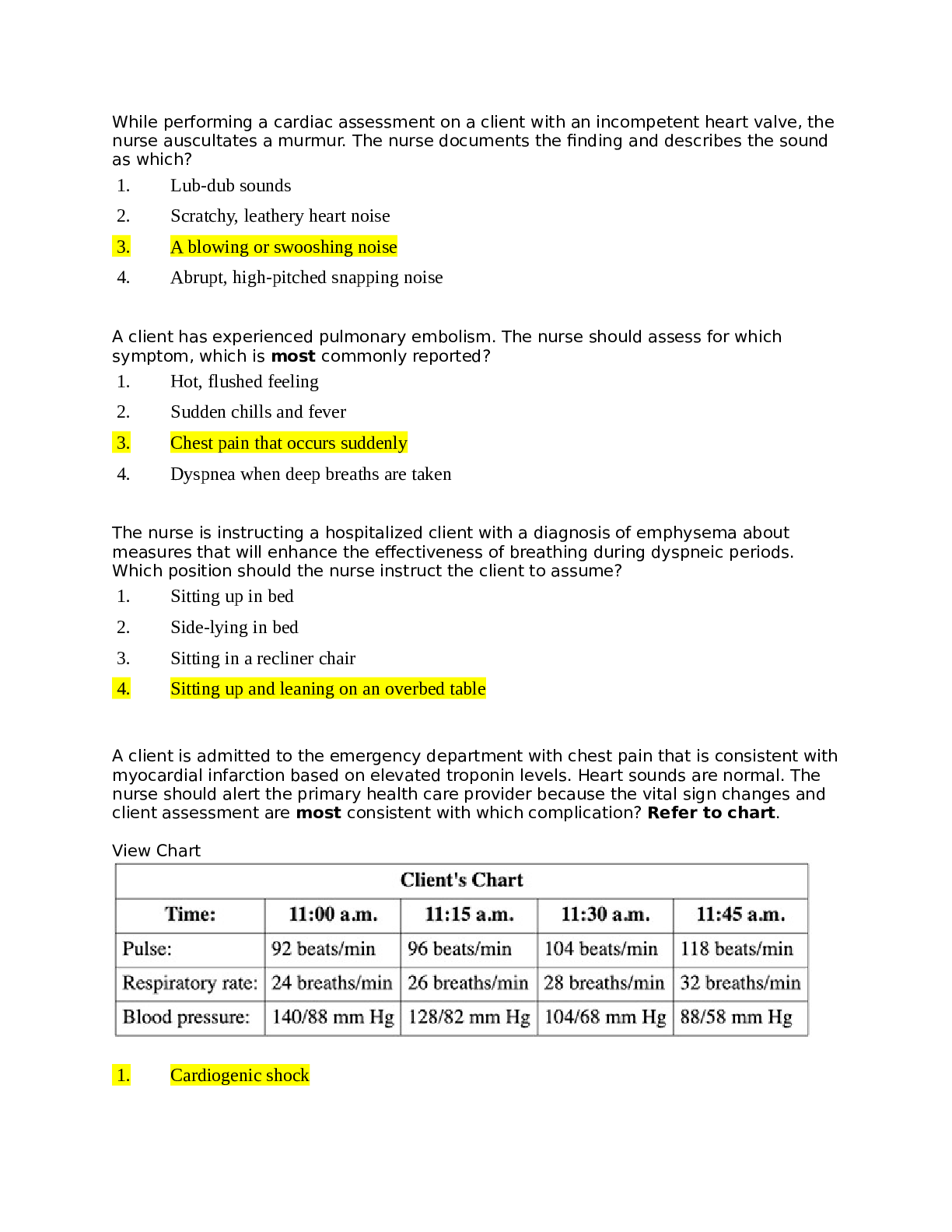
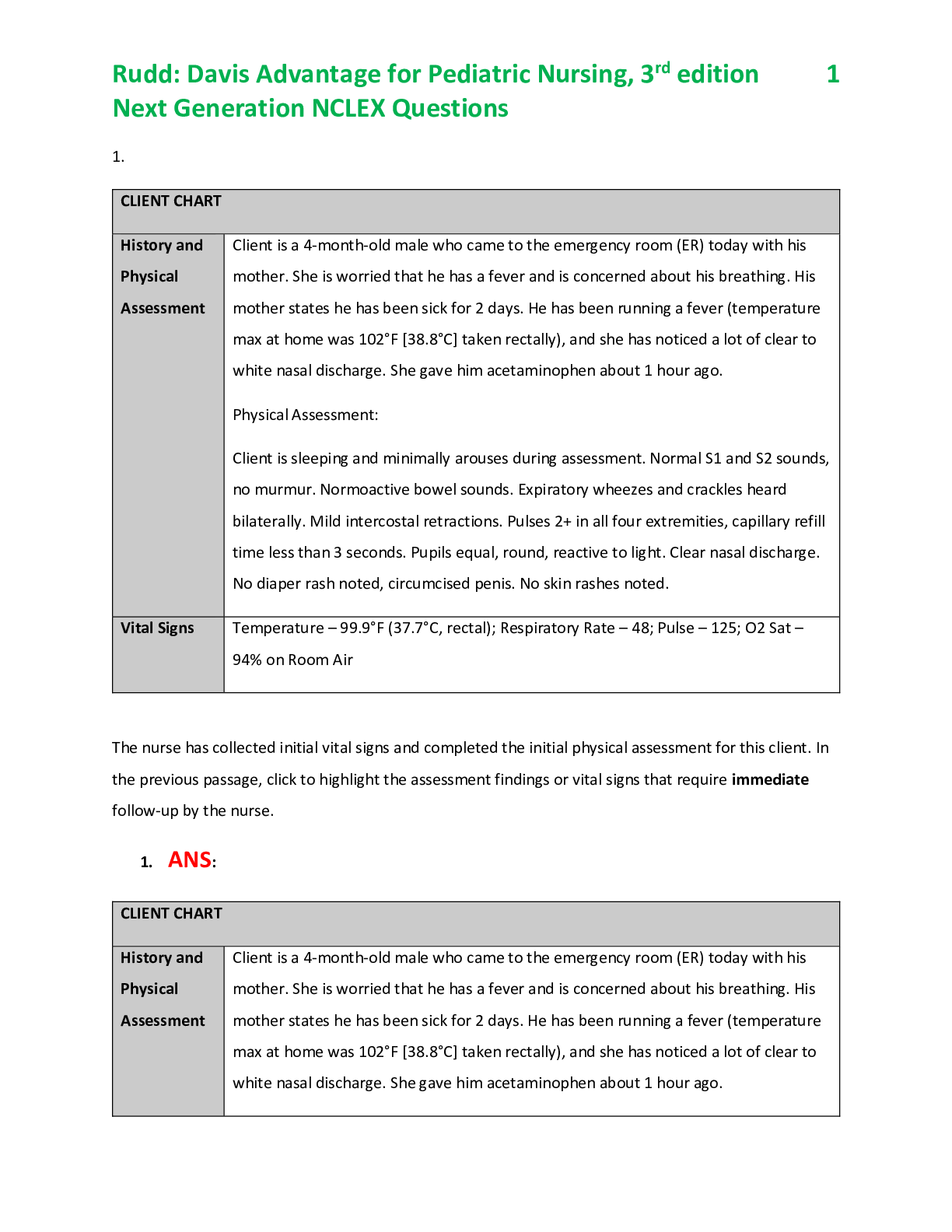
NURS MISC ANCLEX Fundamentals II,100% CORRECT
Document Content and Description Below
NURS MISC ANCLEX Fundamentals II health care provider's prescription reads potassium chloride 20 mEq in 1000 mL normal saline and infuse at 100 mL/hr. The nurse assisting in caring for the client de... termines that the client will receive how many milliequivalents (mEq) of potassium every hour? Fill in the blank. Rationale: Use the ratio and proportion formula to solve this problem, and then solve for x. 20 mEq: 1000 mL :: x mg: 100 mL Multiply means and extremes then divide to solve for x. 1000x = 2000x = 2 mEq Penicillin V 250 mg orally every 8 hours, is prescribed for a child with a respiratory infection. The child's weight is 45 pounds. The safe pediatric dosage is 25 to 50 mg/kg/day. Which statement accurately describes the prescribed dosage for this child? Rationale: Convert pounds to kilograms by dividing by 2.2 and then determine the dosage frequency.Pounds to kilograms:45 lb ÷ 2.2 lb/kg = 20.45 kgDosage parameters:25 mg/kg/day × 20.45 kg = 511.25 mg/day50 mg/kg/day × 20.45 kg = 1022.5 mg/dayDosage frequency:250 mg × 3 doses (every 8 hours) = 750 mg/dayThe dosage is within the safe dosage range. The nurse is assigned to care for an Asian-American client. The nurse develops a plan of care based on which belief? Rationale: Asian Americans believe that illness is caused by an imbalance between yin and yang, by prolonged sitting or lying, or by overexertion. In the African-American culture, illness is viewed as a disharmonious state that may be caused by demons and spirits. Native Americans believe that illness is caused by supernatural forces. An anxious client is experiencing respiratory alkalosis from hyperventilation as a result of anxiety. The nurse should do which action to help the client experiencing this acid-base disorder? Rationale: An anxious client benefits from emotional support and reassurance, which in turn reduces anxiety and may lower the respiratory rate. The client may benefit from the administration of a sedative or antianxiety medication, if it is prescribed. The client should try to breathe more slowly and shallowly. Lying supine provides no benefit to the client. The nurse is assisting in the care of a client receiving codeine sulfate for pain. The nurse should make note of which finding to detect an adverse effect of this medication? Rationale: The client taking codeine sulfate is at risk for constipation. Thus, the nurse monitors the frequency of bowel movements. The nurse also would monitor the client for hypotension, decreased respirations, and urinary retention. The nurse would plan measures to counteract these expected effects such as encouraging fluids, coughing and deep breathing, and increasing mobility to the extent tolerated by the client. A client who takes theophylline (Theo-24) for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is seen in the health care clinic. A theophylline level is drawn, and the nurse determines that the client is compliant with the medication regimen if which laboratory result is reported? Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, administration of theophylline, and note the word compliant. Familiarity with the therapeutic level of theophylline is needed to select the correct option. Remember that the therapeutic range for the serum theophylline level is 10 to 20 mcg/mL. Review: Therapeutic range of theophylline. The health care provider prescribes ibuprofen (children's Motrin) 5 mg per kg for a child who weighs 13 pounds. How many milligrams (mg) should the nurse administer to the child? Fill in the blank. Record your answer using one decimal place. Rationale: A child who weighs 13 pounds weighs 5.9 kg. This is determined by dividing 13 by 2.2 to obtain the weight in kilograms (1 kg = 2.2 lb). Once that is determined, 5.9 is multiplied by 5 mg to yield 29.5 mg. Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Implementation Content Area: Fundamental Skills: Medication/IV Calculations Strategy(ies): Subject Priority Concepts: Clinical Judgment, Safety Diphenhydramine hydrochloride (Benadryl) 25 mg orally every 6 hours is prescribed for a child with an allergic reaction. The child weighs 25 kg. The safe pediatric dosage is 5 mg/kg/day. What should the nurse determine about the medication dosage? Rationale: Calculate the dosage parameters using the safe dosage range identified in the question and the child's weight in kilograms. Next, determine the total daily dosage.Dosage parameters: 5 mg/kg × 25 kg = 125 mg/dayDosage frequency: 25 mg × 4 doses = 100 mg/dayThe dosage is safe. Level of Cognitive Ability: Analyzing Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Data Collection Content Area: Fundamental Skills: Medication/IV Calculations Strategy(ies): Subject Priority Concepts: Clinical Judgment, Safety A health care provider's prescription reads triazolam (Halcion), 125 mcg orally at bedtime daily. The medication bottle is labeled triazolam, 0.125-mg tablets. The nurse prepares how many tablet(s) to administer 1 dose? Fill in the blank. Rationale: Convert 125 mcg to mg. In the metric system, to convert smaller to larger, divide by 1000 or move the decimal three places to the left. Therefore, 125 mcg = 0.125 mg. One tablet is administered. Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Planning Content Area: Fundamental Skills: Medication/IV Calculations Strategy(ies): Subject Priority Concepts: Clinical Judgment, Safety A child with leukemia is experiencing nausea related to medication therapy. The nurse, concerned about the child's nutritional status, should offer which during an episode of nausea? Rationale: When the child is nauseated, it is best to offer frequent intake of cool, clear liquids in small amounts because small portions are usually better tolerated. Cool, clear fluids are also soothing and better tolerated when a client is nauseated. It is best not to offer favorite foods when the child is nauseated because foods eaten during times of nausea will be associated with being sick. It is best to offer small, frequent meals of high-protein and high-calorie content once the nausea has been controlled with medication or has subsided. Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Implementation Content Area: Fundamental Skills: Nutrition Strategy(ies): Subject Priority Concepts: Cellular Regulation, Nutrition The nurse is caring for an older client who had a hip pinned after being fractured. In planning nursing care, which should the nurse avoid to minimize the chance for further injury? Rationale: Safe nursing actions intended to prevent injury to the client include keeping side rails up, having the bed in a low position, and providing a call bell that is within the client's reach. Responding promptly to the client's use of the call light minimizes the chance that the client will try to get up alone, which could result in a fall. Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Safe and Effective Care Environment Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Implementation Content Area: Fundamental Skills: Safety Strategy(ies): Subject Priority Concepts: Clinical Judgment, Safety The nurse is caring for a client with kidney failure. The nurse is told that the blood gas results indicate a pH of 7.30 and a HCO3– of 20 mm Hg, and that the client is experiencing metabolic acidosis. The nurse reviews the laboratory results and expects to note which? Rationale: Signs/symptoms of metabolic acidosis include weakness, malaise, and headache. Hyperkalemia will occur because the cells will draw hydrogen into the cell and in exchange will push potassium out of the cell into the blood. The pH will be lower than 7.35, and the HCO3– ion level will be lower than 22 mEq/L. The remaining options identify normal laboratory values, whereas a potassium level of 5.6 mEq/L indicates hyperkalemia. Level of Cognitive Ability: Analyzing Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Data Collection Content Area: Fundamental Skills: Acid-Base Strategy(ies): Comparable or Alike Options Priority Concepts: Clinical Judgment, Acid-Base Balance A clear liquid diet has been prescribed for a client with gastroenteritis. Which item is appropriate to offer to the client? Rationale: A clear liquid diet consists of foods that are relatively transparent. Soft custard and orange juice would be included in a full liquid diet because they are opaque, not clear. Clam chowder is opaque and also includes pieces of clams, thus eliminating it from a full liquid diet. Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Implementation Content Area: Fundamental Skills: Nutrition Strategy(ies): Subject Priority Concepts: Inflammation, Nutrition The chart describes characteristics of various types of enemas. Which type of enema has the highest risk of complications? Refer to chart. View Chart Rationale: Tap water is hypotonic, creating a lower osmotic pressure than the fluid in interstitial spaces. With repeated tap water enemas, fluid can escape from the bowel lumen into interstitial spaces and can cause circulatory overload if the body absorbs too much water. Normal saline enemas are the safest type of enema because of having the same osmotic pressure as fluid in the interstitial spaces around the bowel. Thus, enemas using normal saline do not cause any fluid shifts. Castile soap is incorrect because it can be mixed with either water or saline, and if mixed with saline, there should not be any risk of fluid overload. Castile soap is the only safe soap to use for a soapsuds enema because harsh soaps may cause inflammation of the bowel. Hypertonic solution is incorrect because hypertonic fluids pull fluid from the interstitial spaces into the colon. Although this could have the potential for dehydration, it does not pose as high of risk of complications as the tap water enema. A Fleets enema is the most common type of hypertonic enema. Level of Cognitive Ability: Analyzing Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Data Collection Content Area: Fundamental Skills: Elimination Strategy(ies): Subject Priority Concepts: Clinical Judgment, Elimination The nurse needs to increase the calcium in the diet of a client who is lactose intolerant. Which food items should the nurse encourage? Select all that apply. Rationale: Lactose-intolerant clients should not eat dairy products. Therefore, these clients need high- calcium foods from nondairy sources. Tofu, broccoli, mustard greens, and sardines are foods that are high in calcium that do not come from dairy sources. Although milk and cheese are high in calcium, they are dairy products, which lactose-intolerant clients need to avoid. Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Implementation Content Area: Fundamental Skills: Nutrition Strategy(ies): Comparable or Alike Options Priority Concepts: Health Promotion, Nutrition The health care provider prescribes a three-way bladder irrigation of normal saline to be infused at a rate of 200 mL per hour, which infused without problem. There is 1850 mL in the collection receptacle at the conclusion of the 8-hour shift. Which is the client's true urine output for the shift? Fill in the blank. Rationale: 200 mL × 8 hr = 1600, which is the amount of normal saline infused. 1850 - 1600 = 250 (total in receptacle minus irrigation) Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Communication and Documentation Content Area: Fundamental Skills: Elimination Strategy(ies): Subject Priority Concepts: Clinical Judgment, Elimination The health care provider prescribes a three-way bladder irrigation of normal saline to be infused at a rate of 200 mL per hour, which infused without problem. There is 1850 mL in the collection receptacle at the conclusion of the 8-hour shift. Which is the client's true urine output for the shift? Fill in the blank. Rationale: 200 mL × 8 hr = 1600, which is the amount of normal saline infused. 1850 - 1600 = 250 (total in receptacle minus irrigation) Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Communication and Documentation Content Area: Fundamental Skills: Elimination Strategy(ies): Subject Priority Concepts: Clinical Judgment, Elimination The nurse is preparing a session regarding nutrition for a group of culturally diverse pregnant women. The nurse determines that the priority nursing intervention includes which action? Rationale: The priority nursing intervention is to identify the cultural food preferences of each client. This information is needed in order to adequately provide information regarding appropriate nutrition. The socioeconomic status may be an important component, particularly when the nurse is determining whether a client's financial situation permits the purchase of appropriate food items. A baseline weight also may be important. Encouraging appropriate nutrition and the need to avoid fast-food restaurants is also important. However, an adequate nutritional plan can be formulated only if cultural food preferences are identified. Level of Cognitive Ability: Analyzing Client Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Teaching and Learning Content Area: Fundamental Skills: Cultural Awareness Strategy(ies): Strategic Words Priority Concepts: Culture, Nutrition The health care provider's prescription reads "levothyroxine (Synthroid), 150 mcg orally daily." The medication label reads "levothyroxine, 0.1 mg/tablet." The nurse prepares to administer how many tablet(s) to the client? Fill in the blank. Record your answer using one decimal place. Rationale: Convert 150 mcg to milligrams. In the metric system, to convert smaller to larger, divide by 1000, or move the decimal three places to the left. Therefore, 150 mcg = 0.15 mg. Formula: Desired × tablet(s) ––––––––––––––––––– = tablet(s) per dose Available 0.15 mg × 1 tablet –––––––––––––––––– = 1.5 tablets 0.1 mg Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Planning Content Area: Fundamental Skills: Medication/IV Calculations Strategy(ies): Subject Priority Concepts: Clinical Judgment, Safety A licensed practical nurse (LPN) is asked to prepare an intravenous (IV) infusion of 1000 mL 5% dextrose in lactated Ringer's at 80 mL/hr to be administered to an assigned client. The LPN time-tapes the bag with a start time of 09:00. After making hourly marks on the time- tape, the LPN notes that which time would mark the completion time for the bag? Rationale: At a rate of 80 mL per hour, the 1000-mL bag will be finished infusing in 12½ hours. This brings the end time to 21:30, using military time. Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Safe and Effective Care Environment Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Implementation Content Area: Fundamental Skills: Medication/IV Calculations Strategy(ies): Subject Priority Concepts: Fluid and Electrolyte Balance, Safety The nurse determines that an adult male client admitted with dehydration and a hematocrit level of 56% has received adequate fluid volume replacement if which repeat hematocrit level is noted? Rationale: The normal hematocrit level for an adult male is 42% to 52%. Thus, 48% is the only correct choice. The client who is dehydrated has an elevated level as a result of hemoconcentration. The client's level may be expected to drift back down to within the normal range after the fluid volume has been adequately restored. The remaining options are too high and indicate fluid replacement is still indicated. Level of Cognitive Ability: Evaluating Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Evaluation Content Area: Fundamental Skills: Laboratory Values Strategy(ies): Subject Priority Concepts: Clinical Judgment, Fluid and Electrolyte Balance A client with atrial fibrillation who is receiving maintenance therapy with warfarin sodium (Coumadin) has a prothrombin time (PT) of 30 seconds. The nurse anticipates that which will be prescribed? Rationale: The normal PT is 9.6 to 11.8 seconds for the adult male and 9.5 to 11.3 seconds for the adult female. The goal of oral anticoagulation with warfarin sodium therapy is to achieve a PT at 1.5 to 2 times the laboratory control value. A PT of 30 seconds places the client at risk for bleeding, so the nurse should anticipate that the client would not receive further doses at this time. If the level is too high, the antidote (vitamin K) may be prescribed. The remaining options would make the client even more prone to bleeding. A client having preadmission testing before surgery has blood drawn for the determination of serum electrolyte levels. The nurse determines that which result warrants a call to the health care provider by the nurse? Rationale: The normal serum electrolyte ranges for adults are as follows: sodium, 135 to 145 mEq/L; potassium, 3.5 to 5.0 mEq/L; chloride, 98 to 107 mEq/L; and bicarbonate (venous), 22 to 29 mEq/L. The only abnormal value identified is the serum sodium level. The nurse determines that sodium polystyrene sulfonate (Kayexalate) has been effective in a client if which laboratory result is noted? Rationale: The normal serum potassium level in the adult is 3.5 to 5.0 mEq/L. Sodium polystyrene (Kayexalate) is a medication that is used to treat hyperkalemia. The laboratory values in the remaining options are slightly elevated; in addition, this medication would have no effect on these other electrolytes. A client with a history of cardiac disease is scheduled for a dose of furosemide (Lasix). Which serum potassium level warrants a call to the health care provider by the nurse before administering the furosemide? Rationale: The normal adult serum potassium level is 3.5 to 5.0 mEq/L. A serum potassium level of 3.2 mEq/L is the only value that falls below the therapeutic range. Administering furosemide (Lasix) to a client with a low potassium level and a cardiac history could precipitate ventricular dysrhythmias in the client. Even though a result of 5.2 mEq/L is high, administration of the furosemide can only assist with excretion of the excess potassium. A client with a history of gastrointestinal bleeding has a platelet count of 300,000 cells/mm3. Which action by the nurse is most appropriate after reading this report? Rationale: A normal platelet count ranges from 150,000 to 400,000 cells/mm3. The nurse should place the report that contains the normal laboratory value into the client's medical record. The remaining options are incorrect and unnecessary. The nurse is reviewing the serum magnesium results for a group of clients. Which results warrant a call to the health care provider by the nurse? Select all that apply. Rationale: The normal magnesium level in an adult client is 1.6 to 2.6 mg/dL. Magnesium levels that are below or above the normal range should be reported to the health care provider. A client has a history of mild renal insufficiency. Which serum creatinine level should the nurse determine is consistent with this problem? Rationale: The normal serum creatinine level is 0.6 to 1.3 mg/dL. The client with mild renal insufficiency would have a slightly elevated level, which would be the value of 1.9 mg/dL. Creatinine levels of 3.5 mg/dL may be associated with acute kidney injury or chronic kidney disease. A client with a seizure disorder is taking phenytoin (Dilantin). A sample for a serum phenytoin level is drawn, and the nurse determines that the next dose of the medication may be administered if which laboratory result is noted? Rationale: The therapeutic range for serum phenytoin (Dilantin) level is 10 to 20 mcg/mL, so the next dose of phenytoin should be given if the level is 17 mcg/mL. If the level is too high, such as in the remaining options, the client could experience phenytoin toxicity. A client was diagnosed with acute pancreatitis 10 days ago. The nurse interprets that the episode of acute pancreatitis is fully resolved if the serum lipase level drops to which value? Rationale: The normal serum lipase level is 10 to 140 units/L. The client who is recovering from acute pancreatitis usually has elevated lipase levels for approximately 10 days after the onset of symptoms. This makes lipase a valuable test for monitoring the client's pancreatic function. The serum lipase level of 135 units/L indicates resolution of the acute pancreatitis because it is a normal value. The remaining options identify elevated lipase levels. A client arrives in the emergency department complaining of chest pain that began 4 hours ago. A troponin T blood specimen is obtained, and the results indicate a level of 0.6 ng/mL. How should the nurse correctly interpret these results? Rationale: Troponins are regulatory proteins that are found in striated muscle. The troponins function together in the contractile apparatus for striated muscle in the skeletal muscle and the myocardium. Increased amounts of troponins are released into the bloodstream when an infarction causes damage to the myocardium. A troponin T level greater than 0.1 to 0.2 ng/mL is consistent with a myocardial infarction. A normal troponin I level is less than 0.6 ng/mL, whereas a level greater than 1.5 ng/mL is consistent with a myocardial infarction. A troponin T level of 0.6 is not normal, so that option can be eliminated. Troponin T does not test for gastritis or angina, so those options can also be eliminated. A client has a hemoglobin level of 10.8 g/dL. The nurse interprets that this result is most likely the result of which factor in the client's history? Rationale: The normal hemoglobin level for an adult female client is 12 to 15 g/dL and 14 to 16.5 for a male client. A low hemoglobin level usually indicates anemia. Iron deficiency anemia can result in lower hemoglobin levels. Heart failure and COPD may increase the hemoglobin level as a result of the body's need for more oxygen-carrying capacity. Dehydration may increase the hemoglobin level by hemoconcentration. A client is a lacto-vegetarian. Which food item should the nurse remove from the tray? Rationale: Eggs are not consumed by lacto-vegetarians. Other dairy and plant products are eaten by lacto-vegetarians. Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Implementation Content Area: Fundamental Skills: Nutrition Strategy(ies): Comparable or Alike Options, Subject Priority Concepts: Adherence, Nutrition A low-sodium diet has been prescribed for a client with hypertension. Which food selected from the menu by the client indicates an understanding of this diet? Rationale: Regular soup (1 cup) contains 900 mg of sodium. Fresh shellfish (1 oz) contains 50 mg of sodium. Poultry (1 oz) contains 25 mg of sodium. The nurse is providing dietary instructions to a client with gout. The nurse should tell the client to avoid which food item? Rationale: Scallops should be omitted from the diet of a client who has gout because of the high purine content. The food items identified in the remaining options have negligible purine content and may be consumed by the client with gout. The nurse reinforces instructions to a client to increase the amount of riboflavin in the diet. The nurse should tell the client to select which food item that is high in riboflavin? Rationale: Food sources of riboflavin include milk, lean meats, fish, and grains. Tomatoes and citrus fruits are high in vitamin C. Green leafy vegetables are high in folic acid. Which of these clients are most likely to develop fluid (circulatory) overload? Select all that apply. Rationale: Clients with cardiac, respiratory, renal, or liver diseases and older and very young clients cannot tolerate an excessive fluid volume. The risk of fluid (circulatory) overload exists with these clients. A client has a prescription to receive 1000 mL of 5% dextrose in 0.45% sodium chloride. After gathering the appropriate equipment, the nurse takes which action first before spiking the IV bag with the tubing? Rationale: The nurse should first clamp the tubing to prevent the solution from running freely through the tubing after it is attached to the IV bag. The nurse should next uncap the proximal (spike) portion of the tubing and attach it to the IV bag. The IV bag is elevated and the roller clamp is then opened slowly, and the fluid is allowed to flow through the tubing in a controlled fashion to prevent air from remaining in parts of the tubing. The nurse is preparing an intravenous (IV) solution and tubing for a client who requires IV fluids. While preparing to prime the tubing, the tubing drops and hits the top of the medication cart. The nurse should plan to take which action? Rationale: The nurse should change the IV tubing. The tubing has become contaminated, and, if used, it could result in a systemic infection in the client. Wiping or scrubbing the tubing is insufficient to prevent systemic infection. The nurse is caring for a client with a health care–associated infection caused by methicillin- resistant Staphylococcus aureus who is on contact precautions. The nurse prepares to provide colostomy care to the client. Which protective items will be required to perform this procedure? Rationale: Goggles are worn to protect the mucous membranes of the eye during interventions that may produce splashes of blood, body fluids, secretions, and excretions. In addition, contact precautions require the use of gloves, and a gown should be worn if direct client contact is anticipated. Shoe protectors are not necessary. The nurse is assisting with planning care for a client with an internal radiation implant. Which should be included in the plan of care? Select all that apply. Rationale: A private room with a private bath is essential if a client has an internal radiation implant. This is necessary to prevent the accidental exposure of other clients to radiation. The remaining options identify interventions that are necessary for a client with a radiation device. The nurse is administering a cleansing enema to a client with a fecal impaction. Before administering the enema, the nurse should assist the client to which position? Rationale: When administering an enema, the client is placed in a left Sims' position so that the enema solution can flow by gravity in the natural direction of the colon. The head of the bed is not elevated. The nurse is assigned to assist with caring for a client with esophageal varices who had a Sengstaken-Blakemore tube inserted because other treatment measures were unsuccessful. The nurse should check the client's room to ensure that which priority item is at the bedside? Rationale: When the client has a Sengstaken-Blakemore tube, a pair of scissors must be kept at the client's bedside at all times. The client needs to be observed for sudden respiratory distress, which occurs if the gastric balloon ruptures and the entire tube moves upward. If this occurs, the registered nurse is notified immediately and the balloon lumens will be cut. An obturator and a Kelly clamp are kept at the bedside of a client with a tracheostomy. An irrigation set may also be kept at the bedside, but it is not the priority item. The nurse is preparing to administer medication through a nasogastric (NG) tube that is connected to suction. Which indicates the accurate procedure for medication administration? Rationale: If a client has an NG tube connected to suction, the nurse should wait up to 30 minutes before reconnecting the tube to the suction apparatus to allow adequate time for medication absorption. Aspirating the NG tube will remove the medication that has just been administered. Low intermittent suction will also remove the medication. The client should not be placed in the supine position because of the risk for aspiration. Which laboratory result would verify the diagnosis of bacterial meningitis? Rationale: A diagnosis of meningitis is made by testing the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) obtained by lumbar puncture. In the case of bacterial meningitis, findings usually include increased pressure, cloudy cerebrospinal fluid, a high protein level, and a low glucose level. The nurse is told that an assigned client is suspected of having methicillin- resistant Staphylococcus aureus(MRSA). Which precautions should the nurse institute during the care of the client? Rationale: Wear a gown and gloves. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends the wearing of gowns and gloves when in close contact with a person who has methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus(MRSA). Masks are not necessary. Transmission via clothing and other inanimate objects is uncommon. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is contagious and is spread to others by direct contact with infected skin or infected articles. Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Safe and Effective Care Environment Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Implementation Content Area: Fundamental Skills: Infection Control Strategy(ies): Subject Priority Concepts: Infection, Safety The nurse is reinforcing teaching to a client about an upcoming colonoscopy procedure. The nurse should include in the instructions that the client will be placed in which position for the procedure? Rationale: The client is placed in the left Sims' position for the procedure. This position takes the best advantage of the client's anatomy for ease in introducing the colonoscope. The other options are incorrect. A client with ascites is scheduled for a paracentesis. The nurse is assisting the health care provider in performing the procedure. Which position should the nurse assist the client into for this procedure? Rationale: An upright position allows the intestine to float posteriorly and helps prevent intestinal laceration during catheter insertion. Options 1, 3, and 4 are incorrect positions. The client has just undergone computed tomography (CT) scanning with a contrast medium. Which statement by the client demonstrates an understanding of postprocedure care? Rationale: After CT scanning, the client may resume all usual activities. The client should be encouraged to take in extra fluids to replace those lost with diuresis from the contrast dye. Options 2, 3, and 4 are unnecessary. Hypernatremia is described as having a serum sodium level that exceeds 145 mEq/L. Signs and symptoms would include dry mucous membranes, loss of skin turgor, thirst, flushed skin, elevated temperature, oliguria, muscle twitching, fatigue, confusion, and seizures. Interventions include monitoring fluid balance, monitoring vital signs, reducing dietary intake of sodium, monitoring electrolyte levels, and increasing oral intake of water. Sodium replacement therapy would not be prescribed for a client with hypernatremia. The nurse checks the food on a tray delivered for an Orthodox Jewish client and notes that the client has received a cheeseburger and potato fries with whole milk as a beverage. Which action should the nurse take? Rationale: In the Orthodox Jewish tradition, members avoid meat from carnivores, pork products, and certain fish. The nurse should not deliver the food tray to the client and should ask the dietary department to deliver a different meal. Meat and dairy are served separately, thus the dairy–meat combination is not acceptable, making option 2 incorrect. Option 4 is incorrect because pork and pork products are also not allowed in the diet. Which electrocardiogram changes would the nurse note on the cardiac monitor with a client whose potassium (K+) level is 2.7 mEq/L? Rationale: A serum potassium level less than 3.5 mEq/L is indicative of hypokalemia. Potassium deficit is the most common electrolyte imbalance and is potentially life threatening. Cardiac changes with hypokalemia may include peaked P waves, flattened T waves, depressed ST segment, and the presence of U waves. The nurse is preparing to administer an enema to an adult client. Which interventions should the nurse plan to perform for this procedure? Select all that apply. Rationale: The administration of an enema is a clean procedure, and standard precautions must be used. The nurse applies disposable gloves when administering an enema to prevent the transfer of microorganisms. To administer an enema, the nurse places the client in the left Sims' position because the enema solution will flow downward by gravity along the natural curve of the sigmoid colon and rectum, improving retention of the enema solution. The tube is lubricated for easy insertion and is inserted approximately 3 to 4 inches in an adult. If the client complains of cramping or discomfort during the procedure, the nurse clamps the tubing until the discomfort subsides. The container containing the enema solution is hung about 12 to 18 inches above the client's anus. A flow of solution that is too forceful can damage the bowel. The temperature of the solution should be between 100° F (37.8° C) and 105° F (40.5° C). Solution that is too hot will burn the client, and solution that is too cool will cause cramping. The nurse is preparing a list of home care instructions regarding stoma and laryngectomy care to a client. Which instructions should be included in the list? Select all that apply. Rationale: The nurse should teach the client how to care for the stoma, depending on the type of laryngectomy performed. Most interventions focus on protection of the stoma and the prevention of infection. Interventions include avoiding swimming and using caution when showering, avoiding exposure to people with infections, preventing debris from entering the stoma, and obtaining a Medic-Alert bracelet. Additional interventions include wearing a stoma guard or high-collar clothing to cover the stoma, increasing the humidity in the home, and increasing fluid intake to 3000 mL/day to keep the secretions thin. The nurse is preparing to set up a sterile field using the principles of aseptic technique to perform a dressing change. Which should the nurse include in the preparations? Select all that apply. Rationale: Sterile packages are opened away from the nurse's body, and the distal flap of a sterile package is opened first. This prevents contaminating the pack by reaching over the exposed sterile contents after the other flaps are opened (option 2). To avoid contamination, the sterile field should be prepared just before the planned procedure, and supplies should be used immediately (option 3). The outer 1-inch border of the sterile field must be considered unsterile, and sterile items are not placed within this 1-inch area (option 6). A dry table that is above waist level is used to set up a sterile field. Moisture will contaminate the sterile field, and anything below waist level is considered contaminated, according to the principles of surgical asepsis. The sterile field must be kept in sight at all times, and the nurse should not turn away from it. If this happens, the nurse cannot be sure that it is still sterile. Sterile gloves, not clean gloves, are used. An unsterile item touching a sterile item contaminates the sterile item. The nurse is caring for a client with kidney failure. The laboratory results reveal a magnesium level of 3.6 mg/dL. Which sign does the nurse expect to note in the client, based on this magnesium level? Rationale: The normal magnesium level is 1.6 to 2.6 mg/dL. A client with a magnesium level of 3.6 mg/dL is experiencing hypermagnesemia. Loss of deep tendon reflexes is characteristic of this condition. Twitching, irritability and hyperactive reflexes should be noted in a client with hypomagnesemia. The nurse is caring for a group of clients. Which client is most likely to have a serum phosphorus level of 2.0 mg/dL? Rationale: The normal serum phosphorus level is 2.7 to 4.5 mg/dL, so a value of 2.0 mg/dL is indicative of hypophosphatemia. Causative factors include decreased nutritional intake and malnutrition. A poor nutritional state is associated with alcoholism. Hypoparathyroidism, chemotherapy, and vitamin D intoxication are causative factors of hyperphosphatemia. The nurse is reinforcing instructions to a client regarding how to decrease the intake of phosphorus in the diet. The nurse should tell the client that which food item contains the least amount of phosphorus? Rationale: An orange contains the least amount of phosphorus. Foods high in phosphorus include fish, pork, beef, chicken, organ meats, nuts, whole-grain breads, and cereals. The nurse is told in a report that the client has hypocalcemia and a positive Chvostek's sign. Which signs should the nurse expect to note during the data collection? Select all that apply. Rationale: A positive Chvostek's sign is indicative of hypocalcemia. Other signs and symptoms include tachycardia, hypotension, paresthesias, twitching, cramps, tetany, a positive Trousseau's sign, diarrhea, seizures, hyperactive bowel sounds, and a prolonged QT interval. A client with diabetes mellitus has a glycosylated hemoglobin A (HbA1c) level of 8%. Which instruction does the nurse plan to reinforce to the client based on this test result? Rationale: Elevations of the HbA1c value indicate a need for teaching related to the prevention of hyperglycemic episodes. The HbA1c value measures the amount of glucose that has become permanently bound to the red blood cells. Elevations in blood glucose levels will cause elevations in the amount of glycosylation. Thus, this test is useful for detecting clients who have periods of hyperglycemia that are undetected in other ways. Values are expressed as a percentage of the total hemoglobin and based on the health care provider's preference, include the following: diabetic client with good control, 7.5% or less; diabetic client with fair control, 7.6% to 8.9%; and diabetic client with poor control, 9% or greater. Some health care providers prefer levels lower that these noted. Avoiding infection relates to a low white blood cell count rather than the HbA1c level. Taking in enough fluids relates to an increased hematocrit level rather than the HbA1c level. Increasing iron relates to a low red blood cell count and hemoglobin level rather than the HbA1c level. HbA1c relates to glucose. The nurse is caring for a client with a diagnosis of cancer who is immunosuppressed. The nurse knows that neutropenic precautions will be implemented if the client has which white blood cell (WBC) count? Rationale: The normal WBC count ranges from 4500 to 11,000 cells/mm3. The client who is immunosuppressed has a decrease in the number of circulating WBCs. The nurse implements neutropenic precautions when the client's values fall sufficiently below the low- normal level. Two of the options (5800 cells/mm3 and 8400 cells/mm3) are within normal limits, and one option is slightly elevated (11,500 cells/mm3). The nurse is reviewing the laboratory results of several clients receiving pharmacologic therapy. Which laboratory test results indicate a therapeutic value and that the nurse can safely administer the medication as prescribed? Select all that apply. Rationale: The gentamicin, theophylline, and carbamazepine levels are within the normal therapeutic range; all other results are abnormal (too high). Therapeutic medication levels include the following: gentamicin, 5 to 10 mcg/mL; tobramycin 5 to 10 mcg/mL; digoxin (Lanoxin), 0.5 to 2 ng/mL; phenytoin (Dilantin), 10 to 20 mcg/mL; theophylline, 10 to 20 mcg/mL; and carbamazepine (Tegretol), 5 to 12 mcg/mL. Diphenhydramine hydrochloride (Benadryl), 25 mg orally every 6 hours, is prescribed for a child with an allergic reaction. The child weighs 25 kg. The safe pediatric dosage is 5 mg/kg/day. Which conclusion should the nurse infer? Rationale: Use the formula for calculating a safe dosage range.Safe dose parameter:5 mg/kg/day × 25 kg = 125 mg/dayDosage frequency:25 mg × 4 doses (every 6 hours) = 100 mg/dayThe dose is within the safe dosage range. A pediatric client with a ventricular septal defect repair is placed on a maintenance dose of digoxin (Lanoxin). The safe dose is 0.03 mg/kg/day, and the client's weight is 7.2 kg. The health care provider (HCP) prescribes the digoxin to be given twice daily. How much digoxin should the nurse administer to the client at each dose? Rationale: Calculate the dosage by weight first; therefore, 0.03 mg/day × 7.2 kg = 0.21 mg/day. Next, note that the HCP prescribes digoxin to be given twice daily; therefore, 2 doses in 24 hours will be administered, and 0.21 mg/day divided by 2 doses = 0.1 mg for each dose. The nurse is monitoring the laboratory results of a client receiving an antineoplastic medication by the intravenous (IV) route. The nurse plans to initiate bleeding precautions if which laboratory result is noted? Rationale: Bleeding precautions need to be initiated when the platelet count decreases. The normal platelet count is 150,000 to 450,000/mm3. When the platelets are lower than 50,000/mm3, any small trauma can lead to episodes of prolonged bleeding. The normal white blood cell count is 5000 to 10,000/mm3. When the white blood cell count drops, neutropenic precautions need to be implemented. The normal clotting time is 8 to 15 minutes. The normal ammonia value is 10 to 80 mcg/dL. The nurse caring for a male client with a diagnosis of gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding reviews the client's laboratory results and notes a hematocrit level of 30%. Which action should the nurse take? Rationale: The normal hematocrit level in a male client ranges from 39% to 52%, depending on age. A hematocrit level of 30% is a low level and should be reported to the registered nurse and health care provider because it indicates blood loss. Therefore, the remaining options are incorrect. The nurse is monitoring a client who is attached to a cardiac monitor and notes the presence of U waves. The nurse checks the client and then reviews the results of the client's recent electrolyte results. The nurse expects to note which electrolyte value? Rationale: The normal sodium level is 135 to 145 mEq/L. The normal potassium level is 3.5 to 5.0 mEq/L. A serum potassium level below 3.5 mEq/L is indicative of hypokalemia. In hypokalemia, the electrocardiogram (ECG) changes that occur include inverted T waves, ST segment depression, heart block, and prominent U waves. The nurse provides dietary instructions to a client at risk for hypokalemia about the foods high in potassium that should be included in the daily diet. The nurse tells the client that the fruit highest in potassium is which selection? Rationale: Foods that are high in potassium include bananas, cantaloupe, kiwifruit, and oranges. Fruits low in potassium include apples, cherries, grapefruit, peaches, pineapple, and cranberries. Which cardiovascular sign should the nurse expect to note in a client with a diagnosis of hypocalcemia? Rationale: Cardiovascular manifestations that occur with hypocalcemia include decreased heart rate, diminished peripheral pulses, and hypotension. On the ECG, the nurse should note a prolonged ST segment and a prolonged QT interval. The registered nurse is preparing to insert a nasogastric (NG) tube in a client and asks the licensed practical nurse (LPN) to obtain supplies needed for the procedure. Which supply obtained by the LPN indicates a need for further teachingregarding this procedure? Rationale: Water-soluble lubricant is used to lubricate 3 inches of the tube at the insertion end. An oil lubricant is not used because if the tube accidentally enters the bronchus, pneumonia can develop. Half-inch tape is used to secure the tube after correct placement is verified. A 50- mL catheter tip syringe is used to aspirate gastric contents to confirm placement. The client will be asked to take a sip of water through a straw to help with the passage of the tube. The nurse assists a health care provider with the insertion of a Miller-Abbott tube. After insertion of the tube, the nurse should assist the client to which position? Rationale: A Miller-Abbott tube is an intestinal tube that has a double lumen, one for a tungsten balloon and the other for suction or drainage. After insertion of the tube, the tube is allowed to advance for several hours. The client is positioned in high-Fowler's and on the right side to facilitate passage through the pylorus of the stomach and into the small intestine. The other positions are incorrect. The nurse is preparing to administer a continuous tube feeding to a client with a nasogastric tube. The health care provider has prescribed an amount of 100 mL/hr. How much formula should the nurse plan to add to fill the feeding bag? Rationale: Feeding can be hung at room temperature for a period of 4 hours. If 100 mL/hr is prescribed, the nurse should fill the feeding bag with a maximum amount of 400 mL. Feeding hung longer than 4 hours at room temperature creates the risk of bacterial invasion in the formula. The nurse is preparing to suction a client through a tracheostomy tube. The nurse should avoid which action when performing this procedure? Rationale: Suction is not placed on the catheter when the catheter is introduced into the tracheostomy tube. Suction draws out oxygen, and placing suction on the catheter at this time could traumatize tracheal tissue. The remaining options are appropriate components of the plan of care for suctioning. The nurse is reviewing the laboratory results of a client scheduled for surgery. Which laboratory result should indicate to the nurse that the surgery might be postponed? Rationale: Routine screening tests include a complete blood cell count, serum electrolyte analysis, coagulation studies, and serum creatinine tests. The complete blood count includes the hemoglobin analysis. All these values are within normal range, except the hemoglobin. If a client has a low hemoglobin level, the surgery may be postponed. The nurse volunteering at the health screening clinic reinforces instructions to a 22-year-old client that diet and exercise should be used as tools to keep the total cholesterol level under at least which level? Rationale: The cholesterol level should be at least less than 199 mg/dL. The client should be counseled to keep the total cholesterol level under 200 mg/dL. This will aid in prevention of atherosclerosis, which can lead to a number of cardiovascular disorders later in life. The option of 130 mg/dL is a healthy value yet a low one, and the options of 250 mg/dL and 300 mg/dL aretoo high. A client is suspected of having a myocardial infarction. The nurse should expect elevations in which isoenzyme value reported with the creatine kinase (CK) level? Rationale: The MB band reflects CK from cardiac muscle, which is the level that increases with myocardial infarction. The MM band reflects CK from skeletal muscle. The BB band reflects CK from the brain. There is no MK band. Several laboratory tests are prescribed for a client, and the nurse reviews the results of the tests. Which laboratory results warrant a call to the health care provider (HCP)? Select all that apply. Rationale: The normal values include the following: white blood cells, 4500 to 11,000 cells/mm3; thyroid-stimulating hormone, 0.2 to 5.4 microunits/mL; magnesium, 1.6 to 2.6 mg/dL; calcium, 8.6 to 10.0 mg/dL; blood urea nitrogen, 5 to 20 mg/dL; and serum creatinine, 0.6 to 1.3 mg/dL. Therefore, values that are abnormal should be reported to the HCP. A client who takes theophylline for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is seen in the urgent care center for respiratory distress. Just before initiating treatment for the respiratory distress, a sample for a theophylline level is drawn. The nurse determines that the client may not be compliant with medication therapy if which result is obtained? Rationale: The therapeutic range for the serum theophylline level is 10 to 20 mcg/mL. A level of 6 mcg/mL is below the therapeutic range, indicating the client may not be compliant. With a low level, the client may experience frequent exacerbations of the disorder. If the level is within the therapeutic range as indicated in the remaining options, the client is most likely compliant with medication therapy. The nurse is assigned to a hospitalized client with chronic pancreatitis. The nurse reviews the client's record and expects to note a serum amylase level that is most alike to which value? Rationale: The normal serum amylase level is 25 to 151 units/L. In chronic cases of pancreatitis, the rise in the serum amylase level usually does not exceed three times the normal value. In acute pancreatitis, the value may exceed five times the normal value. Therefore, 300 units/L is correct because the remaining options are normal values. A client has been admitted for urinary tract infection and dehydration. The nurse determines that the client has received adequate volume replacement if the blood urea nitrogen (BUN) level drops to which value? Rationale: The normal blood urea nitrogen value for the adult is 10 to 20 mg/dL. Thus the value of 15 mg/dL is correct. Values of 29 and 35 mg/dL reflect continued dehydration. Option 1 reflects a lower than normal value, which may occur with fluid overload, among other conditions. The nurse is instructing a client on how to decrease the intake of magnesium in the diet. The nurse tells the client that which food item contains the least amount of magnesium? Rationale: Drinking water that has been processed through a water softener is low in magnesium. Peanut butter, spinach, and broccoli are magnesium-containing foods and should be avoided by the client on a magnesium-restricted diet. The nurse instructs a client at risk for hypokalemia about the foods high in potassium that should be included in the daily diet. The nurse tells the client that which food provides the least amount of potassium? Rationale: An apple provides approximately 3 mEq of potassium per serving. Spinach and carrots (½ cup cooked) and four apricots provide approximately 7 mEq of potassium per serving. Renal/Reproductive The nursing instructor asks a nursing student to list the functions of the amniotic fluid. The student responds correctly by stating that which are functions of amniotic fluid? Select all that apply. Allows for fetal movement Is a measure of kidney function Surrounds, cushions, and protects the fetus Maintains the body temperature of the fetus The nursing student is asked to describe the size of the uterus in a nonpregnant client. Which response indicates an understanding of the anatomy of this structure? "The uterus weighs about 2 ounces." Methylergonovine is prescribed for a woman to treat postpartum hemorrhage. Before the administration of methylergonovine, the nurse should check which priority item? Blood pressure The nurse is monitoring a preterm labor client who is receiving magnesium sulfate intravenously. The nurse should monitor for which adverse effects of this medication? Select all that apply. Flushing Depressed respirations Extreme muscle weakness A pregnant client is receiving magnesium sulfate for the management of preeclampsia. The nurse determines that the client is experiencing toxicity from the medication if which is noted on data collection? Respirations of 10 breaths per minute Epidural analgesia is administered to a woman for pain relief after a cesarean birth. The nurse assigned to care for the woman ensures that which medication is readily available if respiratory depression occurs? Naloxone (Narcan) Rho(D) immune globulin (RhoGAM) is prescribed for a woman after the delivery of a newborn infant, and the nurse provides information to the woman about the purpose of the medication. The nurse determines that the woman understands the purpose of the medication if the woman states that it will protect her next baby from which condition? Being affected by Rh incompatibility A woman with preeclampsia is receiving magnesium sulfate. Which indicates to the nurse that the magnesium sulfate therapy is effective? Seizures do not occur. Methylergonovine is prescribed for a client with postpartum hemorrhage. Before administering the medication, the nurse should question administration of the medication if which condition is documented in the client's medical history? Peripheral vascular disease The nursing instructor asks a nursing student to describe the procedure for administering erythromycin ointment to the eyes of a neonate. The instructor determines that the student needs to research this procedure further if the student makes which statement? "I will flush the eyes after instilling the ointment." A 31-week preterm labor client dilated to 4 centimeters has been started on magnesium sulfate. Her contractions have stopped. If the client's labor can be inhibited for the next 48 hours, which medication does the nurse anticipate will be prescribed? Betamethasone The nurse is caring for a client who is receiving oxytocin (Pitocin) to induce labor. The nurse should discontinue the oxytocin infusion and notify the registered nurse if which is noted on data collection of the client? Uterine hyperstimulation The nurse is caring for the client with epididymitis. Which treatment modalities should be implemented? Select all that apply. Bed rest Sitz bath Antibiotics Scrotal elevation A client has epididymitis as a complication of a urinary tract infection (UTI). The nurse is giving the client instructions to prevent a recurrence. The nurse determines that the client needs further teachingif the client states the intention to do which? Continue to take antibiotics until all symptoms are gone. The nurse is collecting data from a client who has had benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) in the past. To determine if the client is currently experiencing exacerbation of BPH, the nurse should ask the client about the presence of which early symptom? Decreased force in the stream of urine A client newly diagnosed with chronic kidney disease has recently begun hemodialysis. Which are signs/symptoms of disequilibrium syndrome? Headache, deteriorating level of consciousness, and twitching A client with chronic kidney disease has been on dialysis for 3 years. The client is receiving the usual combination of medications for the disease, including aluminum hydroxide as a phosphate-binding agent. The client now has mental cloudiness, dementia, and complaints of bone pain. Which does this data indicate? Aluminum intoxication A hemodialysis client with a left arm fistula is at risk for arterial steal syndrome. The nurse monitors this client for which signs/symptoms of this disorder? Pallor, diminished pulse, and pain in the left hand The nurse is reviewing the medical record of a client with a diagnosis of pyelonephritis. Which disorder noted on the client's record should the nurse identify as a risk factor for this disorder? Diabetes mellitus The nurse is reviewing the client's record and notes that the health care provider has documented that the client has a renal disorder. Which laboratory results would indicate a decrease in renal function? Select all that apply. Elevated serum creatinine level Decreased red blood cell (RBC) count Elevated blood urea nitrogen (BUN) level A client is scheduled for intravenous pyelography (IVP). Which priority nursing action should the nurse take? Determine a history of allergies. After a renal biopsy, the client complains of pain at the biopsy site, which radiates to the front of the abdomen. Which would this indicate? Bleeding The nurse monitoring a client receiving peritoneal dialysis notes that the client's outflow is less than the inflow. The nurse should take which actions? Select all that apply. Check the level of the drainage bag. Reposition the client to his or her side. Place the client in good body alignment. Check the peritoneal dialysis system for kinks. The nurse is collecting data on a newly admitted client with a diagnosis of bladder cancer. Which sign/symptom should be noted first? Hematuria A client with benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH) undergoes a transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) and is receiving continuous bladder irrigations postoperatively. Which are the signs/symptoms of transurethral resection (TUR) syndrome? Bradycardia and confusion A client with prostatitis resulting from kidney infection has received instructions on management of the condition at home and prevention of recurrence. Which statement indicates that the client understood the instructions? Use warm sitz baths and analgesics to increase comfort. The nurse is monitoring an older client suspected of having a urinary tract infection (UTI) for signs of the infection. Which sign/symptom should occur first? Confusion The client who has a cold is seen in the emergency department with an inability to void. Because the client has a history of benign prostatic hyperplasia, the nurse determines that the client should be questioned about the use of which medication? Decongestants A sulfonamide is prescribed for a client with a urinary tract infection. On review of the client's record, the nurse notes that the client is taking warfarin sodium (Coumadin) daily. Which prescription should the nurse anticipate for this client? A decrease in the warfarin sodium (Coumadin) dosage Methenamine (Urex), a urinary antiseptic, is prescribed for the client. The nurse reviews the client's medical record and should contact the health care provider regarding which documented finding to verify the prescription? Refer to chart. Renal insufficiency Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMZ) is prescribed for a client. The nurse should instruct the client to report which symptom if it developed during the course of this medication therapy? Sore throat Phenazopyridine hydrochloride (Pyridium) is prescribed for a client for symptomatic relief of pain resulting from a lower urinary tract infection. Which should the nurse reinforce to the client? A reddish-orange discoloration of the urine may occur. Bethanechol chloride (Urecholine) is prescribed for a client with urinary retention. Which disorder should be a contraindication to the administration of this medication? Urinary strictures The nurse who is administering bethanechol chloride (Urecholine) is monitoring for acute toxicity associated with the medication. The nurse should check the client for which sign of toxicity? Bradycardia Oxybutynin chloride (Ditropan XL) is prescribed for a client with neurogenic bladder. Which sign would indicate a possible toxic effect related to this medication? Restlessness After kidney transplantation, cyclosporine (Sandimmune) is prescribed for a client. Which laboratory result would indicate an adverse effect from the use of this medication? Elevated blood urea nitrogen level The nurse is reinforcing discharge instructions to a client receiving sulfadiazine. Which should be included in the list of instructions? Maintain a high fluid intake. The nurse is reinforcing discharge instructions to a client receiving sulfisoxazole. Which should be included in the plan of care for instructions? Maintain a high fluid intake. The nursing instructor asks the nursing student about the physiology related to the cessation of ovulation that occurs during pregnancy. Which response by the student indicates an understanding of this physiological process? "Ovulation ceases during pregnancy because the circulating levels of estrogen and progesterone are high." The nurse is inspecting the stoma of a client after creation of an ureterostomy. Which appearance should the nurse expect to note? A red and moist stoma The nurse is assessing the patency of an arteriovenous fistula in the left arm of a client who is receiving hemodialysis for the treatment of chronic kidney disease. Which finding indicates that the fistula is patent? Palpation of a thrill over the fistula A client newly diagnosed with renal failure will be receiving peritoneal dialysis. During the infusion of the dialysate, the client complains of abdominal pain. Which action by the nurse is appropriate? Explain that the pain will subside after the first few exchanges. The nurse is instructing a client with diabetes mellitus about peritoneal dialysis. The nurse tells the client that it is important to maintain the dwell time for the dialysis at the prescribed time because of risk for which complication? Hyperglycemia A client is diagnosed with polycystic kidney disease, and the nurse provides information to the client about the treatment plan. The nurse determines that the client needs further teaching if the client states that which component is part of the treatment plan? Sodium restriction The client with chronic kidney disease who is scheduled for hemodialysis this morning is due to receive a daily dose of enalapril (Vasotec). When should the nurse plan to administer this medication? On return from dialysis The nurse is caring for a client who had a renal biopsy. Which interventions should the nurse include in the plan of care for the client after this procedure? Select all that apply. Administering pain medication as prescribed Monitoring vital signs and the puncture site frequently Testing serial urine samples with dipsticks for occult blood A client is admitted to the emergency department following a fall from a horse. The health care provider (HCP) prescribes the insertion of an indwelling urinary catheter. The nurse notes blood at the urinary meatus while preparing for the procedure. Which action should the nurse take? Notify the health care provider. A male client has a tentative diagnosis of urethritis. The nurse collects data from the client knowing that which are signs/symptoms of this disorder? Dysuria and penile discharge A male client is diagnosed with urethritis caused by chlamydial infection. The unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) assigned to the client asks the nurse what measures are necessary to prevent a contraction of the infection during care. Which instruction should the nurse give the UAP? Standard precautions are sufficient because the infection is transmitted sexually. The nurse is caring for a client with epididymitis. The nurse anticipates noting which group of findings on data collection? Fever, nausea and vomiting, and painful scrotal edema A client receiving nitrofurantoin (Macrodantin) calls the health care provider's office complaining of side effects related to the medication. Which side effect indicates the need to stop treatment with this medication? Chest pain A client with chronic kidney disease is receiving epoetin alfa (Epogen, Procrit). Which laboratory result should indicate a therapeutic effect of the medication? Hematocrit of 32% The nurse provides home care instructions to a client undergoing hemodialysis with regard to care of an arteriovenous (AV) fistula. Which statement by the client indicates an understanding of the instructions? "I should check the fistula every day by feeling it for a vibration." Methylergonovine is prescribed for a client with postpartum hemorrhage caused by uterine atony. Before administering the medication the nurse checks which important client parameter? Blood pressure The licensed practical nurse (LPN) is assisting a school nurse in conducting a session with female adolescents regarding the menstrual cycle. The LPN tells the adolescents that the normal duration of the menstrual cycle is which? 28 days The maternity nursing instructor asks a nursing student to identify the hormones that are produced by the ovaries. Which hormone(s) identified by the student indicates an understanding of the hormones produced by this endocrine gland? Estrogen and progesterone The maternity nurse is describing the ovarian cycle to a group of nursing students and asks a nursing student to identify the phases of the cycle. Which phase stated by the nursing student indicates a need for further teaching in this area? Proliferative phase The nurse prepares to administer sodium polystyrene sulfonate (Kayexalate) to a client with chronic kidney disease for which laboratory abnormality? Potassium level of 7.2 mEq/L The nurse is reinforcing instructions to a client about the types of fluids that assist in prevention and treatment of urinary tract infections (UTIs). The nurse instructs the client to consume which fluids? Select all that apply. Prune juice Apple juice Cranberry juice A client has been examined in the clinic and has been diagnosed with endometriosis. The client asks the nurse to describe this condition. Which description of endometriosis by the nurse is accurate? "Endometriosis is the presence of tissue outside the uterus that resembles the endometrium." The nurse is assisting in conducting a teaching session with a group of adolescents. The nurse tells the adolescents that the hormone that induces the growth of pubic and axillary hair at puberty is which? testosterone Which statement made by the nursing student demonstrates an understanding of the hormone oxytocin? "It causes contractions of the uterus during birth." The nurse is collecting data from a client who is suspected of having mittelschmerz. Which should the nurse expect to note? Sharp pain located on the right side of the pelvis The nurse has reinforced instructions to the client with a cystocele about Kegel exercises. The nurse determines that the client has not fully understood the directions if the client makes which statement? "Begin voiding and then stop the stream, holding residual urine for an hour." The nurse is reviewing the health record of a client who is suspected of having mittelschmerz. Which should the nurse expect to note documented in the client's record? Sharp pain located on the right side of the pelvis An alkaline-ash diet is prescribed for a client with renal calculi. Which diet menu does the nurse advise the client to select? A spinach salad, milk, and a banana The nurse is assisting in planning a diet for a client with acute kidney injury (AKI). The nurse plans to restrict which dietary component from this client's diet? Potassium A client who suffered a crush injury to the leg has a highly positive urine myoglobin level. The nurse plans to monitor this particular client carefully for signs of which complication? Acute tubular necrosis The nurse is caring for a client with kidney failure. The serum phosphate level is reported as 7 mg/dL. Which medication should the nurse plan to administer as prescribed to the client? Aluminum hydroxide gel A client is seen in the health care clinic with a diagnosis of mild anemia. The anemia is believed to be a result of the menstrual period. The woman asks the nurse how much blood is lost during a menstrual period. Which is a normal amount of blood loss during a menstrual period that the nurse should compare with the client's loss? 40 mL A nursing instructor asks a nursing student to describe Montgomery's tubercles of the breast. Which response by the student indicates an understanding of this anatomical structure? "These are sebaceous glands that are located in the areola." A maternity nurse is providing an in-service educational session to nursing students regarding the process of conception. The nurse determines that a nursing student understands this process if the student states that fertilization of a mature ovum occurs in which areas? In the distal third of the fallopian tube A nursing student is asked to describe the corpus of the uterus. Which response by the student indicates an understanding of the anatomy of the uterus? "It is the uppermost part of the uterus." A client hospitalized with urolithiasis has a sudden significant decrease in urine output. The nurse should perform which action? Notify the registered nurse. The nurse is caring for a client undergoing peritoneal dialysis. The nurse checks the client and notes that the drainage from the outflow catheter is cloudy. The nurse notifies the registered nurse and plans to take which action? Obtain a culture and sensitivity of the drainage. The postpartum nurse is caring for a client following a cesarean birth who received epidural analgesia. The client is lethargic and is exhibiting signs of respiratory depression. The nurse suspects that the respiratory depression is caused by the epidural analgesia. The nurse notifies the registered nurse immediately and prepares the client for the administration of which medication? Naloxone (Narcan) The nursing student is assigned to care for a 30-week gestational woman who is admitted to the maternity unit in preterm labor. Betamethasone is prescribed to be administered to the mother. The nursing instructor asks the student about the purpose of the medication. Which statement by the student indicates an understanding of the purpose of this medication? "This medication will promote fetal lung maturity." The nurse is caring for a hospitalized client following cystoscopy and is monitoring for signs of complications associated with the procedure. Which result noted in the first few hours following the procedure indicates the need to notify the registered nurse? Bloody urine with clots The nurse is admitting a client to the nursing unit who has returned from the postanesthesia care unit following prostatectomy. The client has a three-way Foley catheter with continuous bladder irrigation. The nurse should maintain the flow rate of the continuous bladder infusion to maintain which urine output characteristic? Pale yellow or slightly pink The nurse is providing dietary instructions to a client with renal calculi, and the laboratory analysis has revealed that the calculus is composed of uric acid. The nurse tells the client that it would be helpful to make which dietary changes? Increase intake of legumes in the diet. In reviewing the admission assessment data and health care provider's prescriptions for a client with peptic ulcer disease, the nurse notes that the client has a history of renal disease. Based on this data, the nurse determines that which antacid should be prescribed for this client? Aluminum hydroxide (Amphojel) A client with a history of prostatic hypertrophy has purchased the over-the- counter medication, diphenhydramine (Benadryl), to treat symptoms of a runny nose. The nurse explains to the client that this medication combined with prostatic hypertrophy could cause exacerbation of which symptom? Urinary retention Bethanechol (Urecholine) is prescribed for the client with urinary retention, and an injectable form of bethanechol is available for use as prescribed. The nurse informs the client of the health care provider's prescription, knowing that the medication will be administered by which route? Subcutaneously A client has undergone a transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) a few hours ago to treat symptoms of benign prostatic hypertrophy. The nurse notes bright red blood and clots in the urinary catheter drainage bag. Which response should be the nurse's initial action? Increase the flow rate of the continuous bladder irrigation. Magnesium sulfate is prescribed for a client with severe preeclampsia. Which statement by the student nurse supports the need for further teaching regarding the action of this medication? "It increases acetylcholine and blocks neuromuscular transmission." A client with severe preeclampsia is receiving magnesium sulfate by intravenous infusion. The nurse reviews the laboratory results, knowing that which value is a therapeutic magnesium level? 6 mg/dL A client diagnosed with severe preeclampsia is on magnesium sulfate by continuous intravenous infusion. Which finding suggests to the nurse that the next dose of this medication should be held? Absence of deep tendon reflexes A client has been prescribed allopurinol (Zyloprim). The nurse reinforces which information concerning the administration of the medication? Drink at least eight glasses of fluid every day. The nurse is reinforcing dietary instructions to a client who is currently prescribed probenecid (Benemid). Which food should the nurse encourage the client to continue to eat? Spinach The nurse is caring for a client diagnosed with Parkinson's disease who is prescribed benztropine mesylate (Cogentin) daily. The nurse reinforces instructions to both the client and the spouse regarding the side effects of this medication and the need to report which side effect if it occurs? Inability to urinate The nurse is providing instructions to the client regarding the complications of peritoneal dialysis. The nurse instructs the client that which symptom is likely associated with the onset of peritonitis? Fever A client who is performing peritoneal dialysis at home calls the clinic and reports that the outflow from the dialysis catheter seems to be decreasing in amount. The nurse appropriately asks which question first? "Have you experienced any constipation recently?" A client complains of leaking urine whenever she sneezes, coughs, or laughs. The nurse recognizes that this report is consistent with which type of incontinence? Stress The nurse is caring for a client in preterm labor who is receiving terbutaline sulfate to stop uterine activity. During this medication therapy, the nurse implements nursing interventions to monitor which specific body organs that can be affected by this medication? Heart and lungs The nurse documents that the urine collected from a client diagnosed with early stage polycystic kidney disease is dilute with a low-specific gravity. Based on this documentation, which specific gravity result was likely present? 1.000 The nurse is reinforcing instructions to a client with glaucoma receiving acetazolamide (Diamox) daily. Which statement by the client indicates an understanding of the adverse effects related to the medication? "I need to call the doctor if I notice dark urine and stools." The nurse is assisting a client with cystitis to select foods that are appropriate for an acid-ash diet. The nurse encourages the client to eat which food? Cheese The nurse is assigned to care for a client who has just returned to the nursing unit after having hemodialysis for the first time. The nurse monitors the client carefully for which signs and symptoms of disequilibrium syndrome? Vomiting and headaches A client is seen in the health care clinic and acute pyelonephritis is suspected. The nurse reviews the client's record and should expect to note which associated signs and symptoms documented? Select all that apply Chills General weakness Nausea and vomiting The use of peritoneal dialysis for the treatment of chronic kidney disease would be contraindicated for which client? The client with severe emphysema Which conditions places the client at risk for developing acute postrenal failure? Hydronephrosis The nurse is assessing a client with suspected acute kidney injury. Which finding would support a diagnosis of acute intrarenal failure? Urine analysis positive for casts and cellular debris A client diagnosed with chronic kidney disease is being treated at home with continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. The client notes that there is a decrease in the catheter outflow following the prescribed 6-hour dwell time and calls the nurse to report this occurrence. The nurse should reinforce instructing the client to take which action? Ambulate in the home. Which statements indicate an understanding of the necessary dietary modifications of a client diagnosed with chronic kidney disease? Select all that apply. "I should avoid eggs, and a bagel is preferable." "I should consume approximately 40 g of protein daily." The nurse is assigned to care for a client who has returned to the nursing unit following a left nephrectomy. The nurse places the highest priorityon monitoring which data? Hourly urine output A client with acute kidney injury (AKI) has been treated with sodium polystyrene sulfonate (Kayexalate) by mouth. The nurse evaluates this therapy as effective if which value is noted on follow-up laboratory testing? Potassium, 4.9 mEq/L The nurse is admitting a client with chronic kidney disease (CKD) to the nursing unit. The nurse monitors the client for which frequent cardiovascular sign that occurs in CKD? Hypertension The nurse is assisting in preparing a plan of care for a client who will be receiving a calcium antagonist to prevent preterm delivery. Which action does the nurse include in the plan of care for the client to detect a side effect of the medication? Monitor for increases in maternal and fetal heart rates. The nursing student is asked to describe the size of the uterus in a nonpregnant client. Which response by the student indicates an understanding of the anatomy of this structure? "The uterus weighs about 2 ounces." The nurse is urging a client to cough and deep breathe after a nephrectomy. The client tells the nurse, "That's easy for you to say! You don't have to do this." The nurse interprets that the client's statement is likely a result of which contributing factor? Pain that is intensified because the location of the incision is near the diaphragm A client has received instructions on self-management of peritoneal dialysis. The nurse determines that the client needs further teachingif the client makes which statement? "I will use a strong adhesive tape to anchor the catheter dressing." The nurse notes that a client's urinalysis report contains a notation of positive red blood cells (RBCs). The nurse interprets that this finding is unrelated to which item that is part of the client's medical record? Diabetes mellitus A client with acute glomerulonephritis had a urinalysis sent to the laboratory. The report reveals that there is hematuria and proteinuria in the urine. The nurse interprets that these results are which? Consistent with glomerulonephritis A client with acute pyelonephritis is scheduled for a voiding cystourethrogram. Which information about this procedure should the nurse give to the client? The client must void while the micturition process is filmed. The nurse is assisting in monitoring a preterm infant in the neonatal intensive care unit who received surfactant (Infasurf). The nurse monitors for which desired therapeutic outcome of this medication? Decreased tachypnea and nasal flaring The nurse in the delivery room is caring for a newborn delivered 10 minutes ago. The nurse assists to prepare which medications that will be prescribed to be given within the first hour of life? Select all that apply. Erythromycin eye drops Phytonadione (vitamin K) The client with diabetes mellitus receiving peritoneal dialysis asks the nurse why it is important to leave the dialysate infused only for a specific amount of time. The nurse responds that not adhering to the dwell time can increase the risk of the client experiencing which complication? Hyperglycemia The nurse is reinforcing dietary instructions to a client diagnosed with acute glomerulonephritis. The nurse determines that the client understands the information presented if the client states the intention to do which action? Limit protein intake. A client has been diagnosed with pyelonephritis. The nurse interprets that which health problem has placed the client at risk for this disorder? Diabetes mellitus The nurse is collecting data from a client with epididymitis. The nurse should expect to note which signs and symptoms of this problem? Fever, nausea and vomiting, and painful scrotal edema A client arrives at the ambulatory care clinic with low abdominal pain. A routine urine specimen reveals hematuria. The client does not have a fever. The nurse should next ask the client about a history of which condition? Blow or trauma to the bladder or abdomen A client's kidneys are retaining greater amounts of sodium. The nurse anticipates that the kidneys are also retaining greater amounts of which other substances? Chloride and bicarbonate The spouse of a client with acute kidney injury secondary to heart failure asks the nurse how this could happen. The nurse plans to base a response in part on the fact that which statement is true? The kidneys generally require and receive about 20% to 25% of the resting cardiac output. The use of peritoneal dialysis for the treatment of chronic kidney disease would be contraindicated for which clients? The client with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) An adolescent is admitted to the hospital with complaints of lower right abdominal pain. The health care provider prescribes laboratory tests to rule out ectopic pregnancy rather than appendicitis. Which is most significant in ruling out an ectopic pregnancy? Serum human chorionic gonadotropin A male client has a history of urinary tract infections due to urinary retention. Which intervention should the nurse implement to decrease the risk of infection? Assist the client to stand for voiding. The nurse is teaching breast self-examination (BSE) to a client who has had a hysterectomy. Which time of the month should the nurse tell the client to perform breast self-examination? On a specific day of the month and on that same day every month thereafter The nurse is caring for a client who has been diagnosed as having a kidney mass. The client asks the nurse the reason for a renal biopsy, when other tests such as computed tomography (CT) and ultrasound are available. In formulating a response, the nurse incorporates the knowledge that a renal biopsy serves which purpose? Gives specific cytological information about the lesion The nurse is assisting in planning a teaching session with a client diagnosed with urethritis caused by infection with Chlamydia. The nurse should plan to include which point in the teaching session? The most serious complication of this infection is sterility. A client with chlamydial infection has received instructions on self-care and prevention of further infection. The nurse determines that the client needs further teaching if the client states which? I will use an antibiotic prophylactically to prevent symptoms of Chlamydia. A client who has a cold is seen in the emergency department with an inability to void. Because the client has a history of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), the nurse questions the client about use of which medication? Decongestants A client who had a prostatectomy has learned perineal exercises to gain control of the urinary sphincter. The nurse determines that the client needs further teaching if the client states that he will perform which action as part of these exercises? Perform the Valsalva maneuver. The nurse is working with a client newly diagnosed with chronic kidney disease (CKD) to set up a schedule for hemodialysis. The client states, "This is impossible! How can I even think about leading a normal life again if this is what I'm going to have to do?" The nurse determines that the client is exhibiting which reaction? Anger A urinary analgesic is prescribed for a client with a urinary tract infection. When should the nurse tell the client that it is best to take the medication? With meals Bethanechol chloride (Urecholine) is prescribed for a client. When should the nurse tell the client to take the medication? Two hours after meals Propantheline bromide (Pro-Banthine) is prescribed for a client with bladder spasms. Which disorder, noted in the client's record, alerts the nurse to question the prescription for this medication? Glaucoma Aluminum hydroxide is prescribed for the client with chronic kidney disease (CKD). When should the nurse instruct the client to take this medication? With meals The nurse is reinforcing dietary instructions to a client with renal calculi who must learn to eat an alkaline-ash diet. The nurse determines that the client has properly understood the information presented if the client chooses which selection from a diet menu? A spinach salad, milk, and a banana The nurse must ambulate a client who has a nephrostomy tube attached to a drainage bag. The nurse plans to do this most safely and effectively by performing which action? Changing the drainage bag to a leg collection bag A long-term care nurse notes that a female client has leakage of urine when sneezing, coughing, or laughing. The nurse reports that this client has which type of incontinence? Stress incontinence The nurse caring for a client taking tamsulosin (Flomax) determines that which finding indicates the need for follow-up? Pulse rate of 120 beats per minute A client has just undergone renal biopsy. In planning care for this client, the nurse should avoid which intervention? Ambulate in the room and hall for short distances. The nurse has a prescription to collect a 24-hour urine specimen from a client. The unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) has been instructed on the collection technique. Which action by the UAP demonstrates the UAP needs further teaching? Asks the client to void, save the specimen, and note the start time The nurse is preparing a client scheduled for an intravenous pyelogram (IVP). The nurse should take which important action before the test? Ask about allergies to iodine or shellfish. A female client has a prescription for a clean-catch urine culture. After providing a sterile specimen cup to the client, the nurse should give which instruction so that the specimen is collected properly? Cleanse the labia using cleansing towels, begin to void into toilet, and then collect the specimen. A client with new-onset renal failure is having a first hemodialysis treatment. The nurse is especially careful to monitor the client for which signs/symptoms after the dialysis treatment? Headache, decreasing level of consciousness, and seizures The nurse is assisting a client who is new to a low-potassium diet to select food items from the menu. Which food item is lowest in potassium and should be recommended to the client on this dietary restriction? Lima beans A client is admitted to the surgical nursing unit following transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) for benign prostatic hypertrophy. The client has a bladder irrigation infusing, and output is light cherry colored. The blood pressure is 134/82 mm Hg, the pulse is 84 beats per minute, and the client is afebrile with a respiratory rate of 18 breaths per minute. The licensed practical nurse (LPN) assisting in caring for the client collects assessment data 1 hour after admission to the nursing unit. The LPN notifies the registered nurse (RN) if which is noted on data collection? Blood pressure of 102/50 mm Hg, pulse 110 beats per minute A client with acute glomerulonephritis is admitted to the nursing unit. The nurse should plan to do which action immediately on admission? Remove the water pitcher from the bedside. A client with a urinary tract infection with dysuria is given a prescription for phenazopyridine hydrochloride (Pyridium) for symptom relief. Which should the nurse reinforce instructing the client about this medication? Expect the urine to become reddish orange. The nurse is preparing a subcutaneous dose of bethanechol chloride (Urecholine) prescribed for a client with urinary retention. Before giving the dose, the nurse checks to see that which medication is available on the emergency cart? Atropine sulfate The nurse suspects the client has a urinary tract infection (UTI). Which signs/symptoms suggest a UTI? Select all that apply. Dysuria Hematuria Frequency Flank pain Cloudy urine A client with end stage kidney disease (ESKD) undergoes a surgical procedure to create an arteriovenous fistula for hemodialysis in the upper extremity. The nurse should take which actions when the client returns from surgery? Select all that apply. Monitor pain and administer analgesics. Monitor bleeding and swelling at the site. Check for audible bruit and palpable thrill at the fistula site. A client contacts the health care provider's office to report she is not feeling well, has burning with urination, and suspects she may have a urinary tract infection. The nurse instructs the client to collect a urine specimen for testing. Which urinalysis findings indicate the presence of a urinary tract infection? Select all that apply. Nitrites, present White blood cells, 10 Leukoesterase, present A client with end stage kidney disease (ESKD) begins peritoneal dialysis. The nurse observes for which signs/symptoms indicating peritonitis? Select all that apply. Nausea and vomiting Abdominal tenderness Cloudy peritoneal effluent Oral temperature of 38° C A client who underwent a kidney transplant 6 months earlier is seen in the clinic for a routine monthly appointment. The nurse reviews how the client has been doing and observes for signs/symptoms of acute rejection. Which signs/symptoms suggest acute rejection of the transplanted kidney? Select all that apply. Oliguria Elevation of blood pressure over baseline Abdominal tenderness on the side of the kidney transplant Elevation of serum blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine The nurse is speaking with a client who underwent a minimally invasive procedure treatment for recurrent urolithiasis. Which instructions are appropriate to reinforce in the teaching plan? Select all that apply. Drink at least 3000 mL of fluid each day. Complete the full course of prescribed antibiotics. Filter urine and collect any stones to take to the urological health care provider. A client, on the waiting list for a renal transplant, receives a hemodialysis treatment. Which findings indicate to the nurse that the treatment has been effective? Select all that apply. Serum potassium level is within the normal range. The client's weight is 2 kilograms less than predialysis weight. Serum blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine levels are lower than predialysis. Which observations by the nurse caring for clients on a hospital medical- surgical unit should be immediately reported to the health care provider? Select all that apply. New confused mental state and pulse rate of 106 beats per minute in a 72-year-old client A volume of 105 mL of urine over 4 hours in the collection bag of a 1- day postoperative client A client tells the nurse she completed an educational program to manage her stress incontinence but is now discouraged. Which information from the client indicates the need for further teaching? Select all that apply. She performs the Kegel exercises every other day. She quit drinking coffee with cream but drinks diet cola. She has begun an exercise program that includes lifting weights. A client, who had experienced significant blood loss in an automobile crash, was admitted to the hospital 2 days earlier. The nurse observes the client for which signs/symptoms that indicate acute kidney injury (AKI)? Select all that apply. Elevated urine specific gravity Rising serum blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine levels Urine output averaging 25 mL per hour while receiving an intravenous infusion at 150 mL/hour The nurse is evaluating the data results of a client with sepsis and acute kidney injury with related azotemia and oliguria. Which are the primary features of azotemia and oliguria? Select all that apply. Increase in serum creatinine Increase in blood urea nitrogen (BUN) Urine output less than 0.5 mL/kg/hour The nurse is caring for a 58-year-old client with renal failure who is on peritoneal dialysis. Which finding is considered most important by the nurse, requiring health care provider notification? Refer to chart. WBC 15,000 cells/mL The nurse is caring for a client who received a recent kidney transplant. Besides actual rejection of the transplant, which are some of the most important complications this client is at risk for? Select all that apply. Malignancies Cardiovascular disease Susceptibility to infection Corticosteroid-related complications The nurse is evaluating the assessment of a client's arteriovenous fistula being used for hemodialysis. Which findings would prompt the nurse to notify the health care provider immediately? Select all that apply. No thrill palpated at fistula site No bruit auscultated at the fistula site Absent pulse distal to the arteriovenous fistula The nurse is caring for a hemodialysis client who has been receiving treatment for several years and is not a candidate for kidney transplant. The nurse knows that the majority of deaths of hemodialysis clients are related to which causes? Select all that apply. Stroke Infectious complications Myocardial infarction (MI) The nurse is caring for a client with a possible ectopic pregnancy. The nurse should perform the following actions in which priority order? Arrange the actions in the order they should be performed. All options must be used. Prepare the client for ultrasound. Assess the client for signs of increased pain or vaginal bleeding. Assess the emotional state of the client. Obtain a urine specimen. The nurse in a women's health clinic is reinforcing instructions to a client that is being treated for pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). Which information would be essential for the nurse to reinforce before discharge? Select all that apply. Get plenty of rest and increase fluid intake. Refrain from sexual activity for 3 weeks. Inform your sexual partner of the need for treatment, even if no symptoms are present. The nurse at an outpatient cardiology clinic is reviewing the medical history of a 48-year-old man during a routine exam. The client is complaining of the inability to maintain an erection and asks the nurse what could be causing it. Which information should the nurse include as possible contributing factors to his erectile dysfunction? Select all that apply. Weight 245 lb Total cholesterol 223 mg/dL Serum creatinine 1.86 mg/dL The nurse is caring for a female 45-year-old client. The client has 3 healthy children, all born via spontaneous vaginal birth. The client has been diagnosed with mild uterine prolapse and asks the nurse what she can do to prevent further prolapse. The nurse should include which instruction in her teaching? Select all that apply. Lose weight. Perform Kegel exercises. Eat a diet high in fiber. Take a stool softener daily as needed. The nursing student is assigned to care for an adolescent female client in the health care clinic, and the instructor reviews the menstrual cycle with the student. The instructor determines that the student understands the process of the secretion of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) if the student makes which statement? "FSH and LH are released from the anterior pituitary gland." A client has an arteriovenous (AV) shunt in place for hemodialysis. The nurse should take which priorityprecaution, knowing that bleeding is a potential complication? Ensure that small clamps are attached to the AV shunt dressing. Cardio NCLEX 1. The nurse is assigned to assist with caring for a client after cardiac catheterization. The nurse should plan to maintain bed rest for this client in which position? - Head elevation of no more than 30 degrees 2. A postcardiac surgery client with a blood urea nitrogen (BUN) level of 45 mg/dL and a serum creatinine level of 2.2 mg/dL has a total 2-hour urine output of 25 mL. The nurse understands that the client is at risk for which? - Acute kidney injury 3. The nurse is preparing to ambulate a postoperative client after cardiac surgery. The nurse plans to do which to enable the client to best tolerate the ambulation? - Premedicate the client with an analgesic before ambulating. 4. A client is wearing a continuous cardiac monitor, which begins to alarm at the nurse's station. The nurse sees no electrocardiographic complexes on the screen. The nurse should do which first? - Check the client status and lead placement. 5. The nurse in a medical unit is caring for a client with heart failure. The client suddenly develops extreme dyspnea, tachycardia, and lung crackles, and the nurse suspects pulmonary edema. The nurse immediately notifies the registered nurse and expects which interventions to be prescribed? Select all that apply. - Administering oxygen - Inserting a Foley catheter - Administering furosemide (Lasix) - Administering morphine sulfate intravenously 6. The nurse is monitoring a client following cardioversion. Which observations should be of highest priority to the nurse? - Status of airway 7. The nurse is assisting in caring for the client immediately after insertion of a permanent demand pacemaker via the right subclavian vein. The nurse prevents dislodgement of the pacing catheter by implementing which intervention? - Limiting movement and abduction of the right arm 8. A client diagnosed with thrombophlebitis 1 day ago suddenly complains of chest pain and shortness of breath, and the client is visibly anxious. The nurse understands that a life-threatening complication of this condition is which? - Pulmonary embolism 9. A 24-year-old man seeks medical attention for complaints of claudication in the arch of the foot. The nurse also notes superficial thrombophlebitis of the lower leg. The nurse should check the client for which next? - Smoking history 10. The nurse has reinforced instructions to the client with Raynaud's disease about self-management of the disease process. The nurse determines that the client needs further teaching if the client states which? - "Moving to a warmer climate should help." 11. A client with myocardial infarction suddenly becomes tachycardic, shows signs of air hunger, and begins coughing frothy, pink-tinged sputum. The nurse listens to breath sounds, expecting to hear which breath sounds bilaterally? - Crackles 12. The nurse is collecting data on a client with a diagnosis of right-sided heart failure. The nurse should expect to note which specific characteristic of this condition? - Dependent edema 13. The nurse is checking the neurovascular status of a client who returned to the surgical nursing unit 4 hours ago after undergoing an aortoiliac bypass graft. The affected leg is warm, and the nurse notes redness and edema. The pedal pulse is palpable and unchanged from admission. The nurse interprets that the neurovascular status is which? - Normal, caused by increased blood flow through the leg 14. A client with a diagnosis of rapid rate atrial fibrillation asks the nurse why the health care provider is going to perform carotid massage. The nurse responds that this procedure may stimulate which? - Vagus nerve to slow the heart rate 15. A client is admitted to the hospital with possible rheumatic endocarditis. The nurse should check for a history of which type of infection? - Streptococcal infection 16. A client has an Unna boot applied for treatment of a venous stasis leg ulcer. The nurse notes that the client's toes are mottled, and cool and the client verbalizes some numbness and tingling of the foot. Which interpretation should the nurse make of these findings? - The boot has been applied too tightly. 17. A client with angina complains that the anginal pain is prolonged and severe and occurs at the same time each day, most often in the morning. On further data collection, the nurse notes that the pain occurs in the absence of precipitating factors. How should the nurse best describe this type of anginal pain? - Variant angina 18. The nurse is monitoring a client with an abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA). Which finding is probably unrelated to the AAA? - Hyperactive bowel sounds in the area 19. An emergency department client who complains of slightly improved but unrelieved chest pain for 2 days is reluctant to take a nitroglycerin sublingual tablet offered by the nurse. The client states, "I don't need that—my dad takes that for his heart. There's nothing wrong with my heart." Which description best describes the client's response? - Denial 20. A client is scheduled for a cardiac catheterization using a radiopaque dye. The nurse checks which most critical item before the procedure? - Prior reaction to contrast media 21. A client is scheduled for a dipyridamole thallium scan. The nurse should check to make sure that the client has not consumed which substance before the procedure? - Caffeine 22. An ambulatory clinic nurse is interviewing a client who is complaining of flulike symptoms. The client suddenly develops chest pain. Which question best assists the nurse to discriminate pain caused by a noncardiac problem? - "Does the pain get worse when you breathe in?" 23. A client with myocardial infarction (MI) has been transferred from the coronary care unit (CCU) to the general medical unit with cardiac monitoring via telemetry. The nurse assisting in caring for the client expects to note which type of activity prescribed? -Bathroom privileges and self-care activities 24. The nurse is preparing to care for a client who will be arriving from the recovery room after an above-the-knee amputation. The nurse ensures that which priority item is available for emergency use? -Surgical tourniquet 25. A client is diagnosed with thrombophlebitis. The nurse should tell the client that which prescription is indicated? - Bed rest, with elevation of the affected extremity 26. A client returns to the nursing unit after an above knee amputation of the right leg. In which position should the nurse place the client? - With the foot of the bed elevated 27. The nurse is collecting data from a client about medications being taken, and the client tells the nurse that he is taking herbal supplements for the treatment of varicose veins. The nurse understands that the client is most likely taking which? - Bilberry 28. The nurse is planning to reinforce instructions to a client with peripheral arterial disease about measures to limit disease progression. The nurse should include which items on a list of suggestions to be given to the client? Select all that apply. - Be careful not to injure the legs or feet. - Walk each day to increase circulation to the legs. - Cut down on the amount of fats consumed in the diet. 29. A client is at risk for developing disseminated intravascular coagulopathy (DIC). The nurse should become concerned with which fibrinogen level? - 90 mg/dL 30. A hospitalized client with a history of angina pectoris is ambulating in the corridor. The client suddenly complains of severe substernal chest pain. The nurse should take which action first? - Assist the client to sit or lie down. 31. The nurse notes bilateral 2+ edema in the lower extremities of a client with known coronary artery disease who was admitted to the hospital 2 days ago. Based on this finding, the nurse should implement which action? - Reviews the intake and output records for the last 2 days 32. A client brings the following medications to the clinic for a yearly physical. The nurse realizes which medication has been prescribed to treat heart failure? - Digoxin (Lanoxin) 33. A student nurse is assigned to assist in caring for a client with acute pulmonary edema who is receiving digoxin (Lanoxin) and heparin therapy. The nursing instructor reviews the plan of care formulated by the student and tells the student that which intervention is unsafe? - Restricting the client's potassium intake 34. A client has an inoperable abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA). Which measure should the nurse anticipate reinforcing when teaching the client? - Antihypertensives 35. The nurse finds a client tensing while lying in bed staring at the cardiac monitor. Which is the nurse's best response when the client states, "There sure are a lot of wires around there. I sure hope we don't get hit by lightning!"? - "Yes, this equipment is a little scary. Can we talk about how the cardiac monitor works?" 36. In order to assess the dorsalis pedis pulse of a client diagnosed with arterial vascular disease, the nurse palpates which anatomical location? Refer to figure. - 4 37. The nurse is asked to assist another health care member in providing care to a client who is placed in a modified Trendelenburg's position. The nurse interprets that the client is likely being treated for which condition? - Shock 38. A client is seen in the health care provider's office for a physical examination after experiencing unusual fatigue over the last several weeks. Height is 5 feet, 8 inches, with a weight of 220 pounds. Vital signs are temperature 98.6° F oral, pulse 86 beats per minute, respirations 18 breaths per minute, and blood pressure 184/96 mm Hg. Random blood glucose is 110 mg/dL. In order to best collect relevant data, which question should the nurse ask the client first? - "When was the last time you had your blood pressure checked?" 39. The client scheduled for a right femoropopliteal bypass graft is at risk for compromised tissue perfusion to the extremity. The nurse takes which action before surgery to address this risk? - Marking the location of the pedal pulses on the right leg 40. When preparing a client for a pericardiocentesis, which position does the nurse place the client in? - Supine with the head of bed elevated at a 45- to 60-degree angle 41. For a client diagnosed with pulmonary edema, the nurse establishes a goal to have the client participate in activities that reduce cardiac workload. Which client activities will contribute to achieving this goal? - Using a bedside commode for stools 42. The nurse is caring for a client who is developing pulmonary edema. The client exhibits respiratory distress, but the blood pressure is unchanged from the client's baseline. As an immediate action before help arrives, the nurse should perform which action? - Place the client in high-Fowler's position 43. The nurse has reinforced home care instructions to a client who had a permanent pacemaker inserted. Which educational outcome has the greatest impact on the client's long-term cardiac health? - The ability to take an accurate pulse in either the wrist or neck 44. The clinic nurse is obtaining cardiovascular data on a client. The nurse prepares to check the client's apical pulse and places the stethoscope in which position? - At the midclavicular line at the fifth left intercostal space 45. The nurse is caring for a client who has been admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of angina pectoris. The client is receiving oxygen via nasal cannula at 2 L. The client asks the nurse why the oxygen is necessary. The nurse bases the response on which information? - Deficient oxygenation to heart cells results in angina pectoris pain. 46. The licensed practical nurse (LPN) is assisting in caring for a client with a diagnosis of myocardial infarction (MI). The client is experiencing chest pain that is unrelieved by the administration of nitroglycerin. The registered nurse administers morphine sulfate to the client as prescribed by the health care provider. Following administration of the morphine sulfate, the LPN plans to monitor which indicator(s)? - Respirations and blood pressure 47. A client diagnosed with angina pectoris returns to the nursing unit after experiencing an angioplasty. The nurse reinforces instructions to the client regarding the procedure and home care measures. Which statement by the client indicates an understanding of the instructions? - "I need to adhere to my dietary restrictions." 48. The nurse is caring for a client with a diagnosis of myocardial infarction (MI) and is assisting the client in completing the diet menu. Which beverage does the nurse instruct the client to select from the menu? - Lemonade 49. The nurse is collecting data on a client with a diagnosis of angina pectoris who takes nitroglycerin for chest pain. During the admission, the client reports chest pain. The nurse immediately asks the client which question? - "Where is the pain located?" 50. The nurse has reinforced dietary instructions to a client with coronary artery disease. Which statement by the client indicates an understanding of the dietary instructions? - "I should routinely use polyunsaturated oils in my diet." 51. The nurse is assisting in caring for a client in the telemetry unit who is receiving an intravenous infusion of 1000 mL 5% dextrose with 40 mEq of potassium chloride. Which occurrence observed on the cardiac monitor indicates the presence of hyperkalemia? - Tall, peaked T waves 52. The nurse is assisting in caring for a client in the telemetry unit and is monitoring the client for cardiac changes indicative of hypokalemia. Which occurrence noted on the cardiac monitor indicates the presence of hypokalemia? - ST-segment depression 53. While the nurse is involved in preparing a client for a cardiac catheterization, the client says, "I don't want to talk with you. You're only the nurse. I want my doctor." Which response by the nurse should be therapeutic? - "So you're saying that you want to talk to your health care provider?" 54. The nurse reinforces instructions to a client at risk for thrombophlebitis regarding measures to minimize its occurrence. Which statement by the client indicates an understanding of this information? - "I should avoid sitting in one position for long periods of time." 55. A client with a history of angina pectoris tells the nurse that chest pain usually occurs after going up two flights of stairs or after walking four blocks. The nurse interprets that the client is experiencing which type of angina? - Stable 56. The nurse is teaching the client with angina pectoris about disease management and lifestyle changes that are necessary in order to control disease progression. Which statement by the client indicates a need for further teaching? - "It is best to exercise once a week for an hour." 57. The nurse is working with a client who has been diagnosed with Prinzmetal's (variant) angina. The nurse plans to reinforce which information about this type of angina when teaching the client? - Prinzmetal's angina is generally treated with calcium channel blocking agents. 58. The nurse working in a long-term care facility is collecting data from a client experiencing chest pain. The nurse should interpret that the pain is likely a result of myocardial infarction (MI) if which observation is made by the nurse? - The pain has not been unrelieved by rest and nitroglycerin tablets. 59. The nurse is discussing smoking cessation with a client diagnosed with coronary artery disease (CAD). Which statement should the nurse make to the client to try to motivate the client to quit smoking? - "If you quit now, your risk of cardiovascular disease will decrease to that of a nonsmoker in 3 to 4 years." 60. A client with heart failure is scheduled to be discharged to home with digoxin (Lanoxin) and furosemide (Lasix) as ongoing prescribed medications. The nurse teaches the client to report which sign/symptom that indicates the medications are not producing the intended effect? - Weight gain of 2 to 3 pounds in a few days 61. A client has experienced an episode of pulmonary edema. The nurse determines that the client's respiratory status is improving if which breath sounds are noted? - Crackles in the lung bases 62. A client in pulmonary edema has a prescription to receive morphine sulfate intravenously. The licensed practical nurse assisting in caring for the client determines that the client experienced an intended effect of the medication if which is noted? - Relief of apprehension 63. The nurse is providing discharge teaching for a post– myocardial infarction (MI) client who will be taking 1 baby aspirin a day. The nurse determines that the client understands the use of this medication if the client makes which statement? - "I will take this medication every day." 64. The nurse determines that a client with coronary artery disease (CAD) needs further teaching about disease management if the client makes which statement? - "I will avoid walking for exercise." 65. An older client with ischemic heart disease has experienced an episode of dizziness and shortness of breath. The nurse reviews the plan of care and notices documentation of decreased cardiac output, dyspnea, and syncopal episodes. The nurse plans to take which important action? - Place the client on a cardiac monitor. 66. The nurse is planning adaptations needed for activities of daily living for a client with cardiac disease. The nurse should incorporate which instruction in discussion with the client? - Take in adequate daily fiber to prevent straining during a bowel movement. 67. An adult client just admitted to the hospital with heart failure also has a history of diabetes mellitus. The nurse calls the health care provider to verify a prescription for which medication that the client was taking before admission? - Chlorpropamide 68. Acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) is prescribed for a client before a percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA). When the nurse takes the aspirin to the client, the client asks the nurse about its purpose. What is the purpose of the aspirin? - To prevent the formation of clots 69. The nurse is caring for a client with coronary artery disease, and a topical nitrate is prescribed for the client. Why is acetaminophen (Tylenol) usually prescribed to be taken before the administration of the topical nitrate? - Headache is a common side effect of nitrates. 70. The nurse is assisting in developing a plan of care for a client who will be returning to the nursing unit following a cardiac catheterization via the femoral approach. Which nursing intervention should be included in the postprocedure plan of care? - Encourage the client to increase fluid intake. 71. The nurse is reinforcing dietary instructions to a client with heart failure (HF). The nurse determines that the client understands the instructions if the client states that which food item will be avoided? - Catsup 72. A client seeks medical attention for intermittent episodes in which the fingers of both hands become cold, pale, and numb. The client states that they then become reddened and swollen with a throbbing, achy pain and Raynaud's disease is diagnosed. Which factor would precipitate these episodes? - Ingestion of coffee or chocolate 73. A client is admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of pericarditis. The nurse reviews the client's record for which sign or symptom that differentiates pericarditis from other cardiopulmonary problems? - Pericardial friction rub 74. The nurse is beginning to ambulate a client with activity intolerance caused by bacterial endocarditis. The nurse determines that the client is best tolerating ambulation if which parameter is noted? - Blood pressure that increases from 114/82 to 118/86 mm Hg 75. The nurse is assisting a hospitalized client who is newly diagnosed with coronary artery disease (CAD) to make appropriate selections from the dietary menu. The nurse encourages the client to select which meal? - Fresh strawberries, steamed vegetables, and baked fish 76. A client with known coronary artery disease (CAD) begins to experience chest pain while getting out of bed. The nurse should take which action? - Have the client stop and lie back down in bed. 77. The nurse is setting up the bedside unit for a client being admitted to the nursing unit from the emergency department with a diagnosis of coronary artery disease (CAD). The nurse should place highest priority on making sure that which is available at the bedside? - Oxygen tubing and flowmeter 78. The nurse determines that a client with coronary artery disease (CAD) understands disease management if the client makes which statement? - "I will walk for one-half hour daily." 79. A client has just completed an information session about measures to minimize the progression of coronary artery disease (CAD). Which statement indicates an initial understanding of lifestyle alterations? - I should eat a diet that is low in fat and cholesterol. 80. The nurse is collecting data on a client who was just admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of coronary artery disease (CAD). The client reveals having been under a great deal of stress recently. Which should the nurse do next? - Explore with the client the sources of stress in life. 81. A client with a diagnosis of myocardial infarction has a new activity prescription allowing the client to have bathroom privileges. As the client stands and begins to walk, the client begins to complain of chest pain. The nurse should take which action? - Assist the client to get back into bed. 82. A client being seen in the emergency department for complaints of chest pain confides in the nurse about regular use of cocaine as a recreational drug. The nurse takes which important action in delivering holistic nursing care to this client? - Teaches about the effects of cocaine on the heart and offers referral for further help 83. The nurse is reinforcing instructions to a client with angina pectoris about measures to reduce recurrence of chest pain. The nurse should stress to the client the importance of taking which measure? - Avoiding exposure to either very hot or very cold weather 84. The nurse is planning measures to decrease the incidence of chest pain for a client with angina pectoris. The nurse should do which intervention to effectively accomplish this goal? - Provide a quiet and low-stimulus environment. 85. A client in a long-term care facility who has a history of angina pectoris wants to go for a short walk outside with a family member. It is a sunny but chilly December day. The nurse should perform which intervention to care for this client in a holistic manner? - Instruct the family member to dress the client warmly before going outside. 86. The nurse carries out a standard prescription for a stat electrocardiogram (ECG) on a client who has an episode of chest pain. The nurse should take which action next? - Give sublingual nitroglycerin (Nitrostat) per the health care provider's prescriptions. 87. A client admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of myocardial infarction (MI) tells the nurse that the pain likely resulted from the fried chicken sandwich that the client had for lunch. The nurse's response is based on which fact? - Denial is a common occurrence early after MI. 88. The nurse is preparing to provide a therapeutic environment for a client who recently had a myocardial infarction (MI). Which are characteristics of a therapeutic environment? - Low stimulus, low stress 89. A client who experienced a myocardial infarction (MI) tells the nurse that he is fearful about not being able to return to a normal life. Which action by the nurse is therapeutic at this time? - Explore the specific concerns with the client. 90. A client complaining of chest pain has an as-needed (PRN) prescription for sublingual nitroglycerin (Nitrostat). Before administering the medication to the client, the nurse should first check which? - Blood pressure 91. A client who has undergone femoropopliteal bypass grafting says to the nurse, "I hope I don't have any more problems that could make me lose my leg. I'm so afraid that I'll have gone through this for nothing." Which is an appropriate nursing response? - "You are concerned about losing your leg?" 92. The nurse is teaching a hospitalized client who has had aortoiliac bypass grafting about measures to improve circulation. The nurse should tell the client to do which? - Keep the ankles uncrossed. 93. A client is admitted to the hospital with possible rheumatic heart disease. The nurse collects data from the client and checks the client for which signs/symptoms? - Fever and sore throat 94. A client with infective endocarditis is at risk for heart failure. The nurse monitors the client for which signs and symptoms of heart failure? - Lung crackles, peripheral edema, and weight gain 95. A client has just returned from the cardiac catheterization laboratory. The left femoral vessel was used as the access site. After returning the client to bed and conducting an initial assessment, the nurse assisting in caring for the client expects the health care provider to write a prescription for the client to remain on bed rest. In which position should the bed be positioned? - With the head of bed elevated no more than 30 degrees 96. The nurse is collecting data from a client with varicose veins. Which finding would the nurse identify as an indication of a potential complication associated with this disorder? - The client complains of leg edema, and skin breakdown has started. 97. A client with coronary artery disease has selected guided imagery to help cope with psychological stress. Which statement by the client indicates understanding of this stress reduction measure? - "The best thing about this is that I can use it anywhere, anytime." 98. A client, who is 36 hours post–myocardial infarction, has ambulated for the first time. The nurse determines that the client best tolerated the activity if which observation is made? - The preactivity pulse rate is 86 beats per minute; the postactivity pulse rate is 94 beats per minute. 99. The nurse is planning a dietary menu for a client with heart failure being treated with digoxin (Lanoxin) and furosemide (Lasix). Which would be the best dinner choice from the daily menu? - Baked pollock, mashed potatoes, and carrot-raisin salad 100. A client has received instructions about an upcoming cardiac catheterization. The nurse determines that the client has the best understanding of the procedure if the client knows to report which symptoms? - Chest pain 101. The nurse is caring for a client diagnosed with Buerger's disease. Which finding should the nurse determine is a potential complication associated with this disease? - Numbness and tingling in the legs 102. The nurse has completed nutritional counseling with an overweight client about weight reduction to modify the risk for coronary artery disease (CAD). The nurse should determine the teaching is successful if the client states that which weight loss goal is safe? - Two pounds per week 103. The nurse has reinforced instructions to the family of an older client who seems anxious about being discharged after cardiac surgery. The nurse understands further teaching is needed if a family member makes which statement? - "A daily half-mile–long brisk walk generally helps people bounce back more quickly and provides more of a sense of control." 104. The nurse monitors the laboratory data on a client at risk for coronary artery disease. A fasting blood glucose reading of 200 mg/dL is recorded on the chart. The nurse analyzes this result as indicative of which finding? - Elevated, signaling the presence of diabetes mellitus, a risk factor of coronary artery disease 105. The nurse has completed counseling about smoking cessation with a client with coronary artery disease (CAD). The nurse determines that the client has understood the material best if the client makes which statement? - "A smoker has twice the risk of having a heart attack as a nonsmoker." 106. The nurse has given simple instructions on preventing some of the complications of bed rest to a client who experienced a myocardial infarction. The nurse should intervene if the client was performing which of these contraindicated activities? - Isometric exercises of the arms and legs 107. A client with a diagnosis of heart failure (HF) is preparing for discharge to home from the hospital. Which condition indicates the client is ready for discharge to home? - The client can verbally describe the daily medications, doses, and times to be administered. 108. A client admitted to the hospital with coronary artery (CAD) disease complains of dyspnea at rest. The nurse determines that which would be of most help to the client? - Elevating the head of the bed to at least 45 degrees 109. The nurse is evaluating the effects of care for the client with deep vein thrombosis. Which limb observations should the nurse note as indicating the least success in meeting the outcome criteria for this problem? - Pedal edema that is 3+ 110. A client is at risk for complications of heart failure. Which is the nurse's priority for early detection of the most likely cause of complications with this client? - Evaluating total body fluid 111. A female client complains of an "odd, left-sided, twinge- like pain" along the anterior axillary line and states she has had this feeling for the past 3 days. Which is the initial action? - Determine if the pain is cardiac in origin. 112. A client's blood pressure is 100/78 mm Hg; the client has tachycardia and is cool and pale. The nurse assists the client to which position to promote tissue oxygenation and alleviate hypoxia? - Semi-Fowler's 113. The nurse notes this rhythm on the client's cardiac monitor. The nurse next reports that the client is experiencing which heart rhythm? Refer to figure. - Atrial fibrillation 114. The client's B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) level is 691 pg/mL. Which intervention should the nurse institute when providing care for the client? - Take daily weights and monitor trends. 115. The nurse is using a stethoscope to listen to the client's heart and hears this sound. (Refer to audio.) To assist in identifying the sound, the nurse should take which initial and best action? - Palpate the carotid pulse for a pulsation. 116. The nurse is caring for a client who has a malignant lung neoplasm and has developed cardiopulmonary complications. On auscultation, the nurse hears these breath sounds over the left lower sternal border (over the apical area) and interprets the sounds as which? (Refer to audio.) - Pericardial friction rub 117. The nurse is auscultating a client's heart sounds and hears these sounds. (Refer to audio.) The nurse identifies these as being produced during which phase of the cardiac cycle? - Passive filling phase of ventricles 118. A hypertensive client who has been taking metoprolol (Lopressor) has been prescribed to decrease the dose of the medication. The client asks the nurse why this must be done over a period of 1 to 2 weeks. In formulating a response, the nurse incorporates the understanding that abrupt withdrawal could affect the client in which way? - Precipitate rebound hypertension 119. A client is admitted to the hospital with a venous stasis leg ulcer. The nurse inspects the ulcer expecting to note which observation? - The ulcer has a brownish or "brawny" appearance. 120. A client has just returned from the cardiac catheterization laboratory. The left femoral vessel was used as the access site. After returning the client to bed, the nurse places a sign above the bed stating that the client should remain on bed rest and in which position? -With the head of the bed elevated no more than 15 degrees 121. A client's serum calcium level is 7.9 mg/dL. The nurse is immediately concerned, knowing that this level could lead to which complication? - Cardiac arrest 122. A client has a history of left-sided heart failure. The nurse should look for the presence of which finding to determine whether the problem is currently active? - Bilateral lung crackles 123. The nurse is told during shift report that a client is having occasional ventricular dysrhythmias. The nurse reviews the client's laboratory results, recalling that which electrolyte imbalance could be responsible for this development? - Hypokalemia 124. A licensed practical nurse (LPN) is assisting in the care of a client who is having central venous pressure (CVP) measurements taken by the registered nurse (RN). The LPN should assist the RN by placing the bed in which position for the reading? - Flat 125. The nurse is assisting a client who will wear a Holter monitor for continuous cardiac monitoring over the next 24 hours. The nurse takes which action to assist the client? - Gives the client a device holder to wear around the waist 126. A client is admitted with an arterial ischemic leg ulcer. The nurse expects to note that this ulcer has which typical characteristic? - Deep and painful 127. The nurse is assisting in the care of a client with myocardial infarction who should reduce intake of saturated fat and cholesterol. The nurse should help the client comply with diet therapy by selecting which food items from the dietary menu? - Baked haddock, steamed broccoli, herbed rice, sliced strawberries 128. The nurse is assisting a client admitted to the hospital with pulmonary edema to prepare for discharge. The nurse should reinforce with the client the importance of complying with which measure to prevent a recurrence? - Weigh self every morning before breakfast. 129. The nurse is assisting in the care of a client diagnosed with rheumatic heart disease. The nurse should reinforce instructions to the client to notify the dentist before dental procedures for which reason? - The client requires prophylactic antibiotics before treatment. 130. A client with a history of angina pectoris complains of substernal chest pain. The nurse checks the client's blood pressure and administers nitroglycerin 0.4 mg sublingually. Five minutes later, the client is still experiencing chest pain. If the blood pressure is still stable, the nurse should take which action next? - Administer another nitroglycerin tablet. 131. The health care provider is discharging a client with a diagnosis of chronic heart failure. Which health maintenance instructions should the nurse reinforce in the discharge teaching plan? Select all that apply. - Obtain annual influenza vaccination. - Avoid adding salt to foods or in cooking. - Report a weight gain of 3 or more pounds in a week. 132. The nurse is preparing for a health fair about tobacco use and the development of coronary heart disease. Which information should the nurse include? Select all that apply. - Nicotine decreases oxygen to the heart. - Hypnosis may be helpful to stop smoking. - Avoid exposure to environmental tobacco smoke. 133. The nurse is caring for a client with a new onset of atrial fibrillation. Which prescribed treatments should the nurse expect? Select all that apply. - Digoxin (Lanoxin) - Warfarin (Coumadin) - Electrical cardioversion 134. A client with hyperlipidemia is seen in the clinic for a follow-up visit. Which dietary modifications should the nurse include to lower the risk of coronary heart disease? Select all that apply. - Use liquid vegetable oil. - Increase intake of fruits. - Choose whole grain foods. - Remove skin from poultry. 135. The nurse is caring for a client with left-sided heart failure. Which clinical signs are most important for the nurse to communicate to the health care provider? Select all that apply. - Pink-tinged frothy sputum - Increase in respiratory rate - Auscultation of crackles throughout the lungs 136. The nurse is admitting a client with acute pericarditis who reports chest pain. When planning the client's care, which position should the nurse encourage the client to assume to alleviate the chest pain? Select all that apply. - Sitting up and leaning forward - Head of bed elevated to 45 degrees 137. The health care provider is discharging a client with a diagnosis of primary hypertension. Which health maintenance instructions should the nurse reinforce in the discharge teaching plan? Select all that apply. - Monitor the blood pressure at home. - Restrict sodium intake as prescribed. - Eye examinations with an ophthalmoscope should be routine. - Follow-up appointments for blood pressure checks are important. 138. The nurse is caring for a client in the cardiac care unit with heart disease. The nurse knows that the direction of blood flows through the heart and lungs in which order? Please arrange the blood flow in the direction of flow. All options must be used. - Blood flows to the right atrium from the superior and inferior vena cavae. - Blood flows from the right atrium to the right ventricle via the tricuspid valve. - Blood flows from the right ventricle to the lungs for oxygenation. - Blood flows from the lungs to the left atrium. - Blood flows from the left atrium via the mitral valve to the left ventricle. - Blood flows from the left ventricle to the aorta and then to the systemic circulation. Neurology NCLEX 1. The nurse is reinforcing home-care instructions to a client and family regarding care after cataract removal from the right eye. Which statement made by the client indicates an understanding of the instructions? Answer: "I should not sleep on my right side." 2. The nurse is assisting with caring for a client after a craniotomy. Which is the best position for the client to be placed? Answer: Semi-Fowler's position 3. The nurse is caring for a client following a supratentorial craniotomy, in which a large tumor was removed from the left side. In which position can the nurse safely place the client? Refer to Figures. Answer: A 4. The nurse is preparing to communicate with an older client who is hearing impaired. Which intervention should be implemented initially? Answer: Stand in front of the client. 5. Which intervention should be implemented for the older client with presbycusis who has a hearing loss? Answer: Use low-pitched tones. 6. The nurse is preparing to reinforce a teaching plan for a client who is undergoing cataract extraction with intraocular implant. Which home care measures should the nurse include in the plan? Select all that apply. Answer: To avoid activities that require bending over To place an eye shield on the surgical eye at bedtime To contact the surgeon if a decrease in visual acuity occurs To take acetaminophen (Tylenol) for minor eye discomfort 7. The nurse is assisting in developing a teaching plan for the client with glaucoma. Which instruction should the nurse suggest to include in the plan of care? Answer: Eye medications will need to be administered for the rest of your life. 8. The nurse is assigned to care for a client with a detached retina. Which finding should the nurse expect to be documented in the client's record? Answer: A sense of a curtain falling across the field of vision 9. The nurse is assigned to care for a client with a diagnosis of detached retina. Which finding would indicate that bleeding has occurred as a result of retinal detachment? Answer: Complaints of a burst of black spots or floaters 10. A client arrives in the emergency department after an automobile crash. The client's forehead hit the steering wheel, and a hyphema has been diagnosed. Which position should the nurse prepare to position the client? Answer: On bed rest in a semi-Fowler's position 11. A client sustains a contusion of the eyeball after a traumatic injury with a blunt object. The nurse should take which immediate action? Answer: Apply ice to the affected eye. 12. A client sustains a chemical eye injury from a splash of battery acid. The nurse should prepare the client for which immediate measure? Answer: Irrigating the eye with sterile normal saline 13. The nurse is caring for a client after enucleation and notes the presence of bright red drainage on the dressing. The nurse should take which appropriate action? Answer: Report the finding to the registered nurse (RN). 14. The nurse is preparing to administer eardrops to an adult client. The nurse administers the eardrops by which technique? Answer: Pulling the pinna up and back 15. The nurse is caring for a client who is hearing-impaired and should take which approach to facilitate communication? Answer: Speak in a normal tone. 16. A client arrives at the emergency department with a foreign body in the left ear that has been determined to be an insect. Which initial intervention should the nurse anticipate to be prescribed? Answer: Instillation of mineral oil or diluted alcohol 17. The nurse notes that the health care provider has documented a diagnosis of presbycusis on the client's chart. The nurse understands that this condition is accurately described as which? Answer: A sensorineural hearing loss that occurs with aging 18. A client with Ménière's disease is experiencing severe vertigo. The nurse reinforces instructions to the client to do which to assist in controlling the vertigo? Answer: Avoid sudden head movements. 19. The nurse is assigned to care for a client hospitalized with Ménière's disease. The nurse expects that which would most likely be prescribed for the client? Answer: Low-sodium diet 20. A client is diagnosed with glaucoma. Which data gathered by the nurse indicate a risk factor associated with glaucoma? Answer: Cardiovascular disease 21. Betaxolol hydrochloride (Betoptic) eyedrops have been prescribed for the client with glaucoma. Which nursing action is most appropriate related to monitoring for the side/adverse effects of this medication? Answer: Monitoring blood pressure 22. The nurse assists to prepare the client for ear irrigation as prescribed by the health care provider. Which action should the nurse plan to take? Answer: Warm the irrigating solution to 98° F. 23. In preparation for cataract surgery, the nurse is to administer cyclopentolate (Cyclogyl) eyedrops. The nurse administers the eyedrops knowing that the purpose of this medication is which? Answer: Dilate the pupil of the operative eye. 24. The nurse is providing instructions to a client who will be self- administering eyedrops. To minimize the systemic effects that eyedrops can produce, the client is instructed to perform which? Answer: Occlude the nasolacrimal duct with a finger over the inner canthus for 30 to 60 seconds after instilling the drops. 25. The client is receiving an eyedrop and an eye ointment to the right eye. Which action should the nurse take? Answer: Administer the eyedrop first, followed by the eye ointment. 26. The nurse is caring for a client with glaucoma. Which medication prescribed for the client should the nurse question? Answer: Atropine sulfate (Isopto Atropine) 27. The nurse is preparing to administer eyedrops. Which interventions should the nurse take to administer the drops? Select all that apply. Answer: Wash hands. Put on gloves. Place the drop in the conjunctival sac. Pull the lower lid down against the cheekbone. 28. A client was just admitted to the hospital to rule out a gastrointestinal (GI) bleed. The client has brought several bottles of medications prescribed by different specialists. During the admission assessment, the client states, "Lately, I have been hearing some roaring sounds in my ears, especially when I am alone." Which medication should the nurse determine to be the cause of the client's complaint? Answer: Acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) 29. Pilocarpine hydrochloride (Isopto Carpine) is prescribed for the client with glaucoma. Which medication should the nurse plan to have available in the event of systemic toxicity? Answer: Atropine sulfate 30. A miotic medication has been prescribed for the client with glaucoma. The client asks the nurse about the purpose of the medication. The nurse should tell the client which? Answer: "The medication causes the pupil to constrict and will lower the pressure in the eye." 31. A client with a seizure disorder is being admitted to the hospital. Which should the nurse plan to implement for this client? Select all that apply. Answer: Pad the bed's side rails. Place an airway at the bedside. Place oxygen equipment at the bedside. Place suction equipment at the bedside. 32. The nurse is caring for a client with increased intracranial pressure (ICP). Which change in vital signs would occur if ICP is rising? Answer: Increasing temperature, decreasing pulse, decreasing respirations, increasing BP 33. The nurse observes the unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) positioning the client with increased intracranial pressure (ICP). Which position would require intervention by the nurse? Answer: Head turned to the side 34. The client recovering from a head injury is arousable and participating in care. The nurse determines that the client understands measures to prevent elevations in intracranial pressure (ICP) if the nurse observes the client doing which activity? Answer: Exhaling during repositioning 35. The client has clear fluid leaking from the nose after a basilar skull fracture. The nurse determines that this is cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) if the fluid meets which criteria? Answer: Separates into concentric rings and tests positive for glucose 36. The client is admitted to the hospital for observation with a probable minor head injury after an automobile crash. The nurse expects the cervical collar will remain in place until which time? Answer: The health care provider reviews the x-ray results. 37. The client was seen and treated in the emergency department (ED) for a concussion. Before discharge, the nurse explains the signs/symptoms of a worsening condition. The nurse determines that the family needs further teaching if they state they will return to the ED if the client experiences which sign/symptom? Answer: Minor headache 38. The nurse is caring for a client who has undergone craniotomy with a supratentorial incision. The nurse should plan to place the client in which position postoperatively? Answer: Head of bed elevated 30 to 45 degrees, head and neck midline 39. The client with a cervical spine injury has Crutchfield tongs applied in the emergency department. The nurse should perform which essential action when caring for this client? Answer: Comparing the amount of prescribed weights with the amount in use 40. The nurse has provided discharge instructions to a client with an application of a halo device. The nurse determines that the client needs further teaching if which statement is made? Answer: "I will drive only during the daytime." 41. The nurse is caring for the client who has suffered spinal cord injury. The nurse further monitors the client for signs of autonomic dysreflexia and suspects this complication if which sign/symptom is noted? Answer: Severe, throbbing headache 42. The client with spinal cord injury is prone to experiencing autonomic dysreflexia. The least appropriate measure to minimize the risk of autonomic dysreflexia is which action? Answer: Limiting bladder catheterization to once every 12 hours 43. The client with spinal cord injury suddenly experiences an episode of autonomic dysreflexia. After checking vital signs, which immediate action should the nurse take? Answer: Raise the head of the bed and remove the noxious stimulus. 44. The nurse is assigned to care for an adult client who had a stroke and is aphasic. Which interventions should the nurse use for communicating with the client? Select all that apply. Answer: Face the client when talking. Speak slowly and maintain eye contact. Use gestures when talking to enhance words. Give the client directions using short phrases and simple terms. 45. The nurse is admitting a client with Guillain-Barré syndrome to the nursing unit. The client has an ascending paralysis to the level of the waist. Knowing the complications of the disorder, the nurse should bring which items into the client's room? Answer: Electrocardiographic monitoring electrodes and intubation tray 46. The nurse is attempting to communicate with a hearing-impaired client. Which strategy by the nurse would be least helpful when talking to this client? Answer: Smiling continuously during conversation 47. The nurse is reviewing the record of a client with mastoiditis. The nurse should expect to note which documented characteristic regarding the results of the otoscopic examination? Answer: Red, dull, thick, and immobile tympanic membrane 48. A client is diagnosed with a disorder involving the inner ear. The nurse caring for the client understands that which is the most common client complaint associated with a disorder involving the inner ear? Answer: Tinnitus 49. The nurse is reviewing the health care record of a client with a diagnosis of otosclerosis. The nurse should expect to note documentation of which early symptom of this disorder? Answer: Ringing in the ears 50. The nurse provides discharge instructions to the client who was hospitalized for an acute attack of Ménière's disease. Which statement made by the client indicates a need for further teaching? Answer: "It is not necessary to restrict salt in my diet." 51. The nurse is reinforcing instructions to a client regarding the use of a hearing aid. Which statement by the client indicates a need for further teaching? Answer: "I should turn the hearing aid off after removing it from my ear." 52. Tonometry is performed on the client with a suspected diagnosis of glaucoma. The nurse reviews the test and determines that the intraocular pressure is normal if which result is noted? Answer: 15 mm Hg 53. The nurse is assisting in developing a plan of care for the client scheduled for cataract surgery. The nurse makes suggestions regarding the plan, knowing that which problem is specifically associated with this type of surgery? Answer: Sensory perceptual alteration 54. The nurse is reviewing the health record of a client diagnosed with a cataract. The initial sign/symptom that the nurse should expect to note in the early stages of cataract formation is which? Answer: Blurred vision 55. The nurse is assigned to care for a client following a cataract extraction. The nurse plans to place the client in which position? Answer: On the nonoperative side 56. During the early postoperative stage, the cataract extraction client complains of nausea and severe eye pain over the operative site. Which action should the nurse implement? Answer: Report the client's complaints. 57. The nurse is caring for a client with an intracranial aneurysm who was previously alert. Which finding should be an early indication that the level of consciousness (LOC) is deteriorating? Answer: Drowsiness 58. The nurse is planning to put aneurysm precautions in place for the client with a cerebral aneurysm. Which item should be included as part of the precautions? Answer: Maintaining the head of the bed at 15 degrees 59. The nurse is caring for a client who begins to experience seizure activity while in bed. Which action by the nurse would be contraindicated? Answer: Restrain the client's limbs. 60. The nurse is planning care for the client with hemiparesis of the right arm and leg. Where should the nurse plan to place objects needed by the client? Answer: Within the client's reach, on the left side 61. The nurse is reinforcing instructions to the family of a stroke client who has homonymous hemianopsia about measures to help the client overcome the deficit. The nurse determines that the family understands the measures to use if they state that they will do which? Answer: Remind the client to turn the head to scan the lost visual field. 62. A client has experienced an episode of myasthenic crisis. The nurse collects data to determine whether the client has experienced which precipitating factor? Answer: Omitted doses of medication 63. A client with Parkinson's disease is embarrassed about the symptoms of the disorder and is bored and lonely. The nurse should plan which approach as therapeutic in assisting the client to cope with the disease? Answer: Encourage and praise perseverance in exercising and performing ADL. 64. The nurse has given suggestions to the client with trigeminal neuralgia about strategies to minimize episodes of pain. The nurse determines that the client needs further teaching if the client made which statement? Answer: "I will try to eat my food either very warm or very cold." 65. A client has an impairment of cranial nerve II. Specific to this impairment, the nurse plans to do which to ensure client safety? Answer: Provide a clear path for ambulation without obstacles. 66. The nurse reinforces home care instructions to a client after cataract removal and placement of an intraocular implant in the right eye. Which statement by the client indicates a need for further teaching? Answer: "I need to remove the eye dressing as soon as I get home and place a warm pack on my eye." 67. The nurse provides dietary instructions to a client with Ménière's disease. The nurse tells the client that which food or fluid item is acceptable to consume? Answer: Sugar-free Jell-O 68. The nurse is caring for a client who will be undergoing surgical treatment for Ménière's disease. The nurse plans care based on which expected outcome? Answer: The surgery relieves pressure from accumulation of inner ear fluid in the endolymphatic sac. 69. A clinic nurse notes that following several eye examinations the health care provider has documented a diagnosis of legal blindness in the client's chart. Which should the nurse expect to note documented as the result of the Snellen chart test? Answer: 20/200 vision 70. The nurse is assigned to administer the prescribed eye drops for a client preparing for cataract surgery. Which type of eye drops should the nurse expect to be prescribed? Answer: A mydriatic medication 71. A client is being discharged from the ambulatory care unit following cataract removal, and the nurse provides instructions regarding home care. Which statement by the client indicates an understanding of the instructions? Answer: "I will wear my eye shield at night and my glasses during the day." 72. A client with glaucoma asks the nurse if complete vision will return. The nurse should make which response to the client? Answer: "Although some vision has been lost and cannot be restored, further loss may be prevented by adhering to the treatment plan." 73. A client with retinal detachment is admitted to the outpatient nursing unit in preparation for a scleral buckling procedure. Which prescription should the nurse anticipate? Answer: Placing an eye patch over the client's affected eye 74. The nurse should check for vision loss in a client with which condition? Answer: Diabetes mellitus 75. The nurse is assisting the health care provider with performing a Weber tuning fork test on a client. What does this test assess for? Answer: Hearing loss 76. The nurse is providing discharge instructions for a client who has had a fenestration procedure for the treatment of otosclerosis. Which statement by the client indicates an understanding of the instructions? Answer: "I will take stool softeners as prescribed by my doctor." 77. The nurse is caring for a client following craniotomy for removal of an acoustic neuroma. The nurse understands that assessment of which cranial nerve should identify a complication specifically associated with this surgery? Answer: Cranial nerve VII, facial nerve 78. The nurse is monitoring a client with a blunt head injury sustained from a motor vehicle crash. Which would indicate a basal skull fracture as a result of the injury? Answer: Bloody or clear drainage from the auditory canal 79. The nurse is assigned to care for a client with a diagnosis of Ménière's disease. Which part of the ear is affected with Ménière's disease? Answer: Inner ear 80. Surgery has been recommended for the client with otosclerosis. The client tells the nurse that she would prefer not to have surgery and asks the nurse about alternative methods to improve hearing. The nurse should make which appropriate response to the client? Answer: "A hearing aid may improve your hearing." 81. The nurse is caring for a client hospitalized with an acute attack from Ménière's disease. The client verbalizes concern because the client has experienced a hearing loss as a result of the attack. Which response should the nurse make to the client regarding the hearing loss? Answer: "The attack leaves a hearing loss in the involved ear." 82. The nurse is reviewing the health care provider's prescriptions for a client admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of an acute attack of Ménière's disease. Which prescription noted on the client's chart should the nurse question? Answer: The administration of a vasoconstrictor 83. A client with a diagnosis of otosclerosis is admitted to the ambulatory care unit for stapedectomy, and the nurse reinforces instructions to the client regarding home care following the procedure. Which statement by the client indicates a need for further teaching? Answer: "I need to avoid air travel for at least 6 months." 84. The nurse is reinforcing discharge instructions with a client who is being discharged following a fenestration procedure for the treatment of otosclerosis. Which should be included on the list of instructions prepared for the client? Answer: "You need to avoid air travel." 85. A myringotomy is performed on a client in the ambulatory care center. The ambulatory care nurse calls the client 24 hours after the procedure to evaluate the status of the client. The client reports to the nurse that a small amount of brownish drainage has been coming from the ear. Which instruction should the nurse provide to the client? Answer: "Continue to monitor the drainage because this is normal and may occur for 24 to 48 hours following the surgery." 86. A client has a cerebellar lesion. The nurse determines that the client is adapting successfully to this problem if the client demonstrates proper use of which item? Answer: Walker 87. The nurse is planning care for a client who displays confusion secondary to a neurological problem. Which approach by the nurse would be least helpful in assisting this client? Answer: Encouraging multiple visitors at one time 88. A client with a neurological impairment experiences urinary incontinence. Which nursing action should help the client adapt to this alteration? Answer: Establishing a toileting schedule 89. The nurse has obtained a personal and family history from a client with a neurological disorder. Which finding in the client's history is least likely associated with a risk for neurological problems? Answer: Allergy to pollen 90. A client with right leg hemiplegia is experiencing difficulty with mobility. The nurse determines that the family needs reinforcement of teaching if the nurse observes which action by the family? Answer: Encouraging the client to stand unassisted on the leg 91. The nurse is preparing a client who is scheduled to have cerebral angiography performed. Which should the nurse check before the procedure? Answer: Allergy to iodine or shellfish 92. A client admitted to the hospital with a neurological problem indicates to the nurse that magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be done. Which finding noted in the client history indicates that the client may be ineligible for this diagnostic procedure? Answer: Prosthetic valve replacement 93. A client is somewhat nervous about having magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Which statement by the nurse should provide reassurance to the client about the procedure? Answer: "Even though you are alone in the scanner, you will be in voice communication with the technologist during the procedure." 94. The nurse is trying to help the family of an unconscious client cope with the situation. Which intervention should the nurse plan to incorporate into the care routine for the client? Answer: Explaining equipment and procedures on an ongoing basis 95. The nurse is suctioning an unconscious client who has a tracheostomy. The nurse should avoid which action during this procedure? Answer: Making sure not to suction for longer than 30 seconds 96. The nurse has applied a hypothermia blanket to a client with a fever. The nurse should inspect the skin frequently to detect which complication of hypothermia blanket use? Answer: Skin breakdown 97. The nurse is caring for an unconscious client who is experiencing persistent hyperthermia with no signs and symptoms of infection. The nurse understands that there may be damage to the client's thermoregulatory center which is located in which part of the brain? Answer: Hypothalamus 98. A client seeking treatment for an episode of hyperthermia is being discharged to home. The nurse determines that the client needs clarification of discharge instructions if the client makes which statement? Answer: "I can resume a full activity level immediately." 99. The family of an unconscious client with increased intracranial pressure is talking at the client's bedside. They are discussing the gravity of the client's condition and wondering if the client will ever recover. How should the nurse interpret the client's situation? Answer: It is possible the client can hear the family. 100. The nurse is providing care to a client with increased intracranial pressure (ICP). Which approaches would be beneficial in controlling the client's ICP from an environmental viewpoint? Select all that apply. Answer: Reducing environmental noise Maintaining a calm atmosphere Allowing the client uninterrupted time for sleep 101. The nurse is preparing to give the postcraniotomy client medication for incisional pain. The family asks the nurse why the client is receiving codeine sulfate and not "something stronger." The nurse should formulate a response based on which understanding of codeine? Answer: Codeine does not alter respirations or mask neurological signs as do other opioids. 102. The nurse reinforces home care instructions to the postcraniotomy client. Which statement by the client indicates the need for further teaching? Answer: "I will not hear sounds clearly unless they are loud." 103. The nurse notes documentation that a postcraniotomy client is having difficulty with body image. The nurse determines that the client is still working on the postoperative outcome criteria when the client indicates which altered personal appearance? Answer: Indicates that facial puffiness will be a permanent problem 104. A client with spinal cord injury becomes angry and belligerent whenever the nurse tries to administer care. Which is the best response by the nurse? Answer: Acknowledge the client's anger and continue to encourage participation in care. 105. A client with a spinal cord injury expresses little interest in food and is very particular about the choice of meals that are actually eaten. How should the nurse interpret this? Answer: Meal choices represent an area of client control and should be encouraged as much as is nutritionally reasonable. 106. A client who is paraplegic after spinal cord injury has been taught muscle-strengthening exercises for the upper body. The nurse determines that the client will derive the least muscle-strengthening benefit from which activity? Answer: Doing active range of motion to finger joints 107. A client with diplopia has been taught to use an eye patch to promote better vision and prevent injury. The nurse determines that the client understands how to use the patch if the client states that he or she will do which? Answer: Wear the patch continuously, alternating eyes each day. 108. The nurse is planning care for a client in spinal shock. Which action would be least helpful in minimizing the effects of vasodilation below the level of the injury? Answer: Moving the client quickly as one unit 109. The nursing instructor asks a nursing student about the points to document if the client has had a seizure. The instructor determines that the student needs to research seizures and related documentation points if the student states which assessment is important? Answer: Client's diet in the 2 hours preceding seizure activity 110. The nurse is planning to institute seizure precautions for a client who is being admitted from the emergency department. Which measure should the nurse avoid in planning for the client's safety? Answer: Putting a padded tongue blade at the head of the bed 111. The nurse has given medication instructions to the client receiving phenytoin (Dilantin). The nurse determines that the client understands the instructions if the client makes which comment? Answer: "Good oral hygiene is needed, including brushing and flossing." 112. A client with a stroke (brain attack) has residual dysphagia. When a diet prescription is initiated, the should nurse avoid which action? Answer: Giving the client thin liquids 113. The nurse is trying to communicate with a stroke (brain attack) client with aphasia. Which action by the nurse would be least helpful to the client? Answer: Completing the sentences that the client cannot finish 114. A client receives a dose of edrophonium (Enlon). The client shows improvement in muscle strength for a period of time following the injection. The nurse should interpret this finding as indicative of which disease process? Answer: Myasthenia gravis 115. A client with myasthenia gravis is having difficulty speaking. The client's speech is dysarthric and has a nasal tone. The nurse should use which communication strategies when working with this client? Select all that apply. Answer: Listening attentively Asking yes and no questions when able Using a communication board when necessary Repeating what the client said to verify the message 116. The nurse is teaching the client with myasthenia gravis about prevention of myasthenic and cholinergic crises. The nurse tells the client that this is most effectively done by which activity? Answer: Taking medications on time to maintain therapeutic blood levels 117. The nurse has instructed the client with myasthenia gravis about ways to manage his or her own health at home. The nurse determines that the client needs further teaching if the client makes which statements? Answer: "Going to the beach will be a nice, relaxing form of activity." 118. A client with Parkinson's disease is experiencing a parkinsonian crisis. The nurse should immediately place the client where? Answer: In a quiet, dim room with respiratory and cardiac support available 119. The nurse has given instructions to the client with Parkinson's disease about maintaining mobility. The nurse determines that the client understands the directions if the client states that he or she will perform which activity? Answer: Rock back and forth to start movement with bradykinesia. 120. An adult client had a cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis after lumbar puncture. The nurse interprets that a negative value of which is consistent with normal findings? Answer: Red blood cells 121. The nurse is collecting data on a client with a diagnosis of meningitis and notes that the client is assuming this posture. (Refer to figure.) The nurse contacts the health care provider and reports that the client is exhibiting which? Answer: Opisthotonos 122. An older gentleman is brought to the emergency department by a neighbor who heard him talking and wandering in the street at 3 am. The nurse should first determine which about the client? Answer: Whether this is a change in his usual level of orientation 123. An 84-year-old client in an acute state of disorientation was brought to the emergency department by the client's daughter. The daughter states that this is the first time that the client experienced confusion. The nurse determines from this piece of information that which is unlikely to be the cause of the client's disorientation? Answer: Alzheimer's disease 124. A resident in a long-term care facility prepares to walk out into a rainstorm after saying, "My father is waiting to take me for a ride." An appropriate response by the nurse is which? Answer: "I'm glad you told me that. Let's have a cup of coffee and you can tell me about your father." 125. The nurse observes that a client with Parkinson's disease has very little facial expression. The nurse attributes this piece of data to which information? Answer: Masklike facies is a component of Parkinson's disease. 126. The nurse is communicating with a client who is hard of hearing in both ears. To facilitate communication with this client, the nurse should perform which? Answer: Lower the voice pitch and face the client when speaking. 127. The nurse overhears the term sundowning used to describe the behavior of a client newly admitted to the nursing unit during the previous evening shift. Of which diagnosis is sundowning a symptom? Answer: Alzheimer's disease 128. The nurse has reinforced discharge instructions to the client who has had ocular surgery of the right eye. The nurse determines that the client needs further teaching if the client states which? Answer: "I will call the health care provider if a temperature of 99° F is present." 129. A client with glaucoma has suffered significant eye damage before diagnosis and now has impaired vision. The nurse determines that the client needs further assistance in adapting to this situation if the client makes which statement? Answer: "There is no difficulty driving at dusk." 130. A client in the emergency department is diagnosed with Bell's palsy. The nurse collecting data on this client expects to note which observation? Answer: A lag in closing the bottom eyelid 131. An adult client with suspected meningitis has undergone lumbar puncture to obtain cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) for analysis of a bacterial infection. The nurse checks for which value indicating a bacterial infection of the CSF? Answer: Decreased glucose level 132. A client reports to the health care clinic for an eye examination, and a diagnosis of primary open-angle glaucoma is suspected. Which question will elicit information regarding the signs/symptoms associated with this disorder? Answer: "Have you had difficulty with peripheral vision?" 133. The nurse is preparing to reinforce instructions to a client with glaucoma regarding the prescribed treatment measures for the disorder. The nurse prepares the instructions based on which treatment goal? Answer: Maintaining intraocular pressure at a reduced level 134. The nurse in the outpatient unit is preparing a client who is scheduled for a laser trabeculoplasty for the treatment of primary open-angle glaucoma. Which instructions should the nurse reinforce to the client? Answer: "You may return to work 1 or 2 days following the procedure." 135. The nurse reinforces instructions to a client with glaucoma regarding measures that will prevent an increase in intraocular pressure in the eyes. Which statement by the client indicates a need for further teaching? Answer: "I can tie my shoelaces by bending over slowly." 136. A clinic nurse is reviewing the record of a client recently diagnosed with a cataract. Which clinical manifestation associated with this disorder should the nurse expect to be documented in the client's record? Answer: Painless, progressive loss of vision 137. Prescriptive glasses are prescribed for a client with bilateral aphakia, and the nurse reinforces instructions to the client regarding the use of the glasses. Which statement by the client indicates the need for further teaching? Answer: "The prescriptive glasses will correct my visual field of sight." 138. A client is brought to the ambulatory care department by the spouse one day following a cataract extraction procedure. A diagnosis of hyphema is made, which occurred as a result of the surgical procedure. The nurse reinforces instructions to the client and spouse regarding the treatment for the complication and makes which statement? Answer: "Maintain bed rest and patching of both eyes." 139. The nurse is reinforcing preoperative instructions to a client scheduled for cataract surgery and prepares a written list of instructions for the client. Which statement by the client indicates a need for further teaching? Answer: "I can drink any liquids that I want to on the morning of the surgery." 140. The nurse collects data from a client with a diagnosis of macular degeneration of the eye. The nurse should expect the client to report which symptom? Answer: Blurred central vision 141. The nurse is reinforcing instructions to a client with a diagnosis of hordeolum regarding the treatment plan. Which instruction should the nurse include in the teaching plan for the client? Answer: Apply a warm compress for 15 minutes four times daily. 142. The nurse in the ambulatory care unit is caring for a client following cataract extraction. The client suddenly complains of nausea and severe eye pain in the surgical eye. The nurse should take which action? Answer: Notify the registered nurse. 143. A client arrives at the emergency department after experiencing a traumatic blow to the eye and a hyphema is diagnosed. In which position should the nurse place the client? Answer: In semi-Fowler's position 144. A client who was hit in the eye with a baseball bat sustains a contusion of the eyeball. The emergency department nurse implements which immediate action? Answer: Applies ice to the affected eye 145. A client arrives in the emergency department with an eye injury caused by metal fragments that hit the eye while the client was drilling into metal. The nurse checks the eye and notes small pieces of metal floating on the eyeball. Which action should the nurse plan to assist with first? Answer: Irrigate the eye with sterile saline. 146. A client arrives in the emergency department with a chemical eye injury. The nurse immediately performs which action? Answer: Irrigates the eye with copious amounts of sterile normal saline 147. The nurse is reviewing the plan of care developed by a nursing student for a client scheduled for keratoplasty. The nurse discusses the plan with the student if which incorrect intervention is listed in the plan? Answer: Administering medications that will dilate the pupil 148. The nurse is providing discharge instructions to a client following a keratoplasty. Which statement by the client indicates the need for further teaching? Answer: "Sutures are removed in 2 weeks." 149. The nurse is caring for a client following enucleation. On data collection, the nurse notes staining and bleeding on the dressing. The nurse should take which action? Answer: Notify the registered nurse. 150. The nurse is monitoring a client with a head injury and notes that the client is assuming the posture shown in the figure. What is the client exhibiting that would require the nurse to notify the registered nurse immediately? Refer to the figure. Answer: Decorticate posturing 151. The nurse is inserting soft contact lenses into the eyes of a client. Which direction does the nurse tell the client to look? Answer: Straight ahead 152. The nurse is providing client and family instructions for a client who has been recently diagnosed with glaucoma. Which statement indicates that the client's family member needs further teaching regarding the eye drop application of pilocarpine hydrochloride (Isopto Carpine)? Select all that apply. Answer: "I should apply the eye drops directly over my family member's pupil." "I have to contact the prescriber if my family member develops a small pupil." "I need to wipe off the tip of the eye drop bottle with a tissue between administrations." 153. The nurse is assisting in caring for a client who sustained a traumatic head injury following a motor vehicle crash. The nurse documents that the client is exhibiting decerebrate posturing. The nurse bases this documentation on which observation? Answer: Extension of the extremities and pronation of the arms 154. The nurse is caring for a client diagnosed with Bell's palsy 1 week ago. Which data would indicate a potential complication associated with Bell's palsy? Answer: Excessive tearing 155. The nurse is collecting data on a client suspected of having Alzheimer's disease. The priority data should focus on which characteristic of this disease? Answer: Recent memory loss 156. The nurse is monitoring a client with a C5 spinal cord injury for spinal shock. Which findings would be associated with spinal shock in this client? Select all that apply. Answer: Bowel sounds are absent. The client's abdomen is distended. Respiratory excursion is diminished. Accessory muscles of respiration are areflexic. 157. The nurse is ambulating a client with a known seizure disorder. The client says, "I'm seeing those flashing lights again," then loses consciousness and develops a clonic-tonic seizure. Which would be the nurse's initial action? Answer: Assist the client to the floor. 158. The nurse is collecting data on a client with myasthenia gravis. The nurse determines that the client may be developing myasthenic crisis if the client makes which statement? Answer: "I can't swallow very well today." 159. The nurse is providing client teaching regarding glaucoma. Which instructions are important to include in the teaching plan? Select all that apply. Answer: Follow a low-sodium, minimal-caffeine diet with plenty of fiber. Be sure to report halos of light or increased eye pain to your health care provider. 160. A client arrives at the emergency department following a blow to the eye from a softball. Which intervention should be implemented by the nurse initially? Answer: Apply ice to the affected eye. 161. While at home, the nurse receives a telephone call from a neighbor, who reports that while accidentally breaking a mirror, a piece of glass flew into her eye. Which is the appropriate initial nursing action after observing that the large glass shard is protruding from the neighbor's eye? Answer: Secure a paper cup over the affected eye. 162. A client arrives at the emergency department following an eye injury in which an acid used to clean the brick on the fireplace splashed into the eye. Which question should the nurse ask initially? Answer: "Did you flush the eye following the injury?" 163. The nurse is caring for a client following enucleation. Which postsurgical observation requires immediate attention by the nurse? Answer: Bright red drainage on the dressing 164. Which instruction is appropriate for the nurse to provide to a client who reports via telephone that he is certain an insect has flown into his ear because he can hear it "buzzing"? Answer: Use a flashlight to coax the insect out of the ear. 165. Which statement by the nurse indicates an understanding of the diagnosis of presbycusis? Answer: "It is a sensorineural type of hearing loss that occurs with aging." 166. The nurse determines that the client diagnosed with Ménière's disease understands the reinforced dietary instructions when the client states that which food will be avoided in the diet? Answer: Hot dogs 167. The nurse is assisting in developing a plan of care for a client following the surgical removal of an acoustic neuroma. Which assessment will be included in the plan of care for this specific intervention? Answer: Assessment of cranial nerve VII (facial) 168. A client is being discharged from the ambulatory care unit following cataract removal. Which instruction from the discharge teaching plan should the nurse reinforce? Answer: Take acetaminophen (Tylenol) if any discomfort occurs. 169. The nurse is reinforcing instructions to a client following a cataract extraction on the right eye. Which statement by the client indicates a need for further teaching? Answer: "I need to wear an eye shield all the time." 170. When the nurse documents the results of a Snellen vision test as 20/80 vision, the client asks the nurse to describe what these numbers mean. Which statement is the appropriate response? Answer: "You can read at a distance of 20 feet what a client with normal vision can read at 80 feet." 171. Which information will the nurse reinforce to the client scheduled for a lumbar puncture? Answer: An informed consent will be required. 172. The nurse is reinforcing instructions to a client taking divalproex sodium (Depakote). The nurse tells the client to return to the clinic for follow-up laboratory studies related to which test? Answer: Liver function studies 173. Which data collection finding supports the possible diagnosis of Bell's palsy? Answer: Speech or chewing difficulties accompanied by facial droop 174. The nurse reviews the health care provider's treatment plan for a client with Guillain-Barré syndrome. Which prescription noted in the client's record should the nurse question? Answer: Clear liquid diet 175. A client has a halo vest that was applied following a C6 spinal cord injury. The nurse performs which action to determine whether the client is ready to begin sitting up? Answer: Compares the client's pulse and blood pressure when both flat and sitting 176. A client is admitted to the emergency department with a C4 spinal cord injury. The nurse performs which intervention first when collecting data on the client? Answer: Monitoring the respiratory rate 177. A client with myasthenia gravis is experiencing prolonged periods of weakness. The health care provider prescribes a test dose of edrophonium (Enlon) and the client becomes weaker. The nurse interprets this outcome as indicative of which result? Answer: Cholinergic crisis 178. The nurse is assisting in gathering data on cranial nerve XII of a client who sustained a brain attack (stroke). The nurse understands that the client should be asked to perform which action? Answer: Extend the tongue. 179. The nurse is assisting to perform a Romberg test on a client being seen in the clinic. The nurse performs this test to make which determination? Answer: The ability of the vestibular apparatus in the inner ear 180. A perforated eardrum is suspected in a client who was hit in the ear with a basketball. Which documented observation concerning an otoscopic examination supports this suspicion? Answer: A round or oval darkened area on the eardrum 181. The nurse is assisting in performing a confrontation test on a client seen in the clinic. The nurse understands that this test is performed to check which client ability? Answer: The ability to demonstrate effective peripheral vision 182. The nurse in a health care clinic is assisting to test the client for accommodation. The nurse should ask the client to perform which initial action? Answer: Focus on a distant object. 183. The nurse is reviewing the medical record of a client diagnosed with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Which initial sign/symptom of this disorder supports this diagnosis? Answer: Mild clumsiness 184. The nurse is assisting in caring for a client with a supratentorial lesion. The nurse monitors which criterion as the critical index of central nervous system (CNS) dysfunction? Answer: Level of consciousness 185. The nurse caring for a client following a craniotomy monitors for signs of increased intracranial pressure (ICP). Which indicates an early sign of increased ICP? Answer: Confusion 186. Acetazolamide is prescribed for a client with a diagnosis of a supratentorial lesion. The nurse monitors the client for effectiveness of this medication, knowing which is its primary action? Answer: Decrease cerebrospinal fluid production 187. Which sign/symptom is observed in the clonic phase of a seizure? Answer: Extension spasms of the body 188. The nurse is preparing for the admission of a client with a prescription for seizure precautions. Which supplies will the nurse make available to this client? Select all that apply. Answer: Suction machine Oxygen administration Padding for the side rails Prescribed diazepam (Valium) 189. The nurse is preparing for the admission of a client with a diagnosis of early stage Alzheimer's disease. The nurse assists in developing a plan of care, knowing that which is a characteristic of early Alzheimer's disease? Answer: Forgetfulness 190. The clinic nurse is reviewing the medical record of a client scheduled to be seen in the clinic. The nurse notes that the client is prescribed selegiline hydrochloride (Eldepryl). The nurse understands that this medication is prescribed for which diagnosis? Answer: Parkinson's disease 191. The nurse is reviewing the record of a client with a suspected diagnosis of Huntington's disease. Which documented early symptom supports this diagnosis? Answer: Vertigo 192. The nurse is assisting in caring for a client with a suspected diagnosis of meningitis. The nurse reinforces to the client information regarding which diagnostic test that is commonly used to confirm this diagnosis? Answer: Lumbar puncture 193. The nurse is preparing for the admission of a client with a suspected diagnosis of herpes simplex encephalitis. Which diagnostic test should be prescribed to confirm this diagnosis? Answer: Brain biopsy 194. The nurse is caring for a client with a diagnosis of multiple sclerosis who has been prescribed oxybutynin (Ditropan). The nurse evaluates the effectiveness of the medication by asking the client which question? Answer: "Are you getting up at night to urinate?" 195. The nurse is preparing for the admission of a client with a suspected diagnosis of Guillain-Barré syndrome. Which sign/symptom is considered a primary symptom of this syndrome? Answer: Development of muscle weakness 196. A thymectomy via a median sternotomy approach is performed on a client with a diagnosis of myasthenia gravis. The nurse has assisted in developing a plan of care for the client and includes which nursing action in the plan? Answer: Monitor the chest tube drainage. 197. The nurse is caring for a client with a diagnosis of right (nondominant) hemispheric brain attack (stroke). The nurse notes that the client is alert and oriented to time and place. Based on these findings, the nurse makes which determination? Answer: The client may have perceptual and spatial disabilities. 198. The nurse is preparing to care for a client with a diagnosis of brain attack (stroke). The nurse notes in the client's record that the client has anosognosia. The nurse plans care, knowing which is a characteristic of anosognosia? Answer: The client neglects the affected side. 199. The nurse is preparing a plan of care for a client with a brain attack (stroke) who has global aphasia. The nurse incorporates communication strategies in the plan of care, knowing that the client's speech should fit which characterization? Answer: Associated with poor comprehension 200. The nurse is caring for a client with a diagnosis of brain attack (stroke) with anosognosia. To meet the needs of the client with this deficit, which action does the nurse plan? Answer: Increase the client's awareness of the affected side. 201. The nurse is caring for a client who sustained a spinal cord injury. While administering morning care, the client developed signs and symptoms of autonomic dysreflexia. Which is the initial nursing action? Answer: Elevate the head of the bed. 202. Prescriptive eyeglasses are prescribed for a client with bilateral aphakia. When reinforcing teaching instructions regarding the eyeglasses, the nurse determines the need for further teaching when the client makes which statement? Answer: "My peripheral vision will not be distorted." 203. The nurse has reinforced instructions to a client who is scheduled for a cataract extraction. Which statement by the client indicates a need for further teaching? Answer: "No eating or drinking for at least 18 hours before the surgery." 204. The nurse in the recovery room area is preparing to care for a client following cataract extraction of the right eye. Which position does the nurse prepare to place the client? Answer: On the left side with the head of the bed elevated 205. A client who sustained an eye injury arrives at the emergency department. Which is the initial nursing action? Answer: Obtain a history regarding the cause of the injury. 206. A client arrives at the emergency department for treatment of an injury to the eye after being hit by a baseball bat. On data collection, the nurse notes that the eye is bleeding. Which nursing action is appropriate? Answer: Cover the eye with cold, sterile saline gauze. 207. A client arrives in the emergency department following an eye injury from a chemical solution. Which is the initial nursing action? Answer: Test the eye pH with litmus paper. 208. The nurse is reviewing the preoperative prescriptions of a client scheduled for a keratoplasty. Which prescriptions noted in the client's chart should the nurse question? Answer: Administer medication to dilate the affected pupil. 209. The nurse has reinforced instructions to a client following a right keratoplasty. Which statement by the client indicates a need for further teaching? Answer: "In 1 week, I'll return to have the sutures removed." 210. The nurse caring for a client in the postoperative period following an enucleation notes bloody staining on the surgical eye dressing. Which is the appropriate nursing action? Answer: Contact the health care provider. 211. A client reporting recent right eye discomfort is diagnosed with chalazion of the right eye. The nurse reinforces instructions to the client regarding care to the eye. Which statement by the client indicates an understanding of the measures? Answer: "I should apply warm packs to my eye." 212. The nurse is reinforcing home care instructions to a client who has a hordeolum (sty) of the right eye. Which statement by the client indicates an understanding of the instructions? Answer: "I should apply antibiotic ointment as prescribed." 213. The nurse is assisting the health care provider in performing a caloric test on a client. Following instillation of cool water into the ear, the nurse observes the presence of nystagmus. The nurse should document the findings of this test as indicative of which result? Answer: Normal 214. The nurse is assisting the health care provider in performing a caloric test on a client. Following instillation of warm water into the ear, the client complains of vertigo. The nurse documents the findings of this test as indicative of which result? Answer: Normal 215. The nurse is assisting a health care provider in performing a caloric test on a client. Following instillation of warm water into the ear, the nurse notes that nystagmus does not occur. The nurse should document the findings of this test as indicative of which result? Answer: Positive 216. A caloric test is prescribed for a client suspected of having a disease of the labyrinth. The nurse obtains which essential item in preparation for this test? Answer: An otoscope 217. A nursing instructor asks a student about cochlear implants. The student understands that which clients are candidates for such a procedure? Select all that apply. Answer: A client who has a profound hearing loss in both ears A client who has received no benefit from conventional hearing aids 218. A female client with myasthenia gravis comes to the health care provider's office for a scheduled office visit. The client is very concerned and tells the nurse that her husband seems to be avoiding her because she is very unattractive. Which is the appropriate nursing response? Answer: "Have you thought about sharing your feelings with your husband?" 219. The nurse assigned to care for a hearing-impaired client should use which approach to communication in order to enhance communication and preserve the client's self-esteem? Select all that apply. Answer: Speaking slowly and clearly Standing directly in front of the client while speaking Turning down the volume on the radio or TV when talking 220. The nurse is reinforcing discharge instructions to a client going home after same-day eye surgery. During the postoperative period, the nurse stresses that the client may safely perform which activity? Answer: Watch television. 221. The nurse is reinforcing discharge instructions to a client who has had ocular surgery of the left eye. Which statement by the client indicates a need for further teaching? Answer: "I need to call the doctor if I develop any fever." 222. A client who had previously undergone cataract surgery tells the nurse that she has begun seeing flashing lights and floaters in the eye. Based on the client's history, the nurse interprets that the client is at risk for which? Answer: Detached retina 223. A client diagnosed with primary open-angle glaucoma has been prescribed pilocarpine ophthalmic drops. When the client asks the nurse how this medication lowers intraocular pressure, which information does the nurse tell the client? Answer: The medication increases the outflow of aqueous humor. 224. The nurse interprets that a client diagnosed with glaucoma needs information about the expected effects of this condition when the client makes which statement? Answer: "Taking my daily walk right around dusk each evening has proven to be so enjoyable." 225. The nurse is preparing to instill an otic solution into the adult client's right ear. The nurse should include which action while performing this procedure? Select all that apply. Answer: Pulling the auricle of the right ear upward Pulling the auricle of the right ear backward Warming the solution to room temperature Placing the client in a left side-lying position 226. A client has a diagnosis of presbycusis. The nurse interprets that which behavior indicates that the client has successfully adapted to this disorder? Answer: Agrees to use a prescribed hearing aid, especially when home alone 227. Immediately following cataract repair, the client's affected conjunctiva and eyelids are edematous. Which statement by the nurse accurately characterizes these findings for the client? Answer: "The edema is normal and should subside within 3 days." 228. A client who has undergone cataract removal without an intraocular lens implant is visibly upset because his vision is still blurry. Which action should the nurse perform to provide realistic reassurance to this client? Answer: Explain that vision will improve with adjustment to aphakic lenses. 229. A client with a history of ear problems telephones the ambulatory care nurse to cancel an appointment because he will be away on business. The client mentions that he will be flying during this trip. The nurse advises the client to engage in which activity to prevent barotrauma during takeoff and landing? Select all that apply. Answer: Chewing gum Yawning occasionally Swallowing a few times Sucking on a piece of hard candy 230. A client has had same-day surgery to insert a ventilating tube in the tympanic membrane. The nurse reinforces to the client to be sure to perform which action until the postoperative assessment by the health care provider? Answer: Use a shower cap to protect the ears if taking a shower. 231. An adult client with a history of ear infections reports a right earache accompanied by a sensation of fullness. The client also reports nausea and has a temperature of 100.6° F. The nurse questions the client about which aspect of the client's history? Answer: Whether the client has had a recent upper respiratory infection (URI) 232. A client is recovering at home after suffering a brain attack (stroke) 2 weeks ago. A home caregiver tells the home health nurse that the client has some difficulty swallowing food and fluids. Which nursing action would be appropriate? Answer: Observe the client feeding himself or herself. 233. When reinforcing information to a client regarding how to appropriately care for a new hearing aid, the nurse should provide the client with which instruction? Answer: To check the battery regularly to ensure that it is working before use 234. A client susceptible to motion sickness asks the nurse about the use of medication to prevent an occurrence. The nurse plans to incorporate into the discussion that the medication works effectively if which guideline is followed? Answer: Taking the medication 1 hour before a triggering event. 235. The nurse is collecting data from a client who has a history of untreated cataracts. The nurse checks the client for which associated manifestation? Answer: Difficulty with driving a car at night 236. A client has been diagnosed with open-angle glaucoma and asks the nurse to repeat the health care provider's explanation of the disorder. The nurse should offer the client which explanation? Answer: The pressure increases within the eye from excess fluid or blocking of drainage. 237. The nurse is reinforcing education to a client who has just obtained a hearing aid about its use and maintenance. The nurse tells the client that it is helpful to follow which practice? Answer: Keep an extra battery readily available. 238. A client has sought treatment in the ambulatory care clinic after an insect has become trapped in the external ear canal. The nurse prepares to assist the health care provider to instill which acceptable solutions into the ear to remove the insect? Select all that apply. Answer: Lidocaine Mineral oil Ether solution 239. The nurse is collecting neurological data on a poststroke adult client. Which technique should the nurse perform to adequately check proprioception? Answer: Hold the sides of the client's great toe, and while moving it, ask what position it is in. 240. After a routine eye examination, a client has been told there are refractive errors in both eyes. The nurse explains to the client that this problem is primarily treated with which intervention? Answer: Prescription of corrective lenses 241. The nurse is reinforcing discharge teaching to a client following right eye cataract surgery. The nurse determines that the client needs further teaching about ways to avoid strain on the operative eye when the client makes which statements? Select all that apply. Answer: "I can lie on my right side." "I will wear my eye shield only during the daytime." 242. The nurse develops a plan of care for a client following a lumbar puncture. Which interventions should be included in the plan? Select all that apply. Answer: Monitor the client's ability to void. Maintain the client in a flat position. Monitor the client's ability to move the extremities. Inspect the puncture site for swelling, redness, and drainage. 243. A client with Parkinson's disease "freezes" while ambulating, increasing the risk for falls. Which suggestion should the nurse include in the client's plan of care to alleviate this problem? Answer: Consciously think about walking over imaginary lines on the floor. 244. The nurse is assisting in checking for Tinel's sign in a client suspected of having carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS). Which technique should the nurse expect to be used to elicit this sign? Answer: Percuss the medial nerve at the wrist as it enters the carpal tunnel, and monitor for tingling sensations. 245. The nurse is monitoring a client with a spinal cord injury who is experiencing spinal shock. Which assessment will provide the nurse with the best information about recovery from the spinal shock? Answer: Reflexes 246. The nurse is caring for a client with a cerebral aneurysm who is on aneurysm precautions and is monitoring the client for signs of aneurysm rupture. The nurse understands that an early sign of rupture is which? Answer: A decline in the level of consciousness 247. The nurse is caring for a client with a head injury and is monitoring the client for signs of increased intracranial pressure (ICP). Which sign if noted in the client should the nurse report immediately? Answer: The client vomits. 248. The nurse is caring for a client with a spinal cord injury. High-top sneakers on the client's feet will prevent the occurrence of which? Answer: Foot drop 249. A halo vest is applied to a client following a cervical spine fracture. The nurse reinforces instructions to the client regarding safety measures related to the vest. Which statement by the client indicates a need for further teaching? Answer: "I will bend at the waist, keeping the halo vest straight to pick up items." 250. The nurse is preparing a plan of care to monitor for complications in a client who will be returning from the operating room following transsphenoidal resection of a pituitary adenoma. Which intervention does the nurse document in the plan as the priority nursing intervention for this client? Answer: Monitor urine output. 251. The nurse is reinforcing discharge instructions to a client who has undergone transsphenoidal surgery for a pituitary adenoma. Which statement by the client indicates the client understands the discharge instructions? Answer: "I need to call the doctor if I develop frequent swallowing or postnasal drip." 252. The nurse is collecting admission data on a client with Parkinson's disease. The nurse asks the client to stand with the feet together and the arms at the side and then to close the eyes. The nurse notes that the client begins to fall when the eyes are closed. Based on this finding, the nurse documents which in the client's record? Answer: Positive Romberg's test 253. A nursing student is collecting data on a client recently diagnosed with meningitis. The student expects to note which signs and symptoms? Select all that apply. Answer: Tachycardia Photophobia Red, macular rash Positive Kernig's sign 254. The nurse is reinforcing discharge instructions to a client following right eye cataract surgery about ways to avoid strain on the operative eye. The nurse determines that the client needs further teaching if the client makes which statement? Answer: "I can lie on my right side." 255. The nurse is caring for a client with acute otitis media. The nurse plans care knowing which treatment for this problem is likely to be included? Answer: Myringotomy 256. The nurse is assisting in preparing a teaching plan for a client with Ménière's disease. The nurse places highest priority on teaching the client information related to which information? Answer: Safety 257. The nurse is reviewing the results of an eye examination on a client. Which tests can detect glaucoma? Select all that apply. Answer: Tonometry Visual field check 258. A client is suspected of having a diagnosis of Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS). Which findings would support a diagnosis of Guillain-Barré syndrome? Select all that apply. Answer: Visual and hearing disturbances Ascending symmetrical muscle weakness 259. The nurse is preparing a plan of care for a client being admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of retinal detachment. Which measure should the nurse include in the plan of care? Answer: Place an eye patch over the affected eye. 260. The nurse is reinforcing home care instructions to a client following a fenestration procedure for the treatment of otosclerosis. Which instruction should the nurse give the client? Answer: Increase fluids and take a stool softener daily. 261. The nurse is reviewing the health care record of a client suspected of having mastoiditis. Which finding does the nurse expect to note if this disorder is present? Answer: Swelling behind the ear 262. A nursing student is caring for a client in the health care clinic who has been diagnosed with glaucoma. The nursing instructor asks the student to describe the types of medication that will likely be prescribed for the client to treat the eye disorder. Which drug classification will facilitate the outflow of aqueous humor? Answer: Cholinergic miotic agents 263. A nursing student is preparing to assist with an ear irrigation on an assigned client who has a buildup of cerumen in the left ear. The nursing instructor asks the student about the procedure for the irrigation. The student nurse should perform the procedure in which correct order? Arrange the actions in the order that they should be used. All options must be used. Answer: Warm the prescribed solution to body temperature (95° F to 105° F). Have the client sit up holding an emesis basin under the ear to be irrigated with a drape under the basin. Straighten the external canal of an adult by pulling the auricle up and back. Select an irrigating syringe or bulb syringe with a tip that is smaller than the canal. Direct the solution toward the top of the canal in a steady stream, not toward the eardrum. 264. A clinic nurse is reinforcing home care instructions to a client with a diagnosis of glaucoma. Which statement by the client indicates an understanding of the treatment plan for glaucoma? Answer: "I need to take my eye drops for the rest of my life." 265. The nurse is observing an unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) talk to a client who is hearing impaired. The nurse should intervene if which action is performed by the UAP during communication with the client? Answer: The UAP speaks directly into the impaired ear. 266. A clinic nurse is reinforcing instructions to a client regarding the use of a hearing aid. Which statement by the client indicates a need for further teaching? Answer: "I should turn the hearing aid off after removing it from my ear." 267. The nurse is collecting data on a client diagnosed with Parkinson's disease. Which finding indicates a serious complication of this disorder? Answer: Congested cough and coarse rhonchi heard during auscultation 268. The nurse notices that a client with trigeminal neuralgia has been withdrawn, is having frequent episodes of crying, and is sleeping excessively. Which method is the best way for the nurse to explore issues with the client regarding these behaviors? Answer: Have the client express the feelings in writing. 269. A client with suspected Guillain-Barré syndrome has a lumbar puncture performed. The cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) protein is 750 mg/dL. The nurse analyzes these results as which? Answer: Higher than normal, supporting the diagnosis of Guillain- Barré 270. A client with a T4 spinal cord injury is to be monitored for autonomic dysreflexia (hyperreflexia). Which finding is indicative of this complication? Answer: The client complains of a headache, and the blood pressure is elevated. 271. The nurse is monitoring a client with a spinal cord injury for signs of spinal shock. Which sign is indicative of this complication of a spinal cord injury? Answer: Areflexia below the level of injury 272. A client with tetraplegia complains bitterly about the nurse's slow response to the call light and the rigidity of the therapy schedule. Which interpretation of this behavior should serve as a basis for planning nursing care? Answer: The client is reacting to loss of control. 273. A client with Parkinson's disease is developing dementia. Which action should the nurse plan to assist the client in maintaining self-care abilities? Answer: Break down activities into small steps. 274. The nurse is caring for a client that is comatose and notes in the client's chart that the client is exhibiting decerebrate posturing. The nurse understands that which definition describes decerebrate posturing? Answer: The extension of the extremities and pronation of the arms 275. A client recovering from a craniotomy complains of a "runny nose." Based on the interpretation of the client's complaint, which action should the nurse take? Answer: Notify the registered nurse. 276. The nurse is planning care for a client with Bell's palsy. Which measure should be included in the plan? Answer: Instill artificial tears and wear a patch over the affected eye at night. 277. A client with Guillain-Barré syndrome has been asking many questions about the condition, and the nursing staff feels that the client is very discouraged about her condition. It is important for the nurse to include which information in discussions with the client? Answer: Generally, a vast number of people recover from this condition. 278. The nurse is monitoring a client who sustained a head injury and suspects that the client has a skull fracture. This conclusion is based on which findings? Select all that apply. Answer: Drainage from ear Bruising around the eyes Pink-tinged drainage from the nose 279. The nurse notes that the client's eyes are reddened, and the client states that an eye infection has been diagnosed. The nurse interprets that the client is most likely referring to infection of which structure that provides a protective covering for the eye? Answer: Conjunctiva 280. The client has undergone funduscopic examination of the eye. The documented results indicate that the blood vessels are without tortuosity, narrowing, pulsation, or nicking. The nurse interprets that this report indicates which finding? Answer: Normal retinal examination 281. The nurse notes that the client's physical examination record states the client's eyes moved normally through the six cardinal fields of gaze. The nurse makes which interpretation? Answer: The client has normal ocular movements. 282. The nurse assesses that a client with glaucoma has vision that is lost because of obstruction of aqueous humor flow by the trabecular meshwork. The nurse interprets that this client is suffering from which disorder? Answer: Primary open-angle glaucoma 283. The nurse is listening to a health care provider explain the results of an eye examination to a client. The health care provider states that the client has glaucoma resulting from a congenitally narrow anterior chamber angle, which has suddenly become blocked by the base of the iris. The nurse interprets that the health care provider is describing which type of glaucoma? Answer: Angle-closure glaucoma 284. A client is experiencing double vision, or diplopia. The nurse interprets that this client is experiencing a loss of which normal function of the eye? Answer: Binocular vision 285. After an eye examination, a client has been diagnosed with acute angle-closure glaucoma. The nurse collecting data from the client asks the client about an accompanying history of which sign/symptom? Answer: Eye pain 286. A client is experiencing blockage of the eustachian tubes. The nurse teaches the client that which activities by the client may forcibly open the eustachian tube? Answer: Performing the Valsalva maneuver 287. The nursing student is developing information for use in a clinical conference about hearing disorders. In the presentation, the student plans to include the statement that the ear is housed in which bones of the skull? Answer: Temporal 288. Which nursing interventions are appropriate for a client recovering from surgery for retinal detachment? Select all that apply. Answer: Monitor for hemorrhage. Administer eye medications. Maintain the eye patch or shield. Assist with activities of daily living. Educate regarding symptoms of retinal detachment. 289. A client experiences an episode of Bell's palsy and complains about increasing clumsiness. The nurse should prepare the client for which diagnostic study (studies) to determine the cause of the complaints? Select all that apply. Answer: Cerebral angiography Lumbar puncture (LP) Computed tomography 290. When the nurse taps at the level of the client's facial nerve, the following response is noted. How should the nurse document this finding on the client record? Refer to figure. Answer: Positive Chvostek's sign 291. The nurse is collecting neurological data on an unconscious client. On application of a central noxious stimulus, the nurse observes this response. How should the nurse document this response on the client's record? Refer to figure. Answer: Client demonstrated decerebrate posturing. 292. The nurse suspects neurogenic shock in a client with complete transection of the spinal cord at the T3 (thoracic 3) level if which clinical symptoms are observed? Answer: Hypotension and bradycardia 293. The nurse is told in report that a client has a positive Chvostek's sign. Which other data should the nurse expect to find on data collection? Select all that apply. Answer: Tetany Diarrhea Possible seizure activity Positive Trousseau's sign 294. A client with glaucoma and an acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) has a new prescription to receive carteolol HCl (Ocupress) eye drops. Which action by the nurse is most appropriate? Answer: Withhold the dose and notify the registered nurse. 295. The nurse determines that motor function of which cranial nerve is intact if the client can perform this action? Refer to figure. Answer: Facial 296. A client complains of pain in the lower back and pain and spasms in the hamstrings when the nurse attempts to extend the client's leg. How should the nurse record this finding on the client's medical record? Refer to figure. Answer: Positive Kernig's sign 297. A client with a stroke (brain attack) is experiencing residual dysphagia. The nurse should remove which food items that arrived on the client's meal tray from the dietary department? Answer: Peas 298. The nurse is reinforcing instructions to a client regarding the use of ice packs to treat an eye injury. The nurse instructs the client to do which action? Answer: Wrap a plastic bag filled with ice with a pillowcase and place it on the eye. 299. The nurse is caring for a client following craniotomy who has a supratentorial incision. The nurse reviews the client's plan of care, expecting to note that the client should be maintained in which position? Answer: Semi-Fowler's position 300. A client is about to undergo a lumbar puncture (LP). The nurse tells the client that which position will be used during the procedure? Answer: Side-lying with the legs pulled up and the head bent down onto the chest 301. The nurse is speaking with a client with a hearing impairment. The nurse refrains from doing which least likely helpful action when communicating with this client? Answer: Using many exaggerated hand gestures while talking 302. The nurse is gathering data from a client with a history of untreated cataracts. The nurse asks the client about the presence of which sign of a cataract? Answer: Difficulty with driving at night and blurred vision 303. The nurse is assisting a client who has just been given a hearing aid to wear for the first time. When reinforcing client teaching, the nurse should include which instruction? Answer: "The hearing aid should not be worn if an ear infection is present." 304. The nurse is attempting to inspect the lacrimal apparatus of a client's eye. Because of its anatomical location the nurse should do which action? Answer: Retract the upper eyelid and ask the client to look down. 305. A client has been newly diagnosed with glaucoma. As part of the discharge instructions, the nurse should plan to reinforce which information? Answer: The need for lifelong medication therapy 306. A client is diagnosed with hyphema after experiencing a traumatic blow to the eye. The nurse explains to the client that which activity limitation needs to be implemented following this type of injury? Answer: Bed rest with the head in semi-Fowler's position 307. A client arrives in the emergency department with an eye injury resulting from metal fragments that hit the eye while the client was drilling into metal. The nurse checks the eye and notes small pieces of metal floating on the eyeball. Which action should the nurse take first? Answer: Irrigate the eye with sterile saline. 308. A client has been diagnosed with glaucoma. The nurse who is teaching the client principles of self-care should encourage the client to limit or refrain from which usual activity on a repeated basis? Answer: Picking objects up off the floor 309. The nurse is explaining how sound is conducted from the middle ear to the inner ear in teaching a client who is experiencing hearing loss. The nurse plans to use a diagram that illustrates how which bones connects to the cochlea at the oval window? Answer: Stapes 310. The nurse is developing a poster to use in teaching clients about the prevention of hearing loss. The nurse should diagram which structure as part of the inner ear? Answer: Cochlea 311. An adult client has increased fluid in the middle ear, which is causing vertigo. The nurse checks this client for which associated signs and symptoms of this condition? Answer: Nausea and vomiting 312. The nurse has been assigned to a client with a hearing impairment. To enhance nurse-client communication, the nurse should plan to communicate with the client by speaking in which manner? Answer: In a normal tone while facing the client 313. The nurse is reviewing the medication list for an assigned client. Which medication is the only one on the client's prescription sheet that does not have an ototoxic effect? Answer: Acetaminophen (Tylenol) 314. A client has just undergone lumbar puncture (LP). The nurse assists the client into which optimal position? Answer: Prone, with a pillow under the abdomen 315. A client with Bell's palsy exhibits facial asymmetry and cannot close the eye completely on one side. The client is also drooling and has loss of tearing in one eye. The nurse documents that the client displays symptoms of involvement of which cranial nerves (CNs)? Answer: CN VII 316. The nurse is caring for the client with a head injury secondary to a motor vehicle crash. The nurse observes the client's status regularly, monitoring closely for which change in vital signs that could indicate increased intracranial pressure? Answer: Decreasing pulse, decreasing respirations, increasing BP 317. A client who sustained a closed head injury has a new onset of copious urinary output. Urine output for the previous 8-hour shift was 3300 mL, and 2800 mL for the shift before that. The findings have been reported to the health care provider, and the nurse anticipates a prescription for which medication? Answer: Desmopressin (DDAVP) 318. A client who suffered a cervical spine injury had Crutchfield tongs applied in the emergency department. The nurse should avoid which action in the care of the client? Answer: Removing the weights when repositioning the client 319. The nurse is reinforcing instructions to the client who has just been fitted for a halo vest. Which statement by the client indicates the need for further teaching? Answer: "I will avoid driving at night because the vest limits the ability to turn the head." 320. A client with spinal cord injury has experienced more than one episode of autonomic dysreflexia. The nurse should avoid which action that could trigger an episode of this complication? Answer: Allowing the client's bladder to become distended 321. The nurse is assisting in admitting a client who experienced seizure activity in the emergency department. The nurse avoids which action when managing this client's environment? Answer: Keeping the bed position raised to the nurse's waist level 322. The nurse is assisting in the care of a client who is being evaluated for possible myasthenia gravis. The health care provider gives a test dose of edrophonium (Enlon). The nurse recalls that the client should have which reaction if the client has this disease? Answer: An increase in muscle strength within 1 to 3 minutes 323. A client with myasthenia gravis becomes increasingly weaker. The health care provider injects a dose of edrophonium (Enlon) to determine whether the client is experiencing a myasthenic crisis or a cholinergic crisis. The nurse expects that the client will have which reaction if the client is in cholinergic crisis? Answer: A temporary worsening of the condition 324. Which symptoms would validate the diagnosis of a cluster headache? Select all that apply. Answer: A runny nose Burning sensation in the eye Tearing on the affected eye 325. A client, who frequently experiences hearing loss due to built-up cerumen in the ears, asks the nurse about ways to deal with the problem including irrigating the ears. Which information is correct for the nurse to include in the teaching plan? Select all that apply. Answer: Irrigate the ear canal with lukewarm tap water around 98° F. The ear irrigation should be stopped if the client becomes dizzy or nauseous. Instill drops of mineral oil and hydrogen peroxide for several days to soften dried cerumen before irrigation. 326. The nurse administers meclizine hydrochloride (Antivert) to a client diagnosed with an attack of Ménière's disease. Which observations demonstrate to the nurse that the medication is effective? Select all that apply. Answer: Decrease in nausea Decrease in vertigo 327. The nurse is reinforcing discharge instructions to a client who just underwent a myringotomy with placement of a polyethylene tube in the left ear. Which statement by the client indicates a need for further teaching? Select all that apply. Answer: "I may wash my hair tomorrow." "I will irrigate the ear with gentle pressure." "I can expect to feel pressure inside the ear." 328. The nurse determines that motor function of which cranial nerve is intact if the client can perform this action? Refer to figure. Answer: Facial A client complains of pain in the lower back and pain and spasms in the hamstrings when the nurse attempts to extend the client's leg. How should the nurse record this finding on the client's medical record? Refer to figure. Answer: Positive Babinski's sign The nurse is caring for a client following a supratentorial craniotomy, in which a large tumor was removed from the left side. In which position can the nurse safely place the client? Refer to Figures. 1. A client has died, and the nurse asks a family member about the funeral arrangements. The family member refuses to discuss the issue. Which is the appropriate nursing action? -Remain with the family member without discussing funeral arrangements. 2. The nursing instructor asks a nursing student to describe the procedure for relieving an airway obstruction on an unconscious pregnant woman at 8 months' gestation. How should the student describe the procedure correctly? -Place a rolled blanket under the right abdominal flank and hip area. 3. The nurse on the day shift walks into a client's room and finds the client unresponsive. The client is not breathing and does not have a pulse, and the nurse immediately calls out for help. The next nursing action is which? -Start chest compressions. 4. The nurse witnesses a neighbor's husband sustain a fall from the roof of his house. The nurse rushes to the victim and determines the need to open the airway. The nurse opens the airway in this victim with the use of which method? -Jaw thrust maneuver 5. The nurse understands that which is a correct guideline for adult cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) for a health care provider? -Each rescue breath should be given over 1 second and should produce a visible chest rise. 6. The nurse attempts to relieve an airway obstruction on a 6-year-old conscious child. Which location is the correct placement of the hands to perform this maneuver? -Between the umbilicus and the xiphoid process 7. The nurse is performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) on an adult. The nurse should deliver how many breaths per minute to the client? -10 8. The nurse is performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) on an infant. When performing chest compressions, which is the compression rate for an infant? -100 times per minute 9. Which is the most appropriate location for assessing the pulse of an infant who is less than 1 year old? -Brachial 10. The nurse educator is teaching principles of cardiopulmonary resuscitation to a group of nursing students. The nurse asks a student to describe the reason why blind finger sweeps are avoided in infants. The nurse determines that the student understands the reason if the student makes which statement? -"The object may be forced back further into the throat." 11. The nurse is performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) on an adult client. How far should the sternum be depressed in an adult client for effective chest compressions? -2 inches 12. The nurse is caring for an older client who is reminiscing about past life experiences in a positive manner. The nurse plans care with the understanding that this behavior indicates which? -A normal psychosocial response 13. The nurse is preparing to care for a dying client, and several family members are at the client's bedside. Which therapeutic techniques should the nurse use when communicating with the family? Select all that apply. -Encourage expression of feelings, concerns, and fears. -Touch and hold the client's or family member's hand if appropriate. -Be honest and let the client and family know that they will not be abandoned by the nurse. 14. Upon palpation of the fontanel of a 3-month-old newborn, the nurse notes that the anterior fontanel has not closed and is soft and flat. Which action should the nurse take? -Document the findings. 15. An older client has been prescribed digoxin (Lanoxin). The nurse understands that which age-related change would place the client at risk for digoxin toxicity? -Decreased lean body mass and glomerular filtration rate 16. The nurse should plan which to encourage rebreak in the client who is a resident in a long-term care facility? -Choosing his social activities 17. When the nurse is collecting data from the older adult, which findings should be considered normal physiological changes? Select all that apply. -Decline in visual acuity -Increased susceptibility to urinary tract infections -Increased incidence of awakening after sleep onset 18. The nurse is providing an education class to healthy older adults. Which exercise will best promote health maintenance? -Walking three to five times a week for 30 minutes 19. The nurse should implement which activity to promote reminiscence among older clients? -Having storytelling hours 20. The clinic nurse is assisting to perform a focused data collection process on a client who is complaining of symptoms of a cold, a cough, and lung congestion. Which should the nurse include for this type of data collection? Select all that apply. -Auscultating lung sounds -Obtaining the client's temperature -Obtaining information about the client's respirations 21. A client with a diagnosis of asthma is admitted to the hospital with respiratory distress. Which type of adventitious lung sounds should the nurse expect to note documented in the health record when collecting data related to the respiratory system for this client? -Wheezes 22. The nurse is reviewing the client's health record and notes that the client elicited a positive Romberg sign. The nurse understands that this indicates which finding? -A significant sway when the client stands erect with feet together, arms at the side, and the eyes closed 23. The nurse notes documentation that a client is exhibiting Cheyne-Stokes respirations. On data collection of the client, the nurse expects to note which finding? -Rhythmic respirations with periods of apnea 24. The nurse notes documentation that a client has conductive hearing loss. The nurse understands that which is a cause of this type of hearing loss? -A physical obstruction to the transmission of sound waves 25. While collecting data related to the cardiac system on a client diagnosed with an incompetent heart valve, the nurse auscultates a murmur. Which best describes the sound of a heart murmur? -Gentle, blowing or swooshing noise 26. The nurse is preparing to assist the health care provider to test the extraocular movements in a client for muscle weakness in the eyes. The nurse anticipates that which physical assessment technique will be done to assess for muscle weakness in the eye? -Testing the six cardinal positions of gaze 27. The nurse is reinforcing instructions for a client in how to perform a testicular self- examination (TSE). The nurse explains that which is the best time to perform this exam? -After a shower or bath 28. The nurse notes that the physical assessment findings for a client with meningeal irritation indicate a positive Brudzinski sign. The nurse understands that which observation was made? -The client passively flexes the hip and knee in response to neck flexion and reports pain in the vertebral column. 29. The nurse in the newborn nursery receives a telephone call to prepare for the admission of a neonate born at 43 weeks' gestation with Apgar scores of 1 and 4. When planning for the admission of this infant which is the nurse's highest priority? -Connecting the resuscitation bag to the oxygen outlet 30. The nurse is preparing to perform an abdominal examination. The initial step should be which? -Inspection 31. The nurse is caring for a client on a cardiac monitor who is alone in a room at the end of the hall. The client has a short burst of ventricular tachycardia (VT), followed by ventricular fibrillation (VF). The client suddenly loses consciousness. Which intervention should the nurse do first? -Call for help and initiate cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). 32. To use an external cardiac defibrillator on a client, which action should be performed to check the cardiac rhythm? -Applying the adhesive patch electrodes to the skin and moving away from the client 33. The nurse is preparing to care for a dying client, and several family members are at the client's bedside. Which therapeutic techniques should the nurse use when communicating with the family? Select all that apply. -Encourage expression of feelings, concerns, and fears. -Extend, touch, and hold the client's or family member's hand if appropriate. -Be honest and truthful, and let the client and family know that you will not abandon them. 34. Which data would indicate a potential complication associated with age-related changes in the musculoskeletal system? -Overall sclerotic lesions 35. The nurse is caring for an older client who is terminally ill. Which signs indicate to the nurse that death may be imminent? -Irregular, noisy breathing and cold, clammy skin 36. The nursing student is asked to describe the correct steps for performing adult cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). Arrange the steps of adult CPR in the order of priority. -Determine unconsciousness by shaking the client and asking, "Are you OK?" -Perform chest compressions. -Open the client’s airway -Initiate breathing 37. The nurse is preparing to auscultate a client's abdomen for bowel sounds. The nurse listens for bowel sounds in which abdominal quadrant first? Refer to figure. #3 38. The nurse is checking a dark-skinned client for the presence of petechiae. Which body area is best for the nurse to check in this client? -Oral mucosa 39. The nurse is reinforcing instructions regarding cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) to a group of nursing students. The nurse tells the group that when performing chest compressions on adults, the sternum should be depressed to least which depth? -2 inches 40. An older client confides to the visiting nurse the fear of falling while going to the bathroom at night. Which statement indicates an understanding of the visual changes affecting the older client? -"Keep a red light on in the bathroom at night." 41. The nurse is providing information to unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) regarding caring for the older adult. The nurse tells the UAPs that which situation portrays ageism? -Advising older adults to forgo aggressive treatment 42. The nurse assigned to care for an older adult client places an extra blanket in the client's room. The nurse understands that the older adult is less able to regulate hot and cold body changes because of alterations in the activity of which gland? -Sweat glands 43. The nurse is collecting data from an older adult client. Which indicates a potential complication associated with the skin of this client? -Crusting 44. The nurse is collecting medication information from a client, and the client states that she is taking garlic as an herbal supplement. The nurse understands that the client is most likely treating which condition? -Hyperlipidemia 45. The nurse is asked to test the visual acuity of a client using a Snellen chart. The nurse prepares to perform the test, knowing that which identifies the accurate procedure for this visual acuity test? -The right eye is tested, followed by the left eye, and then both eyes are tested. 46. A client's vision is tested with a Snellen chart. The results of the test are documented as 20/60. How should the nurse interpret this result? -The client can read at a distance of 20 feet what a client with normal vision can read at 60 feet. 47. The nurse is preparing the client for eye testing, and the examiner is planning to test the eyes using the confrontational method. What should the nurse tell the client about the purpose of the test? -Examines visual fields or peripheral vision 48. An older client is at risk for falls. When developing an individualized plan of care for this client, the nurse recalls that which concept is least relevant to maintenance of balance for the older client? -Older clients cannot think quickly enough to respond to emergencies. 49. In planning care for older clients in a long-term care facility, the nurse recalls that which is accurate regarding sexuality and the older client? -Although responses may be slower, sexual ability is present in later years of life. 50. The nurse is working with an older client and family about discharge following hospitalization. When initiating discussions with the group, the nurse understands that older persons usually prefer which? -To live independently, but close to their children 51. An older client is taking multiple medications for a variety of health problems. The nurse should monitor the results of which most important laboratory test(s) when evaluating adverse effects of medication therapy in the older adult? -Creatinine 52. The nurse working in a long-term care facility is approached by the son of a resident, who wants his 78-year-old father to have a heating pad because "his feet are always cold at night." The nurse should incorporate which concept when formulating a response to the family member? -Older adults often have slower neurological response times and are therefore more at risk for burns. 53. The nurse has gathered data regarding an older client. The nurse understands that which indicator of fluid imbalance is not reliable for a client in this age group? -Thirst 54. The nurse is told by an older woman that she has begun to be incontinent of urine at night and now drinks no fluids after 6:00 pm. The nurse's response should be guided by which knowledge? -Incontinence at any age deserves urological attention. 55. The nurse is preparing to perform an abdominal assessment on a client. The nurse places the client in which best position to perform the assessment? #2 56. A client who has been seen in the clinic has been diagnosed with endometriosis and asks the nurse to describe this condition. The nurse bases the response on what information? -Endometriosis is the presence of tissue outside the uterus that resembles the endometrium. 57. A nursing instructor asks a nursing student about the reason for the reduction of anesthetic medication dosage in the older person. Which statement is an appropriate response? -"The increase of fatty tissue allows anesthetic agents, which have an affinity for fatty tissue, to concentrate in body fat." 58. The nurse recognizes that which intervention is unlikely to facilitate effective communication between a dying client and the family? -The nurse makes decisions for the client and family in order to relieve them of unnecessary demands 59. A 39-year-old man learned today that his 36-year-old wife has an incurable cancer and is expected to live not more than a few weeks. The nurse identifies which response by the husband as indicative of effective individual coping? -He expresses his anger at God and the health care providers for allowing this to happen. 60. The nurse determines that a student in a basic cardiac life support (BCLS) course correctly performs cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) on an infant when the nurse observes which rate of chest compressions delivered to the infant mannequin? -100 times per minute 61. A client and her husband are being discharged from the hospital after delivering a stillborn infant. They ask about the possibility of attending a bereavement support group in the community. Which response should this request indicate to the nurse? -Normal grieving 62. Which observation indicates that the nurse is performing a whispered voice hearing assessment test procedure correctly? -Asks the client to block one ear at a time 63. The nurse is preparing to collect client data by examining the abdomen. The nurse should begin the assessment by performing which action first? -Inspecting the abdomen 64. The nurse is caring for a client with terminal cancer who is close to death. In reviewing the plan of care, the nurse determines that which action is a priority? -Maintain the client's dignity and self-esteem, and make the client as comfortable as possible. 65. The nurse provides information to a client regarding breast self-examination (BSE). Which client statement indicates a need for further teaching regarding BSE? -"I don't need to do that; I'm too old for that." 66. A nursing student enrolled in a physical assessment course is asked to describe the probable signs of pregnancy. Which are probable signs indicating possible pregnancy? Select all that apply. -Hegar's, Chadwick's, McDonald’s 67. A client who was struck by a car while jogging is brought to the emergency department by the ambulance team. The client is unconscious, and a ruptured spleen is suspected. Emergency measures are instituted but are unsuccessful. The client's fiancée is with the client and tells the nurse that the client is an organ donor. In anticipation that the client's eyes will be donated, which should the nurse implement? -Close the deceased client's eyes and place a small ice pack on the eyes. 68. The nurse is checking the apical heart rate of a client with a complaint of angina. The nurse places the stethoscope in which anatomical area? Refer to figure. #4 69. When collecting physical assessment data, the nurse understands that the spleen is located in which abdominal quadrant? Refer to figure. #2 70. When performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), the nurse should deliver how many breaths per minute to an adult client? -10 71. The nurse is providing cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) to an adult cardiac arrest victim. Which is the proper compression-to-ventilation ratio for one-person CPR? -30:2 72. The nurse caring for the older adult client understands that dosages of many medications are reduced in this population because of which fact? -Serum albumin levels are decreased. 73. The nurse prepares to discharge a client who is experiencing family-related stress. Which goal does the nurse include to help the client achieve the primary developmental task? -Help the client resume her familial role. 74. A client has a terminal illness, and her spouse is distraught about the unrelenting pain she experiences. Which should the nurse implement as the most effective measure to alleviate the spouse's distress? -Engage the spouse in providing comfort. 75. A client's spouse becomes distraught when thinking about his wife's grave prognosis. Which action should the nurse implement to promote hope for the spouse? -Encourage formation of achievable goals. 76. To assess for the presence of the posterior tibialis pulse, the nurse should palpate which areas? -In the groove behind the medial malleolus and the Achilles tendon 77. A licensed practical nurse (LPN) is providing instructions to an unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) who is preparing to care for a deceased client whose eyes will be donated. The nurse intervenes if the UAP performs which action? -Places a dry sterile dressing over the open eyes 78. A licensed practical nurse (LPN) is a certified basic life support (BLS) instructor. The LPN is conducting a BLS recertification class and is discussing automated external defibrillation. A member of the class asks the LPN to identify the correct location for the placement of conductive gel pads to treat ventricular fibrillation. The LPN tells the class that the conductive gel pads are placed in which location on the client's chest? -Under the right clavicle and to the left of the precordium 79. The nurse is initiating cardiopulmonary resuscitation on an adult client. The nurse should place the hands in which position to begin chest compressions? -On the lower half of the sternum 80. The nurse should use which best method to open the victim's airway if the victim sustained a neck injury? -Jaw thrust maneuver 81. The nurse notes that an 8-year-old child is choking but is awake and alert at this time. As the nurse rushes to aid the child, the nurse plans to place the hands between which landmarks to remove the foreign body? -The umbilicus and xiphoid process 82. The nurse employed in the pediatric unit working on the 11:00 ᴘᴍ to 7:00 ᴀᴍ shift finds an infant unresponsive and without respiration or a pulse. The nurse plans to deliver chest compressions at a rate of at least which? -100 times per minute 83. The nurse arrives at the scene of a code and begins to assist in performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) on an adult client. After determining proper hand placement, the nurse begins delivering compressions by pushing down on the chest at which depth? -2 inches 84. An automatic external defibrillator (AED) is available to treat a client who goes into cardiac arrest. The nurse uses this equipment to determine cardiac rhythm by doing which? -Applying the adhesive patch electrodes to the skin and moving away from the client 85. An automatic external defibrillator (AED) interprets that the rhythm of a pulseless client is ventricular fibrillation. The nurse takes which action next? -Orders personnel away from the client, charges the machine, and depresses the discharge buttons 86. The nurse witnesses a person starting to choke in the hospital cafeteria. Before performing abdominal thrusts, which action should the nurse perform? -Ask the client, "Are you choking?" 87. The nurse is conducting a teaching session on basic life support (BLS) for nursing students. Which statement made by a nursing student indicates a need for further teaching? -"I will remember the algorithm airway, breathing, and compressions to guide my actions when providing BLS." 88. The nurse-midwife is conducting a session on the process of fertilization with a group of nursing students. The nurse-midwife asks a nursing student to identify the structure in which fertilization of an ovum takes place. The student answers correctly by identifying which location? -Fallopian tube 89. The nurse is collecting data from a client who is suspected of having mittelschmerz. Which finding should the nurse expect to note on data collection of the client? -Sharp pain located on the right side of the pelvis 90. The nurse employed in the emergency department is collecting data on a 7-year- old child with a fractured arm. The child is hesitant to answer questions that the nurse is asking and consistently looks at the parents in a fearful manner. The nurse suspects physical abuse and continues with the data collection procedures. Which finding would most likely assist in verifying the suspicion? -Bald spots on the scalp 91. The nurse is auscultating bowel sounds. Which are appropriate data collection methods? Select all that apply. -Divide the abdomen into four quadrants at the umbilicus. -Do not feed the client if no sounds are audible in 5 minutes. -Listen in each quadrant for gurgling sounds indicating movement. 92. The nurse is caring for an 8-year-old child in the late stage of a terminal illness. The child is semiconscious. The nurse notices that the child has a dry mouth and the family believes the child is thirsty. The family is attempting to give the child a large glass of apple juice. Which actions should the nurse take? Select all that apply. -Perform frequent oral care with mouth swabs. -Encourage the family to participate in oral care as much as desired. -Give the child small sips of water or ice chips if alert and requested by the child. 93. The nurse is caring for a client at the end of life. Which late cardiovascular and respiratory findings should the nurse expect to note while collecting data? Select all that apply. -Irregular heart rate -Decreased pulse rate -Decreased blood pressure -Irregular breathing patterns 94. The nurse is creating a care plan for a client with a terminal illness. Which nursing actions should be included? Select all that apply. -Respond to requests from the client and family promptly. -Support the client's decision-making in order to promote client control. -Provide information about what to expect during the dying process to the client and family. 95. The nurse is caring for a client at the end of life. Which gastrointestinal findings indicate that death is approaching? Select all that apply. -Nausea -Incontinence -Accumulation of gas -Abdominal distention 96. The nurse is caring for a client at the end of life. Which skin changes would the nurse expect to note? Select all that apply. -Waxlike texture -Mottling of arms, legs, hands, and feet -Cyanosis of the nose, nail beds, and knees 97. The nurse is caring for a client at the end-of-life. The client is withdrawn and agitated and is experiencing visual hallucinations. Which actions should the nurse take to provide end-of-life psychological care? Select all that apply. -Provide privacy to the client and family. -Encourage the family to talk with and reassure the client. -Encourage visits by appropriate spiritual services as desired. 98. The nurse is caring for a client who has just died. Which end-of-life information needs to be documented in the client's medical record? Select all that apply. -Time and date of death -Time of body transfer and destination -Name of health care provider certifying death -Medical tubes, devices, or lines left in the body The nurse is caring for a client who had a renal biopsy. Which interventions should the nurse include in the plan of care for the client after this procedure? Select all that apply. Administering pain medication as prescribed Monitoring vital signs and the puncture site frequently Testing serial urine samples with dipsticks for occult blood [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 234 pages
Instant download

Instant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jan 05, 2022
Number of pages
234
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jan 05, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
118