*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > NUR 641E Midterm Exam Study Guide GRAND CANYON UNIVERSITY Score100% (All)
NUR 641E Midterm Exam Study Guide GRAND CANYON UNIVERSITY Score100%
Document Content and Description Below
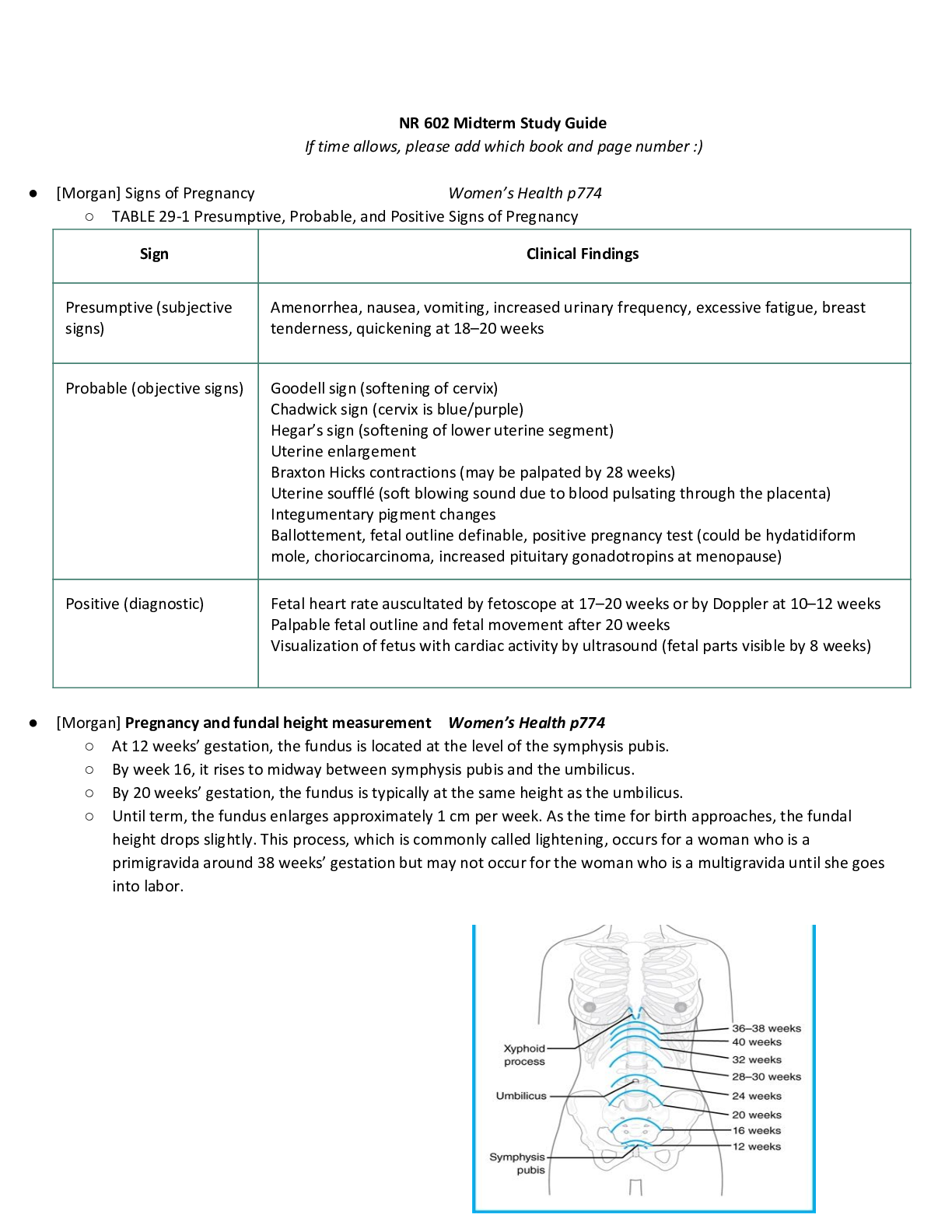
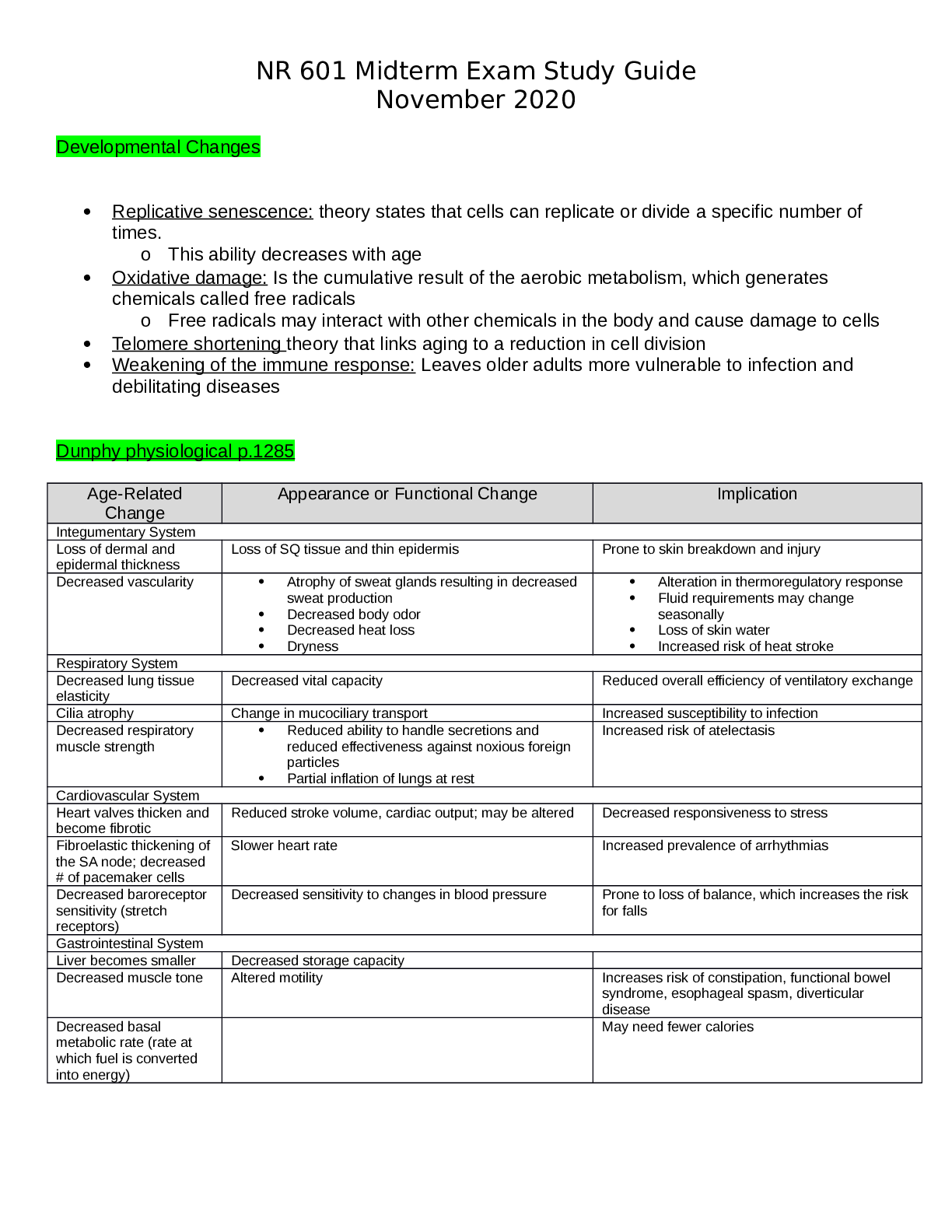
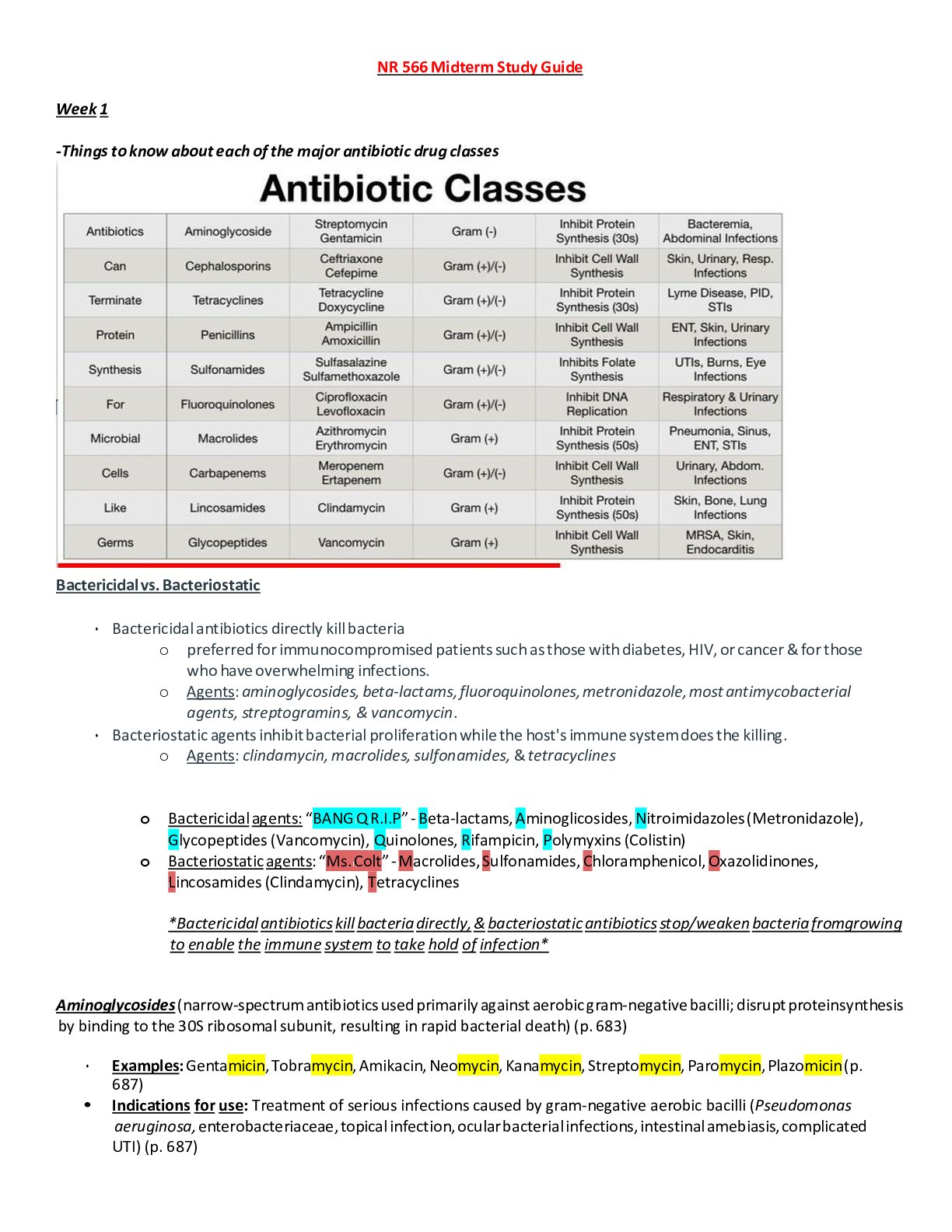
NUR-641E Mid-Term Exam Study Guide Note: Read the questions: the questions only have one answer unless the question specifically states there is more than one correct answer. ANSWERED SO FAR Under... stand what a prodrug is, and activation/inactivation by liver enzymes, and how it differs from active drugs. The liver is the principal site of drug metabolism. Although metabolism typically inactivates drugs, some drug metabolites are pharmacologically active—sometimes even more so than the parent compound. An inactive or weakly active substance that has an active metabolite is called a prodrug, especially if designed to deliver the active moiety more effectively. Know what Bioavailability (BA) a term used in pharmacology and nutritional and environmental sciences. In pharmacology, it refers to the degree and rate at which an administered drug is absorbed by the body's circulatory system, the systemic circulation. Bioavailability is an essential measurement tool since it determines the correct dosage for non-intravenous administration of a drug availability means Bioavailability. In pharmacology, bioavailability (BA or F ) is a subcategory of absorption and is the fraction of an administered dose of unchanged drug that reaches the systemic circulation Bioavailability is affected by chemical instability, solubility and first-pass metabolism The first pass effect- is a phenomenon of drug metabolism whereby the concentration of a drug is greatly reduced before it reaches the systemic circulation. It is the fraction of drug lost during the process of absorption which is generally related to the liver and gut wall. Bioequivalence does not affect bioavailability Bioequivalence is the similarity of two drugs that share the same desired outcome for patients. Pharmaceutical equivalence means two drugs release the active ingredient into This study source was downloaded by 100000831988016 from CourseHero.com on 01-26-2022 10:53:19 GMT -06:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/38661995/NUR-641E-Study-Guide-1midtermdocx/ the bloodstream at the same amount and same rate. When assessing how well a generic drug works, scientists evaluate its bioequivalence to the name-brand version. Understand what the Cytochrome P450 system is in the liver Cytochrome P450 enzymes are primarily found in liver cells but are also located in cells throughout the body. ... Cytochrome P450 enzymes account for 70 percent to 80 percent of enzymes involved in drug metabolism. Cytochrome P450 enzymes also function to metabolize potentially toxic compounds, including drugs and products of endogenous metabolism such as bilirubin, principally in the liver. Clopidogrel (Plavix) is a prodrug and must be activated by hepatic CYP2C19 metabolism; individuals who are poor metabolizers may not form the active metabolite and have reduced antiplatelet response. A drug’s half-life determines how often the drug is administered? The elimination half-life of a drug is a pharmacokinetic parameter that is defined as the time it takes for the concentration of the drug in the plasma or the total amount in the body to be reduced by 50%. In other words, after one half-life, the concentration of the drug in the body will be half of the starting dose. Steady state of a drug is reached in approximately 5 to 6 times the half-life Inhalation, oral and parenteral drug action and onset of effects? Inhalational administration can be used. The lungs serve as an effective route of administration of drugs. The pulmonary alveoli represent a large surface and a minimal barrier to diffusion. The lungs also receive the total cardiac output as blood flow. Thus, absorption from the lungs can be very rapid and complete. Bioavailability of drugs administered orally varies greatly. Parenteral administration refers to any routes of administration that do not involve drug absorption via the GI tract (par = around, enteral = gastrointestinal), including the IV, intramuscular (IM), subcutaneous (SC or SQ), and transdermal routes Know the mechanism of action of anticoagulants (e.g., warfarin, apixaban, heparin). Warfarin competitively inhibits the vitamin K epoxide reductase complex 1 (VKORC1), which is an essential enzyme for activating the vitamin K available in the body. Through this mechanism, warfarin can deplete functional vitamin K reserves and therefore reduce the synthesis of active clotting factors This study source was downloaded by 100000831988016 from CourseHero.com on 01-26-2022 10:53:19 GMT -06:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/38661995/NUR-641E-Study-Guide-1midtermdocx/ Heparin produces rapid anticoagulation by binding with antithrombin III, and inhibits factors IXa, Xa, XIIa, and XIII. Monitor heparin with a PTT (low dose SC heparin [5000 units BID] does not require aPTT monitoring). Warfarin inhibits vitamin K-dependent blood factors II, VII, IX and X; takes several days for its anticoagulant effect. Monitor the International Normalized Ratio (INR) when warfarin is used. Blood Factor IIa inhibitor (direct thrombin inhibitor): dabigatran (Pradaxa). An antidote to dabigatran-induced hemorrhage is idarucizumab. Blood Factor Xa inhibitors: apixaban (Eliquis), edoxaban (Savaysa), rivaroxaban (Xarelto), fondaparinux (Arixtra). Know what pulmonary emboli are, where they come from and what these emboli do in the body Pulmonary embolism is a blockage in one of the pulmonary arteries in your lungs. In most cases, pulmonary embolism is caused by blood clots that travel to the lungs from the legs or, rarely, other parts of the body (deep vein thrombosis). Know the risk factors for cerebrovascular accident (CVA) Some stroke risk factors, such as gender, age and family history, can't be controlled. Lifestyle factors that increase your risk of stroke include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, high blood cholesterol levels, heavy drinking, high salt and high fat diet and lack of exercise. Know the elements involved in the action potential of myocardial tissue Calcium…?? Know what tuberculosis is and its epidemiology in the world. Tuberculosis (TB) is one of the top 10 causes of death worldwide. In 2017, 10 million people fell ill with TB, and 1.6 million died from the disease (including 0.3 million among people with HIV). [Show More]
Last updated: 5 months ago
Preview 1 out of 7 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jan 26, 2022
Number of pages
7
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jan 26, 2022
Downloads
10
Views
476




























.png)



