*NURSING > UWorld > UWorld Neuro Nursing- Med Surg. This exam Study Guide Contains the Last minute Information you NEED (All)
UWorld Neuro Nursing- Med Surg. This exam Study Guide Contains the Last minute Information you NEED to pass the UWorld Neuro Exam. An easy to read layout.
Document Content and Description Below
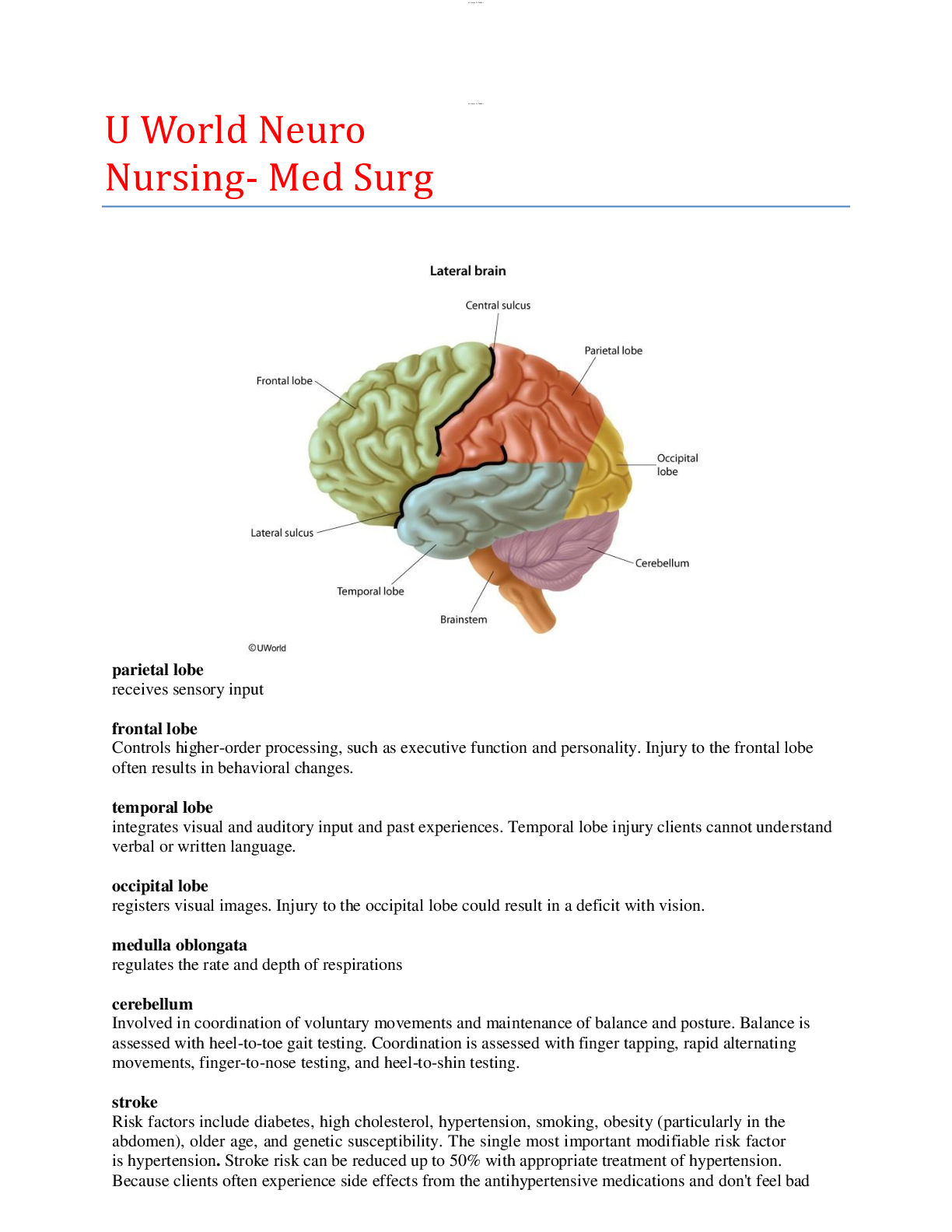
lOMoARcPSD|784381 U World Neuro Nursing- Med Surg parietal lobe receives sensory input frontal lobe Controls higher-order processing, such as executive function and personality.. tem... poral lobe integrates visual and auditory input and past experiences. occipital lobe medulla oblongata cerebellum Involved in coordination of voluntary movements and maintenance of balance and posture. Balance is assessed with heel-to-toe gait testing. stroke Risk factors include diabetes, high cholesterol, hypertension, smoking, obesity (particularly in the Supraglottic swallow Clients are instructed to: 1. Inhale deeply Coup-contrecoup Injury occurs when a body in motion stops suddenly (eg, head hits car windshield), causing contusions Quadriplegia (tetraplegia) occurs when the lower limbs are completely paralyzed and there is complete or partial paralysis of the Huntington disease is an incurable autosomal dominant disease that causes progressive nerve degeneration, which impairs St. John's wort Herbal product commonly used by many clients to treat depression. However, it may interact with Levetiracetam (Keppra) a medication often used to treat seizures in various settings.. Dexamethasone a corticosteroid, is used to treat cerebral edema associated with a brain injury/tumor by decreasing inflammation. Malignant hyperthermia (MH) a rare but life-threatening inherited muscle abnormality that is triggered by specific, inhaled anesthetic Parkinson Disease Caused by low levels of dopamine in the brain. S&S- stooped posture, rigidity, flexed elbows & wrists, Carbidopa-levodopa combination medication most helpful for treating bradykinesia in Parkinson disease and can also improve Myasthenia gravis an autoimmune disease involving a decreased number of acetylcholine receptors at the neuromuscular Phenytoin (Dilantin) an anticonvulsant drug, is used to treat generalized tonic-clonic seizures Increased ICP Clients with should avoid anything that increases intrathoracic or intraabdominal pressure as these also Cushing's triad related to increased intracranial pressure (ICP). Early signs include change in level of consciousness. Serial neurologic assessments Are important as neurologic abnormalities are often initially subtle, making it important to note the Trigeminal neuralgia sudden, sharp pain along the distribution of the trigeminal nerve. symptoms are usually unilateral and primarily in the maxillary and mandibular branches. Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) dissolves clots and restores perfusion in clients with ischemic stroke. It must be administered within a 3- cranial nerve (CN) VIII, the vestibulocochlear (or auditory) nerve Symptoms of impairment may include loss of hearing, dizziness, vertigo, and motion sickness, which place the client at a high risk for falls. Autonomic dysreflexia (autonomic hyperreflexia) a massive, uncompensated cardiovascular reaction by the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) in a spinal Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) an acute, immune-mediated polyneuropathy that is most often accompanied by ascending muscle Bell's palsy an inflammation of cranial nerve VII (facial) that causes motor and sensory alterations. Clients are Tricyclic antidepressants (amitriptyline, nortriptyline, desipramine, imipramine) are commonly used for neuropathic pain. Side Due to the increased risk of falling, the priority nursing action is to teach the client to get up slowly from the bed or a sitting position. Interventions to help decrease aspiration and resulting aspiration pneumonia in susceptible clients (eg, elderly, neurologic dysfunction, decreased cough or gag reflexes, decreased immunity, chronic disease), Multiple sclerosis (MS) a progressive, demyelinating disease of the central nervous system that interrupts nerve impulses, causing Concussion considered a minor traumatic brain injury and results from blunt force or an acceleration/deceleration head injury. Typical signs of concussion include: Aphasia Broca (expressive) aphasia Wernicke (receptive) aphasia Global aphasia Thrombolytic agents (eg, alteplase, tenecteplase, reteplase) Transsphenoidal hypophysectomy surgical removal of the pituitary gland, an endocrine gland that produces, stores, and excretes hormones Seizures Manifestations generally are classified into 4 phases: Seizure precautions • Raising the upper side rails on the bed to prevent the client from falling to the floor during a • airway. Suction equipment and oxygen equipment are set up at the bedside • Lumbar puncture Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is assessed for color, contents, and pressure. Normal CSF is clear and Mannitol (Osmitrol) an osmotic diuretic used to treat cerebral edema (increased intracranial pressure) and acute glaucoma. Melatonin Evening primrose Ginseng Head injury discharging a client Spinal immobilization is not a benign procedure. An acronym to help determine the need for spinal immobilization is NSAIDs: Ischemic stroke a loss of brain tissue perfusion due to blockage in blood flow. Elevated blood pressure is common and . Status epilepticus a serious and life-threatening emergency in which a client has been seizing for 5 minutes or longer. Ruptured cerebral aneurysm a surgical emergency with a high mortality rate. Cerebral aneurysms are usually asymptomatic unless Sumatriptan is prescribed for moderate to severe, acute migraine headaches that are characterized by Meningitis an inflammation of the meninges covering the brain and spinal cord. The key clinical manifestations of Hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel ruptures in the brain and causes bleeding. Seizure activity may occur due to Arteriovenous malformation A congenital deformity of tangled blood vessels often occurring in the brain. These vessels may weaken and rupture, causing an intracranial hemorrhage. Epidural hematoma An accumulation of blood between the skull bone and dura mater ** Apraxia refers to loss of the ability to perform a learned movement (eg, whistling, clapping, dressing) due to neurological impairment. [Show More]
Last updated: 2 months ago
Preview 1 out of 12 pages
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 02, 2020
Number of pages
12
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 02, 2020
Downloads
1
Views
169