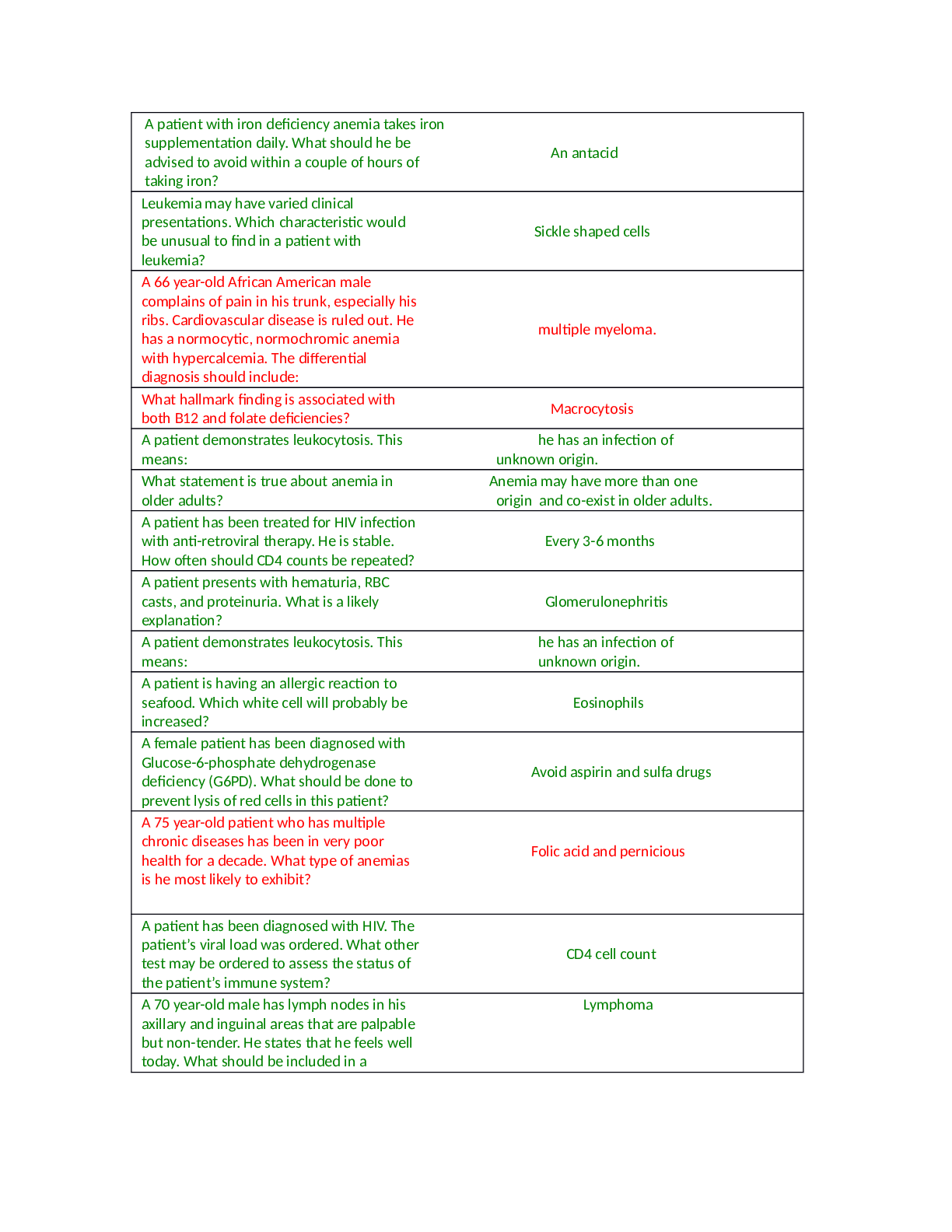
Business Administration > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > BPL 5100 Chapters 1-12 Complete Test Bank Questions & Answers Rationales, Summer 2020. (All)
BPL 5100 Chapters 1-12 Complete Test Bank Questions & Answers Rationales, Summer 2020.
Document Content and Description Below
BPL 5100 Chapters 1-12 Complete Test Bank Questions & Answers Rationales 1. Nortel, like other firms, suffered from a drop in overall industry demand for telecommunications equipment during 2000 and ... 2001. According to the text, this would be an example of the "romantic" perspective of leadership. True False 2. Strategic management consists of the analyses, decisions, and actions an organization undertakes in order to create and sustain competitive advantages. True False 3. Strategic management includes strategy analysis, strategy formulation, and strategy implementation. True False 4. Management innovations such as total quality, benchmarking, and business process reengineering often lead to sustainable competitive advantage. True False 5. Strategic management recognizes the trade-offs between effectiveness and efficiency. True False 6. The best firms always realize their intended strategy. True False 7. According to the text, formulating strategy includes taking into consideration strategy at the business, international, and corporate levels. In addition managers must formulate effective entrepreneurial initiatives. True False 8. Business-level strategy focuses on two issues, (1) what businesses to compete in, and (2) how businesses can be managed to achieve synergy. True False 9. Corporate-level strategy addresses how firms compete and outperform their rivals as well as achieve and sustain competitive advantages. True False 10. Effective leadership can play a large role in fostering corporate entrepreneurship. Corporate entrepreneurship can have a very positive impact on a firm's bottom line. True False 11. The three primary participants in corporate governance are: (1) the shareholders; (2) management (led by the chief executive officer); and, (3) employees. True False 12. Decisions by Boards of Directors are always consistent with shareholder interests. True False 13. Former Chrysler vice chairman Robert Lutz stated: "We are here to serve the shareholder and create shareholder value. I insist that the only person who owns the company is the person who paid good money for it." This is an example of a symbiotic approach to stakeholder management. True False 14. Stockholders in a company are the only individuals with an interest in the financial performance in the company. True False 15. Stockholders, employees, and the community-at-large are among a firm's stakeholders. True False 16. Symbiosis is the ability to recognize interdependencies among the interests of multiple stakeholders within and outside an organization. True False 17. One of the benefits of crowdsourcing is that stakeholders are restricted to one narrow role. True False 18. Social responsibility is the idea that organizations are not only accountable to stockholders but also to the community-at-large. True False 19. The concept of "shared value" redefines the purpose of the corporation as creating shared value in order to create a more even distribution of the profits to all employees, not just top level executives. True False 20. Shell, NEC, and Procter & Gamble have been measuring their performance according to what has been called a "triple bottom line." This technique involves an assessment of financial, social, and environmental performance. True False 21. The strategic management process should be addressed only by top-level executives. Mid-level and low- level employees are best equipped to implement the organization's strategies. True False 22. Organizational vision statements are the beginning point for the hierarchy of goals throughout the organization. An organization's vision statement should be massively inspiring, overarching, and long term. True False 23. Strategic objectives are more specific than vision statements. True False 24. According to the text, a mission statement is an overarching statement that is massively inspiring, long term, and only discusses the purpose of the company. True False 25. A mission statement encompasses both the purpose of the company as well as the basis of competition and competitive advantage. True False 26. Some excellent examples of mission statements are: "To be the happiest place on earth" (Disneyland) and "Restoring patients to full life" (Medtronic). True False 27. Strategic objectives should be measurable, specific, appropriate, and realistic, but not constrained by time deadlines. True False 28. Much research has supported the notion that individuals work much harder when they are asked to "do their best" rather than when they are striving toward a specific goal. True False 29. Objectives in organizations should be clear, stated, and known by employees throughout the organization. True False 30. Strategic management should only include short-term objectives. Long-term objectives are covered in the organization's vision statement. True False 31. Organizational goals and objectives should be vague in order to allow for changes in strategy. True False 32. The text addresses two perspectives of leadership as well as their implications. These two perspectives are A. romantic and unromantic. B. romantic and internal control. C. external control and unromantic. D. romantic and external control. 33. A CEO made a lot of mistakes such as committing errors in assessing the market and competitive conditions and improperly redesigning the organization into numerous business units. Such errors led to significant performance declines. According to the text, this example illustrates the perspective of leadership. A. external control B. romantic C. internal mechanism D. operational 34. According to the text, the strategic management process entails three ongoing processes: A. analyses, actions, and synthesis. B. analyses, decisions, and actions. C. analyses, evaluation, and critique. D. analyses, synthesis, and antithesis. 35. Management innovations such as total quality, benchmarking, and business process reengineering cannot lead to sustainable competitive advantage because A. companies that have implemented these techniques have lost money. B. there is no proof that these techniques work. C. they cost too much money and effort to implement. D. every company is trying to implement them and hence it does not make a company different from others. 36. The "organizational versus individual rationality" perspective suggests that A. what is good for a functional area is always good for the organization. B. what is good for the organization is always good for a functional area. C. what is best for a functional area may not be best for the organization. D. the "incremental" perspective may be best for functional areas while the "rational" perspective may be best for the organization. 37. The four key attributes of strategic management include the idea that A. strategy must be directed toward overall organizational goals and objectives. B. strategy must be focused on long-term objectives. C. strategy must be focused on one specific area of an organization. D. strategy must focus on competitor strengths. 38. The four key attributes of strategic management include all of the following EXCEPT: A. including multiple stakeholder interests in decision making. B. incorporating both short-term and long-term perspectives. C. recognizing the trade-offs between effectiveness and efficiency. D. emphasis on the attainment of short-term objectives. 39. "Effectiveness" is often defined as A. doing things right. B. stakeholder satisfaction. C. doing the right thing. D. productivity enhancement. 40. All of the following are ambidextrous behaviors EXCEPT: A. taking initiative and being alert to opportunities beyond the confines of one's own job. B. being cooperative and seeking opportunities to combine one's efforts with others. C. intensely focusing on one's own responsibilities and maximizing the output of one's department in an organization. D. being brokers, always looking to build internal linkages. 41. According to Henry Mintzberg, the realized strategies of a firm A. are a combination of deliberate and emergent strategies. B. are a combination of deliberate and differentiation strategies. C. must be based on a company's strategic plan. D. must be kept confidential for competitive reasons. 42. According to Henry Mintzberg, decisions following from a firm's strategic analysis are its A. emergent strategy. B. deliberate strategy. C. intended strategy. D. realized strategy. 43. may be considered the "advance work" that must be done in order to effectively formulate and implement strategies. A. Goal setting B. Corporate entrepreneurship C. Strategy analysis D. Organizational design 44. involves ensuring proper strategic controls and organizational designs. A. Corporate governance B. Corporate-level strategy C. Strategy implementation D. Business-level strategy 45. The three participants in corporate governance are A. the shareholders, board of directors, and employees. B. the shareholders, labor unions, and employees. C. the shareholders, board of directors, and management. D. the shareholders, banks and lending institutions, and management. 46. While working to prioritize and fulfill their responsibilities, members of an organization's board of directors should A. represent their own interests. B. represent the interests of the shareholders. C. direct all actions of the CEO. D. emphasize the importance of short-term goals. 47. Members of Boards of Directors are A. appointed by the Securities and Exchange Commission. B. elected by the shareholders as their representatives. C. elected by the public. D. only allowed to serve one term of four years. 48. An organization is responsible to many different entities. In order to meet the demands of these groups, organizations must participate in stakeholder management. Stakeholder management means that A. interests of the stockholders are not the only interests that matter. B. stakeholders are second in importance to the stockholders. C. stakeholders and managers inevitably work at cross-purposes. D. all stakeholders receive financial rewards. 49. Stakeholders are A. a new way to describe stockholders. B. individuals, groups, and organizations who have a stake in the success of the organization. C. creditors who hold a lien on the assets of the organization. D. attorneys and their clients who sue the organization. 50. Outback Steakhouse has developed a sophisticated quantitative model and found that there were positive relationships between employee satisfaction, customer satisfaction, and financial results. According to the text, this is an example of A. zero-sum relationship among stakeholders. B. stakeholder symbiosis. C. rewarding stakeholders. D. emphasizing financial returns. 51. There are several perspectives of competition. One perspective is zero-sum thinking. Zero-sum thinking means that A. all parts of the organization gain at no loss. B. in order for someone to gain others must experience no gain or benefit. C. one can only gain at the expense of someone else. D. everyone in the organization shares gains and losses equally. 52. Managers should do more than just focus on short-term financial performance. One concept that helps managers do this is stakeholder symbiosis. This means that A. stakeholders are dependent on each other for their success. B. stakeholders look out for their individual interests. C. one can only gain at the expense of someone else. D. all stakeholders want to maximize shareholder returns. 53. Crowdsourcing can be defined as A. using surveys to get supplier input. B. using multiple sources for a firm's raw material inputs. C. tapping the latent talent of the online crowd. D. addressing strategic issues directly with managers and employees. 54. Firms must be aware of goals other than short-term profit maximization. One area of concern should be social responsibility which is A. the expectation that business will strive to improve the overall welfare of society. B. the idea that organizations are solely responsible to local citizens. C. the fact that court costs could impact the financial bottom line. D. the idea that businesses are responsible to maintain a healthy social climate for their employees. 55. According to the text, the "triple bottom line" approach to corporate accounting includes three components: A. financial, environmental, and customer. B. financial, organizational, and customer. C. financial, environmental, and social. D. financial, organizational, and psychological. 56. Many organizations have a large number of functional areas with very diverse, and sometimes competing, interests. Such organizations will be most effective if A. each functional area focuses on achieving their own goals. B. functional areas work together to attain overall goals. C. goals are defined at the bottom and implemented at the top. D. management and employees have separate goals. 57. Strategy formulation and implementation is a challenging ongoing process. To be effective, it should involve A. the CEO and the board of directors. B. the board of directors, CEO, and CFO. C. line and staff managers. D. all of these. 58. The text argues that a strategic perspective in an organization should be emphasized A. at the top of the organization. B. at the middle of the organization. C. throughout the organization. D. from the bottom up. 59. Peter Senge, of MIT, recognized three types of leaders. are individuals that, although having little positional power and formal authority, generate their power through the conviction and clarity of their ideas. A. Local line leaders B. Executive leaders C. Internal networkers D. Shop floor leaders 60. Peter Senge, of MIT, recognized three types of leaders. champion and guide ideas, create a learning infrastructure, and establish a domain for taking action. A. Local line leaders B. Executive leaders C. Internal networkers D. Shop floor leaders 61. Leadership is a necessary (but not sufficient) condition for organizational success. Leaders should emerge at which level(s) of an organization? A. only at the top B. in the middle C. throughout the organization D. only during times of change 62. The hierarchy of organizational goals is in this order (least specific to most specific): A. vision statements, strategic objectives, mission statements. B. mission statements, strategic objectives, vision statements. C. vision statements, mission statements, strategic objectives. D. mission statements, vision statements, strategic objectives. 63. Vision statements are used to create a better understanding of the organization's overall purpose and direction. Vision statements A. are very specific. B. provide specific objectives. C. set organizational structure. D. evoke powerful and compelling mental images. 64. Effective vision statements include A. all strategic directions of the organization. B. a brief statement of the company's direction. C. strategic posturing and future objectives D. financial objectives and projected figures. 65. Examples of include: "To be the happiest place on earth" (Disneyland), and "Restoring patients to full life" (Medtronic). A. vision statements B. mission statements C. strategic objectives D. operational objectives 66. WellPoint Health Network states: "WellPoint will redefine our industry: through a new generation of consumer-friendly products that put individuals back in control of their future." This is an example of a A. strategic objective. B. vision statement. C. vague statement of direction. D. line manager's individual goal. 67. In contrast to an organization's vision, its mission should A. be shorter in length. B. encompass both the purpose of the company as well as the basis of competition. C. encompass all the major rules and regulations of the corporate work force. D. be less detailed. 68. An organization's mission statement and vision statement set the overall direction of the organization. Strategic objectives A. operationalize the mission statement. B. modify the mission statement. C. are a shorter version of the mission statement. D. are only clarified by the board of directors. 69. Successful organizations are effective in motivating people. Employees work best when A. they are asked to "do their best." B. work requirements are vague and unclear. C. they are striving toward specific goals. D. they are guided by an abstract mission statement. 70. Fortune Brands states they will "cut corporate overhead costs by $30 million a year." This is an example of a A. nonfinancial strategic objective. B. financial strategic objective. C. vision statement. D. mission statement. 71. "We want to be the top-ranked supplier to our customers." (PPG) This is an example of a A. nonfinancial strategic objective. B. financial strategic objective. C. vision statement. D. mission statement. 72. In large organizations, conflicts can arise between functional areas. In order to resolve these conflicts, strategic objectives A. put financial objectives above human considerations. B. align departments toward departmental goals. C. help resolve conflicts through their common purpose. D. cause debate and increase conflict. 73. The strategic management process includes strategy analysis, strategy formulation, and strategy implementation. Discuss each of these steps. 74. Discuss the key elements of corporate governance. 75. A firm has a variety of stakeholders. Identify several possible stakeholders a firm may have and discuss how the firm may achieve stakeholder symbiosis. 76. Leadership is a topic that is often discussed in the management literature. The text suggests that leaders should be at all levels in an organization. Discuss why it is important to have leaders throughout an organization. 77. According to the text, vision statements should be massively inspiring, overarching, and long term. Provide several examples of potential vision statements for various organizations and discuss how such vision statements would inspire employees around a cause. 78. A mission statement encompasses the purpose of the company as well as the basis of competition and competitive advantage. Compare the purpose of a mission statement to that of a vision statement and a strategic objective. 79. Organizations must focus on financial and nonfinancial objectives. Select an organization and discuss possible financial and nonfinancial objectives the organization may have. 80. The text discusses several characteristics of effective strategic objectives. List several of these and discuss why a firm's strategic objectives should meet these criteria. 33. (p. 5) 34. (p. 8) 35. (p. 8) A CEO made a lot of mistakes such as committing errors in assessing the market and competitive conditions and improperly redesigning the organization into numerous business units. Such errors led to significant performance declines. According to the text, this example illustrates the perspective of leadership. A. external control B. romantic C. internal mechanism D. operational According to the text, the strategic management process entails three ongoing processes: A. analyses, actions, and synthesis. B. analyses, decisions, and actions. C. analyses, evaluation, and critique. D. analyses, synthesis, and antithesis. Management innovations such as total quality, benchmarking, and business process reengineering cannot lead to sustainable competitive advantage because A. companies that have implemented these techniques have lost money. B. there is no proof that these techniques work. C. they cost too much money and effort to implement. D. every company is trying to implement them and hence it does not make a company different from others. The popular management innovations of the last two decades—total quality, just-in-time, benchmarking, business process reengineering, outsourcing—are all about operational effectiveness. Each of these is important, but none lead to sustainable competitive advantage because everyone is doing them. Strategy is all about being different. 36. (p. 9) The "organizational versus individual rationality" perspective suggests that A. what is good for a functional area is always good for the organization. B. what is good for the organization is always good for a functional area. C. what is best for a functional area may not be best for the organization. D. the "incremental" perspective may be best for functional areas while the "rational" perspective may be best for the organization. 37. (p. 9) 38. (p. 9) The four key attributes of strategic management include the idea that A. strategy must be directed toward overall organizational goals and objectives. B. strategy must be focused on long-term objectives. C. strategy must be focused on one specific area of an organization. D. strategy must focus on competitor strengths. The four key attributes of strategic management include all of the following EXCEPT: A. including multiple stakeholder interests in decision making. B. incorporating both short-term and long-term perspectives. C. recognizing the trade-offs between effectiveness and efficiency. D. emphasis on the attainment of short-term objectives. 39. (p. 10) "Effectiveness" is often defined as A. doing things right. B. stakeholder satisfaction. C. doing the right thing. D. productivity enhancement. 40. (p. 11) All of the following are ambidextrous behaviors EXCEPT: A. taking initiative and being alert to opportunities beyond the confines of one's own job. B. being cooperative and seeking opportunities to combine one's efforts with others. C. intensely focusing on one's own responsibilities and maximizing the output of one's department in an organization. D. being brokers, always looking to build internal linkages. 41. (p. 12) According to Henry Mintzberg, the realized strategies of a firm A. are a combination of deliberate and emergent strategies. B. are a combination of deliberate and differentiation strategies. C. must be based on a company's strategic plan. D. must be kept confidential for competitive reasons. 42. (p. 11-12) According to Henry Mintzberg, decisions following from a firm's strategic analysis are its A. emergent strategy. B. deliberate strategy. C. intended strategy. D. realized strategy. Topic: The Strategic Management Process 43. may be considered the "advance work" that must be done in order to effectively (p. 12) formulate and implement strategies. A. Goal setting B. Corporate entrepreneurship C. Strategy analysis D. Organizational design 44. involves ensuring proper strategic controls and organizational designs. (p. 14) A. Corporate governance B. Corporate-level strategy C. Strategy implementation D. Business-level strategy 45. 45. (p. 15) The three participants in corporate governance are A. the shareholders, board of directors, and employees. B. the shareholders, labor unions, and employees. C. the shareholders, board of directors, and management. D. the shareholders, banks and lending institutions, and management. 46. 46. (p. 15) While working to prioritize and fulfill their responsibilities, members of an organization's board of directors should A. represent their own interests. B. represent the interests of the shareholders. C. direct all actions of the CEO. D. emphasize the importance of short-term goals. 47. 47. (p. 15) Members of Boards of Directors are A. appointed by the Securities and Exchange Commission. B. elected by the shareholders as their representatives. C. elected by the public. D. only allowed to serve one term of four years. 48. 48. (p. 16) An organization is responsible to many different entities. In order to meet the demands of these groups, organizations must participate in stakeholder management. Stakeholder management means that A. interests of the stockholders are not the only interests that matter. B. stakeholders are second in importance to the stockholders. C. stakeholders and managers inevitably work at cross-purposes. D. all stakeholders receive financial rewards. 49. 49. (p. 17) Stakeholders are A. a new way to describe stockholders. B. individuals, groups, and organizations who have a stake in the success of the organization. C. creditors who hold a lien on the assets of the organization. D. attorneys and their clients who sue the organization. 50. 50. (p. 18) Outback Steakhouse has developed a sophisticated quantitative model and found that there were positive relationships between employee satisfaction, customer satisfaction, and financial results. According to the text, this is an example of A. zero-sum relationship among stakeholders. B. stakeholder symbiosis. C. rewarding stakeholders. D. emphasizing financial returns. 51. 51. (p. 17) There are several perspectives of competition. One perspective is zero-sum thinking. Zero-sum thinking means that A. all parts of the organization gain at no loss. B. in order for someone to gain others must experience no gain or benefit. C. one can only gain at the expense of someone else. D. everyone in the organization shares gains and losses equally. In the "zero-sum" view, the role of management is to look upon the various stakeholders as competing for the organization's resources. In essence, the gain of one individual or group is the loss of another individual or group. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 01 #51 Learning Objective: 01-03 The vital role of corporate governance and stakeholder management as well as how "symbiosis" can be achieved among an organizations stakeholders. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: The Role of Corporate Governance and Stakeholder Management 52. 52. (p. 18) Managers should do more than just focus on short-term financial performance. One concept that helps managers do this is stakeholder symbiosis. This means that A. stakeholders are dependent on each other for their success. B. stakeholders look out for their individual interests. C. one can only gain at the expense of someone else. D. all stakeholders want to maximize shareholder returns. Organizations can achieve mutual benefit through stakeholder symbiosis, which recognizes that stakeholders are dependent upon each other for their success and well-being. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 01 #52 Learning Objective: 01-03 The vital role of corporate governance and stakeholder management as well as how "symbiosis" can be achieved among an organizations stakeholders. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: The Role of Corporate Governance and Stakeholder Management 53. 53. (p. 18) Crowdsourcing can be defined as A. using surveys to get supplier input. B. using multiple sources for a firm's raw material inputs. C. tapping the latent talent of the online crowd. D. addressing strategic issues directly with managers and employees. In June 2006, Jeff Howe of Wired magazine defined crowdsourcing as the tapping of the "latent talent of the (online) crowd." AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 01 #53 Learning Objective: 01-03 The vital role of corporate governance and stakeholder management as well as how "symbiosis" can be achieved among an organizations stakeholders. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: The Role of Corporate Governance and Stakeholder Management 54. 54. (p. 21) 55. 55. (p. 23) 56. 56. (p. 24) Firms must be aware of goals other than short-term profit maximization. One area of concern should be social responsibility which is A. the expectation that business will strive to improve the overall welfare of society. B. the idea that organizations are solely responsible to local citizens. C. the fact that court costs could impact the financial bottom line. D. the idea that businesses are responsible to maintain a healthy social climate for their employees. Social responsibility is the expectation that businesses or individuals will strive to improve the overall welfare of society. From the perspective of a business, this means that managers must take active steps to make society better by virtue of the business being in existence. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 01 #54 Learning Objective: 01-04 The importance of social responsibility; including environmental sustainability; and how it can enhance a corporations innovation strategy. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: The Role of Corporate Governance and Stakeholder Management According to the text, the "triple bottom line" approach to corporate accounting includes three components: A. financial, environmental, and customer. B. financial, organizational, and customer. C. financial, environmental, and social. D. financial, organizational, and psychological. Many companies are now measuring what has been called a "triple bottom line." This involves assessing financial, social, and environmental performance. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 01 #55 Learning Objective: 01-04 The importance of social responsibility; including environmental sustainability; and how it can enhance a corporations innovation strategy. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: The Role of Corporate Governance and Stakeholder Management Many organizations have a large number of functional areas with very diverse, and sometimes competing, interests. Such organizations will be most effective if A. each functional area focuses on achieving their own goals. B. functional areas work together to attain overall goals. C. goals are defined at the bottom and implemented at the top. D. management and employees have separate goals. Strategic management requires managers to take an integrative view of the organization and assess how all of the functional areas and activities fit together to help an organization achieve its goals and objectives. This cannot be accomplished if only the top managers in the organization take an integrative, strategic perspective of issues facing the firm and everyone else "fends for themselves" in their independent, isolated functional areas. Instead, people throughout the organization must strive toward overall goals. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 01 #56 Learning Objective: 01-05 The need for greater empowerment throughout the organization. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: The Strategic Management Perspective: An Imperative throughout the Organization 57. 57. (p. 25) 58. 58. (p. 25) 59. 59. (p. 25) Strategy formulation and implementation is a challenging ongoing process. To be effective, it should involve A. the CEO and the board of directors. B. the board of directors, CEO, and CFO. C. line and staff managers. D. all of these. To develop and mobilize people and other assets, leaders are needed throughout the organization. No longer can organizations be effective if the top "does the thinking" and the rest of the organization "does the work." Everyone must be involved in the strategic management process. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 01 #57 Learning Objective: 01-05 The need for greater empowerment throughout the organization. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: The Strategic Management Perspective: An Imperative throughout the Organization The text argues that a strategic perspective in an organization should be emphasized A. at the top of the organization. B. at the middle of the organization. C. throughout the organization. D. from the bottom up. No longer can organizations be effective if the top "does the thinking" and the rest of the organization "does the work." Everyone must be involved in the strategic management process. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 01 #58 Learning Objective: 01-05 The need for greater empowerment throughout the organization. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: The Strategic Management Perspective: An Imperative throughout the Organization Peter Senge, of MIT, recognized three types of leaders. are individuals that, although having little positional power and formal authority, generate their power through the conviction and clarity of their ideas. A. Local line leaders B. Executive leaders C. Internal networkers D. Shop floor leaders Internal networkers, although they have little positional power and formal authority, generate their power through the conviction and clarity of their ideas. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 01 #59 Learning Objective: 01-05 The need for greater empowerment throughout the organization. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: The Strategic Management Perspective: An Imperative throughout the Organization 60. 60. (p. 25) 61. 61. (p. 25) 62. 62. (p. 26) Peter Senge, of MIT, recognized three types of leaders. champion and guide ideas, create a learning infrastructure, and establish a domain for taking action. A. Local line leaders B. Executive leaders C. Internal networkers D. Shop floor leaders Executive leaders champion and guide ideas, create a learning infrastructure, and establish a domain for taking action. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 01 #60 Learning Objective: 01-05 The need for greater empowerment throughout the organization. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: The Strategic Management Perspective: An Imperative throughout the Organization Leadership is a necessary (but not sufficient) condition for organizational success. Leaders should emerge at which level(s) of an organization? A. only at the top B. in the middle C. throughout the organization D. only during times of change To develop and mobilize people and other assets, leaders are needed throughout the organization. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 01 #61 Learning Objective: 01-05 The need for greater empowerment throughout the organization. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: The Strategic Management Perspective: An Imperative throughout the Organization The hierarchy of organizational goals is in this order (least specific to most specific): A. vision statements, strategic objectives, mission statements. B. mission statements, strategic objectives, vision statements. C. vision statements, mission statements, strategic objectives. D. mission statements, vision statements, strategic objectives. Organizations express priorities best through stated goals and objectives that form a hierarchy of goals, which includes its vision, mission, and strategic objectives. What visions may lack in specificity, they make up for in their ability to evoke powerful and compelling mental images. On the other hand, strategic objectives tend to be more specific and provide a more direct means of determining if the organization is moving toward broader, overall goals. Exhibit 1.6 depicts the hierarchy of goals and its relationship to two attributes: general versus specific and time horizon. Refer to Exhibit 1.6 AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 01 #62 Learning Objective: 01-06 How an awareness of a hierarchy of strategic goals can help an organization achieve coherence in its strategic direction. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Ensuring Coherence in Strategic Direction 63. 63. (p. 26) Vision statements are used to create a better understanding of the organization's overall purpose and direction. Vision statements A. are very specific. B. provide specific objectives. C. set organizational structure. D. evoke powerful and compelling mental images. A vision is an organizational goal(s) that evoke(s) powerful and compelling mental images. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 01 #63 Learning Objective: 01-06 How an awareness of a hierarchy of strategic goals can help an organization achieve coherence in its strategic direction. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Ensuring Coherence in Strategic Direction 64. 64. (p. 26) 65. 65. (p. 28) Effective vision statements include A. all strategic directions of the organization. B. a brief statement of the company's direction. C. strategic posturing and future objectives D. financial objectives and projected figures. A vision is a goal that is "massively inspiring, overarching, and long term." It represents a destination that is driven by and evokes passion. What visions may lack in specificity, they make up for in their ability to evoke powerful and compelling mental images. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 01 #64 Learning Objective: 01-06 How an awareness of a hierarchy of strategic goals can help an organization achieve coherence in its strategic direction. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Ensuring Coherence in Strategic Direction Examples of include: "To be the happiest place on earth" (Disneyland), and "Restoring patients to full life" (Medtronic). A. vision statements B. mission statements C. strategic objectives D. operational objectives One of the most famous examples of a vision is Disneyland's: "To be the happiest place on earth." Another example is "Restoring patients to full life." (Medtronic) AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 01 #65 Learning Objective: 01-06 How an awareness of a hierarchy of strategic goals can help an organization achieve coherence in its strategic direction. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Ensuring Coherence in Strategic Direction 66. 66. (p. 28-29) WellPoint Health Network states: "WellPoint will redefine our industry: through a new generation of consumer-friendly products that put individuals back in control of their future." This is an example of a A. strategic objective. B. vision statement. C. vague statement of direction. D. line manager's individual goal. Effective visions provide a fundamental statement of an organization's values, aspirations, and goals. Such visions go well beyond narrow financial objectives, of course, and strive to capture both the minds and hearts of employees. Refer to Exhibit 1.7 AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 01 #66 Learning Objective: 01-06 How an awareness of a hierarchy of strategic goals can help an organization achieve coherence in its strategic direction. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Ensuring Coherence in Strategic Direction 67. 67. (p. 29) 68. 68. (p. 30) In contrast to an organization's vision, its mission should A. be shorter in length. B. encompass both the purpose of the company as well as the basis of competition. C. encompass all the major rules and regulations of the corporate work force. D. be less detailed. A company's mission statement differs from its vision in that it encompasses both the purpose of the company as well as the basis of competition and competitive advantage. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 01 #67 Learning Objective: 01-06 How an awareness of a hierarchy of strategic goals can help an organization achieve coherence in its strategic direction. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Ensuring Coherence in Strategic Direction An organization's mission statement and vision statement set the overall direction of the organization. Strategic objectives A. operationalize the mission statement. B. modify the mission statement. C. are a shorter version of the mission statement. D. are only clarified by the board of directors. Strategic objectives are used to operationalize the mission statement. That is, they help to provide guidance on how the organization can fulfill or move toward the "higher goals" in the goal hierarchy—the mission and vision. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 01 #68 Learning Objective: 01-06 How an awareness of a hierarchy of strategic goals can help an organization achieve coherence in its strategic direction. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Ensuring Coherence in Strategic Direction 69. 69. (p. 31) 70. 70. (p. 30) 71. 71. (p. 30) Successful organizations are effective in motivating people. Employees work best when A. they are asked to "do their best." B. work requirements are vague and unclear. C. they are striving toward specific goals. D. they are guided by an abstract mission statement. Challenging objectives can help to motivate and inspire employees to higher levels of commitment and effort. Much research has supported the notion that people work harder when they are striving toward specific goals instead of being asked simply to "do their best." AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 01 #69 Learning Objective: 01-06 How an awareness of a hierarchy of strategic goals can help an organization achieve coherence in its strategic direction. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Ensuring Coherence in Strategic Direction Fortune Brands states they will "cut corporate overhead costs by $30 million a year." This is an example of a A. nonfinancial strategic objective. B. financial strategic objective. C. vision statement. D. mission statement. Exhibit 1.8 lists several firms' strategic objectives—both financial (like this one from Fortune Brands) and nonfinancial. Refer to Exhibit 1.8 AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 01 #70 Learning Objective: 01-06 How an awareness of a hierarchy of strategic goals can help an organization achieve coherence in its strategic direction. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Ensuring Coherence in Strategic Direction "We want to be the top-ranked supplier to our customers." (PPG) This is an example of a A. nonfinancial strategic objective. B. financial strategic objective. C. vision statement. D. mission statement. Exhibit 1.8 lists several firms' strategic objectives—both financial and nonfinancial (like this one from PPG). Refer to Exhibit 1.8 AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 01 #71 Learning Objective: 01-06 How an awareness of a hierarchy of strategic goals can help an organization achieve coherence in its strategic direction. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Ensuring Coherence in Strategic Direction 72. 72. (p. 32) 73. 73. (p. 12-15) In large organizations, conflicts can arise between functional areas. In order to resolve these conflicts, strategic objectives A. put financial objectives above human considerations. B. align departments toward departmental goals. C. help resolve conflicts through their common purpose. D. cause debate and increase conflict. There is always the potential for different parts of an organization to pursue their own goals rather than overall company goals. Although well intentioned, these may work at cross-purposes to the organization as a whole. Meaningful objectives thus help to resolve conflicts when they arise. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 01 #72 Learning Objective: 01-06 How an awareness of a hierarchy of strategic goals can help an organization achieve coherence in its strategic direction. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Ensuring Coherence in Strategic Direction The strategic management process includes strategy analysis, strategy formulation, and strategy implementation. Discuss each of these steps. Answers will vary. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 01 #73 Learning Objective: 01-02 The strategic management process and its three interrelated and principal activities. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: The Strategic Management Process 74. 74. (p. 15-16) Discuss the key elements of corporate governance. Answers will vary. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 01 #74 Learning Objective: 01-03 The vital role of corporate governance and stakeholder management as well as how "symbiosis" can be achieved among an organizations stakeholders. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: The Role of Corporate Governance and Stakeholder Management 75. 75. (p. 16-18) A firm has a variety of stakeholders. Identify several possible stakeholders a firm may have and discuss how the firm may achieve stakeholder symbiosis. Answers will vary. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 01 #75 Learning Objective: 01-03 The vital role of corporate governance and stakeholder management as well as how "symbiosis" can be achieved among an organizations stakeholders. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: The Role of Corporate Governance and Stakeholder Management 76. 76. (p. 24-26) Leadership is a topic that is often discussed in the management literature. The text suggests that leaders should be at all levels in an organization. Discuss why it is important to have leaders throughout an organization. Answers will vary. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Apply Dess - Chapter 01 #76 Learning Objective: 01-05 The need for greater empowerment throughout the organization. Level of Difficulty: 3 Hard Topic: The Strategic Management Perspective: An Imperative throughout the Organization 77. 77. (p. 26-29) 78. 78. (p. 26-32) 79. 79. (p. 30-32) 80. 80. (p. 30-32) According to the text, vision statements should be massively inspiring, overarching, and long term. Provide several examples of potential vision statements for various organizations and discuss how such vision statements would inspire employees around a cause. Answers will vary. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Apply Dess - Chapter 01 #77 Learning Objective: 01-06 How an awareness of a hierarchy of strategic goals can help an organization achieve coherence in its strategic direction. Level of Difficulty: 3 Hard Topic: Ensuring Coherence in Strategic Direction A mission statement encompasses the purpose of the company as well as the basis of competition and competitive advantage. Compare the purpose of a mission statement to that of a vision statement and a strategic objective. Answers will vary. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 01 #78 Learning Objective: 01-06 How an awareness of a hierarchy of strategic goals can help an organization achieve coherence in its strategic direction. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Ensuring Coherence in Strategic Direction Organizations must focus on financial and nonfinancial objectives. Select an organization and discuss possible financial and nonfinancial objectives the organization may have. Answers will vary. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Apply Dess - Chapter 01 #79 Learning Objective: 01-06 How an awareness of a hierarchy of strategic goals can help an organization achieve coherence in its strategic direction. Level of Difficulty: 3 Hard Topic: Ensuring Coherence in Strategic Direction The text discusses several characteristics of effective strategic objectives. List several of these and discuss why a firm's strategic objectives should meet these criteria. Answers will vary. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 01 #80 Learning Objective: 01-06 How an awareness of a hierarchy of strategic goals can help an organization achieve coherence in its strategic direction. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Ensuring Coherence in Strategic Direction Ch01 Summary Category # of Questions AACSB: Analytic 80 Blooms: Apply 3 Blooms: Remember 42 Blooms: Understand 35 Dess - Chapter 01 80 Learning Objective: 01-01 The definition of strategic management and its four key attributes. 13 Learning Objective: 01-02 The strategic management process and its three interrelated and principal activities. 11 Learning Objective: 01- 18 03 The vital role of corporate governance and stakeholder management as well as how "symbiosis" can be achieved among an orga nizations stakeholders. Learning Objective: 01- 5 04 The importance of social responsibility; including environmental sustainability; and how it can enhance a corporations innovati on strategy. Learning Objective: 01-05 The need for greater empowerment throughout the organization. 8 Learning Objective: 01- 25 06 How an awareness of a hierarchy of strategic goals can help an organization achieve coherence in its strategic direction. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy 41 Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium 36 Level of Difficulty: 3 Hard 3 Topic: Ensuring Coherence in Strategic Direction 25 Topic: The Role of Corporate Governance and Stakeholder Management 23 Topic: The Strategic Management Perspective: An Imperative throughout the Organization 8 Topic: The Strategic Management Process 11 Topic: What is Strategic Management? 13 Ch02 Student: 1. Environmental scanning and competitor intelligence provide important inputs for forecasting activities. True False 2. Environmental monitoring deals with tracking changes in environmental trends that are often uncovered during the environmental scanning process. True False 3. Competitor Intelligence (CI) is a tool that can provide management with "early warnings" about both threats and opportunities. True False 4. Competitive intelligence generally does not benefit very much from gathering information on competitors from sources in the public domain. True False 5. Even with all of the advances in recent years, forecasting is typically considered more of an art than a science and it is of little use in generating accurate predictions. True False 6. Scenario planning is usually concerned with short-term forecasts. True False 7. Although changes in the general environment may often adversely or favorably impact a firm, they seldom alter an entire industry. True False 8. The same environmental trend can often have very different effects on firms within the same industry. True False 9. A major sociocultural trend in the United States is the increased educational attainment by women. True False 10. Technological innovations can create entirely new industries and alter the boundaries of industries. True False 11. There is generally a weak relationship between equity markets (e.g., New York Stock Exchange) and economic indicators. True False 12. The Internet provides an electronic "staging area" for several forms of digital communications. True False 13. Porter's Five-Forces model is designed to help us understand how social attitudes and cultural values impact U.S. businesses. True False 14. Porter's Five-Forces model helps to determine both the nature of competition in an industry and the industry's profit potential. True False 15. In some industries, high switching costs can act as an important barrier to entry. True False 16. Industries characterized by high economies of scale typically attract fewer new entrants. True False 17. The power of a buyer group is increased if the buyer group has less concentration than the supplier group. True False 18. Buyer power tends to be higher if suppliers provide undifferentiated or standard products. True False 19. Supplier power tends to be highest in industries where products are vital to buyers, where switching from one supplier to another is very costly, and where there are many suppliers. True False 20. The power of suppliers will be enhanced if they are able to maintain a credible threat of forward integration. True False 21. The more attractive the price/performance ratio of substitute products, the more tightly it constraints an industry's ability to charge high prices. True False 22. Rivalry is most intense when there are high exit barriers and high industry growth. True False 23. Rivalry will be most intense when there is a lack of differentiation or switching costs. True False 24. In most industries, new entrants will be a bigger threat because the Internet lowers entry barriers. True False 25. The Internet and digital technologies suppress the bargaining power of buyers by providing them with more information to make buying decisions. True False 26. An end user's switching costs are potentially much higher because of the Internet. True False 27. Because of the Internet and digital technologies, it is very difficult for suppliers to create purchasing techniques that lower switching costs. True False 28. Reintermediation is responsible for an overall reduction in business opportunities. True False 29. The Internet heightens the threat of substitutes because it creates new ways to accomplish the same task. True False 30. Five-Forces analysis implicitly assumes a zero-sum game, a perspective that can be short-sighted. True False 31. Michael Porter's Five-Forces Analysis is a dynamic tool for analyzing industry attractiveness. True False 32. Complementary products are products that typically have a negative impact on the value of a firm's own products or services. True False 33. Competition tends to be more intense among firms within a strategic group than between strategic groups. True False 34. The same environmental trend or event may have a very different impact on different strategic groups within the same industry. True False 35. The use of the strategic groups concept is generally not helpful in charting the future directions of firms' strategies. True False 36. The strategic groups in the world-wide automobile industry have been very stable and unchanging in recent years. True False 37. Two of the key inputs to developing forecasts discussed in the text are A. environmental scanning and stakeholder identification. B. environmental scanning and competitor intelligence. C. assessing internal strengths and environmental scanning. D. environmental scanning and a SWOT analysis. 38. tracks the evolution of environmental trends, sequences of events, or streams of activities. A. Environmental scanning B. Environmental monitoring C. Environmental surveying D. Competitive intelligence 39. Scanning the general environment would identify information on A. substitute goods. B. the aging population and ethnic shifts. C. customer and firm bargaining power. D. competitive rivalry. 40. Gathering "competitive intelligence" A. is good business practice. B. is illegal. C. is considered unethical. D. minimizes the need to obtain information in the public domain. 41. Environmental forecasting involves developing plausible projections about the of environmental change. A. direction B. scope C. speed D. all of these 42. A danger of forecasting discussed in the text is that A. in most cases, the expense of collecting the necessary data exceeds the benefit. B. forecasting's retrospective nature provides little information about the future. C. managers may view uncertainty as "black and white" while ignoring important "gray areas." D. it can create legal problems for the firm if regulators discover the company is making forecasts. 43. The aging of the population, changes in ethnic composition, and effects of the baby boom are A. macroeconomic changes. B. demographic changes. C. global changes. D. sociocultural changes. 44. Increasingly larger numbers of women entering the work force since the early 1970s is an example of A. demographic changes. B. political and legal environmental changes. C. sociocultural changes. D. technological developments. 45. Emerging sociocultural changes in the environment include A. changes in the ethnic composition. B. the increasing educational attainment of women in the past decade. C. progressively less disposable income by consumers. D. changes in the geographic distribution of the population. 46. All of the following are important elements of the political/legal segment of the general environment EXCEPT A. the deregulation of utilities. B. the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). C. the increased use of Internet technology. D. increases in the federally mandated minimum wage. 47. Which of the following would be considered part of a firm's general environment? A. Decreased entry barriers. B. Higher unemployment rates. C. Increased bargaining power of the firm's suppliers. D. Increased competitive intensity. 48. Interest-rate increases have a impact on the residential home construction industry and a effect on industries that produce consumer necessities such as prescription drugs or basic grocery items. A. positive; negligible B. negative; negligible C. negative; positive D. positive; negative 49. To illustrate interrelationships among different segments of the general environment: The persistence of large U.S. trade deficits ( ) has led to greater demand for protectionist measures, such as trade barriers and quotas ( ). These measures lead to higher prices for U.S. consumers and fuel inflation ( ). A. macroeconomic, sociocultural, political/legal B. macroeconomic, political/legal, economic C. macroeconomic, technological, economic D. macroeconomic, global, economic 50. Which is considered a force in the "Five-Forces" model? A. Increased deregulation in an industry. B. The threat of government intervention. C. Rivalry among competing firms. D. Recent technological innovation. 51. Which of the following firms would likely pose the least competitive threat? A. A firm in the same industry and in the same strategic group. B. A firm that produces substitute goods to your product line. C. A competitor to your product where a high switching cost exists. D. A firm in the same industry and in the nearest strategic group looking to join your group. 52. The threat of new entrants is high when there are A. low economies of scale. B. high capital requirements. C. high switching costs. D. high differentiation among competitors' products and services. 53. Product differentiation by incumbents act as an entry barrier because A. new entrants cannot differentiate their products. B. incumbents will take legal action if new entrants do not differentiate their products. C. new entrants will have to spend heavily to overcome existing customer loyalties. D. it helps a firm to derive greater economies of scale. 54. Which of the following would be an entry barrier? A. large economies of scale B. low switching costs C. easy access to raw materials D. low capital requirements 55. A large fabricator of building components purchased a steel company to provide raw materials for its production process. This is an example of A. backward integration. B. economies of scale. C. forward integration. D. product differentiation. 56. The bargaining power of the buyer is greater than that of the supplier when A. volume of purchase is low. B. threat of backward integration by buyers is low. C. cost savings from the supplier's product are minimal. D. the buyer's profit margin is low. 57. Buyer power will be greater when A. the products purchased are highly differentiated. B. there are high switching costs. C. the industry's product is very important to the quality of the buyer's end products or services. D. it is concentrated or purchases large volumes relative to seller sales. 58. The bargaining power of suppliers increases as A. more suppliers enter the market. B. importance of buyers to supplier group increases. C. switching costs for buyers decrease. D. threat of forward integration by suppliers increases. 59. An independent group of suppliers, such as farmers, gather to form a cooperative to sell their products to buyers directly, replacing their former distributor. This is an example of A. threat of entry. B. backward integration. C. forward integration. D. threat of substitute products. 60. The bargaining power of suppliers is enhanced under the following market condition: A. no threat of forward integration. B. low differentiation of the suppliers' products. C. greater availability of substitute products. D. dominance by a few suppliers. 61. In Porter's Five-Forces model, conditions under which a supplier group can be powerful include all the following EXCEPT A. lack of importance of the buyer to the supplier group. B. high differentiation by the supplier. C. dominance by a few suppliers. D. readily available substitute products. 62. A supplier group would be most powerful when there is/are A. many suppliers. B. few substitute products. C. low differentiation of products supplied. D. high threat of backward integration by the buyers. 63. Threat of substitute products comes from A. other companies in the same industry. B. foreign companies which can use cheap labor in their countries. C. firms in other industries that produce products or services that satisfy the same customer need. D. all of these. 64. Firms would be most likely to face intense rivalry with competitors when they A. are in a high growth industry with low fixed costs. B. are in a protected market. C. have high fixed costs, in a slow growth industry with high exit barriers. D. have low exit barriers for easy transition to another industry. 65. The most intense rivalry results from A. numerous equally balanced competitors, slow industry growth, high fixed or storage costs. B. few competitors, slow industry growth, lack of differentiation, high fixed or storage costs. C. numerous equally balanced competitors, manufacturing capacity increases only in large increments, low exit barriers. D. a high level of differentiation. 66. Exit barriers arise from A. specialized assets with no alternative use. B. governmental and social pressures. C. strategic interrelationships with other business units within the same company. D. all of these. 67. Because the Internet lowers barriers to entry in most industries, it A. decreases the threat of new entrants. B. increases the threat of new entrants. C. makes it easier to build customer loyalty. D. increases supplier power. 68. End users are A. the final consumers in a distribution channel. B. usually the C in B2C. C. likely to have greater bargaining power because of the Internet. D. all of these. 69. Incumbent firms may enjoy increased bargaining power because the Internet A. focuses marketing efforts on end users. B. diminishes the power of many distribution channel intermediaries. C. increases channel conflict. D. has reduced the number of wholesalers and distributors. 70. Supplier power has increased because of the Internet for all of the following reasons EXCEPT A. the growth of new Web-based businesses has created more outlets for suppliers to sell to. B. some suppliers have created Web-based purchasing systems that encourage switching. C. the process of disintermediation makes it possible for some suppliers to reach end users directly. D. software that links buyers to a supplier's website has created rapid, low-cost order capabilities. 71. In general, the threat of substitutes is heightened because the Internet A. introduces new ways to accomplish the same task. B. lowers switching costs. C. lowers barriers to entry. D. increases output per unit of cost. 72. How do infomediaries and consumer information websites increase the intensity of competitive rivalry? A. by shifting customers away from issues of price B. by making competitors in cyberspace seem less equally balanced Cby consolidating the marketing message that consumers use to make a purchase decision to a few key . pieces of information that the selling company has little control over D. by highlighting a firm's unique selling advantages 73. The value net is a game-theoretic approach that A. extends the value chain analysis. B is a way to analyze all the players in a game and analyze how their interactions affect a firm's ability to . generate and appropriate value. C. helps us to understand the evolution of the five forces over time. D. uses network analysis to understand the relationships among different companies. 74. In the value net analysis, complementors are A. firms that produce substitute products. B. customers who compliment the company for their good products and services. C. firms that produce products or services that have a positive impact on the value of a firm's products or services. D. firms that supply critical inputs to a company. 75. Strategic groups consist of A. a group of top executives who make strategies for a company. B. a group of firms within an industry that follow similar strategies. C. a group of executives drawn from different companies within an industry that makes decisions on industry standards. D a group of firms within an industry that decide to collude rather than compete with each other so that . they can increase their profits. 76. Which of the following statements about strategic groups is FALSE? A. Two assumptions are made: (1) no two firms are totally different, (2) no two firms are exactly the same. B. Strategic groupings are of little help to a firm in assessing mobility barriers that protect a group from attacks by other groups. C. Strategic groups help chart the future directions of firms' strategies. D. Strategic groups are helpful in thinking through the implications of each industry trend for the group as a whole. 77. Explain how competitor intelligence can be improved by gathering information about competitors in the public domain. Provide examples. 78. Discuss some of the limitations of forecasting. 79. Discuss the six segments of the general environment. Provide examples of how they might be related. 80. Explain the important barriers to entry in an industry. Provide examples. 81. Discuss and provide examples of factors that would lead to greater buyer power. 82. What are some of the factors that would cause a supplier group to become powerful? Illustrate. 83. Several factors usually interact which result in intense rivalry among competitors. Explain. 84. Address how Internet and digital technologies affect Porter's five-forces. 85. Explain how the value net analysis adds to the Five-Forces analysis. Be sure to include examples from at least two industries. 86. What value is the strategic groups concept as a tool in analyzing an industry? Ch02 Summary Category # of Questions AACSB: Analytic 86 Blooms: Apply 4 Blooms: Remember 26 Blooms: Understand 56 Dess - Chapter 02 86 Learning Objective: 02-01 The importance of developing forecasts of the business environment. 2 Learning Objective: 02- 02 Why environmental scanning; environmental monitoring; and collecting competitive intelligence are critical inputs to forecastin g. 10 Learning Objective: 02- 03 Why scenario planning is a useful technique for firms competing in industries characterized by unpredictability and change. 2 Learning Objective: 02-04 The impact of the general environment on a firms strategies and performance. 14 Learning Objective: 02- 05 How forces in the competitive environment can affect profitability; and how a firm can improve its competitive position by incr easing its power vis-à-vis these forces. 32 Learning Objective: 02- 06 How the Internet and digitally based capabilities are affecting the five competitive forces and industry profitability. 19 Learning Objective: 02-07 The concept of strategic groups and their strategy and performance implications. 7 Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy 26 Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium 56 Level of Difficulty: 3 Hard 4 Topic: Creating the Environmentally Aware Organization 14 Topic: The Competitive Environment 58 Topic: The General Environment 14 Ch03 Student: 1. One advantage of SWOT analysis is that it helps managers to identify strengths that are almost always sources of competitive advantages that are sustainable. True False 2. Value-chain analysis assumes that a firm's basic economic purpose is to create value and it is a useful framework for analyzing a firm's strengths and weaknesses. True False 3. In value-chain analysis, value is measured by the market value of the total stock outstanding of the company. True False 4. Primary activities contribute to the physical creation of a product or service, its sale and transfer to the buyer, and its service after the sale. True False 5. The value-chain concept assumes that both primary and support activities are capable of producing value for customers. True False 6. Inbound logistics include all activities associated with transforming inputs into the final product form such as machining, packaging, assembly, equipment, testing, printing, and facility operations. True False 7. Support activities provide support for primary activities, but not each other. True False 8. Establishing a customer service hotline to handle customer complaints would be considered a primary activity in value-chain analysis. True False 9. Technology development is a much broader concept than research and development. True False 10. In value-chain analysis, finance and accounting are considered part of a firm's general administration. True False 11. Managers should focus their attention on interrelationships among value-chain activities within the firm, NOT on relationships among activities within the firm and other organizations (such as suppliers and customers). True False 12. Some leading edge companies are applying the "prosumer" concept. Here, firms team up with their suppliers and alliance partners to satisfy their customers' needs. True False 13. Value-chain analysis can only be applied to manufacturing operations. True False 14. The resource-based view of the firm focuses solely on the internal analysis of a firm's operations and competencies. 15. Tangible resources are assets that are relatively easy to identify such as financial and physical assets. True False 16. A firm's intangible resources refer to its capacity to deploy tangible resources over time and leverage those resources effectively. True False 17. Products and services that are difficult to imitate help firms sustain their profitability. True False 18. Path dependency has no impact on the inimitability of resources. True False 19. Capabilities that exhibit causal ambiguity are difficult to imitate. True False 20. For a resource to provide a firm with potential sustainable advantages it must satisfy only two criteria: rareness and difficulty in substitution. True False 21. Firms that are successful in creating competitive advantages that are sustainable for a period of time do not have to be concerned about profits being retained (or "appropriated") by employees or managers. True False 22. Employee exit cost is a factor that can increase an employee's bargaining and help him or her appropriate a firm's profits. True False 23. Financial analysis provides an accurate way to assess the relative strengths of firms and can be used as a complete guide to study companies. True False 24. Leverage ratios provide measures of a firm's capacity to meet its long-term financial obligations. True False 25. Historical comparisons are most appropriate during periods of recession or economic boom. True False 26. When using industry norms as a standard of comparison, managers must be sure that the firms used in the comparisons are representative of all sizes and strategies within the industry. True False 27. A primary benefit of the "balanced scorecard" is that it complements financial indicators with operational measures of customer satisfaction, internal processes, and the organization's innovation and improvement activities. True False 28. The balanced scorecard enables managers to evaluate their business from only two perspectives: customer and financial. True False 29. An important implication of the balanced scorecard is that managers need NOT look at their job as primarily balancing stakeholder demands. True False 30. One strength of the balanced scorecard is that it is very easy to implement and that there is little need for executive sponsorship. 31. Evaluation activities add value by helping firms finalize transactions including negotiating contracts, making payments, and taking delivery. True False 32. Content such as entertainment programming does little to improve the value proposition of a website. True False 33. Business models can be defined as methods companies use to create value and earn profits in a competitive environment. True False 34. A commission-based business model, when applied to the Internet, is similar to the broadcast television model in which viewers watch shows produced with revenues from commission fees. True False 35. Which of the following is NOT a limitation of SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunity, Threats) analysis? A. Organizational strengths may not lead to competitive advantage. B. SWOT's focus on the external environment is too broad and integrative. C. SWOT gives a one-shot view of a moving target. D. SWOT overemphasizes a single dimension of strategy. 36. In value-chain analysis, the activities of an organization are divided into two major categories of value activities: primary and support. Which of the following is a primary activity? A. Purchasing key inputs. B. Recruiting and training employees. C. Repairing the product for the consumer. D. Monitoring the cost of producing the product through a cost accounting system. 37. Inbound logistics include A. machining and packaging. B. warehousing and inventory control. C. repair and parts supply. D. promotion and packaging. 38. In assessing its primary activities, an airline would examine A. employee training programs. B. baggage handling. C. criteria for lease versus purchase decisions. D. the effectiveness of its lobbying activities. 39. Advertising is a activity. Supply of replacement parts is a activity. A. primary; primary B. support; primary C. support; secondary D. primary; support 40. Which of the following examples demonstrates how successful organizations manage their primary activities? A. By employing JIT inventory systems, Hewlett Packard has been able to cut lead time from five days to one. B. Motorola has revised its compensation system to reward employees who learn a variety of skills. C National Steel improved its efficiency by consolidating, reducing the number of job classifications, and . broadening worker responsibilities. D Walmart implemented a sophisticated information system that resulted in reduced inventory carrying . costs and shortened customer response time. 41. Which of the following is not an advantage of Just-In-Time inventory systems? A. Reduced raw material storage costs. B. Minimized idle production facilities and workers. C. Reduced work-in-process inventories. D. Reduced dependence on suppliers. 42. XYZ Corp. is focusing on the objective of low-cost, high quality, on-time production by minimizing idle productive facilities and workers. The XYZ Corp. is taking advantage of a system. A. Last In, First Out (LIFO) B. Just-in-time (JIT) C. First In, First Out (FIFO) D. Highly mechanized 43. is/are associated with collecting, storing, and distributing the product or service to buyers. They consist of warehousing, material handling, delivery operation, order processing, and scheduling. A. Services B. Inbound logistics C. Outbound logistics D. Operations 44. Customer service would include A. product promotion. B. product distribution. C. parts supply. D. procurement of critical supplies. 45. Which of the following is a support activity? A. Inbound logistics. B. Operations. C. Technology development. D. Customer service. 46. Which of the following lists consists of support activities? A. Human resource management, technology development, customer service, and procurement. B. Human resource management, customer service, marketing and sales, and operations. C. Human resource management, technology development, procurement, and firm infrastructure. D. Customer service, information systems, technology development, and procurement. 47. Human resource management consists of activities involved in recruiting, hiring, training, development, and compensation of all types of personnel. It A. supports only individual primary activities. B. supports only individual support activities. C. supports both individual primary and support activities and the entire value chain. D. supports mostly support activities but does have some impact on primary activities. 48. According to value-chain analysis, which of the following would be considered part of a firm's general administration? A. Human resource management. B. Information systems. C. Technology development. D. Procurement. 49. Although general administration is often viewed only as overhead expense, it can become a source of competitive advantage. Examples include all of the following EXCEPT A. negotiating and maintaining ongoing relations with regulatory bodies. B. effective information systems contributing significantly to a firm's overall cost leadership strategy. C. marketing expertise increasing a firm's revenues and enabling it to enter new markets. D. top management providing a key role in collaborating with important customers. 50. For firm's such as Walgreen Co. (a chain of drugstores), information systems have been a source of competitive advantage by enabling them to A. differentiate service. B. automate some operations. C. respond to consumer needs. D. all of these. 51. A marketing department that promises delivery faster than the production department's ability to produce is an example of a lack of understanding of the A. interrelationships among functional areas and firm strategies. B. need to maintain the reputation of the company. C. organizational culture and leadership. D. synergy of the business units. 52. The resource-based view (RBV) of the firm combines two perspectives: A. the primary and support activities of the firm. B. the interrelationships among the primary activities of the firm and corporate management. C. the internal analysis of the firm as well as the external analysis of the industry and competitive environment. D. the industry and the competitive environment. 53. The three key types of resources that are central to the resource-based view of the firm's are A. tangible resources, intangible resources, and organizational structure. B. culture, tangible resources, intangible resources. C. tangible resources, intangible resources, and organizational capabilities. D. tangible resources, intangible resources, and top management. 54. Examples of tangible resources (in the resource-based view of the firm) include: A. financial resources, human resources, and firm competencies. B. financial resources, physical resources, and the capacity to combine intangible resources. C. financial resources, physical resources, and technological resources. D. outstanding customer service, innovativeness of products, and reputation. 55. are typically embedded in unique routines and practices that have evolved and accumulated over time - such as trust and effective work teams. A. Tangible resources B. Intangible resources C. Reputational resources D. Organizational capabilities 56. Gillette combines several technologies (e.g., metallurgy, physiology, physics) to attain unparalleled success in the wet shaving industry. This is an example of their A. tangible resources. B. intangible resources. C. organizational capabilities. D. strong primary activities. 57. are the competencies or skills that a firm employs to transform inputs into outputs. A. Tangible resources B. Intangible resources C. Reputational resources D. Organizational capabilities 58. For a resource to provide a firm with the potential for a sustainable competitive advantage, it must have four attributes. Which of the following is not one of these attributes? A. Rare. B. Easy for competitors to substitute. C. Valuable. D. Difficult for competitors to imitate. 59. A competitive advantage based on inimitability can be sustained for at least some time if it has the following characteristics: A. physical uniqueness, path dependency, causal ambiguity, and social complexity. B. psychographic uniqueness, path dependency, causal ambiguity, and substitutability. C. rarity, path dependency, causal ambiguity, and social substitutability. D. geographic uniqueness, cause dependency, social ambiguity, and path complexity. 60. A crash R&D program by one firm cannot replicate a successful technology developed by another firm when research findings cumulate. This is an example of A. social complexity. B. path dependency. C. physical uniqueness. D. causal ambiguity. 61. A variety of firm's resources include interpersonal relations among managers in the firm, its culture, and its reputation with its suppliers and customers. Such competitive advantages are based upon A. social complexity. B. path dependency. C. physical uniqueness. D. tangible resources. 62. The following are examples of socially complex organizational phenomena EXCEPT A. a firm's culture. B. interpersonal relations among a firm's managers. C. complex physical technology. D. leadership and trust. 63. A resource is valuable and rare but neither difficult to imitate nor without substitutes. This should enable the firm to attain A. no competitive advantage. B. competitive parity. C. a temporary competitive advantage. D. a sustainable competitive advantage. 64. Employees will be able to obtain a proportionately high level of profits they generate (relative to the firm) if A. suppliers are loyal to the firm. B. the cost to the firm of replacing them is high. C. their expertise is firm-specific. D. the firm's resources are path dependent. 65. Historical comparisons provide information to managers about changes in a firm's competitive position. Historical comparisons are often misleading A. if the overall strategy of the firm is the same. B. in periods of recession or economic boom. C. if the firm shows constant growth. D. if the firm's stock is publicly traded. 66. The best measure of a company's ability to meet imminent financial obligations is known as the A. current ratio. B. total asset turnover. C. debt ratio. D. profit margin. 67. Which of the following would be most difficult to assess? A. The liquidity position of a firm. B. The legitimacy and reputation of a firm. C. Market share growth. D. The efficiency with which a firm utilizes its assets. 68. Which of these categories of financial ratios is used to measure a company's ability to meet its short-term financial obligations? A. Leverage ratios. B. Profitability ratios. C. Activity ratios. D. Liquidity ratios. 69. Ratios that reflect whether or not a firm is efficiently using its resources are known as A. turnover ratios. B. leverage ratios. C. liquidity ratios. D. profitability ratios. 70. The "balanced scorecard" provides top managers with a view of the business. A. detailed and complex B. fast but comprehensive C. simple and routine D. long-term financial 71. The "balanced scorecard" developed by Kaplan and Norton helps to integrate A. financial analysis and a firm's reputation. B. intangible resources and operational measures. C. financial analysis and stakeholder perspectives. D. short-term perspectives and strategic positioning. 72. The balanced scorecard enables managers to consider their business from all of the following perspectives EXCEPT A. customer perspective. B. internal perspective. C. innovation and learning perspective. D. ethical perspective. 73. An important implication of the "balanced scorecard" approach is that Amanagers need to recognize tradeoffs in stakeholder demands and realize that such demands represent . a "zero-sum" game in which one stakeholder will gain only at another's loss. B. the key emphasis on customer satisfaction and financial goals are only a means to that end. Cmanagers should not look at their job as primarily balancing stakeholder demands; increasing . satisfaction among multiple stakeholders can be achieved simultaneously. D. gains in financial performance and customer satisfaction must often come at a cost of employee satisfaction. 74. Four Internet-based activities that are enhancing firms' capabilities to use the Internet to add value include A. outsourcing, problem-solving, bill-paying, and delivery. B. evaluating, bill-paying, customizing, and returning. C. search, rescue, repair, return. D. search, evaluation, problem-solving, and transaction. 75. Internet search activities include A. generating action plans. B. considering alternatives. C. gathering information. D. making payments and taking delivery. 76. The value-adding activity known as problem-solving A. involves streamlining operations. B. is typically used in the context of providing unique services. C. refers to comparing the costs and benefits of various options. D. creates access to products ratings and price comparisons. 77. Unique content will not add value to an Internet website under the following condition(s): A. the cost of developing the content exceeds the benefits gained. B. visitors to the website do not value or use the content. C. the content is unreliable. D. all of these. 78. Examples of value-adding content often found on websites include all of the following except A. customer feedback. B. advertising. C. expertise. D. entertainment programming. 79. Internet business models A. outline methods that online businesses use to create value. B. cannot be used by traditional businesses. C. outline specific actions a firm needs to take to be profitable. D. cannot be combined to create additional competitive advantages. 80. All of the following are examples of Internet business models EXCEPT A. referral-based model. B. subscription-based model. C. prescription-based model. D. production-based model. 81. What are some of the key strengths and limitations of SWOT analysis? 82. What are the key advantages of value-chain analysis over SWOT analysis? 83. What are some ways in which a firm's general administration can help create (or enhance) competitive advantages? 84. How can a firm develop (or enhance) its advantages in the marketplace by having strong, positive interrelationships among its value chain activities and those of its suppliers and customers? Provide an example. 85. The resource-based view (RBV) combines both the internal analysis of the firm and the external analysis of the environment. Discuss and provide examples. 86. Explain the four attributes that a resource must have to provide a firm with a sustainable competitive advantage. 87. What are the benefits and limitations of making historical comparisons in analyzing a firm's performance? 88. What are the four perspectives that the "balanced scorecard" enables managers to evaluate their business? 89. What are some of the most important implications of using the "balanced scorecard" approach? 90. Address some of the limitations and potential downsides of the balanced scorecard. 91. Briefly explain the role of search, evaluation, problem-solving and transaction activities in helping firms use the Internet to add value. Provide examples of companies that exhibit each of these value-adding activities. 92. Discuss the function of a business model and its role, if any, in creating competitive advantages. Provide examples of companies that illustrate each of the seven Internet business models—commission, advertising, and Digital Technologies Add Value Ch03 Summary Category # of Questions AACSB: Analytic 92 Blooms: Apply 4 Blooms: Remember 33 Blooms: Understand 55 Dess - Chapter 03 92 Learning Objective: 03-01 The benefits and limitations of SWOT analysis in conducting an internal analysis of the firm. 10 Learning Objective: 03-02 The primary and support activities of a firms value chain. 19 Learning Objective: 03-03 How value- 5 chain analysis can help managers create value by investigating relationships among activities within the firm and between the firm and its customers and suppliers. Learning Objective: 03-04 The resource- 10 based view of the firm and the different types of tangible and intangible resources; as well as organizational capabilities. Learning Objective: 03- 14 05 The four criteria that a firms resources must possess to maintain a sustainable advantage and how value created can be appropri ated by employees and managers. Learning Objective: 03- 10 06 The usefulness of financial ratio analysis; its inherent limitations; and how to make meaningful comparisons of performance acr oss firms. Learning Objective: 03- 11 07 The value of the "balanced scorecard" in recognizing how the interests of a variety of stakeholders can be interrelated. Learning Objective: 03-08 How firms are using Internet technologies to add value and achieve unique advantages. (Appendix) 13 Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy 33 Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium 55 Level of Difficulty: 3 Hard 4 Topic: Evaluating Firm Performance: Two Approaches 21 Topic: How the Internet and Digital Technologies Add Value 13 Topic: The Resource-Based View of the Firm 24 Topic: Value-Chain Analysis 34 Ch04 Student: 1. According to the text, for most of the twentieth century, managerial efforts were directed more toward the efficient allocation of labor and capital - the two traditional factors of production. True False 2. The importance of human capital has decreased in recent years. For this reason, many firms have placed greater attention on attracting, but not on developing or retaining talent. True False 3. The more reliance a firm has on intellectual capital, the closer its book value will be to its market value. True False 4. The difference between the market value and book value of a firm is its social capital. True False 5. In today's economy, reliance on the three traditional financial statements: income statement, balance sheet, and statement of cash flow, has increased. True False 6. Firms such as Oracle, Google, and Genentech will tend to have a higher ratio of market value to book value than "industrial companies" such as International Paper and Nucor Steel. True False 7. Creation of new knowledge typically involves the continual interaction of explicit and tacit knowledge. True False 8. Knowledge workers are more loyal to their companies than traditional workers. True False 9. Technical skills are a necessary and sufficient condition for hiring an employee. True False 10. One of the most important elements in a good employee is his or her attitude. Firms should follow the adage "hire for attitude, train for skill." True False 11. Companies have found that referrals from their own employees are generally an ineffective approach to recruiting top talent. True False 12. Many leading companies look for creativity and flexibility in problem solving during the interview process. This helps a firm assess a potential employee's social capital. True False 13. In most effective evaluation and reward systems employees only receive evaluation and feedback from their immediate supervisor. True False 14. 360-degree evaluation and feedback systems address many of the limitations of traditional approaches of evaluating human capital. True False 15. 360-degree evaluation systems are not useful due to the need to integrate large amounts of feedback. True False 16. The most effective method of improving a firm's retention of top talent is to intensify its hiring efforts. True False 17. An internal labor market (to increase an employee's mobility within a firm) is one means of increasing employee retention. True False 18. The text suggests that talented professionals are typically most concerned about financial rewards. Money is the top reason why such employees take and leave jobs. True False 19. Workforces, which reflect demographic changes, will become more homogeneous (or less varied) over the next few decades with regard to gender, race, ethnicity, and nationality. True False 20. Social capital is based on the network of relationships within a firm, not in the skills and abilities of an individual employee. True False 21. Social capital is found in the knowledge, skills, and abilities of individual employees. True False 22. Developing social capital is risky for an organization because social capital is specific to individuals and remains with the employee if he or she leaves the organization. True False 23. Social network analysis can be used to help identify groups or clusters of individuals that comprise the network, individuals who link the clusters, and other network members. True False 24. Developing and protecting social capital requires independence—that is, individuals must spend most of their time working individually. True False 25. In social networks, in bridging relationships, one member is central to the communication flows in a group. True False 26. Closure, in contrast to bridging relationships, stresses the importance of ties connecting heterogeneous people. True False 27. From an individual's perspective, social networks deliver three unique advantages: private information, access to diverse skill sets, and power. True False 28. One potential downside of building social capital in an organization is "groupthink." This means everyone in the group thinks on his or her own and comes up with new ideas. True False 29. The role of technology in the recruitment of human capital has lowered individuals' reliance on the use of social networks. True False 30. The use of e-mail can be distracting to employees. Some firms limit the time that employees spend using e-mail. True False 31. Since electronic teams (e-teams) seldom meet face-to-face, it is NOT important for them to be concerned with how to combine individual contributions effectively. True False 32. Once a knowledge asset (e.g., software) is developed and paid for, it can be used many times at very low cost as long as it doesn't have to be substantially modified each time. True False 33. According to the text, effective e-teams identified group members with a proper balance of technical and interpersonal skills. True False 34. Explicit knowledge is generally known to everyone in the firm and is not a critical concern of management. True False 35. Intellectual property rights are easier to define and protect than property rights for physical assets (e.g., plant and equipment). True False 36. The makeup of goods and services in the Gross Domestic Products of developed countries has changed over the last decade. More than 50% of the value of GDP of developed countries is based on A. clothing and apparel. B. capital accumulation. C. financial management. D. knowledge. 37. As the competitive environment changes, strategic management must focus on different aspects of the organization. Recently, strategic management has moved from focusing on A. intangible resources to tangible resources. B. tangible resources to intangible resources. C. working capital to fixed capital. D. fixed capital to working capital. 38. Changes in our economy have forced firms to be more concerned with protecting their A. knowledge workers. B. social capital. C. intellectual capital. D. all of these. 39. In the knowledge economy, if a large portion of a firm's value is in intellectual and human assets, the difference between the company's market value and book value should a company with mostly physical and financial assets. A. be equal to B. be smaller than C. be larger than D. not be correlated with 40. According to the text, intellectual capital is the difference between the market value and the book value of a firm. Intellectual capital can be increased by A. increasing retention of below average workers. B. attracting and retaining knowledgeable workers. C. decreasing labor costs. D. increasing the turnover of employees. 41. Which of the following firms would you expect to have the highest ratio of market value to book value? A. Union Pacific (railroad) B. Google C. International Paper D. Nucor (steel) 42. Human capital includes A. an individual's capabilities, knowledge, and skills. B. the relationships between people. C. the output from assembly line employees. D. an improved product. 43. includes creativity and problem solving ability. A. Physical capital B. Human capital C. Social capital D. Emotional capital 44. can be defined as the "network of relationships that individuals have throughout the organization." A. Human capital B. Social capital C. Intellectual capital D. Tacit knowledge 45. Tacit knowledge A. is the same as explicit knowledge. B. is found mostly at the lower levels of the organization. C. can be codified but not reproduced. D. can be accessed only with the consent of the employees because it is in the minds of the employees. 46. New knowledge involves the continual interaction between and knowledge. A. intellectual; pragmatic B. theoretical; practical C. tacit; explicit D. detailed; tacit 47. Recently, a knowledge worker's loyalty to his or her employing firm has compared to his or her loyalty to his or her profession and colleagues. A. increased B. decreased C. remained the same D. no correlation when 48. The text discusses three areas a firm must be concerned with in order to keep their best and brightest employees from leaving. These include all of the following EXCEPT A. hiring/selecting. B. sorting/absorbing. C. developing. D. retaining. 49. Managing a knowledge intensive workforce is very challenging. The best way for a firm to manage its workforce is to A. retain knowledge workers. B. attract the brightest employees. C. balance efforts in the attraction, selection, and retention of top talent. D. ensure that it pays higher salaries than its rivals. 50. Firms must compete for top talent. When attracting and selecting employees, firms must strive to select the best fit for both the employee and the firm. In an effort to reduce wasted time and effort in interviewing too many candidates while assuring a good candidate pool, a firm should A. run employment ads in the newspaper. B. use a pre-interview quiz or "bozo filter" (e.g., Cooper Software). C. only let lower level employees interview job candidates. D. refrain from hiring by referrals from present employees. 51. Many companies use referrals by current employees as a source for new hiring and even monetarily reward them for the following reasons: A. it is less expensive than the fees paid to headhunters. B. current employees are normally very careful in recommending someone because their credibility is on the line. C. it is a good test of employee loyalty. Dboth because current employees are careful in their recommendations because of their credibility and . also because it is less expensive than the fees paid to headhunters. 52. ABC, Incorporated desires to have the most qualified people in every position throughout its organization. This is an example of a concern for A. developing human capital. B. developing social networks. C. decreasing labor intensive training. D. leveraging organizational structure. 53. Developing human capital is essential to maintaining a competitive advantage in today's knowledge economy. Efforts and initiatives to develop human capital should be directed A. at top managers. B. at human resource departments. C. at the employees themselves. D. throughout the firm at all levels. 54. Maintaining a competitive workforce is very challenging in today's economy. The role of evaluating human capital, in recent years, has A. increased. B. decreased. C. become less important. D. remained the same. 55. In a 360-degree evaluation and feedback system, rate a person's skill and performance. A. superiors B. direct reports C. colleagues D. all of these 56. Attracting and retaining human capital is a challenge for many firms today. Firms experiencing high turnover should A. focus on increased recruiting. B. decrease money spent on human capital. C. make their work environment less stimulating. D. adopt effective retention strategies. 57. In order to take advantage of investment in human capital, a firm should A. rotate workers through functions in the company as quickly as possible. B. refrain from training individual employees. C. establish practices that will enhance employee retention. D. none of these. 58. The least effective way to retain human capital is A. encouraging employee identification with organizational mission and goals. B. requiring employees to sign agreements that prevent them from working for competitors in the future. C. providing employees with a challenging and stimulating work environment. D. providing employees with financial and nonfinancial rewards and incentives. 59. Generally, employees are most likely to stay with an organization if A. the employer provides high salaries to technology professionals. B. the organization's mission and values align with the employee's mission and values. C. the firm is in a high tech industry. D. the mission and values of the organization change often. 60. Many successful firms use internal labor markets. The most important reason they do this is because A. they want to encourage job rotation. B. if an employee is in the same department for too long, he/she would become indispensable. C. they want to keep highly mobile employees motivated and challenged. D. an employee who moves too much can be identified as unreliable and eliminated. 61. All of the following are the benefits of diversity in a firm's workforce except: A. Creativity Argument. B. Problem-Solving Argument. C. Resource Acquisition Argument. D. Similarity in Perspectives Argument. 62. Human capital and social capital are vital for superior firm performance. If a firm has strong human capital, the firm may exploit this by building social capital. This can be accomplished through A. requiring workers to work independently of each other. B. decreasing the interaction of departments within the firm. C. encouraging the sharing of ideas between employees in the firm. D. structuring the firm with rigid departmental and employee divisions. 63. In an effort to capture key employees from competitors, firms may attract the symbolic leader of a group within a competing firm and hope others will follow. This has been termed A. the "Columbus effect." B. the "Pied Piper effect." C. strategically competitive hiring. D. knowledge integration. 64. Social capital is a source of strength to many firms. Firms leverage their social capital in an effort to create competitive advantages. A firm's social capital is based on A. an employee's individual abilities. B. the relationships among a firm's employees. C. a firm's allocation of financial resources. D. an individual's knowledge. 65. Social network analysis is helpful because the configuration of group members' social ties within and outside the group affects the extent to which members connect to individuals who do all of the following EXCEPT: A. convey needed resources. B. ensure that everyone has the same perspective on strategic and operational issues. C. have the opportunity to exchange information and support. D. have the motivation to treat each other in positive ways. 66. In social network analysis stress(es) the importance of ties connecting heterogeneous people, helping to ensure a wide range of diversity in information and perspective. A. closure B. redundancy C. bridging relationships D. social supports 67. In social network analysis, high levels of often come at a price. For example, groups can become too insular and fail to share what they have learned with people outside the group. A. bridging relationships B. intellect C. closure D. diverse knowledge 68. Advantages of effective social networks for career success include all of the following EXCEPT A. access to private information. B. access to diverse skill sets. C. greater power. D. greater redundancy in knowledge sources. 69. Among the downsides of social capital is/are: A. high social capital may breed "groupthink," i.e., a tendency not to question shared beliefs. B. socialization processes whereby individuals are socialized into the norms and values of the organization may become expensive. C. individuals may become less willing to collaborate on joint projects. D social capital may both breed "groupthink" and the socialization processes to create it (orientation, . training, etc.) can be expensive. 70. Social capital has many potential benefits. However, according to the text, social capital A. is always beneficial to a firm. B. may or may not be beneficial to a firm. C. usually restricts the productivity of employees. D. always hurts firm performance. 71. The use of information technology (e.g., e-mail) has increased in recent years in many organizations. This has helped to A. communicate information efficiently. B. make more effective use of time in every situation. C. restrict social network growth. D. create smaller social networks. 72. The creation of knowledge assets is typically characterized by A. high upfront costs and subsequent high variable costs. B. high fixed costs and high variable costs. C. low upfront costs and high variable costs. D. high upfront costs and low variable costs. 73. Mary Stinson was required to take over a project after the entire team left the company. She was able to reconstruct what the team had accomplished through reading e-mails exchanged by the previous team's members. This is an example of A. using explicit knowledge. B. inefficient use of information management. C. using tacit knowledge. D. all of these. 74. The management of intellectual property involves all of the following EXCEPT A. patents. B. contracts with confidentiality and noncompete clauses. C. converting explicit knowledge to tacit knowledge. D. copyrights and trademarks. 75. Dynamic capabilities include all of the following EXCEPT: A. learning and innovating. B. the ability of an organization to challenge the conventional industry in its industry and market. C. becoming more efficient in operational processes. D. continuously adopting new ways of serving the evolving needs of the market. 76. What is intellectual capital and what is its effect on the ratio of a firm's market value to book value? 77. Effective human capital is a benefit to any organization. What are some challenges firms face when attempting to attract and develop top talent? 78. Discuss the adage "hire for attitude, train for skill." What are its implications for the attraction, training, and retention of top talent? 79. In an effort to attract and retain top talent, firms provide financial and nonfinancial rewards to their employees. Give examples of each and describe how the incentives you have chosen may impact individual employees. 80. The workforce in the United States will become increasingly diverse over the next few decades. What strategies should firms undergo to take full advantage of this emerging trend? 81. Describe social capital. Where does it come from and how can a firm attempt to build it? 82. What are some of the key tradeoffs between "closure" and "bridging relationships" in social network theory? What are some implications for career success? 83. Address some of the potential limitations (or downsides) of social capital. Answers will vary. 84. Discuss how technology has impacted the attraction, training, and retention of professionals. How has technology helped firms to enhance their human capital and social capital? 85. Address some of the challenges associated with protecting intellectual property. 1 Ch04 Summary Category # of Questions AACSB: Analytic 85 Blooms: Apply 6 Blooms: Remember 21 Blooms: Understand 58 Dess - Chapter 04 85 Learning Objective: 04- 21 01 Why the management of knowledge professionals and knowledge itself are so critical in todays organizations. Learning Objective: 04- 30 02 The importance of recognizing the interdependence of attracting; developing; and retaining human capital. Learning Objective: 04-03 The key role of social capital in leveraging human capital within and across the firm. 6 Learning Objective: 04-04 The importance of social networks in knowledge management and in promoting career success. 15 Learning Objective: 04-05 The vital role of technology in leveraging knowledge and human capital. 3 Learning Objective: 04- 6 06 Why "electronic" or "virtual" teams are critical in combining and leveraging knowledge in organizations and how they can be m ade more effective. Learning Objective: 04-07 The challenge of protecting intellectual property and the importance of a firms dynamic capabilities. 4 Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy 21 Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium 58 Level of Difficulty: 3 Hard 6 Topic: Human Capital: The Foundation of Intellectual Capital 31 Topic: Protecting the Intellectual Assets of the Organization: Intellectual Property and Dynamic Capabilities 4 Topic: The Central Role of Knowledge in Todays Economy 19 Topic: The Vital Role of Social Capital 22 Topic: Using Technology to Leverage Human Capital and Knowledge 9 Ch05 Student: 1. Michael Porter's three generic strategies can be depicted on two dimensions: competitive advantage and product life cycle. True False 2. Concentrating solely on one form of competitive advantage generally leads to the highest possible level of profitability. True False 3. A firm striving for cost leadership will typically spend relatively more on product related R&D than on process related R&D. True False 4. To generate above-average returns, a firm following an overall cost leadership position should NOT be concerned with attaining parity or proximity on the basis of differentiation relative to its peers. True False 5. The experience curve concept suggests that production costs tend to decrease as production increases regardless of where an industry is at in its life cycle. True False 6. Firms that compete on overall cost leadership are vulnerable if all rivals share a common input or raw material that contributes a significant amount to total costs. True False 7. The example of Lexus automobiles in the text points out that a firm can strengthen its differentiation strategy by achieving integration at multiple points along the value chain. True False 8. A successful differentiation strategy lowers entry barriers because of customer loyalty and the firm's ability to provide uniqueness in its products and services. True False 9. A successful differentiation strategy increases rivalry since buyers become more price-sensitive. True False 10. If a firm has a successful differentiation strategy, it is NOT necessary to attain parity on cost. True False 11. One potential pitfall of a differentiation strategy is that a brand's identification in the marketplace may become diluted through excessive product line extensions. True False 12. With a focus strategy, creating a niche by differentiating one's product or service often allows small firms to compete successfully with market leaders. True False 13. Focus, by itself, often constitutes a competitive advantage. True False 14. A potential pitfall of a focus strategy is that focusers can become too focused to satisfy buyer needs. True False 15. A disadvantage of firms that successfully integrate overall cost leadership and differentiation strategies is that they are relatively easy for competitors to imitate. True False 16. Mass customization enables manufacturers to be more responsive to customer demands for high quality products. True False 17. An important idea behind the "profit pool" concept is that there is always a strong relationship between the generation of revenues and the capturing of profits. True False 18. An important potential pitfall of an integrated overall cost leadership and differentiation strategy is that firms may fail to implement either one and become "stuck-in-the-middle." True False 19. Most analysts agree that use of the Internet will lower transaction costs. True False 20. One way the Internet and digital technologies are creating opportunities for firms with differentiation strategies is by enabling mass customization. True False 21. The Internet offers few advantages for focusers because niche players and small companies cannot implement capabilities as effectively as their larger competitors. True False 22. The Internet has provided a small subset of companies with greater tools for managing costs. True False 23. Incumbent firms that thought a niche market was too small to enter in the past may use Internet technologies to enter that segment with focusers. True False 24. The market life cycle should be used as a short-run forecasting device because it provides a conceptual framework for understanding what changes typically occur. True False 25. An important advantage of first movers or "pioneers" in a market is that they may establish brand recognition that may later serve as an important switching cost. True False 26. During the growth stage of the market life cycle, customers are very likely to establish brand loyalty. True False 27. Given the attractiveness of premium pricing during the growth stage of the market life cycle, managers should emphasize short-term results to increase profits. True False 28. As markets mature, competition on the basis of differentiation is preferable to price competition. True False 29. As markets mature, the magnitude of differentiation and cost leadership advantages among competitors decrease. True False 30. With reverse positioning, a strategy to be used during the mature stage of the industry life cycle, a product escapes its category by deliberately associating with a different one. True False 31. Businesses that compete in markets that are in decline should simply be harvested or divested since they are no longer profitable. True False 32. During the decline stage of the product life cycle, a harvesting strategy means that a firm keeps a product going without significantly reducing marketing support, technological development, or other investments, while hoping that competitors will exit the market. True False 33. The decline stage of the industry life cycle stage is inevitably followed by death. True False 34. Many firms facing a turnaround situation try to reduce their costs by outsourcing the production of many inputs. True False 35. The primary aim of strategic management at the business level is A. maximizing risk-return tradeoffs through diversification. B. achieving a low cost position. C. maximizing differentiation of products and/or services. D. achieving competitive advantage(s). 36. Primary value chain activities that involve the effective layout of receiving dock operations (inbound logistics) and support value chain activities that include expertise in process engineering (technology development) characterize what generic strategy? A. differentiation B. overall cost leadership C. differentiation focus D. stuck-in-the-middle 37. A manufacturing business pursuing cost leadership will likely A. focus on a narrow market segment. B. rely on experience effects to raise efficiency. C. use advertising to build brand image. D. put heavy emphasis on product engineering. 38. One aspect of using a cost leadership strategy is that experience effects may lead to lower costs. Experience effects are achieved by A. hiring more experienced personnel. B. repeating a process until a task becomes easier. C. spreading out a given expense or investment over a greater volume. D. competing in an industry for a long time. 39. The experience curve suggests that cutting prices is a good strategy A. if it can induce greater demand and thereby help a firm travel down the experience curve faster. B. in industries characterized by high economies of scale. C. in the maturity stage of the industry life cycle. D. in the decline stage of the industry life cycle. 40. Convincing rivals not to enter a price war, protection from customer pressure to lower prices, and the ability to better withstand cost increases from suppliers characterize which type of competitive strategy? A. Overall cost leadership. B. Differentiation. C. Differentiation focus. D. Cost leadership focus. 41. Which of the following is a risk (or potential pitfall) of cost leadership? A. Cost cutting may lead to the loss of desirable features. B. Attempts to stay ahead of the competition may lead to gold plating. C. Cost differences increase as the market matures. D. Producers are more able to withstand increases in suppliers' cost. 42. A firm can achieve differentiation through all of the following means EXCEPT A. improving brand image. B. better customer service. C. offering lower prices to frequent customers. D. adding additional product features. 43. Support value chain activities that involve excellent applications engineering support (technology development) and facilities that promote a positive firm image (firm infrastructure) characterize what generic strategy? A. Differentiation. B. Overall cost leadership. C. Differentiation focus. D. Stuck-in-the middle. 44. High product differentiation is generally accompanied by A. higher market share. B. decreased emphasis on competition based on price. C. higher profit margins and lower costs. D. significant economies of scale. 45. Which of the following is FALSE regarding how a differentiation strategy can help a firm to improve its competitive position vis-à-vis Porter's five forces? A. By increasing a firm's margins, it avoids the need for a low cost position. B. It helps a firm to deal with supplier power and reduces buyer power since buyers lack comparable alternatives. C. Supplier power is increased because suppliers will be able to charge higher prices for their inputs. D. Firms will enjoy high customer loyalty, thus experiencing less threat from substitutes than its competitors. 46. A differentiation strategy enables a business to address the five competitive forces by A. lessening competitive rivalry by distinguishing itself. B. having brand-loyal customers become more sensitive to prices. C. increasing economies of scale. D. serving a broader market segment. 47. All of the following are potential pitfalls of a differentiation strategy EXCEPT: A. uniqueness that is not valuable. B. too high a price premium. C. all rivals share a common input or raw material. D. perceptions of differentiation may vary between buyers and sellers. 48. Which statement regarding competitive advantages is true? A. If several competitors pursue similar differentiation tactics, they may all be perceived as equals in the mind of the consumer. B. With an overall cost leadership strategy, firms need not be concerned with parity on differentiation. C. In the long run, a business with one or more competitive advantages is probably destined to earn normal profits. D. Attaining multiple types of competitive advantage is a recipe for failure. 49. A narrow market focus is to a differentiation-based strategy as a A. broadly-defined target market is to a cost leadership strategy. B. growth market is to a differentiation-based strategy. C. growth market is to a cost-based strategy. D. technological innovation is to a cost-based strategy. 50. A firm following a focus strategy A. must focus on governmental regulations. B. must focus on a market segment or group of segments. C. must focus on the rising cost of inputs. D. must avoid entering international markets. 51. All of the following are potential pitfalls of a focus strategy EXCEPT A. erosion of cost advantages within the narrow segment. B. all rivals share a common input or raw material. C. even product and service offerings that are highly focused are subject to competition from new entrants and from imitation. D. focusers can become too focused to satisfy buyer needs. 52. Research has consistently shown that firms that achieve both cost leadership and differentiation advantages tend to perform A. at about the same level as firms that achieve either cost or differentiation advantages. B. about the same as firms that are "stuck-in-the-middle." C. lower than firms that achieve differentiation advantages but higher than firms that achieve cost advantages. D. higher than firms that achieve either a cost or a differentiation advantage. 53. The text discusses three approaches to combining overall cost leadership and differentiation competitive advantages. These are the following EXCEPT A. automated and flexible manufacturing systems. B. exploiting the profit pool concept for competitive advantage. C. coordinating the "extended" value chain by way of information technology. D. deriving benefits from highly focused and high technology markets. 54. A can be defined as the total profits in an industry at all points along the industry's value chain. A. profit maximizer B. revenue enhancer C. profit pool D. profit outsourcing 55. All of the following are potential pitfalls of an integrated overall low cost and differentiation strategy EXCEPT: A. firms that fail to attain both strategies may end up with neither and become "stuck-in-the-middle." B. targeting too large a market that causes unit costs to increase. C. underestimating the challenges and expenses associated with coordinating value-creating activities in the extended value chain. D. miscalculating sources of revenue and profit pools in the firm's industry. 56. Which of the following is NOT one of the ways the Internet is lowering transaction costs? A. eliminating supply chain intermediaries B. evaluating employee performance C. minimizing office expenses D. reducing business travel 57. Dell Computer has an online ordering system that allows consumers to configure their own computers before Dell builds them. This capability is an example of A. electronic data interchange. B. knowledge management. C. collaborative design. D. mass customization. 58. Which of the following methods of implementing a differentiation strategy has been greatly enhanced because of Internet technologies? A. celebrity endorsements B. prestige packaging C. exceptional service D. mass customization 59. Which of the following phrases best completes this sentence: Because of the Internet, firms that use a focus strategy have new opportunities to A. respond quickly to customer requests. B. provide more services and features. C. access markets less expensively. D. access niche markets in a highly specialized fashion. 60. One of the reasons the Internet is eroding sustainable competitive advantages is A. incumbent firms are entering market segments that they previously considered to be too small. B. nearly all competitors will have greater access to tools for managing costs making it hard for any one to achieve an advantage. C. differentiators have been able to preserve the unique advantages that have always been the hallmark of their success. D. firms are ignoring opportunities to offer high-end services in niche markets. 61. Which of these statements regarding the industry life cycle is correct? A. Part of the power of the market life cycle is its ability to serve as a short-run forecasting device. B. Trends suggested by the market life cycle model are generally not reversible or repeatable. C. It has important implications for a firm's generic strategies, functional areas, value-creating activities, and overall objectives. D. It points out the need to maintain a differentiation advantage and a low cost advantage simultaneously. 62. Which of the following statements about the introduction stage of the market life cycle is TRUE? A. It produces relatively large, positive cash flows. B. Strong brand recognition seldom serves as an important switching cost. C. Market share gains by pioneers are usually easily sustained for many years. D. Products or services offered by pioneers may be perceived as differentiated simply because they are new. 63. In the stage of the industry life cycle, the emphasis on product design is very high, the intensity of competition is low, and the market growth rate is low. A. introduction B. growth C. maturity D. decline 64. The growth stage of the industry life cycle is characterized by A. "in-kind" competition (from the same type of product). B. premium pricing. C. a growing trend to compete on the basis of price. D. retaliation by competitors whose customers are stolen. 65. In the stage of the industry life cycle, there are many segments, competition is very intense, and the emphasis on process design is high. A. introduction B. growth C. maturity D. decline 66. In a given market, key technology no longer has patent protection, experience is not an advantage, and there is a growing need to compete on price. What stage of its life cycle is the market in? A. introduction B. growth C. maturity D. decline 67. A market that mainly competes on the basis of price and has stagnant growth is characteristic of what life cycle stage? A. introduction B. growth C. maturity D. decline 68. As markets mature, A. costs continue to increase. B. application for patents increase. C. differentiation opportunities increase. D. there is increasing emphasis on efficiency. 69. The size of pricing and differentiation advantages between competitors decreases in which stage of the market life cycle? A. introduction B. growth C. maturity D. decline 70. Which of the following is most often true of mature markets? A. Some competitors enjoy a significant operating advantage due to increasing experience effects. B. The market supports premium pricing, which attracts additional competitors. C. Advantages that cannot be duplicated by other competitors are difficult to achieve. D. The magnitude of pricing differences and product differentiation is larger than in the growth stage. 71. In the stage of the industry life cycle, there are few segments, the emphasis on process design is low, and the major functional areas of concern are general management and finance. A. introduction B. growth C. maturity D. decline 72. The most likely time to pursue a harvest strategy is in a situation of A. high growth. B. strong competitive advantage. C. mergers and acquisitions. D. decline in the market life cycle. 73. During the decline stage of the industry life cycle, refers to obtaining as much profit as possible and requires that costs be decreased quickly. A. maintaining B. harvesting C. exiting D. consolidating 74. Research shows that the following are all strategies used by firms engaged in successful turnarounds EXCEPT A. asset and cost surgery. B. selective product and market pruning. C. global expansion. D. piecemeal productivity improvements. 75. Piecemeal productivity improvements during a turnaround typically does NOT involve A. business process reengineering. B. increased capacity utilization. C. benchmarking. D. expansion of a firm's product market scope. 76. Use the value chain as a framework to explain how a firm can achieve a competitive advantage of overall cost leadership. 77. Explain how a cost leadership strategy permits a firm to address the five forces in their competitive environment so it can enjoy higher-than-normal profits. 78. Discuss how a competitive advantage can be attained through differentiation using the value chain concept. 79. Explain how a differentiation strategy enables a business to address the five competitive forces in such a way that it can enjoy high levels of profitability. 80. Discuss the risks associated with each of these forms of competitive advantage: overall cost leadership, differentiation, and focus. 81. What are the benefits and risks associated with combining overall cost leadership and differentiation strategies? 82. Discuss the uses and limitations associated with the industry life cycle concept as a framework for studying strategy formulation at the business level. 83. Describe the two positioning strategies—reverse positioning and breakaway positioning that firms can use when faced with the maturity phase of the industry life cycle. 84. Briefly explain the advantages of the four alternatives—maintaining, harvesting, exiting, consolidating— associated with the decline stage of the market life cycle. 85. Discuss some of the effective turnaround strategies. Ch05 Summary Category # of Questions AACSB: Analytic 85 Blooms: Apply 1 Blooms: Remember 16 Blooms: Understand 68 Dess - Chapter 05 85 Learning Objective: 05- 12 01 The central role of competitive advantage in the study of strategic management; and the three generic strategies: overall cost lea dership; differentiation; and focus. Learning Objective: 05-02 How the successful attainment of generic strategies can improve a firms relative power vis-à- 2 vis the five forces that determine an industrys average profitability. Learning Objective: 05-03 The pitfalls managers must avoid in striving to attain generic strategies. 23 Learning Objective: 05-04 How firms can effectively combine the generic strategies of overall cost leadership and differentiation. 8 Learning Objective: 05-06 How Internet-enabled business models are being used to improve strategic positioning. 10 Learning Objective: 05-07 The importance of considering the industry life cycle to determine a firms business- 26 level strategy and its relative emphasis on functional area strategies and value-creating activities. Learning Objective: 05- 4 08 The need for turnaround strategies that enable a firm to reposition its competitive position in an industry. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy 16 Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium 68 Level of Difficulty: 3 Hard 1 Topic: How the Internet and Digital Technologies Affect the Competitive Strategies 10 Topic: Industry Life Cycle Stages: Strategic Implications 30 Topic: Types of Competitive Advantage and Sustainability 45 Ch06 Student: 1. Whenever an organization diversifies, it represents investing a stockholder's funds in a way in which the individual investor is unable. True False 2. Diversification that results in strengthening the value chain and increasing competitive advantages is the best possible example of investing stockholders' funds in a way that individual investors cannot. True False 3. When firms diversify into unrelated businesses, the primary potential benefits are horizontal relationships, i.e., businesses sharing tangible and intangible resources. True False 4. Individual investors are dependent upon the corporation's managers to A. diversify the stockholder's investments in order to reduce risk. B. add value to their investments in a way that the stockholders could not accomplish on their own. C. achieve risk reduction at a lower cost than stockholders could obtain on their own. D. maximize short-term returns in the form of dividends. 5. McKesson, a large distribution company, sells many product lines such as pharmaceuticals and liquor through its super warehouses. This is an example of A. achieving economies of scope through related diversification. B. achieving market power through related diversification. C. attaining the benefits of restructuring through unrelated diversification. D. attaining the benefits of parenting through unrelated diversification. 6. The corporate office of Cooper Industries adds value to its acquired businesses by performing such activities as auditing their manufacturing operations, improving their accounting activities, and centralizing union negotiations. This is an example of A. achieving economies of scope through related diversification. B. achieving market power through related diversification. C. attaining the benefits of horizontal integration. D. attaining the benefits of parenting through unrelated diversification. 7. What are the primary benefits and risks associated with related diversification? 8. Briefly explain the advantages and disadvantages of vertical integration. 9. What are some of the key issues to take into account when considering whether or not to vertically integrate? 10. Explain how transaction cost analysis can provide insights into vertical integration decisions. 11. What are the primary benefits and risks associated with unrelated diversification? 12. Explain the uses and limitations of portfolio management matrices such as the growth-share matrix developed by the Boston Consulting Group (BCG). 13. Summarize the advantages and disadvantages of mergers and acquisitions as a means of diversification. 14. Discuss some of the potential benefits of divestment. 15. Strategic alliances are arrangements in which two firms join forces and form a cooperative partnership. Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of strategic alliances as well as guidelines for reducing conflict between the partners. 16. Discuss how the potential benefits of diversification may be adversely affected by conflicts between managers' interests and stockholders' interests. Hint: Egotism, growth for growth's sake, antitakeover tactics. Ch06 Summary Category # of Questions AACSB: Analytic 16 Blooms: Apply 1 Blooms: Understand 15 Dess - Chapter 06 16 Learning Objective: 06-02 How managers can create value through diversification initiatives. 6 Learning Objective: 06- 4 03 How corporations can use related diversification to achieve synergistic benefits through economies of scope and market power. Learning Objective: 06- 2 04 How corporations can use unrelated diversification to attain synergistic benefits through corporate restructuring; parenting; and portfolio analysis. Learning Objective: 06-05 The various means of engaging in diversification-mergers and acquisitions; joint ventures/ 3 strategic alliances; and internal development. Learning Objective: 06-06 Managerial behaviors that can erode the creation of value. 1 Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium 15 Level of Difficulty: 3 Hard 1 Topic: How Managerial Motives Can Erode Value Creation 1 Topic: Making Diversification Work: An Overview 6 Topic: Related Diversification: Economies of Scope and Revenue Enhancement 4 Topic: The Means to Achieve Diversification 3 Topic: Unrelated Diversification: Financial Synergies and Parenting 2 Ch07 Student: 1. The trend towards worldwide markets makes it easier to predict where competitors will spring up. True False 2. Because many countries are investing in countries other than their own, each country is becoming more autonomous and independent. True False 3. An advantage of international expansion is that competition within foreign countries is generally very similar to that of the United States. True False 4. In Michael Porter's "diamond of national advantage," there are four broad attributes that, as a system, constitute a nation's competitiveness in an industry. True False 5. The factor endowments of a country are inherited and cannot be created. True False 6. With regard to "factor conditions," the pool of resources that a firm (or nation) has is much more important than the speed and efficiency with which these resources are deployed. True False 7. Demanding domestic consumers tend to push firms to move ahead of companies in other countries where consumers are less demanding and more complacent. True False 8. High levels of environmental awareness in Denmark have led to a decline in Denmark's industrial competitiveness in the international marketplace. True False 9. Countries with a strong supplier base benefit by adding efficiency to downstream activities. True False 10. Typically, intense rivalry in domestic markets does not force firms to look outside their national boundaries for new markets. True False 11. Many international firms are increasing their efforts to market their products and services to countries such as India and China as the ranks of their middle class continue to increase. True False 12. International expansion can extend the life cycle of a product that is in its maturity stage in a firm's home country. True False 13. An advantage of international expansion is that it can enable a firm to optimize the location of every activity in its value chain. True False 14. The laws, and the enforcement of laws, associated with the protection of intellectual property rights, represent a significant currency and management risk to multinational firms. 15. Differences in foreign markets such as culture, language, and customs can represent significant management risks when firms enter foreign markets. True False 16. Offshoring takes place when a firm decides to shift an activity that they were previously performing in a domestic location to a foreign location. True False 17. Two opposing pressures that managers face when they compete in foreign markets are cost reduction and adaptation to local markets. True False 18. Theodore Levitt has argued that people around the world are willing to sacrifice preferences in product features, functions, and design if they are offered lower prices and high quality. True False 19. Among Theodore Levitt's assumptions that would favor a global strategy is that consumers around the world are becoming less price-sensitive. True False 20. Within a worldwide market, the most effective strategies are neither purely multidomestic nor purely global. True False 21. Industries in which proportionally more value is added in upstream activities are more likely to benefit from a global strategy than those in which more value is added downstream (closer to the customer). True False 22. In a global strategy a firm operates all its businesses under a single common strategy regardless of location. True False 23. A multidomestic strategy is the most appropriate strategy for international operations because it drives economies of scale as far as possible and provides a middle-of-the-road product appealing to the largest number of consumers in every market. True False 24. The need to attain economies of scale encourages multinational firms to operate under a multidomestic strategy. True False 25. Corporations with multiple foreign operations that act very independently of one another are following a multidomestic strategy. True False 26. A multidomestic strategy would likely include the use of high volume, centralized production facilities to maximize economies of scale. True False 27. A limitation of a multidomestic strategy is that it may lead to "overadaptation" as conditions change. True False 28. Multinational firms following a transnational strategy strive to optimize the trade-offs associated with efficiency, local adaptation, and learning. True False 29. A key tenet of a transnational strategy is improved adaptation to all competitive situations as well as flexibility by capitalizing on communication and knowledge flows throughout the organization. 30. According to studies by Rugman and Verbeke, most of the world's 500 firms are global, not regional or biregional. True False 31. A franchise generally expires after a few years whereas a license is designed to last into perpetuity. True False 32. Typically, joint ventures involve less control and risk than franchising. True False 33. Typically, the best method of entry into a foreign market is the establishment of a wholly owned foreign subsidiary so that the parent organization can maintain a high level of control. True False 34. A major trend in international developments includes A. greater international trade and operations. B. a growing recognition of an international managerial perspective. C. a large increase in international investment. D. all of these. 35. The reasons that explain why some governments make better use of the inflows from foreign investment and know-how than others include all of the following EXCEPT A. governmental practices that are business-friendly. B. local entrepreneurs that can train workers and invest in modern technology. C. high tariffs and taxes on foreign investors and multinational corporations provide income to improve living conditions. D. sound management of broader economic factors such as interest rates and inflation. 36. Michael Porter's framework all of the following factors affect a nation's competitiveness EXCEPT A. factor conditions. B. demand characteristics. C. related and supported industries. D. policies that protect the nation's domestic competitors. 37. Rivalry is intense in nations with conditions of consumer demand, supplier bases, and new entrant potential from related industries. A. weak; weak; high B. strong; strong; low C. strong; strong; high D. weak; weak; low 38. According to Michael Porter, firms that have experienced intense domestic competition are A. unlikely to have the time or resources to compete abroad. B. most likely to design strategies aimed primarily at the domestic market. C. more likely to design strategies and structures that allow them to successfully compete abroad. D. more likely to demand protection from their governments. 39. All of the factors below have made India's software services industry extremely competitive on a global scale EXCEPT A. large pool of skilled workers. B. large network of public and private educational institutions. C. tax and antitrust legislation that protect the dominant players in the industry. D. large, growing market and sophisticated customers. 40. All of the following would be viewed as advantages of global diversification EXCEPT A. fewer social and political risks than domestic operations. B. a firm not being solely dependent on the domestic market. C. a firm with large margins at home helping subsidize its operations in other nations. D. the potential to lower costs of operation even if the primary market is at home. 41. Optimizing the location of every activity in the value chain can yield all of the following strategic advantages EXCEPT A. performance enhancement. B. cost reduction. C. extending the life cycle of the product of service. D. risk reduction. 42. Microsoft decided to establish a corporate research laboratory in Cambridge, England A. because England is an ally of the United States. Bto access the outstanding technical and professional talent available there so that they can attain world- . class excellence in selected value-creating activities. C. because the local language is English. D.because the company views the United States as a risky place to expand due to the actions of the U.S. Department of Justice. 43. The sale of Boeing's commercial aircraft and Microsoft's operating systems in many countries enable these companies to benefit from A. higher prices in their domestic markets. B. economies of scale. C. optimizing the location for many activities in their value chain. D. reducing their exposure to currency risks. 44. Many U.S. multinational companies set up maquiladora operations south of the U.S.-Mexico border primarily A. to sell products into the growing Mexican market. B. as part of US government-initiated measures to discourage illegal immigration. C. to take advantage of the lower tax rates in Mexico. D. to take advantage of the low cost of labor. 45. Appreciation of the U.S. dollar will have the following impact on McDonald's: A. lower sales abroad because foreign customers cannot afford McDonalds' products. B. more transfer of ingredients from the U.S. to branches abroad to take advantage of the higher dollar. C. lower profits, because foreign profits will be reduced when measured in dollars. D. no impact at all. 46. occurs when a firm decides to utilize other firms to perform value-creating activities that were previously performed in-house. A. Offshoring B. A global strategy C. Outsourcing D. A transnational strategy 47. Which one of the following is one of Theodore Levitt's assumptions supporting a pure global strategy? A. Consumers are willing to pay more for specific product features. B. Customer needs and interests are becoming more dissimilar. C. If the world markets are treated as heterogeneous, substantial economies of scale are easily achieved. D. MNCs can compete with aggressive pricing on low cost products that meet the common needs of global consumers. 48. Pressures to "reduce costs" require that A. a company should not trade idiosyncratic preferences in product features for higher economic returns. B a company must pursue what is economically beneficial to the company including maximizing . economies of scale and learning curve effects. C. the manager should follow a multidomestic strategy to maximize the economic benefits to the company. D. the company needs to supplement the local foreign economy in a manner specified by the local government. 49. Low pressure for local adaptation combined with low pressure for lower costs would suggest what type of strategy? A. international B. global C. multidomestic D. transnational 50. High pressure for local adaptation combined with low pressure for lower costs would suggest what type of international strategy? A. Global B. Multidomestic C. Transnational D. Overall cost leadership 51. Software Tech, Inc., a company in the computer software industry, invests heavily in R&D and product design. Thus, most of its value is added A. upstream. B. in its infrastructure. C. downstream. D. midstream. 52. Industries in which proportionally more value is added in activities are more likely to benefit from a strategy. A. downstream; global B. upstream; multidomestic C. upstream; global D. manufacturing; multidomestic 53. Which of the following types of international firms are most likely to benefit from a global strategy as opposed to a multidomestic strategy? A. Firms that compete in industries in which consumer preferences vary substantially in each country. B. Firms in industries that are expanding very rapidly. C. Firms in industries that have value added by sales and marketing departments. D. Firms in industries that have much value added in research and design or manufacturing. 54. Recent trends that might lead managers of multinational corporations (MNCs) to adopt a more decentralized strategy for their operations would include all of the following EXCEPT A. customers' needs, interests, and tastes are becoming increasingly homogenized or similar. B. consumers around the world are increasingly willing to tradeoff idiosyncratic preferences in product features for lower price. C flexible manufacturing trends have allowed a decline in the minimum volume required to reach . acceptable levels of production efficiency. D. fluctuating exchange rates. 55. Firms following a global strategy strive to offer products and services as well as locate manufacturing, R&D, and marketing activities in locations. A. a wide variety of; several B. a wide variety of; few C. standardized; several D. standardized; few 56. Gillette's worldwide success with its Sensor razor demonstrates A. the importance of merging global and multidomestic strategies. B. the values of establishing joint ventures with several multinational corporations. C. that a global marketing effort can sometimes be successful. D. the usefulness of a multidomestic strategy. 57. As in the case of Siebel Systems (now part of Oracle), elements of a global strategy may facilitate the competitive advantage of differentiation by A. increased freedom of individual business units to adapt to local tastes. B. the creation of a worldwide network to achieve consistent service regardless of location. C. flexibility in applying R&D to meet country-specific needs. D. tailoring products to meet country-specific needs. 58. All of the following are risks associated with a global strategy EXCEPT A.a firm with only one manufacturing location must export its product—some of which may be a great distance from the operation. B. the geographic concentration of any activity may also tend to isolate that activity from the targeted markets. C. concentrating an activity in a single location makes the rest of the firm dependent on that location. D. the pressures for local adaptation may elevate the firm's cost structure. 59. All of the following are limitations of a global strategy EXCEPT A. limited ability to adapt to local markets. B. the ability to locate activities in optimal locations. C. the concentration of activities may increase dependence on a single facility. D. single locations may lead to higher tariffs and transportation costs. 60. Elements of a multidomestic strategy may facilitate the competitive advantage of cost leadership by A. flexibility in adjusting to local laws and customs. B. decreased duplication of inventories which are often involved in having multiple plants producing similar products. C. decreased shipping and transportation costs inherent in local production. D. economies of scale gained through centralized production of standardized products. 61. All of the following are limitations of a multidomestic strategy EXCEPT A. less ability to realize cost savings through scale economies. B. greater difficulty in transferring knowledge across countries. C. single locations may lead to higher tariffs and transportation costs. D. may lead to "overadaptation" as conditions change. 62. High pressure for local adaptation combined with high pressure for lower costs would suggest what type of international strategy? A. global B. multidomestic C. transnational D. differentiation 63. Units coordinate their activities with headquarters and with one another, units adapt to special circumstances only they face, and the entire organization draws upon relevant corporate resources. These are all attributes of which type of strategy? A. global B. transnational C. international D. multidomestic 64. Which of the following is a disadvantage of a transnational strategy? A. Less ability to realize cost savings through scale economies. B. Limited ability to adapt to local markets. C. Unique managerial challenges in fostering knowledge transfer. D. Single locations may lead to higher tariffs and transportation costs. 65. In order to realize the strongest competitive advantage, firms engaged in worldwide competition must A. require that all of their various business units follow the same strategy regardless of location. B. ensure that all business units follow a strategy strictly tailored to their respective locations. C pursue a strategy that combines the uniformity of a global strategy and the specificity of a . multidomestic strategy in order to achieve optimal results. D. attempt to use the strategy that was most successful in their home country. 66. According to studies by Rugman and Verbeke, approximately how many of the world's largest 500 firms are global, that is, they have at least 20% of their total revenues each in North America, Asia, and Europe? A. 9 B. 59 C. 79 D. 159 67. Which of the following describes the most typical order of entry into foreign markets? A. franchising, licensing, exporting, joint venture, and wholly owned subsidiary B. exporting, licensing, franchising, joint venture, and wholly owned subsidiary C. licensing, exporting, franchising, joint venture, and wholly owned subsidiary D. exporting, franchising, licensing, joint venture, and wholly owned subsidiary 68. A domestic corporation considering expanding into international markets for the first time will typically A. start off by implementing a wholly owned foreign subsidiary so it can maintain standards identical to those at home. B. consider licensing or franchising its operations. C. consider implementing a low risk/low control strategy such as exporting. D. form a joint venture with a reputable foreign producer. 69. The form of entry strategy into international operations that offers the lowest level of control would be A. franchising. B. licensing. C. joint venture. D. exporting. 70. Fees that a multinational receives from a foreign licensee in return for its use of intellectual property (trademark, patent, trade secret, technology) are usually called A. transfer prices. B. dividends. C. royalties. D. intra-corporate inflows. 71. The difference between a franchise and licensing contract is that A. a franchise contract is more specific and usually longer in duration. B. a franchise contract must include a foreign government. C. a licensing contract covers more aspects of operations. D. a franchise contract involves less control and less risk. 72. entail the creation of a third-party legal entity, whereas do not. A. Licensing agreements; joint ventures B. Joint ventures; strategic alliances C. Strategic alliances; joint ventures D. Franchising agreements; strategic alliances 73. A is a business in which a multinational company owns 100 percent of the stock. A. joint venture B. strategic alliance C. wholly owned subsidiary D. franchising operation 74. are most appropriate where a firm already has the appropriate knowledge and capabilities that it can leverage rather easily through multiple locations in many countries. A. Joint ventures B. Strategic alliances C. Licensing agreements D. Wholly owned subsidiaries 75. Explain Michael Porter's "diamond of national advantage." 76. Summarize the most important benefits and risks associated with diversification into global markets. 77. What are the main benefits of offshoring and outsourcing? 78. Explain how the two opposing forces facing MNC managers, cost reduction and local adaptation, create pressures to operate with a global or multidomestic strategy, respectively. 79. According to Theodore Levitt, what are the three assumptions that favor the pursuit of a "pure" global strategy? Briefly provide counterarguments to each assumption. 80. What are some of the primary benefits and risks of transnational strategies? 81. What are the key arguments that Rugman and Verbeke make in favor of regional strategies as opposed to global strategies? 82. What are the major advantages and disadvantages of the four types of entry strategies for international expansion? Ch07 Summary Category # of Questions AACSB: Analytic 82 Blooms: Apply 3 Blooms: Remember 15 Blooms: Understand 64 Dess - Chapter 07 82 Learning Objective: 07-01 The importance of international expansion as a viable diversification strategy. 5 Learning Objective: 07- 02 The sources of national advantage; that is; why an industry in a given country is more (or less) successful than the same industr y in another country. 12 Learning Objective: 07- 03 The motivations (or benefits) and the risks associated with international expansion; including the emerging trend for greater offs horing and outsourcing activity. 16 Learning Objective: 07-04 The two opposing forces-cost reduction and adaptation to local markets- that firms face when entering international markets. 8 Learning Objective: 07- 05 The advantages and disadvantages associated with each of the four basic strategies: international; global; multidomestic; and tra nsnational. 27 Learning Objective: 07-06 The difference between regional companies and truly global companies. 3 Learning Objective: 07-07 The four basic types of entry strategies and the relative benefits and risks associated with each of them. 12 Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy 15 Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium 64 Level of Difficulty: 3 Hard 3 Topic: Achieving Competitive Advantage in Global Markets 38 Topic: Entry Modes of International Expansion 12 Topic: Factors Affecting a Nations Competitiveness 12 Topic: International Expansion: A Companys Motivations and Risks 15 Topic: The Global Economy: A Brief Overview 5 Ch08 Student: 1. Small businesses and entrepreneurial firms create the majority of new jobs in the U. S. economy. True False 2. Most small businesses in the U.S. are in retail trade and construction industries. True False 3. Opportunity recognition is the process of identifying, selecting, and developing entrepreneurial opportunities. True False 4. Opportunity recognition involves two phases of activity: discovery and evaluation. True False 5. The evaluation phase of opportunity recognition includes the "Aha!" experience that often leads to new venture development. True False 6. The majority of entrepreneurial start-ups are financed with personal savings and the contributions of family and friends. True False 7. The majority of entrepreneurial firms are started with financing from venture capitalists and banks. True False 8. Angel investors are private individuals who provide equity investments for seed capital during the early stages of a new venture. True False 9. 9 As investors, venture capitalists rarely provide any help or services to entrepreneurial firms other than financing. True False 10. Venture capital funding for entrepreneurial ventures is usually available only after the start-up has become a going concern and established a track record. True False 11. The term "angel investors" refers to private individuals who provide seed capital to young ventures. True False 12. Venture capital is a form of public equity financing used to help young firms grow rapidly. True False 13. To obtain venture capital financing, business founders often have to give up some ownership and control of their business. True False 14. According to the text, venture capitalists and angel investors regard the management team as the most important asset of an entrepreneurial venture. True False 15. Because of the Small Business Administration and government regulations, small businesses are rarely allowed to bid on government contracts. 16. An entry wedge, according to the text, is a type of entrepreneurial strategy firms can use to enter into business. True False 17. Founders using a pioneering new entry strategy look for opportunities to capitalize on proven market successes. True False 18. Adaptive new entry involves offering a radical new product or highly innovative service. True False 19. Rather than fighting over existing customers, firms pursuing a "blue ocean" strategy seek opportunities in uncontested markets. True False 20. "Blue ocean" strategies rarely provide sustainable advantages because they are easily imitated. True False 21. Because new ventures are typically small, they usually don't have high economies of scale relative to competitors. True False 22. Entrepreneurial firms are often in a strong position to use combination strategies because they have the flexibility to approach situations uniquely. True False 23. Entrepreneurial competitive dynamics refers to a cycle of actions and responses between firms competing for the same customers. True False 24. Entrepreneurial new entry is often perceived as a competitive threat because most market needs are being met, either directly or indirectly, by an existing firm. True False 25. 25 Market commonality is the extent to which rivals draw from the same types of resources. True False 26. Market commonality refers to the extent to which competitors are vying for the same customers in the same markets. True False 27. When attacked, older and larger firms tend to respond more quickly, but their responses are often more predictable. True False 28. Cutting prices or increasing marketing efforts are examples of tactical competitive actions. True False 29. In the context of competitive dynamics, tactical actions involve major commitments of distinctive and specific resources to strategic initiatives. True False 30. Refinements or extensions of existing strategies are often referred to as tactical actions. True False 31. Forbearance is a particularly aggressive type of competitive attack. True False 32. Co-opetition, where competitors work together behind the scenes, is a form of illegal tacit collusion. 33. In the opening case, iSold It, a firm that helped others sell products on eBay, went from one of the fastest growing franchise businesses to a firm that saw a number of its franchises close and declining sales in a matter of months. What was a major challenge iSold It faced that led to these problems? A. It did not have the financial resources to maintain the rapidly growing firm. B. The company lacked knowledgeable executives in key positions. C. Its concept was rapidly imitated by others. D. It had weak operational systems and could not maintain control of the growing network of stores. 34. According to the text, for an entrepreneurial start-up to be successful, three ingredients are critical. What are they? A. good ideas, a team of investors, and a business plan B. a viable opportunity, available resources, and a qualified and motivated founding team C. an opportunity, a marketing plan, and office space D. management, marketing, and money 35. Which of the following is a common source of new business opportunities? A. current or past work experiences B. suggestions by family or friends C. chance event D. all of these 36. 36 The process of identifying, selecting, and developing new venture opportunities is known as A. innovativeness. B. bootstrapping. C. opportunity recognition. D. brainstorming. 37. Generally speaking, the opportunity recognition process consists of two phases of activity. They are A. Global Search and Recycling Profits. B. Value Creation and Affordability. C. Discovery and Evaluation. D. none of these. 38. Which of the following is NOT one of the characteristics of an entrepreneurial opportunity? A. attractive B. affordable C. achievable D. value creating 39. When an opportunity is attractive long enough for it to be successfully developed and deployed, it is said to be A. value creating. B. affordable. C. achievable. D. durable. 40. Which of the following terms is used to refer to opportunities that are practical and physically possible? A. durable B. valuable C. achievable D. sustainable 41. Financing for entrepreneurial start-ups includes which of the following? A. investments by family and friends B. personal savings C. private investors D. all of these 42. Which of the following sources of entrepreneurial financing are available to ventures that have already started to conduct business and generate sales? A. bank financing B. venture capital C. public financing D. all of these 43. The majority of entrepreneurial start-ups are financed with A. bank financing. B. public financing (e.g., SBA loans). C. venture-capital financing. D. personal savings and the contributions of family and friends. 44. Private individuals who provide seed capital to young ventures are known as A. angels. B. gazelles. C. cash cows. D. rising stars. 45. All of the following statements about venture capital are true EXCEPT A. entrepreneurs raise venture capital by selling shares of ownership in their business. B. venture capital is a form of public equity financing. C. venture capital is used to finance rapid growth or large capital expenditures. D. venture capital groups can often provide helpful management advice. 46. Based on statistics reported in the text, which of the following statements is FALSE? A. Firms that obtain venture-capital funding receive an average of over $1 million each. B. Total investment in start-up firms averages about $80,000 in the firm's first year. C Among the 100 fastest-growing new businesses identified by Entrepreneur magazine, 61 percent . obtained start-up funding from personal savings. D. Ninety percent of the companies financed with venture capital funds fail. 47. According to the text, new ventures launched by entrepreneurial teams are more likely to be successful than ventures launched by A. established corporations. B. bootstrappers. C. "lone wolf" entrepreneurs. D. all of these. 48. Which of the following types of resources contribute to the success of entrepreneurial firms? A. social capital B. financial resources C. human resources D. All of these contribute to the success of entrepreneurial firms. 49. provide(s) a key avenue for growth for many young and small firms through partnering to obtain resources and/or expand into new markets. A. Strategic alliances B. Bootstrappers C. "Lone wolf" entrepreneurs D. Research & development 50. The U.S. Small Business Administration supports small business through all of the following EXCEPT A. government contracting. B. underwriting loans. C. investing venture capital. D. training and counseling. 51. Which of the following is NOT one of the three characteristics of entrepreneurial leadership mentioned by the text? A. vision B. dedication and drive C. commitment to excellence D. clarifying job responsibilities 52. Why is vision such an important element of entrepreneurial leadership? A. Because the entrepreneur has to envision realities that do not yet exist. B. Because a vision statement must be part of the documentation used to obtain venture financing. C. Because organizations cannot function without a detailed and operational vision. D. All of these 53. Which of the following is NOT a common new entry strategy according to the text? A. imitative new entry B. adaptive new entry C. proactive new entry D. pioneering new entry 54. Seeking products or services that have been successful in one market and introducing the same basic product or service in another segment of the market is referred to as A. imitative new entry. B. adaptive new entry. C. proactive new entry. D. pioneering new entry. 55. Which of the following is NOT a key element of a blue ocean strategy? A. Pursue low cost and differentiation advantages simultaneously. B. Make the competition irrelevant. C. Highlight incremental improvements to capture market share. D. Create new demand in uncharted territory. 56. Cirque du Soleil is an example of a firm that successfully enacted a "blue ocean" strategy. Which of the following is a feature of the strategy it enacted? A. It developed its own musical scores for its circus performances. B. It discontinued traditional parts of the circus, such as animal acts. C. It researched customers to learn what circus features are more in demand. D. All of these. 57. "Doing more with less", by holding down costs or making more efficient use of resources is one of the ways entrepreneurs achieve success. This is an example of how entrepreneurs use A. an imitative strategy. B. a low-cost leader strategy. C. a differentiation strategy. D. a combination strategy. 58. Entrepreneurial firms that pursue a low-cost leadership strategy use which of the following to achieve lower costs? A. cost-saving technology such as the Internet B. simple organizational structures C. rapid decision making D. all of these 59. When an industry is mature, a strategy is considered to be one of the most effective approaches for a new entrant. A. focus B. differentiation C. overall low-cost D. small business 60. According to the text, all of the following might make it difficult for entrepreneurial firms to effectively pursue a strategy of differentiation EXCEPT A. incumbent firms are constantly seeking opportunities to specialize in market niches. B. differentiation strategies are often expensive to enact. C. it may be difficult for a young firm to establish a strong brand identity. D. implementing superior new technologies may be challenging for entrepreneurial firms. 61. Intense rivalry involving actions and responses among similar competitors vying for the same customers in a marketplace is known as A. competitive dynamics. B. resource similarity. C. threat of substitutes. D. pioneering new entry. 62. Which of the following is NOT one of the reasons a company might launch new competitive actions? A. to obtain first mover advantages B. to improve market position C. to capitalize on growing demand D. to find new sources of raw materials 63. Netflix CEO Reed Hastings made this important observation about dealing with rivals: A. "In a highly competitive marketplace, firms must be paranoid about the multitude of potential rivals." B "You can afford to ignore rivals in small markets, but you can never ignore rivals in large markets, such . as online video companies like YouTube." C"There are tens and maybe hundreds of start-ups who think that they are going to eat Netflix's lunch. . The challenge for a management team is to figure out which are real threats and which aren't." D. "Netflix's position is so strong that I don't worry about new entrants." 64. Aircraft makers Boeing and Airbus have a high degree of because they make very similar products and have many buyers in common. A. dynamic capabilities B. market commonality C. first mover advantages D. equity funding 65. The Wall Street Journal and the New York Times have seen the intensity of their rivalry increase. One factor driving this is that the Wall Street Journal has moved from financial news reporting to general national and global news reporting and finally, to adding local New York news. The rivalry of these two news providers has increased due to A. increased dynamic capabilities. B. increased market commonality. C. erosion of first mover advantages. D. the choice of tactical over strategic actions. 66. Which of the following questions should a firm ask itself before responding to a competitive attack? A. How serious is the impact of the attack? B. What is our competitive intent—do we want to blunt the attack or enhance our competitive position with our response? C. What resources do we have available for a response? D. All of these. 67. Which of the below best describes the competitive tendencies of small firms? A Because they lack legitimacy in the marketplace, small firms tend to signal their competitive actions . long before they launch those actions. B. Small firms typically have more resources available as they undertake competitive attacks than do large firms. C. Small firms are more nimble and can respond quickly to competitive attacks. D. All of these. 68. Cirrus Aircraft, a leading manufacturer of small airplanes, sees a market opportunity and has decided to double its plant capacity over the next two years. What type of competitive action does this represent? A. A tactical action because the move is an attempt to fill a gap in service. B. A strategic action because such a large plant expansion will require a major commitment of resources. C. A strategic action because the firm can easily reverse the action at any time, thus giving Cirrus more strategic flexibility. D. A guerilla offensive because it is fast and will surprise its rivals. 69. All of the following are examples of strategic actions a firm might take EXCEPT A. acquire with competitors to reduce competition. B. expand into neglected markets. C. change product packaging. D. tie up raw materials sources. 70. The best example of a tactical action that a company might use in response to a competitive attack is to A. acquire the competitor. B. target the rival's markets. C. expand into new geographical areas. D. offer price discounts and rebates. 71. All of the below are factors that affect how a competitor will respond to a competitive attack EXCEPT A. how dependent the competitor is on that industry or particular market segment. B. the degree of market power and reputation of the company that initiated the attack. C. the resources which are available for a firm to respond. D. the stock market reaction to the initial competitive attack. 72. Which of the following refers to a situation where a company has a high concentration of its business in a particular industry's market? A. competitor's resources B. market dependence C. resource similarity D. actor's reputation 73. A firm is considering a large price cut on its leading product as a way to gain market share. One executive strongly disagrees with the price cut and states, "We are in the same marketplace as our rivals, and we do not have any competitive advantages in our cost structure. If we cut prices, our competitors will likely do the same. The end result is that we will all make less money." These arguments are an example of A. a strategy of forbearance. B. a strategy of co-opetition. C. a hardball strategy whereby competitive actions are not undertaken without a clear advantage. D. a weakness strategy that leads a company into constant decline. 74. What is the role of opportunity recognition in the new venture development process? 75. Discuss the four characteristics of an entrepreneurial opportunity. Explain why each is important for the opportunity to be viable. 76. Discuss the role of informal investments versus venture-capital financing as it is used by entrepreneurial ventures. What are the advantages and disadvantages of each type? 77. What are the advantages and disadvantages of using venture capital to finance new ventures? 78. 78 In what ways are human capital and social capital valuable to an entrepreneurial start-up? Provide examples of each. 79. Compare and contrast the three most common new venture entry strategies: pioneering, imitative, and adaptive. 80. Define the term "competitive dynamics." Then, describe the cycle of actions and responses that are characteristic of a competitive dynamics process. 81. Compare and contrast market commonality and resource similarity. 82. According to competitive dynamics, competitors are more likely to respond when attacked in a market where the competitor relies on that market for a large portion of its sales. Why is this so? That is, what "dynamic" is at work in this situation that would cause that response? 83. What are the differences between strategic actions and tactical actions? What are the implications of each approach to the competitive dynamics process? 84. In the context of competitive dynamics, what factors determine the likelihood of a competitive response? Ch08 Summary Category # of Questions AACSB: Analytic 84 Blooms: Apply 3 Blooms: Remember 25 Blooms: Understand 56 Dess - Chapter 08 84 Learning Objective: 08-01 The role of new ventures and small businesses in the U.S. economy. 4 Learning Objective: 08-02 The role of opportunities; resources; and entrepreneurs in successfully pursuing new ventures. 36 Learning Objective: 08-03 Three types of entry strategies-pioneering; imitative; and adaptive- commonly used to launch a new venture. 10 Learning Objective: 08- 04 How the generic strategies of overall cost leadership; differentiation; and focus are used by new ventures and small businesses. 6 Learning Objective: 08- 05 How competitive actions; such as the entry of new competitors into a marketplace; may launch a cycle of actions and reactions among close competitors. 4 Learning Objective: 08-06 The components of competitive dynamics analysis- new competitive action; threat analysis; motivation and capability to respond; types of competitive actions; and likelihood of comp etitive reaction. 25 Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy 25 Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium 56 Level of Difficulty: 3 Hard 3 Topic: Competitive Dynamics 28 Topic: Entrepreneurial Strategy 16 Topic: Recognizing Entrepreneurial Opportunities 40 Ch09 Student: 1. The "traditional" approach to strategic control is interactive, while the "contemporary" approach to strategic control is sequential. True False 2. The traditional approach to strategic control relies on feedback from performance measurement to formulate strategy. True False 3. For firms competing in highly unstable and turbulent industries, "traditional" strategic controls are most appropriate. True False 4. Sales quotas, operating budgets, and production schedules are examples of "traditional" controls. True False 5. In "single loop" learning, the organization's assumptions, premises, goals, and strategies are continuously monitored, tested, and reviewed. True False 6. "Contemporary" strategic controls involve comparing actual performance to predetermined goals. True False 7. Informational control is primarily concerned with whether or not the organization is "doing the right things." True False 8. Continuous monitoring enhances an organization's ability to respond with speed and flexibility. True False 9. As firms downsize, a control system based on rewards and culture becomes dysfunctional. True False 10. For young managers who see themselves as free agents, behavioral controls such as rewards and culture can be an effective way to enhance organizational loyalty. True False 11. Once a strong and healthy organizational culture has been established, it becomes self-sustaining. True False 12. The collective sum of individual behaviors of an organization's employees generally results in what is best for the organization; thus, individual rationality assures organizational rationality. True False 13. An organization's reward system is typically a weak method of motivating employees. True False 14. Different functional areas within an organization often have different reward systems. True False 15. Rewards systems that reinforce an organization's core values and contribute to organizational cohesiveness are the least effective type. 16. For a reward system to be effective, it must be perceived as fair and equitable. True False 17. Boundaries and constraints are just used to maintain order in an organization and have little effect on the organization's strategic priorities. True False 18. Short-term objectives and action plans are types of boundaries that channel the efforts of employees toward goal accomplishment. True False 19. Unexpected events (such as wildcat strikes or new government regulations) have little effect on short- term objectives that need to remain fixed to be effective. True False 20. Action plans permit a degree of autonomy for managers who sometimes must modify activities to achieve the desired outcome. True False 21. Boundaries and constraints, when used properly, can minimize improper and unethical conduct. True False 22. Rule-based controls are appropriate in organizations where most of the employees are unskilled. True False 23. The primary participants in corporate governance, according to Monks and Minow, are (1) the shareholders, (2) board of directors, and (3) employees. True False 24. Central to agency theory is the relationship between two primary players, the principals (stockholders) and agents (management). True False 25. Research has shown that executives who have large holdings of stock in their firm were more likely to have diversification strategies more consistent with shareholder interests, like increasing long-term returns. True False 26. One of the most critical roles of the board of directors is to create incentives that align the interests of the CEO and top executives with the interests of shareholders. True False 27. The risk of being acquired by hostile raiders is often referred to as the takeover constraint. True False 28. Auditors are appointed by the Securities and Exchange Commission to audit a company's financial statements. True False 29. Stock analysts generally issue more "sell" recommendations than "buy" recommendations. True False 30. Public companies are required by law to disclose information regarding executive compensation packages. True False 31. The Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 requires that CEOs and CFOs of publicly-listed companies must reveal off-balance-sheet finances and vouch for the accuracy of information provided. 32. The Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 stipulates that executives of a firm will still be able to sell their shares in the firm when other employees cannot. True False 33. In emerging economies and continental Europe, principal-principal conflicts are frequent. These consist of conflicts between controlling shareholders and executives. True False 34. Principal-principal (PP) conflicts frequently result in expropriation, which is defined as activities to enrich minority shareholders to assure their support. True False 35. The "traditional" approach to strategic control is sequential. Which of the following is not one of the steps in the sequence? A. Action plans are submitted by lower level managers. B. Performance is measured against the predetermined goal. C. Strategies are implemented. D. Strategies are formulated and top management sets goals. 36. The primary drawback of "traditional" strategic control systems is A. they are only appropriate when the environment is stable and simple. B. goals and objectives cannot be measured with a high level of certainty. C. they lead to complacency. D. they lack the flexibility needed to adjust to changes in the environment. 37. For businesses facing complex and turbulent business environments A. goals and objectives that are uncertain prevent opportunism. B. traditional strategic controls are usually inappropriate. C. complacency about predetermined milestones can prevent adaptability. D. detailed plans are needed to maintain order. 38. Contemporary approaches to strategic control rely primarily on A. feedback controls. B. single-loop learning. C. double-loop learning. D. comparative learning. 39. Informational control systems ask A. Is the organization "doing things right"? B. Is the organization "doing the right things"? C. Are rules and regulations being followed as information is processed? D. Is the organization's environment a necessary and sufficient condition for success? 40. The benefits of continuous monitoring include A. enhancing the organization's ability to respond with speed and flexibility. B. replacing the time-consuming process of organizational learning. C. dramatically altering the organization's response to its competitive environment. D. all of these. 41. Which of the following is NOT one of the characteristics of a contemporary control system? A. It is a key catalyst for an ongoing debate about underlying data, assumptions, and action plans. B. It must focus on constantly changing information that is strategically important. C. It circumvents the need for face-to-face meetings among superiors, subordinates, and peers. D. It generates information that is important enough to demand regular and frequent attention. 42. Top managers at ABC Company meet every Friday to review daily operational reports and year-to-date data. This is an example of A. behavioral control. B. informational control. C. strategy formulation. D. strategy implementation. 43. Complete the following sentence: "As firms simultaneously downsize and face the need for increased coordination across organizational boundaries, a control system based primarily on is dysfunctional." A. boundaries and constraints B. culture and rewards C. organizational loyalty D. innovation and risk taking 44. All of the following are examples of how organizational culture exerts behavioral control EXCEPT A. culture helps maintain control by creating behavioral norms. B. culture generates unwritten standards of acceptable behavior. C. culture encourages individual identification with the organization and its objectives. D. culture sets explicit boundaries. 45. The late Sam Walton, founder of Walmart, used to give pep rallies at local Walmart stores. What purpose did this serve? A. It was used to remind employees of Walmart's rules and regulations. B. It helped reinforce and sustain Walmart's culture. C. It demonstrated to employees the importance of articulating explicit goals and objectives. D. It made Walmart's reward system very explicit. 46. Which of the following is NOT one of the characteristics of reward and incentive systems? A. They represent a poor means of influencing an organization's culture. B. They focus efforts on high-priority tasks. C. They motivate high levels of individual and collective task performance. D. They represent an effective control mechanism. 47. Complete the following sentence: "Individual rationality organizational rationality." A. is a good indicator of B. will ensure C. is often the opposite of D. does not always guarantee 48. When subcultures emerge that have shared values opposite from the dominant culture of an organization A. organizational cohesiveness increases. B. information is shared rather than hoarded. C. individuals begin working at cross purposes. D. individuals gain insights into overarching goals and objectives. 49. All of the following are characteristics of effective reward and incentive systems EXCEPT A. performance measures are clear and highly visible. B. the structure is fixed to assure employees of consistency. C. the compensation system is perceived as fair and equitable. D. objectives are well understood, and broadly accepted. 50. The causes of counterproductive behavior in organizations include A. lack of a clear understanding of organizational goals and objectives. B. motivated self-interest. C. outright malfeasance. D. all of these. 51. Effective boundaries and constraints A. tend to inhibit efficiency and effectiveness. B. distract employees who are trying to focus on organizational priorities. C. minimize improper and unethical conduct. D. tend to limit organizational growth. 52. Effective short-term objectives have all of the following priorities EXCEPT A. an emphasis on "do your best" goals. B. being achievable yet challenging. C. providing a specific time horizon for their attainment. D. being specific and measurable. 53. Which of the following statements about action plans is TRUE? A. Action plans, though specific, should permit a degree of autonomy to managers and not be constrained by budgets. B Action plans must be specific so that managers will have a clear understanding of the resource . requirements necessary to implement the plan. C. Action plans should not be constrained by a time frame in order to allow for modification. DAlthough managers must be held accountable for implementing action plans, this accountability often . erodes the managers' motivation to implement the plan on a timely basis. 54. Rules and regulations are examples of A. implicit controls. B. informational controls. C. cultural norms. D. boundaries and constraints. 55. Cadbury Schweppes has a policy that all payments, no matter how unusual, are recorded in the company's books. This rule is A. overly cumbersome. B. aimed at encouraging managers to make better budgetary decisions. C. directed at protecting client confidentiality. D. designed to minimize improper and unethical conduct. 56. Which of the following approaches to behavioral strategic control should be utilized least in an organization in which there is a great need for innovation and a high degree of autonomy? A. culture B. rewards C. boundaries D. all of these are equally important 57. Most successful organizations minimize the need for explicit rules, regulations, and other boundaries by A. posting written statements of the organization's goals and objectives. B. discouraging the formation of subcultures that isolate work groups. C. designing effective reward systems. D. encouraging employees to see themselves as free agents. 58. Rule-based controls are most appropriate in organizations with all of the following characteristics EXCEPT A. environments are stable and predictable. B. employees are highly skilled and independent. C. consistency in product and service. D. the risk of malfeasance is extremely high. 59. Rules and regulations, rather than culture or rewards, would be used for strategic control at which type of company? A. software developer B. stock brokerage firm C. manufacturer of mass produced products D. high tech research facility 60. The primary participants in corporate governance are all of the following EXCEPT A. the shareholders. B. key stakeholders such as financial institutions. C. the management (led by the chief executive officer). D. the board of directors. 61. Intel's exemplary corporate governance practices include all of the following EXCEPT A. a mix of inside and outside directors. B. all outside directors to assure objectivity in decision-making. C. board presentations and access to employees. D. formal evaluation of officers. 62. CEO duality refers to a situation in which A. the CEO formulates and implements strategies. B. the CEO serves as both the CEO and the chair of the board of directors. C. the CEO is responsible for acting as CEO and serving on the compensation committee. D. the CEO is responsible for acting as CEO and Chief Operating Officer (COO). 63. External governance control mechanisms include all of the following EXCEPT A. auditors. B. analysts. C. competitors. D. the market for corporate control. 64. If the market value of a firm becomes less than its book value, A. it becomes an attractive takeover target. B. the firm will be delisted by the stock exchange. C the Securities and Exchange Commission will not allow it to declare dividends until the market value . once again exceeds the book value. D. the firm will be unable to service its debt. 65. By takeover constraint, we mean A. constraints placed by the firm on raiders who want to takeover the firm. B. legal constraints that limit the ability of the raiders to acquire a firm. C. provisions in the charter of a company that prevents it from attempting a takeover of other companies. D. the risk of being acquired by a hostile raider. 66. It is generally argued that the takeover constraint A. deters management from engaging in opportunistic behavior. B. deters management from considering acquiring other companies. C. deters management from declaring dividends. D. deters management from increasing a firm's level of borrowing. 67. The failure of many auditing firms to raise red flags about accounting irregularities in companies such as Enron and WorldCom is generally attributed to all of the following factors EXCEPT A. the desire to get future auditing contracts from the company. B. the desire to get consulting work from the company because most audit firms also do consulting work. C. the fact that auditors are appointed by the firm. D. the failure of U.S. audit firms to hire technically qualified professionals. 68. The reasons analyst recommendations are often more optimistic than warranted by an objective analysis of a firm's prospects include all of the following EXCEPT A. many analysts fail to grasp the gravity of the problems facing a company. B. "sell" recommendations generate lower commissions than buy recommendations. C. the firms for which analysts work may have lucrative investment banking relationships with the firm. D analysts are often pressured by their superiors to overlook negative information or tone down their . criticisms of the firms they analyze. 69. All of the following are types of information that a firm is required to disclose EXCEPT A. quarterly and annual filings of financial information. B. stock trading by insiders. C. details of new products under development. D. details of executive compensation packages. 70. In emerging economies and continental Europe, firms often can be characterized by all of the following EXCEPT A. concentrated ownership. B. low family ownership and control. C. business group structures. D. weak legal protection for minority shareholders. 71. In principal-principal conflicts (conflicts between controlling shareholders and minority shareholders), the ownership (of equity) is A. widely dispersed (5-20% is considered "concentrated ownership"). B. controlled almost completely by management. C. concentrated; often greater than 50% of equity is controlled by controlling shareholders. D. often held by employee stock ownership programs. 72. Conditions for principal-principal (PP) conflicts (conflicts between controlling shareholders and minority shareholders) to occur include all of the following EXCEPT A. a dominant owner or group of owners who have interests that are distinct from minority shareholders. B. legislation that protects the interests of minority shareholders. C. a motivation for the controlling shareholders to exercise their dominant position to their advantage. Dfew formal (such as legislation or regulatory bodies) or informal constraints that discourage or prevent . the controlling shareholders from exploiting their advantageous positions. 73. Expropriation of minority shareholders means that A. minority shareholders must sell their shares upon demand. B. minority shareholders cannot own shares in foreign firms. C. minority shareholders do not receive dividends. D. minority shareholders are adversely affected by the actions of controlling shareholders. 74. What are the advantages and disadvantages associated with using "traditional" approaches to strategic control? 75. What are the advantages and disadvantages associated with using "contemporary" approaches to strategic control? 76. What are the four characteristics of effective contemporary control systems? Give examples of how firms apply these practices. 77. Why is it important to have a balance among the three behavioral controls (culture, rewards, and boundaries)? Is there a danger associated with emphasizing one behavioral approach more than another? 78. Discuss the benefits and risks of using reward and incentive systems as a means of strategic control. 79. What are the characteristics of short-term objectives? Provide examples of practical applications of these characteristics by organizations. 80. What are the three key means to align the interests of owners (shareholders) and managers in a corporation? 81. Is CEO duality "good" or "bad"? Summarize the two schools of thought that represent alternate positions on this issue. 82. What is meant by the term "market for corporate control?" How does the market for corporate control act as an external control mechanism? 83. Identify at least three external control mechanisms. Discuss the role played by each of these. 84. What is meant by principal-principal (PP) conflict? What are the implications for sound corporate governance? (p. 319) Ch10 Student: 1. In a simple structure where the owner manager makes most of the important decisions, extensive rules and regulations are used to maintain order. True False 2. A small firm with a simple structure often fosters creativity and individualism because of its informal atmosphere. True False 3. A simple organizational structure may lead to problems such as unclear boundaries of authority and few career advancement options. True False 4. As firms grow, owner managers often need to hire functional specialists to handle the increased information-processing burden. True False 5. To enhance integration and control of related product market activities, the functional structure minimizes centralization. True False 6. One disadvantage of a functional structure is that differences in functional orientation may impede organization coordination and communication. True False 7. Operational decision making in a large business places excessive demands on the firm's top management. True False 8. A major disadvantage of adopting a divisional structure is the tendency for managers to focus on short- term objectives. True False 9. A major disadvantage of a divisional structure is that when divisions are separated to manage individual product-markets, there is a separation of strategic and operational control. True False 10. The strategic business unit (SBU) and holding company structure are variants of the functional form of structure. True False 11. The strategic business unit (SBU) structure is also referred to as the conglomerate structure. True False 12. One major advantage of the holding company form of organization structure is that it minimizes the duplication of functional activities between product lines. True False 13. The matrix structure attempts to combine the advantages of the functional and product-oriented structure. True False 14. A matrix organization is organized strictly along product lines. True False 15. A major disadvantage of the matrix structure is that it duplicates the use of specialized personnel, equipment, and facilities. True False 16. A worldwide product division structure is used when global strategies require that each division be responsible for overall efficiency and performance. True False 17. A global startup typically benefits from lower communication, coordination, and transportation costs. True False 18. A firm's structure typically has almost no effect on its strategy. True False 19. For firms that compete on the basis of cost leadership, incentives tend to be primarily based on explicit financial targets. True False 20. For firms following a differentiation strategy, behavioral and intangible incentives are not an effective means of motivating employees. True False 21. For firms following related diversification strategies, reward and evaluation systems should rely primarily on behavioral indicators, since the organization needs to reward and reinforce behaviors that facilitate sharing and collaboration. True False 22. According to the text, boundaryless organizational structures are most effective when they replace rather than complement traditional organizational structures. True False 23. The purpose of boundaryless forms of organizing is to facilitate the widespread sharing of knowledge and information across internal and external boundaries of the organization. True False 24. In a barrier-free organization, differences in skills, authority, and talent disappear. True False 25. An advantage of the barrier-free form of organizing is that internal cooperation and shared objectives are not required for it to work. True False 26. According to the text, the factor that most distinguishes a "superior" team from a "good" team is talent. True False 27. Because the modular form of organizing involves outsourcing vital functions, modular firms often forfeit full strategic control. True False 28. Modular companies can achieve rapid growth because they don't require large investments in fixed assets. True False 29. Outsourcing relieves companies of the requirement to maintain skill levels needed to manufacture essential components. True False 30. One of the risks of outsourcing is a loss of cross-functional skills. True False 31. The virtual type of organization is a network of independent companies linked together to share skills, costs, and access to one another's markets. True False 32. The virtual organization is characterized by participating firms which pursue a collective strategy that enables them to cope with environmental uncertainty through cooperative efforts. True False 33. Managing virtual structures requires new and difficult-to-acquire managerial skills. True False 34. Horizontal organization structures facilitate resource sharing and help create a sense of common purpose. True False 35. One of the advantages of boundaryless structures is that they can be implemented without upgrading the skills of workers and managers. True False 36. Firms must create ambidextrous organizations primarily to help manage operations in multiple countries. True False 37. It is challenging to become an ambidextrous organization and get the proper balance of "alignment" and "adaptability." True False 38. Generally speaking, discussions of the relationship between strategy and structure strongly imply that A. strategy follows structure. B. structure follows strategy. C. strategy can effectively be formulated without considering structural elements. D. structure typically has a very small influence on a firm's strategy. 39. When an organization with a simple structure increases its sales revenue and volume of outputs, it is most likely to develop a A. divisional structure. B. functional structure. C. product-market structure. D. geographic structure. 40. When an organization with a functional structure diversifies into related product-markets, it generally A. maintains its functional structure. B. develops a divisional structure. C. develops a matrix structure. D. develops a worldwide product-division structure. 41. A strategy of related diversification requires most firms to organize around geographical areas or product lines. This type of organizational growth leads to a(n) A. divisional structure. B. functional structure. C. matrix structure. D. international structure. 42. All of the following statements about simple organizational structures are true EXCEPT which? A. Small firms with a narrow product-market scope will adopt such a structure. B. Decision making authority is highly centralized. C. There is little specialization of tasks. D. Creativity and individualism are rare. 43. A simple structure is characterized by A. high specialization and low centralization. B. low specialization and high centralization. C. low formality and low creativity. D. high formality and low centralization. 44. Functional structures are usually found in organizations where there is A. high volume production. B. unrelated product lines or service offerings. C. very little vertical integration. D. a strong need to decentralize decision making. 45. At ABC Corporation, work is divided into units that specialize in production, marketing, research and development, and other management tasks. This is an example of a A. simple structure. B. functional structure. C. divisional structure. D. matrix structure. 46. Which of the following is an advantage of a functional type of organizational structure? A. Decentralized decision-making enhances an organization-wide perspective across functions. B. It facilitates the development of general management talent. C. Pooling of specialists enhances coordination and control. D. It is easy to establish uniform performance standards. 47. Which of the following is a disadvantage of a functional type of organizational structure? A. Differences in functional orientation may impede communication and coordination. B. Use of managerial and technical talent is inefficient due to pooling of expertise in functional areas. C. Decision making is centralized at the top of the organization. D. Managers tend to be overly concerned with long-term strategies that minimize the importance of functional area strengths. 48. A divisional structure A. is organized around functional area departments. B. typically improves the performance of firms pursuing a strategy of vertical integration. C. facilitates the development of general managers. D. enhances centralized decision making. 49. Which of the following is an advantage of a divisional type of organizational structure? A. Efficient use of managerial and technical talent. B. An enhanced ability to respond quickly to changes in the external environment. C. High degree of emphasis on long-term performance. D. Uniformity in image and quality across divisions. 50. All of the following are disadvantages of a divisional type of organizational structure EXCEPT A. it can be very expensive compared to a functional organizational structure. B. there is a strong tendency for divisions to focus on short-term performance. C. there can be dysfunctional competition among divisions. D. there is separation of strategic and operating control. 51. An organization such as ConAgra that has dozens of different divisions with similar products will probably have the greatest success with which form of organization structure? A. Functional structure B. Matrix structure C. Strategic business unit structure D. Holding company structure 52. All of the following are advantages of a strategic business unit (SBU) type of organizational structure EXCEPT A. divisions with similar products, markets, or technologies are formed into homogeneous groups that can achieve synergies. B. divisional executives can respond quickly to market changes and opportunities. C. planning and control by the corporate office is more manageable. D. the corporate office is more removed from the individual divisions. 53. Important advantages of a holding company structure include A. savings in personnel and overhead expenses associated with a small corporate office. B. a high level of awareness at the corporate office of issues facing individual divisions. C. a high level of control of division executives by executives at the corporate level. D. gaining synergistic benefits across businesses. 54. Strategic business unit (SBU) and holding company structures result from extensive A. diversification. B. vertical integration. C. international expansion. D. organizational flattening. 55. Complete the following sentence: "Strategic business unit (SBU) structures are best suited for corporations pursuing , whereas holding company structures are best suited for companies with strategies." A. product-market diversification; international B. international diversification; product-market C. related diversification; unrelated diversification D. unrelated diversification; related diversification 56. A matrix organizational structure is characterized by A. dual reporting relationships. B. a combination of functional and divisional organization structures. C. efficient use of resources and expertise. D. all of these. 57. Complicated working relationships, intense power struggles, and excessive reliance on group processes are disadvantages of what type of organizational structure? A. divisional B. matrix C. holding company D. functional 58. Which of the following is considered to be an advantage of a matrix structure? A. the layering of matrices B. increased clarity in reporting relationships C. increased responsiveness to the market D. fewer power struggles and reduced conflict 59. If an international firm has a multidomestic strategy and a relatively high level of product diversity, the best choice for its organizational structure is A. worldwide functional. B. worldwide product division. C. worldwide matrix. D. international division. 60. If an international firm has a global strategy and a relatively low level of product diversity, the best choice for its organizational structure is A. worldwide functional. B. worldwide product division. C. worldwide matrix. D. international division. 61. The relationship between strategy and structure can be best described as A. strategy determines structure but structure does not determine strategy. B. structure determines strategy but strategy does not determine structure. C. strategy and structure influence each other. D. a third force determines both strategy and structure. 62. In firms with overall low cost strategies, the culture should foster levels of interdependence and rewards should be based primarily on measures of output. A. low; financial B. low; behavioral C. high; financial D. high; behavioral 63. In firms with differentiation strategies, the culture should foster levels of interdependence and rewards should be based primarily on measures of output. A. low; financial B. low; behavioral C. high; financial D. high; behavioral 64. In firms with related diversification strategies, the culture should foster levels of interdependence and rewards should be based primarily on measures of output. A. low; financial B. low; behavioral C. high; financial D. high; behavioral 65. In firms with unrelated diversification strategies, the culture should foster levels of interdependence and rewards should be based primarily on measures of output. A. low; financial B. low; behavioral C. high; financial D. high; behavioral 66. Which of the following is not a boundaryless organizational design? A. virtual B. modular C. matrix D. barrier-free 67. Which of the following is NOT an advantage of teams? A. Because teams interact so closely, coordination and integration becomes unnecessary. B. Teams substitute peer-based control for hierarchical control of work. C. Because of sharing, teams often develop more creative solutions. D. Teams permit the absorption of administrative tasks previously performed by specialists. 68. According to the text, there are elements of team building that influence a team's success. These include all of the following EXCEPT A. work. Work should be relevant and meaningful to group members. B. people bonding during the "heat of the battle." Team members become more unified during a crisis. C. titles. Titles are important to a team's success. D. teams taking care of their own. Team members look after each other's best interest. 69. Organizations are increasingly using teams for many reasons. The difference between a good team and an outstanding team has been found to be A. the combined technical skills of the members. B. similarities in the way team members solve problems. C. the way team members treat each other. D. similarities in the age and experience of team members. 70. Which of the following is NOT a disadvantage of the barrier-free form of organization? A. Lack of strong leadership can lead to coordination problems. B. Democratic process can be time-consuming and difficult to manage. C. Additional integration issues result is a slower response to market changes. D. If trust among employees is not sufficiently high, organizational performance may suffer. 71. What type of organization is defined as "a central hub surrounded by networks of outside suppliers and specialists"? A. matrix B. virtual C. modular D. barrier-free 72. What is the name of the practice that many modular organizations use to grow? A. operational effectiveness B. outsourcing C. strategic leveraging D. strategic enabling 73. What advantages does outsourcing provide an organization? A. accessing best in class goods and services B. enabling rapid expansion with relatively low capital investment C. focusing scarce resources on core competencies D. all of these 74. Which of the following is NOT a strategic risk of outsourcing? A. loss of critical skills B. loss of cross-functional skills C. loss of control over a supplier D. loss of non-vital functions 75. Nike is a company that makes use of the concept of "product expatriates." Product expatriates are A. managers from the home country sent abroad to oversee the marketing of a company's products. B. managers from suppliers who come to work at a company's headquarters. C. managers of the company sent abroad to work at the plants of its suppliers. D. local nationals hired by the company in the countries from which it sources products. 76. The phrase that best defines a virtual organization is A. a dot.com company. B. a type of modular structure. C. an organization that uses information technology to integrate different functions. D. a continually evolving network of independent companies. 77. Lockheed Martin uses a coalition of three entities, its own company, academia, and government, to achieve its goals. This is an example of a A. matrix organization. B. modular organization. C. virtual organization. D. divisional structure. 78. Complete the following sentence: "Virtual organizations whereas modular organizations ." A. are usually permanent; are usually temporary B. accept interdependent destinies; pursue collective strategies C. pursue collective strategies; forfeit strategic control D. give up part of their strategic control; retain full strategic control 79. Which of the following is not a disadvantage of virtual structures? A. difficulty in individual and organizational knowledge sharing B. potential loss of operational control among partners C. loss of strategic control over emerging technology D. difficulty in determining where one company ends and another begins due to close interdependencies 80. Technical Computer Graphics uses small project teams and forms alliances with its teams, customers, and suppliers to accomplish projects. This is an example of A. combining forms of boundaryless organizations. B. outsourcing. C. horizontal systems and processes. D. democratic management control. 81. Organizations generally tend to become internally focused when faced with A. resource scarcity. B. declining performance. C. external pressures. D. all of these. 82. Tools and techniques used to achieve effective coordination and integration of key activities in an organization include all of the following EXCEPT A. horizontal organization structures. B. horizontal systems and processes. C. horizontal diversification. D. communications and information technologies. 83. Effective ambidextrous organizations have alignment, which means that A. employees are rewarded according to both profit and sales growth. B. managers are focused on growth opportunities. C. there is a clear sense of how value is being created in the short-term and how activities are properly integrated and coordinated. D. divisional-level goals are consistent with overall corporate goals. 84. According to the study by O'Reilly and Tushman, effective ambidextrous structures had all of the following attributes EXCEPT A. a clear and compelling vision. B. managerial efforts were highly focused on revenue enhancement. C. cross-fertilization among business units. D. established units were shielded from the distractions of launching new businesses. 85. How do organizational structures change as organizations grow and mature? What are the dominant patterns of growth? 86. Describe the attributes of a simple organizational structure. What are the advantages and disadvantages associated with using the simple organizational form? 87. Describe the attributes of a functional organizational structure. What are the advantages and disadvantages associated with using the functional organizational form? 88. Describe the attributes of a divisional organizational structure. What are the advantages and disadvantages associated with using the divisional organizational form? 89. Briefly describe the strategic business unit (SBU) and holding company organizational structures. Under what circumstances do organizations choose these forms of organizing? 90. Describe the attributes of a matrix organizational structure. What are the advantages and disadvantages associated with using the matrix organizational form? 91. Briefly describe global start-ups. What advantages do they have and what challenges do they face? 92. Discuss the contingent nature of reward and evaluation systems as they relate to both business-level and corporate-level strategies. 93. Discuss how changes in today's workforce and the business environment have contributed to growth in the use of boundaryless organizational designs. 94. Discuss the uses and limitations of the barrier-free organizational structure. What is the role of teams in the barrier-free organization? 95. Discuss the uses and limitations of the modular organizational structure. What is the role of outsourcing in the modular organization? 96. Describe the virtual organizational form. How and why are organizations choosing to implement this approach to organizing? Provide examples of organizations that have used a virtual organizational structure. 97. What are ambidextrous organizations? When should they be used and how can they be made effective? 1. (p. 359) 2. (p. 359) 3. (p. 359) 4. (p. 359) Ch11 Student: 1. Three key interdependent strategic leadership activities are: designing the organization; determining its direction; and, nurturing a culture dedicated to excellence and ethical behavior. True False 2. Setting a direction is the leadership activity that involves developing a strategic vision of what the organization could become. True False 3. Designing the organization is the leadership activity that involves building structures, teams, systems, and processes that facilitate the implementation of a leader's vision. True False 4. Leaders play an important role in sustaining an organization's culture, but they are powerless to change it. True False 5. Leaders are not expected to accept personal responsibility for ethical behavior in an organization because ethics is a matter of individual choice. True False 6. Conventional decision making involves considering two conflicting ideas simultaneously without dismissing one of the ideas or becoming discouraged about reconciling them. True False 7. Integrative thinking is the process by which people reconcile opposing thoughts to identify creative solutions that provide them with more options and new alternatives. True False 8. The tendency of many individuals to throw "good money at bad decisions" despite negative performance feedback is referred to as "escalation." True False 9. Systemic barriers to change refer to elements of an organization's design, structure, and reporting relationships that impede the flow of information. True False 10. Behavioral barriers to change occur because of conflicts between departments, conflicts arising from power relationships, and refusal to share information. True False 11. The two broad bases of a leader's power are organizational and hierarchical. True False 12. "Referent power" refers to a manager's identification with his or her employees. True False 13. "Coercive power" is the power exercised by use of fear of punishment for errors of either omission or commission by employees. True False 14. Emotional Intelligence (EI) is one of the components of a high Intelligence Quotient (IQ). True False 15. Emotional Intelligence (EI) is generally a better predictor of life success than Intelligence Quotient (IQ). True False 16. Empathy, one of the components of Emotional Intelligence (EI), refers to one's proficiency in managing relationships and building networks. True False 17. Organizational learning works best when an organization's leaders gather information and teach it to employees who are like their students. True False 18. Successful learning organizations have a proactive, creative approach to the unknown. True False 19. A key function of the leaders in a learning organization is to generate an organization-wide commitment to the status quo. True False 20. Inspiring and motivating people with a mission or purpose is a necessary and sufficient condition for developing a learning organization. True False 21. To successfully empower employees to achieve organizational goals, leaders must perform the tasks of resource allocation and power brokering. True False 22. In the "top-down" approach to empowerment, leaders clarify the mission, delegate responsibility, and hold people accountable for results. True False 23. The "top-down" view of empowerment is concerned with risk taking, change, and "doing the right thing." True False 24. The trend among many organizations is toward forms of empowerment that rely on trust, team building, and the expertise of employees at all levels. True False 25. The phrase "Lead, follow, or get out of the way" is indicative of the bottom-up approach to empowerment. True False 26. "Open book" management is a technique for gathering and disseminating internal information so that all employees can be involved in decision making and management. True False 27. Internal benchmarking is discouraged in most organizations because it creates competition and internal rivalries that are counterproductive. True False 28. In order to gather information from informal sources, successful executives must be good listeners. True False 29. Competitive benchmarking is a method of seeking the best examples of practices or processes that have essentially the same function regardless of industry. True False 30. Establishing a culture of dissent can be an effective means of questioning the status quo. True False 31. Although many organizations encourage creativity and risk taking, few successful companies tolerate failure. True False 32. Leaders who fail to institute proper systems and controls that facilitate ethical conduct share responsibility with those who conceive, execute, and knowingly benefit from corporate misdeeds. True False 33. Ethical crises are bad for an organization's reputation but they rarely have any financial consequences. True False 34. There are many advantages of an ethical organization, but it generally has little to do with employee commitment and motivation to excel. True False 35. A compliance-based approach to ethics management combines a concern for law with an emphasis on managerial responsibility for ethical behavior. True False 36. Corporate codes of conduct provide norms and expectations for employees to not commit unethical acts. True False 37. An effective way to instill ethical behavior in an organization is to distribute rewards strictly on the basis of outcomes. True False 38. Inappropriate reward systems seldom cause individuals at all levels throughout an organization to commit unethical acts since people are either unethical or ethical in their behavior. True False 39. Which of the following is an important characteristic of a leader? A. goal-oriented B. satisfied with the status quo C. reactive D. focused on past performance 40. All of the following statements about leadership are true EXCEPT A. leadership is focused on the creation and implementation of a creative vision. B. leadership is the process of transforming organizations from what they are to what the leader would have them become. C. leaders support the status quo and seek control mechanisms to maintain it. D. effective implementation of strategy is essential for successful leadership. 41. According to the text, effective leadership is like a three-legged stool consisting of all of the following EXCEPT A. dedication to maintaining the status quo. B. nurturing a culture dedicated to excellence and ethical behavior. C. determining a direction. D. designing the organization. 42. The leader's role in developing a strategic vision provides many benefits including A. a clear future direction. B. a framework for their organization's mission and goals. C. enhanced employee communication and commitment. D. all of these. 43. Poor organizational design by leaders can result in all of the following EXCEPT A. insufficient mechanisms that integrate and coordinate activities across the firm. B. inadequate accountability among managers and employees. C. inappropriate budgeting and control systems. D. teams, systems, and organizational processes that facilitate implementation. 44. XYZ's CEO scrapped the company's commission-based reward system because it was rewarding employees for inappropriate behavior. This is an example of A. setting a direction. B. designing the organization. C. unethical behavior. D. failure to maintain the status quo. 45. Leaders play a key role in developing and sustaining an organization's A. status quo. B. culture. C. reporting relationships. D. rules and regulations. 46. The process by which people reconcile opposing thoughts to identify creative solutions that provide them with more options and new alternatives is known as A. designing the organization. B. conservative thinking. C. ethical planning. D. integrative thinking. 47. All of the following stages are part of the integrative thinking and deciding process EXCEPT A. causality. B. conservation. C. architecture. D. salience. 48. In the integrative thinking and deciding process, making a mental map of the causal relationships between the elements of a decision to evaluate how the elements relate to one another is known as A. architecture. B. causality. C. visualization. D. multidimensionality. 49. Barriers in which the design of the organization's structure, information processing, and reporting relationships, impede the proper flow and evaluation of information are known as A. systemic barriers. B. behavioral barriers. C. political barriers. D. barriers to entry. 50. Barriers associated with a manager's tendency to look at issues from a biased or limited perspective are known as A. systemic barriers. B. behavioral barriers. C. political barriers. D. barriers to exit. 51. Refusal to share information, conflicts over resources, conflicts between departments and divisions, and petty interpersonal differences are symptoms of which type of barrier to change? A. systemic barriers B. political barriers C. behavioral barriers D. all of these 52. Which of the following explains why organizations are prone to inertia and slow to change? A. personal time constraints B. political barriers C. vested interests in the status quo D. all of these 53. All of the following constitute organizational bases of a leader's power EXCEPT A. legitimate power. B. reward power. C. referent power. D. coercive power. 54. Expert power A. is derived from organizationally conferred decision-making authority. B. arises from a manager's access, control, and distribution of information that is not freely available to everyone in an organization. C. is derived from referent power. D. is derived from the leader's capability and knowledge in a particular field. 55. Coercive power is A. the power exercised by use of fear of punishment for errors of omission or commission by employees. B. the power of persuasion exercised by a charismatic leader to get compliance from reluctant subordinates. C is the type that arises from a manager's access, control, and distribution of information that is not freely . available to everyone in an organization. D. the ability of the leader or manager to confer rewards for positive behaviors or outcomes. 56. The source of referent power is A. a subordinate's identification with the leader. B. a leader's identification with the subordinates. C. derived from the fact that the manager can potentially act as a reference when the employee applies for another job. D. derived from the manager's ability to provide effective incentives to employees. 57. The three broad sets of capabilities that a leader should possess include all of the following EXCEPT A. technical skills. B. cognitive abilities. C. calculative abilities. D. emotional intelligence. 58. All of the following are components of Emotional Intelligence (EI) EXCEPT A. self-awareness. B. self-regulation. C. self-promotion. D. empathy. 59. Which component of Emotional Intelligence (EI) enables a manager to have a deep understanding of the existence and importance of cultural and ethnic differences? A. self-awareness B. empathy C. social skills D. self-regulation 60. The following two components of Emotional Intelligence (EI) deal with a person's ability to manage relationships with others: A. motivation and self-awareness. B. self-regulation and empathy. C. empathy and social skill. D. motivation and empathy. 61. Complete the following sentence. The days when a company's leader are gone; today, all employees need to be involved in . A. learned for the organization; learning and adapting B. managed from the top; self-management C. delegated authority; assuming responsibility and control D. was held in high regard; holding leaders accountable for their actions 62. What happens to organizations that get caught up in day-to-day work activities? A. They fail to think objectively about themselves and their business. B. They fail to refresh their strategies or reengineer their work processes. C. They fail to ask probing questions about their basic assumptions. D. All of these. 63. Which of the following is not a characteristic of a successful learning organization? A. They create a proactive, creative approach to the unknown. B. They actively solicit the involvement of employees at all levels. C. They regularly engage in activities to reinforce the status quo. D. They enable everyone to use their intelligence and apply their imagination. 64. Complete the following sentence. "Inspiring and motivating people with a mission or purpose is a for developing an organization that can learn and adapt." A. necessary and sufficient condition B. necessary, but not a sufficient condition C. goal, but not a necessary condition D. goal and a required pre-condition 65. In order to create an environment where employees can achieve their potential as they move the organization towards its goals, the manager's role needs to be that of A. resource allocator. B. resource controller. C. a flexible resource. D. an advocator of the status quo. 66. The "top-down" perspective of empowerment A. encourages intelligent risk taking. B. trusts people to perform. C. encourages cooperative behavior. D. delegates responsibility. 67. The "bottom-up" perspective of empowerment A. clarifies the organization's values and mission. B. builds teams to encourage cooperative behavior. C. communicates specific plans. D. encourages employees to "ask permission rather than forgiveness." 68. The empowerment perspective that involves trusting people to "do the right thing," take intelligent risks, and act with a sense of ownership is known as A. the leadership perspective. B. the top-down approach. C. the bottom-up approach. D. the risk-taking model. 69. An empowerment perspective that delegates responsibility, focuses on accountability, and relies on clearly specified rewards to motivate is known as A. the leadership perspective. B. the top-down approach. C. the bottom-up approach. D. the accounting model. 70. Manufacturing employees at Chaparral Steel are directly involved with customers and have access to the new innovative knowledge being developed in its manufacturing processes. This is an example of A. hierarchical control. B. knowledge management. C. enabling heroes and drones. D. employee empowerment. 71. Which of the following is NOT one of the three core activities in the "open book" management system pioneered by Jack Stack? A. Information is generated daily that reflects the work performance and production costs of each employee. B. The information is aggregated once a week and shared with employees at every level. C. Information about customer expectations and feedback is distributed monthly. D. Extensive training in how to use and interpret the numbers is provided to all employees. 72. At Whole Foods, the "no secrets" management philosophy allows employees access to most of the company's operating and financial data. This is an example of A. information sharing. B. employee advocacy. C. bottom-up empowerment. D. internal benchmarking. 73. Internal benchmarking at Whole Foods A. is used by teams to compete against other teams in their stores. B. is used by teams which compete against their own goals for sales, growth, and productivity. C. is used by teams to compete against similar teams at different stores and regions. D. all of these. 74. Functional benchmarking A. is not very useful for organizations with a divisional organizational structure. B. endeavors to determine best practices regardless of industry. C. restricts the search for best practices to competitors. D. is useful when researching industry-specific standards. 75. All of the following are guidelines an organization can use to promote the challenging of the status quo EXCEPT A. establishing a "culture of dissent." B. forcefully creating a sense of urgency. C. fostering a culture that encourages risk taking. D. creating a results-based reward system. 76. Companies that cultivate cultures of experimentation and curiosity make sure that is not, in essence, to be avoided at all costs. A. experimentation B. failure C. authority D. risk taking 77. Which of the following statements about ethics is FALSE? A. Ethics may be defined as a system of right and wrong. B. Ethics assists individuals in deciding when an act is moral or immoral. C. Ethics is NOT concerned with whether or not an act is socially desirable. D. Business ethics is the application of ethical standards to commercial enterprises. 78. As a manager, when faced with ethical crises you should A. focus on issues most relevant to stockholders. B. wait for the other party to make the first move. C. take the initiative to address the problem. D. cover up as much as possible. 79. All of the following statements about ethical organizations are true EXCEPT A. the potential benefits of an ethical organization are few but direct. B. ethical values shape the search for opportunities. C. organizational ethics define what a company is and what it stands for. D. ethics provide a common frame of reference that serves as a unifying force. 80. Proactive measures to prevent organizational ethics problems include all of the following EXCEPT A. instituting a reward system which considers outcomes as its primary criterion. B. using leaders as role models of ethical behavior. C. issuing statements describing the organization's commitment to certain standards of behavior. D. using the organization's information systems as a control system. 81. Which of the following statements would least likely be found in a corporate credo? A. Maximize financial benefits for stakeholders. B. Provide secure and stable employment for employees. C. Establish an environment that enhances professional growth. D. Support community organizations and projects. 82. Briefly discuss the three interdependent activities that are critical for effective leadership. 83. What are the four stages of the integrative thinking and deciding process? Discuss how these relate to each other and how they might or might not be part of a conventional thinking process. 84. Discuss the organizational and personal bases of a leader's power. 85. Identify the five components of Emotional Intelligence (EI). Discuss how each of these factors contributes to the success of a leader or manager. 86. What are some of the potential drawbacks of emotional intelligence? 87. What are the five elements of a learning organization? What is the value of a learning organization in today's global marketplace? 88. What is the difference between "top-down" and "bottom-up" approaches to empowerment? Discuss how these differences impact the effectiveness of empowerment efforts. 89. What is "open book" management? Why is this and other approaches to accumulating and sharing internal information being used increasingly in today's organizations? 90. What is the leader's role in establishing an ethical organization? 91. How can developing and maintaining a high ethical standard benefit an organization? Give examples and describe the effects the examples have had on the organization and/or its stakeholders. 92. Discuss the differences between integrity-based and compliance-based approaches to organizational ethics. 93. What is a corporate credo? How can it be helpful in shaping the moral dimensions of an organization? 94. Briefly discuss how an organization's reward and evaluation systems can be used to promote organizational ethics. 1. (p. 396) 2. (p. 397) 3. (p. 398) 4. (p. 398) Ch11 Key Three key interdependent strategic leadership activities are: designing the organization; determining its direction; and, nurturing a culture dedicated to excellence and ethical behavior. TRUE Many authors contend that successful leaders must recognize three interdependent activities that must be continually reassessed for organizations to succeed. As shown in Exhibit 11.1, these are: (1) setting a direction, (2) designing the organization, and (3) nurturing a culture dedicated to excellence and ethical behavior. Refer to Exhibit 11.1 AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 11 #1 Learning Objective: 11-01 The three key interdependent activities in which all successful leaders must be continually engaged. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Leadership: Three Interdependent Activities Setting a direction is the leadership activity that involves developing a strategic vision of what the organization could become. TRUE Setting a direction includes developing a knowledge of all of the company's stakeholders and other salient environmental trends and events. Managers must integrate this knowledge into a vision of what the organization could become. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 11 #2 Learning Objective: 11-01 The three key interdependent activities in which all successful leaders must be continually engaged. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Leadership: Three Interdependent Activities Designing the organization is the leadership activity that involves building structures, teams, systems, and processes that facilitate the implementation of a leader's vision. TRUE When designing the organization, successful leaders are actively involved in building structures, teams, systems, and organizational processes that facilitate the implementation of their vision and strategies. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 11 #3 Learning Objective: 11-01 The three key interdependent activities in which all successful leaders must be continually engaged. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Leadership: Three Interdependent Activities Leaders play an important role in sustaining an organization's culture, but they are powerless to change it. FALSE Leaders play a key role in changing, developing, and sustaining an organization's culture. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #4 Learning Objective: 11-01 The three key interdependent activities in which all successful leaders must be continually engaged. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Leadership: Three Interdependent Activities 5. (p. 400) 6. (p. 401) 7. (p. 401) 8. (p. 402) Leaders are not expected to accept personal responsibility for ethical behavior in an organization because ethics is a matter of individual choice. FALSE Managers and top executives must accept personal responsibility for developing and strengthening ethical behavior throughout the organization. They must consistently demonstrate that such behavior is central to the vision and mission of the organization. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #5 Learning Objective: 11-01 The three key interdependent activities in which all successful leaders must be continually engaged. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Leadership: Three Interdependent Activities Conventional decision making involves considering two conflicting ideas simultaneously without dismissing one of the ideas or becoming discouraged about reconciling them. FALSE In Roger L. Martin's book The Opposable Mind, he contends that people who can consider two conflicting ideas simultaneously, without dismissing one of the ideas or becoming discouraged about reconciling them, often make the best problem solvers because of their ability to creatively synthesize the opposing thoughts. In contrast to conventional thinking, this reconciling of opposing thoughts is called integrative thinking. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #6 Learning Objective: 11-02 Three elements of effective leadership: integrative thinking; overcoming barriers to change; and the effective use of power. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Elements of Effective Leadership Integrative thinking is the process by which people reconcile opposing thoughts to identify creative solutions that provide them with more options and new alternatives. TRUE In contrast to conventional thinking, which tends to focus on making choices between competing ideas from a limited set of alternatives, integrative thinking is the process by which people reconcile opposing thoughts to identify creative solutions that provide them with more options and new alternatives. Exhibit 11.2 outlines the four stages of the integrative thinking and deciding process. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 11 #7 Learning Objective: 11-02 Three elements of effective leadership: integrative thinking; overcoming barriers to change; and the effective use of power. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Elements of Effective Leadership The tendency of many individuals to throw "good money at bad decisions" despite negative performance feedback is referred to as "escalation." TRUE Many people have vested interests in the status quo. People tend to be risk averse and resistant to change. There is a broad stream of research on "escalation," wherein certain individuals continue to throw "good money at bad decisions" despite negative performance feedback. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 11 #8 Learning Objective: 11-02 Three elements of effective leadership: integrative thinking; overcoming barriers to change; and the effective use of power. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Elements of Effective Leadership 9. (p. 402) 10. (p. 403- 404) 11. (p. 404) 12. (p. 404) Systemic barriers to change refer to elements of an organization's design, structure, and reporting relationships that impede the flow of information. TRUE Organizations at all levels are prone to inertia and are slow to learn, adapt, and change because there are systemic barriers. The design of the organization's structure, information processing, reporting relationships, and so forth impede the proper flow and evaluation of information. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 11 #9 Learning Objective: 11-02 Three elements of effective leadership: integrative thinking; overcoming barriers to change; and the effective use of power. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Elements of Effective Leadership Behavioral barriers to change occur because of conflicts between departments, conflicts arising from power relationships, and refusal to share information. FALSE Behavioral barriers cause managers to look at issues from a biased or limited perspective due to their education, training, work experiences, and so forth. Political barriers refer to conflicts arising from power relationships. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #10 Learning Objective: 11-02 Three elements of effective leadership: integrative thinking; overcoming barriers to change; and the effective use of power. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Elements of Effective Leadership The two broad bases of a leader's power are organizational and hierarchical. FALSE A leader derives his or her power from several sources or bases. The simplest way to understand the bases of power is by classifying them as organizational and personal, as shown in Exhibit 11.3. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 11 #11 Learning Objective: 11-02 Three elements of effective leadership: integrative thinking; overcoming barriers to change; and the effective use of power. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Elements of Effective Leadership "Referent power" refers to a manager's identification with his or her employees. FALSE The source of referent power is a subordinate's identification with the leader. A leader's personal attributes or charisma might influence subordinates and make them devoted to that leader. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 11 #12 Learning Objective: 11-02 Three elements of effective leadership: integrative thinking; overcoming barriers to change; and the effective use of power. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Elements of Effective Leadership 13. (p. 404) 14. (p. 407) 15. (p. 407) 16. (p. 407) "Coercive power" is the power exercised by use of fear of punishment for errors of either omission or commission by employees. TRUE Coercive power is the power a manager exercises over employees using fear of punishment for errors of omission or commission. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 11 #13 Learning Objective: 11-02 Three elements of effective leadership: integrative thinking; overcoming barriers to change; and the effective use of power. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Elements of Effective Leadership Emotional Intelligence (EI) is one of the components of a high Intelligence Quotient (IQ). FALSE Exhibit 11.4 identifies the five components of EI: self-awareness, self-regulation, motivation, empathy, and social skill. Findings indicate that EI is a better predictor of life success (economic well- being, satisfaction with life, friendship, family life), including occupational attainments, than IQ. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 11 #14 Learning Objective: 11-03 The crucial role of emotional intelligence (EI) in successful leadership as well as its potential drawbacks. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Emotional Intelligence: A Key Leadership Trait Emotional Intelligence (EI) is generally a better predictor of life success than Intelligence Quotient (IQ). TRUE Findings indicate that EI is a better predictor of life success (economic well-being, satisfaction with life, friendship, family life), including occupational attainments, than IQ. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #15 Learning Objective: 11-03 The crucial role of emotional intelligence (EI) in successful leadership as well as its potential drawbacks. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Emotional Intelligence: A Key Leadership Trait Empathy, one of the components of Emotional Intelligence (EI), refers to one's proficiency in managing relationships and building networks. FALSE According to Exhibit 11.4, empathy is the ability to understand the emotional makeup of other people, and skill in treating people according to their emotional reactions. Social skill is proficiency in managing relationships and building networks and an ability to find common ground and build rapport. Refer to Exhibit 11.4 AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 11 #16 Learning Objective: 11-03 The crucial role of emotional intelligence (EI) in successful leadership as well as its potential drawbacks. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Emotional Intelligence: A Key Leadership Trait 17. (p. 410) 18. (p. 411) 19. (p. 411) 20. (p. 412) Organizational learning works best when an organization's leaders gather information and teach it to employees who are like their students. FALSE As noted by today's leading expert on learning organizations, MIT's Peter Senge, the days when Henry Ford, Alfred Sloan, and Tom Watson "learned for the organization" are gone. "In an increasingly dynamic, interdependent, and unpredictable world, it is simply no longer possible for anyone to "figure it all out at the top." The old model, "the top thinks and the local acts," must now give way to integrating thinking and acting at all levels." AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #17 Learning Objective: 11-04 The value of creating and maintaining a learning organization in todays global marketplace. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Developing a Learning Organization Successful learning organizations have a proactive, creative approach to the unknown. TRUE Successful learning organizations create a proactive, creative approach to the unknown, actively solicit the involvement of employees at all levels, and enable all employees to use their intelligence and apply their imagination. Higher-level skills are required of everyone, not just those at the top. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #18 Learning Objective: 11-04 The value of creating and maintaining a learning organization in todays global marketplace. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Developing a Learning Organization A key function of the leaders in a learning organization is to generate an organization-wide commitment to the status quo. FALSE A learning environment involves organization-wide commitment to change, an action orientation, and applicable tools and methods. It must be viewed by everyone as a guiding philosophy and not simply as another change program. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #19 Learning Objective: 11-04 The value of creating and maintaining a learning organization in todays global marketplace. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Developing a Learning Organization Inspiring and motivating people with a mission or purpose is a necessary and sufficient condition for developing a learning organization. FALSE Inspiring and motivating people with a mission or purpose is a necessary but not sufficient condition for developing an organization that can learn and adapt to a rapidly changing, complex, and interconnected environment. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #20 Learning Objective: 11-04 The value of creating and maintaining a learning organization in todays global marketplace. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Developing a Learning Organization 21. (p. 412) 22. (p. 412) 23. (p. 412) 24. (p. 412) To successfully empower employees to achieve organizational goals, leaders must perform the tasks of resource allocation and power brokering. FALSE To empower employees at all levels, a manager's role becomes one of creating an environment where employees can achieve their potential as they help move the organization toward its goals. Instead of viewing themselves as resource controllers and power brokers, leaders must envision themselves as flexible resources willing to assume numerous roles as coaches, information providers, teachers, decision makers, facilitators, supporters, or listeners, depending on the needs of their employees. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #21 Learning Objective: 11-04 The value of creating and maintaining a learning organization in todays global marketplace. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Developing a Learning Organization In the "top-down" approach to empowerment, leaders clarify the mission, delegate responsibility, and hold people accountable for results. TRUE In the top-down perspective, empowerment is about delegation and accountability. It encompasses the following: start at the top, clarify the organization's mission, vision, and values, clearly specify the tasks, roles, and rewards for employees, delegate responsibility, and hold people accountable for results. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 11 #22 Learning Objective: 11-04 The value of creating and maintaining a learning organization in todays global marketplace. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Developing a Learning Organization The "top-down" view of empowerment is concerned with risk taking, change, and "doing the right thing." FALSE In contrast with the top-down perspective, the bottom-up view looks at empowerment as concerned with risk taking, growth, and change. It involves trusting people to "do the right thing" and having a tolerance for failure. It encourages employees to act with a sense of ownership and typically "ask for forgiveness rather than permission." AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 11 #23 Learning Objective: 11-04 The value of creating and maintaining a learning organization in todays global marketplace. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Developing a Learning Organization The trend among many organizations is toward forms of empowerment that rely on trust, team building, and the expertise of employees at all levels. TRUE Many leading-edge organizations are moving in the direction of the bottom-up view of empowerment, recognizing the need for trust, cultural control, and expertise at all levels instead of the extensive and cumbersome rules and regulations inherent in hierarchical control. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #24 Learning Objective: 11-04 The value of creating and maintaining a learning organization in todays global marketplace. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Developing a Learning Organization 25. (p. 412- 413) 26. (p. 413- 414) 27. (p. 413) 28. (p. 413- 414) The phrase "Lead, follow, or get out of the way" is indicative of the bottom-up approach to empowerment. FALSE The phrase "Lead, follow, or get out of the way" is not indicative of the bottom-up approach to empowerment, which recognizes the need for trust, cultural control, and expertise at all levels. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #25 Learning Objective: 11-04 The value of creating and maintaining a learning organization in todays global marketplace. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Developing a Learning Organization "Open book" management is a technique for gathering and disseminating internal information so that all employees can be involved in decision making and management. TRUE "Open book" management is a technique for gathering and disseminating internal information so that all employees can be involved in decision making and management. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #26 Learning Objective: 11-04 The value of creating and maintaining a learning organization in todays global marketplace. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Developing a Learning Organization Internal benchmarking is discouraged in most organizations because it creates competition and internal rivalries that are counterproductive. FALSE An important benefit of the sharing of internal information at Whole Foods becomes the active process of internal benchmarking. Competition is intense at Whole Foods. Teams compete against their own goals for sales, growth, and productivity; they compete against different teams in their stores; and they compete against similar teams at different stores and regions. There is an elaborate system of peer reviews through which teams benchmark each other. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #27 Learning Objective: 11-04 The value of creating and maintaining a learning organization in todays global marketplace. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Developing a Learning Organization In order to gather information from informal sources, successful executives must be good listeners. TRUE Leaders have to develop means to tap into some of the more informal sources of internal information. In a recent survey, respondents were asked what differentiated the successful candidates for promotion. The consensus: The executive was seen as a person who listens. According to Peter Meyer, the author of the study, "The value of listening is clear: You cannot succeed in running a company if you do not hear what your people, customers, and suppliers are telling you Listening and understanding well are key to making good decisions." AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #28 Learning Objective: 11-04 The value of creating and maintaining a learning organization in todays global marketplace. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Developing a Learning Organization 29. (p. 414) 30. (p. 415) 31. (p. 416) 32. (p. 417) Competitive benchmarking is a method of seeking the best examples of practices or processes that have essentially the same function regardless of industry. FALSE Benchmarking is used to seek out the best examples of a particular practice as part of an ongoing effort to improve the corresponding practice in their own organization. Competitive benchmarking restricts the search for best practices to competitors, while functional benchmarking endeavors to determine best practices regardless of industry. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 11 #29 Learning Objective: 11-04 The value of creating and maintaining a learning organization in todays global marketplace. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Developing a Learning Organization Establishing a culture of dissent can be an effective means of questioning the status quo. TRUE Establishing a "culture of dissent" can be an effective means of questioning the status quo and serving as a spur toward creativity. Here norms are established whereby dissenters can openly question a superior's perspective without fear of retaliation or retribution. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #30 Learning Objective: 11-04 The value of creating and maintaining a learning organization in todays global marketplace. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Developing a Learning Organization Although many organizations encourage creativity and risk taking, few successful companies tolerate failure. FALSE Companies that cultivate cultures of experimentation and curiosity make sure that failure is not, in essence, an obscene word. They encourage mistakes as a key part of their competitive advantage. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #31 Learning Objective: 11-04 The value of creating and maintaining a learning organization in todays global marketplace. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Developing a Learning Organization Leaders who fail to institute proper systems and controls that facilitate ethical conduct share responsibility with those who conceive, execute, and knowingly benefit from corporate misdeeds. TRUE Ethics is as much an organizational as a personal issue. Leaders who fail to provide proper leadership to institute proper systems and controls that facilitate ethical conduct share responsibility with those who conceive, execute, and knowingly benefit from corporate misdeeds. AACSB: Ethics Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #32 Learning Objective: 11-05 The leaders role in establishing an ethical organization. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Creating an Ethical Organization 33. (p. 417) 34. (p. 419) 35. (p. 419- 420) 36. (p. 421) Ethical crises are bad for an organization's reputation but they rarely have any financial consequences. FALSE Ethical crises can be very expensive, both in terms of financial costs and in the erosion of human capital and overall firm reputation. Merely adhering to the minimum regulatory standards may not be enough to remain competitive in a world that is becoming more socially conscious. AACSB: Ethics Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #33 Learning Objective: 11-05 The leaders role in establishing an ethical organization. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Creating an Ethical Organization There are many advantages of an ethical organization, but it generally has little to do with employee commitment and motivation to excel. FALSE The advantages of a strong ethical orientation can have a positive effect on employee commitment and motivation to excel. This is particularly important in today's knowledge-intensive organizations, where human capital is critical in creating value and competitive advantages. AACSB: Ethics Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #34 Learning Objective: 11-05 The leaders role in establishing an ethical organization. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Creating an Ethical Organization A compliance-based approach to ethics management combines a concern for law with an emphasis on managerial responsibility for ethical behavior. FALSE Integrity-based ethics programs combine a concern for law with an emphasis on managerial responsibility for ethical behavior. It is broader, deeper, and more demanding than a legal compliance initiative. AACSB: Ethics Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 11 #35 Learning Objective: 11-06 The difference between integrity-based and compliance-based approaches to organizational ethics. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Creating an Ethical Organization Corporate codes of conduct provide norms and expectations for employees to not commit unethical acts. TRUE Corporate credos and codes of conduct are mechanisms that provide statements of norms and beliefs as well as guidelines for decision making. They provide employees with a clear understanding of the organization's policies and ethical position. Such guidelines also provide the basis for employees to refuse to commit unethical acts and help to make them aware of issues before they are faced with the situation. AACSB: Ethics Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #36 Learning Objective: 11-07 Several key elements that organizations must have to become an ethical organization. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Creating an Ethical Organization 37. (p. 423) 38. (p. 423) An effective way to instill ethical behavior in an organization is to distribute rewards strictly on the basis of outcomes. FALSE A flaw in an organization's reward structure may inadvertently cause individuals to act in an inappropriate manner if rewards are seen as being distributed on the basis of outcomes rather than the means by which goals and objectives are achieved. AACSB: Ethics Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #37 Learning Objective: 11-07 Several key elements that organizations must have to become an ethical organization. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Creating an Ethical Organization Inappropriate reward systems seldom cause individuals at all levels throughout an organization to commit unethical acts since people are either unethical or ethical in their behavior. FALSE Inappropriate reward systems may cause individuals at all levels throughout an organization to commit unethical acts that they might not otherwise commit. AACSB: Ethics Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #38 Learning Objective: 11-07 Several key elements that organizations must have to become an ethical organization. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Creating an Ethical Organization 39. (p. 395) Which of the following is an important characteristic of a leader? A. goal-oriented B. satisfied with the status quo C. reactive D. focused on past performance Leadership is proactive, goal-oriented, and focused on the creation and implementation of a creative vision. Leadership is the process of transforming organizations from what they are to what the leader would have them become. This definition implies a lot: dissatisfaction with the status quo, a vision of what should be, and a process for bringing about change. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #39 Learning Objective: 11-01 The three key interdependent activities in which all successful leaders must be continually engaged. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Leadership: Three Interdependent Activities 40. (p. 395) 41. (p. 396) 42. (p. 397) All of the following statements about leadership are true EXCEPT A. leadership is focused on the creation and implementation of a creative vision. B. leadership is the process of transforming organizations from what they are to what the leader would have them become. C. leaders support the status quo and seek control mechanisms to maintain it. D. effective implementation of strategy is essential for successful leadership. Leadership is proactive, goal-oriented, and focused on the creation and implementation of a creative vision. Leadership is the process of transforming organizations from what they are to what the leader would have them become. This definition implies a lot: dissatisfaction with the status quo, a vision of what should be, and a process for bringing about change. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #40 Learning Objective: 11-01 The three key interdependent activities in which all successful leaders must be continually engaged. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Leadership: Three Interdependent Activities According to the text, effective leadership is like a three-legged stool consisting of all of the following EXCEPT A. dedication to maintaining the status quo. B. nurturing a culture dedicated to excellence and ethical behavior. C. determining a direction. D. designing the organization. Many authors contend that successful leaders must recognize three interdependent activities that must be continually reassessed for organizations to succeed. As shown in Exhibit 11.1, these are: (1) setting a direction, (2) designing the organization, and (3) nurturing a culture dedicated to excellence and ethical behavior. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #41 Learning Objective: 11-01 The three key interdependent activities in which all successful leaders must be continually engaged. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Leadership: Three Interdependent Activities The leader's role in developing a strategic vision provides many benefits including A. a clear future direction. B. a framework for their organization's mission and goals. C. enhanced employee communication and commitment. D. all of these. A strategic vision provides many benefits: a clear future direction; a framework for the organization's mission and goals; and enhanced employee communication, participation, and commitment. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #42 Learning Objective: 11-01 The three key interdependent activities in which all successful leaders must be continually engaged. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Leadership: Three Interdependent Activities 43. (p. 398) 44. (p. 398) 45. (p. 398) Poor organizational design by leaders can result in all of the following EXCEPT A. insufficient mechanisms that integrate and coordinate activities across the firm. B. inadequate accountability among managers and employees. C. inappropriate budgeting and control systems. D. teams, systems, and organizational processes that facilitate implementation. Many leaders have difficulty implementing their vision and strategies. Such problems may stem from a variety of issues in the design of the organization, such as: a lack of understanding of responsibility and accountability among managers, reward systems that do not motivate individuals (or collectives such as groups and divisions) toward desired organizational goals, inadequate or inappropriate budgeting and control systems, or insufficient mechanisms to integrate activities across the organization. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #43 Learning Objective: 11-01 The three key interdependent activities in which all successful leaders must be continually engaged. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Leadership: Three Interdependent Activities XYZ's CEO scrapped the company's commission-based reward system because it was rewarding employees for inappropriate behavior. This is an example of A. setting a direction. B. designing the organization. C. unethical behavior. D. failure to maintain the status quo. In designing the organization, successful leaders are actively involved in building structures, teams, systems, and organizational processes that facilitate the implementation of their vision and strategies. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #44 Learning Objective: 11-01 The three key interdependent activities in which all successful leaders must be continually engaged. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Leadership: Three Interdependent Activities Leaders play a key role in developing and sustaining an organization's A. status quo. B. culture. C. reporting relationships. D. rules and regulations. Leaders play a key role in changing, developing, and sustaining an organization's culture. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #45 Learning Objective: 11-01 The three key interdependent activities in which all successful leaders must be continually engaged. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Leadership: Three Interdependent Activities 46. (p. 401) 47. (p. 401- 402) 48. (p. 401) The process by which people reconcile opposing thoughts to identify creative solutions that provide them with more options and new alternatives is known as A. designing the organization. B. conservative thinking. C. ethical planning. D. integrative thinking. In contrast to conventional thinking, which tends to focus on making choices between competing ideas from a limited set of alternatives, integrative thinking is the process by which people reconcile opposing thoughts to identify creative solutions that provide them with more options and new alternatives. Exhibit 11.2 outlines the four stages of the integrative thinking and deciding process. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #46 Learning Objective: 11-02 Three elements of effective leadership: integrative thinking; overcoming barriers to change; and the effective use of power. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Elements of Effective Leadership All of the following stages are part of the integrative thinking and deciding process EXCEPT A. causality. B. conservation. C. architecture. D. salience. Exhibit 11.2 outlines the four stages of the integrative thinking and deciding process. These stages are salience, causality, architecture, and resolution. Refer to Exhibit 11.2 AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 11 #47 Learning Objective: 11-02 Three elements of effective leadership: integrative thinking; overcoming barriers to change; and the effective use of power. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Elements of Effective Leadership In the integrative thinking and deciding process, making a mental map of the causal relationships between the elements of a decision to evaluate how the elements relate to one another is known as A. architecture. B. causality. C. visualization. D. multidimensionality. Exhibit 11.2 outlines the four stages of the integrative thinking and deciding process. Causality refers to making a mental map of the causal relationships between the features, that is, how the various features are related to one another. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #48 Learning Objective: 11-02 Three elements of effective leadership: integrative thinking; overcoming barriers to change; and the effective use of power. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Elements of Effective Leadership 49. (p. 402) 50. (p. 403) 51. (p. 404) Barriers in which the design of the organization's structure, information processing, and reporting relationships, impede the proper flow and evaluation of information are known as A. systemic barriers. B. behavioral barriers. C. political barriers. D. barriers to entry. Organizations at all levels are prone to inertia and are slow to learn, adapt, and change because there are systemic barriers. The design of the organization's structure, information processing, reporting relationships, and so forth impede the proper flow and evaluation of information. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 11 #49 Learning Objective: 11-02 Three elements of effective leadership: integrative thinking; overcoming barriers to change; and the effective use of power. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Elements of Effective Leadership Barriers associated with a manager's tendency to look at issues from a biased or limited perspective are known as A. systemic barriers. B. behavioral barriers. C. political barriers. D. barriers to exit. Behavioral barriers cause managers to look at issues from a biased or limited perspective due to their education, training, work experiences, and so forth. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 11 #50 Learning Objective: 11-02 Three elements of effective leadership: integrative thinking; overcoming barriers to change; and the effective use of power. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Elements of Effective Leadership Refusal to share information, conflicts over resources, conflicts between departments and divisions, and petty interpersonal differences are symptoms of which type of barrier to change? A. systemic barriers B. political barriers C. behavioral barriers D. all of these Political barriers refer to conflicts arising from power relationships. This can be the outcome of a myriad of symptoms such as vested interests, refusal to share information, conflicts over resources, conflicts between departments and divisions, and petty interpersonal differences. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 11 #51 Learning Objective: 11-02 Three elements of effective leadership: integrative thinking; overcoming barriers to change; and the effective use of power. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Elements of Effective Leadership 52. (p. 402- 404) 53. (p. 404) Which of the following explains why organizations are prone to inertia and slow to change? A. personal time constraints B. political barriers C. vested interests in the status quo D. all of these Organizations at all levels are prone to inertia and are slow to learn, adapt, and change because many people have vested interests in the status quo, there are systemic, behavioral, and political barriers, and some people have personal time constraints. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #52 Learning Objective: 11-02 Three elements of effective leadership: integrative thinking; overcoming barriers to change; and the effective use of power. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Elements of Effective Leadership All of the following constitute organizational bases of a leader's power EXCEPT A. legitimate power. B. reward power. C. referent power. D. coercive power. Organizational bases of power refer to the power that a person wields because of holding a formal management position. These include legitimate power, reward power, coercive power, and information power. The personal bases of power include referent power and expert power. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 11 #53 Learning Objective: 11-02 Three elements of effective leadership: integrative thinking; overcoming barriers to change; and the effective use of power. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Elements of Effective Leadership 54. (p. 404) Expert power A. is derived from organizationally conferred decision-making authority. B. arises from a manager's access, control, and distribution of information that is not freely available to everyone in an organization. C. is derived from referent power. D. is derived from the leader's capability and knowledge in a particular field. The source of expert power is the leader's expertise and knowledge in a particular field. The leader is the expert on whom subordinates depend for information that they need to do their jobs successfully. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 11 #54 Learning Objective: 11-02 Three elements of effective leadership: integrative thinking; overcoming barriers to change; and the effective use of power. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Elements of Effective Leadership 55. (p. 404) Coercive power is A. the power exercised by use of fear of punishment for errors of omission or commission by employees. B. the power of persuasion exercised by a charismatic leader to get compliance from reluctant subordinates. C is the type that arises from a manager's access, control, and distribution of information that is not . freely available to everyone in an organization. D. the ability of the leader or manager to confer rewards for positive behaviors or outcomes. Coercive power is the power a manager exercises over employees using fear of punishment for errors of omission or commission. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 11 #55 Learning Objective: 11-02 Three elements of effective leadership: integrative thinking; overcoming barriers to change; and the effective use of power. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Elements of Effective Leadership 56. (p. 404) 57. (p. 405) The source of referent power is A. a subordinate's identification with the leader. B. a leader's identification with the subordinates. C. derived from the fact that the manager can potentially act as a reference when the employee applies for another job. D. derived from the manager's ability to provide effective incentives to employees. The source of referent power is a subordinate's identification with the leader. A leader's personal attributes or charisma might influence subordinates and make them devoted to that leader. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 11 #56 Learning Objective: 11-02 Three elements of effective leadership: integrative thinking; overcoming barriers to change; and the effective use of power. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Elements of Effective Leadership The three broad sets of capabilities that a leader should possess include all of the following EXCEPT A. technical skills. B. cognitive abilities. C. calculative abilities. D. emotional intelligence. Leadership traits may be grouped into three broad sets of capabilities: purely technical skills (like accounting or operations research), cognitive abilities (like analytical reasoning or quantitative analysis), and emotional intelligence (like self-management and managing relationships). 58. (p. 407) 59. (p. 408) 60. (p. 409) All of the following are components of Emotional Intelligence (EI) EXCEPT A. self-awareness. B. self-regulation. C. self-promotion. D. empathy. Exhibit 11.4 identifies the five components of EI: self-awareness, self-regulation, motivation, empathy, and social skill. Refer to Exhibit 11.4 AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 11 #58 Learning Objective: 11-03 The crucial role of emotional intelligence (EI) in successful leadership as well as its potential drawbacks. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Emotional Intelligence: A Key Leadership Trait Which component of Emotional Intelligence (EI) enables a manager to have a deep understanding of the existence and importance of cultural and ethnic differences? A. self-awareness B. empathy C. social skills D. self-regulation Empathy means thoughtfully considering an employee's feelings, along with other factors, in the process of making intelligent decisions. Globalization typically involves cross-cultural dialogue that can easily lead to miscues. Empathetic people are attuned to the subtleties of body language; they can hear the message beneath the words being spoken. They have a deep understanding of the existence and importance of cultural and ethnic differences. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 11 #59 Learning Objective: 11-03 The crucial role of emotional intelligence (EI) in successful leadership as well as its potential drawbacks. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Emotional Intelligence: A Key Leadership Trait The following two components of Emotional Intelligence (EI) deal with a person's ability to manage relationships with others: A. motivation and self-awareness. B. self-regulation and empathy. C. empathy and social skill. D. motivation and empathy. While the first three components of EI are all self-management skills, the last two, empathy and social skill, concern a person's ability to manage relationships with others. 61. (p. 410) 62. (p. 411) 63. (p. 411) Complete the following sentence. The days when a company's leader are gone; today, all employees need to be involved in . A. learned for the organization; learning and adapting B. managed from the top; self-management C. delegated authority; assuming responsibility and control D. was held in high regard; holding leaders accountable for their actions As noted by today's leading expert on learning organizations, MIT's Peter Senge, the days when Henry Ford, Alfred Sloan, and Tom Watson "learned for the organization" are gone. "In an increasingly dynamic, interdependent, and unpredictable world, it is simply no longer possible for anyone to "figure it all out at the top." The old model, "the top thinks and the local acts," must now give way to integrating thinking and acting at all levels." AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #61 Learning Objective: 11-04 The value of creating and maintaining a learning organization in todays global marketplace. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Developing a Learning Organization What happens to organizations that get caught up in day-to-day work activities? A. They fail to think objectively about themselves and their business. B. They fail to refresh their strategies or reengineer their work processes. C. They fail to ask probing questions about their basic assumptions. D. All of these. Many organizations get so caught up in carrying out their day-to-day work that they rarely, if ever, stop to think objectively about themselves and their businesses. They often fail to ask the probing questions that might lead them to call into question their basic assumptions, to refresh their strategies, or to reengineer their work processes. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #62 Learning Objective: 11-04 The value of creating and maintaining a learning organization in todays global marketplace. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Developing a Learning Organization Which of the following is not a characteristic of a successful learning organization? A. They create a proactive, creative approach to the unknown. B. They actively solicit the involvement of employees at all levels. C. They regularly engage in activities to reinforce the status quo. D. They enable everyone to use their intelligence and apply their imagination. A learning organization is one that creates a proactive, creative approach to the unknown, characterized by (1) inspiring and motivating people with a mission and purpose, (2) empowering employees at all levels, (3) accumulating and sharing internal knowledge, (4) gathering and integrating external information, and (5) challenging the status quo and enabling creativity. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #63 Learning Objective: 11-04 The value of creating and maintaining a learning organization in todays global marketplace. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Developing a Learning Organization 64. Complete the following sentence. "Inspiring and motivating people with a mission or purpose is a (p. 412) for developing an organization that can learn and adapt." A. necessary and sufficient condition B. necessary, but not a sufficient condition C. goal, but not a necessary condition D. goal and a required pre-condition Inspiring and motivating people with a mission or purpose is a necessary but not sufficient condition for developing an organization that can learn and adapt to a rapidly changing, complex, and interconnected environment. 65. 65. (p. 412) AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #64 Learning Objective: 11-04 The value of creating and maintaining a learning organization in todays global marketplace. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Developing a Learning Organization In order to create an environment where employees can achieve their potential as they move the organization towards its goals, the manager's role needs to be that of A. resource allocator. B. resource controller. C. a flexible resource. D. an advocator of the status quo. Instead of viewing themselves as resource controllers and power brokers, leaders must envision themselves as flexible resources willing to assume numerous roles as coaches, information providers, teachers, decision makers, facilitators, supporters, or listeners, depending on the needs of their employees. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #65 Learning Objective: 11-04 The value of creating and maintaining a learning organization in todays global marketplace. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Developing a Learning Organization 66. 66. (p. 412) The "top-down" perspective of empowerment A. encourages intelligent risk taking. B. trusts people to perform. C. encourages cooperative behavior. D. delegates responsibility. In the top-down perspective, empowerment is about delegation and accountability; senior management has developed a clear vision and has communicated specific plans to the rest of the organization. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #66 Learning Objective: 11-04 The value of creating and maintaining a learning organization in todays global marketplace. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Developing a Learning Organization 67. 67. (p. 412) 68. 68. (p. 412) 69. 69. (p. 412) The "bottom-up" perspective of empowerment A. clarifies the organization's values and mission. B. builds teams to encourage cooperative behavior. C. communicates specific plans. D. encourages employees to "ask permission rather than forgiveness." The salient elements of empowerment in the "bottom-up" perspective include building teams to encourage cooperative behavior, encouraging intelligent risk taking, and trusting people to perform. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #67 Learning Objective: 11-04 The value of creating and maintaining a learning organization in todays global marketplace. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Developing a Learning Organization The empowerment perspective that involves trusting people to "do the right thing," take intelligent risks, and act with a sense of ownership is known as A. the leadership perspective. B. the top-down approach. C. the bottom-up approach. D. the risk-taking model. The bottom-up view looks at empowerment as concerned with risk taking, growth, and change. It involves trusting people to "do the right thing" and having a tolerance for failure. It encourages employees to act with a sense of ownership and typically "ask for forgiveness rather than permission." AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 11 #68 Learning Objective: 11-04 The value of creating and maintaining a learning organization in todays global marketplace. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Developing a Learning Organization An empowerment perspective that delegates responsibility, focuses on accountability, and relies on clearly specified rewards to motivate is known as A. the leadership perspective. B. the top-down approach. C. the bottom-up approach. D. the accounting model. In the top-down perspective, empowerment is about delegation and accountability; senior management has developed a clear vision and has communicated specific plans to the rest of the organization. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 11 #69 Learning Objective: 11-04 The value of creating and maintaining a learning organization in todays global marketplace. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Developing a Learning Organization 70. 70. (p. 412) 71. 71. (p. 413- 414) 72. 72. (p. 413) Manufacturing employees at Chaparral Steel are directly involved with customers and have access to the new innovative knowledge being developed in its manufacturing processes. This is an example of A. hierarchical control. B. knowledge management. C. enabling heroes and drones. D. employee empowerment. This is an example of empowering employees, enabling them to learn and progress on the job. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Apply Dess - Chapter 11 #70 Learning Objective: 11-04 The value of creating and maintaining a learning organization in todays global marketplace. Level of Difficulty: 3 Hard Topic: Developing a Learning Organization Which of the following is NOT one of the three core activities in the "open book" management system pioneered by Jack Stack? A. Information is generated daily that reflects the work performance and production costs of each employee. B. The information is aggregated once a week and shared with employees at every level. C. Information about customer expectations and feedback is distributed monthly. D. Extensive training in how to use and interpret the numbers is provided to all employees. Information about customer expectations and feedback is not distributed monthly in the "open book" management system. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #71 Learning Objective: 11-04 The value of creating and maintaining a learning organization in todays global marketplace. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Developing a Learning Organization At Whole Foods, the "no secrets" management philosophy allows employees access to most of the company's operating and financial data. This is an example of A. information sharing. B. employee advocacy. C. bottom-up empowerment. D. internal benchmarking. The "no secrets" management philosophy at Whole Foods is an example of information sharing. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #72 Learning Objective: 11-04 The value of creating and maintaining a learning organization in todays global marketplace. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Developing a Learning Organization 73. 73. (p. 413) Internal benchmarking at Whole Foods A. is used by teams to compete against other teams in their stores. B. is used by teams which compete against their own goals for sales, growth, and productivity. C. is used by teams to compete against similar teams at different stores and regions. D. all of these. An important benefit of the sharing of internal information at Whole Foods becomes the active process of internal benchmarking. Competition is intense at Whole Foods. Teams compete against their own goals for sales, growth, and productivity; they compete against different teams in their stores; and they compete against similar teams at different stores and regions. There is an elaborate system of peer reviews through which teams benchmark each other. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #73 Learning Objective: 11-04 The value of creating and maintaining a learning organization in todays global marketplace. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Developing a Learning Organization 74. 74. (p. 414) 75. 75. (p. 415- 416) Functional benchmarking A. is not very useful for organizations with a divisional organizational structure. B. endeavors to determine best practices regardless of industry. C. restricts the search for best practices to competitors. D. is useful when researching industry-specific standards. There are two primary types of benchmarking. Competitive benchmarking restricts the search for best practices to competitors, while functional benchmarking endeavors to determine best practices regardless of industry. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #74 Learning Objective: 11-04 The value of creating and maintaining a learning organization in todays global marketplace. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Developing a Learning Organization All of the following are guidelines an organization can use to promote the challenging of the status quo EXCEPT A. establishing a "culture of dissent." B. forcefully creating a sense of urgency. C. fostering a culture that encourages risk taking. D. creating a results-based reward system. Perhaps the best way to challenge the status quo is for the leader to forcefully create a sense of urgency. Establishing a "culture of dissent" can be another effective means of questioning the status quo and serving as a spur toward creativity. Closely related to the culture of dissent is the fostering of a culture that encourages risk taking. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #75 Learning Objective: 11-04 The value of creating and maintaining a learning organization in todays global marketplace. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Developing a Learning Organization 76. 76. (p. 416) Companies that cultivate cultures of experimentation and curiosity make sure that is not, in essence, to be avoided at all costs. A. experimentation B. failure C. authority D. risk taking Companies that cultivate cultures of experimentation and curiosity make sure that failure is not, in essence, an obscene word. They encourage mistakes as a key part of their competitive advantage. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #76 Learning Objective: 11-04 The value of creating and maintaining a learning organization in todays global marketplace. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Developing a Learning Organization 77. 77. (p. 417) Which of the following statements about ethics is FALSE? A. Ethics may be defined as a system of right and wrong. B. Ethics assists individuals in deciding when an act is moral or immoral. C. Ethics is NOT concerned with whether or not an act is socially desirable. D. Business ethics is the application of ethical standards to commercial enterprises. Ethics may be defined as a system of right and wrong. Ethics assists individuals in deciding when an act is moral or immoral, socially desirable or not. Business ethics is the application of ethical standards to commercial enterprise. AACSB: Ethics Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #77 Learning Objective: 11-05 The leaders role in establishing an ethical organization. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Creating an Ethical Organization 78. 78. (p. 417) As a manager, when faced with ethical crises you should A. focus on issues most relevant to stockholders. B. wait for the other party to make the first move. C. take the initiative to address the problem. D. cover up as much as possible. Ethical leaders must take personal, ethical responsibility for their actions and decision making. Leaders who exhibit high ethical standards become role models for others and raise an organization's overall level of ethical behavior. AACSB: Ethics Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #78 Learning Objective: 11-05 The leaders role in establishing an ethical organization. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Creating an Ethical Organization 79. 79. (p. 417) 80. 80. (p. 423) 81. 81. (p. 421) All of the following statements about ethical organizations are true EXCEPT A. the potential benefits of an ethical organization are few but direct. B. ethical values shape the search for opportunities. C. organizational ethics define what a company is and what it stands for. D. ethics provide a common frame of reference that serves as a unifying force. The ethical organization is characterized by a conception of ethical values and integrity as a driving force of the enterprise. Ethical values shape the search for opportunities, the design of organizational systems, and the decision-making process used by individuals and groups. They provide a common frame of reference that serves as a unifying force across different functions, lines of business, and employee groups. Organizational ethics helps to define what a company is and what it stands for. There are many potential benefits of an ethical organization, but they are often indirect. AACSB: Ethics Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #79 Learning Objective: 11-05 The leaders role in establishing an ethical organization. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Creating an Ethical Organization Proactive measures to prevent organizational ethics problems include all of the following EXCEPT A. instituting a reward system which considers outcomes as its primary criterion. B. using leaders as role models of ethical behavior. C. issuing statements describing the organization's commitment to certain standards of behavior. D. using the organization's information systems as a control system. A flaw in the organization's reward structure may inadvertently cause individuals to act in an inappropriate manner if rewards are seen as being distributed on the basis of outcomes rather than the means by which goals and objectives are achieved. AACSB: Ethics Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #80 Learning Objective: 11-07 Several key elements that organizations must have to become an ethical organization. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Creating an Ethical Organization Which of the following statements would least likely be found in a corporate credo? A. Maximize financial benefits for stakeholders. B. Provide secure and stable employment for employees. C. Establish an environment that enhances professional growth. D. Support community organizations and projects. Corporate credos and codes of conduct are mechanisms that provide statements of norms and beliefs as well as guidelines for decision making. They provide employees with a clear understanding of the organization's policies and ethical position. Financial maximization is least likely to be included in such statements. AACSB: Ethics Blooms: Apply Dess - Chapter 11 #81 Learning Objective: 11-07 Several key elements that organizations must have to become an ethical organization. Level of Difficulty: 3 Hard Topic: Creating an Ethical Organization 82. 82. (p. 395- 400) 83. 83. (p. 401- 402) Briefly discuss the three interdependent activities that are critical for effective leadership. Answers will vary. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #82 Learning Objective: 11-01 The three key interdependent activities in which all successful leaders must be continually engaged. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Leadership: Three Interdependent Activities What are the four stages of the integrative thinking and deciding process? Discuss how these relate to each other and how they might or might not be part of a conventional thinking process. Answers will vary. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #83 Learning Objective: 11-02 Three elements of effective leadership: integrative thinking; overcoming barriers to change; and the effective use of power. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Elements of Effective Leadership 84. 84. (p. 404- 405) 85. 85. (p. 407- 409) 86. 86. (p. 409- 410) 87. 87. (p. 411- 416) Discuss the organizational and personal bases of a leader's power. Answers will vary. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #84 Learning Objective: 11-02 Three elements of effective leadership: integrative thinking; overcoming barriers to change; and the effective use of power. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Elements of Effective Leadership Identify the five components of Emotional Intelligence (EI). Discuss how each of these factors contributes to the success of a leader or manager. Answers will vary. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #85 Learning Objective: 11-03 The crucial role of emotional intelligence (EI) in successful leadership as well as its potential drawbacks. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Emotional Intelligence: A Key Leadership Trait What are some of the potential drawbacks of emotional intelligence? Answers will vary. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #86 Learning Objective: 11-03 The crucial role of emotional intelligence (EI) in successful leadership as well as its potential drawbacks. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Emotional Intelligence: A Key Leadership Trait What are the five elements of a learning organization? What is the value of a learning organization in today's global marketplace? Answers will vary. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #87 Learning Objective: 11-04 The value of creating and maintaining a learning organization in todays global marketplace. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Developing a Learning Organization 88. 88. (p. 412- 413) 89. 89. (p. 413- 414) What is the difference between "top-down" and "bottom-up" approaches to empowerment? Discuss how these differences impact the effectiveness of empowerment efforts. Answers will vary. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #88 Learning Objective: 11-04 The value of creating and maintaining a learning organization in todays global marketplace. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Developing a Learning Organization What is "open book" management? Why is this and other approaches to accumulating and sharing internal information being used increasingly in today's organizations? Answers will vary. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #89 Learning Objective: 11-04 The value of creating and maintaining a learning organization in todays global marketplace. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Developing a Learning Organization 90. 90. (p. 417- 419) 91. 91. (p. 417- 424) 92. 92. (p. 419- 420) What is the leader's role in establishing an ethical organization? Answers will vary. AACSB: Ethics Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #90 Learning Objective: 11-05 The leaders role in establishing an ethical organization. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Creating an Ethical Organization How can developing and maintaining a high ethical standard benefit an organization? Give examples and describe the effects the examples have had on the organization and/or its stakeholders. Answers will vary. AACSB: Ethics Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #91 Learning Objective: 11-05 The leaders role in establishing an ethical organization. Learning Objective: 11-06 The difference between integrity-based and compliance-based approaches to organizational ethics. Learning Objective: 11-07 Several key elements that organizations must have to become an ethical organization. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Creating an Ethical Organization Discuss the differences between integrity-based and compliance-based approaches to organizational ethics. Answers will vary. AACSB: Ethics Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #92 Learning Objective: 11-06 The difference between integrity-based and compliance-based approaches to organizational ethics. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Creating an Ethical Organization 93. 93. (p. 421- 422) 94. 94. (p. 423- 424) What is a corporate credo? How can it be helpful in shaping the moral dimensions of an organization? Answers will vary. AACSB: Ethics Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #93 Learning Objective: 11-07 Several key elements that organizations must have to become an ethical organization. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Creating an Ethical Organization Briefly discuss how an organization's reward and evaluation systems can be used to promote organizational ethics. Answers will vary. AACSB: Ethics Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 11 #94 Learning Objective: 11-07 Several key elements that organizations must have to become an ethical organization. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Creating an Ethical Organization Ch11 Summary Category # of Questions AACSB: Analytic 77 AACSB: Ethics 17 Blooms: Apply 2 Blooms: Remember 29 Blooms: Understand 63 Dess - Chapter 11 94 Learning Objective: 11-01 The three key interdependent activities in which all successful leaders must be continually engaged. 13 Learning Objective: 11- 02 Three elements of effective leadership: integrative thinking; overcoming barriers to change; and the effective use of power. 21 Learning Objective: 11- 03 The crucial role of emotional intelligence (EI) in successful leadership as well as its potential drawbacks. 9 Learning Objective: 11-04 The value of creating and maintaining a learning organization in todays global marketplace. 34 Learning Objective: 11-05 The leaders role in establishing an ethical organization. 8 Learning Objective: 11-06 The difference between integrity-based and compliance-based approaches to organizational ethics. 3 Learning Objective: 11-07 Several key elements that organizations must have to become an ethical organization. 8 Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy 29 Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium 63 Level of Difficulty: 3 Hard 2 Topic: Creating an Ethical Organization 17 Topic: Developing a Learning Organization 34 Topic: Elements of Effective Leadership 21 Topic: Emotional Intelligence: A Key Leadership Trait 9 Topic: Leadership: Three Interdependent Activities 13 Ch12 Student: 1. The term "innovation" refers primarily to an invention that uses the latest technologies. True False 2. Radical innovations are evolutionary applications of novel ideas within existing paradigms. True False 3. As an industry matures, there are greater opportunities for change and so innovations tend to be more radical. True False 4. Process innovations are often associated with a low cost leadership strategy. True False 5. Disruptive innovations are those that overturn markets by providing an altogether new approach to meeting customer needs. True False 6. Research indicates that leaders of innovative firms spend 50 percent more time on discovery activities than the leaders of less innovative firms. True False 7. The term "strategic envelope" refers to the scope of a firm's innovation efforts. True False 8. Radical innovation often involves open-ended experimentation which can be very time consuming. True False 9. For innovation team members to work enthusiastically on innovation projects, it is important to separate the performance of individual team members from the performance of the innovation itself. True False 10. A firm's innovation efforts rarely benefit from partnering with non-business entities such as universities and government agencies. True False 11. Strategic renewal and the pursuit of new venture opportunities are the two primary aims of corporate entrepreneurship. True False 12. Corporate entrepreneurship is sometimes called "intrapreneurship." True False 13. Corporate venturing that is focused permeates all parts of the organization and involves every member of the organization. True False 14. Firms using a focused approach to corporate entrepreneurship typically separate corporate venturing activities from ongoing operations of the firm. True False 15. Business incubators are designed to support fledgling entrepreneurial ventures until they can operate as stand-alone businesses. True False 16. Corporate business incubators often provide physical space and business services to internal ventures, but not funding. True False 17. Dispersed approaches to corporate entrepreneurship are often found in organizations with a strong spirit of entrepreneurship. True False 18. Product champions are the employees who identify new product ideas or services. True False 19. According to the text, new venture ideas must pass through two critical stages to be implemented by corporations—project definition and project impetus. True False 20. Product champions are critical during the period after a new venture project has been defined but before it has gained momentum and achieved project impetus. True False 21. Only about 50 percent of corporate venturing efforts reach profitability within six years of their launch. True False 22. The strategic goals of corporate entrepreneurship are often just as important as the financial goals. True False 23. Exit champions are often reluctant to gather hard data about a venture because it might kill the project. True False 24. Real options logic is useful when corporations consider stock options as a way to finance entrepreneurial ventures. True False 25. Corporate ventures that use real options logic in decision making tend to keep total investment low in order to minimize the downside risk of a project. True False 26. Real options analysis helps managers make investment decisions involving large irreversible commitments of financial resources. True False 27. One of the potential pitfalls of real options analysis is that managers may have the incentive and know- how to "game the system." True False 28. The term "skunkworks" is used to refer to a type of in-house facility that corporations use to develop entrepreneurial ideas. True False 29. First movers in an industry often capture above-average profits, but usually find it difficult to maintain early market share gains. True False 30. Competitive aggressiveness is a response to threats whereas proactiveness is a response to opportunities. True False 31. Business risk taking refers to the risk associated with entering untested markets or committing to unproven technologies. True False 32. refers to efforts to create designs and applications of technology to develop new products, while refers to efforts to improve the efficiency of organizational systems such as manufacturing and operations. A. Radical innovation; incremental innovation B. Breakthrough innovation; instrumental innovation C. Product innovation; process innovation D. Product innovation; service innovation 33. Whereas are often associated with a low cost leader strategy, are frequently an important aspect of a differentiation strategy. A. process innovations; product innovations B. product innovations; service innovations C. radical innovations; instrumental innovations D. marketing innovations; management innovations 34. Incremental innovations A. are usually highly disruptive. B. usually represent technological breakthroughs. C. are usually small improvements in products and processes. D. nearly always can be patented. 35. Radical innovations A. often result in quick profits. B. often represent technological breakthroughs. C. usually apply to products and processes simultaneously. D. usually cannot be patented. 36. produce fundamental changes that can transform a company or even revolutionize an industry, while enhance existing practices and often represent evolutionary applications of fundamental breakthroughs. A. Technological breakthroughs; product-market breakthroughs B. New technologies; new paradigms C. Incremental innovations; radical innovations D. Radical innovations; incremental innovations 37. Innovations that extend sales in an existing market, usually by enabling new products or services to be sold at higher margins are known as A. radical innovations. B. disruptive innovations. C. technology innovations. D. sustaining innovations. 38. All of the following are characteristics of a disruptive innovation EXCEPT A. It is usually more sophisticated technologically. B. It appeals to less demanding customers. C. It is typically a less expensive solution for meeting a need. D. It usually takes root in a new market or the low-end of an existing market. 39. All of the following are dilemmas faced by corporations trying to manage the innovation process EXCEPT A. launching incremental rather than "preemptive" innovations. B. emphasizing marketing over management innovations. C. preferring experience over initiative. D. choosing internal rather than external staffing. 40. The innovation dilemma known as building capabilities versus collaborating refers to A. developing innovation skills internally versus partnering with qualified outsiders. B. building innovative products in-house versus outsourcing. C. building credibility by launching products ahead of potential collaboration partners. D. all of these. 41. The innovation dilemma known as seeds versus weeds refers to A. choosing to pursue radical rather than incremental innovations. B. choosing to pursue product rather than process innovations. C. promoting organizational stars onto innovation teams rather than involving all employees in innovation efforts. D. none of these. 42. Creative intelligence involves the ability to see patterns in data, integrating data, and making insights. The four patterns of actions that help build creative intelligence are A. observing, experimenting, cataloging, and networking. B. questioning, observing, integrating, and networking. C. questioning, observing, experimenting, and networking. D. observing, experimenting, cataloging, and integrating. 43. Individuals with highly innovative DNA traits have the ability to connect seemingly unrelated questions, problems, and ideas from different fields, allowing them the opportunity to creatively see opportunities others miss. In the text, this is referred to as A. associating. B. integrating. C. visioning. D. allocating. 44. In the 1990s, DuPont used its knowledge of plastics to develop biodegradable plastic products. This is an example of A. focusing on process rather than product innovation. B. defining its innovation efforts within the context of its "strategic envelope." C. radical innovation. D. public relations, since plastics are not biodegradable. 45. The advantages of collaborating with strategic partners in order to innovate include A. obtaining skills and new knowledge from outside sources. B. making firms identify their own strengths and weaknesses. C. managers clarifying what an innovation project requires to be successful and who will accomplish it. D. all of these. 46. The W. L. Gore organization, a highly innovative company, uses several approaches and "rules of thumb" to encourage innovation. Which of the following is NOT one of them? A. It requests that all risk-taking activities have a financial pay-off within one year. B. It celebrates failure rather than condemning it. C. It promotes person-to-person communications rather than e-mails. D. It uses small teams to promote creativity and autonomy. 47. In a typical corporation, which of the following impact how the people within the corporation recognize entrepreneurial opportunities? A. structural features that guide and constrain action B. corporate culture C. organizational systems that foster learning and manage rewards D. all of these 48. Two common forms of a focused approach to corporate entrepreneurship include A. internal collaboration and internal venturing. B. social capital and collaboration capital. C. business incubators and new venture groups. D. focus groups and business incubators. 49. According to the text, , which support fledgling startups are often used to pursue specific entrepreneurial ventures developed by . A. collaboration partners; strategic partners B. business incubators; new venture groups C. product champions; corporate venture capitalists D. lower-level managers; upper-level managers 50. Corporate business incubators typically provide some or all of the following functions EXCEPT A. physical space. B. mentoring. C. funding. D. student interns. 51. A culture of entrepreneurship is one in which A. the search for venture opportunities permeates every part of the organization. B. every value chain activity is viewed as a source of entrepreneurial value creation. C. employees at every level are attuned to opportunities to help create new businesses. D. all of these occur. 52. Common features of a dispersed approach to corporate entrepreneurship include all of the following EXCEPT A. semi-autonomous new venture groups. B. use of product champions. C. a top-down approach to supporting entrepreneurial behavior. D. an entrepreneurial culture. 53. In corporations with a strong entrepreneurial culture, the willingness and ability to change A. is imposed from the top-down. B. is considered a core capability. C. often leads to instability. D. often worries stakeholders such as suppliers and creditors. 54. Product champions A. are typically senior executives. B. are usually inventors of some sort. C. scavenge for resources and encourage others to back promising new ideas. D. are strong supporters of the status quo. 55. Project involves justifying whether an opportunity is attractive in the marketplace; project involves evaluating the strategic and economic impact of a new venture. A. impetus; definition B. definition; impetus C. reward; development D. development; focus 56. On average, approximately what percentage of corporate ventures reaches profitability within six years? A. 80 percent. B. 65 percent. C. 50 percent. D. 35 percent. 57. Financial reasons for undertaking internal corporate venturing include A. strengthening competitive position. B. obtaining above average returns. C. adding to the corporation's resource base. D. all of these. 58. Strategic reasons for undertaking a corporate venture include which of the following? A. entering into new markets B. expanding capabilities by acquiring new knowledge C. building the corporation's base of resources D. all of these 59. All of the following are questions that should be answered when evaluating the performance of corporate venturing efforts EXCEPT which of these? A. Is the venture attracting external venture funding? B. Is the venture considered to be a market success? C. Does the venture add to the worth of the firm internally? D. Does the value proposition offered by the venture insulate it from competitive attack? 60. A manager whose role is to question the viability of corporate venture projects is known as a(n) A. product champion. B. exit champion. C. rising star. D. mentor. 61. Whereas are willing to violate procedures and operate outside normal channels, gather hard data and develop a strong case for why a project should be killed. A. senior managers; entrepreneurial leaders B. strategic managers; financial managers C. exit champions; product champions D. product champions; exit champions 62. Options exist when the owner of the option has A. the obligation, but not the right to engage in a transaction. B. the right, but not the obligation to engage in a transaction. C. the right and obligation to engage in a transaction. D. neither the right, nor the obligation to engage in a transaction. 63. Real options analysis is most appropriate when A. the total investment required is small, but the environment is uncertain. B. the investment required can be justified by Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) techniques. C. a small investment up front can be followed by a series of subsequent investments. D. there is no prospect of obtaining additional knowledge before making subsequent investments. 64. One of the pitfalls of real options analysis is that managers may have an incentive and know-how to "game the system" and "back-solve" a formula to get a proposal approved. This can give rise to A. managerial conceit. B. the illusion of control. C. escalation of commitment. D. agency problems. 65. Which of the following is NOT one of the dimensions of entrepreneurial orientation? A. proactiveness B. risk taking C. autonomy D. opportunism 66. Which of the following statements about skunkworks is FALSE? A. They are independent work units. B. They are used to encourage creative thinking and brainstorming. C. They refer to a specialized type of outside contractor that corporations use to develop entrepreneurial ideas. D. They help managers set aside their usual routines and practices. 67. After 15 teams created 128 different phones, Chris Galvin, former CEO of Motorola, recently eliminated the autonomous teams being used to develop new wireless phones. This was necessary because such teams A. often lack coordination. B. sometimes waste resources on projects with questionable feasibility. C. sometimes create inefficiencies through duplication of effort. D. all of these. 68. Which of the following dimensions of entrepreneurial orientation is described as "a forward-looking perspective characteristic of a marketplace leader that has the foresight to seize opportunities"? A. proactiveness B. risk taking C. autonomy D. competitive aggressiveness 69. All of the following statements about innovativeness are true EXCEPT which of these? A. It refers to making decisions and taking risks without certain knowledge of probable outcomes. B. It refers to a firm's efforts to find new opportunities and novel solutions. C. It involves creativity and experimentation. D. It is aimed at developing new products, services, and processes. 70. According to the text, which of the following is NOT one of the methods companies can use to enhance their competitive position via innovativeness? A. fostering creativity and experimentation B. investing in new technology, R&D, and continuous improvement C. copying the business practices or techniques of successful competitors D. departing from existing technologies to develop products and practices that go beyond the current state of the art 71. The benefits gained by firms that are the first to enter new markets, establish brand identity, and/or adopt new technologies are known as A. competitive aggressiveness. B. technological capabilities. C. first mover advantages. D. breakthrough innovations. 72. Sony Corporation's mission statement says, "We should always be the pioneers with our products, out front leading the market." This is an example of A. innovativeness. B. proactiveness. C. competitive aggressiveness. D. autonomy. 73. According to the text, firms that want to enhance their entrepreneurial position by being competitively aggressive should A. enter markets with drastically lower prices. B. foster creativity and experimentation. C. continuously seek out new products or services. D. research risk factors to minimize uncertainty. 74. All of the following are types of risks that executives must address EXCEPT A. business risk taking. B. financial risk taking. C. personal risk taking. D. product-market risk taking. 75. Which kind of risk taking requires that a company borrow heavily or commit a large portion of its resources in order to grow? A. business risk taking B. financial risk taking C. personal risk taking D. technological risk taking 76. What are the differences between product and process innovation? What are the strategic implications of each approach to innovation? 77. What is meant by the terms "radical" innovation and "incremental" innovation? Describe the advantages and disadvantages of each type of innovation and provide examples. 78. What are the characteristics of a disruptive innovation? In what way is a disruptive innovation similar to and different than a radical innovation? What are the strategic implications of those differences and similarities? 79. What are the five dilemmas that most firms face when trying to determine the best way to manage the innovation process? 80. Compare and contrast the concepts of focused versus dispersed approaches to corporate entrepreneurship. Provide examples of each approach. 81. What are the five types of support that corporate business incubators provide to entrepreneurial ventures? 82. What are product champions and why are they important to corporate entrepreneurship? 83. Compare and contrast the financial and strategic objectives of corporate entrepreneurship. Provide examples of each type of objective and discuss their benefits and/or costs. 84. By some accounts, only about 50 percent of corporate ventures reach profitability after six years. Is corporate venturing worth it? Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of internal venturing in relation to the extent of its financial success. 85. What are exit champions and how do they further the internal corporate venturing process? 86. Discuss how real options logic can be applied in the context of corporate entrepreneurship. Are there any disadvantages to using this approach to make decision about launching corporate ventures? 87. What are some of the pitfalls of real options analysis (ROA)? 88. Discuss the five dimensions of entrepreneurial orientation. What are the benefits and risks associated with using each of these? 1. (p. 433) 2. (p. 433) 3. (p. 434) Ch12 Key The term "innovation" refers primarily to an invention that uses the latest technologies. FALSE Innovation involves using new knowledge to transform organizational processes or create commercially viable products and services. The sources of new knowledge may include the latest technology, the results of experiments, creative insights, or competitive information. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 12 #1 Learning Objective: 12-01 The importance of implementing strategies and practices that foster innovation. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Managing Innovation Radical innovations are evolutionary applications of novel ideas within existing paradigms. FALSE Radical innovations produce fundamental changes by evoking major departures from existing practices. They tend to be highly disruptive and can transform a company or revolutionize a whole industry. Incremental innovations enhance existing practices or make small improvements in products and processes. They may represent evolutionary applications within existing paradigms of earlier, more radical innovations. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 12 #2 Learning Objective: 12-01 The importance of implementing strategies and practices that foster innovation. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Managing Innovation As an industry matures, there are greater opportunities for change and so innovations tend to be more radical. FALSE Incremental innovations are more likely in mature industries. Because they often sustain a company by extending or expanding its product line or manufacturing skills, incremental innovations can be a source of competitive advantage by providing new capabilities that minimize expenses or speed productivity. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #3 Learning Objective: 12-01 The importance of implementing strategies and practices that foster innovation. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Managing Innovation 4. (p. 433) Process innovations are often associated with a low cost leadership strategy. TRUE Process innovations are more likely to occur in the later stages of an industry's life cycle as companies seek ways to remain viable in markets where demand has flattened out and competition is more intense. As a result, process innovations are often associated with overall cost leader strategies, because the aim of many process improvements is to lower the costs of operations. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 12 #4 Learning Objective: 12-01 The importance of implementing strategies and practices that foster innovation. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Managing Innovation 5. (p. 435) 6. (p. 437) Disruptive innovations are those that overturn markets by providing an altogether new approach to meeting customer needs. TRUE Disruptive innovations are those that overturn markets by providing an altogether new approach to meeting customer needs. Walmart and Southwest Airlines are cited as two disruptive examples. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 12 #5 Learning Objective: 12-01 The importance of implementing strategies and practices that foster innovation. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Managing Innovation Research indicates that leaders of innovative firms spend 50 percent more time on discovery activities than the leaders of less innovative firms. TRUE The leaders of innovative firms have exhibited "discovery skills" that allow them to see the potential in innovations and to move the organization forward in leveraging the value of those innovations. These leaders spend 50 percent more time on these discovery activities than the leaders of less innovative firms. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #6 Learning Objective: 12-02 The challenges and pitfalls of managing corporate innovation processes. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Managing Innovation 7. (p. 438) 8. (p. 440) The term "strategic envelope" refers to the scope of a firm's innovation efforts. TRUE Firms must have a means to focus their innovation efforts. By defining the "strategic envelope", the scope of a firm's innovation efforts, firms ensure that their innovation efforts are not wasted on projects that are outside the firm's domain of interest. Strategic enveloping defines the range of acceptable projects. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 12 #7 Learning Objective: 12-02 The challenges and pitfalls of managing corporate innovation processes. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Managing Innovation Radical innovation often involves open-ended experimentation which can be very time consuming. TRUE The project time line of a radical innovation is typically long term, 10 years or more. Radical innovations often begin with a long period of exploration in which experimentation makes strict timelines unrealistic. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #8 Learning Objective: 12-02 The challenges and pitfalls of managing corporate innovation processes. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Managing Innovation 9. (p. 441) 10. (p. 441) 11. (p. 442- 443) For innovation team members to work enthusiastically on innovation projects, it is important to separate the performance of individual team members from the performance of the innovation itself. TRUE Strategy experts Rita Gunther McGrath and Thomas Keil researched the types of human resource management practices that effective firms use to capture value from their innovation efforts. One practice that is especially important is to separate the performance of individuals from the performance of the innovation. Otherwise, strong players may feel stigmatized if the innovation effort they worked on fails. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #9 Learning Objective: 12-02 The challenges and pitfalls of managing corporate innovation processes. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Managing Innovation A firm's innovation efforts rarely benefit from partnering with non-business entities such as universities and government agencies. FALSE Innovation partners may come from many sources, including research universities and the federal government. Each year the federal government issues requests for proposals (RFPs) asking private companies for assistance in improving services or finding solutions to public problems. Universities are another type of innovation partner. Chip-maker Intel, for example, has benefited from underwriting substantial amounts of university research. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #10 Learning Objective: 12-02 The challenges and pitfalls of managing corporate innovation processes. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Managing Innovation Strategic renewal and the pursuit of new venture opportunities are the two primary aims of corporate entrepreneurship. TRUE Corporate entrepreneurship (CE) has two primary aims: the pursuit of new venture opportunities and strategic renewal. The innovation process keeps firms alert by exposing them to new technologies, making them aware of marketplace trends, and helping them evaluate new possibilities. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #11 Learning Objective: 12-02 The challenges and pitfalls of managing corporate innovation processes. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Corporate Entrepreneurship 12. (p. 443) Corporate entrepreneurship is sometimes called "intrapreneurship." TRUE Corporate new venture creation was labeled "intrapreneuring" by Gifford Pinchot because it refers to building entrepreneurial businesses within existing corporations. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 12 #12 Learning Objective: 12-02 The challenges and pitfalls of managing corporate innovation processes. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Corporate Entrepreneurship 13. (p. 446) Corporate venturing that is focused permeates all parts of the organization and involves every member of the organization. FALSE Two distinct approaches to corporate venturing are found among firms that pursue entrepreneurial aims. The first is focused corporate venturing, in which CE activities are isolated from a firm's existing operations and worked on by independent work units. The second approach is dispersed, in which all parts of the organization and every organization member are engaged in intrapreneurial activities. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #13 Learning Objective: 12-03 How corporations use new venture teams; business incubators; and product champions to create an internal environment and culture that promote entrepreneurial development. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Corporate Entrepreneurship 14. (p. 446) Firms using a focused approach to corporate entrepreneurship typically separate corporate venturing activities from ongoing operations of the firm. TRUE Firms using a focused approach typically separate the corporate venturing activity from the other ongoing operations of the firm. CE is usually the domain of autonomous work groups that pursue entrepreneurial aims independent of the rest of the firm. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #14 Learning Objective: 12-03 How corporations use new venture teams; business incubators; and product champions to create an internal environment and culture that promote entrepreneurial development. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Corporate Entrepreneurship 15. (p. 447) Business incubators are designed to support fledgling entrepreneurial ventures until they can operate as stand-alone businesses. TRUE Business incubators are designed to "hatch" new businesses. They have a specialized purpose, to support and nurture fledgling entrepreneurial ventures until they can thrive on their own as stand- alone businesses. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #15 Learning Objective: 12-03 How corporations use new venture teams; business incubators; and product champions to create an internal environment and culture that promote entrepreneurial development. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Corporate Entrepreneurship 16. (p. 447) Corporate business incubators often provide physical space and business services to internal ventures, but not funding. FALSE Incubators typically provide some or all of the following four functions: funding, physical space, business services, and mentoring. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #16 Learning Objective: 12-03 How corporations use new venture teams; business incubators; and product champions to create an internal environment and culture that promote entrepreneurial development. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Corporate Entrepreneurship 17. (p. 448) Dispersed approaches to corporate entrepreneurship are often found in organizations with a strong spirit of entrepreneurship. TRUE Two related aspects of dispersed entrepreneurship include entrepreneurial cultures that have an overarching commitment to CE activities and the use of product champions in promoting entrepreneurial behaviors. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #17 Learning Objective: 12-03 How corporations use new venture teams; business incubators; and product champions to create an internal environment and culture that promote entrepreneurial development. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Corporate Entrepreneurship 18. (p. 449) Product champions are the employees who identify new product ideas or services. FALSE Product (or project) champions are those individuals working within a corporation who bring entrepreneurial ideas forward, identify what kind of market exists for the product or service, find resources to support the venture, and promote the venture concept to upper management. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 12 #18 Learning Objective: 12-03 How corporations use new venture teams; business incubators; and product champions to create an internal environment and culture that promote entrepreneurial development. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Corporate Entrepreneurship 19. (p. 450) According to the text, new venture ideas must pass through two critical stages to be implemented by corporations—project definition and project impetus. TRUE No matter how an entrepreneurial idea comes to light, however, a new venture concept must pass through two critical stages or it may never get off the ground: project definition and project impetus. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #19 Learning Objective: 12-03 How corporations use new venture teams; business incubators; and product champions to create an internal environment and culture that promote entrepreneurial development. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Corporate Entrepreneurship 20. (p. 450) Product champions are critical during the period after a new venture project has been defined but before it has gained momentum and achieved project impetus. TRUE For a project to advance through the stages of definition and impetus, a product champion is often needed to generate support and encouragement. Champions are especially important during the time after a new project has been defined but before it gains momentum. They form a link between the definition and impetus stages of internal development, which they do by procuring resources and stimulating interest for the product among potential customers. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #20 Learning Objective: 12-03 How corporations use new venture teams; business incubators; and product champions to create an internal environment and culture that promote entrepreneurial development. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Corporate Entrepreneurship 21. (p. 450) 22. (p. 451) 23. (p. 451) 24. (p. 452- 453) Only about 50 percent of corporate venturing efforts reach profitability within six years of their launch. TRUE Not all corporate venturing efforts are financially rewarding. In terms of financial performance, slightly more than 50 percent of corporate venturing efforts reach profitability (measured by ROI) within six years of their launch. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #21 Learning Objective: 12-04 How corporate entrepreneurship achieves both financial goals and strategic goals. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Corporate Entrepreneurship The strategic goals of corporate entrepreneurship are often just as important as the financial goals. TRUE In a successful venture, not only are financial and market acceptance (customer) goals met but so are the internal business and innovation and learning goals. Thus, when assessing the success of corporate venturing, it is important to look beyond simple financial returns and consider a well-rounded set of criteria. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #22 Learning Objective: 12-04 How corporate entrepreneurship achieves both financial goals and strategic goals. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Corporate Entrepreneurship Exit champions are often reluctant to gather hard data about a venture because it might kill the project. FALSE One way to avoid costly and discouraging defeats is to support a key role in the CE process: exit champions. In contrast to product champions and other entrepreneurial enthusiasts within the corporation, exit champions are willing to question the viability of a venture project. By demanding hard evidence and challenging the belief system that is carrying an idea forward, exit champions hold the line on ventures that appear shaky. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #23 Learning Objective: 12-04 How corporate entrepreneurship achieves both financial goals and strategic goals. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Corporate Entrepreneurship Real options logic is useful when corporations consider stock options as a way to finance entrepreneurial ventures. FALSE Real options logic is applied in situations where decisions are made to invest in new ventures or other business activities. Many strategic decisions have the characteristic of containing a series of options. The phenomenon is called "embedded options," a series of investments in which at each stage of the investment there is a go/no-go decision. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #24 Learning Objective: 12-05 The benefits and potential drawbacks of real options analysis in making resource deployment decisions in corporate entrepreneurship contexts. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Real Options Analysis: A Useful Tool 25. (p. 453) Corporate ventures that use real options logic in decision making tend to keep total investment low in order to minimize the downside risk of a project. TRUE The real options logic process of evaluating ideas separates winning ideas from losing ones in a way that keeps investments low. Using real options logic to advance the development process is a key way that firms reduce uncertainty and minimize innovation-related failures. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #25 Learning Objective: 12-05 The benefits and potential drawbacks of real options analysis in making resource deployment decisions in corporate entrepreneurship contexts. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Real Options Analysis: A Useful Tool 26. (p. 452) Real options analysis helps managers make investment decisions involving large irreversible commitments of financial resources. FALSE ROA is appropriate to use when investments can be staged; a smaller investment up front can be followed by subsequent investments. Real options can be applied to an investment decision that gives the company the right, but not the obligation, to make follow-on investments. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #26 Learning Objective: 12-05 The benefits and potential drawbacks of real options analysis in making resource deployment decisions in corporate entrepreneurship contexts. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Real Options Analysis: A Useful Tool 27. (p. 453) One of the potential pitfalls of real options analysis is that managers may have the incentive and know-how to "game the system." TRUE Managers using ROA may have an incentive and the know-how to "game the system." If managers know that a certain option value must be met in order for the proposal to get approved, they can back- solve the model to find a variance estimate needed to arrive at the answer that upper management desires. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #27 Learning Objective: 12-05 The benefits and potential drawbacks of real options analysis in making resource deployment decisions in corporate entrepreneurship contexts. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Real Options Analysis: A Useful Tool 28. (p. 456) The term "skunkworks" is used to refer to a type of in-house facility that corporations use to develop entrepreneurial ideas. FALSE According to Exhibit 12.5, skunkworks are independent work units, often physically separate from corporate headquarters. They allow employees to get out from under the pressures of their daily routines to engage in creative problem solving. Refer to Exhibit 12.5 AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 12 #28 Learning Objective: 12-06 How an entrepreneurial orientation can enhance a firms efforts to develop promising corporate venture initiatives. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Entrepreneurial Orientation 29. (p. 459) 30. (p. 460) 31. (p. 461) First movers in an industry often capture above-average profits, but usually find it difficult to maintain early market share gains. FALSE First movers have several advantages. They often capture unusually high profits because there are no competitors to drive prices down. First movers that establish brand recognition are usually able to retain their image and hold on to the market share gained by being first. Generally, first movers have an advantage that can be sustained until the maturity phase of an industry's life cycle. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #29 Learning Objective: 12-06 How an entrepreneurial orientation can enhance a firms efforts to develop promising corporate venture initiatives. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Entrepreneurial Orientation Competitive aggressiveness is a response to threats whereas proactiveness is a response to opportunities. TRUE Proactiveness is a response to opportunities, the O in SWOT. Competitive aggressiveness, by contrast, is a response to threats, the T in SWOT. A competitively aggressive posture is important for firms that seek to enter new markets in the face of intense rivalry. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #30 Learning Objective: 12-06 How an entrepreneurial orientation can enhance a firms efforts to develop promising corporate venture initiatives. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Entrepreneurial Orientation Business risk taking refers to the risk associated with entering untested markets or committing to unproven technologies. TRUE Business risk taking involves venturing into the unknown without knowing the probability of success. This is the risk associated with entering untested markets or committing to unproven technologies. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 12 #31 Learning Objective: 12-06 How an entrepreneurial orientation can enhance a firms efforts to develop promising corporate venture initiatives. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Entrepreneurial Orientation 32. refers to efforts to create designs and applications of technology to develop new (p. 433) products, while refers to efforts to improve the efficiency of organizational systems such as manufacturing and operations. A. Radical innovation; incremental innovation B. Breakthrough innovation; instrumental innovation C. Product innovation; process innovation D. Product innovation; service innovation Product innovation refers to efforts to create product designs and applications of technology to develop new products for end users. Process innovation, by contrast, is typically associated with improving the efficiency of an organizational process, especially manufacturing systems and operations. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 12 #32 Learning Objective: 12-01 The importance of implementing strategies and practices that foster innovation. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Managing Innovation 33. (p. 433) Whereas are often associated with a low cost leader strategy, are frequently an important aspect of a differentiation strategy. A. process innovations; product innovations B. product innovations; service innovations C. radical innovations; instrumental innovations D. marketing innovations; management innovations Process innovations are often associated with overall cost leader strategies, because the aim of many process improvements is to lower the costs of operations. Product innovations are commonly associated with a differentiation strategy. Firms that differentiate by providing customers with new products or services that offer unique features or quality enhancements often engage in product innovation. 34. Incremental innovations AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #33 Learning Objective: 12-01 The importance of implementing strategies and practices that foster innovation. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Managing Innovation (p. 434) A. are usually highly disruptive. B. usually represent technological breakthroughs. C. are usually small improvements in products and processes. D. nearly always can be patented. Incremental innovations enhance existing practices or make small improvements in products and processes. They may represent evolutionary applications within existing paradigms of earlier, more radical innovations. 35. (p. 433) Radical innovations A. often result in quick profits. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 12 #34 Learning Objective: 12-01 The importance of implementing strategies and practices that foster innovation. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Managing Innovation B. often represent technological breakthroughs. C. usually apply to products and processes simultaneously. D. usually cannot be patented. Radical innovations produce fundamental changes by evoking major departures from existing practices. These breakthrough innovations usually occur because of technological change. They tend to be highly disruptive and can transform a company or even revolutionize a whole industry. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 12 #35 Learning Objective: 12-01 The importance of implementing strategies and practices that foster innovation. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Managing Innovation 36. produce fundamental changes that can transform a company or even revolutionize an (p. 433- 434) 37. (p. 435) industry, while enhance existing practices and often represent evolutionary applications of fundamental breakthroughs. A. Technological breakthroughs; product-market breakthroughs B. New technologies; new paradigms C. Incremental innovations; radical innovations D. Radical innovations; incremental innovations Radical innovations tend to be highly disruptive and can transform a company or even revolutionize a whole industry. Incremental innovations enhance existing practices or make small improvements in products and processes. They may represent evolutionary applications within existing paradigms of earlier, more radical innovations. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 12 #36 Learning Objective: 12-01 The importance of implementing strategies and practices that foster innovation. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Managing Innovation Innovations that extend sales in an existing market, usually by enabling new products or services to be sold at higher margins are known as A. radical innovations. B. disruptive innovations. C. technology innovations. D. sustaining innovations. Sustaining innovations are those that extend sales in an existing market, usually by enabling new products or services to be sold at higher margins. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 12 #37 Learning Objective: 12-01 The importance of implementing strategies and practices that foster innovation. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Managing Innovation 38. (p. 435) All of the following are characteristics of a disruptive innovation EXCEPT A. It is usually more sophisticated technologically. B. It appeals to less demanding customers. C. It is typically a less expensive solution for meeting a need. D. It usually takes root in a new market or the low-end of an existing market. Disruptive innovations are technologically simpler and less sophisticated than currently available products or services, appeal to less demanding customers who are seeking more convenient, less expensive solutions, and take time to take effect and only become disruptive once they have taken root in a new market or low-end part of an existing market. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #38 Learning Objective: 12-01 The importance of implementing strategies and practices that foster innovation. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Managing Innovation 39. (p. 437) 40. (p. 437) All of the following are dilemmas faced by corporations trying to manage the innovation process EXCEPT A. launching incremental rather than "preemptive" innovations. B. emphasizing marketing over management innovations. C. preferring experience over initiative. D. choosing internal rather than external staffing. Innovation is difficult in part because the process involves so many choices. These choices present five dilemmas that companies must wrestle with when pursuing innovation. These include decisions such as: seeds versus weeds, experience versus initiative, internal versus external staffing, building capabilities versus collaborating, and incremental versus preemptive launch. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #39 Learning Objective: 12-02 The challenges and pitfalls of managing corporate innovation processes. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Managing Innovation The innovation dilemma known as building capabilities versus collaborating refers to A. developing innovation skills internally versus partnering with qualified outsiders. B. building innovative products in-house versus outsourcing. C. building credibility by launching products ahead of potential collaboration partners. D. all of these. Innovation projects often require new sets of skills. The "building capabilities versus collaborating" decisions means that firms can seek help from other departments and/or partner with other companies that bring resources and experience as well as share costs of development. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #40 Learning Objective: 12-02 The challenges and pitfalls of managing corporate innovation processes. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Managing Innovation 41. (p. 437) The innovation dilemma known as seeds versus weeds refers to A. choosing to pursue radical rather than incremental innovations. B. choosing to pursue product rather than process innovations. C. promoting organizational stars onto innovation teams rather than involving all employees in innovation efforts. D. none of these. Most companies have an abundance of innovative ideas. They must decide which of these is most likely to bear fruit (the "Seeds") and which should be cast aside (the "Weeds.") AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #41 Learning Objective: 12-02 The challenges and pitfalls of managing corporate innovation processes. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Managing Innovation 42. (p. 438) 43. (p. 439) 44. (p. 438) Creative intelligence involves the ability to see patterns in data, integrating data, and making insights. The four patterns of actions that help build creative intelligence are A. observing, experimenting, cataloging, and networking. B. questioning, observing, integrating, and networking. C. questioning, observing, experimenting, and networking. D. observing, experimenting, cataloging, and integrating. The key attribute that firms need to develop in their managers in order to improve their innovative potential is creative intelligence. Creative intelligence is driven by a core skill of associating (the ability to see patterns in data and integrating different questions, information, and insights) and four patterns of action: questioning, observing, experimenting, and networking. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #42 Learning Objective: 12-02 The challenges and pitfalls of managing corporate innovation processes. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Managing Innovation Individuals with highly innovative DNA traits have the ability to connect seemingly unrelated questions, problems, and ideas from different fields, allowing them the opportunity to creatively see opportunities others miss. In the text, this is referred to as A. associating. B. integrating. C. visioning. D. allocating. Those with the innovator's DNA trait called associating have the ability to connect seemingly unrelated questions, problems, and ideas from different fields. This allows them to creatively see opportunities that others miss. Refer to Exhibit 12.2 AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #43 Learning Objective: 12-02 The challenges and pitfalls of managing corporate innovation processes. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Managing Innovation In the 1990s, DuPont used its knowledge of plastics to develop biodegradable plastic products. This is an example of A. focusing on process rather than product innovation. B. defining its innovation efforts within the context of its "strategic envelope." C. radical innovation. D. public relations, since plastics are not biodegradable. By defining the "strategic envelope", the scope of a firm's innovation efforts, firms ensure that their innovation efforts are not wasted on projects that are outside the firm's domain of interest. In the early 1990s, DuPont sought to use its knowledge of plastics to identify products to meet a growing market demand for biodegradable products. By trying different applications and formulations demanded by customers, the company was finally able to create a product that could be produced economically and had market appeal. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #44 Learning Objective: 12-02 The challenges and pitfalls of managing corporate innovation processes. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Managing Innovation 45. (p. 441- 442) 46. (p. 442- 444) 47. (p. 444, 446) The advantages of collaborating with strategic partners in order to innovate include A. obtaining skills and new knowledge from outside sources. B. making firms identify their own strengths and weaknesses. C. managers clarifying what an innovation project requires to be successful and who will accomplish it. D. all of these. Innovation partners provide the skills and insights that are needed to make innovation projects succeed. Strategic partnering requires firms to identify their strengths and weaknesses and make choices about which capabilities to leverage, which need further development, and which are outside the firm's current or projected scope of operations. To choose partners, firms need to ask what competencies they are looking for and what the innovation partner will contribute. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #45 Learning Objective: 12-02 The challenges and pitfalls of managing corporate innovation processes. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Managing Innovation The W. L. Gore organization, a highly innovative company, uses several approaches and "rules of thumb" to encourage innovation. Which of the following is NOT one of them? A. It requests that all risk-taking activities have a financial pay-off within one year. B. It celebrates failure rather than condemning it. C. It promotes person-to-person communications rather than e-mails. D. It uses small teams to promote creativity and autonomy. Successful innovation involves a companywide commitment because the results of innovation affect every part of the organization. Exhibit 12.3 highlights the policies that help make W. L. Gore an innovation leader. Rules include: the power of small teams, no ranks, no titles, no bosses, take the long view, make time for face time, lead by leading, and celebrate failure. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #46 Learning Objective: 12-02 The challenges and pitfalls of managing corporate innovation processes. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Managing Innovation In a typical corporation, which of the following impact how the people within the corporation recognize entrepreneurial opportunities? A. structural features that guide and constrain action B. corporate culture C. organizational systems that foster learning and manage rewards D. all of these In a typical corporation, many factors determine how entrepreneurial projects will be pursued, including: corporate culture, leadership, structural features that guide and constrain action, and organizational systems that foster learning and manage rewards. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #47 Learning Objective: 12-02 The challenges and pitfalls of managing corporate innovation processes. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Corporate Entrepreneurship 48. (p. 446) Two common forms of a focused approach to corporate entrepreneurship include A. internal collaboration and internal venturing. B. social capital and collaboration capital. C. business incubators and new venture groups. D. focus groups and business incubators. Firms using a focused approach typically separate the corporate venturing activity from the other ongoing operations of the firm. CE is usually the domain of autonomous work groups that pursue entrepreneurial aims independent of the rest of the firm. Two forms—new venture groups (NVGs) and business incubators—are among the most common types of focused approaches. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #48 Learning Objective: 12-03 How corporations use new venture teams; business incubators; and product champions to create an internal environment and culture that promote entrepreneurial development. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Corporate Entrepreneurship 49. (p. 447) According to the text, , which support fledgling startups are often used to pursue specific entrepreneurial ventures developed by . A. collaboration partners; strategic partners B. business incubators; new venture groups C. product champions; corporate venture capitalists D. lower-level managers; upper-level managers Business incubators are designed to "hatch" new businesses. They are a type of corporate new venture group with a somewhat more specialized purpose, to support and nurture fledgling entrepreneurial ventures until they can thrive on their own as stand-alone businesses. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #49 Learning Objective: 12-03 How corporations use new venture teams; business incubators; and product champions to create an internal environment and culture that promote entrepreneurial development. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Corporate Entrepreneurship 50. (p. 447) Corporate business incubators typically provide some or all of the following functions EXCEPT A. physical space. B. mentoring. C. funding. D. student interns. Incubators typically provide some or all of the following five functions: funding, physical space, business services, mentoring, and networking. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #50 Learning Objective: 12-03 How corporations use new venture teams; business incubators; and product champions to create an internal environment and culture that promote entrepreneurial development. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Corporate Entrepreneurship 51. (p. 448) A culture of entrepreneurship is one in which A. the search for venture opportunities permeates every part of the organization. B. every value chain activity is viewed as a source of entrepreneurial value creation. C. employees at every level are attuned to opportunities to help create new businesses. D. all of these occur. A culture of entrepreneurship is one in which the search for venture opportunities permeates every part of the organization. The key to creating value successfully is viewing every value-chain activity as a source of competitive advantage. In companies with an entrepreneurial culture, everyone in the organization is attuned to opportunities to help create new businesses. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #51 Learning Objective: 12-03 How corporations use new venture teams; business incubators; and product champions to create an internal environment and culture that promote entrepreneurial development. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Corporate Entrepreneurship 52. (p. 448) Common features of a dispersed approach to corporate entrepreneurship include all of the following EXCEPT A. semi-autonomous new venture groups. B. use of product champions. C. a top-down approach to supporting entrepreneurial behavior. D. an entrepreneurial culture. A new venture group is characteristic of a focused approach to entrepreneurship, while the dispersed approach often utilizes an entrepreneurial culture and the use of product champions. The latter may also use a top-down approach to provide support and incentives for entrepreneurship. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #52 Learning Objective: 12-03 How corporations use new venture teams; business incubators; and product champions to create an internal environment and culture that promote entrepreneurial development. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Managing Innovation 53. (p. 448) In corporations with a strong entrepreneurial culture, the willingness and ability to change A. is imposed from the top-down. B. is considered a core capability. C. often leads to instability. D. often worries stakeholders such as suppliers and creditors. With the dispersed approach to entrepreneurship, the ability to change is considered to be a core capability. This leads to a second advantage: Because of the firm's entrepreneurial reputation, stakeholders such as vendors, customers, or alliance partners can bring new ideas or venture opportunities to anyone in the organization and expect them to be well-received. Such opportunities make it possible for the firm to stay ahead of the competition. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #53 Learning Objective: 12-03 How corporations use new venture teams; business incubators; and product champions to create an internal environment and culture that promote entrepreneurial development. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Corporate Entrepreneurship 54. (p. 449- 450) Product champions A. are typically senior executives. B. are usually inventors of some sort. C. scavenge for resources and encourage others to back promising new ideas. D. are strong supporters of the status quo. Product (or project) champions are those individuals working within a corporation who bring entrepreneurial ideas forward, identify what kind of market exists for the product or service, find resources to support the venture, and promote the venture concept to upper management. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 12 #54 Learning Objective: 12-03 How corporations use new venture teams; business incubators; and product champions to create an internal environment and culture that promote entrepreneurial development. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Corporate Entrepreneurship 55. (p. 450) Project involves justifying whether an opportunity is attractive in the marketplace; project involves evaluating the strategic and economic impact of a new venture. A. impetus; definition B. definition; impetus C. reward; development D. development; focus In the project definition stage, an opportunity has to be justified in terms of its attractiveness in the marketplace and how well it fits with the corporation's other strategic objectives. For a project to gain impetus, its strategic and economic impact must be supported by senior managers who have experience with similar projects. It then becomes an embryonic business with its own organization and budget. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 12 #55 Learning Objective: 12-03 How corporations use new venture teams; business incubators; and product champions to create an internal environment and culture that promote entrepreneurial development. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Corporate Entrepreneurship 56. (p. 450) On average, approximately what percentage of corporate ventures reaches profitability within six years? A. 80 percent. B. 65 percent. C. 50 percent. D. 35 percent. Not all corporate venturing efforts are financially rewarding. In terms of financial performance, slightly more than 50 percent of corporate venturing efforts reach profitability (measured by ROI) within six years of their launch. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #56 Learning Objective: 12-04 How corporate entrepreneurship achieves both financial goals and strategic goals. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Corporate Entrepreneurship 57. (p. 450- 451) 58. (p. 450- 451) 59. (p. 451) Financial reasons for undertaking internal corporate venturing include A. strengthening competitive position. B. obtaining above average returns. C. adding to the corporation's resource base. D. all of these. Corporations expect a higher return from corporate venturing projects than from normal operations. But there are other important strategic considerations as well that are not financial. These include undertaking a corporate venture to strengthen the competitive position, enter into new markets, expand capabilities by learning and acquiring new knowledge, and build the corporation's base of resources and experience. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #57 Learning Objective: 12-04 How corporate entrepreneurship achieves both financial goals and strategic goals. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Corporate Entrepreneurship Strategic reasons for undertaking a corporate venture include which of the following? A. entering into new markets B. expanding capabilities by acquiring new knowledge C. building the corporation's base of resources D. all of these Corporations expect a higher return from corporate venturing projects than from normal operations. But there are other important strategic considerations as well that are not financial. These include undertaking a corporate venture to strengthen the competitive position, enter into new markets, expand capabilities by learning and acquiring new knowledge, and build the corporation's base of resources and experience. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #58 Learning Objective: 12-04 How corporate entrepreneurship achieves both financial goals and strategic goals. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Corporate Entrepreneurship All of the following are questions that should be answered when evaluating the performance of corporate venturing efforts EXCEPT which of these? A. Is the venture attracting external venture funding? B. Is the venture considered to be a market success? C. Does the venture add to the worth of the firm internally? D. Does the value proposition offered by the venture insulate it from competitive attack? Three questions should be used to assess the effectiveness of a corporation's venturing initiatives: Are the products or services offered by the venture accepted in the marketplace? Are the contributions of the venture to the corporation's internal competencies and experience valuable? Is the venture able to sustain its basis of competitive advantage? External funding may not be critical to success. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #59 Learning Objective: 12-04 How corporate entrepreneurship achieves both financial goals and strategic goals. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Corporate Entrepreneurship 60. (p. 451) 61. A manager whose role is to question the viability of corporate venture projects is known as a(n) A. product champion. B. exit champion. C. rising star. D. mentor. In contrast to product champions and other entrepreneurial enthusiasts within the corporation, exit champions are willing to question the viability of a venture project. By demanding hard evidence and challenging the belief system that is carrying an idea forward, exit champions hold the line on ventures that appear shaky. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 12 #60 Learning Objective: 12-04 How corporate entrepreneurship achieves both financial goals and strategic goals. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Corporate Entrepreneurship Whereas are willing to violate procedures and operate outside normal channels, (p. 451) gather hard data and develop a strong case for why a project should be killed. A. senior managers; entrepreneurial leaders B. strategic managers; financial managers C. exit champions; product champions D. product champions; exit champions Product champions are often thought to be willing to violate procedures and operate outside normal channels. Exit champions reduce ambiguity by gathering hard data and developing a strong case for why a project should be killed. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #61 Learning Objective: 12-04 How corporate entrepreneurship achieves both financial goals and strategic goals. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Corporate Entrepreneurship 62. (p. 452) Options exist when the owner of the option has A. the obligation, but not the right to engage in a transaction. B. the right, but not the obligation to engage in a transaction. C. the right and obligation to engage in a transaction. D. neither the right, nor the obligation to engage in a transaction. Options exist when the owner of the option has the right but not the obligation to engage in certain types of transactions. The most common are stock options. A stock option grants the holder the right to buy (call option) or sell (put option) shares of the stock at a fixed price (strike price) at some time in the future. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 12 #62 Learning Objective: 12-05 The benefits and potential drawbacks of real options analysis in making resource deployment decisions in corporate entrepreneurship contexts. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Real Options Analysis: A Useful Tool 63. (p. 452) Real options analysis is most appropriate when A. the total investment required is small, but the environment is uncertain. B. the investment required can be justified by Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) techniques. C. a small investment up front can be followed by a series of subsequent investments. D. there is no prospect of obtaining additional knowledge before making subsequent investments. ROA is appropriate to use when investments can be staged; a smaller investment up front can be followed by subsequent investments. Real options can be applied to an investment decision that gives the company the right, but not the obligation, to make follow-on investments. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #63 Learning Objective: 12-05 The benefits and potential drawbacks of real options analysis in making resource deployment decisions in corporate entrepreneurship contexts. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Real Options Analysis: A Useful Tool 64. (p. 453) One of the pitfalls of real options analysis is that managers may have an incentive and know-how to "game the system" and "back-solve" a formula to get a proposal approved. This can give rise to A. managerial conceit. B. the illusion of control. C. escalation of commitment. D. agency problems. Managers may have an incentive and the know-how to "game the system." If managers know that a certain option value must be met in order for the proposal to get approved, they can back-solve the model to find a variance estimate needed to arrive at the answer that upper management desires. This is an example of an agency problem that is typically inherent in investment decisions. A manager may have something to gain by not acting in the owner's best interests, or the interests of managers and owners are not co-aligned. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #64 Learning Objective: 12-05 The benefits and potential drawbacks of real options analysis in making resource deployment decisions in corporate entrepreneurship contexts. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Real Options Analysis: A Useful Tool 65. (p. 454) Which of the following is NOT one of the dimensions of entrepreneurial orientation? A. proactiveness B. risk taking C. autonomy D. opportunism An entrepreneurial orientation has five dimensions that permeate the decision-making styles and practices of the firm's members: autonomy, innovativeness, proactiveness, competitive aggressiveness, and risk taking. These factors work together to enhance a firm's entrepreneurial performance. Exhibit 12.4 summarizes the dimensions of entrepreneurial orientation. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 12 #65 Learning Objective: 12-06 How an entrepreneurial orientation can enhance a firms efforts to develop promising corporate venture initiatives. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Entrepreneurial Orientation 66. (p. 456) 67. (p. 456) 68. (p. 458) Which of the following statements about skunkworks is FALSE? A. They are independent work units. B. They are used to encourage creative thinking and brainstorming. C. They refer to a specialized type of outside contractor that corporations use to develop entrepreneurial ideas. D. They help managers set aside their usual routines and practices. Skunkworks are independent work units, often physically separate from corporate headquarters. They allow employees to get out from under the pressures of their daily routines to engage in creative problem solving. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #66 Learning Objective: 12-06 How an entrepreneurial orientation can enhance a firms efforts to develop promising corporate venture initiatives. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Entrepreneurial Orientation After 15 teams created 128 different phones, Chris Galvin, former CEO of Motorola, recently eliminated the autonomous teams being used to develop new wireless phones. This was necessary because such teams A. often lack coordination. B. sometimes waste resources on projects with questionable feasibility. C. sometimes create inefficiencies through duplication of effort. D. all of these. Autonomous teams often lack coordination. Excessive decentralization has a strong potential to create inefficiencies, such as duplication of effort and wasting resources on projects with questionable feasibility. For example, Chris Galvin, former CEO of Motorola, scrapped the skunkworks approach the company had been using to develop new wireless phones. Fifteen teams had created 128 different phones, which led to spiraling costs and overly complex operations. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #67 Learning Objective: 12-06 How an entrepreneurial orientation can enhance a firms efforts to develop promising corporate venture initiatives. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Entrepreneurial Orientation Which of the following dimensions of entrepreneurial orientation is described as "a forward-looking perspective characteristic of a marketplace leader that has the foresight to seize opportunities"? A. proactiveness B. risk taking C. autonomy D. competitive aggressiveness Proactiveness is a forward-looking perspective characteristic of a marketplace leader that has the foresight to seize opportunities in anticipation of future demand. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 12 #68 Learning Objective: 12-06 How an entrepreneurial orientation can enhance a firms efforts to develop promising corporate venture initiatives. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Entrepreneurial Orientation 69. (p. 456) 70. (p. 456- 458) 71. (p. 459) All of the following statements about innovativeness are true EXCEPT which of these? A. It refers to making decisions and taking risks without certain knowledge of probable outcomes. B. It refers to a firm's efforts to find new opportunities and novel solutions. C. It involves creativity and experimentation. D. It is aimed at developing new products, services, and processes. Innovativeness refers to a firm's efforts to find new opportunities and novel solutions. It involves creativity and experimentation that result in new products, new services, or improved technological processes. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #69 Learning Objective: 12-06 How an entrepreneurial orientation can enhance a firms efforts to develop promising corporate venture initiatives. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Entrepreneurial Orientation According to the text, which of the following is NOT one of the methods companies can use to enhance their competitive position via innovativeness? A. fostering creativity and experimentation B. investing in new technology, R&D, and continuous improvement C. copying the business practices or techniques of successful competitors D. departing from existing technologies to develop products and practices that go beyond the current state of the art Innovativeness requires that firms depart from existing technologies and practices and venture beyond the current state of the art. Exhibit 12.6 describes two innovation techniques: foster creativity and experimentation, and invest in new technology, R&D, and continuous improvement. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #70 Learning Objective: 12-06 How an entrepreneurial orientation can enhance a firms efforts to develop promising corporate venture initiatives. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Entrepreneurial Orientation The benefits gained by firms that are the first to enter new markets, establish brand identity, and/or adopt new technologies are known as A. competitive aggressiveness. B. technological capabilities. C. first mover advantages. D. breakthrough innovations. The benefit gained by firms that are the first to enter new markets, establish brand identity, implement administrative techniques, or adopt new operating technologies in an industry is called first mover advantage. 72. (p. 459) 73. (p. 461) 74. (p. 461) Sony Corporation's mission statement says, "We should always be the pioneers with our products, out front leading the market." This is an example of A. innovativeness. B. proactiveness. C. competitive aggressiveness. D. autonomy. Sony's mission states, "We should always be the pioneers with our products—out front leading the market." This philosophy has made Sony technologically strong with industry-leading products such as the PlayStation and Vaio laptop computers. According to Exhibit 12.7, this is an example of proactiveness. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #72 Learning Objective: 12-06 How an entrepreneurial orientation can enhance a firms efforts to develop promising corporate venture initiatives. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Entrepreneurial Orientation According to the text, firms that want to enhance their entrepreneurial position by being competitively aggressive should A. enter markets with drastically lower prices. B. foster creativity and experimentation. C. continuously seek out new products or services. D. research risk factors to minimize uncertainty. According to Exhibit 12.8, one competitive aggressiveness technique is to enter markets with drastically lower prices. An example is California-based Zimbra, Inc. Using open-source software, it has become a leader in messaging and collaboration software. Its product costs about one third less than its direct competitor Microsoft Exchange. Zimbra now has over 60 million users. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #73 Learning Objective: 12-06 How an entrepreneurial orientation can enhance a firms efforts to develop promising corporate venture initiatives. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Entrepreneurial Orientation All of the following are types of risks that executives must address EXCEPT A. business risk taking. B. financial risk taking. C. personal risk taking. D. product-market risk taking. Three types of risk that organizations and their executives face are business risk, financial risk, and personal risk. 75. (p. 461) 76. (p. 433) 77. (p. 433- 435) 78. (p. 433- 435) 79. (p. 437) Which kind of risk taking requires that a company borrow heavily or commit a large portion of its resources in order to grow? A. business risk taking B. financial risk taking C. personal risk taking D. technological risk taking Financial risk taking requires that a company borrow heavily or commit a large portion of its resources in order to grow. In this context, risk is used to refer to the risk/return trade-off that is familiar in financial analysis. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Remember Dess - Chapter 12 #75 Learning Objective: 12-06 How an entrepreneurial orientation can enhance a firms efforts to develop promising corporate venture initiatives. Level of Difficulty: 1 Easy Topic: Entrepreneurial Orientation What are the differences between product and process innovation? What are the strategic implications of each approach to innovation? Answers will vary. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #76 Learning Objective: 12-01 The importance of implementing strategies and practices that foster innovation. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Managing Innovation What is meant by the terms "radical" innovation and "incremental" innovation? Describe the advantages and disadvantages of each type of innovation and provide examples. Answers will vary. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #77 Learning Objective: 12-01 The importance of implementing strategies and practices that foster innovation. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Managing Innovation What are the characteristics of a disruptive innovation? In what way is a disruptive innovation similar to and different than a radical innovation? What are the strategic implications of those differences and similarities? Answers will vary. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #78 Learning Objective: 12-01 The importance of implementing strategies and practices that foster innovation. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Managing Innovation What are the five dilemmas that most firms face when trying to determine the best way to manage the innovation process? Answers will vary. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #79 Learning Objective: 12-02 The challenges and pitfalls of managing corporate innovation processes. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Managing Innovation 80. (p. 446- 450) Compare and contrast the concepts of focused versus dispersed approaches to corporate entrepreneurship. Provide examples of each approach. Answers will vary. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Apply Dess - Chapter 12 #80 Learning Objective: 12-03 How corporations use new venture teams; business incubators; and product champions to create an internal environment and culture that promote entrepreneurial development. Level of Difficulty: 3 Hard Topic: Corporate Entrepreneurship 81. (p. 447- 448) What are the five types of support that corporate business incubators provide to entrepreneurial ventures? Answers will vary. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #81 Learning Objective: 12-03 How corporations use new venture teams; business incubators; and product champions to create an internal environment and culture that promote entrepreneurial development. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Corporate Entrepreneurship 82. (p. 449- 450) What are product champions and why are they important to corporate entrepreneurship? Answers will vary. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #82 Learning Objective: 12-03 How corporations use new venture teams; business incubators; and product champions to create an internal environment and culture that promote entrepreneurial development. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Corporate Entrepreneurship 83. (p. 450- 451) 84. (p. 450- 451) Compare and contrast the financial and strategic objectives of corporate entrepreneurship. Provide examples of each type of objective and discuss their benefits and/or costs. Answers will vary. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #83 Learning Objective: 12-04 How corporate entrepreneurship achieves both financial goals and strategic goals. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Corporate Entrepreneurship By some accounts, only about 50 percent of corporate ventures reach profitability after six years. Is corporate venturing worth it? Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of internal venturing in relation to the extent of its financial success. Answers will vary. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #84 Learning Objective: 12-04 How corporate entrepreneurship achieves both financial goals and strategic goals. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Corporate Entrepreneurship 85. (p. 451) 86. (p. 452- 454) What are exit champions and how do they further the internal corporate venturing process? Answers will vary. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #85 Learning Objective: 12-04 How corporate entrepreneurship achieves both financial goals and strategic goals. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Corporate Entrepreneurship Discuss how real options logic can be applied in the context of corporate entrepreneurship. Are there any disadvantages to using this approach to make decision about launching corporate ventures? Answers will vary. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #86 Learning Objective: 12-05 The benefits and potential drawbacks of real options analysis in making resource deployment decisions in corporate entrepreneurship contexts. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Real Options Analysis: A Useful Tool 87. (p. 453- 454) What are some of the pitfalls of real options analysis (ROA)? Answers will vary. AACSB: Analytic Blooms: Understand Dess - Chapter 12 #87 Learning Objective: 12-05 The benefits and potential drawbacks of real options analysis in making resource deployment decisions in corporate entrepreneurship contexts. Level of Difficulty: 2 Medium Topic: Real Options Analysis: A Useful Tool 88. (p. 454- 462) Discuss the five dimensions of entrepreneurial orientation. What are the benefits and risks associated with using each of these? Answers will vary. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 401 pages
Instant download

Instant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jul 14, 2020
Number of pages
401
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jul 14, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
175













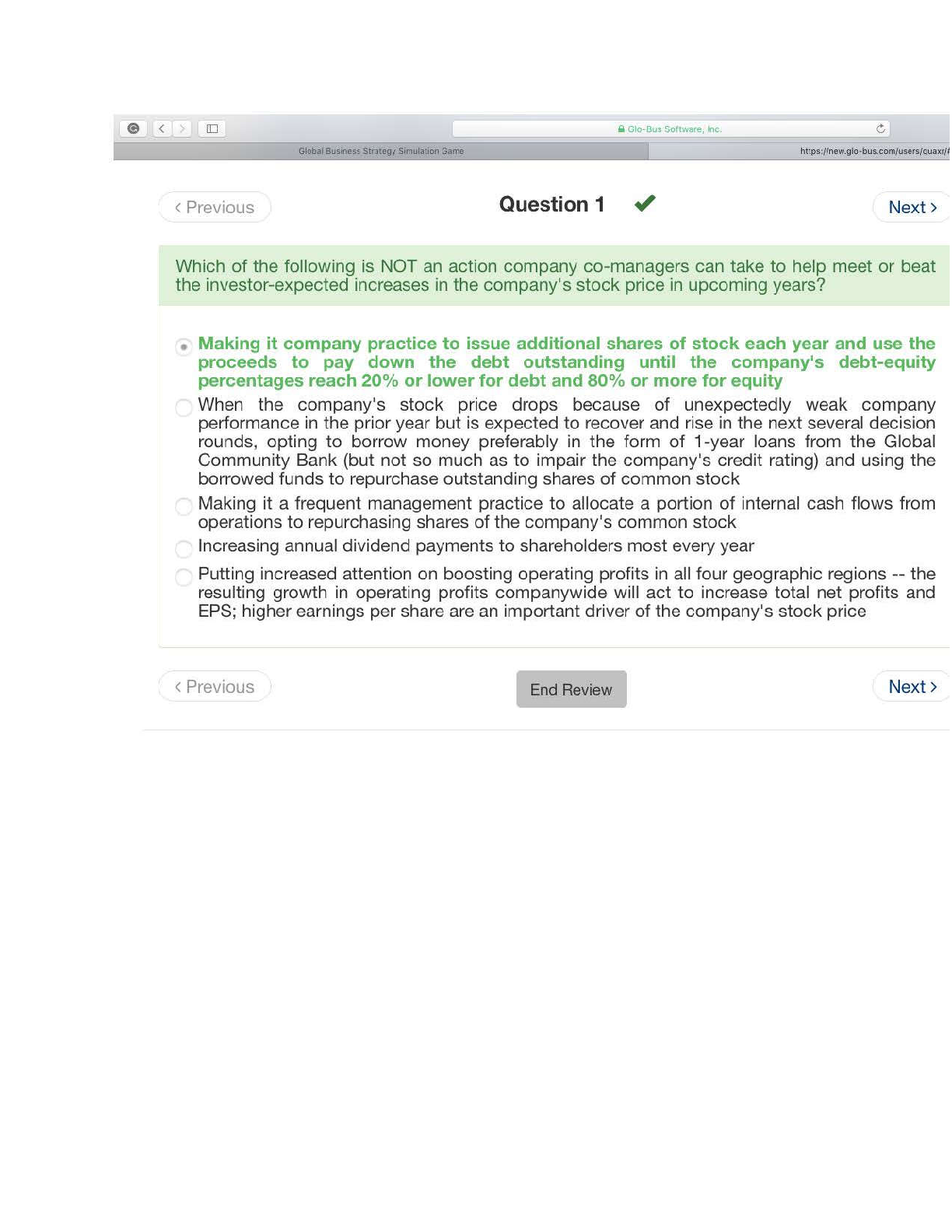







.png)
.png)