Complex Oxygenation - ATI Practice Exam 9 Detailed Answer Key
Document Content and Description Below
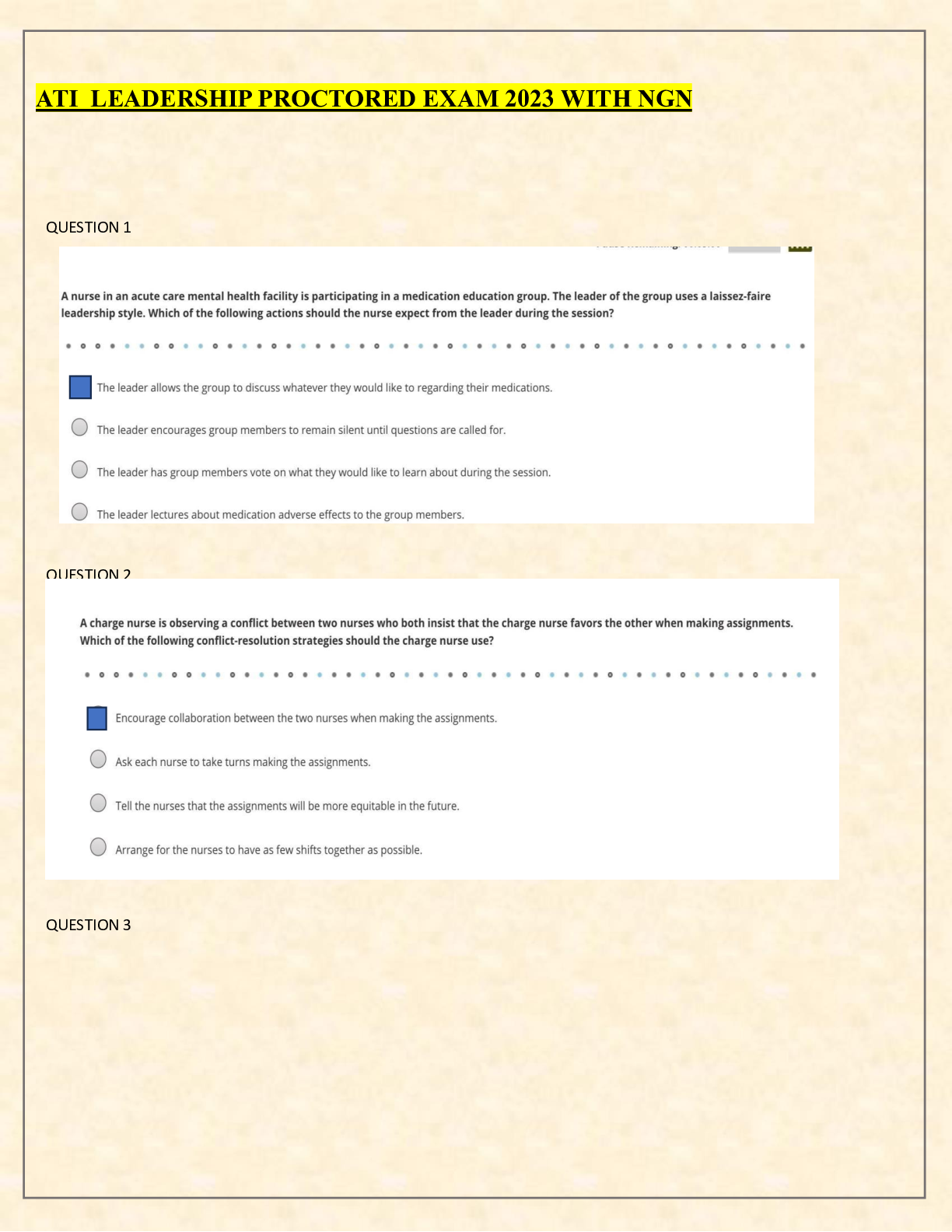
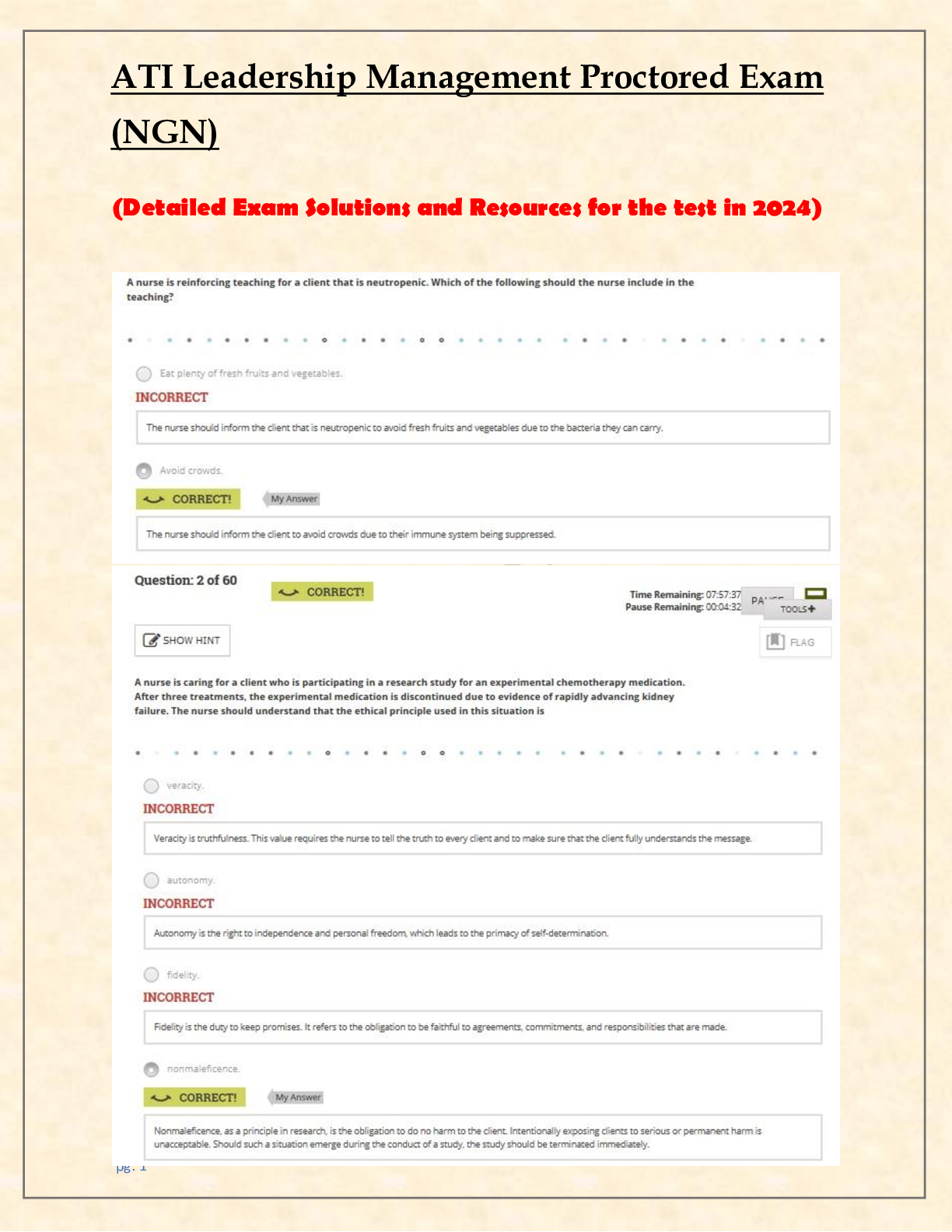
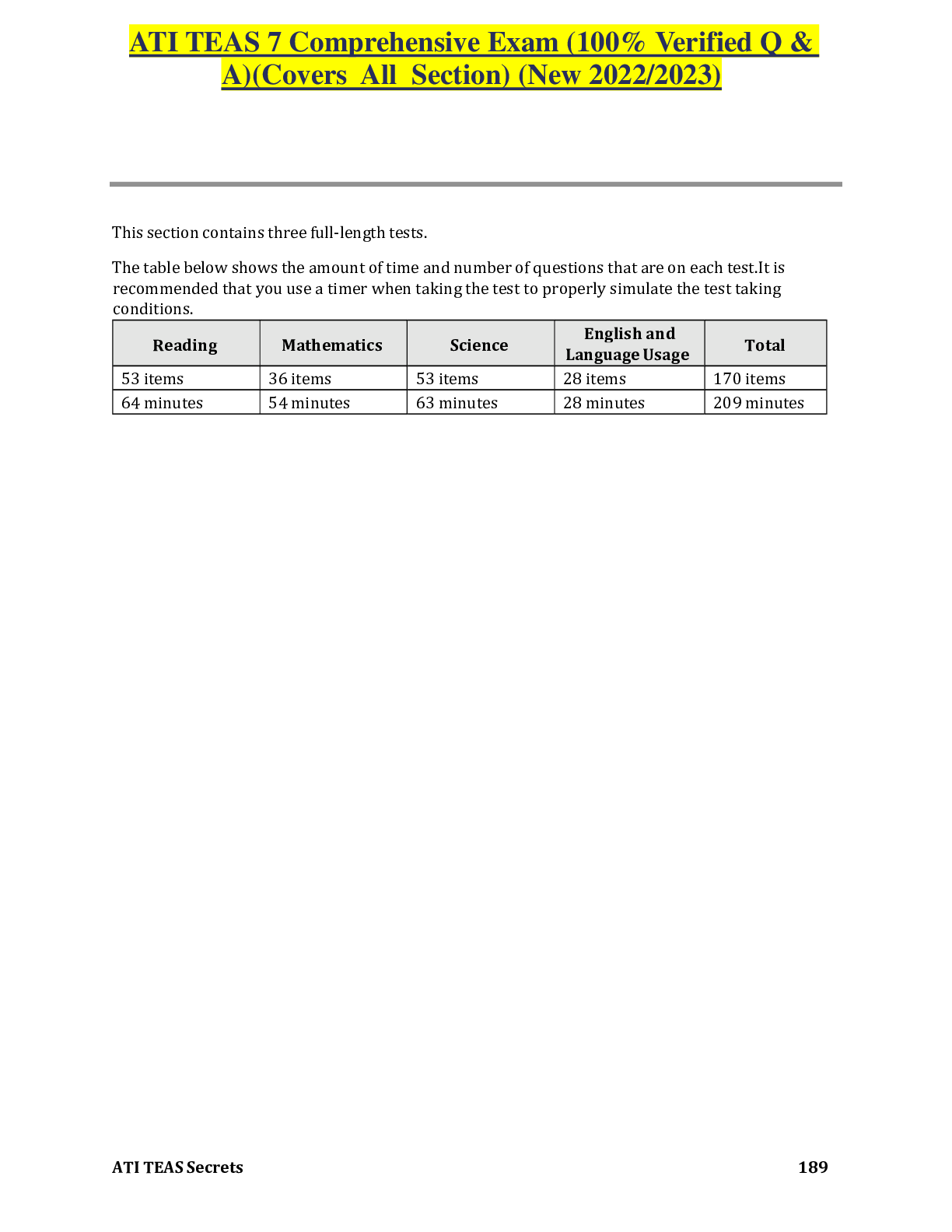
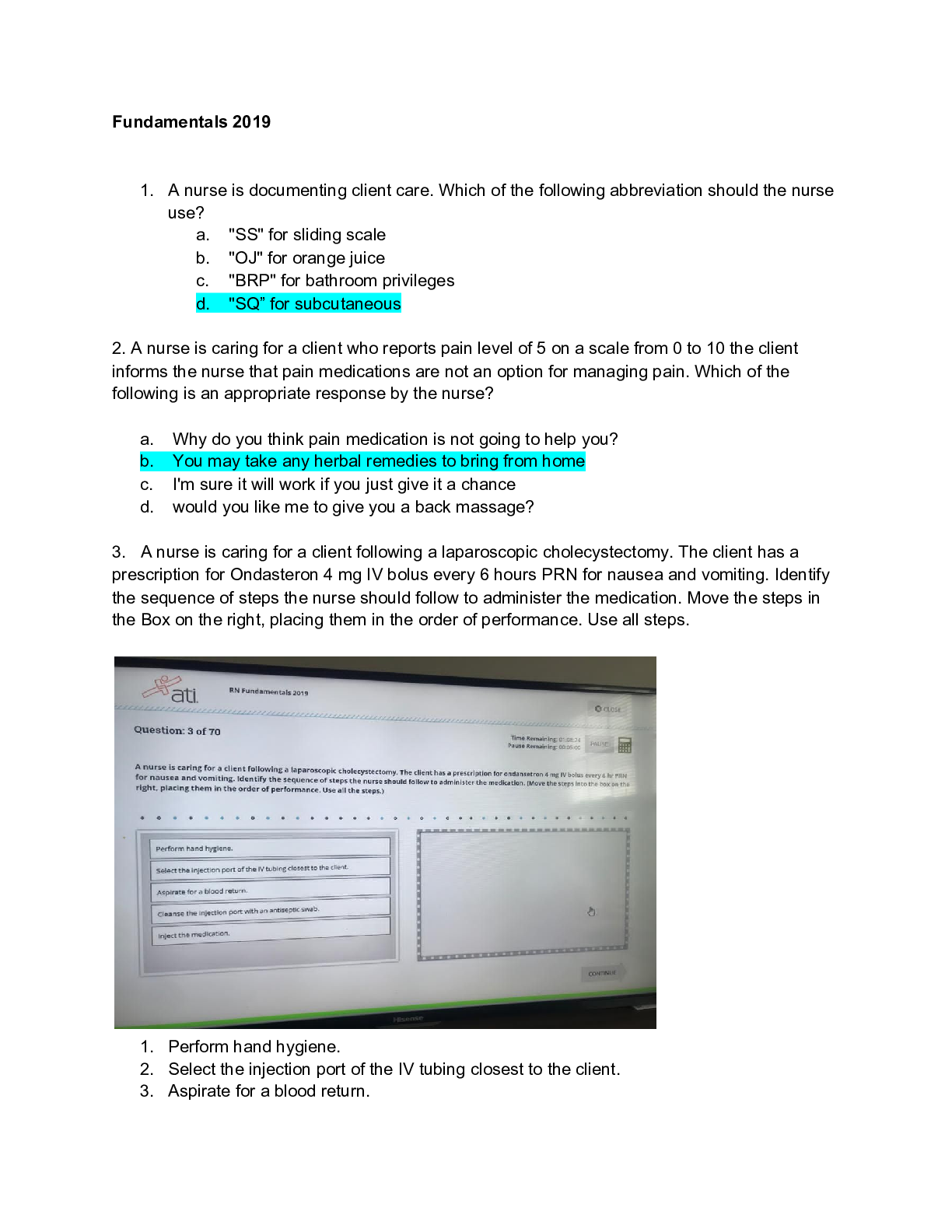
.A nurse is conducting a primary survey of a client who has sustained life-threatening injuries due to a motor-vehicle crash. Identify the sequence of actions the nurse should take. (Move the actions... into the box on the right, placing them in the selected order of performance. Use all the steps.) C. Open the airway using a jaw-thrust maneuver. D. Determine effectiveness of ventilator efforts. B. Establish IV access. A. Perform a Glasgow Coma Scale assessment. E. Remove clothing for a thorough assessment. 2.A nurse is caring for a client who has active pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) and is to be started on intravenous rifampin therapy. The nurse should instruct the client that this medication can cause which of the following adverse effects? A. Constipation Rationale: Rifampin does not cause constipation. More common gastrointestinal effects are diarrhea and nausea. B. Black colored stools Rationale:It is most commonly iron supplements that cause stools to turn black, not rifampin. C. Staining of teeth Rationale: Teeth may be stained from taking liquid iron preparations, not from taking rifampin. D. Body secretions turning a red-orange color Rationale: Rifampin is used in combination with other medicines to treat TB. Rifampin will cause the urine, stool, saliva, sputum, sweat, and tears to turn reddish-orange to reddish-brown. 3.A nurse is caring for a client who has returned from the surgical suite following surgery for a fractured mandible. The client had intermaxillary fixation to repair and stabilize the fracture. Which of the following actions is the priority for the nurse to take? A. Prevent aspiration. Rationale: When using the airway, breathing, circulation approach to client care, the nurse should determine that the priority goal is to prevent the client from aspirating. Because the client's jaws are wired together, aspiration of emesis is a possibility. Therefore, the client should be given medication for nausea, and wire cutters should be kept at the bedside in case of vomiting. B. Ensure adequate nutrition. Rationale: Created on:08/03/2018 Page 1 Detailed Answer Key Complex Oyxgenation ATI Practice The client should be NPO initially after surgery until the gag reflex has returned. Once the client is able to eat, the client may advance to a calorie-appropriate, high-protein liquid diet. However, this is not the priority at this time. C. Promote oral hygiene Rationale: The client will have an incision inside the mouth. While it is important that the client receive frequent mouth cleaning, this is not the priority at this time. D. Relieve the client's pain. Rationale: While the client may be in pain and will need to be medicated, this is not the priority at this time. 4.A nurse caring for a client who has hypertension and asks the nurse about a prescription for propranolol. The nurse should inform the client that this medication is contraindicated in clients who have a history of which of the following conditions? A. Asthma Rationale:Propranolol, a beta-blocker, is contraindicated in clients who have asthma because it can cause bronchospasms. Propranolol blocks the sympathetic stimulation, which prevents smooth muscle relaxation. B. Glaucoma Rationale:Beta-blockers are contraindicated in clients who have cardiogenic shock, but are not contraindicated in a client who has glaucoma. C. Depression Rationale:Beta-blockers are contraindicated in clients who have AV heart block, but are not contraindicated in clients who have depression. D. Migraines Rationale:Beta-blockers are used for prophylactic treatment of migraine headaches. 5.A nurse is caring for a client who has acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), and requires mechanical ventilation. The client receives a prescription for pancuronium. The nurse recognizes that this medication is for which of the following purposes? A. Decrease chest wall compliance Rationale: Neuromuscular blocking agents, such as pancuronium, induce paralysis by relaxing skeletal muscles, which improves chest wall compliance. B. Suppress respiratory effort Rationale: Neuromuscular blocking agents, such as pancuronium, induce paralysis and suppress the client's respiratory efforts to the point of apnea, allowing the mechanical ventilator to take over the work of breathing for the client. This therapy is especially helpful for a client who has ARDS [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 32 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jul 16, 2022
Number of pages
32
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jul 16, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
170

















.png)
.png)