Surgery > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Surgery Week Quiz Series - Part 9 [GRADED A+] (All)
Surgery Week Quiz Series - Part 9 [GRADED A+]
Document Content and Description Below
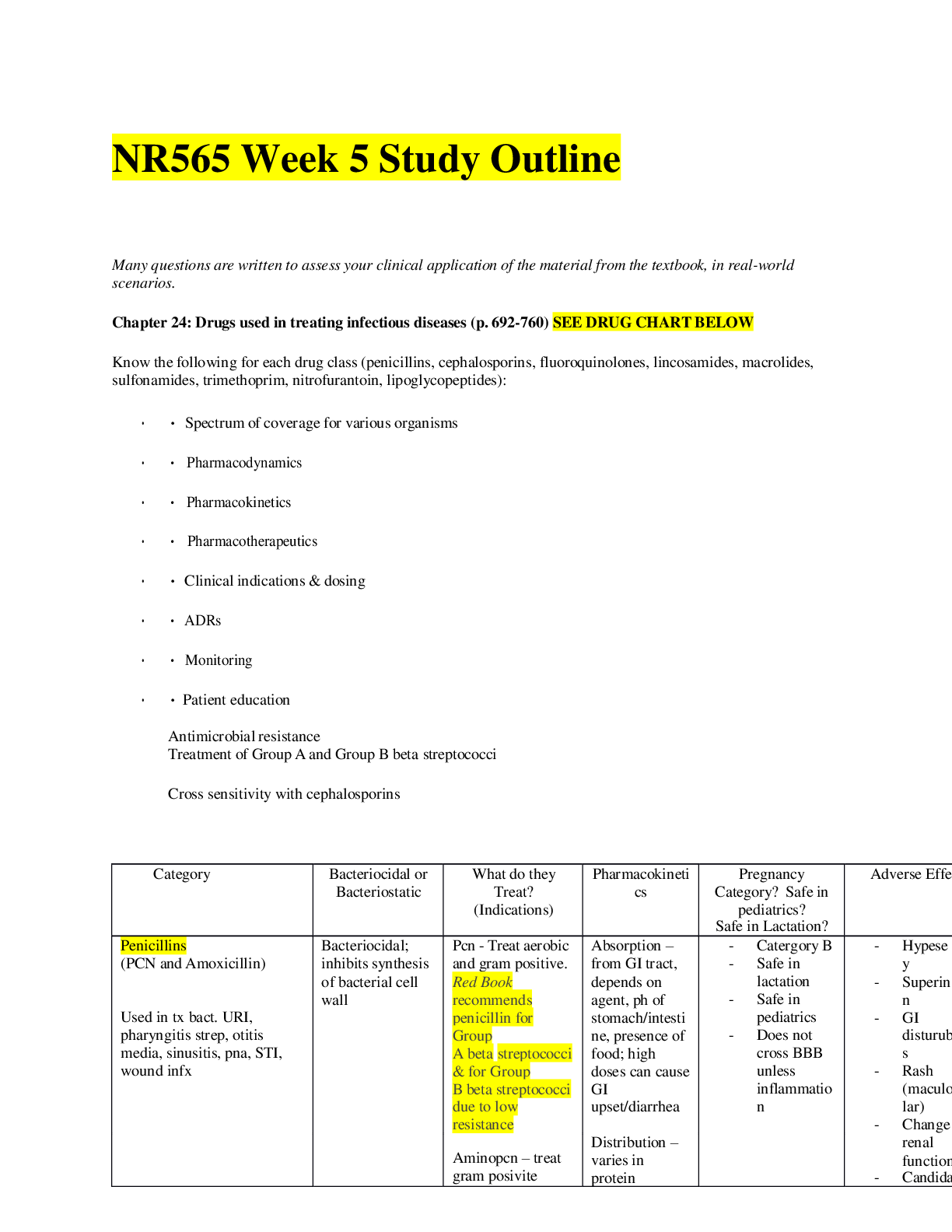
surgery week 9 quiz Q # 1 of 50 - 1 Points USMLE Step 2 CK Medical Subject Review 1. An otherwise healthy 24-year-old basketball player discovers that he has a 2-day history of scrotal 'swelling.'... There is no pain or redness. The examining doctor finds that when the patient is standing, the left scrotal sac is enlarged with a tubular, worm-like, freely movable nontender mass. The mass is not palpable when he is supine. The most likely diagnosis is A. Cystocele B. Epididymal cyst C. Indirect inguinal hernia D. Spermatocele E. Hydrocele F. Varicocele 2. A 30-year-old married woman comes to your clinic with a 2-month history of urgency in urination. She complains of increased frequency of urination. She also complains of pain in the lower abdominal area, which decreases considerably as her bladder gets full and she feels the need to urinate. Her symptoms get worse during menstruation, and she sometimes experiences pain during sexual intercourse. You order urinalysis, urine culture, cystoscopy, and biopsy of the bladder wall to be done. Which of the following statements is characteristic of the above disease? A. Many eosinophils are seen in the bladder epithelium B. Multiple plaques made up of foamy macrophage are a characteristic feature C. Immune suppressed patients most frequently suffer from this type of cystitis D. Inflammation and fibrosis of all layers of the urinary bladder are seen E. Males are more frequently affected than females 3. A 59-year-old man is admitted to the hospital with complaints of weight loss, flank pain, hypertension, supraclavicular lymphadenopathy, and malaise. He had been reasonably healthy all of his life and had never been hospitalized before. A full work-up was done, including blood work, abdominal X-ray, and CT. Vital signs are as follows: BP 155/100 mm of Hg, P 88 beats/min, RR 16 per min, T 98.9 degrees Fahrenheit. Lab tests revealed a CBC within normal limits and hypercalcemia. Urinalysis was normal except for trace hematuria. The abdominal CT showed a 1cm solid mass in the left kidney. Which of the following concerning renal cell carcinoma is true? A. Women are affected more than men B. The classic triad of flank pain, hematuria, and flank mass is most commonly seen and indicates advanced disease C. Approximately 30% of patients present with metastatic disease D. The most common presentation is hypertension E. The disease is more common in those of Asian and African descent 4. A 47-year-old female is brought to the emergency room with hematuria, flank pain, anemia, malaise, and weight loss. Her past medical history is significant for several years of smoking. Her vital signs are as follows: BP 128/86 mm of Hg, P 74/ min, RR 14/min, T 98.4 degrees Fahrenheit. Blood work and urinalysis were normal with the exception of hypercalcemia and hematuria. An abdominal CT shows a 3.2cm solid mass near the pelvis of the right kidney. The most likely diagnosis is A. Pyelonephritis B. Wilm's tumor C. Renal abscess D. Renal cell carcinoma E. Pheochromocytoma 5. An 18-year-old Eurasian woman has a 2-day history of tea-colored urine. All her urine is discolored, she has normal urine volume and frequency, and she has had pharyngitis for 3 days. She has taken no medications or illicit drugs and has not eaten any beets or other dark colored foods recently. She is on the 22nd day of her menstrual cycle and is not sexually active. Her blood pressure is 115/78 mm Hg without orthostatic changes. She has oropharyngeal erythema and no adenopathy. The remainder of her exam is normal. Her rapid pharyngeal streptococcal culture is negative. Given her history, what is the most important diagnostic study to do next? A. Renal biopsy B. Urinalysis with microscopy C. Renal ultrasound D. Renal CT scan E. Renal MRI 6. A 24-year-old Caucasian male comes to your office to establish care. In taking his history, you learn that he had an episode of painless hematuria during a pharyngeal infection while in college. He was told at the time that his blood pressure and blood kidney tests were normal, but that he should have follow up in the future. He is asymptomatic. His blood pressure is 115/80 mm hg and his exam is normal. Given his history of hematuria, what diagnostic studies are MOST appropriate for his health maintenance? A. Urinalysis, serum creatinine, KUB X-ray, and electrolytes B. Urine culture, serum creatinine, and serum electrolytes C. Urinalysis with microscopy, urine albumin/creatinine ratio, and serum creatinine D. Complete blood count, serum electrolytes, and creatinine E. Urinalysis with microscopy and polarizing light, urine albumin/creatinine ratio [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 20 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 08, 2023
Number of pages
20
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 08, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
40

























.png)

.png)




.png)
.png)

.png)

