Biology > EXAM > A&P 1 101 Module 6 Lab Exam (GRADED A+) Questions and Answers- Portage Learning (All)
A&P 1 101 Module 6 Lab Exam (GRADED A+) Questions and Answers- Portage Learning
Document Content and Description Below
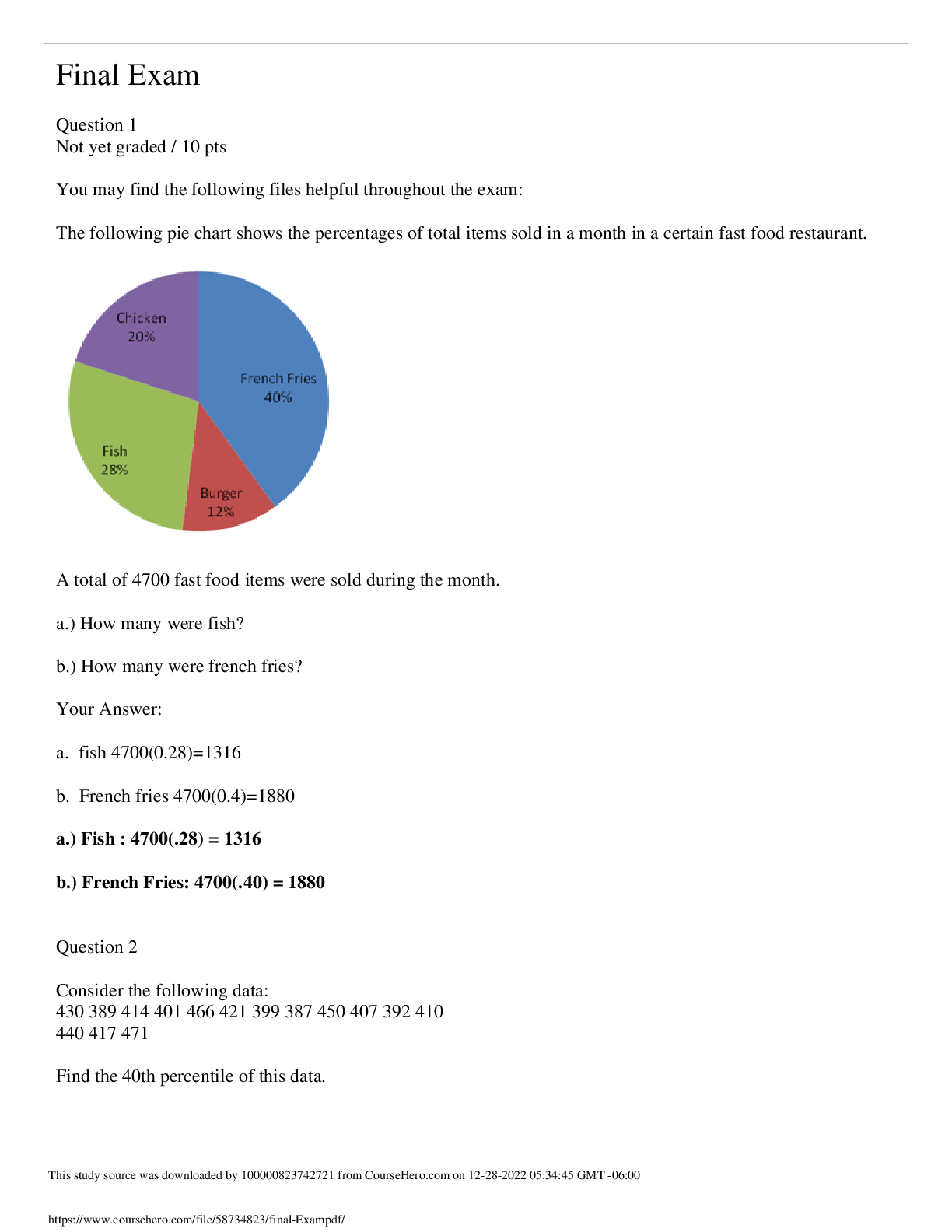
Answer the following questions. 1. Explain two reasons why a woman with low levels of LH would not be able to become pregnant. (1) LH acts on the ovary to cause ovulation to occur. (2) L... H causes progesterone release to facilitate potential fertilization of the egg and pregnancy. Progesterone is a key hormone for the maintenance of pregnancy. 2. Would you expect a female to have testosterone in their bloodstream? Explain why or why not. (1) Yes. Both male and female bodies produce “all” the sex hormones. However, the ratios are different. (2) The adrenal glands are largely responsible for producing this “opposite” hormone that the ovaries would not. Label the endocrine glands (A-C) A: Pineal gland B: Hypothalamus C: Pituitary gland 1. Explain the concept of negative feedback and how it helps to maintain homeostasis. 1- The effect or increased level of the hormone acts to shut down the continued release of the hormone. 2- The brain is constantly monitoring hormone levels to keep levels within a certain range or set- point (homeostasis). Negative feedback is a way of “turning off” hormone production when the desired level is achieved Answer the following five questions: 1. This type of hormone is derived from cholesterol: A. Peptide hormones B. Catecholamines C. Steroid hormones D. Tyrosine C. Steroid hormones 2. Growth hormone A. is most active during childhood/adolescence. B. can cause disease if levels are not correct. C. cannot affect an adult. D. A &B D. A &B 3. Neurons in the hypothalamus are called A. Neurosecretory B. Vasopressin C. Melanocytes D. Somatotropic A. Neurosecretory 4. Which hormone production is increased with sunlight? A. MSH –melanocyte stimulating hormone B. Melatonin C. Cortisol D. GH -Growth hormone A. MSH –melanocyte stimulating hormone 5. The posterior pituitary stores these two hormones: A. ADH and LH B. ADH and Oxytocin C. LH and FSH D. TSH and Prolactin B. ADH and oxytocin 1. List the hormone best describes each of the four statements below: A. I lower the level of calcium in the blood by depositing calcium into bone. Calcitonin B. I am the secreted by the pituitary and stimulate the gonads. FSH or LH (Gonadotropic hormones) C. I am secreted by the pituitary to stimulate the adrenal cortex. ACTH D. I secreted by the alpha cells of the pancreas. Glucagon Answer the following question. 1. Explain in detail how PTH and calcitonin work to maintain calcium balance. Calcitonin: produced by the thyroid glands, deposits calcium into bone. Calcitonin opposes the action of PTH. When the blood calcium level reaches the appropriate level through all these means, the parathyroid glands stop producing PTH through negative feedback. PTH: produced by the parathyroid glands increase the amount of calcium in the blood. (Any one of the following explanations of PTH is acceptable) PTH stimulates the increased absorption of calcium from the intestines. PTH retains calcium through excreting phosphate at the kidneys. In the bones, PTH promotes the activity of osteoclasts to demineralize of the bone, increasing the amount of calcium in the blood. Answer the following multiple choice questions: 1. Which hormone/s are involved in milk production? A. Thyroxin B. Oxytocin C. Prolactin D. B &C E. A&B C. Prolactin 2. Which cells mature in the thymus? A. B cells B. T cells C. Red blood cells D. the islets of Langerhans E. A & B B. T Cells 3. Iodine is needed to produce which hormone/s? A. T3/T4 B. Gonadotropic C. ACTH D. TSH E. A & D A. T3/T4 4. Which of the following is NOT a function of oxytocin? A. Uterine contraction B. Bone growth C. Milk letdown D. Given to aide in childbirth process B. Bone growth 5. Which hormones are produced in the anterior pituitary? A. TSH, MSH, and calcitonin B. ADH, GH, and prolactin C. PTH, TSH, and FH D. ACTH, GH, and prolactin D. ACTH, GH, and prolactin Answer the following question: 1. Aldosterone is involved in the regulation of sodium and potassium in the body. Explain how too much aldosterone could contribute to high blood pressure. Aldosterone’s primary target organ is the kidney, where it promotes renal absorption of sodium and renal excretion of potassium. The blood sodium level is particularly important to the maintenance of blood pressure. Too much sodium causes retention of fluid and increases blood pressure. Therefore, too much aldosterone will cause increased and potentially high blood pressure. Matching each of the following conditions with the one best explanation (1-5): 1. Jet Lag F. Melatonin production is produced according to body’s normal rhythm 2. Pituitary dwarf A. Underproduction of GH as a child 3. Acromegaly C. Overproduction of GH as an adult 4. Inflammation E. Cortisol helps to counteract this condition 5. Tetany D. Results if PTH is not produced in response to low blood calcium A. Underproduction of GH as a child B. Overproduction of GH as a child C. Overproduction of GH as an adult D. Results if PTH is not produced in response to low blood calcium E. Cortisol helps to counteract this condition F. Melatonin production is produced according to body’s normal rhythm G. Lack of erythropoietin to act on the bone marrow H. Results if calcitonin is not produced in response to low blood calcium Answer the following five questions. 1. In addition to the endocrine system, the hypothalamus is also part of which system? A. Excretory B. Nervous C. Circulatory D. Digestive B. Nervous 2. What hormone/s are produced by the adrenal medulla? A. Epinephrine B. Glucocorticoids C. Mineralocorticoids D. B & C A. Epinephrine 3. Which of the following is true regarding aldosterone? A. It is regulated by the anterior pituitary. B. It causes the kidneys to retain potassium and excrete sodium. C. It causes the kidneys to excrete potassium and retain sodium. D. It causes “fight or flight” responses in times of emergency. E. It decreases blood pressure. C. It causes the kidneys to excrete potassium and retain sodium. 4. If you were experiencing kidney disease, what hormone level would be low and what would occur? A. PTH, tetany B. Calcitonin, tetany C. Erythropoietin, anemia D. Erythropoietin, stress response C. Erythropoietin, anemia 5. Which of the following is false regarding testosterone? A. Production is highest in childhood. B. It causes growth of the sex organs. C. It is required for the maturation of sperm. D. It causes males to have a wider pelvis (compared to females). D. It causes males to have a wider pelvis. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 9 pages

Also available in bundle (1)

A&P 1 101 Module 1-8 Exam BUNDLE (GRADED A+) Comprehensive set Portage Learning 2021
A&P 1 101 Module 1-8 Exam BUNDLE (GRADED A+) Comprehensive set Portage Learning 2021
By A+ Solutions 2 years ago
$13.5
23
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Aug 19, 2021
Number of pages
9
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Aug 19, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
63



.png)



















 (1).png)



