid causing pain. d. Radiographs should always be obtained prior to examination so as not to cause further injury to the patient. ____ 5. You are performing muscle strength testing on a patient presenting with musculoskeletal pain and find that the patient has complete ROM with gravity eliminated. Which numeric grade of muscle strength would you give this patient? a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 4 e. 5 ____ 6. Mrs. Gray is a 55-year-old woman who presents with tightness, pain, and limited movement in her right shoulder. She denies any history of trauma. Her examination reveals a 75% reduction in both active and passive ROM of the right shoulder. Mrs. Gray also is experiencing tenderness with motion and pain at the deltoid insertion. Her medical history is significant for type 1 diabetes mellitus and hypertension. Her social history reveals that she is a secretary and that she is right-handed. Based on her examination and medical history, you suspect adhesive capsulitis, or “frozen shoulder.” Which clue in Mrs. Gray’s history supports this diagnosis? a. History of hypertension b. Her affected shoulder is also her dominant arm. c. Her history of diabetes mellitus d. Her work as a secretary predisposes her to repetitive motions. ____ 7. Jennifer is an 18-year-old who comes to the emergency room after a fall during a soccer game. Jennifer explains that she fell on her left side and kept her arm out straight to break her fall. She has been experiencing severe pain and limited ROM in her left shoulder. The clinician has diagnosed Jennifer with a dislocated shoulder. Which of the following statements are true concerning shoulder dislocation? a. Posterior dislocations are more common than anterior dislocations. b. There is a risk of neurovascular and neurosensory trauma, so the clinician should check for distal pulses. c. Recurrent dislocations are uncommon and would require great force to result in injury. d. Surgery is most commonly the treatment of choice. ____ 8. Mrs. Anderson is a 35-year-old woman who has been recently diagnosed with carpal tunnel syndrome. She has two young children and asks the clinician what the chances are that they also will develop carpal tunnel syndrome. Which of the following responses would be correct regarding the risk of developing carpal tunnel syndrome? a. Carpal tunnel syndrome commonly occurs in families. Genetic factors are thought to account for about one-half the risk of developing carpal tunnel. b. Only people with occupations that require repeated flexion extension of the wrist, use of hand tools that require forceful gripping, or use of hand tools that vibrate are at risk for developing carpal tunnel. c. An underlying musculoskeletal disorder must be present for a person to develop carpal tunnel. d. Carpal tunnel syndrome only occurs in the presence of a hormonal imbalance. ____ 9. Which of the following statements is true regarding the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome? a. The goal of treatment is to prevent flexion and extension movements of the wrist. b. Splints are used in carpal tunnel syndrome, because they allow for free movement of the fingers and thumb while maintaining the wrist in a neutral position. c. Corticosteroid injections are discouraged in the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome because of the risks for median nerve damage, scarring, and infection. d. All of the above ____ 10. Sam is a 25-year-old who has been diagnosed with low back strain based on his history of localized low back pain and muscle spasm along with a normal neurological examination. As the clinician, you explain to Sam that low back pain is a diagnosis of exclusion. Which of the following symptoms would alert the clinician to the more serious finding of a herniated nucleus pulposus or ruptured disc? a. Morning stiffness and limited mobility of the lumbar spine b. Unilateral radicular pain symptoms that extend below the knee and are equal to or greater than the back pain c. Fever, chills, and elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate d. Pathologic fractures, severe night pain, weight loss, and fatigue ____ 11. The clinician has instructed Sam, a 25-year-old patient with low back strain, to use NSAIDs to manage his symptoms of pain and discomfort. Which of the following statements would be most appropriate when teaching Sam about the use of NSAIDs? a. “You should start with the lowest dose that is effective in managing your pain, because long-term use of NSAIDs can result in gastrointestinal (GI) disorders such as ulcers and hemorrhage.” b. “You should start with the lowest dose that is effective in managing your pain to avoid developing tolerance to the medication.” c. “You should take the maximum recommended dose of NSAIDs so that you will not need to take narcotics to control your pain.” d. “It is important to take NSAIDs on an empty stomach in order to increase absorption.” ____ 12. Janet is a 30-year-old who has recently been diagnosed with a herniated disc at the level of L5-S1. She is currently in the emergency room with suspicion of cauda equina compression. Which of the following is a sign or symptom of cauda equina compression? a. Gastrocnemius weakness b. A reduced or absent ankle reflex c. Numbness in the lateral foot d. Paresthesia of the perineum and buttocks ____ 13. Which of the following statements is true concerning the management of the client with a herniated disc? a. Muscle relaxants and narcotics can be used to control moderate pain but should be discontinued after 3 weeks of use. b. An epidural injection is helpful in reducing leg pain that has persisted for at least 3 weeks after the herniation occurred. c. Intolerable pain for more than a 3-month period is an indication for surgical intervention. d. All of the above ____ 14. John is a 16-year-old boy who presents to the emergency room after hurting his knee in a football game. He described twisting his knee and then being unable to extend it completely. John tells the clinician that he heard a pop when the injury occurred and has been experiencing localized pain. The clinician suspects a meniscal tear. Which test would be most appropriate to assess for the presence of a meniscal tear? a. Valgus stress test b. McMurray circumduction test c. Lachman test d. Varus stress test ____ 15. The clinician suspects that a client has patellar instability. In order to test for this, the client is seated with the quadriceps relaxed, and the knee is placed in extension. Next the patella is displaced laterally, and the knee flexed to 30°. If instability is present, this maneuver displaces the patella to an abnormal position on the lateral femoral condyle, and the client will perceive pain. Testing for patellar instability in this way is known as: a. Apprehension sign b. Bulge sign c. Thumb sign d. None of the above ____ 16. The clinician is caring for Diane, a 22-year-old woman who presents with an injured ankle. Diane asks the clinician if she will need an x-ray. The clinician explains to Diane that an x-ray is not always necessary for an injured ankle and that the decision to obtain radiographs is dependent on the examination and Diane’s description of her injury. Which of the following clues in Diane’s examination or history would alert the clinician to the need for obtaining radiographs? a. Inability to bear weight immediately after the injury b. Development of marked ankle swelling and discoloration after the injury c. Crepitation with palpation or movement of the ankle d. All of the above ____ 17. Mr. Jackson is a 65-year-old man recently diagnosed with osteoarthritis. The clinician has explained to Mr. Jackson that the goals for managing osteoarthritis include controlling pain, maximizing functional independence and mobility, minimizing disability, and preserving quality of life. Mr. Jackson explains to the clinician that his first choice would be to use complementary therapies to control his condition and asks what therapies are most effective in treating osteoarthritis. What would be the most appropriate response from the clinician? a. “Complementary therapies should be considered only if surgical interventions are not successful.” b. “I am unfamiliar with the available complementary therapies for osteoarthritis and prefer to discuss more mainstream treatments, such as NSAIDs and physical therapy, to manage your condition.” c. “I would be happy to discuss all the treatment options available to you. Complementary therapies, such as acupuncture, acupressure, and tai-chi, are being studied for use in the treatment of osteoarthritis and have shown promise when used with standard medical therapy.” d. “It would be crazy to use complementary therapies to treat such a serious condition.” ____ 18. Normal estrogen function is important for preventing osteoporosis in both men and women. Estrogen works to prevent osteoporosis in which of the following ways? a. By decreasing the erosive activity of osteoclasts b. By promoting osteoclastogenesis c. By inhibiting osteoclast apoptosis d. All of the above ____ 19. Which of the following tests is considered the gold standard for definitively diagnosing osteoporosis? a. Bone alkaline phosphatase levels b. Urinary N-telopeptide assay c. Bone mass density measurement by densitometry d. Magnetic resonance imaging ____ 20. What is the recommended daily calcium intake for adults over the age of 50 with low bone mass? a. 1,200 mg/day b. 1,000 mg/day c. 1,300 mg/day d. 1,500 mg/day ____ 21. Mrs. Allen is a 60-year-old woman who has been diagnosed with osteoporosis. She is very concerned about the risk of breast cancer associated with hormone replacement therapy and is wondering what other treatments are available to her. The clinician explains that bisphosphonates are another class of drugs used in the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. What teaching should the clinician give Mrs. Allen in regard to taking bisphosphonates? a. Taking bisphosphonates can result in hypercalcemia, so calcium intake should be decreased while taking this class of drugs. b. There is potential for upper GI irritation, so these medications are contraindicated in people with abnormalities of the esophagus or delayed esophageal emptying. c. This class of drugs can be taken at any time of the day without regard to meals. d. None of the above ____ 22. Which stage of Paget’s disease is characterized by elevated numbers of osteoblasts, resulting in abnormal increases in bone remodeling and leading to an irregular deposition of collagen fibers? a. Lytic b. Mixed c. Sclerotic d. All of the above ____ 23. Which of the following statements concerning the treatment of fibromyalgia syndrome is true? a. There is currently no cure for the disorder; however, patients should be made aware that symptom relief is possible. b. Treatment is directed toward controlling discomfort, improving sleep, and maintaining function. c. Fibromyalgia syndrome can be difficult to manage, requiring a variety of approaches and multiple medications. d. All of the above ____ 24. One of the most frequent presenting signs/symptoms of osteoporosis is: a. Goiter b. Abnormal serum calcium c. Elevated urine biochemical markers d. Bony fracture ____ 25. Mrs. Thomas was seen in the office complaining of pain and point tenderness in the area of her elbow. The pain has increased following a day of gardening one week ago. A physical finding that differentiates the diagnosis and is most consistent with lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow) is: a. Ecchymosis, edema, and erythema over the lateral epicondyle b. Pain at the elbow with resisted movements at the wrist and forearm c. Inability to supinate and pronate the arm d. Inability to flex or extend the elbow against resistance ____ 26. A 70-year-old female has fallen 2 weeks ago and developed immediate pain in her left wrist. She thought she just bruised it but is worried because it has not improved. She has used Tylenol® and ice at home, and that has helped slightly. You examine her and find she has moderate swelling and ecchymosis but no overtly obvious deformity. Her ROM is uncomfortable and severely diminished due to the pain. No crepitus is heard or felt. Her fingers are warm; her pulse is strong; and capillary refill is less than 2 seconds. What should you do? a. Make an immediate referral for an orthopedic evaluation without further assessment. b. Tell her that it takes time for these bruises to improve, so she should be patient. c. Obtain a wrist x-ray and place her wrist in a splint or prescribe a splint. d. Send her to the emergency room for reduction of this obvious wrist fracture. True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. ____ 1. Osteoarthritis is primarily a noninflammatory condition. ____ 2. The presence of a positive rheumatoid factor is always indicative of rheumatoid arthritis. Chapter 16. Endocrine/Metabolic Problems Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. A patient is 66 inches in height, weighing 200 pounds, and newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM). Her fasting plasma glucose level is 215 mg/dL. What is the best initial treatment? a. No treatment at this time b. Diet and exercise for 6-week trial c. Diet, exercise, and oral medication d. Diet, exercise, and exogenous insulin ____ 2. The clinician suspects that a client seen in the office has hyperthyroidism. Which of the following tests should the clinician order on the initial visit? a. High sensitivity thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and free T4 b. Free T4 and serum calcium c. Free T3 and T4 d. TSH and thyroxin antibodies ____ 3. A patient with type 2 diabetes asks the clinician why she needs to exercise. In order to answer her, the clinician must understand that exercise has what effect on the patient with type 2 diabetes? a. Reduces postprandial blood glucose b. Reduces triglycerides and increases high-density lipoprotein (HDL) c. Reduces total cholesterol d. All of the above ____ 4. A patient with type 1 diabetes comes to the clinic complaining of feeling nervous and clammy. He states that he took his insulin this morning but was late for work and did not eat breakfast. Which action should the clinician take first? a. Check his blood sugar. b. Have him drink 4 ounces of juice. c. Call 911. d. Ask him about his usual eating habits. ____ 5. A patient with type 2 diabetes comes to the clinic after reading about metformin in a magazine. Which of the following conditions that the patient also has would be a contraindication to taking metformin? a. Ketoacidosis b. Cirrhosis c. Hypoglycemic episodes d. All of the above ____ 6. A 25-year-old patient presents to the clinic with fatigue, cold intolerance, weight gain, and constipation for the past 3 months. On physical examination, the clinician notices a sinus bradycardia; muscular stiffness; coarse, dry hair; and a delay in relaxation in deep tendon reflexes. Which of the following tests should be ordered next? a. Serum calcium b. TSH c. Electrolytes d. Urine specific gravity ____ 7. The clinician has been doing diabetic teaching for a patient with type 1 diabetes. Which of the following statements by the patient would indicate that teaching has been effective? a. “As long as I don’t need glasses, I don’t have to worry about going blind.” b. “I know I need to have my eyes checked every year.” c. “My optometrist checks my eyes.” d. “I will see my eye doctor when my vision gets blurry.” ____ 8. A 64-year-old man with type 2 diabetes presents to the clinic with the complaint of “my feet feel like they are on fire.” He has a loss of vibratory sense, +1 Achilles reflex, and a tack embedded in his left heel. Which of the following would be an appropriate treatment? a. Tricyclic antidepressants b. Capsaicin cream c. Vitamin B12 injections d. Insulin ____ 9. After removing a tack from a type 2 diabetic’s heel and evaluating the site for infection, what is the best plan for this patient? a. Suggest she use a heating pad to improve circulation. b. Refer to a podiatrist for a foot care treatment plan. c. Send her for acupuncture treatments. d. All of the above ____ 10. Joyce is seen in the clinic complaining of vague symptoms of nervousness and irritability. She says that her hair will not hold a permanent wave anymore. On physical examination, the clinician finds an irregular heartbeat and brisk reflexes. The differential diagnosis should include which of the following conditions? a. Myxedema b. Thyrotoxicosis c. Cushing’s syndrome d. Pan-hypopituitarism ____ 11. The patient is prescribed radioactive iodine (RAI) and asks the clinician how this drug works. The clinician’s response should include which of the following data? a. RAI prevents the peripheral conversion of T4 to T3. b. RAI binds free T4. c. RAI destroys thyroid tissue. d. RAI reduces freely circulating iodine. ____ 12. A patient is diagnosed with hypothyroidism. Which of the following electrocardiogram changes should the clinician expect as a manifestation of the disease? a. Sinus bradycardia b. Atrial fibrillation c. Supraventricular tachycardia d. U waves ____ 13. After 6 months of Synthroid therapy, the clinician should expect which of the following in the repeat thyroid studies? a. Elevated TSH b. Normal TSH c. Low TSH d. Undetectable TSH ____ 14. Which of the following laboratory findings should the clinician expect in a patient with untreated Graves’ disease? a. Elevated TSH b. Elevated T4 c. Elevated thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) d. All of the above ____ 15. The clinician prescribes glipizide (Glucotrol) for a diabetic patient. Which statement made by the patient would indicate that your teaching has been effective? a. “I’ll take my pill at least 30 minutes before breakfast.” b. “I’ll take my Glucotrol before bedtime.” c. “It is important to take my medication right after I eat.” d. “Since I only like to eat two meals a day, I can take the pill between my meals.” ____ 16. A diabetic patient asks the clinician why he needs to check his blood sugar at home even when he feels good. Which of the following responses would be most appropriate? a. “Control of glucose will help postpone or delay complications.” b. “Regularly checking blood sugar will help establish a routine.” c. “Monitoring glucose will promote a sense of control.” d. All of the above ____ 17. How often should the clinician examine the feet of a person with diabetes? a. Once a year b. Every 6 months c. Every 3 months d. Every visit ____ 18. The clinician sees a patient who is 5 feet tall and weighs 150 pounds. How would the clinician classify this patient? a. Overweight b. Mild obesity c. Moderate obesity d. Morbid obesity ____ 19. Mr. S presents in the clinic with pain, tenderness, erythema, and swelling of his left great toe. The clinician suspects acute gout. Which of the following should the clinician expect in the initial test results for this patient? a. Elevated uric acid level b. Elevated blood urea nitrogen c. Decreased urine pH d. Decreased C-reactive protein ____ 20. Mr. W, 53 years old, is seen in the clinic with concerns about his left foot. He has a 40-year history of type 1 diabetes with “fairly good” control on twice-daily insulin. He denies injury but states that he tripped a few months ago and that his foot is sore when he walks. Physical examination reveals an edematous, erythremic, and warm foot. There is a superficial ulcer on the plantar surface. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis? a. Fallen arch b. Arthritis c. Charcot joint d. Sprained ankle ____ 21. Which of the following tests should you order to confirm Mr. W’s diagnosis? a. Bone scan b. Computed tomography (CT) scan c. X-ray of the foot d. Culture of the ulcer ____ 22. A vegetarian patient with gout asks the clinician about food he should avoid. The clinician should advise the patient to avoid which of the following foods? a. Rice b. Carrots c. Spinach d. Potatoes ____ 23. The clinician should question the patient with suspected gout about use of which of these medications? a. Low-dose aspirin b. Thiazide diuretics c. Ethambutol d. All of the above ____ 24. The clinician finds numerous nodules on the thyroid of a 65-year-old woman. The clinician suspects thyroid cancer. Which of the following data would be most significant for this patient? a. A history of tonsillectomy in the 1940s b. Recent exposure to mumps c. Vegetarian diet d. Allergy to iodine ____ 25. Which of the following is essential for diagnosing thyroid cancer? a. Fine needle aspiration b. Thyroid ultrasound c. CT scan d. Magnetic resonance imaging ____ 26. Which of the following are common signs of type 2 DM? a. Anorexia b. Recurrent yeast infection c. Weight gain d. Elevated HDL cholesterol ____ 27. Which of the following medications can cause hyperglycemia? a. Prednisone b. Metformin c. Synthroid d. Cephalexin ____ 28. Which of the following is diagnostic for diabetes mellitus? a. A1C 7.0 on one occasion b. Fasting blood sugar (FBS) of 100 mg/dL on two occasions c. Random glucose of 200 mg/dL on two occasions d. Two-hour post-load plasma glucose of 300 mg/dL on one occasion ____ 29. Which of the following medications for type 2 diabetes mellitus should not be prescribed during pregnancy? a. Insulin b. Metformin c. Glucotrol d. Precose ____ 30. A 35-year-old woman presents with symptoms of hypoglycemia. There is no history of diabetes mellitus. Which of the following should be included in the differential diagnosis? a. Anxiety disorder b. Pheochromocytoma c. Psychosis d. All of the above True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. ____ 1. Metformin is the first line of pharmacologic treatment for type 2 DM. ____ 2. Fruit juice with added sugar is the treatment of choice for anyone experiencing hypoglycemia. ____ 3. Lifestyle modification is the treatment of choice for metabolic syndrome. ____ 4. A BMI of 29 kg/m2 is considered obesity. ____ 5. Urine-free cortisol is one of four diagnostic tests recommended for Cushing’s syndrome. Chapter 17. Hematologic and Immune Problems Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. Sandra is 42 years old and has just been diagnosed with leukemia. She is complaining of bone and joint pain. Which type of leukemia is most likely the culprit? a. Acute lymphocytic leukemia b. Acute myelogenous leukemia c. Chronic myelogenous leukemia d. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia ____ 2. Which type of bone marrow transplant is obtained from an identical twin? a. Autogenic b. Autologous c. Allogeneic d. Syngeneic ____ 3. During treatment for anaphylaxis, what site is used for the initial injection of epinephrine? a. IV b. Abdomen c. Upper lateral thigh d. Deltoid ____ 4. After the initial treatment for anaphylaxis, which medication should be added to prevent late-phase anaphylactic reactions? a. Albuterol b. Diphenhydramine c. An H2 blocker d. Corticosteroids ____ 5. When analyzing synovial fluid, if it is opaque, white, or translucent; has 5,000 leukocytes/Ml; 80% polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN); and a low red blood cell count, it may be indicative of which of the following conditions? a. This is a normal result. b. Scleroderma c. Rheumatoid arthritis d. Sickle cell disease ____ 6. Which of the following disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs is a folic acid antagonist? a. Methotrexate (Rheumatrex) b. Etanercept (Enbrel) c. Rituximab (Rituxan) d. Anakinra (Kineret) ____ 7. Which statement about HIV postexposure prophylaxis (PEP) for health-care workers is the most accurate? a. PEP should be started within hours of exposure. b. PEP should be started within 72 hours of exposure. c. Renal and hepatic function tests should be done 6 weeks after beginning PEP. d. PEP will prevent potential hepatitis C infection if present. ____ 8. Which household solution should be used to clean a bathroom if sharing with a friend who has HIV? a. 100% bleach b. 50% bleach and 50% vinegar c. Nine parts H2O to one part bleach d. The friend must have his or her own bathroom. ____ 9. Reuben, age 24, has HIV and just had a routine viral load test done. The results show a falling viral load. What does this indicate? a. A favorable prognostic trend b. Disease progression c. The need to be more aggressive with Reuben’s medications d. The eradication of the HIV ____ 10. If the international normalized ratio (INR) result is above the therapeutic range in a patient with atrial fibrillation on warfarin, what might the clinician do? a. Stop the warfarin for 1 week, and then repeat the INR. b. Withhold one or more days of anticoagulant therapy. c. Restart therapy at a lower dose immediately. d. The prothrombin time and INR should be reevaluated within 1 month of the dosage adjustments. ____ 11. Which of the following is identified as an eating disorder in which a person craves food substitutes, such as clay, ice chips, and cotton, and is considered an objective finding associated with severe iron deficiency? a. Ferritin b. Porter’s syndrome c. Hypochromasia d. Pica ____ 12. As a rule of thumb, the estimated level of hematocrit is how many times the value of the hemoglobin? a. Two b. Three c. Four d. Five ____ 13. What is the most common cause of microcytic anemia? a. Anemia of chronic disease b. Sideroblastic anemia c. Iron-deficiency anemia d. Thalassemia ____ 14. The cardinal subjective symptom of sickle cell crisis is which of the following? a. Pain b. Nausea c. Light-headedness d. Palpitations ____ 15. In the United States, what is the second most common connective tissue disease and the most destructive to the joints? a. Osteoarthritis b. Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) c. Rheumatoid arthritis d. Sjögren’s syndrome ____ 16. Which blood test is a nonspecific method and most helpful for evaluating the severity and course of an inflammatory process? a. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate b. White blood cell count c. Polymorphonuclear cells d. C-reactive protein (CRP) ____ 17. Infectious mononucleosis results from an acute infection with which of the following? a. Epstein-Barr virus b. Acute HIV infection c. Guillain-Barré d. Hepatitis ____ 18. What is the most common cause of generalized musculoskeletal pain in women ages 20 to 55? a. Chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) b. Anemia c. Fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS) d. Sports-related injuries ____ 19. After returning from visiting his grandchildren in England, George, age 59, complains of a flulike illness, including fever, chills, and myalgia. He reports having discovered a rash or red spot that grew in size on his right leg. What disease are you considering? a. A viral syndrome b. Lyme disease c. Rocky Mountain spotted fever d. Relapsing fever ____ 20. Dryness of the eyes and mouth is typical of which condition? a. Sjögren’s syndrome b. CFS c. FMS d. Hypothyroidism ____ 21. Triggering factors for acute exacerbations of which of the following conditions include exposure to ultraviolet (UV)-B and UV-A rays? a. Rheumatoid arthritis b. Scleroderma c. SLE d. Sjögren’s syndrome ____ 22. The current goal of treatment for a patient with HIV infection is which of the following? a. Viral suppression of HIV to undetectable levels in the peripheral blood b. Compete eradication of the virus c. Encouraging the person to have no contact with uninfected individuals d. Complete abstinence ____ 23. The most cost-effective screening test for determining HIV status is which of the following? a. Western blot b. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay c. Venereal Disease Research Laboratory test d. Viral load ____ 24. An important complication of antiretroviral (ARV) therapy in patients with advanced AIDS is which of the following? a. Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome b. Improvement in opportunistic infections c. Restoration of immune system to preinfection status d. Progression to AIDS ____ 25. Which drug category of ARV therapy is generally effective in crossing the blood–brain barrier and may be useful in managing HIV-associated dementia? a. Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors b. Protease inhibitors c. Integrase inhibitors d. Nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors ____ 26. Spontaneous bruising may be seen with platelet counts below what level? a. 100,000 cells/mL b. 75,000 cells/mL c. 50,000 cells/mL d. 30,000 cells/ml ____ 27. Which type of the following is characterized by fatigue on awakening that may improve with exercise? a. Functional fatigue b. Fatigue with an organic origin c. Fatigue of chronic anemia d. Fatigue of depression and anxiety ____ 28. Early rheumatoid disease is characterized by: a. Pain and swelling in both small and large peripheral joints b. Rigid joints with diminished range of motion c. Joint swelling and immobility on rising d. A cardiac rub or pulmonary friction rub ____ 29. Which test is diagnostic of rheumatoid arthritis? a. Rheumatoid factor b. ESR c. CRP d. Anti-CCP titers ____ 30. What is the mainstay of management for infectious mononucleosis? a. Antivirals b. Symptom control c. Corticosteroids d. Isolation ____ 31. CFS tends to occur in which individuals? a. Active, highly functional adults b. Depressed middle-aged persons c. Individuals with a depressed immune system d. Individuals who are hypochondriacs ____ 32. The exanthem of Lyme disease is: a. Erythema infectiosum b. Laterothoracic exanthem c. Erythema migrans d. Morbilli exanthem ____ 33. If left untreated, this condition will progress to complaints that include multiple joint arthritis. a. Sjögren’s syndrome b. HIV/AIDS c. Guillain-Barré d. Lyme disease ____ 34. Keratoconjunctivitis sicca is a classic sign of which condition? a. SLE b. Sjögren’s syndrome c. CFS/FMS d. Lyme disease ____ 35. Which person is four times more likely to develop SLE than a Caucasian? a. Persons of African descent b. Asians c. Hispanics d. Middle Eastern Jews Chapter 18. Psychosocial Problems Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. The effectiveness of benzodiazepines in treating anxiety disorders suggests that which of the following neurotransmitters plays a role in anxiety? a. Acetylcholine b. Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) c. Dopamine d. Serotonin ____ 2. The criteria for diagnosing generalized anxiety disorder in the American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th edition (text revision) state that excessive worry or apprehension must be present more days than not for at least: a. 1 month b. 3 months c. 6 months d. 12 months ____ 3. A patient presents to the clinician after experiencing four episodes in the last month of sweating, palpitations, chest pain, nausea, and shaking. Each episode lasted about 10 minutes. The patient is now becoming very fearful of future events and has been reluctant to leave the house. The clinician suspects panic disorder but wants to rule out any possible medical causes. Which of the following medical conditions can mimic the symptoms of a panic attack? a. Pheochromocytoma b. Hyperthyroidism c. Cardiac arrhythmias d. All of the above ____ 4. Which of the following is considered first-line treatment for panic disorders? a. Benzodiazepines b. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) c. Tricyclic antidepressants d. Cognitive behavioral therapy ____ 5. Which of the following symptoms is not part of the diagnostic criteria for post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)? a. Hypersomnolence b. Blunted feelings c. Loss of interest in significant activities d. Intrusive recurrent recollections of the event ____ 6. Which of the following neuroendocrine abnormalities is implicated in depression? a. Decrease in adrenal size b. Increased cortisol and corticotrophin-releasing hormone c. An exaggerated response of thyrotropin (TRH) to infusion of thyroid-releasing hormone d. Increased inhibitory response of glucocorticoids to dexamethasone ____ 7. The clinician has chosen to prescribe an SSRI instead of a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) for a patient fitting the diagnostic criteria for depression. Which of the following is not true concerning SSRIs in comparison to tricyclic antidepressants? a. SSRIs are more effective than TCAs. b. SSRIs take less time to work than TCAs. c. SSRIs have a more favorable side-effect profile than TCAs. d. SSRIs are not lethal in overdose. ____ 8. After discontinuing fluoxetine, how long must a person wait before starting a monoamine oxidase inhibitor? a. 2 weeks b. 3 weeks c. 4 weeks d. 5 weeks ____ 9. It is important to educate patients with depression and their family members about reporting signs of increasing depression and suicidal thoughts. This is especially true during which time period? a. Before the initiation of treatment b. 1 to 2 weeks after the initiation of treatment c. When switching to a different medication d. 1 to 2 weeks after tapering off medications ____ 10. A patient is experiencing extrapyramidal side effects from his antipsychotic medications. The clinician would most likely take which of the following approaches to treating these side effects? a. Give the patient a “drug holiday” until the symptoms resolve and then restart the medication. b. Switch the patient to a different antipsychotic. c. Treat the patient with anticholinergics. d. Treat the patient with anticonvulsants. ____ 11. According to Kübler-Ross, the stages of grief occur in which order? a. Anger, denial, depression, bargaining, acceptance b. Anger, denial, bargaining, acceptance, depression c. Denial, anger, depression, bargaining, acceptance d. Denial, anger, bargaining, depression, acceptance ____ 12. The clinician is educating a patient about the effects of marijuana. The patient stated she has been smoking for years and believes the use does not interfere with her life. What is a significant long-term sequelae of marijuana use that the clinician should educate this patient about? a. Memory impairment b. Sexual dysfunction c. Dry mouth d. There are no long-term consequences of marijuana use. ____ 13. Cocaine acts as a stimulant by blocking the reuptake of which neurotransmitter? a. GABA b. Acetylcholine c. Dopamine d. Serotonin ____ 14. What blood alcohol level corresponds with the signs of stupor and confusion? a. 0.05 b. 0.1 c. 0.2 d. 0.3 ____ 15. Rapid eye movement (REM) sleep occurs how frequently during non-REM sleep? a. Every 30 minutes b. Every 60 minutes c. Every 90 minutes d. Every 180 minutes ____ 16. Which of the following is a laboratory finding commonly found in patients with anorexia nervosa? a. Hypercholesterolemia b. Hypermagnesmia c. Leukocytosis d. Decreased TRH ____ 17. Which of the following is the only drug for bulimia approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration? a. Sertraline b. Fluoxetine c. Citoprolam d. Imipramine ____ 18. Which of the following would be important to monitor in a child receiving methylphenidate for treatment of attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)? a. Liver function b. Vision c. Growth parameters d. Renal function ____ 19. It is important for the clinician to discuss the long-term effects of sexual assault with survivors. Which of the following is the most common long-term effect of sexual assault? a. Depression b. Obsessive-compulsive disorder c. Substance abuse d. PTSD ____ 20. Women are at the highest risk for developing postpartum depression for up to how long after childbirth? a. 2 weeks b. 1 month c. 3 months d. 6 months ____ 21. Which is the most prevalent psychiatric condition in the United States? a. Depression b. Anxiety c. Substance-related addictions d. Gambling ____ 22. What is recorded as clinical category two of the American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th edition (text revision)? a. Clinical disorder or focus of clinical attention b. Personality or environmental problems c. Environmental and psychosocial stressors d. Global assessment of functioning ____ 23. Which of the following may be used to evaluate a person’s suicide risk? a. CAGE b. SANE c. SAD PERSONAS d. DIGFAST ____ 24. Assessing for adherence with prescribed medications and developing a plan for what to do if they are stopped is a major treatment issue for which of the following diagnostic groups? a. ADHD b. Bipolar c. Depression d. Anxiety ____ 25. Bipolar disorder requires differential diagnosis from all of the following except? a. Substance abuse and medication effects b. Medical and neurological disorders c. Cluster B personality disorders and depression d. Obsessive-compulsive disorder True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. ____ 1. The use of benzodiazepines in the patient with generalized anxiety disorder and comorbid depression can exacerbate depressive symptoms. ____ 2. Depressive episodes associated with bipolar disorder are treated the same as major depressive disorder. ____ 3. Women in abusive relationships have a greater chance of being killed by their batterers when they leave the relationship than women who stay. ____ 4. Adults must show childhood onset of symptoms to receive a diagnosis of ADHD. ____ 5. Parkinson’s disease and dementing illnesses may commonly manifest depressive symptoms. ____ 6. The best predictor of suicide risk is a history of suicide attempts. ____ 7. A no-suicide contract can prevent a suicide attempt. ____ 8. Depression is the most chronic disabling and economically catastrophic medical disorder of the severe mental illnesses. ____ 9. Clozapine (Clozaril) requires laboratory monitoring at specified frequencies with results reported to a national registry. ____ 10. When combined with certain other medications, serotonin-specific antidepressants can have significant liver P450-interaction effects. Chapter 19. Emergency Problems Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. Which type of heat-related illness involves a core body temperature of at least 104.9°F, acute mental status changes, absent sweat, and tachypnea? a. Heat cramps b. Heat syncope c. Heat exhaustion d. Heat stroke ____ 2. What percentage of burns is involved using the rule of nines if both front legs are burned? a. 9% b. 18% c. 24% d. 36% ____ 3. Which drug commonly prescribed for burns is active against a wide spectrum of microbial pathogens and is the most frequently used agent for partial- and full-thickness thermal injuries? a. Clotrimazole cream (Lotrimin) b. Mafenide acetate (Sulfamylon) c. Silver nitrate d. Silver sulfadiazine (Silvadene) ____ 4. A sunscreen with a sun-protection factor of at least what number will block most harmful ultraviolet radiation? a. 4 b. 8 c. 10 d. 15 ____ 5. Which clinical feature is the first to be affected in increased intracranial pressure? a. Decrease in level of consciousness b. Headache c. Nausea d. Widening pulse pressure ____ 6. What is the normal number for the Glasgow Coma Scale? a. 7 b. 9 c. 10 d. 15 ____ 7. Which diagnostic test is the best to diagnose a subdural hematoma? a. History b. Positron emission tomography c. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) d. Computed tomography (CT) scan ____ 8. Patients with a spontaneous pneumothorax should be counseled that up to what percentage may experience a reoccurrence at some point? a. 10% b. 20% c. 30% d. 50% ____ 9. Most adult poisonings are: a. Intentional and self-inflicted b. Accidental c. Caused by someone wishing to do harm to the person d. Not attributed to any reason ____ 10. Which method is used to remove heavy metals, such as lead, that are ingested as poisons? a. Chelation b. Dialysis c. Gastric lavage d. Bowel irrigation ____ 11. If a previously frostbitten area becomes frostbitten again after it has healed, what might occur? a. Permanent tissue damage may occur, resulting in necrosis to that body part. b. The area will be super sensitive. c. The area is prone to a repeat frostbite. d. The area is as susceptible as any other area. ____ 12. What percentage of all visits to the emergency department (ED) are related to wounds? a. 5% b. 12% c. 18% d. 24% ____ 13. Which solution should be used when irrigating lacerated tissue over a wound on the arm? a. Dilute povidone-iodine solution b. Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) c. Saline solution infused with an antibiotic d. Saline irrigation or soapy water ____ 14. Which type of burn injury results in destruction of the epidermis with most of the dermis, yet the epidermal cells lining hair follicles and sweat glands remain intact? a. Superficial burns b. Superficial partial-thickness burns c. Deep partial-thickness burns d. Full-thickness burns ____ 15. Which carboxyhemoglobin (COHb) level correlates with the clinical symptoms of confusion, lethargy, and ST-segment depression on the electrocardiogram? a. Less than 10% b. 20% COHb c. 30% COHb d. 40% to 60% COHb ____ 16. Which causes the greatest percentage of mammalian bites? a. Dogs b. Cats c. Humans d. Rodents ____ 17. Which arthropod bite can contain cytotoxic and hemolytic toxins that may destroy tissue? a. Tick b. Brown recluse spider c. Wasp d. Stinging caterpillar ____ 18. Which of the following characteristics separates anaphylaxis from a vasovagal reaction? a. Bradycardia b. Extreme diaphoresis c. Severe bronchoconstriction d. Hypotension ____ 19. Delayed serum sickness–type reactions in response to multiple bee, wasp, or fire ant stings can be managed with which of the following? a. A corticosteroid such as prednisone (Deltasone), 60 to 100 mg, tapered over 2 weeks b. An oral antihistamine, such as hydroxyzine, for 2 weeks c. An H2 blocker such as cimetidine for 1 week d. 0.1 mg (1 mL of 1:10,000 solution epinephrine) in 10 mL of normal saline and administer as a slow intravenous push over 10 minutes ____ 20. After a head injury, what is it called when air enters into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)–filled spaces within the head? a. Pneumocephalus b. Hemotympanum c. Battle’s sign d. Raccoon sign ____ 21. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) may leak through the cribriform plate region of the skull following a head injury and cause which of the following? a. Ear CSF otorrhea b. Leakage of CSF from the eye c. Nasal CSF rhinorrhea d. Leakage of CSF from the mouth ____ 22. Which classic feature of an epidural hematoma may distinguish it from other skull hematomas? a. Unilateral hemiparesis b. Loss of speech c. Temporary hearing loss d. A brief loss of consciousness, then a brief “lucid” moment, followed by momentary unconsciousness minutes after the injury ____ 23. A patient with a basilar skull fracture may experience an impaired downward gaze or diplopia from which affected cranial nerve? a. CN II b. CN III c. CN IV d. CN V ____ 24. A history of overuse or excessive force, as opposed to a fall, hyperextension, or the twisting of a joint, is more likely related to which musculoskeletal injury? a. A sprain b. A strain c. A partial fracture d. A fracture ____ 25. In a healthy adult, the process of remodeling after a fracture of the humerus takes how long? a. Approximately 4 weeks b. 2 months c. 3 months d. 4 months ____ 26. A patient who sustains blunt chest trauma and/or penetrating chest trauma must have which of the following imaging examinations? a. Upright chest x-ray film b. Supine chest x-ray c. Lateral chest x-ray d. MRI ____ 27. Josie, age 30, has a pneumothorax. It may be treated conservatively without a chest tube if it is deflated by what percentage? a. 30% b. 45% c. 60% d. All pneumothoraxes require a chest tube. ____ 28. Hepatic necrosis with jaundice may occur after ingesting massive doses of which medication? a. Phenobarbital b. Diazepam c. Ritalin d. Acetaminophen ____ 29. Pink, cherry red tissues and skin may result from which type of poisoning? a. Arsenic b. Lead c. Carbon monoxide d. Strychnine ____ 30. In which type of burn is the injury more extensive than it appears, and the cardiac conduction system may be affected, leading to sudden death or arrhythmias? a. Chemical burns b. Electrical burns c. Radiation burns d. Thermal burns ____ 31. Eddie, age 4, presents to the ED with a live insect trapped in his ear canal causing a lot of distress. What should be your first step? a. Remove the insect with tweezers. b. Immobilize the insect with 2% lidocaine. c. Sedate Eddie with diazepam. d. Shine a light in the ear for the insect to “find its way out.” ____ 32. When giving discharge instructions to a patient with a laceration injury to his lower leg, which is the most important one? a. Recommend isometric exercises to prevent a deep vein thrombosis (DVT). b. Recommend cleansing the wound every 4 hours to prevent an infection. c. Keep the leg elevated at waist level to prevent any edema. d. Keep the leg completely immobile to prevent extension of the laceration. ____ 33. Cerebellar function may be assessed by performing which examination/test? a. Gag reflex b. Pupillary response c. Romberg’s test d. Apley’s test ____ 34. In the epithelialization phase of wound healing, the wound will have only what percent of its normal tensile strength at 3 weeks? a. Less than 15% b. 15% to 20% c. 25% to 40% d. Greater than 50% ____ 35. Which of the following statements is true about antibiotic prophylaxis for most wounds? a. It is not indicated for most wounds and does not affect the infection rate. b. Antibiotics should always be ordered for a wound. c. Antibiotics need to be ordered for at least 2 weeks. d. Antibiotics should be ordered only if sutures are in place. Chapter 20. Palliative Care Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. Which of the following statements is true regarding pain? a. If a patient complains of pain but has no physical signs, he or she is most likely exhibiting drug-seeking behaviors. b. Acute pain is more intense and severe than chronic pain. c. Pain is a subjective experience related to actual or potential tissue damage. d. All of the above ____ 2. Which of the following would be a cause of visceral pain? a. Bone metastases b. Intra-abdominal metastases c. Musculoskeletal inflammation d. Postsurgical incisional pain ____ 3. According to the World Health Organization’s analgesic ladder, which drug combination would be most appropriate in an opiate-naïve patient who presents with moderate pain? a. Ibuprofen/imipramine b. Naproxen/morphine c. Aspirin/fentanyl d. Indomethacin/hydrocodone ____ 4. A 75-year-old man is being treated as an outpatient for metastatic prostate cancer. Which of the following statements is true regarding the management of pain with opioids in the elderly? a. Opioids with a long half-life, such as methadone, are a good choice, because they stay in the system longer, and patients do not have to remember to take multiple pills. b. Serum creatinine is the best measurement of renal function in the elderly and should be done prior to the initiation of treatment with opioids. c. Renal clearance of medications is faster in the elderly, so higher dosages of medications are needed to adequately control pain. d. None of the above ____ 5. A patient had a transdermal fentanyl patch placed 2 hours ago and is not getting any pain relief. What would be the most appropriate intervention? a. Remove the current patch and replace with a new fentanyl patch at a higher dose. b. Prescribe a short-acting opioid for breakthrough pain. c. Remove the patch and switch to a different intravenous opioid. d. Tell the patient not to worry, as it takes about 12 hours for the patch’s effects to be felt, and he will have relief at that time. ____ 6. A patient is preparing to be discharged to home with hospice. She is on a morphine patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) in the hospital. She is concerned as to whether she can stay on her morphine PCA at home even when she is not able to give herself boluses. What would be an appropriate response from the clinician? a. “We are unable to prescribe a PCA for use at home. If you are comfortable on the PCA, you should remain in the hospital.” b. “It would be possible for your nurse or another trained family member to activate the dosing button when you are unable to do so.” c. “A PCA is not an appropriate method of pain medication delivery once you are unable to use the dosing button. I will switch you to another form of pain control.” d. “You should not be concerned about your pain management at home. It will be taken care of for you.” ____ 7. A patient taking PO hydromorphone for pain control has developed dysphagia. The clinician decides to switch the patient to IV hydromorphone. What ratio of IV:PO hydromorphone does the clinician need to know to calculate the proper dose? a. 1:1 b. 1:2 c. 1:5 d. 1:7 ____ 8. A patient is receiving long-acting oxycodone for pain control. The clinician thinks that he also will benefit from a short-acting oxycodone for breakthrough pain. How will the clinician figure out what the dose of short-acting oxycodone should be? a. The short-acting dose should be 10% to 20% of the total 24-hour long-acting dose. b. The short-acting dose should be 40% to 50% of the total 24-hour long-acting dose. c. The short-acting dose should be 10% to 20% of each long-acting dose. d. The short-acting dose should be 40% to 50% of each long-acting dose. ____ 9. A patient is being switched from hydromorphone to methadone in an attempt to achieve better pain control. How much should the dose of methadone be reduced when calculating the equianalgesic dose of the two drugs? a. 0% b. 20% c. 50% d. 90% ____ 10. If a patient requires six rescue doses for breakthrough pain in a 24-hour period, what would be an appropriate intervention? a. Increase the dose of the baseline long-acting medication. b. Increase the dose of the rescue short-acting medication. c. Switch to a different short-acting rescue medication. d. Do nothing, because this is appropriate, and the patient’s pain is well controlled. ____ 11. A patient with bone metastases from prostate cancer inquires whether he is a candidate for radiopharmaceuticals. Which of the following conditions would exclude him as a candidate? a. Karnofsky performance status of 65 b. Pathologic fracture c. Life expectancy of 5 months d. Hypocalcemia ____ 12. Which of the following is the best description of dyspnea? a. An oxygen saturation of less than 90% b. Respiratory rate greater than 24 c. A psychological state resulting in the feeling of air hunger d. A subjective feeling of breathlessness ____ 13. What would be an appropriate dose of morphine to give an opioid-naïve patient to manage tachypnea associated with dyspnea? a. 5 mg PO every 4 hours b. 15 mg PO every 4 hours c. 30 mg PO every 4 hours d. 40 mg PO every 4 hours ____ 14. Glycopyrrolate (Robinul) is one drug of choice to manage which of the following conditions that can contribute to dyspnea? a. Copious secretions b. Cough c. Anxiety d. Effusion ____ 15. Which characteristic of delirium helps to distinguish it from dementia? a. Abrupt onset b. Impaired attention c. Affective changes d. Delusions ____ 16. Which of the following classes of drugs should be used as first-line therapy for treatment of delirium? a. Benzodiazepines b. Antipsychotics c. Anticonvulsants d. Antidepressants ____ 17. Which of the following is a role of the advanced practice nurse in palliative cancer care? a. Detecting cancer in asymptomatic patients or those with specific symptoms b. Arranging for follow-up care, including psychosocial and spiritual support c. Identifying and managing complications of care d. All of the above True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. ____ 1. Patients who are receiving life-prolonging therapies do not qualify for palliative care. ____ 2. Some anticonvulsant drugs can be used as an adjuvant treatment for mild pain. ____ 3. Oxygen has shown no benefit in alleviating dyspnea in patients without hypoxemia. Chapter 21. Ethical and Legal Issues of a Caring-Based Practice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. Which statement about the American Nurses Association Code of Ethics is accurate? a. The state’s legal requirements exceed those of the Code of Ethics. b. The primary purpose of the Code is to show physicians that nurses are professional. c. The Code was formulated by physicians for all nurses. d. The Code sets forth the values and ethical principles that guide clinical decisions. ____ 2. Which ethical principle reflects respect for all persons and their self-determination? a. Autonomy b. Beneficence c. Justice d. Veracity ____ 3. When may confidentiality be overridden? a. When personal information is available on the computer b. When a clinician needs to share information with a billing company c. When an insurance company wants to know the results of a breast cancer gene test d. When a patient has a communicable disease ____ 4. In an outpatient setting, what is the most common reason for a malpractice suit? a. Failure to treat a condition b. Failure to diagnose correctly c. Ordering the wrong medication d. Failure to manage care ____ 5. Which type of liability insurance covers only situations in which the incident occurred and the claim was made while the policy was in effect? a. Claims made policy b. Occurrence policy c. An employment coverage policy d. A “tail” policy ____ 6. Which insurance plan was the first to allow members to choose nurse practitioners as their primary care provider and pay them the same rate as physicians for the same care? a. Blue Cross/Blue Shield b. Medicare/Medicaid c. The Oxford Health Plan d. United Health Insurance ____ 7. Constructing a decision tree is helpful in analyzing ethical dilemmas, because a decision tree: a. Shows the best solution b. Explains the ethical principles c. Delineates the legal parameters d. Allows all the options to be considered ____ 8. In the consensus model for Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN) regulation, the “C” of LACE represents? a. Commitment b. Consensus c. Certification d. Collaboration ____ 9. The main mechanism for avoiding a lawsuit involves: a. Good liability insurance b. A collaborating physician c. Good documentation d. Open communication skills ____ 10. Paternalism in health care: a. Assumes the physician knows what is best b. Is never warranted c. Is in effect after an informed consent is signed d. Requires a court order ____ 11. The Nurse Practice Act of each state is responsible for: a. Establishing the legal standards b. Promoting high-quality nursing care c. Protecting the public from unethical nursing practice d. Exceeding the requirements of the Code of Ethics for Nurses ____ 12. Deontology is: a. The greatest amount of happiness or the least amount of harm for the greatest number b. The consideration of consequences and the calculation of benefits c. The belief that the ends justify the means d. The principle of universalizability ____ 13. A situation that requires informed consent involves: a. Therapeutic privilege b. An emergency situation c. Invasive procedures d. The therapeutic use of placebos ____ 14. Which ethical principle is the foundation on which health care rests? a. Autonomy b. Nonmaleficence c. Beneficence d. Justice ____ 15. The Joint Commission mandates that all health-care organizations have: a. A mechanism in place for the consideration of ethical issues b. An Ethics committee c. A resident parish nurse d. Legal counsel who is knowledgeable about ethics ____ 16. The relationship between ethics and law is such that: a. What is ethical is also legal b. What is unethical is also illegal c. Legal actions may be both ethical and unethical d. There is no relationship between the law and ethics ____ 17. An APRN’s scope of practice includes all of the following statements EXCEPT: a. The scope of practice defines the duties and responsibilities of the APRN b. The scope of practice delineates the permissible boundaries of the professional practice c. The scope of practice is defined by statute, rule, or a combination of the two d. Each APRN defines his/her own scope of practice and includes it in their protocol ____ 18. Which board administers and defines advanced nursing practice in all states? a. The Board of Nursing b. The Board of Medicine c. The Board of Pharmacy d. It is different for each state. ____ 19. Three components must be present to establish malpractice. Which one does NOT apply? a. The APRN must be paid for the services in question. b. The provider must have a duty to the patient. c. The standard of care must have been deviated from or breached. d. Harm or damages must have occurred as a result of the duty and a breach of the standards of care. ____ 20. The Institute of Medicine stresses interprofessional collaboration between physicians and APRNs. Which statement supports this? a. The physician supervises the APRN. b. The physician sponsors the APRN. c. There is a collegial relationship between the two providers. d. The physician pays the APRN’s salary. Chapter 22. Business of Advanced Practice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. Identify the primary challenge for insurance carriers in today’s health delivery model. a. Preventing illness b. Screening for disease c. Educating the public d. Reducing health-care spending ____ 2. Medicare benefits were offered to U.S. beneficiaries beginning in 1965. What was the service added with the Medicare D plan in 2006? a. Health-care screening b. Health-care education c. Pharmaceutical coverage d. Durable medical equipment coverage ____ 3. With the growing shortage of primary care physicians, the demand for advanced practice registered nurses (APRNs) will increase between 2014 and 2016 from: a. 5 to 15 million b. 15 to 35 million c. 20 million to 30 million d. 30 million to 40 million ____ 4. Maintaining optimum cash flow is a basic fundamental concept in all businesses. Cash flow is impacted at the initial request for appointment and is affected by practices that include: a. Billing within 15 days of services b. Beneficiary verification of patient c. Timely processing of denials d. Identifying payment below contract rate ____ 5. Patients require insurance counseling prior to accessing health-care services for the following reason: a. Many patients do not understand policy benefits and payment responsibility. b. Services may change across the beneficiary year. c. Copayments and deductibles may have already been met by the patient. d. Coding may need to be adjusted to meet the terms of the patient’s benefits. ____ 6. Health-care billing is a significant reason for bankruptcy in the United States. The following provision of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) legislation was included to reduce this from occurring with insured patients: a. Consumer assistance programs b. Preventative care options standardized c. Young adult coverage (under 26 years) d. Elimination of lifetime limits ____ 7. Accounting keeps track of the financial state of a business. The accounting report that demonstrates the growth in assets is: a. Net income statement b. Balance sheet c. Cash flow statement d. Operating statement ____ 8. Medicare advantage plans, also called Medicare HMO Plans, are plans approved by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) as alternative carriers for Medicare beneficiaries. Which of the following is not a characteristic of these plans? a. Offer additional benefits b. Offer lower copayments c. Follow Medicare benefit rules d. Follow the Commercial Carriers rules ____ 9. Current procedural terminology (CPT) coding offers the uniformed language used for reporting medical services and procedures performed by physician and nonphysician practitioners. Clinicians are paid based on calculated resource costs that, in turn, are based on practice components. Which of the following is a part of the components used to calculate the per CPT code payment rate? a. Clinician education loans b. Clinician practice liability and malpractice expense c. Clinician reported cost reduction efforts d. Clinician volume of patients treated ____ 10. Beginning in 2014, all medical practices will be required by the CMS to adopt a certified electronic medical record software system for documenting and billing for medical services. What is a primary reason for this implementation mandate? a. Allows CMS to audit all medical practices’ performance b. Standardizes the billing rules for all clinicians c. Reduces the duplication of services noted in the current system d. Reduces costs related to multiple billing systems ____ 11. All health-care practices should develop a compliance plan. Compliance plans offer practice safeguards that prevent which of the following? a. Malpractice claims b. Conflict of interest claims c. Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act violations d. Occupational Safety and Health Administration violations ____ 12. Clinicians who learn how to code and document Evaluation and Management and clinician services will be more successful in gaining timely payment for care delivery. Which of the following CMS practices is designed to financially penalize clinicians who do not bill according to CMS guidelines? a. Audits and probes b. Add-on codes c. Modifier codes d. HAC guidelines ____ 13. Each state has criteria defining the level of collaboration required between the APRN and an oversight physician. Which is among the questions an APRN should seek when selecting a practice setting? a. List of practice limitations as an APN b. Standard hourly rate as office staff c. Expectation for net revenue generation d. Standard benefit package offered to office staff ____ 14. Identify one of the primary reasons for an APRN to develop a business plan? a. To monitor monthly actual expense to budgeted expense b. To reduce the likelihood of litigation action c. To identify the marketing needed to grow the APRN practice d. To assure accreditation standards are met ____ 15. Despite the growth in the numbers of advanced practice registered nurses (APRNs) over the last decades, the role of the profession is often not understood by the public. What actions should APRNs undertake to market their services to the public? a. Request that the physician act as an APRN spokesperson. b. Increase articles in nursing professional journals about the APRN role. c. Personally seek out the news media to communicate their value. d. Rely on patients to communicate their benefits to neighbors. Chapter 23. The 15-Minute Hour Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. According to World Health Organization data on 1,500 patients in 15 separate world sites, how many patients presenting with medical/somatic complaint had a psychiatric problem? a. Fully one-third of all patients b. One-quarter of all patients c. One-half of all patients d. 60% of all patients ____ 2. Integrating mental health techniques and approaches, such as the 15-minute hour, into the primary care patient encounter is important for a number of reasons. These include: a. Decreasing the patient’s stress and increasing your reimbursement b. Encouraging coping strategies and increasing professional satisfaction c. Assisting patients in reliving traumatic experiences d. Decreasing care clinician stress ____ 3. Valliant (1979) discusses the “ubiquity of stress.” Ubiquity of stress maintains that: a. In a current and rapidly changing society, stress can be viewed as a positive. b. Eustress is counterproductive. c. The overwhelmed can functionally regress. d. Dream therapy has been found to be an effective treatment of overwhelming stress. ____ 4. Basic human needs are identified as: a. Autonomy and feeling valued by others b. Exhilaration and productivity c. Spirituality d. Career success and material rewards ____ 5. Commonalities among psychotherapeutic techniques include the following: a. Dream therapy, listening, and reflection b. Psychodrama, group psychotherapy, and 12-step programs c. Self-help groups d. Obtaining external perspective and participation in a helping relationship ____ 6. The goals of the 15-minute hour approach include: a. Enhance self-esteem, expand behavioral repertoire, prevent dire consequences, and reestablish premorbid levels of functioning b. Emerge with a higher level of functioning and commitment to long-term psychotherapy c. Accept need for antidepressant therapy and psychiatric referral; share concerns with primary care clinician d. Improve family functioning and sexual performance as well as accept need for antidepressant medication ____ 7. BATHEing the patient refers to: a. A technique used in primary care to get the patient to accept the need for psychological or psychiatric referral b. A technique used to facilitate cultural understanding c. A technique used to perform psychotherapy d. A technique that is a quick screen for psychiatric issues and interventions for psychological problems ____ 8. BATHEing the patient is an advanced practice nursing intervention that allows the practitioner to: a. Develop a therapeutic relationship without “owning” the patient’s problem b. Conduct psychological counseling within the context of the primary care encounter c. Focus on the “process” and not the assessment d. Make the patient and family happier ____ 9. The BATHE technique was developed more than 20 years ago and has been used extensively in primary care and family practice. The new “Positive BATHE” stresses: a. A belief that all things are possible through positive affirmations b. A belief that one should only refer to practitioners who embrace the viewpoint of positive psychology c. Personal accomplishment, thankfulness, autonomy, and general positive effect d. The patient’s problems and concerns ____ 10. Which of the following scenarios best demonstrates the relationship between physical health and distress? a. A patient’s high calorie diet contributes to his diagnosis of type 2 diabetes. b. A patient with an elevated HbA1C reports that he was recently evicted from his home. c. A patient with depression reports an increase in suicidal thoughts. d. A patient reports feeling “numb” after learning her malignant tumor is inoperable. ____ 11. One benefit of BATHEing a patient is that: a. It allows providers an in-depth exploration of patient’s presenting problems. b. It assumes that ambivalence is a normal part of the change process. c. It utilizes the therapeutic relationship to help patients in a time-sensitive approach. d. It can be done only with extensive training in therapeutic technique. ____ 12. One benefit of motivational interviewing (MI) is: a. It assumes that ambivalence is a normal part of the change process. b. It can be utilized during routine office visits. c. It is a therapeutic technique which is not necessarily time intensive. d. All are benefits of MI. ____ 13. Which is not a basic principle of MI? a. People often continue behaviors with negative consequences for reasons unknown to the provider. b. The patient is the expert on his/her behavior. c. Providers are obligated to inform each patient of the negative consequences of their behaviors. d. Helping patients understand ambivalence for change is often more powerful than direct instruction. ____ 14. The primary purpose of the “Positive BATHE” is intended to help patients by: a. Focusing on autonomy and accomplishment b. Creating a stronger therapeutic alliance c. Helping the patient change negative behaviors d. Engaging the patient during the psychosocial assessment Chapter 24. Putting Caring into Practice: Caring for Self Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. The World Health Organization defines self-care as: a. An important global activity for all health-care providers b. A set of deliberate actions that all individuals, families, and communities should engage in to maintain good health c. Essential to efficacious advanced practice nursing (APRN) practice d. An awareness by the APRN of their self-care behaviors as related to diet, activity, and mental attitude ____ 2. Nurse theorist Dorothea Orem defines self-care activities as: a. Attainment of professional self-development goals b. Ability to persevere through hardship c. Striving to attain balance and harmony in one’s life d. Comprising activities that are performed independently by an individual to promote and maintain well-being throughout life ____ 3. Self-care and personal development are built into the standards of practice of: a. The American Holistic Nurses Association b. The American Nurses Association c. The American Association of Nurse Practitioners d. The American Academy of Nursing ____ 4. There are many pressures inherent in primary care practice today for APRNs. These pressures include all of the following: a. Electronic medical record, the Affordable Care Act, and the implementation of socialized medicine b. Patient care outcomes being tied to reimbursement, role diffusion with physicians and physician assistants c. Uncertainty, the team approach to care, and the need for patient-centered care d. Availability of medical information on the internet, educational programs for patients, and Medicare drug benefits ____ 5. A new era of health care leads to: a. Greater opportunity for independent practice, yet increased legal risk in accountability for patients b. Lowered reimbursement for all health-care services and providers c. Decrease in status for health-care providers d. No ability to individualize care ____ 6. Compassion fatigue is another side-effect of today’s health-care delivery system. This term means: a. The APRN feels sudden guilt and distress when he or she cannot rescue or save an individual, such as when bad health habits persist despite the best efforts of the APRN. b. This happens over time related to the need to see increasing numbers of patients in busy primary care practices. c. This may persist over time, even when the APRN transfers to a new and different setting. d. Patients’ problems and circumstances can be so overwhelming that the APRN needs to set severe boundaries to maintain safe function. ____ 7. Another term used, burn out, is differentiated by: a. Numbness of feelings leading to substance abuse b. How novice APRNs feel at the end of the day in primary care c. Feelings of aloneness, desperation, and despair d. A gradual response to the inability to achieve one’s goals with patients in the work setting; it is characterized by frustration and diminishing morale ____ 8. The following statement is true: a. APRNs are often sensitive to patients’ deficiencies but not their own. b. APRNs always respond appropriately to patients, families, and team members. c. APRNs are well-equipped from their APRN educational programs to care for self. d. Relicensure in some states mandates continuing education units in self-care. ____ 9. Self-compassion is the ability to be compassionate to one’s self and is positively correlated with emotional intelligence. Emotional intelligence is defined as: a. Being highly attuned to the needs of others b. The ability to engage in self-care c. Being aware of self, having the capacity to self-regulate, possessing motivation, empathy, and social skills d. The holistic integration of self-care and self-development practices ____ 10. APRNs need to develop their own self-management plans. Two key elements of self-management plans are: a. Taking vacations and keeping up with new knowledge and developments in medicine b. Resilience and positive intentionality c. Family support and a healthy diet d. Being physically and emotionally “fit” ____ 11. The term resilience implies: a. Ability to look to a higher power to get you through a crisis b. Response to difficult and adverse circumstances through positively adjusting to stressors c. That the APRN can weather any emergency d. Learning to set appropriate boundaries ____ 12. Qualities associated with resilience include: a. Hope, self-efficacy, and optimism b. Stick-to-it-ness, belief in a higher power c. Education, self-regulation, and use of activity to decrease stress d. Ability to take vacations and the availability of support systems and a secure work environment ____ 13. Patsy, a 42-year-old experienced APRN, is orienting a new APRN to the Minute Clinic, where she has worked for more than 5 years. Patsy loves her work and was concerned when the new APRN, Sue, expressed her dissatisfaction with this setting. “I hate the idea of being here on my own, with no back-up and support after orientation” was one of Sue’s concerns. Sue confessed that this was the only job she could find. Patsy felt good in her independent role and felt she had worked to create a positive atmosphere for her patients at all times. She derived joy and satisfaction from her ability to do this for her patients. Patsy found Sue’s endless complaints debilitating. Patsy demonstrated resiliency by using which of the following strategies? a. Patsy distanced Sue by listening to her as little as possible. b. Patsy openly shared her positive feelings about the work environment and took a risk by sharing with Sue that she found her endless complaining draining. c. Patsy spoke privately with their supervisor, Pamela, stating that she did not think Sue could be successful in this environment. d. Patsy requested that Sue be assigned to a different APRN for orientation. ____ 14. The qualities of resilience that Patsy demonstrated when responding to Sue include: a. Protecting her own positive attitude by lessening her contact with Sue, a negative person b. The ego strength to admit failure in her ability to orient Sue, a destructive person c. Protecting her organization by sharing Sue’s deficiencies with their supervisor d. Asserting her positive approach and basic optimism by initiating an honest discussion with Sue and having the emotional insight to recognize Sue’s negative effect on her ____ 15. According to nurse theorist Jean Watson, a focus on positive intentionality—holding caring thoughts, loving kindness, and open receptivity—enhances caring energy, which leads to healing. How can the APRN bring this to their practice? a. Spiritual readings, centering oneself before patient encounters, engaging in behaviors that help build positive energy b. Review of materials on primary care before going into the work environment to increase one’s confidence, leading to caring energy c. Travel to sacred places d. Helping the poor and homeless—volunteering at a domestic violence shelter, for example—in addition to one’s regular practice [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 110 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Aug 15, 2021
Number of pages
110
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Aug 15, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
41


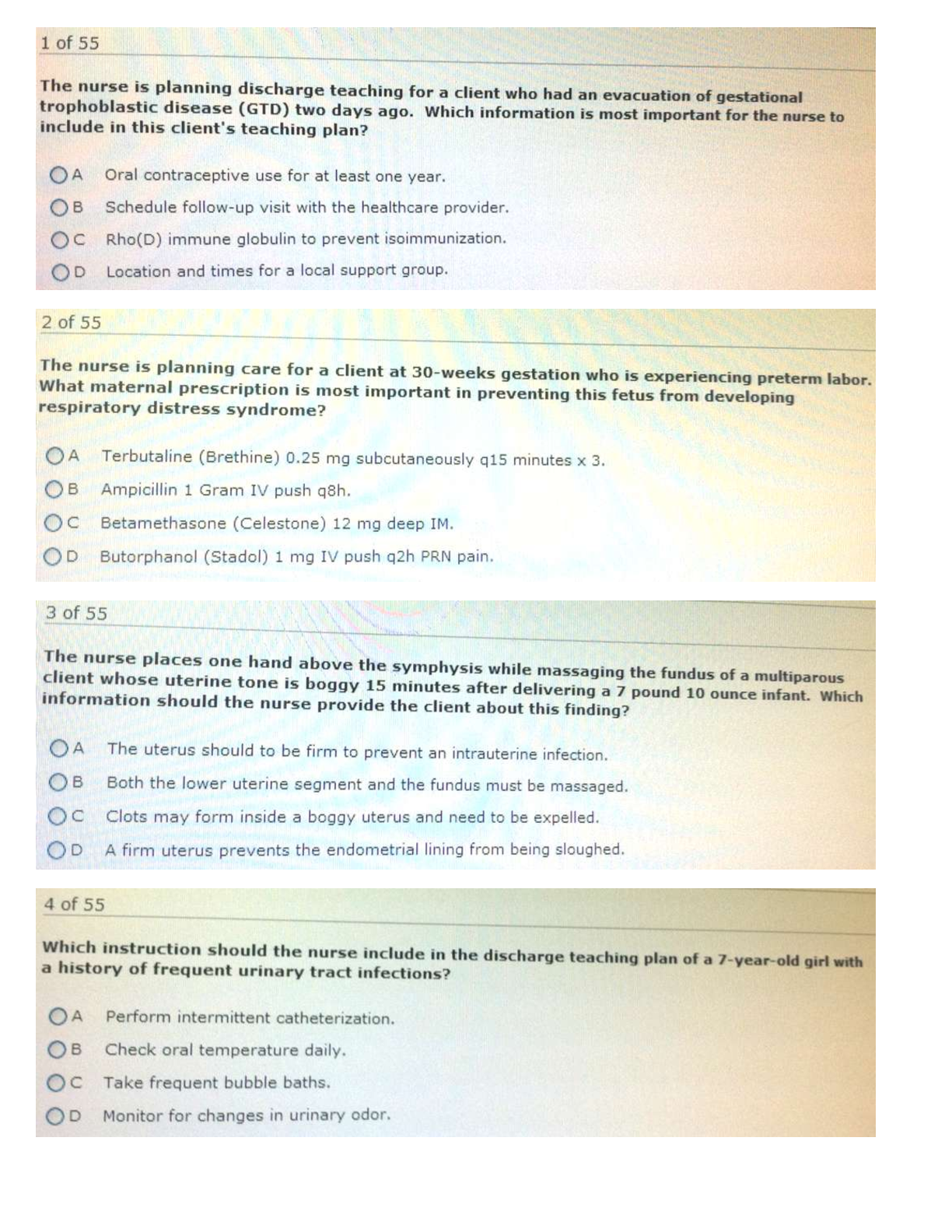


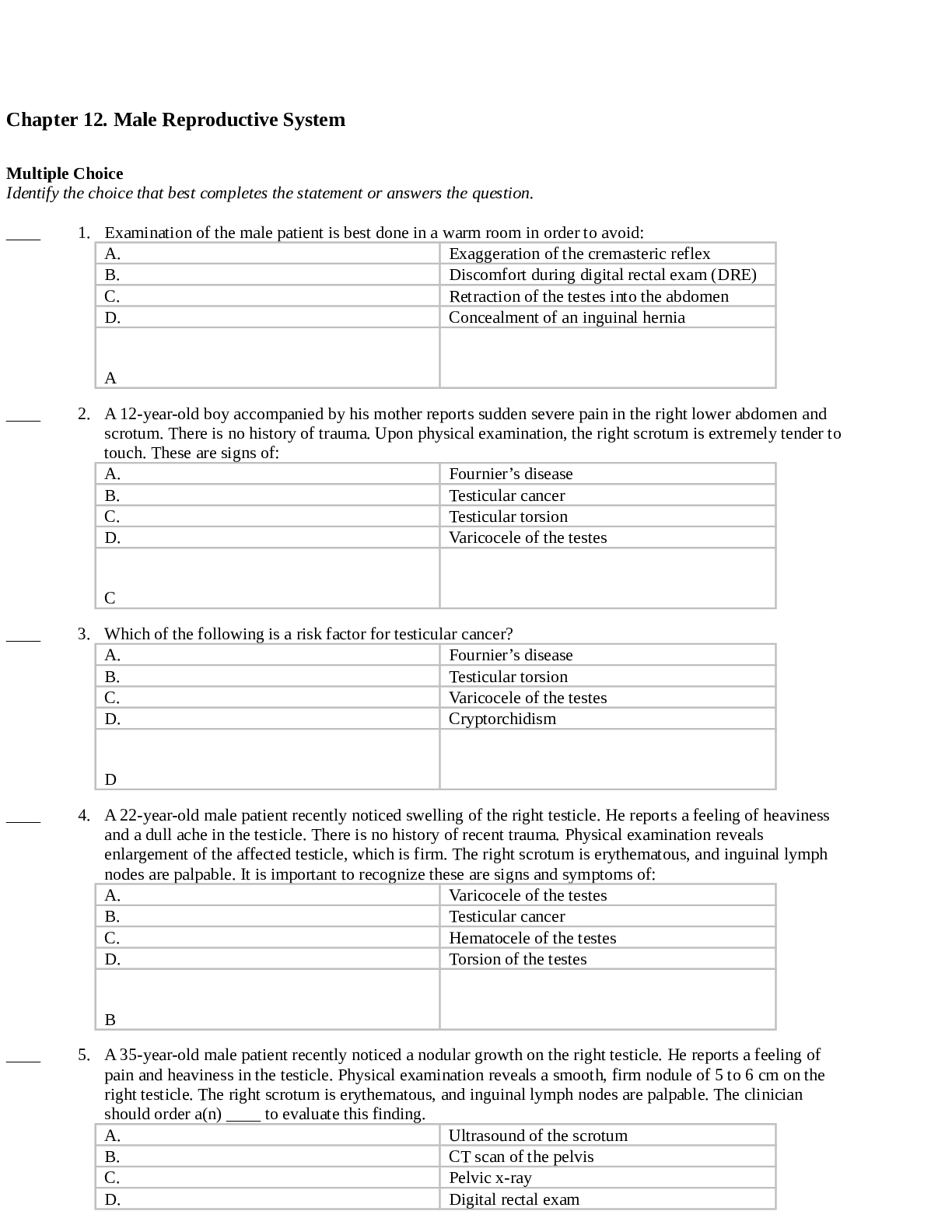





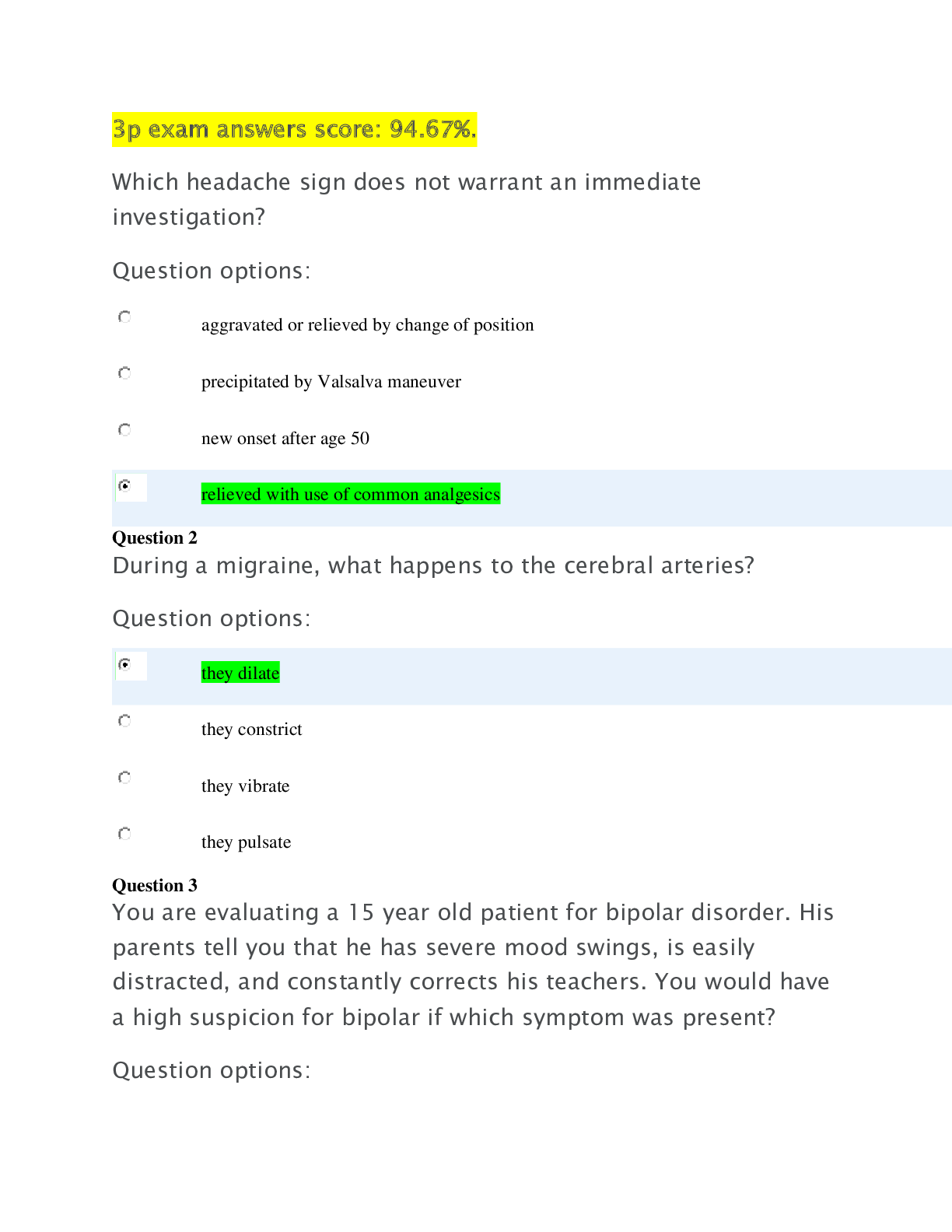

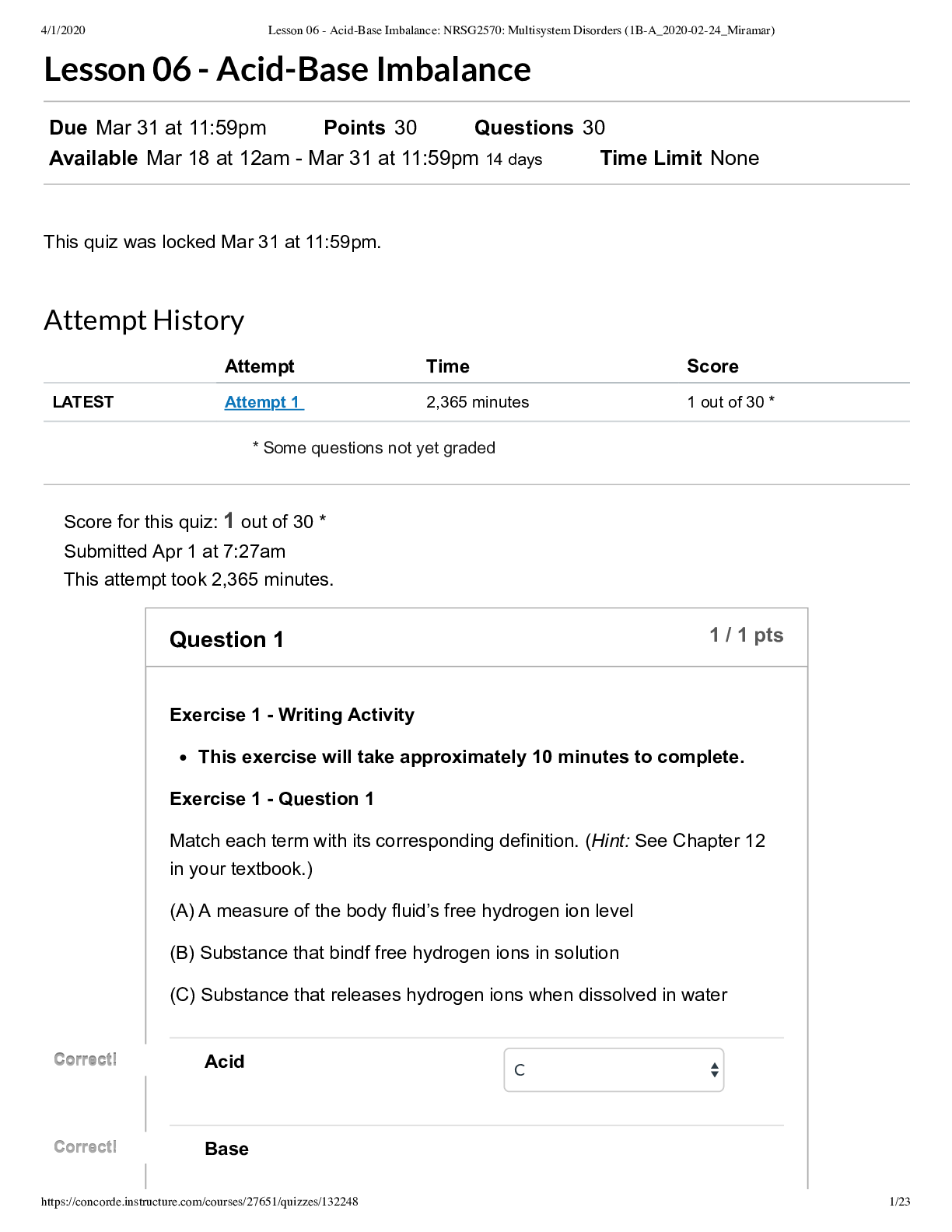







.png)


 AANP-FNP LIGHTNING ROUND REVIEW-2.png)







 LATEST VERIFIED GUIDE FOR EXAM PREPARATION, Graded A.png)


