*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > NURS 611 Exam 2 Study Guide. Week 4 Neurological Functions: chapters 16, 17, 18 & 19 (All)
NURS 611 Exam 2 Study Guide. Week 4 Neurological Functions: chapters 16, 17, 18 & 19
Document Content and Description Below
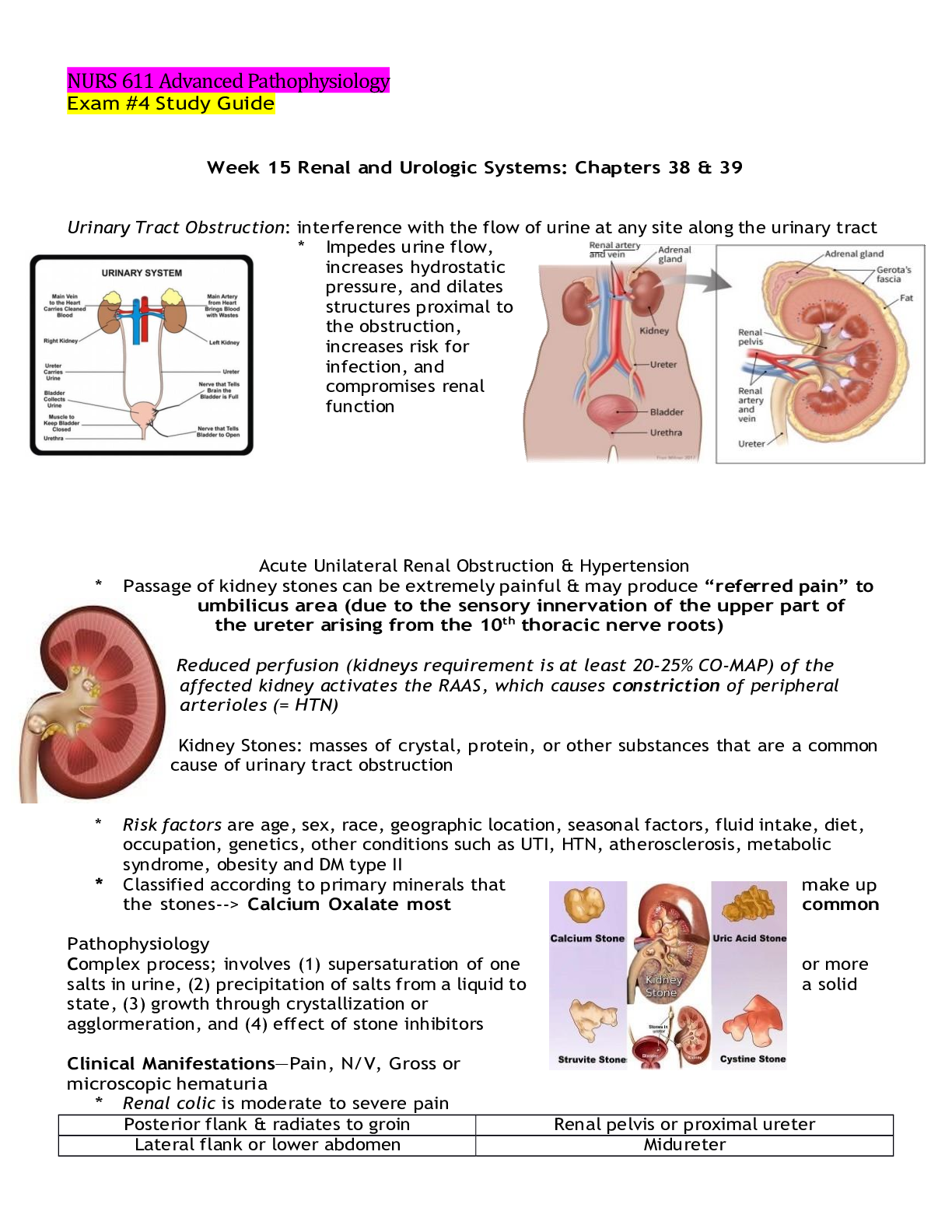
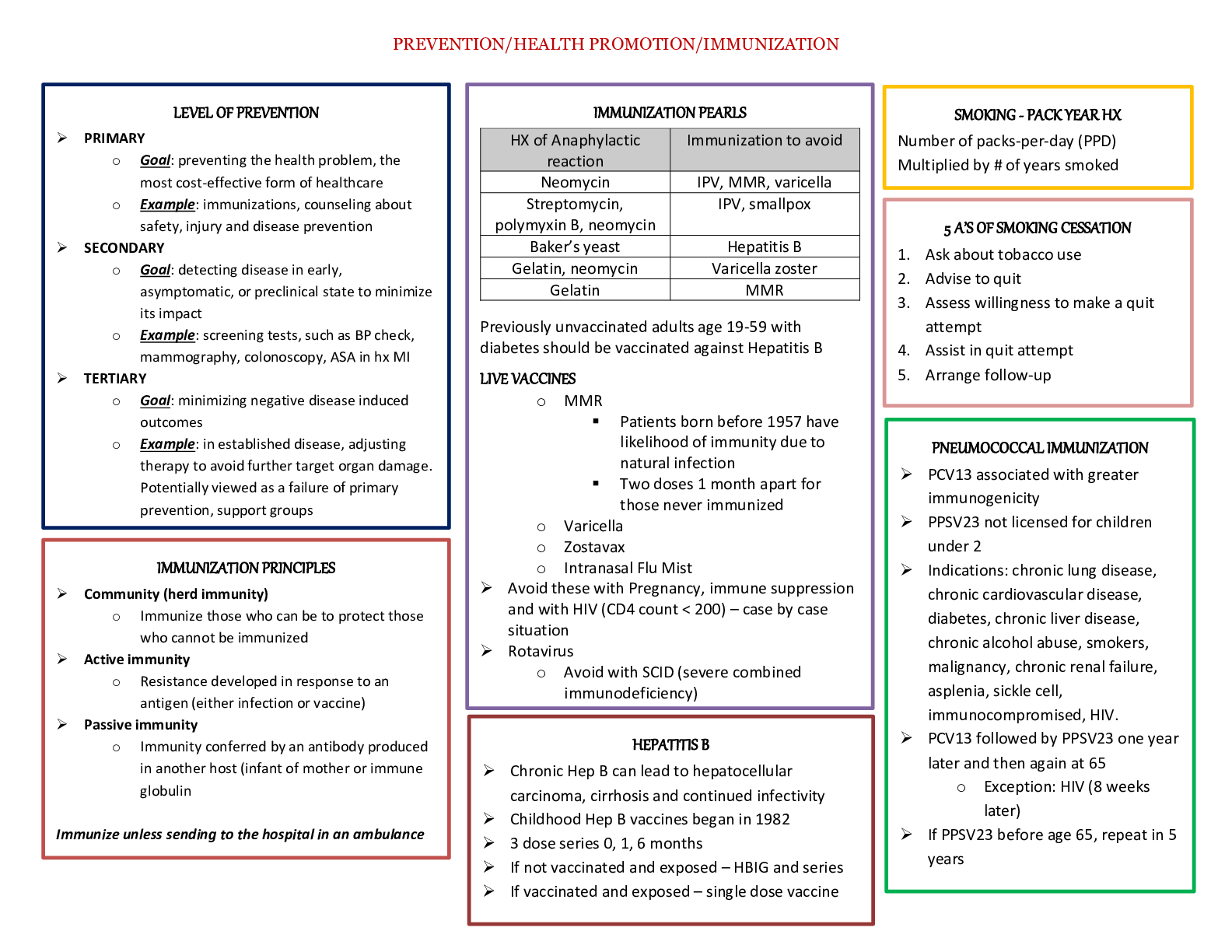
Week 4 Neurological Functions: chapters 16, 17, 18 & 19 Central Nervous System- Brain & spinal cord I. Brain * Ability to reason, function intellectually, express personality & mood, perceive &... interact with the environment A. Forebrain (telencephalon: cerebral hemispheres & diencephalon: interbrain) a. Cerebral cortex (largest portion of the brain) b. Basal ganglia (several nuclei) c. Cerebral cortex: outer layer of neurons (grey matter) that receive, integrate, store & transmit info & white matter (beneath the cerebral cortex) composed of myelinated nerve fibers Telencephalon Frontal lobe (central sulcus): future planning, self-management, decision-making * Speech & language issues (Broca’s area: helps put thoughts into words), ability to speak, understand language, produce speech aka aphasia & dysphagia * Motor skills (primary motor cortex) such as coordinate voluntary movements (walking & running) * Comparing objects * Forming memories (long-term) * Empathy * Personality * Reward-seeking behavior & motivation (dopamine-sensitive neurons) * Attention, selective attention Parietal lobe: somatic sensory input (storage, analysis, interpretation of sensory stimuli) * Touch, temperature, vibratory sense * Hemiplegia * Differentiate between right & left * Difficulty with reading, writing & math * Apraxia Occipital lobe: primary visual cortex * Homonomous hemianopia Temporal lobe: primary auditory cortex * Receptive aphasia or dysphagia (Wernicke’s area: sensory speech, responsible for reception & interpretation of speech * Memory consolidating issues * Hearing: auditory agnosia, verbal agnosia, illusions & hallucinations * Memory, emotion & behavior: loss of short & long term memory, aggressive behavior, lack of interest (depression) * Seizures, vertigo, abnormal perception of time, disturbances of smell & taste Corpus callosum: bundle of myelinated fibers that connects the two cerebral hemispheres Basal ganglia (contains substantia nigra): coordination of voluntary movements, cognitive & emotional function Extrapyramidal system: motor control system that causes involuntary reflexes, has a stabilizing effect on motor control Limbic System (group of interconnected structures located between the telencephalon & diencephalon): mediates emotion, long-term memory, behavioral responses, visceral reaction to emotion, motivation, mood, feeding behaviors, biologic rhythms, sense of smell Amygdala Hippocampus Fornix Hypothalamus Diencephalon Thalamus: major integrating system for afferent (sensory) stimuli to the cerebral cortex * Relay center for info from basal ganglia & cerebellum to the appropriate motor area * Cortical processing for interpretation Hypothalamus: maintain constant internal environment & implement behavioral patterns * Autonomic (sympathetic & parasympathetic NS) nervous system function, regulate body temperature, endocrine function- hormone synthesis, adjust emotional expression B. Midbrain Superior colliculi: voluntary & involuntary visual motor movements (eyes to track moving objects) Inferior colliculi: similar motor activities; involve movements affecting the auditory system Tegmentum (composed of the red nucleus & substantia nigra): Red nucleus- receives ascending sensory info from the cerebellum, substantia nigra- synthesizes dopamine (PD) C. Hindbrain (metencephalon & myelencephalon) Metencephalon Cerebellum: two lobes; reflexive, involuntary fine-tuning of motor control, maintaining balance & posture through extensive neural connections with the medulla * Ipsilateral (same side) control of the body (contrast to cerebral cortex) Pons: transmits info from the cerebellum to the brainstem between the two cerebellar hemispheres * Nuclei of the 5th to the 8th cranial nerves Myelencephalon (Medulla oblongata) Lowest portion of brainstem * * Reflex activities such as HR, RR, BP, coughing, sneezing, swallowing & vomiting * Nuclei of cranial nerves 9th to 12th II. Spinal cord * Transmit long motor & sensory tracts that originate in the brain and synapse with cell bodies in gray matter of the spinal cord before exiting to the body * Somatic & autonomic reflexes, motor pattern control centers, sensory & motor modulation * Divided into sections: 8 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral & 1 coccygeal Peripheral Nervous System * Nerves outside the CNS * Somatic NS controls voluntary muscle movement (efferent nerves) and sensory info (afferent nerves) * Cranial & spinal nerves Autonomic Nervous System * Regulates involuntary function of internal organs * Part of the efferent division of the PNS * Separated by two divisions: sympathetic nervous system & parasympathetic nervous system Parasympathetic & Sympathetic NS Body organs are innervated by these two nervous systems The two divisions cause opposite responses (Ex: sympathetic stimulation of the GI tract causes peristalsis, whereas parasympathetic stimulation peristalsis) Release acetylcholine via cholinergic transmission [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 27 pages

Also available in bundle (1)
NURS 611 Exam 1 - Exam 4 Study Guides. ALL A+ RATED
NURS 611 Exam 1 - Exam 4 Study Guides. ALL A+ RATED
By Quality Suppliers 3 years ago
$30.5
4
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 07, 2021
Number of pages
27
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 07, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
55





























.png)



