NSG 122 Exam 3 - Questions and Answers
Document Content and Description Below
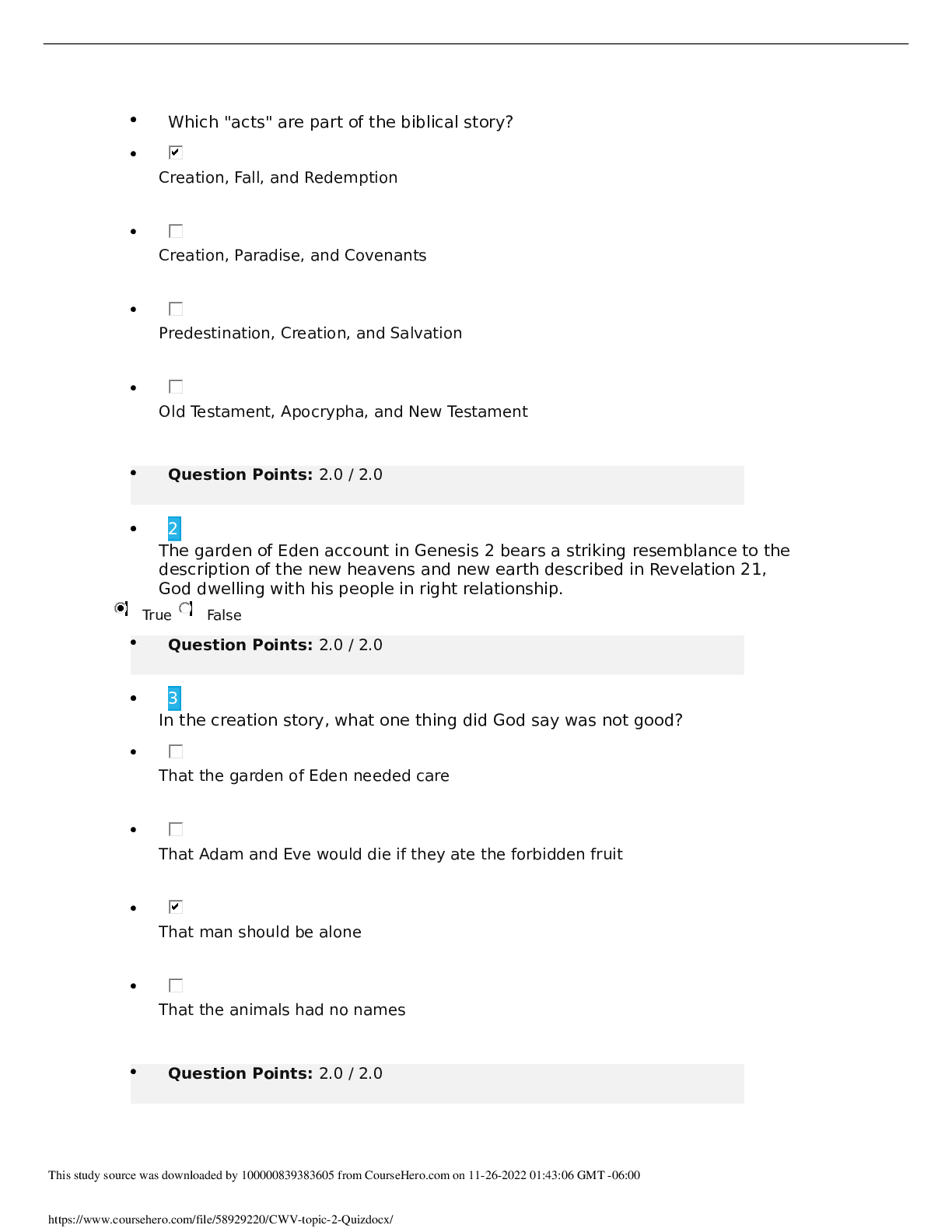
NSG 122 Exam 3 - Questions and Answers Pertinent lab data for nutrition - hemoglobin: 12-18 g/dL (decreased = anemia) - hematocrit: 40-50% (decreased = anemia, increased = dehydration) - serum album... in: 3.5-5.5 g/dL (decreased = malnutrition, low protein) - transferrin: 240-480 mg/dL (decreased = anemia, protein deficiency) - blood urea nitrogen (BUN): 17-18 mg/dL (decreased = malnutrition, overhydration, increased = starvation, severe dehydration) - creatinine: 0.4-1.5 mg/dL (decreased = severe malnutrition, increased = dehydration) Renal diet - reduce kidney workload - limit protein 0.6 - 1 g/kg/day - Na restriction 1000 - 3000 mg/day - potassium restriction - fluid restriction Clear liquid diet - clear fluids or foods that are liquid at body temperature - clear broth - coffee - tea - clear fruit juice - gelatin - popsicles Full liquid diet - includes clear liquids and liquids that cannot be seen through - milk - pudding - vegetable juice Nursing interventions for nutrition - teach nutritional information - monitor nutritional status - stimulate appetite (smells) - calorie count (portion size documentation) - assist with feeding - provide long-term nutritional support - ensure home safety (fridge, food storage) Nutritional interventions for patients with dysphagia - provide 30-minute rest period prior to meals - sit patient upright in chair or 90-degree angle in bed - provide oral care immediately prior to enhance taste - avoid rushed feeding - alternate solids and liquids - allow patient to control eating process if possible - collaborate for speech therapy consult - initiate nutrition consult for appropriate food preparation Nutritional interventions for patients with dementia - avoid clutter/distractions - maintain pleasant, well-lit room - keep food as close to original form as possible - check food temperature - assist patient as needed - provide one food at a time - serve meals in the same place at the same time - closely supervise Prior to administering enteral feeding, what is done? - aspirate gastric contents - check pH (< 5.5 - gastric, > 7.0 - intestinal) - check color (green - gastric, straw-colored - intestinal) - measure amount of residual gastric contents NG tube placement verification - perform hand hygiene - identify patient - explain procedure - assemble equipment - perform abdominal assessment - raise head of bed to 30-45 degrees - confirm placement of NG tube in stomach - apply gloves - aspirate 5-10mL gastric contents, check pH and color (must be at least 1 hour after medication or feeding) - aspirate all gastric contents to assess residual - measure residual, then return contents through tube - flush tube with 30-50mL of sterile water - disconnect syringe - remove gloves before proceeding with tube feeding NG tube bolus feeding steps - verify NG tube placement and check residual (separate steps) - if residual is > 500mL, do not proceed with enteral feeding - apply new gloves - attach 30 - 60mL syringe to feeding tube - pour pre-measured formula into syringe - open clamp on feeding tube and allow formula to enter tube (do not use the plunger) - when almost complete, add 30-60mL of sterile water to syringe - when empty, hold syringe high and clamp the tube - disconnect the syringe, cover the tube with cap - have patient remain in upright position for at least 1 hour Kidneys functions include: - urine formation to eliminate waste - pH regulation - body fluid and electrolyte regulation - blood pressure regulation - erythropoiesis Autonomic bladder when the bladder is no longer controlled by the brain because of illness or injury; voiding occurs by reflex only Polyuria excessive urination (common in diabetic patients) Oliguria below normal urine output (common symptom of kidney failure) Anuria absence of urine (common symptom in kidney failure) Hematuria blood in the urine (symptom of bladder cancer) Nocturia urination at night (can be sign of heart failure) Dysuria painful urination (symptom of UTI) Urinary retention inability to empty the bladder (can be sign of prostate enlargement or symptom of bedridden patient due to position) [Show More]
Last updated: 1 month ago
Preview 1 out of 19 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 13, 2024
Number of pages
19
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 13, 2024
Downloads
0
Views
6