*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > ATI PHARMACOLOGY 2016 A, 2016 B, 2019 A, 2019B Test Bank (all answers correct) (All)
ATI PHARMACOLOGY 2016 A, 2016 B, 2019 A, 2019B Test Bank (all answers correct)
Document Content and Description Below
ATI PHARMACOLOGY 2016 A, 2016 B, 2019 A, 2019B Practice questions ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ATI Pharmacology 2019 A ... 1) A nurse is preparing to administer medication to a pt who has gout. The nurse discovers that an error was made during the previous shift and the pt received atenolol instead of allopurinol. Which of the following actions should the nurse take first? -Obtain the client's blood pressure. = When using the nursing process, the first action the nurse should take to prevent injury to the client is to assess the client for adverse effects of atenolol, such as hypotension. -Contact the client's provider. The nurse should contact the provider, who can provide direction to the nurse to prevent injury to the client. However, there is another action the nurse should take first. -Inform the charge nurse. The nurse should alert the charge nurse about the medication error. However, there is another action the nurse should take first. -Complete an incident report. The nurse should complete an incident report, which is used as part of a facility's quality assurance program. However, there is another action the nurse should take first. 2) A nurse is teaching a pt about Cyclobenzaprine. Which of the following pt statements should indicate to the nurse that the teaching is effective? -"I will have increased saliva production." The client should use gum or sip on water to prevent dry mouth, which is an adverse effect of cyclobenzaprine. -"I will continue taking the medication until the rash disappears." The client should take cyclobenzaprine for treatment of muscle spasms. This medication does not affect skin rashes. -"I will taper off the medication before discontinuing it." = The client should taper off cyclobenzaprine before discontinuing it to prevent abstinence syndrome or rebound insomnia. -"I will report any urinary incontinence." The client should report any urinary retention because of the anticholinergic effects caused when taking cyclobenzaprine. 3) A nurse is assessing a pt 1 hour after administering Morphine for pain. The nurse should identify which of the following findings as the best indication that the Morphine has been effective? -The client's vital signs are within normal limits. Vital signs can be within normal limits for clients who have pain. -The client has not requested additional medication. Clients often do not request medicine even when they are experiencing pain. -The client is resting comfortably with eyes closed. The client might rest with their eyes closed as a method to try to manage pain. However, this does not indicate that the pain is controlled. -The client rates pain as 3 on a scale from 0 to 10. = The client's description of the pain is the most accurate assessment of pain. 4) The nurse is assessing a pt after administering a second dose of Cefazolin IV. The nurse notes the pt has anxiety, hypotension, and dyspnea. Which of the following medications should the nurse administer first? -Diphenhydramine The nurse should administer diphenhydramine, an antihistamine, as a second-line medication to decrease angioedema and urticaria following anaphylaxis. However, evidence-based practice indicates that administering another medication is the priority. -Albuterol inhaler The nurse should administer albuterol, a bronchodilator, for a client who has dyspnea from bronchospasms during anaphylaxis. However, evidence-based practice indicates that administering another medication is the priority. -Epinephrine = According to evidence-based practice, the nurse should administer epinephrine first to induce vasoconstriction and bronchodilation during anaphylaxis. -Prednisone The nurse should plan to administer prednisone, a glucocorticoid, for the urticaria following anaphylaxis and to prevent a delayed anaphylactic reaction from occurring. However, evidence-based practice indicates that administering another medication is the priority. 5) A nurse is providing teaching to a pt who is to begin taking Oxybutynin for urinary incontinence. Which of the following adverse effects should the nurse include in the teaching? (select all that apply) -Dry mouth= Oxybutynin is an anticholinergic agent that can cause dry mouth. -Dry eyes= Oxybutynin is an anticholinergic agent that can cause dry eyes and mydriasis, or pupil dilation. -Blurred vision= Oxybutynin is an anticholinergic agent that can cause blurred vision due to an increase in intraocular pressure. -Bradycardia Oxybutynin can cause several cardiovascular adverse effects such as a prolongation of the QT interval, palpitations, hypertension, and tachycardia. -Tinnitus Oxybutynin can cause several sensory adverse effects including increased intraocular pressure. The nurse should instruct the client to report eye pain, seeing colored halos around lights, and a decreased ability to perceive light changes. However, tinnitus is not an adverse effect associated with oxybutynin administration. 6) A nurse is preparing to administer PO Sodium Polystyrene Sulfonate to a pt who has hyperkalemia. Which of the following actions should the nurse plan to take? -Hold the client's other oral medications for 8 hr post administration. The nurse should hold the client's other oral medications for 6 hr before and after administration of sodium polystyrene sulfonate. -Inform the client that this medication can turn stool a light tan color. Sodium polystyrene sulfonate will not alter the color of the client's stool. -Keep the client's solution in the refrigerator for up to 72 hr. Sodium polystyrene sulfonate solution is stable for 24 hr when refrigerated. -Monitor the client for constipation. = The nurse should monitor the client for the adverse effect of constipation and report it to the provider because this can lead to fecal impaction. 7) A nurse is preparing to administer Heparin subcutaneously to a pt. Which of the following actions should the nurse plan to take? -Administer the medication outside the 5-cm (2-in) radius of the umbilicus.= The nurse should administer the heparin by subcutaneous injection to the abdomen in an area that is above the iliac crest and at least 5 cm (2 in) away from the umbilicus. -Aspirate for blood return before injecting. The nurse should not aspirate by pulling back on the plunger of the heparin syringe to check for a blood return, because this will cause the injection site to bruise. -Rub vigorously after the injection to promote absorption. The nurse should apply firm pressure to the injection site for 1 to 2 min after the administration of the heparin to prevent bruising. -Place a pressure dressing on the injection site to prevent bleeding. The nurse does not need to apply a dressing over the injection site if pressure is held for at least 1 min to prevent bleeding. 8) A nurse is teaching a pt who is to begin taking Tamoxifen for the treatment of breast cancer. Which of the following adverse effects should the nurse include in the teaching? -Hot flashes = The estrogen receptor blocking action of tamoxifen commonly results in the adverse effect of hot flashes. -Urinary retention Tamoxifen can cause genitourinary adverse effects such as vaginal discharge and uterine cancer. However, urinary retention is not an expected adverse effect of tamoxifen. -Constipation Gastrointestinal adverse effects of tamoxifen include nausea and vomiting. However, constipation is not an expected adverse effect of tamoxifen. -Bradycardia Tamoxifen is an antiestrogen medication that works by blocking estrogen receptors. Cardiovascular adverse effects of the medication include chest pain, flushing, and the development of thrombus. However, bradycardia is not an expected adverse effect of tamoxifen. 9) A nurse is reviewing the lab results of a pt who is taking Digoxin for heart failure. Which of the following results should the nurse report to the provider? -Calcium level 9.2 mg/dL A calcium level of 9.2 mg/dL is within the expected reference range of 9.0 to 10.5 mg/dL. The nurse should report a calcium level that is outside the expected reference range to the provider. -Magnesium level 1.6 mEq/L A magnesium level of 1.6 mEq/L is within the expected reference range of 1.3 to 2.1 mEq/L. The nurse should report a magnesium level that is outside the expected reference range to the provider. -Digoxin level 1.1 ng/mL A digoxin level of 1.1 ng/mL is within the expected reference range of 0.8 to 2 ng/mL. The nurse should report a digoxin level that is outside the expected reference range to the provider for a dosage adjustment. -Potassium level 2.8 mEq/L = A potassium level of 2.8 mEq/L is below the expected reference range of 3.5 to 5 mEq/L. The nurse should notify the provider if a client has hypokalemia prior to administration of digoxin due to the increased risk of developing digoxin toxicity and cardiac dysrhythmias. 10) A nurse is providing teaching to a pt who has peptic ulcer disease and is to start a new prescription for Sucralfate. Which of the following actions of Sucralfate should the nurse include in the teaching? -Decreases stomach acid secretion Peptic ulcer disease manifests as an erosion of the gastric or duodenal mucosa. The acid production in the stomach causes further irritation and pain. H2 receptor antagonists, such as famotidine, decrease stomach acid secretion. -Neutralizes acids in the stomach Acid production in the stomach causes further irritation and pain to a client who has a peptic ulcer. Antacids, such as aluminum hydroxide, neutralize acids in the stomach and prevent pepsin formation, a digestive enzyme that can further damage the eroded epithelium. -Forms a protective barrier over ulcers = Secretions by the parietal and chief cells, hydrochloric acid and pepsin, can further irritate the ulcerated areas. Sucralfate, a mucosal protectant, forms a gel-like substance that coats the ulcer, creating a barrier to hydrochloric acid and pepsin. -Treats ulcers by eradicating H. pylori A common cause of peptic ulcers is a bacterial infection with Helicobacter pylori. Treatment of the ulcer includes a combination of antibiotics, such as metronidazole, tetracycline, clarithromycin, or amoxicillin, to eradicate the H. pylori infection. 11) A nurse is assessing a pt who has Myasthenia gravis and is taking Neostigmine. Which of the following findings should indicate to the nurse that the pt is experiencing an adverse effect? -Tachycardia Neostigmine can cause bradycardia, rather than tachycardia, due to the excessive muscarinic stimulation. -Oliguria Neostigmine can cause urinary urgency, rather than decreased urinary output, due to the excessive muscarinic stimulation. -Xerostomia Neostigmine can cause increased salivation, rather than dry mouth, due to the excessive muscarinic stimulation. -Miosis = Miosis, which is pupillary constriction, is a common adverse effect of neostigmine due to the excessive muscarinic stimulation that causes difficulty with visual accommodation. 12) A nurse is preparing to give Ciprofloxin 15mg/kg PO every 12hr to a child who weighs 44lbs. How many mg should the nurse administer per dose? (Round to nearest whole #; do not use trailing zero) 300mg/dose = give 300 mg/dose every 12 hr. 13) A nurse on the acute care unit is caring for a pt who is receiving Gentamicin IV. The nurse should report which of the following findings to the provider as an adverse effect of the medication? -Constipation Gentamicin, an aminoglycoside used to treat serious infections, can cause several gastrointestinal adverse effects, such as inflammation of the liver and spleen. However, it does not cause constipation. -Tinnitus= Aminoglycosides, such as gentamicin, are ototoxic, which can manifest as tinnitus and deafness. The nurse should monitor the client for high-pitched ringing in the ears and headaches and should notify the provider if these occur. -Hypoglycemia Gentamicin, an aminoglycoside used to treat serious infections, can cause alternations in the functions of the liver and spleen. However, pancreatic function, mainly insulin production, is not affected by this medication. -Joint pain Aminoglycosides, such as gentamicin, can result in neuromuscular adverse effects such as twitching or flaccid paralysis. However, joint pain is not an adverse effect of gentamicin. 14) A nurse is teaching a group of unit nurses about medication reconciliation. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching? -The client's provider is required to complete medication reconciliation. The nurse or a member of the health care team, such as the pharmacist, is required to complete medication reconciliation. -Medication reconciliation at discharge is limited to the medication ordered at the time of discharge. Medication reconciliation at discharge includes medications ordered at the time of discharge, over-the-counter medications, vitamins, herbal supplements, nutritional supplements, and other medications the client is taking. -A transition in care requires the nurse to conduct medication reconciliation. = The nurse should conduct medication reconciliation anytime the client is undergoing a change in care such as admission, transfer from one unit to another, or discharge. A complete listing of all prescribed and over-the-counter medications should be reviewed. -Medical reconciliation is limited to the name of the medications that the client is currently taking. The name of the current medication and new medication, over-the-counter medications, vitamins, herbal supplements, and nutritional supplements are included at the medication reconciliation. The indication, route, dosage size, and dosing interval are also required. 15) A nurse is caring for a pt who is experiencing acute alcohol withdrawal. For which of the following pt outcomes should the nurse administer Chlordiazepoxide? -Minimize diaphoresis The client should take clonidine or a beta-adrenergic blocker, such as atenolol, to minimize autonomic components, such as diaphoresis, during alcohol withdrawal. -Maintain abstinence The client should take acamprosate to help maintain abstinence from alcohol by decreasing anxiety and other uncomfortable manifestations. -Lessen craving The client should take propranolol to decrease cravings during alcohol withdrawal. -Prevent delirium tremens = The client should take chlordiazepoxide to prevent delirium tremens during acute alcohol withdrawal. 16) A nurse is reviewing the lab results for a pt who is receiving Heparin via continuous infusion for DVT. The nurse should discontinue the medinfusion for which of the following pt findings? -Potassium 5.0 mEq/ L Although heparin can cause an increase in potassium levels, the client's potassium level is within the expected reference range of 3.5 to 5 mEq/L. -aPTT 2 times the control This is a therapeutic aPTT level for a client receiving heparin and is not an indication to stop the heparin infusion. -Hemoglobin 15 g/dL An Hgb of 15 g/dL is within the expected reference range of 14 to 18 g/dL for a male and 12 to 16 g/dL for a female and is not an indication to stop the heparin infusion. -Platelets 96,000/mm3= A platelet count of 96,000/mm3 is below the expected range of 150,000 to 400,000/mm3. A platelet count less than 100,000/mm3 while receiving heparin can indicate heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, a potentially fatal condition that requires stopping the infusion. 17) A nurse administers a dose of Metformin to a pt instead of the prescribed dose of Metoclopramide. Which of the following actions should the nurse take first? -Report the incident to the charge nurse. The nurse should report the incident to the charge nurse to protect the client from injury. However, there is another action the nurse should take first. -Notify the provider. The nurse should notify the provider to protect the client from injury. However, there is another action the nurse should take first. -Check the client's blood glucose. = The first action the nurse should take using the nursing process is to assess the client. The client is at risk for hypoglycemia. The nurse should monitor the client's blood glucose and provide the client with a snack to reduce the risk for hypoglycemia. -Fill out an incident report. The nurse should fill out an incident report to document the incident. However, there is another action the nurse should take first. The incident report alerts the risk manager to the incident, who then determines the cause and a plan of action to reduce the risk of reocurrence. 18) A nurse in an ED/ER is caring for a pt who has Myasthenia gravis and is in a cholinergic crisis. Which of the following meds should the nurse plan to administer? -Potassium iodide Potassium iodide is a thyroid hormone antagonist used in the treatment of radioactive iodine exposure. -Glucagon Glucagon is an antihypoglycemic medication used in the treatment of low blood glucose levels. -Atropine = A cholinergic crisis is caused by an excess amount of cholinesterase inhibitor, such as neostigmine. The nurse should plan to administer atropine, an anticholinergic agent, to reverse cholinergic toxicity. -Protamine Protamine is a heparin antagonist that is administered to reverse heparin toxicity evidenced by an aPTT greater than 70 seconds. 19) A nurse is caring for a pt who is receiving Filgrastim. Which of the following findings should the nurse document to indicate the effectiveness of the therapy? -Increased neutrophil count = Filgrastim stimulates the bone marrow to produce neutrophils/ more WBCs. For clients receiving chemotherapy, the risk of infection is minimized. -Increased RBC count Filgrastim stimulates the bone marrow to produce neutrophils and has no effect on a client's RBC count. -Decreased prothrombin time Prothrombin time measures the effectiveness of warfarin therapy. Filgrastim therapy does not cause a decrease in prothrombin time. -Decreased triglycerides Triglycerides are a form of lipids found in the blood stream. Increased levels are associated with an increased risk for heart disease. Decreased levels can occur in clients who have malnutrition or malabsorption disorders. Filgrastim is used to treat chemotherapy-induced neutropenia and has no effect on a client's triglyceride levels. 20) A nurse in an ED/ER is caring for a pt who has heroin toxicity. The pt is unresponsive with pinpoint pupils and a resp rate of 6/min. Which of the following meds should the nurse plan to administer? -Methadone The nurse should administer methadone, an opioid agonist, to a client who has heroin toxicity to decrease manifestations of opioid withdrawal and suppress the euphoria the client feels when using heroin. However, the client should not receive methadone in an emergency. -Naloxone = The nurse should administer Naloxone also known as Narcan, an opioid antagonist, to a client who has heroin toxicity to reverse the respiratory depressive effects of the heroin. However, the nurse should not administer naloxone too quickly because naloxone can cause hypertension, tachycardia, nausea, vomiting, and might cause the client to enter a state of opioid withdrawal. -Diazepam The nurse should administer diazepam, a benzodiazepine, to a client who has alcohol toxicity to decrease the manifestations of alcohol withdrawal and prevent withdrawal seizures. -Bupropion The nurse should administer bupropion, an atypical antidepressant, to a client who is trying to quit nicotine to decrease the manifestations of nicotine withdrawal and ease the client's cravings for nicotine. 21) A nurse is providing teaching to a pt who has a prescription for Ergotamine sublingual to treat migraine headaches. Which of the following info should the nurse include in the instructions? -"Take one tablet three times a day before meals." Ergotamine, an alpha-adrenergic blocking medication, is not used prophylactically because this can result in ergotamine dependence. -"Take one tablet at onset of migraine."= The client should take one tablet immediately after the onset of aura or headache. -"Take up to eight tablets as needed within a 24-hour period." The client can take up to a maximum of three tablets in a 24-hr period. Excessive dosing can lead to ergotism, which can cause peripheral gangrene due to vasoconstriction and ischemia. -"Take one tablet every 15 minutes until migraine subsides." The client can take one sublingual tablet every 30 min for a maximum of three tablets in a 24-hr period to manage a migraine. 22) A nurse is teaching a pt about the use of Risedronate for the treatment of osteoporosis. The nurse should identify which of the following statements as an indication that the pt understands the teaching? -"I will drink a glass of milk when I take the risedronate." The nurse should reinforce that risedronate should be taken with a full glass of water, rather than any other liquid. -"I will take the risedronate 15 minutes after my evening meal." Although the delayed release form of the medication can be taken after eating, the immediate release form of the medication should be taken at least 30 min prior to consuming food or other liquids. Both forms of medication should be taken in the morning. -"I should take an antacid with the risedronate to avoid nausea." The absorption of risedronate, a bisphosphonate, will be reduced if it is taken with antacids containing calcium, aluminum, or magnesium. The nurse should instruct the client to take the antacid 2 hr after taking risedronate. -"I should sit up for 30 minutes after taking the risedronate."= Sitting upright for at least 30 min after taking risedronate will reduce the adverse gastrointestinal effects of esophagitis and dyspepsia. Risedronate is contraindicated for a client who cannot sit or stand upright for this length of time. 23) A nurse is collecting a med history from a pt who has a new prescription for Lithium. The nurse should identify that the pt should discontinue which of the following OTC medications? -Aspirin Although most NSAIDs interact with lithium to increase lithium levels, aspirin does not interact with lithium. -Ibuprofen= Most NSAIDs can significantly increase lithium levels. Therefore, the client should not take ibuprofen and lithium concurrently. -Ranitidine There are no known medication interactions between ranitidine and lithium. -Bisacodyl There are no known medication interactions between bisacodyl and lithium. 24) A nurse is planning care for a pt who is prescribed Metoclopramide following bowel surgery. For which of the following adverse effects should the nurse monitor? -Muscle weakness Metoclopramide is a central dopamine receptor antagonist that increases gastrointestinal motility and prevents nausea. Tardive dyskinesia is an adverse effect of metoclopramide. However, metoclopramide does not cause muscle weakness. -Sedation = Metoclopramide has multiple CNS adverse effects, including dizziness, fatigue, and sedation. -Tinnitus Metoclopramide does not cause ringing in the ears. -Peripheral edema Metoclopramide does not cause peripheral edema. 25) A nurse is caring for a pt who is taking Acetazolamide for chronic open angle glaucoma. For which of the following adverse effects should the nurse instruct the pt to monitor and report? -Tingling of fingers= The nurse should instruct the client to report the adverse effect of paresthesia, a tingling sensation in the extremities, when taking acetazolamide. -Constipation Diarrhea is an adverse effect of acetazolamide due to gastrointestinal disturbances. -Weight gain Weight loss is an adverse effect of acetazolamide due to gastrointestinal disturbances causing reduced appetite. -Oliguria Polyuria, rather than oliguria, is an adverse effect of acetazolamide. 26) A nurse is planning care for a pt who has hypertension and is starting to take Metoprolol. Which of the following interventions should the nurse include in the plan of care? -Weigh the client weekly. The nurse should weigh the client daily to monitor for the development of heart failure and weight gain. -Determine apical pulse prior to administering.= Life-threatening bradycardia is an adverse effect that might affect this client. Therefore, the nurse should assess the client's apical pulse prior to administering the medication. If the client's pulse rate is less than 60/min, the nurse should withhold the medication and notify the provider. -Administer the medication 30 min prior to breakfast. The nurse should administer metoprolol following meals or at bedtime if orthostatic hypotension occurs. -Monitor the client for jaundice. The nurse should monitor the client for adverse effects such as hypotension. However, jaundice is not associated with this medication. 27) A nurse in an ED/ER is caring for a pt whose family reports the pt has taken large amounts of Diazepam. Which of the following meds should the nurse anticipate administering? -Ondansetron Ondansetron is an antiemetic that is used to treat nausea and vomiting. -Magnesium sulfate Magnesium sulfate is an electrolyte replacement that is used to treat clients who are at risk for seizure activity. -Flumazenil= The nurse should anticipate administering flumazenil, an antidote used to reverse benzodiazepines such as diazepam. -Protamine sulfate Protamine sulfate is an antidote for heparin and is used to reverse an elevated aPTT caused by taking heparin. 28) A nurse is administering Donepezil to a pt who has Alzheimer’s disease. Which of the following findings should the nurse report to the provider immediately? -Dyspepsia The nurse should report dyspepsia to the provider because dyspepsia can cause discomfort and irritation to the esophageal tissues. However, the nurse should report another finding first. -Diarrhea The nurse should report diarrhea to the provider because diarrhea can result in electrolyte and fluid imbalances. However, the nurse should report another finding first. -Dizziness The nurse should report dizziness to the provider because dizziness can place the client at an increased risk for falls. However, the nurse should report another finding first. -Dyspnea = When using the airway, breathing, circulation approach to client care, the nurse should report the adverse effect of dyspnea, caused by bronchoconstriction, to the provider first. Bronchoconstriction, dyspepsia, diarrhea, and dizziness are caused by the increase in acetylcholine levels, which is a primary effect of donepezil. 29) A nurse is caring for a pt who is in labor. The Pt is receiving Oxytocin by continuous IV infusion with a maintenance IV solution. The external FHR monitor indicates late decelerations. Which of the following actions should the nurse take first? -Turn the client to a side-lying position. = The greatest risk to the fetus experiencing late decelerations is injury from uteroplacental insufficiency. Therefore, the priority action the nurse should take is to place the client in a lateral position. -Disconnect the client's oxytocin from the maintenance IV. The nurse should discontinue the oxytocin to reduce uterine contractions. However, another action is the nurse's priority. -Apply oxygen to the client by face mask. The nurse should apply oxygen by face mask to provide supplemental oxygen to the fetus. However, another action is the nurse's priority. -Increase the client's maintenance IV infusion rate. The nurse should increase the client's maintenance IV infusion rate to maintain adequate blood flow and promote placental perfusion. However, another action is the nurse's priority. 30) A nurse is developing a teaching plan for a pt who has a new prescription for Simvastatin. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include in the teaching plan? (select all that apply) -Report muscle pain to the provider= Myopathy is an adverse effect of simvastatin that can lead to rhabdomyolysis. The nurse should instruct the client to report this to the provider. -Avoid taking the medication with grapefruit juice= When taken with grapefruit juice, simvastatin increases the risk of muscle injury from elevations in creatine kinase. -Expect therapy with this medication to be lifelong= If medication therapy is discontinued, cholesterol levels will return to their pretreatment range within several weeks to months. -Take the medication in the early morning is incorrect. This medication is most effective when taken in the evening because cholesterol production generally increases overnight. -Expect a flushing of the skin as a reaction to the medication is incorrect. The nurse should identify flushing of the skin as an adverse effect of the medication niacin, which can be used to decrease the client's triglyceride levels. 31) A nurse is caring for a pt who is receiving Heparin therapy via continuous infusion to treat a pulmonary embolism. Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as an adverse effect of the med and report to the provider? -Vomiting Vomiting is not an expected adverse effect of heparin therapy. The nurse should assess the client for other causes for vomiting. -Blood in the urine = The nurse should report blood in the urine to the provider because this can be a manifestation of heparin toxicity. Other manifestations can include bruising, hematomas, hypotension, and tachycardia. -Positive Chvostek's sign A Chvostek's sign is seen in clients who have hypocalcemia or hypomagnesemia. -Ringing in the ears Ringing in the ears is not an expected adverse effect of heparin therapy. Aminoglycosides, such as vancomycin, are medications that cause ringing in the ears. 32) A nurse is assessing a pt who is taking a Propylthiouracil for the treatment of Grave’s disease. Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as an indication that the medication has been effective? -Decrease in WBC count Propylthiouracil is a thyroid hormone antagonist used in the treatment of hyperthyroidism, or thyroid storms. A decreased WBC count is an adverse effect of propylthiouracil, which can cause myelosuppression. Therefore, a decrease in WBC count indicates the medication has not been effective. -Decrease in amount of time sleeping Graves' disease, a form of hyperthyroidism, has neurologic manifestations, including insomnia. Therefore, a decrease in the amount of time sleeping indicates the medication has not been effective. -Increase in appetite Graves’ disease can result in gastrointestinal manifestations such as increased appetite, weight loss, and increased gastrointestinal motility. Therefore, an increase in appetite indicates the medication has not been effective. -Increase in ability to focus = A client who has Graves' disease can experience psychological manifestations such as difficulty focusing, restlessness, and manic-type behaviors. Propylthiouracil is a thyroid hormone antagonist that decreases the circulating T4 hormone, reducing the manifestations of hyperthyroidism. An increased ability to focus indicates that the medication has been effective. 33) A nurse is assessing a pt who is postoperative following an outpatient endoscopy procedure using Midazolam. The nurse should monitor for which of the following findings as an indication that the pt is ready for discharge? -The client's capnography has returned to baseline.= The nurse should identify that the client is ready for discharge when the capnography level indicates that gas exchange is adequate. -The client can respond to their name when called. The client is considered ready for discharge when the state of arousal is at the preprocedure level. -The client is passing flatus. The nurse should monitor for the passing of flatus for a client who received general anesthesia. -The client is requesting oral intake. A request for oral intake does not indicate the client is ready for discharge. The nurse should assess for a return of the gag reflex for a client who is postoperative following an endoscopy. 34) A nurse is providing discharge teaching about handling medication to a pt who is to continue taking oral transmucosal Fentanyl raspberry flavored lozenges on a stick. Which of the following info should the nurse include in the teaching? -Chew on the medication stick to release the medication. The nurse should instruct the client to place the fentanyl stick between their cheek and lower gum and actively suck it for increased absorption of the medication. -Leave the medication stick in one location of the mouth until melted. The nurse should instruct the client to periodically move the medication stick to a different location in the mouth for best absorption. -Allow the medication 1 hr for analgesia effects to begin. The nurse should instruct the client to expect the medication's analgesia effects to begin within 10 to 15 min. -Store unused medication sticks in a storage container. = The nurse should instruct the client to store unused, used, or partially used medication sticks in the safe storage container that comes in the kit when the medication is initially prescribed. 35) A nurse is providing teaching to a pt who has multiple sclerosis and a new prescription for Methylprednisolone. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include? (select all that apply) -Blood glucose levels will be monitored during therapy = The nurse should monitor the client for hyperglycemia while providing methylprednisolone to the client. Glucocorticoids, such as methylprednisolone, increase serum glucose levels and can require management with insulin or antihyperglycemics. -Avoid contact with people who have known infections = The nurse should instruct the client to avoid exposure to infectious agents, such as contact with those who have active infections or illnesses. Glucocorticoids, such as methylprednisolone, depress the immune system, placing the client at an increased risk for developing an infection. Grapefruit juice can increase the effects of the medication= The nurse should instruct the client that grapefruit and grapefruit juice can increase the level of methylprednisolone in the body. -Take the medication 1 hr before breakfast is incorrect. The nurse should instruct the client to take the medication with food or milk to decrease gastrointestinal upset. -Decrease dietary intake of foods containing potassium is incorrect. The nurse should instruct the client to increase dietary intake of potassium-rich foods while taking this medication. Glucocorticoids, such as methylprednisolone, deplete potassium in the body, which manifests as hypokalemia. 36) A nurse is planning to teach about the use of a spacer to a child who has a new prescription for a Fluticasone inhaler to treat chronic asthma. The nurse should include that the spacer decreases the risk for which of the following adverse effects of the med? -Oral candidiasis = Dysphonia and oral candidiasis are adverse effects of inhaled corticosteroids. Using a spacer and rinsing the mouth after inhalation will minimize the amount of medication remaining in the oropharynx, preventing the development of these adverse effects. -Headache Fluticasone can cause neurologic adverse effects such as dizziness, fatigue, nervousness, and headaches. However, the use of a spacer will not decrease systemic adverse effects of fluticasone, such as headaches. -Joint pain Fluticasone can cause musculoskeletal adverse effects such as bone loss, muscle aches, and joint pain. However, the use of a spacer will not decrease systemic adverse effects of fluticasone, such as joint pain. -Adrenal suppression Fluticasone is a glucocorticoid medication that decreases bronchoconstriction. Inhaled glucocorticoids can cause adrenal suppression, although this occurs more often with oral glucocorticoids. The nurse should monitor the client for manifestations of adrenal suppression such as weakness, fatigue, hypotension, and hypoglycemia. However, the use of a spacer will not decrease systemic adverse effects of fluticasone, such as adrenal suppression. 37) A nurse is caring for a pt who has cancer and is taking oral Morphine and Docusate Sodium. The nurse should instruct the pt that taking the Docusate Sodium daily can minimize which of the following adverse effects of Morphine? -Constipation= Constipation is a common adverse effect of morphine that can be minimized by taking docusate sodium, a stool softener that promotes easier evacuation of stool by increasing water and fat in the intestine. -Drowsiness Drowsiness is not an adverse effect of morphine that can be minimized by taking docusate sodium. -Facial flushing Facial flushing is not an adverse effect of morphine that can be minimized by taking docusate sodium. -Itching Itching is not an adverse effect of morphine that can be minimized by taking docusate sodium. 38) A nurse is providing teaching to a pt who is taking Bupropion as an aid to quit smoking. Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as an adverse effect of the med? -Cough Bupropion, an atypical antidepressant, does not cause coughing. -Joint pain Bupropion can cause neurologic adverse effects such as bradykinesia. However, it does not cause joint pain. -Alopecia Bupropion can cause sensory adverse effects such as changes in vision and hearing. However, it does not cause alopecia. -Insomnia = Bupropion, an atypical antidepressant, has stimulant properties, which can result in agitation, tremors, mania, and insomnia. 39) A nurse is teaching a pt about Warfarin. The pt asks if they can take Aspirin while taking Warfarin. Which of the following responses should the nurse make? -“It is safe to take an enteric-coated aspirin." Although it is common for clients to consider an occasional aspirin harmless, salicylates inhibit platelet aggregation and increase the potential for hemorrhage. Therefore, the client should avoid taking enteric-coated aspirin. -"Aspirin will increase the risk of bleeding."= Aspirin inhibits platelet aggregation and can potentiate the action of the anticoagulant warfarin. Therefore, the client should avoid taking aspirin because it increases the risk for bleeding. -"Acetaminophen may be substituted for aspirin." Acetaminophen, an analgesic, can potentiate the action of the anticoagulant warfarin when administered in high doses and is not a safe substitute for aspirin. -"The INR lab work must be monitored more frequently if aspirin is taken." The client should continue to follow the provider's prescription for monitoring the PT and INR levels to adjust warfarin dosages. However, the nurse should discourage the client from using aspirin products because these medications increase the antiplatelet action of the warfarin and can result in bleeding. 40) A nurse is instructing a pt on the application of Nitroglycerin transdermal patches. Which of the following statements by the pt indicates an understanding of the teaching? -"I should apply a patch every 5 minutes if I develop chest pain." Nitroglycerin sublingual tablets are used to treat new onset of angina pain. A client who uses sublingual tablets should place one tablet under their tongue at the onset of angina pain and continue taking a tablet every 5 min for a total of three doses of nitroglycerin. The effects of a nitroglycerin patch will take 30 to 60 min to occur and are not useful to prevent an ongoing angina attack. -"I will take the patch off right after my evening meal." = Clients should remove the patch each evening for a medication free time of 12 to 14 hr before applying a new patch to avoid developing a tolerance to the medication's effects. -"I will leave the patch off at least 1 day each week." Nitroglycerin is an antianginal medication that results in dilation of the coronary vessels. Clients should apply the patch daily to sustain prophylaxis. -"I should discard the used patch by flushing it down the toilet." Medication remains in the transdermal patch after removing it from the body and must be discarded safely. The nurse should instruct the client to fold the patch ends together with the medication on the inside and place the discarded patch in a closed container so that children and pets cannot gain access to the medication. 41) A nurse is preparing to administer a scheduled antibiotic at 0800 to a pt and discovers the antibiotic is not present in the pt’s medication drawer. The nurse should identify that administration of that med can occur at which of the following time periods without requiring an incident report? -1000 The nurse should identify that administering an antibiotic 2 hr after the scheduled time is too late and requires filing an incident report. -0900 The nurse should identify that administering an antibiotic 1 hr after the scheduled time is too late and requires filing an incident report. -0830 = The nurse should identify that an antibiotic can be administered 30 min before or after the scheduled time to maintain therapeutic blood levels without requiring an incident report. -1200 The nurse should identify that administering an antibiotic 4 hr after the scheduled time is too late and requires filing an incident report. 42) A nurse is providing discharge instructions to a pt who has heart failure and a new prescription for Captopril. Which of the following pt statements indicates an understanding of the teaching? -"I should take the medication with food." The client should take captopril on an empty stomach because food reduces absorption of the medication. The nurse should instruct the client to take the medication 1 hr before or 2 hr after a meal. -"I should take naproxen if I develop joint pain." Naproxen and other NSAIDs can interact with captopril, which can decrease the effect of the antihypertensive and increase the risk of kidney dysfunction. -"I should tell my provider if I develop a sore throat." = The client should report a sore throat to the provider because this can indicate neutropenia, a serious adverse effect of captopril. Neutropenia can be reversed if it is identified early and the medication is promptly discontinued. -"I should expect the medication to cause my urine to look orange." Captopril affects the urinary system by causing dysuria, urinary frequency, and changes in the normal amount of urine. However, captopril does not affect the color of the urine. 43) A nurse is preparing to administer meds to a pt who tells the nurse “ I don't want to take my fluid pill until I get home today.” Which of the following actions should the nurse take? -Document the refusal and inform the client's provider. = The nurse has the responsibility to verify that the client understands the risks of refusing the medication so that an informed decision can be made. The nurse should then document the refusal in the client's medical record and notify the health care provider. -File an incident report with the risk manager. The nurse does not need to complete an incident report if a client refuses to take a medication. An incident report is necessary for a medication error. -Contact the pharmacist to pick up the medication. The nurse should follow facility protocols for discarding the medication. It is not the role of the pharmacist to retrieve medications that a client refuses to take. -Give the client the medication to take at home and document that it was administered. The nurse should not give the client a scheduled medication to take at home and then document that it was administered, because this violates the ethical principle of accountability. 44) A nurse is reviewing the med administration record of a pt who has hypocalcemia and a new prescription for IV Calcium Gluconate. The nurse should identify that which of the following meds can interact with Calcium Gluconate? -Felodipine Calcium gluconate does not interact with felodipine. -Guaifenesin Calcium gluconate does not interact with guaifenesin. -Digoxin = The nurse should identify that calcium gluconate can cause hypercalcemia, which increases the risk of digoxin toxicity. -Regular insulin Calcium gluconate does not interact with insulin. 45) A nurse is assessing a pt who has schizophrenia and is taking Haloperidol. The nurse should report which of the following findings to the provider as a manifestation of neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS)? -Temperature of 39.7° C (103.5° F) = The nurse should report fever to the provider as an indication of NMS, an acute life-threatening emergency. Other manifestations can include respiratory distress, diaphoresis, and either hyper- or hypotension. -Urinary retention The nurse should report incontinence as a manifestation of NMS. -Heart rate 56/min The nurse should report tachycardia as a manifestation of NMS. -Muscle flaccidity The nurse should report severe muscle rigidity as a manifestation of NMS. 46) A nurse is providing teaching to a pt who is to start treatment for asthma with Beclomethasone and Albuterol inhalers. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include in the teaching? -"Take beclomethasone to avoid an acute attack." The client should take albuterol, a short-acting beta2-adrenergic agonist, to avoid an acute asthma attack. -"Use beclomethasone 5 minutes before using albuterol." The client should use the bronchodilator, albuterol, prior to taking beclomethasone, a glucocorticoid inhaler, to enhance its absorption. -"Limit your calcium and vitamin D intake when taking beclomethasone." The client should increase the intake of calcium and vitamin D to minimize bone loss while taking beclomethasone, a glucocorticoid inhaler. -"Rinse your mouth after inhaling the beclomethasone." = The client should rinse their mouth after using beclomethasone, a glucocorticoid inhaler, to prevent oropharyngeal candidiasis and hoarseness. 47) A nurse is caring for the parent of a newborn. The parents asks the nurse when their newborn should receive the first diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis vaccine (DTaP). The nurse should instruct the parent that their newborn should receive the immunization at which of the following ages? -At birth According to the current recommended immunization schedule, only the hepatitis B vaccine is given at birth. -2 months = The CDC recommends that newborns receive the first dose of the five-dose series of the DTaP immunization at 2 months of age. -6 months The CDC recommends that newborns receive the third dose of the five-dose series of the DTaP immunization at 6 months of age. -15 months The CDC recommends that newborns receive the fourth dose of the five-dose series of the DTaP immunization between 15 to 18 months of age. 48) A nurse is caring for a pt who has acute acetaminophen toxicity. The nurse should anticipate administering which of the following medications? -Vitamin K Vitamin K is used to treat increased warfarin serum levels, indicated by elevated levels of PT/INR. -Acetylcysteine= Acetylcysteine is a specific antidote for acetaminophen toxicity. It can prevent severe injury when given orally or by IV infusion within 8 to 10 hr. -Benztropine Benztropine is an anticholinergic medication used to treat adverse effects of Parkinson's disease by reducing rigidity and tremors. -Physostigmine Physostigmine is an effective antidote for antimuscarinic poisoning from medications such as atropine, scopolamine, some antihistamines, phenothiazines, and tricyclic antidepressants. It has no effect on acetaminophen toxicity. 49) A nurse is reviewing the ECG of a pt who is receiving IV Furosemide for heart failure. The nurse should identify which of the following findings as an indication of hypokalemia? -Tall, tented T-waves The nurse should identify tall, tented T-waves as a manifestation of hyperkalemia. Flattened or inverted T-waves are a manifestation of hypokalemia. -Presence of U-waves= The nurse should identify the presence of U-waves as a manifestation of hypokalemia, an adverse effect of furosemide. -Widened QRS complex The nurse should identify a widened QRS complex as a manifestation of hyperkalemia. -ST elevation The nurse should identify ST elevation is an indication of ischemia. ST depression is a manifestation of hypokalemia. 50) A nurse at an urgent care clinic is collecting a history from a female pt who has a UTI. The nurse anticipates a prescription for Ciprofloxacin. The nurse should identify that which of the following pt statements indicates a contraindication for administering this med? -"I have tendonitis, so I haven't been able to exercise." = The nurse should identify tendonitis as a contraindication for taking ciprofloxacin due to the risk of tendon rupture. -"I take a stool softener for chronic constipation." Ciprofloxacin is not contraindicated for the client who takes a stool softener for chronic constipation. Diarrhea is an adverse effect of the medication. -"I take medicine for my thyroid." Ciprofloxacin does not affect thyroid function and is not contraindicated for the client who takes thyroid medication. -"I am allergic to sulfa." Ciprofloxacin is a quinolone antibiotic. Therefore, the client who has a sulfa allergy can take this medication. 51) A nurse is assessing a pt’s vital signs prior to the administration of PO Digoxin. The pt’s BP is 144/86 and heart rate is 55/min and resp rate is 20/min. The nurse should withhold the med and contact the provider for which of the following findings? -Diastolic BP Digoxin increases cardiac output and reduces the heart rate. A diastolic BP of 86 mm Hg is not a cause for withholding the medication and contacting the provider. -Systolic BP Digoxin increases cardiac output and reduces the heart rate. A systolic BP of 140 mm Hg is not a cause for withholding the medication and contacting the provider. -Heart rate= Digoxin slows the conduction rate through the SA and AV nodes, thereby decreasing the heart rate. The nurse should withhold the medication and notify the provider for a heart rate of 55/min because this is an early indication of digoxin toxicity. -Respiratory rate Digoxin increases cardiac output and reduces heart rate. A respiratory rate of 20/min is not a cause for withholding the medication and contacting the provider. 52) A nurse is providing teaching to a pt who has gastric ulcer and a new prescription for Ranitidine. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include? -"Take the medication on an empty stomach for full effectiveness." The client can take ranitidine with or without food because food does not affect the medication's effectiveness. -"You may discontinue this medication when stomach discomfort subsides." For clients who have a gastric ulcer, ranitidine is prescribed to inhibit gastric secretion and must be taken for the full course of therapy to be effective. -"Report yellowing of the skin."= Ranitidine can be hepatotoxic and cause jaundice. The nurse should instruct the client to monitor for and report yellowing of the skin or eyes to the provider. -"Store the medication in the refrigerator." The client should store ranitidine at room temperature. 53) A nurse is teaching a pt who is to start taking Hydrocodone with Acetaminophen tablets for pain. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching? -The medication should be taken 1 hr prior to eating. The client should take hydrocodone and acetaminophen with food or milk to decrease gastric irritation. -It takes 48 hr for therapeutic effects to occur. The nurse should instruct the client that they should experience the effects of hydrocodone with acetaminophen within 20 min of administration and that pain relief should last for 4 to 6 hr. -Tablets should not be crushed or chewed. The client should avoid crushing, chewing, or breaking the extended release or immediate release hydrocodone tablets to prevent an immediate increase in CNS effects. Hydrocodone with acetaminophen tablets can be crushed if needed. -Decreased respirations might occur.= The nurse should instruct the client that hydrocodone with acetaminophen might cause respiratory depression, which is an adverse effect of the medication. The client should avoid taking over-the-counter medications or newly prescribed medications without consulting their provider to avoid increased respiratory depression. 54) A nurse is reviewing the med list of a pt who wants to begin taking oral contraceptives. The nurse should identify that which of the following pt medications will interfere with the effectiveness of oral contraceptives? -Carbamazepine= Carbamazepine causes an accelerated inactivation of oral contraceptives because of its action on hepatic medication-metabolizing enzymes. -Sumatriptan There is no medication interaction between oral contraceptives and sumatriptan, which is a medication to treat migraines. -Atenolol There is no medication interaction between oral contraceptives and atenolol, a beta blocker. -Glipizide There is no medication interaction between oral contraceptives and glipizide, an antidiabetic medication. 55) A nurse at a clinic is providing followup care to a pt who is taking Fluoxetine for depression. Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as an adverse effect of the medication? -Tingling toes Fluoxetine is an SSRI that can cause muscle twitching. However, distorted sensations in the extremities are not adverse effects of fluoxetine. -Sexual dysfunction= Sexual dysfunction, including a decreased libido, impotence, and delayed orgasm, or anorgasmia, is a common adverse effect of fluoxetine and occurs in about 70% of clients who take this SSRI antidepressant. -Absence of dreams Fluoxetine can cause CNS adverse effects including abnormal dreaming, sedation, delusions, hallucinations, and psychosis. However, an absence of dreams is not associated with fluoxetine. -Pica Fluoxetine can cause neurologic adverse effects such as agitation, euphoria, and sedation. However, an eating disorder such as pica is not associated with fluoxetine. 56) A nurse is preparing to administer Dextrose 5% in water (D5W) 400mL IV to infuse over 1 hour. The drop factor of the manual IV tubing is 15gtt/mL. The nurse should set the manual IV infusion to deliver how many gtt/min? (Round to nearest whole #, do not use trailing zeros) 100 gtt/min = It makes sense to administer 100 gtt/min 57) A nurse is planning care for a pt who is receiving Mannitol via continuous IV infusion. The nurse should monitor the pt for which of the following adverse effects. -Weight loss Mannitol is an osmotic diuretic used to promote diuresis, decrease intracranial pressure, and improve renal function. An expected therapeutic effect of mannitol is weight loss resulting from diuresis. - Increased intraocular pressure An indication for the use of mannitol is increased intraocular pressure. Mannitol decreases the intraocular pressure by creating an osmotic gradient between the intraocular fluid and the plasma. -Auditory hallucinations Mannitol has several neurologic adverse effects, including increased intracranial pressure, seizures, confusion, and headaches. However, it does not cause auditory hallucinations. -Bibasilar crackles = Mannitol, an osmotic diuretic, can precipitate heart failure and pulmonary edema. Therefore, the nurse should recognize lung crackles as an indicator of a potential complication and stop the infusion. 58) A nurse is caring for a 20 year old female pt who has a prescription for Isotretinoin for severe nodulocystic acne vulgaris. Before the pt can obtain a refill the nurse should should advise the pt that which of the following tests is required? -Serum calcium The client does not need to have a laboratory test for serum calcium levels while taking isotretinoin. -Pregnancy test= The nurse should instruct the client that isotretinoin has teratogenic effects; therefore, pregnancy must be ruled out before the client can obtain a refill. The client must provide two negative pregnancy tests for the initial prescription and one negative test before monthly refills. -24-hr urine collection for protein The client does not need to have a 24-hr urine test for protein levels when taking isotretinoin. -Aspartate aminotransferase level The client should have a laboratory test for aspartate aminotransferase levels prior to starting isotretinoin, 1 month after starting the medication, and periodically thereafter. However, a laboratory test for aspartate aminotransferase is not required to renew a prescription for isotretinoin. 59) A nurse receives a verbal order from the provider to administer Morphine 5mg every 4 hours subcutaneously for severe pain as needed. The nurse should identify which of the following entries as the correct format for the MAR? -MSO4 5 mg subcut every 4 hr PRN severe pain The use of the abbreviation MSO4 is prohibited by The Joint Commission. The medication name of morphine must be spelled out to reduce the risk for error. -Morphine 5 mg subcut every 4 hr PRN severe pain= The nurse should identify this entry as the correct format for the MAR. The medication name is spelled out and there are not any abbreviations from The Joint Commission's "Do Not Use" list included in the transcription. -MSO4 5 mg SQ every 4 hr PRN severe pain The use of the abbreviations MSO4 and SQ are prohibited by The Joint Commission. The abbreviation SQ can be mistaken for SL and, therefore, this route should be written as subcut, subq, or subcutaneously. -Morphine 5.0 mg subcutaneously every 4 hr PRN severe pain The trailing zero on 5.0 can be mistaken for 50 if the decimal point is missed. Therefore, the dosage should be written as 5 mg without a trailing zero. 60) A nurse is caring for a pt who received 0.9% Sodium Chloride 1L over 4 hours instead of over 8 hours as prescribed. Which of the following information should the nurse enter as a complete documentation of the incident? -IV fluid infused over 4 hr instead of the prescribed 8 hr. Client tolerated fluids well, provider notified. The nurse should only chart factual information in the client's medical record without indicating the error that occurred. -0.9% sodium chloride 1 L IV infused over 4 hr. Vital signs stable, provider notified.= The nurse should document the type and amount of fluid, how long it took to infuse, provider notification, and the client's physical status. -1 L of 0.9% sodium chloride completed at 0900. Client denies shortness of breath. This documentation is not complete because it does not include the amount of fluid that was infused over the amount of time. -IV fluid initiated at 0500. Lungs clear to auscultation. This documentation is not complete because it does not include the amount of fluid that was infused over the amount of time. ATI Pharmacology 2019 B 1) A nurse is caring for a pt who is receiving Haloperidol. The nurse should identify which of the following findings as an adverse effect of the med? -Akathisia = An adverse effect associated with haloperidol is the development of extrapyramidal manifestations such as dystonia, pseudoparkinsonism, and akathisia. -Paresthesia Haloperidol, an antipsychotic neuroleptic medication, can cause CNS adverse effects such as seizures, confusion, and neuroleptic syndrome. However, paresthesia is not an adverse effect of haloperidol. -Excess tear production Haloperidol has anticholinergic properties that can cause sensory adverse effects such as increased intraocular pressure, blurred vision, and dry eyes. -Anxiety Haloperidol can be prescribed to treat severe agitation as well as psychotic manifestations. 2) A nurse is providing teaching to a pt who is to start taking Sumatriptan. Which of the following adverse effects should the nurse instruct the pt to monitor for and report to the provider? -Chest pressure= Sumatriptan is an antimigraine agent which can cause coronary vasospasms, resulting in angina. The client should report chest pressure or heavy arms to the provider. -White patches on the tongue White patches on the tongue can indicate a fungal infection, which is not an adverse effect of sumatriptan. -Bruising Ecchymosis can indicate thrombocytopenia, which is not an adverse effect of sumatriptan. -Insomnia Sumatriptan can cause drowsiness and sedation as an adverse effect of the medication. 3) A nurse is teaching a pt who is starting to take Amitriptyline. Which of the following findings should the nurse include in the teaching as an adverse effect of the med? -Diarrhea Constipation is an adverse effect of amitriptyline. -Cough Developing a cough is not an adverse effect of amitriptyline. -Urinary retention = The nurse should instruct the client that amitriptyline causes the anticholinergic effect of urinary retention. -Increased libido A decrease in libido is an adverse effect of amitriptyline. 4) A nurse is assessing a pt who is taking Tamoxifen to treat breast cancer. Which of the following findings is the priority for the nurse to report to the provider? -Hot flashes The client is at risk for hot flashes as an adverse effect of tamoxifen; however, another finding is the priority to report to the provider. The nurse should encourage the client to avoid caffeine and spicy foods to prevent hot flashes. -Gastrointestinal irritation The client is at risk for gastrointestinal irritation (GI) as an adverse effect of tamoxifen; however, another finding is the priority to report to the provider. The nurse should administer the medication with food or fluids to reduce GI irritation. -Vaginal dryness The client is at risk for vaginal dryness as an adverse effect of tamoxifen; however, another finding is the priority to report to the provider. The nurse should encourage the client to use vaginal moisturizers if dryness occurs. -Leg tenderness = The greatest risk to this client is the development of a thromboembolism, which is an adverse effect of tamoxifen. The nurse should also monitor the client for other manifestations of a thromboembolism, including leg tenderness, redness, swelling, and shortness of breath. 5) A nurse is teaching a pt who is taking Allopurinol for the treatment of gout. Which of the following info should the nurse include in the teaching? -Plan to increase the dosage each week by 200 mg increments. The nurse should instruct the client to increase the dosage each week by 50 to 100 mg until they experience relief or reach a maximum of 800 mg daily. -Prolonged use of the medication can cause glaucoma. The nurse should instruct the client that the prolonged use of allopurinol can cause cataracts; therefore, the client should have periodic ophthalmic checkups. -Drink 2 L of water daily. = The nurse should instruct the client to drink at least 2 L of water each day to prevent renal stone formation and kidney injury, because allopurinol is eliminated through the kidneys. -A fine red rash is transient and can be treated with antihistamines. The nurse should instruct the client to report a rash to the provider immediately as this can be an indication of hypersensitivity syndrome, a life-threatening toxicity. Treatment for allopurinol toxicity can require hemodialysis or the administration of glucocorticoid medications 6) A nurse is caring for a pt who has diabetes mellitus and is taking Glyburide. The pt reports feeling confused and anxious. Which of the following actions should the nurse take first? -Perform a capillary blood glucose test. = The greatest risk to this client is injury from hypoglycemia. Therefore, the nurse should perform a capillary blood glucose test to determine the client's blood glucose status. Manifestations of hypoglycemia include weakness, anxiety, confusion, sweating, and seizures. -Provide the client with a protein-rich snack. The nurse should provide the client with a protein-rich snack after determining the client's blood glucose value and providing a carbohydrate first. However, there is another action that the nurse should take first. -Give the client 120 mL (4 oz) of orange juice. The nurse should give the client 10 to 15 g of carbohydrates, such as 4 oz of orange juice, to treat hypoglycemia. However, there is another action that the nurse should take first. -Schedule an early meal tray. The nurse should schedule an early meal tray to maintain the client's blood glucose level following the initial interventions for hypoglycemia. However, there is another action the nurse should take first. 7) A nurse is administering Cefotetan via intermittent IV bolus to a pt who suddenly develops dyspnea and widespread hives. Which of the following actions should the nurse take first? -Administer epinephrine 0.5 mL via IV bolus. The nurse should administer epinephrine, which is a beta-adrenergic agonist that can stimulate the heart, cause vasoconstriction of blood vessels in the skin and mucous membranes, and cause bronchodilation in the lungs. However, there is another action the nurse should take first. -Discontinue the medication IV infusion. = The greatest risk to the client is respiratory arrest from anaphylaxis. Therefore, the first action the nurse should take is to discontinue the medication IV infusion to prevent the client from receiving more medication. However, the nurse should not remove the IV catheter. Instead, the nurse should change the tubing and administer 0.9% sodium chloride by continuous IV infusion. -Elevate the client's legs above the level of the heart. The nurse should elevate the client's legs and feet to a level above the client's heart to facilitate blood flow to the vital organs. However, there is another action the nurse should take first. -Collect a blood specimen for ABGs. The nurse should collect a blood specimen for ABGs levels to evaluate the client's respiratory status. However, there is another action the nurse should take first. 8) A nurse is preparing to administer 0.9% Sodium Chloride 1000mL IV over 8hr to a pt. The drop factor of the manual IV tubing is 15gtt/mL. The nurse should set the manual IV infusion to deliver how many gtt/min? (round to nearest whole #, do not use trailing zero) The nurse should set the manual IV infusion to deliver 0.9% sodium chloride IV at 31 gtt/min. = 9) A nurse is teaching about a new prescription for Ciprofloxan to a pt who has a UTI. The nurse should identify which of the following statements as an indication that the pt understands the teaching? -"I will take this medication with an antacid to prevent gastrointestinal upset." The client should avoid taking ciprofloxacin with an antacid containing aluminum, magnesium, or calcium because this can decrease the effectiveness of the medication. The nurse should instruct the client to take antacids 2 hr before or 6 hr after the ciprofloxacin. -"I will stop taking this medication when I no longer have pain upon urination." The client should take the full course of ciprofloxacin to prevent reoccurring colonization of bacteria. -"I will report any signs of tendon pain or swelling." = Ciprofloxacin, a fluoroquinolone, is associated with a risk of tendon rupture. This risk is increased in older adult clients, so the client should notify the provider at the onset of tendon pain or swelling. -"I will take this medication with milk." The client should take ciprofloxacin with water and increase fluids to 2 to 3 L daily to avoid the development of crystals in the kidneys. Milk products will decrease the absorption of the medication. 10) A nurse is preparing to teach a pt who is to start a new prescription for extended release Verapamil. Which of the following instructions should the nurse plan to include? -Take the medication on an empty stomach. The nurse should instruct the client to take extended release verapamil with food to minimize gastric distress. -Avoid crowds. Avoiding crowds is not necessary for the client who is taking verapamil because it does not cause an immunosuppression disorder. -Discontinue the medication if palpitations occur. The nurse should instruct the client that verapamil can cause palpitations, which should be reported to the provider. The client should never discontinue the medication abruptly because the client might experience chest pain. -Change positions slowly. = The nurse should instruct the client to change positions gradually to prevent orthostatic hypotension and syncope. -A nurse is caring for a pt who is refusing to take their scheduled morning Furosemide. Which of the following statements should the nurse make? -"By not taking your furosemide, you might retain fluid and develop swelling." = The nurse should respect the client's right to refuse the medication and inform the client of the risks of not taking the medication, notify the provider, and document the refusal. Furosemide is a loop diuretic given to reduce edema. -"You can double your dose of furosemide this evening if that would be better for you." The nurse should respect the client's right to refuse the medication and identify that the client should not double the medication dose if missed. -"If you do not take your furosemide, we might get in trouble." The nurse should respect the client's right to refuse the medication and inform the client of the risks of not taking the medication, notify the provider, and document the refusal. This response uses nontherapeutic communication because the nurse is threatening the client. -"I'll go ahead and mix the furosemide into your breakfast cereal." The nurse should respect the client's right to refuse the medication and inform the client of the risks of not taking the medication, notify the provider, and document the refusal. This response is dismissing the client's right to refuse a medication. -A nurse is providing teaching to a pt who has a prescription for Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include in the teaching? -Take the medication with food. The nurse should instruct the client to take the medication on an empty stomach either 1 hr before or 2 hr after meals. -Expect a fine, red rash as a transient effect. The nurse should instruct the client to notify the provider if a rash develops, because this can be an indication of Stevens-Johnson syndrome. However, the client should not expect to have a fine, red rash as a transient effect. -Drink 8 to 10 glasses of water daily. = The nurse should instruct the client to increase water intake to 1,920 to 2,400 mL (65 to 81 oz) a day to decrease the chance of kidney damage from crystallization. -Store the medication in the refrigerator. The nurse should inform the client to store trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole in a light-resistant container at room temperature. 13) A nurse in a clinic is caring for a pt who is taking Aspirin for treatment of arthritis. The nurse should identify which of the following findings as an indication that the pt is beginning to exhibit salicylism? -Gastric distress Gastric distress is a possible adverse effect of aspirin therapy, but it is not an indication of salicylism. Gastric distress can be minimized by taking aspirin with food or an enteric form of the medication. -Oliguria Kidney impairment is an adverse effect associated with aspirin use. Manifestations include reduced urinary output, weight gain, and elevated BUN and creatinine levels. However, oliguria is not an indication of salicylism. -Excessive bruising Excessive bruising is a possible adverse effect of aspirin therapy, caused by the antiplatelet effects of the medication. However, excessive bruising is not an indication of salicylism. -Tinnitus = Tinnitus is a manifestation of aspirin toxicity, also called salicylism. Other manifestations include sweating, headache, and dizziness. 14) A nurse is caring for a pt who has heart failure and a prescription for Enalapril. The nurse should monitor the pt for which of the following findings as an adverse effect of the med? -Bradycardia Enalapril is an ACE inhibitor that has several cardiovascular adverse effects including hypotension, tachycardia, and dysrhythmias. -Hyperkalemia = Enalapril improves cardiac functioning in clients who have heart failure and can cause hyperkalemia due to potassium retention by the kidneys. -Loss of smell Enalapril can cause several sensory adverse effects such as a loss of taste. However, it does not cause a loss of smell. -Hypoglycemia Enalapril does not cause hypoglycemia. 15) A circulating nurse is planning care for a pt who is scheduled for surgery and has a latex allergy. Which of the following actions should the nurse include in the plan of care? -Schedule the client for the last surgery of the day. The nurse should schedule the client for the first surgery of the day to minimize the client's exposure to latex, including latex dust. -Place monitoring cords and tubes in a stockinet. = The nurse should place monitoring devices in a stockinet to prevent direct contact with the client's skin. -Choose rubber injection ports for fluid administration. The nurse should ensure that latex-free products are used in the care of this client. Rubber injection ports contain latex, which puts the client at risk for a severe allergic reaction. -Ensure phenytoin IV is readily available. The nurse should ensure that epinephrine is readily available in the operating room in case of an anaphylactic reaction caused by an accidental exposure to latex. 16) A nurse is precepting a newly licensed nurse who is caring for 4 pts. The nurse should complete an incident report for which of the following actions by the newly licensed nurse? -Administers isosorbide mononitrate to a client who has BP 82/60 mm Hg = Isosorbide mononitrate is a nitrate used for clients with angina. Taking isosorbide mononitrate leads to vasodilation, which can result in hypotension. The nurse should withhold the medication and notify the provider if the client's systolic blood pressure is below the expected reference range of 120/80. -Administers digoxin to a client who has a heart rate of 92/min Digoxin is a cardiac glycoside used for clients who have heart failure because it strengthens the contractility of the heart, increasing cardiac output. A slowing of the heart rate is an effect of digoxin, so it should be withheld if the client's heart rate is less than 60/min. -Administers regular insulin to a client who has a blood glucose of 250 mg/dL Insulin is a hormone that promotes the uptake of glucose into the cells, thereby decreasing circulating glucose. A blood glucose value of 250 mg/dL is above the expected reference range, so the nurse should administer regular insulin. -Administers heparin to a client who has an aPTT of 70 seconds Heparin is an anticoagulant that decreases the coagulability of the blood and is used for clients who have thrombus. Dosing of heparin is dependent upon achieving a therapeutic aPTT level. An aPTT of 70 seconds is within the expected reference range when administering heparin. 17) A nurse is caring for a pt who has sickle cell anemia and is taking Hydroxyurea. Which of the following findings should the nurse report to the provider? (Select all that apply) -Hemoglobin 7.0 g/dL = correct A hemoglobin level of 7.0 g/dL indicates hydroxyurea toxicity. This hemoglobin level is below the expected reference range of 14 to 19 g/dL for a male client and 12 to 16 g/dL for a female client. Therefore, the nurse should report this finding to the provider. -Platelets 75,000/mm3 = correct A platelet level of 75,000/mm3 indicates hydroxyurea toxicity. This platelet level is below the expected reference range of 150,00 to 400,000/mm3. Therefore, the nurse should report this finding to the provider. -Potassium 5.2 mEq/L = correct A potassium level of 5.2 mEq/L indicates tumor lysis syndrome. This potassium level is above the expected reference range of 3.5 to 5 mEq/L. Therefore, the nurse should report this finding to the provider. -Creatinine 1 mg/dL A creatinine level of 1 mg/dL is within the expected reference range of 0.5 mg/dL to 1.2 mg/dL. -RBC 4.7 million/mm3 An RBC count of 4.7 million/mm3 is within the expected reference range of 4.7 to 6.1 million/mm3 for a male client and 4.2 to 5.4 million/mm3 for a female client. 18) A nurse is caring for a pt who has a magnesium level of 3.1mEq/L. The nurse should expect to administer which of the following meds? -Magnesium gluconate A magnesium level of 3.1 mEq/L is above the expected reference range of 1.3 to 2.1 mEq/L. Magnesium gluconate is administered to treat hypomagnesemia. -Cinacalcet Cinacalcet is administered to treat hypercalcemia. -Calcium gluconate = The nurse should expect to administer IV calcium gluconate to the client and prepare to provide ventilatory support. This client is at risk for respiratory depression and cardiac dysrhythmias because a magnesium level of 3.1 mEq/L is above the expected reference range of 1.3 to 2.1 mEq/L. -Regular insulin Regular insulin is administered to treat hyperkalemia. 19) A nurse is preparing to mix and administer Dantrolene via IV bolus to a pt who has developed malignant hyperthermia during surgery. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? -Administer the reconstituted medication slowly over 5 min. The nurse should administer reconstituted dantrolene via IV bolus rapidly through a large bore IV or central line. -Store the reconstituted medication in the refrigerator. The nurse should store the reconstituted medication at room temperature and protect it from light until use. -Use the reconstituted medication within 12 hr. The nurse should use the reconstituted medication within 6 hr. -Reconstitute the initial dose with 60 mL of sterile water without a bacteriostatic agent = The nurse should dilute the medication with 60 mL of sterile water without a bacteriostatic agent and inject rapidly. 20) A nurse contacts a pt’s provider on the telephone to obtain a prescription for pain medication. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? -Write the order on a prescription pad designated for the client's provider. The nurse should write the order on the provider's order form in the client's medical record or place the order into the computer on the provider's order form according to facility policy. -Have the provider spell out the unfamiliar medication names = The nurse should ask the provider to spell out the name of the medication if the stated name is one the nurse is not familiar with. -Read the prescription back to the provider using abbreviations. The nurse should read the prescription back to the provider using words in place of abbreviations to reduce the risk of error. The nurse should ask the provider to acknowledge that the prescription is correct after having it read back. -Consult with a second nurse for any questions regarding dosage. The nurse should consult the provider about any questions concerning the prescription. 21) A nurse is providing teaching for a pt who has multiple sclerosis and a new prescription for Methylprednisolone. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include? (select all that apply) -Blood glucose levels will be monitored during therapy = The nurse should monitor the client for hyperglycemia while providing methylprednisolone to the client. Glucocorticoids, such as methylprednisolone, increase serum glucose levels and can require management with insulin or antihyperglycemics. -Avoid contact with people who have known infections = The nurse should instruct the client to avoid exposure to infectious agents, such as contact with those who have active infections or illnesses. Glucocorticoids, such as methylprednisolone, depress the immune system, placing the client at an increased risk for developing an infection. Grapefruit juice can increase the effects of the medication= The nurse should instruct the client that grapefruit and grapefruit juice can increase the level of methylprednisolone in the body. -Take the medication 1 hr before breakfast is incorrect. The nurse should instruct the client to take the medication with food or milk to decrease gastrointestinal upset. -Decrease dietary intake of foods containing potassium is incorrect. The nurse should instruct the client to increase dietary intake of potassium-rich foods while taking this medication. Glucocorticoids, such as methylprednisolone, deplete potassium in the body, which manifests as hypokalemia. 22) A nurse is teaching about Zolpidem to a pt who has insomnia. The nurse should identify that which of the following pt statements indicates an understanding of the teaching? -"I will need to get laboratory testing prior to a refill of this medication." Laboratory testing is not needed when taking this medication for sleep. -"I will use this medication for a short period of time." = Zolpidem is used for short-term treatment of insomnia. Therefore, the provider should reassess the client before refilling the prescription. -"I will need to take this medication for 1 week before results are seen." The client who takes zolpidem should experience improved sleep within 2 days of starting this medication. -"I will need to change the medications to prevent building up a tolerance." The client who takes zolpidem should not build up a tolerance to the medication with short-term use. 23) A nurse is providing teaching to a pt about the use of Ethinyl estradiol/ norelgestromin. The nurse should identify that which of the following statements by the pt indicates an understanding of the teaching? -"I will apply the patch once a week for 2 weeks." The client should apply the patch once a week for 3 weeks and then go without the patch for 1 week to promote menstruation. -"I will leave the existing patch on for 4 hours after applying the new patch." The client should remove and dispose the old patch before applying a new patch to prevent toxicity by combining the remaining medication on the old patch with the medication on the new patch. -"I will fold the sticky sides of the old patch together before disposing it." = The client should fold the sticky sides of the old patch together and then place it in a childproof container to ensure safe disposal of the patch. -"I will apply the patch within 14 days of menses." The client should apply the patch within 7 days of menses to prevent ovulation and the need for another contraceptive method. 24) A nurse is providing teaching to a pt who has a new prescription for Ferrous sulfate. THe nurse should instruct the pt to take the medication with which of the following to promote absorption? -Vitamin E Vitamin E has no effect on iron absorption. -Orange juice The absorption of ferrous sulfate is enhanced by a vitamin C source, such as orange juice. -Milk Milk inhibits iron absorption. -Antacids Antacids inhibit iron absorption. 25) A nurse is reviewing the lab results of a pt who is taking Carbamazepine for a seizure disorder. Which of the following findings should the nurse report to the provider? -Potassium 4.1 mEq/L A potassium level of 4.1 mEq/L is within the expected reference range of 3.5 to 5 mEq/L. The nurse does not need to monitor potassium levels for a client taking carbamazepine; however, the nurse should monitor sodium levels due to the potential adverse effect of hyponatremia. -24-hour urine glucose 300 mg/day A 24-hour urine glucose of 300 mg/day is within the expected reference range of 50 to 300 mg/day. The nurse should continue to monitor this value because carbamazepine can cause an elevation in urine glucose levels. -Carbamazepine level 7 mcg/mL A carbamazepine level of 7 mcg/mL is within the expected reference range of 5 to 12 mcg/mL and is an expected finding -WBC 3,500/mm3 = A WBC count of 3,500/mm3 is below the expected reference range of 5,000 to 10,000/mm3. Leukopenia is an adverse effect of carbamazepine. The nurse should report this finding to the provider and monitor the client for manifestations of infection. 26) A nurse is reviewing the medical record of a pt who has schizophrenia and a prescription for Clozapine. Which of the following lab tests should the nurse review before administering the medication? -Troponin The nurse should review the troponin level of a client who has chest pain and possible myocardial infarction. -Total cholesterol = The nurse should review the client's total cholesterol before administering clozapine, because this medication can cause hyperlipidemia. -Creatinine Clozapine is not metabolized by the kidneys. Therefore, the nurse does not need to review the creatinine level before administering the medication. -Thyroid stimulating hormone The nurse should review the thyroid stimulating hormone level of a client who has hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism. 27) A nurse is planning to teach about inhalant medications to a pt who has a new diagnosis of exercise induced asthma. Which of the following medications should the nurse plan to instruct the pt to use prior to physical activity? -Cromolyn = Cromolyn sodium stabilizes mast cells, which inhibit the release of histamine and other inflammatory mediators. The client should use cromolyn 10 to 15 min before planning to exercise to prevent bronchospasms. -Beclomethasone Beclomethasone is a prophylactic glucocorticoid inhalant medication that suppresses the inflammatory and humoral immune responses. Beclomethasone should be administered with a fixed schedule, not for PRN use before physical exercise. -Budesonide Budesonide is a glucocorticoid medication used to treat asthma as a long-term inhaled agent. This medication is administered by inhalation twice daily, not prior to physical activity. -Tiotropium Tiotropium is an anticholinergic medication that decreases mucus production and produces bronchodilation. Tiotropium is used for maintenance therapy of bronchospasms and has a duration of 24 hr. 28) A nurse is providing teaching to a pt who is to start therapy with Digoxin. For which of the following adverse effects should the nurse instruct the pt to monitor and report to the provider? - Dry cough Clients taking an ACE inhibitor, such as captopril, might develop a dry cough due to a buildup of bradykinin and should report this adverse effect to the provider. However, respiratory adverse effects are not associated with digoxin. -Pedal edema Clients taking a calcium channel blocker, such as verapamil, might develop pedal edema and should report this adverse effect to the provider. However, peripheral edema is not associated with digoxin. -Bruising Clients taking an anticoagulant, such as enoxaparin, might develop bruising and should report this adverse effect to the provider. However, hematologic adverse effects are not associated with digoxin. -Yellow-tinged vision = The nurse should instruct the client to monitor for and report yellow-tinged vision, which is a sign of digoxin toxicity. Other manifestations of digoxin toxicity include nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, and fatigue. As the digoxin levels increase, the client can experience cardiac dysrhythmias. -A nurse is caring for a pt who is to receive treatment for opiod use disorder. Which of the following medications should the nurse expect to administer? -Bupropion The nurse should administer bupropion to assist the client with smoking cessation. -Disulfiram The nurse should administer disulfiram as an aversion therapy to assist with maintaining abstinence from alcohol. -Methadone = The nurse should expect to administer methadone for treatment of opioid use disorder. Methadone can be administered for withdrawal and to assist with maintenance and suppressive therapy. -Modafinil The nurse should administer modafinil to assist with the fatigue and prolonged sleep from methamphetamine withdrawal. 30) A nurse is caring for a pt who has heart failure and is receiving an IV infusion of Dopamine. Which of the following findings indicates that the medication is effective? -Decreased blood pressure Dopamine is an adrenergic that causes a receptor specificity effect, which increases blood pressure. -Increased heart rate Tachycardia is an adverse effect of dopamine and does not indicate the medication's effectiveness. -Increased cardiac output = Dopamine is an adrenergic that causes a receptor specificity effect, which increases cardiac output and improves perfusion. -Decreased serum potassium Dopamine does not affect serum potassium levels. 31) A nurse administered Digoxin immune Fab to a pt who received the incorrect dose of Digoxin over a period of 3 days. The nurse should identify that which of the following findings indicates the antidote was effective? -Normal sinus rhythm = Dysrhythmias are a life-threatening adverse effect of digoxin toxicity. The return of the heart to normal sinus rhythm indicates a therapeutic response to the antidote. Digoxin immune Fab is administered to a client who is experiencing severe digoxin toxicity. It binds with digoxin and works to reduce the client's blood digoxin level. -Digoxin level of 2.5 ng/mL A digoxin level of 2.5 ng/mL is above the expected reference range of 0.8 to 2 ng/mL. Therefore, this finding does not indicate a therapeutic response to the antidote. -Decrease in blood pressure A decrease in blood pressure is not an indication of a therapeutic response to the antidote. -Potassium level of 3.2 mEq/L A potassium level of 3.2 mEq/L is below the expected reference range of 3.5 to 5.0 mEq/L. A decreased potassium level can lead to toxicity in a client who is taking digoxin. However, digoxin immune Fab is administered only for severe toxicity. 32) A nurse is caring for a pt who has hypocalcemia and is receiving Calcium citrate. The nurse should identify that which of the following findings indicates a therapeutic response to the medication? -Positive Chvostek's sign A positive Chvostek's sign is a manifestation of hypocalcemia and does not indicate a therapeutic response to calcium citrate. -Client report of decreased paresthesia = Paresthesia is a manifestation of hypocalcemia. A client report of a decrease in paresthesia is an indication of a therapeutic response to calcium citrate. The nurse should also monitor for a decrease in other manifestations of hypocalcemia, including muscle twitching and cardiac dysrhythmias. -Client report of increased thirst An increase in thirst is a manifestation of hypercalcemia and can be an indication of calcium toxicity. The nurse should monitor the client for other manifestations of hypercalcemia, such as nausea, vomiting, or anorexia. -Calcium level of 8.8 mg/dL A calcium level of 8.8 mg/dL is below the reference range of 9.0 to 10.5 mg/dL and does not indicate a therapeutic response to calcium citrate. 33) A nurse is caring for a pt who is taking Atorvastatin for hyperlipidemia. Which of the following pt laboratory values should the nurse monitor? -Creatinine kinase = The client who is taking atorvastatin can develop an adverse effect called rhabdomyolysis, which causes muscle weakness or pain and can progress to myositis. Creatinine kinase levels rise in response to enzymes released with muscle injury. -Erythrocyte sedimentation rate Erythrocyte sedimentation rates (ESR) evaluate the speed at which red blood cells settle in plasma over a set amount of time. The nurse should monitor ESR for clients who have multiple myeloma, rheumatoid arthritis, and systemic lupus erythematosus. However, ESR is not affected by statins, such as atorvastatin. -International normalized ratio The international normalized ratio (INR) measures clotting abilities of the blood. The nurse should monitor INR for clients who are receiving warfarin therapy. -Potassium Potassium is a major electrolyte that maintains acid-base balance, oncotic pressure, and cardiac rhythm. The nurse should monitor potassium levels in clients who are receiving loop diuretics, such as bumetanide. 34) A nurse is caring for a pt who is receiving end of life care and has a prescription for Fentanyl patches. Which of the following information regarding the adverse effects of Fentanyl should the nurse plan to give to the pt and family? -The provider will prescribe naloxone at home for respiratory depression. Naloxone is only for use in an acute care setting for the reversal of severe respiratory depression. -Remove the patch to reverse the adverse effects immediately. After removing the patch, the effects will persist for several hours due to the absorption of the residual medication on the skin. -Expect an increase in urinary output. Urinary retention is an adverse effect of opioids, including fentanyl. -Take a stool softener on a daily basis = CORRECT ASNWER Constipation is an adverse effect of opioid use. Stool softeners can decrease the severity of this adverse effect. 35) A nurse is preparing to administer 0.9% Sodium Chloride (NaCl) 1,500 mL to infuse over 8hr to a client who is postoperative. The nurse should set the IV pump to deliver how many mL/hr? (Round to nearest whole #. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero) 187.5 mL/hr = 188 mL/hr. The nurse should set the IV pump to deliver 0.9% sodium chloride IV at 188 mL/hr. = 36) A nurse is providing discharge instructions to a pt who is to self administer insulin at home. Which of the following pt statements should indicate to the nurse that the teaching is effective? -"I should avoid getting rid of the air bubble in the syringe." The nurse should instruct the client to expel all air bubbles in the syringe to ensure an accurate dosage is delivered. -"I should inject the insulin into my thigh for the fastest absorption." The nurse should instruct the client that the fastest absorption of insulin occurs with abdominal injections. Absorption is slowest when the injection is into the thigh. -"I will store my unopened bottles of insulin in the refrigerator." = The client should store unopened vials of insulin in the refrigerator to maintain medication viability. Once opened, the insulin can remain at room temperature for up to 1 month. -"I need to shake the insulin before using it to make sure it is well mixed." The nurse should instruct the client to mix insulin by rolling the insulin in the palm of their hand to prevent frothing, which can cause the drawing up of an inaccurate dose of insulin. 37) A nurse is caring for a pt who has developed hypomagnesemia due to long term therapy with Lansoprazole. The nurse should monitor the client for which of the following manifestations? -Bradycardia The nurse should monitor the client for tachycardia as a manifestation of hypomagnesemia. -Hypotension The nurse should monitor the client for hypertension as a manifestation of hypomagnesemia. -Muscle weakness The nurse should monitor the client for neuromuscular irritability, such as tremors, as a manifestation of hypomagnesemia. -Disorientation = The nurse should monitor the client for disorientation and confusion as manifestations of hypomagnesemia. The nurse should also assess the client for a positive Chvostek's and Trousseau's signs. 38) A nurse is teaching a pt who has a new prescription for Docusate sodium about the medication’s mechanism of action. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching?\ -Docusate sodium reduces the surface tension of the stools to change their consistency = Docusate sodium is a surfactant that softens stool by reducing surface tension, allowing water to penetrate more easily into the stool. -Docusate sodium causes rectal contractions. Osmotic laxatives, such as glycerin suppositories, act by lubricating the lower colon and initiating reflex contractions of the rectum. -Docusate sodium acts as a fiber agent, increasing bulk in the intestines. Bulk-forming laxatives, such as methylcellulose, mimic the action of dietary fiber, forming a viscous compound that softens the fecal mass and increases its bulk, which stimulates peristalsis. -Docusate sodium stimulates the motility of the intestines. Stimulant laxatives, such as bisacodyl, stimulate the intestinal wall to cause peristalsis by pulling water into the intestines. 39) A nurse is administering Baclofen for a pt who has a spinal cord injury. Which of the following findings should the nurse document as a therapeutic outcome? -Increase in seizure threshold A client who has a seizure disorder and takes baclofen can have a decrease in the seizure threshold, which can result in seizure activity. -Decrease in flexor and extensor spasticity = A client who has a spinal cord injury and takes baclofen can experience a decrease in the frequency and severity of muscle spasms and in flexor and extensor spasticity. -Increase in cognitive function A client who takes baclofen can experience the adverse effect of memory impairment and a decrease in cognitive function. -Decrease in paralysis of the extremities A client who takes baclofen can experience the adverse effect of inhibited reflexes at the spinal level; however, this medication does not decrease the effects of paralysis. 40) A nurse in a provider’s office is assessing a pt who has been taking Aspirin daily for the past year. For which of the following findings should the nurse notify the provider immediately? -Hyperventilation = When using the urgent vs. nonurgent approach to client care, the nurse should determine that the priority finding is hyperventilation. This finding indicates the client might have acute salicylate poisoning, which causes respiratory alkalosis in the early stages. -Heartburn Heartburn is nonurgent because the client who is taking aspirin can experience gastrointestinal distress. Therefore, there is another finding that is the nurse's priority. -Anorexia Anorexia is nonurgent because the client who is taking aspirin can experience a decrease in appetite. Therefore, there is another finding that is the nurse's priority. -Swollen ankles Swollen ankles are nonurgent because the client who is taking aspirin can experience sodium and fluid retention. Therefore, there is another finding that is the nurse's priority. 41) A nurse is monitoring for adverse effects of Hydrochlorothiazide after administering the medication to an older adult pt who has heart failure. Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as an adverse effect of the medication? -Hypoglycemia Hydrochlorothiazide is an antihypertensive thiazide diuretic medication, which can cause hyperglycemia. -Orthostatic hypotension = The nurse should identify that hydrochlorothiazide is an antihypertensive thiazide diuretic medication, which can cause orthostatic hypotension and light headedness. Therefore, the nurse should instruct the client to rise slowly when moving from a recumbent to a standing position. -Bradycardia The nurse should identify palpitations as an adverse effect of hydrochlorothiazide, which is an antihypertensive thiazide diuretic medication. -Xanthopsia The nurse should identify that hydrochlorothiazide is an antihypertensive thiazide diuretic medication and has an adverse effect of blurred vision. Xanthopsia causes objects to appear yellow and is not an adverse effect of this medication. 42) A nurse is preparing to administer a new prescription of Amoxicillin / Clavulanic to a client. The client tells the nurse that they are allergic to Penicillin. Which of the following actions should the nurse take first? -Update the client's medical record. It is important to update the client's medical record to have complete information available; however, the nurse should take another action first. -Notify the provider. It is important to notify the provider because the client will need a new prescription; however, the nurse should take another action first. -Withhold the medication = When using the urgent vs nonurgent approach to client care, the nurse should determine that the priority action is to withhold the medication to prevent injury to the client. -Inform the pharmacist of the client's allergy to penicillin. It is important to inform the pharmacist of the allergy to promote continuity of care; however, the nurse should take another action first. 43) A nurse is providing teaching to a client who has depression and a new prescription for Fluoxetine. Which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching? -"I should start to feel better within 24 hours of starting this medication." The nurse should inform the client that the therapeutic levels of fluoxetine can take between 1 and 4 weeks to achieve desired effects. The client should take the medication as prescribed and use other strategies to manage depression in the interim. -"I will be sure to follow a strict diet to avoid foods with tyramine." Clients taking fluoxetine, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, are not required to restrict their dietary intake of tyramine. A client who is taking an MAOI, such as selegiline, should avoid products containing tyramine. -"I will continue to take St. John's Wort to increase the effects of the medication." Concurrent use of St. John's Wort and fluoxetine can increase the client's risk for serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening complication. Manifestations of serotonin syndrome include confusion, hallucinations, hyperreflexia, excessive sweating, and fever. -"I should take acetaminophen instead of ibuprofen for my headaches while taking this medication." = Fluoxetine suppresses platelet aggregation, which increases the risk of bleeding when used concurrently with NSAIDs and anticoagulants. Therefore, clients who are taking fluoxetine should take acetaminophen for headaches or pain, since acetaminophen does not suppress platelet aggregation. 44) A nurse is assessing a client who has received Atropine eye drops during an eye examination. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect as an adverse effect of the medication? -Difficulty seeing in the dark A client who has received atropine eye drops can experience photosensitivity, which causes difficulty seeing in brightly lit areas due to the muscarinic receptors causing mydriasis. -Pinpoint pupils Dilation of pupils, or mydriasis, is an expected finding following the administration of atropine eye drops. -Blurred vision = CORRECT ASNWER Blurred vision is an expected finding following the administration of atropine eye drops. This is due to the cycloplegic effects of the medication, which cause distant objects to appear blurry to the client. -Excessive tearing Excessive tearing is not an expected finding following the administration of atropine eye drops. 45) A nurse is providing discharge teaching to a client who has a new prescription for Furosemide twice daily. The nurse should include which of the following instructions in the teaching? (Select all that apply) -"Increase intake of potassium-rich foods"= correct Loop diuretics, such as furosemide, act at the loop of Henle by blocking the resorption of sodium, water, and potassium. An adverse effect of the medication is the development of electrolyte imbalances such as hyponatremia, hypochloremia, and hypokalemia. To prevent hypokalemia, the client should increase intake of potassium-rich foods, such as potatoes, spinach, dried fruit, and nuts. "Monitor for muscle weakness" = correct. Furosemide, a loop diuretic, causes a loss of potassium, which can result in manifestations of hypokalemia such as difficulty concentrating, shallow respirations, hyporeflexia, and muscle weakness. The nurse should instruct the client to monitor for these manifestations and report them to the provider. "Dangle your legs from the side of the bed before standing" = correct. Loop diuretics, such as furosemide, reduce vascular tone and increase fluid excretion. These effects decrease blood return to the heart and can manifest as dizziness and lightheadedness when going from a lying to a standing position. The client should change positions slowly to minimize orthostatic hypotension. -"Take the second dose at bedtime" Furosemide is a loop diuretic that causes diuresis. When taken twice daily, the client should take the second dose of furosemide by 1400 hr to prevent nocturia. -"Obtain your weight weekly" Loop diuretics cause an increase in fluid excretion and can cause dehydration. While manifestations of dehydration, such as increased thirst and decreased urine output, can assist in the diagnosis of dehydration, the most reliable method of identifying the onset of dehydration is by loss of weight. The client should obtain daily weights to monitor for the diuresis effect of the medication. 46) A nurse is teaching a client who is to start taking Ranitidine for peptic ulcer disease. Which of the following client statements should the nurse identify as understanding of the teaching? -"I will stop taking ranitidine when my stomach pain is gone." The nurse should instruct the client to take ranitidine on a continuous basis for the prescribed time. -"I know smoking makes ranitidine less effective" = The nurse should instruct the client that smoking decreases the effectiveness of ranitidine by exacerbating the ulcer manifestations. -"I will take ranitidine anytime my stomach hurts." The nurse should instruct the client to take ranitidine on a continuous basis for the prescribed time. -"I know that ranitidine will turn my stools black." Ranitidine does not cause stools to appear black. However, a bleeding peptic ulcer can cause a client's stools to turn black. 47) A nurse is preparing to administer Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) to a client. Which of the following actions should the nurse take prior to administering the medication? -Ask the client to drink 8 oz of water. HCTZ is a thiazide diuretic administered to promote urine output and reduce blood pressure and edema. The client does not need to drink 8 oz of water prior to taking the medication. -Review the client's most recent Hgb level. HCTZ does not affect Hgb levels. The nurse should monitor the client's electrolytes, especially potassium, before and periodically while the client is taking this medication. -Obtain the client's blood pressure = HCTZ is a thiazide diuretic administered to promote urine output and reduce blood pressure and edema. The nurse should obtain the client's blood pressure prior to administration of the medication. -Determine if the client is allergic to NSAIDs. The nurse should assess the client for an allergy to sulfonamides due to the potential of cross-sensitivity with HCTZ. NSAIDs can decrease the effectiveness of HCTZ. 48) A nurse is caring for a client who is recovering from deep vein thrombosis DVT and is to start taking Warfarin. For which of the following findings should the nurse monitor as an adverse effect to Warfarin? -Hypertension The nurse should monitor for hypotension, which can indicate bleeding. -Low INR The nurse should monitor the INR daily until it increases to a therapeutic level. -Constipation The nurse should monitor for gastrointestinal irritation, which can include diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. -Bleeding gums = The nurse should monitor the client for bleeding gums, which is an adverse effect of warfarin, an anticoagulant. 49) A nurse is planning discharge teaching for a client who has a prescription for Furosemide. The nurse should plan to include which of the following statements in the teaching? -"This medication increases your risk for hypertension." The client who takes furosemide has an increased risk of hypotension due to fluid loss from the diuretic effect of the medication. -"Avoid potassium-rich foods in your diet." The client who takes furosemide has an increased risk for potassium loss because of the diuretic effect of the medication that causes excretion of potassium through the kidneys. The client should increase their intake of potassium-rich foods. -"Take each dose of medication in the evening before bed." The client should take each dose of medication in the morning to avoid sleep disturbances from nocturia. -"Drink a glass of milk with each dose of medication" = The client should take furosemide with food or milk to reduce gastric irritation. 50) A nurse is teaching a client who is starting to take Diltiazem. Which of the following statements should the nurse identify as an indication that the client understands the teaching? -"I will stop taking the medication if I get dizzy." Diltiazem is a calcium channel blocker that causes vascular dilation, which can result in orthostatic hypotension. The client should rise slowly when standing and avoid hazardous activities until there is a stabilization of the medication and dizziness no longer occurs. -"I should not drink orange juice while taking this medication." The client should not drink grapefruit juice while taking diltiazem because it can interfere with metabolism of the medication by increasing the blood levels of diltiazem and leading to toxicity. -"I should expect to gain weight while taking this medication." Diltiazem, a calcium channel blocker, can decrease myocardial contraction, which can lead to heart failure. If the client gains weight or develops shortness of breath, they should notify the provider. -"I will check my heart rate before I take the medication" = CORRECT ASNWER Diltiazem, a calcium channel blocker, has cardio-suppressant effects at the SA and AV nodes, which can lead to bradycardia. The client should check their heart rate before taking the medication and notify the provider if it falls below the expected reference range. 51) A nurse is administering Diazepam to a client who is having a colonoscopy. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? -Ensure flumazenil is available to administer for toxicity management = The nurse should monitor the client for manifestations of diazepam toxicity, such as respiratory depression and hypotension. The nurse should be prepared to administer flumazenil to reverse the effects of diazepam. -Monitor the client for an increase in blood pressure. The nurse should monitor the client for the adverse effect of hypotension. -Expect the client to become unconscious within 30 seconds. When diazepam is administered IV for induction of anesthesia, the nurse should expect the client to develop the full effect of the medication in 2 min. -Measure the capnography level every hour until the client is awake and oriented. The nurse should measure the capnography level every 15 to 30 min until the client is awake and oriented and vital signs have returned to baseline. 52) A nurse is caring for a client who has pneumonia. The client tells the nurse she is pregnant and that she has not told her provider yet. The nurse should identify that pregnancy is a contraindication for receiving which of the following medications? -Acetaminophen Acetaminophen treats mild pain and is not contraindicated for the client at this time. Acetaminophen IV is used with caution among clients who are pregnant or lactating. -Ipratropium Ipratropium is a long-acting bronchodilator and is not contraindicated for a client who is pregnant. -Benzonatate Benzonatate is a cough suppressant and is not contraindicated for a client who is pregnant. -Doxycycline = CORRECT ASNWER Doxycycline is a tetracycline antibiotic. The nurse should identify that doxycycline can cause teratogenic effects such as staining of the infant's teeth when exposed to this medication. Therefore, this medication is contraindicated for the client. 53) A nurse is caring for a client who reports lethargy and myalgia after taking Clozapine for 6 months. Which of the following actions should the nurse plan to take? -Infuse 0.9% sodium chloride 1,000 mL IV fluid bolus. The client who is dehydrated can receive 0.9% sodium chloride IV bolus, but it is not used to treat the adverse effects of lethargy, myalgia, and weakness associated with clozapine. -Schedule the client for an electroencephalogram. The client who develops seizures can have an electroencephalogram, but it is not used to treat or diagnose the client who has lethargy and myalgia. -Obtain WBC with absolute neutrophil count = The client who takes clozapine can develop lethargy and myalgia caused by the adverse effect of agranulocytosis. Therefore, monitoring the WBC with absolute neutrophil count weekly for the first 6 months of treatment is recommended. After 6 months, monitoring can occur every 2 weeks up to 1 year. -Place the client on a tyramine-free diet. The client can take clozapine with or without food and does not need to follow a tyramine-free diet. A client who is taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors should follow a tyramine-free diet. 54) A nurse is assessing a client who is taking Amitriptyline for depression. Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as an adverse effect of the medication? -Tinnitus Amitriptyline is a tricyclic antidepressant medication that has anticholinergic properties. The nurse should assess for sensory-neurologic adverse effects such as blurred vision or an increased sensitivity to light. However, tinnitus is not an expected finding. -Urinary frequency The nurse should assess the client for genitourinary anticholinergic effects such as urinary hesitancy or retention due to the blocking of acetylcholine receptors that cause anticholinergic responses. However, urinary frequency is not an expected finding. -Dry mouth = The nurse should expect the client to have a dry mouth due to the blocking of acetylcholine receptors that cause anticholinergic responses. -Diarrhea The nurse should assess the client for gastrointestinal anticholinergic effects such as constipation. However, diarrhea is not an expected finding. 55) A nurse administers Ceftazidime to a client who has a severe Penicillin allergy. The nurse should identify which of the following client findings as an indication that she should complete an incident report? -The client reports shortness of breath = A severe penicillin allergy is a contraindication for taking ceftazidime, a cephalosporin antibiotic, due to the potential for cross-sensitivity. Shortness of breath can indicate the client is developing anaphylaxis. -The client is also taking lisinopril. Lisinopril is an ACE inhibitor medication that has no known interaction with cephalosporins. -The client's pulse rate is 60/min. Cephalosporins do not affect the client's pulse rate. The client's pulse rate of 60/min is within the expected reference range. -The client's WBC count is 14,000/mm3. An elevated WBC count is an indication the client has an infection and should receive antibiotic therapy. 56) A nurse is reviewing laboratory results for a client who is to receive a dose of Ceftazidime via intermittent IV bolus. Which of the following laboratory Findings is the priority for the nurse to report to the provider before administering the medication? -Total bilirubin 0.4 mg/dL Ceftazidime, a cephalosporin, can cause elevated liver function tests, such as bilirubin. However, a total bilirubin value of 0.4 mg/dL is within the expected reference range. -Alanine aminotransferase 26 units/L Ceftazidime can cause elevated liver function tests, such as alanine aminotransferase. However, an alanine aminotransferase value of 26 units/L is within the expected reference range. -Platelet count 360,000/mm3 Ceftazidime can cause thrombocytopenia. However, a platelet count of 360,000/mm3 is within the expected reference range. -Creatinine 2.6 mg/dL = Ceftazidime is excreted primarily by the renal system. A serum creatinine level above 1.3 mg/dL can indicate a kidney disorder requiring a reduction in the dose administered. The nurse should notify the provider, who is likely to prescribe a lowered dose of medication. 57) A nurse is assessing a client who is receiving Epoetin alfa to treat anemia. Which of the following findings should the nurse monitor? -Paresthesia Epoetin alfa stimulates the bone marrow to increase production of red blood cells. Adverse effects include neurological manifestations such as seizures, headache, and dizziness. However, epoetin alfa does not cause paresthesia. -Increased blood pressure = The therapeutic effect of epoetin alfa is an increase in hematocrit levels, which can result in an increase in a client's blood pressure. If the client's hematocrit level rises too rapidly, hypertension and seizures can result. The nurse should monitor the client's blood pressure and ensure hypertension is controlled prior to administering the medication. -Fever Adverse effects of epoetin alfa include neurological manifestations such as coldness and sweating. However, it does not cause fever. -Respiratory depression Heart failure is an adverse effect of epoetin alfa. The nurse should monitor the client's respiratory status and notify the provider if the client develops crackles or rhonchi. However, epoetin alfa does not cause respiratory depression. 58) A nurse is completing an incident report for a medication error. Which of the following information should the nurse include on the report? -This could have been avoided if I had double checked the medication administration record with the client's identification band. The incident report should clearly and thoroughly report the facts of the error. It should not include the nurse's opinion as to how the error might have been prevented. -It was easy to get confused because another client is receiving a similar sounding medication. The incident report should clearly and thoroughly report the facts of the error. It should not include the nurse's opinion as to why the error might have occurred. -Administered propranolol 80 mg PO at 1800 to the client who did not have a prescription for the medication = The incident report should clearly and thoroughly report the facts of the error. -While I rarely make medication errors, the client was given 80 mg of propranolol by mistake at 1800. The incident report should clearly and thoroughly report the facts of the error. It should not include statements by the nurse regarding personal characteristics. 59) A nurse is teaching about self administration of transdermal medication with a male client who has a prescription for Nitroglycerin. The nurse should identify that which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching? -"I can apply the patch to a chest area that has hair." The client should apply the patch to an area of the skin that is hairless to enhance absorption of the medication. -"I can take this medication while using an erectile dysfunction product." The client should not use erectile dysfunction products while taking nitroglycerin because this combination can cause severe hypotension and death. -"I will remove the patch after 14 hours" = The client should remove the patch after 12 to 14 hr to prevent tolerance of the medication. -"I need to apply a new patch to the same area every day." The client should rotate the location of the patch daily to avoid irritation of the skin. 60) A nurse is reviewing the medical record of a client who has hypertension. The nurse should identify which of the following findings as a contraindication for receiving Propanolol? -Cholelithiasis Cholelithiasis is not a contraindication for receiving propranolol. -Asthma = Asthma is a contraindication for receiving propranolol. Propranolol is an adrenergic antagonist which blocks the beta2 receptors in the lungs, causing bronchoconstriction and leading to serious airway resistance and possibly respiratory arrest. -Angina pectoris The client who has angina pectoris can receive propranolol to decrease heart rate and contractility, resulting in a reduction of oxygen demand. Propranolol is contraindicated for use when a client has vasospastic angina. -Tachycardia Tachycardia is not a contraindication for receiving propranolol. Propranolol is administered to slow a client's heart rate and decrease oxygen demand. ATI PHARMACOLOGY 2016 PRACTICE A 1) A nurse is caring for a client who has sickle cell anemia and is taking hydroxyurea. Which of the following findings should the nurse report to the provider? (select all that apply) -Hemoglobin 7.0 g/dL = A hemoglobin level of 7.0 g/dL indicates hydroxyurea toxicity, and the nurse should report it to the provider. -Platelets 75,000/mm3 = A platelet level of 75,000/mm3 indicates hydroxyurea toxicity, and the nurse should report it to the provider. -Potassium 5.2 mEq/L = A potassium level of 5.2 mEq/L indicates tumor lysis syndrome, and the nurse should report it to the provider. -Creatinine 1 mg/dL A creatinine level of 1 mg/dL is within the expected reference range. RBC 4.7 million/mm3 A RBC 4.7 million/mm3 is within the expected reference range. 2) A nurse is assessing a client who has myasthenia graves and is taking Neostigmine. Which of the following findings should indicate to the nurse the client is experiencing an adverse effect? -Tachycardia Neostigmine can cause bradycardia, rather than tachycardia, due to the excessive muscarinic stimulation. -Oliguria Neostigmine can cause urinary urgency, rather than decreased urinary output, due to the excessive muscarinic stimulation. -Xerostomia Neostigmine can cause increased salivation, rather than dry mouth, due to the excessive muscarinic stimulation. -Miosis = CORRECT ASNWER Miosis, which is pupillary constriction, is a common adverse effect of neostigmine due to the excessive muscarinic stimulation that causes difficulty with visual accommodation. 3) A nurse is monitoring a client who is receiving Amphotericin B intermittent IV bolus for the treatment of histoplasmosis. Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as an adverse reaction to the medication? -Tachycardia Bradycardia, not tachycardia, is an adverse effect of amphotericin B. -Oliguria = Oliguria can indicate renal compromise in a client who is taking amphotericin B. The nurse should report this finding to the provider. -Hyperkalemia Hypokalemia, not hyperkalemia, is an adverse effect of amphotericin B due to the medication causing damage to the kidneys. -Weight gain Weight loss, not weight gain, is an adverse effect of amphotericin B. 4) A nurse is reviewing the medical record of a client who has schizophrenia and a prescription for Clozapine. Which of the following laboratory tests should the nurse review before administering the medication? -Troponin The nurse should review the troponin level of a client who has chest pain and possible myocardial infarction. -Total cholesterol = The nurse should review the client's total cholesterol before administering clozapine, because this medication can cause hyperlipidemia. -Creatinine Clozapine is not metabolized by the kidneys. Therefore, the nurse does not need to review the creatinine level before administering the medication. -Thyroid stimulating hormone The nurse should review the thyroid stimulating hormone level of a client who has hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism. 5) A nurse is teaching about Zolpidem with a client who has insomnia. The nurse should identify that which of the following client statements indicates an understanding of the teaching? -"I will need to get laboratory testing prior to a refill of this medication." Laboratory testing is not needed when taking this medication for sleep. -"I will use this medication for a short period of time." = Zolpidem is used for short-term treatment of insomnia. Therefore, the provider should reassess the client before refilling the prescription. -"I will need to take this medication for 1 week before results are seen." The client who takes zolpidem should have improved sleep within 2 days of starting this medication. -"I will need to change the medications to prevent building up a tolerance." The client who takes zolpidem should not build up a tolerance with short-term use. 6) A nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for Phenytoin. Which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching? -"I should take my medication with antacids to minimize gastric upset." The client should not take phenytoin with antacids because they can decrease the effects of phenytoin. If needed, antacids should be taken 2 hr before or after the phenytoin. -"This type of medication does not require blood monitoring." The client should receive instructions to have blood levels of phenytoin monitored to determine effective dosage. Subtherapeutic and toxic levels can result in poor outcomes. -"I should let my dentist know I'm taking this medication" = Phenytoin commonly causes gingival hyperplasia. As a result, the client should notify his dentist. -"I should expect to experience some unusual eye movement when taking this medication." The client should not expect to experience unusual eye movement when taking phenytoin. However, nystagmus is a serious adverse effect when taking phenytoin that the client should report to the provider. 7) A nurse is caring for a client who reports lethargy and myalgia after taking clozapine for 6 months. Which of the following actions should the nurse plan to take? -Infuse 0.9% sodium chloride 1,000 mL IV fluid bolus. The client who is dehydrated may receive 0.9% sodium chloride IV bolus, but it is not used to treat the adverse effects of lethargy, myalgia, and weakness from taking clozapine. -Schedule the client for an electroencephalogram. The client who develops seizures may have an electroencephalogram, but it is not used to treat or diagnose the client who has lethargy and myalgia. -Obtain WBC with absolute neutrophil count = The client who takes clozapine can develop lethargy and myalgia caused by the adverse effect of agranulocytopenia. Therefore, monitoring the WBC with absolute neutrophil count weekly for the first 6 months of treatment is recommended. After 6 months, monitoring can be changed to occur every 2 weeks up to 1 year. -Place the client on a tyramine-free diet. The client can take clozapine with or without food and does not need to follow a tyramine-free diet, The client will follow a tyramine-free diet if taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors. 8) A nurse is providing discharge teaching about handling medication to a client who is to continue taking oral transmucosal Fentanyl raspberry flavored lozenges on a stick. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching? -Chew on the medication stick to release the medication. The nurse should instruct the client to place the fentanyl stick between her cheek and lower gum and to actively suck it for increased absorption of the medication. -Leave the medication stick in one location of the mouth until melted. The nurse should instruct the client to periodically move the medication stick to a different location in the mouth for best absorption. -Allow the medication 1 hr for analgesia effects to begin. The nurse should instruct the client to expect the medication's analgesia effects to begin within 10 to 15 min. -Store unused medication sticks in a storage container = The nurse should instruct the client to store unused, used, or partially used medication sticks in the safe storage container that comes in the kit when the medication is initially prescribed. 9) A nurse is administering Cefotetan via intermittent IV bolus to a client who suddenly develops dyspnea and widespread hives. Which of the following actions should the nurse take first? -Administer epinephrine 0.5 mL via IV bolus. The nurse should administer epinephrine, which is a beta-adrenergic agonist that can stimulate the heart, cause vasoconstriction of blood vessels in the skin and mucous membranes, and cause bronchodilation in the lungs. However, there is another action the nurse should take first. -Discontinue the medication IV infusion = The greatest risk to the client is respiratory arrest from anaphylaxis. Therefore, the first action the nurse should take is to discontinue the medication IV infusion to prevent the client from receiving more medication. However, the nurse should not remove the IV catheter. Instead, the nurse should change the tubing and administer 0.9% sodium chloride by continuous IV infusion. -Elevate the client's legs above the level of the heart. The nurse should elevate the client's legs and feet to a level above the client's heart to facilitate blood flow to the vital organs. However, there is another action the nurse should take first. -Collect a blood specimen for ABGs. The nurse should collect a blood specimen for ABGs levels to evaluate the client's respiratory status. However, there is another action the nurse should take first. 10) A nurse is teaching a client who is to start taking Ranitidine for peptic ulcer disease. Which of the following client statements should the nurse identify as understanding of the teaching? -"I will stop taking ranitidine when my stomach pain is gone." The nurse should instruct the client to take ranitidine on a continuous basis for the prescribed time. -"I know smoking makes ranitidine less effective" = The nurse should instruct the client that smoking decreases the effectiveness of ranitidine by exacerbating the ulcer manifestations. -"I will take ranitidine anytime my stomach hurts." The nurse should instruct the client to take ranitidine on a continuous basis for the prescribed time. -"I know that ranitidine will turn my stools black." Ranitidine does not cause stools to appear black. However, a bleeding peptic ulcer can cause a client's stools to turn black. 11) A nurse is teaching a client who is to start taking Diltiazem. The nurse should instruct the client to report which of the following findings as an adverse effect of the medication? -Blurred vision The client who is taking diltiazem, a calcium channel blocker, has no visional adverse effects. Digoxin can have non-cardiac signs of toxicity, which can include blurred or yellow vision, nausea, vomiting, anorexia, and fatigue. -Shortness of breath = The client who is taking diltiazem, a calcium channel blocker, can experience shortness of breath as an adverse effect and should report the finding to the provider immediately. -Muscle twitching The client who is taking diltiazem, a calcium channel blocker, can have weakness, insomnia, tremors and paresthesia but not muscle twitching, which may indicate the client has hyponatremia. -Dry cough The client who is taking diltiazem, a calcium channel blocker, can have adverse effects of rhinitis, dyspnea, and pharyngitis. A cough is an adverse effect of an ACE inhibitor. 12) A nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a prescription for a MAOI inhibitor. Which of the following foods should the nurse instruct the client to avoid while taking this medication? -Smoked sausage = The nurse should instruct the client to avoid eating smoked sausage because it contains tyramine. Tyramine can interact with MAOIs and result in hypertensive crisis. -Cottage cheese The nurse should inform the client that it is safe to eat cottage cheese, which contains little to no tyramine, when taking MAOI medications. -Green beans The nurse should inform the client that it is safe to eat green beans, which contain little to no tyramine, when taking MAOI medications. -Apple pie The nurse should inform the client that it is safe to eat apple pie, which contains little to no tyramine, when taking MAOI medications. 13) A nurse is providing teaching to a client who is to start taking Lisinopril. Which of the following findings is an adverse effect that the nurse should instruct the client to monitor and report to the provider? -Hair loss Alopecia, or hair loss, is not an adverse effect of lisinopril. -Ringing in the ears Tinnitus, or ringing in the ears, is not an adverse effect of lisinopril. -Facial flushing Facial flushing is not an adverse effect of lisinopril. However, facial edema is a serious effect that the client should report to the provider. -Dry cough = A buildup of bradykinin from taking lisinopril can cause a client to have a dry cough and lead to life-threatening consequences. The client should report the finding to the provider. 14) A nurse is providing teaching to a client who is to start taking Sumatriptan. Which of the following adverse effects should the nurse instruct the client to monitor for and report to the provider? -Chest pressure Sumatriptan is an antimigraine agent which can cause coronary vasospasms, resulting in angina. The client should report chest pressure or heavy arms to the provider. -White patches on the tongue White patches on the tongue can indicate a fungal infection, which is not an adverse effect of sumatriptan. -Bruising Ecchymosis can indicate thrombocytopenia, which is not an adverse effect of sumatriptan. -Insomnia Sumatriptan can cause drowsiness and sedation as an adverse effect of the medication. 15) A nurse is preparing to administer Amoxicillin 250 mg PO to a school age child. The amount available is amoxicillin oral suspension 200 mg/5 mL. How many mL should the nurse administer per dose? (Round to nearest tenth. Use a trailing sero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero) 6.25 = 6.3 6.3 = The nurse should administer amoxicillin 6.3 mL PO. 16) A nurse is monitoring for adverse effects of Hydrochlorothiazide after administering the medication to an older adult client who has heart failure. Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as an adverse effect of the medication? -Hypoglycemia Hydrochlorothiazide is an antihypertensive thiazide diuretic medication, which can cause hyperglycemia. -Orthostatic hypotension = The nurse should identify that hydrochlorothiazide is an antihypertensive thiazide diuretic medication, which can cause orthostatic hypotension and light headedness in clients who are taking the medication. Therefore, the nurse should instruct the client to rise slowly when moving from a recumbent to a standing position. -Bradycardia The nurse should identify palpitations as an adverse effect of hydrochlorothiazide, which is an antihypertensive thiazide diuretic medication. -Xanthopsia The nurse should identify that hydrochlorothiazide is an antihypertensive thiazide diuretic medication and has an adverse effect of blurred vision. Xanthopsia causes objects to appear yellow and is not an adverse effect of this medication. 17) A nurse is reviewing the medical record of a client who has hypertension. The nurse should identify which of the following findings as a contraindication to receiving Propranolol? -Cholelithiasis Cholelithiasis is not a contraindication to receiving propranolol. -Asthma = Asthma is a contraindication to receiving propranolol. Propranolol is an adrenergic antagonist which blocks the beta2 receptors in the lungs, causing bronchoconstriction and leading to serious airway resistance and possibly respiratory arrest. -Angina pectoris The client who has angina pectoris can receive propranolol to decrease heart rate and contractility, resulting in a reduction of oxygen demand. Propranolol is contraindicated for use when a client has vasospastic angina. -Tachycardia Tachycardia is not a contraindication to receiving propranolol. Propranolol is administered to slow a client's heart rate and decrease oxygen demand. 18) A nurse is preparing to administer Heparin subcutaneously to a client. Which of the following actions should the nurse plan to take? -Administer the medication outside the 5-cm (2-in) radius of the umbilicus. = The nurse should administer the heparin by subcutaneous injection to the abdomen in an area that is above the iliac crest and at least 2 inches away from the umbilicus. -Aspirate for blood return before injecting. The nurse should not aspirate by pulling back on the plunger of the heparin syringe to check for a blood return, because it will cause the injection site to bruise. -Rub vigorously after the injection to promote absorption. The nurse should apply firm pressure to the injection site for 1 to 2 min after the administration of the heparin to prevent bruising. -Place a pressure dressing on the injection site to prevent bleeding. The nurse does not need to apply a dressing over the injection site if pressure is held for at least 1 min to prevent bleeding. 19) A circulating nurse is planning care for a client who is scheduled for surgery and has a latex allergy. Which of the following actions should the nurse include in the plan of care? -Schedule the client for the last surgery of the day. The circulating nurse should schedule the client for the first surgery of the day to minimize the client's exposure to latex, including latex dust. -Place monitoring cords and tubes in a stockinet. = The circulating nurse should place monitoring devices in a stockinet to prevent direct contact with the client's skin. -Choose rubber injection ports for fluid administration. The circulating nurse should ensure that latex-free products are used in the care of this client. Rubber injection ports contain latex, which would place the client at risk for a severe allergic reaction. -Ensure phenytoin IV is readily available. The nurse should ensure that epinephrine is readily available in the operating room in case of an anaphylactic reaction of accidental exposure to latex. 20) A nurse is caring for the mother of a newborn. The mother asks the nurse when her newborn should receive his first diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis vaccine (DTaP). The nurse should instruct the mother that her newborn should receive the immunization at which of the following ages? -Birth According to the current recommended immunization schedule, only the hepatitis B vaccine is given at birth. -2 months = The CDC recommends that newborns receive the first dose of the five-dose series of the DTaP immunization at 2 months of age. -6 months The CDC recommends that newborns receive the third dose of the five-dose series of the DTaP immunization at 6 months of age. -15 months The CDC recommends that newborns receive the fourth dose of the five-dose series of the DTaP immunization between 15 to 18 months of age. 21) A nurse is caring for a client who has heart failure and is receiving an IV infusion of Dopamine. Which of the following findings indicates that the medication is effective. -Decreased blood pressure Dopamine is an adrenergic that causes a receptor specificity effect, which increases blood pressure. -Increased heart rate Tachycardia is an adverse effect of dopamine, and it does not indicate the medication's effectiveness. -Increased cardiac output = Dopamine is an adrenergic that causes a receptor specificity effect, which increases cardiac output and improves perfusion. -Decreased serum potassium Dopamine does not affect serum potassium levels. 22) A nurse is providing teaching about insulin Glargine to a client who has type 1 diabetes mellitus. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the instructions? -Observe for hypoglycemia when the insulin peaks. Insulin glargine does not cause peaks. Instead, it maintains a steady blood level up to a 24-hr period, which reduces the risk of hypoglycemia. -Administer the insulin immediately before meals. The client can inject glargine once or twice a day, any time during the day, but always at the same time every day. -Do not mix this medication in a syringe with other insulin. = The client should not mix insulin glargine with any other type of insulin in the same syringe, because this procedure can alter the medication's effects. -Rotate the bottle gently prior to drawing up the insulin. Insulin glargine is clear. Therefore, there is no need for the client to rotate the bottle prior to drawing up the insulin. 23) A nurse is preparing to administer to client 0.9%sodium chloride 1000 mL IV over 8 hr. The drop factor of the manual IV tubing is 15 gtt/mL. The nurse should set the manual IV infusion to deliver how many gtt/min? Round to nearest whole #. 31.25 = 31 31 = The nurse should set the manual IV infusion to deliver 0.9% sodium chloride IV at 31 gtt/min. 24) A nurse is reviewing the medication list of a client who wants to begin taking oral contraceptives. The nurse should identify that which of the following client medications will interfere with the effectiveness of oral contraceptives? -Carbamazepine = Carbamazepine causes an accelerated inactivation of oral contraceptives because of its action on hepatic medication-metabolizing enzymes. -Sumatriptan There is no medication interaction between oral contraceptives and sumatriptan, which is a medication to treat migraines. -Atenolol There is no medication interaction between oral contraceptives and atenolol, a beta blocker. -Glipizide There is no medication interaction between oral contraceptives and glipizide, an antidiabetic medication. 25) A nurse is providing teaching for a client who has multiple sclerosis and a new prescription for Methylprednisolone. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include? (select all that apply) Blood glucose levels will be monitored during therapy = The nurse should monitor the client for hyperglycemia while providing this medication to the client. Glucocorticoids, such as methylprednisolone, increase serum glucose levels and can require management with insulin or antihyperglycemics. Avoid contact with people who have known infections = The nurse should instruct the client to avoid exposure to infectious agents, such as contact with those who have active infections or illnesses. Glucocorticoids, such as methylprednisolone, depress the immune system, placing the client at an increased risk for developing an infection. Grapefruit juice can increase the effects of the medication = The nurse should instruct the client that grapefruit and grapefruit juice can increase the level of methylprednisolone in the body. Take the medication 1 hr before breakfast The nurse should instruct the client to take the medication with food or milk to decrease gastrointestinal upset. Decrease dietary intake of foods containing potassium The nurse should instruct the client to increase dietary intake of potassium-rich foods while taking this medication. Glucocorticoids, such as methylprednisolone, deplete potassium in the body, which manifests as hypokalemia. 26) A nurse is preparing to administer medication to a client who has gout. The nurse discovers that an error was made during the previous shift and the client received atenolol instead of allopurinol. Which of the following actions should the nurse take first? -Obtain the client's blood pressure = The first action the nurse should take to prevent injury to the client when using the nursing process is to assess the client for adverse effects of atenolol, such as hypotension. -Contact the client's provider. The nurse should contact the provider, who can provide direction to the nurse to prevent injury to the client. However, there is another action the nurse should take first. -Inform the charge nurse. The nurse should alert the charge nurse to the medication error. However, there is another action the nurse should take first. -Complete an incident report. The nurse should complete an incident report, which is used as part of a facility's quality assurance program. However, there is another action the nurse should take first. 27) A nurse is caring for a 20 year old female client who has a prescription for Isotretinoin for severe nodulocystic acne vulgaris. Before the client can obtain a refill, the nurse should advise the client that which of the following tests is required? -Serum calcium The client does not need to have a laboratory test for serum calcium levels when taking isotretinoin. -Pregnancy test = The client who is pregnant or might become pregnant must not take isotretinoin because this medication has teratogenic effects. Pregnancy testing is mandatory before the initial prescription (two tests) and before monthly refills (one test). -24 hr urine collection for protein The client does not need to have a 24 hr urine test for protein levels when taking isotretinoin. -Aspartate aminotransferase level The client does not need to have a laboratory test for aspartate aminotransferase levels when taking isotretinoin. 28) A nurse is preparing to administer a scheduled antibiotic at 0800 to a client and discovers the antibiotic is not present in the client's medication drawer. The nurse should identify that administration of the medication can occur at which of the following time periods without requiring an incident report? -1000 The nurse should identify that administering an antibiotic 2 hr after the scheduled time is too late and requires filing an incident report. -0900 The nurse should identify that administering an antibiotic 1 hr after the scheduled time is too late and requires filing an incident report. -0830 = The nurse should identify that an antibiotic can be administered 30 min before or after the scheduled time to maintain therapeutic blood levels without requiring an incident report. -1200 The nurse should identify that administering an antibiotic 4 hr after the scheduled time is too late and requires filing an incident report. 29) A nurse is providing teaching about adverse effects of Clindamycin to a client. Which of the following findings should the nurse instruct the client to report to the provider? -Orange urine The client who takes clindamycin can develop jaundice, which can cause the urine to turn dark brown in color. -Watery diarrhea = The client who takes clindamycin can have an adverse effect of watery diarrhea that can lead to Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea or pseudomembranous colitis. The client should report these findings immediately to the provider. -Weight gain The client who takes clindamycin can have the adverse effect of weight loss. -Headache The client who takes clindamycin will not have adverse effects that involve the central nervous system or cause a headache. 30) A nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a prescription for Trimethoprim /Sulfamethoxazole. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include in the teaching? -Take the medication with food. The nurse should instruct the client to take the medication on an empty stomach either 1 hr before or 2 hr after meals. -Expect a fine, red rash as a transient effect. The nurse should instruct the client to notify the provider if a rash develops, as this can be an indication of Stevens-Johnson syndrome. However, the client should not expect to have a fine, red rash as a transient effect. -Drink 8 to 10 glasses of water daily = The nurse should instruct the client to increase water intake to 1,920 to 2,400 mL (64 to 80 oz) a day to decrease the chance of kidney damage from crystallization. -Store the medication in the refrigerator. The nurse should inform the client to store trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole in a light-resistant container at room temperature. 31) A nurse is developing a teaching plan for a client who has a new prescription for Simvastatin. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include in the teaching plan? (select all that apply) -Report muscle pain to the provider = Myopathy is an adverse effect of simvastatin that can lead to rhabdomyolysis, so it should be reported to the provider. -Avoid taking the medication with grapefruit juice = When taken with grapefruit juice, simvastatin increases the risk of muscle injury from elevations in creatine kinase. - Expect therapy with this medication to be lifelong = If medication therapy is discontinued, cholesterol levels will return to their pretreatment range within several weeks to months. - Take the medication in the early morning is incorrect. This medication is most effective when taken in the evening because cholesterol production generally increases overnight. -Expect a flushing of the skin as a reaction to the medication is incorrect. The nurse should identify flushing of the skin as an adverse effect of the medication niacin, which can be used to decrease the client's triglyceride levels. 32) A nurse is teaching about self-administration of transdermal medication with a male client who has a new prescription for Nitroglycerin. The nurse should identify that which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching? -"I can apply the patch to a chest area that has hair." The client should apply the patch to an area of the skin that is hairless to enhance absorption of the medication. -"I can take this medication if using an erectile dysfunction product." The client should not use erectile dysfunction products with nitroglycerin because this combination can cause severe hypotension and death. -"I will remove the patch after 14 hours" = The client should remove the patch after 12 to 14 hr to prevent tolerance of the medication. -"I need to apply a new patch to the same area every day." The client should rotate the location of the patch daily to avoid irritation of the skin. 33) A nurse is providing teaching to a client about the use of Ethinyl Estradiol / Norelgestromin. The nurse should identify that which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching? -"I will apply the patch once a week for 2 weeks." The client should apply the patch once a week for 3 weeks and then no patch for 1 week to promote menstruation. -"I will leave the existing patch on for 4 hours after applying the new patch." The client should remove and dispose the patch before applying a new patch to prevent an overdose of the medication by combining the remaining medication on the old patch with the medication on the new patch. -"I will fold the sticky sides of the old patch together before disposing it." = The client should fold the sticky sides of the old patch together and then place it in a childproof container to ensure safe disposal of the patch. -"I will apply the patch within 14 days of menses." The client should apply the patch within 7 days of menses to prevent ovulation and the need for another contraceptive method. 34) A nurse is teaching a client about Cyclobenzaprine. Which of the following client statements should indicate to the nurse that the teaching is effective? -"I will have increased saliva production." The client should use gum or sip on water to prevent dry mouth, which is an adverse effect of cyclobenzaprine. -"I will continue taking the medication until the rash disappears." The client should take cyclobenzaprine for treatment of muscle spasms. This medication does not have an effect on skin rashes. -"I will taper off the medication before discontinuing it" = The client should taper off cyclobenzaprine before discontinuing it to prevent the return of the musculoskeletal condition. -"I will report any urinary incontinence." The client should report any urinary retention because of the anticholinergic effects created when taking cyclobenzaprine. 35) A nurse is caring for a client who has diabetes mellitus and is taking Glyburide. The client reports feeling confused and anxious. Which of the following actions should the nurse take first? -Perform a capillary blood glucose test = The greatest risk to this client is injury from hypoglycemia. Therefore, the nurse should perform a capillary blood glucose test to determine the client's blood glucose status. Manifestations of hypoglycemia include weakness, anxiety, confusion, sweating, and seizures. -Provide the client with a protein-rich snack. The nurse should provide the client with a protein-rich snack after determining the client's blood glucose value and providing a carbohydrate first. However, there is another action that the nurse should take first. -Give the client 120 mL (4 oz) of orange juice. The nurse should give the client 10 to 15 g of carbohydrates, such as 4 oz of orange juice, to treat hypoglycemia. However, there is another action that the nurse should take first. -Schedule an early meal tray. The nurse should schedule the client an early meal tray to maintain the client's blood glucose level following the initial interventions for hypoglycemia. However, there is another action the nurse should take first. 36) A nurse is caring for a client who is in labor. The client is receiving oxytocin by continuous IV infusion with a maintenance IV solution. The external FHR monitor indicates late decelerations. Which of the following actions should the nurse take first? -Turn the client to a side-lying position = The greatest risk to the fetus experiencing late decelerations is injury from uteroplacental insufficiency. Therefore, the priority intervention the nurse should take is to place the client in a lateral position. -Disconnect the client's oxytocin from the maintenance IV. The nurse should discontinue the oxytocin to reduce uterine contractions. However, another action is the nurse's priority. -Apply oxygen to the client by face mask. The nurse should apply oxygen by face mask to provide supplemental oxygen to the fetus. However, another action is the nurse's priority. -Increase the client's maintenance IV infusion rate. The nurse should increase the client's maintenance IV infusion rate to maintain adequate blood flow and promote placental perfusion. However, another action is the nurse's priority. 37) A nurse is reviewing the prescriptions of a client who has tuberculosis. The nurse should identify that which of the following medications are used to treat tuberculosis? (select all that apply) -Rifampin = This medication is given to treat tuberculosis by inhibiting the production of mycobacteria. -Isoniazid = This medication is given to treat tuberculosis by inhibiting the production of mycobacteria. -Mirtazapine This medication is given to treat depression. -Temazepam This medication is given to treat insomnia. -Infliximab This medication is given to treat moderate to severe Crohn's disease or arthritis. 38) A nurse is caring for a client who is receiving end of life care and has a prescription for fentanyl patches. Which of the following information regarding the adverse effects of fentanyl should the nurse plan to give to the client and family? -The provider will prescribe naloxone at home for respiratory depression. Naloxone is only for use in an acute care setting for the reversal of severe respiratory depression. -Remove the patch to reverse the adverse effects immediately. After removing the patch, the effects will persist for several hours due to the absorption of the residual medication on the skin. -Expect an increase in urinary output. Urinary retention is an adverse effect of opioids, including fentanyl. -Take a stool softener on a daily basis = Constipation is an adverse effect of opioid use and stool softeners can decrease the severity of this adverse effect. 39) A nurse is caring for a client who is receiving long-term treatment for systemic lupus erythematosus with Prednisone. The nurse should inform the client to expect to undergo which of the following diagnostic tests to monitor for long-term complications of prednisone? -Pulmonary function tests Pulmonary function tests are not indicated for a client who is taking prednisone. -Electrocardiograms Routine echocardiograms are not indicated for a client who is taking prednisone. -Liver function studies Liver function studies are not indicated for a client who is taking prednisone. -Bone density scans = The client who is taking prednisone, which is a glucocorticoid, should have regularly scheduled bone density scans to monitor for the adverse effects of osteoporosis. 40) A nurse is providing teaching to a client who is to start treatment for asthma with Beclomethasone and Albuterol inhalers. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include in the teaching? -"Take beclomethasone to avoid an acute attack." The client should take albuterol, a short-acting beta2-adrenergic agonist, to avoid an acute asthma attack. -"Use beclomethasone 5 minutes before using albuterol." The client should use the bronchodilator, albuterol, prior to taking beclomethasone, a glucocorticoid inhaler, to enhance its absorption. -"Limit your calcium and vitamin D intake when taking beclomethasone." The client should increase the intake of calcium and vitamin D to minimize bone loss while taking beclomethasone, a glucocorticoid inhaler. -"Rinse your mouth after inhaling the beclomethasone" = The client should rinse her mouth after using beclomethasone, a glucocorticoid inhaler, to prevent oropharyngeal candidiasis and hoarseness. 41) A nurse is caring for a client who is taking Atenolol. Which of the following findings should indicate to the nurse that the medication is effective? -The client has an increase in urinary output. Atenolol, a beta-adrenergic blocking agent, has no direct effect on kidney function. -The client reports an improvement in memory. Atenolol, a beta-adrenergic blocking agent, has an adverse effect of memory loss. -The client has a decrease in blood pressure = Atenolol, a beta-adrenergic blocking agent, lowers blood pressure by decreasing peripheral vascular resistance. -The client reports having an increase in libido. Atenolol, a beta-adrenergic blocking agent, can cause a decrease in libido and sexual ability. 42) A nurse is assessing a client who has received Atropine eye drops during an eye examination. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect as an adverse effect of the medication? -Difficulty seeing in the dark The client who has received atropine eye drops can have photosensitivity, which causes difficulty seeing in brightly lit areas due to the muscarinic receptors causing mydriasis. -Pinpoint pupils Dilation of pupils, or mydriasis, is an expected finding following the administration of atropine eye drops. -Blurred vision = Blurred vision is an expected finding following the administration of atropine eye drops. This is due to the cycloplegic effects of the medication, which cause distant objects to appear blurry to the client. -Excessive tearing Excessive tearing is not an expected finding following the administration of atropine eye drops. 43) A nurse is teaching a client who is to start taking Temazepam. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include? -Limit continuous use to 7 to 10 weeks. The nurse should include in the teaching to limit use of temazepam to 7 to 10 days. -Schedule doses for early morning before breakfast. The nurse should instruct the client to administer temazepam at bedtime to treat insomnia. -Expect that it will take 4 nights before benefits are noticed. The nurse should include in the teaching that it will take 2 nights before benefits are noticed. -Plan to withdraw from the medication gradually. = The nurse should include in the teaching to have the client plan to withdraw from taking temazepam gradually to avoid mild withdrawal syndrome. 44) A nurse is caring for a client who is recovering from a deep vein thrombosis and is to start taking warfarin. For which of the following findings should the nurse monitor as an adverse effect of warfarin? -Hypertension The nurse should monitor for hypotension, which may indicate bleeding. -Low INR The nurse should monitor the INR daily until it increases to a therapeutic level. -Constipation The nurse should monitor for gastrointestinal irritation, which can include diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. -Bleeding gums = The nurse should monitor the client for bleeding gums, which is an adverse effect of warfarin, an anticoagulant. 45) A nurse is preparing to teach a client who is to start a new prescription for extended release Verapamil. Which of the following instructions should the nurse plan to include? -Take the medication on an empty stomach. The nurse should instruct the client to take extended release verapamil with food to minimize gastric distress. -Avoid crowds. Avoiding crowds is not necessary for the client who is taking verapamil because it does not cause an immunosuppression disorder. -Discontinue the medication if palpitations occur. The nurse should instruct the client that verapamil can cause palpitations, which should be reported to the provider. The client should never discontinue the medication abruptly because the client may experience chest pain. -Change positions slowly = The nurse should instruct the client to change positions gradually to prevent orthostatic hypotension and syncope. 46) A nurse is caring for a client who has pneumonia. The client tells the nurse she is pregnant and that she has not told her provider yet. The nurse should identify that pregnancy is a contraindication to receiving which of the following medication? -Acetaminophen Acetaminophen treats mild pain and is a category B medication of the FDA pregnancy risk categories, indicating the client should use acetaminophen with caution during pregnancy. The nurse should inform the provider of the client's pregnancy. However, this medication is not contraindicated for the client at this time. -Ipratropium Ipratropium is a long-acting bronchodilator and is a category B medication of the FDA pregnancy risk categories, indicating the client should use ipratropium with caution during pregnancy. The nurse should inform the provider of the client's pregnancy. However, this medication is not contraindicated for the client at this time. -Benzonatate Benzonatate is a cough suppressant and is not contraindicated for the client who is pregnant. -Doxycycline = Doxycycline is a tetracycline antibiotic and is contraindicated for a client who is pregnant because the medication is a category D medication of the FDA pregnancy risk categories, which indicates the medication has fetal risks that can cause fetal damage. The client should only take doxycycline for a life-threatening condition. 47) A nurse is caring for a client who has cancer and is taking oral Morphine and Docusate sodium. The nurse should instruct the client that taking the decussate sodium on a daily basis can minimize which of the following adverse effects of morphine? -Constipation = Constipation is a common adverse effect of morphine that will minimize when the client takes docusate sodium, a stool softener that promotes easier evacuation of stool by increasing water and fat in the intestine. -Drowsiness Drowsiness is not an adverse effect of morphine that will be minimized while taking docusate sodium. -Facial flushing Facial flushing is not an adverse effect of morphine that will be minimized while taking docusate sodium. -Itching Itching is not an adverse effect of morphine that will be minimized while taking docusate sodium. 48) A nurse is caring for a client who is taking Acetazolamide for chronic open angle glaucoma. For which of the following adverse effects should the nurse instruct the client to monitor and report? -Tingling of fingers = The nurse should instruct the client to report the adverse effect of paresthesia, a tingling sensation in the extremities, when taking acetazolamide. -Constipation Diarrhea is an adverse effect of acetazolamide due to gastrointestinal disturbances. -Weight gain Weight loss is an adverse effect of acetazolamide due to gastrointestinal disturbances causing reduced appetite. -Oliguria Polyuria, rather than oliguria, is an adverse effect of acetazolamide. 49) A nurse is providing discharge instruction to a client who is to self-administer insulin at home. Which of the following client statements should indicate to the nurse that the teaching is effective? -"I should avoid getting rid of the air bubble in the syringe." The nurse should instruct the client to expel all air bubbles in the syringe to ensure an accurate dosage is delivered. -"I should inject the insulin into my thigh for the fastest absorption." The nurse should instruct the client that the fastest absorption of insulin occurs with abdominal injections. Absorption is slowest when the injection is into the thigh. -"I will store my unopened bottles of insulin in the refrigerator" = The client should store unopened vials of insulin in the refrigerator to maintain medication viability. Once opened, the insulin may remain at room temperature for up to 1 month. -"I need to shake the insulin before using it to make sure it is well mixed." The nurse should instruct the client to mix insulin by rolling the insulin in the palm of his hand to prevent frothing, which can cause the drawing up of an inaccurate dose of insulin. 50) A nurse in an emergency department is caring for a client whose family reports the client has taken large amounts of Diazepam. Which of the following medications should the nurse anticipate administering? -Ondansetron Ondansetron is an antiemetic and the nurse should administer the medication to treat nausea and vomiting. -Magnesium sulfate Magnesium sulfate is an electrolyte replacement and the nurse should administer the medication to treat the risk of seizure activity. -Flumazenil = Flumazenil is an antidote and the nurse should administer the medication to reverse benzodiazepines, such as diazepam. -Protamine sulfate Protamine sulfate is an antidote for heparin and the nurse should administer the medication to reverse an elevated aPTT caused by the use of heparin. 51) A nurse is teaching a client who has an upper respiratory infection about Guaifenesin. Which of the following statements should the nurse include in the teaching? -"Constipation is an expected adverse effect of this medication." The nurse should inform the client that diarrhea, not constipation, is an expected adverse effect of guaifenesin. -"Increase your fluid intake to at least 2 liters each day while taking this medication" = The nurse should instruct the client to increase fluid intake to at least 2 L per day while taking guaifenesin. An increase in fluid intake facilitates the removal of secretions and helps to create a more productive cough. -"Store your medication in the refrigerator." The nurse should instruct the client to store the medication at room temperature. Refrigeration can alter the properties of the medication. -"You can expect to experience insomnia while taking this medication." The nurse should inform the client that drowsiness, not insomnia, is an expected adverse effect of this medication. The client should avoid driving or other potentially hazardous activities while taking this medication if drowsiness occurs. 52) A nurse is teaching a client who is starting to take Amitriptyline. Which of the following findings should the nurse include in the teaching as an adverse effect of the medication? -Diarrhea Constipation is an adverse effect of amitriptyline. -Cough Developing a cough is not an adverse effect of amitriptyline. -Urinary retention = The nurse should instruct the client that amitriptyline causes the anticholinergic effect of urinary retention. -Increased libido A decrease in libido is an adverse effect of amitriptyline. 53) A nurse administers Ceftazidime to a client who has a severe penicillin allergy. The nurse should identify which of the following client findings as an indication that she should complete an incident report? -The client reports shortness of breath = A severe penicillin allergy is a contraindication for taking ceftazidime, a cephalosporin antibiotic, due to the potential for cross-sensitivity. Shortness of breath can indicate the client is developing anaphylaxis. -The client is also taking lisinopril. Lisinopril is an ACE inhibitor medication that has no known interaction with cephalosporins. -The client's pulse rate is 60/min. Cephalosporins do not affect the client’s pulse rate. The client’s puls rate of 60/min is within the expected reference range. -The client's WBC count is 14,000/mm3. An elevated WBC count is an indication the client has an infection and should receive antibiotic therapy. 54) nurse is teaching a client who is starting to take Ketorolac. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching? -"Check for bruising while taking this medication" = The nurse should instruct the client to check for bruising because ketorolac can increase the risk of bleeding by interfering with platelet aggregation. -"Take the medication on an empty stomach." Ketorolac should be taken with food to prevent gastrointestinal distress. -"The medication can cause anxiety." There is no indication that ketorolac causes anxiety. -"Increase iron intake with this medication." There is no indication that the client should increase iron intake. 55) A nurse is providing teaching for a client who has a new prescription for Ferrous sulfate. The nurse should instruct the client to take the medication with which of the following to promote absorption? -Vitamin E Vitamin E has no effect on iron absorption. -Orange juice = The absorption of ferrous sulfate is enhanced by a vitamin C source, such as orange juice. However, increasing the dosage of ferrous sulfate can provide the same benefit to increase the amount of iron uptake. -Milk Milk inhibits iron absorption. -Antacids Antacids inhibit iron absorption. 56) A nurse in a provider's office is assessing a client who has been taking Aspirin daily for the past year. For which of the following findings should the nurse notify the provider immediately? -Hyperventilation = When using the urgent vs. nonurgent approach to client care, the nurse should determine that the priority finding is hyperventilation. This indicates the client might have acute salicylate poisoning, which causes respiratory alkalosis in the early stages. -Heartburn Heartburn is nonurgent because the client who is taking aspirin can experience gastrointestinal distress. Therefore, there is another finding that is the nurse's priority. -Anorexia Anorexia is nonurgent because the client who is taking aspirin can experience a decrease in appetite. Therefore, there is another finding that is the nurse's priority. -Swollen ankles Swollen ankles are nonurgent because the client who is taking aspirin can experience sodium and fluid retention. Therefore, there is another finding that is the nurse's priority. 57) A nurse is planning discharge teaching for a client who has a prescription for Furosemide. The nurse should plan to include which of the following statements in teaching? -"This medication increases your risk for hypertension." The client who takes furosemide has an increased risk of hypotension due to the fluid loss from the diuretic effect of the medication. -"Avoid potassium-rich foods in your diet." The client who takes furosemide has an increased risk for potassium loss because of the diuretic effect of the medication that causes excretion of potassium through the kidneys. The client should increase the intake of potassium-rich foods. -"Take each dose of medication in the evening before bed." The client should take each dose of medication in the morning to avoid sleep disturbances from nocturia. -"Drink a glass of milk with each dose of medication" = The client should take furosemide with food or milk to reduce gastric irritation. 58) A nurse at an urgent care clinic is collecting a history from a female client who has a urinary tract infection. The nurse anticipates a prescription for Ciprofloxacin. The nurse should identify that which of the following client statements indicates a contraindication for administering this medication? -"I have tendonitis, so I haven't been able to exercise" = The nurse should identify tendonitis is a contraindication for taking ciprofloxacin due to the risk of tendon rupture. -"I take a stool softener for chronic constipation." Ciprofloxacin is not contraindicated for the client who takes a stool softener for chronic constipation. An adverse effect of the medication is diarrhea. -"I take medicine for my thyroid." Ciprofloxacin does not affect thyroid function and is not contraindicated for the client who takes thyroid medication. -"I am allergic to sulfa." Ciprofloxacin is a quinolone antibiotic. Therefore, the client who has a sulfa allergy can take this medication. 59) A nurse is administering Baclofen for a client who has a spinal cord injury. Which of the following should the nurse document as a therapeutic outcome? -Increase in seizure threshold The client who has a seizure disorder and takes baclofen can have a decrease in the seizure threshold, which can result in seizure activity. -Decrease in flexor and extensor spasticity = The client who has a spinal cord injury and takes baclofen can experience a decrease in the frequency and severity of muscle spasms and in flexor and extensor spasticity. -Increase in cognitive function The client who takes baclofen can experience the adverse effect of memory impairment and a decrease in cognitive function. -Decrease in paralysis of the extremities The client who takes baclofen can experience the adverse effect of inhibited reflexes at the spinal level, but the medication does not decrease the effects of paralysis. 60) A nurse in an emergency department is caring for a client who has heroin toxicity. The client is unresponsive with pinpoint pupils and a respiratory rate of 6/min. Which of the following medications should the nurse plan to administer? -Methadone The nurse should administer methadone, an opioid agonist, to a client who has heroin toxicity to decrease manifestations of opioid withdrawal and to suppress the euphoria the client feels when using heroin. However, the client should not receive methadone in an emergency. -Naloxone = The nurse should administer naloxone, an opioid antagonist, to a client who has heroin toxicity to reverse the respiratory depressive effects of the heroin. However, the nurse should not administer naloxone too quickly because naloxone can cause hypertension, tachycardia, nausea, vomiting, and might cause the client to enter a state of opioid withdrawal. -Diazepam The nurse should administer diazepam, a benzodiazepine, to a client who has alcohol toxicity to decrease the manifestations of alcohol withdrawal and prevent withdrawal seizures. -Bupropion The nurse should administer bupropion, an atypical antidepressant, for a client who is trying to quit smoking cigarettes to decrease the manifestations of nicotine withdrawal and ease the client's cravings for nicotine. ATI PHARMACOLOGY 2016 PRACTICE B 1) A nurse is planning care for a pt who is receiving Mannitol via continuous IV infusion. The nurse should monitor the pt for which of the following adverse effects. -Weight loss Mannitol is an osmotic diuretic used to promote diuresis, decrease intracranial pressure, and improve renal function. An expected therapeutic effect of mannitol is weight loss resulting from diuresis. -Increased intraocular pressure An indication for the use of mannitol is increased intraocular pressure. Mannitol decreases the intraocular pressure by creating an osmotic gradient between the intraocular fluid and the plasma. -Auditory hallucinations Mannitol has several neurologic adverse effects, including increased intracranial pressure, seizures, confusion, and headaches. However, it does not cause auditory hallucinations. -Bibasilar crackles = Mannitol, an osmotic diuretic, can precipitate heart failure and pulmonary edema. Therefore, the nurse should recognize lung crackles as an indicator of a potential complication and stop the infusion. 2) A nurse is planning to teach about inhalant medications to a pt who has a new diagnosis of exercise induced asthma. Which of the following medications should the nurse plan to instruct the pt to use prior to physical activity? -Cromolyn = Cromolyn sodium stabilizes mast cells, which inhibit the release of histamine and other inflammatory mediators. The client should use cromolyn 10 to 15 min before planning to exercise to prevent bronchospasms. -Beclomethasone Beclomethasone is a prophylactic glucocorticoid inhalant medication that suppresses the inflammatory and humoral immune responses. Beclomethasone should be administered with a fixed schedule, not for PRN use before physical exercise. -Budesonide Budesonide is a glucocorticoid medication used to treat asthma as a long-term inhaled agent. This medication is administered by inhalation twice daily, not prior to physical activity. -Tiotropium Tiotropium is an anticholinergic medication that decreases mucus production and produces bronchodilation. Tiotropium is used for maintenance therapy of bronchospasms and has a duration of 24 hr. 3) A nurse is caring for a pt who has acute acetaminophen toxicity. The nurse should anticipate administering which of the following medications? -Vitamin K Vitamin K is used to treat increased warfarin serum levels, indicated by elevated levels of PT/INR. -Acetylcysteine= Acetylcysteine is a specific antidote for acetaminophen toxicity. It can prevent severe injury when given orally or by IV infusion within 8 to 10 hr. -Benztropine Benztropine is an anticholinergic medication used to treat adverse effects of Parkinson's disease by reducing rigidity and tremors. -Physostigmine Physostigmine is an effective antidote for antimuscarinic poisoning from medications such as atropine, scopolamine, some antihistamines, phenothiazines, and tricyclic antidepressants. It has no effect on acetaminophen toxicity. 4) A nurse is assessing a client who is receiving Epoetin alfa to treat anemia. Which of the following findings should the nurse monitor? -Paresthesia Epoetin alfa stimulates the bone marrow to increase production of red blood cells. Adverse effects include neurological manifestations such as seizures, headache, and dizziness. However, epoetin alfa does not cause paresthesia. -Increased blood pressure = The therapeutic effect of epoetin alfa is an increase in hematocrit levels, which can result in an increase in a client's blood pressure. If the client's hematocrit level rises too rapidly, hypertension and seizures can result. The nurse should monitor the client's blood pressure and ensure hypertension is controlled prior to administering the medication. -Fever Adverse effects of epoetin alfa include neurological manifestations such as coldness and sweating. However, it does not cause fever. -Respiratory depression Heart failure is an adverse effect of epoetin alfa. The nurse should monitor the client's respiratory status and notify the provider if the client develops crackles or rhonchi. However, epoetin alfa does not cause respiratory depression. 5) A nurse is teaching a pt who is to start taking Hydrocodone with Acetaminophen tablets for pain. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching? -The medication should be taken 1 hr prior to eating. The client should take hydrocodone and acetaminophen with food or milk to decrease gastric irritation. -It takes 48 hr for therapeutic effects to occur. The nurse should instruct the client that they should experience the effects of hydrocodone with acetaminophen within 20 min of administration and that pain relief should last for 4 to 6 hr. -Tablets should not be crushed or chewed. The client should avoid crushing, chewing, or breaking the extended release or immediate release hydrocodone tablets to prevent an immediate increase in CNS effects. Hydrocodone with acetaminophen tablets can be crushed if needed. -Decreased respirations might occur.= The nurse should instruct the client that hydrocodone with acetaminophen might cause respiratory depression, which is an adverse effect of the medication. The client should avoid taking over-the-counter medications or newly prescribed medications without consulting their provider to avoid increased respiratory depression. 6) A nurse is caring for a pt who is experiencing acute alcohol withdrawal. For which of the following pt outcomes should the nurse administer Chlordiazepoxide? -Minimize diaphoresis The client should take clonidine or a beta-adrenergic blocker, such as atenolol, to minimize autonomic components, such as diaphoresis, during alcohol withdrawal. -Maintain abstinence The client should take acamprosate to help maintain abstinence from alcohol by decreasing anxiety and other uncomfortable manifestations. -Lessen craving The client should take propranolol to decrease cravings during alcohol withdrawal. -Prevent delirium tremens = The client should take chlordiazepoxide to prevent delirium tremens during acute alcohol withdrawal. 7) A nurse is instructing a pt on the application of Nitroglycerin transdermal patches. Which of the following statements by the pt indicates an understanding of the teaching? -"I should apply a patch every 5 minutes if I develop chest pain." Nitroglycerin sublingual tablets are used to treat new onset of angina pain. A client who uses sublingual tablets should place one tablet under their tongue at the onset of angina pain and continue taking a tablet every 5 min for a total of three doses of nitroglycerin. The effects of a nitroglycerin patch will take 30 to 60 min to occur and are not useful to prevent an ongoing angina attack. -"I will take the patch off right after my evening meal." = Clients should remove the patch each evening for a medication free time of 12 to 14 hr before applying a new patch to avoid developing a tolerance to the medication's effects. -"I will leave the patch off at least 1 day each week." Nitroglycerin is an antianginal medication that results in dilation of the coronary vessels. Clients should apply the patch daily to sustain prophylaxis. -"I should discard the used patch by flushing it down the toilet." Medication remains in the transdermal patch after removing it from the body and must be discarded safely. The nurse should instruct the client to fold the patch ends together with the medication on the inside and place the discarded patch in a closed container so that children and pets cannot gain access to the medication. 8) A nurse is assessing a pt who is taking a Propylthiouracil for the treatment of Grave’s disease. Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as an indication that the medication has been effective? -Decrease in WBC count Propylthiouracil is a thyroid hormone antagonist used in the treatment of hyperthyroidism, or thyroid storms. A decreased WBC count is an adverse effect of propylthiouracil, which can cause myelosuppression. Therefore, a decrease in WBC count indicates the medication has not been effective. -Decrease in amount of time sleeping Graves' disease, a form of hyperthyroidism, has neurologic manifestations, including insomnia. Therefore, a decrease in the amount of time sleeping indicates the medication has not been effective. -Increase in appetite Graves’ disease can result in gastrointestinal manifestations such as increased appetite, weight loss, and increased gastrointestinal motility. Therefore, an increase in appetite indicates the medication has not been effective. -Increase in ability to focus = A client who has Graves' disease can experience psychological manifestations such as difficulty focusing, restlessness, and manic-type behaviors. Propylthiouracil is a thyroid hormone antagonist that decreases the circulating T4 hormone, reducing the manifestations of hyperthyroidism. An increased ability to focus indicates that the medication has been effective. 9) A nurse is caring for a client who recently began taking oral Amoxicillin / Clavulanate and reports urticaria. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? -Request a change in the type of the antibiotic. = Manifestations of urticaria after taking a penicillin-based medication indicate a mild allergic reaction. Therefore, it is appropriate for the nurse to request a change in the type of antibiotic. -Ask for a change in the route of the administration. The client is experiencing a mild allergic reaction to the medication. Changing the route of administration puts the client at risk for further manifestations of the allergy. -Check for pitting edema. Pitting edema is not an expected manifestation of a mild allergic reaction. The nurse should assess the client's heart rate and pulmonary status when the client is experiencing a mild allergic reaction. -Check the client's WBC count. The client is experiencing a mild allergic reaction to the medication and checking the client's WBC count does not indicate why the client is having urticaria. 10) A nurse is reviewing the health history of a client who has Diabetes Mellitus and will begin taking insulin. Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as a factor that might cause the client to have difficulty safely self administering insulin? -Macular degeneration = A client who has macular degeneration loses central vision, making it difficult to accurately draw up insulin for self-administration or dial the insulin pen to the appropriate dosage. The nurse should determine that adaptive equipment is necessary for the client who has macular degeneration. -Right-sided heart failure A client who has right-sided heart failure has hypertension and peripheral edema because the right ventricle is unable to completely empty. However, this condition will not affect the client's ability to prepare and administer insulin. -Hyperlipidemia A client who has hyperlipidemia has developed an accumulation of plaques and fat within the venous system placing the client at risk for hypertension, stroke, or myocardial infarction. However, this condition will not affect the client's ability to prepare and administer insulin. -Stage II chronic kidney disease A client who has diabetes mellitus can also have chronic kidney disease due to changes in the microvasculature caused by hyperglycemia. However, this condition will not affect the client's ability to prepare and administer insulin. 11) A nurse is collecting a med history from a client who has a new prescription for Lithium. The nurse should identify that the client should discontinue which of the following over the counter OTC medications? -Aspirin Although most NSAIDs interact with lithium to increase lithium levels, aspirin does not interact with lithium. -Ibuprofen= Most NSAIDs can significantly increase lithium levels. Therefore, the client should not take ibuprofen and lithium concurrently. -Ranitidine There are no known medication interactions between ranitidine and lithium. -Bisacodyl There are no known medication interactions between bisacodyl and lithium. 12) A nurse is providing teaching to a pt who has a prescription for Ergotamine sublingual to treat migraine headaches. Which of the following info should the nurse include in the instructions? -"Take one tablet three times a day before meals." Ergotamine, an alpha-adrenergic blocking medication, is not used prophylactically because this can result in ergotamine dependence. -"Take one tablet at onset of migraine."= The client should take one tablet immediately after the onset of aura or headache. -"Take up to eight tablets as needed within a 24-hour period." The client can take up to a maximum of three tablets in a 24-hr period. Excessive dosing can lead to ergotism, which can cause peripheral gangrene due to vasoconstriction and ischemia. -"Take one tablet every 15 minutes until migraine subsides." The client can take one sublingual tablet every 30 min for a maximum of three tablets in a 24-hr period to manage a migraine. 13) A nurse on the acute care unit is caring for a pt who is receiving Gentamicin IV. The nurse should report which of the following findings to the provider as an adverse effect of the medication? -Constipation Gentamicin, an aminoglycoside used to treat serious infections, can cause several gastrointestinal adverse effects, such as inflammation of the liver and spleen. However, it does not cause constipation. -Tinnitus= Aminoglycosides, such as gentamicin, are ototoxic, which can manifest as tinnitus and deafness. The nurse should monitor the client for high-pitched ringing in the ears and headaches and should notify the provider if these occur. -Hypoglycemia Gentamicin, an aminoglycoside used to treat serious infections, can cause alternations in the functions of the liver and spleen. However, pancreatic function, mainly insulin production, is not affected by this medication. -Joint pain Aminoglycosides, such as gentamicin, can result in neuromuscular adverse effects such as twitching or flaccid paralysis. However, joint pain is not an adverse effect of gentamicin. 14) A nurse is precepting a newly licensed nurse who is caring for four clients. The nurse should complete an incident report for which of the following actions by the newly licensed nurse? -Administers isosorbide mononitrate to a client who has BP 82/60 mm Hg = Isosorbide mononitrate is a nitrate used for clients with angina. Taking isosorbide mononitrate leads to vasodilation, which can result in hypotension. The nurse should withhold the medication and notify the provider if the client's systolic blood pressure is below the expected reference range of 120/80. -Administers digoxin to a client who has a heart rate of 92/min Digoxin is a cardiac glycoside used for clients who have heart failure because it strengthens the contractility of the heart, increasing cardiac output. A slowing of the heart rate is an effect of digoxin, so it should be withheld if the client's heart rate is less than 60/min. -Administers regular insulin to a client who has a blood glucose of 250 mg/dL Insulin is a hormone that promotes the uptake of glucose into the cells, thereby decreasing circulating glucose. A blood glucose value of 250 mg/dL is above the expected reference range, so the nurse should administer regular insulin. -Administers heparin to a client who has an aPTT of 70 seconds Heparin is an anticoagulant that decreases the coagulability of the blood and is used for clients who have thrombus. Dosing of heparin is dependent upon achieving a therapeutic aPTT level. An aPTT of 70 seconds is within the expected reference range when administering heparin. 15) A nurse is planning to teach about the use of a spacer to a child who has a new prescription for a Fluticasone inhaler to treat chronic asthma. The nurse should include that the spacer decreases the risk for which of the following adverse effects of the med? -Oral candidiasis = Dysphonia and oral candidiasis are adverse effects of inhaled corticosteroids. Using a spacer and rinsing the mouth after inhalation will minimize the amount of medication remaining in the oropharynx, preventing the development of these adverse effects. -Headache Fluticasone can cause neurologic adverse effects such as dizziness, fatigue, nervousness, and headaches. However, the use of a spacer will not decrease systemic adverse effects of fluticasone, such as headaches. -Joint pain Fluticasone can cause musculoskeletal adverse effects such as bone loss, muscle aches, and joint pain. However, the use of a spacer will not decrease systemic adverse effects of fluticasone, such as joint pain. -Adrenal suppression Fluticasone is a glucocorticoid medication that decreases bronchoconstriction. Inhaled glucocorticoids can cause adrenal suppression, although this occurs more often with oral glucocorticoids. The nurse should monitor the client for manifestations of adrenal suppression such as weakness, fatigue, hypotension, and hypoglycemia. However, the use of a spacer will not decrease systemic adverse effects of fluticasone, such as adrenal suppression. 16) A nurse is caring for a pt who is receiving Heparin therapy via continuous infusion to treat a pulmonary embolism. Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as an adverse effect of the med and report to the provider? -Vomiting Vomiting is not an expected adverse effect of heparin therapy. The nurse should assess the client for other causes for vomiting. -Blood in the urine = The nurse should report blood in the urine to the provider because this can be a manifestation of heparin toxicity. Other manifestations can include bruising, hematomas, hypotension, and tachycardia. -Positive Chvostek's sign A Chvostek's sign is seen in clients who have hypocalcemia or hypomagnesemia. -Ringing in the ears Ringing in the ears is not an expected adverse effect of heparin therapy. Aminoglycosides, such as vancomycin, are medications that cause ringing in the ears. 17) A nurse is assessing a client who is taking Amitriptyline for depression. Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as an adverse effect of the medication? -Tinnitus Amitriptyline is a tricyclic antidepressant medication that has anticholinergic properties. The nurse should assess for sensory-neurologic adverse effects such as blurred vision or an increased sensitivity to light. However, tinnitus is not an expected finding. -Urinary frequency The nurse should assess the client for genitourinary anticholinergic effects such as urinary hesitancy or retention due to the blocking of acetylcholine receptors that cause anticholinergic responses. However, urinary frequency is not an expected finding. -Dry mouth = The nurse should expect the client to have a dry mouth due to the blocking of acetylcholine receptors that cause anticholinergic responses. -Diarrhea The nurse should assess the client for gastrointestinal anticholinergic effects such as constipation. However, diarrhea is not an expected finding. 18) A nurse is teaching a client who is starting to take Diltiazem. Which of the following statements should the nurse identify as an indication that the client understands the teaching? -"I will stop taking the medication if I get dizzy." Diltiazem is a calcium channel blocker that causes vascular dilation, which can result in orthostatic hypotension. The client should rise slowly when standing and avoid hazardous activities until there is a stabilization of the medication and dizziness no longer occurs. -"I should not drink orange juice while taking this medication." The client should not drink grapefruit juice while taking diltiazem because it can interfere with metabolism of the medication by increasing the blood levels of diltiazem and leading to toxicity. -"I should expect to gain weight while taking this medication." Diltiazem, a calcium channel blocker, can decrease myocardial contraction, which can lead to heart failure. If the client gains weight or develops shortness of breath, they should notify the provider. -"I will check my heart rate before I take the medication" = CORRECT ASNWER Diltiazem, a calcium channel blocker, has cardio-suppressant effects at the SA and AV nodes, which can lead to bradycardia. The client should check their heart rate before taking the medication and notify the provider if it falls below the expected reference range. 19) A nurse is preparing to administer a new prescription of Amoxicillin / Clavulanic to a client. The client tells the nurse that they are allergic to Penicillin. Which of the following actions should the nurse take first? -Update the client's medical record. It is important to update the client's medical record to have complete information available; however, the nurse should take another action first. -Notify the provider. It is important to notify the provider because the client will need a new prescription; however, the nurse should take another action first. -Withhold the medication = When using the urgent vs nonurgent approach to client care, the nurse should determine that the priority action is to withhold the medication to prevent injury to the client. -Inform the pharmacist of the client's allergy to penicillin. It is important to inform the pharmacist of the allergy to promote continuity of care; however, the nurse should take another action first. 20) A nurse is teaching a client who has tuberculosis about the adverse effects of Isoniazid. The nurse should instruct the client to report to the provider which of the following as an adverse effect of the medication? -Reddish-orange urine Rifampin, another antituberculosis medication, can cause body fluids to take on a reddish-orange color. However, isoniazid does not alter urine color. -Photosensitivity Isoniazid can cause sensory adverse effects including blurred vision and optic neuritis. However, photosensitivity is not an adverse reaction of isoniazid. -Yellowish skin tones = Isoniazid is a hepatotoxic medication that can cause hepatitis. The nurse should instruct the client to monitor for and report signs of hepatitis, such as malaise, nausea, and yellowish skin tones, to the provider. -Headache Isoniazid is associated with a number of CNS adverse effects including dizziness, memory impairment, seizures, and psychosis. However, it does not cause headaches. 21) A nurse is providing teaching to a pt who has peptic ulcer disease and is to start a new prescription for Sucralfate. Which of the following actions of Sucralfate should the nurse include in the teaching? -Decreases stomach acid secretion Peptic ulcer disease manifests as an erosion of the gastric or duodenal mucosa. The acid production in the stomach causes further irritation and pain. H2 receptor antagonists, such as famotidine, decrease stomach acid secretion. -Neutralizes acids in the stomach Acid production in the stomach causes further irritation and pain to a client who has a peptic ulcer. Antacids, such as aluminum hydroxide, neutralize acids in the stomach and prevent pepsin formation, a digestive enzyme that can further damage the eroded epithelium. -Forms a protective barrier over ulcers = Secretions by the parietal and chief cells, hydrochloric acid and pepsin, can further irritate the ulcerated areas. Sucralfate, a mucosal protectant, forms a gel-like substance that coats the ulcer, creating a barrier to hydrochloric acid and pepsin. -Treats ulcers by eradicating H. pylori A common cause of peptic ulcers is a bacterial infection with Helicobacter pylori. Treatment of the ulcer includes a combination of antibiotics, such as metronidazole, tetracycline, clarithromycin, or amoxicillin, to eradicate the H. pylori infection. 22) A nurse is preparing to administer 0.9% Sodium Chloride (NaCl) 1,500 mL to infuse over 8hr to a client who is postoperative. The nurse should set the IV pump to deliver how many mL/hr? (Round to nearest whole #. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero) 187.5 mL/hr = 188 mL/hr. The nurse should set the IV pump to deliver 0.9% sodium chloride IV at 188 mL/hr. = 23) A nurse is assessing a pt 1 hour after administering Morphine for pain. The nurse should identify which of the following findings as the best indication that the Morphine has been effective? -The client's vital signs are within normal limits. Vital signs can be within normal limits for clients who have pain. -The client has not requested additional medication. Clients often do not request medicine even when they are experiencing pain. -The client is resting comfortably with eyes closed. The client might rest with their eyes closed as a method to try to manage pain. However, this does not indicate that the pain is controlled. -The client rates pain as 3 on a scale from 0 to 10. = The client's description of the pain is the most accurate assessment of pain. 24) A nurse is providing follow up care to a client who is taking Lisinopril. Which of the following manifestations should the nurse instruct the client to report as an adverse effect of Lisinopril? -Drowsiness Lisinopril is an ACE inhibitor used in the treatment of hypertension, heart failure, and myocardial infarction. Lisinopril can cause a number of neurologic adverse effects including insomnia. However, drowsiness is not an adverse effect of lisinopril. -Hallucinations Lisinopril can cause a number of neurologic adverse effects including depression, paresthesia, and stroke. However, hallucinations are not an adverse effect of lisinopril. -Persistent cough = Lisinopril is an ACE inhibitor that can cause a persistent, dry, irritating, nonproductive cough from an excessive buildup of bradykinin. The client should report this adverse effect to the provider. -Weight gain Lisinopril can cause a number of gastrointestinal adverse effects including vomiting, anorexia, constipation, pancreatitis, and liver failure. However, lisinopril has not been associated with weight gain. 25) A nurse in an emergency department is caring for a client who has Myasthenia gravis and is in a cholinergic crisis. Which of the following medications should the nurse plan to administer? -Potassium iodide Potassium iodide is a thyroid hormone antagonist used in the treatment of radioactive iodine exposure. -Glucagon Glucagon is an antihypoglycemic medication used in the treatment of low blood glucose levels. -Atropine = A cholinergic crisis is caused by an excess amount of cholinesterase inhibitor, such as neostigmine. The nurse should plan to administer atropine, an anticholinergic agent, to reverse cholinergic toxicity. -Protamine Protamine is a heparin antagonist that is administered to reverse heparin toxicity evidenced by an aPTT greater than 70 seconds. 26) A nurse is teaching a client who is to begin taking Tamoxifen for the treatment of breast cancer. Which of the following adverse effects should the nurse include in the teaching? -Hot flashes = The estrogen receptor blocking action of tamoxifen commonly results in the adverse effect of hot flashes. -Urinary retention Tamoxifen can cause genitourinary adverse effects such as vaginal discharge and uterine cancer. However, urinary retention is not an expected adverse effect of tamoxifen. -Constipation Gastrointestinal adverse effects of tamoxifen include nausea and vomiting. However, constipation is not an expected adverse effect of tamoxifen. -Bradycardia Tamoxifen is an antiestrogen medication that works by blocking estrogen receptors. Cardiovascular adverse effects of the medication include chest pain, flushing, and the development of thrombus. However, bradycardia is not an expected adverse effect of tamoxifen. 27) A nurse is planning care for a client who is prescribed Metoclopramide following bowel surgery. For which of the following adverse effects should the nurse monitor? -Muscle weakness Metoclopramide is a central dopamine receptor antagonist that increases gastrointestinal motility and prevents nausea. An adverse effect of metoclopramide is tardive dyskinesia. However, metoclopramide does not cause muscle weakness. -Sedation = Metoclopramide has multiple effects on the CNS, including dizziness, fatigue, and sedation. -Tinnitus Metoclopramide does not cause ringing in the ears. -Peripheral edema Metoclopramide does not cause peripheral edema. 28) A nurse is teaching a pt about Warfarin. The pt asks if they can take Aspirin while taking Warfarin. Which of the following responses should the nurse make? -“It is safe to take an enteric-coated aspirin." Although it is common for clients to consider an occasional aspirin harmless, salicylates inhibit platelet aggregation and increase the potential for hemorrhage. Therefore, the client should avoid taking enteric-coated aspirin. -"Aspirin will increase the risk of bleeding."= Aspirin inhibits platelet aggregation and can potentiate the action of the anticoagulant warfarin. Therefore, the client should avoid taking aspirin because it increases the risk for bleeding. -"Acetaminophen may be substituted for aspirin." Acetaminophen, an analgesic, can potentiate the action of the anticoagulant warfarin when administered in high doses and is not a safe substitute for aspirin. -"The INR lab work must be monitored more frequently if aspirin is taken." The client should continue to follow the provider's prescription for monitoring the PT and INR levels to adjust warfarin dosages. However, the nurse should discourage the client from using aspirin products because these medications increase the antiplatelet action of the warfarin and can result in bleeding. 29) A nurse is providing care for a client who is postoperative following an open cholecystectomy with the placement of a closed suction drain and is receiving Morphine via patient controlled analgesia for pain. Which of the following assessments is the nurse’s priority? -Respiratory rate = When using the airway, breathing, circulation approach to client care, the nurse should determine that the priority assessment is the client's respiratory rate due to the risk of respiratory depression. Morphine and other opioid medication can cause respiratory depression, constipation, and urinary retention. -Bowel sounds The nurse should monitor the bowel sounds for a client who is postoperative following open cholecystectomy. The administration of anesthesia will slow bowel function and suppress bowel sounds. However, there is another assessment that is the nurse's priority. -Drainage amounts The nurse should assess the amount and characteristics of the client's drainage to monitor for bleeding, fluid, and electrolyte imbalances. However, there is another assessment that is the nurse's priority. -Wound appearance The nurse should assess the client’s wound following surgery to monitor for bleeding or separation of the incision. However, there is another assessment that is the nurse's priority. 30) A nurse has administered 2 doses of Betamethasone to a client in preterm labor. After delivery of the newborn the nurse understands the medication was effective when she observes which of the following? -The newborn is free of infection. Betamethasone is a glucocorticoid medication. The newborn being free of infection is not an indication that the administration of betamethasone was effective. -The newborn has normal respiratory patterns = The newborn having a normal respiratory pattern is an indication that the administration of betamethasone was effective. This medication stimulates surfactant production, which improves oxygenation and lung compliance in neonates. -Mother's blood pressure is within the expected reference range. Maternal hypertension can be treated with hydralazine, labetolol, or nifedipine. However, betamethasone is not used for treatment of preeclampsia. -Mother's postpartum bleeding is minimal. Postpartum bleeding is controlled with the administration of oxytocin, a hormone that produces uterine contractions. However, betamethasone is not used for treatment of postpartum bleeding. 31) A nurse is reviewing laboratory results for a client who is to receive a dose of Ceftazidime via intermittent IV bolus. Which of the following laboratory Findings is the priority for the nurse to report to the provider before administering the medication? -Total bilirubin 0.4 mg/dL Ceftazidime, a cephalosporin, can cause elevated liver function tests, such as bilirubin. However, a total bilirubin value of 0.4 mg/dL is within the expected reference range. -Alanine aminotransferase 26 units/L Ceftazidime can cause elevated liver function tests, such as alanine aminotransferase. However, an alanine aminotransferase value of 26 units/L is within the expected reference range. -Platelet count 360,000/mm3 Ceftazidime can cause thrombocytopenia. However, a platelet count of 360,000/mm3 is within the expected reference range. -Creatinine 2.6 mg/dL = Ceftazidime is excreted primarily by the renal system. A serum creatinine level above 1.3 mg/dL can indicate a kidney disorder requiring a reduction in the dose administered. The nurse should notify the provider, who is likely to prescribe a lowered dose of medication. 32) A nurse is teaching a pt who has a new prescription for Docusate sodium about the medication’s mechanism of action. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching? -Docusate sodium reduces the surface tension of the stools to change their consistency = Docusate sodium is a surfactant that softens stool by reducing surface tension, allowing water to penetrate more easily into the stool. -Docusate sodium causes rectal contractions. Osmotic laxatives, such as glycerin suppositories, act by lubricating the lower colon and initiating reflex contractions of the rectum. -Docusate sodium acts as a fiber agent, increasing bulk in the intestines. Bulk-forming laxatives, such as methylcellulose, mimic the action of dietary fiber, forming a viscous compound that softens the fecal mass and increases its bulk, which stimulates peristalsis. -Docusate sodium stimulates the motility of the intestines. Stimulant laxatives, such as bisacodyl, stimulate the intestinal wall to cause peristalsis by pulling water into the intestines. 33) A nurse is providing teaching to a pt who is taking Bupropion as an aid to quit smoking. Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as an adverse effect of the med? -Cough Bupropion, an atypical antidepressant, does not cause coughing. -Joint pain Bupropion can cause neurologic adverse effects such as bradykinesia. However, it does not cause joint pain. -Alopecia Bupropion can cause sensory adverse effects such as changes in vision and hearing. However, it does not cause alopecia. -Insomnia = Bupropion, an atypical antidepressant, has stimulant properties, which can result in agitation, tremors, mania, and insomnia. 34) A nurse is caring for a client who has heart failure and is prescribed Enalapril. The nurse should monitor the client for which of the following findings as an adverse effect of the medication? -Bradycardia Enalapril is an ACE inhibitor that has several cardiovascular adverse effects including hypotension, tachycardia, and dysrhythmias. -Hyperkalemia = Enalapril improves cardiac functioning in clients who have heart failure and can cause hyperkalemia due to potassium retention by the kidneys. -Loss of smell Enalapril has several sensory adverse effects including tinnitus, double vision, and a loss of taste. However, it does not cause a loss of smell. -Hypoglycemia Enalapril does not cause hypoglycemia. 35) ) A nurse is teaching a pt who is taking Allopurinol for the treatment of gout. Which of the following info should the nurse include in the teaching? -Plan to increase the dosage each week by 200 mg increments. The nurse should instruct the client to increase the dosage each week by 50 to 100 mg until they experience relief or reach a maximum of 800 mg daily. -Prolonged use of the medication can cause glaucoma. The nurse should instruct the client that the prolonged use of allopurinol can cause cataracts; therefore, the client should have periodic ophthalmic checkups. -Drink 2 L of water daily. = The nurse should instruct the client to drink at least 2 L of water each day to prevent renal stone formation and kidney injury, because allopurinol is eliminated through the kidneys. -A fine red rash is transient and can be treated with antihistamines. The nurse should instruct the client to report a rash to the provider immediately as this can be an indication of hypersensitivity syndrome, a life-threatening toxicity. Treatment for allopurinol toxicity can require hemodialysis or the administration of glucocorticoid medications 36) A nurse is caring for a pt who is receiving Filgrastim. Which of the following findings should the nurse document to indicate the effectiveness of the therapy? -Increased neutrophil count = Filgrastim stimulates the bone marrow to produce neutrophils/ more WBCs. For clients receiving chemotherapy, the risk of infection is minimized. -Increased RBC count Filgrastim stimulates the bone marrow to produce neutrophils and has no effect on a client's RBC count. -Decreased prothrombin time Prothrombin time measures the effectiveness of warfarin therapy. Filgrastim therapy does not cause a decrease in prothrombin time. -Decreased triglycerides Triglycerides are a form of lipids found in the blood stream. Increased levels are associated with an increased risk for heart disease. Decreased levels can occur in clients who have malnutrition or malabsorption disorders. Filgrastim is used to treat chemotherapy-induced neutropenia and has no effect on a client's triglyceride levels. 37) A nurse is caring for a pt who is taking Atorvastatin for hyperlipidemia. Which of the following pt laboratory values should the nurse monitor? -Creatinine kinase = The client who is taking atorvastatin can develop an adverse effect called rhabdomyolysis, which causes muscle weakness or pain and can progress to myositis. Creatinine kinase levels rise in response to enzymes released with muscle injury. -Erythrocyte sedimentation rate Erythrocyte sedimentation rates (ESR) evaluate the speed at which red blood cells settle in plasma over a set amount of time. The nurse should monitor ESR for clients who have multiple myeloma, rheumatoid arthritis, and systemic lupus erythematosus. However, ESR is not affected by statins, such as atorvastatin. -International normalized ratio The international normalized ratio (INR) measures clotting abilities of the blood. The nurse should monitor INR for clients who are receiving warfarin therapy. -Potassium Potassium is a major electrolyte that maintains acid-base balance, oncotic pressure, and cardiac rhythm. The nurse should monitor potassium levels in clients who are receiving loop diuretics, such as bumetanide. 38) The nurse is assessing a pt after administering a second dose of Cefazolin IV. The nurse notes the pt has anxiety, hypotension, and dyspnea. Which of the following medications should the nurse administer first? -Diphenhydramine The nurse should administer diphenhydramine, an antihistamine, as a second-line medication to decrease angioedema and urticaria following anaphylaxis. However, evidence-based practice indicates that administering another medication is the priority. -Albuterol inhaler The nurse should administer albuterol, a bronchodilator, for a client who has dyspnea from bronchospasms during anaphylaxis. However, evidence-based practice indicates that administering another medication is the priority. -Epinephrine = According to evidence-based practice, the nurse should administer epinephrine first to induce vasoconstriction and bronchodilation during anaphylaxis. -Prednisone The nurse should plan to administer prednisone, a glucocorticoid, for the urticaria following anaphylaxis and to prevent a delayed anaphylactic reaction from occurring. However, evidence-based practice indicates that administering another medication is the priority. 39) A nurse is planning care for a pt who has hypertension and is starting to take Metoprolol. Which of the following interventions should the nurse include in the plan of care? -Weigh the client weekly. The nurse should weigh the client daily to monitor for the development of heart failure and weight gain. -Determine apical pulse prior to administering.= Life-threatening bradycardia is an adverse effect that might affect this client. Therefore, the nurse should assess the client's apical pulse prior to administering the medication. If the client's pulse rate is less than 60/min, the nurse should withhold the medication and notify the provider. -Administer the medication 30 min prior to breakfast. The nurse should administer metoprolol following meals or at bedtime if orthostatic hypotension occurs. -Monitor the client for jaundice. The nurse should monitor the client for adverse effects such as hypotension. However, jaundice is not associated with this medication. 40) A nurse is caring for a client in the emergency department following a Diazepam overdose. Which of the following medications should the nurse anticipate administering to the client? -Naloxone Naloxone is an opioid antagonist used for the treatment of opioid-induced respiratory depression. -Leucovorin Leukovorin, a form of the vitamin folic acid, is used as an antidote for methotrexate toxicity. -Neostigmine Neostigmine is a reversible cholinesterase inhibitor that increases the amount of acetylcholine available for neuromuscular and muscarinic responses. It is used in the treatment of myasthenia gravis and as a reversal agent for neuromuscular blocking agents, such as those used in surgery. -Flumazenil = Flumazenil is a benzodiazepine receptor antagonist that can decrease the sedative effects of benzodiazepines, such as diazepam. The nurse should administer the medication via IV bolus, titrating doses as needed, for a maximum of 3 mg. However, the medication can precipitate seizures and might not reverse respiratory depression, so airway support may be necessary. 41) A nurse in a clinic is caring for a pt who is taking Aspirin for treatment of arthritis. The nurse should identify which of the following findings as an indication that the pt is beginning to exhibit salicylism? -Gastric distress Gastric distress is a possible adverse effect of aspirin therapy, but it is not an indication of salicylism. Gastric distress can be minimized by taking aspirin with food or an enteric form of the medication. -Oliguria Kidney impairment is an adverse effect associated with aspirin use. Manifestations include reduced urinary output, weight gain, and elevated BUN and creatinine levels. However, oliguria is not an indication of salicylism. -Excessive bruising Excessive bruising is a possible adverse effect of aspirin therapy, caused by the antiplatelet effects of the medication. However, excessive bruising is not an indication of salicylism. -Tinnitus = Tinnitus is a manifestation of aspirin toxicity, also called salicylism. Other manifestations include sweating, headache, and dizziness. 42) A nurse is preparing to give Ciprofloxin 15mg/kg PO every 12hr to a child who weighs 44lbs. How many mg should the nurse administer per dose? (Round to nearest whole #; do not use trailing zero) 300 mg/dose = give 300 mg/dose every 12 hr. 43) A nurse is caring for a pt who is receiving Haloperidol. The nurse should identify which of the following findings as an adverse effect of the med? -Akathisia = An adverse effect associated with haloperidol is the development of extrapyramidal manifestations such as dystonia, pseudoparkinsonism, and akathisia. -Paresthesia Haloperidol, an antipsychotic neuroleptic medication, can cause CNS adverse effects such as seizures, confusion, and neuroleptic syndrome. However, paresthesia is not an adverse effect of haloperidol. -Excess tear production Haloperidol has anticholinergic properties that can cause sensory adverse effects such as increased intraocular pressure, blurred vision, and dry eyes. -Anxiety Haloperidol can be prescribed to treat severe agitation as well as psychotic manifestations. 44) A nurse is administering Donepezil to a pt who has Alzheimer’s disease. Which of the following findings should the nurse report to the provider immediately? -Dyspepsia The nurse should report dyspepsia to the provider because dyspepsia can cause discomfort and irritation to the esophageal tissues. However, the nurse should report another finding first. -Diarrhea The nurse should report diarrhea to the provider because diarrhea can result in electrolyte and fluid imbalances. However, the nurse should report another finding first. -Dizziness The nurse should report dizziness to the provider because dizziness can place the client at an increased risk for falls. However, the nurse should report another finding first. -Dyspnea = When using the airway, breathing, circulation approach to client care, the nurse should report the adverse effect of dyspnea, caused by bronchoconstriction, to the provider first. Bronchoconstriction, dyspepsia, diarrhea, and dizziness are caused by the increase in acetylcholine levels, which is a primary effect of donepezil. 45) A nurse at a clinic is providing followup care to a pt who is taking Fluoxetine for depression. Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as an adverse effect of the medication? -Tingling toes Fluoxetine is an SSRI that can cause muscle twitching. However, distorted sensations in the extremities are not adverse effects of fluoxetine. -Sexual dysfunction= Sexual dysfunction, including a decreased libido, impotence, and delayed orgasm, or anorgasmia, is a common adverse effect of fluoxetine and occurs in about 70% of clients who take this SSRI antidepressant. -Absence of dreams Fluoxetine can cause CNS adverse effects including abnormal dreaming, sedation, delusions, hallucinations, and psychosis. However, an absence of dreams is not associated with fluoxetine. -Pica Fluoxetine can cause neurologic adverse effects such as agitation, euphoria, and sedation. However, an eating disorder such as pica is not associated with fluoxetine. 46) A nurse is preparing to administer Dextrose 5% in water (D5W) 400mL IV to infuse over 1 hour. The drop factor of the manual IV tubing is 15gtt/mL. The nurse should set the manual IV infusion to deliver how many gtt/min? (Round to nearest whole #, do not use trailing zeros) 100 gtt/min = It makes sense to administer 100 gtt/min 47) A nurse is teaching a group of unit nurses about medication reconciliation. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching? -The client's provider is required to complete medication reconciliation. The nurse or a member of the health care team, such as the pharmacist, is required to complete medication reconciliation. -Medication reconciliation at discharge is limited to the medication ordered at the time of discharge. Medication reconciliation at discharge includes medications ordered at the time of discharge, over-the-counter medications, vitamins, herbal supplements, nutritional supplements, and other medications the client is taking. -A transition in care requires the nurse to conduct medication reconciliation. = The nurse should conduct medication reconciliation anytime the client is undergoing a change in care such as admission, transfer from one unit to another, or discharge. A complete listing of all prescribed and over-the-counter medications should be reviewed. -Medical reconciliation is limited to the name of the medications that the client is currently taking. The name of the current medication and new medication, over-the-counter medications, vitamins, herbal supplements, and nutritional supplements are included at the medication reconciliation. The indication, route, dosage size, and dosing interval are also required. 48) A nurse is providing teaching to a client who has depression and a new prescription for Fluoxetine. Which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching? -"I should start to feel better within 24 hours of starting this medication." The nurse should inform the client that the therapeutic levels of fluoxetine can take between 1 and 4 weeks to achieve desired effects. The client should take the medication as prescribed and use other strategies to manage depression in the interim. -"I will be sure to follow a strict diet to avoid foods with tyramine." Clients taking fluoxetine, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, are not required to restrict their dietary intake of tyramine. A client who is taking an MAOI, such as selegiline, should avoid products containing tyramine. -"I will continue to take St. John's Wort to increase the effects of the medication." Concurrent use of St. John's Wort and fluoxetine can increase the client's risk for serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening complication. Manifestations of serotonin syndrome include confusion, hallucinations, hyperreflexia, excessive sweating, and fever. -"I should take acetaminophen instead of ibuprofen for my headaches while taking this medication." = Fluoxetine suppresses platelet aggregation, which increases the risk of bleeding when used concurrently with NSAIDs and anticoagulants. Therefore, clients who are taking fluoxetine should take acetaminophen for headaches or pain, since acetaminophen does not suppress platelet aggregation. 49) A nurse is providing discharge instructions to a pt who has heart failure and a new prescription for Captopril. Which of the following pt statements indicates an understanding of the teaching? -"I should take the medication with food." The client should take captopril on an empty stomach because food reduces absorption of the medication. The nurse should instruct the client to take the medication 1 hr before or 2 hr after a meal. -"I should take naproxen if I develop joint pain." Naproxen and other NSAIDs can interact with captopril, which can decrease the effect of the antihypertensive and increase the risk of kidney dysfunction. -"I should tell my provider if I develop a sore throat." = The client should report a sore throat to the provider because this can indicate neutropenia, a serious adverse effect of captopril. Neutropenia can be reversed if it is identified early and the medication is promptly discontinued. -"I should expect the medication to cause my urine to look orange." Captopril affects the urinary system by causing dysuria, urinary frequency, and changes in the normal amount of urine. However, captopril does not affect the color of the urine. 50) A nurse is teaching a pt about the use of Risedronate for the treatment of osteoporosis. The nurse should identify which of the following statements as an indication that the pt understands the teaching? -"I will drink a glass of milk when I take the risedronate." The nurse should reinforce that risedronate should be taken with a full glass of water, rather than any other liquid. -"I will take the risedronate 15 minutes after my evening meal." Although the delayed release form of the medication can be taken after eating, the immediate release form of the medication should be taken at least 30 min prior to consuming food or other liquids. Both forms of medication should be taken in the morning. -"I should take an antacid with the risedronate to avoid nausea." The absorption of risedronate, a bisphosphonate, will be reduced if it is taken with antacids containing calcium, aluminum, or magnesium. The nurse should instruct the client to take the antacid 2 hr after taking risedronate. -"I should sit up for 30 minutes after taking the risedronate."= Sitting upright for at least 30 min after taking risedronate will reduce the adverse gastrointestinal effects of esophagitis and dyspepsia. Risedronate is contraindicated for a client who cannot sit or stand upright for this length of time. 51) A nurse is reviewing lab results for a client who is receiving Heparin via continuous IV infusion for deep vein thrombosis. The nurse should discontinue the medication infusion for which of the following client findings? -Potassium 5.0 mEq/ L Although heparin can cause an increase in potassium levels, the client's potassium level is within the expected reference range. -aPTT 2 times the control This is a therapeutic aPTT level for a client receiving heparin, which is not an indication to stop the heparin infusion. -Hemoglobin 15 g/dL An Hgb of 15 g/dL is within the expected reference range and is not an indication to stop the heparin infusion. -Platelets 96,000/mm3 = A platelet count less than 100,000/mm3 while receiving heparin can indicate heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, a potentially fatal condition, which requires stopping the infusion. 52) A nurse is caring for a client who is receiving Cefazolin IV. The nurse should identify what which of the following medications can potentiate nephrotoxicity if administered concurrently? -Famotidine Famotidine, an H2-histamine receptor antagonist used in the treatment of GERD, is primarily metabolized in the liver. Although it is excreted in the kidneys, it is not nephrotoxic and will not potentiate renal damage if administered concurrently with cefazolin. -Levofloxacin Levofloxacine, a fluoroquinolone used to treat infections, can cause hepatotoxicity. However, it will not potentiate renal damage if administered concurrently with cefazolin. -Metoclopramide Metoclopramide is an antiemetic that can cause tardive dyskinesia. However, it will not potentiate renal damage if administered concurrently with cefazolin. -Gentamicin = Gentamicin, an aminoglycoside antibiotic, can damage renal function. When combined with a penicillin or cephalosporin, such as cefazolin, the client is at increased risk for nephrotoxicity. 53) A nurse is providing discharge teaching to a client who has a new prescription for Furosemide twice daily. The nurse should include which of the following instructions in the teaching? (Select all that apply) -"Increase intake of potassium-rich foods"= correct Loop diuretics, such as furosemide, act at the loop of Henle by blocking the resorption of sodium, water, and potassium. An adverse effect of the medication is the development of electrolyte imbalances such as hyponatremia, hypochloremia, and hypokalemia. To prevent hypokalemia, the client should increase intake of potassium-rich foods, such as potatoes, spinach, dried fruit, and nuts. "Monitor for muscle weakness" = correct. Furosemide, a loop diuretic, causes a loss of potassium, which can result in manifestations of hypokalemia such as difficulty concentrating, shallow respirations, hyporeflexia, and muscle weakness. The nurse should instruct the client to monitor for these manifestations and report them to the provider. "Dangle your legs from the side of the bed before standing" = correct. Loop diuretics, such as furosemide, reduce vascular tone and increase fluid excretion. These effects decrease blood return to the heart and can manifest as dizziness and lightheadedness when going from a lying to a standing position. The client should change positions slowly to minimize orthostatic hypotension. -"Take the second dose at bedtime" Furosemide is a loop diuretic that causes diuresis. When taken twice daily, the client should take the second dose of furosemide by 1400 hr to prevent nocturia. -"Obtain your weight weekly" Loop diuretics cause an increase in fluid excretion and can cause dehydration. While manifestations of dehydration, such as increased thirst and decreased urine output, can assist in the diagnosis of dehydration, the most reliable method of identifying the onset of dehydration is by loss of weight. The client should obtain daily weights to monitor for the diuresis effect of the medication. 54) A nurse is providing teaching for a client who has multiple sclerosis and a new prescription for Methylprednisolone. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include? (select all that apply) -Blood glucose levels will be monitored during therapy = The nurse should monitor the client for hyperglycemia while providing this medication to the client. Glucocorticoids, such as methylprednisolone, increase serum glucose levels and can require management with insulin or antihyperglycemics. -Avoid contact with people who have known infections = The nurse should instruct the client to avoid exposure to infectious agents, such as contact with those who have active infections or illnesses. Glucocorticoids, such as methylprednisolone, depress the immune system, placing the client at an increased risk for developing an infection. -Grapefruit juice can increase the effects of the medication = The nurse should instruct the client that grapefruit and grapefruit juice can increase the level of methylprednisolone in the body. -Take the medication 1 hr before breakfast The nurse should instruct the client to take the medication with food or milk to decrease gastrointestinal upset. -Decrease dietary intake of foods containing potassium The nurse should instruct the client to increase dietary intake of potassium-rich foods while taking this medication. Glucocorticoids, such as methylprednisolone, deplete potassium in the body, which manifests as hypokalemia. 55) A nurse is providing teaching to a pt who is to start therapy with Digoxin. For which of the following adverse effects should the nurse instruct the pt to monitor and report to the provider? - Dry cough Clients taking an ACE inhibitor, such as captopril, might develop a dry cough due to a buildup of bradykinin and should report this adverse effect to the provider. However, respiratory adverse effects are not associated with digoxin. -Pedal edema Clients taking a calcium channel blocker, such as verapamil, might develop pedal edema and should report this adverse effect to the provider. However, peripheral edema is not associated with digoxin. -Bruising Clients taking an anticoagulant, such as enoxaparin, might develop bruising and should report this adverse effect to the provider. However, hematologic adverse effects are not associated with digoxin. -Yellow-tinged vision = The nurse should instruct the client to monitor for and report yellow-tinged vision, which is a sign of digoxin toxicity. Other manifestations of digoxin toxicity include nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, and fatigue. As the digoxin levels increase, the client can experience cardiac dysrhythmias. 56) A nurse is providing teaching to a pt who is to begin taking Oxybutynin for urinary incontinence. Which of the following adverse effects should the nurse include in the teaching? (select all that apply) -Dry mouth= Oxybutynin is an anticholinergic agent that can cause dry mouth. -Dry eyes= Oxybutynin is an anticholinergic agent that can cause dry eyes and mydriasis, or pupil dilation. -Blurred vision= Oxybutynin is an anticholinergic agent that can cause blurred vision due to an increase in intraocular pressure. -Bradycardia Oxybutynin can cause several cardiovascular adverse effects such as a prolongation of the QT interval, palpitations, hypertension, and tachycardia. -Tinnitus Oxybutynin can cause several sensory adverse effects including increased intraocular pressure. The nurse should instruct the client to report eye pain, seeing colored halos around lights, and a decreased ability to perceive light changes. However, tinnitus is not an adverse effect associated with oxybutynin administration. 57) A nurse is preparing to mix and administer Dantrolene via IV bolus to a pt who has developed malignant hyperthermia during surgery. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? -Administer the reconstituted medication slowly over 5 min. The nurse should administer reconstituted dantrolene via IV bolus rapidly through a large bore IV or central line. -Store the reconstituted medication in the refrigerator. The nurse should store the reconstituted medication at room temperature and protect it from light until use. -Use the reconstituted medication within 12 hr. The nurse should use the reconstituted medication within 6 hr. -Reconstitute the initial dose with 60 mL of sterile water without a bacteriostatic agent = The nurse should dilute the medication with 60 mL of sterile water without a bacteriostatic agent and inject rapidly. 58) A nurse is providing teaching to a pt who has gastric ulcer and a new prescription for Ranitidine. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include? -"Take the medication on an empty stomach for full effectiveness." The client can take ranitidine with or without food because food does not affect the medication's effectiveness. -"You may discontinue this medication when stomach discomfort subsides." For clients who have a gastric ulcer, ranitidine is prescribed to inhibit gastric secretion and must be taken for the full course of therapy to be effective. -"Report yellowing of the skin." = Ranitidine can be hepatotoxic and cause jaundice. The nurse should instruct the client to monitor for and report yellowing of the skin or eyes to the provider. -"Store the medication in the refrigerator." The client should store ranitidine at room temperature. 59) A nurse is teaching about neural tube defects to a client who is planning a pregnancy. Which of the following vitamins should the nurse instruct the client to start taking before becoming pregnant? -Folic acid = The nurse should instruct all female clients who could become pregnant to take at least 400 mcg of folic acid daily in addition to foods containing folic acid to prevent neural tube defects in the developing fetus. Enriched rice and breakfast cereals are good sources of folic acid but might not provide enough folic acid without supplements. -Thiamine Thiamine, or vitamin B1deficiency, can cause beriberi or Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome that affect the CNS. However, thiamine does not prevent neural tube defects in the developing fetus. -Pyridoxine Pyridoxine, or vitamin B6, can help a client who is predisposed to neuropathy from diabetes or alcohol use disorder. However, pyridoxine does not prevent neural tube defects in the developing fetus. -Riboflavin Riboflavin, or vitamin B2, can help a client who has a vitamin deficiency and can be used to treat migraine headaches. However, riboflavin does not prevent neural tube defects in the developing fetus. 60) A nurse is teaching about a new prescription for Ciprofloxan to a pt who has a UTI. The nurse should identify which of the following statements as an indication that the pt understands the teaching? -"I will take this medication with an antacid to prevent gastrointestinal upset." The client should avoid taking ciprofloxacin with an antacid containing aluminum, magnesium, or calcium because this can decrease the effectiveness of the medication. The nurse should instruct the client to take antacids 2 hr before or 6 hr after the ciprofloxacin. -"I will stop taking this medication when I no longer have pain upon urination." The client should take the full course of ciprofloxacin to prevent reoccurring colonization of bacteria. -"I will report any signs of tendon pain or swelling." = Ciprofloxacin, a fluoroquinolone, is associated with a risk of tendon rupture. This risk is increased in older adult clients, so the client should notify the provider at the onset of tendon pain or swelling. -"I will take this medication with milk." The client should take ciprofloxacin with water and increase fluids to 2 to 3 L daily to avoid the development of crystals in the kidneys. Milk products will decrease the absorption of the medication. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 57 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 23, 2020
Number of pages
57
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 23, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
76















.png)


.png)

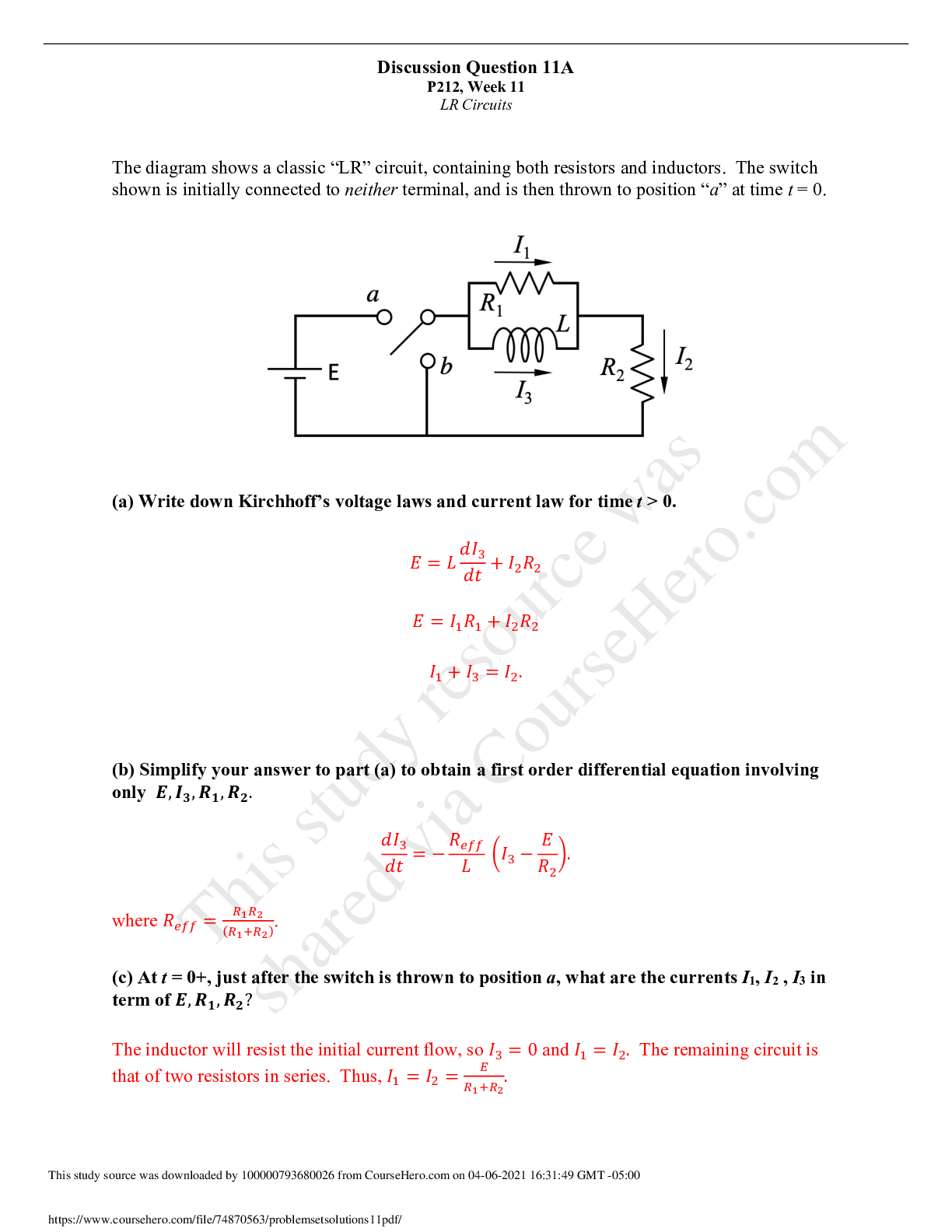
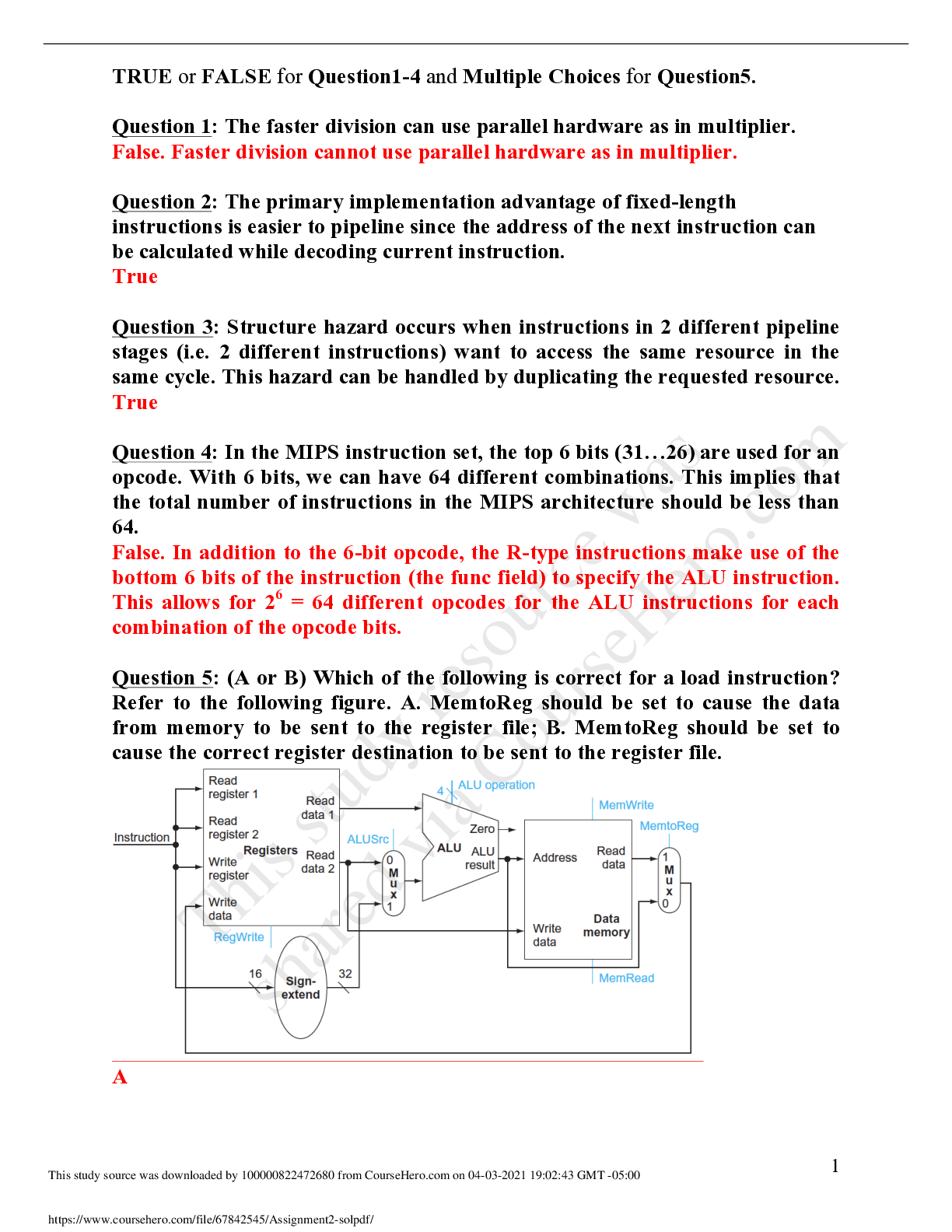



.png)



.png)

