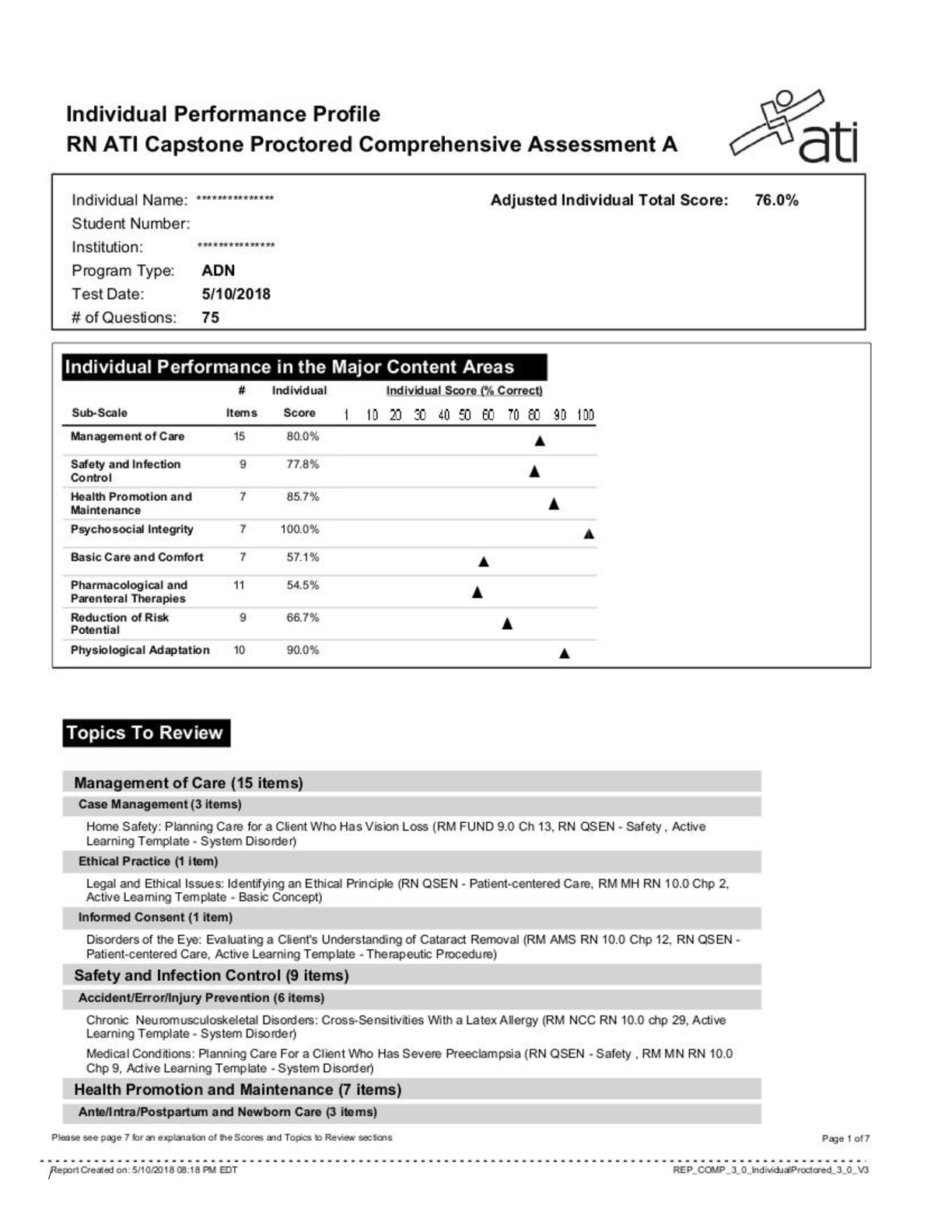
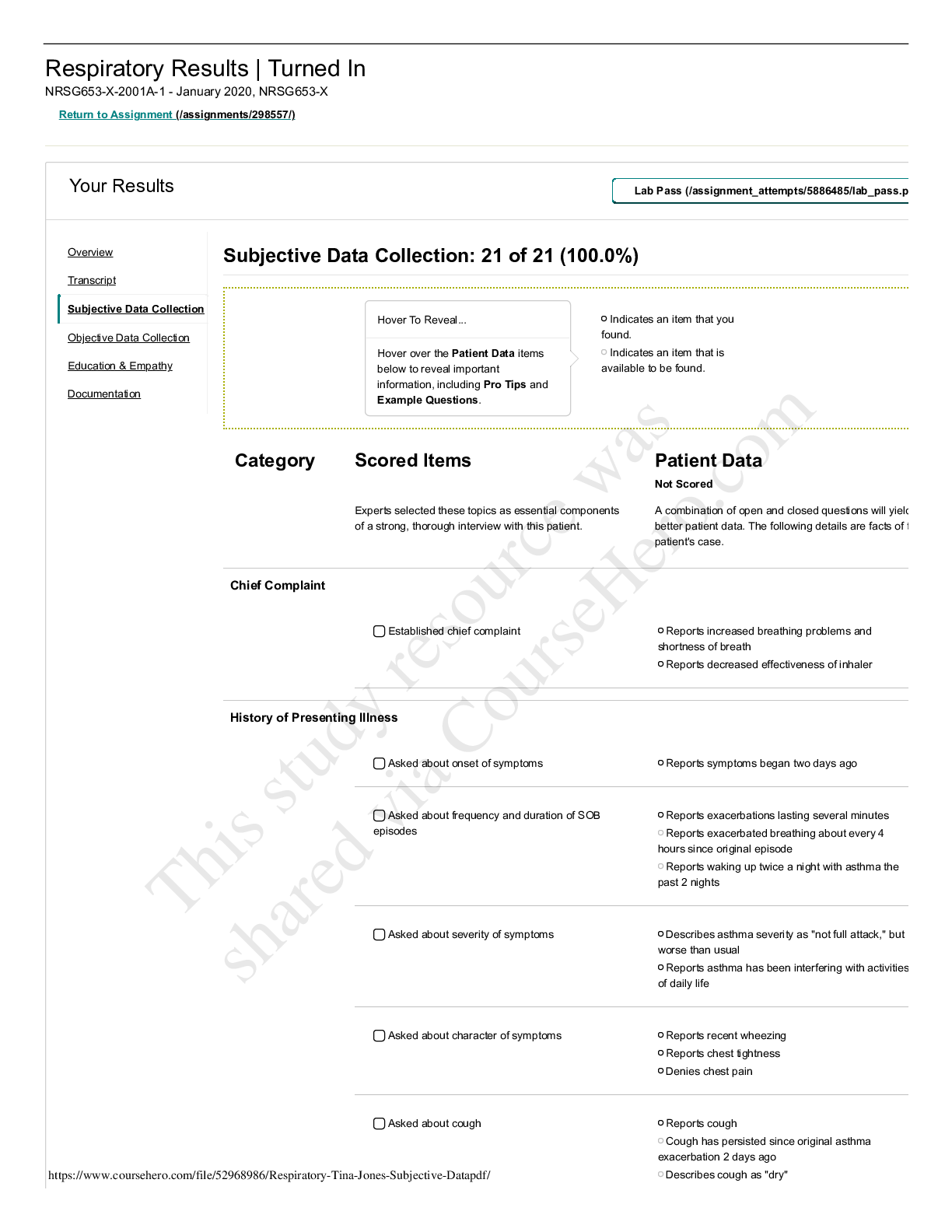
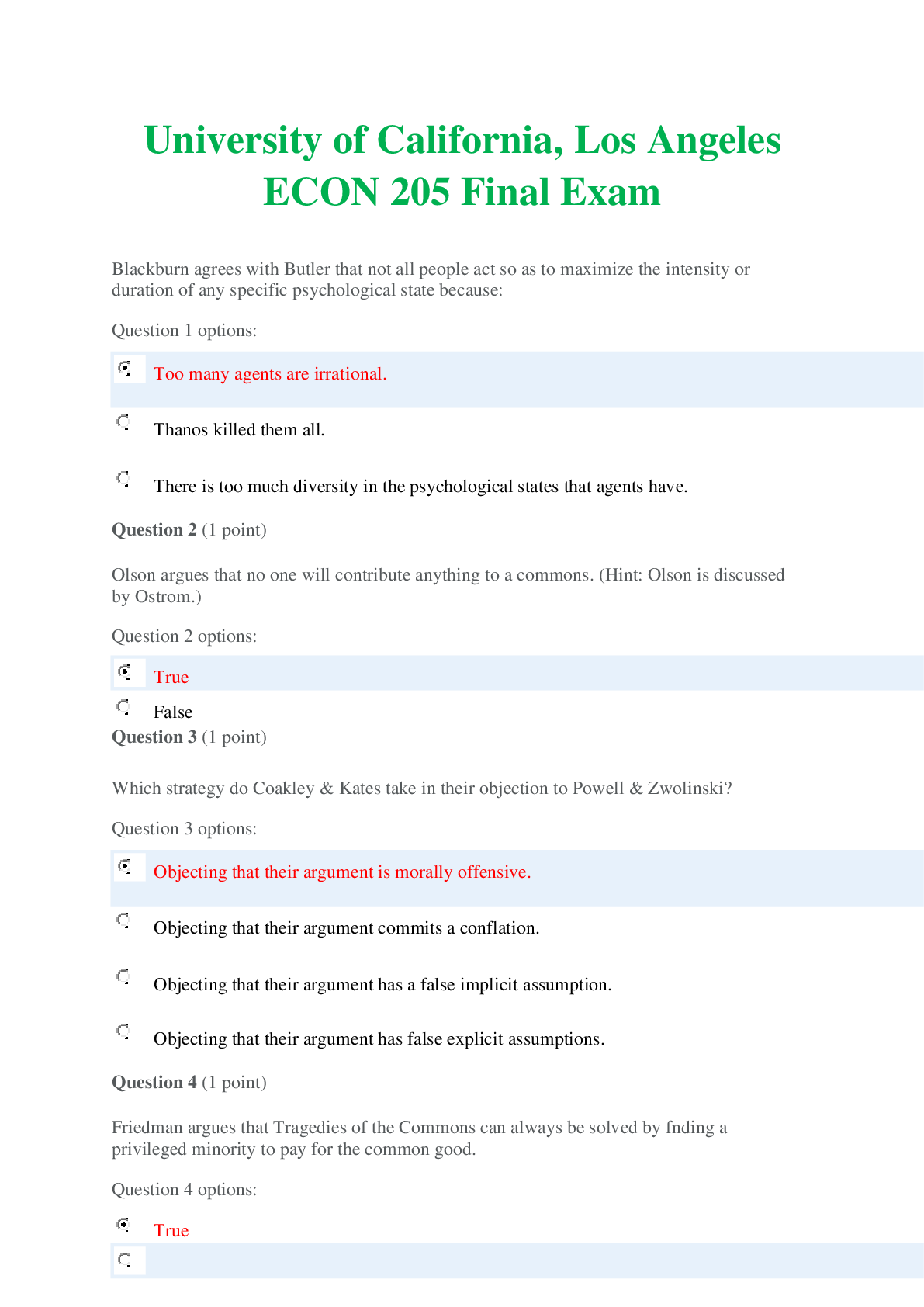
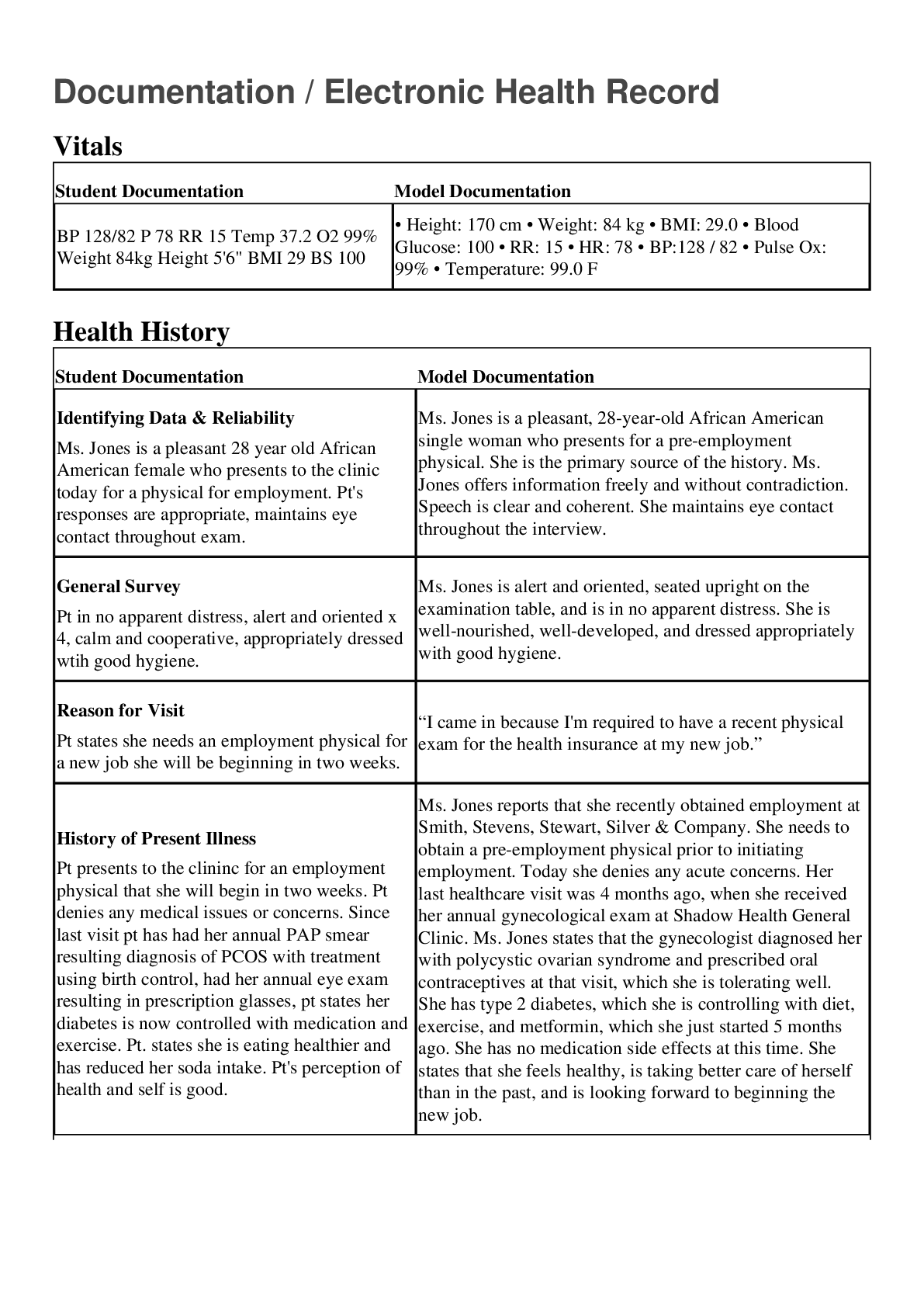
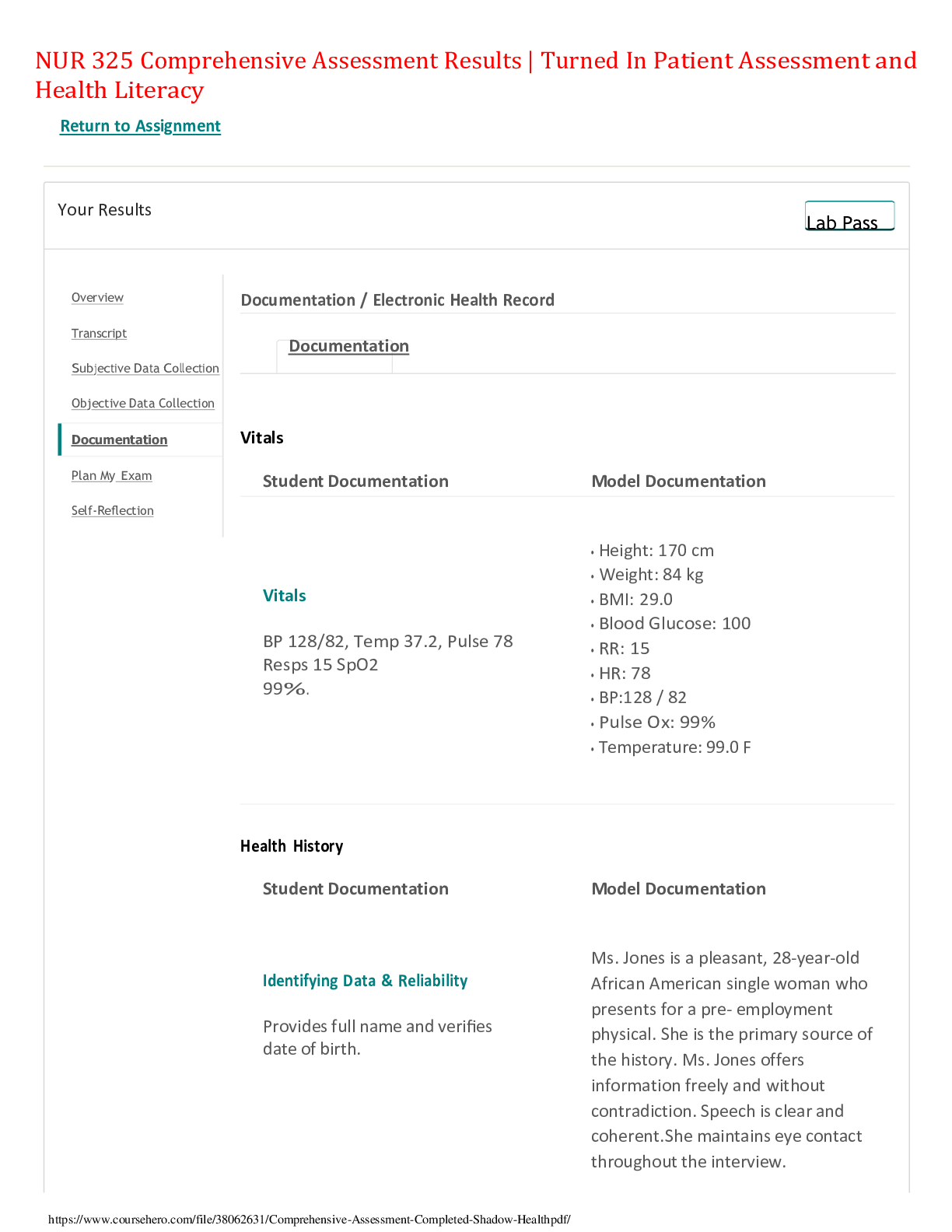
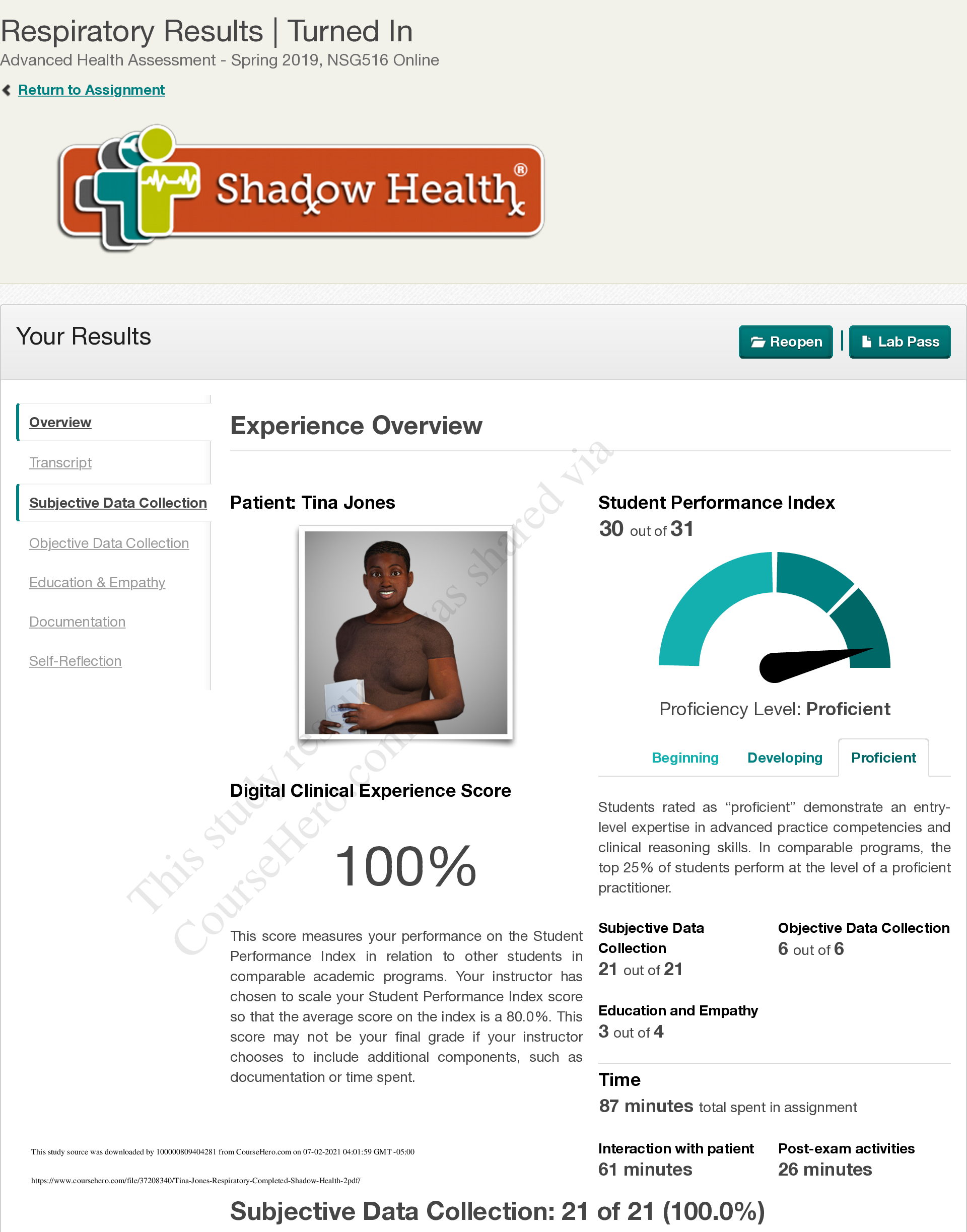
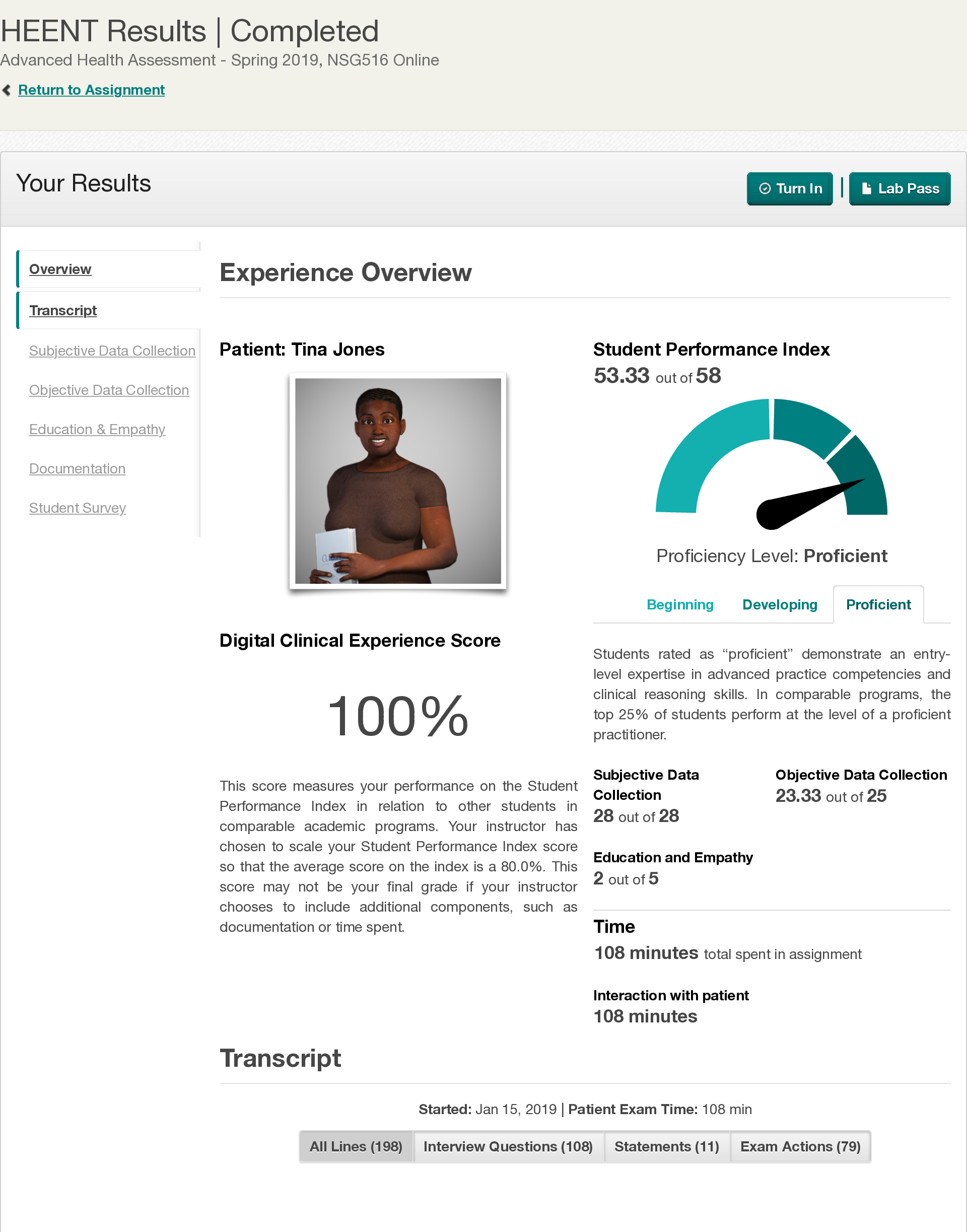
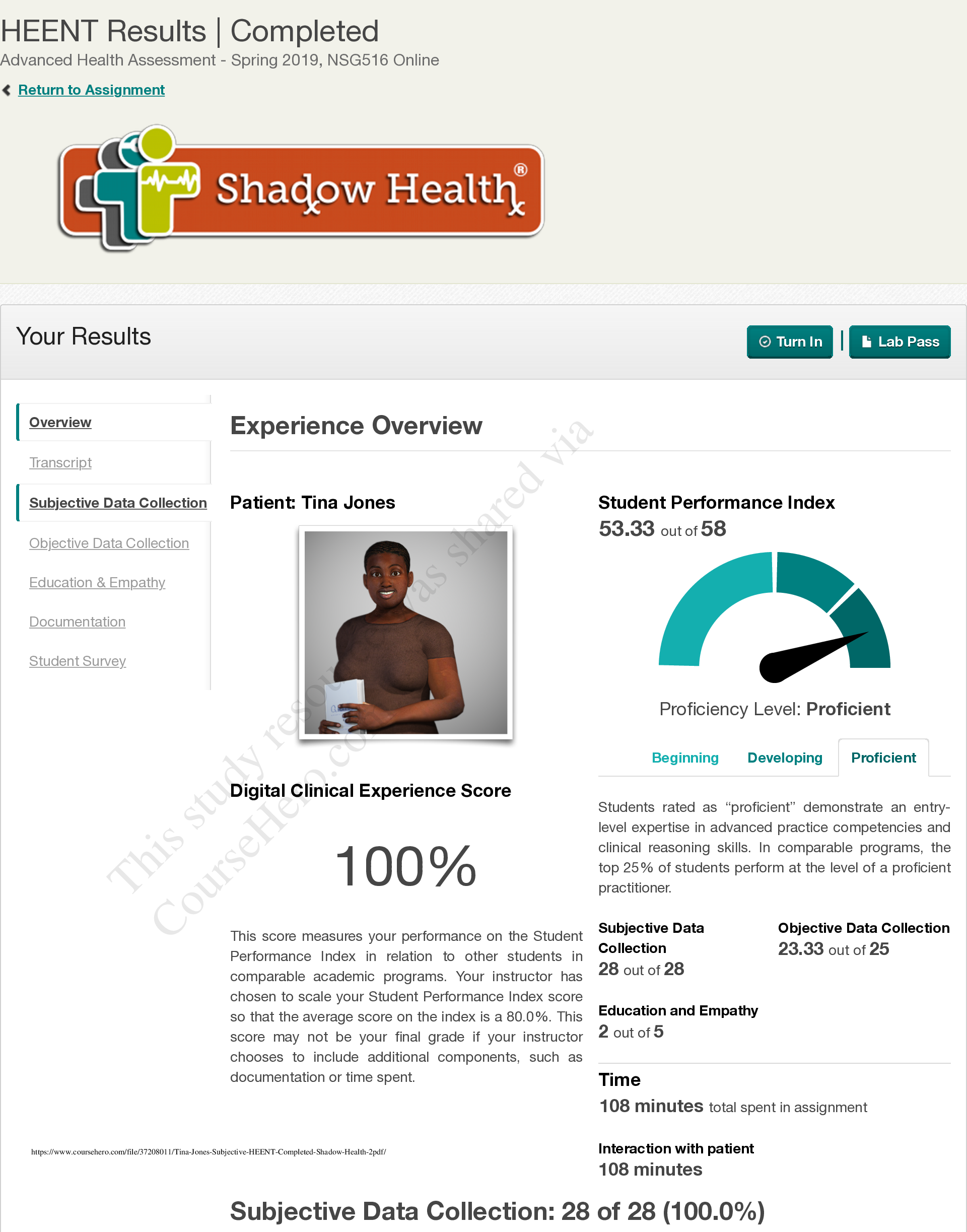
NSG 6020 Health Assessment - South University. Final Exam Review.
Document Content and Description Below
NSG6020 Final Exam Review Breast and Lymphatics Statement by the patient would indicate a need for further teaching? A. "The best time to check my breasts is a week before my cycle." B. "I will... check my breasts in the shower one week after my cycle." C. "I will exam my breast in a clock-like sequence so that I don't miss any surface area." D. "I will be sure to check my arm pits." A pregnant woman who has breast implants asks the nurse if she can still breastfeed. What is the nurse's best response? A. "You should not have any problems breast feeding because your implants do not affect milk production." B. "When the breast implants are inserted they usually affect the milk glands, and breastfeeding is not possible." C. "This would depend on which type of implants were placed and which procedure was used by the surgeon. Check with your surgeon to see if your milk production will be affected." Statement by the patient would indicate a need for further teaching? A. "The best time to check my breasts is a week before my cycle." B. "I will check my breasts in the shower one week after my cycle." C. "I will exam my breast in a clock-like sequence so that I don't miss any surface area." D. "I will be sure to check my arm pits." A pregnant woman who has breast implants asks the nurse if she can still breastfeed. What is the nurse's best response? A. "You should not have any problems breast feeding because your implants do not affect milk production." B. "When the breast implants are inserted they usually affect the milk glands, and breastfeeding is not possible." C. "This would depend on which type of implants were placed and which procedure was used by the surgeon. Check with your surgeon to see if your milk production will be affected." Which of the following statements is true regarding the internal structures of the breast? The breast is: A)mainly muscle, with very little fibrous tissue. B)composed of fibrous, glandular, and adipose tissue. C)composed mostly of milk ducts, known as lactiferous ducts. D)composed of glandular tissue, which supports the breast by attaching to the chest wall. In performing a breast examination, the nurse knows that it is especially important to examine the upper outer quadrant of the breast. The reason for this is that the upper outer quadrant is: A)the largest quadrant of the breast. B)the location of most breast tumors. C)where most of the suspensory ligaments attach. D)more prone to injury and calcifications than other locations in the breast. In performing an assessment of a woman's axillary lymph system, the nurse should assess which of these nodes? A)Central, axillary, lateral, and sternal nodes B)Pectoral, lateral, anterior, and sternal nodes C)Central, lateral, pectoral, and subscapular nodes D)Lateral, pectoral, axillary, and suprascapular nodes If a patient reports a recent breast infection, then the nurse should expect to find _____ node enlargement. A)nonspecific B)ipsilateral axillary C)contralateral axillary D)inguinal and cervical A 9-year-old girl is in the clinic for a sports physical. After some initial shyness she finally asks, "Am I normal? I don't seem to need a bra yet, but I have some friends who do. What if I never get breasts?" The nurse's best response would be: A)"Don't worry, you still have plenty of time to develop." B)"I know just how you feel, I was a late bloomer myself. Just be patient and they will grow." C)"You will probably get your periods before you notice any significant growth in your breasts." D)"I understand that it is hard to feel different from your friends. Breasts usually develop between 8 and 10 years of age." A patient contacts the office and tells the nurse that she is worried about her 10-year-old daughter having breast cancer. She describes a unilateral enlargement of the right breast with associated tenderness. She is worried because the left breast is not enlarged. What would be the nurse's best response? A)Tell the mother that breast development is usually fairly symmetric and she should be examined right away. B)Tell the mother that she should bring her daughter in right away because breast cancer is fairly common in preadolescent girls. C)Tell the mother that, although an examination of her daughter would rule out a problem, it is most likely normal breast development. D)Tell the mother that it is unusual for breasts that are first developing to feel tender because A 14-year-old girl is anxious about not having reached menarche. When taking the history, the nurse should ascertain which of the following? The age: A)she began to develop breasts B)her mother developed breasts C)she began to develop pubic hair D)she began to develop axillary hair. A woman is in the family planning clinic seeking birth control information. She states that her breasts "change all month long" and that she is worried that this is unusual. What is the nurse's best response? A)Tell her that it is unusual. The breasts of nonpregnant females usually stay pretty much the same all month long. B)Tell her that it is very common for breasts to change in response to stress and that she should assess her life for stressful events. C)Tell her that, because of the changing hormones during the monthly menstrual cycle, cyclic breast changes are common. D)Tell her that breast changes normally occur only during pregnancy and that a pregnancy test is needed at this time. A woman has just learned that she is pregnant. What are some things the nurse should teach her about her breasts? A)She can expect her areolae to become larger and darker in color. B)Breasts may begin secreting milk after the fourth month of pregnancy. C)She should inspect her breasts for visible veins and report this immediately. D)During pregnancy, breast changes are fairly uncommon; most of the changes occur after the birth. The nurse is teaching a pregnant woman about breast milk. Which statement by the nurse is correct? A)"Your breast milk is present immediately after delivery of the baby." B)"Breast milk is rich in protein and sugars (lactose) but has very little fat." C)"The colostrum, which is present right after birth, does not contain the same nutrition as breast milk does." D)"You may notice a thick, yellow fluid expressed from your breasts as early as the fourth month of pregnancy." A 65-year-old patient remarks that she just can't believe that her breasts sag so much. She states it must be from lack of exercise. What explanation should the nurse offer her? A)After menopause, only women with large breasts experience sagging. B)After menopause, sagging is usually due to decreased muscle mass within the breast. C)After menopause, a diet that is high in protein will help maintain muscle mass, which keeps the breasts from sagging. D)After menopause, the glandular and fat tissue atrophies, causing breast size and elasticity to diminish, resulting in breasts that sag. In examining a 70-year-old male patient, the nurse notices that he has bilateral gynecomastia. Which of the following describes the nurse's best course of action? A)Recommend that he make an appointment with his physician for a mammogram. B)Ignore it; it is not unusual for men to have benign breast enlargement. C)Explain that this condition may be the result of hormonal changes and recommend that he see his physician. D)Tell him that gynecomastia in men is usually associated with prostate enlargement and recommend that he be screened thoroughly. During an examination of a 7-year-old girl, the nurse notices that the girl is showing breast budding. What should the nurse do next? A)Ask her if her periods have started. B)Assess the girl's weight and body mass index (BMI). C)Ask the girl's mother at what age she started to develop breasts. D)Nothing; this is a normal finding. The nurse is reviewing statistics regarding breast cancer. Which woman, aged 40 years in the United States, has the highest risk for development of breast cancer? A)African-American B)White C)Asian D)American Indian The nurse is preparing for a class in early detection of breast cancer. Which statement is true with regard to breast cancer in African-American women in the United States? A)Breast cancer is not a threat to African-American women. B)African-American women have a lower incidence of regional or distant breast cancer than white women. C)African-American women are more likely to die of breast cancer at any age. D)Breast cancer incidence in African-American women is higher than that of white women after age 45. During a breast health interview, a patient states that she has noticed pain in her left breast. The nurse's most appropriate response to this would be: A)"Don't worry about the pain; breast cancer is not painful." B)"I would like some more information about the pain in your left breast." C)"Oh, I had pain like that after my son was born; it turned out to be a blocked milk duct." D)"Breast pain is almost always the result of benign breast disease." During a history interview, a female patient states that she has noticed a few drops of clear discharge from her right nipple. What should the nurse do next? A)Contact the physician immediately to report the discharge. B)Ask her if she is possibly pregnant. C)Ask her some additional questions about the medications she is taking. D)Immediately obtain a sample for culture and sensitivity testing. During a physical examination, a 45-year-old woman states that she has had a crusty, itchy rash on her breast for about 2 weeks. In trying to find the cause of the rash, which of these would be important for the nurse to determine? A)Is the rash raised and red? B)Does it appear to be cyclic? C)Where did it first appear—on the nipple, the areola, or the surrounding skin? D)What was she doing when she first noticed the rash, and do her actions make it worse? A patient is newly diagnosed with benign breast disease. The nurse recognizes that which statement about benign breast disease is true? The presence of benign breast disease: A)makes it harder to examine the breasts. B)frequently turns into cancer in a woman's later years. C)is easily reduced with hormone replacement therapy. D)is usually diagnosed before a woman reaches childbearing age. . During an annual physical exam, a 43-year-old patient states that she doesn't perform monthly breast self-examinations (BSE). She tells the nurse that she believes that mammograms "do a much better job than I ever could to find a lump." The nurse should explain to her that: A)BSEs may detect lumps that appear between mammograms. B)breast self-examination is unnecessary until the age of 50 years. C)she is correct, mammography is a good replacement for breast self-examination. D)she doesn't need to perform breast self-examination as long as a physician checks her breasts yearly. During an interview, a patient reveals that she is pregnant. She states that she is not sure whether she will breastfeed her baby and asks for some information about this. Which of these statements by the nurse is accurate with regard to breastfeeding? A)"Breastfed babies tend to be more colicky." B)"Breastfeeding provides the perfect food and antibodies for your baby." C)"Breastfed babies eat more often than infants on formula." D)"Breastfeeding is second nature and every woman can do it." The nurse is reviewing risk factors for breast cancer. Which of these women have risk factors that place them at a higher risk for breast cancer? A)37 year old who is slightly overweight B)42 year old who has had ovarian cancer C)45 year old who has never been pregnant D)65 year old whose mother had breast cancer During an examination of a woman, the nurse notices that her left breast is slightly larger than her right breast. Which of these statements is true about this finding? A)Breasts should always be symmetric. B)This finding is probably due to breastfeeding and is nothing to worry about. C)This finding is not unusual, but the nurse should verify that this change is not new. D)This finding is very unusual and means she may have an inflammation or growth. The nurse is assisting with a self-breast examination clinic. Which of these women reflect abnormal findings during the inspection phase of breast examination? A)Woman whose nipples are in different planes (deviated) B)Woman whose left breast is slightly larger than her right C)Nonpregnant woman whose skin is marked with linear striae D)Pregnant woman whose breasts have a fine blue network of veins visible under the skin During the physical examination, the nurse notices that a female patient has an inverted left nipple. Which statement regarding this is most accurate? A)Normal nipple inversion is usually bilateral. B)A unilateral inversion of a nipple is always a serious sign. C)It should be determined whether the inversion is a recent change. D)Nipple inversion is not significant unless accompanied by an underlying palpable mass. The nurse is performing a breast examination. Which of these statements best describes the correct procedure to use when screening for nipple and skin retraction during a breast examination? Have the woman: A)bend over and touch her toes. B)lie down on her left side and notice any retraction. C)shift from a supine position to a standing position; notice any lag or retraction. D)slowly lift her arms above her head and note any retraction or lag in movement. The nurse is palpating a female patient's breasts during an examination. Which of these positions is most likely to make significant lumps more distinct during breast palpation? A)Supine with arms raised over her head B)Sitting with arms relaxed at the sides C)Supine with arms relaxed at the sides D)Sitting with arms flexed and fingertips touching shoulders Which of these clinical situations would the nurse consider to be outside normal limits? A)A patient has had one pregnancy. She states that she believes she may be entering menopause. Her breast examination reveals breasts that are soft and sag slightly. B)A patient has never been pregnant. Her breast examination reveals large pendulous breasts that have a firm, transverse ridge along the lower quadrant in both breasts. C)A patient has never been pregnant. She reports that she should begin her period tomorrow. Her breast examination reveals breast tissue that is nodular and somewhat engorged. She states that the examination was slightly painful. D)A patient has had two pregnancies and she breastfed both of her children. Her youngest child is now 10 years old. Her breast examination reveals breast tissue that is somewhat soft and she has a small amount of thick yellow discharge from both nipples. A patient states during the interview that she noticed a new lump in the shower a few days ago. It was on her left breast near her axilla. The nurse should plan to: A)palpate the lump first. B)palpate the unaffected breast first. C)avoid palpating the lump because it could be a cyst, which might rupture. D)palpate the breast with the lump first but plan to palpate the axilla last. The nurse has palpated a lump in a female patient's right breast. The nurse documents this as a small, round, firm, distinct, lump located at 2 o'clock, 2 cm from the nipple. It is nontender and fixed. There is no associated retraction of skin or nipple, no erythema, and no axillary lymphadenopathy. Which of these statements reveals the information that is missing from the documentation? It is missing information about: A)the shape of the lump. B)the lump's consistency. C)the size of the lump. D)whether the lump is solitary or multiple. The nurse is conducting a class about breast self-examination (BSE). Which of these statements indicates proper BSE technique? A)The best time to perform BSE is in the middle of the menstrual cycle. B)The woman needs to do BSE only bimonthly unless she has fibrocystic breast tissue. C)The best time to perform BSE is 4 to 7 days after the first day of the menstrual period. D)If she suspects that she is pregnant, the woman should not perform a BSE until her baby is born. The nurse is preparing to teach a woman about breast self-examination (BSE). Which statement by the nurse is correct? A)"BSE is more important than ever for you because you have never had any children." B)"BSE is so important because one out of nine women will develop breast cancer in her lifetime." C)"BSE on a monthly basis will help you feel familiar with your own breasts and their normal variations." D)"BSE will save your life because you are likely to find a cancerous lump between mammograms." A 55-year-old postmenopausal woman is being seen in the clinic for a yearly examination. She is concerned about changes in her breasts that she has noticed over the past 5 years. She states that her breasts have decreased in size and that the elasticity has changed so that her breasts seem "flat and flabby." The nurse's best reply would be: A)"This change occurs most often because of long-term use of bras that do not provide enough support to the breast tissues." B)"This is a normal change that occurs as women get older. It is due to the increased levels of progesterone during the aging process." C)"Decreases in hormones after menopause causes atrophy of the glandular tissue in the breast. This is a normal process of aging." D)"Postural changes in the spine make it appear that your breasts have changed in shape. Exercises to strengthen the muscles of the upper back and chest wall will help to prevent the changes in elasticity and size." A 43-year-old woman is at the clinic for a routine examination. She reports that she has had a breast lump in her right breast for years. Recently, it has begun to change in consistency and is becoming harder. She reports that 5 years ago her physician evaluated the lump and determined that it "was nothing to worry about." The examination validates the presence of a mass in the right upper outer quadrant at 1 o'clock, approximately 5 cm from the nipple. It is firm, mobile, nontender, with borders that are not well defined. The nurse's recommendation to her is: A)"Because of the change in consistency of the lump, it should be further evaluated by a physician." B)"The changes could be related to your menstrual cycles. Keep track of changes in the mass each month." C)"This is probably nothing to worry about because it has been present for years and was determined to be noncancerous at that time." D)"Because you are experiencing no pain and the size has not changed, continue to monitor the lump and return to the clinic in 3 months." During a discussion about breast self-examination with a 30-year-old woman, which of these statements by the nurse is most appropriate? A)"The best time to examine your breasts is during ovulation." B)"Examine your breasts every month on the same day of the month." C)"Examine your breasts shortly after your menstrual period each month." D)"The best time to examine your breasts is immediately before menstruation." The nurse is discussing breast self-examination with a postmenopausal woman. The best time for postmenopausal women to perform breast self-examination is: A)the same day every month. B)daily, during the shower or bath. C)1 week after her menstrual period. D)every year with her annual gynecologic examination. While inspecting a patient's breasts, the nurse finds that the left breast is slightly larger than the right with the presence of Montgomery's glands bilaterally. The nurse should: A)palpate over the Montgomery's glands, checking for drainage. B)consider these normal findings and proceed with the examination. C)ask extensive history questions regarding the woman's breast asymmetry. D) continue with examination and then refer the patient for further evaluation of the Montgomery's glands. During an examination, the nurse notes a supernumerary nipple just under the patient's left breast. The patient tells the nurse that she always thought it was a mole. Which statement about this finding is correct? A)It is a normal variation and not a significant finding. B)It is a significant finding and needs further investigation. C)It also contains glandular tissue and may leak milk during pregnancy and lactation. D)The patient is correct—it is actually a mole that happens to be located under the breast. While examining a 75-year-old woman, the nurse notices that the skin over her right breast is thickened and the hair follicles are exaggerated. This condition is known as: A)dimpling. B)retraction. C)peau d'orange. D)benign breast disease. When a breastfeeding mother is diagnosed with a breast abscess, which of these instructions from the nurse is correct? The mother needs to: A)continue to nurse on both sides to encourage milk flow. B)discontinue nursing immediately to allow for healing. C)temporarily discontinue nursing on affected breast and manually express milk and discard it. D)temporarily discontinue nursing on affected breast but can manually express milk and give it to the baby. A new mother calls the clinic to report that part of her left breast is red, swollen, tender, very hot, and hard. She has a fever of 101° F. She has also had symptoms of the flu, such as chills, sweating, and feeling tired. The nurse notices that she has been breastfeeding for 1 month. From her description, what condition does the nurse suspect? A)Mastitis B)Paget's disease C)Plugged milk duct D)Mammary duct ectasia During a breast examination on a female patient, the nurse notices that the nipple is flat, broad, and fixed. The patient states it "started doing that a few months ago." This finding suggests: A)dimpling. B)a retracted nipple. C)nipple inversion. D)deviation in nipple pointing. A 54-year-old man comes to the clinic with a "horrible problem." He tells the nurse that he has just discovered a lump on his breast and is fearful of cancer. The nurse knows that which statement about breast cancer in males is true? A)Breast masses in men are difficult to detect because of minimal breast tissue. B)Breast cancer in men rarely spreads to the lymph nodes. C)One percent of all breast cancer occurs in men. D)Most breast masses in men are diagnosed as gynecomastia. . The nurse is assessing the breasts of a 68-year-old woman and discovers a mass in the upper outer quadrant of the left breast. When assessing this mass, the nurse keeps in mind that characteristics of a cancerous mass include which of the following? Select all that apply. A)Nontender mass B)Dull, heavy pain on palpation C)Rubbery texture and mobile D)Hard, dense, and immobile E)Regular border F)Irregular, poorly delineated border The nurse is examining a 62-year-old man and notes that he has gynecomastia bilaterally. The nurse should explore his history for which related conditions? Select all that apply. A)Obesity B)Malnutrition C)Hyperthyroidism D)Type 2 diabetes mellitus E)Liver disease F)History of alcohol abuse Which of the following statements is true regarding the internal structures of the breast? The breast is made up of: Fibrous, glandular, and adipose tissues. Clinical breast exam should be performed every - 3 years - GU WOMEN MENORRHAGIA - INREASED AMOUNT OF BLEEDING METORRHAGIA - BLEEDNG BETWEEN PERIODS CERVICAL CANCER SCREENING WITH PAP SHOULD BE DONE EVERY - 3 YEARS Normal ovary size - 2-3CM What is the confirmatory test for HIV? A. ELISA B. Western Blot C. HIV polymerease chain reaction test D. HIV antibody B. Remember that the Western Blot is the confirmatory test for HIV but ELISA is the initial test. If this test is positive then you confirm with the Western Blot. What medication would a patient with HIV be taking everyday for the prevention of pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (pneumocystis jirovecci)? A. Bactrim B. Penicillin C. Doxycyline D. Erythromcycin - A. Bactrim must be taken daily for the prevention of pneumocytis carinii pneumonia. A patient comes into your office complaining of night sweats, weight loss, and fever. You want to test for: A. HIV B. Syphilis C. pneumonia D. chancroid Remember early HIV looks like the flu. How long does it take a patient with HIV to serconvert? A. 6 months to 1 year B. 3 months to 1 year C. 3 weeks to 6 months D. Over one year What is a normal T-cell (CD4) count? A. 800 B. 400 C. 200 D. None A. That they are stable B. That they are severely immunocomprimised C. There immune response is high. Chancroid is a: A. Gram positive organism B. Gram negative bacillus C. Co-factor for HIV transmission D. Both B and C The degree to which those who have a disease screen/test positive is known as: A. Specificity B. Sensitivity - B. Sensitivity: Think how many people are positive. Don't get tricked. This has nothing to do with how many people might be negative. If a patient complains of pain upon urination and does not have a urinary tract infection you suspect: A. Chlamydia B. Syphilus C. PID D. Trichimoniasis Patients who are diagnosed with gonorrhea are also treated for following because of high rates of coinfection: A. Mycoplasma pneumoniae B. Chlamydia trachomatis C. Syphilis D. Pelvic inflammatory disease Human papilloma virus (HPV) infection of the larynx has been associated with: A. Laryngeal cancer B. Esophageal stricture C. Cervical cancer D. Metaplasia of squamous cells The pap smear result on a 20 year old sexually active student who uses condoms inconsistently show a large amount of inflammation. Which of the following is the best follow-up. A. The NP needs to do cervical cultures to verify the presence of gonorrhea B. Treat the patient with metronidazole vaginal cream over the phone C. Call the patient and tell her she needs a repeat pap smear in 6 months. D. Advise her to use a betadine douche at H (half strength) for three days. - C. A- Gonorrhea can cause cervicitis in women Fitz Hugh Curtis Syndrome is associated with which of the following infections: A. Syphilis B. Chlamydia trachomatis C. Herpes gentitalis D. Lymhogranuloma venereum A 13 year old adolescent who is not sexually active is brought in by her mother for an immunization update and physical examination. According to the mother her daughter had two doses of hepatitis 1 year ago. All of the following are indicated for this visit except: A. Hapatitis B Vaccine B. Tetanus vaccine C. Screen for depression D. HIV test The ELISA and Western Blot tests are both used to test for the HIV virus. Which of the following statements is correct. A. They are both tests to detect viral RNA B. A positive ELISA screening does not mean the person has HIV infection C. They are both tests used to detect for antibodies against HIV virus. D. They are both the best diagnostic tests for HIV All of the following are infections affecting the vagina or labia except: A. Bacterial Vaginosis B. Candidiasis C. Trichomoniasis D. Chlamydia Trachomatis The KOH prep (potassium hydroxide) will help you diagnose all of the following conditions except: A. Tinea infections B. Candida albicans infections of the skin C. Bacterial vaginosis D. Atypical bacterial infections KOH potassium hydroxide skin scraping will reveal - hyphae Trichomoniasis characteristics of vaginal discharge - foul, frothy, grayish, strawberry spots, motile porotozoa Bacterial vaginosis characteristics - fishy, white-yellow, creamy, clue cells and whiff test on wet prep Chlamydia characteristics/gonorrhea - yellowish, no odor, purulent discharge, numerous white cells on wet prep All of the following are reportable diseases except: A. Lyme disease B. Gonorrhea C. Nongonococcal urethritis D. Syphilis A 20 year old woman who is sexually active complains of copious milk like vaginal discharge. On microscopy the slide reveals a large number of mature squamous epithelial cells. The vaginal pH is 5.o. There are very few leukocytes and no red blood cells seen on the wet smear. Which of the following is most likely. A. Atrophic vaginits B. Bacterial Vaginosis C. Trichomoniasis D. This is a normal finding All of the following are clinical findings associated with syphilis except: A. Condyloma lata B. Condyloma acuminata C. Painless chancre D. Rashes on the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet The differential diagnosis for genital ulcerations includes all of the following except: A. Syphilis B. Genital herpes C. Chancroid D. Molluscum contagiosum Which type of hepatitis infection is more likely to result in cirrhosis of the liver and the risk of developing heaptocellular carcinoma. A. Hepatitis A virus B. Hepatitis B Virus C. Hepatitis C virus D. Both B and C A 19 year old male has recently been diagnosed with acute hepatitis B. He is sexually active and is monogamous and reports using condoms inconsistently. Which of the following is recommended for his male sexual partner, who was also recently tested for hepatitis with the following result HBsAG (-); anti-HBs (-); anti-HVC (-); anti HAV (+). A. Hepatitis B Vaccination B. Hepatitis B immuno globulin C. Hepatitis B vaccination and hepatitis immune globulin D. No vaccination is needed at this time. Which of the following is recommended for the treatment of a patient with bacterial vaginosis? A. Azithromycin (Zithromax) B. Doxycyline (Dynapin) C. Ceftriaxone (Rocephin) D. Metronidazole (Flagyl) All of the following sexually transmitted diseases can become disseminated if not treated except: A. Neissieria gonorrhoeae B. Treponema pallidum C. HIV D. Chlamydia Trahomatis A homeless middle aged male complains of migratory arthritis and dysuria. Currently, his right knee is swollen and painful. On examination, green colored purulent discharge is noted. Which of the following do you most likely suspect? A. Gonorrhea B. Chlamydia C. Nongonococcal urethritis D. Acute epididymitis Which of the following methods is used to diagnose gonorrheal proctitis? A. Serum chlamydia titer B. Gen-Probe C. Thayer Martin culture D. PRP (rapid plasma reagent) and VDRL (venereal disease research lab test) A 34 year old female is diagnosed with pelvic inflammatory disease. The cervical gen probe result is positive for Neisseria gonorrhoeae and negative for chlamydia trachomatis. All of the following treatments are true regarding the management of this patient except: A. This patient should be treated for chlamydia even though the gen-probe for chlamydia is negative B. Ceftriaxone 250 mg IM and doxycyline 100 mg po BID x 14 days are appropriate treatment for this patient? C. Advise the patient to return to the clinic for repeat pelvic examination in 48 hours D. Repeat Gen-Probe test for chlamydia to ensure that the previous test was not a false negative result A 25 year old woman comes into your office complaining of dysuria, pruritis, and purulent vaginal dischage. Pelvic examination reveals a cervix with punctate superficial petechiae (strawberry cervix) and irritated reddened vulvar area, with frothy discharge. Microscopic examination of the discharge reveals unicellular organisms. The correct pharmacological treatment for this condition is: A. Oral metronidazole (Flagyl) B. Ceftriaxone sodium (Rocephin) injection C. Doxycycline hyclate (vibramycin) D. Clotrimazole (Gyne-Lotrimin) cream or suppositories Prophylaxis for pneumocystis carinii pneumonia includes all of the following drugs except: A. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim) B. Dapsone C. Aerosolized pentamidine D. Nedocromil sodium Tilade Which of the following is recommended for treatment by the CDC for a case of uncomplicated gonorrheal and chlamydia infection? A. Metronidazole 250 mg po three times daily for seven days B. Valacylcovir 500 mg po bid for 10 days C. Azithromycin 1 g orally or Doxyclycline 100 mg twice daily for seven days D. One dose of oral Fluconazole 150 mg A patient diagnosed with bacterial vaginosis should be advised that her sexual partner be treated with: A. Ceftriazone (Rocephin) 250 mg with doxycycline 100 mg po bid x 14 days B. Flagyl 500 mg BID x 7 days with 1 dose of azithromycin C. Her partner does not need to be treated D. Lotrimin cream to the penis twice daily for 14 days A 38 year old active Asian woman with a history of infertility treatment and severe endometriosis complains to the nurse practitioner in the emergency department of right sided pelvic pain that is steadily getting worse. She also reports small amounts of yellow vaginal discharge on her underwear for the last week. The patient reports expecting her period which has not appeared in the last two months. Which of the following should be performed initially? A. Follicle stimulating hormone and culture and sensitivity testing for vaginal discharge B. Serum quantitative pregnancy test and quantitative cervical Gen-Probe testing C. Pelvic ultrasound and serum quantitative pregnancy test D. Microscopy of vaginal discharge and complete blood count with white cell differential? Which of the following is the most important differential diagnosis to consider in a 38 year old sexually active Asian woman with a history of infertility treatment and severe endometrosis with right sided pelvic pain that is steadily getting worse and small amounts of yellow colored discharge? A. Tubal ectopic pregnancy and pelvic inflammatory disease B. Mucopurulent cervicitis and tubal ectopic pregnancy C. Human papilloma virus infection of the cervix and pelvic inflammatory disease D. Ovarian cysts and severe endometriosis Vaginal candidiasis is best diagnosed in the primary care arena by the following method: A. Microscopy B. Tzanck smear C. KOH smear whiff test D. Clinical findings only - *Tzanck test is scraping of an ulcer base to look for tazanck cells, sometimes also called the chickenpox skin test and the herpes skin test. For which diagnosis is the consideration of whether the patient has a bubo necessary. A. Chancroid B. Syphilis C. Genital herpes A 21 year old Latino male comes into your office presenting with a sore on his penis x2 weeks. On exam, you note an indurated chancre that is painless, along with mild regional lymphadenopathy. Based on your diagnosis, which of the following is your most appropriate order? A. Ceftriaxone B. PCN G C. Azithromycin D. Acylcolovir the nurse practitioner knows that asymptomatic shedding should be considered with which STD/STI? A. Syphilis B. Chlamydia C. HSV-2 D. Gonorrhea In teaching a patient about seroconversion with HIV the nurse practitioner knows: A. Most patients seroconvert within 3-4 weeks of exposure B. Once seroconversion occurs the diagnosis of AIDS is usually made and medication is started in most patients C. Enough antigens have built up in the blood by 6 months to usually detect a virus D. Once seroconversion occurs, the patient may or may not show symptoms. All of these are considered part of HIV/AIDS except: A. Fatigue/vague abdominal pain B. Weight loss C. Night Sweats D. Fever The pap smear result on a 20 year old sexually active student who uses condoms inconsistently shows a large amount of inflammation. Which of the following is the best follow-up? A. The NP needs to do cervical cultures to verify the presence of gonorrhea B. Treat the patient with metronidazole vaginal cream C. Call the patient and tell her she needs a repeat pap smear in six months D. Advise her to use a betadine douche at half strength for three days. MALE GU A normal prostate is described as - Rubbery and non tender A 32 y.o. male comes into your office complaining of a superficial, painful ulcer, surrounded by an erythematous halo on the shaft of his penis with a unilateral bubo. You suspect: A. Chancroid B. Lymphogranuloma venereum C. condylomata acuminata D. molluscum contagiosum NEUROLOGICAL SYSTEM The two parts of the nervous system are the: Central and peripheral. The wife of a 65-year-old man tells the nurse that she is concerned because she has noticed a change in her husband's personality and ability to understand. He also cries very easily and becomes angry. The nurse recalls that the cerebral lobe responsible for these behaviors is the __________ lobe. Frontal Which statement concerning the areas of the brain is true? The hypothalamus controls body temperature and regulates sleep. The area of the nervous system that is responsible for mediating reflexes is the: Spinal cord. While gathering equipment after an injection, a nurse accidentally received a prick from an improperly capped needle. To interpret this sensation, which of these areas must be intact? Lateral spinothalamic tract, thalamus, and sensory cortex A patient with a lack of oxygen to his heart will have pain in his chest and possibly in the shoulder, arms, or jaw. The nurse knows that the best explanation why this occurs is which one of these statements? The sensory cortex does not have the ability to localize pain in the heart; consequently, the pain is felt elsewhere. The ability that humans have to perform very skilled movements such as writing is controlled by the: Corticospinal tract. A 30-year-old woman tells the nurse that she has been very unsteady and has had difficulty in maintaining her balance. Which area of the brain that is related to these findings would concern the nurse? Cerebellum Which of these statements about the peripheral nervous system is correct? The peripheral nerves carry input to the central nervous system by afferent fibers and away from the central nervous system by efferent fibers. A patient has a severed spinal nerve as a result of trauma. Which statement is true in this situation? The adjacent spinal nerves will continue to carry sensations for the dermatome served by the severed nerve. A 21-year-old patient has a head injury resulting from trauma and is unconscious. There are no other injuries. During the assessment what would the nurse expect to find when testing the patient's deep tendon reflexes? Reflexes will be normal. A mother of a 1-month-old infant asks the nurse why it takes so long for infants to learn to roll over. The nurse knows that the reason for this is: Myelin is needed to conduct the impulses, and the neurons of a newborn are not yet myelinated. During an assessment of an 80-year-old patient, the nurse notices the following: an inability to identify vibrations at her ankle and to identify the position of her big toe, a slower and more deliberate gait, and a slightly impaired tactile sensation. All other neurologic findings are normal. The nurse should interpret that these findings indicate: Normal changes attributable to aging. A 70-year-old woman tells the nurse that every time she gets up in the morning or after she's been sitting, she gets "really dizzy" and feels like she is going to fall over. The nurse's best response would be: "You need to get up slowly when you've been lying down or sitting." During the taking of the health history, a patient tells the nurse that "it feels like the room is spinning around me." The nurse would document this finding as: Vertigo. When taking the health history on a patient with a seizure disorder, the nurse assesses whether the patient has an aura. Which of these would be the best question for obtaining this information? "Do you have any warning sign before your seizure starts?" While obtaining a health history of a 3-month-old infant from the mother, the nurse asks about the infant's ability to suck and grasp the mother's finger. What is the nurse assessing? Reflexes In obtaining a health history on a 74-year-old patient, the nurse notes that he drinks alcohol daily and that he has noticed a tremor in his hands that affects his ability to hold things. With this information, what response should the nurse make? "Does the tremor change when you drink alcohol?" A 50-year-old woman is in the clinic for weakness in her left arm and leg that she has noticed for the past week. The nurse should perform which type of neurologic examination? Complete neurologic examination During an assessment of the CNs, the nurse finds the following: asymmetry when the patient smiles or frowns, uneven lifting of the eyebrows, sagging of the lower eyelids, and escape of air when the nurse presses against the right puffed cheek. This would indicate dysfunction of which of these CNs? Motor component of CN VII The nurse is testing the function of CN XI. Which statement best describes the response the nurse should expect if this nerve is intact? The patient: Moves the head and shoulders against resistance with equal strength. During the neurologic assessment of a "healthy" 35-year-old patient, the nurse asks him to relax his muscles completely. The nurse then moves each extremity through full range of motion. Which of these results would the nurse expect to find? Mild, even resistance to movement When the nurse asks a 68-year-old patient to stand with his feet together and arms at his side with his eyes closed, he starts to sway and moves his feet farther apart. The nurse would document this finding as: Positive Romberg sign. The nurse is performing an assessment on a 29-year-old woman who visits the clinic complaining of "always dropping things and falling down." While testing rapid alternating movements, the nurse notices that the woman is unable to pat both of her knees. Her response is extremely slow and she frequently misses. What should the nurse suspect? Dysfunction of the cerebellum During the taking of the health history of a 78-year-old man, his wife states that he occasionally has problems with short-term memory loss and confusion: "He can't even remember how to button his shirt." When assessing his sensory system, which action by the nurse is most appropriate? Before testing, the nurse would assess the patient's mental status and ability to follow directions. The assessment of a 60-year-old patient has taken longer than anticipated. In testing his pain perception, the nurse decides to complete the test as quickly as possible. When the nurse applies the sharp point of the pin on his arm several times, he is only able to identify these as one "very sharp prick." What would be the most accurate explanation for this? This response is most likely the result of the summation effect. The nurse is performing a neurologic assessment on a 41-year-old woman with a history of diabetes. When testing her ability to feel the vibrations of a tuning fork, the nurse notices that the patient is unable to feel vibrations on the great toe or ankle bilaterally, but she is able to feel vibrations on both patellae. Given this information, what would the nurse suspect? Peripheral neuropathy The nurse places a key in the hand of a patient and he identifies it as a penny. What term would the nurse use to describe this finding? Astereognosis (inability to identify objects correctly, and it occurs in sensory cortex lesions) The nurse is testing the deep tendon reflexes of a 30-year-old woman who is in the clinic for an annual physical examination. When striking the Achilles heel and quadriceps muscle, the nurse is unable to elicit a reflex. The nurse's next response should be to: Ask the patient to lock her fingers and pull. In assessing a 70-year-old patient who has had a recent cerebrovascular accident, the nurse notices right-sided weakness. What might the nurse expect to find when testing his reflexes on the right side? Hyperactive reflexes When the nurse is testing the triceps reflex, what is the expected response? Extension of the forearm The nurse is testing superficial reflexes on an adult patient. When stroking up the lateral side of the sole and across the ball of the foot, the nurse notices the plantar flexion of the toes. How should the nurse document this finding? Plantar reflex present In the assessment of a 1-month-old infant, the nurse notices a lack of response to noise or stimulation. The mother reports that in the last week he has been sleeping all of the time, and when he is awake all he does is cry. The nurse hears that the infant's cries are very high pitched and shrill. What should be the nurse's appropriate response to these findings? Refer the infant for further testing. Which of these tests would the nurse use to check the motor coordination of an 11-month-old infant? Denver II To assess the head control of a 4-month-old infant, the nurse lifts up the infant in a prone position while supporting his chest. The nurse looks for what normal response? The infant: Raises the head, and arches the back. While assessing a 7-month-old infant, the nurse makes a loud noise and notices the following response: abduction and flexion of the arms and legs; fanning of the fingers, and curling of the index finger and thumb in a C position, followed by the infant bringing in the arms and legs to the body. What does the nurse know about this response? This reflex should have disappeared between 1 and 4 months of age. To test for gross motor skill and coordination of a 6-year-old child, which of these techniques would be appropriate? Ask the child to: Hop on one foot. During the assessment of an 80-year-old patient, the nurse notices that his hands show tremors when he reaches for something and his head is always nodding. No associated rigidity is observed with movement. Which of these statements is most accurate? These findings are normal, resulting from aging. While the nurse is taking the history of a 68-year-old patient who sustained a head injury 3 days earlier, he tells the nurse that he is on a cruise ship and is 30 years old. The nurse knows that this finding is indicative of a(n): Decreased level of consciousness. The nurse is caring for a patient who has just had neurosurgery. To assess for increased intracranial pressure, what would the nurse include in the assessment? Level of consciousness, motor function, pupillary response, and vital signs During an assessment of a 22-year-old woman who sustained a head injury from an automobile accident 4 hours earlier, the nurse notices the following changes: pupils were equal, but now the right pupil is fully dilated and nonreactive, and the left pupil is 4 mm and reacts to light. What do these findings suggest? Increased intracranial pressure A 32-year-old woman tells the nurse that she has noticed "very sudden, jerky movements" mainly in her hands and arms. She says, "They seem to come and go, primarily when I am trying to do something. I haven't noticed them when I'm sleeping." This description suggests: Chorea. During an assessment of a 62-year-old man, the nurse notices the patient has a stooped posture, shuffling walk with short steps, flat facial expression, and pill-rolling finger movements. These findings would be consistent with: Parkinsonism. During an assessment of a 32-year-old patient with a recent head injury, the nurse notices that the patient responds to pain by extending, adducting, and internally rotating his arms. His palms pronate, and his lower extremities extend with plantar flexion. Which statement concerning these findings is most accurate? This patient's response: Is a very ominous sign and may indicate brainstem injury. A 78-year-old man has a history of a cerebrovascular accident. The nurse notes that when he walks, his left arm is immobile against the body with flexion of the shoulder, elbow, wrist, and fingers and adduction of the shoulder. His left leg is stiff and extended and circumducts with each step. What type of gait disturbance is this individual experiencing? Spastic hemiparesis In a person with an upper motor neuron lesion such as a cerebrovascular accident, which of these physical assessment findings should the nurse expect? Hyperreflexia A 59-year-old patient has a herniated intervertebral disk. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect to see on physical assessment of this individual? Hyporeflexia A patient is unable to perform rapid alternating movements such as rapidly patting her knees. The nurse should document this inability as: Presence of dysdiadochokinesia. The nurse knows that determining whether a person is oriented to his or her surroundings will test the functioning of which structure(s)? Cerebrum During an examination, the nurse notices severe nystagmus in both eyes of a patient. Which conclusion by the nurse is correct? Severe nystagmus in both eyes: May indicate disease of the cerebellum or brainstem. The nurse knows that testing kinesthesia is a test of a person's: Position sense. The nurse is reviewing a patient's medical record and notes that he is in a coma. Using the Glasgow Coma Scale, which number indicates that the patient is in a coma? 6 A man who was found wandering in a park at 2 AM has been brought to the emergency department for an examination; he said he fell and hit his head. During the examination, the nurse asks him to use his index finger to touch the nurse's finger, then his own nose, then the nurse's finger again (which has been moved to a different location). The patient is clumsy, unable to follow the instructions, and overshoots the mark, missing the finger. The nurse should suspect which of the following? Acute alcohol intoxication The nurse is assessing the neurologic status of a patient who has a late-stage brain tumor. With the reflex hammer, the nurse draws a light stroke up the lateral side of the sole of the foot and inward, across the ball of the foot. In response, the patient's toes fan out, and the big toe shows dorsiflexion. The nurse interprets this result as: Positive Babinski sign, which is abnormal for adults. A 69-year-old patient has been admitted to an adult psychiatric unit because his wife thinks he is getting more and more confused. He laughs when he is found to be forgetful, saying "I'm just getting old!" After the nurse completes a thorough neurologic assessment, which findings would be indicative of Alzheimer disease? Select all that apply. b.Difficulty performing familiar tasks, such as placing a telephone call cMisplacing items, such as putting dish soap in the refrigerator eRapid mood swings, from calm to tears, for no apparent reason f.Getting lost in one's own neighborhood bone marrow- the musculoskeletal system functions to encase and protect the inner vital organs, to support the body, to produce red blood cells in the bone marrow - hematopoiesis) and to store minerals. Fibrous bands running directly from one bone to another that strengthen the joint and help prevent movement in undesirable directions are called: ligaments The nurse notices that a woman in an exercise class is unable to jump rope. The nurse is aware that to jump rope, one's shoulder has to be capable of: Circumduction is defined as moving the arm in a circle around the shoulder. The other options are not correct. Of the 33 vertebrae in the spinal column, there are: 7 cervical 12 thorasic, 5 lumbar/sacral 3-4 cocccygeal vertebrae an imaginary line connecting the highest point on each iliac crest would cross the ....... vertebra forth sacral The nurse is explaining to a patient that there are shock absorbers in his back to cushion the spine and to help it move. The nurse is referring to his: Intervertebral disks are elastic fibrocartilaginous plates that cushion the spine similar to shock absorbers and help it move. other landmarks are the The vertebral column is the spinal column itself. The nucleus pulposus is located in the center of each disk. The vertebral foramen is the channel, or opening, for the spinal cord in the vertebrae. an injury to the rotator cuff involves which shoulder joint glenohumeral joint which enclosed by a group of four powerful muscles and tendons that support and stabilize it- other definitions are: the nucleus pulposus is located in the center of each intervertebral disk. The articular processes are projections in each vertebral disk that lock onto the next vertebra, thereby stabilizing the spinal column. The medial epicondyle is located at the elbow. A patient is visiting the clinic for an evaluation of a swollen, painful knuckle. The nurse notices that the knuckle above his ring on the left hand is swollen and that he is unable to remove his wedding ring. This joint is called the _________ joint. metacarpophalangeal joint. 2. The interphalangeal joint is located distal to the metacarpophalangeal joint. 3. The tarsometatarsal and tibiotalar joints are found in the foot and ankle. The nurse is assessing a patient's ischial tuberosity. To palpate the ischial tuberosity, the nurse knows that it is best to have the patient: The ischial tuberosity lies under the gluteus maximus muscle and is palpable when the hip is flexed. The nurse is examining the hip area of a patient and palpates a flat depression on the upper, lateral side of the thigh when the patient is standing. The nurse interprets this finding as the: The greater trochanter of the femur is palpated when the person is standing, and it appears as a flat depression on the upper lateral side of the thigh. 2. The iliac crest is the upper part of the hip bone; 3. the ischial tuberosity lies under the gluteus maximus muscle and is palpable when the hip is flexed; and the gluteus muscle is part of the buttocks. The ankle joint is the articulation of the tibia, fibula, and: The ankle or tibiotalar joint is the articulation of the tibia, fibula, and talus. The nurse is explaining the mechanism of the growth of long bones to a mother of a toddler. Where does lengthening of the bones occur? Lengthening occurs at the epiphyses, or growth plates. The other options are not correct. A woman who is 8 months pregnant comments that she has noticed a change in her posture and is having lower back pain. The nurse tells her that during pregnancy, women have a posture shift to compensate for the enlarging fetus. This shift in posture is known as: Lordosis compensates for the enlarging fetus, which would shift the center of balance forward. This shift in balance, in turn, creates a strain on the low back muscles, felt as low back pain during late pregnancy by some women. 2. Scoliosis is lateral curvature of portions of the spine; 3. ankylosis is extreme flexion of the wrist, as observed with severe rheumatoid arthritis; and 4. kyphosis is an enhanced thoracic curvature of the spine. An 85-year-old patient comments during his annual physical examination that he seems to be getting shorter as he ages. The nurse should explain that decreased height occurs with aging because: 1. Postural changes are evident with aging; decreased height is most noticeable and is due to shortening of the vertebral column. 2. Long bones do not shorten with age. 3. Intervertebral disks actually get thinner with age. 4. Subcutaneous fat is not lost but is redistributed to the abdomen and hips. A patient has been diagnosed with osteoporosis and asks the nurse, "What is osteoporosis?" The nurse explains that osteoporosis is defined as: After age 40 years, a loss of bone matrix (resorption) occurs more rapidly than new bone formation. The net effect is a gradual loss of bone density, or osteoporosis. The nurse is teaching a class on preventing osteoporosis to a group of perimenopausal women. Which of these actions is the best way to prevent or delay bone loss in this group? Physical activity, such as fast walking, delays or prevents bone loss in perimenopausal women. The faster the pace of walking, the higher the preventive effect is on the risk of hip fracture. A teenage girl has arrived complaining of pain in her left wrist. She was playing basketball when she fell and landed on her left hand. The nurse examines her hand and would expect a fracture if the girl complains of a: A fracture causes sharp pain that increases with movement. A patient is complaining of pain in his joints that is worse in the morning, better after he moves around for a while, and then gets worse again if he sits for long periods. The nurse should assess for other signs of what problem? Rheumatoid arthritis is worse in the morning when a person arises. Movement increases most joint pain, except the pain with rheumatoid arthritis, which decreases with movement. A patient states, "I can hear a crunching or grating sound when I kneel." She also states that "it is very difficult to get out of bed in the morning because of stiffness and pain in my joints." The nurse should assess for signs of what problem? Crepitation is an audible and palpable crunching or grating that accompanies movement and occurs when articular surfaces in the joints are roughened, as with rheumatoid arthritis. The other options are not correct. A patient is able to flex his right arm forward without difficulty or pain but is unable to abduct his arm because of pain and muscle spasms. The nurse should suspect: Rotator cuff lesions may limit range of motion and cause pain and muscle spasms during abduction, whereas forward flexion remains fairly normal. A professional tennis player comes into the clinic complaining of a sore elbow. The nurse will assess for tenderness at the: The epicondyles, the head of the radius, and the tendons are common sites of inflammation and local tenderness, commonly referred to as tennis elbow. The other locations are not affected. The nurse suspects that a patient has carpal tunnel syndrome and wants to perform the Phalen test. To perform this test, the nurse should instruct the patient to: For the Phalen test, the nurse should ask the person to hold both hands back to back while flexing the wrists 90 degrees. Acute flexion of the wrist for 60 seconds produces no symptoms in the normal hand. The Phalen test reproduces numbness and burning in a person with carpal tunnel syndrome. An 80-year-old woman is visiting the clinic for a checkup. She states, "I can't walk as much as I used to." The nurse is observing for motor dysfunction in her hip and should ask her to: abduct her hip while she is lying on her back. Limited abduction of the hip while supine is the most common motion dysfunction found in hip disease. The nurse has completed the musculoskeletal examination of a patient's knee and has found a positive bulge sign. The nurse interprets this finding to indicate: A positive bulge sign confirms the presence of swelling caused by fluid in the suprapatellar pouch. During an examination, the nurse asks a patient to bend forward from the waist and notices that the patient has lateral tilting. When his leg is raised straight up, the patient complains of a pain going down his buttock into his leg. The nurse suspects: Lateral tilting and sciatic pain with straight leg raising are findings that occur with a herniated nucleus pulposus. The nurse is examining a 3-month-old infant. While the nurse holds his or her thumbs on the infant's inner mid thighs and the fingers on the outside of the infant's hips, touching the greater trochanter, the nurse adducts the legs until the his or her thumbs touch and then abducts the legs until the infant's knees touch the table. The nurse does not notice any "clunking" sounds and is confident to record a: 1. negative ortolans sign. Normally, this maneuver feels smooth and has no sound. 2. With a positive Ortolani sign, however, the nurse will feel and hear a "clunk," as the head of the femur pops back into place. A positive Ortolani sign also reflects hip instability. 3. The Allis test also tests for hip dislocation but is performed by comparing leg lengths. During a neonatal examination, the nurse notices that the newborn infant has six toes. This finding is documented as: 1. Polydactyly is the presence of extra fingers or toes. 2. Syndactyly is webbing between adjacent fingers or toes. A mother brings her newborn baby boy in for a checkup; she tells the nurse that he does not seem to be moving his right arm as much as his left and that he seems to have pain when she lifts him up under the arms. The nurse suspects a fractured clavicle and would observe for: For a fractured clavicle, the nurse should observe for limited arm range of motion and unilateral response to the Moro reflex. A 40-year-old man has come into the clinic with complaints of extreme pain in his toes. The nurse notices that his toes are slightly swollen, reddened, and warm to the touch. His complaints would suggest: acute gout consist of redness, swelling, heat, and extreme pain like a continuous throbbing. Gout is a metabolic disorder of disturbed purine metabolism, associated with elevated serum uric acid. A young swimmer comes to the sports clinic complaining of a very sore shoulder. He was running at the pool, slipped on some wet concrete, and tried to catch himself with his outstretched hand. He landed on his outstretched hand and has not been able to move his shoulder since. The nurse suspects: A dislocated shoulder occurs with trauma involving abduction, extension, and external rotation A 68-year-old woman has come in for an assessment of her rheumatoid arthritis, and the nurse notices raised, firm, nontender nodules at the olecranon bursa and along the ulna. These nodules are most commonly diagnosed as: Subcutaneous nodules- these are raised, firm, and nontender and occur with rheumatoid arthritis in the olecranon bursa and along the extensor surface of the ulna A woman who has had rheumatoid arthritis for years is starting to notice that her fingers are drifting to the side. The nurse knows that this condition is commonly referred to as: Ulnar deviation . Fingers drift to the ulnar side because of stretching of the articular capsule and muscle imbalance caused by chronic rheumatoid arthritis. A radial drift is not observed. A patient who has had rheumatoid arthritis for years comes to the clinic to ask about changes in her fingers. The nurse will assess for signs of what problems? Changes in the fingers caused by chronic rheumatoid arthritis include swan-neck and boutonniere deformities. 2. Heberden nodes and Bouchard nodules are associated with osteoarthritis. 3. Dupuytren contractures of the digits occur because of chronic hyperplasia of the palmar fascia A patient's annual physical examination reveals a lateral curvature of the thoracic and lumbar segments of his spine; however, this curvature disappears with forward bending. The nurse knows that this abnormality of the spine is called: 1. Functional scoliosis - it is flexible and apparent with standing but disappears with forward bending. 2. Structural scoliosis is fixed; the curvature shows both when standing and when bending forward. A 14-year-old boy who has been diagnosed with Osgood-Schlatter disease reports painful swelling just below the knee for the past 5 months. Which response by the nurse is appropriate? "Your disease is due to repeated stress on the patellar tendon. It is usually self-limited, and your symptoms should resolve with rest." Osgood-Schlatter disease is a painful swelling of the tibial tubercle just below the knee and most likely due to repeated stress on the patellar tendon. It is usually self-limited, occurring during rapid growth and most often in boys. The symptoms resolve with rest. The other responses are not appropriate. When assessing muscle strength, the nurse observes that a patient has complete range of motion against gravity with full resistance. What grade of muscle strength should the nurse record using a 0- to 5-point scale? Complete range of motion against gravity is normal muscle strength and is recorded as grade 5 muscle strength. The nurse is examining a 6-month-old infant and places the infant's feet flat on the table and flexes his knees up. The nurse notes that the right knee is significantly lower than the left. Which of these statements is true of this finding? Finding one knee significantly lower than the other is a positive Allis sign and suggests hip dislocation. Normally, the tops of the knees are at the same elevation. The nurse is assessing a 1-week-old infant and is testing his muscle strength. The nurse lifts the infant with hands under the axillae and notices that the infant starts to "slip" between the hands. The nurse should asses that An infant who starts to "slip" between the nurse's hands shows weakness of the shoulder muscles. An infant with normal muscle strength wedges securely between the nurse's hands. nurse is examining a 2-month-old infant and notices asymmetry of the infant's gluteal folds. The nurse should assess for other signs of what disorder? hip dislocation-Unequal gluteal folds may accompany hip dislocation after 2 to 3 months of age, but some asymmetry may occur in healthy children. Further assessment is needed. The other responses are not correct. The nurse should use which test to check for large amounts of fluid around the patella? Ballottement of the patella is reliable when large amounts of fluid are present. 2. The Tinel sign and the Phalen test are used to check for carpal tunnel syndrome. 3. The McMurray test is used to test the knee for a torn meniscus. A patient tells the nurse that, "All my life I've been called 'knock knees'." The nurse knows that another term for knock knees is: Genu valgum is also known as knock knees and is present when more than 2.5 cm is between the medial malleoli when the knees are together. A man who has had gout for several years comes to the clinic with a problem with his toe. On examination, the nurse notices the presence of hard, painless nodules over the great toe; one has burst open with a chalky discharge. This finding is known as: 1. Tophi are collections of monosodium urate crystals resulting from chronic gout in and around the joint that cause extreme swelling and joint deformity. They appear as hard, painless nodules (tophi) over the metatarsophalangeal joint of the first toe and they sometimes burst with a chalky discharge When performing a musculoskeletal assessment, the nurse knows that the correct approach for the examination should be The musculoskeletal assessment should be performed in an orderly approach, head to toe, proximal to distal, from the midline outward. ... ... The nurse is assessing the joints of a woman who has stated, "I have a long family history of arthritis, and my joints hurt." The nurse suspects that she has osteoarthritis. name different symptoms asymmetric joint involvement, pain with motion of affected joints, affected joints are swollen with hard bony protuberances you have just assessed the muscle strength of your patient. you determine that the patient's knee strength is fair and exhibits active motion with gravity. you should document the patient's muscle strength as: 3/5 you are assessing your patient for range of motion movement. you ask him to move his arm in towards the center of his body. this movement is called: adduction a female patient is 8 months pregnant. she comments that she has noticed a change in posture and is having lower back pain. the nurse tells her that during pregnancy women have a posture shift to compensate for the enlarging fetus. this shift is posture is known as: lordosis the nurse is checking the range of motion in a patient's knee and knows that the knee is capable of which movements? flexion and extension the nurse notes that there is an audible clicking sound when the patient opens and closes the mouth. what is the appropriate response of the nurse at this time? documenting this finding as expected if no other signs or symptoms are found the nurse asks the patient to rest the left arm on a table and to move the lower arm so that the palm of the hand is up and then down. what motion is the nurse testing? supination and pronation of the elbow upon inspection of a patient's hands, the nurse notices ulnar deviation and swan-neck deformities bilaterally. the nurses correlates this finding with which disorder? rheumatoid arthritis when performing a musculoskeletal assessment, the nurse knows the correct approach for the examination should be: proximal to distal a patient is able to flex his right arm forward without difficulty or pain; but is unable to abduct his arm because of pain and muscle spasms. the nurse should suspect: rotator cuff injury the nurse is assessing the joints of a woman who has stated, "I have a long family history of arthritis, and my joints hurt." the nurse suspects that she has osteoarthritis. which of these is a symptom of osteoarthritis? Terms in this set (47) two parts of the nervous system are the: ANS: central and peripheral. The cns includes the brain and spinal cord. The pns 12 pairs of cranial nerves, 31 pairs of spinal nerves, and branches. The wife of a 65-year-old man has change in personality and ability to understand. He also cries. The nurse recalls that the cerebral lobe responsible for these behaviors is the _____ lobe. The frontal lobe has areas concerned with personality, behavior, emotions, and intellectual function. The parietal lobe has areas concerned with sensation; the occipital lobe is responsible for visual reception; and the temporal lobe is concerned with hearing, taste and smell. Which of these statements concerning areas of the brain is true? The cerebellum-motor coordination, equilibrium, balance. The basal ganglia control autonomic movements of the body. The area of the nervous system that is responsible for reflexes a nurse accidentally received a prick from an improperly capped needle. To interpret this sensation? . A patient with lack of oxygen, yet pain in his chest and possibly the shoulder, arms, ANS: The sensory cortex does not have the ability to localize pain in the heart, so the pain is felt elsewhere. The ability that humans have to perform very skilled movements such as writing is controlled by the: Corticospinal fibers mediate voluntary movement, particularly very skilled, discrete, purposeful movements, such as writing. A 30-year-old woman tells the nurse that she has been very unsteady and has had difficulty in maintaining her balance. coordinates movement, maintains equilibrium, and helps maintain posture. Which of these statements about the peripheral nervous system is correct? A patient has a severed spinal nerve as a result of trauma. A dermatome is a circumscribed skin area that is supplied mainly from one spinal cord segment through a particular spinal nerve. A 21-year-old patient has a head injury resulting from trauma. what is expected when testing the patient's deep tendon reflexes? A reflex is a defense mechanism of the nervous system. A mother of a 1-month-old infant asks the nurse why it takes so long for infants to learn to roll over. During an assessment of an 80-year-old patient, the nurse notices slightly impaired tactile sensation. All other neurologic findings are normal. A 70 yr woman tells the nurse that every time she gets up in the morning. she gets "really dizzy" During the history, a patient tells the nurse that "it feels like the room is spinning around me." The nurse would document this as: Dizziness is a lightheaded, Syncope is a sudden loss of consciousness. . When taking the history on a patient with a seizure disorder, the nurse assesses whether the patient has an aura. Aura is a subjective sensation that precedes a seizure; it could be auditory, visual, or motor. While obtaining a history of a 3-month-old infant, the nurse asks about the infant's ability to suck and grasp mother's finger. In 74-year-old patient the nurse notes that he drinks alcohol daily and that he has noticed a tremor in his hands. Senile tremor is relieved by alcohol, although this is not a recommended treatment. the nurse finds the following: asymmetry when the patient smiles uneven lifting of eyebrows, sagging of the lower eyelids, and escape of air when the nurse presses against the right puffed cheek. The nurse is testing the function of cranial nerve XI. intact? ANS: moves the head and shoulders against resistance with equal strength. Checking the patient's ability to hear CN VIII. stick out the tongue checks the function of CN XII. Testing the eyes CN III, IV, and VI. assessment of a "healthy" 35-year-old patient, the The nurse then moves each extremity through full range of motion. When the nurse asks a 68-year-old patient to stand with feet together and his eyes closed, he starts to sway and moves his feet farther apart. Positive Romberg sign is loss of balance that is increased by closing of the eyes. Ataxia is unsteady gait. Homans' sign is used to test the legs for deep vein thrombosis. a 29-year-old woman who visits the clinic complaining of "always dropping things and falling down." the woman is unable to pat both her knees. During the history of a 78-year-old man, he occasionally has short-term memory loss and confusion: "He can't even remember how to button his shirt." The assessment of a 60-year-old patient has taken longer than anticipated. In testing his pain perception the nurse decides to complete the test as quickly as possible. When the nurse applies the sharp point of the pin on his arm several times, he is only able to identify these as one "very sharp prick." What would be the most accurate explanation for this? Let at least 2 seconds elapse between each stimulus to avoid summation. With summation, frequent consecutive stimuli are perceived as one strong stimulus. The other responses are incorrect. The nurse is performing a neurologic assessment on a 41-year-old woman with a history of diabetes. When testing her ability to feel the vibrations of a tuning fork, the nurse notices that the patient is unable to feel vibrations on the great toe or ankle bilaterally, but she is able to feel vibrations on both patellae. Given this information, what would the nurse suspect? Loss of vibration sense occurs with peripheral neuropathy (e.g., diabetes and alcoholism). Peripheral neuropathy is worse at the feet and gradually improves as the examiner moves up the leg, as opposed to a specific nerve lesion, which has a clear zone of deficit for its dermatome. The nurse places a key in the hand of a patient and he identifies it as a penny. What term would the nurse use to describe this finding? Stereognosis is the person's ability to recognize objects by feeling their forms, sizes, and weights. Astereognosis is an inability to identify objects correctly, and it occurs in sensory cortex lesions. . In the assessment of a 1-month-old infant, the nurse notices a lack of response to noise or stimulation. The mother reports that in the last week he has been sleeping all the time, and when he is awake all he does is cry. The nurse hears that the infant's cries are very high pitched and shrill. What should be the nurse's appropriate response to these findings? A high-pitched, shrill cry or cat-sounding screech occurs with central nervous system damage. Lethargy, hyporeactivity, hyperirritability, and parent's report of significant change in behavior all warrant referral. The other options are not correct responses. Which of these tests would the nurse use to check the motor coordination of an 11-month-old infant? Denver II- to screen gross and fine motor coordination, the nurse should use the Denver II While assessing a 7-month-old infant, the nurse makes a loud noise and notices the following response: abduction and flexion of arms and legs; fanning of fingers, and curling of index and thumb in a C position followed by infant bringing in arms and legs to body. What does the nurse know about this response? The Moro reflex is present at birth and disappears at 1 to 4 months. To test for gross motor skill and coordination of a 6-year-old child, which of these techniques would be appropriate? During the assessment of an 80-year-old patient, the nurse notices that his hands show tremors when he reaches for something and his head is always nodding. There is no associated rigidity with movement. Which of these statements is most accurate? Senile tremors occasionally occur. These benign tremors include an intention tremor of the hands, head nodding (as if saying yes or no), and tongue protrusion. Tremors associated with Parkinson disease include rigidity, slowness, and weakness of voluntary movement. The other responses are incorrect. While the nurse is taking the history of a 68-year-old patient who sustained a head injury 3 days earlier, he tells the nurse that he is on a cruise ship and is 30 years old. The nurse knows that this finding is indicative of: A change in consciousness may be subtle. The nurse should notice any decreasing level of consciousness, disorientation, memory loss, uncooperative behavior, or even complacency in a previously combative person. The other responses are incorrect. The nurse is caring for a patient who has just had neurosurgery. To assess for increased intracranial pressure, what would the nurse include in the assessment? . assessment of a 22-year who has a head injury, the nurse notices the right pupil is fully dilated and nonreactive, left pupil is 4 mm and reacts to light. . During an assessment of a 62-year-old man the nurse notices the patient has a stooped posture, shuffling walk with short steps, flat facial expression, and pill-rolling finger movements. 32-year-old patient with head injury, the patient responds to pain by extending, adducting, and irotating his arms. palms pronate and his lower extremities extend with plantar flexion. In a person with an upper motor neuron lesion such as a cerebrovascular accident, which of these physical assessment findings should the nurse expect to see? Hyperreflexia, diminished or absent superficial reflexes, and increased muscle tone or spasticity can be expected with upper motor neuron lesions. A 59-year-old patient has a herniated intervertebral disk. With a herniated intervertebral disk or lower motor neuron lesion there is loss of tone, flaccidity, atrophy, A patient is not able to perform rapid alternating movements such as patting her knees rapidly. The nurse should document this as: Slow clumsy movements and the inability to perform rapid alternating movements are condition of dysdiadochokinesia. Ataxia is uncoordinated or unsteady gait. Astereognosis is the inability to identify an object by feeling it. Kinesthesia is the person's ability to perceive passive movement of the extremities, or the loss of position sense. determining whether a person is oriented to his or her surroundings will test ? The cerebral cortex is responsible for thought, memory, reasoning, sensation, and voluntary movement. During an examination, the nurse notices severe nystagmus in both eyes of a patient. Which of these conclusions by the nurse is correct? This may indicate disease of the cerebellum or brainstem. End-point nystagmus at an extreme lateral gaze occurs normally. The nurse knows that testing kinesthesia is a test of a person's: Kinesthesia, or position sense, is passive movements of the extremities. Using the Glasgow Coma Scale, which number indicates that the patient is in a coma? ANS: 6 A fully alert, normal person has a score of 15, whereas a score of 7 or less reflects coma on the Glasgow Coma Scale. a patient who has a late-stage brain tumor. the patient's toes fan out, and the big toe shows dorsiflexion. The nurse interprets this result as: Dorsiflexion of the big toe and fanning of all toes is a positive Babinski's sign, also called "upgoing toes A 69-year-old patient has been admitted to an adult psychiatric unit because his wife thinks he is getting more and more confused. Alzheimer's disease? Rapid mood swings, from calm to tears, Getting lost in one's own neighborhood During the assessment of deep tendon reflexes, the nurse finds that a patient's responses are normal bilaterally. What number is used to indicate "normal" deep tendon reflexes when the documenting this finding. _____+ Responses to assessment of deep tendon reflexes are graded on a 4-point scale. A rating of 2+ indicates normal or average response. A rating of 0 indicates no response, and a rating of 4+ indicates very brisk, hyperactive response with clonus, which is indicative of disease. $2.99 STUDY GUIDE Neuro System55 Terms starliightz 4 Chapter 23 JARVIS 256 Terms During an examination the nurse observes a female patient's vestibule and expects to see the Cervix urethral meatus and vaginal orifice During a speculum inspection of the vagina, the nurse would expect to see what at the end of the vaginal canal? The uterus is usually positioned tilting forward and superior to the bladder. This position is Anteverted and anteflexed A postmenopausal woman should be aware that she is at increased risk for dyspareunia because of decreased vaginal secretions. A 54 year old woman who has just completed menopause is in the clinic today for a yearly physical examination. Which of these statements should the nurse include in patient education? Stress incontinence A 52 year old patient states that when she sneezes or coughs she "wets herself a little." She is very concerned that something may be wrong with her. The nurse suspects that the problem is The nurse is preparing to interview a postmenopausal woman. Which of these statements is true with regard to the history of a postmenopausal woman? The nurse should ask a postmenopausal woman if she ever has vaginal bleeding Multiple nontender sebaceous cysts. The nurse has just completed an inspection of a nulliparous woman's external genitalia. Which of these would be a description of a finding within normal limits? The nurse is preparing for an internal genitalia examination of a woman. Which order of the examination is correct? Speculum, bimanual, rectovaginal Candidiasis During a vaginal examination of a 38 year old woman, the nurse notices that the vulva and vagina are erythematous and edematous with thick, white, curdlike discharge adhering to the vaginal walls. The woman reports intense pruritus and thick white discharge from her vagina. The nurse knows that these history and physical examination findings are most consistent with which of these conditions? Pelvic inflammatory disease A 25 year old woman comes to the emergency department with a sudden fever of 101 degrees F and abdominal pain. Upon examination, the nurse notices that she has a rigid, boardlike lower abdominal musculature. When the nurse tries to perform a vaginal examination, the patient has severe pain when the uterus and cervix are moved. The nurse knows that these signs and symptoms are suggestive of - FACT #1: The lymphatics of the testes drain into the abdominal lymph nodes FACT #2: The cremaster muscle contracts in response to cold and draws the testicles closer to the body. A male patient with possible fertitility problems asks the nurse where sperm is produced. The nurse knows that sperm production occurs in the – A 62 year old man states that his doctor told him that he has an "inguinal hernia." He asks the nurse to explain what a hernia is. When the nurse is performing a genital examination on a male patient, the patient has an erection. The nurse's most appropriate action or response is to- reassure the patient that This is a normal response and then continue with the examination Smegma may be present under the foreskin of an uncircumcised male. The nurse is examining the glans and knows that which of these is a normal finding for this area? Hypospadias When performing a genitourinary assessment, the nurse notices that the urethral meatus is positioned ventrally. This finding is Men with a history of cryptorchidism are at greatest risk for development of testicular cancer. The nurse is aware that which of these statements is true regarding the incidence of testicular cancer? The nurse is describing how to perform a testicular self-examination to a patient. Which of these statements is most appropriate? If you notice an enlarged testicle or a painless lump, call you health care provider. When performing a genital assessment on a middle-aged man, the nurse notices multiple soft, moist, painless papules in the shape of cauliflower-like patches scattered across the shaft of the penis. These lesions are characteristic of Genital wart A 15 year old boy is seen in the clinic for complaints of "dull pain and pulling" in the scrotal area. On examination the nurse palpates a soft, irregular mass posterior to and above the testis on the left. The mass collapses when the patient is supine and refills when he is upright. This description is Variocele ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS YOU ARE PERFORMING A PAP, HOW CAN YOU MAKE THE PERSON MORE COMFORTABLE - HAVE THEM PUT ARMS BEHIND HEAD - RAISE HEAD AND SHOULDER TO MAINTAIN EYE CONTACT How venous blood returns back to the heart WHAT IS ASSOCIATED WITH RA What does a majenta tongue mean A long term homeless person what is the cause of his problems There is no pulse felt in tibial pulse at 0/0-4 what should be pulse be A guy is lifting something heavy and has incontinence A patient has pain while lying in bed, relieved by dangling legs what does he have What is a characteristic of venous insufficiency Pt has low albumin what can you conclude - I put that there are other causes for low albumin A patient with chronic emphysema and bronchitis what would you expect to see Pt has a nevi that has changed, what is most concerning about the findings After menopause, the glandular and fat tissue atrophies, causing breast size and elasticity to diminish, resulting in breasts that sag. “Puberty usually begins about age fifteen.” “The first sign of puberty is enlargement of the testes.” “Penis size does not increase until about the age of sixteen.” "The development of pubic hair precedes testicular or penis enlargement.” 4. During an examination, the nurse notes severe nystagmus in both eyes of a patient. Which of the following conclusions is correct? 1.This is a normal occurrence. 2.This may indicate disease of the cerebellum or brainstem. 3.This is a sign that the patient is nervous about the examination. 4.This indicates a visual problem and a referral to an ophthalmologist is indicated. End-point nystagmus at an extreme lateral gaze occurs normally. Assess any other nystagmus carefully. Severe nystagmus occurs with disease of the vestibular system, cerebellum, or brainstem. 1. A 43-year-old woman is at the clinic for a routine examination. She reports that she has had a breast lump in her right breast for years. Recently, it has begun to change in consistency and is becoming harder. She reports that 5 years ago her physician evaluated the lump and determined that it “was nothing to worry about.” The examination validates the presence of a mass in the right upper outer quadrant at 1 o’clock, approximately 5 cm from the nipple. It is firm, mobile, nontender, with borders that are not well defined. The nurse’s recommendation to her is: 1. A patient's mother has noticed that her son, who has been to a new babysitter, has some blisters and scabs on his face and buttocks. On examination, the nurse notices moist, thin-roofed vesicles with a thin erythematous base and suspects: 9. A 16-yr-old girl is being seen at clinic for gastrointestinal complaints+weight loss. Nurse determines that many of her complaints may be related to erratic eating patterns, eating predominantly fast foods, + high caffeine intake. In this situation, which is most appropriate when collecting current dietary intake information? I picked keep a log of 2 work days and 1 weekend 10. A patient has a positive Homans' sign. The nurse knows that a positive Homans' sign may indicate: 9. A 15-year-old boy is seen in the clinic for complaints of “dull pain and pulling” in the scrotal area. On examination the nurse palpates a soft, irregular mass posterior to and above the testis on the left. This mass collapses when the patient is supine and refills when he is upright. This description is consistent with: 10. The nurse is bathing an 80-year-old man and notices that his skin is wrinkled, thin, lax, and dry. This finding would be related to which factor? An increased loss of elastin and a decrease in subcutaneous fat in the elderly 17. In assessment of 1-month-old, nurse notes a lack of response to noise or stimulation. mother reports that in the last week he has been sleeping all the time + when awake all he does is cry. nurse hears that infant’s cries are very high pitched and shrill. What would be nurse’s appropriate response? 1.Refer the infant for further testing. 2.Talk with the mother about eating habits. 3.Nothing; these are expected findings for an infant this age. 4.Tell the mother to bring the baby back in a week for a recheck. 11. A 14-year-old girl is anxious about not having reached menarche. When taking the history, the nurse should ascertain which of the following? The age: 12. During an examination, the nurse notes a supernumerary nipple just under the patient’s left breast. The patient tells the nurse that she always thought it was a mole. Which statement about this finding is correct? 23. In a person with an upper motor neuron lesion such as a cerebrovascular accident, which of the following physical assessment findings would the nurse expect to see? 1.Hyperreflexia 2.Fasciculations 3.Loss of muscle tone and flaccidity 4.Atrophy and wasting of the muscles 27. uring an examination, you note that a male patient has a red, round, superficial ulcer with a yellowish-serous discharge on his penis. Upon palpation, you note a nontender base that feels like a small button between your thumb and fingers. At this point you suspect that this patient has: 28. During an interview, a patient reveals that she is pregnant. She states that she is not sure whether she will breastfeed her baby and asks for some information about this. Which of these statements by the nurse is accurate with regard to breastfeeding? 30. The nurse practitioner is examining only the rectal area of a woman and should place the woman in what position? use the left lateral decubitus 33. A man found wandering in park at 2AM has been brought to emergency department for examination because he said he fell+hit head. During examination, nurse asks him to use his index finger to touch nurse’s finger, then own nose, then nurse’s finger again (moved to a different location). patient is clumsy, unable to follow the instructions, + overshoots mark, missing finger. nurse suspects... 1.Cerebral injury 2.Cerebrovascular accident 3.Acute alcohol intoxication 4.Peripheral neuropathy . During an assessment, the nurse notes that a patient's left arm is swollen from the shoulder down to the fingers, with nonpitting edema. The right arm is normal. The patient had a mastectomy 1 year ago. The nurse suspects which problem? Lymphedema . The assessment of an 80-year-old patient, the nurse notes that his hands show tremors when he reaches for something and that his head is always nodding. There is no associated 44. Which of the following statements is true regarding the arterial system? 45. A patient who is visiting the clinic complains of having "stomach pains for 2 weeks" and describes his stools as being "soft and black" for about the last 10 days. He denies taking any medications. The NP is aware that these symptoms are most indicative of: 47. When assessing a patient the nurse practitioner documents the left femoral pulse as 0/0-4+. Which of the following findings would the nurse practitioner expect at the dorsalis pedis pulse? 0/0-4+ Pulsations are graded on a four-point scale: 0, absent; 1+, weak; 2+, normal; 3+, increased; 4+, bounding. If a pulse is absent at the femoral site, one would expect the dorsalis pedis pulse to be absent also. 49. The nurse practitioner is doing an assessment on a 29-year-old woman who visits the clinic complaining of "always dropping things and falling down." While testing rapid alternating movements, the nurse practitioner notices that the woman is unable to pat both her knees. Her response is very slow and she misses frequently. What might the nurse practitioner suspect? 50. The wife of a 65 year old man tells the nurse that she is concerned because she has noted a change in her husband's personality and ability to understand. He also cries and becomes angry very easily. The nurse recalls that the cerebral lobe responsible for these behaviors is which of the following? Frontal 51. A male patient with possible fertility problems asks the nurse where sperm is produced. The nurse knows that sperm production occurs in the: 52. Which of the following statements reflects the best approach to teaching a woman about breast self-examination (BSE)? 53. When assessing a patient's pulse, the nurse practitioner notes that the amplitude is weaker during inspiration and stronger during expiration. When the nurse practitioner measures the blood pressure, the reading decreases 20 mm Hg during inspiration and increases with expiration. This patient is experiencing: . 57. Assessment of a 60-yr-old patient has taken longer than anticipated. in testing pain perception nurse decides to complete the test as quickly as possible. When nurse applies sharp point of pin on his arm several times, he is only able to identify these as one 'very sharp prick.' most accurate explanation? 1.has hyperesthesia as a result of aging process 2.most likely the result of the summation effect. 3.The nurse was probably not poking hard enough with the pin in the other areas. 4.The patient most likely has analgesia in some areas of arm and hyperalgesia in others. 57. Assessing a 7-month-old infant you make a loud noise and note the following response: Abduction and flexion of arms and legs; fanning of fingers and curling of index finger and thumb in C-position; followed by infant bringing in arms and legs to body. What do you know about this? 1.This could indicate brachial nerve palsy 2.This is an expected startle response at this age 3.This reflex should disappear between 1 and 4 months of age 4.It is normal as long as movements are symmetrical bilaterally 61. Which of the following veins are responsible for most of the venous return in the arm? 62. A man who has had gout for several years comes to the clinic with a "problem with my toe." On examination, the nurse practitioner notes the presence of hard, painless nodules over the great toe; one had burst open with a chalky discharge. This finding is known as: Tophi are collections of sodium urate crystals resulting from chronic gout in and around the joint 64. A 70-year-old patient is scheduled for open-heart surgery. The surgeon plans to use the great saphenous vein for the coronary bypass grafts. The patient asks, “What happens to my circulation when the veins are removed?” The nurse should reply: 65. When observing the vestibule, the nurse practitioner should be able to see the: 66. When the nurse is conducting sexual history from a male adolescent, which statement would be most appropriate to use at the beginning of the interview? Often boys your age have questions about sexual activity 70. Mrs. A has had arthritis for years and is starting to notice that her fingers are drifting to this side. This is commonly referred to as: 72. A 14-year-old boy who has been diagnosed with Osgood-Schlatter disease reports painful swelling just below the knee for the past 5 months. Which response by the nurse practitioner is appropriate? 75. The nurse practitioner has completed the musculoskeletal examination of a patient’s knee and has found a positive bulge sign. The nurse suspects: 76. Which of the following statements is true with regard to the history of a postmenopausal woman? ASK IF SHE EVER HAS VAGINAL BLEEDING 78. During a physical examination, a 45-year-old woman states that she has had a crusty, itchy rash on her breast for about 2 weeks. In trying to find the cause of the rash, which of these would be important for the nurse to determine? ??? CONCERN FOR PAGETS DISEASE 80. The patient is in her first trimester of pregnancy. She complains of feeling nauseated and has vomited on occasion. She tells the nurse that she did not have this with her first pregnancy. She asks the nurse, "What is causing this and when will it end?" How should the nurse respond? 81. A professional tennis player comes in complaining of a sore elbow. You suspect that he has tenderness at: 85. In examining a 70-year-old male patient, the nurse notices that he has bilateral gynecomastia. Which of the following describes the nurse’s best course of action? 88. During an annual check-up of a 55 y/o patient, the nurse discusses the early detection measures for colon cancer. The nurse should mention the need for a 89. What are the two main parts of the nervous system? 90. While obtaining a history of a 3-month old infant from the mother, the nurse practitioner asks about the baby's ability to suck and grasp the mother's finger. What is the nurse practitioner assessing? [Show More]
Last updated: 1 month ago
Preview 1 out of 54 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jul 12, 2020
Number of pages
54
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jul 12, 2020
Downloads
2
Views
157