*NURSING > EXAM > NR 508 Advanced Pharmacology Quiz 3_Chamberlain College Of Nursing: Verified Answers( Download To Ge (All)
NR 508 Advanced Pharmacology Quiz 3_Chamberlain College Of Nursing: Verified Answers( Download To Get An A)
Document Content and Description Below
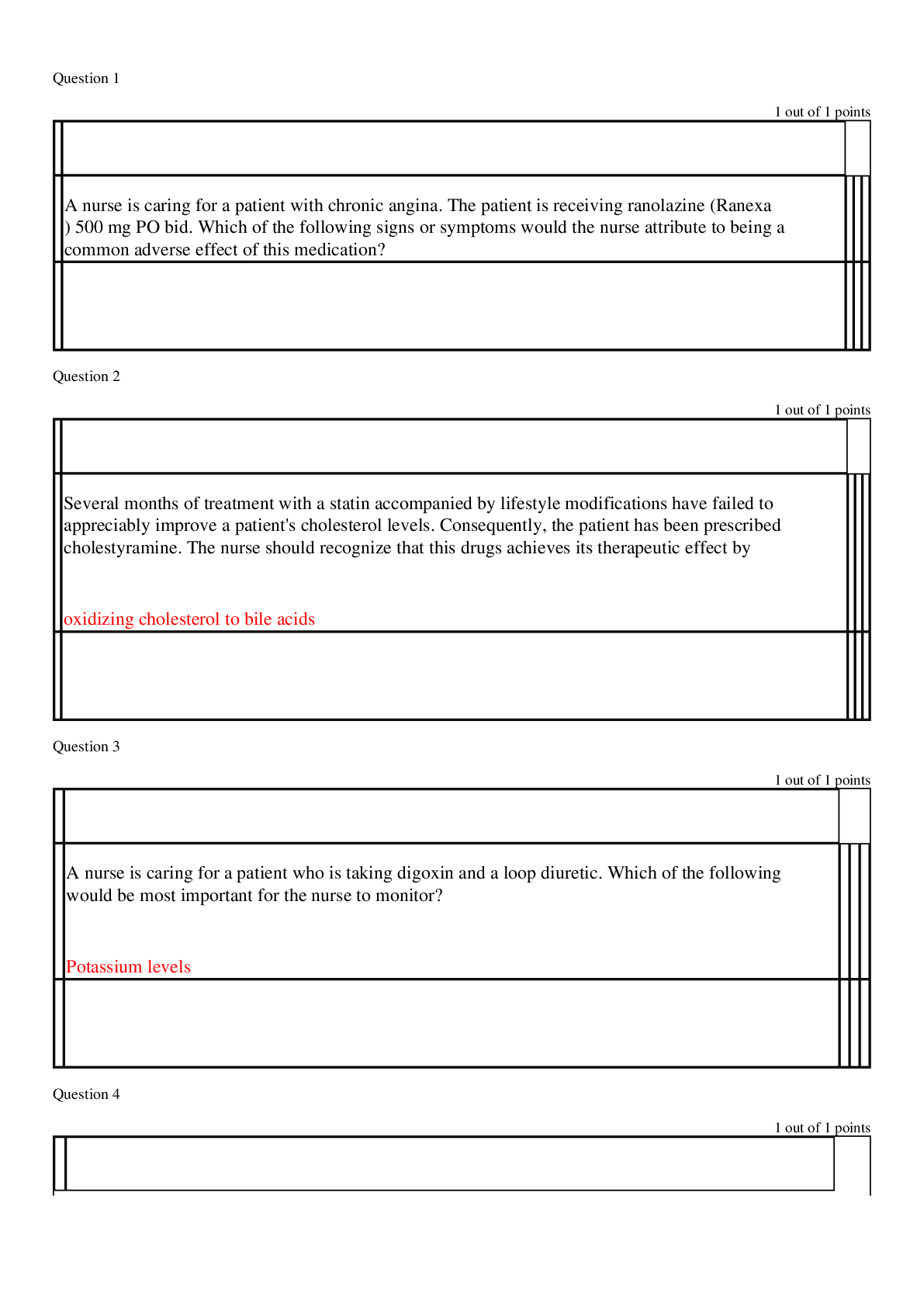
NR 508Advanced Pharmacology Quiz 3 1. A patient who has been taking digoxin 0.25 mg daily for 6 months reports that it is not working as well as it did initially. The primary care NP should: (Point... s : 2) recommend a reduced potassium intake. increase the dose of digoxin to 0.5 mg daily. hold the next dose of digoxin and obtain a serum digoxin level. contact the patient’s pharmacy to ask if generic digoxin was dispensed. Question 2.2. A patient with a history of coronary heart disease develops atrial fibrillation. The primary care NP refers the patient to a cardiologist who performs direct current cardioversion. The NP should expect the patient to begin taking which -blocker medication? (Points : 2) Nadolol (Corgard) Sotalol (Betapace) Timolol (Blocadren) Propranolol (Inderal) Question 3.3. A patient comes to the clinic with a complaint of gradual onset of left-sided weakness. The primary care NP notes slurring of the patient’s speech. A family member accompanying the patient tells the NP that these symptoms began 4 or 5 hours ago. The NP will activate the emergency medical system and expect to administer: (Points : 2) 325 mg of chewable aspirin. LMWH. intravenous alteplase and aspirin. warfarin (Coumadin) and aspirin. Question 4.4. The primary care NP sees a new patient for a routine physical examination. When auscultating the heart, the NP notes a heart rate of 78 beats per minute with occasional extra beats followed by a pause. History reveals no past cardiovascular disease, but the patient reports occasional syncope and shortness of breath. The NP should: (Points : 2) order an ECG and refer to a cardiologist. schedule a cardiac stress test and a graded exercise test. order a complete blood count (CBC) and electrolytes and consider a trial of procainamide. prescribe a -blocker and anticoagulant and order 24-hour Holter monitoring. Question 5.5. The primary care NP refers a patient to a cardiologist who diagnoses long QT syndrome. The cardiologist has prescribed propranolol (Inderal). The patient exercises regularly and is not obese. The patient asks the NP what else can be done to minimize risk of sudden cardiac arrest. The NP should counsel the patient to: (Points : 2) drink extra fluids when exercising. reduce stress with yoga and hot baths. ask the cardiologist about an implantable defibrillator. ask the cardiologist about adding procainamide to the drug regimen. Question 6.6. A patient who takes a thiazide diuretic will begin taking an ACE inhibitor. The primary care NP should counsel the patient to: (Points : 2) report wheezing and shortness of breath, which may occur with these drugs. take care when getting out of bed or a chair after the first dose of the ACE inhibitor. discuss taking an increased dose of the thiazide diuretic with the cardiologist. minimize fluid intake for several days when beginning therapy with the ACE inhibitor. Question 7.7. A female patient who is underweight tells the primary care NP that she has been using bisacodyl (Dulcolax) daily for several years. The NP should: (Points : 2) prescribe docusate sodium (Colace) and decrease bisacodyl gradually. suggest she use polyethylene glycol (MiraLAX) on a daily basis instead. tell her that long-term use of suppositories is safer than long-term laxative use. counsel the patient to discontinue the laxative and increase fluid and fiber intake. Question 8.8. A woman who is 4 months pregnant comes to the clinic with acute diarrhea and nausea. Her husband is experiencing similar symptoms. The primary care nurse practitioner (NP) notes a temperature of 38.5° C, a heart rate of 92 beats per minute, and a blood pressure of 100/60 mm Hg. The NP should: (Points : 2) prescribe attapulgite to treat her diarrhea. obtain a stool culture and start antibiotic therapy. instruct her to replace lost fluids by drinking Pedialyte. refer her to an emergency department for intravenous (IV) fluids. Question 9.9. A patient who has had four to five liquid stools per day for 4 days is seen by the primary care NP. The patient asks about medications to stop the diarrhea. The NP tells the patient that antidiarrheal medications are: (Points : 2) not curative and may prolong the illness. useful in cases of acute infection with elevated temperature. most beneficial when symptoms persist longer than 2 weeks. useful when other symptoms, such as hematochezia, develop. Question 10.10. An 80-year-old patient asks a primary care NP about OTC antacids for occasional heartburn. The NP notes that the patient has a normal complete blood count and normal electrolytes and a slight elevation in creatinine levels. The NP should recommend: (Points : 2) calcium carbonate (Tums). aluminum hydroxide (Amphojel). sodium bicarbonate (Alka-Seltzer). magnesium hydroxide (Milk of Magnesia). Question 11.11. A patient who takes digoxin reports taking psyllium (Metamucil) three or four times each month for constipation. The primary care NP should counsel this patient to: (Points : 2) decrease fluid intake to avoid cardiac overload. change the laxative to docusate sodium (Colace). take the digoxin 2 hours before taking the psyllium. ask the cardiologist about taking an increased dose of digoxin. Question 12.12. A patient who has a history of chronic constipation uses a bulk laxative to prevent episodes of acute constipation. The patient reports having an increased frequency of episodes. The primary care NP should recommend: (Points : 2) adding docusate sodium (Colace). polyethylene glycol (MiraLAX) and bisacodyl (Dulcolax). lactulose (Chronulac) and polyethylene glycol (MiraLAX). adding nonpharmacologic measures such as biofeedback. Question 13.13. A patient with peptic ulcer disease is taking a histamine-2 blocker and tells the primary care NP that over-the-counter antacid tablets help with the discomfort. The NP should tell this patient to: (Points : 2) discontinue the antacid. discontinue the histamine-2 blocker. take the antacid and the histamine-2 blocker at the same time. take the histamine-2 blocker 2 hours before taking the antacid. Question 14.14. A patient who has GERD with erosive esophagitis has been taking a PPI for 4 weeks and reports a decrease in symptoms. The patient asks the primary care NP if the medication may be discontinued. The NP should tell the patient that: (Points : 2) the dose may be decreased for long-term therapy. antireflux surgery must be done before the PPI can be discontinued. the condition may eventually be cured, but therapy must continue for years. once the symptoms have cleared completely, the medication may be discontinued. Question 15.15. A 12-year-old patient has acute diarrhea and an upper respiratory infection. Other family members have had similar symptoms, which have resolved. The primary care NP should recommend: (Points : 2) diphenoxylate (Lomotil). attapulgite (Kaopectate). an electrolyte solution (Pedialyte). bismuth subsalicylate (Pepto-Bismol). Question 16.16. A 2-year-old child has chronic “toddler’s” diarrhea, which has an unknown but benign etiology. The child’s parent asks the primary care NP if a medication can be used to treat the child’s symptoms. The NP should recommend giving: (Points : 2) diphenoxylate (Lomotil). attapulgite (Kaopectate). an electrolyte solution (Pedialyte). bismuth subsalicylate (Pepto-Bismol). Question 17.17. A primary care NP sees a 3-year-old patient who has been vomiting for several days. The child has had fewer episodes of vomiting the past day and is now able to take sips of fluids without vomiting. The child has dry oral mucous membranes, 2-second capillary refill, and pale but warm skin. The child’s blood pressure is 88/46 mm Hg, the heart rate is 110 beats per minute, and the temperature is 37.2° C. The NP should: (Points : 2) prescribe promethazine. prescribe a scopolamine patch. begin oral rehydration therapy. send the child to the hospital for IV fluids. Question 18.18. A patient comes to the clinic with a 4-day history of 10 to 12 liquid stools each day. The patient reports seeing blood and mucus in the stools. The patient has had nausea but no vomiting. The primary care NP notes a temperature of 37.9° C, a heart rate of 96 beats per minute, and a blood pressure of 90/60 mm Hg. A physical examination reveals dry oral mucous membranes and capillary refill of 4 seconds. The NP’s priority should be to: (Points : 2) obtain stool cultures. begin rehydration therapy. consider prescribing metronidazole. administer opioid antidiarrheal medications. Question 19.19. A patient has been taking furosemide 80 mg once daily for 4 weeks and returns for a follow-up visit. The primary care NP notes a blood pressure of 100/60 mm Hg. The patient’s lungs are clear, and there is no peripheral edema. The patient’s serum potassium is 3.4 mEq/L. The NP should: (Points : 2) continue furosemide at the current dose. decrease furosemide to 60 mg once daily. increase furosemide to 80 mg twice daily. change furosemide dose the 40 mg twice daily. Question 20.20. A patient who is about to begin chemotherapy expresses concern to the primary care NP about gastrointestinal side effects of the treatments. The NP should reassure the patient that: (Points : 2) most newer chemotherapeutic agents do not cause nausea and vomiting. antiemetics will be administered as needed if nausea and vomiting occur. taking ondansetron before chemotherapy decreases nausea and vomiting. a scopolamine patch is an effective way to prevent nausea and vomiting. Question 21.21. A patient has been diagnosed with IBS and tells the primary care NP that symptoms of diarrhea and cramping are worsening. The patient asks about possible drug therapy to treat the symptoms. The NP should prescribe: (Points : 2) mesalamine (Asacol). dicyclomine (Bentyl). simethicone (Phazyme). metoclopramide (Reglan). Question 22.22. A patient who has congestive heart failure and arthritis has been taking chlorthalidone (Zaroxolyn) 25 mg daily for 6 months. The primary care NP notes a persistent blood pressure of 145/90 mm Hg. The NP should: (Points : 2) ask the patient which medications are used for pain. add furosemide (Lasix) to the patient’s drug regimen. increase the dose of chlorthalidone to 100 mg daily. recommend that the patient use salt substitutes to season foods. Question 23.23. A primary care NP sees a patient who is about to take a cruise and reports having had motion sickness with nausea on a previous cruise. The NP prescribes the scopolamine transdermal patch and should instruct the patient to apply the patch: (Points : 2) daily. every 3 days. as needed for nausea. 1 hour before embarking. Question 24.24. A patient takes hydrochlorothiazide to treat hypertension and asks the primary care NP why it is necessary to reduce sodium intake while taking this medication. The NP should explain that decreasing sodium is necessary to: (Points : 2) prevent renal insufficiency. minimize the risk of hypokalemia. prevent postdiuretic sodium retention. increase the likelihood that the drug may be discontinued. Question 25.25. A patient who has IBS has been taking dicyclomine and reports decreased pain and diarrhea but is now having occasional constipation. The primary care NP should recommend: (Points : 2) beginning treatment with an SSRI. beginning therapy with a TCA. over-the-counter (OTC) laxatives as needed when constipated. increasing the amounts of raw fruits and vegetables in the diet. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 13, 2020
Number of pages
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 13, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
12

























.png)






