*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Chamberlain College of Nursing - NR 661/NR 661 Ears, Eyes, Nose, and Throat (EENT) Exam 2020(all ans (All)
Chamberlain College of Nursing - NR 661/NR 661 Ears, Eyes, Nose, and Throat (EENT) Exam 2020(all answers explained) Graded A+.
Document Content and Description Below
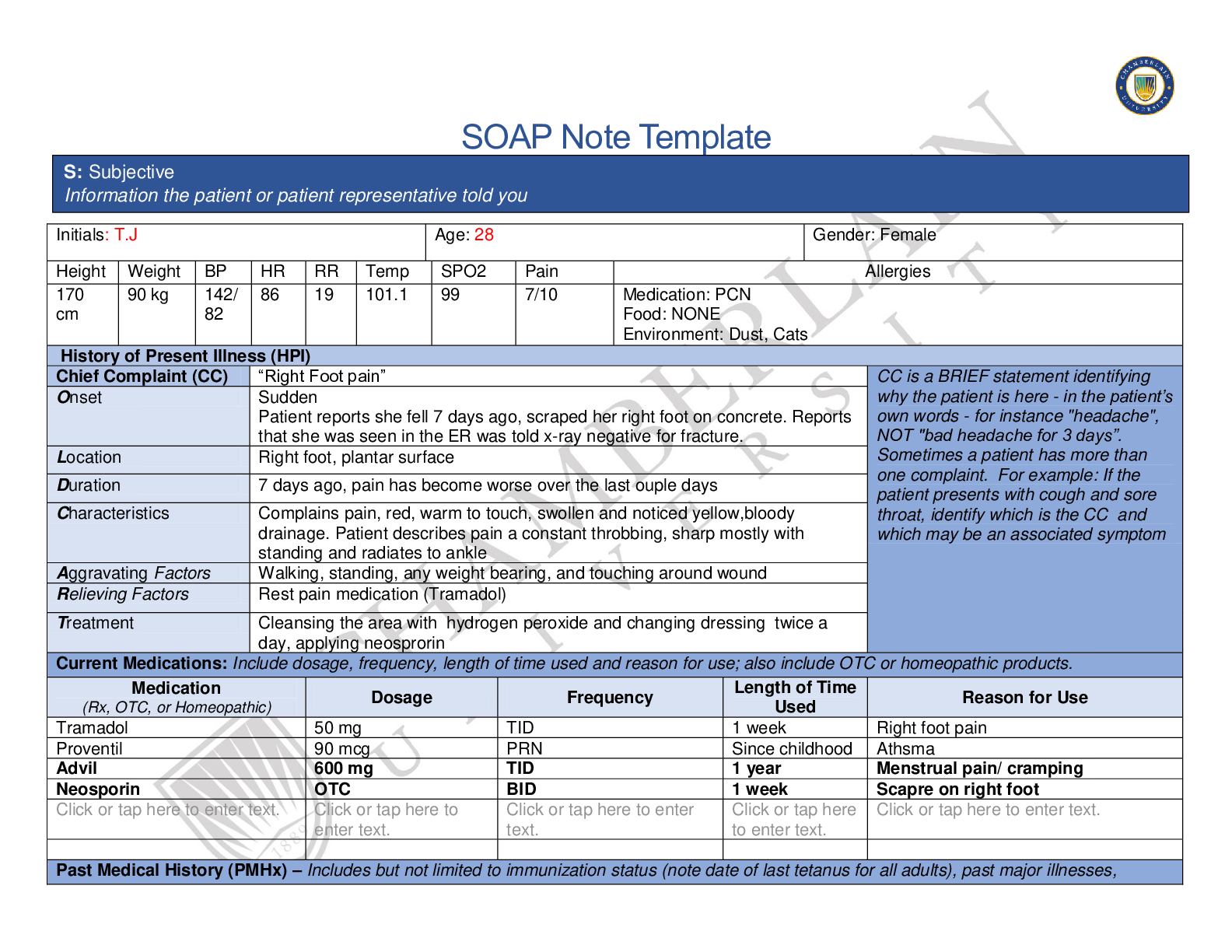
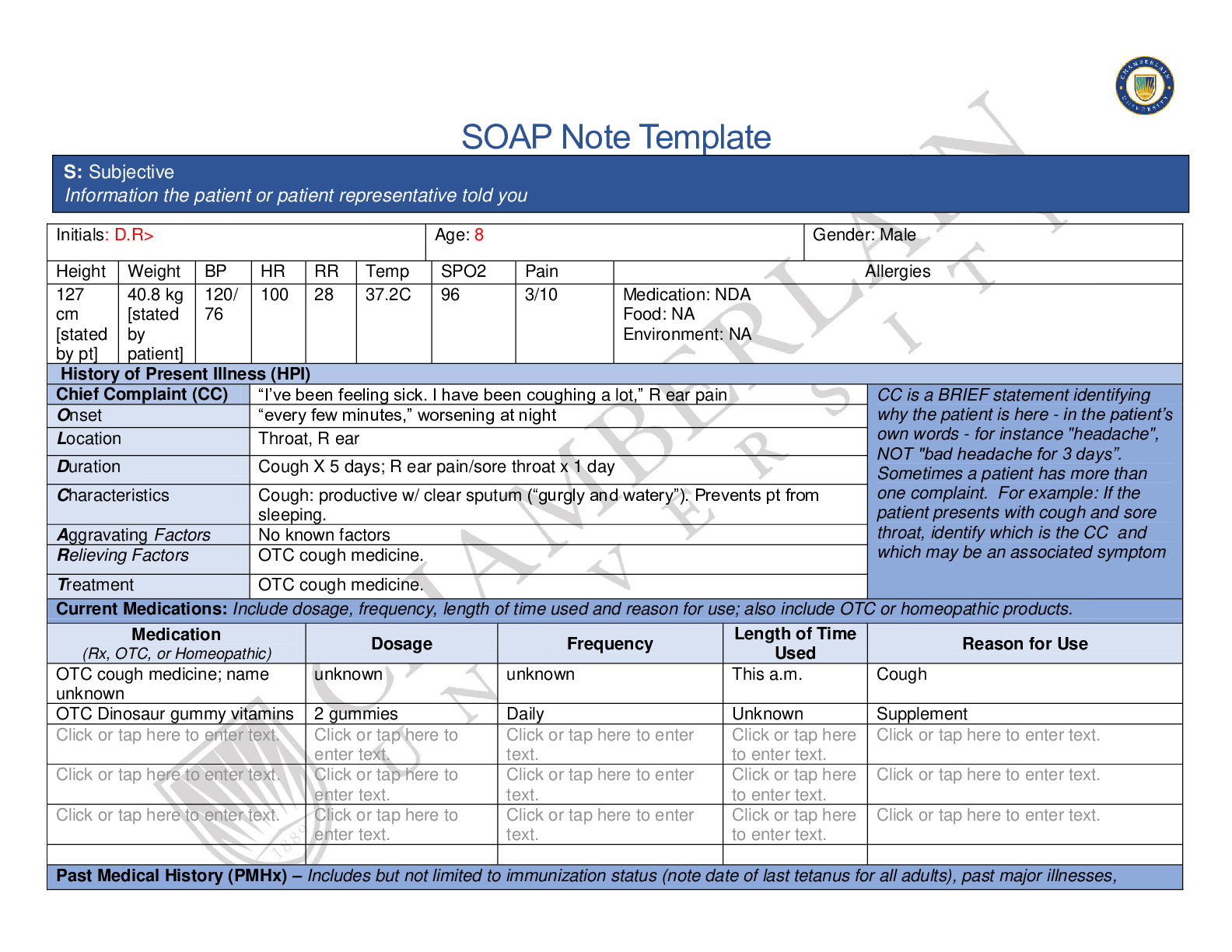
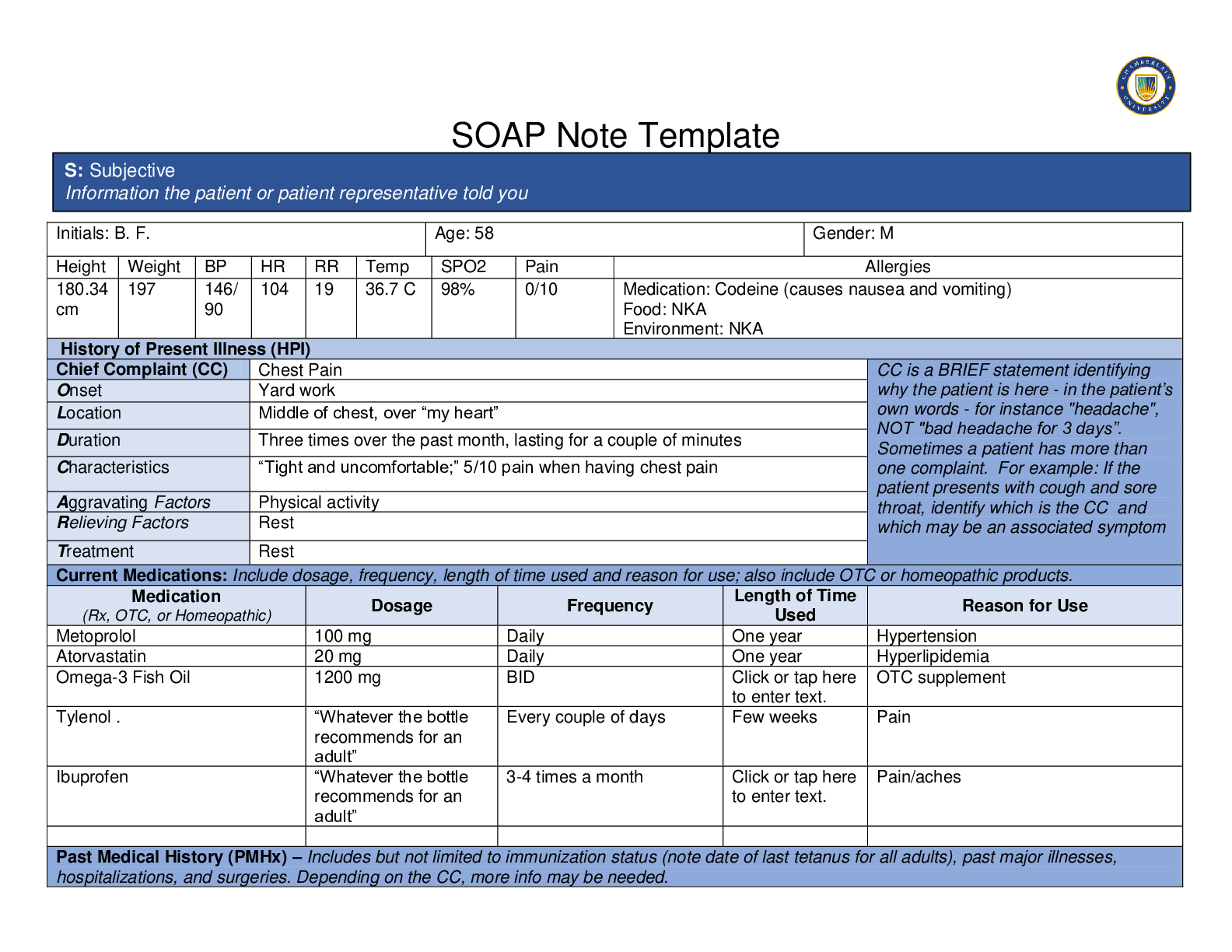
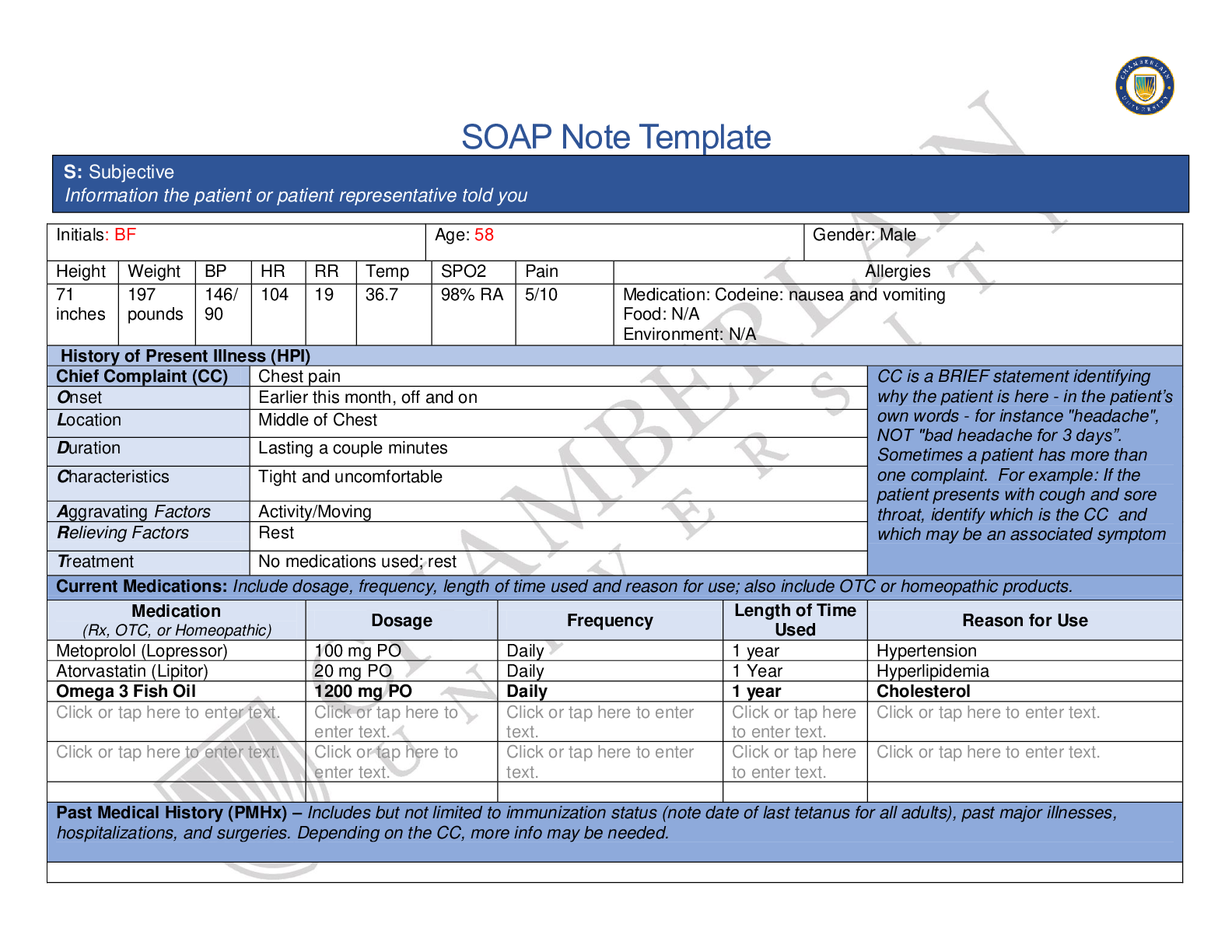
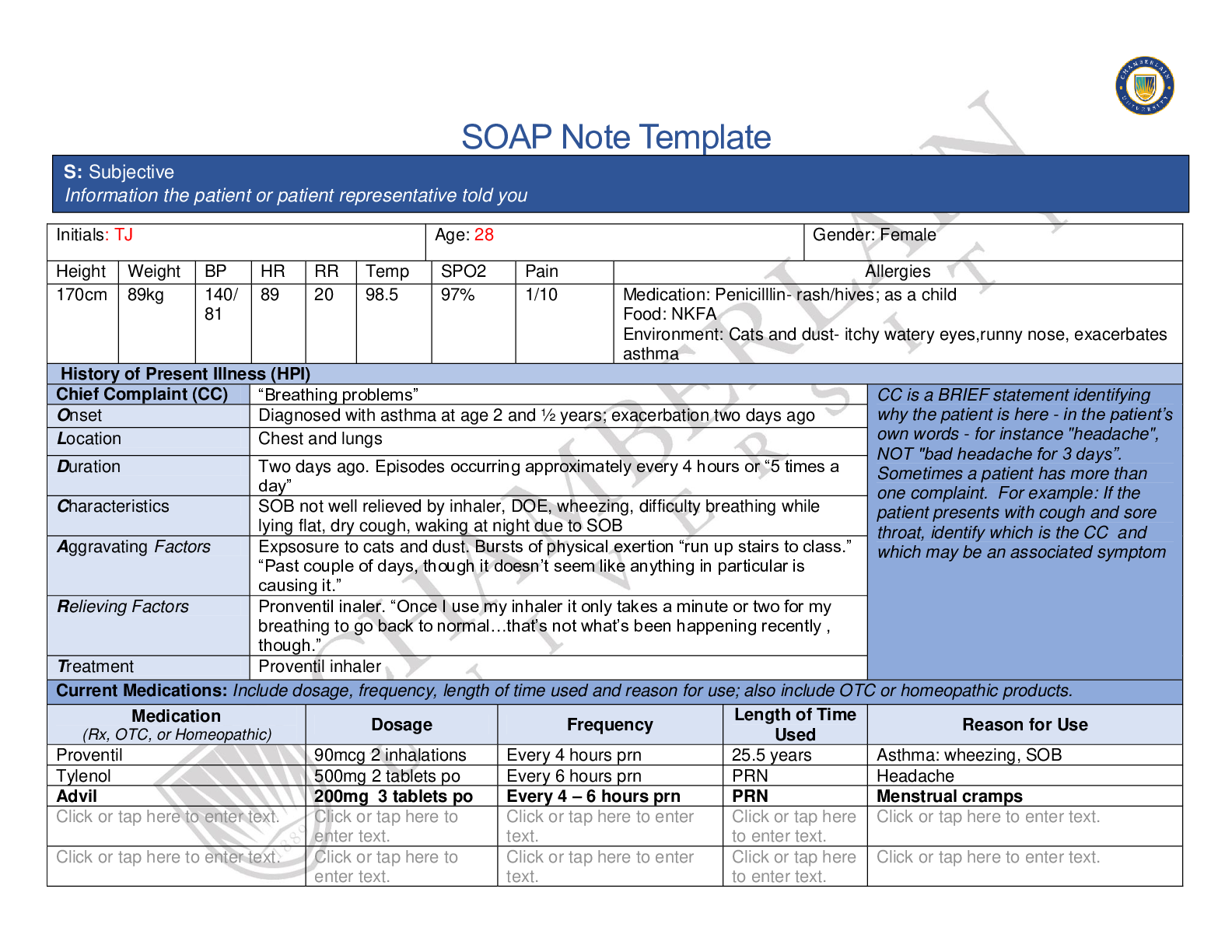
NR 661 Ears, Eyes, Nose, and Throat (EENT) Exam2020 1. A 30 year old male has been diagnosed with non-allergic rhinitis. What finding is more likely in non-allergic rhinitis than allergic rhinitis? ... Older age of symptom onset Male gender Post nasal drip Sneezing Older age of symptom onset Explanation: Non-allergic rhinitis, often called vasomotor rhinitis, is very common in the US. It is typically diagnosed and differentiated from allergic rhinitis by history. Although both conditions may co-exist in patients, non-allergic rhinitis typically has onset after age 20 years. Allergic rhinitis typically presents prior to age 20 years. The most common symptoms associated with non-allergenic rhinitis are nasal congestion and post-nasal drip. It is predominantly reported in females. Common precipitants of non-allergic rhinitis symptoms can occur with exposure to spicy foods, cigarette smoke, strong odors, perfumes, and alcohol consumption. This is frequently treated with topical azelastine. 2. The throat swab done to identify Streptococcal infection was negative in a 12 year-old female with tonsillar exudate, fever, and sore throat. What statement is true regarding this? A second swab should be done to repeat the test. The patient does not have Strept throat. The patient probably has mononucleosis. A second swab should be collected and sent to microbiology. A second swab should be collected and sent to microbiology. Explanation: A second swab is collected, but it is not used to repeat the test. The second swab is sent to microbiology for culture. The sensitivity varies in office Strept tests. Some are as low as 50% and a second swab should be collected. If beta-hemolytic Strept organisms are grown out, then the patient can be diagnosed with Streptococcal infection 3. What is the usual age for vision screening in young children? 2 years 3 years 4 years 5 years 3 years Explanation: Initial vision screening should take place at 3 years of age. If the child is not cooperative, screening should be attempted 6 months later. If the child is still not cooperative at 3.5 years, it should be attempted at 4 years. Generally, children are cooperative at 4 years of age. The usual vision of a 3 yearold is 20/50 4. Epstein-Barr virus is responsible for: mononucleosis. the most common cause of pharyngitis. most teenage cases of pharyngitis. viral pharyngitis in young children. mononucleosis. Explanation: Infectious mononucleosis is caused by Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). This commonly affects adolescents but can affect various age groups. The most prominent feature of mononucleosis is fever, fatigue and pharyngitis. 5. A patient with environmental allergies presents to your clinic. She takes an oral antihistamine every 24 hours. What is the most effective single maintenance medication for allergic rhinitis? Antihistamine Decongestant Intranasal glucocorticoids Leukotriene blockers Intranasal glucocorticoids Explanation: These agents are particularly effective in the treatment of nasal congestion and would be a good choice for the patient in this scenario. Intranasal glucocorticoids are effective in relieving nasal congestion, discharge, itching, and sneezing. A trial of stopping the oral antihistamine could be tried in this patient. Symptoms would determine whether the antihistamine should be resumed. 6. Conjunctivitis: produces blurred vision in the affected eye. usually begins as a viral infection. produces anterior cervical lymphadenopathy. is common in patients who are nearsighted. usually begins as a viral infection. Explanation: Conjunctivitis or "pink eye" usually begins as a viral infection. As the conjunctiva becomes irritated, the eye is rubbed and fingers introduce bacteria. A secondary bacterial infection develops. Conjunctivitis produces a red (or pink) eye, but should never produce blurred vision. A patient with a red eye and blurred vision should be referred to ophthalmology. The pre-auricular nodes may be palpable when a patient has conjunctivitis, not the anterior cervical ones. 7. At what age would it be unusual to see thrush? At birth 2 months 6 months 8 months At birth Explanation: Thrush is an infection in the oral cavity caused by yeast. Yeast grow in a warm, dark, moist environment. It is not unusual to see thrush in young infants who are breast or bottle fed. It would be unusual to see thrush in a newborn. In fact, this should cause concern regarding an immunocompromised state in the infant or hyperglycemia in the mother. 8. A patient presents with severe toothache. She reports sensitivity to heat and cold. There is visible pus around the painful area. What is this termed? Pulpitis Caries Gingivitis Periodontitis Pulpitis Explanation: The predominant symptom of patients who exhibit pulpitis is pain especially elicited by thermal changes, cold and hot. The pain can become severe and patients are ill appearing. Pus may be seen around the gum area or may be restricted to the pulp cavity. Caries and gingivitis do not produce pus. Periodontitis is characterized by gingival inflammation and pain. Pus is not present in this disease. A periodontal abscess produces pain and pus, but the pus is usually only expressed after probing. 9. How long should a 6 year old with acute otitis media be treated with an antibiotic? 5 days 5-7 days 10 days Until the erythema has resolved 5-7 days Explanation: The recommendations from the American Academy of Pediatrics are 5-7 days of an antibiotic for children 6 years and older who have mild to moderate acute otitis media (AOM). Children less than 2 years of age should be treated for 10 days. Children 2 years and older may be treated for 5-7 days for AOM if they do not have a history of recurrent AOM. 10. A patient is diagnosed with otitis externa. He complains of tragal pain, otic discharge, otic itching, and fever. What is the cardinal symptom of otitis externa? Tragal pain Otic discharge Otic itching Fever Tragal pain Explanation: Otitis externa is "swimmer's ear". This is a superficial infection usually caused by Pseudomonas in the external canal. Fever, a typical systemic symptom is inconsistent with otitis externa since the infection is superficial. The other symptoms listed are typical of patients who are diagnosed with otitis externa. However, the cardinal symptom is tragal pain. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 49 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Oct 26, 2020
Number of pages
49
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Oct 26, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
28










 (1).png)


 A+ Guide.png)




.png)