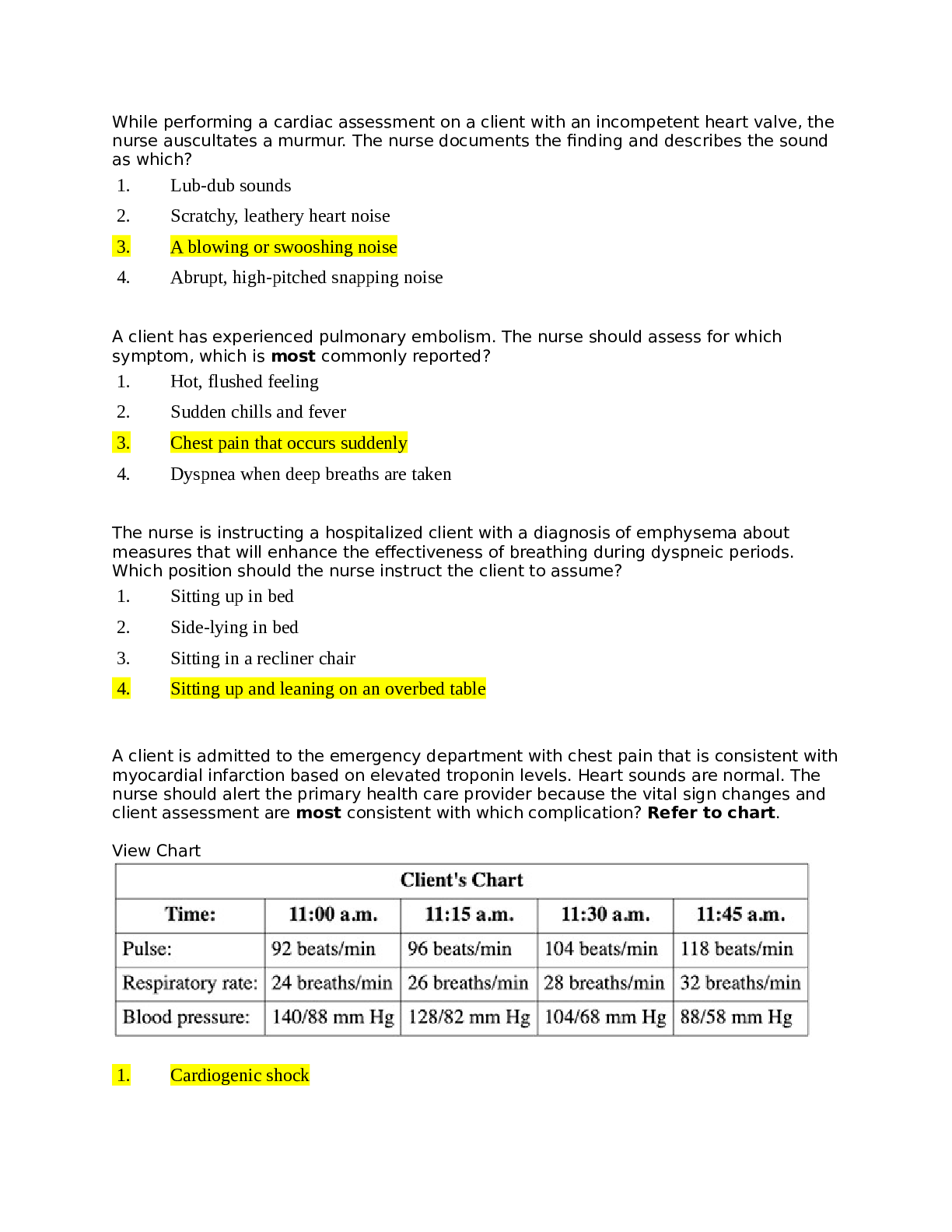
*NURSING > NCLEX > Family Development and Family Nursing Assessment Stanhope: Foundations of Population Health for Comm (All)
Family Development and Family Nursing Assessment Stanhope: Foundations of Population Health for Community/Public Health Nursing, 5th Edition,100% CORRECT
Document Content and Description Below
Family Development and Family Nursing Assessment Stanhope: Foundations of Population Health for Community/Public Health Nursing, 5th Edition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The following people enter the health ... clinic together: an unmarried man and his year-old son, an unmarried woman with a year-old daughter, and the man’s married brother, who is separated from his wife. During the assessment it is determined that both men work and contribute to the household, where all of them live. Which of the following best describes the “family”? a. The group consists of three families: the man and his son, the woman and her daughter, and the brother, who is married even though he and his wife are separated. b. There are two families involved: first, the unmarried man and woman and their two children, and second, the brother, who is married even though he and his wife are separated. c. There is no family here, only three adults sharing resources between themselves and two biologically related children. d. The family includes whoever the adults state are family members. ANS: D Nurses working with families should ask an adult member to identify all those considered to be family members and then include those members in health care planning. A “family” may range from the traditional nuclear model with extended family to such “postmodern” family structures as single-parent families, stepfamilies, same-gender families, and families consisting of friends. The incorrect answers have the nurse determining who is and who is not part of a family. This is not an appropriate action for the nurse to take, rather the nurse should let the client describe and define his/her family. 2. The nurse in community health needs to conduct a family assessment within a commune but is uncertain how to proceed because family lines appear blurred. The best way to determine the family of a mother and her child is to ask the woman which of the following questions? a. “How many children do you have, and who is the father of each?” b. “Is there a register of families who are members of this commune?” c. “Tell me about your significant other.” d. “Who are the members of your and your child’s family?” ANS: D The members of a family are self-defined. The family includes whoever the woman says are family members. The nurse should include all those members in health care planning. Asking who the father of each child is does not help define the family; the client needs to define the family. Knowing if there is or is not a register of families on the commune does not help the client define her own family. The client may or may not include the significant other in her definition of a family, so this may not assist in making this determination. 3. In taking a family history, the nurse in community health finds that this is the second marriage for the previously divorced parents and that the male partner is the stepparent to the oldest child. For which of the following aspects of the family assessment is data being gathered? a. Dynamics b. Function c. Structure d. System ANS: C Family structure refers to the organization of the family. This defines the roles and positions of the family members. The family functions refers to the activities and purposes of the family. The family as a system accomplishes activities that serve the individual and society. Family dynamics refers to the interactions and relationships within the family. 4. Which of the following statements best explains why family functions and structures create unique challenges in family nursing? a. Function and structure change over time. b. Function and structure do not apply to all family units. c. Some clients do not have families. d. Traditional families are rare in society. ANS: A The functions that families serve evolve and change over time. Some become more important and others less so. Family structures also change over time. The great speed with which changes in family structure, values, and relationships are occurring makes working with families at the beginning of the 21st century exciting and challenging. All familiy units have functions (activities and purposes) and structure (organization). These functions and structures many be very different among family members, but they do exist. All clients are part of a family, even if they define their family as only themselves. Nurses should be open-minded and recognize that all families are different and a “traditional” family structure may mean something different to different individuals. 5. A nurse is working with a family who is confronting major challenges to their health. Which of the following approaches would be most helpful for the nurse to use? a. Allowing the family to be noncompliant b. Building on the family’s strengths and resilience c. Labeling the family as resistant d. Recognizing that the family is dysfunctional ANS: B Families are neither all good nor all bad; families have both strengths and difficulties and have seeds of resilience. Recognizing the family’s strengths gives the nurse assets on which to draw in planning care. The labels of dysfunctional, noncompliant, resistant, or unmotivated all denote families who are not functioning well; however, such labels do not create an environment conducive for positive family change and intervention and should not be used. 6. The nurse is told that a healthy, functional family consisting of a 25-year-old man and a 24-year-old woman, who are expecting their first child, would appreciate a nurse coming to their apartment for anticipatory guidance in preparing themselves and their apartment for the baby. Based on that statement, which of the following assumptions can the nurse safely make about the family? a. The family is lacking a strong support system. b. The family’s basic needs are being met. c. The couple’s in-laws are unavailable to share their expertise about child care. d. The married couple is excited about their first baby. ANS: B In functional, healthy, or resilient families, the basic survival needs are met. Healthy families exist based on attachment and affection. There is nothing in the example to suggest that they are married, that their income is low, or that they lack other resources or support systems. 7. A nurse focuses on the care of the individual while viewing the client’s family as a background resource or possible stressor. Which of the following conceptualizations of family does this nurse’s view represent? a. Client b. Component of society c. Context d. System ANS: C Family as the context, or structure, has a traditional focus that places the individual first and the family second. In the “family as context” concept, the family serves as either a resource or a stressor to individual health and illness. When family is the the client, the family is placed first, and individuals are second. The family is seen as the sum of individual family members. When family is the system, the focus is on the family as the client, and the family is viewed as an interacting system in which the whole is more than the sum of its parts. When the family is seen as a component of society, it is seen as one of many institutions of society, along with health, education, religious, or financial institutions. 8. A nurse asks a family member, “What has changed between you and your spouse since your child’s head injury?” Which of the following focuses of the family is the nurse assessing? a. The context b. The client c. A system d. A component of society ANS: C When the focus is on the family as a system, the family is viewed as an interactional system in which the whole is more than the sum of its parts. The approach simultaneously focuses on individual members and the family as a whole at the same time. The interactions between family members are the target for nursing interventions. When family is the the client, the family is placed first, and individuals are second. The family is seen as the sum of individual family members. When the family is seen as a component of society, it is seen as one of many institutions of society, along with health, education, religious, or financial institutions. When family is the context, the individual is placed first and the family second. In the “family as context” concept, the family serves as either a resource or a stressor to individual health and illness. 9. Which of the following theories views the family as a whole with boundaries that are affected by the environment? a. Family developmental b. Exosystems c. Bioecological systems d. Family systems ANS: D The theory that views the family as a whole with boundaries that are affected by the environment is the family systems theory. In this theory, the emphasis is on the whole rather than on individuals. Families are viewed from both a subsystem and suprasystem approach. The family developmental theory focuses on common tasks of family life and provides a longitudinal view of the family life cycle. The bioecological systems theory describes how environments and systems outside of the family influence the development of a child over time. The definition of exosystems is found within the bioecological systems theory; these are the external environments that have an indirect influence on the family. 10. A nurse organizes care for a family by focusing on the common tasks of family life and considering a longitudinal view of the family life cycle. Which theory is being applied? a. Family systems b. Bioecological systems c. Family developmental d. Family nursing ANS: C The family developmental theory focuses on common tasks of family life and provides a longitudinal view of the family life cycle. In the family systems theory, families are considered social systems, composed of a set of organized, complex, interacting elements. The bioecological systems theory describes how environments and systems outside of the family influence the development of a child over time. Family nursing theory is an evolving synthesis of the scholarship from three different traditions: family social science, family therapy, and nursing. 11. A new mother is a full-time college student who lives with her parents, because the baby’s father has been imprisoned related to theft and drug abuse. The infant’s grandmother, although also employed, cares for the child while the young mother attends classes. Which of the following theoretical frameworks would be most helpful to the nurse when assessing this family’s needs? a. Developmental b. Family nursing c. Bioecological d. Systems ANS: A Developmental theory explains and predicts the changes that occur to humans or groups over time. Achievement of family developmental tasks helps individual members accomplish their tasks. In this case the new mother has tasks, whereas her parents have temporarily interrupted their progress in response to their daughter’s (and grandchild’s) needs. In the family systems theory, families are considered social systems, composed of a set of organized, complex, interacting elements. The bioecological systems theory describes how environments and systems outside of the family influence the development of a child over time. Family nursing theory is an evolving synthesis of the scholarship from three different traditions: family social science, family therapy, and nursing. 12. A nurse considers how the environment outside of the family influences the development of a child when planning care for a family. Which of the following theories is being used by the nurse? a. Bioecological systems theory b. Family systems approach c. Family developmental theory d. Family nursing theory ANS: A The bioecological systems theory describes how environments and systems outside of the family influence the development of a child over time. In the family systems theory, families are considered social systems, composed of a set of organized, complex, interacting elements. The family developmental theory focuses on common tasks of family life and provides a longitudinal view of the family life cycle. Family nursing theory is an evolving synthesis of the scholarship from three different traditions: family social science, family therapy, and nursing. 13. A nurse is in the termination phase of the nurse-family relationship. Which of the following strategies would the nurse most likely implement? a. Increasing sessions with the nurse b. Making referrals when appropriate c. Providing a formative evaluation of the relationship d. Refusing additional communication with the family ANS: B Making referrals when appropriate is part of the termination phase as the nurse ends the relationship with the family. It also includes decreasing contact with the nurse, extending invitations to the family for follow-up, and a summative evaluation meeting for formal closure. If sessions were the nurse were to increase, it would be unlikely that the relationship was going to be soon terminated or ended. Formative evaluation occurs throughout the relationship and is ongoing; an evaluation that would be done at the closure of the relationship would be summative. It would be appropriate for the nurse to extend an invitation for follow-up, not refuse additional communication. 14. A nurse is making an appointment with a family for a nursing visit. Which of the following describes a potential barrier the nurse may encounter? a. The assessment cannot be done unless the extended family is present. b. It may be difficult to find a convenient time for all family members to be present. c. Nurses have limited time to do home visits. d. Families are often scattered over a large area, making access difficult. ANS: B It is important to encourage all family members to attend the meeting. However, it can be difficult to find a convenient time for all family members to attend. Many times late afternoon or evening appointments are necessary to accommodate the needs of the family. It is probably most important that the immediate, not necessarily the extended, family is present. If the nurse is making an appointment with a family this would be part of the role of the nurse, and it would be within the scope of the nurse’s practice to make time to complete home visits. The nurse may need to be creative in how to best meet the needs of the family to arrange a meeting. The larger barrier is finding a common time, not distance of the family member. 15. Which of the following factors must be considered before deciding on an appropriate plan of action? a. Family agrees to the nurse’s plan. b. Family is capable of the required actions. c. Family will learn better coping skills from the nurse’s plan. d. Nurse has informed family how to complete the required actions. ANS: B Family theorists stress that any intervention plan must be developed in collaboration with the family, using and enhancing family strengths and increasing independence of family members. The family must have the skills and commitment necessary and to complete the developed plan. The plan cannot be the nurse’s choice alone. Further, the plan must be within the information and skill level of the family, and the family must be committed to the plan and have adequate resources available to implement the plan. 16. Which of the following terms refers to government actions that have a direct or indirect effect on families? a. Family funding b. Family legislation c. Family planning d. Family policy ANS: D Government actions that have a direct or indirect effect on families are called family policy. The range of social policy decisions that affect families is vast, such as health care access and coverage, low-income housing, Social Security, welfare, food stamps, pension plans, affirmative action, and education. Family planning is only one example of family policy that can have a direct or indirect effect on families. Family funding may occur through programs administered by the government, but these programs are developed from family policy. Family policy is broader than only addressing legislative action. 17. A nurse is using the provisions of the Family Medical Leave legislation. Which of the following actions is the nurse most likely to take? a. Resigning from employment, but retaining health insurance b. Sharing family information with colleagues c. Providing Medicaid to a family who cannot afford health insurance d. Taking a defined time off of work for family events without fear of job loss ANS: D The Family Medical Leave legislation allows for a family member to take a defined amount of leave for family events, such as births and deaths, without fear of losing his or her job. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountabilty Act (HIPAA) allows for familys to retain health insurance after resigning from employment. HIPAA prevents family information from being shared with colleagues unless they have a need to know based on the care they are providing for the family. The provision of Medicaid is not part of the Family Medical Leave legislation. 18. A nurse is conducting a family assessment. Which of the following behaviors would the nurse recognize as suggestive of a family with problems? a. Before eating, the family prayed, expressing gratitude for their blessings. b. During family play, jokes and laughter were heard. c. Each person had a private room with a door for alone time. d. Most of the conversation was between the father and the eldest daughter. ANS: D Limited communication or certain families members dominating the conversation can be suggestive of problems within the family. Evidence of healthy families can be seen in a variety of observations, including open communication among all members, mutual play with humor, balanced interactions among all members, expressions of a religious core or other value system, and each member being allowed some privacy. 19. The hospital-based nurse has worked with a client at some length regarding appropriate diet. Based on the family systems theory, which of the following will most likely occur when the client returns home? a. The family member who prepares food will probably suggest the newly discharged member eat the meals everyone in the family enjoys. b. The family member who prepares food will probably try to modify family meals without obvious change for the family as a whole. c. The family member who prepares food will probably prepare meals based on the diet plan for all the family. d. The family member who prepares food will probably prepare special meals for the newly discharged member. ANS: B Family systems typically maintain stable patterns, although families do change constantly in response to stresses. Change in one part of the family affects the total system. However, if family members are supportive, they will want to try to help the ill member. Therefore, the member who prepares the meals will probably compromise by trying to meet the ill member’s needs without making drastic changes in the overall eating patterns of the family. It is not realistic to expect the whole family to change eating patterns immediately based on the needs of one family member. Because of the rapid change and stress in American society, preparing different sets of meals is not very realistic. If the family member who prepares the meals does not attempt to make some changes, this would not be therapeutic for the family member who is ill. 20. A nurse has just met a family and is completing their family assessment. Which of the following actions should the nurse take before engaging in self-disclosure? a. Confirm the reason for the appointment. b. Demonstrate cultural awareness. c. Take time to build trust. d. Understand the family dynamics. ANS: C The family assessment process is interactive. As the nurse is evaluating the family, the family is evaluating the nurse. Too much disclosure during the early contacts between the family and nurse may scare the family away. The nurse should slow the process down, and take time to build trust. Components of building trust with the family would include confirming the reason for the appointment so that the family knows the nature of the visit and demonstrating cultural awareness during interactions. As the nurse completes the family assessment, the nurse will note the dynamics of the family; understanding the family dynamics is not important before engaging in self-disclosure. 21. A nurse is completing a tertiary prevention activity in a predominantly poor community, where eating clay (pica) is a common practice. Which of the following actions would the nurse most likely take? a. Assist those who eat large amounts of clay to obtain food stamps after explaining that clay, although filling, does not provide necessary nutrients. b. Initiate early intervention in the school system through education programs designed to focus on healthy food choices. c. Provide laboratory testing and physical assessments to assess for nutritional deficits resulting from clay intake. d. Survey families in the community to determine whether they eat clay and how much clay they eat. ANS: A Tertiary prevention is undertaken to prevent additional health problems when a problem has occurred. If the family members are eating clay, this demonstrates that a problem already exists. Early intervention in the school system is an example of primary prevention. Lab testing and surveying families are screening activities to determine whether a problem is present and to catch it in the early phases; such screening activities are representative of secondary prevention. MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1. A nurse requests to meet a newly referred family in their home. Which of the following best explains the rationale for this request? (Select all that apply.) a. The nurse can assess the family environment. b. The family will feel more comfortable. c. Families typically welcome others into their home. d. More family members can typically be involved. ANS: A, B, D Advantages to meeting in the family home include the fact that it allows the nurse to see the everyday family environment and observe typical family interactions. Also, more family members can be present, and families are often more comfortable in their own environment. However, a disadvantage to meeting in the family s home is that family members may view this as an intrusion into the only place they feel safe from outside observation; thus, the nurse must be highly skilled in guiding the interactions and setting limits. 2. In comparison with traditional norms, which family functions have become increasingly important in modern American society? (Select all that apply.) a. Conferring appropriate social status b. Educating the younger members c. Ensuring physical and mental health d. Fostering interpersonal relationships and support ANS: C, D Today, the more important functions are fostering relationships (emphasizing how people get along and their level of satisfaction) and promoting physical and mental health. Historically, families have had several functions including financial survival, reproduction, protection from hostile forces, and enculturation, including religious faith, education, conferring social status. 3. Which of the following must be firmly established before beginning a family assessment? (Select all that apply.) a. Why the data are needed b. How best to interview each individual in the family c. The most convenient time for you to visit the family d. The rationale or purpose of the visit ANS: A, C, D Assessment of families requires an organized plan, including the purpose of seeing the family, which family members can be present, what you are assessing and why, and how will you obtain the necessary data. The preferred time to visit is when most family members will be available. It is more informative to interview the family as a whole so that you can observe family interaction (rather than focusing on interviewing each individual Chapter 31: The Nurse in the Schools Stanhope: Foundations of Population Health for Community/Public Health Nursing, 5th Edition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following activities are expectations for a school health nurse? a. Ensuring that children with health problems are accepted by their peers b. Driving children home if parents can’t pick them up c. Giving emergency care in the school or during school events d. Giving medications as needed if children are ill ANS: C School nursing responsibilities include making sure that children get the health care they need, including emergency care in the school; keeping track of the state-required vaccinations that children have received; carrying out the required screening of the children based on state law; and ensuring that children with health problems are able to learn in the classroom. The nurse cannot convince children to accept other children as peers, although certainly efforts should be made. HIPAA would not allow individual examples of health problems to be shared, other than providing group statistics. It would not be appropriate for the school nurse to provide transportation services to the students attending the school. 2. Which of the following statements best explains why many school nurses are not able to ensure that all children receive needed health care in the schools? a. There is a shortage of baccalaureate-prepared nurses with national school health nurse certification. b. Most nurses prefer to be employed in hospitals giving direct care. c. Most school districts are unable to afford a nurse in every school. d. School districts and taxpayers see no need for nurses in schools. ANS: C In Healthy People 2020, objective ECBP-5 states that there should be one nurse for every 750 children in each school (U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, 2010). Most schools have not achieved this objective. In 2006, approximately 40% of the nation’s schools met that standard. The new objective is that 44.7% of the country’s elementary, middle, junior high, and senior high schools have this many nurses by 2020 (U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, 2010). Having fewer nurses in the schools means that the nurses are expected to perform many different functions. It is therefore possible that they are unable to provide the amount of comprehensive care that the students need. There is not a national requirement that school nurses must have baccalaureate preparation or school nurse certification. Preference of employers by nurses does not impact why school nurses are unable to ensure that adequate care if provided. School districts may see that the need for nurses is important, but may have insufficent funds to be able to afford to pay for their services. 3. A school health nurse is requested by the board of education to assist in choosing new playground equipment for an elementary school that meets safety standards. Which of the following best describes the nurse’s role in this scenario? a. Case manager b. Consultant c. Counselor d. Health educator ANS: B The school nurse is the person best able to provide health information to school administrators, teachers, and parent–teacher groups. As a consultant, the school nurse can provide professional information about proposed changes in the school environment and their effect on the health of the children. The nurse also can recommend changes in the school’s policies or ask community organizations to help make the children’s schools healthier places. As a case manager, the school nurse helps to coordinate the health care for children with complex health problems. As a counselor, the school nurse is considered a trustworthy person to whom the children can go if they are in trouble or when they need to talk. In the health educator role, the school nurse may be asked to teach children both individually and in the classroom. 4. At the annual community health fair, the school health nurse displays a science booth that examines the hazards of ineffective hand washing. Which of the following best describes the nurse’s role in this scenario? a. Consultant b. Community outreach c. Counselor d. Researcher ANS: B When participating in community outreach, nurses reach out to residents in the community. One common way this occurs is when nurses are involved in activities such as community health fairs or festivals in the schools. As a consultant, the school nurse can provide professional information about proposed changes in the school environment and their effect on the health of the children. As a counselor, the school nurse is considered a trustworthy person to whom the children can go if they are in trouble or when they need to talk. As a researcher, the nurse can study outcomes related to school nursing services which may advance the practice of school nursing. 5. Which of the following best explains why school nurses are involved in helping teachers with the task of teaching children how to practice problem solving, communication, and other life skills? a. Teacher shortages have required nurses to be increasingly involved in teaching life skills. b. Because so many nurses want to be employed in schools, this responsibility was assumed to increase employment opportunities. c. States are requiring nurses to screen and to teach life skills. d. Nurses have been enlisted in this role to help reduce risk factors for future health problems in school children. ANS: D Nurses fulfilling the health educator role assist in teaching children both individually and in the classroom. This teaching should assist in helping reduce the risk factors among children in the future. Potential teacher shortages have not impacted the role of the school nurse as a health educator. Use of the role of health educator has not changed the need for school nurses in the school setting. There are not state requirements for required school screening or teaching life skills. 6. Which of the following best describes services that are offered at a school-based health center? a. Employee care at a discounted cost at the school b. Family-centered care for preK-12 grade students c. Sex education, birth control, family planning, and care throughout pregnancy d. Referral and networking with other health care services in the community ANS: B These are family-centered, community-based clinics that are run within school, often in low income populations. These centers provide primary care services to students of preK-12 and may offer expanded health services, including mental health and dental care. The intention of school-based health centers is to provide care specifc to preK-12 grade students, not employees. These clinics provide a variety of services, depending on the clinic. Based on the size and services of the clinic, they may not provide family planning services, referral, or networking with other health care services. 7. The school health nurse has enlisted the assistance of high school role models in the areas of sports and scholarship to provide an antidrug presentation to their peers. Which of the following levels of prevention is being implemented? a. Primary b. Secondary c. Tertiary d. Both primary and secondary ANS: A Primary prevention interventions by the school nurse include educating children and adolescents about the effects of drugs. In preventing use, students are taught by the school nurse to stay away from drugs such as marijuana, cocaine, crack, heroin, and alcohol. Secondary prevention involves screening and intervening with at risk populations. Tertiary prevention aims for rehabilitation and returning to the highest functioning possible. 8. Which of the following best describes the primary reason that school health nurses spend so much time on educational programs that teach children the importance of water and fire safety, using a seatbelt in the car, and wearing a helmet when biking or skateboarding? a. Because children won’t know if someone doesn’t tell them b. Because injuries are the leading cause of death in children and most injuries are preventable c. Because it is a dangerous world and someone has to warn children about the dangers d. Because teaching is easy and more fun than passing out bandages and documenting care ANS: B The school nurse, as the trusted person at school, is able to quickly give information to help prevent injuries from occurring, since most injuries are preventable. Injuries are the leading cause of death in children and teenagers. The nurse is a trustworthy person, but the children may likely have heard this information from someone else. The role of health educator is an appropriate and important role of the school nurse which is the same as the role of the direct caregiver in caring for injured children and documenting care. 9. A nurse would like to implement a primary prevention effort to decrease the leading cause of death among children and teenagers. Which of the following actions would the nurse most likely take? a. Educate students about injury prevention measures. b. Provide free condoms to sexually active students. c. Screen for signs and symptoms of cancer. d. Invite a guest speaker to talk about living with HIV. ANS: A Injuries are the leading cause of death in children and teenagers; therefore, prevention measures should focus on injury prevention. Because the question asks for primary prevention efforts, the intervention must occur before injury. Common interventions by the school nurse include educational programs reminding children to use their seatbelts or bicycle helmets to prevent injuries. Other classes can be on crossing the street, water safety, and fire safety. Providing free condoms to sexually active students would be an secondary prevention intervention as these students are at risk to contract a sexually transmitted disease. Screening for signs and symptoms of cancer is an example of secondary prevention, aimed at early detection. Inviting a guest speaker to speak about HIV would address primary prevention, but it does not address the leading cause of death among children. 10. The school nurse has arranged for volunteers to help check each child’s hearing and vision. Any child that the volunteers feel did not “pass” will be sent to the nurse for follow-up. The nurse will then send a note to the parents that a physician should be seen. Which of the following levels of prevention is being implemented? a. Primary b. Secondary c. Tertiary d. Both primary and secondary ANS: B Because secondary prevention involves caring for children when they need health care, this is the largest responsibility for the school nurse. This includes caring for ill or injured students and school employees. It also involves screening and assessing children and referral to appropriate health agencies or providers. Primary prevention involves providing education before a problem or disease occurs. Tertiary prevention aims at rehabilitation after the disease or problem has occurred and intends to get the client to the highest possible level of functioning. 11. Which of the following would be the best way for the school nurse to fulfill his or her responsibilities in an emergency situation? a. Tell all staff to call 911 if the nurse is not in the building. b. Arrange to always be available, even if only by phone. c. Create and share an emergency plan with all teachers and staff. d. Wear a pager so that the nurse can come as soon as humanly possible. ANS: C The American Health Association recommends that the school nurse create an emergency plan with at least two different staff members identified and responsible for implementing the plan if the nurse is not in the building at the time of the emergency. The plan would include when to call 911 and how to get a child to the hospital via ambulance if needed. Depending on the emergency, it may or may not be appropriate to call 911; thus, having an emergency plan in place is a more appropriate response. It is impossible for the nurse to be available at all times. Depending on where the nurse is and what other roles the nurse is fulfilling, it may not be possible for the nurse to respond quickly to an emergency. 12. A school nurse is administering medications at the school. Which of the following guidelines should be followed? a. A current drug reference should be available in case information is needed b. The nurse should administer medications brought in from home by the child in a plastic bag c. Medications cannot be administered without a physician order d. Narcotics and controlled substances should be kept in a locked cabinet ANS: A A current drug reference should always be available so that it can be consulted for information. The nurse should develop a series of guidelines to help with the legal administration of medications in the school. The prescribed drugs should have the original prescription label on it and be in the original container. There should be a current, signed parental consent form for giving the medication, and the nurse should have a means of contacint a pharmacist to ask questions. A physican’s order is not needed to administer the medications. All medications, including narcotics, should be kept in a locked container so that they are not accessible to others. 13. An upset mother calls the school nurse and says, “How dare you say my child has lice? My child is clean and I keep a clean house! You’ve obviously made an error.” Which of the following would be the best response by the nurse? a. “I’m sorry you’re upset, but your child cannot return to school until this problem is addressed.” b. “Most lice are found in clean hair. Children often share combs. Let me tell you how to fix the problem.” c. “You may have been traveling. Lice are often found in motels.” d. “I’m sure you’re correct; one of my volunteers probably made an error. I’ll recheck.” ANS: B The nurse must reassure the mother that no insult was intended; in fact, lice are most often found on middle-class children with clean hair. Lice travel easily when children share items such as combs or other property in school. Lice are not life-threatening, and the necessary shampoo and other items to treat lice are widely available over the counter. Most school policies are more caring and less exclusionary and allow children with lice to attend school. It is more likely that the student contracted the lice from another student than from traveling to a motel. If the nurse has delegated the reponsibility of assessing for lice to a volunteer, the nurse should reassess the findings of the volunteer to confirm that the child has lice before contating the parent. 14. A school nurse listens as one student talks about another student being upset because his father frequently spanks him with a leather belt that leaves big marks on the student’s back. But the student begs the nurse not to tell anyone because he promised the friend that the information would never be shared. Which of the following actions should be taken by the nurse? a. Ask the student if abuse has occurred. b. Call in the named student and ask him to remove his shirt. c. Discuss the conversation with the student’s parents. d. Notify the legal authorities. ANS: D When the nurse identifies a child who may be abused or who receives information from someone else that a child may have been abused, the nurse must contact the appropriate legal authorities and the school’s principal. Asking the student about the abuse will not always elicit a truthful answer, because children will protect their parents. A confidential file should be made about the incident; however, the nurse should let the government authorities, usually the state or county child protection department, look into the suspected case. In all cases, the child should be protected from harm, and those who have no right to know that child abuse or neglect is suspected should not be given any information. 15. A school nurse suggests to teachers that they have a session on coping strategies and stress management techniques. The nurse also sets up a peer counseling program. Which of the following is the school nurse most likely trying to prevent? a. Suicide b. Bullying c. Obesity d. Violence ANS: A Suicide is the second leading cause of death among adolescents, ages 15 to 19. To reduce the incidence of suicide in teenagers, the nurse can emphasize coping strategies and stress management techniques and organize a peer assistance program to help teenagers cope with school stresses. Bullying may result in adolescents feeling that suicide is the only answer. However, the strategies that the nurse is completing would not necessarily promote a decrease in bullying. The strategies suggested would not impact the prevalence of obesity or the incidence of violence. 16. A disaster has occurred in the community. Which of the following actions should be taken by the school nurse? a. Continue activities as much as possible as if nothing had happened b. Continue to assess for shock and stress c. Help teachers discuss the disaster with their class d. Maintain school routines and activities ANS: B After a disaster, the school nurse has many responsibilities—for instance, continuing to assess the school community for the presence of shock and stress; encouraging parents to minimize how much their children view the disaster coverage on TV; providing grief counseling; continuing to communicate with the children, parents, and school personnel; and following up with assessment of children for anxiety, depression, regression, and posttraumatic stress disorder. It would not be appropriate for the nurse to ignore that a disaster has occurred or to assume that routines will remain the same; it is important for the nurse to assist the community to cope with the disaster. The nurse may use counselors in the community to assist the children to cope with the disaster as this may not be an appropriate role for the nurse or for the teacher to perform. 17. Which of the following is the leading cause of children being absent from school because of a chronic illness? a. Allergies b. Asthma c. Diabetes d. Upper respiratory infections ANS: B Asthma is one of the leading cause of children being absent from school because of a chronic illness. Upper respiratory infections are an acute problem, not a chronic one. Diabetes and allergies are not leading causes of chronic disease that result in children being absent from school. 18. A school nurse is demonstrating the use of a peak flow meter to help children with chronic asthma recognize when they need to use a rescue inhaler. Which of the following levels of prevention is being used by the nurse? a. Primary b. Secondary c. Tertiary d. Both primary and secondary ANS: C Tertiary prevention includes caring for children with long-term health needs, including asthma and disabling conditions. The nurse is teaching disease management (i.e., when to use an inhaler). Primary prevention involves providing education before a problem or disease occurs. Secondary prevention addresses screening and early detection of the disease or problem. 19. A school nurse has developed a special class for pregnant teens to teach them everything from anticipated body changes to methods for managing common pregnancy-associated problems. The classes also allow the nurse to be in close frequent contact with the students to monitor their health status. Which of the following levels of prevention is being used by the nurse? a. Primary prevention b. Secondary prevention c. Tertiary prevention d. Both primary and secondary prevention ANS: C Many teenage girls who are pregnant attend school; therefore, the school nurse may provide ongoing care to the mother. Although this may appear to be secondary prevention, it is tertiary prevention because adolescent pregnancies are considered to be high risk. Primary prevention involves providing education before a problem or disease occurs. Secondary prevention addresses screening and early detection of the disease or problem. Because the teenager is already pregnant, the nurse is addressing how to assist the teen to achieve the highest level of functioning possible (tertiary prevention). 20. A pregnant teen asks the school nurse to provide information on abortion and a list of health care providers who offer such services. If the school nurse has very strong personal beliefs against abortion, which of the following actions should be taken by the nurse? a. Call in another nurse to care for this client. b. Explain, from the nurse’s perspective, all the reasons that abortion should be made illegal. c. Offer the student a combination of oral contraceptives to induce spontaneous abortion. d. Provide information on alternatives to abortion and give the client information on adoption agencies. ANS: A This creates an ethical dilemma for the nurse. If the nurse feels so strongly that he or she cannot work with the situation, another school nurse should be called for help or the student should be referred to other health providers who can provide the care the student needs. It is important that the nurse be able to keep an open mind when working when this teen, and if that is not possible, another nurse needs to be asked to care for this client. The incorrect options all address the nurse discussing his/her personal beliefs against abortion which may not be therapeutic for the teen. 21. Which of the following is most important for school nurses to master in order to prepare for health care delivery in the future? a. Complementary and alternative therapies b. Computer and technology use c. Psychoanalytical techniques d. Self-defense techniques ANS: B In the future, school nursing will use telehealth and telecounseling to teach health education. School nurses will use the Internet to work with children and parents. Complementary and alternative therapies are already being widely used; most likely the nurse will not be the one providing such care so it would not be necessary for the nurse to master these skills. Psychoanalytical techniques would not be necessary for the nurse to master as the nurse is able to refer students who require this type of care to appropriate providers. There would not be a need for school nurses to master self-defense techniques. 22. The principal of a school was upset over a rumor that one of the children had engaged in a violent activity that injured a younger sibling. The principal asked the nurse who the children were so that the involved teachers could both support the injured child and guard other children from the violent child. Which of the following would be the best response by the nurse? a. “I’ll get the names to you and the involved teachers immediately.” b. “Let me get the parents’ consent, and then I’ll get you the names.” c. “Rumors are often inaccurate; let me follow up and see what happened and what needs to be done.” d. “Why don’t we coordinate a school-wide program on preventing accidents instead?” ANS: C The school nurse is responsible for maintaining school health office policies, including privacy and safety of health records. When a rumor is involved, it is always wise to check its accuracy. If a child was indeed hurt, the nurse needs to make sure both children involved receive (or have already received) appropriate care. The nurse must follow the HIPAA privacy rules while also ensuring the safety of children at school. The question about having a school-wide program may be appropriate, but this behavior was apparently purposeful, not accidental. 23. The mother of a high school student newly diagnosed with a condition that will require special health care services is concerned that the student will be required to be home-schooled away from the friends he has developed. Which of the following would be the most appropriate response by the school nurse? a. “Federal legislation requires that the school make provisions for those with various challenges, so your child will be able to remain in school as long as he is able.” b. “I realize that this will be a difficult adjustment, but home-schooling has improved over recent decades and the Internet will allow your child to connect with friends.” c. “Whether your child can remain in school will depend on state funding for those with disabilities. You might want to contact your congressman on this issue.” d. “Your child may remain in school as long as he can manage the course requirements and doesn’t flunk out.” ANS: A Federal legislation specifies that children cannot be excluded from schools because of a disability. The school must provide health services that each child needs. Legislation further requires the school district’s committee on the disabled to develop individualized education plans (IEPs) for children. Federal legislation will support this child continuing in the current school; thus, it would not be necessary to counsel the parent about concerns related to the child needing to be home schooled. Depending on the diagnosis, special educational needs may need to be addressed for the child through an IEP which may assist the child in being successful in the coursework. 24. A group of nursing students are scheduled to present a program on healthy hearts to various community groups, with a daycare center being the first location. What of the following advice should be given to them by their instructor? a. Base the program on the audience’s development and maturity. b. Bring (borrow if necessary) a model of the heart to help explain its functioning. c. Focus on entertaining the learners. d. Have lots of handouts to reinforce the lesson. ANS: A For younger learners, it is important to keep the lesson to no more than 20 minutes in length; to use plenty of examples, pictures, and stuffed animals in the talk; and to remember the developmental stage of the children when teaching them. It will be important for the nurse to assess the developmental level of the audience in order to determine if models or handouts are appropriate to be used. Keeping the presentation short should assist in keeping the learner’s attention. MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1. Which of the following activities are included in the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s school health program? (Select all that apply.) a. Ensuring a healthy school environment b. Assisting teachers with education related to health c. Encouraging nutritious school meals d. Giving immunizations to students, staff, teachers, and their families ANS: A, B, C The federal government, through the coordination of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, developed a plan that school health programs should follow, including health education, physical education, health services, nutrition services, counseling, psychological and social services, healthy school environment, health promotion for staff, and family/community involvement. Unfortunately, schools cannot afford to give immunizations to everyone who might want such a benefit. 2. Which of the following best explains why the federal government is beginning to fund school-based health centers? (Select all that apply.) a. These centers help young children avoid becoming addicted to drugs while still in elementary school. b. Attendance and learning are higher in schools with health clinics. c. These centers help keep children in school longer by distributing birth control and thus avoiding pregnancies. d. Many children have no other source of health care services. ANS: B, D The U.S. government began funding school-based health centers essentially because many school children may not receive health care services otherwise. These are family-centered, community-based clinics run within the schools. Certainly, avoiding pregnancy and drug addiction are among the goals of school-based health centers, but these are not reasons the government began funding them. 3. A new student’s parents had not yet submitted an immunization record, although the nurse had sent a reminder home with the student twice. Which of the following actions should be taken by the nurse to keep the child in school? (Select all that apply.) a. Call the parents or mail another reminder. b. Report the problem to the teacher and the principal. c. Send the child home with a note saying the child cannot return until the immunization record is received. d. Suggest to the parents that if they don’t have health care insurance, they may qualify for programs that provide immunizations free. ANS: A, D There are many problems with children not being immunized or having incomplete vaccination records, especially in families who have moved many times or who may not have a regular physician. The parents may have no idea whether the child has received the required shots. Families may also be without health care insurance to pay for the immunizations, or they may have insurance that does not pay for preventive care. In these cases, they may lack the resources to pay for the immunizations themselves. Therefore, the nurse’s role is to be sure parents are aware of the problem, to help them obtain the records if they have been misplaced, and to suggest ways to obtain the injections without charge, even if there is no obvious evidence that lack of funds is the problem. Telling the teacher or principal won’t resolve the problem. Sending home a note saying the child can not return to school does not assist the family with obtaining the immunization for the child which may be a burden for the family or a potential underlying reason why the child has not received the immunization. 4. Which of the following supplies or equipment should a nurse have available in the school health office? (Select all that apply.) a. Cervical spine collars b. Complete emergency kit that fulfills American Hospital Association requirements c. Epinephrine autoinjector kit d. Material for splints ANS: A, C, D The school nurse needs much equipment to deal with emergencies in the school. Basic necessary equipment includes full oxygen tanks with oxygen masks of different kinds, splints, cervical spine collars, sterile dressings, and an epinephrine autoinjector kit in case a child goes into anaphylactic shock after exposure to an allergen. A hospital-oriented emergency kit would become quickly outdated (medications) and extremely expensive. 5. A school nurse would like to improve the safety of everyone at the school by creating policies to decrease the likelihood that violence will occur. Which of the following actions would the nurse likely take? (Select all that apply.) a. Engaging parents in school activities b. Creating a zero tolerance police for weapons on school property c. Encouraging children to participate in the after school program at a local community center d. Developing mentoring programs for at-risk youth ANS: A, B, D Interventions that are aimed at preventing violence from occurring are: engaging parents in school activities that promote connections with their children, and foster communication, problem solving, limit setting, and monitoring of children; supporting/assisting with creating policies of zero tolerance for weapons on school property, including school grounds; and developing mentoring programs for at-risk youth and families. Encouraging students to attend the after school program at a local community center may assist with the students having additional supervision, but it does not contribute to the students having an increased loyalty or connection to the school. It is important to facilitate student connectedness to the school community. 6. A child has multiple disabilities, and caring for the child has been both expensive and time consuming for the school. Once the child turns 16, which of the following actions should be taken by the nurse? (Select all that apply.) a. As an adult, the child is no longer eligible for school services without charge. b. The school must continue to provide needed appropriate education for the child. c. The school can exclude the child from any extracurricular activities. d. The school should prepare an updated individualized education plan. ANS: B, D Educational services must be offered by the schools for all disabled children from birth through age 22 years. Children cannot be excluded from activities because of a disability. The school must always develop an individualized education plan for each child and update it at appropriate intervals. Turning 16 does not make a child an adult; thus the child is still able to receive services of the school and participate in extra curricular activities. Chapter 29: The Faith Community Nurse Stanhope: Foundations of Population Health for Community/Public Health Nursing, 5th Edition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following best describes the primary difference between parish nursing and all other nursing positions? a. Affiliation with a church or congregation b. Incorporation of spiritual aspects into nursing care c. Provision of holistic nursing care d. Residence within the community of service ANS: A In 1998 the American Nurses Association accepted parish nursing as the most recognized term for the practice of nurses working with congregations or faith communities. All nurses may choose to incorporate spiritual aspects into holistic nursing care. 2. To help congregation members better meet their nutritional needs, the parish nurse organized members to participate in activities that focused on fellowship while providing healthy meals to homebound members and serving “healthy heart” church suppers. Which of the following activities is being completed? a. Holistic care b. Health ministries c. Partnerships d. Pastoral care practices ANS: B Health ministries are those activities and programs in faith communities organized around health and healing to promote wholeness in health across the life span. These services include activities such as visiting the homebound, providing meals for families in crisis or when returning home after hospitalization, organizing prayer circles, serving “healthy heart” church suppers, and holding regular grief support groups. Holistic care is concerned with the relationship of body, mind, and spirit in a constantly changing envrionment. Providing a healthy meal does not address these multiple components. Partnerships may be among individuals, groups, and health care professionals within the congregation. It may involve partnerships to provide these meals; however, the focus is on the overall health ministry provided by this activity, not the partnerships which may be necessary to develop the program. Pastoral care practices invloves stresing the spiritual dimension of nursing, lending support duirng times of joy and sorrow, guiding the person through health and illness throughout life, and helping identify the spiritual strengths that assist in coping with particular events. These practices related to pastoral care are not provided through this meal. 3. Which of the following best describes why it is helpful to be a member of a faith community? a. Belief and traditions help with coping. b. Members can ask others in the group for help. c. It is a social outlet. d. Members are able to get others to contribute to the causes they support. ANS: A Persons who encounter assaults with physical and emotional illness and brokenness and who are able to call upon their faith beliefs and religious traditions are able to increase coping skills and realize spiritual growth even during adversity. Family communities do allow for a social outlet, asking others for help, and getting others to contribute to causes the support. However, the common connect of faith and traditions is what connects the members together and allows them to accomplish these other things. 4. Which of the following principles is central to the role of the parish nurse? a. Advanced nursing practice education and skills b. Faith consistent with the community and its leadership c. Spiritual dimension of care d. Willingness to serve anyone in need ANS: C The spiritual dimension of health care is central to the practice of parish nursing. Advanced nursing practice education and skills, although helpful, is not necessary for a nurse to become a parish nurse. Having a faith that is consistent with those who the nurse is working with is helpful, but not essential to the role of the parish nurse. Willingness to serve others is not specific to the role of the parish nurse, but rather a role that all nurses should embrace. 5. A young woman had been away from home several years before she returned home sick and disheartened. Her mother called a nurse to help. Which of the following behaviors would suggest that the caregiver who arrived was a parish nurse? a. Advanced nursing practice education and skills b. Compassionate, skilled, dedicated touch c. Offered a prayer with the daughter and mother d. Willingness to do whatever was needed by mother or daughter ANS: C The spiritual dimension of health care is central to the practice of parish nursing. Both nursing functions and pastoral care functions are performed by parish nurses, whose visits often involve prayer and reference to scripture, symbols, sacraments, and liturgy of the faith community. Advanced nursing practice is not required for a parish nurse, so this would not suggest that the nurse was a parish nurse. All nurses should demonstrate compassionate, skilled, and dedicated touch; thus, this would not be specific to the role of the parish nurse. Nurses should be willing to complete tasks that are within the scope of their practice, and this does not specifically describe what that scope of practice would be for a parish nurse. 6. Which of the following statements best describes how clients and parish nurses typically perceive spiritual health? a. It exists at the point that cure is attained. b. It has a tangential relation to well-being. c. It is part of an ongoing dynamic process. d. It is usually unchanging across the life span. ANS: C Health, spiritual health, and healing are considered parts of an ongoing, dynamic process. Because spiritual health is central to well-being, influences are evident in the total individual and noted in a healthy congregation. Well-being and illness may occur simultaneously; spiritual healing or well-being can exist in the absence of cure. Spiritual health and its definition is an ongoing and dynamic process; thus, it changes across the lifespan. 7. Which of the following statements suggests that faith community nursing is a nationally recognized specialty of nursing? a. Academic programs now offer a clinical specialty in parish nursing. b. Faith community nurses are increasingly receiving salaries for their efforts. c. Faith community nursing is being adapted in other countries and to non-Christian faiths. d. Scope and standards of faith community practice have been developed and revised. ANS: D The 2005 Faith Community Nursing: Scope and Standards of Practice revised the original 1998 document in describing the who, what, where, when, why, and how of the practice of faith community nursing. The most recent edition, released in 2012, focuses on faith community nurses but is also aimed at other healthcare providers, spiritual leaders, families, and members of faith communities. Specialty areas within professional nursing achieve a major milestone when the standards and scope common to that practice are recognized. Academic programs do not offer a clinical specialty in parish nursing; however, there may be ways to obtain specialty certification in the practice after becoming a registered nurse. Many faith community nurses work as volunteers. The majority of parish nurses are found in Protestant congregations, but they can be found around the world and in other faiths; however, there is nothing to suggest that the practice needs to be adapted when working with these other populations. 8. A group of parish nurses affiliated with a number of faith-based communities located in different regions across the state are attending a quarterly meeting. Which of the following statements made by one of them indicates a lack of understanding of parish nursing? a. “I always make sure to have new clients sign a release of information form to obtain their health record from their previous parish nurse.” b. “Because I work for and within the church, I am immune from civil laws.” c. “The pastor and I work together for the spiritual health of the community.” d. “Yes, I am happy to pray with my clients and help them worship.” ANS: B A nurse stating immunity to civil laws does not understand the role of the parish nurse. Parish nurses must abide by all of the parameters of the nurse practice act of the state just as other registered nurses. The nurse must personally and professionally abide by the parameters of the nurse practice act of the jurisdiction and maintain an active license of that state. 9. A nurse is considering accepting the parish nursing position within his congregation. Which of the following educational preparation is crucial for the nurse to have received? a. Baccalaureate education including community health nursing experience b. Graduate education in community health nursing c. Passing the national certifying exam for parish health nursing d. Worship experiences for the process of ministry ANS: A Current educational preparation for the parish nurse includes the successful completion of extensive continuing education contact hours or designated coursework in parish nurse preparation at the baccalaureate or graduate level, as well as a thorough grasp of the scope and standards of the practice. These basic programs provide an orientation to the role and functions of the parish nurse, as well as worship experiences for the process of ministry. Graduate education is not necessary to be employed as a parish nurse. A national certification exam for parish health nurses does not exist at this time. The parish nurse must be a member of the faith community and be comfortable with worship practices and traditions to function; however, the main function of the parish nurse is not ministry. 10. A family shared their concerns, including sexual issues, in strictest confidence with a faith community nurse. When the nurse returned to the church office, the pastor asked why the family wanted to see her. Which of the following statements would be the best response by the nurse? a. “Because you are my supervisor, I will summarize what was said for you.” b. “I will include that information in my report to our church’s wellness committee.” c. “They just wanted me to assess their health needs and make some suggestions.” d. “The family had some issues they wanted to discuss in confidence, which I will keep in confidence.” ANS: D Issues of privacy and confidentiality as well as record management should be discussed upon accepting a position. Regardless, if the nurse agreed to keep the information confidential, the nurse is morally obligated to do so. If the practice is to share all information with the pastor, then the family must be told this before they choose to share any information with the nurse. In order to keep this inforamtion confidential, the nurse should not disclose to the pastor that the nurse spoke with them about their health needs, as this may lead to further questions by the pastor. Additionally, because of confidentialty, the nurse would not share this information iwht the church’s wellness committee. 11. A father confides to the parish nurse that his wife has been hurting their 3-year-old daughter. The nurse examines the daughter and finds evidence of physical abuse. In the parish nurse role, which of the following actions should the nurse take first? a. Contact the pastor for guidance in handling this situation. b. Recommend that the family be removed from the faith community. c. Refer the family to pastoral services for counseling. d. Report the findings to child protective services. ANS: D As an advocate of client and group rights, the nurse identifies and reports neglect, abuse, and illegal behaviors to the appropriate legal sources. This is necessary regardless of the feelings of the pastor or the father because the nurse is bound legally to report abuse to a child, confirmed or suspected. Referral for counseling is appropriate; however, the child’s present state of well-being is paramount. Parish nurses must obey the nurse practice act and laws of the state. The nurse should not need to contact the pastor, as it is within the scope of nursing practice to report suspected abuse. 12. A faith community nurse is partnering with a local public health department to develop programs for primary, secondary, and tertiary prevention activities. Which of the following should be used as the primary guide for development? a. Contemporary articles in nursing journals b. Evidence-based practice guidelines for treatment of disease c. Healthy People 2020 goals and objectives d. Preferences of partners who are funding the programs ANS: C Healthy People 2020 guidelines are basic to the planning of health care. Contemporary nursing articles may be limited in scope and it may be very time consuming for the nurse to search multiple articles to find examples of these various levels of prevention. Evidence-based practice is for treatment, not for program development. Preferences of partners should not be used as the primary guide for development, rather after reviewing Healthy People 2020, the nurse may want to decide on which community partners would be appropriate for program devleopment. 13. A parish nurse is evaluating health programs that provide holistic care across the life span. Which of the following methods would be the most appropriate approach? a. Bringing families together to plan programs to meet the needs of individuals b. Establishing a wellness committee to assist in the evaluation process c. Matching financial resources with program objectives and goals d. Revisiting assessment data to be certain that planning reflects actual problems observed ANS: B The nurse and members of the congregation assess, plan, implement, and evaluate programs. The process of providing holistic care is enhanced by an active wellness committee or health cabinet. These incorrect options deal with factors other than program evaluation. 14. Which of the following statements by a parish nurse exhibits a lack of understanding of the concept of pastoral care? a. “By working with my clients to help them identify their spiritual strengths, I am drawing on pastoral care aspects of practice.” b. “To incorporate pastoral care, I should involve the pastor in ministering to the members of the congregation.” c. “I use pastoral care when I emphasize the spiritual dimension of nursing when providing care.” d. “When I lend support to my clients during times of joy, as well as during their times of sorrow, this illustrates an important aspect of pastoral care.” ANS: B Pastoral care is a service ministry formalized by a church or faith community, not necessarily involving the pastor. The nurse fulfills the role of pastoral care through stressing the spiritual dimension of nursing, lending support during times of joy and sorrow, guiding the person through health and illness throughout life, and helping identify the spiritual strengths that assist in coping with particular events. 15. A parish nurse is using the institution-based model to plan care for a client with a chronic illness. Which of the following activities would the nurse most likely implement? a. Bringing in family members to work with the client and nurse in decision making b. Partnering with outlying health care centers for coordinating optimal care c. Pulling from the collective strengths of faith-based community members for social support for the client d. Relying on congregational prayer as a component of healing ANS: B The institution-based model includes greater collaboration and partnerships. The nurse may be in a contractual relationship with hospitals, medical centers, long-term care establishments, or educational institutions. Thus, based on the institution-based model is partnering with outlying health care centers is appropriate. The other options are better examples of the nurse implementing the congregation-based model. In this practice, the nurse usually practice autonomously and is accountable to the congregation and its governing body. There are not specific partnerships in this model. 16. A nurse would like to maximize her autonomy in her parish nursing practice. Which of the following models would most likely be preferred by the nurse? a. Congregation-based model b. Institution-based model c. Teamwork model d. Partnership model ANS: A In the congregation-based model, the nurse is usually autonomous. The development of a parish nurse/health ministry program arises from the individual community of faith. The nurse is accountable to the congregation and its governing body. The institution-based model includes greater collaboration and partnerships. The nurse may be in a contractual relationship with hospitals, medical centers, long-term care establishments, or educational institutions. The teamwork and partnership models are not models of parish nursing. 17. A parish nurse organizes the annual health fair for the congregation, inviting community agencies to attend the event and display the health resources that are available in the community. What function of the parish nurse is being demonstrated? a. Health advocate b. Referral agent c. Health educator d. Coordinator of volunteers ANS: D As the coordinator of volunteers, the parish nurse recruits, trains, and supervises volunteers to expand ministry and outreach; organizes a health ministry team to guide and direct faith and health initiatives; and utilizes the gifts and talents of congregation and community members. As a health advocate, the parish nurse empowers congregation members to obtain needed health care services. Using the function of referral agent, the parish nurse provides information for referrals to appropriate agencies and services. As a health educator, the parish nurse focuses on the teaching role of the nurse; organizing a health fair enables others to complete that health teaching, not the parish nurse. 18. A parish nurse is implementing a primary prevention measure related to obesity among the school-age members of the church. Which of the following activities is most likely being used by the nurse? a. Establishing a walking program that is sufficiently challenging yet not too strenuous for those who are obese b. Partnering with youth camp cooks to ensure that food is nutritious c. Supervising height and weight measurements taken by clinic assistants d. Working with parents of obese children to implement family lifestyle changes ANS: B An example of primary prevention is encouraging healthy snacks and meals for youth outings and at educational hour and parenting sessions. The incorrect options all deal with secondary prevention activities, which are focused on decreasing obesity. MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1. The parish nurse is working with the wellness committee to develop health programming for the congregation. Which of the following activities would the nurse most likely completed? (Select all that apply.) a. Provide regular blood pressure screening for members of the congregation. b. Create a bulletin board to display information about the signs and symptoms of stroke. c. Implement a program to speak with adolescents about stress management. d. Research evidence-based approaches for chronic wound healing. ANS: A, B As a member of the wellness committee, the parish nurse is concerned with reducing the risk of development of disease or disorder among all of the members of the congregation. Thus, implementing strategies that are related to health promotion would be appropriate for the nurse to implement. These would include blood pressure screenings, creating a bulletin board about stroke, and implementing a stress management program for adolescents. Researching evidence-based guidelines for chronic wound healing would not address health promotion strategies within the congregation. Also, it is unlikely that the parish nurse is providing direct care services, such as caring for chronic wounds, for members of the congregation. 2. A parish nurse has been using pastoral activities when providing care to clients. Which of the following interventions is the nurse most likely using? (Select all that apply.) a. Helping families plan healthy nutritious meals and get plenty of rest b. Giving health education classes to the congregation c. Using hymns and scripture as a source of guidance and comfort d. Helping identify spiritual strengths that may assist in coping ANS: C, D When the nurse fulfills pastoral care, the nurse stresses the spiritual dimension, lends support during times of joy and sorrow, guides the person through health and illness, and helps identify the spiritual strengths that assist in coping with particular events. The incorrect responses represent nursing functions, not functions of pastoral care. Chapter 19: Family Health Risks Stanhope: Foundations of Population Health for Community/Public Health Nursing, 5th Edition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. A nurse was preparing for a home visit to a family where the mother had just been discharged from trauma care after being hit by a drunk driver. The nurse hoped the family was able to care for her. Which of the following comments from the husband would suggest an energized family? a. “I make most of the decisions so the kids don’t notice much difference.” b. “My daughter is pretty independent; she’s active in both sports and theater.” c. “My son is old enough to get a job and help pay all these medical bills.” d. “My wife taught our daughter how to cook simple meals.” ANS: B Pratt proposed the energized family as being an ideal family type that was most effective in meeting health needs. The energized family is characterized by active contact with a variety of groups and organizations (Boy Scouts, church, sports, theater), flexible role relationships, equal power structure, and a high degree of autonomy by each member. Flexible role relationships is not being demonstrated if only the daughter is taught how to cook and only the son is expected to get a job. Equal power structure is not being displayed if the husband makes all the decisions. 2. Using the Neuman Systems Model, which of the following questions would the nurse ask a client to assess physiological health? a. “What helps you to cope with situations involving your wife’s cancer?” b. “How has your child’s illness affected the behavior of your other children?” c. “Tell me about any illnesses your other family members have.” d. “Who do you turn to for support outside your immediate family?” ANS: C Physiological health involves issues related to physical wellness or illness. Other components of health in Neuman’s model include psychological health, sociocultural health, developmental health, and spiritual health. Asking about coping and support addresses psychological health, not physiological health. Inquiring about the behavior of the other children addresses developmental health. 3. A nurse is working with a family member to reduce his health risk. Which of the following recommendations would most likely be made by the nurse? a. “Be sure to take a 30-minute walk each day.” b. “Call our office if you have any questions or concerns at all.” c. “Come back in 2 weeks for follow-up on your surgery.” d. “Continue to take the drug until it is gone, even if you’re feeling better earlier.” ANS: A The factors that determine or influence whether disease or other unhealthy results occur are called health risks. The major categories of risk include inherited biological risk, social and physical environmental risk, and behavioral risk. Exercising for 30 minutes a day reduces the risk for many diseases. All the other options are treatment oriented rather than risk avoidance. 4. A nurse is appraising health risks. Which of the following questions would most likely be asked by the nurse? a. “Does your 4-year-old have a booster seat in the car?” b. “Have you noticed any physical problems as you go about your daily routine?” c. “What concerns do you have today? d. “Why did you decide to come in for a checkup?” ANS: A Health risk appraisal refers to the process of assessing for the presence of specific factors in each of the categories that have been identified as being associated with an increased likelihood of an illness, such as cancer, or an unhealthy event, such as an automobile accident. Inquiring about why the client came in for the visit, asking about concerns, and physical problmes does not address potential health risks that may need to be addressed for the client. 5. A nurse is conducting a health risk appraisal. Which of the following activities is the nurse assessing when using this tool? a. Health promotion activities b. Illness prevention activities c. Risk reduction activities d. Unhealthy activities ANS: D Health risk appraisal refers to the process of assessing the presence of specific factors in each of the categories that have been identified as being associated with an increased likelihood of an illness, such as cancer, or an unhealthy event, such as an automobile accident. Therefore, the nurse would assess for unhealthy behavior and activities in the areas of biological and age-related risk, social and physical environment risk, and behavioral risk. Incorrect Activities to promote health, prevent illness, or reduce risks would be advantageous, not risky. 6. A nurse is implementing risk reduction interventions with a family. Which of the following questions is most important for the nurse to ask? a. “Did any of the hunters in your family kill a deer this year?” b. “How do you keep your rifles safe from curious children?” c. “Where do you shoot with your handguns?” d. “Where do you keep your rifles locked when it is not hunting season?” ANS: C Risk reduction is a complex process that requires knowledge of risks and families’ perceptions of the nature of the risk. In this situation the nurse was asking questions to determine the family’s perception of risks associated with owning guns. If the family does not perceive the behavior (having guns in the house) as risky, but rather as necessary for food or sport, the nurse must first educate or persuade the family that others may be more comfortable if certain precautionary measures are taken (such as locks on the guns). Rifles are used for food and sport but handguns are often used in crimes and accidents resulting in death. Asking about how guns are kept safe or locked up does not address the families perception of the nature of the risk. Asking if any of the hunters killed a deer this year makes the assumption that the family uses the guns for hunting. This perception by the nurse may be inaccurate, it would be more appropriate for the nurse to ask how the guns are used in the home rather than assuming that they are used for deer hunting. 7. A nurse is completing a health risk appraisal with a client. Which of the following comments would cause the nurse to probe further to determine if the family is in crisis? a. “I can’t visit my husband in the hospital when I’m at work all day. How can I be sure he’s all right?” b. “My husband always handled our finances. Now that he’s gone, I’ll have to learn how to do this.” c. “I don’t know what to do now that my husband is dead. There is no way I can go back to work and also take care of our three children.” d. “What am I supposed to do now that everything we own is gone? Are there any agencies that can help me?” ANS: C A family crisis occurs when the family is not able to cope with an event and becomes disorganized or dysfunctional. When the demands of the situation exceed the resources of the family, a family crisis exists. Only the correct response is the person overwhelmed and unable to conceive of how to cope. In incorrect responses, the survivor is considering the problem and trying to learn how to cope or seek resources to cope. 8. A nurse has completed health risk appraisals with several different families. Which of the following families would be of most concern to the nurse? a. An older couple who has just retired and sold their house, who talk about their new condo in a retirement community. b. Newlyweds who have been saving their money, who want to discuss birth control and family planning in preparation for future pregnancies. c. Parents who come with their child for his prekindergarten physical exam and want to be sure all the child’s immunizations are up to date. d. A woman who is very pleased with her new position at the hospital and wants to have her preemployment exam and drug screen. ANS: A Transitions (movement from one stage or condition to another) are times of potential risk for families. Age-related or life-event risks often occur during transitions from one developmental stage to another. Transitions present new situations and demands for families. Moving from the family home to a smaller condo represents a major change in lifestyle. The incorrect responses do not represent major transitions. If the event is normative, or anticipated, it is possible for families to prepare for the event and its consequences. 9. Which of the following best describes a normative life event that can increase the risk for illness? a. A family is involved in a motor vehicle crash. b. A group of teens experiment with recreational drugs. c. A woman is pregnant with her first child. d. The family wage earner is laid off from his job. ANS: C Life events can increase the risk for illness and disability. Normative events are those that are generally expected to occur at a particular stage of development or of the life span. Although pregnancy is a normal condition, it carries risks such as the development of eclampsia or more minor health problems such as constipation and hemorrhoids. Additionally, pregnancy (and the birth that follows) will alter family dynamics and may increase risk for psychological stressors. The incorrect responses are not normative life events. 10. A nurse is drawing a genogram. Which of the following would the nurse use to demonstrate a marriage relationship between two individuals? a. A broken horizontal line b. An X through a circle c. A solid horizontal line d. A solid vertical line ANS: C Marriage is indicated by a solid line on a genogram. A broken horizontal line indicates a divorce or separation. An X through a circle or square indicates a death. A solid vertical line indicates offspring and children. 11. Which of the following best describes the use of genomic health care? a. Assists with understanding family relationships b. Assists with determining familial health risks c. Useful in learning about environmental risk factors d. Useful in detecting risk for developing cancer ANS: B Genomic health care can give health care providers the tools that they need to use a person’s unique genomic information to design and prescribe the most effective treatment for each person and to help clients and families understand some of their health risks that are influenced by their genetic make-up. When nurses obtain a family history and learn about the illnesses and causes of death of biologically related family members, they can then learn about shared genes, environment and lifestyle behaviors that can increase a person’s risks for the same diseases that other family members experienced. Genomic health care involves assesing for health risks based on genetic make-up, not environmental risks or risks posed by relationships or or family functioning. Genomic health care is broader than detecting risk for developing cancer. 12. Which of the following families is at high risk for health problems? a. A man agrees that he needs to eat better and exercise more but also expresses how busy he is at his job. b. A man knows that his grandfather, father, and older brother all died of cardiac disease. c. A man is currently unemployed and despairs about finding a position. d. A man expresses disappointment that, having been laid off as an executive, his new position pays only about two thirds of his original salary. ANS: C A person who is unemployed and despairing of finding employment is at serious economic risk, which is one of the foremost predictors of health problems. Economic risk is determined by the relationship between family financial resources and the demands on those resources. Having adequate financial resources means that a family is able to purchase the necessary services and goods related to health, such as adequate housing, clothing, food, education, and health or illness care. A man who says he needs to eat better and exercixe more appears to have adequate resources as he is employed. The man who has a family history of cardiac disease is not displaying any known risk factors related to income. The man who has been laid off stil is receiving an income which should assist him in being able to afford the necessary goods and services he needs in the immediate future. 13. A home health nurse who is visiting a family for the first time asks, “Could we review your extended family and other persons or groups with whom you interact each week?” Which of the following provides the best rationale for the nurse asking this question? a. To assess the family’s environment and social resources and risks b. To communicate with relevant others as needed c. To determine financial assets available to the family in case of serious need d. To understand the extended family relationships ANS: A The question by the nurse indicates that she is trying to obtain an ecomap. Ecomaps can provide information about relationships that the family has with others (such as relatives and neighbors), the family’s connections with other social units (such as church, school, work, clubs, and organizations), and the flow of energy, positive or negative, in the family. An ecomap represents the family’s interactions with other groups and organizations. Environmental or social risk and resources can be assessed from an ecomap. An ecomap does not assess extended family relationships or financial assets. An ecomap is not used as a communication method. 14. Which of the following clients would cause the nurse the most concern? a. The client who is currently unemployed but actively seeking a position and frequently walking from one interview to another b. The client who is not employed but spending time at the gym keeping fit and studying the benefits of organic natural uncooked foods c. The client who is employed and often works 12 hours a day without moving from the computer desk d. The client who is employed but always leaves promptly at 5:00 to pick up the children from the day care center ANS: C Personal health habits continue to contribute to the major causes of morbidity and mortality. The pattern of personal health habits and behavioral risk defines individual and family lifestyle risk. The client who doesn’t move from the computer desk is creating great stress and strain on personal physiology and needs to be educated on the benefits of exercise and the risks of cumulative trauma on the body. Multiple health benefits of regular physical activity have been identified; regular physical exercise is effective in promoting and maintaining health and preventing disease. The client who is currently unemployed is demonstrating positive health behaviors by actively seeking employment and walking frequently. The client who spends time at the gym and studies the benefits of organic foods is displaying positive health behaviors by being active and wanting to eat healthy. The client who leaves work to pick up the children at 5:00 is displaying healthy behaviors as he/she is balancing family and work. 15. An occupational health nurse is developing an educational program to address the importance of healthy personal health habits. Which of the following topics would be most important for the nurse to address? a. Avoidance of alcohol b. Regular physical exercise c. Daily consumption of calcium-rich foods d. Monthly self-breast and testicular exams ANS: B Many family health risks can be reduced by careful attention to diet, exercise, and stress management. Regular physical exercise is effective in promoting and maintaining health and in preventing disease. Physical activity can help to prevent obesity, diabetes, heart disease, cancer, osteoporosis, and depression. Avoidance of alcohol and daily consumption of calcium-rich foods are not recommendations for improving personal health habits. 16. A home health nurse is about to visit a family at their home. However, the nurse is feeling uncomfortable about getting out of her car because a group of young adults across the street are drinking and fighting among themselves. Which of the following actions should be taken by the nurse? a. Call the agency and ask what she should do. b. Call the family, explain the situation, and try to reschedule. c. Fulfill the nurse’s commitment to the family and enter the home quickly. d. Drive away and notify the family from a safer location. ANS: D Personal safety is an issue. Home visits are generally very safe; however, as with all worksites, the possibility of violence exists. Therefore, the nurse needs to use caution. If a reasonable question exists about the safety of making a visit, the nurse should not make the visit. The home health nurse should be educated about what to do in this situation before it occurs and should not need to call the agency to ask for their advice when faced with this situation. The priority would be to leave the situation before calling the family. The nurse should not place him/herself in a potentially violent situation by choosing to enter the home. 17. A nurse arrives at a home at the appointment time established with the client over the phone. However, no one answers the door. Finally a teenager comes out and says, “My mom said she couldn’t see you and you should go away.” Which of the following actions should be taken by the nurse? a. Demand the teen let the nurse into the home to talk to the mother. b. Interview the child as to how the family is doing. c. Leave a card with information on how to get in touch with the nurse. d. Point out that legally once an appointment has been made the mother needs to be seen. ANS: C The contact may be terminated as requested if the nurse determines that either the situation has been resolved or services have been obtained from another source and if the family understands that services are available and how to contact the agency if desired. However, the nurse should leave open the possibility of future contact. Obviously, the nurse cannot force entrance into the home. It would not be appropriate to coerce a child with misinformation or to interview a child about health concerns without a parent being present. 18. A nurse is completing an initial home visit with a family. Which of the following actions should be taken first by the nurse? a. Assess the family and the home setting for both strengths and problems. b. Determine the family’s expectations of a home visit. c. Establish rapport between the nurse and the family. d. Engage in extended social interaction as would be expected from any guest. ANS: C The initial home visit includes the nurse’s self-identification and clarification of role, establishing rapport with the family, assessing the situation, and then determining the client’s expectations. However, without rapport between the nurse and the client, the nurse will be notably less effective at other tasks. Although in some senses the nurse is a guest in the home, the nurse is not there for social purposes but to help the family with health concerns. Building rapport between the nurse and family should occur as the nurse is determining the family’s expectations, as well assessing the family and home setting. 19. A home health nurse is preparing to terminate the first home visit with teenage parents and their new baby. Which of the following actions will the nurse take before leaving? a. Determine the family’s willingness for another home visit b. Establish the purpose of the visit c. Review the family’s learning and other accomplishments of the visit d. Review the family record and reason for referral ANS: C During the termination phase, the nurse reviews the visit with the family, summarizes what has occurred and what has been accomplished, and may make plans for future visits. The incorrectoptions listed occur during the pre-visit phase. 20. During which phase of the home visit does the nurse document what was accomplished? a. Previsit phase b. In-home phase c. Termination phase d. Postvisit phase ANS: D A major task of the postvisit phase is documenting the visit and services provided. Major tasks of the pre-visit phase are to initiate contact with the family and schedule the home visit. During the in-home phase, the nurse-client relationshp is established. During the termination phase the visit is reviewed with the family and plan for future visits is made. 21. A nurse has just witnessed the signing of an agreement between two parents in which the parents pledge not to yell at each other in the presence of their children. Which of the following is being demonstrated through this action? a. Contracting b. Family crisis c. Empowerment d. Health risk reduction ANS: A Contracting is making an agreement between those involved in a shared effort by both nurse and family. The premise of contracting is family control. It is assumed that when the family has legitimate control, their ability to make healthful choices is increased. A family crisis ocurs when the family is not able to cope with an event and becomes disorganized or dysfuntional. Making a pledge through contracting is a way to cope with a family crisis. Empowerment reflects a family seeking help with access and control over needed resources, decision-making and problem-solving abilities, and the ability to communicate and to obtain needed resources. The pledge does not address the multiple components of empowerment. Health risk reduction is based on the assumption that decreasing the number or the magnitude of risks will decrease the probability of an undesired event occurring. The pledge does not address multiple health risks. 22. A nurse wants to empower the family of a mother who has been newly diagnosed with breast cancer. Which of the following actions would the nurse most likely take? a. Apply for emergency financial assistance on the family’s behalf. b. Arrange for community members to assist with child care. c. Invite the mother to join a cancer support group. d. Teach the family how to navigate the health care system. ANS: D Definitions of empowerment reflect three characteristics of the empowered family seeking help: access and control over needed resources, decision-making and problem-solving abilities, and the ability to communicate and to obtain needed resources. Approaches for helping individuals and families assume an active role in their health care should focus on empowering, rather than giving direct help. 23. A nurse has been successful in creating improvement in a family’s health. Which of the following characteristics is most likely displayed by the nurse? a. Skilled at recognizing and strengthening the family’s competencies b. Skilled at obtaining referrals and resources for the family c. Skilled at communication and interpersonal relationships d. Skilled at assessing the family’s main problems ANS: A The nurse’s approach to the family should be positive and focused on competencies rather than on problems or deficits. The incorrect responses do not address the strengths of the family, rather they focus on obtaining necessary resources, improving relationships, and assessing for problems. 24. Which of the following should be the initial consideration made by a nurse who is working with lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgendered (LGBT) families? a. Understanding of same sex marriage laws within the state b. Understanding of personal feelings of working with members of this community c. Assessment of the family structure within the LGBT family d. Assessment of sexual orientation in a safe environment ANS: B Nurses have an ethical obligation to provide culturally competent care to LGBT families. Some nurses may feel a degree of discomfort discussing sexual orientation with their patients. However, it is important to overcome this barrier to care for LGBT families. Thus, nurses should provide a safe environment for patients to discuss their sexual orientation. After understanding one’s own feelings when providing care for this population, it may be important for the nurse to investigate same sex marriage laws and family structure. It is important to provide clients a safe environment to discuss sexual orientation; however, the nurse must be aware of his/her own feelings before beginning this discussion. 25. A nurse notes that the community has an unusually high prevalence of sexually transmitted infections among teens. Which of the following best describes a secondary prevention action the nurse could take? a. Conducting a sexual behavior survey with the adolescents b. Establishing in-school education related to transmission of sexual infections c. Providing free condoms at schools and universities d. Providing follow-up educational programs for those diagnosed with an STI ANS: A Secondary prevention would include screening for risky behavior. Education and distribution of condoms are both primary prevention measures, and follow-up education for those diagnosed and being treated is tertiary to prevent further problems. MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1. A family asks the nurse to please meet at their home rather than at the clinic. Which of the following best describes why the family prefers to meet in their home? (Select all that apply.) a. The family won’t have to travel. b. It is cheaper for the family because of reimbursement requirements. c. Meeting at home is much more convenient for the family. d. The nurse won’t be distracted by other clients or responsibilities. e. It would save money for the nurse and the clinic. ANS: A, C Advantages of a home visit include client convenience and client control, as well as the fact that it facilitates clients who are unable to travel, it allows more individualized services, and it provides a natural relaxed environment for discussion. However, home visits are expensive for the nurse and the nurse’s employer because of travel costs and the amount of time spent with just one family. Unfortunately, nurses can be distracted by other tasks regardless of setting. Home visits are cheaper for insurance companies, not for the family. 2. Which of the following factor(s) may help determine how many home visits are made to a particular family? (Select all that apply.) a. Agency’s policies regarding eligibility for services b. Family’s feelings about the home visit and willingness to continue c. Nurse’s perception of the amount of time needed to complete required tasks d. Reimbursement policies of third-party payers ANS: A, B, D Although it is not unusual to have only one home visit with a family, often multiple visits are made. The frequency and intensity of home visits vary not only with the needs of the family but also with the eligibility of the family for services as defined by agency policies and priorities. Although the textbook does not directly discuss the issue, the family’s willingness to work with the nurse is a factor. Also, the nurse cannot make visits unless the agency is being reimbursed for the nurse’s time and expenses, so reimbursement policies of third-party payers are a major influence on the number of visits for which the family may be eligible. The nurse’s perception of the time needed to give quality care must unfortunately be secondary to other variables, which can control the time available. 3. The nurse and the family have agreed on an ambitious goal to improve family functioning, but as the family later expresses with some dismay, they have not been able to change their behavior as easily and quickly as they had hoped. Which of the following must be remembered throughout this process? (Select all that apply.) a. A reassessment of resources should be done if the plan does not work. b. Individual family members must all be willing to make the plan their first priority. c. Goals must be realistic and feasible. d. Ongoing negotiation is central to the process. ANS: C, D In contracting, an important aspect is obtaining the family’s view of the situation and its needs and problems. Goals must be mutually set and realistic. A pitfall for nurses and clients who are new to contracting is to set overly ambitious goals. Because contracting is a process characterized by ongoing renegotiating, the goals are not static. The family’s inability to change “as easily and quickly as they had hoped” does not mean the plan is not workable—only that more time and effort may be necessary. The plan does not need to be the “first priority” for all family members for it to be effective. The plan does need to be mutually set, but depending on the situation it may be difficult for this to be the priority for all members of the family. The plan may not be working for a variety of reasons, lack of resources may not be the reason. 4. A nurse enters a family’s home for the first time. Which of the following goals should the nurse have? (Select all that apply.) a. Assessing each family member in detail both physically and psychologically b. Collaborating with the family to establish goals and a plan for meeting them c. Determining the exact relationship between each member of the family d. Exploring the family’s perception of their problems and needs ANS: B, D During the beginning phase of the nurse-family interaction, three activities occur—mutual data collection and exploration of needs and problems; mutual establishment of goals; and mutual development of a plan. Assessment of each family member and determining the exact relationship between each member of the family are not part of nurse-family interactions. 5. A nurse calls a family to arrange for the first home visit. Which of the following information should the nurse share with the family? (Select all that apply.) a. The reason for the visit b. Everything the nurse knows about the family c. How many visits will be planned d. The cost of the visit and how this may be paid ANS: A, D The nurse should include the reason for the visit, how or from whom the referral was obtained, and a brief summary of what is known about the family’s situation. The nurse should negotiate a time for the visit, preferably when most family members are available. Clients should be told the fee and possible methods of payment before the nurse assesses the family’s willingness for a home visit. If the family does not have a phone, mail can be used to share information. It would be inappropriate for the nurse to share everything that she knows about the family with the family as there may be some information that the family does not need to know. Without visiting the family first, the nurse may not yet know the number of visits that may be planned. Chapter 20: Health Risks Across the Life Span Stanhope: Foundations of Population Health for Community/Public Health Nursing, 5th Edition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. A school nurse wants to decrease the rate of obesity among children. Which of the following actions in the community would be most effective? a. Lobby legislators to enact stronger legislation regarding school lunches and snack machines in schools. b. Increase nutrition programs in schools that teach children to make healthy food choices. c. Involve the entire family in the planning and managing of nutrition, especially when a child in the family is obese. d. Provide after-school and summer camps that focus on diet and exercise. ANS: C Interventions need to be based on goals of lifestyle changes for the entire family. The goal is to modify the way the family eats, exercises, and plans daily activities. Although it is important to teach nutrition, exercise, and proper food choice, if the family does not, for example, prepare the proper foods from which they can choose, the knowledge of the child is insignificant. Changes need to be made at a more direct level, such as by working with the family, to establish a change. Community-level changes may not impact what is happening within the family in regards to diet and exercise. 2. A nurse wants to establish a program to decrease the death rate among children. Which of the following health problems should be the target of this program? a. Accidents and injuries b. AIDS c. Childhood obesity d. Vaccine-preventable diseases ANS: A Injuries are the number one cause of death for children (and young adults up to age 21 years) in the United States. Injuries and accidents are the most important causes of preventable disease, disability, and death among children. Most are preventable. Obesity, although a significant problem, is not a common cause of death in children. AIDS and vaccine-preventable diseases are not common causes of death among children. 3. A nurse wants to establish a program to decrease the death rate among adolescents. Which of the following programs should be developed? a. Antialcohol program b. Antismoking program c. Careful driving program d. Safe sex program ANS: C Motor vehicle accidents are the leading cause of death among children and teenagers. The use of tobacco is a leading cause of preventable death among adults, but not among adolescents. The use of alcohol and sexually transmitted diseases are not related to common causes of death among teenagers. 4. Which of the following is of the greatest concern for the nurse who works with high school students? a. Alcohol use b. Motor vehicle accidents c. Sports-related injuries d. Unprotected sex ANS: B Motor vehicle-related injuries and violence are the leading causes of morbidity and mortality for adolescents. Thus, this would be the greatest concern for the nurse working with high school students. Alcohol use, sport-related injuries, and unprotected sex are not related to the major causes of morbidity and mortality among adolescents. So, although these topics may impact this population they should not be the priority for the nurse. 5. A mother says, “My son wants me to let him buy a car. I must admit, I certainly get tired of driving him around to all his sports and other activities. Do you think I should let him have a car?” Which of the following statements would be the best response by the nurse? a. “Absolutely, it will help him recognize the cost of gas and maintenance.” b. “Certainly. Most young men want their own car, and peer pressure can be painful.” c. “It depends on whether you trust your son to drive safely.” d. “No, adolescent males cannot be trusted with an automobile.” ANS: C Motor vehicle-related injuries and violence are the leading causes of morbidity and mortality for adolescents. Males are more likely to take risks, and injury death rates for boys are twice as high as those for girls. Thus, the response by the nurse should take these factors into consideration in response and encourage the mother to individualize her decision for her son. The incorrect reponses do not take into account the individual risk factors that the nurse should encourage the mother to consider. The nurse should encourage the mother to think about the risky behaviors specific to this population and how they apply to her son. 6. Which of the following children is most at risk for being abused? a. A 1-year-old b. A 6-year-old c. A 9-year-old d. A teenager ANS: A Children under the age of 4 and children with special needs are at highest risk for abuse. A 6 year old, 9 year old, and teenager are not as at high of risk for being abused because they are older. Literature states that those under the age of 4 years are at highest risk for abuse. 7. If underlying causes were listed on autopsy reports, which of the following would be the most common cause of unnecessary death in the United States? a. Alcohol b. Guns c. Lack of exercise d. Unprotected sex ANS: C Heart disease is the leading cause of death in the United States. Routine physical activity has been found to prevent early death and chronic diseases, including coronary artery disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes mellitus, depression, and some types of cancer. Alcohol, guns, and unprotected sex are not related to common causes of unnecessary death among adults in the United States. 8. A client has designated someone else to make health care decisions when he or she is unable to do so. Which of the following methods is the client using to make health care decisions? a. An advance directive b. A living will c. A durable power of attorney d. A Do-Not-Resuscitate (DNR) order ANS: C Durable power of attorney is the legal way for a client to designate someone else to make health care decisions when he or she is unable to do so. Advance directives is a broad category that includes both living wills and durable power of attorney. A living will allows the client to express wishes regarding the use of medical treatments in the event of a terminal illness. A DNR order is a specific order from a physician not to use cardiopulmonary resuscitation. 9. A woman needs to take some time off from work to care for her invalid mother. Which of the following health policies allows her to take an extended leave from work to care for a family member? a. Patient Self-Determination Act b. Personal Responsibility and Work Opportunity Reconciliation Act c. Temporary Assistance for Needy Families (TANF) d. Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA) ANS: D The FMLA provides job protection and continuous health benefits where applicable for eligible employees who need extended leave for their own illness or to care for a family member. The Patient Self-Determination Act requires that providers receiving Medicare and Medicaid funds give clients written inforamtion regarding their legal options for treatment choices if they become incapacitated. The Personal Responsibility and Work Opportunity Reconciliation Act is commonly known as “welfare reform”. This law created the TANF program. The Temporary Assistance for Needy Families program is a work program that mandates that women heads of households find employment to retain their benefits. 10. Which of the following situations would most likely indicate elder abuse? a. A daughter refuses to visit her mother due to work commitments. b. A child runs around a grandparent’s house breaking items. c. A young man repeatedly steals money from his grandmother. d. An elderly person demands that the family come for dinner. ANS: C Theft or mismanagement of money or resources is an element of abuse. A daughter refusing to visit, children breaking items, and an elderly person demanding that the family come for dinner are not situations that indicate elder abuse. None of these situations should cause alarm for the nurse as they all may normally occur within a family. 11. A nurse would like to learn more about the overall health of a population. Which of the following indicators would the nurse most likely use? a. Life expectancy b. Mortality rate c. Morbidity rate d. Health status ANS: A Life expectancy is a measure that is often used to gauge the overall health of a population. Health status indicators are the quantitative or qualitative measures used to describe the level of well-being or illness present in a defined population or to describe related attributes or risk factors. Morbidity rate is the frequency that a disease occurs within a population. Mortality rate is the number of deaths in a given area or period. Both morbidity and mortality rates are health status indicators. 12. A nurse is new to the community but wants to begin planning immediately for health promotion programs. Even though the nurse does not yet know the community, which of the following programs would be good to plan first? a. Alcohol and tobacco cessation programs b. Cancer screening programs c. Cardiac health education programs d. Exercise for life programs ANS: C Heart disease is one of the most significant public health problems in the United States, responsible for premature mortality and disability. Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in the United States. Good nutrition and exercise programs, while both good health promotion programs, are too narrow in focus to represent the greatest need in the community. Cancer is the second leading cause of death so may be the nurse’s second focus. 13. A nurse is caring for a child who has been diagnosed with a chronic health condition. Which of the following conditions would the child most likely have? a. Heart disease b. Down syndrome c. Emphysema d. Arthritis ANS: B Common chronic conditions seen in children are Down syndrome, spina bifida, cerebral palsy, asthma, ADHD, diabetes, congenital heart disease, cancer, hemophilia, brochopulmonary dysplagia, and AIDS. Heart diease, emphysema, and arthritis are common chronic health conditions of adults, not children. 14. A nurse has just met the parents of a 10-year-old child who has been diagnoses with a congenital heart defect. When interviewing the parents, which of the following would be a priority question for the nurse to ask? a. What are the learning needs of your child? b. What does your child eat on a typical day? c. Does your child have a good peer support network? d. Does your child have a medical home? ANS: D The use of a medical home, in which one provider or clinic has all of the child’s records, is important for this population. Communication among all providers who are working with this child is essential in order for the child to achieve optimal health and functioning. Learning needs, nutritional needs, and peer relationships are important for a 10 year old child. However, without having the coordination and consistency of a medical home to coordinate medical care these other things may be insignficant. 15. Which statement about eating disorders is correct? a. Individuals with anorexia frequently complain about weight loss. b. Purging is associated with anorexia. c. Most women with bulimia are concerned with the shape and weight of their body. d. Bulimia is considered to have more medical complications than anorexia. ANS: C Those with bulimia are usually concerned with the shape and weight of their body. Those with anorexia view themselves as normal or overweight, purging is associated with bulimia, and anorexia is considered to have more complications than bulimia. 16. A nurse is providing contraceptive counseling to a female client. Which of the following is the most appropriate outcome of this counseling? a. Encourage the individual to choose abstinence. b. Ensure the individual is educated to make an informed choice about reproduction. c. Advocate for increased funding for reproductive services. d. Reduce the health risks of the individual. ANS: B The goal of contraceptive counseling is to ensure that women have appropriate instruction to make informed choices about reproduction. The nurse should provide a nonjudgmental approach during counseling and allow the woman to choose the appropriate contraceptive method. Nurses do advocate for reproductive services for women, but that is not a goal of contraceptive counseling. Reduction in the health risks of the individual is a goal of pre-conceptual counseling. 17. A nurse is providing preconceptual counseling to a young woman. Which of the following supplements would the nurse most likely recommend? a. Iron b. Calcium c. Folic acid d. Vitamin C ANS: C Research has shown that intake of folic acid can significantly reduce the occurrence of serious and often fatal neural tube defects. A recommendation was made that women capable of or planning a pregnancy take 400 mcg of folic acid daily (USDHHS, 2010). Iron, calcium, and vitamin C are not used as routine prenatal supplements. 18. Which of the following best describes the current research findings related to the use of hormone replacement therapy (HRT)? a. HRT does not prevent heart disease. b. Use of HRT is recommended to prevent osteoporosis. c. When used with complementary therapies, HRT is most effective. d. HRT is a contributing cause of breast cancer. ANS: A HRT does not prevent heart disease. To prevent heart disease women should avoid smoking, reduce fat and cholesterol intake, limit salt and alcohol, maintain a healthy weight, and be physically active. HRT is not recommended to promote osteoporosis. HRT is not a contributing cause of breast cancer. There is no evidence that HRT is most effective when used with complementary therapies. 19. Which of the following best describes where health care dollars in the United States be focused to improve breast cancer cure rates? a. Education for women about breast cancer b. Early detection programs with referral to ongoing access to a care provider c. Primary prevention programs d. Tertiary care through long-term follow-up ANS: B Early detection can promote a cure, whereas late detection typically ensures a poor prognosis. The differences in the outcomes between women of color and white women point to issues associated with early detection, access to health care, and follow-up by a regular care provider. Education for women about breast cancer is not as effective as early detection programs. Screening must be completed which is accomplished through secondary, not primary prevention. Tertiary care does not occur until after diagnosis has occurred and this is too late. 20. Which of the following behaviors results in men being less healthy than women? a. Concentration on sports, hunting, and other dangerous recreational choices b. Employment in stressful positions more so than women c. Preference to spend money on priorities other than health care d. Reluctance to visit physicians ANS: D A major obstacle to improving men’s health is their apparent reluctance to consult their primary care provider. Men are not well connected to the health care system. Men do not participate in health care at the same level as women, apparently because of the traditional masculine gender role learned through socialization (Bonhomme, 2007). Only 57% of US men see a doctor, nurse practitioner, or physician assistant compared with 74% of women (AHRQ, 2010). Hobbies, employment, and preference on how to spend money may influence a man’s decision to seek medical care. However, these have not been identified as major obstacles in comparance to overall reluctance to seek care. 21. Which of the following characteristics indicates a man is at a higher risk for developing prostate cancer? a. Being of Caucasian descent b. Has not had a PSA test c. Has a father or brother who has had prostate cancer d. Has benign prostatic hypertrophy ANS: C Having a father or brother who has had prostate cancer places a man at higher risk for developing prostate cancer. African American males have a mortality rate from prostate cancer that is nearly twice as high as any other group. The PSA test is not accurate in terms of sensitivity or specificity. This blood test produces many false-positive results because many factors can elevate the PSA. There is not a relationship between benign prostatic hypertrophy and the development of prostate cancer. 22. Which of the following factors has the largest impact on health disparities among all populations? a. Ethnicity b. Education level c. Lifestyle choices d. Poverty ANS: D Poverty is a strong and underlying current factor that affects all special groups. Ethnicity, education level, and lifestyle choices do not have as large of an impact on health disparities than income level related to poverty. 23. A nurse is conducting a screening for type 2 diabetes for children attending a local school. In addition to an elevated BMI, which of the following risk factors should the nurse consider? a. Caucasian descent b. Family history of type 2 diabetes c. Birthweight greater than 9 pounds d. Poverty ANS: B Screening for type 2 diabetes mellitus is recommended for children with a BMI from the 85th to 95th percentile with two or more for the following risk factors: family history of type 2 diabetes in a first or second degree relative; Native American, African American, latino, Asian American or Pacific Islander descent; signs of insulin resistance or conditions associated with insulin resistance; or maternal history of diabetes or GDM during the child’s gestation. Native American, African American, latino, Asian American or Pasific Islander descent is a risk factor, not Caucasian descent. Elevated birthweight and poverty have not been identified by the American Diabetes Association as significant risk factors that indicate the need for additional screening. 24. A nurse is providing nutrition counseling to the parents of a 4-year-old. Which of the following recommendations is the nurse most likely to provide? a. It is recommended that the child consume approximately 10 ounces of grains on a daily basis. b. It is recommended that the child consume approximately four cups of dairy on a daily basis. c. It is recommended that the child consume approximately four cups of fruits and vegetables daily. d. It is recommended that the child consume approximately 10 ounces of protein on a daily basis. ANS: C It is recommended that children of 4 to 8 years old consume 1.5–2.5 cups of vegetables and 1–2 cups of fruits on a daily basis. It is recommended that children 4 to 8 years old consume 4-6 ounces of grains on a daily basis. It is recommended that children 4 to 8 years old consume 2 cups of dairy on a daily basis. It is recommended that children 4 to 8 years old consume 3-5.5 ounces of proteins on a daily basis. 25. A nurse is implementing Wagner’s Chronic Care Model (CCM). Which of the following actions would the nurse most likely take? a. Educate a community group about hypertension control. b. Create a budget for chronic disease management. c. Administer immunizations to community members. d. Conduct depression screenings in the community. ANS: A Use of electronic health records, provider reminders for key evidence-based care components, interprofessional teams communicating regularly, and community health classes to educate people with chronic diseases are various ways the CCM is being implemented. Creating a budget is not a way to use CCM. Administration of immunizations and conducting depression screenings do not address the management of the most common and costly chronic diseases: heart disease, diabetes, stroke, cancer, and arthritis. 26. Toward whom is the TLC model targeted? a. Caregivers of older persons with health problems b. Community organizations that offer services for the elderly c. Elderly clients with health problems d. Nurses who care for older clients ANS: A The TLC model is focused toward caregivers (primarily families) in an effort to relieve caregiver burden. Components are T = training in care techniques, safe medication use, recognition of abnormalities, available resources; L = leaving the care situation periodically to obtain respite and relaxation and maintain their normal living needs; and C = care for themselves (the caregiver) through adequate sleep, rest, exercise, nutrition, socialization, solitude, support, financial aid, and health management. The TLC model is not focused on community organizations, elderly clients, or nurses, rather it focuses on caregivers and relieving caregiver burden. 27. A client explains to the nurse that it is just impossible for her and her husband to continue to have his mother in the home alone during the day while they work because the woman becomes confused and has fallen twice. Which of the following community resources should the nurse recommend? a. Adult day health b. Home health c. Long-term care d. Senior center ANS: A Adult day health is for individuals whose mental and/or physical function requires additional health care and supervision. Typically, individuals return home to their caregivers at night. Adult day health serves as more of a medical model than the senior center.Long-term care would take the client out of the home. Home health would leave the patient for periods of unsupervised time in which the patient could have problems and help would not be available. 28. An elderly person is in the last stages of dying. Which type of care would be the best for him? a. Home health b. Assisted living c. Nursing home d. Hospice ANS: D Hospice would be the best form of care for a person in the last stages of dying. The other options are not specifically designed for persons in the last stages of dying. Home health provides care in the home, but is not specific to meet the needs of the dying patient and his/her family. Assisted living relates to a living situation where the client receives different amentities depending on the level of care needed. This type of living arrangment is not specific to care for the dying patient. Nursing homes provide long-term care and are not specific to care needed for a dying patient. 29. Which of the following is the best way to ensure good nutrition in infants? a. Breastfeeding only b. Feed them brand-name baby foods c. Feed them only homemade cereals d. Supplement breastfeeding with brand-name formulas ANS: A Breastfeeding is the preferred method of infant feeding. Breast milk provides appropriate nutrients and antibodies for the infant. Breastfed infants have fewer illnesses and allergies. Breastfeeding is associated with a lower risk in developing childhood obesity. Feeding brand-name foods, homemade cereals, and supplementing with formula are not the best ways to ensure good nutrition in infants. Breastfeeding is the best option to ensure good nutrition. 30. A nurse is implementing a tertiary prevention program to promote health among middle-aged women with diabetes. Which of the following best describes the intervention being implemented by the nurse? a. Developing lifestyle improvement programs for women at risk for diabetes b. Presenting lifestyle management presentations at women’s conferences c. Monitoring blood glucose levels closely and modifying diet accordingly d. Screening glucose levels of women at risk for development of diabetes ANS: C Tertiary prevention includes activities that are aimed to reduce the complications of the disease process. Only monitoring blood glucose levels is directed toward preventing problems in women who already are diagnosed with diabetes. Developing lifestyle improvement programs for women at risk for diabetes is an example of secondary prevention as this group is at risk for developing the problem. Presenting lifestyle management at women’s conferences is an example of primary prevention, preventing the disease before it occurs. Screening glucose levels is an example of secondary prevention, as all screening tests are secondary prevention. 31. A nurse advises a client who has HIV not to donate blood, plasma, or organs. Which of the following levels of prevention is being used? a. Primary prevention b. Secondary prevention c. Tertiary prevention d. Health promotion ANS: C Tertiary prevention includes those interventions aimed at disability limitations and rehabilitation from disease, injury, or disability. Primary prevention and health promotion both address the use of interventions before the disease occurs and to reduce the risk of developing the disease. Secondary prevention is aimed at detecting the disease early through screening programs and early intervention for at risk individuals. 32. A nurse wants to promote improved health for obese children in the community. Which of the following best describes a tertiary prevention measure that the nurse would implement? a. Establish lifestyle improvement programs through local youth organizations. b. Evaluate the food intake of a group of children for a 48-hour period. c. Provide education programs to overweight expectant parents. d. Evaluate the body mass index of children at regularly scheduled well-child exams. ANS: A Tertiary prevention includes activities aimed to reduce the complications of the disease process. Only lifestyle improvement programs are directed toward preventing problems in children who are already obese. Evaluating food intake and evaluating BMI are types of screening programs (secondary prevention). Providing education programs to overweight expectant parents does not involve children. MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1. Which of the following adolescent(s) would receive care from the advanced practice nurse without parental consent? (Select all that apply.) a. A 16-year-old who is living on his own (not with his parents) b. A pregnant adolescent c. An adolescent in an emergency situation d. An adolescent whose diagnosis has a serious prognosis ANS: A, B, C Most states have enacted laws allowing health care providers to treat adolescents in certain situations without parental consent. These situations include emergency care, substance abuse, pregnancy, and birth control. All 50 states recognize the “mature minors doctrine.” This allows youths 15 years of age and older to give informed medical consent if it is apparent that they are capable of understanding the risks and benefits and if the procedure is medically indicated. If an adolescent has a diagnosis that has a serious prognosis, parental consent will be neededed as this is not a situation that involves emergency care, substance abuse, pregnancy, and birth control. 2. Which of the following interventions would the nurse most likely implement when addressing the problem of asthma among school-aged children? (Select all that apply.) a. Assess schools and day care centers for environmental “friendliness.” b. Share nutritional information with all students in the school. c. Develop home and environmental assessment guides. d. Teach all school personnel how to use rescue inhalers. ANS: A, C Population-focused strategies for asthma management include education programs for families of children and adolescents who have asthma, development of home and environmental assessment guides to identify triggers, education and outreach efforts in high-risk populations to aid in case finding (e.g., in areas with low income, high unemployment, and substandard housing, where there is exposure to secondhand smoke), development of community clean air policies (e.g., no burning of leaves, use of smoke-free zones), improved access to care for asthmatic patients (e.g., developing clinic services with consistent health care providers to decrease emergency department use), and assessment of schools and day-care centers for lack of asthma triggers. Sharing nutritional information is not related to the care of asthma patients. It is not necessary that all school personnel know how to use rescue inhalers, rather those who are in direct contact with the child with asthma. 3. A health care provider is working with elderly clients who have ongoing chronic disease. Which of the following strategies can best assist them with healing? (Select all that apply.) a. Advocating for increased support for elderly persons b. Eliminating signs and symptoms of disease c. Managing any chronic diseases to prevent complications and delay deterioration d. Maximizing self-care capacity ANS: C, D With chronic illness, the focus is on healing (a unique process resulting in a shift in the body/mind/spirit system) rather than curing (elimination of the signs and symptoms of disease). Appropriate goals include maximizing self-care capacity, managing chronic diseases effectively, preventing complications, delaying deterioration and decline, and achieving the highest possible quality of life before dying with comfort, peace, and dignity. It is probably impossible to eliminate signs and symptoms of the disease with a client who has a chronic disease. Advocating for increased support for elderly persons is not related to assisting the client with healing from the chronic disease. 4. After seeing a public education program on the need for screening colonoscopy and the dangers of colorectal cancer, an older friend asks the nurse, “I’m really scared of getting cancer. What can I do to avoid that kind of cancer?” Which of the following recommendations should be made by the nurse? (Select all that apply.) a. Avoid smoking or much alcohol. b. Choose poultry or fish rather than red or processed meat. c. Eat lots of fruits, vegetables, and fiber every day. d. Try to get at least 8 hours of sleep a night. ANS: A, B, C Obesity, physical inactivity, smoking, heavy alcohol consumption, a diet high in red or processed meats, and insufficient intake of fruits and vegetables are risk factors for colorectal cancer. Getting an adequate amount of sleep is not a risk factor for the development of colorectal cancer. 5. A nurse’s mother leans forward and says, “My best friend fell the other day and now she’s in the hospital. I’m really worried about getting osteoporosis. What do you think I should do?” What should the nurse recommend? (Select all that apply.) a. Ask your doctor for hormone replacement therapy. b. Continue to abstain from alcohol and not use tobacco. c. Eat foods high in calcium such as fortified skim milk. d. Eat lots of green leafy vegetables. ANS: B, C It is estimated that one of every two American women older than 50 years will experience an osteoporosis-related fracture in her lifetime. Primary prevention activities include a diet rich in calcium and vitamin D; exposure to sunlight for 20 minutes a day; exercise, especially weight-bearing activities such as walking, running, stair climbing, and weight lifting, to improve bone density; limiting alcohol consumption; and avoiding smoking. Use of hormone replacement therapy and consumption of green leafy vegetables are not related to decreasing the risk of developing osteoporosis. Chapter 10: Caring for Families Chapter 10: Caring for Families Potter et al.: Fundamentals of Nursing, 9th Edition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. A nurse is assessing the family unit to determine the family’s ability to adapt to the change of a member having surgery. Which area is the nurse monitoring? a. Family durability b. Family resiliency c. Family diversity d. Family forms ANS: B Family resiliency is the ability of the family to cope with expected and unexpected stressors; it’s the families’ ability to adapt to changes. Family diversity is the uniqueness of each family unit. Every person within a family unit has speci쪻 c needs, strengths, and important developmental considerations. Family durability is a system of support and structure within a family that extends beyond the walls of the household. Family forms are patterns of people considered by family members to be included in the family. DIF:Apply (application)REF:117 | 122 OBJ: Discuss how the term family re 庯蔶ects family diversity. TOP: Assessment 10/15/2016 Chapter 10: Caring for Families | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter10caringforfamilies/ 2/13 MSC: Psychosocial Integrity 2. A nurse reviews the current trends a ecting the family. Which trend will the nurse 쪻 nd? a. Mothers are staying at home. b. Adolescent mothers usually live on their own. c. More grandparents are raising their grandchildren. d. Teenage fathers usually have stronger support systems. ANS: C More grandparents are raising their grandchildren. The majority of women work outside the home, and about 60% of mothers are in the workforce. The majority of adolescent mothers continue to live with their families. Teenage fathers usually have poorer support systems and fewer resources to teach them how to parent. DIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:118-119 OBJ: Discuss current trends in the American family. TOP: Assessment MSC: Psychosocial Integrity 3. A spouse brings the children in to visit their mother in the hospital. The nurse asks how the family is doing. The husband states, “None of her jobs are getting done, and I don’t do those jobs, so the house and the kids are falling apart.” How will the nurse interpret this 쪻 nding? a. The family structure is resilient. b. The family structure is 庯蔶exible. c. The family structure is hardy. d. The family structure is rigid. 10/15/2016 Chapter 10: Caring for Families | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter10caringforfamilies/ 3/13 ANS: D A rigid structure speci쪻 cally dictates who is able to accomplish die limits the number of rent tasks and also persons outside the immediate family allowed to assume these tasks. Resiliency helps to evaluate healthy responses when individuals and families are experiencing stressful events. An extremely 庯蔶 exible structure also presents problems for the family. There is sometimes an absence of stability that would otherwise lead to automatic action during a crisis or rapid change. Hardiness is the internal strength and durability of the family unit characterized by a sense of control over the outcome of life and an active, rather than passive, orientation in adapting to stressful events. DIF:Apply (application)REF:121 OBJ:Explain how the relationship between family structure and patterns of functioning ae the health of cts individuals within the family and the family as a whole. TOP: Assessment MSC: Psychosocial Integrity 4. A nurse cares for the family’s as well as the patient’s needs using available resources. Which approach is the nurse using? a. Family as context b. Family as patient c. Family as system d. Family as caregivers ANS: C When you care for the family as a system, you are caring for each family member (family as context) and the family unit (family as patient), using all available environmental, social, psychological, and community resources. When you view the family as context, the primary focus is on the health and development of an individual member existing within a speci쪻 c environment (i.e., the patient’s family). When you view the family as patient, the family processes and relationships (e.g., parenting or family caregiving) are the primary focuses of nursing care. There is no approach for family as caregivers; rather it is a term to describe family members caring for other family members usually at home. DIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:123 10/15/2016 Chapter 10: Caring for Families | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter10caringforfamilies/ 4/13 OBJ:Compare family as context to family as patient and explain the way these perspectives in 庯蔶uence nursing practice.TOP:Implementation MSC:Management of Care 5. A nurse is caring for a patient who needs constant care in the home setting and for whom most of the care is provided by the patient’s family. Which action should the nurse take to help relieve stress? a. Encourage caregiver to do as much as possible. b. Focus primarily on the patient. c. Point out weaknesses. d. Provide education. ANS: D Providing education to the family and caregiver helps relieve some of the stress of caregiving. Help the family focus on their strengths instead of on problems and weaknesses. While caregivers desire to care for the loved one, they often feel extreme pressure to do everything; therefore, encouraging the caregiver to do more will add stress. Focusing primarily on the patient will not be bene쪻 cial; the entire family is the patient. DIF:Apply (application)REF:127-128 OBJ iscuss the role of families and family members as caregivers. TOP: Implementation MSC: Psychosocial Integrity 6. A nurse is working with a patient. When the nurse asks about family members, the patient states that it includes my spouse, children, and aunt and uncle. How will the nurse describe this type of family? a. Nuclear b. Blended c. Extended 10/15/2016 Chapter 10: Caring for Families | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter10caringforfamilies/ 5/13 d. Alternative ANS: C The extended family includes relatives (aunts, uncles, grandparents, and cousins) in addition to the nuclear family. The nuclear family consists of husband and wife (and perhaps one or more children). The blended family is formed when parents bring unrelated children from prior adoptive or foster parenting relationships into a new, joint living situation. Relationships include multi-adult households, “skip- generation” families (grandparents caring for grandchildren), communal groups with children, “nonfamilies” (adults living alone), cohabitating partners, and homosexual couples. DIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:118 OBJ iscuss common family forms and their health implications. TOP: Assessment MSC: Psychosocial Integrity 7. A nurse is assessing a child that lives in a car with family members who presents to the emergency department. Which area should the nurse assess closely? a. Ears b. Eyes c. Head d. Hands ANS: A Children of homeless families are often in fair or poor health and have higher rates of asthma, ear infections, stomach problems, and mental illness. Eyes, head, and hands are not as important as the ears. DIF:Apply (application)REF:119 OBJ: Discuss factors that promote or impede family health. TOP: Assessment MSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance 10/15/2016 Chapter 10: Caring for Families | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter10caringforfamilies/ 6/13 8. The nurse is interviewing a patient who is being admitted to the hospital. The patient’s family went home before the nurse’s interview. The nurse asks the patient, “Who decides when to come to the hospital?” What is the rationale for the nurse’s action? a. To assess the family form b. To assess the family function c. To assess the family structure d. To assess the family generalization ANS: C To assess the family structure, the nurse asks questions that determine the power structure and patterning of roles and tasks (e.g., “Who decides where to go on vacation?”). When focusing on family form, the nurse should begin the family assessment by determining the patient’s de쪻 nition of family. Family function is the ability of the family to provide emotional support and to cope with health problems or situations. The question asked by the nurse will not assess that. Nurses do not assess family generalization. DIF:Apply (application)REF:121 | 124 | 125 OBJ:Explain how the relationship between family structure and patterns of functioning ae the health of individuals within the family and the family as a whole. TOP: Assessment MSC: Psychosocial Integrity 9. A nurse is caring for a patient from a motor vehicle accident. Which action by the unlicensed assistive personnel will cause the nurse to intervene? a. Tells the family not to leave the bedside b. Oers the family a sandwich c. Gives the family a blanket d. Sits with the family 10/15/2016 Chapter 10: Caring for Families | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter10caringforfamilies/ 7/13 ANS: A The action of telling the family not to leave is inappropriate and should be corrected. Sometimes telling the family that you will stay with their loved one while they are gone is all they need to feel comfortable in leaving. cts Oering a sandwich, giving a blanket, and sitting with the family are appropriate and do not require the nurse to intervene. When the victim of trauma is hospitalized, take time to make sure that the family is comfortable. You can bring them something to eat or drink, give them a blanket, or encourage them to get a meal. DIF:Analyze (analysis)REF:120 OBJ: Discuss factors that promote or impede family health. TOP: Implementation MSC:Management of Care 10. A nurse is using the family as context approach to provide care to a patient. What should the nurse do next? a. Assess family patterns versus individual characteristics. b. Assess how much the family provides the patient’s basic needs. c. Use “family as patient” and “family as context” approaches simultaneously. d. Plan care to meet not only the patient’s needs but those of the family as well. ANS: B When the nurse views the family as context, the primary focus is on the health and development of an individual member existing within a speci쪻 c environment (i.e., the patient’s family). Although the focus is on the individual’s health status, the nurse assesses how much the family provides the individual’s basic needs. Family patterns are in the realm of “family as patient” approach. Often, the nurse will use the two simultaneously (family as context and family as patient) with the approach of “family as system.” “Family as patient” involves planning to meet the needs of the patient and those of the family as well. DIF:Apply (application)REF:123 OBJ:Compare family as context to family as patient and explain the way these perspectives in 庯蔶uence nursing practice.TOP:Implementation 10/15/2016 Chapter 10: Caring for Families | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter10caringforfamilies/ 8/13 MSC:Management of Care 11. The nurse is caring for a patient in hospice. The nurse notes that the patient is getting adequate care, but the spouse is not sleeping well. The nurse also assesses the need for better family nutrition and meals assistance. The nurse discusses these needs with the patient and family and develops a plan of care with them using community resources. Which approach is the nurse using? a. Family as context b. Family as patient c. Family as system d. Family as caregiver ANS: C When you care for the family as a system, you are caring for each family member (family as context) and the family unit (family as patient), using all available environmental, social, psychological, and community resources. In family as context, the primary focus is on the health of an individual member. In family as patient, family processes and relationships are the primary focus. Family as caregiver is not an approach to familyfocused nursing but is a term used to describe a family member caring for another family member. DIF:Apply (application)REF:123 OBJ:Compare family as context to family as patient and explain the way these perspectives in 庯蔶uence nursing practice.TOP:Implementation MSC:Management of Care 12. The nurse is caring for an older adult patient who has no apparent family. When questioned about family and the de쪻 nition of family, the patient states, “I have no family. They’re all gone.” When asked, “Who prepares your meals?” the patient states, “I do, or I go out.” Which approach should the nurse use for this patient? a. Family as context b. Family as patient 10/15/2016 Chapter 10: Caring for Families | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter10caringforfamilies/ 9/13 c. Family as system d. Family as caregiver ANS: A If only one family member receives nursing care, it is realistic and practical to use the approach “family as context.” Although family nursing is based on the assumption that all people regardless of age are a member of some type of family form, the patient insists that there is no family. The nurse should investigate further. However, at this time, family as patient or as system is not appropriate. Family as caregiver is not an approach but rather is a term to describe a family member caring for another family member. DIF:Analyze (analysis)REF:123 OBJ: Compare family as context to family as patient and explain the way these perspectives in 庯蔶uence nursing practice. TOP: Evaluation MSC: Management of Care 13. The nurse is caring for an older adult patient at home who requires teaching for dressing changes. The spouse and adult child are also involved in changing the dressing. Which statement by the nurse will most likely elicit a positive response from the patient and family? a. “You’re doing that all wrong. Let me show you how to do it.” b. “I don’t know who showed you how to change a dressing, but you’re not doing it right. Let me show you again.” c. “You’re hesitant about changing the dressing like I was before I was shown an easier way; would you like to see?” d. “I used to change the dressing the same way you are doing it: the wrong way. I’ll show you the right way to do it.” ANS: C When the nurse is con쪻 dent and skillful instead of coming across as an authority on the subject, the patient’s/family’s defenses will be down, making the patient/family more willing to listen without feeling embarrassed. Respectful communication is necessary. Saying that you’re doing it wrong, you’re not doing it right, or the wrong way is not respectful or necessary. DIF:Analyze (analysis)REF:126 10/15/2016 Chapter 10: Caring for Families | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter10caringforfamilies/ 10/13 OBJ iscuss the role of families and family members as caregivers. TOP:Communication and Documentation MSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance 14. The nurse is providing discharge teaching for an older-adult patient who will need tube feedings at home. The spouse is the only source of care and states “I will not be able to perform the feedings due to arthritis.” Which action should the nurse take? a. Obtain extra feeding supplies. b. Arrange for home care. c. Cancel the discharge. d. Teach the spouse. ANS: B Discharge planning with a family involves an accurate assessment of what will be needed for care at the time of discharge, along with any shortcomings in the home setting. If no one can do the feedings properly, the nurse will need to arrange for a home care service referral. Extra feeding supplies will not help the situation if the spouse cannot use them. Canceling the discharge is not an option. Teaching the spouse will not be eective since the spouse is unable to perform the feeding. DIF:Apply (application)REF:125 OBJ: Use the nursing process to provide for the health care needs of the family. TOP:ImplementationMSC:Management of Care MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1. A nurse is assessing threats concerning the family. Which areas will the nurse include in the assessment? (Select all that apply.) a. Homelessness 10/15/2016 Chapter 10: Caring for Families | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter10caringforfamilies/ 11/13 b. Domestic violence c. Presence of illness d. Changing economic status e. Rise of homosexual families ANS: A, B, C, D Social scientists have identi쪻 ed 쪻 ve trends as threats facing the family. These include (1) Changing economic status, (2) homelessness, (3) domestic violence, (4) the presence of acute or chronic illness or trauma, and (5) end-of-life care. Homosexual families are not a threat facing the family; in fact, many homosexual couples now de쪻 ne their relationship in family terms. DIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:119 OBJ: Discuss current trends in the American family. TOP: Assessment MSC: Psychosocial Integrity 2. A nurse is assessing the realms of family life. Which processes will the nurse assess? (Select all that apply.) a. Developmental b. Interactive c. Integrity d. Coping e. Life ANS: A, B, C, D 10/15/2016 Chapter 10: Caring for Families | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter10caringforfamilies/ 12/13 The 쪻 ve realms of family life that should be assessed include: developmental, interactive, integrity, coping, and health, not life. DIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:122 OBJ: Use the nursing process to provide for the health care needs of the family. TOP: Assessment MSC: Psychosocial Integrity MATCHING A nurse is focusing on the interactive processes of family life and is asking the patient questions. Match the questions the nurse will ask to the interactive process. a. Intimacy expression b. Social support c. Roles d. Family nurturing 1. Who is the “peacekeeper” of the family? 2. How are house rules established? 3. How often does the family hug each other? 4. Who at your workplace is close to the family? Chapter 12: Conception Through Adolescence Chapter 12: Conception Through Adolescence Potter et al.: Fundamentals of Nursing, 9th Edition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. A mother has delivered a healthy newborn. Which action is priority? a. Encourage close physical contact as soon as possible after birth. b. Isolate the newborn in the nursery during the 町祗 rst hour after delivery. c. Never leave the newborn alone with the mother during the 町祗 rst 8 hours after delivery. d. Do not allow the newborn to remain with parents until the second hour after delivery. ANS: A After immediate physical evaluation and application of identi 町祗 cation bracelets, the nurse promotes the parents’ and newborn’s need for close physical contact. Early parent-child interaction encourages parent-child attachment. Most healthy newborns are awake and alert for the 町祗 rst half-hour after birth. This is a good time for parent-child interaction to begin. No evidence in the scenario suggests that the baby cannot be left alone with the parents during the 町祗 rst 8 hours or that the baby should remain in the nursery during the 町祗 rst hour. DIF:Apply (application)REF:142 OBJ: Discuss common physiological and psychosocial health concerns during the transition of the child from intrauterine to extrauterine life. TOP: Implementation 10/15/2016 Chapter 12: Conception Through Adolescence | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter12conceptionthroughadolescence/ 2/19 MSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance 2. A nurse teaches a new mother about the associated health risks to the infant. Which statement by the mother indicates a correct understanding of the teaching? a. “I will feed my baby every 4 hours around-the-clock.” b. “I need to leave the blankets oᏲ ඤ my baby to prevent smothering.” c. “I need to remind friends who want to hold my baby to wash their hands.” d. “I will throw away the bulb syringe now because my baby is breathing 町祗 ne.” ANS: C Good handwashing technique is the most important factor in protecting the newborn from infection. You can help prevent infection by instructing parents and visitors to wash their hands before touching the infant. The nurse can help parents identify ways to meet needs by counseling them to feed their baby on demand rather than on a rigid schedule. Newborns are susceptible to heat loss and cold stress. Place the healthy newborn directly on the mother’s abdomen, covering with warm blankets. Removal of nasopharyngeal and oropharyngeal secretions remains a priority of care to maintain a patent airway; keeping the bulb syringe is important. DIF:Apply (application)REF:142 OBJ: Discuss common physiological and psychosocial health concerns during the transition of the child from intrauterine to extrauterine life. TOP: Teaching/Learning MSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance 3. A nurse is working in the delivery room. Which action is priority immediately after birth? a. Open the airway. b. Determine gestational age. c. Monitor infant-parent interactions. 10/15/2016 Chapter 12: Conception Through Adolescence | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter12conceptionthroughadolescence/ 3/19 d. Promote parent-newborn physical contact. ANS: A Opening the airway is the priority. The most extreme physiological change occurs when the newborn leaves the utero circulation and develops independent respiratory functioning. Direct nursing care includes maintaining an open airway, stabilizing and maintaining body temperature, and protecting the newborn from infection. After immediate physical evaluation and application of identi 町祗 cation bracelets, the nurse promotes the parents’ and newborn’s need for close physical contact. Following a comprehensive physical assessment, the nurse assesses gestational age and interactions between infant and parents. DIF:Apply (application)REF:142 OBJ: Discuss common physiological and psychosocial health concerns during the transition of the child from intrauterine to extrauterine life. TOP: Implementation MSC:Management of Care 4. A nurse is assessing a newborn that was just born. Which newborn 町祗 nding will cause the nurse to intervene immediately? a. Molding b. A lack of re 冡exes c. Cyanotic hands and feet d. A soft, protuberant abdomen ANS: B A lack of re 冡exes must be addressed quickly. Assessment of these re 冡exes is vital because the newborn depends largely on re 冡exes for survival and in response to its environment. Molding, or overlapping of the soft skull bones, allows the fetal head to adjust to various diameters of the maternal pelvis and is a common occurrence with vaginal births. Normal physical characteristics include the continued presence of lanugo on the skin of the back; cyanosis of the hands and feet for the 町祗 rst 24 hours; and a soft, protuberant abdomen. 10/15/2016 Chapter 12: Conception Through Adolescence | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter12conceptionthroughadolescence/ 4/19 DIF:Analyze (analysis)REF:143 OBJ: Discuss common physiological and psychosocial health concerns during the transition of the child from intrauterine to extrauterine life. TOP: Assessment MSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance 5. A nurse performs an assessment on a healthy newborn. Which assessment 町祗 nding will the nurse document as normal? a. Cyanosis of the feet and hands for the 町祗 rst 48 hours b. Triangle-shaped anterior fontanel c. Sporadic motor movements d. Weight of 4800 grams ANS: C Movements in the newborn are generally sporadic, but they are symmetric and involve all four extremities. Cyanosis of the hands and feet is normal for the 町祗 rst 24 hours, not 48 hours. The diamond shape of the anterior fontanel and the triangular shape of the posterior fontanel are found between the unfused bones of the skull. The average newborn is 2700 to 4000 grams (6 to 9 pounds), not 4800 grams. DIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:143 OBJ: Describe characteristics of physical growth of the unborn child and from birth to adolescence. TOP:AssessmentMSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance 6. A nurse is teaching the staᏲ ඤ about development. Which information indicates the nurse needs to follow up? a. “Development proceeds in a cephalocaudal pattern.” b. “Development proceeds in a proximal-distal pattern.” c. “Development proceeds at a slower rate during the embryonic stage.” 10/15/2016 Chapter 12: Conception Through Adolescence | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter12conceptionthroughadolescence/ 5/19 d. “Development proceeds at a predictive rate from the moment of conception.” ANS: C Development proceeds at a slower rate during embryonic stage indicates the nurse needs to follow up to correct the misconception. From the moment of conception until birth, human development proceeds at a predictive and rapid rate. All the rest of the information is correct and does not need follow- up. Development proceeds in a cephalocaudal and proximal-distal pattern. DIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:141 OBJ: Describe characteristics of physical growth of the unborn child and from birth to adolescence. TOP: Teaching/Learning MSC: Health Promotion and Maintenance 7. A nurse is comparing physical growth patterns between school-aged children and adolescents. Which principle should the nurse consider? a. Physical growth usually slows during the adolescent period. b. Secondary sex characteristics usually develop during the adolescent years. c. Boys usually exceed girls in height and weight by the end of the school years. d. The distribution of muscle and fat remains constant during the adolescent years. ANS: B Sexual maturation in adolescence occurs with the development of primary and secondary sexual characteristics. Physical growth usually slows during the school-aged period, and then a growth spurt occurs during adolescence. Girls usually exceed boys in height and weight by the end of the school years. As height and weight increase during adolescence, the distribution of muscle and fat changes. DIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:153 OBJ: Describe characteristics of physical growth of the unborn child and from birth to adolescence. 10/15/2016 Chapter 12: Conception Through Adolescence | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter12conceptionthroughadolescence/ 6/19 TOP lanningMSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance 8. The parent brings a child to the clinic for a 12-month well visit. The child weighed 6 pounds 2 ounces and was 21 inches long at birth. Which 町祗 nding will cause the nurse to intervene? a. Height of 30 inches b. Weight of 16 pounds c. Is not yet potty-trained d. Is not yet walking up stairs ANS: B Size increases rapidly during the 町祗 rst year of life. Birth weight doubles in approximately 5 months and triples by 12 months. This infant should weigh at least 18 (6 × 3) pounds by this calculation. This child needs the nurse to intervene for further assessment. Height increases an average of 1 inch during each of the 町祗 rst 6 months and about 1/2 inch each month until 12 months: 21 + 6 + 3 = 30 (30 inches is the predicted height). Patterns of body function are just now starting to stabilize. It is quite normal for a 12-month-old child to not be potty-trained or walking up stairs yet. These milestones usually occur in the toddler period of development (12 to 36 months). DIF:Analyze (analysis)REF:145 OBJ: Describe characteristics of physical growth of the unborn child and from birth to adolescence. TOP:AssessmentMSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance 9. A nurse is assessing the cognitive changes in a preschooler. Which standard will the nurse use to determine normal? a. The ability to think abstractly and deal eᏲ ඤ ectively with hypothetical problems b. The ability to think in a logical manner about the here and now c. The ability to assume the view of another person d. The ability to classify objects by size or color 10/15/2016 Chapter 12: Conception Through Adolescence | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter12conceptionthroughadolescence/ 7/19 ANS: D Preschoolers demonstrate their ability to think more complexly by classifying objects according to size or color. Cognitive changes that provide the ability to think in a logical manner about the here and now occur during the school-aged years. It is during the teenaged years when the individual thinks abstractly and deals eᏲ ඤ ectively with hypothetical problems. The toddler is unable to assume the view of another. DIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:149 OBJ: Describe cognitive and psychosocial development from birth to adolescence. TOP:AssessmentMSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance 10. The nurse is teaching a parenting class. One of the topics is development. Which statement from a parent indicates more teaching is needed? a. “The toddler may use parallel play.” b. “The preschooler has the ability to play in small groups.” c. “The school-aged child still needs total assistance in all safety activities.” d. “The toddler may have temper tantrums from parent’s acting on safety rules.” ANS: C At this age (school-age), encourage children to take responsibility for their own safety. The toddler continues to engage in solitary play but also begins to participate in parallel play, which is playing beside rather than with another child. The play of preschool children becomes more social after the third birthday as it shifts from parallel to associative play with others in small groups. The toddler’s strong will is frequently exhibited in negative behavior when caregivers attempt to direct actions. Temper tantrums result when parental restrictions frustrate toddlers. DIF:Apply (application)REF:153 OBJ: Describe cognitive and psychosocial development from birth to adolescence. 10/15/2016 Chapter 12: Conception Through Adolescence | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter12conceptionthroughadolescence/ 8/19 TOP: Teaching/Learning MSC: Health Promotion and Maintenance 11. The nurse is observing a 2-year-old hospitalized patient in the playroom. Which activity will the nurse most likely observe? a. Seeking out same sex children to play with b. Participating as the leader of a small group activity c. Sitting beside another child while playing with blocks d. Separating building blocks into groups by size and color ANS: C The child beside another child and playing is exhibiting parallel play, characteristic of a toddler. Participating as a group leader does not usually occur until around age 5. Preschoolers (ages 3 to 5) demonstrate their ability to think more complexly by classifying objects according to size or color. A 2-year-old child does not have this ability yet. Gender does not become a factor until the child reaches school-age when the child prefers same sex peers to opposite sex peers. DIF:Analyze (analysis)REF:148 OBJ: Explain the role of play in the development of a child. TOP: Assessment MSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance 12. A nurse is communicating with a newly admitted teenaged patient. Which action should the nurse take? a. Avoid questioning the patient about cigarette use when the nurse observes a cigarette lighter lying on the bedside table. b. Complete the admission database as quickly as possible by asking yes and no questions. c. Look for meaning behind the patient’s words and actions. d. Ignore the patient’s withdrawn behavior. 10/15/2016 Chapter 12: Conception Through Adolescence | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter12conceptionthroughadolescence/ 9/19 ANS: C Good communication skills are critical for adolescents. Look for meaning behind the adolescent’s words and actions. Following are some hints for communicating with adolescents: Do not avoid discussing sensitive issues. Asking questions about sex, drugs, and school opens the channels for further discussion. Ask openended questions. (Yes and no questions are closed-ended questions.) The nurse should inquire about a patient’s withdrawn behavior to seek out the meaning of such behaviors. Be alert to clues about adolescents’ emotional states. DIF:Apply (application)REF:154 OBJ: Describe cognitive and psychosocial development from birth to adolescence. TOP: Implementation MSC: Health Promotion and Maintenance 13. A nurse is caring for a preschooler. Which fear should the nurse most plan to minimize? a. Fear of bodily harm b. Fear of weight gain c. Fear of separation d. Fear of strangers ANS: A The greatest fear of preschoolers appears to be that of bodily harm; this is evident in children’s fear of the dark, animals, thunderstorms, and medical personnel. Toddlers who become ill and require hospitalization are most stressed by the separation from their parents. Persons with anorexia nervosa have an intense fear of gaining weight. By 8 months, most infants are able to diᏲ ඤ erentiate a stranger from a familiar person and respond diᏲ ඤ erently to the two. DIF:Apply (application)REF:150 OBJ: Describe cognitive and psychosocial development from birth to adolescence. TOP lanningMSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance 10/15/2016 Chapter 12: Conception Through Adolescence | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter12conceptionthroughadolescence/ 10/19 14. A nurse is teaching a class about the eᏲ ඤ ects of nutrition on fetal growth and development. A pregnant patient asks the nurse how much weight should normally be gained over the pregnancy. Which information should the nurse share with the patient? a. About 10 to 20 pounds b. About 15 to 25 pounds c. About 20 to 30 pounds d. About 25 to 35 pounds ANS: D The diet of a woman both before and during pregnancy has a signi 町祗 cant eᏲ ඤ ect on fetal development. For women who are at normal weight for height, the recommended weight gain is 25 to 35 pounds over three trimesters. Weight gains of 10 to 20, 15 to 25, and 20 to 30 pounds are too low. DIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:142 OBJ: Discuss common physiological and psychosocial health concerns during the transition of the child from intrauterine to extrauterine life. TOP: Teaching/Learning MSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance 15. The nurse is caring for an infant. Which activity is most appropriate for the nurse to oᏲ ඤ er to the infant? a. Set of cards to organize and separate into groups b. Set of sock puppets with movable eyes c. Set of plastic stacking rings d. Set of paperback book ANS: C 10/15/2016 Chapter 12: Conception Through Adolescence | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter12conceptionthroughadolescence/ 11/19 Adults and nurses facilitate infant learning by planning activities that promote the development of milestones and providing toys that are safe for the infant to explore with the mouth and manipulate with the hands such as rattles, wooden blocks, plastic stacking rings, squeezable stuᏲ ඤ ed animals, and busy boxes. Preschoolers demonstrate their ability to think more complexly by classifying objects according to size or color, making the cards more appropriate for them. Neither group is ready for paperback books. The sock puppet with movable eyes could create a choking hazard if one of the eyes comes oᏲ ඤ. DIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:146 OBJ: Explain the role of play in the development of a child. TOP: Implementation MSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance 16. A mother expresses concern because her 5-year-old child frequently talks about friends who don’t exist. What is the nurse’s best response to this mother’s concern? a. “Have you considered a child psychological evaluation?” b. “You should stop your child from playing electronic games.” c. “Pretend play is a sign your child watches too much television.” d. “It’s very normal for a child this age to have imaginary playmates.” ANS: D At age 5, some children have imaginary playmates. Imaginary playmates are a sign of health and allow the child to distinguish between reality and fantasy. The child does not need a psychological evaluation because this is normal behavior. Television, videos, electronic games, and computer programs help support development and the learning of basic skills. However, these should be only one part of the child’s total play activities. Pretend play is not a sign of watching too much television. DIF:Apply (application)REF:150 OBJ:Explain the role of play in the development of a child. TOP:Communication and Documentation MSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance 10/15/2016 Chapter 12: Conception Through Adolescence | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter12conceptionthroughadolescence/ 12/19 17. A school nurse is encouraging children to play a game of kickball. Which group of children is the nurse most likely addressing? a. Infant b. Toddler c. Preschool d. School-aged ANS: D A game of kickball would be best suited for school-aged children because in this age group, play involves peers and the pursuit of group goals. Although solitary activities are not eliminated, group play overshadows them. Younger children typically are not able to participate cooperatively in groups yet. Infants begin to play simple social games such as patty-cake and peek-a-boo. Toddlers engage in solitary play but also begin to participate in parallel play. Preschoolers playing together engage in similar if not identical activities; however, no division of labor or rigid organization or rules are observed. By the age of 5, the group has a temporary leader for each activity. DIF:Apply (application)REF:152 OBJ: Explain the role of play in the development of a child. TOP: Evaluation MSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance 18. Which assessment 町祗 nding of a school-aged patient should alert the nurse to a possible developmental delay? a. Verbalization of “I have no friends” b. Absence of secondary sex characteristics c. Curiosity about sexuality d. Lack of group identity 10/15/2016 Chapter 12: Conception Through Adolescence | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter12conceptionthroughadolescence/ 13/19 ANS: A School-aged children should begin to develop friendships and to socialize with others. Interaction with peers allows them to de 町祗 ne their own accomplishments in relation to others as they work to develop a positive selfimage. The absence of secondary sex characteristics is a major concern of adolescents, not school- aged children, because physical evidence of maturity encourages the development of masculine and feminine behaviors in the adolescent. Lack of group relationships is also a concern of adolescents, not of school-aged children, because adolescents seek a group identity to ful 町祗 ll their esteem and acceptance needs. Today many researchers believe that school-aged children have a great deal of curiosity about their sexuality. Some experiment, but this is usually transitory. DIF:Analyze (analysis)REF:152 OBJ: Explain the role of play in the development of a child. TOP: Assessment MSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance 19. The nurse is teaching a parent about developmental needs of a 9-month-old infant. Which statement from the parent indicates a correct understanding of the teaching? a. “My child will begin to speak in sentences by 1 year of age.” b. “My child will probably enjoy playing peek-a-boo.” c. “My child will sleep about 7 to 8 hours a night.” d. “My child will be ready to try low-fat milk.” ANS: B By 9 months, infants play simple social games such as patty-cake and peek-a-boo. By 1 year, infants not only recognize their own names but are also able to say three to 町祗 ve words and understand almost 100 words; a 2 year old is generally able to speak in two-word sentences. The use of whole cow’s milk, 2% cow’s milk, or alternate milk products before the age of 12 months is not recommended. By 6 months, most infants are nocturnal and sleep between 9 and 11 hours at night. Total daily sleep averages 15 hours. DIF:Apply (application)REF:152 10/15/2016 Chapter 12: Conception Through Adolescence | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter12conceptionthroughadolescence/ 14/19 OBJ: Discuss ways in which the nurse is able to help parents meet their child’s developmental needs. TOP: Teaching/Learning MSC: Health Promotion and Maintenance 20. A nurse is teaching the parents of a school-aged child about accidents most common in this age group. Which topic should the nurse address? a. Falls b. Fires c. Drownings d. Poisonings ANS: B Because accidents such as 町祗 res and car and bicycle crashes are the leading cause of death and injury in the school-age period, safety is a priority health teaching consideration. Falls, drownings, and poisonings are priority for toddlers. DIF:Apply (application)REF:153 OBJ: Discuss ways in which the nurse is able to help parents meet their child’s developmental needs. TOP: Teaching/Learning MSC: Health Promotion and Maintenance 21. Which information from the parent of an 8-month-old infant will cause the nurse to intervene? a. My baby rides in the front-facing car seat when I go to the grocery store. b. I made sure the slats on the crib were less than 2 inches apart. c. I removed the mobile after my baby could reach it. d. My baby cries every time he sees a new person. 10/15/2016 Chapter 12: Conception Through Adolescence | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter12conceptionthroughadolescence/ 15/19 ANS: A The nurse should intervene when parents let infants and toddlers ride in a front-facing car seat. All infants and toddlers should ride in a rear-facing car safety seat until they are 2 years of age or until they reach the highest weight or height allowed by the manufacturer or their car safety seat. Parents also need to inspect an older crib to make sure the slats are no more than 6 cm (2.4 inches) apart. Instruct parents to remove mobiles as soon as the infant is able to reach them. By 8 months, most infants are able to diᏲ ඤ erentiate a stranger from a familiar person and respond diᏲ ඤ erently to the two; this is a normal 町祗 nding. DIF:Analyze (analysis)REF:144 OBJ: Discuss ways in which the nurse is able to help parents meet their child’s developmental needs. TOP: Implementation MSC: Health Promotion and Maintenance 22. The nurse is preparing to teach a group of parents with infants about growth and development. Which information should the nurse include in the teaching session? a. 3-month-old infants will be able to bang objects together. b. 4-month-old infants will be able to sit alone with support. c. 5-month-old infants will be able to creep on hands and knees. d. 6-month-old infants will be able to turn from back to abdomen. ANS: D 6-month-old infants will be able to turn from back to abdomen. 6 to 8 month olds can sit alone without support and bang objects together. 8 to 10 month olds can creep on hands and knees. DIF:Apply (application)REF:145 OBJ: Discuss ways in which the nurse is able to help parents meet their child’s developmental needs. TOP: Teaching/Learning MSC: Health Promotion and Maintenance 23. Which statement, if made by a parent, will require further instruction from the nurse? 10/15/2016 Chapter 12: Conception Through Adolescence | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter12conceptionthroughadolescence/ 16/19 a. “I should not be surprised that my teenage son has so many friends.” b. “I get worried because my teenage son thinks he’s indestructible.” c. “I should cover for my 10-year-old son when he makes mistakes until he learns the ropes.” d. “I usually have nutritious snacks available because my 10-year-old son is always hungry right after school.” ANS: C The nurse will need to teach the parent of a school-aged child covering for the child’s mistakes; this is a misconception that needs to be corrected. Parents have to learn to allow their school-aged child (6 to 12 years old) to make decisions, accept responsibility, and learn from life’s experiences. All the other statements are normal and do not need further teaching. Teenagers typically are very social and have many friends. Adolescents seek a group identity because they need esteem and acceptance. Adolescents feel they are indestructible, which leads to risk-taking behaviors. School-age children are developing eating patterns that are independent of parental supervision. Having nutritious snacks available is a healthy option. DIF:Apply (application)REF:151 OBJ: Discuss ways in which the nurse is able to help parents meet their child’s developmental needs. TOP: Teaching/Learning MSC: Health Promotion and Maintenance 24. A nurse is teaching parents about appropriate activities for diᏲ ඤ erent age groups. Which toy, if selected by the parent of a 12-month-old infant, will indicate a correct understanding of the teaching? a. Busy box b. Electronic games c. Game requiring two to four people d. Small, plastic alphabet letters and magnets ANS: A 10/15/2016 Chapter 12: Conception Through Adolescence | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter12conceptionthroughadolescence/ 17/19 Adults facilitate infant learning by planning activities that promote the development of milestones and by providing toys that are safe for the infant to explore with the mouth and manipulate with the hands, such as rattles, wooden blocks, plastic stacking rings, squeezable stuᏲ ඤ ed animals, and busy boxes. For the toddler (not the infant), television, videos, electronic games, and computer programs help support development and learning of basic skills. Infants are not capable of participating in small group activities. By age 4, children play in groups of two or three. Adults should provide toys that are safe for the infant to explore with the mouth. Small, plastic letters and magnets could be choking hazards for an infant. DIF:Apply (application)REF:146 OBJ: Discuss ways in which the nurse is able to help parents meet their child’s developmental needs. TOP: Teaching/Learning MSC: Health Promotion and Maintenance MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1. A nurse is teaching a parenting class for families with adolescents. Which health concerns will the nurse include in the teaching session? (Select all that apply.) a. Suicide b. Eating disorders c. Violence/Homicide d. Sexually transmitted infections e. Gonadotropic hormone stimulation ANS: A, B, C, D Suicide is a major leading cause of death in adolescents 15 to 24 years of age. Adolescent overweight and obesity are current concerns in the United States, and most teens try dieting at some time to control weight. Unfortunately the number of eating disorders is on the rise in adolescent girls. Homicide is the second leading cause of death in the 15- to 24-year-old age-group, and for African-American teenagers it is the most likely cause of death. Sexually transmitted diseases annually aᏲ ඤ ect three million sexually active adolescents. Gonadotropic hormones stimulate ovarian cells to produce estrogen and testicular cells to produce testosterone. These hormones are normally occurring and contribute to the development of secondary sex 10/15/2016 Chapter 12: Conception Through Adolescence | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter12conceptionthroughadolescence/ 18/19 characteristics, such as hair growth and voice changes, and play an essential role in reproduction. It is not a health concern. DIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:155-156 OBJ: Discuss ways in which the nurse is able to help parents meet their child’s developmental needs. TOP: Teaching/Learning MSC: Health Promotion and Maintenance MATCHING A nurse is teaching parents about the 䙖ne motor skills of infants to help parents understand development growth and needs. Match the information to the correct age that the nurse should include in the teaching session. a. Can place objects into containers b. Pulls a string to obtain an object c. Can hold a baby bottle d. Holds rattle for short periods e. Uses pincer grasp well 1. 2 to 4 months 2. 4 to 6 months 3. 6 to 8 months 4. 8 to 10 months 5. 10 to 12 months Chapter 13: Young and Middle Adults Chapter 13: Young and Middle Adults Potter et al.: Fundamentals of Nursing, 9th Edition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. A nurse is caring for a young adult. Which goal is priority? a. Maintain peer relationships. b. Maintain family relationships. c. Maintain parenteral relationships. d. Maintain recreational relationships. ANS: B Family is important during young adulthood. Challenges may include the demands of working and raising families. Peer is more important in the adolescent years. Young adults are much freer from parental control. While recreation is important, the family and work are the priorities in young adults. DIF:Apply (application)REF:159 OBJ: List and discuss major life events of young and middle adults and the childbearing family. TOP lanningMSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance 10/15/2016 Chapter 13: Young and Middle Adults | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter13youngandmiddleadults/ 2/15 2. The nurse is caring for a hospitalized young-adult male who works as a dishwasher at a local restaurant. He states that he would like to get a better job but has no education. How can the nurse best assist this patient psychosocially? a. By providing information and referrals b. By focusing on the patient’s medical diagnoses c. By telling the patient that he needs to go back to school d. By expecting the patient to be ᨌ exible in decision making ANS: A Support from the nurse, access to information, and appropriate referrals provide opportunities for achievement of a patient’s potential. Health is not merely the absence of disease (focusing on medical diagnoses) but involves wellness in all human dimensions. Telling a patient what to do (go back to school) is inappropriate. Each person (not the nurse) needs to make these decisions based on individual factors. Insecure persons tend to be more rigid in making decisions. DIF:Analyze (analysis)REF:160 OBJ: Discuss cognitive and psychosocial changes occurring during the adult years. TOP: Implementation MSC: Health Promotion and Maintenance 3. Which goal is priority when the nurse is caring for a middle-aged adult? a. Maintain immediate family relationships. b. Maintain future generation relationships. c. Maintain personal career relationships. d. Maintain work relationships. 10/15/2016 Chapter 13: Young and Middle Adults | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter13youngandmiddleadults/ 3/15 ANS: B Many middle-aged adults ᧴nd particular joy in helping their children and other young people become productive and responsible adults. While immediate family is important, this goal is priority in young adults, not as important in middle-aged adults. During this period, personal and career achievements have often already been experienced; therefore, these goals are not priority. DIF:Apply (application)REF:166 OBJ: List and discuss the major life events of young and middle adults and the childbearing family. TOP lanningMSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance 4. A nurse is teaching young adults about health risks. Which statement from a young adult indicates a correct understanding of the teaching? a. “It’s probably safe for me to start smoking. At my age, there’s not enough time for cancer to develop.” b. “My mother had appendicitis so this increases my chance for developing appendicitis.” c. “Controlling the amount of stress in my life may decrease the risk of illness.” d. “I don’t do drugs. I do drink co ᨌ ee, but ca ᨌ eine is not a drug.” ANS: C Lifestyle habits that activate the stress response increase the risk of illness; so, controlling this will decrease risk. Smoking is a well-documented risk factor for pulmonary, cardiac, and vascular disease as well as cancer in smokers and in individuals who receive secondhand smoke. The presence of certain chronic illnesses (not acute illnesses—appendicitis) in the family increases the family member’s risk of developing a disease. Ca ᨌ eine is a naturally occurring legal stimulant that is readily available. Ca ᨌ eine stimulates catecholamine release, which, in turn, stimulates the central nervous system; it also increases gastric acid secretion, heart rate, and basal metabolic rate. DIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:162 OBJ: Describe health concerns of the young adult, the childbearing family, and the middle adult. TOP: Teaching/Learning MSC: Health Promotion and Maintenance 10/15/2016 Chapter 13: Young and Middle Adults | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter13youngandmiddleadults/ 4/15 5. A nurse is choosing an appropriate topic for a young-adult health fair. Which topic should the nurse include? a. Retirement b. Menopause c. Climacteric factors d. Unplanned pregnancies ANS: D Unplanned pregnancies are a continued source of stress that can result in adverse health outcomes for the mother (young adult), infant, and family. Retirement is an issue for middle-aged, not young adults. The onset of menopause and the climacteric a ᨌ ect the sexual health of the middle-aged adult, not the young adult. DIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:163 OBJ: Describe health concerns of the young adult, the childbearing family, and the middle adult. TOP lanningMSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance 6. A nurse is assessing the risk of intimate partner violence (IPV) for patients. Which population should the nurse focus on most for IVP? a. White males b. Pregnant females c. Middle-aged adults d. Nonsubstance abusers ANS: B 10/15/2016 Chapter 13: Young and Middle Adults | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter13youngandmiddleadults/ 5/15 The greatest risk of violence occurs during the reproductive years. A pregnant woman has a 35.6% greater risk of being a victim of IPV than a nonpregnant woman. White males, middle-aged adults, and nonsubstance abusers are not as high risk as pregnant women. DIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:163 OBJ: Describe health concerns of the young adult, the childbearing family, and the middle adult. TOP:AssessmentMSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance 7. A patient states that she is pregnant and concerned because she does not know what to expect, and she wants her husband to play an active part in the birthing process. Which information should the nurse share with the patient? a. Lamaze classes can prepare pregnant women and their partners for what is coming. b. The frequency of sexual intercourse is key to helping the husband feel valued. c. After the birth, the stress of pregnancy will disappear and will be replaced by relief. d. After the baby is born, the wife should accept the extra responsibilities of motherhood. ANS: A Childbirth education classes (like Lamaze) can prepare pregnant women, their partners, and other support persons to participate in the birthing process. The psychodynamic aspect of sexual activity is as important as the type or frequency of sexual intercourse to young adults; however, this does not relate to the issue the patient reports (lack of knowledge and participation). The stress that many women experience after childbirth has a signi᧴cant impact on the health of postpartum women. Ideally partners should share all responsibilities; however, this does not relate to the patient’s concerns. DIF:Apply (application)REF:161 OBJ: Describe developmental tasks of the young adult, the childbearing family, and the middle adult. TOP: Teaching/Learning MSC: Health Promotion and Maintenance 8. Which information from the nurse indicates a correct understanding of emerging adulthood? 10/15/2016 Chapter 13: Young and Middle Adults | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter13youngandmiddleadults/ 6/15 a. It is a type of young adulthood. b. It is a type of extended adolescence. c. It is a type of independent exploration. d. It is a type of marriage and parenthood. ANS: C This newly identi᧴ed stage of development from age 18 to 25 (emerging adulthood) has been described as neither an extended adolescence, as it is much freer from parental control and is much more a period of independent exploration, nor young adulthood, as most young people in their twenties have not made the transitions historically associated with adult status, especially marriage and parenthood. DIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:159 OBJ iscuss development theories of young and middle adults. TOP: Teaching/Learning MSC: Health Promotion and Maintenance 9. A nurse is planning care for a 30 year old. Which goal is priority? a. Re᧴ne self-perception. b. Master career plans. c. Examine life goals. d. Achieve intimacy. ANS: B From 29 to 34, the person directs enormous energy toward achievement and mastery of the surrounding world. The years from 35 to 43 are a time of vigorous examination of life goals and relationships. Between the ages of 23 and 28, the person re nes self-perception and ability for intimacy. 10/15/2016 Chapter 13: Young and Middle Adults | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter13youngandmiddleadults/ 7/15 DIF:Apply (application)REF:160 OBJ: Discuss cognitive and psychosocial changes occurring during the adult years. TOP lanningMSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance 10. A nurse is planning care for young-adult patients. Which information should the nurse consider when planning care? a. Fertility issues do not occur in young adulthood. b. Young adults tend to su ᨌ er more from severe illness. c. Substance abuse is easy to observe in young-adult patients. d. Young adults are quite active but are at risk for illness in later years. ANS: D Young adults are generally active and experience severe illnesses less frequently. However, their lifestyles may put them at risk for illnesses or disabilities during their middle or older-adult years. An estimated 10% to 15% of reproductive couples are infertile, and many are young adults. Substance abuse is not always diagnosable, particularly in its early stages. DIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:160 OBJ: Describe normal physical changes in young and middle adulthood and pregnancy. TOP lanningMSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance 11. During a routine physical assessment, the nurse obtaining a health history notes that a 50-year-old female patient reports pain and redness in the right breast. Which action is best for the nurse to take in response to this ᧴nding? a. Assess the patient as thoroughly as possible. b. Explain to the patient that breast tenderness is normal at her age. 10/15/2016 Chapter 13: Young and Middle Adults | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter13youngandmiddleadults/ 8/15 c. Tell the patient that redness is not a cause for concern and is quite common. d. Inform her that redness is the precursor to normal unilateral breast enlargement. ANS: A A comprehensive assessment o ᨌ ers direction for health promotion recommendations, as well as for planning and implementing any acutely needed intervention. Redness or painful breasts are abnormal physical assessment ᧴ndings in the middle-aged adult. Increased size of one breast is an abnormal physical assessment ᧴nding in the middle-aged adult. DIF:Apply (application)REF:166 OBJ: Describe normal physical changes in young and middle adulthood and pregnancy. TOP: Implementation MSC: Health Promotion and Maintenance 12. A 55-year-old female presents to the outpatient clinic describing irregular menstrual periods and hot ᨌ ashes. Which information should the nurse share with the patient? a. The patient’s assessment points toward normal menopause. b. Those symptoms are normal when a woman undergoes the climacteric. c. An assessment is not really needed because these problems are normal for older women. d. The patient should stop regular exercise because that is probably causing these symptoms. ANS: A The most signi᧴cant physiological changes during middle age are menopause in women and the climacteric in men. Menopause typically occurs between 45 and 60 years of age. The nurse should continue with the examination because a comprehensive assessment o ᨌ ers direction for health promotion recommendations, as well as for planning and implementing any acutely needed interventions. Exercise should not be stopped, especially in middle-aged adults. DIF:Apply (application)REF:166 10/15/2016 Chapter 13: Young and Middle Adults | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter13youngandmiddleadults/ 9/15 OBJ: Describe normal physical changes in young and middle adulthood and pregnancy. TOP:AssessmentMSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance 13. The nurse is teaching a class to pregnant women about common physiological changes during pregnancy. Which information should the nurse include in the teaching session? a. Pregnancy is not a time to be having sexual activity. b. Urinary frequency will occur early in the pregnancy. c. Breast tenderness should be reported as soon as possible. d. Late in the pregnancy Braxton Hicks contraction may occur. ANS: D During the third trimester (late pregnancy), increases in Braxton Hicks contractions (irregular, short contractions), fatigue, and urinary frequency (not early) occur. Normally, women commonly have morning sickness, breast enlargement and tenderness, and fatigue. Women need to be reassured that sexual activity will not harm the fetus. DIF:Apply (application)REF:165 OBJ: Describe normal physical changes in young and middle adulthood and pregnancy. TOP: Teaching/Learning MSC: Health Promotion and Maintenance 14. A nurse discusses the risks of repeated sun exposure with a young-adult patient. Which response will the nurse most expect from this patient? a. “I should consider participating in a health fair about safe sun practices.” b. “I’ll make an appointment with my doctor right away for a full skin check.” c. “I’ve had this mole my whole life. So what if it changed color? My skin is ᧴ne.” d. “I have a mole that has been bothering me. I’ll call my family doctor for an appointment to get it checked.” 10/15/2016 Chapter 13: Young and Middle Adults | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter13youngandmiddleadults/ 10/15 ANS: C Most typically young adults would say that their skin is ᧴ne. Young adults often ignore physical symptoms and often postpone seeking health care. Making an appointment right away with the doctor and participating in health fairs are not typical behaviors of young adults for the same reason. DIF:Analyze (analysis)REF:160 OBJ: Describe health concerns of the young adult, the childbearing family, and the middle adult. TOP:AssessmentMSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance 15. Upon assessment of a middle-aged adult, the nurse observes uneven weight bearing and decreased range of joint motion. Which area is priority? a. Abuse potential b. Fall precautions c. Stroke prevention d. Self-esteem issues ANS: B With uneven weight bearing and decreased range of joint motion, falling is a priority. Abuse potential would indicate other ᧴ndings such as bruising or unkept appearance. While stroke prevention is important in a middle-aged adult, these are not the signs of stroke. While self-esteem issues may arise from physical changes, safety is a priority over self-esteem issues. DIF:Analyze (analysis)REF:167 OBJ: Describe health concerns of the young adult, the childbearing family, and the middle adult. TOP:AssessmentMSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance 10/15/2016 Chapter 13: Young and Middle Adults | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter13youngandmiddleadults/ 11/15 16. A young-adult patient is brought to the hospital by police after crashing the car in a high- speed chase when trying to avoid arrest for spousal abuse. Which action should the nurse take? a. Question the patient about drug use. b. O ᨌ er the patient a cup of co ᨌ ee to calm nerves. c. Discretely assess the patient for sexually transmitted infections. d. Deal with the issue at hand, not asking about previous illnesses. ANS: A Reports of arrests because of driving while intoxicated, wife or child abuse, or disorderly conduct are reasons for the nurse to investigate the possibility of drug abuse more carefully. Ca ᨌ eine is a naturally occurring legal stimulant that stimulates the central nervous system and is not the choice for calming nerves. Although sexually transmitted infections occur in the young adult, this is not an action a nurse should take in this situation. The nurse may obtain important information by making speci᧴c inquiries about past medical problems, changes in food intake or sleep patterns, and problems of emotional lability. DIF:Apply (application)REF:163 OBJ: Describe health concerns of the young adult, the childbearing family, and the middle adult. TOP: Implementation MSC: Psychosocial Integrity 17. A nurse determines that a middle-aged patient is a typical example of the “sandwich generation.” What did the nurse discover the patient is caught between? a. Job responsibilities or family responsibilities b. Stopping old habits and starting new ones c. Caring for children and aging parents d. Advancing in career or retiring 10/15/2016 Chapter 13: Young and Middle Adults | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter13youngandmiddleadults/ 12/15 ANS: C Middle-aged adults also begin to help aging parents while being responsible for their own children, placing them in the sandwich generation. It does not include job and family responsibilities; old habits and new ones; or career and retiring. DIF:Apply (application)REF:166 OBJ: Discuss the signi᧴cance of family in the life of the adult. TOP: Assessment MSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1. A nurse is assessing a middle-aged patient’s barriers to change in eating habits. Which areas will the nurse assess that are external barriers? (Select all that apply.) a. Lack of facilities b. Lack of materials c. Lack of knowledge d. Lack of social supports e. Lack of short- and long-term goals ANS: A, B, D External barriers to change include lack of facilities, materials, and social supports. Internal barriers are lack of knowledge, insu ᨌ cient skills, and unde᧴ned short- and long-term goals. DIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:169 OBJ: Describe health concerns of the young adult, the childbearing family, and the middle adult. TOP:AssessmentMSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance 10/15/2016 Chapter 13: Young and Middle Adults | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter13youngandmiddleadults/ 13/15 2. A home health nurse is providing care to a middle-aged couple with children at home. The patient has a debilitating chronic illness. Which areas will the nurse need to assess? (Select all that apply.) a. Adherence to treatment and rehabilitation regimens b. Coping mechanisms of patient and family c. Need for community services or referrals d. Knowledge base of patient only e. Use of a doula for care ANS: A, B, C Along with the current health status of the chronically ill middle-aged adult, you need to assess the knowledge base of both the patient and family. In addition, you must determine the coping mechanisms of the patient and family; adherence to treatment and rehabilitation regimens; and the need for community and social services, along with appropriate referrals. A doula is a support person to be present during labor to assist women who have no other source of support. DIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:170 OBJ: Discuss the signi᧴cance of family in the life of the adult. TOP: Assessment MSC: Psychosocial Integrity 3. A nurse is providing prenatal care to a ᧴rst-time mother. Which information will the nurse share with the patient? (Select all that apply.) a. Regular trend for postpartum depression b. Protection against urinary infection c. Strategies for empty nest syndrome d. Exercise patterns 10/15/2016 Chapter 13: Young and Middle Adults | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter13youngandmiddleadults/ 14/15 e. Proper diet ANS: B, D, E Prenatal care includes a thorough physical assessment of the pregnant woman during regularly scheduled intervals. Information regarding STIs and other vaginal infections and urinary infections that will adversely a ᨌ ect the fetus and counseling about exercise patterns, diet, and child care are important for a pregnant woman. Empty nest syndrome occurs as children leave the home. Postpartum depression is rare. DIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:165 OBJ: Describe health concerns of the young adult, the childbearing family, and the middle adult. TOP: Teaching/Learning MSC: Health Promotion and Maintenance MATCHING A nurse is assessing young and middle-aged adults for work-related conditions. Match the job to the work-related conditions that the nurse is assessing. a. Liver disease b. Carpal tunnel syndrome c. Asbestosis d. Farmer’s lung e. Bladder cancer 1. Insulators 2. Dry cleaners 3. Dye workers 4. O ᨌ ce computer workers 10/15/2016 Chapter 13: Young and Middle Adults | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter13youngandmiddleadults/ 15/15 5. Agricultural workers 1.ANS:CDIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:164 Chapter 14: Older Adult Chapter 14: Older Adult Potter et al.: Fundamentals of Nursing, 9th Edition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. A nurse is obtaining a history on an older adult. Which ⤀褅nding will the nurse most typically ⤀褅nd? a. Lives in a nursing home b. Lives with a spouse c. Lives divorced d. Lives alone ANS: B In 2012, 57% of older adults in non-institutional settings lived with a spouse (45% of older women, 71% of older men); 28% lived alone (35% of older women, 19% of older men); and only 3.5% of all older adults resided in institutions such as nursing homes or centers. Most older adults have lost a spouse due to death rather than divorce. DIF:Apply (application)REF:173 OBJ:Identify common myths and stereotypes about older adults. TOP:AssessmentMSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance 10/15/2016 Chapter 14: Older Adult | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/81202/ 2/19 2. A nurse is developing a plan of care for an older adult. Which information will the nurse consider? a. Should be standardized because most geriatric patients have the same needs b. Needs to be individualized to the patient’s unique needs c. Focuses on the disabilities that all aging persons face d. Must be based on chronological age alone ANS: B Every older adult is unique, and the nurse needs to approach each one as a unique individual. The nursing care of older adults poses special challenges because of great variation in their physiological, cognitive, and psychosocial health. Aging does not automatically lead to disability and dependence. Chronological age often has little relation to the reality of aging for an older adult. DIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:173 OBJ:Identify common myths and stereotypes about older adults. TOP lanningMSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance 3. Which information from a co-worker on a gerontological unit will cause the nurse to intervene? a. Most older people have dependent functioning. b. Most older people have strengths we should focus on. c. Most older people should be involved in care decision. d. Most older people should be encouraged to have independence. ANS: A 10/15/2016 Chapter 14: Older Adult | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/81202/ 3/19 Most older people remain functionally independent despite the increasing prevalence of chronic disease; therefore, this misconception should be addressed. It is critical for you to respect older adults and actively involve them in care decisions and activities. You also need to identify an older adult’s strengths and abilities during the assessment and encourage independence as an integral part of your plan of care. DIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:173 OBJ:Identify common myths and stereotypes about older adults. TOP: Implementation MSC: Health Promotion and Maintenance 4. A nurse suspects an older-adult patient is experiencing caregiver neglect. Which assessment ⤀褅ndings are consistent with the nurse’s suspicions? a. Flea bites and lice infestation b. Left at a grocery store c. Refuses to take a bath d. Cuts and bruises ANS: A Caregiver neglect includes unsafe and unclean living conditions, soiled bedding, and animal or insect infestation. Abandonment includes desertion at a hospital, nursing facility, or public location such as a shopping center. Self-neglect includes refusal or failure to provide oneself with basic necessities such as food, water, clothing, shelter, personal hygiene, medication, and safety. Physical abuse includes hitting, beating, pushing, slapping, kicking, physical restraint, inappropriate use of drugs, fractures, lacerations, rope burns, and untreated injuries. DIF:Apply (application)REF:188 OBJ: Describe the multi-faceted aspects of elder mistreatment. TOP: Assessment MSC: Psychosocial Integrity 5. A nurse is teaching a group of older-adult patients. Which teaching strategy is best for the nurse to use? 10/15/2016 Chapter 14: Older Adult | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/81202/ 4/19 a. Provide several topics of discussion at once to promote independence and making choices. b. Avoid uncomfortable silences after questions by helping patients complete their statements. c. Ask patients to recall past experiences that correspond with their interests. d. Speak in a high pitch to help patients hear better. ANS: C Teaching strategies include the use of past experiences to connect new learning with previous knowledge, focusing on a single topic to help the patient concentrate, giving the patient enough time in which to respond because older adults’ reaction times are longer than those of younger persons, and keeping the tone of voice low; older adults are able to hear low sounds better than high-frequency sounds. DIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:184 OBJ: Discuss issues related to psychosocial changes of aging. TOP: Teaching/Learning MSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance 6. An older patient has fallen and su⤀ㄆ ered a hip fracture. As a consequence, the patient’s family is concerned about the patient’s ability to care for self, especially during this convalescence. What should the nurse do? a. Stress that older patients usually ask for help when needed. b. Inform the family that placement in a nursing center is a permanent solution. c. Tell the family to enroll the patient in a ceramics class to maintain quality of life. d. Provide information and answer questions as family members make choices among care options. ANS: D Nurses help older adults and their families by providing information and answering questions as they make choices among care options. Some older adults deny functional declines and refuse to ask for assistance with tasks that place their safety at great risk. The decision to enter a nursing center is never ⤀褅 nal, and a nursing 10/15/2016 Chapter 14: Older Adult | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/81202/ 5/19 center resident sometimes is discharged to home or to another less-acute residence. What de⤀褅nes quality of life varies and is unique for each person. DIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:175 OBJ: Discuss common developmental tasks of older adults. TOP: Implementation MSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance 7. What is the best suggestion a nurse could make to a family requesting help in selecting a local nursing center? a. Have the family members evaluate nursing home sta⤀ㄆ according to their ability to get tasks done e⤀ꀈciently and safely. b. Make sure that nursing home sta⤀ㄆ members get patients out of bed and dressed according to sta⤀ㄆ’s preferences. c. Explain that it is important for the family to visit the center and inspect it personally. d. Suggest a nursing center that has standards as close to hospital standards as possible. ANS: C An important step in the process of selecting a nursing home is to visit the nursing home. The nursing home should not feel like a hospital. It is a home, a place where people live. Members of the nursing home sta⤀ㄆ should focus on the person, not the task. Residents should be out of bed and dressed according to their preferences, not sta⤀ㄆ preferences. DIF:Apply (application)REF:175 OBJ: Discuss common developmental tasks of older adults. TOP: Implementation MSC:Management of Care 8. A 70-year-old patient who su⤀ㄆ ers from worsening dementia is no longer able to live alone. The nurse is discussing health care services and possible long-term living arrangements with the patient’s only son. What will the nurse suggest? a. An apartment setting with neighbors close by 10/15/2016 Chapter 14: Older Adult | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/81202/ 6/19 b. Having the patient utilize weekly home health visits c. A nursing center because home care is no longer safe d. That placement is irrelevant because the patient is retreating to a place of inactivity ANS: C Some family caregivers consider nursing center placement when in-home care becomes increasingly di⤀ꀈ cult or when convalescence from hospitalization requires more assistance than the family is able to provide. An apartment setting and the use of home health visits are not appropriate because living at home is unsafe. Dementia is not a time of inactivity but an impairment of intellectual functioning. DIF:Analyze (analysis)REF:175 OBJ: Discuss common developmental tasks of older adults. TOP: Implementation MSC:Management of Care 9. A nurse is caring for an older adult. Which goal is priority? a. Adjusting to career b. Adjusting to divorce c. Adjusting to retirement d. Adjusting to grandchildren ANS: C Adjusting to retirement is one of the developmental tasks for an older person. A young or middle-aged adult has to adjust to career and/or divorce. A middle-aged adult has to adjust to grandchildren. DIF:Apply (application)REF:174 10/15/2016 Chapter 14: Older Adult | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/81202/ 7/19 OBJ: Discuss common developmental tasks of older adults. TOP: Planning MSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance 10. A nurse is observing for the universal loss in an older-adult patient. What is the nurse assessing? a. Loss of ⤀褅 nances through changes in income b. Loss of relationships through death c. Loss of career through retirement d. Loss of home through relocation ANS: B The universal loss for older adults usually revolves around the loss of relationships through death. Life transitions, of which loss is a major component, include retirement and the associated ⤀褅 nancial changes, changes in roles and relationships, alterations in health and functional ability, changes in one’s social network, and relocation. However, these are not the universal loss. DIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:181 OBJ: Discuss issues related to psychosocial changes of aging. TOP: Assessment MSC: Psychosocial Integrity 11. A nurse is discussing sexuality with an older adult. Which action will the nurse take? a. Ask closed-ended questions about speci⤀褅c symptoms the patient may experience. b. Provide information about the prevention of sexually transmitted infections. c. Discuss the issues of sexuality in a group in a private room. d. Explain that sexuality is not necessary as one ages. 10/15/2016 Chapter 14: Older Adult | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/81202/ 8/19 ANS: B Include information about the prevention of sexually transmitted infections when appropriate. Open-ended questions inviting an older adult to explain sexual activities or concerns elicit more information than a list of closed-ended questions about speci⤀褅 c activities or symptoms. You need to provide privacy for any discussion of sexuality and maintain a nonjudgmental attitude. Sexuality and the need to express sexual feelings remain throughout the human life span. DIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:182 OBJ: Discuss issues related to psychosocial changes of aging. TOP: Implementation MSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance 12. A nurse is teaching a health promotion class for older adults. In which order will the nurse list the most common to least common conditions that can lead to death in older adults? 1. Chronic obstructive lung disease 2. Cerebrovascular accidents 3. Heart disease 4. Cancer a. 4, 1, 2, 3 b. 3, 4, 1, 2 c. 2, 3, 4, 1 d. 1, 2, 3, 4 ANS: B Heart disease is the leading cause of death in older adults followed by cancer, chronic lung disease, and stroke (cerebrovascular accidents). DIF:Apply (application)REF:184 10/15/2016 Chapter 14: Older Adult | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/81202/ 9/19 OBJ: Describe selected health concerns of older adults. TOP: Teaching/Learning MSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance 13. A nurse is observing skin integrity of an older adult. Which ⤀褅nding will the nurse document as a normal ⤀褅nding? a. Oily skin b. Faster nail growth c. Decreased elasticity d. Increased facial hair in men ANS: C Loss of skin elasticity is a common ⤀褅nding in the older adult. Other common ⤀褅ndings include pigmentation changes, glandular atrophy (oil, moisture, and sweat glands), thinning hair (facial hair: decreased in men, increased in women), slower nail growth, and atrophy of epidermal arterioles. DIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:177 OBJ: Describe common physiological changes of aging. TOP: Assessment MSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance 14. An older-adult patient in no acute distress reports being less able to taste and smell. What is the nurse’s best response to this information? a. Notify the health care provider immediately to rule out cranial nerve damage. b. Schedule the patient for an appointment at a smell and taste disorders clinic. c. Perform testing on the vestibulocochlear nerve and a hearing test. d. Explain to the patient that diminished senses are normal ⤀褅 ndings. 10/15/2016 Chapter 14: Older Adult | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/81202/ 10/19 ANS: D Diminished taste and smell senses are common ⤀褅ndings in older adults. Scheduling an appointment at a smell and taste disorders clinic, testing the vestibulocochlear nerve, or an attempt to rule out cranial nerve damage is unnecessary at this time as per the information provided. DIF:Apply (application)REF:177 OBJ: Describe common physiological changes of aging. TOP: Implementation MSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance 15. A nurse is assessing an older adult for cognitive changes. Which symptom will the nurse report as normal? a. Disorientation b. Poor judgment c. Slower reaction time d. Loss of language skills ANS: C Slower reaction time is a common change in the older adult. Symptoms of cognitive impairment, such as disorientation, loss of language skills, loss of the ability to calculate, and poor judgment are not normal aging changes and require further investigation of underlying causes. DIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:177 | 179 OBJ: Describe common physiological changes of aging. TOP: Assessment MSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance 16. An older patient with dementia and confusion is admitted to the nursing unit after hip replacement surgery. Which action will the nurse include in the plan of care? a. Keep a routine. 10/15/2016 Chapter 14: Older Adult | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/81202/ 11/19 b. Continue to reorient. c. Allow several choices. d. Socially isolate patient. ANS: A Patients with dementia need a routine. Continuing to reorient a patient with dementia is nonproductive and not advised. Patients with dementia need limited choices. Social interaction based on the patient’s abilities is to be promoted. DIF:Apply (application)REF:181 OBJ: Identify nursing interventions related to the physiological, cognitive, and psychosocial changes of aging. TOP: Planning MSC: Physiological Adaptation 17. A nurse is helping an older-adult patient with instrumental activities of daily living. The nurse will be assisting the patient with which activity? a. Taking a bath b. Getting dressed c. Making a phone call d. Going to the bathroom ANS: C Instrumental activities of daily living or IADLs (such as the ability to write a check, shop, prepare meals, or make phone calls) and activities of daily living or ADLs (such as bathing, dressing, and toileting) are essential to independent living. DIF:Apply (application)REF:179 10/15/2016 Chapter 14: Older Adult | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/81202/ 12/19 OBJ:Identify nursing interventions related to the physiological, cognitive, and psychosocial changes of aging.TOP:Implementation MSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance 18. A male older-adult patient expresses concern and anxiety about decreased penile ⤀褅 rmness during an erection. What is the nurse’s best response? a. Tell the patient that libido will always decrease, as well as the sexual desires. b. Tell the patient that touching should be avoided unless intercourse is planned. c. Tell the patient that heterosexuality will help maintain stronger libido. d. Tell the patient that this change is expected in aging adults. ANS: D Aging men typically experience an erection that is less ⤀褅rm and shorter acting and have a less forceful ejaculation. Testosterone lessens with age and sometimes (not always) leads to a loss of libido. However, for both men and women sexual desires, thoughts, and actions continue throughout all decades of life. Sexuality involves love, warmth, sharing, and touching, not just the act of intercourse. Touch complements traditional sexual methods or serves as an alternative sexual expression when physical intercourse is not desired or possible. Clearly not all older adults are heterosexual, and there is emerging research on older adult, lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender individuals and their health care needs. DIF:Apply (application)REF:177-178 OBJ:Identify nursing interventions related to the physiological, cognitive, and psychosocial changes of aging.TOP:Implementation MSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance 19. A patient asks the nurse what the term polypharmacy means. Which information should the nurse share with the patient? a. This is multiple side e⤀ㄆects experienced when taking medications. b. This is many adverse drug e⤀ㄆects reported to the pharmacy. 10/15/2016 Chapter 14: Older Adult | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/81202/ 13/19 c. This is the multiple risks of medication e⤀ㄆects due to aging. d. This is concurrent use of many medications. ANS: D Polypharmacy refers to the concurrent use of many medications. It does not have anything to do with side e⤀ㄆects, adverse drug e⤀ㄆects, or risks of medication use due to aging. DIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:187 OBJ: Describe selected health concerns of older adults. TOP: Teaching/Learning MSC harmacological and Parenteral Therapies 20. An outcome for an older-adult patient living alone is to be free from falls. Which statement indicates the patient correctly understands the teaching on safety concerns? a. “I’ll take my time getting up from the bed or chair.” b. “I should dim the lighting outside to decrease the glare in my eyes.” c. “I’ll leave my throw rugs in place so that my feet won’t touch the cold tile.” d. “I should wear my favorite smooth bottom socks to protect my feet when walking around.” ANS: A Postural hypotension is an intrinsic factor that can cause falls. Changing positions slowly indicates a correct understanding of this concept. Environmental hazards outside and within the home such as poor lighting, slippery or wet ⤀褅ooring, and items on ⤀褅oor that are easy to trip over such as throw rugs are other factors that can lead to falls. Impaired vision and poor lighting are other risk factors for falls and should be avoided (dim lighting). Inappropriate footwear such as smooth bottom socks also contributes to falls. DIF:Analyze (analysis)REF:186 10/15/2016 Chapter 14: Older Adult | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/81202/ 14/19 OBJ: Describe selected health concerns of older adults. TOP: Teaching/Learning MSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance 21. A nurse’s goal for an older adult is to reduce the risk of adverse medication e⤀ㄆects. Which action will the nurse take? a. Review the patient’s list of medications at each visit. b. Teach that polypharmacy is to be avoided at all cost. c. Avoid information about adverse e⤀ㄆects. d. Focus only on prescribed medications. ANS: A Strategies for reducing the risk for adverse medication e⤀ㄆects include reviewing the medications with older adults at each visit; examining for potential interactions with food or other medications; simplifying and individualizing medication regimens; taking every opportunity to inform older adults and their families about all aspects of medication use; and encouraging older adults to question their health care providers about all prescribed and over-the-counter medications. Although polypharmacy often re⤀褅ects inappropriate prescribing, the concurrent use of multiple medications is often necessary when an older adult has multiple acute and chronic conditions. Older adults are at risk for adverse drug e⤀ㄆects because of age- related changes in the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of drugs. Work collaboratively with the older adult to ensure safe and appropriate use of all medications—both prescribed medications and over- the-counter medications and herbal options. DIF:Apply (application)REF:188 OBJ: Describe selected health concerns of older adults. TOP: Implementation MSC harmacological and Parenteral Therapies 22. An older-adult patient has developed acute confusion. The patient has been on tranquilizers for the past week. The patient’s vital signs are normal. What should the nurse do? a. Take into account age-related changes in body systems that a⤀ㄆect pharmacokinetic activity. 10/15/2016 Chapter 14: Older Adult | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/81202/ 15/19 b. Increase the dose of tranquilizer if the cause of the confusion is an infection. c. Note when the confusion occurs and medicate before that time. d. Restrict phone calls to prevent further confusion. ANS: A Some sedatives and tranquilizers prescribed for acutely confused older adults sometimes cause or exacerbate confusion. Carefully administer drugs used to manage confused behaviors, taking into account age-related changes in body systems that a⤀ㄆect pharmacokinetic activity. When confusion has a physiological cause (such as an infection), speci⤀褅 cally treat that cause, rather than the confused behavior. When confusion varies by time of day or is related to environmental factors, nonpharmacological measures such as making the environment more meaningful, providing adequate light, etc., should be used. Making phone calls to friends or family members allows older adults to hear reassuring voices, which may be bene⤀褅 cial. DIF:Apply (application)REF:188 OBJ: Describe selected health concerns of older adults. TOP: Implementation MSC harmacological and Parenteral Therapies 23. Which assessment ⤀褅nding of an older adult, who has a urinary tract infection, requires an immediate nursing intervention? a. Confusion b. Presbycusis c. Temperature of 97.9° F d. Death of a spouse 2 months ago ANS: A Confusion is a common manifestation in older adults with urinary tract infection; however, the cause requires further assessment. There may be another reason for the confusion. Confusion is not a normal ⤀褅nding in the 10/15/2016 Chapter 14: Older Adult | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/81202/ 16/19 older adult, even though it is commonly seen with concurrent infections. Di⤀ꀈ culty hearing, presbycusis, is an expected ⤀褅nding in an older adult. Older adults tend to have lower core temperatures. Coping with the death of a spouse is a psychosocial concern to be addressed after the acute physiological concern in this case. DIF:Apply (application)REF:176 | 179 OBJ: Identify nursing interventions related to the physiological, cognitive, and psychosocial changes of aging. TOP: Implementation MSC: Physiological Integrity 24. Which patient statement is the most reliable indicator that an older adult has the correct understanding of health promotion activities? a. “I need to increase my fat intake and limit protein.” b. “I still keep my dentist appointments even though I have partials now.” c. “I should discontinue my ⤀褅tness club membership for safety reasons.” d. “I’m up-to-date on my immunizations, but at my age, I don’t need the in⤀褅 uenza vaccine.” ANS: B General preventive measures for the nurse to recommend to older adults include keeping regular dental appointments to promote good oral hygiene, eating a low-fat, well-balanced diet, exercising regularly, and maintaining immunizations for seasonal in⤀褅uenza, tetanus, diphtheria and pertussis, shingles, and pneumococcal disease. DIF:Analyze (analysis)REF:184 OBJ: Describe selected health concerns of older adults. TOP: Teaching/Learning MSC:Health Promotion and Maintenance 25. A 72-year-old woman was recently widowed. She worked as a teller at a bank for 40 years and has been retired for the past 5 years. She never learned how to drive. She lives in a rural area that does not have public transportation. Which psychosocial change does the nurse focus on as a priority? a. Sexuality 10/15/2016 Chapter 14: Older Adult | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/81202/ 17/19 b. Retirement c. Environment d. Social isolation ANS: D The highest priority at this time is the potential for social isolation. This woman does not know how to drive and lives in a rural community that does not have public transportation. All of these factors contribute to her social isolation. Other possible changes she may be going through right now include sexuality related to her advanced age and recent death of her spouse; however, this is not the priority at this time. She has been retired for 5 years, so this is also not an immediate need. She may eventually experience needs related to environment, but the data do not support this as an issue at this time. DIF:Analyze (analysis)REF:181-182 | 188 OBJ: Discuss issues related to psychosocial changes of aging. TOP: Assessment MSC: Psychosocial Integrity MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1. A recently widowed older-adult patient is dehydrated and is admitted to the hospital for intravenous ⤀褅uid replacement. During the evening shift, the patient becomes acutely confused. Which possible reversible causes will the nurse consider when assessing this patient? (Select all that apply.) a. Electrolyte imbalance b. Sensory deprivation c. Hypoglycemia d. Drug e⤀ㄆects e. Dementia 10/15/2016 Chapter 14: Older Adult | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/81202/ 18/19 ANS: A, B, C, D Delirium, or acute confusional state, is a potentially reversible cognitive impairment that is often due to a physiological event. Physiological causes include electrolyte imbalances, untreated pain, infection, cerebral anoxia, hypoglycemia, medication e⤀ㄆects, tumors, subdural hematomas, and cerebrovascular infarction or hemorrhage. Sometimes it is also caused by environmental factors such as sensory deprivation or overstimulation, unfamiliar surroundings, or sleep deprivation or psychosocial factors such as emotional distress. Dementia is a gradual, progressive, and irreversible cerebral dysfunction. DIF:Apply (application)REF:179 OBJ: Di⤀ㄆerentiate among delirium, dementia, and depression. TOP: Assessment MSC: Physiological Adaptation MATCHING A nurse is using di ᜱ 욐 erent strategies to meet older patients’ psychosocial needs. Match the strategy the nurse is using to its description. a. Respecting the older adult’s uniqueness b. Improving level of awareness c. Listening to the patient’s past recollections d. Accepting describing of patient’s perspective e. O⤀ㄆering help with grooming and hygiene 1. Body image 2. Validation therapy 3. Therapeutic communication 4. Reality orientation 5. Reminiscence 10/15/2016 Chapter 14: Older Adult | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/81202/ 19/19 1.ANS:EDIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:189-190 Concept 05: Spirituality Giddens: Concepts for Nursing Practice, 2nd Edition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The nurse is assessing a patient's spirituality and observes the patient meditating before any treatments. What is the nurse’s best action? a. Document that the patient is not religious b. Offer the patient a copy of the bible to read c. Arrange for quiet time for the patient as needed d. Limit the time patient can meditate before procedures ANS: C The nurse can best promote the patient’s spirituality practices by arranging for the patient to be left alone when possible to meditate. Meditation is an exemplar of spirituality, not necessarily of the Christian faith. The bible is most often read by believers in the Christian faith. Meditation does not imply that the patient is not religious. Time for meditation should not be limited, whenever possible. REF: Page 41 OBJ: NCLEX® Client Needs Category: Safe and Effective Care Environment: Health Promotion and Maintenance 2. When conducting a spiritual assessment of a hospitalized patient, the nurse should remain aware of which potential barrier to effective communication? a. Clarifying the meaning of a patient’s statement b. Multi-tasking while talking to the patient c. Listening to patients’ complete statements d. Discussing patient’s feelings while hospitalized ANS: B Several barriers may result in the nurses’ inability to be totally present and communicate effectively with the patient. First, the nurse may be distracted by other things and may not pay attention to the patient. Multi-tasking while trying to listen to a patient may be a barrier to effective communication. Second, the nurses may miss the meaning of the patient’s message because of failure to clarify the meaning of a word, a phrase, or a facial expression. Third, the nurse may interject personal feelings and reactions into the patient’s situation rather than allow the patient to explore and discuss his own feelings and reactions. The last barrier occurs when the nurse is busy formulating a response while the patient is still talking. In this instance, the nurse never hears the patient’s message. REF: Page 42 OBJ: NCLEX® Client Needs Category: Safe and Effective Care Environment: Psychosocial Integrity 3. A patient uses rosary beads and attends mass once a week. This expression of spirituality is best described with which term? a. Religiosity b. Faith c. Belief d. Authenticity ANS: A There are a few similar and related terms to spirituality worth mentioning to provide distinction and clarification. Faith, as defined by Dyess, refers to an “evolving pattern of believing, that grounds and guides authentic living and gives meaning in the present moment of inter-relating.” Religiosity, another similar term, is an external expression (public or private), in the form of practicing a belief or faith, whereas spirituality is an internalized spiritual identity (or experiential). Specifically, religiosity is defined as “the adherence to religious dogma or creed, the expression of moral beliefs, and/or the participation in organized or individual worship, or sacred practices.” REF: Page 43 OBJ: NCLEX® Client Needs Category: Safe and Effective Care Environment: Psychosocial Integrity 4. When developing a plan of care, the nurse should consider which attribute of the concept of spirituality? a. Spirituality is not a well-known universal concept b. Chronic versus acute illnesses affect spirituality c. Convincing patients to pray is a priority intervention d. Referrals may be needed to spiritual counselors ANS: D The attributes of the concept of spirituality in the context of nursing care are described below. □ Spirituality is universal. All individuals, even those who profess no religious belief, are driven to derive meaning and purpose from life. □ Illness impacts spirituality in a variety of ways. Some patients and families will draw closer to God or however they conceive that higher Power to be in an effort to seek support, healing, and comfort. Others may blame and feel anger towards that Higher Power for any illness and misfortune that may have befallen a loved one or their entire family. Still others will be neutral in their spiritual reactions. □ There has to be willingness on the part of patient and/or family to share and/or act on spiritual beliefs and practices. □ The nurse needs to be aware that specific spiritual beliefs and practices are impacted by family and culture. □ The nurse needs to be willing to assess the concept of spirituality in patients and families and based on this ongoing assessment to integrate the spiritual beliefs of patients and families into care. □ The nurse needs to be willing to refer the patient or family to a Spiritual Expert i.e. a Minister, Priest, Rabbi, an Imam. □ Community based religious organizations can provide supportive care to families and patients and nurses need to be aware of these resources. REF: Page 42 OBJ: NCLEX® Client Needs Category: Safe and Effective Care Environment: Psychosocial Integrity MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1. When completing the FICA tool for spiritual assessment, which questions should the nurse ask the patient? (Select all that apply.) a. What things do you believe in that give meaning to life? b. Are you connected with a faith center in your community? c. How has your illness affected your personal beliefs? d. When was the last time you have been to church? e. What can I do for you? ANS: A, B, C, E The FICA tool for spiritual assessment stands for Faith or beliefs, Importance and influence, Community, and Address. “When was the last time you have been to church?” is not a question included in the FICA assessment. The patient may attend community activities, besides church, that foster his/her spiritual well-being. REF: Page 41 OBJ: NCLEX® Client Needs Category: Health Promotion and Maintenance 2. Which are true statements about the definition of spirituality in nursing? (Select all that apply.) a. Patient’s quality of life, health, and sense of wholeness are affected by spirituality b. An exact definition was developed and adopted in the late 1980s c. Encompasses principle, an experience, attitudes, and belief regarding God d. Head knowledge affects spirituality more than heart knowledge e. Mind, body, spirit, love, and caring are interconnected ANS: A, C, E The concept of Spirituality is an elusive concept to define. Authors that write about spirituality in nursing advocate the position that a patient’s quality of life, health, and sense of wholeness are affected by spirituality, yet still the profession of nursing struggles to define it. Why? There are a number of explanations for this. One explanation is that spirituality represents “heart” not “head” knowledge and “heart” knowledge is difficult to encapsulate into words. A second explanation is that spirituality is unique to each person so a precise definition is somewhat elusive. The definitions of spirituality encompass the following: a principle, an experience, attitudes and belief regarding God, a sense of God, the inner person. Most descriptions of spirituality include not only transcendence but also the connection of mind, body, and spirit, plus love, caring, and compassion and a relationship with the Divine. REF: Page 39 OBJ: NCLEX® Client Needs Category: Safe and Effective Care Environment: Health Promotion and Maintenance 3. The nurse recognizes that which life events can be spiritually life changing? (Select all that apply.) a. Births b. Weddings c. Medical diagnoses d. Career day to day job duties e. Loss of independence ANS: A, B, C, E The meaning and significance of the event might only be experienced by one individual; others who might be participants in the event might be left virtually untouched and unchanged. These life changing spiritual events include just about any occurrence that has intense and personal relevance to those involved in the event. Examples of spiritually life changing events include births, deaths, weddings, divorces, illnesses, diagnoses, and loss of abilities, loss of independence, death and so many more. These events, having the power to change individuals and families, also have the power to draw people towards the transcendent – for many people that transcendent is known as God but this is not universal. Day to day activities are not the best examples of spiritually life changing events. Chapter 36: Spiritual Health Chapter 36: Spiritual Health Potter et al.: Fundamentals of Nursing, 9th Edition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. A co-worker asks the nurse to explain spirituality. What is the nurse’s best response? a. It has a minor e 洅ect on health. b. It is awareness of one’s inner self. c. It is not as essential as physical needs. d. It refers to 밄 re or giving of life to a person. ANS: B Spirituality is often de 밄 ned as an awareness of one’s inner self and a sense of connection to a higher being, to nature, or to some purpose greater than oneself. Spirituality is an important factor that helps individuals achieve the balance needed to maintain health and well-being and to cope with illness. Florence Nightingale believed that spirituality was a force that provided energy needed to promote a healthy hospital environment and that caring for a person’s spiritual needs was just as essential as caring for his or her physical needs. The word spirituality comes from the Latin word spiritus, which refers to breath or wind. The spirit gives life to a person. DIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:733 OBJ iscuss the in 밄 uence of spirituality on patients’ health practices. 10/15/2016 Chapter 36: Spiritual Health | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter36spiritualhealth/ 2/15 TOP:Teaching/LearningMSC:Management of Care 2. The nurse is caring for a patient who is an agnostic. Which information should the nurse consider when planning care for this patient? a. The patient is devoid of spirituality. b. The patient does not believe in God. c. The patient believes there is no known ultimate reality. d. The patient 밄 nds no meaning through relationship with others. ANS: C Some people do not believe in the existence of God (atheist), or they believe that there is no known ultimate reality (agnostic). Nonetheless, spirituality is important regardless of a person’s religious beliefs. Agnostics discover meaning in what they do or how they live because they 밄 nd no ultimate meaning for the way things are. They believe that people bring meaning to what they do. DIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:734 OBJ iscuss the in 밄 uence of spirituality on patients’ health practices. TOP lanningMSC:Management of Care 3. The nurse is caring for an Islam patient who wants a snack. Which action by the nurse is most appropriate? a. O 洅ers a ham sandwich b. O 洅ers a beef sandwich c. O 洅ers a kosher sandwich d. O 洅ers a bacon sandwich 10/15/2016 Chapter 36: Spiritual Health | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter36spiritualhealth/ 3/15 ANS: B Islam religion does allow beef. Islam does not allow pork or alcohol. Ham and bacon are pork. Kosher is allowed for Judaism. DIF:Apply (application)REF:745 OBJ: Discuss nursing interventions designed to promote a patient’s spiritual health. TOP: Implementation MSC: Psychosocial Integrity 4. A nurse is teaching a patient how to meditate. Which information from the patient indicates e 洅ective learning? a. I will lie on the 밄 oor. b. I will breathe quickly. c. I will focus on an image. d. I will do this for 10 minutes every day. ANS: C The steps of meditation include sitting in a comfortable position with the back straight; breathe slowly; and focus on a sound, prayer, or image. Meditation should occur for 10 to 20 minutes twice a day. DIF:Apply (application)REF:745 OBJ: Discuss nursing interventions designed to promote a patient’s spiritual health. TOP: Teaching/Learning MSC: Psychosocial Integrity 5. The nurse is admitting a patient to the hospital. The patient is a very spiritual person but does not practice any speci 밄 c religion. How will the nurse interpret this 밄 nding? a. This indicates a strong religious a 甇 liation. b. This statement is contradictory. 10/15/2016 Chapter 36: Spiritual Health | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter36spiritualhealth/ 4/15 c. This statement is reasonable. d. This indicates a lack of hope. ANS: C The patient’s statement is reasonable and is not contradictory. Many people tend to use the terms spirituality and religion interchangeably. Although closely associated, these terms are not synonymous. Religious practices encompass spirituality, but spirituality does not need to include religious practice. When a person has the attitude of something to live for and look forward to, hope is present. DIF:Apply (application)REF:733 | 735 OBJ:Compare and contrast the concepts of religion and spirituality. TOP: Assessment MSC: Psychosocial Integrity 6. A nurse hears the following comments from di 洅erent patients. Which patient comment does the nurse identify as faith? a. I go to church every Sunday. b. I believe there is life after death. c. I have something to look forward to each day. d. I get a feeling of awe when looking at the sunset. ANS: B Faith allows people to have 밄 rm beliefs despite lack of physical evidence (life after death). Religion refers to the system of organized beliefs and worship that a person practices to outwardly express spirituality (go to church). When a person has the attitude of something to live for and look forward to, hope is present (look forward to each day). Self-transcendence is the belief that there is a force outside of and greater than the person (awe when looking at a sunset). 10/15/2016 Chapter 36: Spiritual Health | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter36spiritualhealth/ 5/15 DIF:Analyze (analysis)REF:734 OBJ: Describe the relationship among faith, hope, and spiritual well-being. TOP: Assessment MSC: Psychosocial Integrity 7. A nurse is caring for a Hindu patient. Which action will the nurse take? a. Allow time to practice the Five Pillars. b. Allow time to practice Blessingway. c. Allow time for Holy Communion. d. Allow time for purity rituals. ANS: D Hindus practice prayer and purity rituals. Blessingway is a practice of the Navajos that attempts to remove ill health by means of stories, songs, rituals, prayers, symbols, and sand paintings. Islams must be able to practice the Five Pillars of Islam. Holy Communion is practiced in the Christian religion. DIF:Apply (application)REF:739 OBJ: Discuss nursing interventions designed to promote a patient’s spiritual health. TOP: Implementation MSC: Psychosocial Integrity 8. The nurse is caring for a patient with a chronic illness who is having con 밄 icts with beliefs. Which health care team member will the nurse ask to see this patient? a. The clergy b. A psychiatrist c. A social worker d. An occupational therapist 10/15/2016 Chapter 36: Spiritual Health | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter36spiritualhealth/ 6/15 ANS: A Other important resources to patients are spiritual advisors and members of the clergy. Spiritual care helps people identify meaning and purpose in life, look beyond the present, and maintain personal relationships, as well as a relationship with a higher being or life force. A psychiatrist is for emotional health. A social worker focuses on social, 밄 nancial, and community resources. An occupational therapist provides care with vocational issues and functioning within physical limitations. DIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:735 | 743-744 OBJ:Explain the importance of establishing caring relationships with patients to provide spiritual care.TOP:ImplementationMSC:Management of Care 9. The nurse is caring for a patient with a terminal disease. The nurse sits down and lightly touches the patient’s hand. Which technique is the nurse using? a. “Doing for” b. Establishing presence c. O 洅ering transcendence d. Providing health promotion ANS: B Establishing presence by sitting with a patient to attentively listen to his or her feelings and situation, talking with the patient, crying with the patient, and simply o 洅ering time are powerful spiritual care approaches. Benner explains that presence involves “being with” a patient versus “doing for” a patient. Transcendence is the belief that a force outside of and greater than the person exists beyond the material world. In settings where health promotion activities occur, patients often need information, counseling, and guidance to make the necessary choices to remain healthy. DIF:Apply (application)REF:744 OBJ:Identify approaches for establishing presence with patients. 10/15/2016 Chapter 36: Spiritual Health | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter36spiritualhealth/ 7/15 TOP: Implementation MSC: Psychosocial Integrity 10. The nurse and the patient have the same religious a 甇liation. Which action will the nurse take? a. Must use a formal assessment tool to determine patient’s beliefs. b. Assume that both have the same spiritual beliefs. c. Do not impose personal values on the patient. d. Skip the spiritual belief assessment. ANS: C It is important not to impose personal value systems on the patient. This is particularly true when the patient’s values and beliefs are similar to those of the nurse because it then becomes very easy to make false assumptions. It is not a must to use a formal assessment tool when assessing a patient’s beliefs. It is important to conduct the spiritual belief assessment; conducting an assessment is therapeutic because it expresses a level of caring and support. DIF:Apply (application)REF:738 OBJ: Explain the importance of establishing caring relationships with patients to provide spiritual care. TOP: Implementation MSC: Psychosocial Integrity 11. A nurse makes a connection with the patient when providing spiritual care. Which type of connectedness did the nurse experience? a. Intrapersonal b. Interpersonal c. Transpersonal d. Multipersonal 10/15/2016 Chapter 36: Spiritual Health | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter36spiritualhealth/ 8/15 ANS: B Interpersonal means connected with others and the environment. Intrapersonal means connected within oneself. Transpersonal means connected with God or an unseen higher power. There is no such term as multipersonal for connectedness. DIF:Apply (application)REF:734 OBJ:Explain the importance of establishing caring relationships with patients to provide spiritual care.TOP:CaringMSC sychosocial Integrity 12. The patient is admitted with chronic anxiety. Which action is most appropriate for the nurse to take? a. Focus on 밄 nding quick remedies for the anxiety. b. Realize that the patient’s only goal is relief of the anxiety. c. Look at how anxiety in 밄 uences the patient’s ability to function. d. Help the patient realize that there is little hope of relief from anxiety. ANS: C Do not just look at the patient’s anxiety as a problem to solve with quick remedies, but rather look at how the anxiety in 밄 uences the patient’s ability to function and achieve goals established in life (not just anxiety relief). Mobilizing the patient’s hope is central to a healing relationship. DIF:Apply (application)REF:744 OBJ: Assess a patient’s spirituality. TOP: Caring MSC: Psychosocial Integrity 13. In caring for the patient’s spiritual needs, the nurse asks 20 questions to assess the patient’s relationship with God and a sense of life purpose and satisfaction. Which method is the nurse using? a. The spiritual well-being scale b. The FICA assessment tool 10/15/2016 Chapter 36: Spiritual Health | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter36spiritualhealth/ 9/15 c. Belief tool d. Hope scale ANS: A The spiritual well-being scale (SWB) has 20 questions that assess a patient’s relationship with God and his or her sense of life purpose and life satisfaction. The FICA assessment tool evaluates spirituality and is closely correlated to quality of life. This does not describe belief or hope. DIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:738 OBJ: Assess a patient’s spirituality. TOP: Assessment MSC: Psychosocial Integrity 14. A male patient in stable condition is in the intensive care unit (ICU) and is asking to see his spouse and two daughters. What should the nurse do? a. Allow only 5 to 10 minutes with the family. b. Allow the wife and daughters to visit at the patient’s request. c. Allow the two daughters to visit, and let the wife visit when they leave. d. Allow the wife and one daughter to enter the ICU but not the other daughter. ANS: B Use of support systems is important in any health care setting. Allowing the family to visit is appropriate since the patient is in stable condition. When patients depend on family and friends for support, encourage them to visit the patient. As long as no interference with active patient care is involved, there is no reason to limit visitation. Limiting the visit is not necessary since the patient is stable. Breaking the family apart is not needed; the patient is stable and can see all three at once. DIF:Apply (application)REF:744 OBJ: Discuss nursing interventions designed to promote a patient’s spiritual health. TOP: Implementation MSC: Psychosocial Integrity 10/15/2016 Chapter 36: Spiritual Health | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter36spiritualhealth/ 10/15 15. The nurse is caring for a patient who has been diagnosed with a terminal illness. The patient states, “I just don’t feel like going to work. I have no energy, and I can’t eat or sleep.” The patient shows no interest in taking part in the care by saying, “What’s the use?” Which response by the nurse is best? a. It sounds like you have lost hope. b. It sounds like you have lost energy. c. It sounds like you have lost your appetite. d. It sounds like you have lost the ability to sleep. ANS: A All of the patient’s description are describing a loss of hope. While losses of energy, appetite, and sleep are indicated, they only address a part of patient’s problems. A loss of hope encompasses the holistic view of the patient. DIF:Apply (application)REF:735 | 744 | 746 OBJ:Explain the importance of establishing caring relationships with patients to provide spiritual care.TOP:CaringMSC sychosocial Integrity 16. The patient is having a di 甇 cult time dealing with an AIDS diagnosis. The patient states, “It’s not fair. I’m totally isolated from God and my family because of this. Even my father hates me for this. He won’t even speak to me.” What should the nurse do? a. Tell the patient to move on and focus on getting better. b. Use therapeutic communication to establish trust and caring. c. Assure the patient that the father will accept this situation soon. d. Point out that the patient has no control and that he or she must face the consequences. ANS: B 10/15/2016 Chapter 36: Spiritual Health | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter36spiritualhealth/ 11/15 Application of therapeutic communication principles and caring helps you establish therapeutic trust with patients. The nurse should not o 洅er false hope (father will accept the situation soon). The nurse should help the patient maintain feelings of control, not no control. The nurse should encourage renewing relationships if possible and establishing connections with self, signi 밄 cant others, and God. DIF:Apply (application)REF:736 OBJ: Discuss nursing interventions designed to promote a patient’s spiritual health. TOP: Implementation MSC: Psychosocial Integrity 17. The nurse is caring for a group of patients. Which patient will the nurse see 밄 rst? a. A patient saying that God has left and there is no reason for living. b. A patient refusing treatment on the Sabbath. c. A patient having a folk healer in the room. d. A patient praying to Allah. ANS: A A patient saying that God has left and there is no reason for living must be seen 밄 rst for safety reasons. It must be determined by the nurse if the patient is planning suicide or is just angry and frustrated. A patient refusing treatment on the Sabbath is within that patient’s right and doesn’t need to be seen 밄 rst. A patient with a folk healer is within the patient’s right and does not need to be seen 밄 rst. A patient praying to Allah is within the patient’s right and does not need to be seen 밄 rst. DIF:Analyze (analysis)REF:739 | 743 OBJ: Assess a patient’s spirituality. TOP: Assessment MSC: Management of Care 18. A nurse is providing spiritual care to patients. Which action is essential for the nurse to take? a. Know one’s own personal beliefs. b. Learn about other religions. 10/15/2016 Chapter 36: Spiritual Health | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter36spiritualhealth/ 12/15 c. Visit churches, temples, mosques, or synagogues. d. Travel to other areas that do not have the same beliefs. ANS: A Because each person has a unique spirituality, you need to know your own beliefs so you are able to care for each patient without bias. While learning about religions, visiting other religious areas of worship, and traveling to areas that do not have the same beliefs are bene 밄 cial, they are not essential. DIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:737 OBJ: Explain the importance of establishing caring relationships with patients to provide spiritual care. TOP: Implementation MSC: Psychosocial Integrity MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1. A nurse is evaluating a patient’s spiritual care. Which areas will the nurse include in the evaluation process? (Select all that apply.) a. Review the patient’s view of the purpose in life. b. Ask whether the patient’s expectations were met. c. Discuss with family and friends the patient’s connectedness. d. Review the patient’s self-perception regarding spiritual health. e. Impress on the patient that spiritual health is permanent once obtained. ANS: A, B, C, D In evaluating care include a review of the patient’s self-perception regarding spiritual health, the patient’s view of his or her purpose in life, discussion with the family and friends about connectedness, and determining whether the patient’s expectations were met. Attainment of spiritual health is a lifelong goal; it is not permanent once obtained. 10/15/2016 Chapter 36: Spiritual Health | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter36spiritualhealth/ 13/15 DIF:Apply (application)REF:746 OBJ: Evaluate patient outcomes related to spiritual health. TOP: Evaluation MSC:Management of Care 2. Spiritual distress has been identi 밄 ed in a patient who has been diagnosed with a chronic illness. Which interventions will the nurse add to the care plan? (Select all that apply.) a. O 洅er to pray with the patient. b. Avoid time with the support group. c. Have the patient avoid church attendance. d. Develop activities to heal body, mind, and spirit. e. Teach relaxation, guided imagery, and meditation. ANS: A, D, E Interventions that are appropriate for spiritual distress include (1) helping the patient develop/identify activities to heal body, mind, and spirit; (2) o 洅ering to pray with the patient; and (3) teaching relaxation, guided imagery, and medication. Attendance at church should be encouraged as well as spending time with a support group. DIF:Apply (application)REF:736 | 743 OBJ: Discuss nursing interventions designed to promote a patient’s spiritual health. TOP lanningMSC:Management of Care MATCHING A nurse is providing spiritual care to a group of patients. Match the group to their belief. a. Nature controls life and health. b. Organ transplantation or donation is not considered. 10/15/2016 Chapter 36: Spiritual Health | Nursing Test Banks http://boostgrade.info/chapter36spiritualhealth/ 14/15 c. Observance of the Sabbath is important. d. Past sins cause illness. e. Nonhuman spirits invading the body cause illness. 1. Hinduism 2. Buddhism 3. Islam 4. Judaism 5. Appalachians 1.ANS DIF:Understand (comprehension)REF:739 [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 183 pages
Instant download

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 20, 2021
Number of pages
183
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 20, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
42