*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > NR 508 Week 1 Quiz (Fall 2019) - 100% correct. (All)
NR 508 Week 1 Quiz (Fall 2019) - 100% correct.
Document Content and Description Below
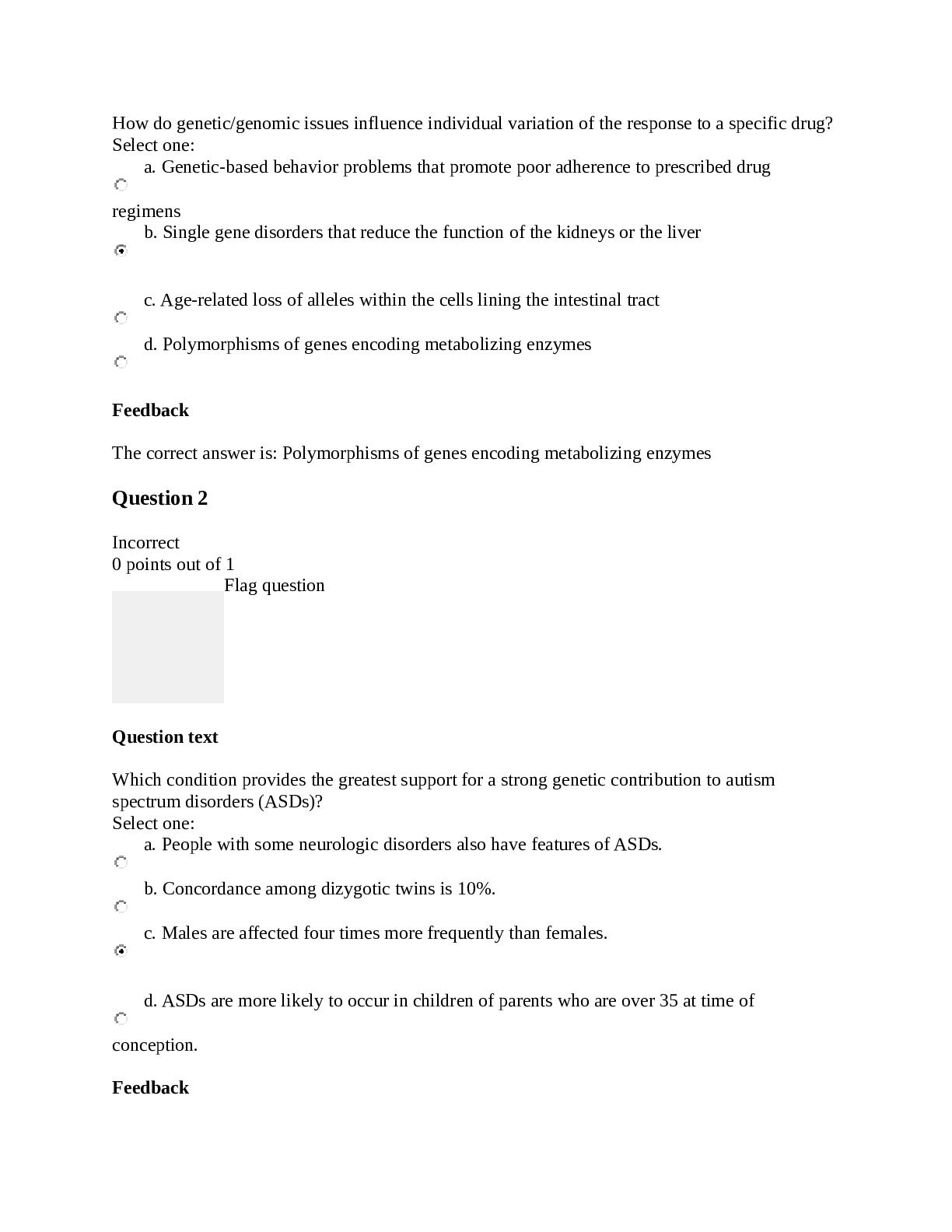
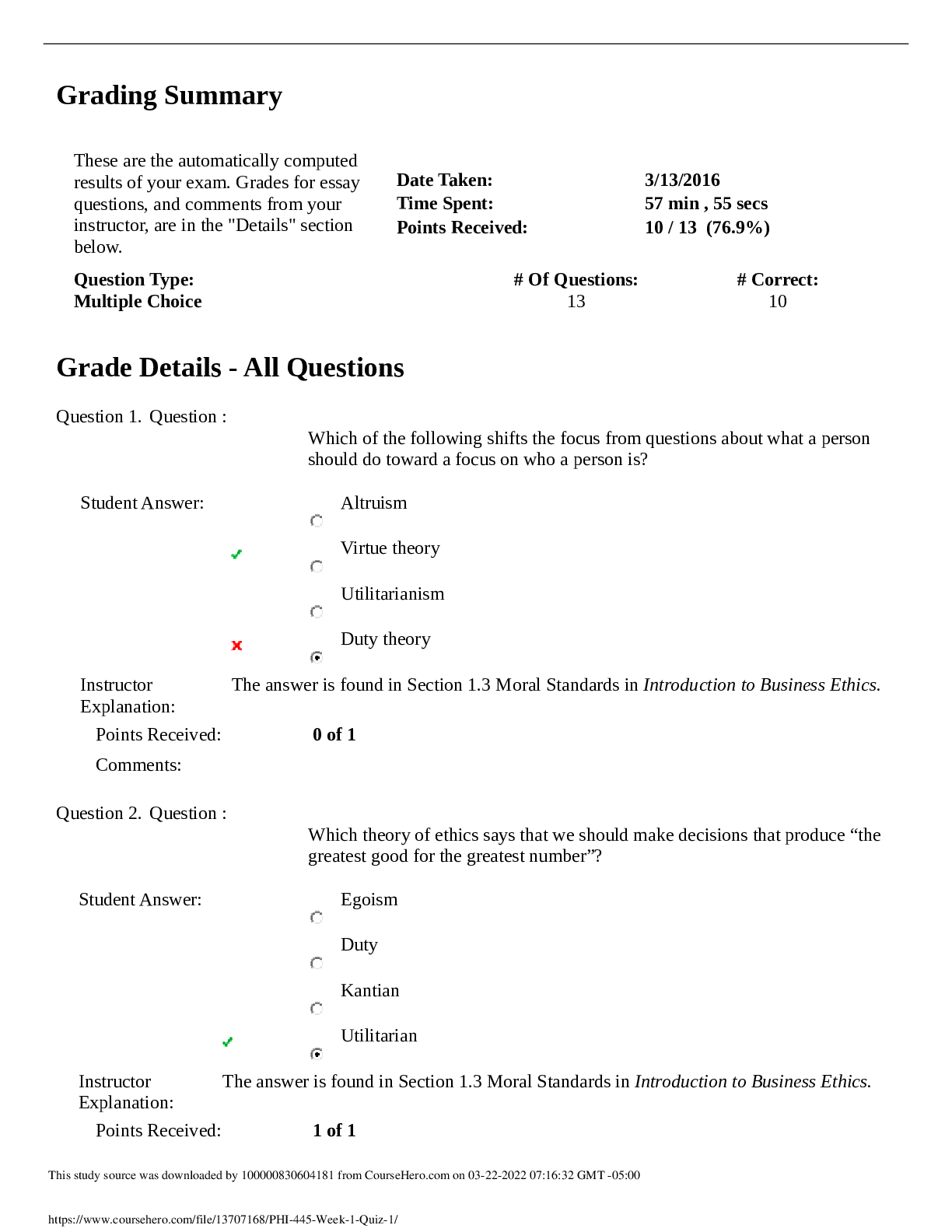
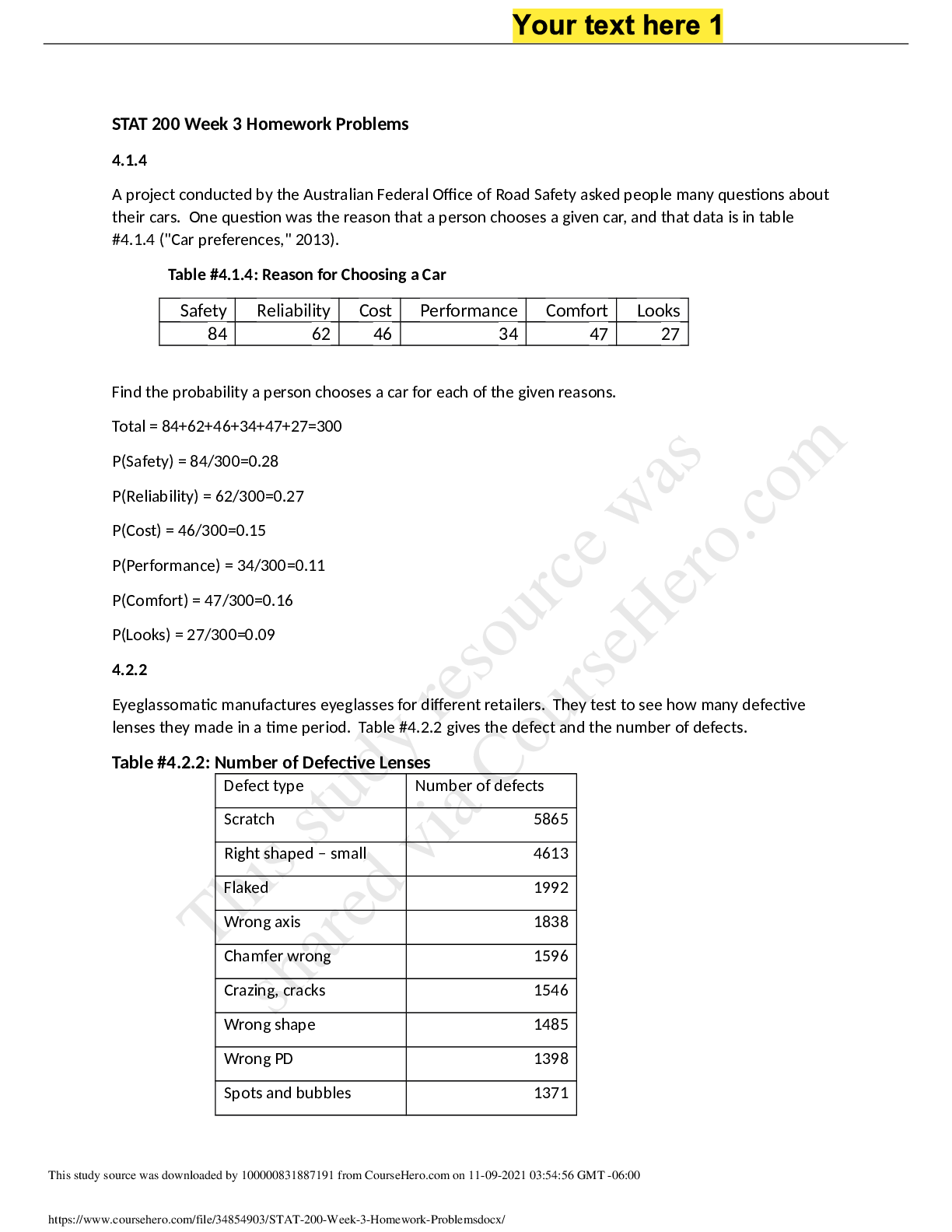
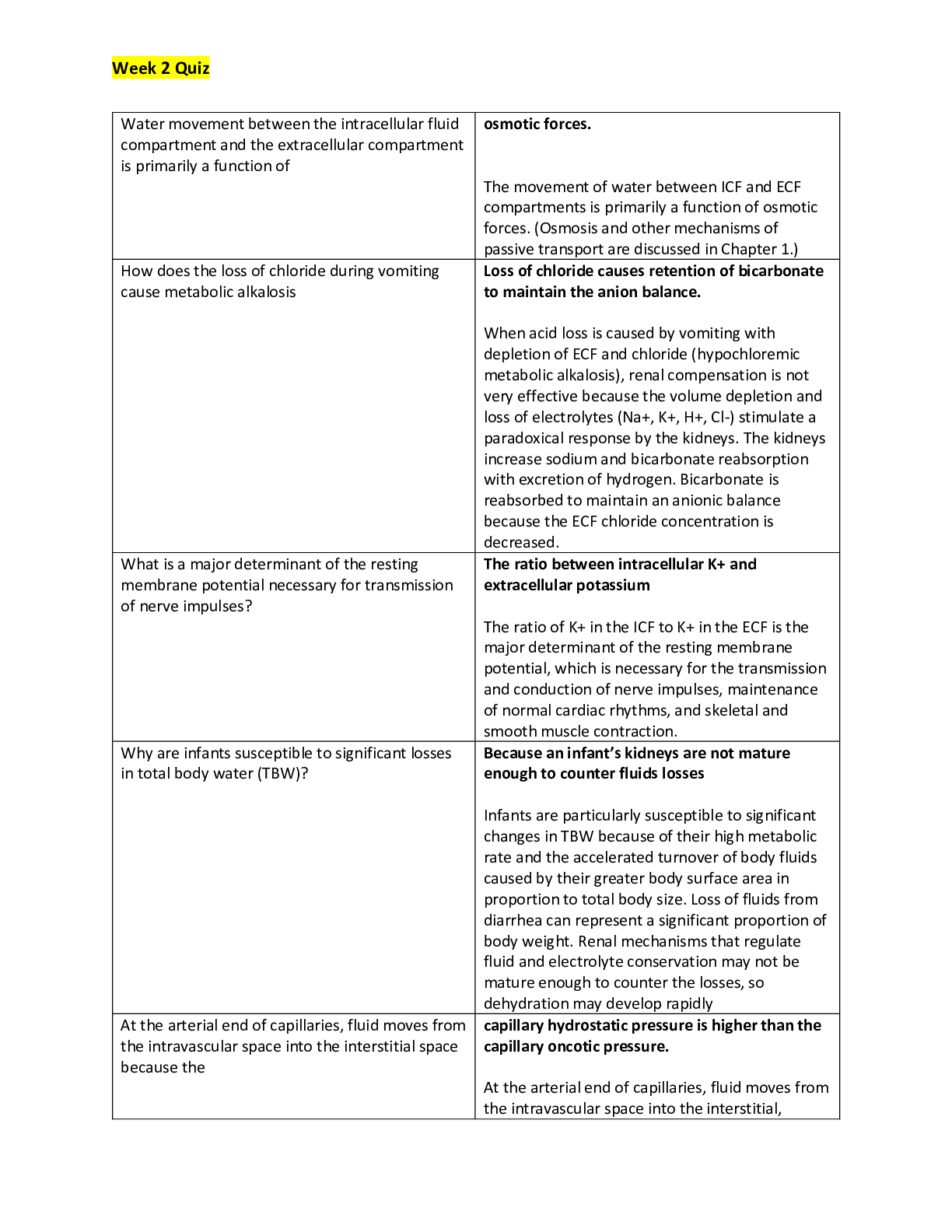
NR 508 Week 1 Quiz (Fall 2019) Question 1.1. A primary care NP is aware that many patients in the community use herbal remedies to treat various conditions. The NP understands the importance of: (Po... ints : 2) learning about the actions, uses, doses, and toxicities of these agents. prescribing these agents when possible to ensure safe dosing. counseling patients to stop using herbal products to avoid toxic side effects. teaching patients that these products are unregulated and unsafe to use. Question 2.2. A woman who began taking a COCP 2 months ago calls the primary care NP to report having nausea every day. She takes a pill at the same time each morning. The NP should tell her to: (Points : 2) try taking the pill in the evening each day. come to the clinic for a urine pregnancy test. take the pill on an empty stomach with water. stop taking the pill for 7 days and then restart. Question 3.3. A primary care NP is performing a previsit health history on a new patient. The patient reports taking vitamins every day. The NP should: (Points : 2) ask the patient to bring all vitamin bottles to the clinic appointment. recommend natural vitamin products over synthetic vitamin products. reassure the patient that vitamins that are high in folic acid are safe to take. tell the patient that some vitamins, such as vitamin C, are safe in large doses. Question 4.4. A patient receives an inhaled corticosteroid to treat asthma. The patient asks the primary care NP why the drug is given by this route instead of orally. The NP should explain that the inhaled form: (Points : 2) is absorbed less quickly. has reduced bioavailability. has fewer systemic side effects. provides dosing that is easier to regulate. Question 5.5. A patient is diagnosed with lupus and reports occasional use of herbal supplements. The primary care NP should caution this patient to avoid: (Points : 2) ginseng. echinacea. ginkgo biloba. St. John’s wort. Question 6.6. A parent brings a child who has moderate-persistent asthma to the clinic and tells the primary care NP that none of the child’s medications are working. The parent says, “Everybody tells me something different. I don’t know what to do.” The NP suspects that the parent is not administering the medications appropriately. The NP should initially: (Points : 2) perform a careful history of the child’s symptoms and the medications that are given. provide a written asthma action plan and encourage the parent to call when symptoms are worse. review what other providers have prescribed in the past and explain these interventions to the parent. explain the different purposes of maintenance and rescue medications and give the parent a schedule for medication administration. Question 7.7. A primary care NP prescribes a COCP for a woman who has never taken oral contraceptives before. The woman is in a monogamous relationship, and she and her partner have been using condoms and wish to stop using them. Her last period was 1 week ago. The NP should: (Points : 2) perform an in-office pregnancy test before starting a COCP. tell the patient to begin the first pill today and to continue using condoms for 7 days. tell the patient to begin the first pill on the Sunday of or following her next menstrual period. tell the patient to begin the first pill today and to return in 2 weeks for a pregnancy test. Question 8.8. A primary care NP will begin practicing in a state in which the governor has opted out of the federal facility reimbursement requirement. The NP should be aware that this defines how NPs may write prescriptions: (Points : 2) without physician supervision in private practice. as CRNAs without physician supervision in a hospital setting. in any situation but will not be reimbursed for this by government insurers. only with physician supervision in both private practice and a hospital setting. Question 9.9. A patient who has asthma and who is known to the primary care NP calls the NP after hours and asks for a refill of an albuterol metered-dose inhaler. The patient has not been seen in the clinic for more than a year. The NP should: (Points : 2) call the pharmacy to order the medication with several refills. send an electronic prescription to the pharmacy for one time only. send the patient to the emergency department for evaluation of symptoms. refill the drug and tell the patient that an office visit is necessary for further refills. Question 10.10. The primary care NP should understand that a drug is at a therapeutic level when it is: (Points : 2) at peak plasma level. past 4 or 5 half-lives. at its steady plasma state. between minimal effective concentration and toxic levels. Question 11.11. A woman who is taking a progestin-only pill has just stopped nursing her 9-month-old infant and tells the primary care NP that she would like to space her children about 2 years apart. The NP should: (Points : 2) discontinue the progestin-only pill. prescribe a COCP and a folic acid supplement. prescribe a progestin-only pill for another 6 months. suggest that she use a barrier method of contraception. Question 12.12. In every state, prescriptive authority for NPs includes the ability to write prescriptions: (Points : 2) for controlled substances. for specified classifications of medications. without physician-mandated involvement. with full, independent prescriptive authority. Question 13.13. A man who has secondary hypogonadism associated with pituitary dysfunction will begin exogenous testosterone therapy. The patient asks the primary care NP about future chances of fathering children. The NP should tell him that: (Points : 2) fertility may improve with testosterone therapy. exogenous testosterone therapy will shut down sperm production. fertility can be restored when testosterone therapy is discontinued. he should store sperm ahead of the initiation of testosterone therapy. Question 14.14. A perimenopausal woman tells the primary care NP that she is having hot flashes and increasingly severe mood swings. The woman has had a hysterectomy. The NP should prescribe: (Points : 2) estrogen-only HT. low-dose oral contraceptive therapy. selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor therapy until menopause begins. estrogen-progesterone HT. Question 15.15. An adolescent girl has chosen Depo-Provera as a contraceptive method and tells the primary care NP that she likes the fact that she won’t have to deal with pills or periods. The primary care NP should tell her that she: (Points : 2) should consider another form of contraception after 1 year. may have irregular bleeding, especially in the first month or so. will need to take calcium and vitamin D every day while using this method. will have to take oral contraceptive pills in addition to Depo-Provera when she takes antibiotics. Question 16.16. A patient has been using an herbal supplement for 2 years that the primary care NP knows may have toxic side effects. The NP should: (Points : 2) tell the patient to stop taking the supplement immediately. inform the patient of the risks of toxic side effects with this supplement. refer the patient to a CAM provider who can manage this patient’s therapy. prescribe another herbal drug that has fewer adverse effects than the one the patient is taking. Question 17.17. A patient who weighs 170 lb wishes to lose weight, with a target weight goal of 125 lb. To initiate a program that will result in a loss of 1 lb per week, the primary care NP should recommend a dietary intake of _____ kcal. (Points : 2) 1000 1200 1700 2000 Question 18.18. A primary care NP has prescribed phentermine for a patient who is obese. The patient loses 10 lb in the first month but reports that the drug does not seem to be suppressing appetite as much as before. The NP should: (Points : 2) discontinue the phentermine. increase the dose of phentermine. continue the phentermine at the same dose. change to a combination of phentermine and topiramate. Question 19.19. A 50-year-old woman reports severe, frequent hot flashes and vaginal dryness. She is having irregular periods. She has no family history of CHD or breast cancer and has no personal risk factors. The primary care NP should recommend: (Points : 2) estrogen-only HT. low-dose oral contraceptive therapy. selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor therapy until menopause begins. estrogen-progesterone HT. Question 20.20. A patient who has an upper respiratory infection reports using over-the-counter cold preparations. The primary care NP should counsel this patient to use caution when taking additional over-the-counter medications such as: (Points : 2) antipyretics. calcium supplements. acid reflux medications. antioxidant supplements. Question 21.21. A primary care NP sees a 60-year-old woman for a physical examination. The woman tells the NP she is taking tamoxifen for treatment of breast cancer. To monitor her response to this medication, the NP should order: (Points : 2) a chest radiograph. bone mineral density testing. serum bilirubin and creatinine. liver enzymes and a complete blood count (CBC). Question 22.22. A 55-year-old woman has not had menstrual periods for 5 years and tells the primary care nurse practitioner (NP) that she is having increasingly frequent vasomotor symptoms. She has no family history or risk factors for coronary heart disease (CHD) or breast cancer but is concerned about these side effects of hormone therapy (HT). The NP should: (Points : 2) tell her that starting HT now may reduce her risk of breast cancer. advise a short course of HT now that may decrease her risk for CHD. tell her that HT will not help control her symptoms during postmenopause. recommend herbal supplements for her symptoms to avoid HT side effects. Question 23.23. A patient will begin taking two drugs that are both protein-bound. The primary care NP should: (Points : 2) prescribe increased doses of both drugs. monitor drug levels, actions, and side effects. teach the patient to increase intake of protein. stagger the doses of drugs to be given 1 hour apart. Question 24.24. A patient asks a primary care NP why herbal supplements are not regulated by the FDA. The nurse practitioner should tell the patient these products are not regulated by the FDA because they are: (Points : 2) natural, plant-based products and not man-made. not marketed as products that can treat or cure disease. regulated by the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act. covered by the Hatch-Richardson Bill of 1992, which allows them to make health claims without FDA approval. Question 25.25. A woman who has been taking a COCP tells the primary care NP that, because of frequent changes in her work schedule, she has difficulty remembering to take her pills. The woman and the NP decide to change to a vaginal ring. The NP will instruct her to insert the ring: (Points : 2) within 7 days after her last active pill. and use a backup contraceptive for 7 days. and continue the COCP for one more cycle. on the same day she stops taking her COCP. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 23 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 13, 2020
Number of pages
23
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 13, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
28









.png)

.png)










.png)




.png)