*NURSING > ATI > ATI NCLEX-PN 2 Final Review Respiratory -S/S of asthma ATI p 125-127, Med-Surg. All the notes for Q (All)
ATI NCLEX-PN 2 Final Review Respiratory -S/S of asthma ATI p 125-127, Med-Surg. All the notes for Quick Exam Revision and Preparation.
Document Content and Description Below
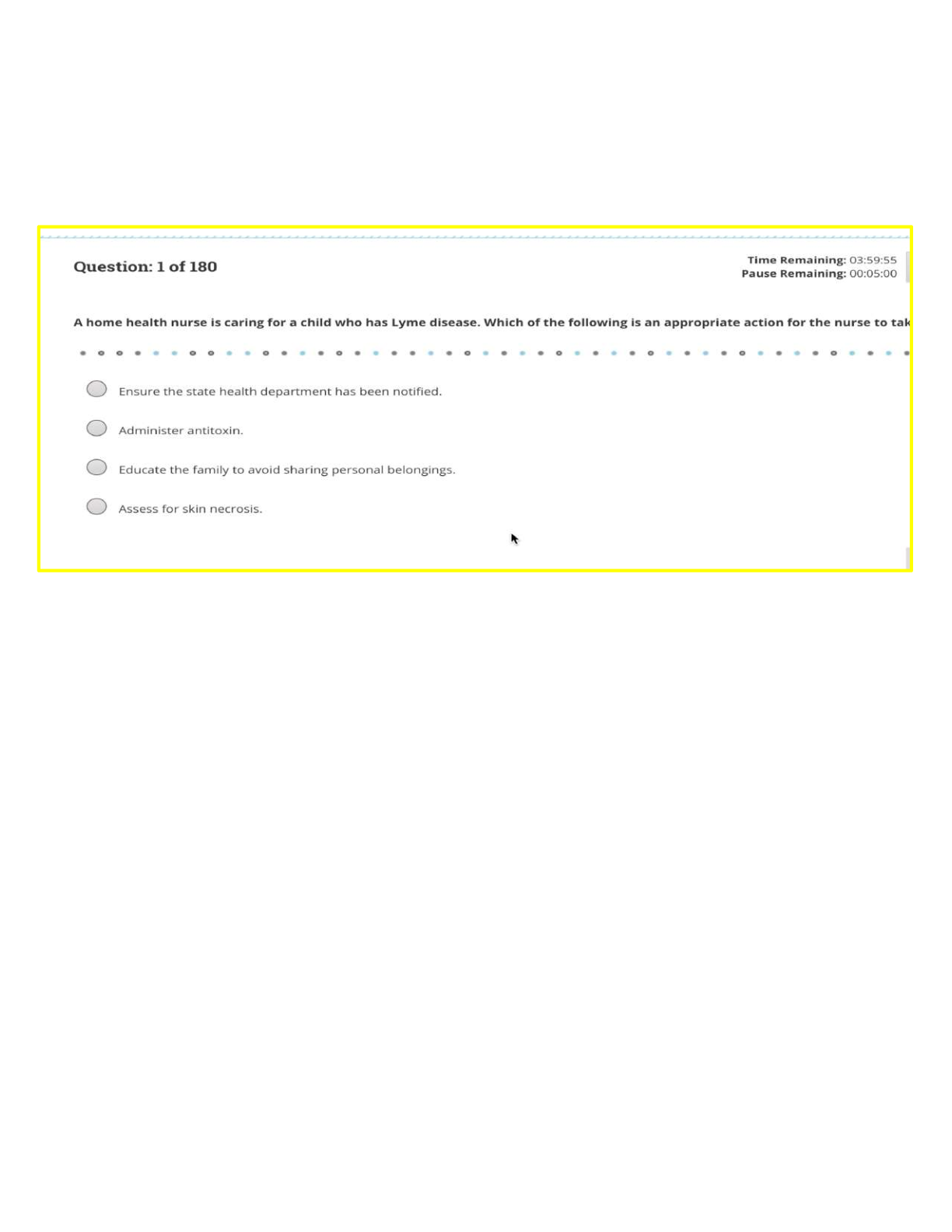
ATI NCLEX-PN 2 Final Review Respiratory -S/S of asthma ATI p 125-127, Med-Surg. Respiratory -S/S of asthma ATI p 125-127, Med-Surgical EXPECTED FINDINGS ●● Dyspnea ●● Chest tightness ... ●● Anxiety or stress PHYSICAL ASSESSMENT FINDINGS ●● Coughing ●● Wheezing ●● Mucus production ●● Use of accessory muscles ●● Prolonged exhalation ●● Poor oxygen saturation (low SaO2) ●● Barrel chest or increased chest diameter Obtain history regarding current and previous asthma exacerbations. ●● Onset and duration ●● Precipitating factors (stress, exercise, exposure to irritant) ●● Changes in medication regimen ●● Medications that relieve symptoms ●● Other medications taken ●● Self‑care methods used to relieve symptoms RISK FACTORS ●● Older adult clients have decreased pulmonary reserves due to physiologic lung changes that occur with the aging process. ◯◯ Older adult clients are more susceptible to infections. ◯◯ The sensitivity of beta‑adrenergic receptors decreases with age. As the beta receptors age and lose sensitivity, they are less able to respond to agonists, which relax smooth muscle and can result in bronchospasms. ●● Family history of asthma ●● Smoking ●● Secondhand smoke exposure ●● Environmental allergies ●● Exposure to chemical irritants or dust ●● Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) The most common indicators of asthma in adults include wheezing (high-pitched whistling sounds on expiration), cough, difficulty breathing, recurrent chest tightness, and history of obstructive symptoms that occur or worsen at night or in the presence of triggers. There may be breathlessness, increased respiration, tachycardia, pulsus paradoxus, hyperexpansion of the thorax, use of accessory muscles to breathe, appearance of hunched shoulders, chest deformity, increased nasal secretion, mucosal swelling, and nasal polyps. The patient may be cyanotic and use a tripod position to breathe. Monitoring Signs and Symptoms Global Assessment “Has your asthma been better or worse since your last visit?” Recent Assessment “In the past two weeks, how many days have you: • Had problems with coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, or chest tightness during the day?” • Awakened at night from sleep because of coughing or other asthma symptoms?” • Awakened in the morning with asthma symptoms that did not improve within 15 minutes of inhaling a short-acting inhaled beta2 agonist?” • Had symptoms while exercising or playing?” Monitoring Pulmonary Function Lung Function “What is the highest and lowest your peak flow has been since your last visit?” “Has your peak flow dropped below ______ L/min (80% of personal best) since your last visit?” “What did you do when this occurred?” Peak Flow Monitoring Technique “Please show me how you measure your peak flow.” “When do you usually measure your peak flow? Monitoring Quality of Life and Functional Status “Since your last visit, how many days has your asthma caused you to: • Miss work or school?” • Reduce your activities?” • (For caregivers) Change your activity because of your child’s asthma?” “Since your last visit, have you had any unscheduled or ED visits or hospital stays?” Monitoring Exacerbation History “Since your last visit, have you had any episodes or times when your asthma symptoms were a lot worse than usual?” • If yes, “what do you think caused the symptoms to get worse?” • If yes, “what did you do to control the symptoms?” “Have there been any changes in your home or work environment (e.g., new smokers or pets)?” Monitoring Pharmacotherapy Medications “What medications are you taking?” “How often do you take each medication?” “How much do you take each time?” “Have you missed or stopped taking any regular doses of your medications for any reason?” “Have you had trouble filling your prescriptions (e.g., for financial reasons or not on formulary)?” How many puffs of your short-acting inhaled beta2 agonist (quick-relief medicine) do you use per day?” “How many [name short-acting inhaled beta2 agonist] inhalers [or pumps] have you been through in the past month?” “Have you tried any other medicines or remedies?” Side Effects “Has your asthma medicine caused you any problems, such as” • “Shakiness, nervousness, bad taste, sore throat, cough, or upset stomach?” Inhaler Technique “Please show me how you use your inhaler.” Monitoring Patient-Provider Communication and Patient Satisfaction “What questions have you had about your asthma daily self-management plan and action plan?” “What problems have you had following your daily self-management plan? Your action plan?” “Has anything prevented you from getting the treatment you need for your asthma from me or anyone else?” “Have the costs of your asthma treatment interfered with your ability to get asthma care?” “How satisfied are you with your asthma care?” “How can we improve your asthma care?” “Let’s review some important information:” • “When should you increase your medications? Which medication(s)?” • “When should you call me [your physician or nurse practitioner]? Do you know the after-hours phone number?” • “If you can’t reach me, what ED would you go to?” -Asthma pt positions NURSING CARE ●● Position the client to maximize ventilation (high‑Fowler’s). ●● Administer oxygen therapy as prescribed. ●● Monitor cardiac rate and rhythm for changes during an acute attack (can be irregular, tachycardic, or with PVCs). ●● Initiate and maintain IV access. ●● Maintain a calm and reassuring demeanor. ●● Provide rest periods for older adult clients who have dyspnea. Design room and walkways with opportunities for rest. Incorporate rest into ADLs. ●● Encourage prompt medical attention for infections and appropriate vaccinations. ●● Administer medications as prescribed. -What are the fast-acting inhalers Quick-relief medications are used only during acute exacerbations and should not be used on a regular schedule. They promote prompt reversal of acute airflow obstruction and relief of accompanying symptoms by direct relaxation of bronchial smooth muscle. Frequent use of quick-relief medications indicates poor asthma control and the need to initiate or increase long-term control therapy. All patients should have a quick-relief medication readily available for acute symptoms of bronchospasm. The drug of choice for acute symptom relief is a short-acting inhaled selective beta2-adrenergic agonist, such as albuterol. An inhaled anticholinergic medication, such as ipratropium, can be used as an alternative for those who are intolerant to beta2-adrendergic agonists. Short-acting bronchodilators should be used only on an as-needed basis. -SE of albuterol Short‑acting beta2 agonists, such as albuterol, provide rapid relief of acute symptoms and prevent exercise‑induced asthma. NURSING CONSIDERATIONS ●● Albuterol: Watch for tremors and tachycardia. -Transmission of Tuberculosis – ATI p 135 - 139, Med-Surg p 858 Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. TB is transmitted through aerosolization (airborne route). Once inside the lung, the body encases the TB bacillus with collagen and other cells. This can appear as a Ghon tubercle on a chest x‑ray. Only a small percentage of people infected with TB actually develop an active form of the infection. The TB bacillus can lie dormant for many years before producing the disease. TB primarily affects the lungs but can spread to any organ in the blood. The risk of transmission decreases after 2 to 3 weeks of antituberculin therapy. Educate the client and family to continue medication therapy for its full duration of 6 to 12 months, even up to 2 years for multidrug‑resistant TB. Emphasize that failure to take the medications can lead to a resistant strain of TB. MEDICATIONS Due to the resistance that is developing against the antituberculin medications, combination therapy of two or more medications at a time is recommended. ●● Because these medications must be taken for 6 to 12 months, medication noncompliance is a significant contributing factor in the development of resistant strains of TB. ●● The current four‑medication regimen includes isoniazid, rifampin, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol. Ethambutol - This medication should not be given to children younger than 8 years of age. Isoniazid - Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) is used to prevent neurotoxicity from isoniazid. Rifampin - Inform the client that urine and other secretions will be orange. Pyrazinamide- Assess for history of gout, as the medication will cause an adverse effect of nongouty polyarthralgias. Streptomycin sulfate - Due to its high level of toxicity, this medication should be used only in clients who have multidrug‑resistant TB (MDR‑TB). Streptomycin can cause ototoxicity, so monitor hearing function and tolerance often. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY The most common indicators of asthma in adults include wheezing (high-pitched whistling sounds on expiration), cough, difficulty breathing, recurrent chest tightness, and history of obstructive symptoms that occur or worsen at night or in the presence of triggers. There may be breathlessness, increased respiration, tachycardia, pulsus paradoxus, hyperexpansion of the thorax, use of accessory muscles to breathe, appearance of hunched shoulders, chest deformity, increased nasal secretion, mucosal swelling, and nasal polyps. The patient may be cyanotic and use a tripod position to breathe. -How long patients take TB Meds Pharmacology Pharmacological treatment depends on cause and epidemiological factors. Four medications are used together for the immediate treatment of TB. Once the susceptible results are complete the treatment should be altered for the individual. Medications include isoniazid (INH), rifampin (RIF), ethambutol (EMB), and pyrazinamide (PZA) (CDC, 2009b). These four medications have proven effective in the treatment of TB. Several side effects can occur while completing the treatment regimen. A common patient compliant is gastrointestinal (GI) distress, including loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, or stomach pain, during the first few weeks of treatment. Stomach irritation with TB treatment regimens are prevalent because the medications must be given on an empty stomach or two hours after meals, which may result in noncompliance with the treatment regimen (Table 32-4 p. 861). -Chest tube care and what to do when ambulating and dislodging Chest drainage systems are a one-piece design containing three chambers. These chambers provide separate functions of fluid that is [Show More]
Last updated: 9 months ago
Preview 1 out of 60 pages

Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Aug 23, 2020
Number of pages
60
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Aug 23, 2020
Downloads
2
Views
271




























_Already Graded A.png)