NUR 155 Exam 1 2023 Full and Revised Study Guide with complete solutions
Document Content and Description Below
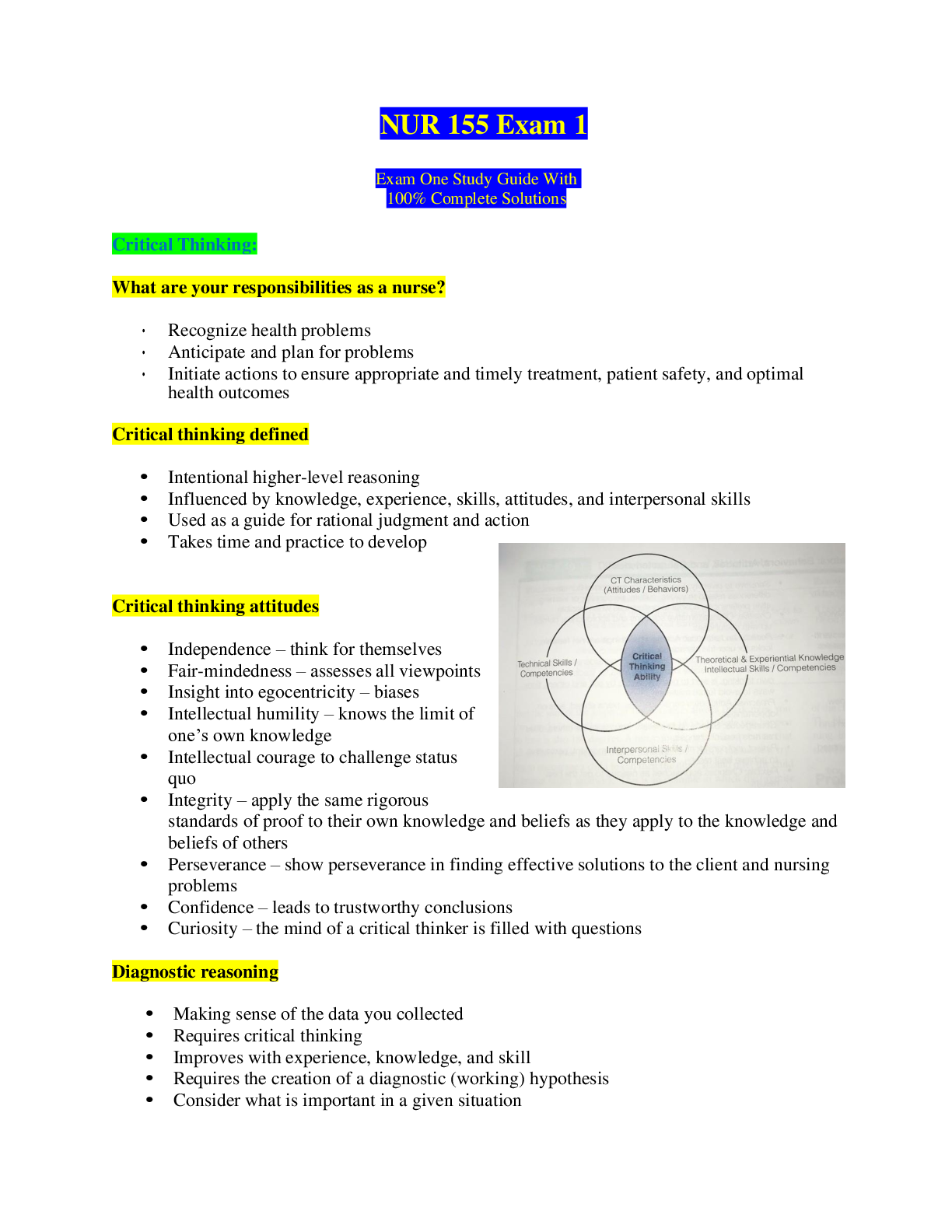
NUR 155 Exam 1 2023 Full and Revised Study Guide. Exam One Study Guide Critical Thinking: What are your responsibilities as a nurse? Recognize health problems Anticipate and plan for problems ... Initiate actions to ensure appropriate and timely treatment, patient safety, and optimal health outcomes Critical thinking defined Intentional higher-level reasoning Influenced by knowledge, experience, skills, attitudes, and interpersonal skills Used as a guide for rational judgment and action Takes time and practice to develop Critical thinking attitudes Independence – think for themselves Fair-mindedness – assesses all viewpoints Insight into egocentricity – biases Intellectual humility – knows the limit of one’s own knowledge Intellectual courage to challenge status quo Integrity – apply the same rigorous standards of proof to their own knowledge and beliefs as they apply to the knowledge and beliefs of others Perseverance – show perseverance in finding effective solutions to the client and nursing problems Confidence – leads to trustworthy conclusions Curiosity – the mind of a critical thinker is filled with questions Diagnostic reasoning Making sense of the data you collected Requires critical thinking Improves with experience, knowledge, and skill Requires the creation of a diagnostic (working) hypothesis Consider what is important in a given situation 1 Four components of diagnostic reasoning Cues (ex. Pt staggers into ER) Diagnostic “working” hypothesis (ex. Pt is intoxicated) Data collection to support hypothesis (ex. No alcohol on breath, clammy skin, diaphoretic, disoriented, blood glucose level is critical at 61) Evaluating hypothesis (ex. Pt isn’t intoxicated, pt is hypoglycemic and requires immediate intervention to prevent life-threatening complications) Critical thinking techniques Critical Thinking – is the process of intentional higher-level thinking to define a pts problem, examine the evidence-based practice in caring for the pt, and make choices in the delivery of care Critical Reasoning – is the cognitive process that uses thinking strategies to gather and analyze pt information, evaluate the relevance of the information, and decide on possible nursing actions to improve the pts physiological and psychosocial outcomes Critical Analysis – is the application of a set of questions to a particular situation or idea to determine essential information and ideas and discard unimportant information and ideas Socratic Questioning – is a technique one can use to look beneath the surface, recognize and examine assumptions, search for inconsistencies, examine multiple points of view, and differentiate what one knows from what one merely believes Inductive Reasoning – generalizations are formed from a set of facts or observations Deductive Reasoning – is reasoning from general premise to the specific conclusion Nursing Process – is a systematic, rational method of planning and providing individualized nursing care. It begins with assessment of the pt and use of clinical reasoning to identify pt problems. Clinical Judgment – is a decision-making process to ascertain the right nursing action to be implemented at the appropriate time in the pt’s care Cognitive Processes – are the thinking processes based on the knowledge of aspects of client care, cognitive skills are learned through reading and applying health-related literature Metacognitive Processes – include reflective thinking and awareness of the skills learned by the nurse in caring for the pt, the nurse reflects on the pt’s status, and through the use of critical thinking skills determines the most effective plan of care 2 Problem solving techniques Trial & Error – in which a number of approaches are tried until a solution is found (least effective, pt could suffer harm) Intuition – is a problem-solving approach that relies on a nurse’s inner sense, 6th sense, hunch, instinct, feeling, or suspicion (experience improves intuition) Research process – evidence-based decisions and care, what do we know works best vs what we’ve always done (pursue answers to pt care problems through research) Concept mapping Concept maps provide an opportunity to “see” thinking The map maker’s prior knowledge influences what is portrayed on the concept map Something to think about Nurses are responsible for a unique dimension of healthcare – “the diagnosis and treatment of human responses to actual or potential health problems” Nurses use knowledge from other disciplines Nurses deal with change in stressful environments Nurses make important decisions Nursing process Is a systematic, rational method of planning and providing individualized nursing care Its purposes are to identify a pt’s health status and actual or potential health care problems or needs, to establish plans to meet identified needs, and to deliver specific nursing interventions to meet those needs The pt may be an individual, a family, a community, or a group The nursing process is… 3 Systematic – the nursing process has an ordered sequence of activities and each activity depends on the accuracy of the activity that precedes it and influences the activity following it Dynamic – the nursing process has great interaction and overlapping among the activities and each activity is fluid and flows into the next activity Client Centered – the nursing process ensures that nurses are client-centered rather than taskcentered Goal-Directed – the nursing process is a means for nurses and clients to work together to identify specific goals and to match them with the appropriate nursing actions Universally applicable – the nursing process allows nurses to practice nursing with well or ill people, young or old, in any type of practice setting ADPIE A – assessment D – diagnosis P – planning I – implementation E – evaluation Assessment Collect data Organize data Validate data Document data Diagnosis Analyze data Identify health problems, risks, and strengths Formulate diagnostic statements Planning Prioritize problems/diagnoses Formulate goals/desired outcomes Select nursing interventions Write nursing interventions Implementation Reassess the pt Determine the nurse’s need for assistance Implement the nursing interventions Supervise delegated care Document nursing activities. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 38 pages
Instant download
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 30, 2023
Number of pages
38
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 30, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
35


.png)
















.png)
.png)

.png)

