BioChemistry > GIZMOS > Biochemistry>Explore Learning: GIZMO Student Exploration: Meiosis 100% Score (All)
Biochemistry>Explore Learning: GIZMO Student Exploration: Meiosis 100% Score
Document Content and Description Below
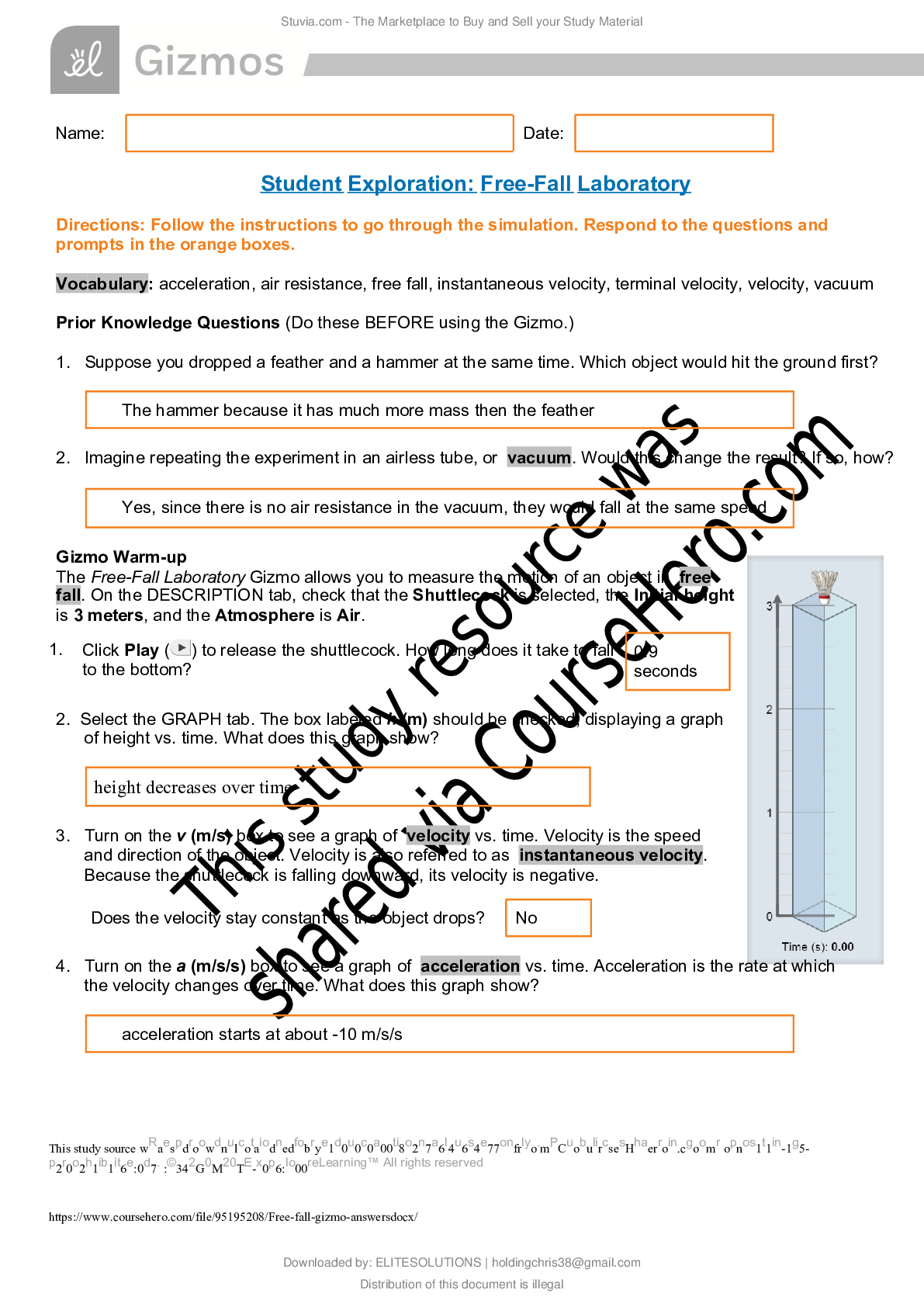
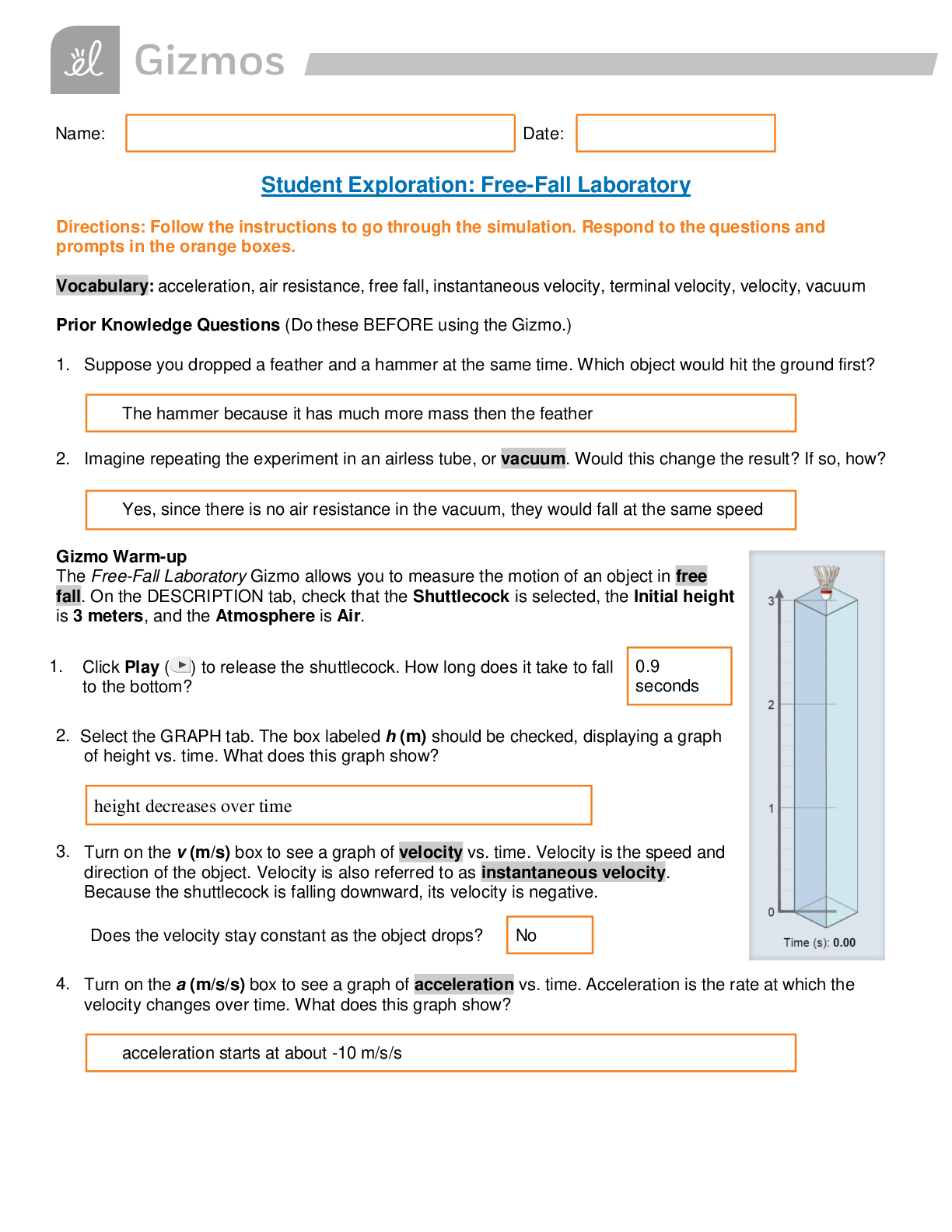
Vocabulary: anaphase, chromosome, crossover, cytokinesis, diploid, DNA, dominant, gamete, genotype, germ cell, haploid, homologous chromosomes, interphase, meiosis, metaphase, mitosis, ovum, phenoty p... e, prophase, recessive, sister chromatid, sperm cell, telophase, zygote Name: Date: Student Exploration: Meiosis Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.) 1. During a single cell divides to produce two daughter cells. What must happen in the original cell so that each of the daughter cells has a complete set of 2. During sexual reproduction, two sex cells fuse to create a fertilized cell with a complete set of chromosomes. What must be true about the number of chromosomes in each sex cell? Gizmo Warm-up Meiosis is a type of cell division that results in four daughter cells with half as many chromosomes as the parent cell. These daughter cells mature into gametes, or sex cells. In the Meiosis Gizmo, you will learn the steps in meiosis and experiment to produce customized sex cells and offspring. On the STEPS tab, click Male. You are looking cell, or a cell that will undergo meiosis to become gametes. 1. Read the description of iat the bottom of the Gizmo. What happens to the cell at the beginning of interphase? 2. Click on the DNA in the nucleus of the cell. Describe what happens. A. The pairs of (chromosomes of similar size with a matching set of genes). In the Gizmo, drag the homologous chromosomes together. Click 2. Observe: (I) - Drag the groups of homologous chromosomes to the metaphase plate, then drag spindle fibers from each of the centrosomes to the chromosomes. Click the centrosome to pull the chromosomes apart. How do the chromosomes separate in anaphase I? 3. Compare: An image of the anaphase step in mitosis is shown to the right. A. How does anaphase I in meiosis differ from anaphase in mitosis? B. At the end of anaphase I (meiosis), how many chromosomes are on each side? 4. Observe: Telophase I and cytokinesis are the final steps of the first half of meiosis. A. Describe what happens when you click on the chromosomes during telophase I. B. Click and drag on the contractile ring. Describe what happened during cytokinesis. 5. Observe: Go through the steps of the second half of meiosis until you reach the end of telophase II, following the instructions at the top right corner. As you proceed, answer the questions below. Use the Back button if you need to see a step again. A. Before prophase II begins, does the DNA in the cell duplicate itself? B. During metaphase II, do homologous chromosomes pair up as in metaphase I C. How does anaphase II differ from anaphase I? D. At the end of anaphase II, how many chromatids are on each side of the cell? E. After cytokinesis, how many cells have been formed from the parent cell? F. Are all of the cells the same size? The original parent cell is called because it contains a complete set of homologous chromosome pairs. Each of the four daughter cells is, meaning that each contains half of the original parent cell’s chromosomes. Each daughter cell contains one chromatid from each homologous pair. 6. Observe: Click on the spermatids. Spermatids that formed from meiosis will develop into mature male gametes called. Sketch a mature sperm cell in the space to the right. Introduction: Although both male and female gametes contain genetic material from the parent organism, they perform different functions. A male gamete delivers genetic material to a female gamete. The fertilized female gamete, called a zygote, then grows into the offspring. 1. Compare: Click on the Female button. For the female cell, proceed through meiosis until you reach the end of anaphase I. Up to this point, did you notice any differences between the development of male and female gametes? Explain. 2. Compare: Proceed through telophase I and cytokinesis I. A. What do you notice about the size of the two resulting cells? B. How does this compare to the two cells at the end of telophase I and cytokinesis I in male cells? 3. Compare: Continue through meiosis until you finish telophase II and cytokinesis II. A. What do you notice about the four cells now? B. What is the largest cell called? The ovum is the largest cell in the human body. In contrast, the sperm cell is the smallest cell in the human body. C. What are the small cells called? Polar bodies are small cells that develop as a byproduct of meiosis in females. In humans and most other animals, these cells play no significant role and soon die. Think and discuss: Why do you think egg cells are large and sperm cells are small? Activity C: Genetic diversity Get the Gizmo ready: • Make sure the STEPS tab is selected. • Click Reset. Introduction: The activities above shows that organisms can produce at least four different gametes. In reality, organisms can produce millions of genetically unique gametes. 1. Experiment: Use the following abbreviations for the chromosomes. Dark green – DG; Light green – LG; Dark purple – DP, Light purple – LP. Choose a cell. A. Proceed though meiosis to anaphase I. Which chromosomes went up and which went down? Up: B. Click Back and run anaphase I again a few times. Did the results ever change? Yes Explain. C. Chromosomes are distributed randomly during anaphase I. What are the possible chromosome combinations in the two daughter cells? (Use DG, LG, DP, and LP.) 2. Experiment: Click Reset. Choose a Male or Female cell. Proceed through meiosis until the chromosomes are condensed in Prophase I. Drag the LG (light green) chromosome to the Allele map on the left. This shows the alleles (or variations of a gene) that are present on the chromosome. A genotype is a list of alleles. The genotype of the LG chromosome, for example, is EEFFGGHHJJ. A. What are the genotypes of the remaining chromosomes? DG: B. After moving the centrosomes, drag the pairs of homologous chromosomes together. Click on a chromosome. What happens? When homologous chromosomes are paired up, they can exchange sections. This exchange of genes is called a C. Click on several segments to create crossovers, and then click Continue. Proceed to anaphase I. Drag each chromosome to the Allele map and write its genotype. 3. Think and discuss: In this Gizmo, only one crossover is allowed in each segment. In reality, crossovers can occur at almost any point along the chromosome. How do the random distribution of chromosomes and crossovers create more variation in the resulting gametes? 4. Explore: Meiosis is a complicated process. What happens when something goes wrong? A. Click Reset and choose a male or female cell. Click Skip. Describe what would happen if meiosis occurred without DNA replication. . B. Click Back. Proceed through meiosis until the chromosomes are lined up along the metaphase plate. Click Skip. Describe what would happen if the chromosomes did not attach to spindle fibers during metaphase I. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 9 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Aug 14, 2021
Number of pages
9
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Aug 14, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
684













, Questions and Answers, All Correct Study Guide, Download to Score A.png)
, Questions and Answers, All Correct Study Guide, Download to Score A.png)
, Questions and Answers, All Correct Study Guide, Download to Score A.png)
, Questions and Answers, All Correct Study Guide, Download to Score A.png)
, Questions and Answers, All Correct Study Guide, Download to Score A.png)
.png)


