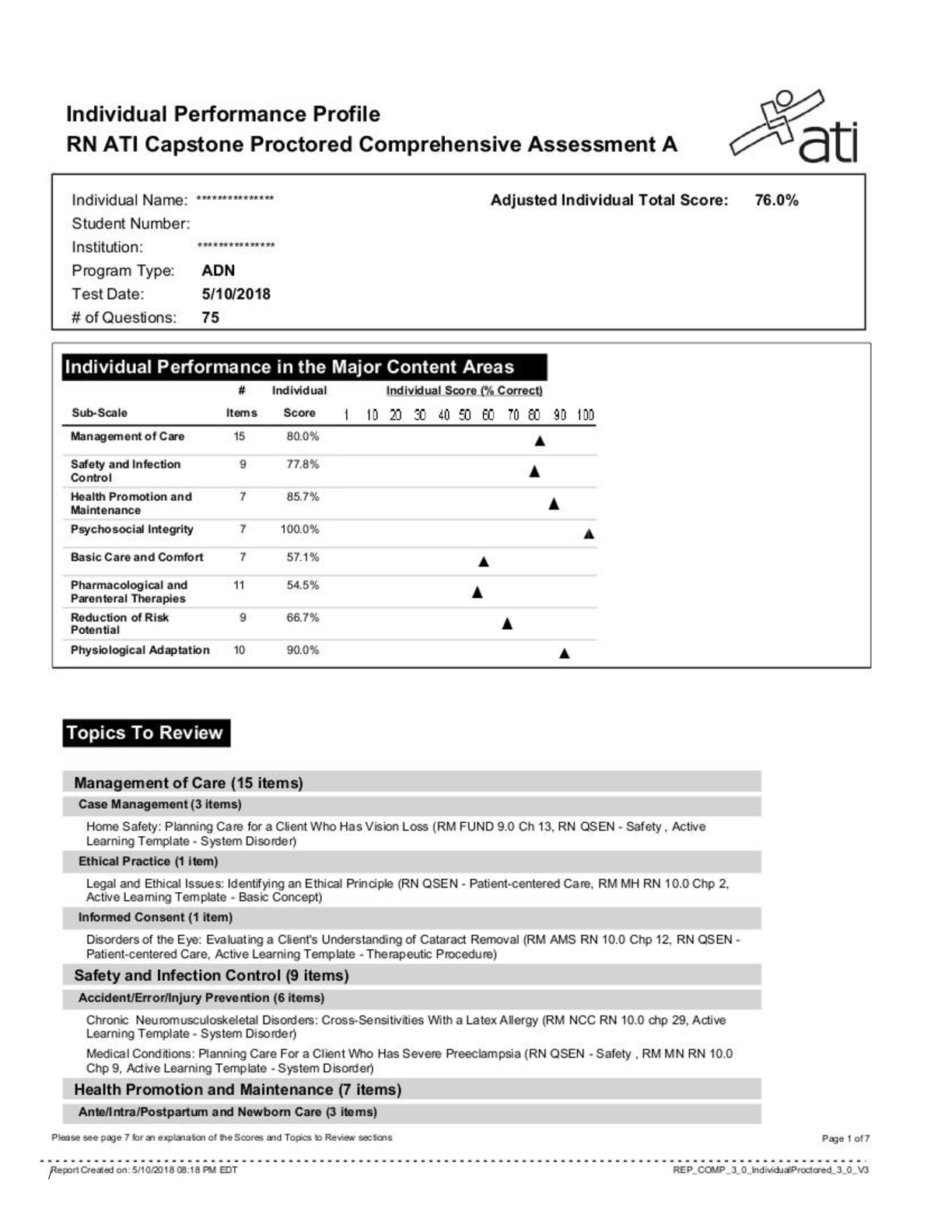
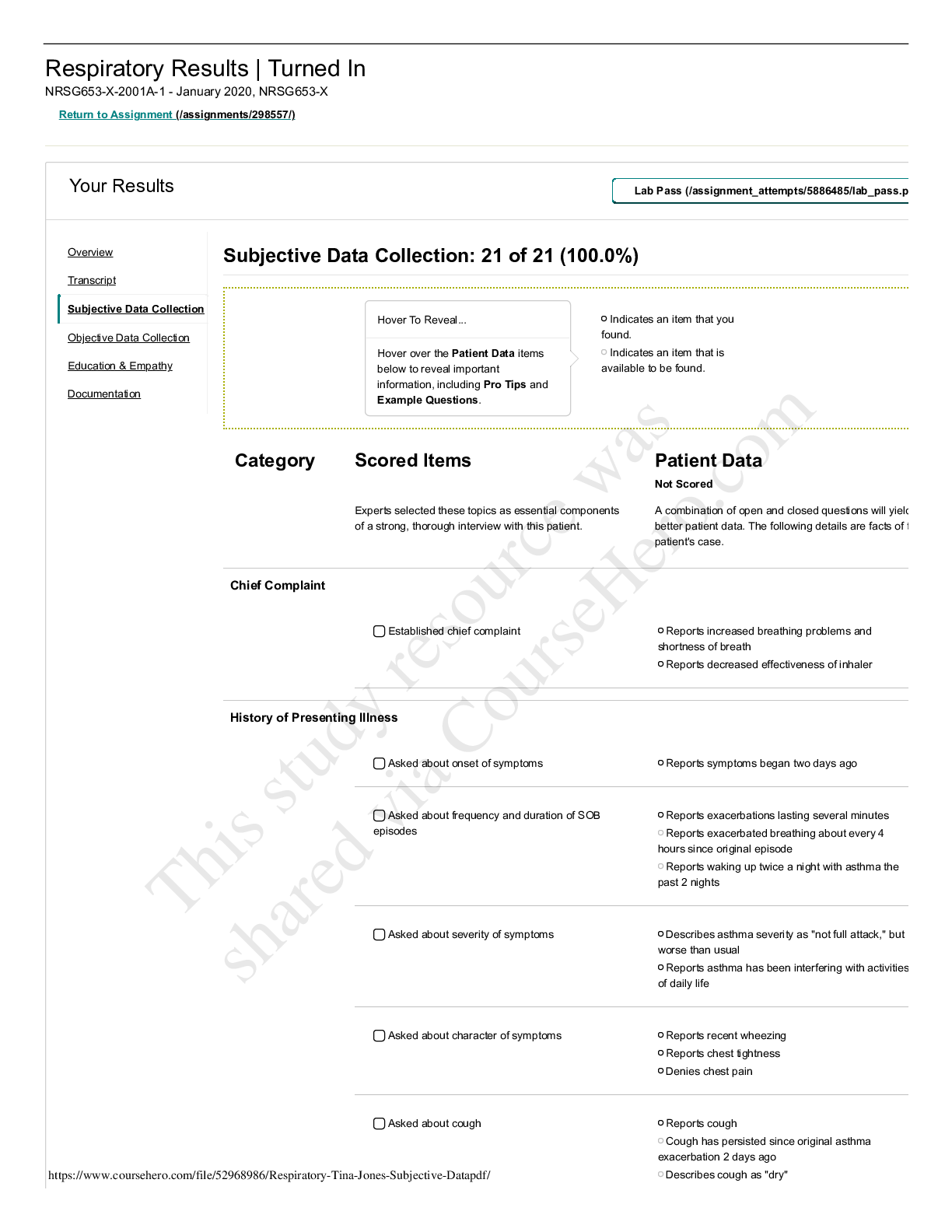
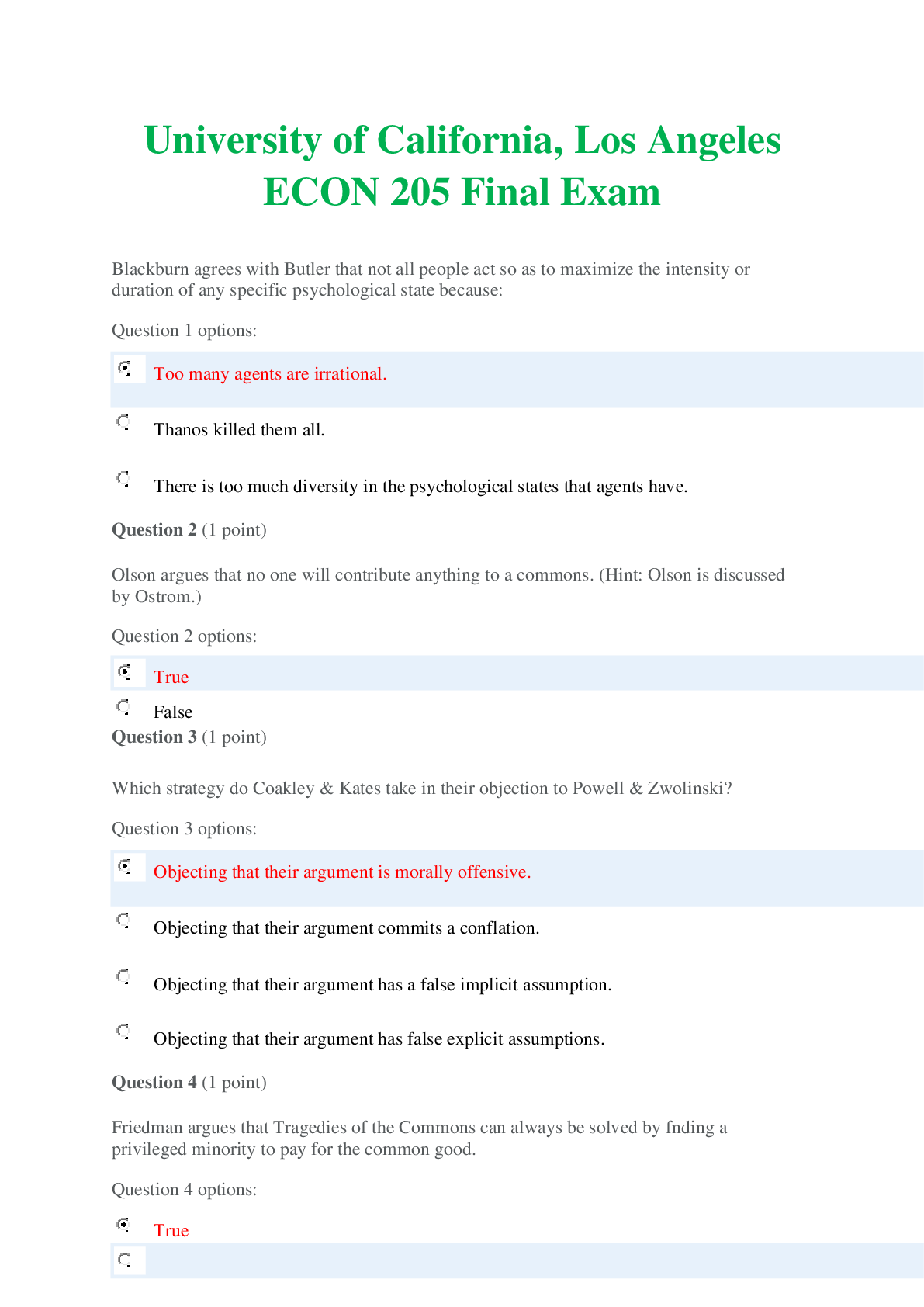
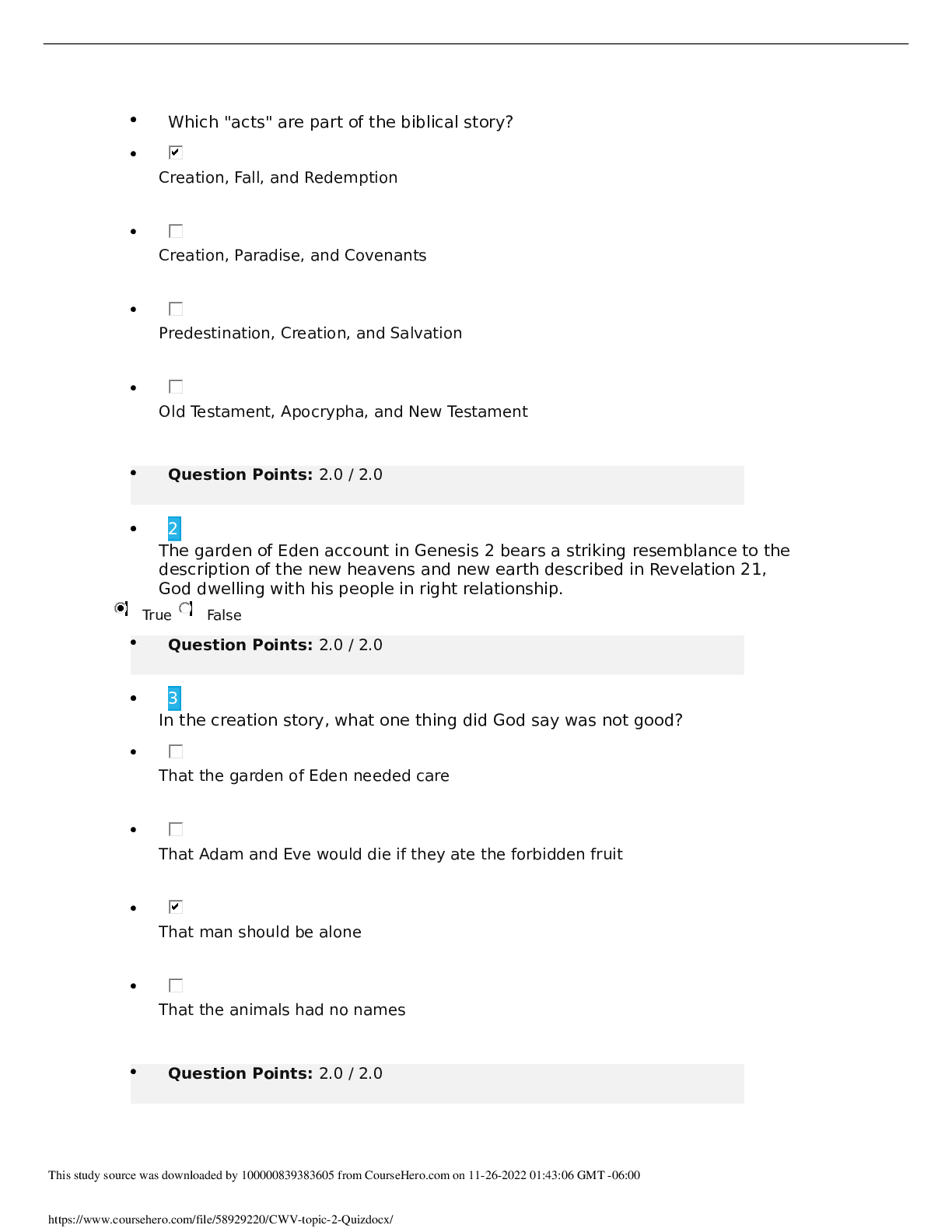
Criminology > EXAM > CMY1501 Criminology: EXAM October 2019, Questions and Answers Introduction to Criminology: Crime, Of (All)
CMY1501 Criminology: EXAM October 2019, Questions and Answers Introduction to Criminology: Crime, Offenders and Criminal Behaviour (University of South Africa). Answers and Explanations Provided
Document Content and Description Below
CMY1501 Criminology: EXAM October 2019, Questions and Answers Introduction to Criminology: Crime, Offenders and Criminal Behaviour (University of South Africa) CMY1501 Criminology AWNSERS AT THE... END WITH PAGE REF. 1. important in righting the wrongs of crime in precolonial Africa? (1) Rehabilitation; treatment (2) Retribution ; punishment (3) Reconciliation ; compensation (4) Reconstruction ; development 2. Literally, what does the word “criminology“ mean the study of? (1) Crime (2) The criminal justice system (3) Culture of crime (4) Society 3. According to the power-control theory, what are gender and social class differences in delinquency linked to? (1) The structure of the family (2) Cultural and ethnic diversity (3) Aggressiveness (4) Lack of opportunities 4. Concerning emotions, which one of the following statements is incorrect? (1) Emotions indicate the desire that a specific result will follow from a specific action. (2) Emotions are short-lived, subjective-physiological and functional –expressive phenomena that orchestrate how we react to events in our lives. (3) Emotions are subjective feelings that make us feel in a particular way such as angry, joyful or sad. (4) Emotions have four components, namely; feelings, bodily arousal, a sense of purpose and social expression. 5. Recently South Africa has been moving away from prison sentences towards which alternative forms of punishment? (1) Treatment of offenders in the community (2) Granting offenders amnesty (3) Permitting medical parole to offenders (4) Short imprisonment term 6. According to research, which of the following factor(s) increase the risk of youth misbehaviour? (1) Poor supervision (2) Parental conflict (3) Family violence (4) All of the above 7. … commences from an early age and characteristically begins with stubborn and rebellious behaviour as a child. (1) The overt pathway (2) Antisocial behaviour (3) The conflict pathway (4) Emotional immaturity 8. Criminal law controls illegal behaviour of citizens. Who or what is it enforced by? (1) The state only (2) Case law (3) Community law (4) Common law 9. The variations in crime rates between racial and ethnic groups reflect three differences among the groups. Indicate which of the following is incorrect. (1) Educational (2) Economic (3) Cultural (4) Social 10. Which one of the following places emphasis on external factors as causes of crime and sees criminals as victims of social conditions over which they have little control? (1) Social milieu school of thought (2) Rational choice theory (3) Deviant socialisation (4) Systematic observation 11. What is the relatively new technique, in terms of which multiple advanced computational methods are used to analyse large data sets involving one or more data sources, known as? (1) Crime mapping (2) Victim survey (3) Data mining (4) Self-report survey 12. Minimal brain damage is a learning disability which is also associated with … (1) hyperactivity. (2) antisocial tendencies. (3) a genetic disorder. (4) epilepsy. 13. Research has shown that stress levels can rise due to long-term exposure to extreme temperatures. What can this relate to an increase in? (1) Instrumental crimes (2) Substance abuse (3) Violent crimes (4) Child abuse 14. Broken homes can contribute to … if the separation of parents results in economic hardships, loss of affection and loss of proper role models necessary for socialisation. (1) gangsterism (2) delinquency (3) low IQ’s (4) truancy 15. In relation to family functioning, criminal risk factors can be associated with interpersonal relationships, functioning and socialisation within the family. Siegel and Senna identified categories that could be associated with delinquency. Choose the correct statement. (1) Factors influenced by the environment (2) Alcohol and drug abuse (3) Mental and physiological disorders (4) Factors associated with criminal activities 16. According to research, with what does deviant behaviour tend to be associated with? (1) Computerised crime maps (2) General antisocial behaviour patterns (3) Psychosocial influences on human behaviour (4) Criminogenic risk factors 17. According to the … theory, human behaviour is shaped by interpersonal conflict and that those who maintain social power will use to it further their own needs. (1) consensus (2) structure (3) conflict (4) process 18. Most theories of delinquency rely heavily on the parent-child relationship and parent practices to explain delinquency. With which one of the following is parental discord associated with? (1) Antisocial behaviour (2) Erratic discipline (3) Truancy (4) Emotional instability 19. Which one of the following does the term volition refer to? (1) Legal rules that were not originally written down (2) An applied discipline within the human sciences (3) Purposeful behaviour an action taken of free will (4) The juridical definition of crime 20. Which one of the following is referred to as an umbrella term for contemporary crime perspectives like feminism, leftist realism, peace-making criminology and integrated theories? (1) Postmodern criminology (2) Social learning theories (3) Content theories (4) Critical criminology 21. Perinatal risk factors are not genetically based, but are the result of destructive parental behaviour during pregnancy. Which of the following perinatal risk factors can be associated with juvenile delinquency and adult crime? (1) Exposure to smoking (2) Inadequate nutrition (3) Substance abuse (4) All of the above 22. According to Farrington, traits present in persistent offenders can be observed as early as the age of eight. With which one of the following types of crime do chronic offenders often begin with? (1) Property (2) Sexual (3) White-collar (4) Drug-related 23. Victim surveys can be regarded as valuable. This is so because they provide information on which one of the following? (1) Crime statistics (2) The dark figure (3) Self-report studies (4) Police statistics 24. The … theory focuses on the way in which society is organised and how it influences peoples’ behaviour. (1) Structure (2) Process (3) Rational choice (4) Instrumental 25. Which of the following are vital components of a “good” theory? (1) Plausibility, falsifiability and predictability (2) Usefulness, validity and policy implications (3) Plausibility , validity and empirical support (4) Reliability, adequacy and empirical support QUESTION 1 The word" criminology" literally means the study of: 1) crime. 2) criminal justice. 3) the culture of violence 4) behaviour. QUESTION 2 Crime statistics were compiled for the first time by: 1) Jerome Neapolitan 2) Ted Chiricos 3) Adolphe Quetelet 4) Gary Kleck QUESTION 3 Some criminologists distinguish criminology as the study of . 2 1) crime and deviant behaviour. 2) crime and criminal justice. 3) criminal and criminal association. 4) criminal and criminal justice behaviour QUESTION 4 In South Africa, police crime statistics are provided by the . 1) Crime Information Analysis Centre (CIAC). 2) Institute for Security Studies (ISS). 3) Crime Information Management (CIM). 4) Institute for Security Studies (ISS). QUESTION 5 zooms in on the political and economic structures of discrimination and exploitation as causes of crime and the reasons for some actions to be classified as crime and others not. 1) Critical criminology 2) Feminist criminology 3) Classical criminology 4) positivist criminology QUESTION 6 Alternative sources of information are needed to establish the true extent of 1) crime trends. 2) crime patterns. 3) trends in society 4) crime fluctuations. QUESTION 7 3 In relation to intelligence as risk indicator for criminal behaviour, studies indicate that a large fraction of offenders' IQ is at the scale. 1) high end of intelligence 2) far end of intelligence 3) middle end intelligence 4) low end of intelligence QUESTION 8 Social refers to the dynamic, multi-dimensional process of being shut out, fully or partially, from the various social, economic, political or cultural system which serves to assist the integration of a person into society. 1) exclusion 2) mobility 3) theory 4) cohesion QUESTION 9 law resolves disputes between private individuals, the chief aim being compensation for a private injustice. 1) Criminal 2) Civil 3) Statutory 4) Common QUESTION 10 Criminology is an applied discipline within the human sciences. Its field of study includes the scientific study of . 1) crime, criminals, victims, punishment and the prevention and control of crime. 2) crime, victims, families of victims and criminals and crime control only. 3) victims, punishment and the prevention and control of unknown offenders. 4) punishment and the prevention and control of law enforcement agencies. QUESTION 11 Generally speaking, criminologists study crime from two points of view, and those points of view are the . 1) classical and modern definitions of crime. 2) cultural and societal definitions of crime. 3) juridical and non-juridical definitions of crime. 4) Juridical and professional definitions of crime. QUESTION 12 12. According to the crime is a product of the capitalist system. 1) Rational choice theory 2) Social process approach 3) Social structure approach 4) Marxist criminology approach QUESTION 13 Recidivism means . 1) prevention of crime 2) punishment of crime. 3) relapses into crime 4) in relation to crime. QUESTION 14 14. A wrongful act can be defined as . 1) an act that conflicts with the legal norm in the form of a prescription or prohibition. 2) a culpable frame of mind in which a person commits a wrongful act. 3) an antisocial conduct that is In conflict with the law or detrimental to the sound normal life of an individual. 4) punishment that comprises a prison sentence, a fine, correctional supervision, a suspended or deferred sentence or a combination of any of these QUESTION 15 Tarde, Guerry and Quetelet were proponents of the social milieu school of thought. Two approaches can be distinguished in this school of thought, namely the . 1) Psycho-social and social structure approach 2) Social structure and social process approaches. 3) positivist and the interpretativist approach. 4) Psychological and social process approach. QUESTION 16 Positivism assumes that . 1) All people are equal in their rights and should be treated equally before the law and people who commit crime are motivated by pleasure. 2) The state is selective and biased, focusing on some acts as being criminal usually those committed by the powerless. 3) Forces beyond the control of individuals determine criminal behaviour. 4) Improved social conditions will prevent crime QUESTION 17 There are three separate but overlapping branches within the . 1) cultural perspective 2) social structure perspective 3) trait theory. 4) strain theory. 6 QUESTION 18 theories focus on psychological processes that affect motivation. 1) Process 2) Content 3) Instrumental 4) Rational choice QUESTION 19 Both the and stereotype female criminals as "sick". 1) classic and positivist criminology 2) critical and postmodern criminology 3) conflict and critical criminology 4) liberal feminist and positivist criminology QUESTION 20 According to the instrumental theories, . 1) focus is on the content of motivation and is essentially about taking action to fulfil needs 2) crime is a functional of conflict between the goals people have and means they can use to obtain them. 3) focus is psychological process that affect motivation 4) the reward or punishment serves as a means to ensure that people act in a particular way QUESTION 21 Lack of self-control is often linked to . 1) criminal behaviour 2) deviant behaviour 3) Impulsive behaviour 4) aggressive behaviour 7 QUESTION 22 Criminal Justice in South Africa is greatly influenced by law. 1) British and French 2) Roman Dutch and British 3) Scottish and Romanian 4) Italian and French QUESTION 23 Criminal justice is directed mainly at punishment and deterrence and its chief objective is to: 1) Compensate for a private injustice. 2) Emphasise the importance of rehabilitation. 3) Protect people against unsanctioned behaviour by others. 4) Control the criminal behaviour. QUESTION 24 The feminist school of thought developed in Western Europe and North America in the mid 1960's and is commonly regarded as the great movement in criminology. 1) first 2) second 3) third 4) fourth QUESTION 25 Classification of crime entails the . 1) arrangement of certain information into particular classes because the data display common characteristics. 2) placing of crime information into a system of convenience because It must be easily accessible 3) arrangement of crime information into simpler combinations because the four pillars require the simplification of information. 4) physical arrangements of certain information into particular crime cases QUESTION 26 Conklin states that there are three facilitating factors that are often present when crimes are committed, namely. 1) physiological disorders, alcohol and firearms. 2) opportunity, alcohol and drugs 3) gangsterism, firearms and drugs. 4) alcohol, drugs and firearms QUESTION 27 The critical school believes in 1) empowering the community by means of development programmes and community courts. 2) the destruction of social control and negotiates transition to democracy and self-defence units. 3) the view that the cause of delinquent behaviour is an impulsive personality 4) the view that human behaviour is shaped by interpersonal conflict. QUESTION 28 Determinism is the ... 1) assumption of positivism that says that individual differences in behaviour are rooted in factors beyond, or at least not entirely within, the control of individuals. 2) basic premise that certain people are born to be criminals through inheritance of a genetic or physiological predisposition to crime. 3) ability to make rational choices among possible actions, and to select one over the others. 4) way in which society is organised and how it Influences people's behaviour. QUESTION 29 Siegel and Welsh (2009), maintain that children growing up in an environment of 9 discord and conflict often exhibit . 1) aggressive delinquent behaviour. 2) learning disabilities later in life. 3) substance abuse 4) antisocial behaviour. QUESTION 30 Historically, criminological theories have developed according to three distinctive viewpoints. Choose the incorrect option. 1) Crime is a congenital trait (biological theories). 2) Crime is a tendency that individuals have acquired. 3) The causes of crime are to be found in the structure and function of society. 4) The excitement of crime is attractive to someone with a poor self-image QUESTION 31 To qualify as a crime, an act has to meet certain requirements. Which one of the following options does NOT meet the juridical requirements for a criminal act? 1) It must be a human act under the control of a human will. 2) It must be a voluntary act. 3) It must be an observable act 4) It must be an act that violates an individual's basic rights QUESTION 32 Which one of the following options represent postmodern criminology perspective? 1) It emphasises transnational and community-based policing, restorative justice and community-based punishments. 2) Crime is attributed mainly to the fact that the colonial powers forced capitalism onto a pre-capitalist continent 3) Crime should be prevented by empowering the people by repealing unjust laws and through diversion rather than imprisonment. 4) The state is selective and biased, focusing on some acts as being criminal usually those committed by powerless people. QUESTION 33 theory is essentially idealistic in unequal societies and economic conditions influence choices. 1) feminist 2) radical 3) classical 4) positivist QUESTION 34 The term "motive" refers to . 1) a causative factor that drives an action to bring about a definite result 2) subjective feelings that stem from physiological needs. 3) the desire that a specific result will follow from a particular action 4) physiological preparedness to meet situational demands QUESTION 35 feel that certain factors make women more vulnerable to crime 1) Radical feminist 2) Liberal feminist 3) Positivist criminologists 4) Postmodern criminologists QUESTION 36 Emotions are multidimensional, which means that they are studied from many different points of view. Which one of the following statements is incorrect? 1) Emotions are subjective feelings that make us feel a particular way, such as angry, joyful or sad. 2) Emotions indicate the desire that a specific result will follow from a particular action. 3) Emotions have four components, namely feelings, bodily arousal, sense of purpose and social expressions 4) Emotions are short-lived, subjective-physiological, functional-expressive phenomena that orchestrate how we react to events in our lives. QUESTION 37 theory developed from the assumption that a chaotic society causes strain which leads to delinquency and crime. 1) Strain 2) Classical 3) Radical 4) Liberal 12 QUESTION 38 Hard determinism assumes that . 1) human behaviour is completely determined by factors outside the conscious person and that choice is irrelevant. 2) people can make choices about their behaviour, but these choices are influenced by genetic and environmental factors. 3) the explanation for individual differences in the tendency to commit criminal acts may be found in a person's level of self-control. 4) exposure to violence at every level (in the news, on television and the radio and films and computer games) entrenches violent behaviour. QUESTION 39 There are four vital components that reflect the ideal characteristics of a "good" theory. Choose the incorrect option. 1) Plausibility 2) Trustworthiness 3) Predictability 4) Falsifiability The correct answer is (2) SG p185 “Four vital components reflect the ideal characteristics of a ``good'' theory: • plausibility • evidence of validity • falsifiability • predictability (Maguire & Radosh 1999:157-158)” QUESTION 40 is the statistical data compiled by the police, courts and corrections and routinely published by governments as indices of the extent of crime. 1) Code of crime list 2) Official crime statistics 3) Crime trends 13 4) Crime patterns The correct answer is (2) SG p40 “Official crime statistics. Statistical data compiled by the police, courts and corrections and routinely published by governments as indices of the extent of crime.” QUESTION 41 Racial differences in the crime rate may be linked to frustration over perceived . 1) ethnic heterogeneity. 2) economic disparity. 3) unemployment 4) social factors The correct answer is (2) SG p76 “Racial differences in the crime rate may be linked to frustration over perceived racism, discrimination and economic disparity (Siegel, Welsh & Senna 2003:42).” QUESTION 42 With which criminological school of thought do you associate the name "Turk"? 1) Postmodern school of thought. 2) Feminist school of thought 3) Classical school of thought. 4) Conflict school of thought QUESTION 43 Personality can be defined as a 1) unique, relatively stable and consistent behaviour pattern, inclusive of emotions and actions that distinguishes one person from another. 2) Unique, relatively stable and consistent behaviour pattern, inclusive of behaviour and thoughts that distinguishes one person from another. 3) Unique, relatively stable and consistent behaviour pattern, inclusive of emotions and behaviour that distinguishes one person from another. 4) Unique, relatively stable and consistent behaviour pattern, inclusive of emotions and thoughts that distinguishes one person from another QUESTION 44 14 According to Sheldon's Somatotypes, delinquent boys are mainly• 1) Ectomorphs 2) Somatotypes 3) Mesomorphs 4) Endomorphs QUESTION 45 Minimal brain disorder (MBO) is associated with . 1) antisocial tendencies 2) chromosomal disorders 3) Tourette syndrome 4) Hyperactivity QUESTION 46 According to the power-control theory, gender and social class differences in delinquency are linked to . 1) social- disorganisation. 2) the structure of the family. 3) cultural and ethnic diversity. 4) Aggressiveness QUESTION 47 Research has shown that stress levels can rise due to long-term exposure to extreme temperatures, which relates to an increase In ... crimes. 1) Violent 2) organised 3) white-collar 4) xenophobi QUESTION 48 With reference to the meaning of the concept of empathy, indicate which of the following options is correct. 1) The degree to which individuals perceive their behaviour to be under their own control. 2) The ability to see things from another person's point of view 3) The ability to exercise self-control and resist the temptation to commit crime. 4) The process whereby individuals acquire insight into their environment. QUESTION 49 Which one of the following is not an element of cognitive component? 1) Memory 2) Thinking 3) Observation 4) Empathy QUESTION 50 To understand why an offender committed a particular crime, it is essential to establish the perpetrators' . 1) intelligence. 2) criminal record. 3) motive. 4) moral reasoning. 16 QUESTION 1 Recently South Africa has been moving away from prison sentences towards alternative forms of punishment, such as 1) giving offenders amnesty 2) short imprisonment term 3) giving medical parole to offenders 4) treatment of offenders in the community QUESTION 2 Concerning emotions, which one of the following statements is incorrect? 1) Emotions indicate the desire that a specific result will follow from a specific action 2) Emotions are short-lived, subjective-physiological and functional-expressive phenomena that orchestrate how we react to events in our lives 3) Emotions are subjective feelings that make us feel in a particular way such as angry, joyful or sad 4) Emotions have four components, namely, feelings, bodily arousal, a sense of purpose and social expression QUESTION 3 Which one of the following concepts was important in righting the wrongs of crime in pre-colonial Africa? 1) Rehabilitation and treatment 2) Retribution and punishment 3) Reconciliation and compensation 4) Reconstruction and development 17 QUESTION 4 According to the power-control theory, gender and social class differences in delinquency are linked to 1) the structure of the family 2) cultural and ethnic diversity 3) aggressiveness 4) social –disorganisation QUESTION 5 In terms, only those acts that are punishable by the state are reckoned as crime 1) juridical 2) criminal justice 3) non-juridical 4) criminological QUESTION 6 emphasizes is on external factors as causes of crime, and criminals are seen as victims of social conditions of which they have little control 1) Critical criminology 2) Feminist criminology 3) Social milieu school of thought 4) Classical theory QUESTION 7 Process theories 1) focuses on the way in which society is organized 18 2) view human behaviour as shaped by interpersonal conflict 3) view crime as acts that are outlawed and in conflict with the rules 4) explain how people become offenders QUESTION 8 In relation to the positivist school of thought, identify the correct statement 1) Criminal behaviour is determined by biological, psychological and socio- economical factors. 2) The purpose of sanctions is not so much to punish, but to provide for treatment and reform 3) It is not bound to a particular school of thought 4) Crime could be prevented by empowering the people QUESTION 9 Intention consists of two elements, namely 1) Cognitive and volitional 2) Affective and intellectual 3) Cognitive and emotional 4) Expressive and intellectual QUESTION 10 To which criminological school of thought does the following quotation relate? "Economic and political discrimination are seen as the causes of crime" 1) Postmodern criminology 2) Positivist criminology 3) Critical criminology 4) Feminist criminology QUESTION 11 According to Sheldon's somatotypes, delinquent boys are mainly 1) ectomorphs 2) endomorphs 3) mesomorphs 4) somorphops QUESTION 12 is a relatively new criminological technique in terms of which multiple advanced computational methods are used to analyse large datasets involving one or more data sources 1) Victim survey 2) Crime mapping 3) Self-report study 4) Data mining QUESTION 13 Farrington identified factors that predict the of criminal offences 1) pattern 2) protection 3) discontinuity 4) continuity QUESTION 14 Personality may be defined as a 20 1) unique, relatively stable and consistent behaviour pattern, inclusive of emotions and actions, that distinguishes one person from another 2) unique, relatively stable and consistent behaviour pattern, inclusive of behaviour and thoughts, that distinguishes one person from another 3) unique, relatively stable and consistent behaviour pattern, inclusive of emotions and behaviour, that distinguishes one person from another 4) unique, relatively stable and consistent behaviour pattern, inclusive of emotions and thoughts, that distinguishes one person from another QUESTION 15 With which criminological school of thought do you associate the name "Turk"? 1) Feminist school of thought 2) Conflict school of thought 3) Postmodern school of thought 4) Classical school of thought QUESTION 16 Tarde, Guerry and Quetelet were proponents of the social milieu school of thought .Two approaches may be distinguished in this, namely the . 1) Positivist and critical approaches 2) social structure and the social process approaches 3) cultural structure and social structural approaches 4) criminological and victim logical approaches QUESTION 17 One of the basic premises of the classic theory is that: 1) crime could be prevented by empowering the people 2) there is no concern with punishment or rehabilitation 3) crime is a voluntary act committed by persons exercising a deliberate choice 4) the emphasis is on the criminal, not on the crime QUESTION 18 Being psychologically present literally implies that children will 1) consciously or unconsciously evaluate their behaviour against their society's opinion of that particular behaviour 2) consciously or unconsciously evaluate behaviour against their community's opinion of that particular act 3) consciously or unconsciously evaluate their behaviour against their peers' opinion of that particular act 4) consciously or unconsciously evaluate their own behaviour against their parents' opinion of that particular act QUESTION 19 Positivist criminology has dominated crime policy and prevention for decades but is now under criticism for its inability to reduce the level of crime. Which one of the following options represents objections to positivist criminology? 1) The main focus is on the criminals' social environment 2) The rejection of the juridical concept and traditional causes of crime 3) Failure to explain crimes committed by people with power 4) Victims of crime are of little or no importance QUESTION 20 Siegel & Welsh (2009) identified three parts of antisocial behaviour that, during the 22 developmental process of a child, may lead to a delinquent career, namely 1) Conflict pathway, covert pathway and overt pathway 2) Conflict pathway, aggressive pathway and overt pathway 3) Conflict pathway, hidden pathway and overt pathway 4) Conflict pathway, covert pathway and aggressive pathway QUESTION 21 Precolonial Africa concerned itself mainly with 1) crime statistics 2) crime victim 3) social fabric crime 4) property-related crime QUESTION 22 Which one of the following social factors is not a contributory factor to the high crime rate among the youth? 1) Materialistic cravings 2) Peer group pressure 3) Social stressors 4) High level of aggression QUESTION 23 Criminogenic risk factors are associated with criminal activities, such as 1) Crime 2) Delinquency 3) Offending 4) All of the above 23 QUESTION 24 The term "dark figure", refers to 1) A statistical survey that measures the amount, nature and patterns of victimisation in the population 2) The number of crimes that are committed but not recorded by the police 3) A means of collecting information about aspects of an individual’s personal experience such as involvement in offending 4) The statistical data compiled by the police, courts and corrections on the extend of crime QUESTION 25 Self -report items aim to 1) explain policy directions in respect of crime and criminal behaviour 2) measure attitudes, values, personal characteristics and behaviours 3) analyse and correlate data to create detailed visuals of crime patterns 4) identify and predict future criminal behaviour or events QUESTION 26 Rational choice theory has its roots in the 1) social milieu school of thought 2) postmodernist approach 3) social structure approach 4) classical school of criminology QUESTION 27 refer/s to the dynamic, multidimensional process of being fully or partially excluded from the various social, economic, political or cultural systems which serve to assist the integration of a person in society 1) Social disorganisation 2) Conflict theories 3) Marginalisation 4) Systematic observation QUESTION 28 Which one of the following is not a contributory factor to crime in South Africa? 1) Rapid structures 2) Political factors 3) Inadequate welfare services 4) The system of migrant labours QUESTION 29 Lack of self-control is often linked to 1) substance abuse 2) impulsive behaviour 3) juvenile delinquency 4) criminal behaviour QUESTION 30 The theorists view the forces operating in run-down lower-class areas as the key determinants of criminal behaviour patterns 1) social structure 2) rational choice 3) social process 4) traits QUESTION 31 is associated with children's lack of internal inhibitions against offending 1) Lack of empathy 2) Deviant socialisation 3) Harsh parental discipline 4) Personality QUESTION 32 According to research on social support, in order to prevent criminal behaviour parents should 1) act as probation or parole agencies willing to guarantee their member's good conduct 2) restrict children's activities and maintain physical surveillance by knowing their whereabouts 3) reduce crime by protecting their home and its occupants against physical, emotional and material harm 4) All of the above QUESTION 33 As far as the functioning of the family is concerned, criminal risk factors may be associated with 1) the structure, functioning and relationships of the family 2) interfamilial abuse, criminality and offending 3) the structure, size and composition of the family 4) interpersonal relationships and socialisation within the family QUESTION 34 Criminology is an applied discipline within the human sciences. Its field of study is 1) Victims, punishment and the prevention and control of unknown offenders 2) Knowledge of a particular discipline, on crime and victims which is systematically controlled 3) Crime, criminals, victims, punishment and the prevention and control of crime 4) Punishment and the prevention and control of all law enforcements agencies QUESTION 35 Criminal justice in South Africa is greatly influenced by law 1) Italian and French 2) Scottish and Romanian 3) Roman Dutch and British 4) British and French QUESTION 36 There are three separate but overlapping branches within the 1) social structure perspective 2) cultural perspective 3) rational theory 4) traits theory QUESTION 37 Instrumental theories state that 1) all persons are equal in their rights and should be treated equally before the law 2) reward or punishment serves as a means to ensure that people act in a particular way 3) punishment should be proportionate to crime and linked to treatment 4) behaviour is linked to factors over which individuals have full control 27 QUESTION 38 According to Burton (2007), one of the risk factors associated with violence with South African youth is: 1) exposure to violence at every level entrenches violent behaviour 2) inadequate education and poor preparation for the labour market 3) the presence of large numbers of illegal immigrants 4) the negotiated transition and destruction of social control QUESTION 39 Parental neglect is often associated with 1) mental and physiological disorders 2) the child's lack of emotional security 3) mental and physiological disorders 4) deprivation of the child's emotional needs QUESTION 40 Which one of the following is not an element of a cognitive component? 1) Thinking 2) Empathy 3) Observation 4) Memory SG p141 QUESTION 41 The and criminology stereotype female criminals as "sick", implying that they need treatment and are psychological disturbed 1) classic, positivist 2) liberal feminists, classic 3) critical , postmodern 4) radical feminist, positivist QUESTION 42 Consensus theories belief that 1) human behaviour is shaped by interpersonal conflict and those that maintain social power will use It to further their own needs 2) Crime is regarded as an event in time and space and various factors have to be present for a crime to occur 3) Human behaviour is determined biological, psychological and socioeconomic factors over which individuals have little control 4) crimes are acts that are outlawed because they conflict with the rules of the majority and are harmful to society QUESTION 43 Historically, criminological theories have developed according to distinctive viewpoints. Choose the incorrect statement 1) Crime is a tendency that individuals have acquired 2) Crime is a congenital trait (biological theories) 3) Causes of crime are found in the structure and function of society 4) The criminal and criminal offenders are considered as separate concepts QUESTION 44 Violent people tend to have that makes it difficult for them to come up with non- aggressive solutions to interpersonal conflicts and disputes 1) cognitive deficiencies 2) Tourette syndrome 3) antisocial behaviour 4) low lQ QUESTION 45 Determinism is: 1) an assumption of positivism that says individual differences In behaviour are rooted in factors beyond, or at least not entirely within, the control of individuals 2) the degree to which individuals perceive their behaviour to be under their own control or under the control of external forces, such as the government 3) a branch of the social structure theories that focus on the breakdown of institutions such as the family, school and employment in the inner city 4) a process by which a pronouncement is made on a bigger group or population on the basis of a study of a limited number of similar cases QUESTION 46 criminology focuses especially on the rights and needs of crime victims, national crime prevention strategies, transnational and community-based policing, restorative justice and community-based punishments 1) Positivist 2) Postmodern 3) Classical 4) Radical QUESTION 47 According to the theory, the traditionally lower crime rate for women could be explained by their "second class" economic and social position 1) power-control 2) liberal feminist 3) structure 4) radical feminist QUESTION 48 Cognitive processes play an important role in appraising available aims when designing a particular strategy. Cognition involves . 1) 1 Thought, judgement, interpretation and understanding 2) 2 Direction, persistence, effort and emotions 3) 3 Goals, needs, interpretation and understanding 4) 4 Needs, judgement, thought and emotions QUESTION 49 Children from broken homes where both parents are missing are normally involved in deviant activities such as 1) gangsterism 2) substance abuse 3) bullying 4) truancy According to the people can make choices about their behaviour, but these choices are influenced by genetic and environmental factors 1) hedonistic principle 2) soft determinism view 3) universal ethical principle 4) hard determinism view October/November 2014 QUESTION 1 One of the premises of the classic crime theory is that: 1) The main focus is on external factors as causes of crime 2) Most crimes are economically determined 3) Political discrimination and exploitation are important causes of crime 4) People are rational and their behaviour is the product of free will QUESTION 2 According to Gottfredson and Hirschi's general theory of crime, crime 1) is basically a problem of poor self-control 2) does not require much skill or planning 3) brings an immediate satisfaction of needs 4) could be prevented by empowering the community QUESTION 3 The emphasis is on external factors as causes of crime, criminals are seen as 32 victims of social conditions over which they have little control. This premise refers to: 1) Social milieu school of thought 2) Critical criminology 3) Feminist criminology 4) Contemporary positivism QUESTION 4 Motive may be defined as: 1) The desire that a specific result will follow from a particular action 2) An inner drive that causes or compels a person to act 3) A physical need that evokes aggression in an unpleasant environment 4) A stimulus caused by frustration as a result of deliberate provocation QUESTION 5 Siegel and Senna (2000) identified categories that could be associated with delinquency. Identify the incorrect option. 1) Alcohol and drug abuse 2) Marital conflict and break-up 3) Interfamilial and interpersonal conflict 4) Parental deviance resulting in the deviant socialisation of children 33 QUESTION 6 With reference to the meaning of the concept of empathy, indicate which of the following options is correct 1) The degree to which individuals perceive their behaviour to be under their own control 2) The ability to see things from another person's point of view 3) The observed social support for antisocial behaviour 4) The process whereby individuals acquire insight into their environment QUESTION 7 Which of the following is NOT a non-juridical definition of crime? 1) Crime as a violation of behavioural norms 2) Crime as a violation of human rights 3) Crime as a form of social deviance 4) Crime as social culture QUESTION 8 is strongly linked to persistent violent offending 1) Substance abuse 2) Broken homes 3) Poverty 4) Delinquency QUESTION 9 There are three forms of intention. Choose the incorrect option 1) Direct intention 2) Dolus eventualis 3) Indirect intention 4) Hedonistic principle 34 QUESTION 10 To which criminological school of thought does the following quotation relate? "Economic and political discrimination are seen as the causes of crime" 1) Postmodern criminology 2) Critical criminology 3) Positivist criminology 4) Feminist criminology QUESTION 11 law is made up of all the legal rules which identify crimes and set down punishments 1) Civil 2) Juridical 3) Common 4) Criminal QUESTION 12 The main task of a criminologist is to 1) Maintain peace, order, love and happiness in society by ensuring that people study and understand criminology 2) Study, define, describe, interpret, explain and indicate policy directions in respect of crime, criminal behaviour and victimisation 3) Legislate and regulate all criminal actions of people in society 4) Protect criminal law and all criminal justice institutions in society QUESTION 13 35 is a relatively new criminological technique in terms of which multiple advanced computational methods are used to analyse large datasets involving one or more data source 1) Data mining 2) Victim survey 3) Dark figure 4) Self-report studies QUESTION 14 Which of the following school of thought emphasises transnational and community- based policing, restorative justice and community-based punishments? 1) Postmodern criminology 2) Feminist criminology 3) Classical criminology 4) Critical criminology QUESTION 15 There are three separate but overlapping branches within the 1) social disorganisation 2) strain theory 3) traits theory 4) social structure perspective QUESTION 16 According to Sheldon's body-type, delinquent boys are mainly 1) Ectomorphs 2) Endomorphs 3) Somatotypes 36 4) Mesomorphs QUESTION 17 Research has shown that children who grow up in an environment of discord often exhibit 1) aggressive behaviour 2) substance abuse 3) antisocial behaviour 4) classroom demeanour QUESTION 18 Lack of self-control is often linked to 1) impulsive behaviour 2) delayed maturity 3) verbal and physical aggression 4) lack of concentration QUESTION 19 Minimal brain dysfunction (MBD) is associated with 1) Tourette syndrome 2) chromosomal disorders 3) antisocial tendencies 4) genetic factors QUESTION 20 The is criticised for its assumption that male dominance is universal whereas anthropological studies have shown that women in matriarchal societies actually 37 have a great deal of power 1) radical feminism 2) contemporary positivism 3) liberal feminism 4) postmodern criminology QUESTION 21 Historically theories have developed according to three distinctive viewpoints. Choose the incorrect statement. 1) Crime is a congenital trait (biological theories) 2) Crime is a tendency that individuals have acquired 3) The causes of crime are to be found in the structure and function of society 4) Crime is a voluntary act committed by person's exercising a deliberate choice QUESTION 22 Wells and Rankin's analysis of studies of broken homes and delinquency found that 1) There are no consistent differences in the impact of broken homes as far as girls and boys or black and white youth are concerned 2) There is consistent evidence of the negative impact of stepparents on juvenile delinquency 3) There is a strong relationship between emotional deprivation or lack of parental love and juvenile delinquency 4) There is positive evidence on the impact of step parents on juvenile delinquency = QUESTION 23 According to Bandura, aggressive behaviour in adolescents is the result of 1) a distorted dependency relationship with the parents 2) children modelling their parents' behaviour 3) a delay In the development and maturation of moral reasoning 4) exposure and socialising with aggressive peers QUESTION 24 Arnold, Robertson and Cooper are of the opinion that motivation comprises of three components , namely: 1) goal, effort and persistence 2) direction, effort and action 3) need, goal and action 4) persistence , direction and effort QUESTION 25 is/are statistical data compiled by the police, the courts and the Department of Correctional Services and are routinely published by governments to indicate the extent of crime found in a country 1) The dark figure 2) The conviction rate 3) The code of crime hst 4) Official crime statistics = QUESTION 26 The theory has its root in the classical school of criminology 1) rational choice 2) social process 3) social structure 4) trait QUESTION 27 The word "criminology” literally means the study of 1) criminal behaviour 2) crime 3) criminal justice 4) criminals QUESTION 28 approach is of view that criminal behaviour is a function in people's interactions with various organisations, institutions and processes in society 1) Postmodernist 2) Social process 3) Radical criminology 4) Social structure QUESTION 29 South African Universities have been teaching criminology as a subject in the faculty of social sciences since 1) 1948 2) 1849 3) 1960 4) 1949 = QUESTION 30 The term " " refers to knowledge and indicates an understanding of a particular discipline that has been systematically collected 1) theory 2) criminology 3) science 4) survey QUESTION 31 Criminal justice in South Africa is greatly influenced by law 1) Italian and French 2) Scottish and Roman 3) British and civil 4) Roman Dutch and British QUESTION 32 The court is the highest decision-making body in the country and can invalidate laws adopted by Parliament if, in terms of the Bill of rights, they infringe on the rights of South Africans 1) Magistrate 2) Constitutional 3) High 4) Regional QUESTION 33 Criminal law controls illegal behaviour by citizens within its jurisdiction it is enforced by the 1) Community 2) High court 3) common law 4) the state only = QUESTION 34 With which criminological school of thought do you associate the name "Turk"? 1) Classical school of thought 2) Feminist school of thought 3) Conflict school of thought 4) Post-modern school of thought QUESTION 35 Recidivism means: 1) Prevention of crime 2) Punishment of crime 3) In relation to crime 4) Relapses to crime QUESTION 36 A wrongful act may be defined as an act that is: 1) conflicting with personal norms in the form of a prescription or prohibition 2) not originally written down, but which have to come to be accepted as the law of the land 3) prohibited by all the international communities 4) conflicting with the legal norm in the form of a prescription or prohibition QUESTION 37 Guilt has a number of meanings, but according to the juridical definition of crime, guilt is defined as a: 1) deviant behaviour determined by tradition and criminal law = 2) culpable frame of mind in which a person commits a wrongful act 3) culpable action in which a person commits any wrongful act 42 4) person's own conscience and admission of the wrongful act QUESTION 38 Which of the following is not an element of cognitive component? 1) Memory 2) Thinking 3) Empathy 4) Observation QUESTION 39 According to the theory, gender and social class differences in delinquency are linked to the structure of the family 1) equal opportunity 2) power-control 3) liberal feminist 4) social process QUESTION 40 In relation to intelligence as risk indicator for criminal behaviour, studies indicate that a large fraction of offenders' lQs are at the 1) Far end of the intelligence scale 2) High end of the intelligence scale 3) Middle of the intelligence scale 4) Low end of the intelligence scale = QUESTION 41 There are a few factors that protect high-risk youths from starting criminal careers. Choose the incorrect option. 1) Having a sociable personality 2) Having few friends at age eight 3) Being regarded highly by their mothers 4) Having non-deviant families QUESTION 42 Social refers to the dynamic, multi-dimensional process of being shut out, fully or partially, from the various social, economic, political or cultural system which serve to assist the integration of a person into society 1) cohesion 2) mobility 3) milieu 4) exclusion QUESTION 43 In order to rear a child correctly, so that he or she develops self-control, certain minimum requirements must be met. Which of the following option is incorrect? 1) If delinquency occurs, the child must be punished 2) The supervisor(s) must be able to identify and detect delinquent behaviour 3) Someone must monitor a child's behaviour 4) The South African children's court must be notified QUESTION 44 Racial differences in the crime rate may be linked to = 1) frustration over perceived racism and discrimination 2) different definitions of crime by different ethnic groups 44 3) overcrowding, poverty and gender inequality 4) variations in homicide rates and ethnic heterogeneity QUESTION 45 To understand why an offender committed a particular crime, it is essential to establish the perpetrators . 1) Previous criminal record 2) Personality characteristics 3) Mental make-up 4) Motive QUESTION 46 Emotions are biological reactions and energy-mobilising responses that prepare the body to adapt to the situation the person is confronted. Which of the following statements does not refer to emotions? 1) Emotions are subjective feelings that make us feel in a particular way such as angry, joyful or sad 2) Emotions are short-lived, subjective-physiological and functional-expressive phenomena that orchestrate how we react to events in our lives 3) Emotions indicate the desire that a specific result will follow from a specific action 4) Emotions have four components , namely feelings, physical arousal, a sense of purpose and social expressions QUESTION 47 What are criminogenic risk factors? 1) Mental and physiological disorders 2) Factors influenced by the environment 3) Factors associated with criminal activities 4) Alcohol and drug abuse = 45 QUESTION 48 Which of the following factor(s) increase the risk of youth misbehaviour? 1) poverty 2) parental conflict 3) Erratic discipline 4) All of the above QUESTION 49 commences from an early age and characteristically begins with stubborn and rebellious behaviour as a child 1) Conflict pathway 2) Criminal personality 3) Low-self control 4) Overt pathway QUESTION 50 law resolves disputes between private individuals, the chief aim being compensation for a private injustice 1) State 2) Case 3) Civil 4) British The correct answer is (3) SG p11 “Civil law resolves disputes between private individuals, the chief aim being compensation for a private injustice.” May/June 2014 QUESTION 1 According to the theory, the cause of delinquent behaviour is an impulsive personality 1) Self-control 2) Radical 3) Liberal 4) Power-control = QUESTION 2 acts as a protective factor against delinquency 1) Social support 2) Differential association 3) Determinism 4) Rational choice QUESTION 3 criminology focuses more particularly on hidden crimes, such as sexual harassment in the workplace 1) Postmodern 2) Critical 3) Feminist 4) Positivist QUESTION 4 is a means of collecting information about aspects of an individual's personal experience, such as involvement in offending 1) Dark figure 2) Self-report survey 3) Victimisation survey 4) Questionnaire QUESTION 5 The concept of is an attempt to account for the acquisition and maintenance of criminal behaviour in terms of contact with particular environments and social groups 1) criminogenic risk factors 2) external events 3) biological dimension 4) differential association = 47 QUESTION 6 Research on violent recidivist indicates that they may be distinguished from other offenders on the basis of their 1) impulsive personality structure 2) pathologically violent offences 3) exposure to delinquent peers 4) genetic and hereditary factors QUESTION 7 Several studies suggest that may be a critical factor in explaining gender differences in delinquency 1) marginalisation 2) social process approach 3) social structure approach 4) differential association QUESTION 8 The general theory of crime advocates that 1) the explanation for individual differences in the tendency to commit criminal acts may be found in a person's level of self-control 2) punishment must be proportionate to the crime and has to be just and fair 3) the purpose of sanctions is not so much to punish, but to provide for treatment 4) the root cause of power-control is due to inadequate child-rearing practices QUESTION 9 exist(s) as subjective, biological, purposive and social phenomena 1) Intent 2) Emotions 3) Needs 4) Motive QUESTION 10 focuses on the criminal's social environment 1) Positivist criminology 2) Social milieu school of thought 3) Classical criminology 4) Conflict theory QUESTION 11 According to Sheldon's somatotypes, an endomorph's personality is associated with being 1) Strong, active, aggressive and sometimes violent 2) Introverted, hypersensitive and intellectual 3) Extroverted, aggressive and violent 4) Extroverted, friendly and sociable QUESTION 12 criminology questions narrow definitions of conventional concepts like" norms", "values", "culture", " "social constraint" and "anomy" and ask who should determine what behaviour should be described as a crime 1) Postmodern 2) Classical 3) Radical 4) Feminist QUESTION 13 Perinatal risk factors associated with juvenile delinquency and adult crime are, among others 1) Inadequate nutrition 2) Temperament 3) Personality 49 4) Physiological disorder QUESTION 14 Personality may be defined as a 1) unique, relatively stable and consistent behaviour pattern, inclusive of emotions and actions, that distinguishes one person from another 2) unique, relatively stable and consistent behaviour pattern, inclusive of behaviour and thoughts, that distinguishes one person from another 3) unique, relatively stable and consistent behaviour pattern, inclusive of emotions and behaviour, that distinguishes one person from another 4) unique, relatively stable and consistent behaviour pattern, inclusive of emotions and thoughts, that distinguishes one person from another QUESTION 15 Involves thinking, perceiving, abstracting, synthesising, organising and conceptualising the nature of the external world and the self 1) Locus of control 2) Moral reasoning 3) Cognition 4) External control QUESTION 16 The escalation of school conflict and violence may be attributed to a variety of causes. Choose the option (s) 1) School staff may lack conflict resolution and management skills 2) The school has no control over social and family conditions 3) School staff may fall to recognise and address conditions within the school that give rise to violence 4) All of the above QUESTION 17 Which school of thought emphasises external factors as causes of crime, and sees criminals as victims of social conditions over which they have little control 1) Social milieu 2) Positivist 3) Critical 4) Conflict QUESTION 18 Content theory is based on 1) the view that human behaviour is shaped by interpersonal conflict 2) the way in which society is organised and how it influences people's behaviour 3) a hierarchy of needs ranging from basic physiological needs to the need for self-actualisation 4) the view that the cause of delinquent behaviour is an impulsive personality QUESTION 19 is a relatively new criminological technique in terms of which multiple advanced computational methods are used to analyse large data sets involving one or more data sources 1) Data mining 2) Crime mapping 3) Dark figure 4) Self-report studies QUESTION 20 Farrington identified factors that predict the of criminal offences 1) mobility 2) continuity 3) pattern 4) discontinuity QUESTION 21 Precolonial Africa concerned itself mainly with reconciliation and compensation which were considered crucial to the righting of wrongs and the restoration of law and order 1) crime statistics 2) crime victims 3) social fabric crime 4) property-related crime QUESTION 22 Intention consists of two elements, namely 1) Cognitive and volitional 2) Cognitive and emotional 3) Expressive and intellectual 4) Affective and intellectual QUESTION 23 Which one of the following is not an element of a cognitive component? 1) Memory 2) Observation 3) Empathy 52 4) Thinking QUESTION 24 Arnold, Cooper and Robertson are of the opinion that there are three components of motivation, namely 1) Goal, effort and persistence 2) Need, goal and action 3) Direction , effort and persistence 4) Direction, need and effort QUESTION 25 Which one of the following is not one of the limitations of victim surveys? 1) Victims always forget an important fact if they are not questioned on the day crime was committed 2) Victim surveys reflect the number of crimes but not the number of offenders 3) The same type of offence is reported by the victim each time 4) Indirect victims do not report a crime as readily as direct victims do QUESTION 26 According to research, is one of the strongest predictors of adolescent violence as far as both males and females are concerned 1) drug abuse 2) poverty 3) aggression 4) low lQ QUESTION 27 The theory is a branch of the social structure theories that focuses on the breakdown of institutions such as the family, school and employment in inner-city neighbourhoods 1) Consensus 2) Postmodernist 3) Social disorganisation 4) Classical QUESTION 28 Lack of self-control is often linked to 1) truancy 2) violent crimes 3) social problem solving 4) impulsive behaviour QUESTION 29 54 The theory suggests that a traditionally lower crime rate for women could be explained by their "second class", economic and social position 1) radical 2) Positivist 3) classical 4) feminist QUESTION 30 refers to the rise and fall in crime in a particular year 1) Crime trends 2) Dark figure 3) Surveys 4) Crime patterns QUESTION 31 commences from an early age and characteristically begins with stubborn and rebellious behaviour as a child 1) Conflict pathway 2) Juvenile delinquency 3) Temperament 4) Personality QUESTION 32 The basic premise of the is that some people are born to be criminals through the inheritance of a genetic or physiological predisposition to crime 1) biological dimension 2) Social learning approach 3) rational choice theory 55 4) classical criminology QUESTION 33 Research conducted by Wilson and Petersilia suggests that in order to prevent criminal behaviour parents should 1) Act as probation or parole agencies willing to guarantee the member's good conduct 2) Reduce crime by protecting their home and Its occupants against physical, emotional and material harm 3) Restrict children 's activities and maintain physical surveillance by knowing their whereabouts 4) All of the above QUESTION 34 Criminology is an applied discipline within the human sciences its field of study includes 1) Victims , punishment and the prevention and control of unknown offenders 2) knowledge of a particular discipline on crime and victims which is systematically controlled 3) crime, criminals, victims, punishment and the prevention and control of crime 4) punishment and the prevention and control of all law enforcements agencies QUESTION 35 Criminal justice in South Africa is greatly influenced by law 1) Italian and French 2) Scottish and Romanian 3) Roman Dutch and British 4) British and French 56 QUESTION 36 The concept of is an attempt to account for the acquisition and maintenance of criminal behaviour. 1) differential association 2) Internal motives 3) determinism 4) social disorganisation QUESTION 37 According to the theory, gender and social class differences in delinquency are linked to the structure of the family 1) structure 2) power-control 3) liberal feminist 4) positivist QUESTION 38 There are vital components that reflect the ideal characteristics of a "good" theory. Choose the correct option. 1) Plausibility 2) Falsifiability 3) Predictability 4) All of the above QUESTION 39 One of the basic premises of the classic crime theory is that 1) crime should be prevented by empowering people 2) the emphasis is on the criminal, not on the crime 3) there is no concern with punishment or rehabilitation 4) crime is a voluntary act committed by persons exercising a deliberate choice QUESTION 40 Research indicates that children are more likely to exhibit delinquent behaviour 1) first born 2) middle 3) last born 4) twin QUESTION 41 indicates the desire that a specific result will follow from a particular action 1) Intent 2) Emotions 3) Thoughts 4) Needs QUESTION 42 criminology has made an important contribution by showing that the juridical crime concept can be unjust and discriminatory 1) Socialist 2) Feminist 3) Critical 4) Positivist QUESTION 43 Minimal brain disorder (MBD) is associated with 1) Chromosomal disorders 58 2) Antisocial tendencies 3) Biochemical factors 4) Tourette syndrome QUESTION 44 is of view that crime is a product of the capitalist system 1) Radical Criminology 2) Trait theory 3) Postmodern Criminology 4) Positivist theory QUESTION 45 Determinism is: 1) an assumption of positivism that says individual differences in behaviour are rooted in factors beyond, or at least not entirely within, the control of individuals 2) the degree to which individuals perceive their behaviour to be under their own control or under the control of external forces, such as the government 3) a branch of the social structure theories that focus on the breakdown of institutions such as the family, school and employment In the inner city 4) a process by which a pronouncement is made on a bigger group or population on the basis of a study of a limited number of similar cases QUESTION 46 The approach focuses on individual crimes in particular 1) social process 2) rational choice 3) social structure 4) radical feminist QUESTION 47 criminology is known as the third movement in the scientific development of criminology and focuses on the political and economic structures of discrimination and exploitation as causes of crime 1) Positivist 2) Classical 3) Critical 4) Conflict QUESTION 48 refer(s) to the inherently characteristic way in which an individual reacts to life's demands and challenges on an emotional level 1) Temperament 2) Familial risk factors 3) Free will 4) Intelligence QUESTION 49 is made up of all the legal rules which identify crimes and set down punishments 1) Common law 2) Criminology 3) Penology 4) Criminal law QUESTION 50 The perinatal risk factors associated with juvenile delinquency and adult crime are . 1) Inadequate nutrition 2) exposure to smoking 60 3) alcohol abuse 4) All of the above October/November 2015 QUESTION 1 From a juridical point of view, no one can be labelled a criminal unless he or she has 1) transgressed the law of a particular country 2) been arrested 3) tried and found guilty of a particular crime 4) All of the above QUESTION 2 The theoretical perspective of classical criminology suggests that 1) people have a free will to choose criminal or conventional behaviours 2) crime can be controlled only by the fear of criminal sanctions 3) people choose to commit crime for reasons of greed or personal need 4) All of the above QUESTION 3 There are various factors that protect high-risk youths from starting criminal careers. Which one of the following statements is correct? 1) A shy personality 2) Few friends at the age of eight 3) Non-deviant families 4) Poor self-control 61 QUESTION 4 In many African states criminology is accepted as a means of explaining and controlling crime 1) critical 2) Positivist 3) radical 4) classic QUESTION 5 The variations in crime rates between racial and ethnic groups reflect three (3) differences among the groups. Indicate which one of the following is incorrect. 1) Social 2) Cultural 3) Educational 4) Economic QUESTION 6 A criminologist's main task is to study, define, describe, interpret, explain and indicate policy directions in respect of crime, criminal behaviour and victimisation. The basic point of departure is to: 1) Identify the complex causes of crime 2) explain these in terms of existing theories 3) develop and scientifically test new theories 4) All of the above 62 QUESTION 7 There are three (3) forms of intention. Choose the incorrect option. 1) Dolus directus 2) Hedonistic principle 3) Indirect intention 4) Dolus eventualis QUESTION 8 Biochemical factors may play a role in criminal behaviour. These are related to an individual’s . 1) diet 2) blood chemistry 3) allergies 4) All of the above QUESTION 9 According to the power-control theory, gender and social class differences in delinquency are linked to the structure of the 1) family 2) neighbourhood 3) schools 4) peers QUESTION 10 Victim surveys are particularly valuable because they provide information on the "dark figure" in crime statistics. The term "dark figure" refers to: 1) those crimes that are committed but not reported to the police 2) the view that crime is a product of the capitalist system 3) a specific pattern In the incidence of crime 4) the rise and fall in crime In a particular year QUESTION 11 Involvement In alcohol and drug abuse may facilitate the drift into delinquency. Youthful misconduct can also simply mean a stage of . 1) deviant socialisation 2) bullying 3) growing up 4) substance abuse QUESTION 12 emphasis is on external factors as causes of crime and criminals are seen as victims of social conditions over which they have little control. 1) Critical criminology 2) Feminist criminology 3) Social milieu school of thought 4) Classical theory QUESTION 13 Competence and a sense of belonging are two needs that arise from the human being's requirement for environmental mastery and warm interpersonal relationships 1) social 2) psychological 3) emotional 4) physiological QUESTION 14 In order to rear a child correctly, so that he or she develops self-control, the following requirement(s) must be met. 1) Someone must monitor or supervise the child's behaviour 2) If delinquency does occur, the child must be punished 3) Supervisor(s) must be able to identity delinquency or detect it if it occurs 4) All of the above 64 QUESTION 15 Emotions are multi-dimensional which means that they are studied from many different 1) patterns 2) school of thoughts 3) points of view 4) theories QUESTION 16 In relation to the positivist school of thought, identify the correct statement(s) 1) The emphasis is on the criminal, not on the crime 2) Crime and victimisation may be prevented by medical treatment. 3) The purpose of sanctions is not so much to punish, but provide treatment 4) All of the above QUESTION 17 Arnold, Robertson and Cooper are of the opinion that motivation comprises of three components of motivation. Which one of the following is a component of motivation? 1) Persistence 2) Goal 3) Action 4) Need 65 QUESTION 18 The perspective assumes that men and women are the same, but women are denied opportunities to do the same things as men, including participation in crime. 1) liberal feminist 2) ethnic diversity 3) feminist 4) differential association QUESTION 19 Rational choice theorists view crime as both specific 1) offender and situational 2) offence and content 3) process and content 4) offence and offender QUESTION 20 To which criminological school of thought does the following quotation relate? "Economic and political discrimination are seen as the causes of crime" 1) Critical 2) Radical criminology 3) New Criminology 4) All of the above QUESTION 21 Social action theory is also known as theory. 1) labelling 2) trait 3) social control 66 4) rational choice QUESTION 22 Data obtained from can be used for testing theories, measuring attitudes toward crime as well as the association between crime and important social variables such as family relations, education and income 1) systematic observation 2) self-report survey 3) crime mapping 4) victimisation survey QUESTION 23 In anger rape, the act of rape can be regarded as the offender's expression of his anger and 1) frustration 2) power 3) sexuality 4) hostility QUESTION 24 is a relatively new criminological technique in terms of which multiple advanced computational methods are used to analyse large data sets involving one or more data sources 1) Victim survey 2) Crime mapping 3) Self-report survey 4) Data mining QUESTION 25 According to Sheldon's somatotypes, a mesomorph's personality type is associated with being 1) Introverted, hypersensitive and intellectual 2) strong, active, aggressive and sometimes violent 3) extroverted, friendly and sociable 4) extroverted, aggressive and violent QUESTION 26 Theories of crime should be able to take account of both men and women's deviant behaviour and highlight factors which operate differently on both genders. Both and criminology stereotype female criminals as "sick" 1) classic, positivist 2) postmodern, classic 3) positivist, radical 4) radical, postmodern QUESTION 27 Minimal brain damage is associated with antisocial tendencies 1) theory 2) perspective 3) learning disability 4) process QUESTION 28 According to researchers in Africa, in order to prevent and control crime, it is important to eradicate poverty and empower the community. Which of the following statement(s) can be associated with crime prevention in Africa? 1) Compulsory education for all 2) The restoration of family values and norms 3) The eradication of poverty and unemployment 4) All of the above QUESTION 29 The theory views crime as a function of a decision-making process in which the potential offender weighs up the potential costs and benefits of an illegal act 1) Social process 2) Rational choice 3) Instrumental 4) Social learning QUESTION 30 Research has shown that stress levels can rise due to long-term exposure to extreme temperatures which relates to an increase in 1) child abuse 2) violent crime 3) Instrumental crimes 4) substance abuse QUESTION 31 According to Conklin, there are three facilitating factors which are often present when crime is committed, namely 1) Friends, families and victims 2) Poverty, alcohol and abuse 3) Firearms, victims and unemployment 4) Alcohol, drugs and firearms 69 QUESTION 32 The school of thought rejects the traditional causes of crime as identified by positivism and expands the juridical crime concept by counting various forms of social bias and the violation of human rights as crimes 1) critical criminology 2) Social milieu 3) positivism 4) postmodern QUESTION 33 The theory focuses on the way in which society is organised and how it influences people's behaviour 1) rational choice 2) liberal feminist 3) structure 4) process QUESTION 34 Crime maps can be used to create graphic presentations of spatial geography of crime. The assist in analysing and correlating data to create detailed visuals of crime patterns 1) data mining 2) dark figure 3) computerised crime maps 4) official crime statistics QUESTION 35 The prenatal risk factors associated with juvenile delinquency and adult crime are 1) exposure to smoking 2) Inadequate nutrition 3) alcohol abuse 4) All of the above QUESTION 36 Rational choice theory has its roots in the school of criminology which was developed by Cesare Beccaria. 1) classical 2) critical 3) radical 4) liberal QUESTION 37 In juridical terms, only those acts that are punishable by the state are considered to be crime. The punishment for a particular crime may be set out in law or in a . 1) civil, correctional facility 2) common, legal prescription 3) criminal, correctional facility 4) common, rehabilitation centre QUESTION 38 act(s) as a blue print or map which determines all aspects of human development 1) Genes 2) Criminogenic risk factors 3) Physical and biological factors QUESTION 39 The theory admits that free will could be constrained by certain forms of pathology (deviance), such as mental illness and incompetence 1) classical 2) neo-classicists 3) new criminology 4) critical criminology SG p20 QUESTION 40 Broken homes can contribute to , if the separation of parents results in economic hardships, loss of affection and loss of a proper role model necessary for socialisation 1) gangsterism 2) truancy 3) delinquency 4) Substance abuse QUESTION 41 Precolonial Africa concerned itself mainly with the 1) Perpetrator 2) colonial power 3) crime victim 4) prevention of crime QUESTION 42 Classical theories focus on laws, government structures and the of the individual 1) free will 2) rights 3) criminality 4) compensation QUESTION 43 Accurate reporting of crime is needed to eliminate the misappropriation and manipulation of crime information. Crime constitute(s) all data and information on crime that are scientifically arranged and tabulated in order to offer a total picture of the crime problem 1) statistics 2) mapping 3) patterns 4) trends 72 QUESTION 44 Emotions are biological reactions and energy-mobilising responses that prepare the body to adapt to the situation the person is confronted with. Which one of the following statements does not refer to emotions? 1) Emotions have four components, namely feelings, body arousal, a sense of purpose and social expression 2) Emotions are short-lived, subjective-physiological and functional-expressive phenomenon that orchestrate how we react to events in our lives 3) Emotions indicate the desire that a specific result will follow from a specific action 4) Emotions are subjective feelings that make us feel in a particular way such as angry, joyful or sad QUESTION 45 The concept of is an attempt to account for the acquisition and maintenance of criminal behaviour in terms of contact, or association with particular environments and social groups. 1) culturally violent offenders 2) power-control 3) differential association 4) Instrumental theories QUESTION 1 Social disorganisation theory is a branch of the that focuses on the breakdown of institutions 73 1) social structure 2) population structure 3) Social learning approach 4) rational choice perspective QUESTION 2 Emotions are short-lived, subjective-physiological and functional-expressive phenomena that orchestrate how we react adequately to the important events in our lives. Emotions organise and comprise several aspects of experiences, such as 1) Feelings 2) Function 3) Expression 4) All of the above QUESTION 3 Desired goods, which cannot be obtained by conventional means, may be obtained through illegal activities, for example selling drugs or stealing valuables from people to obtain food. These are called crimes. 1) expressive 2) Instrumental 3) common 4) commercial QUESTION 4 The term refers to those crimes that are committed but not reported to the police 1) Victim survey 2) self-report studies 3) dark figure 4) data-mining 74 QUESTION 5 According to Siegel (2004' 4), criminology is: 1) made up of all the legal rules that were not originally written down 2) the study of causes of crime and youth offending. 3) the scientific approach to the study of criminal behaviour 4) an applied science within the human sciences QUESTION 6 The theory predicts that male-female differences in delinquency will be greater in patriarchal families and in lower classes 1) social learning 2) power control 3) liberal feminist 4) Social structure QUESTION 7 Historically, criminological theories have developed according to three distinctive viewpoints, namely that 1) Crime is a congenital trait. 2) the causes of crime are to be found in the structure and function of society 3) crime is a tendency that individuals have acquired 4) All of the above. QUESTION 8 Generalised knowledge is . 75 1) a means of collecting information about aspects of an individual's personal experience, such as involvement in offending 2) a process by which scientists gather information from the external or internal environment 3) a concept that refers to a scientific demand that is made of research acts and survey results. 4) a process by which a pronouncement is made on a bigger group on the basis of a study of a limited number of similar cases QUESTION 9 The theories which are environmentally oriented, are sometimes subdivided into structure and process theories because of the differences in their points of departure. 1) Instrumental 2) content 3) explanatory 4) classical QUESTION 10 refers to the inherently characteristic way in which an individual reacts to life's demands and challenges on an emotional level. 1) Aggression 2) Temperament 3) Personality 4) Hereditary QUESTION 11 Parental discord is associated with . 1) antisocial disorder in children 2) aggression and truancy 3) drug and alcohol abuse 4) poor academic progress and criminal activities QUESTION 12 rejects the state definitions of crime 1) Feminist school of thought 2) Postmodern criminology 3) Critical criminology 4) Labelling theory QUESTION 13 Recently South Africa has been moving away from prison sentences towards alternative forms of punishment, such as . 1) permitting medical parole 2) short-term imprisonment 3) granting amnesty or house arrests 4) treatment of offenders in the community QUESTION 14 Physiological disorders have a genetic and psychological influence on human behaviour as well as a labelling impact. Psychological disorders include . 1) Down syndrome 2) Epilepsy 3) Tourette's syndrome 4) All of the above QUESTION 15 Both and criminology stereotype female criminals as "sick", implying that they need treatment. 77 1) classic, positivist 2) postmodern, critical 3) radical, classical 4) feminist, positivist QUESTION 16 In relation to family functioning, criminal risk factors can be associated with the interpersonal relationships. Which one of the following categories is associated with delinquency? 1) Parental neglect 2) Marital conflict 3) Parental deviance 4) All of the above QUESTION 17 There are various motivation theories which aim to describe and explain how behaviour is started, energised, sustained and directed. The theories focus on psychological processes that affect motivation. 1) content 2) Instrumental 3) process 4) rational choice QUESTION 18 According to the view, a person's behaviour is determined by external factors beyond his or her control 1) hard determinism 2) differential association 78 3) soft determinism 4) moral reasoning QUESTION 19 Data mining is a relatively new criminological technique in terms of which multiple advanced computational methods are used to analyse large data sets involving one or more data sources. Its goal is to . 1) create graphic representations of the spatial geography of crime 2) establish the true extent of crime patterns in different areas 3) measure attitudes, values, personal characteristics and behaviours 4) Identify significant and recognisable patterns and trends. QUESTION 20 A is a means of collecting information about aspects, such as, involvement in offending 1) self-report study 2) questionnaire 3) Victimisation survey 4) dark figure QUESTION 21 According to research, there are three facilitating factors which are often present when crimes are committed, namely . 1) alcohol, drugs and firearms 2) friends, drugs and firearms 79 3) poverty, alcohol and abuse 4) firearms, abuse and drugs QUESTION 22 During research, Sheldon identified three basic body types. These body types are characterised by the physical and emotional character traits. According to these body types, delinquent boys are mainly . 1) mesomorphs 2) endomorphs 3) ectomorphs 4) hydromorphs QUESTION 23 The main premise(s) of the feminist school of thought is . 1) It focuses mainly on discrimination against women in the criminal justice system 2) It takes both the juridical and the non-juridical concepts of crime as their point of departure 3) It considers it unjust to expect victims to protect themselves against crime 4) All of the above QUESTION 24 Theorists, who subscribe to the general theory of crime, are of view that . 1) All individuals have the same motivations 2) Economic and political discrimination are the causes of crime 3) Crime could be prevented by empowering the people. 4) The purpose of sanctions is not to punish, but provide treatment and reform SG p197 QUESTION 25 Crime is a social phenomenon that can be analysed and explained with the aid of figures. Crime constitute all data and information on crime that are scientifically arranged and tabulated in order to offer a total picture of crime. 1) statistics 2) patterns 3) trends 4) mapping QUESTION 26 In order to develop a theory events are observed systematically. Which of the following component(s) reflects the ideal characteristics of a "good theory"? 1) Predictability 2) Consensus 3) Generalisation 4) Systematic QUESTION 27 Social exclusion refers to the . 1) dynamic, multidimensional process of being fully or partially excluded from the various social, economic, political or cultural systems which serve to assist the integration of a person in society 2) Social structure theories that focus on the breakdown of institutions such as the family, school and employment in inner-city neighbourhoods 3) belief that the majority of citizens in a society share common ideals and work together towards a common good, that crimes are acts outlawed because they conflict with the rules of the majority and are thus harmful to society 4) sum total of acquired behaviour that enables a person to conform to the rules and expectations in the society, whereby a person learns to become a good member of society as opposed to being a selfish individual. 81 QUESTION 28 Which one of the following is not a contributory factor to Crime in South Africa? 1) Rapid structures arising 2) Political factors 3) Inadequate welfare services 4) The Influx of migrant labourers QUESTION 29 Lack of self-control is often linked to 1) substance abuse 2) Impulsive behaviour 3) juvenile delinquency 4) criminal behaviour QUESTION 30 Most theories of delinquency rely heavily on the parent-child relationship and parent practices. To explain delinquency is associated with antisocial disorder in the children 1) peer pressure 2) aggression 3) parental discord 4) personality QUESTION 31 The perspective assumes that men and women are the same' but women are denied opportunities to do the same things as men, including participation in crime 1) liberal feminist 2) Marxist 82 3) conflict 4) radical feminist QUESTION 32 The criminology school of thought rejects the traditional causes of crime as identified by positivism and expands the juridical crime concept by counting various forms of social bias and the violation of human rights as crime. 1) critical 2) conflict 3) radical 4) All of the above QUESTION 33 There is a close link between motivation and emotion. The component is that communicative aspect of emotion. 1) social-expressive 2) purposive 3) feeling 4) physical arousal QUESTION 34 It is suggested that. theory is a useful model for personal development but fails to explain individual behaviour and the process whereby motivation occurs 1) rational choice 2) Maslow's 3) process 4) Farrington's QUESTION 35 In relation to family functioning risk factors can be associated with the interpersonal relationships, functioning and socialisation within the family 83 1) criminal 2) familial 3) prenatal 4) perinatal QUESTION 36 is the cornerstone of criminology and the basis for all the activities that are embodied in criminal justice, such as the prediction, treatment and prevention of crime. 1) Theory 2) Crime 3) Deviant behaviour 4) Social dimension QUESTION 37 Different theories have been developed to explain crime, but not all such theories comply with the ideal of comprehensiveness in explaining the criminal phenomena. The theory is of view that the cause of delinquent behaviour is an impulsive personality 1) postmodern 2) liberal 3) self-control 4) labelling QUESTION 38 There are various official crime information sources in South Africa, namely the 1) police. 84 2) courts 3) prison statistics 4) All of the above QUESTION 39 Hirschi is of the opinion that family size rather than birth position can be associated with delinquency. However, other research indicates that children are more likely to exhibit delinquent behaviour 1) first-born 2) middle 3) last-born 4) adopted QUESTION 40 indicates the desire that a specific result will follow from a particular action 1) Motive 2) Intent 3) Events 4) Memory QUESTION 41 According to the theory, people become criminals when significant members of society label them as such and they accept those labels as a personal identity. 1) Social control 2) social learning 3) Social action 4) Social process QUESTION 42 The basic premise of is that certain people are born to be criminals through the inheritance of a genetic or physiological predisposition to crime 85 1) biological dimension 2) social learning theory 3) Social exclusion 4) systematic observation QUESTION 43 Historically, criminological theories have developed according to distinctive viewpoints. Choose the incorrect statement relating to this viewpoint. 1) Crime is a tendency that individuals have acquired 2) Crime is a congenital trait (biological theories ) 3) Causes of crime are found in the structure and function of society 4) The criminal and criminal offenders are considered as separate concepts. QUESTION 44 law is directed mainly at punishment and deterrence and its chief objective is to protect people against unsanctioned behaviour by others 1) Roman Dutch 2) Criminal 3) Common 4) Civil QUESTION 45 According to criminology, crime is a product of the capitalist system 1) radical 2) social milieu 86 3) feminist 4) Positivist QUESTION 46 The concept of is an attempt to account for the acquisition and maintenance of criminal behaviour in terms of contact, or association with particular environments and social groups 1) differential association 2) locus of control 3) crime patterns 4) criminogenic risk factors QUESTION 47 Before an act or omission may be defined as a crime, law must regard it as such and a suitable punishment has to be in place. 1) criminal 2) common 3) civil 4) constitutional QUESTION 48 Cognitive processes play an important role in appraising available aims when designing a particular strategy. Cognition involves . 1) Thought, judgement, interpretation and understanding 2) Direction, persistence, effort and emotions 3) Goals, needs, interpretation and understanding 4) Needs, judgement, thought and emotions QUESTION 49 by parents has been associated with an increased risk of the children 87 themselves becoming violent offenders in later life 1) Neglect 2) Substance abuse 3) Physical abuse 4) Erratic discipline QUESTION 50 Minimal brain dysfunction, which is a learning disability, is also associated with . 1) hedonistic principle 2) soft determinism view 3) antisocial tendencies. 4) hard determinism view [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 95 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jul 30, 2020
Number of pages
95
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jul 30, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
299