Pharmacology > EXAM > NR 508 ADVANCED PHARMACOLOGY QUIZZES Weeks 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7. Compilation Complete Questions/Answers (All)
NR 508 ADVANCED PHARMACOLOGY QUIZZES Weeks 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7. Compilation Complete Questions/Answers (Verified Explained Answers: Download To Score An A).
Document Content and Description Below
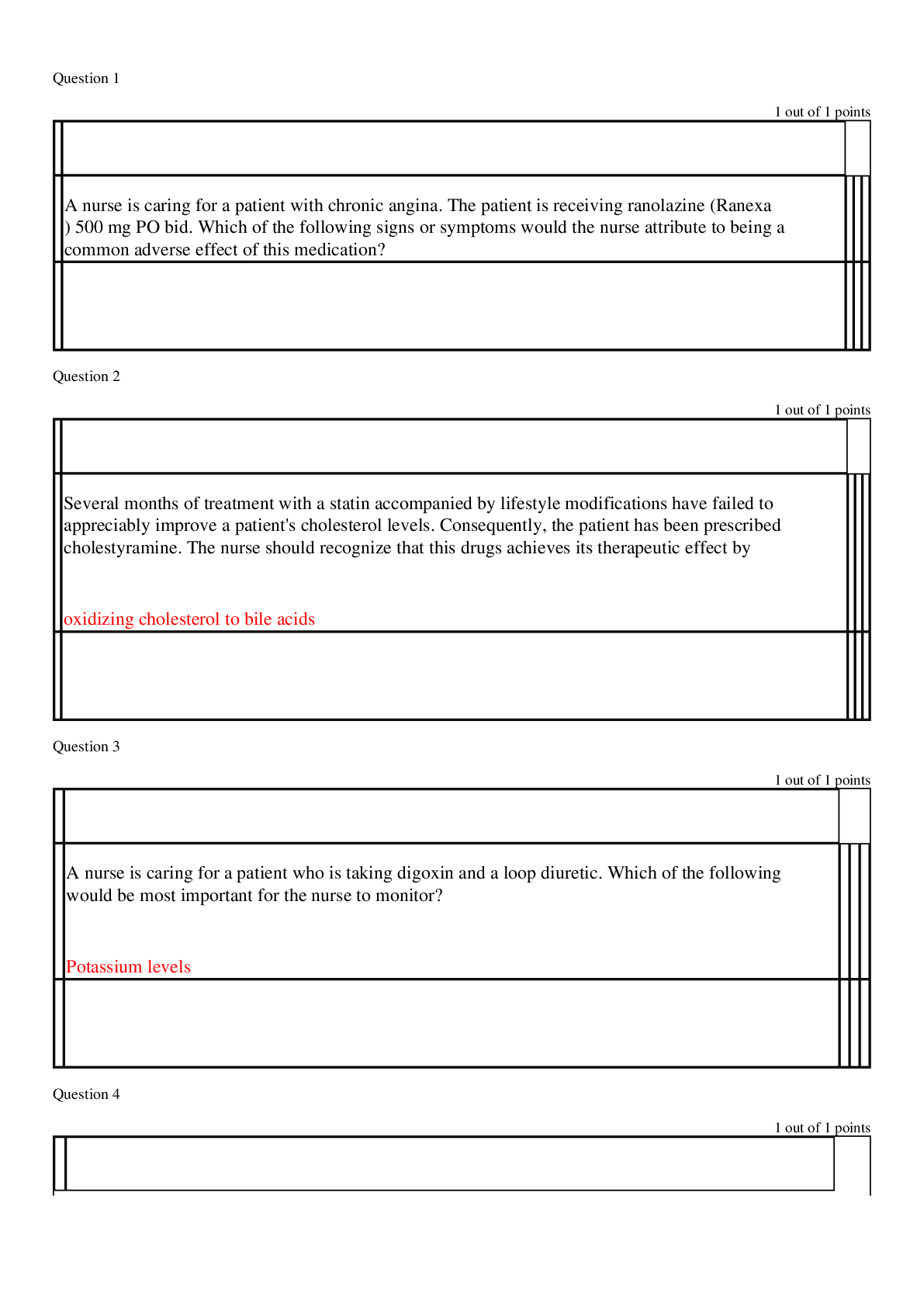
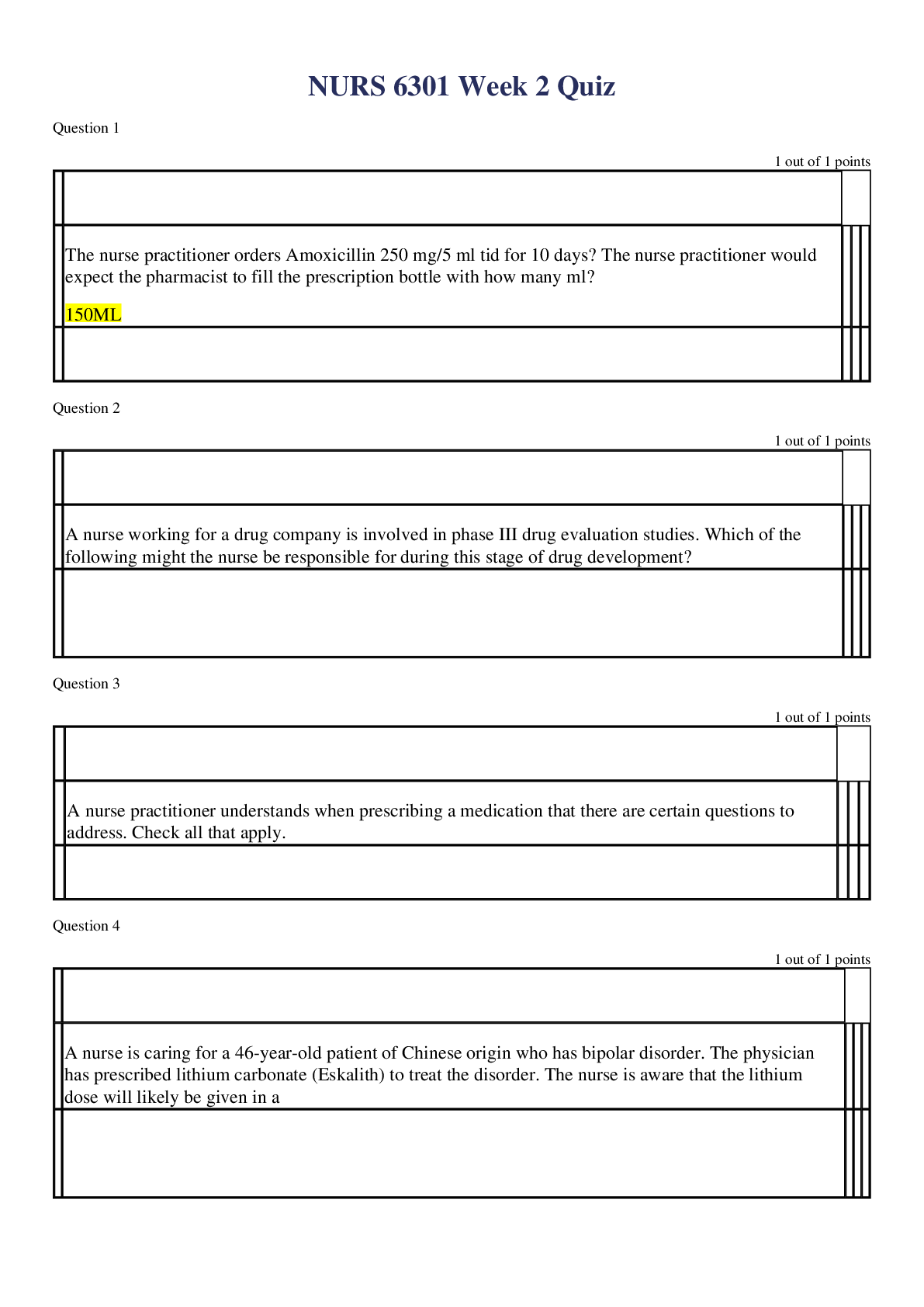
ADVANCED PHARMACOLOGY QUIZZES Question 1 Which of the following statements is true about the prescribing practices of physicians? Antibiotic medications remain in the top five classifications of medic... ations prescribed. Older physicians tend to prescribe more appropriate medications than younger physicians. Correct! The dominant form of drug information used by primary care physicians continues to be that provided by pharmaceutical companies. Most physicians rely on a “therapeutic armamentarium” that consists of less than 100 drug preparations per physician. Even though most physicians claim to place little weight on drug advertisements, pharmaceutical representatives, and patient preference and state that they rely on academic sources for drug information, a study showed that commercial rather than scientific sources of drug information dominated their drug information materials. Younger physicians tend to prescribe fewer and more appropriate drugs. Antibiotics have dropped out of the top five classifications of drugs prescribed. Most physicians have a therapeutic armamentarium of about 144 drugs. Question 2 A primary care NP recommends an over-the-counter medication for a patient who has acid reflux. When teaching the patient about this drug, the NP should tell the patient: not to worry about taking this drug with any other medications. that over-the-counter acid reflux medications are generally safe to take with other medications. Correct! to take the dose recommended by the manufacturer. to avoid taking other drugs that cause sedation while taking this drug. Because patients often increase over-the-counter drug doses themselves, it is important to reinforce the need to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for dosing. As with any drug, interactions may occur with other medications. Antacids do not cause sedation, so patients need not be cautioned to avoid other sedating medications. Question 3 A woman who has been taking a COCP for 2 months tells the primary care NP that she has had several headaches, breakthrough bleeding, and nausea. The NP should counsel the woman: Correct! that these effects will likely decrease in another month. to change to a progestin-only pill. to stop taking the COCP immediately. to use a backup form of contraception. Breakthrough bleeding, nausea, and headaches are common during the first 3 months of therapy and should improve without intervention. Progestin-only pills are used for lactating women only. Prolonged bleeding and severe headache would warrant discontinuation of the COCP. Backup contraception is not indicated. Question 4 A patient asks a primary care nurse practitioner (NP) about using over-the-counter medications to treat an upper respiratory infection with symptoms of cough, fever, and nasal congestion. The NP should: Correct! suggest using single-ingredient products to treat each symptom separately. tell the patient that over-the-counter medications are usually not effective in manufacturer-recommended doses. recommend a cough preparation that also contains acetaminophen. recommend a product containing antitussive, antipyretic, and decongestant ingredients. A basic principle guiding over-the-counter use is to look at specific symptoms and treat each separately because some products contain therapeutic doses of one ingredient and subtherapeutic doses of others. Cough preparations containing acetaminophen often do not contain therapeutic doses, and patients often overdose when they supplement with acetaminophen. Over-the-counter medications are effective at recommended doses. Patients should follow dosing recommendations on the package. Question 5 A patient has recurrent symptoms and tells the primary care NP that she can’t remember to take her medication all the time. The NP should: Correct! ask her about her lifestyle, her schedule, and her understanding of her condition. administer the medication in the clinic to ensure that she takes the drug. give her shortened regimens of the drug to facilitate compliance. provide written information about her condition and the medication. If the attitude is that the patient has a problem for the health care provider to solve, then the provider owns the problem and often hastens to solve it. When patients own their problems, they are more likely to engage in their care and treatment. Giving shortened regimens, providing written information, and administrating medication in the clinic are examples of the provider solving the problem for the patient. Question 6 A postpartum woman will begin taking the minipill while she is nursing her infant. The primary care NP should instruct the patient: that irregular periods while taking the minipill may indicate she is pregnant. that this method does not increase her risk of thromboembolic events. You Answered to use backup contraception while taking the minipill. to continue using the minipill for 6 months after she stops nursing. Minipills are used primarily in breastfeeding women. There is no increased risk for thromboembolic events for women taking these pills. It is not necessary to use a backup method of contraception. Women should be advised to contact the provider when they stop nursing so that a COCP can be prescribed. The more disrupted the bleeding pattern, the more likely it is that ovulation is inhibited. Question 7 A patient who weighs 170 lb wishes to lose weight, with a target weight goal of 125 lb. To initiate a program that will result in a loss of 1 lb per week, the primary care NP should recommend a dietary intake of _____ kcal. 2000 1000 1700 Correct! 1200 To lose weight, a patient must decrease intake to below the level needed to maintain weight. The patient must decrease daily calorie consumption by 500 kcal for each pound he or she wishes to lose weekly. Because it takes approximately 10 kcal per pound to maintain weight, the NP can assume that the patient currently takes in 1700 kcal/day and should recommend a diet of 1200 kcal/day for weight loss. Question 8 A patient who has hypothyroidism and is obese begins therapy with orlistat. The primary care NP teaches the patient about this drug and then asks the patient to describe its use. Which statement by the patient indicates understanding of the teaching? “I can expect the most benefit in the first few months.” “I may eat a high-fat diet while taking orlistat.” You Answered “I should take an increased dose of levothyroxine while I am taking orlistat.” “I should take fat-soluble vitamins each time I take orlistat.” In long-term studies on the use of orlistat, most of the weight loss occurred during the first months. Patients should not be counseled to eat a high-fat diet; the maximum amount of fat excretion is around 25% to 30%. Patients should take fat-soluble vitamins, but the vitamins should be taken at different times and not with orlistat. Orlistat interferes with levothyroxine absorption, so the two drugs should be taken at different times, and thyroid levels should be monitored with an increase in levothyroxine dose only when indicated by thyroid levels. Question 9 A patient with chronic back pain that is unrelieved by prescription analgesic medications asks a primary care nurse practitioner (NP) about acupuncture treatments. The NP should tell this patient: there is no valid research documenting the efficacy of this treatment for pain. biofield therapy has been shown to be more effective than acupuncture. Correct! most studies that show benefits of alternative therapies are based on observation. creatine has been shown to be an effective herbal choice to treat back pain. Current literature does not allow definitive conclusions to be drawn regarding the use of complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) because much of what appears in the literature continues to be based on observational reports and small studies. Biofield therapy has not been shown to be more effective than acupuncture. Creatine is used to increase muscle mass. Question 10 The primary care nurse practitioner (NP) is using critical thinking skills when: Correct! analyzing current research and synthesizing new approaches to patient care. using standardized protocols to guide patient care. adhering to scientific principles to solve a patient problem. following the practices of seasoned mentors when giving care. Practitioners use critical thinking skills by reviewing and analyzing current knowledge and synthesizing approaches to apply to unique patient situations. Using standardized protocols, adhering to scientific principles, and following practices of seasoned mentors may be useful, but these do not encompass the concept of critical thinking, which requires the practitioner to use what is known in new situations. Question 11 The primary care NP prescribes an inhaled corticosteroid for a patient who has asthma. The third-party payer for this patient denies coverage for the brand that comes in the specific strength the NP prescribes. The NP should: order the closest formulary-approved approximation of the drug and monitor effectiveness. provide pharmaceutical company samples of the medication for the patient. inform the patient that the drug must be paid for out of pocket because it is not covered. You Answered write a letter of medical necessity to the insurer to explain the need for this particular medication. The second step of medical decision making takes into account benefits versus costs along with an understanding that it is impossible to do everything because of limited resources. The NP should prescribe what is covered and evaluate its effectiveness; if it does not work, the third-party payer may be approached about the need for the other medication. Providing samples is not always possible, and this practice is being discouraged, so it is not a viable solution. Asking patients to pay out of pocket ultimately may be necessary but carries risks that the patient will not obtain the medication. Writing a letter of medical necessity may be indicated if the available drugs are not effective but is not the initial step. Question 12 A primary care NP prepares to teach a patient about the management of a chronic condition. The patient says, “I don’t want to know all of that. Just tell me what to take and when.” The NP should initially: give the patient basic written instructions about medications, follow up visits, and symptoms. ask the patient to describe the disease process and the medications to evaluate understanding. explain to the patient that without mutual cooperation, the treatment regimen will not be effective. You Answered ask the patient to explore feelings and fears about having a chronic disease and taking medications. The patient has stated expectations about care and treatment for the condition. The NP should begin by respecting that and providing the amount of information the patient wants. As the therapeutic relationship grows, the NP may elicit more active participation and understanding. Question 13 In every state, prescriptive authority for NPs includes the ability to write prescriptions: without physician-mandated involvement. with full, independent prescriptive authority. Correct! for specified classifications of medications. for controlled substances. All states now have some degree of prescriptive authority granted to NPs, but not all states allow authority to prescribe controlled substances. Many states still require some degree of physician involvement with certain types of drugs. Question 14 A primary care NP has prescribed phentermine for a patient who is obese. The patient loses 10 lb in the first month but reports that the drug does not seem to be suppressing appetite as much as before. The NP should: continue the phentermine at the same dose. discontinue the phentermine. You Answered increase the dose of phentermine. change to a combination of phentermine and topiramate. Tolerance to the effects of phentermine usually develops within a few weeks of starting therapy. When this occurs, the drug should be discontinued, not increased. Phentermine use is not recommended longer than a few weeks. Question 15 A patient asks the primary care NP which medication to use for mild to moderate pain. The NP should recommend: APAP. You Answered any over-the-counter pain product. Tylenol. acetaminophen. Providers should use generic drug names when prescribing drugs or recommending them to patients, unless a particular brand is essential for some reason. Because acetaminophen can have many trade names, it is important for patients to understand that the drug is the same for all to avoid overdosing on acetaminophen. APAP is a commonly used abbreviation but should not be used when recommending the drug to patients. Question 16 The primary care NP prescribes an extended-cycle monophasic pill regimen for a young woman who reports having multiple partners. Which statement by the patient indicates she understands the regimen? “This type of pill has fewer side effects than other types.” Correct! “I should expect to have only four periods each year.” “I will need to use condoms for only 7 more days.” “I have to take a pill only every 3 months.” The extended-cycle pills have fewer pill-free intervals, so women have only four periods a year. Patients take pills every day. Because this patient has multiple partners, she should continue to use condoms. This type of pill has the same side effects as other types. Question 17 A patient who has diabetes mellitus and congestive heart failure takes insulin and warfarin. The patient will begin taking exogenous testosterone to treat secondary hypogonadism. The primary care NP should recommend: Correct! more frequent blood glucose monitoring. increasing insulin doses to prevent hypoglycemia. increasing the dose of warfarin. a higher than usual dose of testosterone. Patients with diabetes may require a decrease in insulin dose because of the metabolic effects of androgens. More frequent blood glucose monitoring should be performed. Warfarin doses may need to be decreased because androgens increase sensitivity to anticoagulants. Question 18 A woman who has been taking a COCP tells the primary care NP that, because of frequent changes in her work schedule, she has difficulty remembering to take her pills. The woman and the NP decide to change to a vaginal ring. The NP will instruct her to insert the ring: You Answered and use a backup contraceptive for 7 days. within 7 days after her last active pill. on the same day she stops taking her COCP. and continue the COCP for one more cycle. Patients should be switched from a COCP to a vaginal ring by insertion within 7 days after the last active pill. No backup method is needed. Patients do not need to continue one more cycle of COCPs. Women taking progestin-only pills insert the ring on the last day of the pill pack. Question 19 A primary care NP is developing a clinical practice guideline for management of a patient population in a midsized suburban hospital. The NP should: follow the guideline provided by a third-party payer to help ensure reimbursement. write the guideline to adhere to long-standing practice protocols already in use. Correct! review expert opinion and experimental, anecdotal, correlational study data. use an existing guideline from a leading research hospital. Clinical guidelines should be written using all available evidence as well as expert opinion. Existing guidelines from a different type of hospital may not be based on data generalizable to this population. Third-party payer guidelines are usually weighted toward decreased costs. Long-standing protocols often do not take into account current knowledge and research. Question 20 To increase the likelihood of successful pharmacotherapy, when teaching a patient about using a medication, the primary care nurse practitioner (NP) should: You Answered stress the importance of taking the medication exactly as it is prescribed. give the patient copies of medication package inserts describing the drug use. encourage the patient to participate in the choice of the medication. provide education about the medication actions and adverse effects. It is important that the patient “owns the problem” and has a part in the solution. Providing education about the medication, stressing the importance of following medication instructions, and distributing package inserts may be useful, but it is essential that patients take an active role in their care. Question 21 A 50-year-old woman reports severe, frequent hot flashes and vaginal dryness. She is having irregular periods. She has no family history of CHD or breast cancer and has no personal risk factors. The primary care NP should recommend: selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor therapy until menopause begins. low-dose oral contraceptive therapy. estrogen-progesterone HT. You Answered estrogen-only HT. Oral contraceptive pills are not approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for management of perimenopausal symptoms except to treat irregular menstrual bleeding. This patient has a low risk for CHD and breast cancer, so oral contraceptive pills are relatively safe. She is also at risk for pregnancy, so oral contraceptive pills can help to prevent that. Question 22 A man who has secondary hypogonadism associated with pituitary dysfunction will begin exogenous testosterone therapy. The patient asks the primary care NP about future chances of fathering children. The NP should tell him that: fertility may improve with testosterone therapy. exogenous testosterone therapy will shut down sperm production. You Answered he should store sperm ahead of the initiation of testosterone therapy. fertility can be restored when testosterone therapy is discontinued. Men with secondary hypogonadism may become fertile with exogenous testosterone. Question 23 A 50-year-old woman who is postmenopausal is taking an aromatase inhibitor as part of a breast cancer treatment regimen. She calls her primary care NP to report that she has had hot flashes and increased vaginal discharge but no bleeding. The NP should: recommend that she use a barrier method of contraception. You Answered tell her to stop taking the medication and call her oncologist. schedule her for a gynecologic examination. reassure her that these are normal side effects of the medication. Any abnormal vaginal discharge should be reported immediately and should be evaluated with a gynecologic examination to rule out carcinoma. She is not showing signs of ovulation, so contraception is not necessary. She should not stop taking the medication unless the gynecologic examination is positive. These are common side effects but are not always normal. UnansweredQuestion 24 A patient receives an inhaled corticosteroid to treat asthma. The patient asks the primary care NP why the drug is given by this route instead of orally. The NP should explain that the inhaled form: provides dosing that is easier to regulate. is absorbed less quickly. has reduced bioavailability. has fewer systemic side effects. An inhaled corticosteroid goes directly to the site of action and does not have to pass through gastrointestinal tract absorption or the liver to get to the lungs. It is generally well absorbed at this site, although dosing is not necessarily easier to regulate because it is not always clear how much of an inhaled drug gets into the lungs. Question 25 A patient who takes warfarin (Coumadin) experiences excessive bleeding, even though serum drug levels are normal. The primary care NP should question this patient about the use of: Correct! ginkgo biloba. green tea. feverfew. echinacea. Ginkgo biloba decreases blood viscosity and can enhance the effects of warfarin. Feverfew, echinacea, and green tea do not have this effect. Question 1 The primary care NP is prescribing a medication for an off-label use. To help prevent a medication error, the NP should: tell the patient to ignore the label directions and follow the verbal instructions given in the clinic. You Answered call the pharmacist to explain why the instructions deviate from common use. write “off-label use” on the prescription and provide a rationale. write the alternative drug regimen on the prescription and send it to the pharmacy. When prescribing a drug for an off-label use, the provider should specify this on the written prescription and should provide a rationale so that the pharmacist understands why the prescription is different from the normal use. Calling the pharmacist would not provide written documentation. Merely writing the different instructions can lead to errors if the pharmacist changes the label to conform to usual standards. The patient may forget verbal instructions and follow the usual regimen instead. Question 2 To increase the likelihood of successful pharmacotherapy, when teaching a patient about using a medication, the primary care nurse practitioner (NP) should: give the patient copies of medication package inserts describing the drug use. provide education about the medication actions and adverse effects. encourage the patient to participate in the choice of the medication. You Answered stress the importance of taking the medication exactly as it is prescribed. It is important that the patient “owns the problem” and has a part in the solution. Providing education about the medication, stressing the importance of following medication instructions, and distributing package inserts may be useful, but it is essential that patients take an active role in their care. Question 3 A patient comes to the clinic and asks the primary care NP about using a newly developed formulation of the drug the patient has been taking for a year. When deciding whether or not to prescribe this formulation, the NP should: prescribe the medication if the new drug is available in an extended-release form. review the pharmaceutical company promotional materials about the new medication. prescribe the medication if it is less expensive than the current drug formulation. Correct! tell the patient that when postmarketing data is available, it will be considered. About 6 to 12 months of postmarketing experience can yield information about drug efficacy and side effects, so patients should be cautioned to wait for these data. Drug company promotional materials have biased information. Most new drugs are more expensive, and costs alone should not determine drug choice. Extended-release forms are often more expensive. Question 4 A sexually active patient tells the primary care NP that she has been unable to get her new COCP pill pack until today and has missed 3 days of pills. The NP should tell her to: use backup contraception and take 2 pills each day for the next 2 days. You Answered begin a new pack of pills today and use backup contraception for 7 days. Take a pregnancy test, begin a new pack of pills today, and use backup contraception for 7 days. begin a new pack of pills today, take a Plan B pill, and use backup contraception for 7 days. Patients who miss 2 or more pills at the beginning or end of a pack should use emergency contraceptive pills, such as the Plan B pill, restart a new pill pack, and use backup contraception for 7 days. Question 5 Osteopenia is diagnosed in a 55-year-old woman who has not had a period in 15 months. She has a positive family history of breast cancer. The primary care NP should recommend: Correct! nonhormonal drugs for osteoporosis. estrogen-only therapy. testosterone therapy. estrogen-progesterone therapy for 1 to 2 years. Although estrogen slows the progression of osteoporosis, it also increases the risk of breast cancer when initiated early in menopause. This woman should receive a nonhormonal treatment for osteoporosis and may receive HT in 5 years if menopausal symptoms persist. Testosterone therapy, estrogen-only therapy, and estrogen-progesterone therapy are not indicated. Question 6 A patient asks a primary care NP whether over-the-counter drugs are safer than prescription drugs. The NP should explain that over-the-counter drugs are: Correct! generally safe when label information is understood and followed. less safe because they are not well regulated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). not extensively tested, so claims made by manufacturers cannot be substantiated. safer because over-the-counter doses are lower than prescription doses of the same drug. Over-the-counter products have a wider margin of safety because most of these drugs have undergone rigorous testing before marketing and further refinement through years of over-the-counter use by consumers. When labels are understood and followed, over-the-counter medications are safe. Over-the-counter medications are regulated by the FDA. Question 7 A primary care NP is developing a clinical practice guideline for management of a patient population in a midsized suburban hospital. The NP should: review expert opinion and experimental, anecdotal, correlational study data. You Answered write the guideline to adhere to long-standing practice protocols already in use. use an existing guideline from a leading research hospital. follow the guideline provided by a third-party payer to help ensure reimbursement. Clinical guidelines should be written using all available evidence as well as expert opinion. Existing guidelines from a different type of hospital may not be based on data generalizable to this population. Third-party payer guidelines are usually weighted toward decreased costs. Long-standing protocols often do not take into account current knowledge and research. Question 8 A patient bursts into tears when the primary care NP diagnoses diabetes. The NP should: call in a social worker to assist the patient to obtain equipment and supplies. reassure the patient that the medications and blood tests will become routine. You Answered refer the patient to a diabetes educator to provide teaching about the disease. ask the patient about past experiences with anyone who has this diagnosis. To help patients participate in their disease management, the NP must have an understanding of the patient’s concerns and fears. The first step when the patient is obviously upset is to determine what the patient knows and fears about the disease. Question 9 A patient is diagnosed with lupus and reports occasional use of herbal supplements. The primary care NP should caution this patient to avoid: ginseng. St. John’s wort. You Answered ginkgo biloba. echinacea. Patients with lupus who take echinacea may experience an increase in symptoms, even if the patient is taking immunosuppressants. Question 10 A patient takes an oral medication that causes gastrointestinal upset. The patient asks the primary care NP why the drug information insert cautions against using antacids while taking the drug. The NP should explain that the antacid may: increase stomach upset. Correct! alter drug absorption. alter drug distribution. lead to drug toxicity. Changing the pH of the gastric mucosa can alter the absorption of the drug. Drug distribution is not affected. It may indirectly cause drug toxicity if a significant amount more of the drug is absorbed. It would decrease stomach upset. Question 11 A patient receives an inhaled corticosteroid to treat asthma. The patient asks the primary care NP why the drug is given by this route instead of orally. The NP should explain that the inhaled form: provides dosing that is easier to regulate. has reduced bioavailability. is absorbed less quickly. Correct! has fewer systemic side effects. An inhaled corticosteroid goes directly to the site of action and does not have to pass through gastrointestinal tract absorption or the liver to get to the lungs. It is generally well absorbed at this site, although dosing is not necessarily easier to regulate because it is not always clear how much of an inhaled drug gets into the lungs. Question 12 The primary care NP is reviewing evidence-based recommendations about the off-label use of a particular drug. Which recommendation should influence the NP’s decision about prescribing the medication? Patient reports about effectiveness of the drug for this purpose Correct! Data from randomized, experimental studies Pharmaceutical company reports using anecdotal evidence Endorsement of this use by a leading practitioner in the field Randomized, experimental studies yield the best data about use of medications. Patient reports carry the least weight because bias can occur and other factors can influence outcomes. Pharmaceutical company reports are biased. Question 13 A primary care NP prescribes a COCP for a woman who is taking them for the first time. After teaching, the woman should correctly state the need for using a backup form of contraception if she: delays taking a pill by 5 or 6 hours. You Answered takes nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs several days in a row. has recurrent headaches or insomnia. is having vomiting or diarrhea. Vomiting and diarrhea may cause oral contraceptive failure, so women should be advised to use backup contraception if they experience these. The other conditions do not lead to oral contraceptive failure. Question 14 A patient who has diabetes mellitus and congestive heart failure takes insulin and warfarin. The patient will begin taking exogenous testosterone to treat secondary hypogonadism. The primary care NP should recommend: You Answered a higher than usual dose of testosterone. increasing the dose of warfarin. more frequent blood glucose monitoring. increasing insulin doses to prevent hypoglycemia. Patients with diabetes may require a decrease in insulin dose because of the metabolic effects of androgens. More frequent blood glucose monitoring should be performed. Warfarin doses may need to be decreased because androgens increase sensitivity to anticoagulants. Question 15 A patient asks the primary care NP which medication to use for mild to moderate pain. The NP should recommend: APAP. acetaminophen. You Answered any over-the-counter pain product. Tylenol. Providers should use generic drug names when prescribing drugs or recommending them to patients, unless a particular brand is essential for some reason. Because acetaminophen can have many trade names, it is important for patients to understand that the drug is the same for all to avoid overdosing on acetaminophen. APAP is a commonly used abbreviation but should not be used when recommending the drug to patients. Question 16 The primary care nurse practitioner (NP) writes a prescription for an antibiotic using an electronic drug prescription system. The pharmacist will fill this prescription when: Correct! the electronic prescription is received. the patient brings a written copy of the prescription. the pharmacist accesses the patient’s electronic record to verify. a copy of the written prescription is faxed to the pharmacy. E-sign effectively voids requirements that prescriptions be written on paper or printed as a hard copy. Some scheduled drugs still require written copies. Faxed copies of this drug would be allowed but are not necessary for the pharmacist to fill the prescription. The patient’s electronic medical record stands as evidence of the need for a prescription of a drug but is not needed for the pharmacist to fill the prescription. Question 17 A primary care NP wishes to order a drug that will be effective immediately after administration of the drug. Which route should the NP choose? Topical Correct! Sublingual Rectal Intramuscular The sublingual route is preferred for quick action because the drug is directly absorbed into the bloodstream and avoids the pass through of the liver, where much of an oral drug is metabolized. Rectal routes have unpredictable absorption rates. Topical routes are the slowest. Intramuscular routes are slow. Question 18 A patient develops hepatotoxicity from chronic acetaminophen use. The primary care NP may recommend: milk thistle. You Answered coenzyme Q. glucosamine. chondroitin. Milk thistle has been shown to protect the liver after exposure to hepatotoxins such as acetaminophen, ethanol, and halothane. The other supplements listed do not have this effect. Question 19 A 55-year-old woman has not had menstrual periods for 5 years and tells the primary care nurse practitioner (NP) that she is having increasingly frequent vasomotor symptoms. She has no family history or risk factors for coronary heart disease (CHD) or breast cancer but is concerned about these side effects of hormone therapy (HT). The NP should: advise a short course of HT now that may decrease her risk for CHD. You Answered tell her that HT will not help control her symptoms during postmenopause. recommend herbal supplements for her symptoms to avoid HT side effects. tell her that starting HT now may reduce her risk of breast cancer. The current gap hypothesis regarding breast cancer supports initiating HT 5 years or more after menopause. To decrease risk for CHD, HT should begin at the time of menopause. HT will relieve vasomotor symptoms at all stages of menopause. Herbal supplements have estrogenizing effects and carry the same risks as estrogen therapy. Question 20 Which of the following has influenced an emphasis on primary care education in medical schools? Changes in Medicare reimbursement methods recommended in 1992 The recognition that nonphysicians have variable success providing primary care The need for monopolistic control in the marketplace of primary outpatient care You Answered Competition from nonphysicians desiring to meet primary care shortages The Physician Payment Review Commission in 1992 directly increased financial reimbursement to clinicians who provide primary care. Coupled with a shortage of primary care providers, this incentive led medical schools to place greater emphasis on preparing primary care physicians. Competition from nonphysicians increased coincidentally as professionals from other disciplines stepped up to meet the needs. Nonphysicians have had increasing success at providing primary care and have been shown to be safe and effective. Question 21 A thin 52-year-old woman who has recently had a hysterectomy tells the primary care NP she is having frequent hot flashes and vaginal dryness. A recent bone density study shows early osteopenia. The woman’s mother had CHD. She has no family history of breast cancer. The NP should prescribe: estrogen-only HT in 5 years. You Answered estrogen-progesterone HT now. estrogen-progesterone HT in 5 years. estrogen-only HT now. HT relieves symptoms of menopause and prevents osteoporosis. When started soon after menopause, HT can reduce CHD risk. Breast cancer risk may be decreased if HT is begun 5 years after onset of menopause. This woman has a higher risk of CHD and osteoporosis, so initiating therapy now is a good option. Because she has had a hysterectomy, estrogen-only therapy is indicated. Question 22 A patient reports taking antioxidant supplements to help prevent cancer. The primary care NP should: make sure that the supplements contain large doses of vitamin A. tell the patient that antioxidants are especially important for patients who smoke. tell the patient that evidence shows antioxidants to be effective in preventing cancer. Correct! review healthy dietary practices with this patient. Epidemiologic evidence indicates that people who eat fruits and vegetables regularly have a decreased risk of cancer. Although retrospective studies have suggested major benefits from antioxidants, no intervention studies have determined conclusively that antioxidants prevent cancer. Large doses of vitamin A can produce a yellow hue to the skin. Antioxidants can be beneficial, but in certain populations, such as smokers, they may be harmful. Question 23 When prescribing a medication for a chronic condition, the primary care NP should tell the patient: to contact the pharmacy whenever refills are needed. Correct! about the frequency of clinic visits necessary for the number of refills authorized. that it is necessary to return to the clinic for each monthly refill of the medication. to ask the pharmacist to supply several months’ worth of the medication at a time. Nonscheduled drugs may be ordered with refills so that the patient does not have to be seen each time a refill is needed. It is important to determine how closely a patient should be monitored while taking a drug for a chronic condition and to let the patient know how frequently he or she needs to be seen. Patients may contact a pharmacy when they still have authorized refills to pick up, but this is determined by the clinician. Pharmacists usually cannot dispense more than 30 days’ worth of a medication. Question 24 A patient who has an upper respiratory infection reports using over-the-counter cold preparations. The primary care NP should counsel this patient to use caution when taking additional over-the-counter medications such as: Correct! antipyretics. antioxidant supplements. calcium supplements. acid reflux medications. Cold preparations often contain antipyretics such as acetaminophen or aspirin. Patients should be cautioned about taking additional antipyretics to avoid overdose. Question 25 A patient will begin taking two drugs that are both protein-bound. The primary care NP should: stagger the doses of drugs to be given 1 hour apart. monitor drug levels, actions, and side effects. prescribe increased doses of both drugs. You Answered teach the patient to increase intake of protein. Protein-bound drugs bind to albumin, and serum albumin levels may affect how drugs are distributed. The provider should monitor drug levels, actions, and side effects and change dosing accordingly. Increasing the dose of both drugs is not recommended unless monitoring indicates. Increasing dietary protein does not affect this. Staggering the drugs will not affect this. Question 1 A patient is newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus. The primary care NP reviews this patient’s laboratory tests and notes normal renal function, increased triglycerides, and deceased HDL levels. The NP should prescribe: colesevelam (Welchol). Correct! metformin (Glucophage). glyburide (Micronase). nateglinide (Starlix). Metformin is recommended as initial pharmacologic treatment for type 2 diabetes. It has been shown to decrease triglycerides and LDLs. Question 2 A patient who has type 2 diabetes mellitus will begin taking a bile acid sequestrant. Which bile acid sequestrant should the primary care NP order? Cholestyramine (Questran) Colestipol (Colestid) You Answered Cholestyramine (Questran Light) Colesevelam (Welchol) All bile acid sequestrants are equally effective. Colesevelam has an additional indication to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes and so should be selected when prescribing a bile acid sequestrant for this patient. Question 3 A 55-year-old woman has a history of myocardial infarction (MI). A lipid profile reveals LDL of 130 mg/dL, HDL of 35 mg/dL, and triglycerides 150 mg/dL. The woman is sedentary with a body mass index of 26. The woman asks the primary care NP about using a statin medication. The NP should: begin therapy with atorvastatin 10 mg per day. tell her there is no clinical evidence of efficacy of statin medication in her case. discuss quality-of-life issues as part of the decision to begin medication. You Answered recommend dietary and lifestyle changes first. This woman would be using a statin medication for secondary prevention because she already has a history of MI, so a statin should be prescribed. Dietary and lifestyle changes should be a part of therapy, but not the only therapy. She is relatively young, and quality-of-life issues are not a concern. There is no clinical evidence to support use of statins as primary prevention in women. Question 4 A 40-year-old patient is in the clinic for a routine physical examination. The patient has a body mass index (BMI) of 26. The patient is active and walks a dog daily. A lipid profile reveals low-density lipoprotein (LDL) of 100 mg/dL, high-density lipoprotein (HDL) of 30 mg/dL, and triglycerides of 250 mg/dL. The primary care nurse practitioner (NP) should: consider prescribing metformin (Glucophage). suggest dietary changes and increased exercise. You Answered obtain serum insulin and hemoglobin A1c levels. order a fasting plasma glucose level. Testing for type 2 diabetes should be considered in all adults with a BMI greater than 25 who have risk factors such as HDL less than 35 mg/dL or triglycerides greater than 250 mg/dL. A fasting plasma glucose level greater than 126 mg/dL indicates diabetes. Metformin is not indicated unless testing is positive. Lifestyle changes may be part of the treatment plan. Serum insulin level is not indicated. Question 5 An African-American patient who is obese has persistent blood pressure readings greater than 150/95 mm Hg despite treatment with a thiazide diuretic. The primary care NP should consider prescribing a(n): You Answered β-blocker. angiotensin receptor blocker. calcium channel blocker. ACE inhibitor. African-American patients are considered good candidates for calcium channel blockers to treat hypertension. Treatment with calcium channel blockers as monotherapy in African-American patients has proved to be more effective than some other classes of antihypertensive agents. Question 6 The primary care nurse practitioner (NP) sees a patient in the clinic who has a blood pressure of 130/85 mm Hg. The patient’s laboratory tests reveal high-density lipoprotein, 35 mg/dL; triglycerides, 120 mg/dL; and fasting plasma glucose, 100 mg/dL. The NP calculates a body mass index of 29. The patient has a positive family history for cardiovascular disease. The NP should: consider treatment with an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor. Correct! counsel the patient about dietary and lifestyle changes. reassure the patient that these findings are normal. prescribe a thiazide diuretic. The patient’s blood pressure indicates prehypertension, but the patient does not have cardiovascular risk factors such as hyperlipidemia or hyperinsulinemia. The body mass index indicates that the patient is overweight but not obese. Pharmacologic treatment is not recommended for prehypertension unless compelling reasons are present. The findings are not normal, so it is appropriate to counsel the patient about diet and exercise. Question 7 A patient who has had a previous myocardial infarction has a blood pressure of 135/82 mm Hg. The patient’s body mass index is 28, and the patient has a fasting plasma glucose of 105 mg/dL. The primary care NP should prescribe: You Answered a calcium-channel blocker. a thiazide diuretic. lifestyle modifications. an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor. This patient has prehypertension but has a compelling reason for treatment. Patients who have had a myocardial infarction should be treated with a β-blocker and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB). Question 8 A patient who has stable angina and uses sublingual nitroglycerin tablets is in the clinic and begins having chest pain. The primary care NP administers a nitroglycerin tablet and instructs the patient to lie down. The NP’s next action should be to: call EMS. You Answered obtain an electrocardiogram. give 325 mg of chewable aspirin. administer oxygen at 2 L/minute. When a patient experiences an acute attack of angina in the clinic, the primary care NP should be prepared to treat the condition. After giving nitroglycerin, oxygen should be administered. An electrocardiogram is not immediately indicated. Chewable aspirin is given if the angina is unrelieved and when the patient is being transported to the hospital. EMS should be activated if there is no pain relief 5 minutes after the first dose of nitroglycerin. Question 9 A patient has been taking levothyroxine 100 mcg daily for several months. The patient comes to the clinic with complaints of insomnia and irritability. The primary care NP notes a heart rate of 92 beats per minute. The NP should: change to liothyronine 75 mcg/day. discontinue levothyroxine indefinitely. Correct! order TSH and T4 levels and decrease the dose to 75 mcg/day. order propylthiouracil to counter the increased thyroid levels. When signs of thyrotoxicosis occur, the drug should be decreased or temporarily discontinued for 5 to 7 days. Liothyronine is not indicated. Propylthiouracil is not indicated. Question 10 A patient who takes a calcium channel blocker is in the clinic for an annual physical examination. The cardiovascular examination is normal. As part of routine monitoring for this patient, the primary care NP should evaluate: serum calcium channel blocker level. Correct! liver function tests (LFTs) and renal function. complete blood count and electrolytes. thyroid and insulin levels. Patients who take calcium channel blockers should have periodic renal and LFTs. Question 11 A patient who is newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus has not responded to changes in diet or exercise. The patient is mildly obese and has a fasting blood glucose of 130 mg/dL. The patient has normal renal function tests. The primary care NP plans to prescribe a combination product. Which of the following is indicated for this patient? Metformin/glyburide (Glucovance) You Answered Saxagliptin/metformin (Kombiglyze) Metformin/pioglitazone (ACTOplus met) Insulin and metformin (Glucophage) Obese patients with normal renal function and elevated fasting plasma glucose may be started on a combination of metformin and a second-generation sulfonylurea. Question 12 A 75-year-old patient who has cardiovascular disease reports insomnia and vomiting for several weeks. The primary care NP orders thyroid function tests. The tests show TSH is decreased and T4 is increased. The NP should consult with an endocrinologist and order: You Answered levothyroxine. propylthiouracil. methimazole. thyrotropin. Patients with hyperthyroidism, or Graves’ disease, will require radioactive iodine. Elderly patients and patients with cardiovascular disease should be pretreated with an antithyroid medication such as methimazole. Thyrotropin is used to diagnose thyroid cancer. Levothyroxine is used to treat hypothyroidism. Propylthiouracil is also a thyroid suppressant, but methimazole is preferred. Question 13 A child who has congenital hypothyroidism takes levothyroxine 75 mcg/day. The child weighs 15 kg. The primary care NP sees the child for a 3-year-old check-up. The NP should consult with a pediatric endocrinologist to discuss: stopping the medication and checking TSH and T4 in 4 weeks. You Answered discussing the need for lifetime replacement therapy with the child’s parents. increasing the dose to 90 mcg/day. decreasing the dose to 30 mcg/day. In congenital hypothyroidism, therapy may be stopped for 2 to 8 weeks after the patient reaches 3 years of age. If TSH levels remain normal, thyroid supplementation may be discontinued permanently. Question 14 A primary care NP sees a 46-year-old male patient and orders a fasting lipoprotein profile that reveals LDL of 190 mg/dL, HDL of 40 mg/dL, and triglycerides of 200 mg/dL. The patient has no previous history of coronary heart disease, but the patient’s father developed coronary heart disease at age 55 years. The NP should prescribe: Correct! atorvastatin (Lipitor). gemfibrozil (Lopid). lovastatin/niacin (Advicor). cholestyramine (Questran). HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors are used to treat hyperlipidemia when the LDL is the primary lipid elevation. This patient has risk factors of being a man older than 45 years, with a positive family history of coronary heart disease before age 55 in a male first-degree relative. Gemfibrozil is used for patients with elevated triglycerides and low HDL. Bile acid sequestrants are used as adjunctive and not first-line therapy for reducing LDL. A combination product is not indicated for first-line therapy. Question 15 A patient who has stable angina pectoris and a history of previous myocardial infarction takes nitroglycerin and verapamil. The patient asks the primary care nurse practitioner (NP) why it is necessary to take verapamil. The NP should tell the patient that verapamil: increases the rate of contraction of the cardiac muscle. has a positive inotropic effect to increase cardiac output. increases the force of contraction of the cardiac muscle. Correct! improves blood flow and oxygen delivery to the heart. Verapamil decreases the force of smooth muscle contraction in the smooth muscle of the coronary and peripheral vessels; this results in coronary artery dilation, which lowers coronary resistance and improves blood flow through collateral vessels as well as oxygen delivery to ischemic areas of the heart. Calcium channel blockers do not increase the rate or force of contraction of the heart. Question 16 A patient has three consecutive blood pressure readings of 140/95 mm Hg. The patient’s body mass index is 24. A fasting plasma glucose is 100 mg/dL. Creatinine clearance and cholesterol tests are normal. The primary care NP should order: a thiazide diuretic. You Answered dietary and lifestyle changes. an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor. a β-blocker. The patient has stage I hypertension. Because there are no compelling indications for other treatment, a thiazide diuretic should be used initially to treat the hypertension. Dietary and lifestyle changes should also be recommended but are not sufficient for patients with stage I hypertension. Other drugs may be added later if thiazide diuretic therapy fails. Question 17 A patient who takes nitroglycerin for stable angina pectoris develops hypertension. The primary care NP should contact the patient’s cardiologist to discuss adding: You Answered amlodipine (Norvasc). verapamil HCl (Calan). nifedipine (Procardia XL). diltiazem (Cardizem). Nifedipine and related drugs are potent vasodilators, which makes them more effective for hypertension than verapamil and diltiazem. Amlodipine is not a first-line drug. Question 18 A patient who has a history of angina has sublingual nitroglycerin tablets to use as needed. The primary care nurse practitioner (NP) reviews this medication with the patient at the patient’s annual physical examination. Which statement by the patient indicates understanding of the medication? “I should take aspirin along with the nitroglycerin when I have chest pain.” “I should take nitroglycerin and then rest for 15 minutes before taking the next dose.” “I should call 9-1-1 if chest pain persists 5 minutes after the first dose.” You Answered “I should take 3 nitroglycerin tablets 5 minutes apart and then call 9-1-1.” Although the traditional recommendation is for patients to take up to 3 nitroglycerin doses over 15 minutes before accessing emergency medical services (EMS), more recent guidelines suggest an alternative strategy to reduce delays in emergency care. These include instructions to call 9-1-1 immediately if pain persists for 5 minutes after the first dose. Aspirin is recommended when the patient is being transported to emergency care and is not recommended as an adjunct to nitroglycerin with each episode of chest pain. The three doses of nitroglycerin are given 5 minutes apart over 15 minutes. Question 19 A patient who has type 2 diabetes mellitus takes metformin (Glucophage). The patient tells the primary care NP that he will have surgery in a few weeks. The NP should recommend: You Answered that the patient stop taking metformin several days before surgery. adding a sulfonylurea medication until recovery from surgery is complete. using insulin during the perioperative and postoperative periods. taking the metformin dose as usual the morning of surgery. Insulin should be considered for patients with diabetes during times of physical stress, such as illness or surgery. Question 20 A patient who is taking nifedipine develops mild edema of both feet. The primary care NP should contact the patient’s cardiologist to discuss: You Answered evaluation of left ventricular function. changing to amlodipine. ordering renal function tests. increasing the dose of nifedipine. Mild to moderate peripheral edema occurs in the lower extremities in about 10% of patients; this is caused by arterial dilation, not by left ventricular dysfunction. Amlodipine is less likely to have this effect. Renal function tests are not indicated. Increasing the nifedipine dose would worsen the symptoms. Question 21 A patient who has primary hyperlipidemia and who takes atorvastatin (Lipitor) continues to have LDL cholesterol of 140 mg/dL after 3 months of therapy. The primary care NP increases the dose from 10 mg daily to 20 mg daily. The patient reports headache and dizziness a few weeks after the dose increase. The NP should: recommend supplements of omega-3 along with the atorvastatin. change the patient’s medication to cholestyramine (Questran). You Answered change the atorvastatin dose to 15 mg twice daily. add ezetimibe (Zetia) and lower the atorvastatin to 10 mg daily. When used in combination with a low-dose statin, ezetimibe has been noted to produce an additional 18% reduction in LDL. Because this patient continues to have elevated LDL along with side effects of the statin, the NP should resume the lower dose of the statin and add ezetimibe. Atorvastatin is given once daily. Cholestyramine and omega-3 supplements are not indicated. Question 22 A primary care NP orders thyroid function tests. The patient’s TSH is 1.2 microunits/mL, and T4 is 1.7 ng/mL. The NP should: ask an endocrinologist to evaluate for possible Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. ask the patient about the use of medications such as lithium. You Answered assess the patient for symptoms of hyperthyroidism. tell the patient that the results most likely indicate hypothyroidism. Primary hypothyroidism is the most common form of hypothyroidism. Use of certain drugs, such as lithium, and diseases such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis can cause hypothyroidism but are less likely. The patient does not have signs of hyperthyroidism. Question 23 The primary care NP sees a new patient who has diabetes and hypertension and has been taking a thiazide diuretic for 6 months. The patient’s blood pressure at the beginning of treatment was 150/95 mm Hg. The blood pressure today is 138/85 mm Hg. The NP should: You Answered order a β-blocker. continue the current drug regimen. add an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor. change to an aldosterone antagonist medication. Evidence-based guidelines suggest that optimal control of hypertension to less than 130/80 mm Hg could prevent 37% of cardiovascular disease in men and 56% in women, so this patient, although showing improvement, could benefit from the addition of another medication. An angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor is an appropriate drug for patients who also have diabetes. β-Blockers and aldosterone antagonist medications are not recommended for patients with diabetes. Question 24 A primary care NP prescribes levothyroxine for a patient to treat thyroid deficiency. When teaching this patient about the medication, the NP should: tell the patient that the drug may be stopped when thyroid function tests stabilize. You Answered instruct the patient to stop taking the medication if signs of thyrotoxicosis occur. counsel the patient to take the medication with food. tell the patient that changing brands of the medication should be avoided. Patients should be told not to change brands of the medication; there is potential variability in the bioequivalence between manufacturers. The medication should be taken at approximately the same time each day before breakfast or on an empty stomach. Patients should be instructed to contact the provider if signs of thyrotoxicosis are present. Thyroid replacement medications are usually given for life. Question 25 An 80-year-old male patient will begin taking an α-antiadrenergic medication. The primary care NP should teach this patient to: restrict fluids to aid with diuresis. be aware that priapism is a common side effect. You Answered take the medication in the morning with food. ask for assistance while bathing. All antihypertensives can cause orthostatic hypotension, so patients should be cautioned to avoid sudden changes in position and to use caution when bathing because a hot bath or shower may aggravate dizziness. Older patients are at increased risk for falls and should be cautioned to ask for assistance. Patients taking α-antiadrenergics should consume extra fluids because dehydration can increase the risk of orthostatic hypotension. Patients should take the medication at bedtime because drowsiness is a common side effect. Priapism is not a side effect of these drugs. Question 1 A patient who will begin using nitroglycerin for angina asks the primary care NP how the medication works to relieve pain. The NP should tell the patient that nitroglycerin acts to: prevent catecholamine release. reduce C-reactive protein levels. relax vascular smooth muscle. dissolve atheromatous lesions. Nitrates relax vascular smooth muscle via stimulation of intracellular cyclic guanosine monophosphate production with the major effect being to reduce myocardial oxygen demand. Nitrates do not dissolve atheromatous lesions, prevent catecholamine release, or reduce C-reactive protein levels. UnansweredQuestion 2 A primary care NP sees a 46-year-old male patient and orders a fasting lipoprotein profile that reveals LDL of 190 mg/dL, HDL of 40 mg/dL, and triglycerides of 200 mg/dL. The patient has no previous history of coronary heart disease, but the patient’s father developed coronary heart disease at age 55 years. The NP should prescribe: gemfibrozil (Lopid). cholestyramine (Questran). atorvastatin (Lipitor). lovastatin/niacin (Advicor). HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors are used to treat hyperlipidemia when the LDL is the primary lipid elevation. This patient has risk factors of being a man older than 45 years, with a positive family history of coronary heart disease before age 55 in a male first-degree relative. Gemfibrozil is used for patients with elevated triglycerides and low HDL. Bile acid sequestrants are used as adjunctive and not first-line therapy for reducing LDL. A combination product is not indicated for first-line therapy. UnansweredQuestion 3 A patient who has a history of angina has sublingual nitroglycerin tablets to use as needed. The primary care nurse practitioner (NP) reviews this medication with the patient at the patient’s annual physical examination. Which statement by the patient indicates understanding of the medication? “I should take nitroglycerin and then rest for 15 minutes before taking the next dose.” “I should call 9-1-1 if chest pain persists 5 minutes after the first dose.” “I should take aspirin along with the nitroglycerin when I have chest pain.” “I should take 3 nitroglycerin tablets 5 minutes apart and then call 9-1-1.” Although the traditional recommendation is for patients to take up to 3 nitroglycerin doses over 15 minutes before accessing emergency medical services (EMS), more recent guidelines suggest an alternative strategy to reduce delays in emergency care. These include instructions to call 9-1-1 immediately if pain persists for 5 minutes after the first dose. Aspirin is recommended when the patient is being transported to emergency care and is not recommended as an adjunct to nitroglycerin with each episode of chest pain. The three doses of nitroglycerin are given 5 minutes apart over 15 minutes. UnansweredQuestion 4 The primary care NP sees a new patient who has diabetes and hypertension and has been taking a thiazide diuretic for 6 months. The patient’s blood pressure at the beginning of treatment was 150/95 mm Hg. The blood pressure today is 138/85 mm Hg. The NP should: continue the current drug regimen. order a β-blocker. add an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor. change to an aldosterone antagonist medication. Evidence-based guidelines suggest that optimal control of hypertension to less than 130/80 mm Hg could prevent 37% of cardiovascular disease in men and 56% in women, so this patient, although showing improvement, could benefit from the addition of another medication. An angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor is an appropriate drug for patients who also have diabetes. β-Blockers and aldosterone antagonist medications are not recommended for patients with diabetes. UnansweredQuestion 5 An 80-year-old female patient with a history of angina has increased TSH and decreased T4. The primary care NP should prescribe _____ mcg of _____. 75; levothyroxine 25; levothyroxine 25; liothyronine 75; liothyronine Elderly individuals may experience exacerbation of cardiovascular disease and angina with thyroid hormone replacement. It is advisable to start low at 25 mcg and work up as tolerated. Liothyronine is a synthetic T3. UnansweredQuestion 6 A 45-year-old patient who has a positive family history but no personal history of coronary artery disease is seen by the primary care NP for a physical examination. The patient has a body mass index of 27 and a blood pressure of 130/78 mm Hg. Laboratory tests reveal low-density lipoprotein, 110 mg/dL; high-density lipoprotein, 70 mg/dL; and triglycerides, 120 mg/dL. The patient does not smoke but has a sedentary lifestyle. The NP should recommend: beginning therapy with a statin medication. starting a thiazide diuretic to treat hypertension. taking 81 to 325 mg of aspirin daily. 30 minutes of aerobic exercise daily. This patient is overweight but not obese, and blood lipids are within normal limits. Blood pressure is not elevated. Exercise is recommended as an initial risk reduction strategy because of its positive effects on blood pressure and blood lipids. Aspirin is generally given to patients older than 55 to 65 who are at risk. Statin medications and thiazide diuretics are not indicated. UnansweredQuestion 7 A 55-year-old patient with no prior history of hypertension has a blood pressure greater than 140/90 on three separate occasions. The patient does not smoke, has a body mass index of 24, and exercises regularly. The patient has no known risk factors for cardiovascular disease. The primary care NP should: perform a careful cardiovascular physical assessment. counsel the patient about dietary and lifestyle changes. order a urinalysis and creatinine clearance and begin therapy with a β-blocker. prescribe a thiazide diuretic and an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor. If the patient is younger than 20 or older than 50 years old at the onset of elevated blood pressure, the NP should look for causes of secondary hypertension. The physical examination should include a careful cardiovascular assessment. This patient will need pharmacologic treatment, but not until the underlying cause of hypertension is determined. UnansweredQuestion 8 A patient who has hyperlipidemia has been taking atorvastatin (Lipitor) 60 mg daily for 6 months. The patient’s initial lipid profile showed LDL of 180 mg/dL, HDL of 45 mg/dL, and triglycerides of 160 mg/dL. The primary care NP orde [Show More]
Last updated: 8 months ago
Preview 1 out of 131 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 13, 2020
Number of pages
131
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 13, 2020
Downloads
1
Views
83



















.png)
 (1).png)



