Biology > Class Notes > Course Notes > University of Louisville BIO 240ch 9 cellular respiration and fermentation notes (All)
Course Notes > University of Louisville BIO 240ch 9 cellular respiration and fermentation notes
Document Content and Description Below
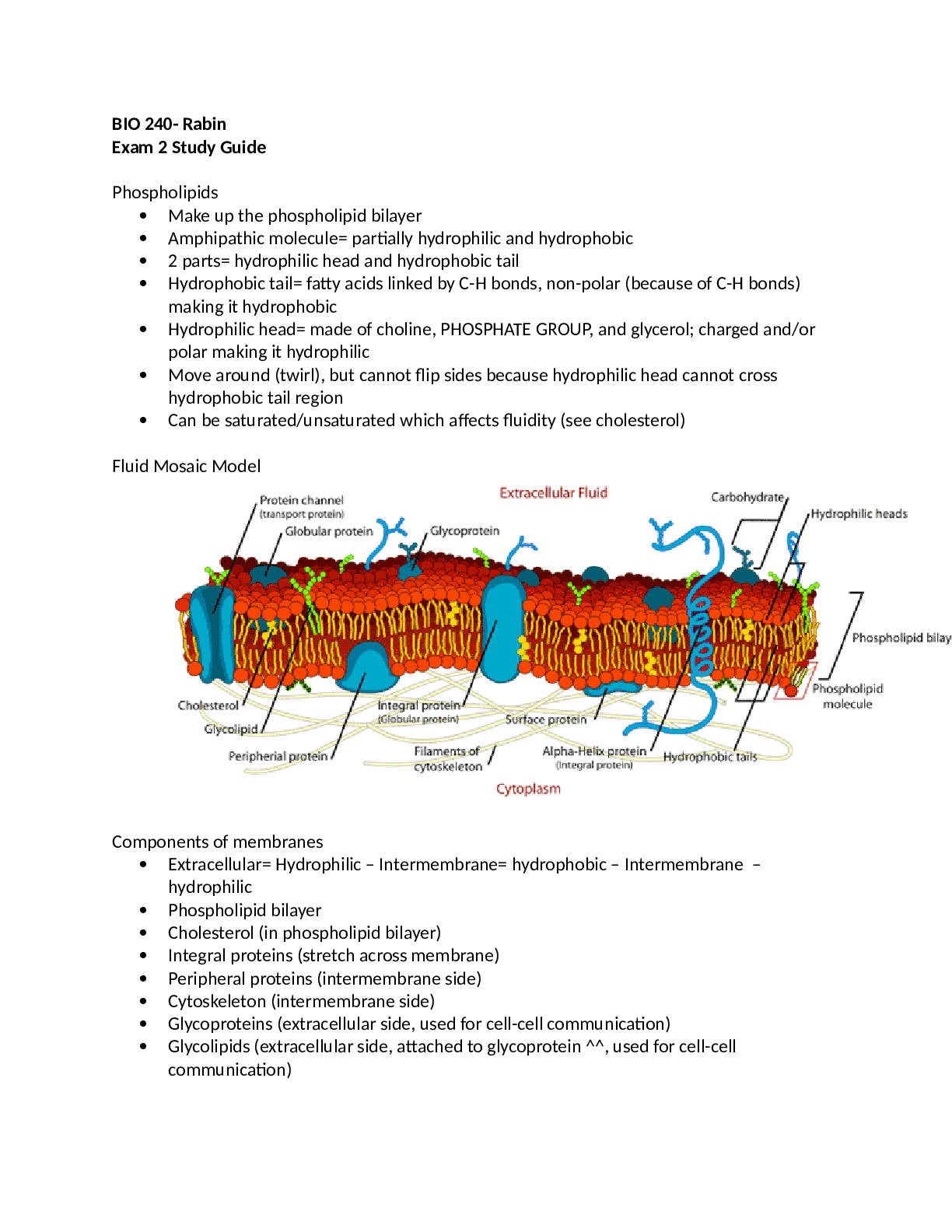
University of Louisville BIO 240 ch 9 cellular respiration and fermentation notes Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Catabolic Pathways yield energy by oxidizing organic fuels o Several pr... ocesses are central to cellular respiration and related pathways o The breakdown of organic molecules is exergonic o Fermentation is a partial degradation of sugars that occur without O2 o Aerobic Respiration consumes molecules and O2 to make ATP o Cellular Respiration includes both aerobic and anaerobic processes Redox Reactions = Oxidation and Reduction o Oxidation - loses electrons o Reduction - accepts electrons o The electron donor is called the reducing agent o The electron acceptor is called the oxidizing agent o NADP+ - electron carrier in respiration 3 Stages of Cellular Respiration (Figure 9.6) o Glycolysis 3 phases of Glycolysis Energy Investment Phase Hexokinase transfers a phosphate group from ATP to glucose, making it more chemically reactive. The charge of the phosphate also traps the sugar in the cell Glucose 6-Phosphate is converted to its isomer, Fructose 6-Phosphate Phosphofructokinase transfers a phosphate group from ATP to the opposite end of the sugar, investing a second molecule of ATP. This is a key step for regulation of glycolysis. Aldolase cleaves the sugar molecule into two different three-carbon sugars (isomers). Isomerase catalyzes the reversible conversion between the two isomers. This reaction never reaches equilibrium: Glyceraldehyde 3-Phosphate is used as the substrate of the next reaction as fast as it forms. Energy Payoff Phase The enzyme catalyzes two sequential reactions. First, the sugar is oxidized by the transfer of elctrons to NAD+, forming NADH Net Oxidates Creates 4 ATP, but uses 2 => Net 2 ATP Sugar-breakdown Glucose -> Pyruvate Glucose is cut in half Producing NADH From the cytosol, it then moves to the matrix of the mitochondria for…. o Pyruvate Oxidation and the Citric Acid/Krebs Cycle Makes ATP Decarboxylation During Oxidative Phosphorylation, Chemiosmosis couples electron transport to ATP synthesis [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 2 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Aug 02, 2022
Number of pages
2
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Aug 02, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
73