*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > NUR 326: ADULT ATI |LABS|complete solution guide, University of Alabama, Birmingham (All)
NUR 326: ADULT ATI |LABS|complete solution guide, University of Alabama, Birmingham
Document Content and Description Below
LABS - ICP 10-15 - IOP 10-21 - pH: 7.35- 7.45 - PaO2: 80-100 - PaCO2: 35-45 - HCO: 21-28 - SaO2: 95-100% - CK-MB: Should be 0%. Elevated for 2-3 days - Troponin I: < 0.03 ng/L. Elevated... for 7-10 days (1 week) - Troponin T: < 0.1 ng/L. elevated for 10-14 days (2 weeks) - Myoglobin: Should be < 90 mcg/L. Elevated for 24 hours - CVP: 2-6 mmHg (> HF) - PAWP: 6-15 (>HF) - CO: 3-6 L/min or 4-8 - Total cholesterol <200 mg/dL - HDL> 55 mg/dL (women); > 45 (men) - LDL < 130 mg/dL - Triglycerides: between 35-135 mg/dL (women), between 40-160 mg/dL (men) - Action for Hearing Loss HA meds Management of Enoxaparin for PE PE interventions TRAVELING LABS FOR RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS BLOOD & BLOOD PRODUCTS - Document pt’s response - All rxns: o Stop infusion o Initiate 0.9% sodium chloride using new tubing Acute hemolytic Febrile Allergic Bacterial PICC LINE TEACHING Primary action for Central Venous Access Device dressing change NTG TEACHING Priority finding for CP: can radiate to shoulder or arm, or present as jaw pain described as crushing or aching pressure tPA admin: give within 3- 4.5 hours of ischemic stroke s/s unless CI by presence of active bleeding TIA s/s slurred speech, numbness, weak extremity, dizziness, visual disturbances (loss of vision in one eye, diplopia), vertigo, transient hemiparesis TPN TRANSVERSE COLOSTOMY DYSRHYTMIAS GO OVER RHYTMS (1ST DEGREE HB, A-FIB***) TX PACING CARDIOVERSION DEFIB - Stable V-tach: IV therapy (amiodarone, procainamide) PANCREATITIS LABS “ S/S OF PERITONITIS TEACHING AFTER GLOSSECTOMY WATER SEAL TEACHING RADIATION EFFECTS Care for pt receiving radiation RENAL CALCULI DIET DEBRIDMENT Mechanical Hydrotherapy Enzymatic - - PRIMARY CARE FOR DKA HIV/AIDS IMMUNIZATION RECOMMENDATIONS SIADH S/S ASSESSING FISTULA presence of bruit, palpable thrill, distal pulses & circulation INTERVENTIONS FOR WOUND DEHISENCE/ DISRUPTION TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION assess for latex allergy HYPOKALEMIA PRIORITY ASSESSMENT respiratory status HF teaching FUROSEMIDE: ingest foods & drinks high in K to counter effects of hypokalemia ABGS nterpreting labs for pt. vomiting MONITORING NEURO STATUS PRIORITY ACTION DURING RESUSCIATION PHASE MENINGITIS MANAGEMENT & s/s S/S PT. TEACHING ABOUT THYROID STORM Raynaud’s S/S Head injury DI interventions AE following Epi admin Lisinopril AE angioedema, skin rash, hypotension, dry cough Valsartan Malnutrition s/s Left sided Cardiac catheterization teaching Hypocalcemia s/s - Decreased HR Pacemaker teaching Monitoring pt. permanent rhythm NERVOUS SYTEM CEREBRAL ANGIOGRAM EEG GSC ICP MONITORING - Allows for visualization of cerebral blood vessels - Catheter is placed into an artery (usually the groin) & threaded up to the blood vessels in the brain, dye is injected, X-rays are taken PRE - NPO 4-6 hrs - Asses for allergies to iodine/shellfish - Assess kidney function (BUN, creatinine) POST - Check insertion for bleeding - Check extremity distal to puncture site (pulses, cap refill, temp. & color) - Analyzes electrical activity in the brain - Identifies seizure activity, sleep disorders & behavioral changes - Electrodes are placed on the scalp - Takes 1 hr PRE - wash hair priorw/ no products - arrive sleep deprived increases seizures - no NPO is needed - avoid stimulants, sedative meds 12-24 hrs - education: flashing lights may be used or the pt. may be instructed to hyperventilate increases electrical activity - scores between 3 & 15 - <8= severe head injury - 9-12= moderate head injury Eye opening (4) 4. Spontaneously 3. In response to voice 2. In response to pain 1. No eye opening Verbal response (5) 5. Coherent/ oriented 4. Incoherent/ disoriented 3. Inappropriate words 2. Sounds, no words 1. No vocalization Motor response (6) 6. Follows commands 5. Local reaction to pain 4. General withdrawal to pain 3. Decorticate posture 2. Decerebrate posture 1. No motor response - Device is inserted into cranial cavity to measure pressure - Huge infection risk - Pt w GSC score <8 s/s of increased ICP - Irritability (early sign) - Widened pulse pressure - Restlessness - Ha - Decreased LOC - Pupil abnormalities - Abnormal breathing (Cheyne strokes deep shallow breaths followed by apnea - Abnormal posturing Normal range: 10-15 LUMBAR PUNCTURE MRI - CSF sample is taken from spinal canal - Used to dx MS, syphilis, meningitis, infection in CSF PRE - Void - Position in cannonball position on their side stretch over table while sitting POST - Lay flat for hours - If dura puncture site doesn’t heal CSF leak ha - Admin meds & increase fluids - Epidural patch can seal off hole - Asses allergy for shellfish/iodine - Assess for hx of claustrophobia - Remove all jewelry - Assess for metal implants pacemaker, orthopedic joints, artificial heart valves, IUDs, aneurysm clips, internal defibrillators - Earplugs can be used PAIN MENINGITIS SEIZURES PARKINSON’S Nociceptive - Damage/ inflammation of tissues (not part of CNS) - Throbbing, aching & localized - Somatic: bones/joints, muscle, connective tissue - Visceral: internal organs - Cutaneous: skin, sub Q tissue Neuropathic - Damaged nerves - Shooting, burning, ‘pins & needles - Antidepressants, muscle relaxants Non-opioid - Mild to moderate pain - Acetaminophen do not exceed 4g/day - Monitor for salicylism w aspirin (tinnitus, vertigo) - Admin w food - Risk for bleeding w/ long term use Opioid - Moderate to severe pain - Constipation, hypotensin, urinary retention, n/v, sedation, respiratory depression - Antidote: naloxone - Admin around the clock - Inflammation of meninges (around spinal cord & brain) - Bacterial is contagious w/ high mortality rate - Prevention: immunizations; Hib for infants; MCV4 for college students in dorm S/S - Nuchal (neck) rigidity - + Kernig’s & Brudzinski sign - Photophobia - Ha - n/v DX - Bacterial: cloudy CSF, dec. glucose content - Viral: clear CSF - Both: elevated WBC & protein MANAGEMENT - Droplet precautions until abx. For 24 hrs - Quiet room, low light, HOB 30 degrees, monitor for inc. ICP, avoid coughing, sneezing, implement seizure precautions - Abx, anticonvulsants (phenytoin) - Uncontrolled electrical discharge neurons - Epilepsy= chronic seizures (2 or more) RFs - Fever, Cerebral edema, Infection, Toxin exposure, Brain tumor, Hypoxia, ETOH/ drug withdrawal, f/e imbalance triggers - stress - fatigue - caffeine - flashing lights DX: EEG TONIC CLONIC preceded by aura. 3 phases: - Tonic: stiffening of muscles, LOC - Clonic: 1-2 min of rhythmic jerking of extremities - Postictal: confusion, sleepiness ABSENCE - Decreased LOC for a few sec - Blank starring, eye fluttering, lip smacking, picking @ clothes MYOCLONIC - brief stiffening of extremities ATONIC: - loss of muscle tone falling STATUS EPILEPTICUS: - Repeated seizure within 30 min or single seizure lasting > 5 min DURING - Protect the head - Turn pt on side - Loosen restrictive clothes - Do not insert airway or restrain pt - Document onset & duration POST - Check VS, neuro checks, reorient pt. seizure precautions, determine trigger - Phenytoin Sx: vagal nerve stimulator, craniotomy to remove brain tissue causing seizures - Degeneration of substantia nigra little dopamine, lotta acetylcholine S/S - Tremor - Muscle rigidity - Slow/ shuffling gait - Bradykinesia - Masklike expression - Drooling - Difficulty swallowing MANAGEMENT - Monitor swallowing/ food intake, thicken food - Sit pt upright - Have suction available - Encourage ROM & exercise, assist w/ ADLs - Levodopa/ carbidopa (increases dopamine), benztropine (dec. acetylcholine) ALZHEIMER’S DZ MULITPLE SCLEROSIS ALS MG - Non-reversible dementia memory loss, problems w judgment & changes in personality Stages 1. No impairment 2. Forgetfulness, no memory probs - Limit choices, do not re-orient 3. Mild cognitive deficits, short-term memory loss noticeable to family 4. Personality changes, obvious memory loss 5. Assistance w/ ADLS 6. Incontinence, wandering 7. Impaired swelling, ataxia, no ability to speak MANAGEMENT - Provide short direction, repetition - Avoid overstimulation - Use single-day calendar - Provide frequent reorientation - Maintain toileting schedule SAFETY - Remove scatter rugs - Install door locks - Good lighting (stairs) - Mark step edges w/ colored tape, remove clutter - Donepezil (prevent Ach breakdown - Autoimmune dz where plaque develops in white matter of CNS - Onset is 20-40 yrs, more common in women - Characterized by periods of relapsing & remitting Triggers: - temperature extremes - stress/injury - pregnancy - fatigue S/S: - eye probs (diplopia/nystagmus) - muscle spasticity & weakness - bowel/bladder dysfunction - cognitive changes - ear probs (tinnitus/ hearing issues) - dysphagia - fatigue - degenerative neuro dz of upper & lower motor neurons progressive paralysis respiratory paralysis within 3-5 years - cognitive function not impacted - no cure S/S - muscle weakness of distal extremities - atrophy MANAGEMENT - Maintain patent airway - Suction/intubate as needed - Monitor for pneumonia, respiratory failure - Meds: Riluzole slows deterioration of motor neurons extend pts life 2-3 mo. - Autoimmune dz severe muscle weakness - Caused by antibodies that interfere w Ach @neuromuscular junction (NMJ) - Characterized by periods of exacerbation & remission - Associated w/ thymus hyperplasia S/S - Drooping eyelids - Incontinence - Muscle weakness (worse w/ activity) - Diplopia - Dysphagia - Impaired respiration DX - Admin edrophonium, increases ACH @NMJ - If s/s improve MG - If s/s do not improve cholinergic crisis (atropine) MANAGEMENT - Maintain patent airway - Risk for aspiration have oral-nasal suction @bedside - Encourage periods of rest - Provide small/ frequent high calorie meals sit upright, thicken liquids - Admin lubricating eye drops, tape eyes shut @ night (prevent damage to the cornea) - Meds: anticholinesterase agents (pyridostigmine or neostigmine) SX - Plasmapheresis: removes antibodies from plasma - Thymectomy: removal of thymus HEADACHES MACULAR DEGENERATION GLAUCOMA MENIERE’S DZ MIGRAINE RFs - Allergies, Bright lights, Fatigue, stress, anxiety, menstrual cycles, MSG, tyramine, nitrites S/S - Photophobia - n/v - unilateral pain (behind one eye/ear) - w/ or w/o aura (visual disturbances, numbness/tingling) - pain persists 4-72 hrs MANAGEMENT - cool/dark/quiet environment - avoid triggering foods - reduce stress levels - meds: NSAIDS (mild), antiemetics (n/v), sumatriptan or ergotamine (severe) CLUSTER S/S - severe, unilateral, non-throbbing pain forehead, temple, cheek - lasts 30 min- 2 hrs. occurs at same time 4-12 weeks - more frequent in fall/spring - more common in men 20-50 yrs - facial sweating - nasal congestion meds: sumatriptan, ergotamine - Central loss of vision - # cause of vision >60 yrs old - No cure S/S - Blurred vision - Loss of central vision - Blindness CATARACTS - Opacity in lens of eye, impairing vision S/S - Decreased visual acuity - Progressive/ painless loss of vision - Diplopia - Halo around lights - Photosensitivity - Absent red reflex POST SX - Wear sunglasses - Avoid increasing IOP don’t bend over @ waist, avoid sneezing/coughing/straining, hyperflexion of head & restrictive clothes, tilting head back to wash hair, limit housework & rapid/ jerky movements - Best vision occurs 4-6 wks after sx - Increase in IOP due to issue w/ optic nerve - Leading cause of blindness OPEN ANGLE - Most common - Aqueous humor outflow decreased gradual increase in IOP S/S - Loss of peripheral vision - Mild eye pain CLOSED-ANGLE - Angle between iris & sclera closes completely sudden increase of IOP S/S - Severe pain - Halos around lights - N IOP: 10-21; measured using tonometry; measure drainage angle w/ gonioscopy Meds - Pilocarpine: constricts pupil - BBs (timolol): reduces aqueous humor production - Mannitol: osmotic diuretic for CAG quickly reduces IOP Eye drop education: - admin 1 drop in each eye 2x/day; wait 5-10 between each eye; do not touch eye w/ applicator; Place pressure on lacrimal ducts POST SX - Wear sunglasses - Avoid increasing IOP don’t bend over @ waist, avoid sneezing/coughing/straining, hyperflexion of head & restrictive clothes, tilting head back to wash hair, limit housework & rapid/ jerky movements - Inner ear dz S/S - Tinnitus - Unilateral sensorineural hearing loss - Vertigo - Vomiting - Balance issues RFs - Viral/bacterial infections - Ototoxic Otoscopic exam - Adults: auricle up & back - Children: auricle down & back - Tympanic membrane should be pearly gray & intact - Light reflex should be @5 for right ear, @7 for left ear EDUCATION - Avoid caffeine & ETOH - Rest in quiet/dark place when experiencing vertigo - Space intake of fluids, dec. Na - Avoid sudden movements SX: stapedectomy, cochlear implant, labyrinthectomy Meds: antihistamines, anticholinergics watch for s/s of urinary retention & sedation HEAD INJURY STROKE/CEREBROVASCULAR ACCCIDENT STROKE: LEFT/RIGHT CEREBRAL HEMISPHERE SCI - 1st priority: stabilize cervical spine S/S - Irritability (early sign) - Cushing’s triad: severe HTN, widening pulse pressure, bradycardia) - Ha - Decreased LOC - Pupil abnormalities INTERVENTIONS TO DEC. ICP - Reduce hypercarbia (hyperventilate pts) - Avoid suctioning - Maintain HOB > 30 degrees - Avoid coughing, blowing nose, extreme neck flexion/ extension, restrictive clothing MEDS - Mannitol: osmotic diuretic to tx cerebral edema - Pentobarbital: induces coma, dec. metabolic demands - Phenytoin: prevents/ tx seizures - Morphine: tx pain SX - Craniotomy to remove nonviable brain tissue (infection, death) semi-fowler’s position CX - Intracranial hemorrhage - Hematoma - SIADH - Brain herniation (downward shift of brain tissue r/t cerebral edema) S/S: - fixed dilated pupils - decreased LOC - abnormal respiration & posturing 1. hemorrhagic - ruptured artery/ aneurysm 2. thrombotic - blood clot in cerebral artery 3. embolic: - blood clot from other part of the body that travels to cerebral artery RFs - Smoking - HTN - Diabetes - AFIB - Hyperlipemia S/S - Visual disturbances - Dizziness - Slurred speech - Weak extremity MANAGEMENT - SBP>180, DBP >110 ischemic stroke - Asses swallowing & gag reflex before clearing to eat - Thicken liquids - Teach pt to swallow w/ head & neck flexed forward - Reposition frequently to prevent pressure injuries - Use scanning technique (turn head from direction of unaffected side to affected side) for homonymous hemianopsia LEFT - Language & math skills - Analytical thinking S/S - Expressive aphasia (inability to speak & understand language) - Reading & writing difficulty - Right sided hemiparesis (weakness) or hemiplegia RIGHT - Visual & spatial awareness S/S - Poor judgement & impulse control - Overstimulation of abilities - One-sided neglect syndrome (ignore left side of body) - Left-sided hemiparesis or hemiplegia MEDS - Anticoags, antiplatelets, thrombolytics (give within 4.5 hrs of initial s/s) SX: carotid artery angioplasty w/ stenting Paraplegia - Injuries below T1 paralysis/ paresis of lower extremities Quadriplegia - Injurie in cervical region paralysis/paresis of all 4 extremities Neurogenic shock - Occurs after SCI for several days-weeks S/S - Hypotension - Dependent edema - Temperature regulation issues Upper motor neuro injuries (above L1/L2) - Spastic muscle tone, spastic neurogenic bladder Lower motor neuron injuries below L1/L2) - Flaccid muscle tone, flaccid neurogenic bladder MEDS - Glucocorticoids (reduces SC edema) - Vasopressors (tx hypotension during neurogenic shock) - Muscle relaxers (baclofen, dantrolene) - Stool softener Autonomic dysreflexia - Injuries above T6 - Stimulation SNS w/ inadequate response from PNS S/S - Extreme HTN - Severe ha - Blurred vision - Diaphoresis MANAGEMENT - Determine cause (distended bladder, fecal impaction, tight clothing, undiagnosed injury) - Tx cause - Admin antihypertensives RESPIRATORY ABGS BRONCHOSCOPY THORACENTESIS CHEST TUBE pH: 7.35- 7.45 PaO2: 80-100 PaCO2: 35-45 HCO: 21-28 SaO2: 95-100% - Perform Allen’s test prior to puncture (compresses ulnar & radial arteries simultaneously) - Hold direct pressure over the site for at least 5 min afterwards (20 min if pt. on anti-coagulants) - If air embolism suspected, place pt. on left side in Trendelenburg position - Allows for visualization of airway (larynx, trachea, bronchi) biopsies, aspiration of deep sputum or excision of lesions PRE - NPO 4-8 hrs - Admin meds (atropine, anti-anxiety, viscous lidocaine) POST - ensure pts. LOC & presence of gag reflex before allowing pt. to eat/ drink - sore/dry throat & small amount of blood-tinged sputum is expected - surgical procedure of chest wall & pleural space w/ a large-bore needle to obtain specimens, inject medication or remove fluid/air S/S - chest pain - SOB - cough Management - have pt. sit upright w/ arms supported on pillows or overbed table - have pt. remain still - amount of fluid removed should not exceed 1L (to prevent CV collapse) - after closely monitor respiratory status CX - mediastinal shift - bleeding - infection - pneumothorax deviated trachea, pain on affected side, unequal movement of chest during inhalation/exhalation, air hunger, tachycardia, shallow respirations) - drains fluid, air or blood from pleural space - chest tube tip positioned UP for pneumothorax & DOWN for hemothorax or pleural effusion drainage collection chamber - chart amount & color of drainage - report drainage >70 ml/hr water seal chamber - add sterile fluid up to 2 cm line, check q 2 hr - chamber must be kept upright & below chest tube insertion site - tidaling expected - lack of tidaling= lung re-expansion or obstruction - continuous bubbling indicates air leak suction control chamber - -20 cm H20 common - Continuous bubbling expected MANAGEMENT - Asses site for erythema, pain, crepitus - Position in semi/high fowler’s position - Obtain x-ray to verify - Keep 2 hemostats, sterile water, occlusive dressing at bedside - Only clamp when ordered; do not strip; milk tubing REMOVAL - Tell pt. to take deep breath, exhale & bear down (or take deep breath & hold it) during removal - Apply sterile petroleum jelly gauze dressing over site CX - If drainage system becomes compromised, place end of tube into sterile water to maintain seal - If chest tube is accidentally removed, place occlusive dressing over insertion site- tape on 3 SIDES - Tension pneumothorax: can result from kink in tubing or obstruction tracheal deviation, absent breath sounds on affected side, respiratory distress, asymmetry of chest O2 DELIVERY MECHANICAL VENTILATION PNEUMONIA ASTHMA Nasal canula - 1-6 L/min - Use humidification for flow rate> 4L/min Simple face mask - 5-8 L/min Partial rebreather mask - 6-11 L/min - Adjust O2 flow to keep reservoir bag from deflating Nonrebreather mask - 10-15 L/min - Keep reservoir bag 2/3 full - Asses valve, flap hourly Venturi - 4-10 L/min - Most precise O2 delivery Aerosol mask/ face tent - Good for pts. w/ facial trauma or burns - Provides high humidification HYPOXEMIA Early - restlessness/irritability - tachypnea - tachycardia - pale skin - HTN - Nasal flaring - Use of accessory muscles - Adventitious lung sounds Late - Confusion - Cyanosis - Bradypnea - Bradycardia - Hypotension - Dysrhythmias TOXICITY - Non-productive cough - Substernal pain - Nasal congestion - n/v - fatigue - ha - sore throat AVOIDING COMBUSTION - post ‘no smoking’ signs - avoid synthetic or wool fabrics - do not use flammable materials (ETOH, acetone) Low pressure alarm - disconnection, cuff leak, or tube displacement High pressure alarm - excess secretions, pt. biting tube, kinks, coughing, pulmonary edema, bronchospasm, pneumothorax MANAGEMENT - suction oral & tracheal secretion - reposition ET tube q 24 hrs - monitor for skin breakdown - provide frequent oral care - have manual resuscitation bag & reintubation equipment at bedside - encourage coughing, deep breathing, use of incentive spirometer, frequent position changes to mobilize secretions S/S - fever - SOB - Chest pain - Cough - Dyspnea - Confusion (in older pts.) - Crackles/wheezes Labs - Obtain sputum sample BEFORE ABX DX - Chest x-ray (shows consolidation) Management - Position pt in high fowlers - Admin O2 as prescribed - Encourage coughing, deep breathing, use of incentive spirometer, increased fluid intake Meds - Abx, bronchodilators (albuterol), anti-inflammatories (glucocorticosteroids) - Chronic inflammatory disorder of the airway; intermittent & reversible S/S - Wheezing - Coughing - Prolonged exhalation - Low SaO2 - Barrel chest - Use of accessory muscles DX - PFTs (FVC, FEV1) Meds - Bronchodilators (short acting: albuterol, long acting: salmeterol) - anticholinergic meds (ipratropium) - anti-inflammatories (corticosteroids) Status asthmaticus - Airway obstruction unresponsive to typical tx - Admin O2, bronchodilators, epinephrine - Prepare for emergency intubation COPD TUBERCULOSIS PULMONARY EMBOLISM RESPIRATORY EMERGENCIES - Emphysema (loss of lung elasticity & hyperinflation of lung tissues) & chronic bronchitis (inflammation of bronchi) - Irreversible - Smoking is primary RF S/S - Dyspnea upon exertion - Crackles/ wheezes - Barrel chest - Use of accessory muscles - Clubbing - Hyperresonance (due to trapped air) - Decreased SaO2 levels - Rapid & shallow respirations - Early satiety LABS - Increased HCT (due to low O2 levels) - PaO2 < 80 - PaCO2 >45 - Respiratory acidosis MANAGEMENT - Position pt. in high fowlers - Encourage coughing, deep breathing, use of incentive spirometer - Ensure proper nutrition (increased calories & protein) Breathing techniques: - Abdominal breathing: take breaths from diaphragm, lie on back w/ knees bent - Pursed lip breathing: breathe in through nose and out through mouth MEDS - Bronchodilators - Anti-inflammatories - Mucolytic agents (acetylcysteine, guaifenesin) CX - Right sided HF dependent edema, distended neck veins, enlarged liver - Infectious dz in lungs caused by Mycobacterium - Tuberculosis S/S - Cough lasting > 3 weeks - night sweats - purulent/ bloody sputum - lethargy - wt. loss DX - Quantiferon gold (blood test) - Mantoux test (skin test) = read within 48-72 hrs. Induration 10 mm= positive result (5 mm for immunocompromised pts.) Those who had the BCG vaccine may get false + result - Chest x-ray: to visualize active lesions in lungs - Acid-fast bacilli culture: use 3 early morning sputum samples MANAGEMENT - Place pt in – air low room - Wear N95 mask in room - Have pt wear N95 mask if they need to leave room - Screen family members for TB - Teach pt. that sputum samples will be needed q 2-4 wks - Pts. Are not infectious after 3 -sputum cultures MEDS - Up to 4 abx are required for 6-12 mo of tx isoniazid, rifampin, pyrazinamide, ethambutol - Life threatening blockage in pulmonary vasculature, most commonly caused by DVT RFs - Immobility - Oral contraceptives - Smoking - Obesity - Sx - AFIB - Long-bone fractures S/S - Anxiety (feelings of doom) - Pain on inspiration - Dyspnea - Pleural friction rub - Tachycardia - Hypotension - Tachypnea - Petechiae - Diaphoresis DX - CT scan - Elevated D-dimer: presence of clot MEDS - Anticoagulants (heparin/enoxaparin, warfarin), thrombolytic therapy (alteplase, streptokinase) SX - Embolectomy (removal of clot) - Vena cava iter (prevents new emboli from entering pulmonary vasculature) MANAGEMENT - Frequent blood draws required to monitor PT/ INR levels (TE= 2-3) - Maintain consistent intake of Vitamin K while on warfarin - Encourage smoking cessation, increased mobility, compression stockings - Reduce risk of bleeding (no aspirin, use electrical shavers, soft toothbrushes, avoid blowing nose) Pneumothorax - Lung collapse due to air in the pleural space - s/s: hyperresonance w/ percussion Tension pneumothorax: - air enters pleural space during inspiration, but cannot exit during expiration - s/s: tracheal deviation Hemothorax - blood accumulates in pleural space - s/s: dull percussion Flail chest - chest wall expansion limited due to multiple fractured ribs - s/s: paradoxical chest wall movement COMMON S/S FOR ALL - respiratory distress - reduced/ absent breath sounds on affected side TX - O2 - Meds (benzodiazepines for anxiety, opioids for pain) - Chest tube (for pneumothorax & hemothorax) CARDIOVASCULAR CARDIAC ENZYMES Cholesterol levels Hemodynamic monitoring CORONARY ANGIOGRAM (cardiac cath) - Released in bloodstream in response to ischemia in heart muscle. Troponin T is most specific - CK-MB: more specific to heart than CK. Should be 0%. Elevated for 2-3 days - Troponin I: < 0.03 ng/L. Elevated for 7-10 days (1 week) - Troponin T: < 0.1 ng/L. elevated for 10-14 days (2 weeks) - Myoglobin: can be elevated due to heart damage OR skeletal muscle damage - Should be < 90 mcg/L. Elevated for 24 hours - Total cholesterol <200 mg/dL - HDL> 55 mg/dL (women); > 45 (men) - LDL < 130 mg/dL - Triglycerides: between 35-135 mg/dL (women), between 40-160 mg/dL (men) - CVP: 2-6 mmHg (> HF) - PAWP: 6-15 (>HF) - CO: 3-6 L/min or 4-8 Level transducer with phlebostatic axis (4th intercostal space, midaxillary line), zero system, confirm placement w/ x-ray - Invasive procedure used to determine if the pt. has a coronary artery blockage or narrowing. - Catheter inserted into femoral artery heart PRE - NPO for 8 hrs - Assess for allergy to iodine/shellfish - Assess kidney function (BUN, creatinine) to determine if kidneys can excrete dye POST - Check insertion site for bleeding, distal to puncture sites (pulses, capillary refill, temperature, color) - Take VS q 15 min x4, q 30 min x2, q 1 hr x 4 - Patient lies flat in bed for 4-6 hrs after procedure CX cardiac tamponade CARDIAC TAMPONADE PICC line/ implanted port IV CX DYSRHTYMIAS - Accumulation of fluid in pericardial sac S/S - Hypotension - Muffled heart sounds - Distended jugular veins - Paradoxical pulse (variance of 10 mmHg or more in SBP between inspiration an expiration DX - Chest x-ray, echocardiogram TX - Pericardiocentesis (removal of fluid from pericardial sac) PICC - Used for long-term admin of IV abx, TPN, chemo. Tip position in lower 1/3 of superior vena cava - Can stay put for 12 mo MANAGAMENT - Assess q 8 hrs - Use 10 mL (or larger) syringe to flush line - Flush w/ 10 mL of 0.9% NaCL before, between, and after meds - Blood draws: withdrawal 10 mL blood and discard, withdrawal 10 mL for sample, flush w/ 20 mL NaCL - No BP on arm w/ PICC line IMPLANTED PORT - For long term (>1 year) vascular access; - Common w/ chemo - Access w non-coring (Huber) needle PHLEBITIS - Erythema - Pain - Warmth - Edema - Indurated or cordlike veins - Red streak * discontinue IV, cool compress, elevation INFILTRATION - Edema - Coolness - Taut skin *discontinue IV, cool compress, elevation AIR EMBOLISM - SOB *place in Trendelenburg position on left side, give O2, notify Dr. Bradycardia (HR < 60) - If symptomatic atropine (AC effects), pacemaker Afib, SVT, ventricular tachycardia w/ pulse - Admin arrhythmic med (amiodarone, adenosine, verapamil) - Cardioversion Cardioversion management - Pt must be on anticoagulation for 4-6 weeks prior - Staff needs to stand clear of pt when shock is delivered - Asses airway, VS, obtain EKG - Monitor for s/s of dislodged clot (PE, stroke, MI) Ventricular tachycardia w/o pulse, V-fib - Admin anti-arrhythmic med (amiodarone, lidocaine, epinephrine) - Defib PACEMAKERS PERCUTANEOUS CORONARY INTERVENTION (PCI) CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT (CABG) PERIPHERAL BYPASS GRAFT - Provide electrical stimulation of heart when natural pacemaker in heart doesn’t maintain proper rhythm - Programmed to pace atrial (A), ventricular (V) or both chambers (AV) Modes - Asynchronous: fires @ constant rate regardless of hearts electrical activity - Synchronous: fires only when heart’s intrinsic rate falls below a certain rate Indications - Symptomatic bradycardia - HB - Sick sinus syndrome Management - Provide sling & instruct pt to minimize shoulder movement - Assess for hiccups pacemaker is pacing the diaphragm - Instruct pt to carry pacemaker ID, take pulse daily, avoid contact sports & heavy lifting for 2 mo - Pacemaker will set off airport security detectors - MRIs are CI - OK to use garage door openers or microwave - Procedure to open coronary arteries - Performed within 3 hrs of onset of MI S/S Types - Atherectomy (removal of plaque in vessel) - Placement of stents - PTCA (inflating a balloon to widen the arterial lumen) Management: same as coronary angiogram CX - artery dissection (monitor for hypotension & tachycardia) - Cardiac tamponade - Bleeding/hematoma @ insertion site - Embolism - Retroperitoneal bleeding (monitor for flank pain and hypotension) - Restenosis of vessel (monitor for CP, asses EKG) - Sx to bypass 1 or more coronary arteries vein d/t blockages and/or persistent ischemia - Saphenous vein often used - Pt’s core temp lowered to decrease metabolic (& O2) demand during procedure Care - Monitor BP - HTN bleeding from grafts - Hypotension collapse of graft - Monitor chest tube: over 150 mL/ hr hemorrhage (call DR.) Teaching - Tx angina w/ sublingual NTG - Quit smoking - Consume heart healthy diet - Participate in cardiac rehab program - Sx to restore blood flow to extremity d/t PAD Management - Obtain consent - NPO for 8 hrs - Closely monitor peripheral pulses, cap refill, skin color & temperature - Bedrest for 18-24 hrs w/ leg straight - Avoid sitting of long periods or crossing legs - Apply antiembolic stocking Monitor for s/s of compartment syndrome - Worsening pain - Swelling - Taut skin *fasciotomy used to relieve pressure ANGINA MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION HF VALVULAR HEART DZ Stable - Occurs w/ exercise, relieved by rest or NTG Unstable - Occurs w/ exercise or @ rest - Increases in duration, occurrence or severity over time Variant - r/t coronary artery spasm - occurs @ rest Angina Vs. MI - pain unrelieved by rest or NTG and lasts more than 30 minutes MI - Mis have other s/s: n, epigastric comfort, diaphoresis, SOB RF - Male, Post-menopausal women, HTN, Smoking, Hyperlipidemia, Diabetes, Stress, Inactivity S/S - Diaphoresis - Cold/clammy skin - Pallor - Tachycardia - Anxiety - CP - Nausea - Acute confusion - Fatigue - palpitations Labs - Elevated cardiac enzymes (CK-MB, Troponin I, Troponin T, myoglobin) EKG changes: ST elevation or depression, T wave inversion, abnormal Q wave Meds - NTG - Analgesics - BBs - Thrombolytics - Antiplatelets - ACs CX - HF - Cardiogenic shock (tachycardia, hypotension, decreased UOP & peripheral pulses, CP, altered LOC - Heart muscle does not pump effectively dec. CO Left sided pulmonary congestion s/s: - SOB - Crackles - Orthopnea - Fatigue - Pink/ frothy sputum Right sided systemic congestion s/s: - JVD - Peripheral edema - Ascites - Hepatomegaly Labs - hBNP > 100 pg/mL (indicates heart problem instead of pulmonary) DX - hemodynamic monitoring: increased CVP, PAWP - decreased CO - Echo: reduced Ejection fraction left: 55-70; right: 45-60 Management - Monitor daily wts, I & Os - High fowlers - Admin O2 - Restricted fluid & Na intake Meds - Diuretics - Afterload-reducing meds (ACE inhibitors, ARBs, CCB) - Inotropic agents (Digoxin) - BBs - NTG - hBNP - ACs Stenosis: narrowed opening Insufficiency: regurgitation of blood RFs - HTN - Rheumatic fever/ dz r/t streptococcal infections - Infective endocarditis r/t streptococcal infection - Older age fibrotic thickening S/S - Murmurs - Extra heart sounds - Arrythmias - SOB w/ mitral stenosis DX - Chest x-ray - EKG - Echo Meds - Diuretics - Afterload reducing meds (ACE, ARBs, BBs, CCBs) - Inotropic agents (Digoxin) - ACs SX - Percutaneous balloon valvuloplasty open values that have stenosis - Valve repair or replace w/ prosthetic valve Teaching - Prophylactic abx before dental work, Sx or invasive procedures INFLAMMATORY HEART DISORDERS PAD PVD VTE Pericarditis - Inflammation of pericardium S/S - CP relieved by sitting up & leaning forward), - Friction rub - SOB Rheumatic endocarditis - Infection of endocardium d/t upper respiratory infection from group A beta- hemolytic streptococcal bacteria - Causes heart lesions to form S/S - Murmurs - Fever - CP - Joint pain - Rash - SOB - Friction rub - tachycardia Infective endocarditis - infection of endocardium d/t streptococcal bacteria - common w / IV drug users S/S - fever - flu-like - murmur - petechiae - red streaks under nailbeds (splinter hemorrhages) Labs - increased WBC - positive blood culture - elevated ESR & CRP d/t inflammation - throat culture + for streptococcal infection Meds - Abx - NSAIDS - Prednisone CX Cardiac tamponade - Inadequate blood flow to lower extremities d/t atherosclerosis - Issue w arteries RFs - HTN - Diabetes - Smoking - Obesity - Hyperlipidemia S/S - Pain in legs during exercise relieved by placing legs in dependent position i.e dangling them - Decreased cap refill of toes & pedal pulses - Lack of hair on calves - Thick toe nails - Pallor w/ elevation, dependent rubor - Ulcers/gangrene on toes Teaching - Walk until point of pain, stop & rest, then walk more - Avoid crossing legs & restrictive garment s - Maintain warm environment, wear insulated socks - Avoid cold, stress, caffeine, nicotine vasoconstriction MEDS - Antiplatelet meds (aspirin, clopidogrel) reduce blood viscosity - Statine SX - Angioplasty (balloon, stent) - Peripheral bypass graft CX - Graft occlusion (reduced pedal pulses) - Increased pain - Pallor - Cold - Compartment syndrome (numbness, pain w/ passive movement) Edema - Issue w/ adequate blood return from the extremities VTE - Blood clot Varicose veins - Enlarged superficial veins Venous insufficiency - Caused by incompetent valves in the deeper veins - Leads to swelling, venous ulcers & cellulitis RFs - Virchow’s triad impaired blood flow, hypercoagulability, endothelial injury) - Hip & knee replacement sx - HF - Immobility - Pregnancy - Oral contraceptives S/S - Calf/ groin pain - Edema in extremity - Warmth/ hardness over blood vessel - SOBPE DX: + D Dimer, venous duplex ultrasonography Management - Elevation of extremity (no pillow or knee gatch under knees) - Warmth/ most compresses - NO massaging limb - Compression stocking - Watch fo rs/s of PE Meds - ACs, thrombolytics VENOUS INSUFFICIENCY VARICOSE VEINS HTN HEMODYNAMIC SHOCK RFs - Sitting/ Standing in one place for a long time - Obesity - pregnancy S/S - Aching pain & feeling of heaviness in legs - Brown discoloration of legs (stasis dermatitis) - BLE edema - Venous stasis ulcers (around ankles) Management - Elevate legs - Avoid crossing legs or restrictive clothing - Compression stockings (apply in morning when swelling is reduced) RFs - Female - Jobs that require prolonged standing - Pregnancy - Obesity - Family hx S/S - Distended/ tortuous veins below the skin surface - Aching - Pruritis Therapeutic procedure - Sclerotherapy (chemical solution is injected into varicose vein to close off the vein) - Vein stripping - Laser tx - Radio frequency Primary: idiopathic RFs - Family hx - Excess Na intake - Inactivity - Obesity - Smoking - Stress - Hyperlipidemia - Race (AA) Secondary: caused by dz or meds RFs - Kidney dz - Cushing’s pheochromocytoma S/S - Ha - Dizzy - Visual issues or no s/s Pre- HTN: SBP 120-139; DBP 80-89 Stage 1: SBP 140-159; DBP 90-99 Stage 2 SBP>160; DBP > 100 HTN crisis SBP > 240; DBP > 120 Meds - Diuretics, CCBs, ACE, ARBs, BBS Teaching - Take BP regularly - Limit ETOH intake - DASH diet (high in fruits & veggies, low fat- dairy, LOW in salt & fat) - Reduce wt & stress - Stop smoking CX - HTN crisis severe ha, blurred vision Cardiogenic - Cardiac pump failure due to HF, MI, dysrhythmias Hypovolemic - Blood loss d/t trauma, sx, burns or fluid loss d/t GI losses, diuresis Obstructive - Blockage of great vessels (PE, tension pneumothorax, cardiac tamponade) Distributive - Extreme vasodilation Septic: endotoxins in bloodstream from infection (gram – bacteria) Neurogenic: loss of sympathetic tone d/t trauma or spinal shock Anaphylactic: antigen- antibody rxn d/t exposure to allergens S/S - Hypoxia - Tachypnea - Hypotension - Tachycardia - Weak pulses - Decreased UOP - Wheezing - Angioedema - Rash w anaphylactic shock Labs - Increased lactic acid - Abnormal ABGs - Increased cardiac enzymes w/ cardiogenic - Decreased Hct/ Hgb w/ hypovolemic shock - + blood cultures w/ septic shock Management - Admin O2 - Prepare for intubation - Modified Trendelenburg Meds - Dobutamine - Vasopressors - Epinephrine - Colloids (hypovolemic, replace volume 1st) - Abx for septic shock CX: MODS, DIC ANEURYSMS Aneurysm - Widening or ballooning in the wall of blood vessel Abdominal aorta aneurysm - Flank/back pain, pulsating abdominal mass Aortic dissection - Feeling of “ripping” or “stabbing” in abdomen or back S/S of hypovolemic shocks: hypotension, tachycardia, dec. pulses, n/v, diaphoresis Thoracic aortic aneurysm - Severe back pain, SOB, diff. swallowing, cough Management - Reduce SBP 100-120 - Admin anti-HTNs - Monitor VS, cardiac rhythm, ABGs, urine output HEMOTOLOGIC BLOOD TRANSFUSIONS BLOOD TRANSFUSION RXNS CAUSES OF ANEMIA COAGULATION DISORDERS - Type A: receive A & O - Type B: can receive type B & O - Type AB: can receive A, B, AB, & O - Type O: can receive O - If a rH- person receives rh- + blood, it will cause hemolysis Blood transfusions - Use 20 gauge or > IV catheter - Confirm pt. ID, blood compatibility, expiration time w/ another RN - Prime admin set w/0.9% NaCl ONLY - Stop transfusion, infuse 0.9% NaCl through separate linesend blood bag to lab Acute hemolytic - Low back pain, fever/chills, tachycardia, hypotension, tachypnea Febrile - Fever/chills, hypotension, tachycardia - Admin antipyretics Mild allergic - Itching, flushing, hives - Admin diphenhydramine Anaphylactic - Wheezing, dyspnea, cyanosis, hypotension Circulatory overload - Dyspnea, tachycardia, tachypnea, crackles, HTN, JVD, - Slow infusion rate, admin diuretics Blood loss - Trauma, GI bleed, menorrhagia Sickle cell anemia - Defective Hgb, malformed RBCs Iron deficient anemia - Common in children & pregnant women - Provide iron supplements: ferrous sulfate, iron dextran Pernicious anemia - Lack on intrinsic factor in gastric mucosa, prevents absorption of B12 - Admin cyanocobalamin (B12) parentally or intranasally Folic acid deficiency - Provide folic acid orally or parentally - Large doses of folic acid can mask B12 deficiency Bone marrow suppression ITP - Autoimmune, where lifespan of platelets is decreased hemorrhage risk DIC - Clotting factors are depleted through formation of thousands of micro-clots in the body - Clots ischemia & lack of clotting factors bleeding S/S - Bleeding from gums/ nose - Oozing/trickling of blood from incisions - Petechia - Tachycardia - Hypotension MANAGEMENT - Admin blood, platelets, clotting factors - Admin O2, fluid volume replacement - Implement bleeding precautions, injury prevention Meds - ITP: corticosteroids, immunosuppressants - DIC: ACs (heparin) FLUID & ELECTROLYTE IMBALANCES FLUID VOLUME DEFICIT FLUID VOLUME EXCESS SODIUM POTASSIUM Causes - GI losses - Diuretics - Hemorrhage - Diaphoresis - DI - Kidney dz - hyperventilation S/S - tachycardia - tachypnea - hypotension - weak pulse - fatigue - weakness - thirst - dry mucous membranes - GI upset - Oliguria - Decreased skin turgor & cap refill - Diaphoresis - Flattened neck veins Labs - Increased Hct - Serum osmolality - Urine specific gravity - BUN serum sodium Management - Fluid replacement - Monitor wt. & I/Os - Notify provider for UOP < 30 ml/hr - Implement fall precautions CX - Hypovolemic shock admin O2, colloids, crystalloids, vasoconstrictors Causes - HF - Steroid use - Kidney dysfunction - Cirrhosis - Burns - Excess Na intake S/S - Tachycardia - Tachypnea - HTN - Bounding pulses - Wt. gain - Edema HIGH RISK FOR SKIN BREAKDOWN - Ascites - SOB - Crackles - Distended neck veins Labs - Decreased Hct & Hgb, Serum/ urine osmolality, Urine specific gravity, BUN Management - Place pt. in semi or high fowler’s position - Monitor wt. daily (1/2 lbs wt. gain in 24 hrs or 3 lbs wt gain in one week call DR.) - monitor I & Os, limit fluid & Na - admin diuretics & O2 CX - pulmonary edema - maintains fluid balance in body, nerve & muscle function HYPONATREMIA Causes - GI loses - Diuretics - Kidney dz - Skin losses - SIADH - Hyperglycemia - HF S/S - Tachycardia - Hypotension - Confusion (elderly) - Fatigue - N/v - ha Management - admin isotonic (0.9% NaCl) - increase Na intake - for acute hyponatremia 3% NaCl (hypertonic solutions) slowly HYPERNATREMIA Causes - water deprivation - excess Na intake - kidney failure - Cushing’s syndrome - DI - Burns - Excess sweating S/S - Tachycardia - Muscle twitching/ weakness - GI upset Management - Admin isotonic (0.9% NaCl) or hypotonic (0.45% NaCl) - IV fluids, decrease Na intake & H20 intake - Maintains ICF, nerve function, regulates muscle & heart contraction HYPOKALEMIA Causes - GI losses - Diuretics (furosemide) - Skin losses - Metabolic alkalosis S/S - Dysrhythmias - Muscle weakness & cramps - Constipation/ ileus - Hypotension - Weak pulse Management - Increase foods in K bananas, cantaloupes, avocadoes, green leafy veggies - Admin supplements (PO, IV phlebitis * mix w/lidocaine) - Cardiac monitoring HYPERKALEMIA Causes - Uncontrolled diabetes (DKA) - Metabolic acidosis - Salt substitutes - Kidney failure - Potassium- sparing diuretics (spironolactone) S/S - Dysrhythmias - Muscle weakness - Numbness/ tingling - Diarrhea Management - Limit foods high in K - Admin loop diuretics - Sodium polystyrene sulfonate (Kayexalate) - Insulin (w/ dextrose) - Calcium gluconate CALCIUM MAGNESIUM ACID BASE BALANCE ACID BASE IMBALANCES - Bone/ teeth formation, nerve & muscle function, clotting - Inverse relationship w/ phosphorous if Ca are high P will be low - Gate keeper for action potential HYPOCALCEMIA Causes - Vitamin D deficiency - Hypoparathyroidism - Hyperphosphatemia - pancreatitis S/S - +Chvostek’s & Trousseau’s sign (C: tap on face cheek face twitching; T: inflate BP cuff muscle & feet spasms) - Muscle spasms - Numbness/ tingling in lips & fingers - GI upset - Hypotension - Decreased HR Management - Increase foods high in Ca - Provide supplements HYPERCALCEMIA Causes - Hyperparathyroidism - Long-term steroid use - Bone cancer S/S - Constipation - Decreased deep tendon reflexes - Kidney stones - Lethargy - Nerve & muscle function, bone formation - Critical for man biochemical rxns in body HYPOMAGNESEMIA Causes - GI losses - Diuretics - Malnutrition - ETOH abuse S/S - Hyperactive deep tendon reflexes - Tetany - Seizures - Constipation/ ileus Management - Increase Mg foods - Provide supplements can cause diarrhea HYPERMAGNESEMIA Causes - Kidney dz - Laxatives containing Mg S/S - Hypotension - Muscle weakness - Lethargy - Respiratory & cardiac arrest Chemical/ protein buffers: hgb, phosphate, HCO3 - 1st LOD - Bind or release H+ ions to quickly change pH Respiratory buffers - 2nd LOD - Chemoreceptors sense change in CO2, send signal to brain to adjust respirations - Increased CO2 inc. rate & depth of respirations (reduces # of H+ ions) - Decreased CO2 decreased rate & depth of respirations (inc. # of H+ ions) Renal buffers - 3rd LOD - Slower to respond, longer duration - Kidneys absorb & produce more HC03 in response to high levels of H+ ions - Kidneys excrete more HC03 in response to low levels of H+ ions RESPIRATORY ACIDOSIS Causes - Respiratory depression - Inadequate chest expansion - Airway obstruction - PE - Pulmonary edema Labs - pH < 7.35 & PaCo2 >45 S/S - tachycardia - tachypnea - shallow breathing - pale/cyanotic skin - confusion Management - O2 & bronchodilators RESPIRATORY ALKALOSIS Causes - Hyperventilation (r/t fear, anxiety, salicylate toxicity) Labs - pH > 7.45 & PaCO2 < 35 S/S - tachypnea - deep & rapid breathing - anxiety - CP - Dysrhythmias Management - Reduce anxiety ACID BASE IMBALANCES METABOLIC ACIDOSIS Causes - DKA - Kidney failure - Diarrhea - Pancreas/ liver failure Labs - pH < 7.35 & HCO3< 22 S/S - bradycardia - hypotension - weak pulses - dysrhythmias - Kussmaul respirations (deep, rapid breathing) - warm/flushed skin Management - admin insulin for DKA - sodium bicarbonate METABOLIC ALKALOSIS Causes - antacid overdose - GI losses (vomiting, NG suctioning) Labs - pH > 7.45 & HCO3 > 26 S/S - tachycardia - dysrhythmias - muscle weakness Management - administer antiemetics for vomiting GI SYSTEM ENDOSCOPY PROCEDURES GI SERIES TPN PARACENTESIS Colonoscopy - allows visualization of anus, rectum, signed, descending, transverse and ascending colon - done under moderate sedation - bowel prep: polyethylene glycol, clear liquid diet, NPO after midnight EGD - allows visualization of esophagus, stomach & duodenum - done under moderate sedation - prep: NPO 6-8 hrs before procedure Sigmoidoscopy - allows visualization of anus, rectum & sigmoid colon - no anesthesia required - bowel prep: polyethylene glycol, clear liquid diet, NPO after midnight - identifies GI abnormalities (ulcers, tumors, obstruction) - pt. drinks barium, x-rays taken as barium moves through GI tract - prep: clear liquid diet, NPO after midnight, no smoking or chewing gum teaching - increase fluid intake to flush out barium - Stools will be white for 24-72 hours after procedure until barium is cleared Indications - Malabsorption - Hypermetabolic state - Chronic malnutrition - Prolonged NPO Admin - Central line (PICC) Management - Gradually increase/ decrease flow rate - Change tubing & bag q 24 hrs - Use micron filter on tubing - Monitor I & Os, daily wts. Electrolyte levels & blood glucose (q 4-6 hrs for 1st 24 hrs) - If the next TPN bag is unavailable, administer dextrose in H2O until it arrives - Do not use TPN line for other fluids or meds - Monitor central line insertion site for S/S of infection erythema, pain, exudate - Insertion of needle through abdominal wall to remove fluid from peritoneal cavity Indications - Ascites (r/t cirrhosis) w/ respiratory distress Management - Have pt. sign consent form - Void before procedure - Take VS, wt. abdominal girth circumference before & after procedure - Monitor for hypovolemia (peritoneal fluid removed is high in protein fluid shift) - Administer albumin as prescribed BARIATRIC SX NG tube OSTOMIES GERD Indications - Morbid obesity Management - Eat only nutrient dense foods - Avoid milk, sweets, high sugar foods - Eat 6 small meals/ day - Allow for 30-60 min to eat - Chew foods thoroughly & slowly - Do not consume liquids w/ meals - Restrict fluids t0 30 mL - Watch for s/s of dumping syndrome abdominal cramping, n/d, diaphoresis, tachycardia, hypotension Indications - Intestinal obstruction vomiting, abnormal bowel sounds, abdominal pain & distention Management - Asses bowel sounds & abdominal girth - Monitor NG tube for displacement - Assess nasal mucosa for breakdown - Provide oral care - Monitor I & Os, electrolytes - Encourage ambulation to increase peristalsis - Performed when part of the bowel must be removed due to dz/ injury - Ileostomies create ileum opening - Colostomies create large intestine opening - Empty ostomy bag when it is ¼- ½ full - Pt can use breath mint in pouch to decrease odor - Cut opening in skin barrier <1/8 in larger than stoma - Gastric contents (including enzymes) back flow into the esophagus pain & mucosal damage (esophagitis, Barrett’s epithelium) RFs - Obesity, ETOH, smoking, older age, pregnancy, ascites, hiatal hernia, supine position, diet high in fatty/ fried foods, caffeine, citrus fruits S/S - Dyspepsia (indigestion) - Throat irritation, bitter taste - Burning pain in esophagus, pain worsens when laying down, improves when sitting up - Chronic cough Meds - Antacids (1-3 hrs after eating, 1 hr before/ after other meds) - H2 receptor antagonists (ranitidine) - PPIs (pantoprazole) - Prokinetics (metoclopramide accelerates gastric emptying, watch for s/s of EPS SX - Fundoplication (fundus of stomach wrapped around esophagus) Teaching - Avoid fatty/ fried/ spicy foods - Eat smaller meals - Remain upright after meals - Avoid tight fitting clothing - Lose wt - Elevate HOB 6-8” w/ blocks - Sleep on right side ESOPHAGEAL VARICES PUD IBS INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTION - Swollen/ fragile blood vessels in esophagus that can hemorrhage (life-threatening) RFs - Portal HTN (increased BP in veins from intestines to live) d/t cirrhosis, hepatitis S/S - Elevated liver enzymes - With bleeding: hypotension, tachycardia, decreased hgb hct Meds - Nonselective BBs (propranolol) - Vasoconstrictors (vasopressin) Procedures - Sclerotherapy, variceal ligation, transjuglar shunt, esophagogastric balloon tamponade (compresses blood vessels in esophagus & stomach), bypass - Erosion in the stomach, esophagus or duodenum mucosa RFs - H. pylori infection, NSAID use, stress S/S - n/v - heartburn - bloating - bloody emesis/ stools - pain: - gastric ulcer: pain 30-60 min after meal, worse in DAY, worse w/ eating - duodenal ulcer: pain 1.5-3 hrs fter meal, worse @ NIGHT, better w/ eating or antacids DX: EGD Meds - MULTIPLE abx to prevent resistance (Metronidazole, amoxicillin, clarithromycin, tetracycline) - H2 receptor antagonist (ranitidine) - PPI (pantoprazole) - Antacids (1-3 hrs after eating, 1 hr before/ after other meds) - Mucosal protectant (sucralfate, given 1 hr before meals & at bedtime) Teaching - Avoid acid-producing foods milk, caffeine, spicy foods - Avoid NSAIDS CX - Perforation hemorrhage - s/s: sever epigastric pain, rigid/board- like abdomen, rebound tenderness, hypotension, tachycardia - an intestinal disorder abdominal pain, gas, diarrhea & constipation Teaching - avoid dairy, eggs, wheat products, ETOH, caffeine - increase fiber intake (30-40 g/day) & fluid intake (2-3L/day) - keep food diary of food intake & bowel patterns Meds - alosetron: for IBS w/ diarrhea (constipation) - lubiprostone: for IBS w/ constipation (diarrhea) Mechanical obstruction causes - adhesions for sx - tumors - diverticulitis - fecal impactionc Non-mechanical obstruction causes (paralytic ileus) - neurogenic disorder - vascular disorder - electrolyte imbalance - inflammation S/S: both: - abdominal distention - obstipation - abdominal pain - high pitched bowel sounds above obstruction - hypoactive bowel sounds below obstruction small bowel only - projectile vomiting w/ fecal odor - severe f & e imbalance - metabolic alkalosis large bowel only - diarrhea or ribbon-like stools around impaction management - NPO - NG tube - Administer IV fluids & electrolytes SX - Colon resection - Colostomy - Lysis of adhesions IBD ULCERATIVE COLLITIS CROHN’S DZ DIVERTICULITIS Ulcerative colitis Crohn’s dz Diverticulitis - Inflammation of the colon continuous lesions S/S - LLQ pain - Fever - 15-20 liquid stools/day - Abdominal distention & pain - Mucus/ blood/ pus in stools - Inflammation & ulceration of the small intestine sporadic lesions - Risk of fistulas S/S - RLQ pain - 5 loose stools/ day - Mucus/ pus in stools - Abdominal distention & pain - Steatorrhea - Inflammation of diverticula (small pouches in the colon) S/S - LLQ pain - n/v - fever - chills Labs - decreased Hct/ Hgb, increased WBC Meds - abx (metronidazole), analgesics Diet - NPO or clear liquid during exacerbations low-fiber diet - Ongoing, eat high fiber diet - Avoid seeds, nuts, popcorn Management - Monitor for s/s peritonitis n/v, rigid/board like, rebound tenderness, hypotension, fever, tachycardia Labs - decreased HCT/ Hgb & albumin - increased ESR, CRP, WBC RFs - genetics, Caucasians, Jewish decent, stress, autoimmune disorder Meds - 5- amino salicylic acid (sulfasalazine) - Corticosteroids (prednisone) - Immunosuppressants (cyclosporine) - Antidiarrheals Management - Monitor for s/s of peritonitis n/v, rigid/board like, rebound tenderness, hypotension, fever, tachycardia - Monitor I & Os, electrolytes (hypokalemia) Diet - NPO during exacerbations - Ongoing eat foods high in protein & calories, low in fiber - Avoid caffeine, ETOH Eat small frequent meals CHOLECYSTISIS CHOLESTECOTOMY PANCREATITIS HEPATITIS - Inflammation of gallbladder - Caused by cholestasis (gallstones) - Gallstones block cystic or common bile duct & cause bile to backup into gallbladder RFs - Female, High-fat diet, Obesity, Genetics, Older age S/S - RUQ pain (possible radiation to right shoulder) - Pain & n/v w/ ingestion of high-fat foods - Jaundice - Clay colored stools - Steatorrhea - Dark urine - Pruritis - Dyspepsia - Gas Labs - Increased WBC - Bilirubin (bile duct blocked) - Amylase & lipase (if pancreas involved) - AST & ALT (if common bile duct blocked) Interventions - Lithotripsy (to break up gallstones) - Cholecystectomy (removal of gallbladder) - Removal of the gallbladder - If done via laparoscopic approach, shoulder pain is expected (encourage ambulation to reduce free air pain) - If done via open approach T-tube may be placed in bile duct Management of T-tube: - Record drainage - >400 mL expected in 1st 24 hrs, then will gradually decrease - Drainage >1,000 mL/ day needs to be reported - Empty drainage bag q 8 hrs - Clamp tube 1-2 hrs to asses for tolerance to eating prior to removal - After removal, stools should return brown color ~ 1 wk Teaching - Low fat diet - Avoid gas-causing foods - Lose wt. Cx - Pancreatitis, peritonitis r/t rupture of gallbladder n/v, rigid/board like, rebound tenderness, hypotension, fever, tachycardia - Autodigestion of the pancreas by pancreatic digestive enzymes that are prematurely activated before reaching the intestines RFs - Bile tract dz, ETOH abuse, GI sx, trauma, medication toxicity S/S - Severe LUQ or epigastric pain (radiating to the back or left shoulder) - n/v - turner’s sign ecchymoses on flanks TURN THE PT OVER & SEE ECCHYMOSIS - Cullen’s sign blue/ grey discoloration around umbilicus EDWARD CULLEN HAS BLUE LIPS - Jaundice - Ascites - Tetany Labs - 9Increased amylase, lipase, WBS, bilirubin, glucose - Decreased Ca, Mg, platelets Management - NPO, NG tube, antiemetics, insulin, IV f/e, opioid analgesics, pancreatic enzymes (pancrelipase) w/ meals & snacks - Progress to bland/ low fat Teaching - No ETOH consumption - Encourage AA meetings - Reduce stress - No smoking CX: - Chronic pancreatitis, pancreatic pseudocysts, Type 1 diabetes - Inflammation of the liver Routes of transmission - Hep A: fecal/oral - Hep B: blood/body fluids - Hep C: blood/body fluids (no vaccine) RFs - IV drug, body piercing, tattoos, unprotected sex, travel to underdeveloped countries, crowded living environments S/S - Flu-like malaise, body aches, fever - Jaundice - Dark-colored urine - Clay-colored stools Labs - Increased ALT, AST, bilirubin CIRRHOSIS CIRRHOSIS CIRRHOSIS - Normal liver tissue is replaced w/ fibrotic scar tissue Post necrotic - D/t viral hepatitis, toxins or meds Laennec’s - D/t chronic alcoholism Biliary - D/t chronic biliary obstruction S/S - Jaundice - Ascites - Petechiae - Spider angiomas - Palmar erythema - Pruritus - Confusion - Fatigue - GI bleeding - Asterixis - Fetor hepaticus (fruity breath) - Peripheral edema Labs - Increased ALT, AST, bilirubin, ammonia - Decreased serum protein, albumin, RBC, Hgb, Hct, platelets Dx - Liver biopsy (most definitive) - Ultrasound - CT - MRI Management - Strict I & Os, restrict fluids & na as ordered - Elevate HOB to help w/ breathing - Measure abdominal girth daily (over largest part) - Wash skin w/ cold water & apply lotion to reduce itching) - Encourage AA Diet - High carb, moderate fat, high protein, low Na - Vitamin & mineral supplements - Several small meals Meds - Lactulose to remove excess ammonia through stool (monitor for hypokalemia) Procedures - Paracentesis: void before - Supine position w/ HOB elevated - Assess for extracted fluid (color & amount) - Liver transplant CX - Encephalopathy (reduce ammonia levels w/ lactulose) - Esophageal varices RENAL SYSTEM HEMODIALYSIS PERITONEAL DIALYSIS KIDNEY TRANSPLANT - 0.6-1.2 - Elevated levels indicate kidney dz - More definitive than BUN BUN - 10-20 - Elevated levels indicate kidney dz or dehydration Urinalysis - Specific gravity 1.01-1.025 - No glucose, protein, ketones, leukocytes or nitrites should be found in urine Cystography/ urography - Check for allergies to iodine, shellfish - NPO after midnight, bowel preparation night before procedure - Encourage increased fluid intake after procedure - Pink tinged urine expected Monitor for s/s of infection cloudy or foul-smelling urine, urinary urgency, urinalysis + for leukoesterase, nitrites - Eliminates excess fluid, electrolytes & waste products from the body - Used in pts w/ acute or chronic kidney dz - Usually done 3x a week PRE - Ensure patent vascular access (check for bruit, thrill, distal pulses) - Assess VS, lab values, wt. INTRA - Monitor for hypotension, cramping, n/v, bleeding - Admin ACs to prevent clots as ordered (admin protamine sulfate to reverse heparin if needed) POST - Decreased BP & lab values expected - Compare wt. to before procedure to estimate fluid removed (1L fluid = 1kg) Teaching - Increase protein intake after, as protein is lost in each exchange - Avoid carrying items w/ arm w/ access site - Don’t sleep on arm w/ access site - Perform hand exercises to mature fistula CX - disequilibrium syndrome n/v, decreased LOC, seizures d/t increased ICP slow dialysis exchange rate - hypotension admin IV fluids or colloids slow exchange rate lower HOB - installation & dwelling of hypertonic dialysate solution in the peritoneal cavity to remove waste - alternate to hemodialysis for: older adults, intolerance to ACs, vascular access difficulties PRE - asses wt. - warm dialysate solution - use sterile technique when accessing catheter insertion site INTRA - compare inflow vs. outflow of dialysate - keep outflow lower than the pt’s abdomen - monitor color of outflow should be clear, light yellow - bloody, cloudy outflow indicates possible infection!! CX - peritonitis fever, purulent drainage, erythema, swelling, discolored dialysate - protein loss (increase protein in diet) - hyperglycemia (admin insulin as needed) - poor inflow/outflow (check for kinks in tubing address constipation, reposition pt., milk tubing to break up clots) PRE - provide immunosuppressant therapy as ordered POST - monitor UOP report output < 30 mL/hr - perform bladder irrigation as ordered - monitor for infection fever, erythema, incisional drainage - monitor for organ rejection fever, HTN, pain @ site types of pain: - hyperacute: within 48 hrs - acute: within 1 week- 2 years - chronic: occurs gradually Teaching - low fat & Na, high fiber & protein - avoid contact sports GLOMERULONEPHRITIS AKI CKD UTI - immune complex dz inflammation of glomerular capillaries RF - streptococcal infections, lupus, HTN, diabetes S/S - decreased UOP fluid volume excessedema, wt. gain, SOB, HTN Labs - throat culture + for strep - + ASO (Antistreptolysin titer) - Decreased GFR (obtained through 24 hr urine collection to determine creatinine clearance - Urinalysis: increased urine specific gravity, proteinuria, hematuria, coffee- colored - Elevated WBC, ESR Management - Monitor wt (report wt. gain of 2 lbs in 24 hrs, or 5lbs in 1 week) - Monitor I & Os - Restrict fluids, Na & protein - Admin abx for strep throat, diuretics & corticosteroids Procedure - Plasmapheresis filter antibody complexes out of blood - Sudden loss of kidney function PRERENAL - d/t decreased blood flow to kidneys (shock, sepsis, hypovolemia, renal vascular obstruction) INTRARENAL - direct damage to kidneys (physical trauma, hypoxic injury, chemical injury d/t toxins or meds) POSTRENAL - d/t obstruction leaving the kidney (stone, tumor, BPH) PHASES Onset - onset to development of oliguria (hrs-days) Oliguria - UOP 100-400 mL/24 hrs (1-3 weeks) Diuresis - Start of kidney recovery, large amount of urine excreted (2-6 weeks) Recovery - Continues until complete recovery (up to 1 yr) Diet - Restrict K, Ph, Mg - Increase protein - Gradual, irreversible loss of kidney function RFs - Gaining, HTN, dehydration, AKI, diabetes, chronic glomerulonephritis, meds (gentamicin, NSADS), autoimmune dz Stages 1. GFR > 90 2. GFR 60-89 3. GFR 30-59 4. GFR 15-29 5. GFR < 15 S/S - Mostly d/t fluid volume overload - JVD - HTN - SOB - Tachypnea - Crackles - Peripheral edema - Pruritus - Lethargy - Uremic frost (crystalized urea deposits on the skin) Labs - Elevates creatinine, BUN, K, Ph, mg - Decreased Na, Ca, Hgb, HCt - Urinalysis: hematuria, proteinuria Management - Weigh pt. daily (1kg wt. gain= 1L fluid retained) - Protect skin from breakdown - Prepare for hemodialysis - Promote frequent rest periods Diet - High carbs, moderate fat, increase Ca - Restrict Na, K, Ph, Mg & proteins - Limit fluid intake Meds - Digoxin, sodium polystyrene (to reduce serum K) - Erythropoietin (to increase RBCS) - Furosemide - Avoid NSAIDS, contrast dye, Mg containing antacids - Infection in lower UT, caused by E. Coli RFs - Female gender (shorter urethra, close proximity to rectum), menopause, sexual intercourse, pregnancy, synthetic underwear, wet bathing suits, frequent baths, urinary catheters, stool incontinence, diabetes, incomplete bladder emptying S/S - Abdominal pain - Dysuria (urinary frequency/ urgency) - Fever - n/v - Hematuria - Pyuria - Cloudy- foul smelling urine - Confusion - Back & flank pain Urinalysis - Presence of bacteria, WBC, + leukocyte esterase & nitrites Meds - Abx (fluoroquinolones, nitrofurantoin, trimethoprime) - Phenazopyridine bladder analgesic warn pt is can turn urine orange CX - Urosepsis hypotension, tachycardia, tachypnea, fever Prevention - Drink > 3L - Maintain good body hygiene - Empty balder regularly (q 3-4 hrs) - Urinate before & after sex - Drink cranberry juice - Wipe front to back - Avoid bubble baths & perfume containing feminine hygiene products - Avoid sitting in wet bathing suits & pantyhose & tight clothing PYLEONEPHRITIS UROLITHIASIS - Kidney infection, usually caused by E. coli - Starts in lower UT kidneys RFs - BPH, kidney stones, pregnancy, increased urine pH, incomplete bladder emptying, chronic dz S/S - Costovertebral tenderness - Fever - Back flank pain - HTN - Chills - Tachypnea - n/v labs - urinalysis + for leukocyte esterase, nitrites, WBC, bacteria - elevated creatinine, BUN, ESR< C- reactive protein meds - abx, opioid analgesics Cx - septic shock hypotension, tachycardia, fever, - CKD HTN - Presence of stones (calculi) in urinary tract, composed of calcium phosphate, calcium oxalate, or uric acid RFs - Male, damage to UT lining, high acidity or alkalinity of urine, urinary retention, dehydration S/S - Severe pain (flank pain abdomen) - Dysuria - Fever - Diaphoresis - n/v - pallor - tachycardia - tachypnea - oliguria - hematuria Management - monitor I & Os - strain all urine (& save stone for lab analysis) - increase fluids to 3 L/ day - encourage ambulation Meds - Opioid analgesics or NSAIDs - Antispasmodics Procedure - Lithotripsy - Uses laser or shock wave energy to break up stones, done under moderate sedation - Strain urine following procedure - Hematuria, bruising@ site is expected - Stenting - Ureter lithotomy (extract stone) Education - Increase fluids 2-3L/day - For calcium phosphate stones, limit intake of animal protein & Na - For oxalate stones, limit foods high in oxalates: spinach, rhubarb, strawberries, beets, chocolate, nuts, tea - For uric acid stones, limit foods high in purines (meat, whole grains, legumes REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM FEMALE DXs MENSTRUAL DZ MENOPAUSE CYSTOCELE/ RETROCELE Pap smear - Tests for cancerous cells in the cervix - Recommended q 3 years starting @21 Mammogram - Tests for breast cancer - Recommended annually starting @ 40 - Avoid use of deodorant, lotion, powders in axillary region prior to exam Menorrhagia - Excess menstrual bleeding (amount/duration) Amenorrhea - Absence of menses - Can be d/t low body fat % or anorexia PMS - Hormonal imbalance before period - Irritability, depression, breast tenderness, bloating, ha Endometriosis - Overgrowth of endometrial tissue outside the uterus - Common cause of infertility - Cessation of menses (no periods in 12 mo) S/S - Hot flashes - Decreased vaginal secretion - Mood swings - Decreased bone density Meds - Hormone therapy-oral, transdermal or intravaginally - Prevents hot flashes, reduces vaginal tissue atrophy & decreases bone fracture risk - Taking HT increases risk of DVT, stroke, MI, & breast cancer Education - Quit smoking immediately - Avoid knee-high stockings & other restrictive socks/ clothing - Avoid sitting for long periods - Move & stretch regularly - Monitor for DVT unilateral leg pain, edema, warmth or MI - Cystocele is protrusion of bladder through anterior vaginal wall - Rectocele is protrusion of rectum through posterior vaginal wall RFs - Obesity, Older age, Chronic constipation, family hx, forceps delivery Tx - Vaginally pessary: device used to provide support & block protrusion of other organs - Kegel exercises - Sx FIBROCYSTIC BREAST CONDITION MALE DXs BPH TURP sx - Noncancerous condition development of fibrotic connective tissue & cysts in the breasts S/S - Breast pain - Rubber-like lumps in upper/outer quadrant of breasts Dx - Breast ultrasound PSA - Measures the amount of protein produced by the prostate gland in the bloodstream - Increased amount of PSA presence of prostate cancer or BPH - Do NOT do DRE prior to drawing blood for PSA - Recommend annually for men >50 - AA men & men w/ family hx should start screening early - PSA >4 ng/mL requires evaluation - Men should not ejaculate 24 hrs prior to test DRE - Palpation of the prostate gland through rectal wall - Dr. inserts finger into the anus - Abnormal finding: enlarged or hard prostate, irregular shapes or lumps - Enlargement of prostate gland that impairs urine outflow from bladder urinary retention increased risk of infection & reflux into kidneys S/S - Urinary frequency - Urgency - Retention - Hesitancy - Incontinence - Post-void dribbling - Reduced urinary stream force - Hematuria - Nocturia - Frequent UTIs Labs - Elevated PSA, WBC w/ UTI, creatinine/ BUN w/ kidney involvement Meds - Androgen inhibitor (finasteride) - Peripherally actin antiadrenergic (Tamsulosin) Sx - Prostatic stent keeps urethra patent - Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP sx) Management - Pt. will have 3 way catheter - Perform continuous bladder irrigation (CBI) w/ NS or prescribed solution - Goal is to keep irrigation outflow light pin - Increase CBI rate if irrigation outflow is bright red, ketchup- appearing or contains clot - If catheter becomes obstructed bladder spasms, reduced outflow turn of CBI, irrigate w/ 50 mL using large piston syringe - Expected: pt. will have continuous need to urinate - Report decreased UOP Meds - Analgesics - Antispasmodics to prevent bladder spasms - Stool softener - Abx prohlylaxis Teaching - Drink 12 or more 8 oz/ day - Avoid caffeine or ETOH (bladder stimulant) - If urine is bloody, stop activity, rest & increase fluid intake MS SYSTEM DXs ARTHROPLASTY KNEE ARTHROPLASTY HIP ARTHTOPLASTY Arthroscopy - Allows visualization of the internal structure of the joint - CI if pt. has infection or cannot bend at least 40 degrees Nuclear scan - Radioactive material injected hrs before scan - Repeat scan at 24, 48 & 72 hours - Bone scan detects tumors, fractures, bone dz - Gallium scan are more sensitive than bone scan DX - Used to determine bone mass & presence of osteoporosis Electromyography - Needles placed into muscle & electrical activity recorded during muscle contraction - Used to dx cause of muscle weakness - Replacement of a dz’d joint w/ prosthetic joint - Used for pts. w/ osteoarthritis, RA, trauma or congenital defects S/S - Joint pain - Crepitus - Swelling CI - Current/ recent infection - Arterial insufficiency to affected extremity PRE - Admin epoetin alfa to increase Hgb, autologous blood donation - Advise pt. to scrub w/ antiseptic soap the night before & morning of sx POST - Initiate continuous passive ROM (CPM) machine immediately after sx (if ordered) - DO NOT place pillow under knee (or use knee gatch), in order to prevent flexion contractures - Wear elastic stockings on both legs - Admin analgesics, abx, ACs, ice therapy - Perform NV checks q 2-4 hrs PT. should NOT kneel or do deep- knee bends POST - Monitor for S/S of DVT unilateral pain, swelling, erythema - Monitor for PE SOB, CP, tachycardia - Apply SCDs or anti-embolic stockings - Encourage early ambulation, foot exercises - Place abduction device between legs - No crossing of legs - Do not allow flexion of hip> 90 degrees - Don’t cross legs at ankles or knees - Externally rotate pt’s toes (do not allow internal rotation) - Monitor for joint dislocation: onset of severe pain, hearing a “pop”, shortened affected extremity, internal rotation - Use elevated toilet seat, avoid low cars AMPUTATIONS OSTEOPOROSIS FRACTURES IMOBLIIZATION DEVICES Indications - Trauma wrap severed extremity in dry sterile gauze, place in sealed plastic bag, submerge in ice water - Infection - PVD reduced pulses, cooler temp, gangrene, cyanosis, decreased sensation Management - Tx phantom limb pain w/ BBs, antiepileptics, antispasmodics, antidepressants - Position stump in dependent position - Perform ROM exercises - To shrink residual limb (in preparation for prosthesis) wrap stump in 8 figure-wrap - Avoid elevating stump for 24 hrs Have pt. lie prone for 20-30 min several x/day - Rate of bone reabsorption exceeds rate of bone formation low bone density & fragile bones - Osteopenia is a precursor RFs - Female, thin/lean body, menopause, insufficient Ca or Vitamin D intake, smoking, EOTH abuse, excess caffeine intake, lack of physical activity, hyperparathyroidism, long-term steroid use, long-term anticonvulsant med use, hx of anorexia nervosa S/S - Back pain - Fractures - Kyphosis - Reduced height Dx - Dual x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) Meds - Calcitonin, estrogen (increased risk of breast cancer & DVT) - Raloxifene, alendronate (remain upright for 30 min after) Teaching - Get sufficient C & vitamin D - Moderate sun exposure using sunscreen - Wt. bearing exercises - Home safety - Measures to prevent falls Closed (simple) - Does not break skin surface Open (compound) - Breaks skin surface, increased risk of infection Complete - Goes through entire bone Incomplete - Goes partly through bone Comminuted - Bone split in multiple pieces Compression - 1 or more bones in spine weakened & collapse (d/t loading force) Oblique - Fracture occurs @oblique angle Spiral - Fracture from twisting motion ABUSE RFS - Osteoporosis, long-term steroid use, falls, trauma, bone cancer, substance abuse S/S - Pain - Crepitus - Deformity in extremity - Muscle spasms - Edema - Ecchymosis Management - Stabilize affected area - Elevate affected limb - Apply ice - Perform NV checks q hr: pain level, sensation (numbness, tingling, lack of sensation), skin temp, cap refill: 2 secs, pulses, movement Meds - Abxs, analgesics, muscle relaxants Sxs - External fixation: pins attached to external fame - Open reduction & internal fixation 9ORIF): pins, plates, screws, rods used internally - Handle plaster casts w/ palms not fingertips & wearing gloves until cast is dry - Elevate cast above level of heart for 1st 24-48 hrs - Tell pt. not to place objects under case - Itching can be relieved by blowing cold air from a hair dryer under cast - Report to provider: hot spots, areas w/ increased drainage, malodorous areas Skin - Wts. attached to pts. skin to decrease muscle spasms & immobilize the extremity before sx - Bryant: for hip dysplasia in kids - Buck’s for hip fractures in adult pts Skeletal - Screws are inserted into the bone - Used for long bone fractures Halo - Used for cervical bone fractures - Make sure wrench to release rods is attached to the vest so CPR can be performed Management - Asses NV status q hr for 1st 24 hrs, then q 4 hrs after - Do not life or remove wts. - Do not left wts. rest on the floor (hang freely) - Muscle spasms are expected & should be treated w/ med, reposition, heat or massage - Report unrelieved muscle spasm to Dr. - For Halo traction, move pt. as a unit & do not apply pressure to rods PIN SITE CARE - Monitor for s/s of infection increased drainage, erythema, loosening of pins, skin tenting @ pin site - Clean pins using NEW cotton tip swab for each pin - DO NOT remove crusting @ pin site COMPARTMENT SYNDROME FAT EMBOLISM OSTEOMYELITIS OSTEOARTHRITIS - Increased pressure within muscle compartment of an extremity that impairs circulation S/S - 5Ps: - Intense pain w/ passive movement - Paresthesia (early sign) - Paralysis (late sign) - Pallor - Pulselessness (late sign) - Hard/swollen muscles Tx - Fasciotomy - Fat globule from bone marrow that travels to lungs, impairing respirations - Long bone & hip** RF: males S/S - Confusion (early) - Petechiae rash on upper body (late) - hypoxemia - Bone infection S/S - Bone pain - Erythema - Edema - Fever - Elevated WBC Tx - Long-term abx therapy - Sx debridement of bone - Hyperbaric O2 therapy - Progressive degermation of articular cartilage in joints RFs - Older age, women, obesity, smoking, repetitive stress on joints S/S - Joint pain/ stiffness - Crepitus - Enlarged joints - Herberden’s nodes distal interphalangeal joints - Bouchard’s nodes proximal interphalangeal joints Management - Apply ice (acute inflammation) or heat - Splinting and/or use of assistive devices - Physical therapy - TENs (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation) Meds - Oral analgesics - Topical analgesics (capsaicin wear gloves when applying, do not apply on areas w/ broken skin, burning sensation is normal - Glucosamine: increases synovial fluid production & helps rebuild cartilage - Injections: glucocorticoids, hyaluronic acid Sx - Total joint arthroplasty RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS OSTEOARTHRITIS - Inflammatory dz process - Pain after rest/immobility, gets better w/ movement - Affects ALL joints, symmetrical - Swan neck & boutonniere deformities - + Rheumatoid factor - Degenerative dz process - Pain w/ activity, gets better w/ rest - Affects specific joints, NOT symmetrical - Heberden’s & Bouchar’s nodes - - rheumatoid factors INTUGMENTARY SYSTEM DX TEST TX OF SKIN INFECTION PSORASIS SEBORRHEIC DERMATITIS Culture & sensitivity - Used to identify & tx bacterial lesions - Get culture prior to starting abx - Final results in 72 hrs - Culture identifies the pathogen - Sensitivity determines which abx can be used to kill pathogen Tzanck smear - Used to dx viral skin lesion KOH test - Used to dx fungal skin lesion Bacterial - Bathe w/antibacterial soap - Remove dried exudate before applying topical antibacterial ointments Viral - Apply Burrow’s solution to promote crusting of lesions - Avoid restrictive clothing - Topical antiviral ointments (acyclovir) Fungal - Apply antifungal cream or powder (clotrimazole) BID for 1-2 weeks after lesions are no longer visible - Autoimmune disorder that results in overproduction of keratin & formation of dry/scaly patches on the skin - Characterized by periods of exacerbations & remissions S/S - Scaly patches - Pitting/ crumbling nails Meds - Topical steroids (triamcinolone) Do not apply to face, skin folds, or broken skin - Tar preparations used in conjunction w/ ultraviolet B light therapy (remove cream before therapy cream may stain skin & clothes). Can increase risk of skin cancer - Immunosuppressants Procedures - Ultraviolet therapy - Admin psoralen 2 hrs before tx (enhances photosensitivity) - Provide eye protection to pt. - Inflammation in areas that contain a high level of sebaceous glands (scalp, forehead, nose, groin, axilla) - Characterized by periods of exacerbations & remissions - Most common: dandruff S/S: - Waxy or flaky plaques or scales in oily parts of the body TX - Topical corticosteroids - Antiseborrheic shampoos (i.e. shampoos containing selenium) - Use several times a week, leave in hair for 2-3 minutes BURNS BURN PHASES BURN MANAGEMENT Rule of nines: calculates % of body burned: - Head 9% - Each arm 9% - Each leg 18% - Anterior torso 18% - Posterior torso 18% - Perineal area 1% Depth of injury Superficial - Damage to the epidermis - Red/pink color, no blisters - sunburn Superficial partial thickness - damage to the epidermis & part of the dermis - red/pink color w/ blisters - no eschar Deep partial thickness - damage to the epidermis & deep into dermis - red/white color - NO blisters - Soft/dry eschar Full thickness - Damage to epidermis, dermis & part of Sub Q tissue - Color varies - Pain may not be present - No blisters, hard eschar Deep full thickness - Damage to all skin layer - Black color Emergent - 1st 24-48 hrs from injury - Initial fluid shift: shifts from interstitial space hypovolemia - Labs: elevated Hct, Hgb, K; hyponatremia Acute - Starts w/ fluid resuscitation is complete & ends when wounds are healed - Fluid immobilization (Diuretic stage): 48-72 hrs after injury - Fluid shifts back into vascular system - Labs: decreased Hct, hgb, protein, albumin hyponatremia, hypokalemia, Rehabilitation - Beings when wounds are healed & ends when reconstructive procedures are complete - Stop burning process - Flush chemical burns w/ large volume of water - Do not apply greasy lotion or butter to burns - Admin tetanus vaccine - Maintain airway - Singed eyebrows, nasal hair or sooty sputum are indications of inhalation damage - Admin humidified O2 - Insert large-bore needles for fluid resuscitation (0.9% NaCl or LR) - Admin colloids or plasma expanders - Monitor for s/s of shock UOP < 30 ml/hr, confusion, fever, decreased bowel sounds, increased capillary refill time - Admin IV opioid analgesics - Avoid IM or Sub Q injections - Prevent infection: no fresh plants/ flowers, no fresh fruits/veggies, limit visitors - Provide nutritional support: increase calorie & protein intake - Provide TPN - Preserve pt. mobility: active & passive ROM exercise to prevent contractures - Apply pressure dressing Parkland formula - Amount of fluid needed in 1st 24 hrs= 4 mL LR x kg wt x BSA burned - Admin ½ in 1st 8hrs - Admin ¼ in 2nd 8hrs - Admin ¼ in 3rd 8hrs Meds - Silver sulfadiazine: antimicrobial, does not penetrate eschar transient neutropenia - Mafenide acetate antimicrobial, does not penetrate eschar metabolic acidosis Skin grafts - Immobilize graft site, elevate extremity, monitor for s/s of infection Allograft - From human cadavers Xenograft - From animals Autograft - From another part of pt’s body ENDOCRINE DX TESTS PHEOCHROMOCYTOMA DIABETES INSIPIDUS SIADH Water deprivation test - Tests to see if the kidneys are able to concentrate urine when blood osmolality increases - If kidneys are unable to concentrate urine nephrogenic DI Vasopressin test - Tests to see if admin of Sub Q vasopressin increase urine specific gravity - If vasopressin causes increase in urine specific gravity neurogenic DI (issue w/ pituitary gland) Dexamethasone suppression - Tests to see if admin of dexamethasone (steroid similar to naturally occurring cortisol) in decreased levels on ACTH & cortisol - If there is NO decrease Cushing’s dz ACTH stimulation test - Tests to see if admin of ACTH increase levels of cortisol in body. - If there is NO increase Addison’s dz - Collect 2 24-hr urine samples (one before & after admin of ACTH) Fasting glucose - No foods or fluids 8 hrs before - Normal < 110 mg/dL Oral glucose tolerance test - Fast for 10-12 hours before - Pt. consumes specific amount of glucose - Blood samples taken q 30 minutes for 2 hors - Normal < 140 HgbA1c - BEST indicator of average blood glucose levels over part 3-4 mo - < 5.7%: no diabetes - 5.7- 6.4: pre-diabetes - >6.5: diabetes - Benign tumor on adrenal gland hypersecretion of catecholamines increased SNS response S/S - Tachycardia - HTN - Diaphoresis - HA - SOB DX - VMA - Catecholamine Meds - Anti-HTNs until sx SX - Remove tumor from adrenal gland - Deficiency of ADH kidneys being able to concentrate urine S/S - Large amounts of diluted urine - Polydipsia - Dehydration tachycardia, hypotension, sunken eyes, dry mucous membranes, weakness, fatigue) Labs - Urine: DECREASED specific gravity < 1.005; decreased osmolality < 200, decreased sodium - Blood: INCREASED serum osmolality > 300 mOsm/L, increased Na DX - Water deprivation test - Vasopressin test Meds - ADH replacement (desmopressin/ vasopressin) - For intranasal admin, clear nasal passageway before inhalation - Excessive release of ADH from posterior pituitary gland increased reabsorption of water (not Na) by kidneys Causes - Brain tumor, head injury, meningitis, meds S/S - Small amount of concentrated urine - Fluid volume excess tachycardia, HTN, crackles, distended neck veins, wt. gain) - Ha - Weakness - Muscle cramping - Confusion - Seizures - Coma Labs - Urine: INCREASED specific gravity > 1.030, osmolarity, Na - Blood: DECREASED serum osmolality <270 mEq/L, Na Management - Fluid restriction - Monitor I & Os (Hyponatremia) - Weigh pt. daily - Provide hypertonic IV fluids - Admin furosemide SYNTHESIS PATHWAYS HYPERTHYROIDISM THYROIDECTOMY HYPOTHYROIDISM Thyroid synthesis - Hypothalamus produces TRH (thyroid releasing hormone) - TRH causes the anterior pituitary gland to produce TSH (Thyroid stimulating hormone) - TSH causes the thyroid gland to produce T3/T4 (thyroid hormones that control metabolism in the body) Cortisol synthesis - Hypothalamus produces CRH (cortisol releasing hormone) - CRH causes the anterior pituitary gland to produce ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) - ACTH causes the adrenal cortex to produce cortisol metabolism, immune function & body’s response to stress - Excess thyroid hormones (T3 & T4) released from the thyroid gland hypermetabolic state Causes Primary - Issue w/ thyroid gland - Graves dz (autoimmune) - thyroid nodule hypersecretion of T3/ T4 Secondary - Issue w/ pituitary gland - Anterior pituitary gland produces too much TSH (due to tumor) Tertiary - Issue w/ hypothalamus - Hypothalamus produces too much TRH S/S - Tachycardia - Hypotension - Heat intolerance (overheated in rising temps) - Exophthalmos - Wt. loss - Insomnia - Diarrhea - Warm/ sweaty skin Labs - Increased T3/ T4 - Decreased TSH (in primary hyperthyroidism) Management - Increase pt’s calories & protein - Monitor I & Os - Exophthalmos: tape eyelids closed, provide eye lubricant Meds - PTU - BBs - Iodine solutions (mix w/ juice to mask taste) - Radioactive iodine: stay away from kids for 2-4 days), flush toilet 3 times, do not share toothbrush, use disposable plates/ utensils CX - Thyroid storm excessively high levels of thyroid hormones, with high mortality rate - Causes: infection, stress, DKA - S/S: HTN, CP, dysrhythmias, SOB, delirium SX - Thyroidectomy (removal of thyroid gland) - Pt. will need thyroid replacement therapy for the rest of their life POST CARE - High fowlers - Prevent & monitor for hemorrhaging - Check dressing & back of neck for bleeding - Support pts. neck & head w/ pillows/sandbags - Teach pt. to avoid neck flexion or extension - Have tracheostomy supplies available at bedside - Monitor for signs of parathyroid gland damage (s/s of hypoglycemia numbness/ tingling around mouth or toes, muscle twitching, + Chvostek’s or Trousseau’s sign - Administer calcium gluconate for tx of hypoglycemia - Admin steroids - Inadequate production of thyroid hormones (T3 & T4) by thyroid gland Causes Primary - Issue w/ thyroid gland - Hashimoto’s dz (autoimmune) - Cretinism (severe hypothyroidism in infants) Secondary - Issue w/ pituitary gland - Anterior pituitary gland produces insufficient TSH (d/t tumor Tertiary - Issue w/ hypothalamus - Hypothalamus produces insufficient TRH S/S - Hypotension - Bradycardia - Lethargy - Cold intolerance (abnormal sensitivity to cold temps) - Constipation - Wt. gain - Thin hair - Brittle fingernails - Depression Labs - Decreased T3 (<70) - Decreased T4< 4 - Increased TSH (w/ primary hypothyroidism - Anemia Management - Encourage frequent rest periods - Low calorie, high fiber & increased activity to promote wt. loss & prevent constipation - No fiber laxatives (interferes w/ levothyroxine absorption) - Provide extra blankets, increase room temperature, no electric blankets Meds - Levothyroxine: start w/ low dose, gradually increase - Take 1 hr before breakfast w/ full glass of water CX - Hyperthyroidism (d/t levothyroxine) - Myxedema coma severe hypothyroidism - Causes: untx’d hypothyroidism, infection/ illness, abrupt discontinuation of levothyroxine - S/S: hypoxia, decreased CO & LOC, bradycardia, hypotension, hypothermia - Management: maintain patent airway, monitor ECG, warm pt. admin large doses of levothyroxine CUSHING’S SYNDROME HYPOPHYSECTOMY ADDISON’S DZ DM - Overproduction of cortisol by adrenal cortex Causes Primary - Adrenal dysfunction - Over secretion of cortisol by the adrenal cortex r/t adrenal hyperplasia or tumor Secondary - Pituitary dysfunction - Over secretion of ACTH by the anterior pituitary gland r/t tumor Long term use of steroids for chronic conditions S/S - Increased infection - Thin/fragile skin - Edema - Wt. gain moon face, buffalo hump, increased abdominal girth - HTN - Tachycardia - Bone pain/ fractures - Hyperglycemia - Gastric ulcer - Hirsutism - Acne - Moon face - Buffalo hump Labs - Elevated cortisol levels in saliva - Increased glucose, Na levels - Decreased K, Ca levels DX - Dexamethasone suppression test Management - Maintain safe environment d/t increased risk of fractures - Prevent infection - Protect pt’s skin from breakdown Diet - Decrease Na intake, increase K, Ca & protein Meds - Ketoconazole (adrenal corticosteroid inhibitor) - Spironolactone SX’s - Cytotoxic agents for tumors causing condition - Hypophysectomy (removal of pituitary gland) - Adrenalectomy (removal of adrenal gland): hormone replacement therapy needed, monitor for adrenal crisis r/t drop in cortisol levels Monitor for CSF leak - Halo sign in drainage (clear in center, yellow on edges) - Sweet tasting drainage - Clear drainage from the nose - HA - Teach pt to AVOID activities that increase ICP coughing, sneezing, blowing nose, bending @ waist, straining during bowel movements - increase fiber intake - Decreased sense of smell expected 3-4 mo - Do not brush teeth for 2 weeks (flossing & rinsing mouth OK) - Inadequate secretion of hormones by adrenal cortex (aldosterone, cortisol, sex hormones) Causes Primary - Adrenal cortical insufficiency - Damage or dysfunction of adrenal cortex r/t autoimmune dysfunction or tumors Secondary - Pituitary dysfunction - Pituitary tumor or hypophysectomy S/S - Wt. loss - Hyperpigmentation (bronze skin) - Lethargy - n/v - hypotension - dehydration Labs - increased K & Ca - decreased Na, glucose, cortisol DX - ACTH stimulation test, admin ACTH measure cortisol response for 30 min, 1 hr Primary- cortisol levels do not rise Secondary- cortisol levels DO rise Management - Admin steroids, f/e - Tx hyperkalemia sodium polystyrene sulfonate, insulin (w/ glucose), Ca, bicarbonate - Tx hypoglycemia food, supplemental glucose CX - Addisonian crisis: rapid onset, medical emergency - Due to infection trauma or abrupt discontinuation of steroids - Chronic hyperglycemia d/t insufficient insulin production by pancreas and/ or insulin resistance of cell in the body Type 1 - Destruction of beta cells in pancreas d/t autoimmune dysfunction - Pts. are insulin dependent - Usually starts @ young age Type 2 - Progressive insulin resistance & decreased insulin production r/t obesity, inactivity & heredity - Usually starts later in life Gestational - High blood glucose during pregnancy RFs - Obesity, HTN, hyperlipidemia, smoking, genetics, race (AA, AI, Hisp), inactivity S/S - 3Ps - Polydipsia - Polyphagia - Polyuria - Hyperglycemia - Wt. loss - Dehydration decreased skin turgor, weak pulse, hypotension, dry mucous membranes - Fruity breath - Kussmaul respirations increased rate & depth - n/v - ha - decreased LOC DX 2 or more of the following on separate days: - casual blood glucose > 200 - fasting glucose > 126 - glucose > 200 w/ oral glucose tolerance test - HgbA1C > 6.5%** (best indicator of tx compliance. Goal is < 7%) Meds - Insulin: rapid (lispro), short (regular), intermediate (NPH), long acting (glargine) - Oral hypoglycemic agents (Type 2 only): metformin, glipizide, repaglinide, pioglitazone, acarbose Teaching - Rotate Sub Q injection sites to prevent lip hypertrophy - Mixing insulins: draw up clear (short-acting regular) before cloudy (longer-acting glargine) - Never mix long-acting insulin (glargine) with other insulins - Monitor for s/s of hypoglycemia confusion, diaphoresis, Ha, shakiness, blurred vision, decreased coordination CX - CV dz: MI, HTN - Cerebrovascular dz: stroke - Diabetic retinopathy: impaired vision - Diabetic neuropathy: nerve damage neuropathic pain, numbness, ischemia, infection - Diabetic nephropathy: kidney damage - DKA - HHS: HYPOGLYCEMIA FOOT CARE FOR DIABETES DKA HHS - Blood glucose < 70 Conscious pts. - Consume 15-20g quickly absorbed carbohydrate (4-6 oz of juice of soft drink) - Recheck blood glucose in 15 min if still < 70, repeat and check again in 15 min - Once blood glucose is >70, consume snack containing protein & carb Unconscious pts. - Admin IM or SubQ glucagon - Repeat in 10 min if pt. is still not conscious - Once pt. is conscious & can swallow safely have pt. consume a carb snack - Inspect feet daily - Test water temp w/ hands, use lukewarm water - Dry feet thoroughly after bathing - Apply moisturizer to feet, not between toes - Wear cotton socks (no synthetic fabrics) - Wear leather shoes or slippers w/ soles. DO not go bare foot or wear open toe/heel shoes - Use foot powder w/ cornstarch on sweaty fet - Cut nails straight across, after bath/shower - Check shoes for objects that can cause injury - Do not use OTC products for corns/ callouses - Do not apply heating pads to feet - life threatening blood glucose > 300 & ketones in blood & urine - metabolic acidosis - rapid onset - more common in type 1 RFs - infection, stress/illness, untx’d or undx’d Type 1 DM, missed insulin S/S - polyuria - polydipsia - polyphagia - wt. loss - fruity breath - Kussmaul respirations - GI upset - Dehydration hypotension, Ha, weakness - - life threatening blood glucose > 600 - no ketosis - severe dehydration - gradual onset - more common in type 2 - metabolic acidosis RFs - older age, inadequate fluid intake, decreased kidney function, infection, stress S/S - polyuria - polydipsia - polyphagia - dehydration hypotension, Ha, weakness Management - tx underlying cause (infection) - admin IV fluids & insulin - check blood glucose hourly (goal < 200) - monitor K. insulin causes K to move back into cells (risk of hypokalemia) - admin Bicarb for metabolic acidosis Teaching - monitor blood glucose more frequently when sick (q 1-4 hrs) - DO NOT skip insulin when sick - Wear medic alert bracelet - Drink 2-3 L/day - Notify Dr. if illness lasts > 1 day or temp > 38.6 degrees C - Notify Dr. for blood glucose > 250 or for urine + for ketones IMMUNE SYSTEM WBCs TYPES TYPES OF IMMUNITTY IMMUNIZATIONS 5,000-10,000/mm^3 Leukopenia - WBC < 4,000 - Can indicate presence of autoimmune dz, BMS, drug toxicity Leukocytosis - WBC >10,000 - Can indicate presence of infection or inflammation Neutropenia - Neutrophil < 2,000 - Indicates compromised immunity “left shift” banded neutrophils - Indicates release of immature neutrophils when body is fighting infection Neutrophils - 55-75% - Increased during acute bacterial infections Lymphocytes - 20-40% - Increased during chronic bacterial or viral infection Monocytes - 2-8% - Increased during protozoal & viral infection, tuberculosis, chronic inflammation Eosinophils - 1-4% - Increased during allergic rxn or parasite infection Basophils - 0.5-1% - Increased d/t leukemia Active natural - Body produces antibodies in response to exposure to live pathogen Active artificial - Body produces antibodies in response to vaccine Passive natural - Antibodies are passed from the mom to the baby to her baby through the placenta or breastmilk Passive artificial - Immunoglobulins are administered to an individual after they have been exposed to a pathogen Pneumococcal - for adults who are immunocompromised, have chronic dz, smoke or live in long-term facility Meningococcal - for individuals living in crowded living environments (students in dorms) Herpes Zoster - for adults > 60 yrs old Expected AE - low grade fever - pain @ injection site - irritability Management - admin antipyretics & cool compresses - encourage pt. to mobilize affected extremity Document: vaccine type, date, route, site, manufacturer, lot #, expiration date, pt’s name/ address/ signature VACCINES HIV/AIDS LUPUS GOUT ARE NOT CI FOR COMMON COLDS OR MINOR ILLNESSES General CI - previous anaphylactic rxn to vaccine - allergy to component of a vaccine - seizure within 3 days of vaccination - pregnancy - severe immunodeficiency (HIV, chemo, long-term steroid use) specific CI - MMR, varicella: allergy to gelatin/ neomycin - Hepatitis B: allergy to baker’s yeast - Influenza: allergy to egg protein HIV - Retrovirus that targets CD4+ lymphocytes (T-Cells) decreased immune function & susceptibility to infections - AIDS= stage 3 (end-stage) HIV infection RFs - Unprotected sex, multiple sex partners, perinatal exposure (all pregnant women should be tested!!), IV drug use, health care workers S/S - Flu-like - Weakness - Night sweats - Ha - Wt. loss - Rash Stage 3 (AIDS) - CD4+ count < 200 S/S - Kaposi’s sarcoma - TB - Pneumonia - Wasting syndrome - Candidiasis of the airways - Herpes - Other infection DX - + ELISA test, confirmed w/ Western blot test Meds - 3-4 antiretroviral meds (-vir) Teaching - Practice good hand hygiene, bathe daily w/ antimicrobial soap - Avoid raw foods - Don’t clean cat litter boxes - Avoid sick ppl - Practice safe sex - Ongoing monitoring of CD4+ counts - Autoimmune disorder chronic inflammation in the body - No cure - Dz is characterized by periods of exacerbations & remissions Discoid - Affects skin (butterfly rash) Systemic - Affects the connective tissues in multiple organs RFs - Females, ages 20-40, race (AA, Asian, NA) S/S - Butterfly rash on face - Joint pain - Fever - Fatigue - Raynaud’s phenomenon - Anemia - Pericarditis - Lymphadenopathy Labs - + ANA titer, decreased serum complement (C3/C4), decreased RBC, WBC, platelets - Increased BUN, creatinine w/ kidney involvement Meds - NSAIDS, immunosuppressants, antimalarials (hydroxychloroquine), topical steroid creams for rash Teaching - Avoid UV/ Sun exposure - Avoid sick ppl (d/t risk of infection w/ immunosuppressants) CX - Renal failure - Inflammatory arthritis formation of uric acid crystals in joints & body tissues RFs - Obesity, ETOH consumption, high purine diet (meat), CV dz, starvation dieting S/S - Severe joint pain (most common in metatarsophalangeal joint in great toe) - Erythema - Swelling - Warmth in affected joint - Tophi w/ chronic gout Meds - Acute gout: Colchicine, NSAIDS, corticosteroids - Chronic gout: allopurinol, probenecid (avoid ASA) RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS CANCER CHEMOTHERAPY RADIATION THERAPY - Chronic, progressive, autoimmune dz inflammation, thickening & deformation of the joints - Joints are affected bilaterally & symmetrically - Characterized by periods of exacerbations & remissions RFs - Female gender, ages 20-50, genetics S/S - Joint pain - Morning stiffness - Fatigue - Joint swelling w/ erythema and warmth - Swan neck & boutonniere deformities in fingers - Sub Q nodules - Fever - Red sclera - Lymphadenopathy Labs - + Rheumatoid factor antibody, + ANA titer - Elevated WBCs, ESR, CRP DX - Arthrocentesis (aspiration of synovial fluid from joint) to test for WBCs, RF Meds - NSAIDS, immunosuppressants, antimalarials Procedures - Plasmapheresis (to remove antibodies from blood) - Total joint arthroplasty Education - Take hot shower to relieve morning stiffness - Physical activity to preserve ROM - Use of assistive devices CX - Sjogren’s syndrome (dry eyes, mouth & vagina) RFs - Older age, genetics, smoking, sun exposure - Diet high in fat and/or red meat - Low in fiber Staging (TNM) T - Tumor (T1-T4) - Size & extent of tumor N - Node (N0-N3) - # of regional lymph nodes involved M - Metastasis (M0, M1) - Presence of metastasis - M0- no metastasis - M1- metastasis present DX - Biopsy - Imaging (MRI, CT, PET scan, ultrasound) TX OPTIONS - Tumor excision - Chemotherapy - Radiation therapy - Hormonal therapy - Immunotherapy CX - Malnutrition d/t increased metabolism, inability to digest and/or absorb nutrients - n/v due to chemo - infection d/t immunosuppression - alopecia - mucositis (inflammation of gums/mouth) - anemia, thrombocytopenia (d/t immunosuppression) - destroys rapidly dividing cells - admin through implanted port or central IV catheter Management - initiate neutropenic precautions for WBC < 1,000 - monitor temp, report > 37.8 C - restrict visitors who are ill - ensure visitors perform hand hygiene - avoid invasive procedures - no fresh flowers, plants - keep dedicated equipment in pts. room - admin filgrastim to increase WBC count - avoid crowds, yard work - do not change cat litter box - do not consume fluids that have been sitting @ room temp > 1 hr - wash dishes in hot water or in dishwasher - wash toothbrush in dishwasher daily or rinse in bleach solution - do not share toiletries w/ others! CX Malnutrition - admin antiemetic meds (ondansetron) - admin meds to increase appetite (megestrol) - avoid drinking liquids w/ meals - eat cold or room-temp foods - consume high calorie/protein, nutrient dense diet - use supplements as needed Mucositis - provide oral care before & after meals - avoid glycerin or ETOH containing mouthwash - rinse mouth w/ saline solution 2x/day - use soft toothbrush - east soft bland foods scrambled eggs (avoid spicy, salty, acidic foods) Anemia/ thrombocytopenia - admin epoetin alfa (increases RBC) & ferrous sulfate - monitor for blood in stool, urine & vomit - avoid IVs & injections - apply prolonged pressure after blood draws or injections - use electric razor, soft toothbrush - avoid blowing nose vigorously - avoid NSAIDS - prevent injury d/t risk of bleeding External - skin over target area will be marked - do not wash off marks - wash skin over affected areas w/ mild sap & water, gently pat dry - do not apply lotions, powders, ointments to irritated skin - wear loose, soft clothing - avoid sun or heat exposure to affected area internal - keep door closed, with warning on door - limit visitor to 30 min, maintain distance of > 6 ft - wear lead apron & dosimeter film badge SKIN CANCER LEUKEMIA/LYMPHOMA BREAST CANCER PROSTATE CANCER - - - - PERIOPERATIVE SX INFORMED CONSENT MALIGNANT HYPERTHERMIA POST-OP CARE - - - - [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 56 pages
Instant download

Instant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 29, 2020
Number of pages
56
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 29, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
38


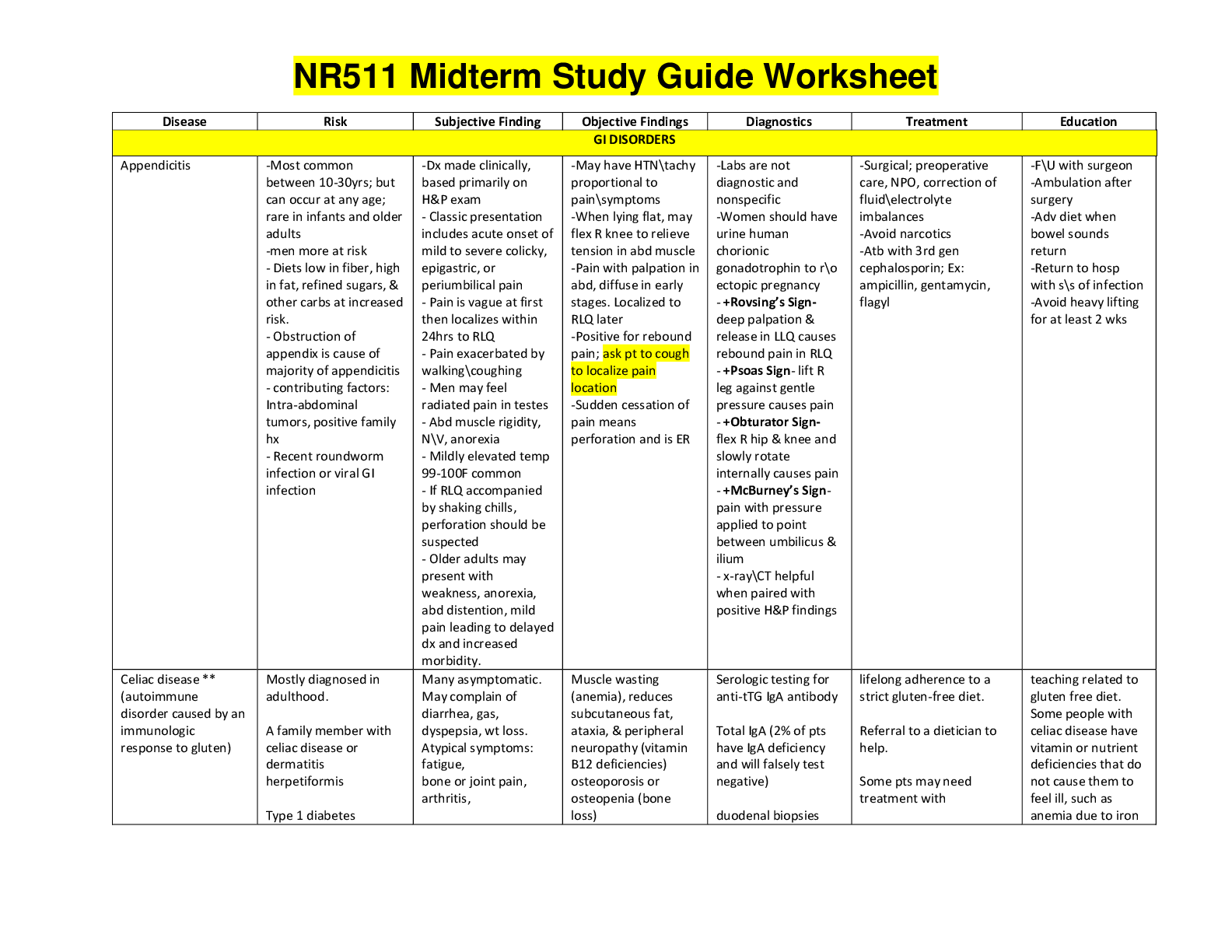






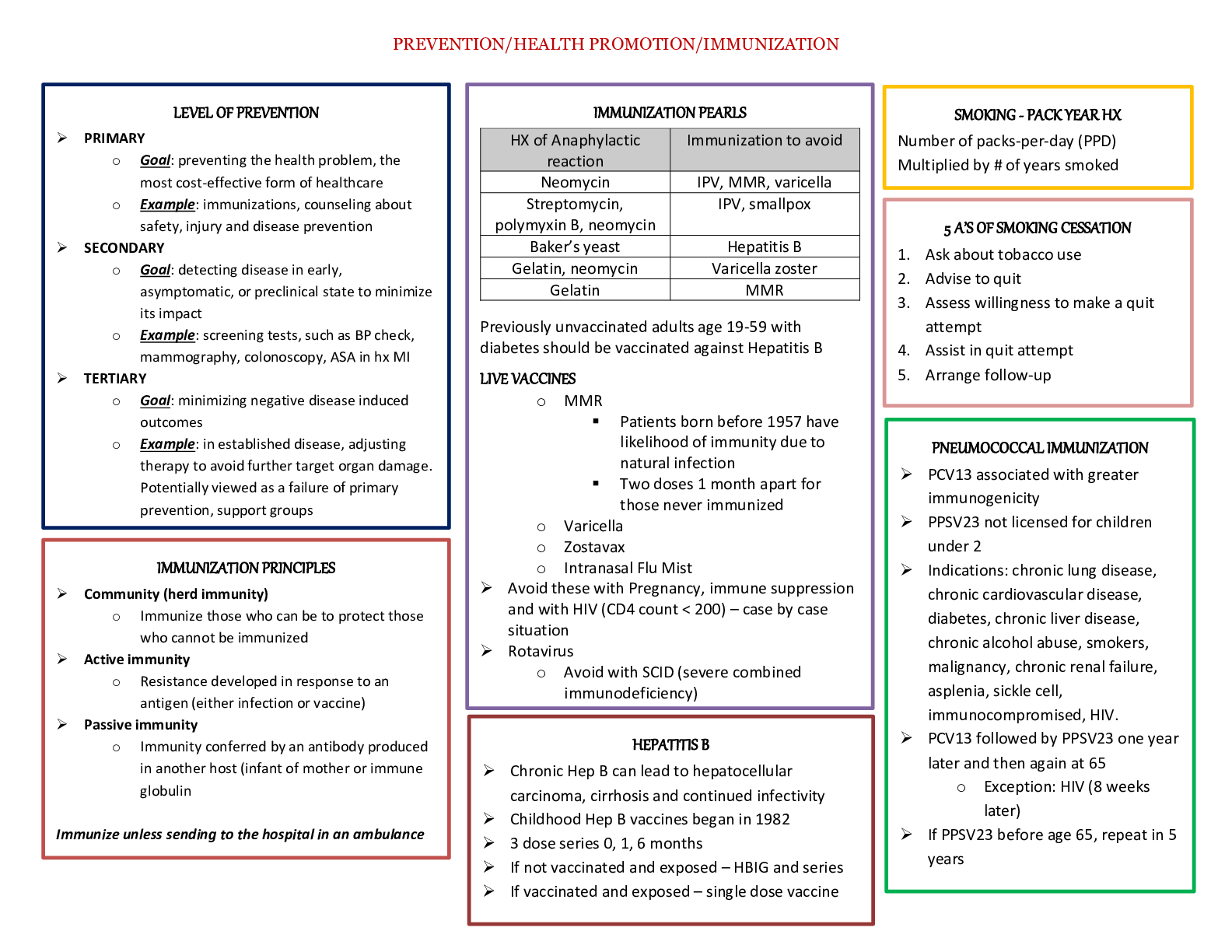






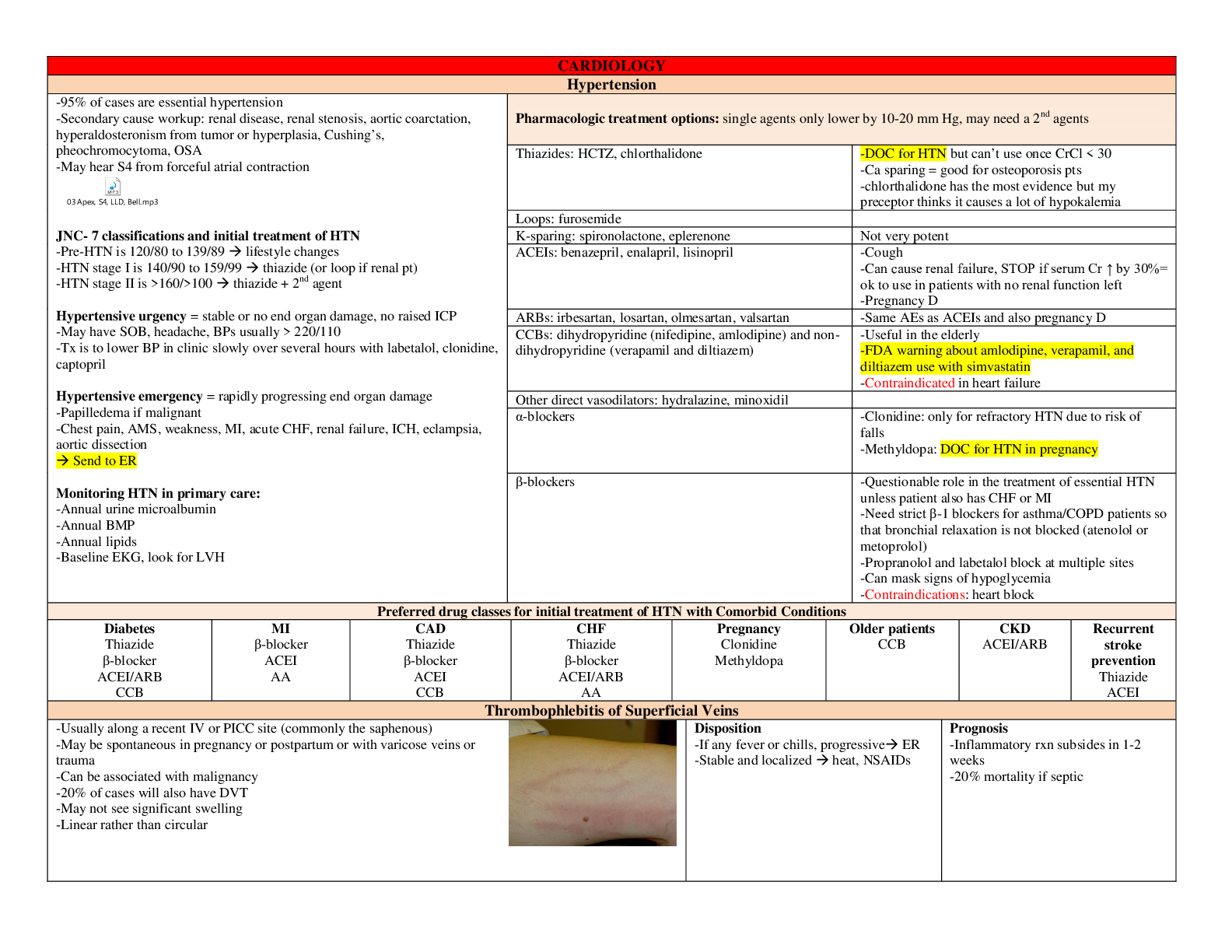


.png)











.png)





