*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > NUR280 COMP 2 REVIEW LATEST UPDATED 2022 ALREADY GRADED A (All)
NUR280 COMP 2 REVIEW LATEST UPDATED 2022 ALREADY GRADED A
Document Content and Description Below
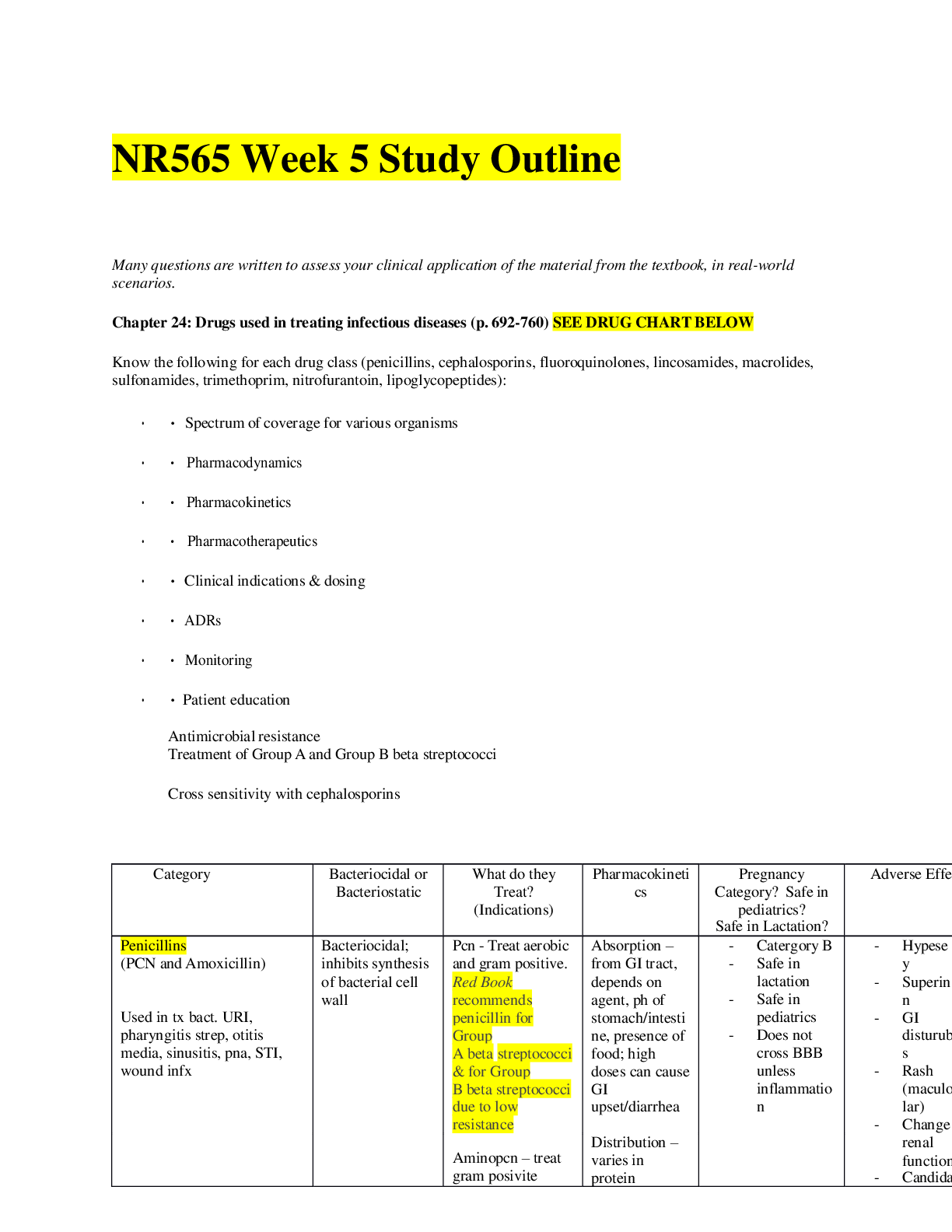
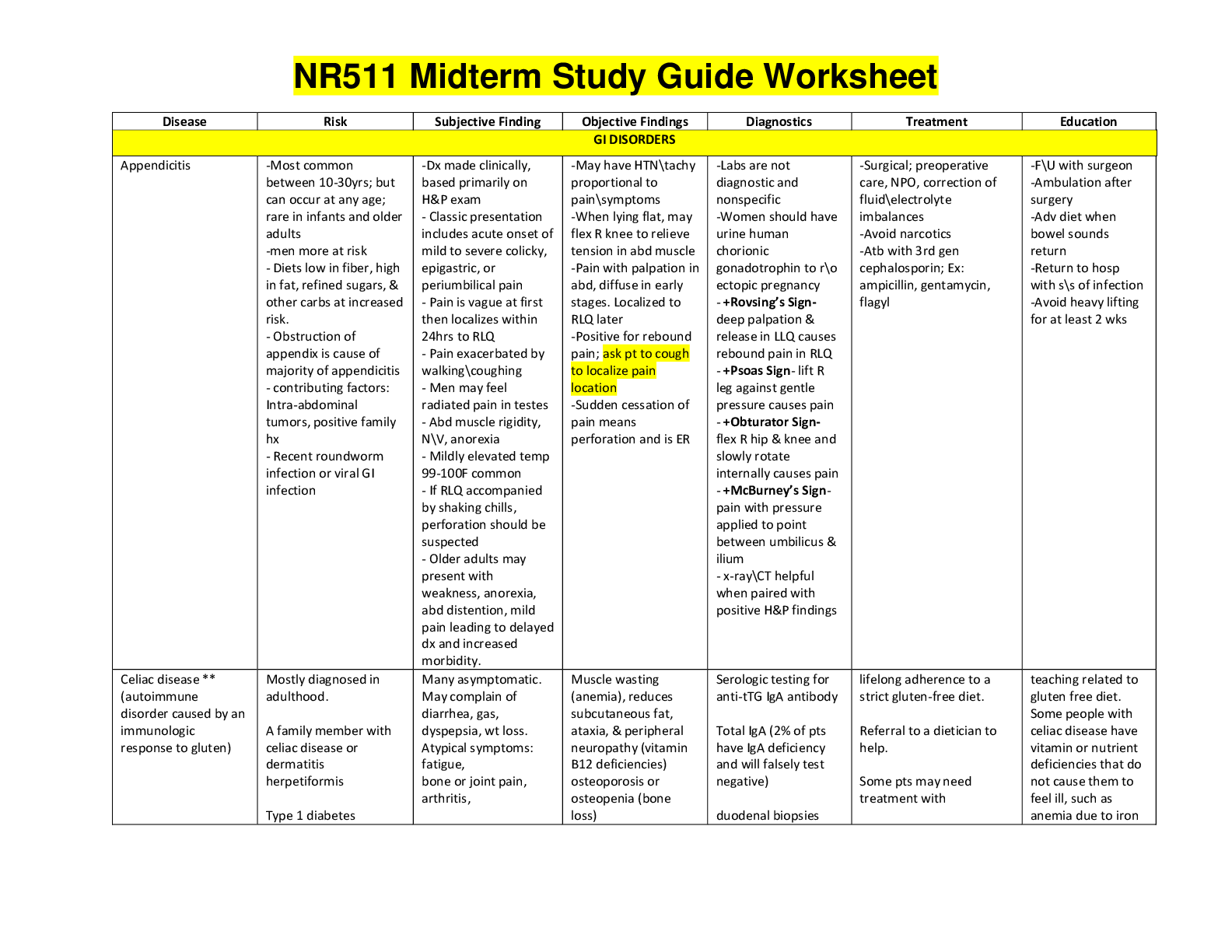
NUR280 COMP 2 REVIEW Prioritization- acute has a higher priority than chronic o Suddenly, new onset, just developed Lab values!!! – don’t just know the ranges, but know how your patient... is going to present if they are high/low o Hypocalcemia-Decreased HR, hypotension, decreased peripheral pulses, hyperactive bowels, cramping causes by diet, parathyroid disease, anticonvulsants, renal failure. o Hypercalcemia- Increased HR, bounding pulses, muscle cramps, N&V, caused by TB or other respiratory issues, dehydration, diuretics and parathyroid disease. o Hypomagnesemia- Tetany and positive chop sticks signs, caused by chronic alcohol abuse and GI losses. o Hypermagnesemia decreased deep tendon reflexes(OB/GYN), hypotension, bradycardia, bradypnea, and asystole, caused by excessive intake of Mg but most commonly causes by renal failure. o Hypokalemia-Psychosis, muscle cramps, palpitations and uncontrolled diabetes, caused by diarrhea, vomiting, alcohol abuse, excessive laxative use, Cushing’s Disease diuretics and anything that relates to metabolic alkalosis. o Hyperkalemia- Arrhythmias, fatigue caused by DKA, metabolic acidosis, Addison’s disease, severe burns, ACE inhibitors. o Hyponatremia- headache, neuro changes, seizures caused by excess water; DI, or renal failure or drinking too much water. o Hypernatremia- Excessive thirst, dry mouth, neuro changes caused by loss of water through skin, heatstroke. Also know dig toxicity s/s and lithium toxicity s/s o Digoxin toxicity- 0.5-2.0 is therapeutic level. Anything greater is toxicity! Things to remember about dig: take apical pulse for 1 full minute before administering. Eat foods high in potassium. Digibind is antidote. Monitor renal efficiency and electrolytes Digoxin is to increase contractility of the heart Dig toxicity- tachycardia, anorexia, n/v, visual disturbances (halos), dysrhythmias! o Lithium toxicity- 1.0-1.5 is therapeutic level. Anything greater is toxicity! Things to remember about lithium: blood levels must be monitored frequently, take with meals to reduced GI distress, takes 1-2 weeks to get in therapeutic level. Should have consistent fluid and sodium intake (2500-3000 mL/day) Lithium is a mood stabilizer- used for bipolar Toxicity- vomiting, diarrhea, drowsiness, muscular weakness, ataxia. Newborn care prioritization o Heat loss is critical! o Respiratory distress- airway!!!! Bulb suctioning- mouth first and then nose! o Apgar score Heart rate, respiratory effort, muscle tone, reflexes, color. 0-3 poor, 4-6 fair, 7-10 excellent. o Bonding- how is mom reacting to baby? Watch for postpartum depression!!! o Shots and drops- vitamin K drops in eyes, and hep B shot o Umbilicus care- 2 arteries and 1 vein Keep it dry, open to air, don’t submerge it. Dab it dry- no alcohol or other substance use IV solution is running late- don’t increase the rate! - fluid overload Besides checking iV site, priority patient assessment is respiratory o Crackles!!!! How are Thyroid storm, organ rejections, and infection alike- increase in temperature! o Tachycardia, o Hyperpyrexia (high fever) Thyroidectomy- have emergency trach kit and ambu bag at bedside o Low or semi-fowler’s o Support head, neck, and shoulders to prevent flexion or hyperextension of suture line; elevate head of bed to 30 degrees o Trach set and suction supplies at bedside o Give fluids as tolerated. o Complications: Laryngeal nerve injury- detected by hoarseness Thyoidtoxicosis- increased temperature, increased pulse, hypertension, abdominal pain, diarrhea, confusion, agitation, seizures Treatment- hypothermia blanket, oxygen, potassium iodine, PTU, propranolol, hydrocortisone, acetaminophen; also caused by trauma, infection, palpation, RAI therapy Hemorrhage- check back of neck and upper chest for bleeding Respiratory obstruction Tetany (from decreased calcium from parathyroid involvement- Chvostek’s and Trousseau’s sign Have IV calcium gluconate or IV calcium chloride available Parathyroid gland removal along with thyroid- hypocalcemia- chovasetk and trousseau’s sign o CATS!!! - hypocalcemia What do ACE inhibitors, Addison’s disease, and potassium sparing diureticshyperkalemia o ACE inhibitors- causes decreased BP, decreased aldosterone secretions- sodium and fluid loss this causes high levels of potassium (end in –pril) o Addison’s disease- remember that you have to ADD cortisol. So, lethargic, dehydration, weight loss, etc. This causes high levels in potassium, but low levels of all other electrolytes. o Potassium sparing diuretics- cause potassium to stay in the system while fluids and electrolytes leave. Salt substitute is essentially potassium, so don’t use, and don’t eat a diet high in potassium. Thoracentesis- removal of fluid from the thoracic cavity in the pleural space o Aspiration of fluid or air from the pleural space. Used to obtain specimen for analysis, relieve lung compression, obtain lung tissue for biopsy, or instill medications into pleural space. Prep/testing: Explain procedure Take vitals Clip area around the needle insertion site Position client is sitting with arms on pillows on over-bed table or lying on side in bed Expect stinging sensation with injection of local anesthetic and feeling of pressure when needle inserted Don’t remove more than 1000 mL fluid at one time Post-nursing care Auscultate breath sounds frequently Monitor vital signs frequently Check for leakage of fluid, location of puncture site, client tolerance Sterile dressing after procedure!!! Chest tube- expected drainage- 100 mL/hr o Anything higher contact the doctor o If more than 100- internal bleeding somewhere o Chest tube- intrapleural drainage system with one or more chest catheters held in pleural space by suture to chest wall, attached to drainage system. o Nursing care: Fill water seal chamber If suction is to be used, fill the suction control chamber with sterile water to the 20 mL Encourage the client to change position and cough and deep breathe frequently Put the drainage system below level of insertion and without kinks! Chest tubes are only clamped momentarily to check air for leaks and to change the drainage apparatus Observe for fluctuations of fluid in the water-seal chamber; stops fluctuating when: Lung re-expands Tubing is obstructed Loop hangs below the rest of the tubing o Removal of the chest tube Instruct the client to do the Valsalva maneuver Chest tube is clamped and quickly removed by the health care provider [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 15 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 25, 2022
Number of pages
15
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 25, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
65