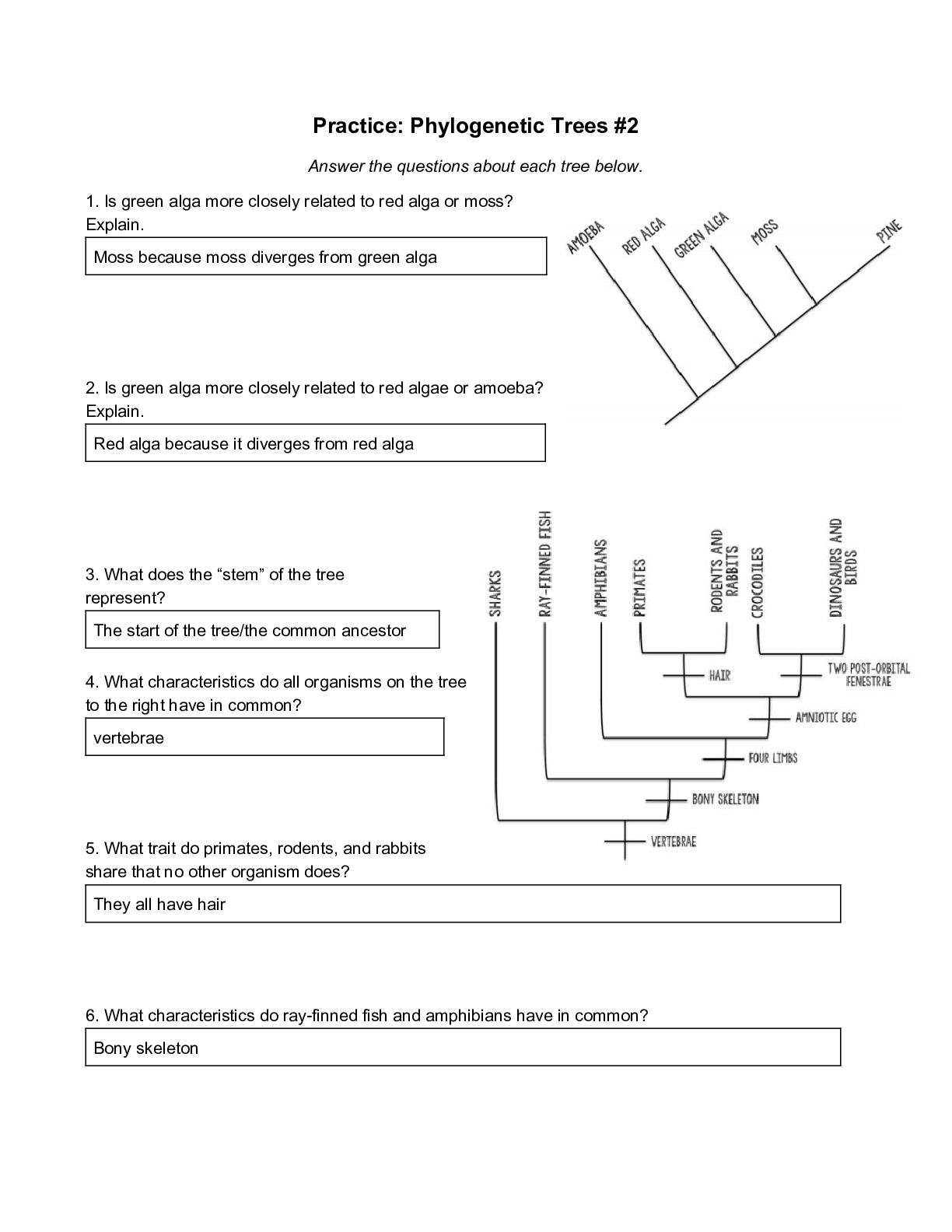
*NURSING > EXAM > Questions Paper > STRATFORD UNIVERSITY – NSG 325 / NSG325 COMPLEX FINAL EXAM 430 HC _ 75 Q&A (CORR (All)
Questions Paper > STRATFORD UNIVERSITY – NSG 325 / NSG325 COMPLEX FINAL EXAM 430 HC _ 75 Q&A (CORRECT Answers Highlighted 100%)
Document Content and Description Below
Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text The nurse admits a patient to the critical care unit following a motorcycle crash. Assessment findings by the nurse include blood pres... sure 100/50 mm Hg, heart rate 58 beats/min, respiratory rate 30 breaths/min, and temperature of 100.5°F. The patient is lethargic, responds to voice but falls asleep readily when not stimulated. Which nursing action is most important to include in this patient’s plan of care? Select one: a. Frequent neurological assessments b. Range-of-motion to extremities c. Frequent oropharyngeal suctioning d. Side to side position changes Question 2 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text The nurse is caring for a burn-injured patient who weighs 154 pounds, and the burn injury covers 40% of his body surface area. The nurse calculates the fluid needs for the first 24 hours after a burn injury using a standard fluid resuscitation formula of 4 mL/kg/% burn of intravenous (IV) fluid for the first 24 hours. The nurse plans to administer what amount of fluid in the first 24 hours? Select one: a. 2800 ml b. 14000 ml c. 11200 ml d. 7000 ml Question 3 Complete 0.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text For patients with major burns, when should you start enteral feedings? Select one: a. A few hours after the injury has occurred b. Not until bowel sounds have returned c. 2 to 3 days after the injury d. After the emergent phase of the injury Question 4 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text After receiving the handoff report from the day shift charge nurse, which patient should the evening charge nurse assess first? Select one: a. A patient with bacterial meningitis on droplet precautions b. Mechanically ventilated patient with a GCS of 6 c. Patient with meningitis complaining of photophobia d. A patient with an intracranial pressure ICP of 20 mm Hg and an oral temperature of 104°F Question 5 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text The charge nurse assigns patients based on their acuity and the level of experience of the critical care nurses on duty. This is an example of implementation of: Select one: a. National patient safety goals b. Healthy work environment c. SBAR communication d. Synergy model Question 6 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text While caring for a patient with a basilar skull fracture, the nurse assesses clear drainage from the patient’s left naris. What is the best nursing action? Select one: a. Place a nasal drip pad under the nose. b. Have the patient blow the nose until clear. c. Suction the left nares until the drainage clears. d. Insert bilateral cotton nasal packing. Question 7 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text The nurse is caring for a patient who was hit on the head with a hammer. The patient was unconscious at the scene briefly but is now conscious upon arrival at the emergency department with a GCS score of 15. One hour later, the nurse assesses a GCS score of 3. What is the priority nursing action? Select one: a. stimulate the patient hourly. b. Continue to monitor the patient. c. Elevate the head of the bed. d. Notify the provider immediately. Question 8 Complete 0.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text The nurse is caring for a patient who has a diminished level of consciousness and who is mechanically ventilated. While performing endotracheal suctioning, the patient’s hands clench and pull into the chest. What is the best interpretation by the nurse? Select one: a. The patient is exhibiting decorticate posturing. b. The patient is exhibiting extension posturing. c. The patient is exhibiting flexion posturing. d. The patient is exhibiting purposeful movement. Question 9 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text Which of the following would be seen in a patient with myxedema coma? Select one: a. Hyperthermia b. Tachycardia c. Hyperventilation d. Decreased reflexes Question 10 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text A patient presents to the emergency department with suspected thyroid storm. The nurse should be alert to which of the following cardiac rhythms while providing care to this patient? Select one: a. Sinus bradycardia b. Atrial fibrillation c. Idioventricular rhythm d. Junctional rhythm Question 11 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text A patient is admitted to the critical care unit with a diagnosis of diabetic ketoacidosis. Following aggressive fluid resuscitation and intravenous (IV) insulin administration, the blood glucose begins to normalize. In addition to glucose monitoring, which of the following electrolytes requires close monitoring? Select one: a. Potassium b. Sodium c. Chloride d. Calcium Question 12 Complete 0.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text diabetic ketoacidosis, the laboratory results are similar to those of hyperosmolar hyperglycemic syndrome, with three major exceptions. What differences would you expect to see in patients with diabetic ketoacidosis? Select one: a. Lower serum glucose, lower osmolality, and higher ketosis b. Higher serum glucose, higher osmolality, and higher ketosis c. Higher serum glucose, higher osmolality, and no ketosis d. Lower serum glucose, lower osmolality, and no ketosis Question 13 Complete 0.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text A patient presents to the emergency department with the following clinical signs: Pulse: 132 beats/min, Blood pressure: 88/50 mm Hg, Respiratory rate: 32 breaths/min, Blood sugar of 60, fatigue, dizziness and darkening of skin. These signs are consistent with which disorder? Select one: a. Thyroid Storm b. Syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone (SIADH) c. Myxedema coma d. Adrenal Crisis Question 14 Complete 0.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text Which of the following patients is at the highest risk for hyperosmolar hyperglycemic syndrome? Select one: a. A 45-year-old woman with type 1 diabetes who forgets to take her insulin in the morning b. An 83-year-old, long-term care resident with type 1 diabetes and new onset Alzheimer’s disease. c. An 18-year-old college student with type 2 diabetes who was diagnosed with the flu d. A 75-year-old man with type 2 diabetes and coronary artery disease who has recently started on insulin injections Question 15 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text The nurse assesses a patient with a skull fracture to have a Glasgow Coma Scale score of 3. Additional vital signs assessed by the nurse include blood pressure 100/70 mm Hg, heart rate 55 beats/min, respiratory rate 10 breaths/min, oxygen saturation (SpO2) 94% on oxygen at 3 L per nasal cannula. What is the priority nursing action? Select one: a. Monitor the patient’s airway patency. b. Support bony prominences with padding. c. Increase supplemental oxygen delivery. d. Elevate the head of the patient’s bed. Question 16 Complete 1.33 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text Which of the following statements is true about the medical management of diabetic ketoacidosis? Select all that apply Select one or more: a. Sodium bicarbonate is used to correct severe acidosis. b. The degree of acidosis is assessed through continuous pulse oximetry. c. Volume replacement and insulin infusion often correct the acidosis. d. Blood glucose levels are used to guide insulin administration. Question 17 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Remove flag Question text Which of the following laboratory values would be found in a patient with syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone? Select one: a. Fasting blood glucose 156 mg/dL b. Serum potassium 5.8 mEq/L c. Urinary sodium 22 mEq/L d. Serum sodium 152 mEq/L Question 18 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text A college student was admitted to the emergency department after being found unconscious by a roommate. The roommate informs emergency medical personnel that the student has diabetes and has been experiencing flulike symptoms, including vomiting, since yesterday. The patient had been up all night studying for exams. The patient used the last diabetes testing supplies 3 days ago and has not had time to go to the pharmacy to refill prescription supplies. Based upon the history, which laboratory findings would be anticipated in this client? Select all that apply: Select one or more: a. pH: 7.40 b. Blood glucose: 524 mg/dL c. HCO3—: 10 mEq/L d. Blood glucose: 43 mg/dL Question 19 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text An individual with type 2 diabetes who takes glipizide has begun a formal exercise program at a local gym. While exercising on the treadmill, the individual becomes pale, diaphoretic, shaky, and has a headache. The individual feels as though she is going to pass out. What is the individual’s priority action? Select one: a. Drink additional water to prevent dehydration b. Eat an apple c. Go to the first-aid station to have glucose checked d. Take another dose of the glipizide Question 20 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text An elderly female patient has presented to the emergency department with altered mental status, hypothermia, and clinical signs of heart failure. Myxedema is suspected. Which of the following laboratory findings support this diagnosis? Select one: a. Elevated adrenocorticotropic hormone b. Elevated cortisol levels c. Elevated T3 and T4 d. Elevated thyroid-stimulating hormone Question 21 Complete 0.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text The nurse is caring for a patient who underwent pituitary surgery 12 hours ago. The nurse will give priority to monitoring the patient carefully for which of the following? Select one: a. Infection b. Congestive heart failure c. Volume overload d. Diabetes Insipidus Question 22 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text Which of the following interventions is a strategy to prevent fat embolism syndrome? Select one: a. Stabilize extremity fractures early. b. Intubate the patient early after the injury to provide mechanical ventilation. c. Administer lipid-lowering statin medications. d. Provide prophylaxis with low–molecular weight heparin. Question 23 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text A 36-year-old driver was pulled from a car after it collided with a tree and the gas tank exploded. What assessment data suggest the patient suffered tissue damage consistent with a blast injury? Select one: a. Crackles (rales) on auscultation of bilateral lung fields b. Irregular heart rate and rhythm c. Responsive only to painful stimuli d. Blood pressure 82/60 mm Hg, heart rate 122 beats/min, respiratory rate 28 breaths/min Question 24 Complete 1.33 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text Which of the following statements are true regarding fluid resuscitation during the care of a trauma patient? Select all that apply Select one or more: a. Only fully crossmatched blood products are administered b. Lactated Ringer’s is recommended for rapid crystalloid infusion. c. Massive transfusions should be avoided to improve patient outcomes. d. IV fluids may need to be warmed to prevent hypothermia. Question 25 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text Which of the following statements about mass casualty triage during a disaster is true? Select one: a. Priority treatments and interventions focus primarily on young victims. b. Color-coded systems in which green indicates the patient of greatest need are used during disasters. c. Disaster victims with the greatest chances for survival receive priority for treatment. d. Once interventions have been initiated, health care providers cannot stop the treatment of disaster victims. Question 26 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text A community-based external disaster is initiated after a tornado moved through the city. A nurse from the medical records review department arrives at the emergency department asking how to assist. The best response by a nurse working for the trauma center would be to Select one: a. Thank the nurse but inform her to return to her department as her skill set is not a good match for patients’ needs. b. Assign the nurse administrative duties, such as obtaining patient demographic information. c. Assign the nurse to a triage room with another nurse from the emergency department. d. Have the nurse assist with transport of patients to procedural areas. Question 27 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text An 18-year-old unrestrained passenger who sustained multiple traumatic injuries from a motor vehicle crash has a blood pressure of 80/60 mm Hg at the scene. This patient should be treated at which level trauma center? Select one: a. Level 1 b. Level IV c. Level II d. Level III Question 28 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text Which of the following interventions would not be appropriate for a patient who is admitted with a suspected basilar skull fracture? Select one: a. Insertion of an indwelling urinary catheter b. Insertion of a nasotracheal tube c. Placement of an oral airway d. Endotracheal intubation Question 29 Complete 1.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text The nurse is caring for a patient admitted with new onset of slurred speech, facial droop, and left-sided weakness 8 hours ago. Diagnostic computed tomography scan rules out the presence of an intracranial bleed. Which actions are most important to include in the patient’s plan of care? Select all that apply Select one or more: a. Prepare for thrombolytic administration. b. Maintain CO2 level at 35-45 mm Hg. c. Maintain MAP greater than 130 mm Hg. d. Make frequent neurological assessments. Question 30 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text A patient with a head injury has an intracranial pressure (ICP) of 18 mm Hg. The blood pressure is 144/90 mm Hg, and mean arterial pressure (MAP) is 90 mm Hg. What is the cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP)? Select one: a. 54 mm Hg b. 126 mm Hg c. 90 mm Hg d. 72 mm Hg Question 31 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text The nurse admits a patient to the emergency department (ED) with a suspected cervical spine injury. What is the priority nursing action? Select one: a. Maintain proper head and neck alignment. b. Keep the neck in the hyperextended position. c. Prepare for immediate endotracheal intubation. d. Remove cervical collar upon arrival to the ED. Question 32 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text While caring for a patient with a traumatic brain injury, the nurse assesses an ICP of 20 mm Hg and a CPP of 55 mm Hg. What is the best interpretation by the nurse? Select one: a. ICP is high; CPP is normal. b. Both pressures are low. c. ICP is high; CPP is low. d. Both pressures are high. Question 33 Complete 0.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text The nurse is caring for a patient admitted to the emergency department in status epilepticus. Vital signs assessed by the nurse include blood pressure 160/100 mm Hg, heart rate 145 beats/min, respiratory rate 36 breaths/min, oxygen saturation (SpO2) 96% on 100% supplemental oxygen by non-rebreather mask. An IV has been established and the patient has been given lorazepam, but the seizures continue. What is the next nursing priority? Select one: a. Obtain stat serum electrolytes. b. Obtain stat portable chest x-ray. c. Administer 2nd lorazepam dose. d. Administer phenytoin. Question 34 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text While caring for a patient with a closed head injury, the nurse assesses the patient to be alert with a blood pressure 130/90 mm Hg, heart rate 60 beats/min, respirations 18 breaths/min, and a temperature of 102°F. To reduce the risk of increased intracranial pressure (ICP) in this patient, what is (are) the priority nursing action(s)? Select one: a. Insert an oral airway and monitor respiratory rate and depth. b. Reduce ambient room temperature and administer antipyretics. c. Ensure adequate periods of rest between nursing interventions. d. Maintain neutral head alignment and avoid extreme hip flexion. Question 35 Complete 0.00 points out of 2.00. Flag question Question text The physician has ordered Dopamine to be administered @ a rate of 5 mcg/kg/min. The patient weighs 145 pounds and the drug is sent to the unit as Dopamine 400 mg in 250 mL D5W. The nurse will set the infusion pump @ Answer 12 mL/hr. 145 /2.2 =65.90/66 5 mcg * 66 * 60 = 19800 250 /400 = 0.625 1/1000= 0.001 19800/1=19800 0.625 x 0.001 x 19800 = 12.375 /12.4/12ml/hr. *Round to the nearest mL at the end of the equation Question 36 Complete 0.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text A patient has been admitted to the ICU for alcohol withdrawl and is ordered lorazepam 10 mg/hr. The pharmacy has sent lorazepam 120 mg in 600 mL of D5W. The nurse will infuse the medication on the infusion pump @ the rate of Answer 50 mL/hr Question 37 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text The patient has hypokalemia and is to receive an IV infusion of potassium chloride. The physician orders the KCl to infuse at a rate of 2 mEq/hr. The pharmacy sends KCL 40mEq/L in D5W. The nurse will set the infusion pump @ Answer 50 mL/hr Question 38 Complete 0.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text The physician has ordered nitroglycerin for a patient with chest pain at a rate of 10 mcg/min. The pharmacy provides Nitroglycerin 25 mg in 250 mL of D5W. The nurse will set the infusion pump @ a rate of Answer 0.1 mL/hr. 250 ml / 25mg= 10 1mg/1000mcg= 0.001 10mcg/1 min= 10 60min /1 hr=60 10 x 0.001 x 10 x 60 = 6 ml/hr. Question 39 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text During the treatment and management of the trauma patient, maintaining tissue perfusion, oxygenation, and nutritional support are strategies to prevent Select one: a. Multisystem organ dysfunction. b. Wound infection c. Disseminated intravascular coagulation. d. Septic shock. Question 40 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text The nurse has admitted a patient to the ED following a fall from a first-floor hotel balcony. The patient smells of alcohol and begins to vomit in the ED. Which of the following interventions is most appropriate? Select one: a. Insert an oral airway to prevent aspiration and to protect the airway. b. Prepare to suction the oropharynx while maintaining cervical spine immobilization. c. Send a specimen of the emesis to the laboratory for analysis of blood alcohol content. d. Offer the patient an emesis basin so that you can measure the amount of emesis. Question 41 Complete 0.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text A 24-year-old unrestrained driver who sustained multiple traumatic injuries from a motor vehicle crash has a blood pressure of 80/60 mm Hg at the scene. The primary survey of this patient upon arrival to the ED Select one: a. Includes a cervical spine x-ray study to determine the presence of a fracture. b. Is done quickly in the first few minutes to get a baseline assessment and establish priorities. c. Involves turning the patient from side to side to get a look at his back. d. Is a methodical head-to-toe assessment identifying injuries and treatment priorities. Question 42 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text The nurse is caring for patient who has been struck by lightning. Because of the nature of the injury, the nurse assesses the patient for which of the following? Select one: a. Stress ulcers b. Infection c. Contractures d. Central nervous system deficits Question 43 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text A 63-year-old patient is admitted with new-onset fever; flulike symptoms; blisters over the arms, chest, and neck; and red, painful oral mucous membranes. The patient should be further evaluated for which possible non– burn-injured skin disorder? Select one: a. Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome b. Toxic epidermal necrolysis c. Graft-versus-host disease d. Necrotizing soft tissue infection Question 44 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text When paramedics notice singed hairs in the nose of a burn patient, it is recommended that the patient be intubated. What is the reasoning for the immediate intubation? Select one: a. The singed hairs and soot in the nostrils will cause dysfunction of cilia in the airways. b. Inhalation injury above the glottis may cause significant edema that obstructs the airway. c. Carbon monoxide poisoning always occurs when soot is visible. d. The patient will have a copious amount of mucus that will need to be suctioned. Question 45 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text In patients with extensive burns, edema occurs in both burned and unburned areas because of Select one: a. Decreased glomerular filtration. b. Loss of integument barrier. c. Catecholamine-induced vasoconstriction. d. Increased capillary permeability. Question 46 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text The nurse is managing the pain of a patient with burns. The provider has prescribed opiates to be given intramuscularly. The nurse contacts the provider to change the prescription to intravenous administration because Select one: a. Burn pain is so severe it requires relief by the fastest route available. b. Tissue edema may interfere with drug absorption of injectable routes. c. Intramuscular injections cause additional skin disruption. d. Hypermetabolism limits effectiveness of medications administered intramuscularly. Question 47 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text The optimal measurement of intravascular fluid status during the immediate fluid resuscitation phase of burn treatment is Select one: a. Serum potassium b. Hourly intake and urine output c. Daily weight d. Blood urea nitrogen. Question 48 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text An autograft is used to optimally treat a partial- or full-thickness wound that Select all that apply Select one or more: a. Involves the face, hands, or feet. b. Involves a joint. c. Is infected. d. Requires less than 2 weeks for healing. Question 49 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text The nurse is caring for a patient who has circumferential full-thickness burns of his forearm. A priority in the plan of care is Select one: a. To splint the forearm. b. Active or passive range-of-motion exercises every hour. c. To keep the extremity in a dependent position. d. To prepare for an escharotomy as a prophylactic measure. Question 50 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text Tissue damage from burn injury activates an inflammatory response that increases the patient’s risk for Select one: a. Acute kidney injury. b. Stress ulcers c. Acute respiratory distress syndrome. d. Infection Question 51 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text A patient with a 60% burn in the acute phase of treatment develops a tense abdomen, decreasing urine output, hypercapnia, and hypoxemia. Based on this assessment, the nurse anticipates interventions to evaluate and treat the patient for Select one: a. Acute respiratory distress syndrome. b. Disseminated intravascular coagulation disorder. c. Intra-abdominal hypertension. d. Acute kidney injury. Question 52 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text The nurse is planning care to meet the patient’s pain management needs related to burn treatment. The patient is alert, oriented, and follows commands. The pain is worse during the day, when various treatments are scheduled. Which statement to the provider best indicates the nurse’s knowledge of pain management for this patient? Select one: a. “The patient’s pain is often unrelieved. It would be best if we can schedule the opioids around the clock.” b. “Can we ask the music therapist to come by each morning to see if that will help the patient’s pain?” c. “The patient’s pain is often unrelieved. I suggest that we also add benzodiazepines to the opioids around the clock.” d. “The patient’s pain varies depending on the treatment given. Can we try patientcontrolled analgesia to see if that helps the patient better?” Question 53 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text Being present during a code can assist family members in: Select one: a. Documenting care that was provided b. Taking a photo of the family member c. Witnessing that everything has been done d. Determining the need for a lawsuit Question 54 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text The nurse recognizes which statement as a potential ethical issue? Select one: a. “If the breathing machine is helping my mother, why is the doctor asking me about removing the breathing tube?” b. . “The physician explained my mother’s poor prognosis.” c. “My mother has designated my brother to make decisions.” d. e. “Can I assist with some of my mother’s care?” Question 55 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text The nurse assesses that there is significant disagreement among family members about what course of treatment is best for the patient. What would be the best response by the nurse? Select one: a. “You need to come to a decision quickly and let us know what you want.” b. “Could we hold a family conference so that we can develop the best plan of care for your loved one?” c. “ Which one of you is the patient’s surrogate to make the decision?” d. “Perhaps you should consult with your pastor or priest.” e. Question 56 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text The nurse asks a patient with chest pain if it travels to the neck or shoulders. This is an assessment of: Select one: a. Quality b. Radiation c. Postion d. Severity Question 57 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text Patients who are not able to meet their nutritional needs orally should be started on enteral nutrition within what time frame? Select one: a. 24-48 hours b. 6-12 hours c. 5 days d. 12-24 hours Question 58 Complete 0.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text A patient with disseminated intravascular coagulation is receiving I.V. albumin, which Select one: a. is isotonic b. decreases intravascular volume c. increases intravascular volume d. increases intersitital volume Question 59 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text Which patient would benefit the most from central venous/right atrial pressure monitoring? Select one: a. Patient admitted with a bowel obstruction b. Patient taking routine doses of furosemide c. Patient receiving two units of blood d. Patient admitted in cardiogenic shock Question 60 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text Interpret these ABGs; patient has a history of COPD: pH 7.37, PaCO2 50 mm Hg, bicarbonate 30 mEq/L; SpO2 93% Select one: a. Combined metabolic and respiratory acidosis b. Compensated respiratory acidosis c. Compensated metabolic alkalosis d. Partly compensated respiratory alkalosis Question 61 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text The nurse is caring for a patient being treated with therapeutic hypothermia post-CPR. Which order should the nurse question? Select one: a. Continuously monitor EEG and ECG b. Draw serum electrolytes stat c. Record tympanic temperature every hour d. Measure blood glucose every 2 hours Question 62 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text Which liver transplant patient being cared for in the ICU is exhibiting signs of acute rejection? Select one: a. Patient with a CVP of 6 mm Hg b. Patient with dark urine and jaundice c. Patient with postoperative pain 6/10 d. Patient with temp of 99.0° F and thirst Question 63 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text The nurse admits a 35-year-old patient to the emergency department following a 3-day history of nausea and vomiting. Vital signs assessed by the nurse include a BP of 70/50 mm Hg, HR 145 beats/min, RR 36 breaths/min, and SpO2 of 92% on room air. The nurse recognizes which classification of shock? Select one: a. Anaphylactic b. Cardiogenic c. Hypovolemic d. Obstructive Question 64 Complete 0.00 points out of 2.00 Remove flag Question text Arterial blood gas alterations in pneumonia include which of the following? Select one: a. Hypoxemia and metabolic acidosis b. Normal values c. Hypoxemia and respiratory alkalosis d. Normal oxygen and respiratory acidosis Question 65 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text Which intervention is most important in assessing fluid balance in the patient with AKI? Select one: a. Intake and Output b. estimated gfr c. Daily weight d. Serum creatinine Question 66 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text The nurse is preparing to admit a patient from the ED who has sustained a complete spinal cord lesion at the C5 level. When planning the patient’s care, which nursing intervention is most important? Select one: a. Give small, frequent feedings. b. Apply warming devices as needed. c. Assist with passive range-of-motion. d. Perform hourly incentive spirometry. Question 67 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text The greatest risk of GI bleeding is: Select one: a. Infection b. Anemia c. Increased cardiac output d. Hypovolemia Question 68 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text A patient suddenly becomes unresponsive as you're speaking to him and develops generalized tonic-clonic seizures. Your priority is to: Select one: a. Notify the primary care provider immediately. b. Administer intravenous diazepam. c. Establish an airway. d. Perform a rapid neurologic exam. Question 69 Complete 0.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text While caring for a patient who is experiencing a postoperative hemorrhage, the healthcare provider notes the rhythm observed on the electrocardiogram (EKG) does not produce a pulse. Which actions should the healthcare provider initiate first? Select one: a. Defibrillation b. Administer epinephrine c. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) d. Syncronized cardioversion Question 70 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text The healthcare provider is caring for a patient on a ventilator with an endotracheal tube in place. What assessment data indicate the tube has migrated too far down the trachea? Select one: a. Low pressure alarm sounds b. High pressure alarm sounds c. Decreased breath sounds on the left side of the chest d. Increased crackles bilaterally Question 71 Complete 0.00 points out of 2.00 Remove flag Question text A patient has a vitamin K deficiency. Which of the following lab results would be expected for a patient with this deficiency? Select one: a. Low platelets b. Prolonged international normalized ration (INR) c. Prolonged activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) d. Normal prothrombin time (PT) Question 72 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text A clinician is providing education to a patient with a recent diagnosis of a transient ischemic attack (TIA). Which of the statements by the patient indicates that the patient understands the information? Select one: a. “Because TIAs don’t cause permanent damage, I do not need to worry if I have another one.” b. “TIAs are usually caused by large bleeds in the brain that resolve on their own.” c. “It is important for you to seek medical attention immediately if you experience these symptoms again because they could mean that you are having a stroke.” d. “Transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) are often caused by small bleeds in the brain that resolve on their own.” Question 73 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text After falling from a 10-foot ladder, a patient is brought to the emergency department. The patient is alert, reports back pain, and difficulty moving the lower extremities. Which additional observation is an indication the patient may be experiencing neurogenic shock? Select one: a. Poor skin turgor b. Cool and pale skin c. Increased systolic blood pressure d. Bradycardia Question 74 Complete 2.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text The healthcare provider is teaching a patient who has been newly diagnosed with second-degree AV block Mobitz type I. The healthcare provider determines teaching has been successful when the patient makes which of the following statements? Select one: a. “I will take my pulse each day before taking my beta blocker medication” b. “If I have symptoms, I will feel tired or I might have chest pain” c. “I will need to learn to use oxygen therapy at home” d. “Each day I will eat foods that are high in vitamin K” Question 75 Complete 0.00 points out of 2.00 Flag question Question text Nursing management of the patient with angina is directed toward: Select one: a. assessment of history of previous anginal episodes b. Immediate administration of nitrates c. assessment and documentation of chest pain episodes d. administration of prophylactic lidocaine for ventricular ectopy [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 34 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jul 05, 2022
Number of pages
34
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jul 05, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
154



.png)




.png)