Biology > Experiment > Comparing DNA Sequences to Understand Evolutionary Relationships with Blast Purpose: The reason for (All)
Comparing DNA Sequences to Understand Evolutionary Relationships with Blast Purpose: The reason for doing this lab is to create cladograms that depict evolutionary relationships and to analyze biological data with an online bioinformatics tool.
Document Content and Description Below
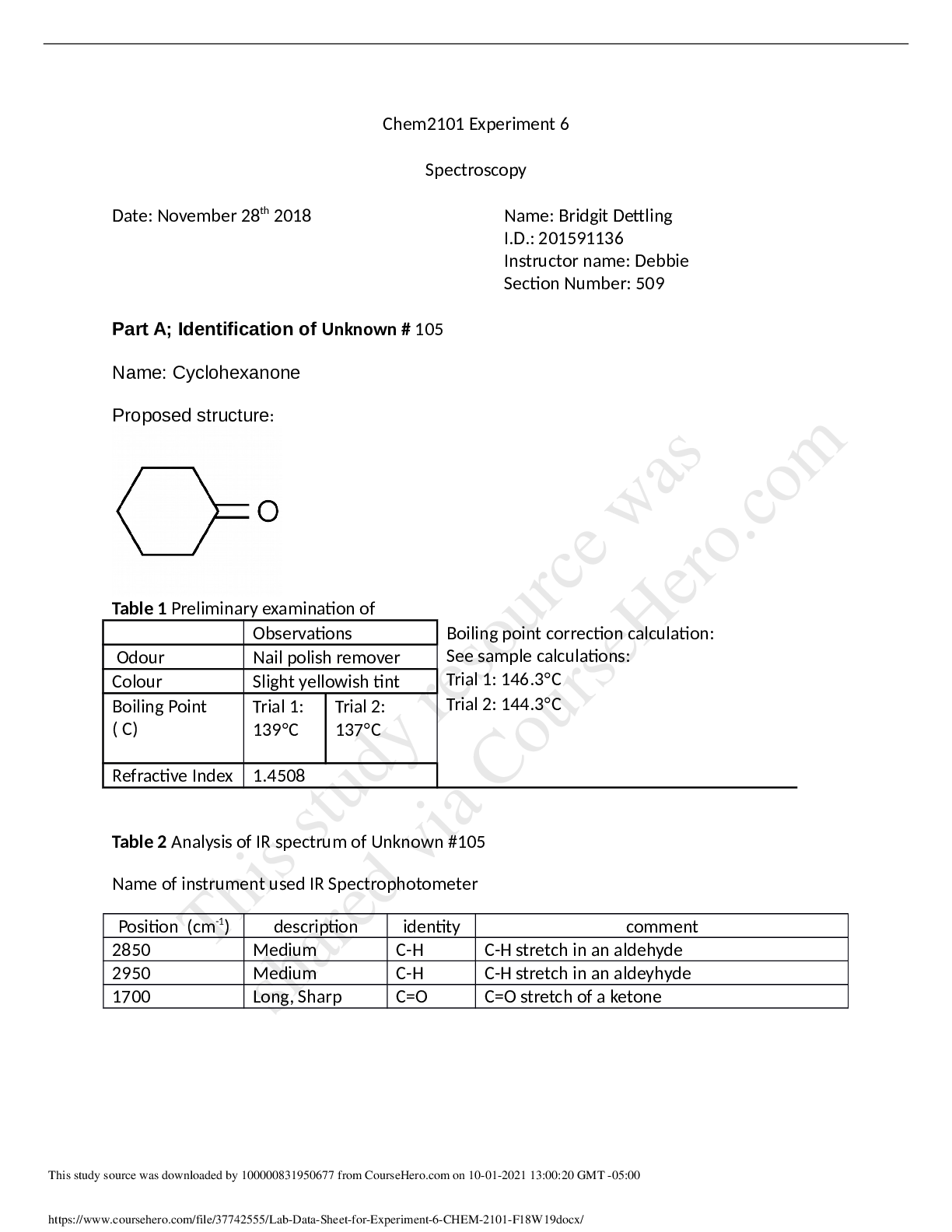
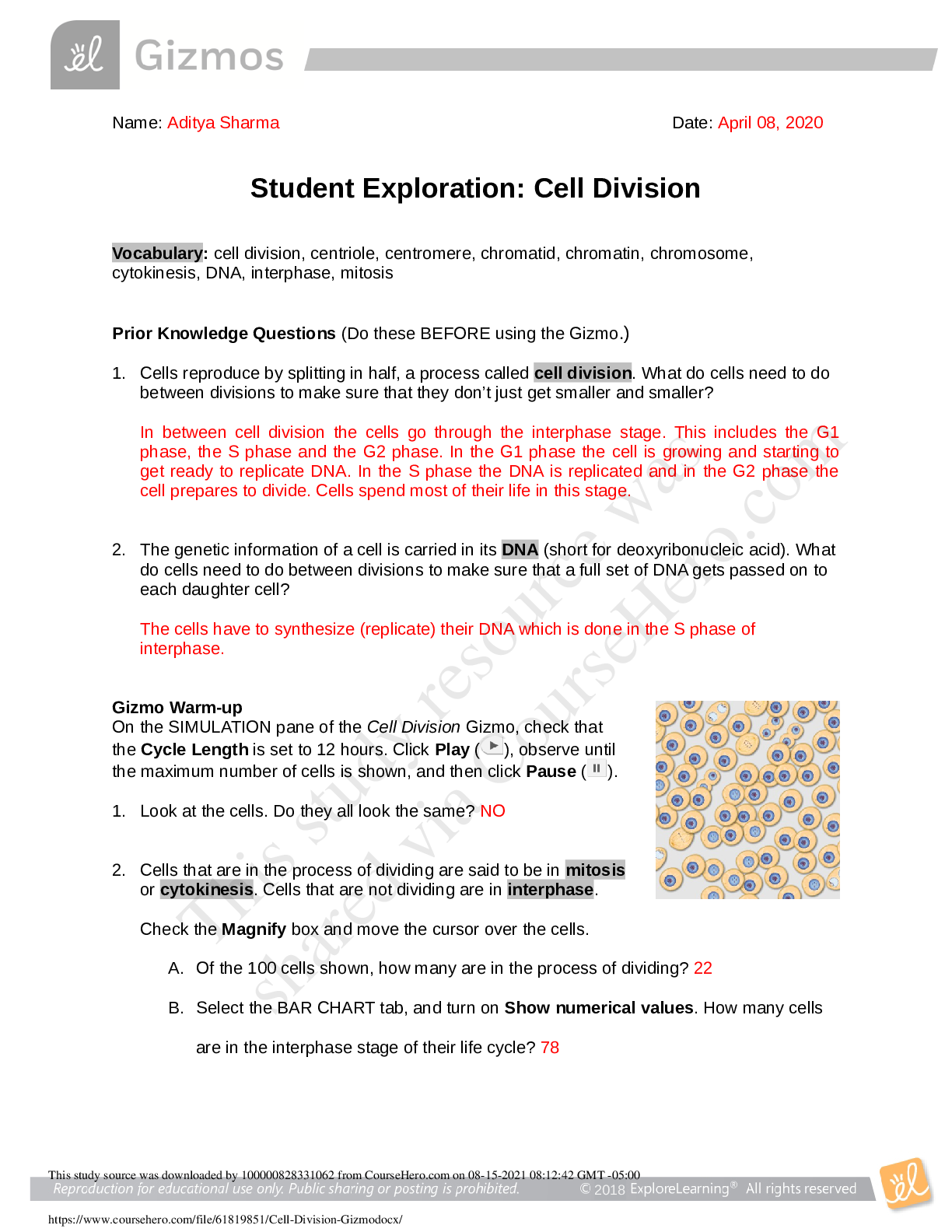
AP Biology Comparing DNA Sequences to Understand Evolutionary Relationships with Blast Purpose: The reason for doing this lab is to create cladograms that depict evolutionary relationships and to ... analyze biological data with an online bioinformatics tool. Hypothesis: The fossil specimen belongs to the crocodilian branch of the fossil cladogram. Materials: ● Online Lab ● Gene Files provided by the College Board ● NIBI Blast Program Procedure: 1. Download gene files from blogging4biology.edublogs.org/2010/08/28/college-board-lab-files/ 2. Upload the gene sequence onto BLAST a. Gene 1: b. Gene 2: c. Gene 3: d. Gene 4: 3. Scroll down to “Sequences producing significant alignments” and click on the most similar gene sequence. 4. After recording the most similar gene sequence, find the second most similar sequence. Data: Gene 1 Gene 2 Gene 3 Our Gene Scientific Name gallus gallus collagen, type V, diphal (COL5A1,) mRNA Drosophila melanogaster FI02063 full insert cDNA Tasehiopygla guttata Ubiquitin - Conjugating Enzyme E2Q Family Member 1 (UBE2Q1,) partial mRNA Homo sapiens bromodomain and WD repeat domain containing 3 (BRWD3), transcript variant X4, misc_RNA Common name Chicken Fruit fly Zebra finch Hemoglobin E Value Ident Pre Lab Questions: 1. Use the following data to construct a cladogram of the major plant groups: Table 1. Characteristics of Major Plant Groups 2. GAPDH (glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase) is an enzyme that catalyzes the sixth step in glycolysis, an important reaction that produces molecules used in cellular respiration. The following data table shows the percentage similarity of this gene and the protein it expresses in humans versus other species. For example, according to the table, the GAPDH gene in chimpanzees is 99.6% identical to the gene found in humans, while the protein is identical. a. Why is the percentage similarity in the gene always lower than the percentage similarity in the protein for each of the species? (Hint: Recall how a gene is expressed to produce a protein.) b. Draw a cladogram depicting the evolutionary relationships among all five species (including humans) according to their percentage similarity in the GAPDH gene. ost lab Questions: 1.What species in the BLAST result has the most similar gene sequence to the gene of interest? 2. Where is that species located on the cladogram? 3. How similar is that gene sequence? 4. What species has the next most similar gene sequence of the gene of interest? Example Procedure 1. On the Entrez Gene website, search “human actin.” 2. Click on the first link that appears and scroll down to the section “NCBI Reference Sequences.” 3. Under “mRNA and Proteins,” click on the first file name “NM 001100.3.” 4. Just below the gene title, click on “FASTA.” 5. e nucleotide sequence displayed is that of the actin gene in humans. 6. Copy the gene sequence and go to the BLAST homepage (http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi). 7. Click on “nucleotide blast” under the Basic BLAST menu. 8. Paste the sequence into the box where it says “Enter Query Sequence.” 9. Give the query a title in the box provided if you plan on saving it for later. 10. Under “Choose Search Set,” select whether you want to search the human genome only, mouse genome only, or all genomes available. 11. Under “Program Selection,” choose whether you want highly similar sequences or somewhat similar sequences. Choosing somewhat similar sequences will provide you with more results. 12. Click BLAST. ATP Synthase: ● ATP Synthase serves to harness the proton gradient present across the inner mitochondrial membranes of mitochondria and the thylakoid membrane in plants and provide a channel for the hydrogen ions to pass through, forming ATP in the process. ● ATP Synthase may be found in all eukaryotes because all eukaryotes need energy to perform metabolic processes. ● It is possible to find the same gene in two organisms but not find the protein because certain genes may be deactivated at certain times, yielding no protein. ● If the gene is found in all organisms tested, it is an indication that it is a very old gene and was present when different species first diverged from each other. ● The usage of DNA sequences is important in the study of evolutionary relationships; however, other factors, such as environment, gene activation, and type of organism must be taken into account, because DNA does not act the same way in all circumstances. Conclusion: [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 10 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 02, 2021
Number of pages
10
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 02, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
121













.png)


.png)