*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > HUN 2201- Study Guide- Exam 2- Spring 2020 (All)
HUN 2201- Study Guide- Exam 2- Spring 2020
Document Content and Description Below
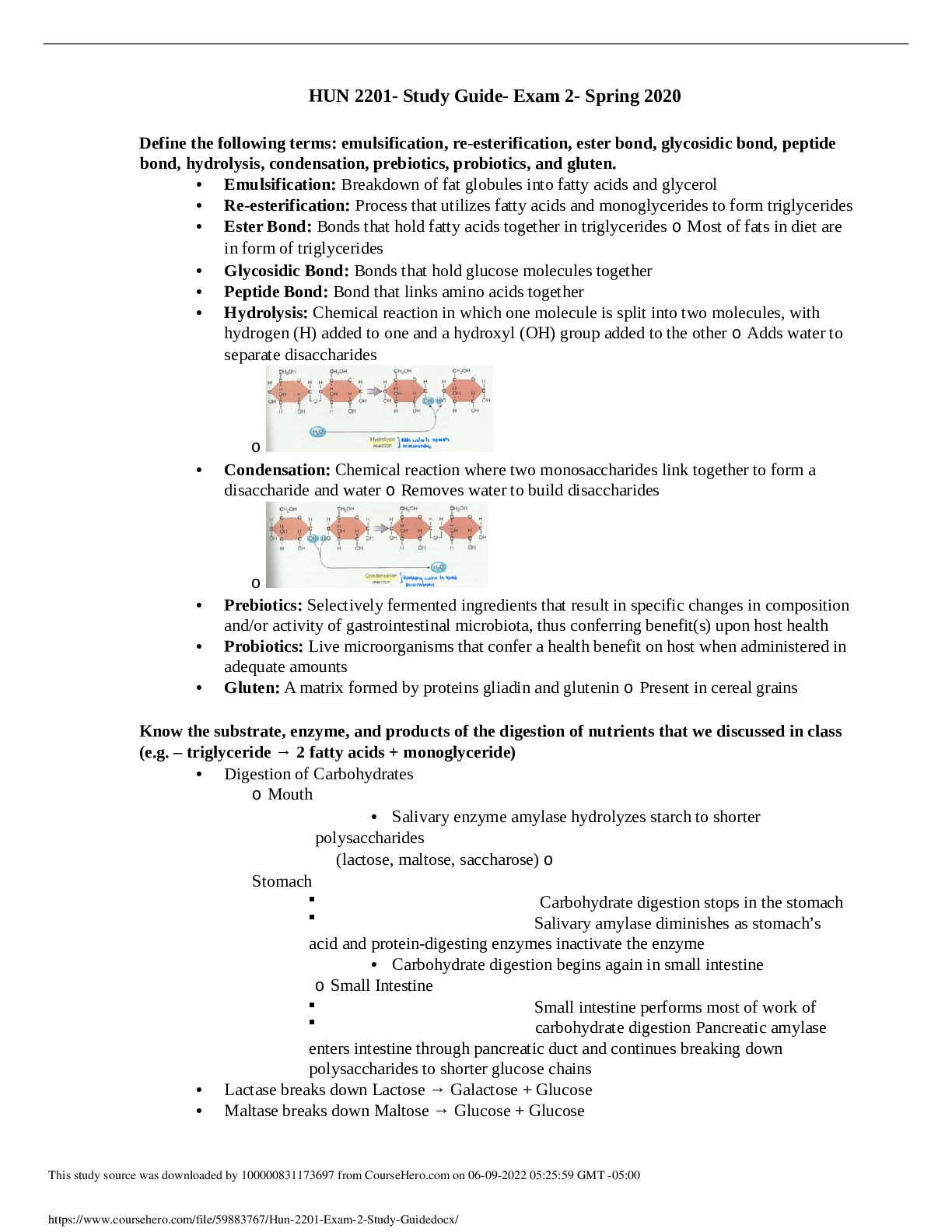
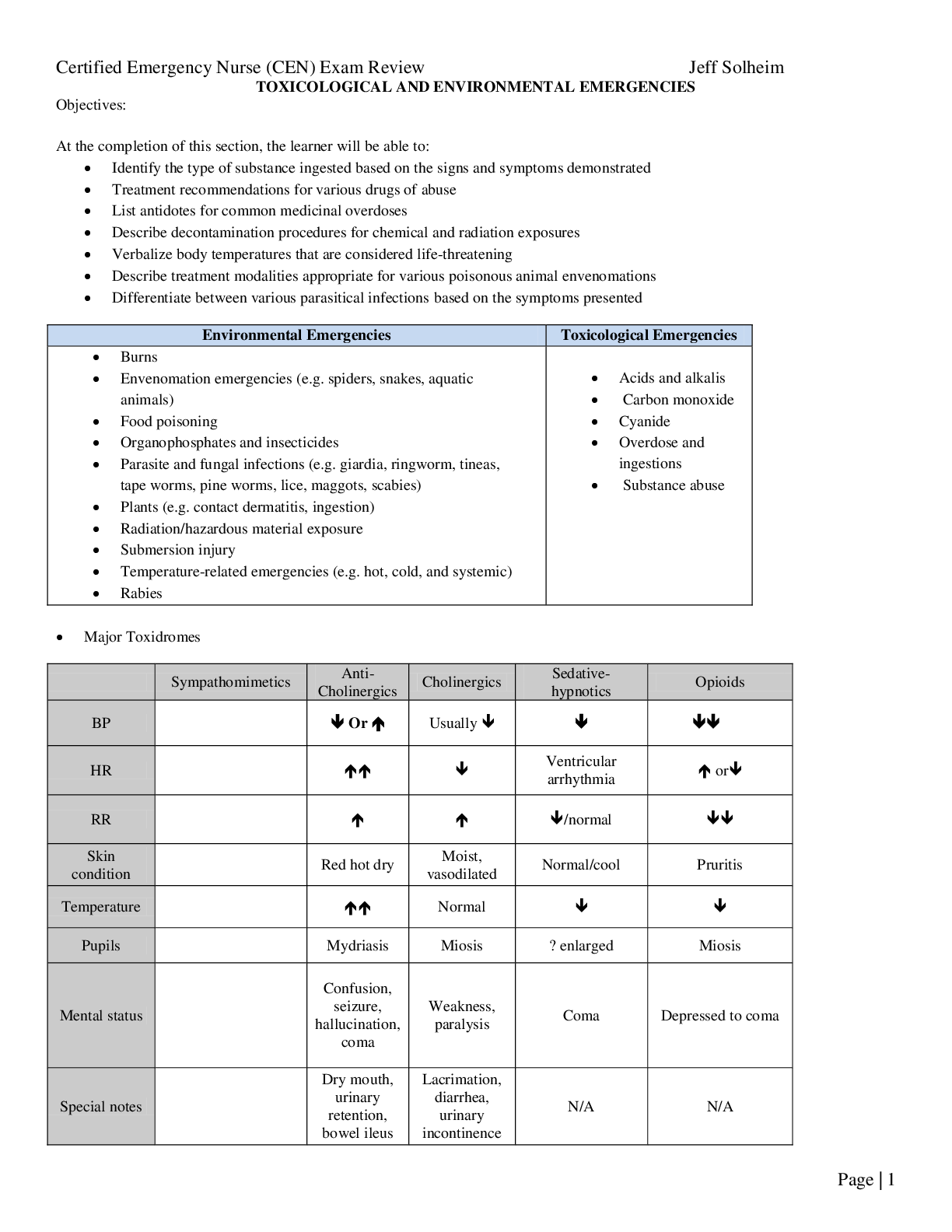
Define the following terms: emulsification, re-esterification, ester bond, glycosidic bond, peptide bond, hydrolysis, condensation, prebiotics, probiotics, and gluten. • Emulsification: Breakdown ... of fat globules into fatty acids and glycerol • Re-esterification: Process that utilizes fatty acids and monoglycerides to form triglycerides • Ester Bond: Bonds that hold fatty acids together in triglycerides o Most of fats in diet are in form of triglycerides • Glycosidic Bond: Bonds that hold glucose molecules together • Peptide Bond: Bond that links amino acids together • Hydrolysis: Chemical reaction in which one molecule is split into two molecules, with hydrogen (H) added to one and a hydroxyl (OH) group added to the other o Adds water to separate disaccharides o • Condensation: Chemical reaction where two monosaccharides link together to form a disaccharide and water o Removes water to build disaccharides o • Prebiotics: Selectively fermented ingredients that result in specific changes in composition and/or activity of gastrointestinal microbiota, thus conferring benefit(s) upon host health • Probiotics: Live microorganisms that confer a health benefit on host when administered in adequate amounts • Gluten: A matrix formed by proteins gliadin and glutenin o Present in cereal grains Know the substrate, enzyme, and products of the digestion of nutrients that we discussed in class (e.g. – triglyceride → 2 fatty acids + monoglyceride) • Digestion of Carbohydrates o Mouth • Salivary enzyme amylase hydrolyzes starch to shorter polysaccharides (lactose, maltose, saccharose) o Stomach Carbohydrate digestion stops in the stomach Salivary amylase diminishes as stomach’s acid and protein-digesting enzymes inactivate the enzyme • Carbohydrate digestion begins again in small intestine o Small Intestine Small intestine performs most of work of carbohydrate digestion Pancreatic amylase enters intestine through pancreatic duct and continues breaking down polysaccharides to shorter glucose chains • Lactase breaks down Lactose → Galactose + Glucose • Maltase breaks down Maltose → Glucose + Glucose [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 9 pages
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Aug 01, 2022
Number of pages
9
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Aug 01, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
50























.png)











