*NURSING > ATI MEDICAL SURGICAL > ATI MED SURG PROCTORED EXAM | (100 Q&A) 100% CORRECT ANSWERS WITH RATIONALES | (LATEST FALL 2021 | D (All)
ATI MED SURG PROCTORED EXAM | (100 Q&A) 100% CORRECT ANSWERS WITH RATIONALES | (LATEST FALL 2021 | DOWNLOAD TO TO SCORE AN A
Document Content and Description Below
1. A nurse is assessing a client who has left-sided heart failure. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect? a. Bradycardia- more tachycardia cuz of a failing ventricle , SNS is activa... ted to compensate . b. Flushed skin- duskly it wIll look like c. Frothy sputum-Left sided- can be blood tinged d. Jugular vein distention→ Right Rationale: ATI MS: pg. 198 ch 32 pdf Left side: dyspnea, orthopnea, fatigue, pulmonary congestion, frothy sputum, organ failure such as oliguria. Right Side: Jugular vein distention, ascending dependent edema, abdominal distention, polyuria ar rest, liver enlargement, 2. A nurse is assessing a client who is experiencing renal colic from a calculus in left renal pelvis. Identify the area where the nurse should expect the client to have referred pain. ( Find “hot spots” in the artwork) Pain travels downward to the inguinal area and lower back Renal colic occurs in the kidney area. Referred pain is somewhere that happens in another place other than where the pain should be felt. 2. A nurse is caring for a client who is receiving peritoneal dialysis and notes a decrease in the dialysate flow rate. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? (Select all the apply?). Check answer i read pg 644-647 med surg it’s not so specific p. 370 ch 57 pdf a. monitor the access site for drainage.- to check for sxs of infection. b. Strip the catheter tubing c. Measure the amount of the dialysate outflow d. Raise the client to high fowlers position- they must lie supine e. Position the client to her other side. 3. A nurse is planning to insert an indwelling catheter for a female client. Which of the following actions should the nurse plan to take? Ati video tutorials foley a. Collect urine specimen from the drainage bag 1 hr after insertion b. Raise the head of the bed to 45 degrees prior to insertion c. Secure the catheter to the client's inner thigh d. Attach the bag to the rail of the bed. –under non movable area 6. A nurse is providing teaching for a client who has age-related macular degeneration which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching a. A possible cause of this problem is long-term lack of dietary protein b. You probably have a Detachment of your retina -vision is like having curtains over eyes c. You probably have noticed a decline in your central vision d. The doctor can perform surgery to correct the start paying the folds in your retina Rationale: ATI MS: PG. 63 Macular degeneration, often called age-related macular degeneration (AMD), is the central loss of vision that affects the macula of the eye. NO cure , happens alot in old people. Sxs: distorted vision, blurred vision, caused by smoking, female, HTN, diet lacking carotene. 7. A nurse is assessing a client who has cirrhosis. Which of the following findings is the priority for the nurse to report? P . 357 ch 55 pdf Med surg a. Platelets 70,000/mm3- risk of bleed normal range is 150,000 - 300,00- ABCS is compromised automatically . b. Distended abdomen- expected c. Alkaline phosphatase 125 units/L -norm normal is 30 -120 D. Clay colored stools- bile not on your shit 8. A nurse is preparing to discontinue long-term total parenteral nutrition (TPN) therapy for a client for a client. The nurse should plan to discontinue the TPN gradually to reduce the risk of which of the following adverse effects? Old med surge docs we used a. Hyperglycemia b. Diarrhea c. Constipation d. Hypoglycemia (Repeat) Since your body is producing enough insulin to take on higher loads, you must taper it down to avoid hypoglycemia with lower concentrations of TPN Abruptly discontinuing TPN will cause rebound hypoglycemia 9. A nurse is preparing to administer a unit of packed RBCs to a client. Which of the following actions should the nurse plan to take? P . 250 chapter 40 pdf p . 678 lewis a. Administer the unit of packed RBC’s over 1 hr- 2- 4 hr its must be given for 2 -4 hours. older adults b. Obtain the client’s first set of vital signs 1 hr after initiating the transfusion- you get vital signs at the initial first 15 to 30 minutes of the transfusion. c. Initiate venous access with a 21-gauge needle - no more than 19, for a regular adult it is 18 or 20 . d. Use Y tubing with 0.9% sodium chloride when administering the transfusion. Pg 249 10. TOXIC SHOCK SYNDROME- same 11. A nurse is providing discharge teaching to an older adult client who had an exacerbation of COPD. The client is to start fluticasone by metered-dose inhaler. WHich of the following instructions should the nurse include? ( C) p . 132 ch 22 a. Use fluticasone as needed for shortness of breath.- fluticasone used to treat inflammation. b. Limit fluid intake to 1 L per day. - drink plenty to avoid dehydration. 2-3 liters. c. Obtain a yearly influenza immunization. - reduce risk of infection. d. Assist use of pursed-lip breathing.- this is also one of the interventions the nurse does but the question ask about fluticasone. It is a steroid, and we all know steroids decresaes inflammation but also depress our immunue system. So getting a flu shot is priority. 12. A nurse is providing discharge teaching to an older adult client following a left total hip arthroplasty. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include in the teaching? a. “You can cross your legs at the ankles when sitting down.” -avoid flexion contraction b. “Clean the incision daily with hydrogen peroxide.”- soap and water c. “Install a raised toilet seat in your bathroom.” Pg 437 also use straight chairs with arms, abduction pillow between the legs, avoid low chairs, and flexion of hip greater than 90 degrees. NO crossing legs , no turing on operative side. d. “You should use an incentive spirometer every 8 hrs.”- once every hour at least 13. Missing 14. A nurse is caring for a client who is postoperative following a femur fracture. Which of the following findings should the nurse report to the provider immediately? a. The client reports shortness of breath - embolism ABCS p . 457 chapter 71 b. The client has a temperature of 38.1 C (100.5F) c. The clients incision is red and warm d. The client reports incision pain 15. A nurse is planning care for a client who Clostridium difficile gastroenteritis. Which of the following is an appropriate nursing action? P . 290 ch 46 pdf a. Place the client in a protective environment b. Obtain a stool specimen with gloves→ CONTACT ISO c. Clean surfaces with chlorhexidine-bleach D. Wash hands with alcohol-based hand rub. 16. A nurse is setting up a sterile field before performing a dressing change on client who is postoperative. Which of the following actions should the nurse plan to take to maintain the sterile field? (select all the apply) a. Grasp 2.5 cm (1 in ) of the outer edge to open the surgical wrap- 1 inch form broder is always non sterile so its ok to touch it . b. Select a work surface at the nurses waist level- body mchiancis . c. Apply sterile gloves before opening the pack- sterile package must be opened first before donning sterile gloves d. Open the first flap of the sterile package toward the nurse's body- must be AWAY first , then sides , then TOWARDS the nurse . e. Place a surgical pack with a sterile drape on the work surface. 17. A nurse is caring for a client who has acute appendicitis. Which of the findings is the priority to the provider? Ch 23 p . 143 PEDIATRICS pdf also p 944 lewis a. Nausea- has not burst b. Flank pain - normal c. Fever - has not burst d. Rigid abdomen - muscles contract because it exploded- can lead to rupture and infection also HR ELEVATED, shallow and rapid respirations, pulse is weak. . 18. A nurse is caring for a client who is receiving radiation. The client reports nauseas since the therapy was initiated. Which of the following considerations should the nurse include when planning the clients meals? P . 583 ch 91 also ch 16 p 269 of the lewis book a. Offer frequent, high-carbohydrate meals- several small meals a day is preffered. b. Offer highly seasoned foods- you want COLD , dry , foods. Cooking stimulates odors that lead to nausea. c. Offer a snack prior to radiation therapy- several small meals a day is recommended. d. Offer hot beverages with meals- hot foods can stimulate nausea. Beverage with meals leads to nausea. 19. A nurse is caring for a client who is receiving mechanical ventilation. Which of the following interventions should the nurse implement? (D) page 208-209 not sure which answer Empty water from the ventilator tubing daily. ( -INFECTION CONTROL: water that collects in the ventilator tubing can create a breeding ground for bacteria which may lead to VAP. Suction the client’s airway every 4 hr.(Suction every 2 hr and as needed. p.157) Maintain the client in supine position. (should reposition pt to help with secretions) Perform oral care every 2 hr.( you do oral care but not every 2hrs ) 20. A nurse in an emergency department is assessing a client who has cirrhosis of the liver. Which of the following is a priority finding? ( C) a. Palmar erythema b. Spider angiomas c. Mental confusion (RM 10 Ch.55 p.359 pdf - too much bilirubin in the blood went to the brain and now caused mental encephalopathy) d. Yellow Sclera 21. A nurse is preparing to administer bumetanide to a client who has heart failure. Which of the following assessment findings should indicate effectiveness of the medication a. Bowel sounds present in 4 quadrants on auscultation b. Alert and oriented to time place and person c. Lung sounds clear - it is Bumex d. Apical pulse 80 Rationale: MS RM 10 Ch.32 p.198-9 23. A nurse is caring for a client who has hypertension and has a new prescription for lisinopril. The nurse should consult with the provider about which of the following medication in the client's medication administration record? a. Potassium chloride ** found on medscape b. evothyroxine c. Acetaminophen d. Metformin Rationale: Pharm RM 7.0 Ch.20 p.151; Hyperkalemia is a complication for Lisinopril; avoid any salt substitutes containing K+. 24. A nurse is planning care for a client who is 1 day postoperative following an open cholecystectomy. Which of the following interventions should the nurse include in the plan or care? a. Avoid use of anticoagulants - use it b. Place pillow under client knees - stasis danger c. Discourage leg exercises while in bed - you need it d. Apply compression stocking in lower extremities Rationale: It’s common post-op, also, resume regular activity after 4-6 wks. 25. What interferes with warfarin therapy a. Potatoes (Potassium) Oranges (Vit C) b. Bananas (Potassium) c. Cauliflower - Huge Vitamin K remember veggies Rationale: Avoid any interaction with Vitamin K when on anticoagulant therapy, and dark, leafy veggies (or just any veggies) are THE source for it. 26. A nurse is administering furosemide 80 to a client with pulmonary edema. Which of the following assessment findings indicates the nurse that the medication is effective? P , 144 ch 19 pharm pdf a. Elevation in BP b. Adventitious breath sounds c. Weight loss of 1.8 kg (4lb) in the past 24 hr d. Respiratory rate of 24/min 27. A nurse is caring for a client who has Cushing’s disease. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect? Ch 80 page 518 a. Weight loss b. Hyponatremia- increased c. Hyperglycemia d. Hypercalcemia- DECREASED ERRYTHANG is UP except K+/Ca+, both HYPO 28. A nurse is monitoring a client who has receiving 2 units packed RBCs. Which of the following manifestations indicates a hemolytic transfusion reaction? (MS RM 10.0 Ch.40 p.250: chills, fever, low-back pain, tachycardia, flushing, hypotension, chest tightening or pain, tachypnea, nausea, anxiety, hemoglobinuria, and an impending sense of doom) a. Back pain b. Bradycardia- should be tachycardia c. Hypertension- hypotension it will cause. d. Chills 29. A PACU nurse is monitoring the drainage from a client’s NG tube following abdominal surgery. Which of the following findings in the first postoperative hour should the nurse report to the provider? a. 75 mL of greenish yellow drainage (Purulent) b. 100 mL of red drainage (Sanguineous/fresh bleeding) c. 200 mL of brown drainage (Purulent) d. 150 mL of serosanguineous drainage 30. A nurse is performing an admission assessment on a client who has severe chronic kidney disease. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect? MS RM 10.0 Ch.59 p.382 pdf a. Lethargy b. Potassium 4.0 mEq/L c. Hypotension- HTN due to fluid overload d. Serum creatinine 0.9 mg/dL- should be increased . Rationale: Expected findings include nausea, fatigue, lethargy, involuntary movement of legs, depression, and intractable hiccups. In most cases of chronic CKD, findings are r/t fluid overload, including both HTN and orthostatic hypotension. 31. Missing 32. A nurse is teaching a client who has hypothyroidism. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching? (select all the apply) pg. 886 med srg a. You will take medication for this condition for several months b. You will need to eat a high-fiber diet to prevent complications of this condition c. You might notice that you perspire more with this condition d. We will perform laboratory tests to monitor the effect of your medication e. This condition can cause you to gain weight. 33. A nurse is caring for a client who is receiving mechanical ventilation when the low pressure alarm sounds on the ventilator. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? P 113 ms ati pdf a. Empty water from the client’s ventilator tubing b. Evaluate the client for a cuff leak - check this first for cause of low pressure c. Suction the client’s airway d. Increase the client’s ventilator flow rate. 34. A nurse is reviewing laboratory results for four clients who are scheduled for surgery. Which of the following laboratory values should the nurse report to the surgeon? a. INR of 1.6 (Normal 1.0-2.0) b. Platelets 95,000/mm3 (low 150,000-350,000) c. Hct 42% (Normal 42%-52% men; 37%-47% women) d. WBC 8,000/mm3 (Normal 5,000-10,000/mm3) Rationale: MS RM 10.0 Ch.39 p.245; Normal labs 35. A nurse is assessing a client who is receiving valsartan to treat heart failure. Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as an indication that the medication is effective? a. Increased potassium level b. Decreased blood pressure ?? ** c. Increased heart rate ( pg 365 md srg valsartan is a afterload reducing agent, angiotensin receptor blocker ) d. Decreased urinary output 36. A nurse is providing teaching to a client following a liver biopsy 1 hour ago. Which of the following positions should the nurse instruct the client to maintain after the procedure??? P. 882 lewis medsurg a. Prone b. Supine c. Right lateral - with minimum 2 hours, with patient bed flat. d. Left lateral Rationale: ATI Capstone question; “Following a liver biopsy, the nurse should instruct the client to lie on the affected side for hemostasis to occur. The liver sits just under the rib cage on the right side of the abdomen.” 37. A nurse is providing discharge teaching to a client following a modified left radical mastectomy with breast expander. Which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching? MS RM 10.0 Ch.92 p.614 a. “I will have to wait 2 months before additional saline can be added to my breast expander” (tissue expanders have ports for additional injection of saline for gradual expansion & is encouraged) b. “I will perform strength building arm exercises using a 15 pound weight” (Squeeze a rubber ball, elbow flexion/extension, hand-wall climbing to promote full ROM and prevent lymphedema) c. “I should expect less than 25 ml of secretions per day in the drainage devices” d. “I will keep my left arm flexed at the elbow as much as possible” (Elbow flexion AND extension) 38. A nurse is teaching a client who has diabetes mellitus about foot care. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include? Ch 82 page 532 a. “Wash your feet twice per day with antibacterial soap and hot water” b. “Wear loose fitting slippers around the house” c. “Wear cotton rather than nylon sock” d. “Use a heating pad to keep your feet warm at night” 39. A nurse is caring for a client following the placement of a transverse colostomy. Which of the following findings indicates a possible complication? a. Client reports pain of 6 on scale from 0 to 10 b. Heart rate 110/min c. Bowel sounds hypoactive d. Stoma appears dry p. 602.. Stoma should be pink , moist , ischemia should be reported to the provider. 40. A nurse is counseling a client who has a family history of hypertension about reducing high risk for high blood pressure. Which of the following strategies should the nurse recommend? P .161 a. Engage is isometric exercises for 15 min daily b. Maintain a body mass index between 31 and 34 c. Lower total cholesterol level <200 mg/dL d. Increase dietary potassium intake 41. A nurse in the PACU is assessing a client who is postoperative following general anesthesia. Which of the following findings is the priority to address? P . 645 a. Piloerection of the skin b. Vomiting upon arousal c. Decreased body temperature- increases risk for wound infection, cardiac dysrhymias, altered absorpton of medication. d. Indistinct, rambling speech 42. A nurse is providing discharge teaching to the partner of a client who has a linear incision site following an open cholecystectomy. Which of the following wound care instructions should the nurse include? a. Change the dressing four times per day b. Use sterile gloves when performing the dressing change ??? ( they dont have to use sterile they can use clean gloves ) c. Clean from the incision to the surrounding skin d. Apply tincture of benzoin prior to removing the dressing 43. A nurse is preparing to administer vancomycin IV bolus to a client who has pneumonia. Which of the following clinical manifestations should the nurse instruct the client to monitor for and report? a. Pallor of the extremities b. Taste of metal in the mouth c. Halo of light around objects d. Ringing in the ears- ototoxic is vanco p 359 pharm ati pdf 44. A nurse is caring for a client who has pancreatitis and has been receiving total parenteral nutrition. Which of the following laboratory tests should the nurse monitor for overall nutritional status? a. Prealbumin b. C reactive protein c. Creatinine d. Lipase 45. A charge nurse is called to a client’s room after a staff nurse reports a client has had a wound evisceration. Which of the following actions should the charge nurse take? Page 650 MS ATI PDF 10.0 im stuck with c and d . its says with cover the wound with a sterile saline soaked towel or dressing a. Attempt to reinsert the protruding viscera- DO NOT ATTEMPT TO REINSERT ORGANS b. Obtain bottles of warm, sterile 0.9% sodium chloride solution = wouldn’t you want to get sterile solution for the dressing cover to put on the wound? c. Place the client in left lateral recumbent position- low fowlers hips knees bent (ati book p1111 “place in supine position with hips and knees bent”)= which is lithotomy position, not recumbent d. Apply a firm pressure dressing across the client’s abdomen <- in practice A/B. confirmed (p1111 ati book “cover wound with sterile dressing”--doesn’t mean apply firm pressure) 46. A nurse is caring for four clients. Which of the following clients is at risk for developing metabolic alkalosis? Pg 283 ati a. A client who is receiving continuous gastric suctioning b. A client who has aspiration pneumonia c. A client who is experiencing an opioid overdose- respiratory acidosis. d. A client who has uncontrolled diabetes mellitus 47. A nurse is caring for a client who is taking digoxin 0.125 mg PO daily and is at risk for developing digoxin toxicity. The nurse should monitor the client for an imbalance of which of the following electrolytes because it can increase the risk for digoxin toxicity? a. Calcium b. Potassium c. Magnesium d. Phosphatase Rationale: Digoxin level and Potassium levels are inversely correlated. So if you have less K+ your digoxin levels shots up leading to digoxin toxicity and if your K+ is high=digoxin level is low. 48. A nurse is assessing the abdominal wound of a client who is 3 days postoperative following a colon resection. Which of the following findings should the nurse report to the provider? a. Erythema (redness can be indicative of infection) b. Ecchymotic skin c. Drainage (expected for 3-4 days?) d. Edema ??? 49. A nurse is completing an admission assessment for a client. The nurse should expect the provider to prescribe which of the following medications for the client? EXHIBIT VITAL SIGNS: Temperature (98.3 F), HR (100/min), RR (20/min), BP (152/94mmHg) a. Atorvastatin b. Allopurinol c. Metoprolol d. levothyroxine 50. A nurse is assessing a client who is near the end of life following a head injury. The client has alternating periods of rapid breathing and apnea. The nurse should document this finding as which of the following respiratory patterns? page 75 ch 14 a. Biot’s respirations- quick shallow respirations followed by apnea. b. Hypoventilatory respirations- opoid overdose c. Kussmaul respirations- hyperglycemia d. Cheyne-Stokes respirations- occurs during INCREASED INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE 51. A nurse is administering a unit of packed RBCs to a client and notes that there are several small clots floating in the IV bag. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? a. Inject 5,000 units of heparin into the unit of packed RBCs b. Place the unit of packed RBCs in a warming unit for 5 min c. Return the unit of packed RBCs to the blood bank- return that shit d. Dilute the unit of packed RBCs using 50 mL of lactated Ringer’s 52. A nurse in a provider’s office is teaching a client about the self-management of GERD. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include? a. “Eat a light meal 1 hour before bedtime”- avoid eating before bedtime b. “Lie down for 30 minutes after each meal”- CANNOT BE SUPINE c. “Increase your caloric intake by 250 calories per day” d. “Sleep with the head of your bed elevated 6 inches”- Rationale: so your acid doesn’t hit your throat when you sleep pg 309 57. A nurse is providing teaching to a client and his partner about performing peritoneal dialysis at home. When discussing peritonitis, which of the following manifestations should the nurse identify as the earliest indication of this complication? a. Generalized abdominal pain b. Cloudy effluent c. Fever d. Increased heart rate Rationale: Peritonitis Assessment Findings : Rigid, board-like abdomen(hallmark), abd distention, N&V, Rebound tenderness, tachycardia, FEVER. 58. A nurse is caring for a client who is receiving enteral nutrition. Which of the following interventions by the nurse will prevent aspiration? a. Check the gastric pH following bolus feedings ( for verifying placement) b. Place the client in supine position before initiating feedings (No; 30 degree) c. Instruct the client to perform the Valsalva maneuver after feedings (no) d. Measure residual volume prior to bolus feedings Rationale: Nursing measures to prevent aspiration include verifying tube placement, checking gastric residuals, assessing bowel function to confirm peristalsis, and elevating the head of the patient’sbed to 30 degrees or more during feeding and at least 1 hour after feeding. Monitor fluid and electrolyte balance carefully; additional water may be prescribed based on the patient’s fluid status. Providing mouth care is particularly important for patients receiving enteral feedings, as is addressing the psychosocial aspects of care. 62. Client has a pressure ulcer. Which indicates wound healing? a. Light yellow exudate (Seropurulent) b. Wound tissue firm to palpation (firm, not healing yet) stage 1. c. Dry brown eschar (dead skin?) d. Dark red granulation tissue p . 330 fundamentals Ratonale: Red: Healthy regeneration of tissue Yellow: Presence of purulent drainage and slough Black: Presence of eschar that hinders healing and requires removal 63. STEPS to use of a peak flow meter a. “Stand upright” 1 b. “Seal your lips around the mouth piece”3 c. “Fill your lungs with a deep breath”2 d. “Exhale forcefully and quickly”4 e. “Record the highest of three consecutive readings”5 Rationale: A,C,B,D,E 1. Stand up or sit up straight. 2. Make sure the indicator is at the bottom of the meter (zero). 3. Take a deep breath in, filling the lungs completely. 4. Place the mouthpiece in your mouth; lightly bite with your teeth and close your lips on it. Be sure your tongue is away from the mouthpiece. 5. Blast the air out as hard and as fast as possible in a single blow. 6. Remove the meter from your mouth. 7. Record the number that appears on the meter and then repeat steps one through seven two times. 8. Record the highest of the three readings in an asthma diary. This reading is your peak expiratory flow (PEF). 67. Client, who is 6 hr postoperative following application of an external fixator for a tibial fracture. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? a. Palpate the dorsalis pedis pulse. b. Maintain the affected extremity in a dependent position (ELEVATE) c. Wrap sterile gauze on the shart point of the pins (NOPE 8-12HRS) d. Adjust the clamps on the fixator flame (NEVER, MD DOES THIS) Rationale: Elevate extremity, Monitor neurovascular status and skin integrity, Assess body image, Perform pin care every 8 to 12 hr, Monitor site for drainage, color, odor, redness, Observe for manifestations of fat and pulmonary embolism, Provide antiembolism stockings and sequential compression device to prevent deep-vein thrombosis (DVT). 68.) A nurse is preparing an in-service presentation about the use of automated external defibrillators (AEDs). Which of the following instructions should the nurse include in the teaching? a. “Perform CPR while the AED is analyzing”-cannot due b/c analysis will be wrong b. “Position the client on a flat surface” c. “Set the AED to 80 joules” (should be 200 joules) d. “Use an AED for a client who has A-fib” (AED is for V-fib & V-tach) Rationale: Process of Elimination and Think. 69. Serum sodium level of 120 mEq/L. Which of the followings findings should the nurse expect? P . 271 a. Hyperreflexia - Decreased DTRs b. Decreased bowel sounds - increased motility , ab cramping, nausea. c. Confusion** d. Increased central venous pressure- Rationale: MANIFESTATION OF HYPONATREMIA :Weakness, Lethargy, CONFUSION, Seizures, Headache, Anorexia, N&V, Muscle Cramps, twitching, Hypotention, Tachycardia, Wt gain and Edema. 271 MS pdf also, headache, lethargy, muslce wekaness to the point of respiratory cimpromise, decreased DTRs, seizures, light headed , dizzy, 70. Pt. taking isoniazid and rifampin, which understands? a. “I will be finished with this medication regimen in 3 months” -9 months b. “I should check the whites of my eyes while taking these medications” - very hepatotoxic c. “I should take my mediation with an antacid if it upsets my stomach” (Taking antacid would decrease effectiveness of the medication so it is not advised or SHOULD not take it during treatment) d. “I will no longer be infectious after two consecutive negative sputum specimens” (THREE) Rationale: Assess for toxicity because both medication are very toxic you are at risk for hepatotoxicity. Other choices are WRONG, Eliminate it. 72. The use of incentive spirometer. a. Position the mouthpiece 2.5cm (1 in) from the mouth (put in ur mouth) b. Place hands on the upper abdomen during inhalation (no hold spirometer) c. Hold breaths about 3-5 secs before exhaling (repeat) d. Exhale slowly through purse lips (With Purse lip breating not Spirometer) Rationale: The client who is using the spirometer should take in a deep breath and hold it for 3 to 5 seconds before exhaling. As the client exhales, the needle of the spirometer rises. This promotes lung expansion. (per ATI med surg) 1. Sit on the edge of your bed if possible, or sit up as far as you can in bed. 2. Hold the incentive spirometer in an upright position. 3. Place the mouthpiece in your mouth and seal your lips tightly around it. 4. Breathe in slowly and as deeply as possible. Notice the yellow piston rising toward the top of the column. The yellow indicator should reach the blue outlined area. 5. Hold your breath as long as possible. Then exhale slowly and allow the piston to fall to the bottom of the column. 6. Rest for a few seconds and repeat steps one to five at least 10 times every hour. 7. Position the yellow indicator on the left side of the spirometer to show your best effort. Use the indicator as a goal to work toward during each slow deep breath. 8. After each set of 10 deep breaths, cough to be sure your lungs are clear. If you have an incision, support your incision when coughing by placing a pillow firmly against it. 9. Once you are able to get out of bed safely, take frequent walks and practice the cough. 73. Pt. who is in septic shock. Which lab findings indicate the patient is developing “multiple organ dysfunction syndrome”? a. Arterial hypoxemia (low / no O2 manifestation of MODS) b. Decreased liver enzymes- Increased c. Decreased BUN - Increased d. Hypoglycemia - body response = increase to save body Rationale: MODS can develop from severe hypotension and reperfusion of ischemic cells, causing further tissue injury. Inadequate tissue perfusion can cause organ failure in the lungs (adult respiratory distress syndrome), kidneys, heart (decreased coronary artery perfusion, decreased cardiac contractility), and the gastrointestinal tract (necrosis).. So MODS happends when no O2 is being delviered 75. A nurse is reviewing a client’s laboratory values and notes a potassium level of 2.8 mEq/L. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect? a. Hyperactive bowel sounds (Hypoactive) b. Increased blood pressure (Hypotension) c. Irregular pulse d. Exaggerated reflexes (CM of Hyperkalemia) Rationale: Manifestion of Hypokalemia: IRREGULAR PULSE, Muscle weakness and cramping, Fatigue, Nausea, Vomiting, Irritability, Confusion, Decrease Bowel sound, Paresthesia, Dysrhythmias, Flat/ inverted T wave, 76. A nurse is caring for a client who is admitted to the medical-surgical unit with a seizure disorder. Which of the following interventions should the nurse include in the plan of care? a. Teach assistive personnel how to apply restraints --> do not attempt to restrain the client b. Keep the side rails in a down position → a) side- rails up with padding to prevent injury c. Keep a padded tongue blade at the client’s bedside → do not use padded tongue blades. d. Maintain peripheral IV access. RATIONALE: ATI MS ATI MS 36 Priority: Maintain peripheral IV access in case of emergency may administer diazepam, or lorazepam IVP followed by IV phenytoin or fosphenytoin. side- rails up with padding to prevent injury 77. A nurse is collecting a medical history from an older adult client who has hypertension and new prescription of nadolol. Which of the following findings should the nurse report to the provider? a. cataracts b. GERD c. Asthma d. Hypothyroidism RATIONALE: ATI PHARM 263 Avoid in clients who have asthma. Bronchoconstriction effect. And if you guys could remember about the JNC8 per Tiamson. 78. A nurse is preparing a client for a Lumbar puncture. Which of the following images indicates the position the nurse should assess the client into for this procedure? (Here are some of the choices) But the correct one is FETAL POSITION. ➔ FETAL POSITION or SITTING FORWARD ON THE TABLE. (ATI MS 21) 78. A nurse is caring for a client who has a diabetes mellitus. The client’s ABG are ph 7.14, PaO2 90 mmHg, PaCO2 35 mmHg, and HCO3 4 mEq/L. The nurse should identify that the client has which of the following acid-base imbalances? a. Respiratory acidosis b. Metabolic alkalosis c. Respiratory alkalosis d. Metabolic acidosis RATIONALE: ATI MS pH 7.35- 7.45 7.14 Acidosis CO2 35-45 35 compensating HCO3 22-26 4 metabolic 80. A nurse is planning care for a client who has developed nephrotic syndrome. Which of the following dietary recommendations should the nurse include? a. Increase Phosphorus b. Increase Potassium c. Decrease protein intake d. Decreased carbohydrate intake. à Increased carbs is what you want RATIONALE: ATI MS Nephrotic syndrome = kidney disorder characterized by massive proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia & edema AVOID excess protein, high amounts of FAT, & minimize Na → more fluid retention 81. A nurse is planning care for a client who has new diagnosis of acute pancreatitis. Which of the ff interventions should the nurse include in the plan of care? a. Administer antihypertensive meds b. Maintain the client on NPO status c. Place client in supine position d. Monitor the client for hypercalcemia RATIONALE: ATI MS 348 NPO: no food until pain-free 82. A nurse is assessing a client who has increased intracranial pressure. The nurse should recognize that which of the following is the first sign of deteriorating neurological status? a. Altered level of consciousness b. Pupillary constriction c. Decorticate posturing d. Cheyne-stokes respirations RATIONALE: ATI MS 19 All manifestation of ICP. But FIRST sign of deteriorating neurological status is ALOC → pupillary constriction → cheyne posturing → Cheyne-stokes respirations. You may use Glasgow coma scale to assess neurological status. 83. A nurse is obtaining a medication history from a client who is to start therapy with naproxen for rheumatoid arthritis. Which of the following medications places the client at risk for bleeding? a.) Captopril → Ace Inhibitor b.) Ibuprofen → NSAIDS c.) Digoxin → antidysrhythmic d.) Phenytoin → anticonvulsant RATIONALE: ATI MS 84. A nurse is caring for an older adult client who is suspected of having septicemia. Which of the following actions is the nurse’s priority? a. Obtain a WBC count with differential b. Obtain a history to determine recent injuries. c. Obtain a blood specimen of culture and sensitivity testing d. Obtain a broad-spectrum antibiotic for rapid administration. RATIONALE: ATI MS 85. A nurse is assessing a client following a kidney biopsy. Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as an indication that the client is experiencing internal bleeding? a. Bradycardia→ Tachycardia, Hemorrhaging b. Polyuria → Urgency, complications c. Flank Pain d. Increase Blood Pressure→ Hypotension, Hemorrhaging RATIONALE: ATI MS 144 Monitor for internal bleeding (measure abdominal girth and abdominal or flank pain) at least Q8hr. TBC 86. A nurse is caring for a client who has diabetes insipidus and has had a urinary output of 3,000 ml in the past 12 hr. which of the following medications should the nurse expect to administer to the client? a. Dopamine b. Desmopressin acetate c. Furosemide d. Spironolactone RATIONALE: ATI Pharm 532 ATI MS 499 Diabetes insipidus has deficiency of ADH. Manifestation of 3 P’s: polyuria, polyphagia, and polydipsia. Administer ADH (desmopressin) to stop polyuria and prevent dehydration. 87. A nurse is admitting a client to a medical unit following placement of a permanent pacemaker. Which of the following findings requires further assessment by the nurse? a. Sneezing b. Presence of a sharp spike prior to the QRS complex on the ECG c. Hiccups d. Presence of intrinsic P waves following a QRS complex on the ECG RATIONALE: ATI MS 177 Assess for hiccups, which can indicate that the generator is pacing the diaphragm. 88. A nurse is caring for a client receiving TPN who weighs 160Lb. If the RDA of protein is 0.8g/kg of body weight. How many g of protein should the client receive? 160 lbs/2.2 = 72.72 kg 0.8 g x 72.72 kg= 58g 89. A nurse is caring for a client who has an arteriovenous graft. Which of the following findings indicates adequate circulation of the graft? (D) a. Dilated appearance of the graft b. Normotensive blood pressure c. Absence of a bruit d. Palpable thrill RATIONALE: ATI MS Adequate circulation of the graft has manifestation of palpable thrill arterial and venous, indicates good blood flow and patency. 90. A nurse is providing discharge teaching for a client who is receiving treatment for genital herpes. Which of the following indicates effective of the teaching? a. I should expect my lesions to resolve in 6 weeks b. I should expect to take my medication for 3 weeks c. I should use natural skin condoms during sex. → Avoid SEX d. I should apply antibiotic ointment to lesions. → Acyclovir – antiviral medication RATIONALE: ATI MS 91. A nurse is caring for a client who has a history of chemotherapy-included nauseas and vomiting. Which of the following medications should the nurse administer prior to chemotherapy? a. Ondansetron b. Sertraline c. Diphenhydramine d. Methylprednisolone RATIONALE: ATI MS 581 Serotonin blockers, such as ondansetron, have been found to be effective and are often administered with corticosteroids, phenothiazines, and antihistamines 92. A nurse is preparing to administer daily medications to a client who is undergoing procedure at 1000 that req IV contrast dye. Which of the following routine meds to give at 0800 should the nurse withhold? a. Metoprolol b. Metformin c. Fluticasone d. Valproic Acid RATIONALE: ATI MS 364 Withhold METFORMIN for 24 hr. before the procedure (risk for lactic acidosis from contrast dye with iodine). 93. A nurse is preparing to assist with the insertion of a non-tunneled central venous catheter for a client who is malnourished. Which of the following actions should the nurse plan to take? a. Confirm the correct position of the line by obtaining a blood sample. - Xray b. Instruct the client to cough as the catheter is inserted. - Cough may shift vessels = danger c. Place the head of the client’s bed lower than the foot. d. Cleanse the site with a hydrogen peroxide solution.- chlorhexidine RATIONALE: ATI MS For central line insertion, tubing change, and line removal, place the client in the Trendelenburg’s position if not contraindicated or in the supine position, and instruct the client to perform the Valsalva maneuver to increase pressure in the central veins when the IV system is open. 94. A nurse is caring for a client who has hypervolemia. Which of the following is an expected assessment finding? a. Hypotension → HYPERTENSION Weight gain→ due to the build of peripheral edema Bradycardia → TACHYCARDIA Loss of skin turgor → this happened when you’re dehydrated. RATIONALE: ATI MS 267 Hypervolemia, as there is excess fluid in the extracellular space. Other signs: peripheral edema due to an excess of fluids within the body and lungs, resulting in weight gain, distended neck veins, and increased urine output. 95. A nurse is reviewing discharge teaching with a client with a client who has a new prescription for warfarin. Which of the following client statements indicates an understanding of the teaching? A. “I know the medication increases my risk for blood clots.” B. “I should avoid taking ibuprofen while taking this medication.” C. “I will increase green leafy vegetables in my diet.” D. “I will return in 1 month to have my blood tested.” Rationale page 143: Warfarin is an anticoagulant. Use to prevent blood clots from getting larger or additional clots from forming. Needs weekly blood draws, not monthly. Do not increase intake in foods high in vitamin K (green leafy vegetables). Vitamin K reduces the anticoagulant effects of warfarin. Aspirin and ibuprofen should not be used as painkillers when taking on warfarin because it increases risk for bleeding and bruising. 96. A nurse is caring for a client who has glaucoma. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect? a. The client reports loss of peripheral vision. b. The client’s eyes are watery c. The client’s pupils are constricted. d. The client reports dark floaters in the affected eye. Rationale: page 65. Glaucoma us a disturbance of the functional or structural integrity of the optic nerve. Decreased fluid drainage or increased fluid secretion increases intraocular pressure (IOP) and can cause atrophic changes of the optic nerve and visual defects. Expected reference range for IOP is 10-21 mm/Hg. ● Two types of glaucoma: ○ Open-angle glaucoma: MORE COMMON. Refers to the angle between the iris and the sclera. The aqueous humor outflow is decreased due to blockages in the eye’s drainage system, causing a rise in IOP. ■ Expected findings: HA, mild eye pain, LOSS OF PERIPHERAL VISION, decreased accommodation, halos seen around lights, elevated IOP ○ Angle-closure glaucoma: IOP rises suddenly. The angle between the iris and the sclera closes suddenly which causes the IOP to increase. NEEDS IMMEDIATE TREATMENT. ■ Expected findings: radif onset of elevated IOP, decreased or blurred vision, colored halos seen around lights, pupils nonreactive to light, severe pain and nausea, and photophobia. 97. A nurse is planning care for a client who has left-sided hemiplegia following a stroke. Which of the following actions should the nurse include in the plan of care? a. Remind the client to use a cane on his left side while ambulating. b. Provide the client with a short-handled reacher. c. Position the bedside table on the client’s left side. d. Place a plate guard on the client’s meal tray. Rationale: place beside table near the patient’s bed on the unaffected side. 99. A nurse is planning to flush an implanted port for a client who is receiving chemotherapy. Which of the following supplies should the nurse plan to use? a. A short peripheral catheter b. A winged infusion needle c. A non-coring needle d. A large-bore needle Rationale: page 166. Access with a noncoring (Huber) needle 100. A nurse is providing discharge teaching to a client who has heart failure and instructs him to limit sodium intake to 2 g per day. Which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching? “I can have mayonnaise on my sandwiches.” 105 mg “I can drink vegetable juice with a meal.” 141 mg “I can season my foods with garlic and onion salts.” “I can have a frozen fruit juice bar for dessert.” 4 mg 101. A nurse in the emergency department is evaluating a young adult client for bacterial meningitis. Which of the following actions should the nurse take as part of the focused assessment? A. Run tongue blade on the outside of the client’s sole and note any flaring of the toes. B. Tap the facial nerve and note any facial twitching - chvostek signs (low Ca) C. Strike the clients patellar tendon with a percussion hammer and note any increase in response D. Gently elevate the client's head and note any nuchal rigidity. Rationale: page 31 Med Surg 2016 → PRIORITY TWO (*did this one*) 1. A nurse is assessing a client who is 12hr postoperative following a colon resection. Which of the following findings should the nurse report to the surgeon? a. Heart rate 90/min b. Absent bowel sounds c. Hgb 8.2 g/dl d. Gastric pH of 3.0 Rationale: Normal Hgb is 13-18M g/dl, 12-16 g/dl. This may indicate a possible hemorrhaging. Since it is 12 hours postoperative there might be absent bowel sounds (normal), but after 24 hours and if there are absent bowel sounds after drinking and eating = should be a concern. 2. A nurse is caring for a client who has diabetes insipidus. Which of the following medications should the nurse plan to administer? a. Desmopressin b. Regular insulin c. Furosemide d. Lithium carbonate Rationale: Diabetes Insipidus has decreased ADH. Administer Desmopressin/Vasopressin increase ADH and to stop patient on urinating. 3. A nurse is admitting a client who has arthritic pain and reports taking ibuprofen several times daily for 3 years. Which of the following test should the nurse monitor? a. Fasting blood glucose b. Stool for occult blood c. Urine for white blood cells d. Serum calcium Rationale: ATI Pharm 16. Pg. 485 Ibuprofen (NSAIDs) monitor for GI bleed (bloody, tarry stools, abdominal pain). 4. A nurse in the emergency department is assessing a client. Which of the following actions should the nurse take first (Click on the “Exhibit” button for additional information about the client. There are three tabs that contain separate categories of data.) a. Obtain a sputum sample for culture b. Prepare the client for a chest x-ray c. Initiate airborne precautions d. Administer ondansertron. Rationale: No idea what the Exhibit is all about; won’t be able to answer it. 5. A nurse is contacting the provider for a client who has cancer and is experiencing breakthrough pain. Which of the following prescriptions should the nurse anticipate? a. Transmucosal fentanyl b. Intramuscular meperidine c. Oral acetaminophen d. Intravenous dexamethasone Rationale: ATI pg. 27 Morphine sulfate and fentanyl are opioid agents used to treat moderate to severe pain. A short-acting pain medication is administered for breakthrough pain. 6. A nurse is admitting a client who reports chest pain and has been placed on a telemetry monitor. Which of the following should the nurse analyze to determine whether the client is experiencing a myocardial infarction? a. PR interval b. QRS duration c. T wave d. ST segment Rationale: ST elevation indicates MI. ST depression indicates ischemia 7. A nurse is teaching a client who has ovarian cancer about skin care following radiation treatment. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include? a. Pat the skin on the radiation site to dry it b. Apply OTC moisturizer to the radiation site c. Cover the radiation site loosely with a gauze wrap before dressing d. Use a soft washcloth to clean the area around the radiation site Rationale: pg. 584. Dry the area thoroughly using patting motions. 8. A nurse is caring for a client who is receiving a blood transfusion. The nurse observes that the client has bounding peripheral pulses, hypertension, and distended jugular veins. The nurse should anticipate administering which of the following prescribed medications? a. Diphenhydramine b. Acetaminophen c. Pantoprazole d. Furosemide Rationale: S/S may indicate fluid retention or heart failure. It is important to administer diuretics to prevent cardiovascular/respiratory distress. 9. A nurse is assessing a client who is receiving magnesium sulfate IV for the treatment of hypomagnesemia. Which of the following findings indicates effectiveness of the medication? a. Lungs clear b. Apical pulse 82/min c. Hyperactive bowel sounds d. Blood pressure 90/50 mm Hg Rationale: pg. 278 Confirmed on answer sheet 10. A nurse is reviewing a client’s ABG results pH 7.42, PaC02 30 mm Hg, and HCO3 21 mEq/L. The nurse should recognize these findings as indication of which of the following conditions? a. Metabolic acidosis b. Metabolic alkalosis c. Compensated respiratory alkalosis d. Uncompensated respiratory acidosis Rationale: because the HCO3 21 trying to compensate for respiratory alkalosis. 11. A nurse is caring for a client who has a deep partial thickness burns over 15% of her body which of the following labs should the nurse expect during the first 24 hours? A. Decreased BUN (elevated due to fluid loss) B. Hypoglycemia (High due to stress) C. Hypoalbuminemia (Low due to fluid loss) D. Decreased Hematocrit (Elevated due to 3rd spacing during resuscitation phase) Rationale: Pg. 481 ATI. Total protein and albumin- low due to fluid loss. 12. A nurse is caring for a client who has dumping syndrome following a gastrectomy, which of the following actions should the nurse takes? a. Offer the client high carbohydrate meal options (High fat, high protein, low fiber, low to moderate carbs page 317, chapter 49 Peptic ulcer disease med surge ATI PDF 10.0) b. Provide the client with four full meals a day (Small frequent meals) c. Encourage the client to drink at least 360 ml of fluids with meals (Eliminate liquids with meals for 1 hr. prior and following a meal) d. Have the client lie down for 30 minutes after meals (Lying down after a meal slows the movement of food within the intestines) Rationale: ATI pg. 318 Dumping syndromes is a term that refers to a constellation of vasomotor symptoms that occurs after eating, especially following a Billroth II procedure. Early manifestations usually occur within 30 minutes of eating and include vertigo, tachycardia, syncope, sweating, pallor, palpitations, and the desire to lie down. The nurse should instruct the client to decrease the amount of fluid taken at meals and to avoid high-carbohydrate foods, including fluids such as fruit nectars; to assume a low-Fowler's position during meals; to lie down for 30 minutes after eating to delay gastric emptying; and to take antispasmodics as prescribed. 12. A nurse is teaching a group of young adult clients about risk factors for hearing loss. Which of the following factors should the nurse include in the teaching? a. Born with a high weight b. Chronic infections of the middle ear c. Use a loop diuretic diuretic such as furosemide and antibiotics like aminoglycoside and gentamicin leads to ototoxic medication d. Perforation of the ear drum e. Frequent exposure to low volume noise Rationale: Pedia ATI pg. 77 Exposure to loud environmental sounds. Hearing defects can be caused by a variety of conditions, including anatomic malformation, maternal ingestion of toxic substances during pregnancy, perinatal asphyxia, perinatal infection, chronic ear infection, and ototoxic medications. 13. A nurse is preparing to administer fresh frozen plasma to a client. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? a. Administer the plasma immediately after thawing b. Transfuse the plasma over 4 hour (Can be in 2 to 4 hours) c. Hold the transfusion if the client is actively bleeding (YOU HAVE TO GIVE IT. That’s the whole point! The patient is losing blood so you have to replace it. We give fresh frozen plasma because he or she may have clotting deficiencies) d. Administer the transfusion through a 24 gauge saline lock (Has to be a 18 or 20 gauge) Rationale: Saunders pg. 164 Fresh-frozen plasma 1. Fresh-frozen plasma may be used to provide clotting factors or volume expansion; it contains no platelets. 2. Fresh-frozen plasma is infused within 2 hours of thawing, while clotting factors are still viable, and is infused over a period of 15 to 30 minutes. 3. Rh compatibility and ABO compatibility are required for the transfusion of plasma products. 4. Evaluation of an effective response is assessed by monitoring coagulation studies, particularly the prothrombin time and the partial thromboplastin time, and resolution of hypovolemia. 14. A nurse is assessing a client who reports numbness and tingling of his toes and exhibits a positive TROUSSEAU. Which of the following electrolyte imbalance should the nurse suspect? a. Hyponatremia b. Hyperchloremia c. Hypermagnesemia d. Hypocalcemia Rationale: (ch 44 page 277 MS ATI PDF 10.0) Positive s/s of CHvostek’s or Trousseau sign indicates HYPOCALCEMIA. 15. A home health nurse is teaching a client how to care for a peripherally central catheter in his right arm. Which of the following statements should the nurse include in the teaching? a. Change the transparent dressing over the insertion site every 48 hours - transparent dressing can be up to 7 days b. Clean the insertion site with mild soap and water - when showering, must insertion site must be covered!!!!! No water can be in it. c. Measure your right arm circumference once weekly- does not say in the chapter d. Use a 10 milliliter syringe when flushing the catheter Rationale: (Chapter 27 cardiovascular diagnostics and therapeutic procedures p. 166 MS ATI PDF 10.0) Use transparent dressing to allow for visualization. Follow facility protocol for dressing changes, usually every 7 days and when indicated (wet, loose, soiled). Shower, cover dressing site to avoid water exposure. Follow the Infusion Nurses Society (INS) practice recommendations for flushing. Use a 10 mL syringe for flushing the PICC line. Do not apply force if resistance is met. 16. A nurse is caring for a client who has a central venous access device. Which of the following assessment findings should the nurse report to the provider? a. RBC count of 4.7 million/mm (4.5-5.3M; 4.1-5.1) b. BUN 22-mg/ dl – (5-25 mg/dl) 10-20 c. WBC count of 16,000/ mm 3 à Elevated; phlebitis is a complication; infection is a complication that can happen 7 days after insertion, also temp increase if 1 degree can happen (5,000-10,000) d. Blood glucose of 120 mg/dl (70-110) Rationale: (P.166 MS ATI PDF 10.0) 17. A nurse is providing dietary teaching to a client who has chronic kidney disease and a decreased glomerular filtration rate. Which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching? a. I will spread my protein allowances over the entire day b. I should increase my intake of canned salmon to three times per week (NO SODIUM) c. I will season my food with lemon pepper rather than salt (We do not want to give the dietary sodium, potassium, phosphorus, and magnesium. I don’t know what lemon pepper has, but we want to RESTRICT sodium, potassium, phosphorus and magnesium.) d. I should limit my intake of hard cheese to 3 ounces each day (NO SODIUM) Rationale: (p.382 chapter 59) Rationale: ATI MS pg. 382-control protein intake based on the client’s stage of CKD and type of dialysis. Restrict sodium intake to prevent fluid retention and hypertension Low GFR indicates CRD. 18. A nurse is caring for a client who has a peripherally inserted central catheter. The client is receiving an antibiotic via intermittent IV bolus. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? a. Administer 20 ml of 0.9 sodium chloride after each dose of medication à (you only flush with 10 ml of NS, not 20. 20 is for flushing blood) b. Flush the catheter using a 5 ml syringe à you use a 10mL syringe to flush c. Verify the placement with an x-ray prior to the initial dose (POSTPROCEDURE) d. Change the transparent membranes dressing daily (dressing can last for up to 7 days) Rationale: (PAGE 166 ch 27 MS ATI PDF 10.0 19. A nurse is teaching a client using a metered dose rescue inhaler. Which of the following statements should the nurse include in the teaching? a. Do not shake your inhaler before use à shake 5-6x. b. Exhale fully before bringing the inhaler to your lips c. Depress the canister after you inhale (depress the inhaler as the patient inhales to go in the lungs). d. Use peroxide to clean the mouthpiece if your inhaler (mild soap and water) Rationale: Pharm ATI pg. 7 Review TABLE for administration of MDI. For an MDI, instruct the client to: ».Remove cap from inhaler. ».Shake inhaler five to six times. ».Hold inhaler with mouthpiece at the bottom. ».Hold inhaler with thumb near mouthpiece and index and middle fingers at top. ».Hold inhaler approximately 2 to 4 cm (1 to 2 in) away from front of mouth. ».Take a deep breath, and then exhale. ».Tilt head back slightly, and press inhaler. While pressing inhaler, begin a slow, deep breath that should last for 3 to 5 seconds to facilitate delivery to the air passages. ».Hold breath for 10 seconds to allow medication to deposit in airways. ».Take inhaler out of mouth, and slowly exhale through pursed lips. ».Resume normal breathing. 20. A nurse is assessing the pain status of a group of clients. Which of the following findings indicate a client is experiencing referred pain? a. A client who has angina reports substernal chest pain b. A client who has pancreatitis reports pain in the left shoulder à referred pain is pain that is felt in another place that is not in the same area as where the pain should be felt. Pain radiates on a certain location of the body. c. A client who is postoperative reports incisional pain d. A client who has peritonitis reports generalized abdominal pain Rationale: ATI MS (page 30) Visceral: in internal organs such as the stomach or intestines. It can cause referred pain in other body locations separate from the stimulus. 21. A nurse is caring for a client who has just returned from surgery with an external fixator to the left tibia. Which of the following assessments findings requires immediate intervention by the nurse? a. The client reports a pain level of 7 on a scale from 0 -10 at the operative site. (The patient just came from surgery so pain is normal for post op patients for first couple of hours.) b. The client’s capillary refill in the left toe is 6 seconds signs and symptoms of compartment syndrome à ABCs are compromised. (Cap refill should be below 3 seconds. This is s/s for compartment syndrome. Untreated can lead to necrosis.) c. The client has an oral temperature of 38.3 (100.9 F) (I wouldn’t pick this because i always see temp 101 as a priority from previous rationales with other atis.) d. The client has 100 ml of blood in the closed suction drained. (I believe this is normal for post-op patients.) Rationale: (p .456 MS ATI PDF 10.0 chapter 71) Assess 5 P’s: pain, paralysis, paresthesia, pallor, pulselessness 22. A nurse is assessing a client who has acute pancreatitis and has been receiving total parenteral nutrition for the past 72 hours. Which of the following findings requires the nurse to intervene? a. Right upper quadrant pain (patient has acute pancreatitis, so it’s normal) b. Capillary blood glucose level of 164 mg/dl - glucose not significantly high c. WBC counts 13,000/mm3 (Infection is one complication of TPN administration d. Crackle in bilateral lower lobes (Priority, FVE/fluid shifts to the lungs may lead to respiratory distress/collapse/failure) life threatening than infection. May need to decrease ml/hr and assess. Rationale: (chapter 47 page 299 MS ATI PDF 10.0) (ABC’s compromised, also one of the complications of TPN is fluid imbalance aka fluid volume excess.) 23. A nurse is caring for a client who has hypotension, cool and clammy skin, tachycardia, and tachypnea. In which of the following positions should the nurse place the client? a. Reverse Trendelenburg (page 232 says for hypotension patients must be flat with legs elevated to increase venous return.) b. Side Lying c. High Fowlers d. Feet elevated Rationale: Manifestations of Heart failure/Cardiogenic Shock Pg. 195. Chapter 31 MS ATI PDF 10.0) 24. A nurse is caring for a client who has tuberculosis and is taking rifampin. The client reports that her saliva has turned red- orange in color. Which of the following responses should the nurse make? a.) “This finding may indicate possible medication toxicity” b.) “Your provider will prescribe a different medication regimen” c.) “This is an expected adverse effect of this medication.” d.) “You will need to increase your fluid intake to resolve this problem” Rationale: pg. 137 ATI MS Expected to be orange in rifampin: urine/secretions 25. A nurse is preparing to administer a unit of packed RBCs for a client who is receiving a continuous IV infusion of 5% dextrose in water. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? a.) Administer the unit through secondary IV tubing (Y-ports) b.) Verify the blood product with assistive personnel (another RN) c.) Begin an IV infusion of 0.9% sodium chloride d.) Insert another 22-gauge IV catheter (18-20 gauge is recommended. 22 is too small) Rationale: ATI Pharm pg. 355 Insert an intravenous (IV) line and infuse normal saline; maintain the infusion at a keep-vein-open rate. An 18- or 19-gauge IV needle will be needed to achieve a maximum flow rate of blood products and to prevent damage to red blood cells; if a smaller gauge needle must be used, red blood cells may be diluted with normal saline (check agency procedure). Use only 0.9% sodium chloride solution to administer with blood products; prime IV and blood tubing with this solution. Use a blood filter for most blood products and either a Y-type or straight tubing set depending on facility policy. 26. A nurse is planning care for a client who is 12 hr. postoperative following a kidney transplant. Which of the following actions should the nurse include in the plan of care? a.) Check the client’s blood pressures every 8 hr. b.) Administer opioids PO c.) Assess urine output hourly ---à prevent shock and mods d.) Monitor for hypokalemia as a manifestation of acute rejection Rationale: Pg. 374 28. A nurse is obtaining a medication history from a client who is to start therapy with naproxen for rheumatoid arthritis. Which of the following medications places the client at risk for bleeding? a.) Captopril –ace inhibitor b.) Ibuprofen --NSAIDS c.) Digoxinà antidysrhythmic d.) Phenytoin-seizure 30. A nurse is assessing the extremities of a client who has Raynaud’s disease. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect? a.) Blanching of the hands à REYNAUD PHENOMENON b.) Hyperactive reflexes c.) Calf pain with foot dorsiflexion d.) Vitiligo on affected extremities Rationale: (P 558 at i MD pdf 10.0) Epiosodic vasospasm in the small peripheral arteries and arterioles, precipitated by exposure to cold or stress usually affects the hands or less often the feet. CREST Calcinosis- calcium deposits in the skin Raynaud phenomenon- spasm of blood vessels in response to cold or stress Esophageal dysfunction- acid reflux and decease in mortility of esophagus Scierodactyly- thickening and tightening of the skin on the fingers and hands Telangiectasias- dilation of capillaries causing red marks on surface of skin. 31. A nurse is caring for a group of clients. The nurse should obtain a blood pressure reading using only the left extremity from which of the following clients? a. A client who has a peripherally inserted central catheter in the left arm b. A client who has left-sided Bell’s palsy c. A client who has a right upper extremity arteriovenous fistula (always use opposite arm from an AV fistula) d. A client who has right-sided weakness due to Parkinson’s disease 32. A nurse is providing teaching to a client who has DVT. Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as a risk factor for the development of DVTs? a. Hypertension b. Cirrhosis c. NSAIDS use d. Oral Contraceptive Use Rationale: page 141 of ATI Book 2016 33. A nurse is caring for client who has Cushing’s disease. Which of the following actions should the nurse takes first? (Click Exhibit button for additional information) a. Check the client’s medication administration record for antihypertensive medication. b. Verify the client’s understanding of sodium restriction. c. Auscultate the client’s lung sound -à due to fluid retention; action first varies on the exhibit d. Determine the need for further glucose monitoring Rationale: cushings disease:increase in cortisol. Hyperglycemia, obesity, striae, moon round face, osteoporosis, buffalo hump, gynecomastia, bruise easily, fluid retention, hypertension 34. A nurse is assessing a client who has nephrotic syndrome. Which of the findings should the nurse expect? a. Proteinuria b. Flank pain c. Hyperalbuminemia d. Hypotension Rationale: Lewis book page 1075. Clinical manifestation of N.S.: peripheral edema, massive proteinuria, HTN, hyperlipidemia, and hypoalbuminemia. 35. A nurse is assessing a client who has right-sided heart failure. Which of the following assessment findings should the nurse expect to find? a. Oliguria (Left) b. S3/S4 galloping heart sounds (Left) c. Poor skin turgor d. Pitting edema Rationale: Page 198 Chapter 32 of ATI Book. Additional source pg. 363 36. A nurse is caring for a client who has newly inserted chest tube. The nurse should clarify which of the following prescriptions with the provider? a. Notify the provider when tidaling ceases. (Yes notify) b. Assisting the client out of bed three times daily. c. Vigorously strip the chest tube twice daily. (Vigorously and BID) d. Administer morphine 2 mg IV bolus every 3 hr PRN for pain. (Don’t need to clarify) Rationale: Page 104 chapter 18 of ATI Book it says that: “Do not strip or milk tubing; only perform when prescribed. Stripping creates a high negative pressure and can damage lung tissue. Stripping tube of clots 37. A nurse is teaching a client who is taking an ACE inhibitor for heart failure. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include for home management of heart failure? a. Obtain daily weight. b. Use of salt substitute. (Avoid it) c. Monitor Intake and Output d. Limit daily activity. Rationale: Pg 199 ATI Book. 38. A nurse is providing discharge teaching to a client who has a permanent pacemaker. Which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching? a. I need to maintain pressure over the pacemaker site with an elastic bandage. b. I need to check my pulse rate every day for a full minute. c. The pacemaker will deliver shock if I develop a dysrhythmia d. When a microwave oven is in use, I need to stay out of the room. Rationale: Chapter 29 pg 177 of ATI book. ATI Pharm pg. 250 ACE inhibitor AE: Angioedema, hyperkalemia, ortho hpn, 39. A nurse in a clinic is providing preventive teaching to an older adult client during well visit. The nurse should instruct the client that which of the following immunization are recommended for healthy adults after age 60? Select all the Apply. a. Herpes Zoster b. Influenza c. HPV d. Meningococcal e. Pneumococcal Polysaccharide 40. A nurse is assessing a client who is 4hr postoperative following arterial revascularization of the left femoral artery. Which of the following findings should the nurse report immediately? a. Bruising around the incision site b. Pallor in the affected extremity c. Urine output 150mL over 4hr d. Temperature of 37.9 (100.2) Rationale: Chapter 35 pg 217. Circulation is compromised 41. A nurse is caring for an older adult client who has not been eating. Which of the following findings indicates dehydration? a. Crackles auscultated bilaterally (signs and symptoms suggestive of fluid overload) b. Capillary refill of 2 seconds (Brisk; normal) c. Diminished peripheral pulses d. Engorged neck veins (Also fluid overload) 42. A nurse is preparing to discharge a client who has a halo device and is reviewing new prescriptions from the provider. The nurse should clarify which of the following prescriptions with the provider? a. Increase intake of fiber rich foods b. May operate a motor vehicle when no longer taking analgesics c. Take tub baths instead of showers d. May place a small pillow under the head when sleeping Rationale Leadership 7.0 page 454-455 ● Traction: uses a pulling force to promote and maintain alignment of the injured area. Traction prescriptions should include the type of traction, amount of weight, and whether traction can be removed for nursing care. ● Goals of traction: prevent soft tissue injury, realign of bone fragments, decrease muscle spasms and pain, and correct or prevent further deformities. ● Halo devices are for skeletal purposes. Screws are inserted into the bone. Can use heavier weights (15 to 30 lb) and longer traction time to realign the bone. Provide pin site care to prevent infection. ● Nursing actions: ○ Assess neurovascular status of the affected body part every hour for 24 hour and every 4 hour after that. ○ Maintain body alignment and realign if the client seems uncomfortable or reports pain. ○ Avoid lifting or removing weights ○ Ensure that weights hang freely and are not resting on the floor ○ If the weights are accidentally displaced, replace the weights. If the problem is not corrected, notify the provider. ○ Ensure the pulley ropes are free of knots, frying, loosening, and improper positioning at least every 6 to 12 hr. ○ Notify the provider if the client experiences severe pain from muscle spasms unrelieved with medications or repositioning. Move the client in halo traction as a unit, without applying pressure to the rods. This will prevent loosening of the pains and pain. ○ Routinely monitor skin integrity and document. ○ Use heat/massage as prescribed to treat muscle spasms. Use therapeutic touch and relaxation techniques. 43. A nurse is assessing for elderly signs of compartment syndrome for a client who has a short leg fiberglass cast. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect? a. Bounding distal pulses b. Capillary refill less than 2 seconds c. Erythema of the toes d. Intense pain with movement Rationale: ATI MS pg. 453 Casts are more effective than splints or immobilizers because the client is unable to remove. Casts, as circumferential immobilizers, are applied once the swelling has subsided (to avoid compartment syndrome). If the swelling continues after cast application and causes unrelieved pain, the cast can be split on one side (univalve) or on both sides (bivalved). Capillary refill: Press nail beds of affected extremity until blanching occurs. Blood return should be within 3 seconds. Prolonged refill indicates decreased arterial perfusion. Nail beds that are cyanotic can indicate venous congestion. 44. A nurse is caring for a client who is postoperative following coronary artery bypass surgery and reports shortness of breath. The nurse administers oxygen at 3L/min and obtains arterial blood gases 60 min later. Which of the following lab findings indicates a positive response to the oxygen therapy? a. PaCO2 34 mmHg b. Bicarbonate 20 mEq/L c. PaO2 90 mmHg (Normal range: 80-100 mmHg) d. ph 7.32 Rationale: 45. A nurse is performing a cranial nerve assessment on a client following a head injury. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect if the client has impaired function of the vestibulocochlear (VIII)? a. Loss of the peripheral vision (CN II, is in charge of this) b. Disequilibrium with movement c. Deviation of the tongue from midline (CN XII) d. Inability to smell (CN I) Rationale: ATI MS Pg. 69 (Vertigo (room spinning) 46. A nurse is caring for a client admitted with a skull fracture. Which of the following assessment findings should be of greatest concern to the nurse? a. Glasgow coma scale score changes from 14 to 9 b. Bilateral pupil diameter changes from 4 to 2 mm c. Pulse pressure changes from 30 to 20 mm Hg d. WBC count changes from 9000 to 16,000 mm3 47. MISSING 48. A nurse is caring for a client who is taking furosemide. The client has a potassium level of 3.1 mEq/L. Which of the following should the nurse assess first? a. Urine output b. Level of orientation c. Cardiovascular statusà dysrhythmia due to potassium d. Muscle weakness- this is an early sign of K imbalance but i would go with C since ABC’s are always first. Rationale: Potassium imbalances causes dysrhythmias, which are the number one reason why potassium levels, are crucial to monitor. Hypokalemia causes ST depression, T wave depression, and elevation of U wave, which is vital for regulating normal electrical activity of the heart. Decreased extracellular potassium causes myocardial hyper excitability with the potential to develop re-entrant arrhythmias. 49. A nurse is caring for a client who is scheduled for an abdominal paracentesis. The nurse should plan to take which of the following actions? a. Instruct the client to take deep breaths and hold them during the procedure b. Administer a stool softener following the procedure c. Ask the client to empty his bladder prior to the procedure d. Assist the client into the left lateral position during the procedure Rationale: Pg. 527 50. A nurse is caring for a client who is 6 hours postoperatively following a thyroidectomy. The client reports tingling and numbness in the hands. The nurse should identify this as a sign of which of following electrolytes imbalances? a. Hyperatremia b. Hypermagnesemia c. Hypokalemia d. Hypocalcemia pg. 874 Rationale: (Parathyroid gland, which is the gland that secretes calcitonin, is right behind the thyroid. When you have a thyroidectomy, you decrease the production of calcitonin, which decreases production of calcium.) 51. A nurse is assessing a client 15 min after the start of a transfusion of 1 unit of packed RBC’s. Which of the following findings is an indication of a hemolytic transfusion reaction? a. Hypotension b. Bradypnea-tachypnea (RR > 20) it will produce c. Bradycardia- tachycardia it will produce d. Hypothermia- FEVER is a complication of a hemolytic reaction Rationale: Page 250 MS ATI PDF 10.0 under acute hemolytic complications 52. A nurse in an emergency department is caring for a client who has sinus bradycardia. Which of the following actions should the nurse take first? a. Prepare the client for temporary pacing. b. Initiate IV fluid therapy for the client c. Measure the client’s blood pressure d. Administer atropine to the client Rational: TX for bradycardia: IDEA: Isiproterenol, Dopamine, Epinephrine, Atropine Additional source is on pg. 275 ATI Pharm; pg. 171 ATI MS 53. A nurse is caring for a client who has a prescription to discontinue a peripherally inserted central catheter. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? a. Apply slight pressure when resistance is met b. Measure the catheter after removal c. Remove the catheter with one continuous motion . Place a dry sterile dressing to the site after remova Rationale: Textbook pg. 132. Removal of CVADs. Immediately apply pressure to the site with sterile gauze to prevent air from entering and to control bleeding. Inspect the catheter to determine that it is intact. After bleeding has stopped, apply an antiseptic ointment and sterile dressing to the site. 54. MISSING 55. A nurse is caring for a client who has a flail chest. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? a. Provide humidified oxygen b. Implement fluid restriction c. Administer antibiotic medication d. Administer acetaminophen orally Rationale: ATI MS pg. 150 Nursing Care: Administer humidified oxygen. 56. A nurse is teaching a group of newly licensed nurses about acute respiratory failure. Which of the following manifestations should the nurse include in the teaching? a. Hypoxemia b. Hyperventilation (Can’t be this because you are forsure going to have HYPERCARBIA and >20 RR will excrete CO2.) c. Hypocarbia- hypercarbia d. Hypervolemia à was highlighted on answer sheet (You’re going to have hypotension during ARF. If you have too much fluid in your body then you would have high blood pressure.) Rationale: Page 153 MS ATI PDF 10.0 57. A nurse is caring for a client who is experiencing a seizure. Which of the following actions should the nurse takes first? a. Obtain the client’s vital signs b. Clear items from the client’s surrounding area ATI PG .35 c. Loosen the client’s restrictive clothing d. Lower the client to the floor (ATI video says this if standing) ATI MS. PG 35 confirmed on answer sheet 58. A nurse is teaching a client who is receiving total parenteral nutrition at home through a central venous access device about transparent dressing changes. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include in the teaching? a. Change the dressing every 48 hr b. Replace the extension tubing with each dressing change c. Use clean technique when changing the dresinsg d. Wear a mask during dressing change (NO) 59. A nurse is caring for a client in the emergency department who experienced a full-thickness burn injury to the lower torso 1 hr ago. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect? a. Decreased respiratory rate- its is increased b. Hypotension c. Bradycardia- tachycardia is what you will find d. Urinary diuresis -decreased urine output is what you will find Rationale: During a major burn the initial phase will activate the Sympathetic nervous system. MS ATI PDF 10.0 page 481 Hypovolemia and shock can result from fluid shifts from the intercellular and intravascular space to the interstitial space. Additional findings include hypotension, tachycardia, and decreased cardiac output. 60. A nurse in an emergency department is assessing a client who has cirrhosis of the liver. Which of the following is a priority finding? a. Spider angiomas (Normal findings for patient have cirrhosis) b. Palmar erythema (Normal findings for patient have cirrhosis) c. Mental confusion à may lead to portal systemic encephalopathy; neuro is deteriorating. d. Yellow Sclera (Normal findings for patient have cirrhosis) Rationale: ATI MS pg. 356; ATI PG 358 MS 61. A nurse is providing instructions about foot care for a client who has a peripheral arterial disease. The nurse should identify which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching? a. “I apply a lubricating lotion to the cracked areas on the soles of my feet every morning” b. “I use my heating pad on a low setting to keep my feet warm.” (Minimal sensation) c. “I soak my feet in hot water before trimming my toenails” (Minimal sesnsation for PAD) d. 7”i rest in my recliner with my feet elevated for about an hour every afternoon Rationale: ATI MS pg. 215 Tell the client to never apply direct heat, such as a heating pad, to the affected extremity because sensitivity is decreased, and this can cause a burn. Tell the client to elevate the legs to reduce swelling, but not to elevate them above the level of the heart because extreme elevation slows arterial blood flow to the feet. 62. A nurse is teaching a client who has a new prescription for alendronate to treat osteoporosis. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include in the teaching? a. Swallow the medication with 120mL (4 oz) of water (Must be 8 oz of water) b. Take the medication with a vitamin E supplement (Pretty sure you need vitamin D instead since this drug is for helping with osteoporosis) c. Sit upright for 30 min after taking the medication (No lying down) d. Take the medication with lunch (Must be taken early morning before eating) Rationale: Page 447 MS ati PDF 10.0. ATI Pharm pg. 452 Instruct client to sit upright or ambulate for 30 min after taking this medication orally. ● Alendronate (Fosamax): Bisphosphonates (inhibits bone resorption) ○ Other drugs in its class: ■ ibandronate (Boniva), risedronate (Actonel) = oral ■ Ibandronate, zoledronic acid, and pamidronate are available as IV preparations. ○ Therapeutic uses: decreases number and actions of osteoclasts, subsequently inhibiting bone resorption for prevention and treatment of osteoporosis, hypercalcemia, and Paget’s disease (interferes with your body's normal recycling process, in which new bone tissue gradually replaces old bone tissue. Over time, the disease can cause affected bones to become fragile and misshapen. Paget's disease of bone most commonly occurs in the pelvis, skull, spine and legs) of the bone. ○ Nursing considerations: ■ Risk for esophagitis and esophageal ulcers ■ Report early signs of indigestion, chest pain, difficulty swallowing, or bloody emesis to provider immediately ■ Take with 8 oz. of water in the early morning before eating ■ Remain upright for 30 minutes after taking medication. ■ Monitor calcium levels in clients receiving IV preparations ■ Clients using IV preparations should have dental examinations and preventive treatment prior to starting therapy to minimize the risk of osteonecrosis of the jaw. ■ You must take alendronate just after you get out of bed in the morning, before you eat or drink anything. Never take alendronate at bedtime or before you wake up and get out of bed for the day. ■ Swallow alendronate tablets with a full glass (6 to 8 ounces [180 to 240 mL]) of plain water. Drink at least a quarter of a cup (2 ounces [60 mL]) of plain water after you take alendronate solution. Never take alendronate tablets or solution with tea, coffee, juice, milk, mineral water, sparkling water, or any liquid other than plain water. ■ Meanwhile, continue all the other measures that help protect and maintain bone density: take 1,200 to 1,500 milligrams of calcium and 800 IU of vitamin D every day; get 30 minutes of weight-bearing exercise at least three times a week; and if you smoke, do your best to stop 64. A nurse is admitting a client to the emergency department after a gunshot wound to the abdomen. Which of the following actions should the nurse take to help prevent the onset of acute kidney failure? a. Initiate beta blocker therapy b. Insert a urinary catheter c. Prepare the client for intravenous pyelogram d. Administer IV fluids to the client Rationale: IV Bolus; Preventing and treating shock with blood and fluid replacement will prevent acute renal failure from hypoperfusion of the kidneys. Significant blood loss is expected in the client with a gunshot wound 65. A nurse is completing an assessment of an older adult client and notes redness areas over the bony prominences, but the client’s skin is intact. Which of the following interventions should the nurse include in the plan of care? a. Apply an occlusive dressing (air to dry only) b. Manage the redness areas three times daily c. Support bony prominences with pillows d. Turn and reposition the client every 4 hr. (Q2 hrs or PRN) Rationale: 66. A nurse is caring for a client who has completed 10 daily cycles of Total parenteral Nutrition (TPN). Which of the following findings indicates that the client is receiving adequate TPN supplementation. Page 298 MS AT PDF. a. Improved Mobility (Doesn’t correlate to TPNs) b. Weight gain of 9.1 kilograms to 20 pounds c. Potassium level of 2.5 meq/l (Potassium should be in normal range since tpn is intended for malnourished patients and contains electrolytes and vitamins that the patient needs.) d. BUN level of 15 mg/dL (Normal level is 6-20 mg/dl) lower than normal may be due to low protein diet, malnutrition, or over-hydration. Rationale: Confirmed (TPNs are intended for patients who are malnourished so gaining 2 pounds in 2 days is good.) 68. A nurse is providing teaching to a client who is post-operative following a partial glossectomy. Which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching? a. I will consume can soup whenever sores appear in my mouth b. I will drink orange juice to increase my vitamin C intake c. I will rinse my toothbrush with hundred peroxide and water after each use d. I will inspect my mouth once each week for sores. 69. A nurse is performing ear irrigation for a client. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? a. Tilt the client's head 45 degrees b. Insert the tip of the syringe to .5 centimeters 1 inch into the ear canal c. Point the tip of the syringe toward the top of the ear canal d. Use cool fluid for irrigation Rationale: Google 70. A nurse is caring for a client who is receiving continuous bladder irrigation following a transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP). The client reports sharp lower abdominal pain. Which of the following actions should the nurse takes first? a. Check the client's urine output b. Reposition the client in bed c. Increase the client's fluid intake d. Administer PRN pain medication 71. A nurse is providing teaching for a client who has diabetes mellitus about the selfadministration of insulin. The client has prescriptions for regular and NPH insulin. Which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching? a. I will draw up regular insulin into the syringe first b. I will insert the needle at a 15-degree angle c. I will store prefilled syringes in the refrigerator with the needle pointing downward d. I will shake the NPH vial vigorously before drawing up the insulin Rationale: Air: NPH then Regular. Aspirate: Regular then NPH 72. Missing 73. Missing 74. A nurse is caring for a client who is receiving Total parenteral Nutrition (TPN). Which of the following nursing actions are appropriate? (Select all the apply) a. Obtain the client's weight daily b. Increase the rate of infusion if administration is delayed. c. Monitor serum blood glucose during infusion. d. In to use 0.9% sodium chloride if the solution is not available. e. Verify the solution with another RN prior to infusion Rationale: ATI pg 298 never ever do this because doing this will alter blood glucose significantly. It says so in the bright yellow box on mage 298. Also HYPERGLYCEMIA can happen if you do. check glucose level every 4 -6 hours for at least 24 hours.have D5 10 % since that is needed in case to prevent hypoglycemia. 75. A nurse is caring for a client in diabetic ketoacidosis dka. Which of the following is the priority intervention by the nurse? a. Check potassium levels b. Administer 0.9% sodium chloride c. Begin bicarbonate continuous IV infusion d. Initiate continuous IV insulin infusion Rationale: ATI pg. 538 Provide rapid isotonic fluid (0.9% sodium chloride) replacement to maintain perfusion to vital organ. 76. A nurse is reviewing the laboratory results of a female client who asked about acupuncture treatment for chemotherapy- induced nausea and vomiting. Which of the following laboratory results contraindication to receiving acupuncture? a. Absolute neutrophil count 5000/mm3 b. C-reactive protein 0.7 mg/dl c. Platelets 160,000/mm3 d. Hemoglobin 12g /dl Rationale: ATI pg 581 Monitor temperature, white blood cell (WBC) count, and absolute neutrophil count (ANC). A fever greater than 37.8° C (100° F) should be reported to the provider immediately. Clients who have neutropenia might not develop a high fever or have purulent drainage even when an infection 77. A nurse is caring for a client following a total knee arthroplasty. The client reports a pain level of 6 on a Pain Scale of 0 to 10. Which of the following should the nurse take? a. Gently massage the area around the clients incision b. Place pillows under the client's knee. No avoid knee gatch and pillows placed behind the knee c. Apply and ice pack to the client’s knee d. Perform range of motion exercises to the client’s knee Rationale: ATI pg. 437 Apply ice or cold therapy to the incisional area to reduce postoperative swelling. 78. A nurse is assessing a client who has heart failure and is receiving a loop diuretic. Which of the following findings indicates hypokalemia? a. Hypertension b. Positive chvostek's sign (hypomagnesemia) c. Muscle weakness d. Oliguria Rationale: ATI pg 274 Signs of hypokalemia includes Weakness, Deep tendon reflexes can be reduced. 79.A nurse at a long-term care facility is assessing an older adult client. Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as an indication that the client has recall memory impairment? a. Inability to state what he has for dinner last night b. Inability to Name the members of his family c. Inability to count backwards from 10 d. Inability to state his current age Rationale: 80. A nurse on an intensive care unit is planning care for a client who has increased intracranial pressure following a head injury. Which of the following IV medications should the nurse plan to administer? a. Chlorpromazine b. Dobutamine c. Mannitol d. Propanol Rationale: ATI pg 77 Mannitol is an osmotic diuretic used to treat cerebral edema. When used for increased ICP, the medication draws fluid from the brain into the blood. 81. A nurse on a medical unit is planning care for a group of clients. Which of the following clients should the nurse attend to First? a. A client who has thrombocytopenia and reports and nosebleed b. A client who has chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and oxygen saturation of 89% (Normal findings for COPD) c. A client who has multiple sclerosis and Ataxia and vertigo d. A client who has left-sided paralysis and slurred speech from a prior stroke Rationale: ATI MS pg. 249 Thrombocytopenia/platelet dysfunction (platelets less than 20,000 or less than 50,000 and actively bleeding) Need to assess nosebleed. Under category C of ABCs 82. A home care nurse is planning to use non-pharmacological pain relief measures for an older client who has severe chronic back pain. Which of the following guidelines should the nurse use? a. Use imagery with clients who have difficulty with focus and concentration. (This is never the answer) b. Pain relief from the use of heat and cold continues for several hours after removal of the stimulus (only works when you have it on) c. Discontinue opioids before trying non-pharmacological methods of pain relief d. Distraction changes the client's perception of pain but does not affect the cause Rationale: ATI Pg 27 Imagery requires an ability to concentrate 83 TO 88 Missing 89. A nurse is caring for a client who has pneumothorax and a chest tube with closed water seal drainage system. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? a. Strip or clear the chest tube every 8 hours b. Refill the water chamber if the fluid is low c. Empty the system at least every 8 hr d. Change the chest to site dressing every 24 hour Rationale: ATI Pg. 104 Monitor the fluid in the suction control chamber, and maintain the prescribed fluid level.check the water seal level every 2 hr, and add fluid as needed. The fluid level should fluctuate with respiratory effort. 90. A nurse is in an emergency department is reviewing a client's ECG reading. Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as an indication that the client has first-degree heart block? a. Prolonged PR intervals b. More p waves than QRS complexes c. Non discernible p waves d. No correlation between p and QRS waves Rationale: As mentioned in class with Tiamson. Confirmed in ECG notes. Consistent prolonged PR intervals. 91. A nurse is preparing to administer a unit of packed RBC's to a client who is anemic. Identify the sequence of steps the nurse should follow. a. Obtain venous access using a 19 gauge needle 3 b. Obtain the unit of packed rbc's from Blood Bank 1 c. Verify blood compatibility with another nurse 2 d. Initiate transfusion of the unit of packed rbc's 4 e. Remain with the client for the first 15 to 30 minutes of the infusion 5 Rationale: ATI PHARM: pg 354-355: or ATI MS pg. 249-250 B, C, A, D, E 92. A nurse is teaching a client who is to begin chemotherapy about peripherally inserted central catheter. Which of the following statements should the nurse include in the teaching? a. We will replace the PICC every month (Not every month) b. We can draw blood samples from the PICC for diagnostic test c. We will change the dressing daily (not daily) d. We can measure your blood pressure in either arm (opposite arm from PICC line) Page 1000- “ a central catheter is usually placed for chemotherapy administration or laboratory blood testing.” 93. A nurse is assessing a client who has Pyelonephritis and reports flank pain. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? a. Assist the client to a sitting position b. Percuss the side of tenderness first c. Auscultate for a bruit over the coastal vertebral area d. Thump the area of tenderness directly with a closed fist 94 A nurse is assessing a client who has acute kidney failure. Which of the following findings should the nurse report to the provider? a. Peripheral pulses 2 + bilaterally (normal findings, no edematous) b. Weight gain 1.1 kilogram to 2.4 pound in 24-hour c. Urine specific gravity 1.045 (1.005 to 1.030 greater than 1.030 indicate dehydration) d. Creatinine 0.8 milliliter (0.5-1.1 mg/dl) Rationale: ATI MS. Pg. 380 Urine specific gravity varies in postrenal type; can be elevated up to 1.030 in prerenal type or diluted as low as 1.000 in intrarenal type. ATI MS Pg. 382. Patient-Centered Care: Weight: 1 kg (2.2 lb) daily weight increase is approximately 1 l of fluid retained and need to report and monitor irregular findings. 95. A nurse is caring for an older adult client who is 72 hour postoperative following a total hip arthroplasty. The client requires a PRN medication prior to ambulation. Which of the following medications should the nurse anticipate administering? a. Indomethacin -> Indocin NSAID b. Meperidine -> Demerol opioid agent; a/e: orthostatic hypotension, sedation c. Naproxen d. Oxycodone à Oxycontin Opioids agent. ATI Pharm: pg. 482 Oxycodone-> A/E : sedation, orthostatic hypotension Rationale: ATI MS pg. 437 Analgesic Opioids (epidural, PCA, IV, oral), NSAIDs Pg. 761-> use NSAID instead of OPIOD because of A/E prior to ambulation. 96. A nurse is caring for a client who has Haemophilus Influenzae type B. which of the following types of isolation should the nurse implement? a. Droplet b. Contact c. Airborne d. Protective Rationale: Fundamentals (this is one is obvious ) 97. A nurse is providing discharge teaching to a client who has pulmonary tuberculosis. Which of the following findings should the nurse include, as an indication the client is no longer infectious? a. Mantoux skin test reveals and induration of less than 1mm b. Client no longer coughing up blood tinged sputum c. Positive Quantiferon TB gold test d. Negative sputum culture for acid fast bacillus Rationale: As mentioned in class with Tiamson. Confirmed on respiratory notes . pg 251 med surg ati obtain 3 early morning sputum samples 98. A nurse working in the emergency department is caring for a client who has a burn injury. After securing the client's Airway which of the following interventions should the nurse take first? a. Cleanse the client wound b. Administer Analgesic medication c. Increase the room temperature d. Start an IV with a large bore needle Rationale: ATI MS pg. 482 pdf book To maintain cardiac output, maintains tissue perfusion, and prevent hypovolemic shock. Initiate IV access using a large bore needle. If burns cover a large area of the body, the client requires insertion of central venous catheter or IO. Fluid replacement is important during the first 24 HR. 99. A nurse is caring for a client who has a central venous access device and notes the tubing has become disconnected. The client develops dyspnea and tachycardia. Which of the following actions should the nurse takes first? a. Obtain ABG values b. Perform an ECG c. Turn the client to his left side d. Clamp the catheter Rationale: I did not find this in the book but I found it on the ATI website under Complications of Central lines. It says if an air embolism is suspected FIRST CLAMP THE CATHETER, then administer o2 and place patient on their left side. 100.A nurse is providing discharge teaching to a client who has impaired immune system due to chemotherapy. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching? a. Wash your perineal area 2 times each day with antimicrobial soap b. Change the water in your drinking glass every 4 hours (avoid fluids sitting in room temp longer than an 1 hour pg 1001 med surg book ati ) c. Wash your toothbrush in the dishwasher once each month (wash toothbrush daily in dishwasher or rinse in bleach solution) d. Change your pet litter box daily (avoid pg 1001 med surg ati book) Rationale : med surg book pg 1001 letter A is the only option after eliminating the others from the book 101. A nurse is caring for a client who has advanced liver disease. Which of the following laboratory results should the nurse monitor when assessing the client? a. Serum Ammonia b. Glucose level c. Phosphate level d. Serum troponin Pg. 618. Ammonia is the only lab test from this list that is in the book. “Amonia levels rise when hepatocellular injury prevents the conversion of ammonia to urea for excretion.” Rationale: For advanced liver disease, you check Serum Ammonia (usually elevated) i got this from my nurse friend ... 102. A nurse is caring for a client who has admitted with nausea, vomiting, and a possible bowel obstruction. An NG tube is placed and set to low intermittent suction. Which of the following findings should the nurse report to the provider? a. The client reports being extremely thirsty with a sore throat b. The amount of drainage is gradually decreasing c. The clients abdomen becomes distended and firm d. The drainage is bright green in color with brown fecal material Rationale: 103. A nurse is caring for a client who takes Lisinopril for HTN. Which of the following client statements indicates an adverse effect of the medication? a. I have a heightened sense of taste b. I have a nagging, dry cough c. I have to urinate frequently d. I seem to be bruising more easily Rationale: ATI MS pg. 227 pdf Teach the client to report a cough, which is an adverse effect of ACE inhibitors. The client should notify the provider of this adverse effect, as the medication can be discontinued due to its persistent nature and occasional relationship to angioedema (swelling of the tissues in the throat that can progress to a life-threatening obstruction). Teach the client to reports manifestations of heart Failure (edema). 104. A nurse is caring for a client who has an endotracheal tube. Which of the following actions should the nurse take to verify tube placement? a. Deflate the cuff to check the tube placement (should be inflated not deflated ) b. Place the client’s head and neck in a flexed position c. Observe for symmetry of chest expansion d. Document the tube length where it passes the chin Rationale : med surg book pg 205 105. A nurse is providing discharge teaching to a client who has chronic urinary tract infections. The client has a prescription for ciprofloxacin 250 mg PO twice daily. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include in the teaching? a. Take a laxative to prevent constipations b. Take an antacid 30 min before taking the medication c. Monitor heart rate once daily d. Drink 2 to 3 L of fluid daily Rationale: ATI MS PDF pg. 388 Nursing Care: Promote fluid intake up to 3 L daily. 106. A nurse is caring for a client who presents to the emergency department after experiencing a heat stroke. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? a. Apply a cooling blanket. b. Assess axillary temperature every 15 min. c. Administer an antipyretic d. Administer lactated Ringers. Rationale: Confirmed 107. A nurse is presenting an in-service program about Parkinson’s disease (PD). Which of the following statements should the nurse include in the teaching? a. PD cause clients to have an increased sympathetic nervous system response b. PD results in the development of neurofibrillary tangles within the client’s brain c. PD results from a decreased amount of dopamine in the client’s brain d. PD manifestations worse due to the clients decreased production of acetylcholine. Rationale: Confirmed see Endocrine notes. Med surg ati book pg 72 108. A nurse is reviewing the medical record of a client who is to undergo open heart surgery. Which of the following findings should the nurse report to the provider as a contraindication to receiving heparin? a. Thrombocytopenia b. Thalassemia c. Rheumatoid arthritis d. COPD Rationale: p.323 ATI Pharm; answer sheet 109. A nurse is assessing a client who has skeletal traction for a femoral fracture. The nurse notes that the weights are testing on the floor. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? a. Pull the client up in bed b. Tie knots in the ropes near the pulleys to shorten them c. Increase the elevation of the affected extremity d. Remove one of the weights (NO) Rationale: : Pg. 792 “Movement of the client's body can alter the traction provided.” Pg. 793. The weights should never touch the floor. 110. A nurse is reviewing a medical record of a client who has acute gout. The nurse expects an increase in which of the following laboratory results? a. Intrinsic factor b. Chloride level c. Uric acid d. Creatinine kinase Rationale: Leadership 7.0 page 559 and 561 (Confirmed answer sheet) ● Gout, also known as gouty arthritis, is a systemic disorder caused by hyperuricemia (increased serum uric acid). Urate levels can be affected by medications, diet, and overproduction in the body. This can cause uric crystal deposits to form in the joints, and a gout attack can occur. ● Gout is the most common inflammatory arthritis. Gout is a systemic disease caused by a disruption in purine metabolism in which uric acid crystals care deposited in the joints and body tissues. Gout is classified as either primary or secondary. ○ Primary gout: ■ Most common ■ Uric acid production is greater than excretion of it by the kidney. ■ Can have genetic component ■ Middle-and older-adult males (peak onset between ages 40 and 50), as well as postmenopausal women are commonly affected. ○ Secondary gout: ■ Caused by another disease or condition (chronic kidney failure, excessive diuretic use) that causes excessive uric acid in the blood ■ Treatment is based on treating the underlying condition ■ Can affect people of any age. 111. A nurse is providing teaching to a client who is to start furosemide therapy for heart failure. Which of the following statements indicates that the client understands a potential adverse effect of this medication? a. “I will check my pulse before I take this medication.” b. “I’ll check my blood pressure so it doesn’t get too high.” c. “I’m going to include more cantaloupe in my diet.” (p. 4115) d. “I will try to limit foods that contain salt.” Med Surg 2016 Re-Take → PRIORITY THREE (note: questions missing b/c repeated questions from above tests) 8. The nurse is preparing the discontinue long term TPN therapy for a client. The nurse should plan to discontinue the TPN gradually to reduce the risk of which of the following adverse effects? A. Hyperglycemia (if speeding up tpn rate) B. Diarrhea C. Constipation D. Hypoglycemia- You taper it off to avoid this!!! Rationale PDF p.298: Never abruptly stop TPN. Speeding up/slowing down the rate is contraindicated. An abrupt rate change can alter blood glucose levels significantly. Rationale PDF nutrition p.58: don’t discontinue abruptly, must taper to prevent rebound hypoglycemia 19. A nurse is preparing a client for an ECG. The client is anxious and says that he is afraid the equipment will give him an electric shock. Which of the following is an appropriate response by the nurse? A. The machine only senses and records electrical currents coming from your heart B. The lead wires and cables are insulated for your safety C. The electrode pads will prevent the conduction of electricity to your skin D. The machine voltage delivery is low enough that you won’t feel any discomfort Rationale PDF p.170: Electrocardiography uses an electrocardiograph to record the electrical activity of the heart over time. 23. A nurse is caring for client who has hypertension and has a new prescription for lisinopril (ACE inhibitor). The nurse should consult with the provider about which of the following medications in the client’s medication administration record? (A) A. Potassium chloride (extra K+ increases risk of hyperkalemia) B. Levothyroxine C. Acetaminophen D. Metformin Rationale PDF p.275: ACE Inhibitor--monitor for increased level of K+ 26. A nurse is administering furosemide (Lasix) 80 mg PO twice daily to a client who has pulmonary edema. Which of the following assessment findings indicates to the nurse that the medication is effective? A. Elevation in blood pressure B. Adventitious breath sounds C. Weight loss of 1.8 kg (4 lb) in the past 24 hr D. Respiratory rate of 24/min Rationale PDF p.383: furosemide--a loop-diuretic administered to excrete excess fluids 32. Couldn't paste the picture on here. But it asked where u can hear pericardial friction rub the best at…Erb’s Point (3rd Intercostal, Central) 33. A nurse is completing discharge teaching with a client who has a new diagnosis of AIDS. Which of the following statements by the nurse indicates an understanding of the teaching? A. I will increase the amount of fresh veggies (avoid raw foods) B. I will wipe up areas soiled with body fluids with alcohol and immediately dispose of the trash (bleach?) C. I will need to take my clothes to the dry cleaners to sterilize them D. Rationale PDF p.556: AIDS/HIV client education/teachings: instruct the client to avoid cleaning pet litter boxes to reduce the risk of toxoplasmosis 35. A nurse is performing a venipuncture on an older adult client whose veins are difficult. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? A. Apply cool compresses (use hot compress for vasodilation) B. Elevate the client’s extremity using a pillow (no, will decrease blood flow to hand) C. Tap the skin around the insertion site (avoid) D. Raise the angle of the catheter to 30 degrees above the insertion site Rationale PDF Funds p.289: Older adult clients, clients taking anticoagulants, or clients who have fragile veins: Avoid tourniquets, Use a blood pressure cuff instead, Do not slap the extremity to visualize veins, Avoid rigorous friction while cleaning the site. Rationale PDF Funds p.290: Use a steady, smooth motion to insert the catheter into the skin at an angle of 10° to 30° with the bevel up 39. A nurse is caring for a client in the ER following a MI. which of the following actions should the nurse anticipate if the client develops asystole? A. Administer atropine (given for bradycardia to increase HR) B. Defibrillate with 200 joules (this is after cpr) C. Starts a continuous lidocaine infusion D. Begin CPR Rationale PDF p.9: Ventricular asystole: a complete absence of electrical activity and ventricular movement of the heart. The client is in complete cardiac arrest and requires implementation of BLS and ACLS protocol. 41. A nurse is caring for a client with severe burn injury. The nurse should recognize which of the following client findings as an indication of hypovolemic shock? A. Potassium 5.2 mEq/L (Individuals with hypovolemic shock due to fluid loss often have disturbances of the blood electrolytes (sodium, potassium, chlorides, and bicarbonates) that must be corrected) B. Capillary refill 1.5 seconds (deceased perfusion would increase capillary refill time) C. Urine output 45 mL/hr (should be decreased urine output r/t dehydration, <30 mL/hr) D. PaCO3 37 mmHg (normal value is 22-26; expected should be respiratory acidosis with hypovolemic shock r/t low perfusion so it should be <22 mmHg) Rationale PDF p.232: hypovolemic shock is central venous pressure is decreased which slows blood flow and perfusion to tissues of the oh Rationale PDF 461: Potassium is increased due to cell destruction (hyperkalemia) 42. A critical care nurse is assessing a client who has a severe head injury. In response to painful stimuli the client does not open her eyes, displays decerebrate posturing, and makes incomprehensible sounds. Which of the following glascow coma scale scores should the nurse assign the client? A. 2 B. 5 (Not open eyes 1, decerebrate 2, Incomp sounds 2) C. 10 D. 13 Rationale PDF p.8: Glasgow Coma Scale Eye Opening Response: 4 spontaneous, 3 to voice, 2 to pain, 1 none Verbal Response: 5 oriented, 4 confused, 3 inappropriate words, 2 mumbling sounds,1 none Motor Response: 6 obeys commands, 5 localizes pain, 4 withdraws, 3 flexion, 2 extension, 1 none 43. A nurse is teaching a client who has heart failure about self management techniques. Which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching? a. I will keep an exercise dairy b. I will take ibuprofen for mild pain - Hypoxic = Angina (NSAIDs worsen HF; evidencebased) c. I will expect swelling in my feet and ankle- indicates worsening condition d. I will weigh myself every other day- daily weights Rationale : Activity may improve the functioning of your heart, by reducing the workload and enabling it to beat more efficiently. This will improve your symptoms. 44. A nurse is providing discharge teaching for a client who has new tracheostomy. Which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching a. Ill insert the obturator after cleaning my stoma b. Ill cut a slit in a clean gauze pad to use as a stoma dressing→ don't cut gauze, instead place fresh split gauze dressing of unraveling material under and around the tracheostomy holder and plate c. Ill cleanse the cannula with half strength hydrogen peroxide→ per SKILLS Perry & Potter 3% of hydrogen peroxide, normal saline, and mild soapy water d. Ill remove the soiled tracheostomy ties prior to cleaning my stoma→ remove last while trying to insert new ones to prevent dislodgement. Secure with new ones before removing soiled ones Rationale: Page 318 Funds PDF ATI, Use surgical asepsis to remove and clean the inner cannula (with the facility-approved solution). Use a new inner cannula if it is disposable. 45. A nurse is caring for a client who has a sealed radiation implant which of the following actions should the nurse take ? a. Limit family member visits to 30 min per day→ limiting time spent in the room and at least 3-6 feet. b. Give the dosimeter badge to the oncoming nurse at the end of the shift c. Apply second pair of gloves before touching the clients implant if it dislodges d. Remove soiled linens from the room after each change Rationale: Med Surg Ati, p. 583, Limit visitors to 30-min visits, and have visitors maintain a distance of 6 feet from the source. 46. A nurse is reviewing the medical record of a client who has pneumonia. Which of the following serum laboratory values should the nurse expect ? a. WBC count 15,000/mm b. Hematocrit 35% c. Sodium 130 mg/dl d. BUN 8 mg/dl 47. A nurse is planning care for a client who has a newly implanted arteriovenous graft in the right arm. Which of the following actions should the nurse include in the plan of care? a. Instruct the client to avoid lifting the right arm for 72 hr b. Check blood pressure in the right arm - NO c. Palpate the site for thrill d. Insert a saline lock into a site 10 cm (4in) distal to the graft Rationale : Assessing for circulation. Lack of bruits or thrills may indicate blood clot and requires surgical intervention 48.a nurse in the emergency department is caring for a client who has a gunshot wound to the abdomen . which of the following should the nurse take first ? a. Check the color of the clients skin - always assess first b. Prepare the client’s clothing c. Remove all the clients clothing d. Administer an opioid analgesic Rationale: Assess! 49. A nurse is assessing a client who has an arteriovenous (AV) fistula in the left forearm. Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as an indication of a complication at the vascular access site. a. Presence of palpable thrill - good sign b. 2 + left radial pulse c. Absence of bruit - obstructed circulation by blood clot d. Dilated appearance of the AV site Rationale: Med Surg Ati p. 367, Assess the patency of a long-term device: arteriovenous (AV) fistula or AV graft (presence of bruit, palpable thrill, distal pulses, and circulation. 50. A nurse is caring for a client who is receiving continuous bladder irrigation following a transurethral resection of the prostate. The client reports spasms and the nurse observes decreased urinary output. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? a. Decrease traction on the catheter b. Remove the indwelling urinary catheter c. Flush the catheter manually with 0.9% sodium chloride- use only normal saline or prescribed d. Administer ibuprofen 400 mg for pain relief 51. A nurse is caring for a client who has contusion of the brainstem and reports thirst. The client’s urinary output was 4,000 mL over the past 24 hr.The nurse should anticipate a prescription for which of the following IV medications? a. Desmopressin - pt is peeing too much, that is why he is thirsty. Give demopressin to retain fluid (diabetes insipidus) b. Epinephrine c. Furosemide d. Nitroprusside Rationale: P. 500 ATI Desmopressin, which is a synthetic ADH, or aqueous vasopressin administered intranasally, orally, or parenterally. Results in increased water absorption from kidneys and decreased urine output. 52. A nurse is preparing to administer daily medications to a client who is undergoing a procedure at 1000 that requires IV contrast dye. Which of the following routine medications to give at 0800 should the nurse withhold? a. Valproic acid b. Metformin -Kidney Overwork -> lactic acidosis c. Metoprolol d. Fluticasone Rationale : p. 530 Stop Metformin for 48 hr before any type of elective radiographic test with iodinated contrast dye and restart 48 hr after (can cause lactic acidosis due to acute kidney injury). 53. A nurse is preparing a client who is to undergo a thoracentesis.The nurse should place the client in which of the following positions? a. On her affected side with her head lowered b. In high-Fowler’s position with her arms at her side c. Prone position with her arms above her head d. Upright on the edge of the bed leaning over the bedside table→ ati ms pg. 100 Rationale p.100 ATI Position the client sitting upright with his arms and shoulders raised and supported on pillows and/or on an overbed table and with his feet and legs well-supported 54. A nurse is teaching a client about the use of an incentive spirometer. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include in the teaching? a. Position the mouthpiece 2.5 cm (1in) from the mouth b. Hold breaths 3 to 5 seconds before exhaling c. Place hands on the upper abdomen during inhalation d. Exhale slowly through pursed lips (exhale completely through mouth/nose) Rationale: exhale first. Put in mouth. Breath in deeply and keep the flow indicator in the target spot. Then hold breath for 3-5 seconds. 56. A nurse is caring for a client who is 2 days postoperative following abdominal surgery and has a prescription for opioid analgesia. Which of the following actions should the nurse implement to help facilitate the client’s recovery? a. Provide analgesic medication prior to physical activities b. Inform the client to monitor for loose stools while taking opioid analgesia c. Withhold analgesic medication unless the client reports pain d. Administer naloxone if the client’s respiratory rate is greater than 24/min (if resp. Depression,, naloxone (For narcotic overdose Rationale: Give analgesic to relieve pain before getting involved in any physical activity. 57. A nurse is preparing to assist the provider with thoracentesis for a client who has left pleural effusion. Which of the following interventions is the priority for the nurse? a. Describe the sensation the client will feel during the procedure b. Reinforce the importance of lying still during the procedure c. Administer a sedative medication d. Determine whether the client has an allergy to local anesthetics - priority Rationale: Ask for allergies before any procedure!!! 58. A nurse is reviewing the medical record of a client who has nephrotic syndrome. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect? a. Decreased serum lipid levels (increased) b. proteinuria c. Hypoalbuminaemia d. Decreased coagulation Rationale: Lewis Ch 46 also edema. Nephrotic syndrome is a kidney disorder characterized by massive proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, edema, and elevated serum lipids, anorexia, and pallor. 59. A nurse is planning care for a client following a cardiac catheterization. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? a. Limit the client’s fluid intake to 1 L per day b. Keep the client on bed rest for 24 hr c. Change the client’s dressing every 8 hr d. Maintain the client’s affected extremity in extension Rationale: Ati Med Surg p. 164, Maintain bedrest in supine position with extremity straight for prescribed time. 60. A nurse is caring for a client who has a traumatic brain injury. The client, who has been quiet and cooperative, becomes agitated and restless. Which of the following assessments should the nurse perform first? a. Urinary output b. Motor responses c. Blood pressure d. Blood glucose Rationale : Ati Med Surg p. 75, Manifestations of increased intracranial pressure: Severe headache, nausea, vomiting. Deteriorating level of consciousness, restlessness,irritability. Dilated or pinpoint nonreactive pupils. Cranial nerve dysfunction: Alteration in breathing pattern (Cheyne-Stokes respirations, central neurogenic hyperventilation, apnea) Deterioration in motor function, abnormal posturing (decerebrate, decorticate, flaccidity) 61. A nurse is providing discharge teaching to a client who has systemic lupus erythematosus. Which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching ( select all that apply). 1. I will use NSAIDS to treat aches and pains 2. I will use cosmetics without moisturizer. 3. I will disinfect skin lesions with rubbing alcohol 4. I will wear long sleeve when outdoor 5. I will increase my intake of sodium Rationale: Med Surg Ati p.560 &561 NSAIDs Used to reduce inflammation and arthritic pain. NURSING CONSIDERATION NSAIDs are contraindicated for clients who have impaired kidney function. Monitor for NSAID-induced hepatitis CLIENT EDUCATION ●● Avoid UV and prolonged sun exposure. Use sunscreen when outside and exposed to sunlight. ●● Use mild protein shampoo and avoid harsh hair treatments. ●● Use steroid creams for skin rash. ●● Report peripheral and periorbital edema promptly. ●● Report evidence of infection related to immunosuppression. ●● Avoid crowds and individuals who are sick, because illness can precipitate an exacerbation. ●● Educate client of childbearing age regarding risks of pregnancy with lupus and treatment medications. 62. A nurse is reviewing the laboratory results of a client who has COPD and severe dyspnea. Which of the following ABG values should the nurse expect? a. PaCO2 50mm Hg- yup CO2 retainer b. pH 7.4 c. PaO2 95 mmHg d. HCO3 20 mEq/L ::::Respiratory acidosis. 63. A nurse is caring for a client who has atrial fibrillation. Which of the following should the nurse expect to administer? a. Dobutamine- for chf-> increase contractility b. Lidocaine - for v tach or v fib c. Atropine- for bradycardia d. Amiodarone page 171 MS ATI PDF ::::Bradycardia (MED: atropine) A-Fib (MED: Amiodarone, adenosine, verapamil) V-tach or V-fib (MED: Amiodarone, lidocaine, epinephrine) 64. A nurse is caring for a client who is receiving epidural analgesia. Which of the following findings is the nurse’s priority? In analgesia SNS system is blocked causing BP decrease which can lead to decreased cardiac output. a. Bladder distention b. Weakness to lower extremities c. Hypotension page 626 MS ATI PDF 10.0 d. Hypoactive bowel sounds ::::ABC prioritization. 65. A nurse is planning care for a client who has chest drainage system set to low suction following a thoracotomy. Which of the following nursing actions is appropriate to include in the plan of care?*^^* a. Check for bubbling in the water seal chamber b. Empty the collection c. Keep the water seal chamber at chest level d. Loop excess tubing below the chest wall ::::Continuous bubbling in the water seal chamber indicates an air leak in the system. p104 66. A nurse is caring for an older adult client who is prescribed packed RBC’s. Which of the following actions is appropriate for the nurse to take? a. Obtain vital signs every hour during transfusion- 15 min b. Administer the transfusion over a 4-hr period. c. Infuse lactated Ringer’s solution while transfusing the blood product.-only with NS d. Use a 24- gauge needle for the transfusion-18 67. A nurse in the intensive care unit is caring for a client who has the following ABG results; pH 7.30; HCO3 19 mEq/L, PaCO2 with the expected reference range. a. Respiratory alkalosis b. Respiratory acidosis c. Metabolic acidosis d. Metabolic alkalosis 68. A nurse is providing discharge teaching to a client who has an impaired immune system due to chemotherapy. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching? a. Change the pet’s litter box daily- never go near this b. Change the water in your drinking glass every 4 hours- page 581 chapter 90 .. CHANGE FLUIDS THATS HAVE BEEN SITTING IN ROOM TEMPERATURE FOR MORE THAN ONE HOUR c. Wash your toothbrush in the dishwasher once each month- EVERY DAY d. Wash your perineal area two times each day with antimicrobial soap- its says 69. A nurse in the emergency department is caring for a client who is in hypovolemic shock. Which of the following actions should the nurse take first? a. Administer IV therapy→ infusion of liquid substances referred to as drips 18-22 gauge commonly used b. 12-14 gauge c. Monitor urine output d. Obtain a blood specimen for type and crossmatch ANSWER IS B. Think TRAUMA not BASIC; pg.1641 (Lewis), Table 67-6 - Interventions 70. A nurse is providing a discharge teaching for a client who has heart failure and is to start therapy with digoxin. Which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching? a. “ I will notify my provider if I experience muscle weakness.” sign of toxicity pg 366 med srg b. “ I will take my digoxin if my pulse is less than 50 beats per minute.”- 60 bpm c. “ I will increase my dose if my vision becomes blurred.” d. “ I will take this medication with fiber to constipation.” 71. A nurse is assessing a client following the insertion of a central venous catheter. Which of the following findings indicates a pneumothorax? a. Diminished breath sounds b. Distended neck veins c. Irregular heart rate d. Itching over the incision ::::S/S of pneumothorax ● Signs of respiratory distress (tachypnea, tachycardia, hypoxia, cyanosis, dyspnea, and use of accessory muscles) ● Tracheal deviation to the UNAFFECTED side (tension pneumothorax) ● REDUCED or ABSENT breath sounds on the affected side 72. A Nurse is caring for a client who is 2 days postoperative following below the knee amputation and asks about the purpose of maintaining an elastic bandage around residual limb of the extremity. Which of the following is an appropriate response by the nurse. a. The elastic bandage will prevent a postoperative wound infection b. The elastic bandage will prevent excessive edema - MS 10.0 p 442 c. The elastic bandage will keep you from seeing the surgical site d. The elastic bandage will keep the sutures from loosening ::::Wrap the stump, using elastic bandages (figure-eight wrap) to prevent restriction of blood flow and decrease edema. 73. A nurse is assessing a client who has malnutrition. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect? a. Hyperproteinemia b. Cachexia (muscle wasting syndrome is loss of weight, muscle atrophy, fatigue, weakness, and significant loss of appetite in someone who is not actively trying to lose weight. c. Diplopia d. hypermagnesemia 74. A nurse is caring for a client who is receiving chemotherapy and requests information about acupuncture to relieve some of the side effects. Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as a contraindication to receiving this alternative therapy? a. Lymphedema (pg 1019, med srg protect client from trauma injections or venipunctures) b. Urticaria c. Mouth sores d. Headaches 75. A nurse is providing discharge teaching to a client who has an ileostomy . which of the following client statements indicates an understanding of the teaching? a. I will take a laxative when i am constipated b. I will expect my stools to be loose pg 533 med srg c. I will eat a higher- fiber diet-low d. I will empty my bag when it is full-half full ::::AVOID foods that cause odor/gas/high fiber Filters, deodorizers, or a breath mint can be placed in the pouch to minimize odor while the pouch is open. 76. A nurse is providing instructions about foot care for a client who has peripheral disease. The nurse should identify that which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching? a. I soak my feet in hot water before trimming my toenails b. I rest in my recliner with my feet elevated for about an hour every afternoon c. I use my heating pad on low setting to keep my feet warm. d. I apply a lubricating lotion to the cracked area on the solos of my feet morning. - repeat 77. A nurse is planning care for a client who has a pulmonary embolism and a prescription for enoxaparin via subcutaneous injection. Which of the following interventions should the nurse include? a. Assess the client’s stools for occult blood b. Massage the injection site c. For 1 min d. Instruct the client to limit vitamin K intake e. Monitor the client's PT levels - for warfarin 78. A nurse is caring for a client who is receiving total parenteral nutrition through central line. The current bag is nearly empty, and a new bag is unavailable from the pharmacy. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? a. Discontinue the infusion and flush the line b. Decrease the rate of the infusion to last until the new bag is available. c. Switch the infusion to a 10% dextrose solution. ::::Dextrose 10% in water (D10W) or Dextrose 20% in water (D20W) should be administered any time there is a temporary delay in TPN therapy. This is a hypertonic fluid which will provide dextrose to the client. The client’s blood glucose level will be maintained and the client is less likely to experience hypoglycemia. This is the safest nursing action. d. Start an infusion of 0.45% sodium chloride solution. 79. A nurse is providing teaching to a client who has tuberculosis. Which of the following is appropriate for the nurse to include in the teaching? a. “ You will need to continue to have yearly tuberculosis skin tests.” b. “ You should expect to take the prescribed medication therapy for 2 months.” c. “ You should avoid consuming fresh fruits and vegetables during therapy d. “ You will no longer be contagious after three consecutive negative sputum specimens.” 80. A nurse is teaching a client who has Graves disease about recognizing the manifestation of thyroid storm. Which of the ff findings should the nurse include in the teaching? (thyroid storm is via INCREASED thyroid hormone (T3) , so every this is up A. Lethargy- INSOMNIA B. C. Dec heart rate- INCREASED HR D. Hypotension- INCREASED BP Rationale: THYROID STORM EVERYTHING IS UP! 81. A nurse is caring for a female client who has toxin shock syndrome. Which of the of findings should the nurse expect? A. Hypertension (Hypotension during shock) B. Generalize rashy C. Elevated platelet count D. Decreased total bilirubin Rationale: Page 232. Physical manifestation includes Rash. Did not mention anything about platelet and bilirubin so I think it would be affected during toxin shock. 82. A nurse is caring for a client who is 5 days post op ff a total abdominal hysterectomy. Which of the ff findings indicated wound dehiscence? A. Incisional pain when coughing or breathing deeply *norm B. Increased serosanguineous drainage from the wound C. Serous crusting along the incision line *norm D. Inflammation of incision edges *norm Rationale: From ATI practice test. (looking for it) 83. A nurse is caring for a client who has bounding pulses, crackles on auscultation, and pink frothy secretions when receiving suctioning. The nurse should recognize these assessment findings as indicating which of the ff? A. Pleural Effusion B. Increased Cardiac Output C. Fluid Volume Excess D. Aspiration Rationale: 267 84. A nurse is preparing instructions for a client who is prescribed metoprolol. Which of the following should the nurse plan to include in the teaching? A. Monitor for hyperglycemia when taking the medication B. Expect excess production of saliva after taking the medication C. Take radial pulse before administering the medication D. Notify the provider if hearing loss occurs. Rationale: Yes because Metoprolol decrease the imbalance between myocardial oxygen supply and demand by reducing afterload and slowing heart rate 85. A nurse is caring for a client who develops third-degree heart block with a heart rate of 30/min/ Which of the following actions should the nurse take? A. Instruct the client to perform the Valsalva Maneuver. )AVOID THIS B. Prepare the client for temporary pacing (YES)→ someone asked me this in clinical if “pacing” is the correct answer. FYI- temporary pacing is an electrical cardiac stimulation to treat bradyarrhythmia or tachyarrhythmia. NOT like temporary pacing around. Lol C. Perform carotid sinus massage NO D. Administer digoxin by IV bolus NO Rationale: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/162007- treatment?pa=fRxjEv2RWk2SiPykK1T5tGaCNdCWeK6LosWnjyBzawc7kXTBWzbdiWc%2F6 n0%2B%2FxO8%2BBE1qPXmoBYm9wbVQZhq23f7Bj2Gvk6BKC47oRZ1BB8%3D#d7 86.A nurse is caring for a client who is receiving TPN. Which of ff nursing actions are appropriate? A. Increase the rate of infusion if administration is delayed. NO B. Monitor serum blood glucose during infusion C. Infuse 0.9% sodium chloride if the solution is not available. 10% dextrose D. Obtain the client wt daily E. Verify the solution with another RN prior infusion. ( Yes, Nutrition ATI pdf Ch 10) 87. A nurse is providing discharge teaching about foot care to a client who is newly diagnosed with type 1 DM. Which of the ff information should the nurse include? A. Apply lotion between the toes. NO B. Trim the toenails straight across. C. Inspect the feet every other day. DAILY D. Soak the feet twice a day DAILY Rationale: Page 532 88. A nurse reviewing the medical record of the client who is 1 day postoperative following an appendectomy. Which of the following findings should the nurse report to the provider? A. Hemoglobin 10 mg/dL (Female: 12-16, Males 14-18) ; B. Serosanguineous exudate noted on dressing change (blood vessel damage, serosanguinous is normal for first few days; purluent exudate is the bad one) C. Reports pain of 4 on a scale when coughing (expected r/t surgery) D. WBC count 8400/mm (within normal limit) Rationale:ATI p444 Hemoglobin is low r/t to possible bleeding/anemia? 89. A nurse is reviewing medications taken at home with a client who has angina. Which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching? A. I should withhold my metoprolol if my heart rate is above 100 bpm (No) B. I should place a nitroglycerin tablet under my tongue every 10min for up to four doses (3 lang and 5min dapat) C. I should lie down before taking dose of isosorbide dinitrate (nitrate) D. I should take my daily aspirin on an empty stomach (wag) RATIONALE: PAGE 170 of PHARM ATI 2016 90. A nurse is instructing a client who has a new diagnosis of type 1 diabetes mellitus about the sick-day rules. Which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching? (A) “I will monitor my blood glucose every 8 hours.”- every 3-4 “I will consume 250 grams of carbohydrates daily while I’m sick.” “I will check my urine for ketones if my blood glucose is greater than 240 mg/dL.”- DKA Rational Page 532 ATI “I will not take my diabetes medications while I am sick.” 91. A nurse is caring for a client who has thrombocytopenia. Which of the following laboratory results should the nurse expect? (A) Platelets 70,000/mm3 (normal is 150,000- 400,000) aPPT 40 seconds- Heparin 30-40 X (1.5-2) INR of 1.0 - warfarin PT 11 seconds- Rationale: ATI p444, thrombocytopenia = low platelets 92. A charge nurse receives a call from the house supervisor requesting room assignments for four new clients. Based on the admission diagnoses, which of the following clients requires a private room? (B) An older adult client who was admitted with aspiration pneumonia A client who reports having fever, night sweats, and cough for 2 days - most likely to spread- signs of TB A client who has diabetes mellitus and is presenting with acute ketoacidosis A client who has a compound fracture of the right femur 93. A nurse is caring for a client who has ulcerative colitis and was admitted to the medicalsurgical unit for management of diarrhea. Which of the following food items should the nurse select for the client’s breakfast tray? (Seedless and Low Residue) Whole grain toast Poached egg Oatmeal - Has most fiber- uhmm no. stay away from high fiber foods. Like bread wheat. grains. Fresh peaches- Has seeds 94. A nurse in a long-term care facility is caring for a bedridden client. Which of the following findings should alert the nurse to a potential complication of the client’s immobility? (A) Confusion because lower oxygen/embolism risk page 83 MS ATI PDF 10.0 Polyuria Blurred vision Diarrhea- more like constipation when you are not moving a lot 95. A nurse is providing teaching to a client who has diabetes mellitus. Which of the following instructions should the nurse provide to the client to help prevent the development of nephropathy? (A) Limiting protein intake Voiding every 2 hr Decreasing potassium intake Controlling hypertension Rationale: nephropathy = damaged kidney r/t htn (overworks kidneys and creates too much pressure) 96. A nurse is teaching a client who has asthma about the use of a peak flow meter. After setting the meter to the zero baseline, what is the sequence of steps the nurse should instruct the client to take? (Use all steps) “Stand upright.”- 1 “Fill your lungs with a deep breath.”-2 “Seal your lips around the mouthpiece.”-3 “Exhale forcefully and quickly.”-4 “Record the highest of three consecutive readings.”- 5 97. A nurse is caring for a client who has rheumatoid arthritis and reports increasing fatigue. The nurse should instruct the client to take which of the following actions to conserve energy? (C) Avoid using large muscle groups Allow others to perform her self-care activities (no, ask for additional assistance when needed, not do it all) - always want them to be independant as much as possible Determine priority activities to accomplish (ATI book p975: teach client measures to conserve energy [ie. space out activities, take rest periods) Limit iron intake. (encourage foods high in vitamins, protein, iron) 98. A nurse is caring for a client who had a total hip arthroplasty. Which of the following actions should the nurse take to prevent hip dislocation? (A)+ Place two bed pillows between the legs when in bed.- Prevent dislocation/Encourage the client to lean forward when attempting to stand. Elevate the knees higher than the hips when sitting. Remove the wedge device when turning. 99. A nurse working in the emergency department is assessing a client admitted with atrial fibrillation. Which of the following findings should the nurse report to the provider immediately? (D) Ventricular rate 120/min → not too high Syncope-fainting from a drop of blood pressure → s/s of a-fib Atrial rate of 350/min normal for A-fib (400-600) AF→ although this is a normal finding for A-FIB, it needed to be treated right away with cardioversion, ANTIDYSRHYTHMIC (amiodarone),, and heparin because blood tends to pool and clot with high risk for EMBOLI STROKE. REVIEW WEBSITE: https://www.heart.org/idc/groups/heartpublic/@wcm/@hcm/documents/downloadable/ucm_300294.pdf Shortness of breath (“sob” is a little different than “dyspnea”) s/s of a-fib Rationale: ATI book 316: complication for dysrhythmia is decreased CO (s/s: hypotension, syncope, increased HR) and HF (s/s:dyspnea, productive cough, edema, venous distention) 100. A nurse is caring for a client who is admitted with heart failure. Which of the following laboratory findings should the nurse report to the provider? Hematocrit 24% (blood cells per volume of blood less= less RBC)(ATI book p444: normal female 37-47%, male 42-52%) Sodium 137 mEq/L Glucose 112 mg/dL BUN 19 mg/dL [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 45 pages
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 11, 2021
Number of pages
45
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 11, 2021
Downloads
1
Views
99








 (1).png)

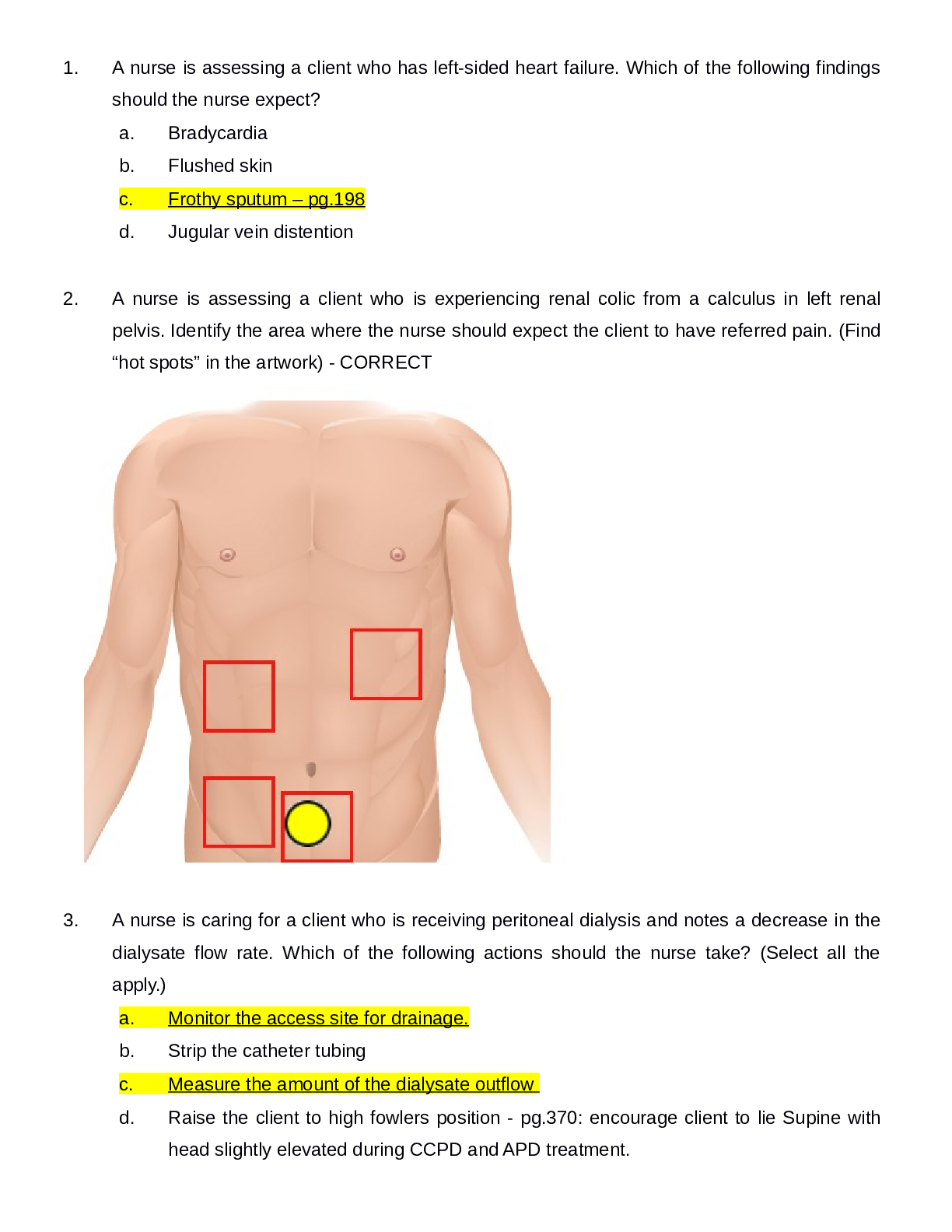









 (2500+ Q & A).png)