*NURSING > EXAM > NR 507 Pathophysiology Week 4 Midterm Exam | Pathophysiology Week 4 Midterm Exam_Graded A (All)
NR 507 Pathophysiology Week 4 Midterm Exam | Pathophysiology Week 4 Midterm Exam_Graded A
Document Content and Description Below
NR 507 Pathophysiology Week 4 Midterm exam (latest) – Chamberlain College of Nursing 1. Question : Hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN) can occur if the mother: Student Answe... r: Is Rh-positive and the fetus is Rh-negative Is Rh-negative and the fetus is Rh-positive Has type A blood and the fetus has type O Has type AB blood and the fetus has type B Instructor Explanation: HDN can occur only if antigens on fetal erythrocytes differ from antigens on maternal erythrocytes. Maternal-fetal incompatibility exists only if the mother and fetus differ in ABO blood type or if the fetus is Rh-positive and the mother is Rh-negative. This erythrocyte incompatibility does not exist in any of the other options. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 2. Question : Examination of the throat in a child demonstrating signs and symptoms of acute epiglottitis may contribute to which life-threatening complication? Student Answer: Retropharyngeal abscess Laryngospasms Rupturing of the tonsils Gagging induced aspiration Instructor Explanation: Examination of the throat may trigger laryngospasm and cause respiratory collapse. Death may occur in a few hours. This selection is the only option that accurately identifies the life-threatening complication that can result from an examination of the throat of a child who demonstrates the signs and symptoms of acute epiglottitis. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 3. Question : If the sinoatrial (SA) node fails, then at what rate (depolarizations per minute) can the atrioventricular (AV) node depolarize? Student Answer: 60 to 70 40 to 60 30 to 40 10 to 20 Instructor Explanation: If the SA node is damaged, then the AV node will become the heart’s pacemaker at a rate of approximately 40 to 60 spontaneous depolarizations per minute. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 4. Question : What is the ratio of coronary capillaries to cardiac muscle cells? Student Answer: 1:1 (one capillary per one muscle cell) 1:2 (one capillary per two muscle cells) 1:4 (one capillary per four muscle cells) 1:10 (one capillary per ten muscle cells) Instructor Explanation: The heart has an extensive capillary network, with approximately 3300 capillaries per square millimeter (ca/mm2) or approximately one capillary per one muscle cell (muscle fiber). Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 5. Question : Which cytokines initiate the production of corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH)? Student Answer: IL–1 and IL-6 IL-2 and TNF- IFN and IL-12 TNF-ß and IL-4 Instructor Explanation: Although a number of stress factors initiate the production of CRH, of the options available, only high levels of IL-1 and IL-6 initiate such a response. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 6. Question : What process allows the kidney to respond to an increase in workload? Student Answer: Glomerular filtration Secretion of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 Increased heart rate Compensatory hypertrophy Instructor Explanation: Compensatory hypertrophy allows the kidney to respond to an increase in workload throughout life. The remaining options are not relevant to accommodating an increased workload. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 7. Question : Which type of antibody is involved in type I hypersensitivity reaction? Student Answer: IgA IgE IgG IgM Instructor Explanation: Type I reactions are only mediated by antigen-specific IgE and the products of tissue mast cells (see Figure 9-1). Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 8. Question : Causes of hyperkalemia include: Student Answer: Hyperparathyroidism and malnutrition Vomiting and diarrhea Renal failure and Addison disease Hyperaldosteronism and Cushing disease Instructor Explanation: Hyperkalemia should be investigated when a history of renal disease, massive trauma, insulin deficiency, Addison disease, use of potassium salt substitutes, or metabolic acidosis exists. The other options are not known to be causes of hyperkalemia. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 9. Question : What is the first stage in the infectious process? Student Answer: Invasion Colonization Spread Multiplication Instructor Explanation: From the perspective of the microorganisms that cause disease, the infectious process undergoes four separate stages of progression: (1) colonization, (2) invasion, (3) multiplication, and (4) spread. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 10. Question : Which statement is true concerning the IgM? Student Answer: IgM is the first antibody produced during the initial response to an antigen. IgM mediates many common allergic responses. IgM is the most abundant class of immunoglobulins. IgM is capable of crossing the human placenta. Instructor Explanation: Typically, IgM is produced first (primary immune response), followed by IgG against the same antigen. The other options are not true statements regarding IgM. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 11. Question : An infant has a loud, harsh, holosystolic murmur and systolic thrill that can be detected at the left lower sternal border that radiates to the neck. These clinical findings are consistent with which congenital heart defect? Student Answer: Atrial septal defect (ASD) Ventricular septal defect (VSD) Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) Atrioventricular canal (AVC) defect Instructor Explanation: On physical examination, a loud, harsh, holosystolic murmur and systolic thrill can be detected at the left lower sternal border. The intensity of the murmur reflects the pressure gradient across the VSD. An apical diastolic rumble may be present with a moderate-to-large defect, reflecting increased flow across the mitral valve. The presentations of the other congenital heart defects are not consistent with the described symptoms. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 12. Question : What is the chief predisposing factor for respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) of the newborn? Student Answer: Low birth weight Alcohol consumption during pregnancy Premature birth Smoking during pregnancy Instructor Explanation: RDS of the newborn, also known as hyaline membrane disease (HMD), is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in premature newborns. None of the other options are considered the chief predisposing factors for RDS. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 13. Question : Which cardiac chamber has the thinnest wall and why? Student Answer: The right and left atria; they are low-pressure chambers that serve as storage units and conduits for blood. The right and left atria; they are not directly involved in the preload, contractility, or afterload of the heart. The left ventricle; the mean pressure of blood coming into this ventricle is from the lung, which has a low pressure. The right ventricle; it pumps blood into the pulmonary capillaries, which have a lower pressure compared with the systemic circulation. Instructor Explanation: The two atria have the thinnest walls because they are low-pressure chambers that serve as storage units and conduits for blood that is emptied into the ventricles. This selection is the only option that correctly identifies which heart chambers have the thinnest walls and why that helps cardiac function. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 14. Question : What is the direct action of atrial natriuretic hormone? Student Answer: Sodium retention Sodium excretion Water retention Water excretion Instructor Explanation: Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) and brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) inhibit the secretion of renin, inhibit angiotensin-induced secretion of aldosterone, vasodilate the afferent and constrict the efferent glomerular arterioles, and inhibit sodium and water absorption by kidney tubules. The other actions are not a result of the atrial natriuretic hormone. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 15. Question : What is the primary site for uncomplicated local gonococci infections in men? Student Answer: Epididymis Lymph nodes Urethra Prostate Instructor Explanation: Uncomplicated local infections are observed primarily as urethral infections in men. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 16. Question : Which statement concerning benign tumors is true? Student Answer: The resulting pain is severe. Benign tumors are not encapsulated. Benign tumors are fast growing. The cells are well-differentiated. Instructor Explanation: A benign tumor is well-differentiated with its tissue appearing similar to the tissue from which it arose. The other options are characteristic of a malignant tumor. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 17. Question : Which of the following is classified as a megaloblastic anemia? Student Answer: Iron deficiency Pernicious Sideroblastic Hemolytic Instructor Explanation: Pernicious anemia is the most common type of megaloblastic anemia. The remaining options are not classified as megaloblastic anemias. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 18. Question : Apoptosis is a(an): Student Answer: Normal mechanism for cells to self-destruct when growth is excessive Antigrowth signal activated by the tumor-suppressor gene Rb Mutation of cell growth stimulated by the TP53 gene Transformation of cells from dysplasia to anaplasia Instructor Explanation: Normal cells have a mechanism that causes them to self-destruct when growth is excessive and cell cycle checkpoints have been ignored. Diverse stimuli, including normal development and excessive growth, trigger this self-destruct mechanism, called apoptosis. The remaining options do not describe apoptosis. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 19. Question : What is the functional unit of the kidney called? Student Answer: Glomerulus Nephron Collecting duct Pyramid Instructor Explanation: The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney. Although the other options are also located in the kidney, they are not its functional units. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 20. Question : Which hepatitis virus is known to be sexually transmitted? Student Answer: A B C D Instructor Explanation: Only hepatitis B virus (HBV) is known to be sexually transmitted. Points Received: 0 of 2 Comments: Question 21. Question : The glomerular filtration rate is directly related to which factor? Student Answer: Perfusion pressure in the glomerular capillaries Diffusion rate in the renal cortex Diffusion rate in the renal medulla Glomerular active transport Instructor Explanation: The filtration of the plasma per unit of time is known as the glomerular filtration rate (GFR), which is directly related to only the perfusion pressure in the glomerular capillaries. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 22. Question : Decreased lung compliance means that the lungs are demonstrating which characteristic? Student Answer: Difficult deflation Easy inflation Stiffness Inability to diffuse oxygen Instructor Explanation: A decrease in compliance indicates that the lungs or chest wall is abnormally stiff or difficult to inflate. This selection is the only option that accurately identifies the meaning of decreased compliance. Points Received: 0 of 2 Comments: Question 23. Question : What is the most common cause of iron deficiency anemia (IDA)? Student Answer: Decreased dietary intake Chronic blood loss Vitamin deficiency Autoimmune disease Instructor Explanation: The most common cause of IDA in well-developed countries is pregnancy and chronic blood loss. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 24. Question : Which drug may be prescribed orally for outbreak management of herpes simplex viral (HSV) infections? Student Answer: Acyclovir (Zovirax) 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) Zidovudine (AZT) (Retrovir) Bichloroacetic acid (BCA) Instructor Explanation: Although no curative treatment for HSV infection is known, only oral acyclovir, valacyclovir, penciclovir, and famciclovir are used for primary and periodic outbreaks and to prevent recurrences. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 25. Question : In a normal, nonmutant state, an oncogene is referred to as a: Student Answer: Basal cell Target cell Caretaker gene Proto-oncogene Instructor Explanation: In its normal nonmutant state, an oncogene is referred to as a proto-oncogene. The other options are not terms used to identify a nonmutant oncogene. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 26. Question : What is the primary cause of respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) of the newborn? Student Answer: Immature immune system Small alveoli Surfactant deficiency Anemia Instructor Explanation: RDS is primarily caused by surfactant deficiency and secondarily by a deficiency in alveolar surface area for gas exchange. None of the other options are related to the cause of RDS. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 27. Question : Fetal hematopoiesis occurs in which structure? Student Answer: Gut Spleen Bone marrow Thymus Instructor Explanation: The spleen is the largest of the secondary lymphoid organs and the site of fetal hematopoiesis. Points Received: 0 of 2 Comments: Question 28. Question : Deficiencies in which element can produce depression of both B- and T-cell function? Student Answer: Iron Zinc Iodine Magnesium Instructor Explanation: Of the options available, only deficient zinc intake can profoundly depress T- and B-cell function. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 29. Question : Phagocytosis involves neutrophils actively attacking, engulfing, and destroying which microorganisms? Student Answer: Bacteria Fungi Viruses Yeasts Instructor Explanation: Invasion is the direct confrontation with an individual’s primary defense mechanisms against only bacteria, which include the complement system, antibodies, and phagocytes, such as neutrophils and macrophages. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 30. Question : Which hormone is synthesized and secreted by the kidneys? Student Answer: Antidiuretic hormone Aldosterone Erythropoietin Angiotensinogen Instructor Explanation: Erythropoietin is produced by the fetal liver and in the adult kidney and is essential for normal erythropoiesis. This statement is not true of the other options. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 31. Question : Which congenital heart defects occur in trisomy 13, trisomy 18, and Down syndrome? Student Answer: Coarctation of the aorta (COA) and pulmonary stenosis (PS) Tetralogy of Fallot and persistent truncus arteriosus Atrial septal defect (ASD) and dextrocardia Ventricular septal defect (VSD) and patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) Instructor Explanation: Congenital heart defects that are related to dysfunction of trisomy 13, trisomy 18, and Down syndrome include VSD and PDA (see Table 33-2). The other defects are not associated with dysfunction of trisomy 13, trisomy 18, and Down syndrome. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 32. Question : Which laboratory test is considered adequate for an accurate and reliable diagnosis of gonococcal urethritis in a symptomatic man? Student Answer: Ligase chain reaction (LCR) Gram-stain technique Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) DNA testing Instructor Explanation: Microscopic evaluation of Gram-stained slides of clinical specimens is deemed positive for Neisseria gonorrhoeae if gram-negative diplococci with the typical “kidney bean” morphologic appearance are found inside polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Such a finding is considered adequate for the diagnosis of gonococcal urethritis in a symptomatic man. The other options are not relevant to the diagnosis of this condition. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 33. Question : During an IgE-mediated hypersensitivity reaction, which leukocyte is activated? Student Answer: Neutrophils Monocytes Eosinophils T lymphocytes Instructor Explanation: Of the options provided, only eosinophils are activated during IgE-mediated hypersensitivity reactions. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 34. Question : What is the life span of platelets (in days)? Student Answer: 10 30 90 120 Instructor Explanation: A platelet circulates for approximately 10 days and ages. Macrophages of the mononuclear phagocyte system, mostly in the spleen, remove platelets. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 35. Question : What is the role of caretaker genes? Student Answer: Maintenance of genomic integrity Proliferation of cancer cells Secretion of growth factors Restoration of normal tissue structure Instructor Explanation: Caretaker genes are responsible for the maintenance of genomic integrity. The other options are not roles assumed by caretaker genes. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 36. Question : Which blood cell type is elevated at birth but decreases to adult levels during the first year of life? Student Answer: Monocytes Platelets Neutrophils Lymphocytes Instructor Explanation: Only monocyte counts are high in the first year of life and then decrease to adult levels. Points Received: 0 of 2 Comments: Question 37. Question : Which term is used to identify the movement of gas and air into and out of the lungs? Student Answer: Perfusion Ventilation Respiration Diffusion Instructor Explanation: Of the options available, ventilation is the only term used to identify the mechanical movement of gas or air into and out of the lungs. Points Received: 0 of 2 Comments: Question 38. Question : In which primary immune deficiency is there a partial-to-complete absence of T-cell immunity? Student Answer: Bruton disease DiGeorge syndrome Reticular dysgenesis Adenosine deaminase deficiency Instructor Explanation: The principal immunologic defect in DiGeorge syndrome is the partial or complete absence of T-cell immunity. The other options are not the result of either a partial or complete absence of T-cell immunity. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 39. Question : Which substance has been shown to increase the risk of cancer when used in combination with tobacco smoking? Student Answer: Alcohol Steroids Antihistamines Antidepressants Instructor Explanation: Alcohol interacts with smoke, increasing the risk of malignant tumors, possibly by acting as a solvent for the carcinogenic chemicals in smoke products. No current research supports the remaining options as having an increased effect on the incidence of cancer when used in combination with tobacco smoking. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 40. Question : Which statement concerning exotoxins is true? Student Answer: Exotoxins are contained in cell walls of gram-negative bacteria. Exotoxins are released during the lysis of bacteria. Exotoxins are able to initiate the complement and coagulation cascades. Exotoxins are released during bacterial growth. Instructor Explanation: Exotoxins are proteins released during bacterial growth. The other options are not true of exotoxins. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 41. Question : Which type of immunity is produced by an individual after either natural exposure to the antigen or after immunization against the antigen? Student Answer: Passive-acquired immunity Active-acquired immunity Passive-innate immunity Active-innate immunity Instructor Explanation: An individual produces active-acquired immunity (active immunity) after natural exposure to an antigen or after immunization, whereas passive-acquired immunity (passive immunity) does not involve the host’s immune response at all. The innate immune system, also known as nonspecific immune system and the first line of defense, is composed of the cells and mechanisms that defend the host from infection by other organisms in a nonspecific manner, which means that the cells of the innate system recognize and respond to pathogens in a generic way. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 42. Question : Research supports the premise that exercise has a probable impact on reducing the risk of which cancer? Student Answer: Liver Endometrial Stomach Colon Instructor Explanation: The World Cancer Research Fund summarizes the effects as convincing for cancers of the colon and probable for postmenopausal breast cancer and endometrial cancer. The relationship is not supported for the remaining options. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 43. Question : What part of the kidney controls renal blood flow, glomerular filtration, and renin secretion? Student Answer: Macula densa Visceral epithelium Juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA) Filtration slits Instructor Explanation: Control of renal blood flow, glomerular filtration, and renin secretion occur at the JGA. Together, the juxtaglomerular cells and macula densa cells form the JGA. The control of renal blood flow, glomerular filtration, and renin secretion is not directed by any of the other options. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 44. Question : What is the fundamental physiologic manifestation of anemia? Student Answer: Hypotension Hyperesthesia Hypoxia Ischemia Instructor Explanation: The fundamental physiologic manifestation of anemia is a reduced oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood, resulting in tissue hypoxia. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 45. Question : Between which months of age does sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) most often occur? Student Answer: 0 and 1 2 and 4 5 and 6 6 and 7 Instructor Explanation: The incidence of SIDS is low during the first month of life but sharply increases in the second month of life, peaking at 2 to 4 months and is unusual after 6 months of age. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 46. Question : What is the purpose of the spirometry measurement? Student Answer: To evaluate the cause of hypoxia To measure the volume and flow rate during forced expiration To measures the gas diffusion rate at the alveolocapillary membrane To determine pH and oxygen and carbon dioxide concentrations Instructor Explanation: Spirometry measures volume and flow rate during forced expiration. The alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient is used to evaluate the cause of hypoxia. Diffusing capacity is a measure of the gas diffusion rate at the alveolocapillary membrane. Arterial blood gas analysis can be used to determine pH and oxygen and carbon dioxide concentrations. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 47. Question : Carcinoma in situ is characterized by which changes? Student Answer: Cells have broken through the local basement membrane. Cells have invaded immediate surrounding tissue. Cells remain localized in the glandular or squamous cells. Cellular and tissue alterations indicate dysplasia. Instructor Explanation: Carcinoma in situ (CIS) refers to preinvasive epithelial malignant tumors of glandular or squamous cell origin. These early stage cancers are localized to the epithelium and have not broken through the local basement membrane or invaded the surrounding tissue. Dysplasia refers to changes in mature cell structure. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 48. Question : The drug heparin acts in hemostasis by which processes? Student Answer: Inhibiting thrombin and antithrombin III (AT-III) Preventing the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin Shortening the fibrin strands to retract the blood clot Degrading the fibrin within blood clots Instructor Explanation: Clinically administered heparin or heparin sulfate (on the surface of endothelial cells) binds to AT-III and induces a conformational change that greatly enhances its activity. Under normal conditions, the presence of endothelial cell heparin sulfate and available AT-III in the circulation cooperate to protect the vessels from the effects of spontaneously activated thrombin. The other options do not accurately describe the role heparin plays in hemostasis. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 49. Question : The coronary ostia are located in the: Student Answer: Left ventricle Aortic valve Coronary sinus Aorta Instructor Explanation: Coronary arteries receive blood through openings in the aorta, called the coronary ostia. Points Received: 0 of 2 Comments: Question 50. Question : Blood vessels of the kidneys are innervated by the: Student Answer: Vagus nerve Sympathetic nervous system Somatic nervous system Parasympathetic nervous system Instructor Explanation: The blood vessels of the kidney are innervated by the sympathetic noradrenergic fibers that cause arteriolar vasoconstriction and reduce renal blood flow. The other options are not involved in this process. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 51. Question : Which term is used to describe a muscle cell showing a reduced ability to form new muscle while appearing highly disorganized? Student Answer: Dysplasia Hyperplasia Myoplasia Anaplasia Instructor Explanation: Anaplasia is defined as the loss of cellular differentiation, irregularities of the size and shape of the nucleus, and the loss of normal tissue structure. In clinical specimens, anaplasia is recognized by a loss of organization and a significant increase in nuclear size with evidence of ongoing proliferation. The remaining options refer to specific changes in the cell. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 52. Question : Which statement best describes a Schilling test? Student Answer: Administration of radioactive cobalamin and the measurement of its excretion in the urine to test for vitamin B12 deficiency Measurement of antigen-antibody immune complexes in the blood to test for hemolytic anemia Measurement of serum ferritin and total iron-binding capacity in the blood to test for iron deficiency anemia Administration of folate and measurement in 2 hours of its level in a blood sample to test for folic acid deficiency anemia. Instructor Explanation: The Schilling test indirectly evaluates vitamin B12 absorption by administering radioactive B12 and measuring excretion in the urine. This selection is the only option that accurately describes a Schilling test. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 53. Question : What is the major concern regarding the treatment of gonococci infections? Student Answer: Development of antibiotic resistance Changes in virulence Changes in pathogenicity Mutations into different strains Instructor Explanation: Several types of drug-resistant strains have been identified; they are penicillinase-producing Neisseria gonorrhoeae (PPNG), which is resistant to penicillin; tetracycline-resistant N. gonorrhoeae (TRNG), which is resistant to tetracycline; chromosomal control of mechanisms of resistance of N. gonorrhoeae (CMRNG), which is resistant to penicillin and tetracycline; and increasingly a fluoroquinolone-resistant N. gonorrhoeae (QRNG). The other options are not major concerns. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 54. Question : What is the action of urodilatin? Student Answer: Urodilatin causes vasoconstriction of afferent arterioles. It causes vasodilation of the efferent arterioles. Urodilatin inhibits antidiuretic hormone secretion. It inhibits salt and water reabsorption. Instructor Explanation: Urodilatin (a natriuretic peptide) inhibits sodium and water reabsorption from the medullary part of collecting duct, thereby producing diuresis. It is not involved in the actions described by the other options. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 55. Question : How is most carbon dioxide (CO2) in the blood transported? Student Answer: Attached to oxygen In the form of bicarbonate Combined with albumin Dissolved in the plasma Instructor Explanation: Approximately 60% of the CO2 in venous blood and 90% of the CO2 in arterial blood are carried in the form of bicarbonate. Points Received: (not graded) Comments: Question 56. Question : The most common site of metastasis for a patient diagnosed with prostate cancer is which location? Student Answer: Bones Brain Bladder Kidney Instructor Explanation: The bone, especially the lumbar spine area, is the most common metastasis site for prostate cancer. Points Received: 0 of 2 Comments: Question 57. Question : Immunoglobulin E (IgE) is associated with which type of hypersensitivity reaction? Student Answer: I II III IV Instructor Explanation: Hypersensitivity reactions have been divided into four distinct types: type I (IgE-mediated) hypersensitivity reactions, type II (tissue-specific) hypersensitivity reactions, type III (immune complex–mediated) hypersensitivity reactions, and type IV (cell-mediated) hypersensitivity reactions. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 58. Question : Which immunoglobulin (Ig) is present in childhood asthma? Student Answer: IgM IgG IgE IgA Instructor Explanation: Included in the long list of asthma-associated genes are those that code for increased levels of immune and inflammatory mediators (e.g., interleukin [IL]–4, IgE, leukotrienes), nitric oxide, and transmembrane proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. None of the other options are associated with childhood asthma. Points Received: 0 of 2 Comments: Question 59. Question : The Papanicolaou (Pap) test is used to screen for which cancer? Student Answer: Ovarian Uterine Cervical Vaginal Instructor Explanation: The Pap test, an examination of cervical epithelial scrapings, readily detects early oncogenic human papillomavirus (HPV)infection. The Pap test is not used for screening the other cancer sites listed. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 60. Question : The risk for respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) decreases for premature infants when they are born between how many weeks of gestation? Student Answer: 16 and 20 20 and 24 24 and 30 30 and 36 Instructor Explanation: Surfactant is secreted into fetal airways between 30 and 36 weeks. The other options are not true regarding the timeframe when the risk for RDS decreases. Points Received: 0 of 2 Comments: [Show More]
Last updated: 8 months ago
Preview 1 out of 39 pages
 – Chamberlain College of Nursing.png)
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 06, 2020
Number of pages
39
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 06, 2020
Downloads
1
Views
86





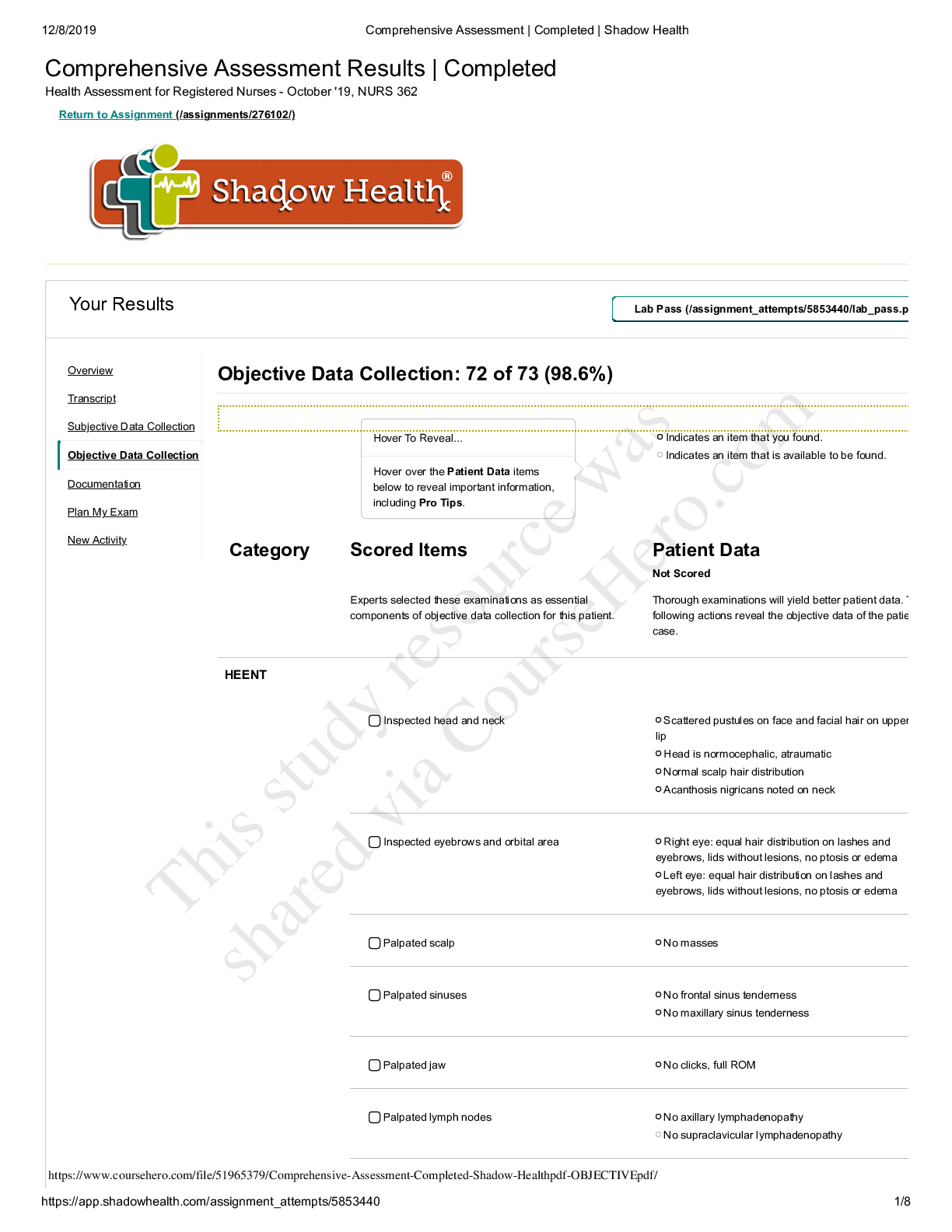








 – CHAMBERLAIN COLLEGE OF NURSING.png)