*NURSING > EXAM > NR507 Final exam Study Guide_Chamberlain College Of Nursing:ALL ANSWERS ARE CORRECT (All)
NR507 Final exam Study Guide_Chamberlain College Of Nursing:ALL ANSWERS ARE CORRECT
Document Content and Description Below
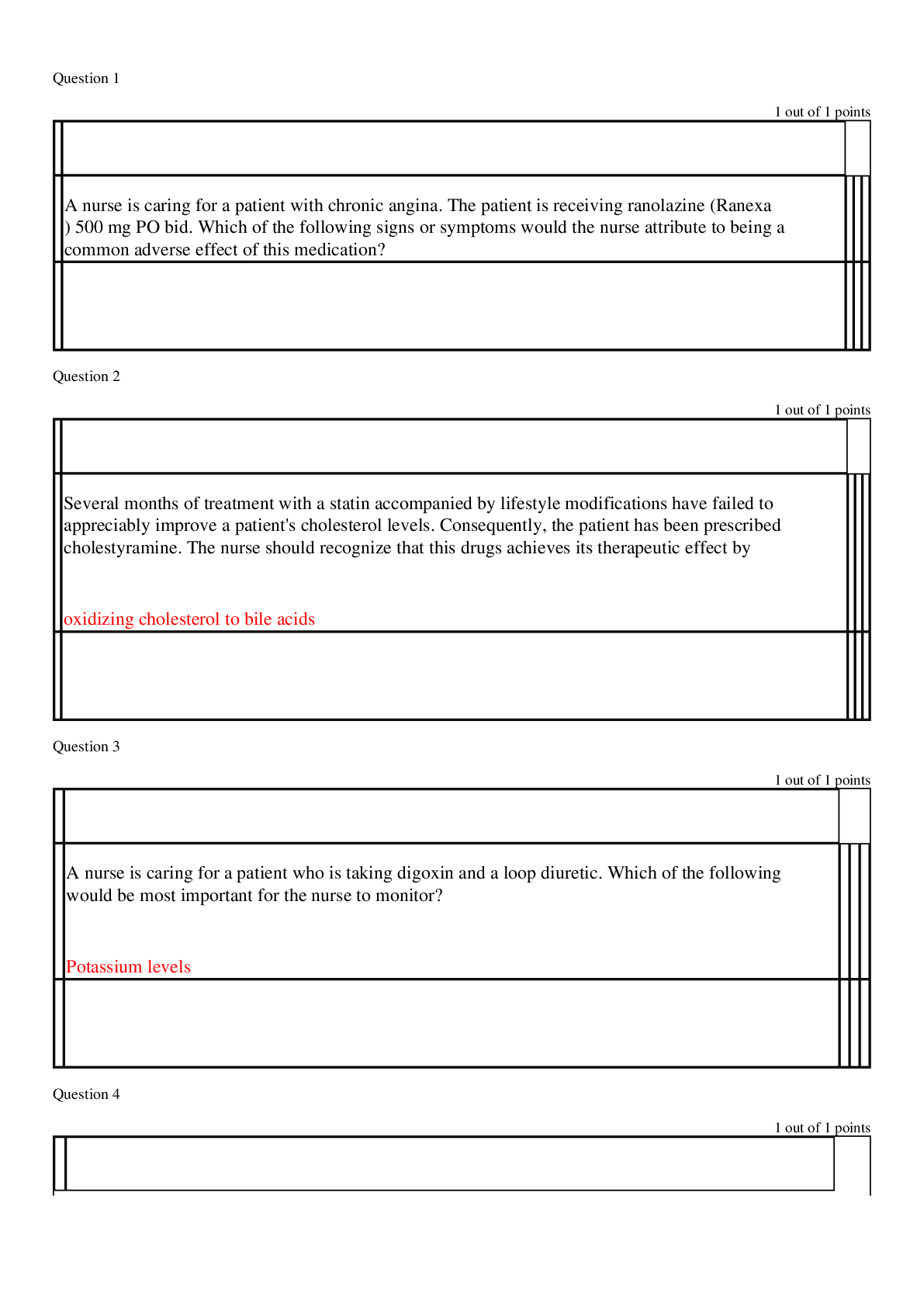
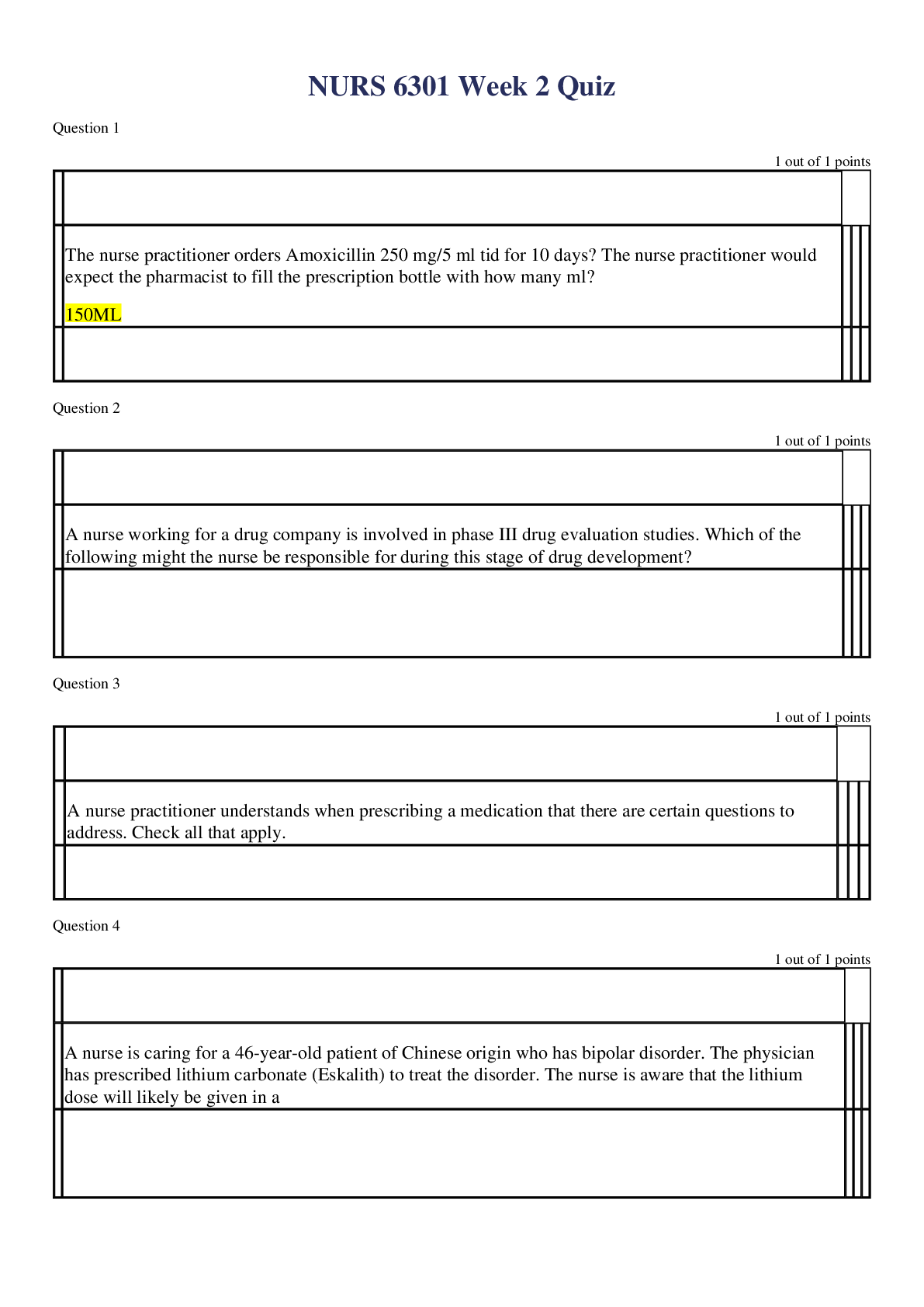
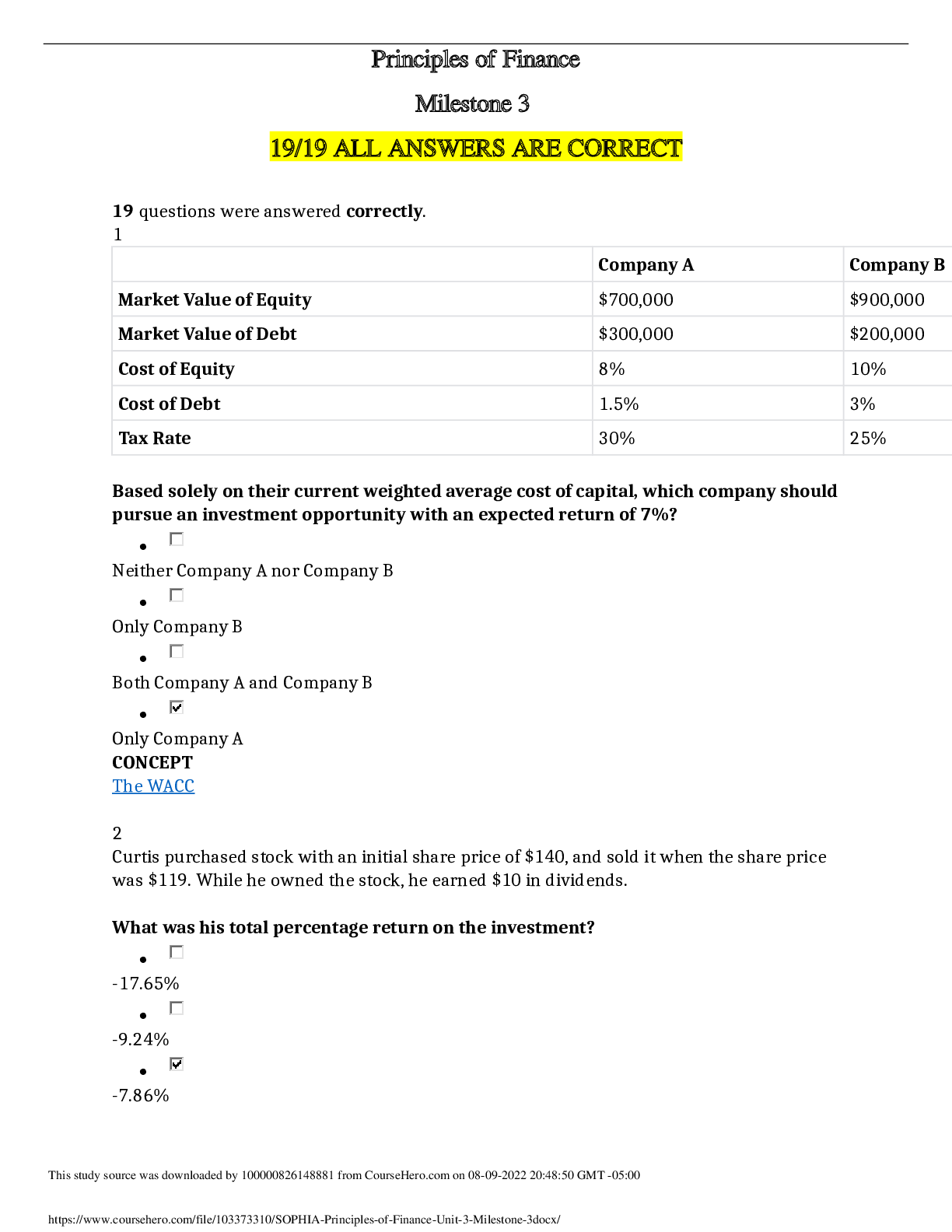
NR-507 Study Guide 1. Types of immunity ch 7 & 8 a. Innate- natural epithelial barrier and inflammation the make innate resistance and protection pg. 191 b. Adaptive/ acquired- immune response or i... mmunity, after innate and inflammation, i. Active (Acquired) -after natural exposure to an antigen or after immunization pg. 227 ii. Passive (Acquired)- preformed antibodies or t lymphocytes are transferred rom a donor to the recipient, maternal to fetus, or bone marrow transplant pg. 227 2. Alveolar ventilation/perfusion- pg. 1239 Ch 34 a. Ratio between the amount of air getting into the alveoli and the amount of blood being sent to the lungs. 3. Dermatologic conditions ch. 46 e.g. pityriasis rosea- benign self-limiting inflammatory disorder that occurs in young adults, with seasonal peaks spring and fall. Harmful in pregnancy. Associated with a virus, starts with a herald patch, circular. Salmon pink, and demarcated, usually on the trunk, acyclovir and erythromycin, and corticosteroid creams for itching. Should go away within a few months. 4. Croup- pg. 1294-1296 Viral, barking cough, winter and spring months, usually affects children 6 mo to 3 yrs, peak at 2 years old, stridor, and fever, 2-5 days. human parainfluenza viruses (HPIVs), RSV, viruses are airborne. Rest, humidity, and lots of fluids. Acute laryngotracheobronchitis 5. Types of anemia pg. 982-1102 C. 28 reduction of the total number of erythrocytes in the circulating blood or a decrease in the quality or quantity of hemoglobin a. Macrocytic-normochromic anemia- large abnormally shaped erythrocytes but normal hemoglobin concentrations (Pernicious- lack of B12, abnormal RNA and DNA synthesis and early cell death, folate deficiency- lack of folate for erythropoiesis premature cell death) b. Microcytic-hypochromic anemia- Small abnormally shaped erythrocytes and reduced hemoglobin concentration (Iron deficiency- lack of Fe for hemoglobin production, insufficient hemo, sideroblastic- dysfunctional iron uptake by erythroblasts and defective porphyrin and heme synthesis, thalassemia- impaired synthesis of alpha and beta chain of hemoglobin, phagocytosis of abnormal erythroblasts in the marrow) c. Normocytic-normochromic anemia- normal size, normal hemo concentration (aplastic- insufficient erythropoiesis, posthemorrhagic- blood lost, hemolytic- premature destruction of mature erythrocytes in the circulation, sickle cell- abnormal hemo synthesis, abnormal cell shape with damage, lysis and phagocytosis, anemia of chronic disease- abnormal demand for new erythrocytes ) 6. The inflammatory process upon injury pg. 195 Ch. 7- blood vessel dilation, increased vascular permeability and leakage of fluid out of the vessel, WBC adherence to the inner walls of the vessel and their migration through vessel walls to the site of injury. Figure 7-2 7. GI symptoms resulting in heart burn- pg. 1429 Ch 41. acid regurg chronic cough, asthma attacks, and laryngitis. Upper abd pain, within 1 hr of eating, worse lying down, chest pain, 8. Pulmonary terminology - dyspnea- SOB, Orthopnea- postural SOB Ch 35 pg. 1248 9. Complications of gastric resection surgery-pg 1440 dumping syndrome, 10. Dermatology terminology-Ch. 46, pg. 1620, macules- freckles, flat moles, change in color, less than1 cm, nevi- moles pg. 1641, etc- 11. Chicken pox- pg. 1660, ch. 47. disease of early childhood, highly contagious virus, vesicles, trunk, scalp, or face, transmission 5-6 days after first vesicle, contagious 1 day prior to rash, contagious for 7-10 days, 12. Maternal immune system- pg. 1059. ABO incompatibility 13. Candidiasis exacerbation- pg. 1638 yeast like fungus in moist areas, 14. Carbuncles- pg. 1635 collection of infected hair follicles occurring usually at the back of the neck, upper back, and lateral thighs 15. Terms such as hypochromic, macrocytic, microcytic, etc pg. 983 Ch 28 a. Hypochromic- lower hemoglobin content b. Macrocytic- higher erythrocyte volume c. Microcytic- lower erythrocyte volume d. Hyperchromic- higher hemoglobin concentration e. Normochromic- hemo concentration normal f. Normocytic- normal erythrocyte concentration 16. Antibodies pg. 229-230 IgG- most abundant 80-85%, protective activity, IgA- normal body secretions highest amount here, IgM- largest first produced in initial or primary response, early in neonatal life, IgD- low concentrations, bcell antigen receptor, IgE least concentrated- mediator of allergic responses 17. Skin cancer- pg. 1641. basal carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma most common 18. Parts of the heart in terms of function Ch. 31 pg. 1085 pericardium- double wall membrane around the heart, prevents displacement of the heart, physical barrier and contracts pain receptors and mechanoreceptors that elicit changes to BP and heart rate 19. Congenital heart defects- pg. 1198 leading cause of death in the first year of life minus prematurity. Etiology usually unknown. 20. Urinary tract obstruction- pg. 1341 Ch 38- interference with the flow of urine at any site along the urinary tract 21. GI symptoms of conditions Ch. 41 a. pyloric stenosis- fullness, nausea, epigatric pain pg. 1430 b. hiatal hernia- asymptomatic, associated with GERd symptoms, dysphagia, epigastric pain pg 1430 c. ulcerative colitis- watery diahhrea, bleeding and cramping, urge to poop, dehydration, weight loss, anemia, and fever pg. 1442 22. Skin cancer lesions-pg. 1642 superficial, nodular, sclerosis/morpheaform, can be pigmented or non pigmented. 23. Gastroesophageal reflux disease- pg, 1429 Ch 41- reflux of acid and pepsin from stomach, to the esophagus, risk factors obesity, hiatal hernia, drugs or chemicals 24. Hypersensitivity reaction- pg. 263 a. Type 1 IgE mediated- immediate, products of mast cells, most common for allergies b. Type 2 tissue specific- immediate, specific cell or tissue being the target of an immune response, IgG and IgM, macrophages in tissues, complement participated frequently, autoimmune thrombocytopenia purpura, graves, hemolytic anemia c. Type 3 immune complex- immediate, IgG and IgM, Neutrophils, completment does participate, systemic lupus d. Type 4 Cell mediated reaction- delayed, no IGs, Lymphocytes, macrohphages, No complement, Poison Ivy and metal sensitivities 25. Congenital intrinsic factor deficiency- pg. 988, genetic disorder tat demonstrates an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern, transporter required for absorption of dietary Vit b12, essential for maturation and DNA synthesis in erythrocytes. Results in Percutaneous anemia (CH. 28) 26. Acid base imbalance- Pg. 126 Ch. 3, See charts 27. Acute epiglottitis- pg. 1296-1297, 25% of cases seen in children, 2-6 years old, high fever, irritable, sore throat, inspiratory stridor and respiratory distress. Do not assess airway 28. Types of gastric ulcers-pg. 1438 Ch. 41. signs and symptoms, characteristics- Stomach ulcers, 55-65 years old, ¼ as common as duodenal ulcers, pain is gone after eating a. Stress ulcer acute form of peptic ulcer b. Ischemic ulcer lack of o2 to an area after another medical event c. Cushing ulcer severe head trauma 29. Lupus- pg. 1632- inflammatory, autoimmune, systemic disease with cutaneous manifestations, lupus nehritis is a complication affecting renal component pg. 1358 30. General adaptation syndrome- pg. 339- 1. Alarm stage or reaction, CNS is aroused and the bodys defenses are mobilized, 2. Resistance or adaptation- mobilization contributes to fight or flight, 3. Stage of exhaustion where continuous stress causes the progressive breakdown of compensatory mechanisms and homeostatis. 31. Ventilation/perfusion ratio- V/Q ratio, normal is 0.8 pg. 1240 32. Bile salt deficiencies- pg. 1440- poor intestinal absorption of fats, and fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E and K), loss via stool and decreased plasma proteins, a- night blindness, d- decrease in calcium with bone demineralization, k- prolongs PT, leading to bruising and petechiae, E- testicular atrophy and neo effects in children, treatment is increasing medium-chain triglycerides in the diet, coconut oil 33. Clonal selection- pg. 226, selection, proliferation and differentiation of individual T and B cells with receptors for a specific antigen 34. Obstructive sleep apnea- pg. 504, ch 16, disorder of sleep characterized by airway obstruction and episodes of apnea with snoring, 35. Large bowel obstruction- pg 1432, s/sx are hypo gastric pain, and abdominal distention 36. Vaginal candidiasis- pg. 1638 table, heat, moisture, occlusive clothing, pregnancy, systemic antibiotics, DM, SEX, itching, white, watery, or creamy discharge, swollen vaginal and labial membranes with erosions, lesions on anus and groin, treated with miconazole cream, nystatin tablets, clotrimazole tablets or cream, loose cotton clothing 37. Folate deficiency- pg. 989 essential vitamin for RNA and DNA synthesis within maturing erythrocyte, dietary intake results in anemia 38. Pancreatic insufficiency- Pg. 1439- deficient production of pancreatic enzymes, lipase, amylase, trypsin, chymotrypsin, causes chronic pancreatitis, pan carcinoma, panc resection, and CF. 39. Types of fractures- Oblique, occult, open, pathologic, segmented, spiral, transverse, green stick, impacted pg. 1541 40. Genetic disorders such as Down Syndrome- pg. 146 – aneuploidy in an autosome is trisomy of the 21 chromosome, low nasal bridge, epicanthal folds, protruding tongue, flat low set ears, Turner Syndrome- pg 147- single X chromosome, no Y only females affected, sex chromosome aneuploidy, sterile, gonadal streaks rather than ovaries, short, webbing of neck, widely spaced nipples, edema in feet and sparse body hair. 41. Vitamin B-12 therapy- 988-989 cobalamin, initial injections of vit b12 are administered weekly, followed by monthly injections for an individuals life, for Pernicious anemia (PA) 42. Glaucoma pg. 510-11- leading cause of visual impairment and blindness, intraocular pressures greater than 12-20mm Hg, family history is a risk factor, 43. Cervical immunoglobulin- A 44. Concept of pain- pg. 485, always subjective, 45. Autosomal dominant diseases-pg. 152-154 inherited one bad gene from one parents that is dominant, they are rare, fewer than 1 in 500 individuals 46. Congenital murmurs- have at birth, innocent or more 47. Lactose intolerance- pg. 1439 inhibits the breakdown of lactose into monosaccharides and there fore prevents lactose digestion and absorption in the intestinal wall, most common in blacks, watery diarrhea, bloating, cramping, pain, diarrhea, flatulence 48. Angiotensin-renin system- pg. 176 Table 49. AIDS- pg. 322, viral disease caused by HIV, infects and depletes a portion of the immune system, Th cells, making people very susceptible to life threatening infections and malignancies. 50. Carcinoma- pg. 364 cancers arising from the epithelial tissues 51. Hormonal regulation of calcium- pg. 119 by parathyroid hormone (PTH), vitamin D and calcitonin 52. Neural tube defect- pg. 168, 663-666 Normally closed at 4 weeks gestation but a defect in closure or subsequent reopening results in defect. Anencephaly, spina bifida, and encephalocele. 53. Types of hormones- pg. 690 Table, 717-767, 804-855 Water soluble, lipid soluble 54. Glycoprotein- pg. 13-15 Proteins attached to carbs, cell surface markers. 55. Kidney stones- pg. 1343-1344 Masses of crystals, protein, or other substances common cause of UTO, most common form is of calcium oxalate or phosphate 56. Type 2 diabetes- 734, 739-742 insulin resistance with relative insulin deficiency to predominately secretory defect with insulin resistance, , insulin requiring, obese, strong genetic predisposition, HTN and dyslipidemia common, older than 40 years old, 57. Pituitary hormone secretion- posterior- (polypeptide hormones) ADH & oxytocin, anterior- ACTH, melanocyte- stimulating hormone (MSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), GH, prolactin, follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and TSH 58. Signs of breast cancer- pg. 873 Chest pain, dilated blood vessels, dimpling of skin, edema, , edema of arm, hemorrhage, local pain, nipple/areolar eczema, nipple discharge, nipple retraction, pitting of skin, reddened skin, skin retraction, ulceration 59. Alzheimer’s disease- Pg. 545-550 leading cause of dementia, and one of the most common causes of severe cognitive dysfunction in older adults, risk factors include low estrogen, being a female, DM, obesity, smoker, HTN, HLD, inactivity, head trauma. Unknown what causes it, 60. Guillain-Barre Syndrome- pg. 622-624 an acquired acute inflammatory demyelinating or axonal polyneuropathy with four subtypes. Autoimmune triggered by a bacterial or viral infection. S/Sx numbness, pain, paresthsia, or weakness in limbs, Diagnosed by CSF- high proteins found, without cellular abnormality. IgG infusions, plasmapheresis, combination therapy. 61. Sympathetic/parasympathetic nervous system- pg. 448 & 473 cranial nerves, which project from the brain, and pass through foramina in the skull, and the spinal nerves, which come from the spinal cord and pass through intervertebral foramina of the vertebrae. 62. ACTH- pg. 339, 699T- corticosteroid, adrenal gland/ cortex is target organ, increased steoridogenesis, synthesis of adrenal proteins contributing to the maintenance of the adrenal gland, made by anterior pituitary 63. Bartholin glands- pg. 772, 817F- open on either side of the introitus, in response to sex they secrete mucus that lubricates the inner labial surfaces. As well as enhances the viability and motility of sperm. 64. Gonococcal disease- pg. 921- contact through epithelial surfaces, Gonorrhea 65. Glomerulonephritis-pg. 1352- 1358, the inflammation of the glomerulus, caused by glomular injury, primary and secondary. 66. Small patent ductus arteriosus-pg. 1202, is a condition in which the ductus arteriosus does not close. The word "patent" means open. The ductus arteriosus is a blood vessel that allows blood to go around the baby's lungs before birth, occurs in 5-10% of congenital defects 67. Risk factors for hypertension- pg. 1136, genetics, DM, obesisy, high sodium intake, smoking, drinking, 68. Loss of language and/or comprehension-pg. 539 aphasia- loss of comprehension or production of language, Dysphagia- impairment of comprehension or production of language, 69. Chronic inflammatory joint disease- pg. 1568- Arthritis, damage or destruction in the synovial membrane, or articular cartilage and by systemic signs of inflammation- fever, leukocytosis, malaise, anorexia and hyperfibrinogenemia. Infectious or non-infectious. 70. Male and female sex hormone production- a. Female- pg. 776 all sex hormones are steroid hormones, synthesized from cholesterol, Estrogen, and progesterone, produced by ovaries, surges at puberty, low levels of testosterone and androgen, leptin in puberty increases caloric demands b. Male- pg. 789, Androgens and testosterone. Leydig cels of the testes and to a lesser degree the adrenal glands produce the hormones 71. Endogenous antigen- is a marker on your own cells that starts an immune response 72. Genital warts- pg. 935 HPV, very contagious, in the low risk strains of HPV, 38-95% contract them when in contact with an infected person, have a vaccine for subtypes 6, 11, 16 and 18, three immunization series. HPV is a noneveloped, circular, double stranded DNA Virus, one of the papoviruses, , may manifest in 2-3 months or not for years, warts are called conylomata acuminate, cause sexual dyspareunia, may bleed 73. Pancreatic enzymes-pg. 1439 lipase, amylase, trypsin, chromotrypain- digest proteins, fats and carbs 74. Process of muscle contraction- Pg. 1533 a. Excitation- spread of action potential, from the nerve terminal to the neuromuscular junction, rapid depolarization, creates the muscle fiber action potential, advances to the t tubules, which triggers voltage sensitive receptors, opening the RyR channels and releasing Ca b. Coupling- migration of Ca ions to the myofilaments, Ca affects troponin and tropomysin, muscle proteins that bind with actin c. Contraction- Ca ions combine with troponin, reaction that overcomes the inhibitory function of the troponin-tropomysin system. Actin moves towards myosin, which shortened after contraction, Cross bridge theory, ATP releases, actin-myosin cross bridges, actin slides on myosin, causing sarcomere to shorten d. Relaxation- As sarcoplasmic reticulum absorbs Ca removing them from the troponin, ca pumped back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum by active transport, cross bridge detaches and the sarcomere lengthens 75. Cervical dysplasia- pg. 827. Caused by HPV, risk of cancer increases with the severity of dysplasia, goes in stages, CIN stage 1-3 76. Consanguinity- pg. 155, marriage between two first cousins, factors into producing children with recessive diseases because related individuals are more likely to have the same recessive genes. 77. Nephrotic syndrome- pg. 1358 excretion of 3.0g or more protein in urine per day, hypoalbumemia, and peripheral edema. S/Sx hematuria, , casts present, proteinuria, [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 6 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 11, 2020
Number of pages
6
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 11, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
49