Health Care > EXAM > Biochemistry WGU C785 - Module 1 questions with complete solutions (All)
Biochemistry WGU C785 - Module 1 questions with complete solutions
Document Content and Description Below
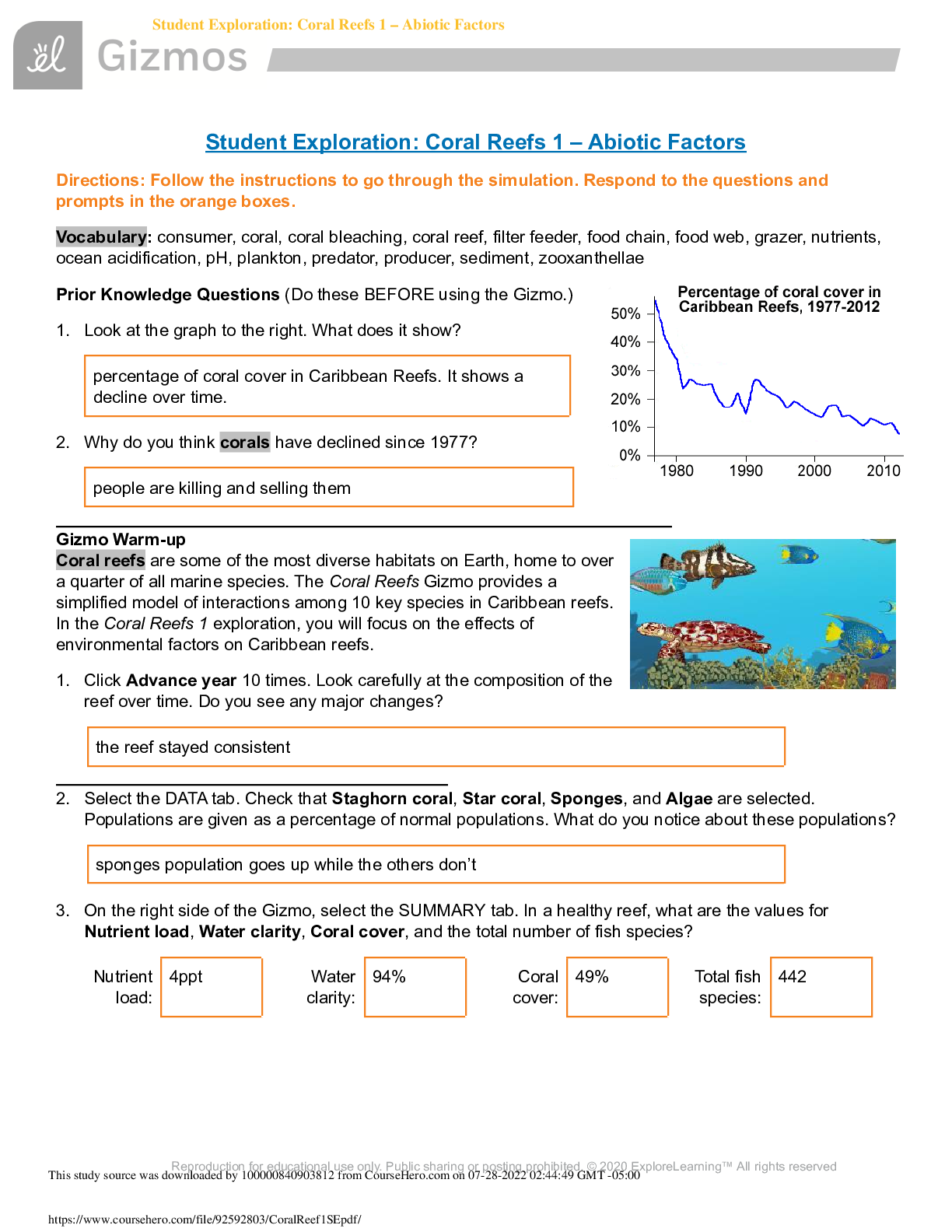
Biochemistry WGU C785 - Module 1 Hydrophilic Correct Answer: Having an affinity for water. Hydrophobic Correct Answer: substances that are not soluble in water. Hydrophobic substances include ... large, uncharged particles like fats and oils solvent Correct Answer: A liquid substance capable of dissolving other substances Solute Correct Answer: A substance that is dissolved in a solution. Adhesive Correct Answer: Having the ability to stick to other surfaces. Cohesive Correct Answer: having the ability to stick together Heat of Vaporization Correct Answer: The amount of energy required for the liquid at its boiling point to become a gas Anticodon Correct Answer: Three-base sequence in a transfer RNA molecule base that pairs with a complementary codon in mRNA Central Dogma of Molecular Biology Correct Answer: DNA -> RNA -> Protein This paradigm was formulated by Grancis Crick: First, a portion of the DNA, a gene, is transcribed to produce a complementary strand of RNA; then RNA is translated into protein Codon Correct Answer: A specific sequence of three adjacent bases on a strand of DNA or RNA that provides genetic code information for a particular amino acid DNA Correct Answer: deoxyribonucleic acid, a self-replicating material present in nearly all living organisms as the main constituent of chromosomes. It is the carrier of genetic information. Dominant Allele Correct Answer: an allele that dominates or masks the presence of another allele and is fully expressed Dominant trait Correct Answer: the trait that is expressed from a dominant allele Recessive allele Correct Answer: the trait that is completely masked and is not expressed Recessive trait Correct Answer: a genetic factor that is blocked by the presence of a dominant factor Epigenetics Correct Answer: the study of environmental influences on gene expression that occur without a DNA change Exons Correct Answer: expressed sequence of DNA; codes for a protein Gene Expression Correct Answer: process by which a gene produces its product and the product carries out its function Histones Correct Answer: they are the chief protein components of chromatin, acting as spools around which DNA winds, and playing a role in gene regulation Inheritance Correct Answer: is the passage of hereditary traits from one generation to the next Introns Correct Answer: Non-coding segments of nucleic acid that lie between coding sequences. Intervening sequences in a newly made mRNA molecule that are removed by splicing before the mRNA is released into the cytoplasm for protein synthesis mRNA Correct Answer: messenger RNA; type of RNA that carries instructions from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosome Peptide Bond Correct Answer: covalent bond formed between amino acids Polypeptides Correct Answer: Promoter Correct Answer: specific region of a gene where RNA polymerase can bind and begin transcription Ribosome Correct Answer: Cytoplasmic organelles at which proteins are synthesized. RNA Correct Answer: ribonucleic acid; a nucleic acid that plays an important role in the production of proteins RNA polymerase Correct Answer: the primary enzyme involved in transcription that reads the DNA sequence of a gene and produces a complementary mRNA molecule. rRNA Correct Answer: Ribosomal RNA part of the ribosome Splicing Correct Answer: the process of removing introns and reconnecting exons in a pre-mRNA Transcription bubble Correct Answer: the region of locally unwound DNA that allows for transcription of mRNA Transcription Factors Correct Answer: Collection of proteins that mediate the binding of RNA polymerase and the initiation of transcription. Transcription start site Correct Answer: is at the beginning (5' end) of a gene and is the location where RNA polymerase begins transcription of that gene Translation Correct Answer: The synthesis of protein by the ribosome using the sequence of messenger RNA as a template. The codons of the mRNA are matched up to their corresponding transfer RNA molecules, which carry the amino acid encoded by the coon. The ribosome then connects the amino acids together using peptide bonds. The resulting protein is also known as a polypetide. tRNA Correct Answer: transfer RNA; type of RNA that carries amino acids to the rib [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 3 pages
Instant download

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jun 27, 2022
Number of pages
3
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jun 27, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
40



.png)