Financial Accounting > TEST BANK > CHAPTER 1 ACCOUNTING IN ACTION: Test Bank for Accounting Principles, Eleventh Edition. This docume (All)
CHAPTER 1 ACCOUNTING IN ACTION: Test Bank for Accounting Principles, Eleventh Edition. This document/TEST BANK Contains 256 Questions With Answers, Worked Solutions and Essay Explanations
Document Content and Description Below
CHAPTER 1 ACCOUNTING IN ACTION SUMMARY OF QUESTIONS BY LEARNING OBJECTIVES AND BLOOM’S TAXONOMY sg This question also appears in the Study Guide. st This question also appears in a self-test... at the student companion website. a This question covers a topic in an appendix to the chapter. SUMMARY OF QUESTIONS BY LEARNING OBJECTIVES AND BLOOM’S TAXONOMY Matching: Q250, Short Answer: Q251-256 SUMMARY OF LEARNING OBJECTIVES BY QUESTION TYPE SUMMARY OF LEARNING OBJECTIVES BY QUESTION TYPE Note: TF = True-False BE = Brief Exercise C = Completion MC = Multiple Choice Ex = Exercise CHAPTER LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Explain what accounting is. 2. Identify the users and uses of accounting. 3. Understand why ethics is a fundamental business concept. 4. Explain generally accepted accounting principles. 5. Explain the monetary unit assumption and the economic entity assumption. 6. State the accounting equation, and define its components. 7. Analyze the effects of business transactions on the accounting equation. 8. Understand the four financial statements and how they are prepared. a9. Explain the career opportunities in accounting. TRUE-FALSE STATEMENTS 1. Owners of business firms are the only people who need accounting information. LO1 BT: K 2. Transactions that can be measured in dollars and cents are recorded in the financial information system. LO1 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: .5 min AACSB: Reflective Thinking 3. The hiring of a new company president is an economic event recorded by the financial information system. LO1 BT: C Difficulty: Easy TOT: .5 min AACSB: Reflective Thinking 4. Management of a business enterprise is the major external user of information. LO2 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: .5 min AACSB: Reflective Thinking 5. Accounting communicates financial information about a business enterprise to both internal and external users. 6. Accounting information is used only by external users with a financial interest in a business enterprise. LO2 BT: C 7. Financial statements are the major means of communicating accounting information to interested parties. LO2 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: .5 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking 8. Bookkeeping and accounting are one and the same because the bookkeeping function includes the accounting process. LO2 BT: C 9. The origins of accounting are attributed to Luca Pacioli, a famous mathematician. 10. The study of accounting will be useful only if a student is interested in working for a profit-oriented business firm. 11. Private accountants are accountants who are not employees of business enterprises. LO2 BT:K 12. The study of accounting is not useful for a business career unless your career objective is to become an accountant. LO2 BT: K 13. A working knowledge of accounting is not relevant to a lawyer or an architect. 14. Expressing an opinion as to the fairness of the information presented in financial statements is a service performed by CPAs. 15. Accountants rely on a fundamental business concept—ethical behavior—in reporting financial information. LO3 BT: K 16. The primary accounting standard-setting body in the United States is the International Accounting Standards Board. LO4 BT: K 17. The Financial Accounting Standards Board is a part of the Securities and Exchange Commission. LO4 BT: K 18. The Securities and Exchange Commission oversees U.S. financial markets and accounting standard-setting bodies. LO4 BT: K 19. The cost and fair value of an asset are the same at the time of acquisition and in all subsequent periods. LO4 BT: K 20. Even though a partnership is not a separate legal entity, for accounting purposes the partnership affairs should be kept separate from the personal activities of the owners. LO5 BT: C Difficulty; Easy TOT: .5 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking 21. A partnership must have more than one owner. LO5 BT: K 22. The economic entity assumption requires that the activities of an entity be kept separate and distinct from the activities of its owner and all other economic entities. LO5 BT: K 23. The monetary unit assumption states that transactions that can be measured in terms of money should be recorded in the accounting records. LO5 BT: K 24. In order to possess future service potential, an asset must have physical substance. LO6 BT: K 25. Owners' claims to total business assets take precedence over the claims of creditors because owners invest assets in the business and are liable for losses. LO6 BT: K 26. The basic accounting equation states that Assets = Liabilities. LO6 BT: K 27. Accountants record both internal and external transactions. LO7 BT: K 28. Internal transactions do not affect the basic accounting equation because they are economic events that occur entirely within one company. LO7 BT: C 29. The purchase of store equipment for cash reduces stockholders’ equity by an equal amount. LO7 BT: C 30. The purchase of office equipment on credit increases total assets and total liabilities. LO7 BT: C 31. The primary purpose of the statement of cash flows is to provide information about the cash receipts and cash payments of a company during a period. LO8 BT: K 32. Net income for the period is determined by subtracting total expenses and drawings from total revenues. 33. The income statement is sometimes referred to as the statement of operations. 34. A balance sheet reports the assets and liabilities of a company for a specific period of time. 35. The ending retained earnings balance is reported on both the retained earnings statement and the balance sheet. 36. Identifying is the process of keeping a chronological diary of events measured in dollars and cents. LO1 BT: K 37. Management consulting includes examining the financial statements of companies and expressing an opinion as to the fairness of their presentation. LO2 BT: K Difficulty; Easy TOT: .5 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking 38. Accountants do not have to worry about issues of ethics. LO3 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: .5 min. AACSB: Ethics 39. At the time an asset is acquired, cost and fair value should be the same. LO4 BT: C 40. The monetary unit assumption requires that all dollar amounts be rounded to the nearest dollar. LO5 BT: K 41. The basic accounting equation is in balance when the creditor and ownership claims against the business equal the assets. LO6 BT: K 42. External transactions involve economic events between the company and some other enterprise or party. LO7 BT: K 43. In the retained earnings statement, revenues are listed first, followed by expenses, and net income (or net loss). LO8 BT: K Answers to True-False Statements MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 44. Accountants refer to an economic event as a a. purchase. b. sale. c. transaction. d. change in ownership. LO1 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 45. The process of recording transactions has become more efficient because a. fewer events can be quantified in financial terms. b. computers are used in processing business events. c. more people have been hired to record business transactions. d. business events are recorded only at the end of the year. LO1 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 46. Communication of economic events is the part of the accounting process that involves a. identifying economic events. b. quantifying transactions into dollars and cents. c. preparing accounting reports. d. recording and classifying information. LO1 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 47. Which of the following events cannot be quantified into dollars and cents and recorded as an accounting transaction? a. The appointment of a new CPA firm to perform an audit. b. The purchase of a new computer. c. The sale of store equipment. d. Payment of income taxes. LO1 BT: C Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 48. The use of computers in recording business events a. has made the recording process more efficient. b. does not use the same principles as manual accounting systems. c. has greatly impacted the identification stage of the accounting process. d. is economical only for large businesses. LO1 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 49. The accounting process involves all of the following except a. identifying economic transactions that are relevant to the business. b. communicating financial information to users by preparing financial reports. c. recording nonquantifiable economic events. d. analyzing and interpreting financial reports. LO1 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 50. The accounting process is correctly sequenced as a. identification, communication, recording. b. recording, communication, identification. c. identification, recording, communication. d. communication, recording, identification. LO1 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 51. Which of the following techniques are not used by accountants to interpret and report financial information? a. Graphs. b. Special memos for each class of external users. c. Charts. d. Ratios. LO1 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 52. Accounting consists of three basic activities which are related to economic events of an organization. These include a. identifying, recording, and communicating b. identifying, calculating, and responding c. classifying, numbering, and reporting d. issuing, reporting, and classifying LO1 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 53. All of the following statements are correct except a. Good decision-making depends on good information. b. A vital element in communicating economic events is the accountant's ability to analyze and interpret reported information. c. The origins of accounting are generally attributed to Socrates, a classical Greek philosopher, who promoted accounting as a social contract. d. The information that a user of financial information needs depends upon the kinds of decisions the user makes. LO2 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 54. Which of the following would not be considered an internal user of accounting data for the GHI Company? a. President of the company. b. Production manager. c. Merchandise inventory clerk. d. President of the employees' labor union. LO2 BT: C Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 55. Which of the following would not be considered an external user of accounting data for the GHI Company? a. Internal Revenue Service Agent. b. Management. c. Creditors. d. Customers. LO2 BT: C Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 56. Which of the following would not be considered internal users of accounting data for a company? a. The president of a company. b. The controller of a company. c. Creditors of a company. d. Salesmen of the company. LO2 BT: C Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 57. Which of the following is an external user of accounting information? a. Labor unions. b. Finance directors. c. Company officers. d. Managers. LO2 BT: C Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 58. Which one of the following is not an external user of accounting information? a. Regulatory agencies. b. Customers. c. Investors. d. All of these are external users. LO2 BT: C Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 59. Bookkeeping differs from accounting in that bookkeeping primarily involves which part of the accounting process? a. Identification. b. Communication. c. Recording. d. Analysis. LO2 BT: C Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 60. The origins of accounting are generally attributed to the work of a. Christopher Columbus. b. Abner Doubleday. c. Luca Pacioli. d. Leonardo da Vinci. LO2 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 61. Financial accounting provides economic and financial information for all of the following except a. creditors. b. investors. c. managers. d. other external users. LO2 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 62. The final step in solving an ethical dilemma is to a. identify and analyze the principal elements in the situation. b. recognize an ethical situation. c. identify the alternatives and weigh the impact of each alternative on stakeholders. d. recognize the ethical issues involved. LO2 BT: C Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 63. The first step in solving an ethical dilemma is to a. identify and analyze the principal elements in the situation. b. identify the alternatives. c. recognize an ethical situation and the ethical issues involved. d. weigh the impact of each alternative on various stakeholders. LO3 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Ethics AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 64. Ethics are the standards of conduct by which one's actions are judged as a. right or wrong. b. honest or dishonest. c. fair or unfair. d. All of these answers are correct. LO3 BT: C Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Ethics AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 65. All of the following are steps in analyzing ethics cases in financial reporting except a. identify and analyze the principle elements in the situation. b. contact law enforcement regarding any violations of corporate ethics codes c. identify the alternatives and weigh the impact of each alternative on various stakeholders. d. recognize an ethical situation and the ethical issues involved. LO3 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 66. In order to increase comparability, in recent years, the FASB and IASB have made efforts to reduce the differences between U.S.GAAP and IFRS through a process known as a. convergence b. monetary unit assumption c. the cost principle d. the fair value principle LO4 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 67. Martin Corporation purchased land in 2007 for $290,000. In 2015, it purchased a nearly identical parcel of land for $460,000. In its 2015 balance sheet, Martin valued these two parcels of land at a combined value of $920,000. By reporting the land in this manner, Martin Corp. has violated the a. historical cost principle b. convergence c. economic entity assumption d. monetary unit assumption LO4 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 68. Andre Dickinson, owner of Andre's Fine Wines, also owns a personal residence that costs $475,000. The market value of his residence is $625,000. During preparation of the financial statements for Andre's Fine Wines, the accounting concept most relevant to the presentation of Andre's home is a. the economic entity assumption. b. the fair value principle. c. the monetary unit assumption. d. convergence. LO4 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 69. Generally accepted accounting principles are a. income tax regulations of the Internal Revenue Service. b. standards that indicate how to report economic events. c. theories that are based on physical laws of the universe. d. principles that have been proven correct by academic researchers. LO4 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 70. The historical cost principle requires that when assets are acquired, they be recorded at a. appraisal value. b. cost. c. market price. d. book value. LO4 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 71. The cost of an asset and its fair value are a. never the same. b. the same when the asset is sold. c. irrelevant when the asset is used by the business in its operations. d. the same on the date of acquisition. LO4 BT: C Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 72. The body of theory underlying accounting is not based on a. physical laws of nature. b. concepts. c. principles. d. definitions. LO4 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 73. The private sector organization involved in developing accounting principles is the a. Feasible Accounting Standards Body. b. Financial Accounting Studies Board. c. Financial Accounting Standards Board. d. Financial Auditors' Standards Body. LO4 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 74. The SEC and FASB are two organizations that are primarily responsible for establishing generally accepted accounting principles. It is true that a. they are both governmental agencies. b. the SEC is a private organization of accountants. c. the SEC often mandates guidelines when no accounting principles exist. d. the SEC and FASB rarely cooperate in developing accounting standards. LO4 BT: C Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 75. GAAP stands for a. Generally Accepted Auditing Procedures. b. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles. c. Generally Accepted Auditing Principles. d. Generally Accepted Accounting Procedures. LO4 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 76. Financial information that is capable of making a difference in a decision is a. faithfully representative. b. relevant. c. convergent. d. generally accepted. LO4 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 77. The Duce Company has five plants nationwide that cost a total of $100 million. The current fair value of the plants is $500 million. The plants will be recorded and reported as assets at a. $100 million. b. $600 million. c. $400 million. d. $500 million. LO4 BT: C Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 78. The fair value principle is applied for a. all assets. b. current assets. c. buildings. d. investment securities. LO4 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 79. The proprietorship form of business organization a. must have at least three owners in most states. b. represents the largest number of businesses in the United States. c. combines the records of the business with the personal records of the owner. d. is characterized by a legal distinction between the business as an economic unit and the owner. LO5 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 80. The economic entity assumption requires that the activities a. of different entities can be combined if all the entities are corporations. b. must be reported to the Securities and Exchange Commission. c. of a sole proprietorship cannot be distinguished from the personal economic events of its owners. d. of an entity be kept separate from the activities of its owner. LO5 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 81. A business organized as a corporation a. is not a separate legal entity in most states. b. requires that stockholders be personally liable for the debts of the business. c. is owned by its stockholders. d. terminates when one of its original stockholders dies. LO5 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 82. The partnership form of business organization a. is a separate legal entity. b. is a common form of organization for service-type businesses. c. enjoys an unlimited life. d. has limited liability. LO5 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 83. Which of the following is not an advantage of the corporate form of business organization? a. Limited liability of stockholders b. Transferability of ownership c. Unlimited personal liability for stockholders d. Unlimited life LO5 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 84. A small neighborhood barber shop that is operated by its owner would likely be organized as a a. joint venture. b. partnership. c. corporation. d. proprietorship. LO5 BT: C Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 85. John and Sam met at law school and decide to start a small law practice after graduation. They agree to split revenues and expenses evenly. The most common form of business organization for a business such as this would be a a. joint venture. b. partnership. c. corporation. d. proprietorship. LO5 BT: C Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 86. Which of the following is true regarding the corporate form of business organization? a. Corporations are the most prevalent form of business organization. b. Corporate businesses are generally smaller in size than partnerships and proprietor-ships. c. The revenues of corporations are greater than the combined revenues of partnerships and proprietorships. d. Corporations are separate legal entities organized exclusively under federal law. LO5 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 87. A basic assumption of accounting that requires activities of an entity be kept separate from the activities of its owner is referred to as the a. stand alone concept. b. monetary unit assumption. c. corporate form of ownership. d. economic entity assumption. LO5 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 88. Ted Leo is the proprietor (owner) of Ted's, a retailer of golf apparel. When recording the financial transactions of Ted's, Ted does not record an entry for a car he purchased for personal use. Ted took out a personal loan to pay for the car. What accounting concept guides Ted's behavior in this situation? a. Pay back concept b. Economic entity assumption c. Cash basis concept d. Monetary unit assumption LO5 BT: C Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 89. A basic assumption of accounting assumes that the dollar is a. unrelated to business transactions. b. a poor measure of economic activities. c. the common unit of measure for all business transactions. d. useless in measuring an economic event. LO5 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 90. The assumption that the unit of measure remains sufficiently constant over time is part of the a. economic entity assumption. b. cost principle. c. historical cost principle. d. monetary unit assumption. LO5 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 91. Owners enjoy limited liability in a a. proprietorship. b. partnership. c. corporation. d. sole proprietorship. LO5 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 92. A problem with the monetary unit assumption is that a. the dollar has not been stable over time. b. the dollar has been stable over time. c. the dollar is a common medium of exchange. d. it is impossible to account for international transactions. LO5 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 93. The common characteristic possessed by all assets is a. long life. b. great monetary value. c. tangible nature. d. future economic benefit. LO6 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 94. Owner's equity is best depicted by the following: a. Assets = Liabilities. b. Liabilities + Assets. c. Residual equity + Assets. d. Assets – Liabilities. LO6 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 95. The basic accounting equation may be expressed as a. Assets = Equities. b. Assets – Liabilities = Stockholders' Equity. c. Assets = Liabilities + Stockholders' Equity. d. All of these answers are correct. LO6 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 96. Liabilities a. are future economic benefits. b. are existing debts and obligations. c. possess service potential. d. are things of value used by the business in its operation. LO6 BT: C Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 97. Liabilities of a company would not include a. notes payable. b. accounts payable. c. salaries and wages payable. d. cash. LO6 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 98. Liabilities of a company are owed to a. debtors. b. benefactors. c. creditors. d. underwriters. LO6 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 99. Stockholders' equity can be described as a. creditorship claim on total assets. b. ownership claim on total assets. c. benefactor's claim on total assets. d. debtor claim on total assets. LO6 BT: C Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 100. Stockholders' equity is often referred to as a. residual equity. b. leftovers. c. spoils. d. second equity. LO6 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 101. When assets are distributed to the owners of a corporation, these distributions are termed a. depletions. b. consumptions. c. dividends. d. a credit line. LO6 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 102. A dividend is a. a distribution of the company's earnings to its stockholders. b. equal to liabilities minus stockholders' equity. c. equal to assets minus stockholders' equity. d. equal to revenues less expenses LO6 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 103. Revenues would not result from a. sale of merchandise. b. issuance of common stock. c. performance of services. d. rental of property. LO6 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 104. Sources of increases to stockholder's equity are a. additional investments by owners. b. purchases of merchandise. c. dividends. d. expenses. LO6 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 105. The basic accounting equation cannot be restated as a. Assets – Liabilities = Stockholders' Equity. b. Assets – Stockholders' Equity = Liabilities. c. Stockholders' Equity + Liabilities = Assets. d. Assets + Liabilities = Stockholders' Equity. LO6 BT: C Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 106. Stockholders' equity is decreased by all of the following except a. sales of stock. b. net losses. c. expenses. d. dividends. LO6 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 107. A net loss will result during a time period when a. liabilities exceed assets. b. dividends exceed investments. c. expenses exceed revenues. d. revenues exceed expenses. LO6 BT: C Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 108. If total liabilities increased by $30,000 and stockholders' equity increased by $20,000 during a period of time, then total assets must change by what amount and direction during that same period? a. $50,000 decrease b. $10,000 decrease c. $10,000 increase d. $50,000 increase LO6 BT: AP Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting Solution: $30,000 $20,000 $50,000 109. If total liabilities decreased by $30,000 and stockholders' equity increased by $20,000 during a period of time, then total assets must change by what amount and direction during that same period? a. $50,000 decrease b. $10,000 decrease c. $10,000 increase d. $50,000 increase LO6 BT: AP Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting Solution: $20,000 $30,000 ($10,000) 110. If total liabilities decreased by $50,000 and stockholders' equity increased by $30,000 during a period of time, then total assets must change by what amount and direction during that same period? a. $80,000 decrease b. $20,000 decrease c. $20,000 increase d. $80,000 increase LO6 BT: AP Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting Solution: $30,000 $50,000 ($20,000) 111. If total liabilities decreased by $30,000 and stockholders' equity decreased by $20,000 during a period of time, then total assets must change by what amount and direction during that same period? a. $50,000 decrease b. $10,000 decrease c. $10,000 increase d. $50,000 increase LO6 BT: AP Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting Solution: ($30,000) ($20,000) ($50,000) 112. If total liabilities increased by $25,000 during a period of time and stockholders' equity decreased by $9,000 during the same period, then the amount and direction (increase or decrease) of the period’s change in total assets is a(n) a. $34,000 decrease. b. $16,000 decrease. c. $16,000 increase. d. $34,000 increase. LO6 BT: AP Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting Solution: $25,000 $9,000 $16,000 increase 113. If total assets equal $345,000 and total stockholders' equity equal $140,000, then total liabilities must equal a. $485,000. b. $205,000. c. $140,000. d. There is not enough information given to determine this. LO6 BT: k Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting Solution: $345,000 $140,000 $205,000 114. Which of the following will not cause a change in the stockholders' equity of a business? a. An increase in prepaid expenses. b. An increase in retained earnings. c. The sale of common stock. d. The declaration and payment of dividends. LO6 BT: k Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 115. The amount of stockholders' equity in a business is not affected by a. The percentage of total assets held in cash. b. Assets consumed in the process of earning revenues. c. The profitability of the business. d. The amount of dividends declared and paid to stockholders. LO6 BT: k Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 116. If the transaction causes an asset account to decrease, which of the following related effects may occur? a. An increase of equal amount in the common stock account. b. An increase in a liability account. c. An increase of equal amount in another asset account. d. An increase in the combined total of liabilities and stockholders' equity. LO6 BT: k Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 117. The accounting equation for Quattro Enterprises is as follows: Assets Liabilities Stockholders' Equity $120,000 = $60,000 + $60,000 If Quattro purchases office equipment on account for $25,000, the accounting equation will change to Assets Liabilties Stockholders' Equity a. $120,000 = $60,000 + $60,000 b. $145,000 = $60,000 + $85,000 c. $145,000 = $72,500 + $72,500 d. $145,000 = $85,000 + $60,000 LO7 BT: C Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting Solution: $120,000 $25,000 $145,000; $60,000 $25,000 $85,000 118. As of June 30, 2015, Actual Tigers Company has assets of $100,000 and stockholders' equity of $40,000. What are the liabilities for Actual Tigers Company as of June 30, 2015? a. $40,000 b. $60,000 c. $100,000 d. $140,000 LO7 BT: AP Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting Solution: $100,000 $40,000 $60,000 119. Stockholders' equity is increased by a. dividends. b. revenues. c. expenses. d. liabilities. LO7 BT: C Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 120. Stockholders' equity is decreased by a. assets. b. revenues. c. expenses. d. liabilities. LO7 BT: C Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 121. If total liabilities increased by $8,000, then a. assets must have decreased by $8,000. b. stockholders' equity must have increased by $8,000. c. assets must have increased by $8,000, or stockholders' equity must have decreased by $8,000. d. assets and stockholders' equity each increased by $4,000. LO7 BT: C Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 122. Collection of a $1,000 Accounts Receivable a. increases an asset $1,000; decreases an asset $1,000. b. increases an asset $1,000; decreases a liability $1,000. c. decreases a liability $1,000; increases stockholders' equity $1,000. d. decreases an asset $1,000; decreases a liability $1,000. LO7 BT: C Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 123. Revenues are a. the cost of assets consumed during the period. b. gross increases in stockholders' equity resulting from business activities. c. the cost of services used during the period. d. actual or expected cash outflows. LO7 BT: C Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 124. If an individual asset is increased, then a. there must be an equal decrease in a specific liability. b. there must be an equal decrease in stockholders' equity. c. there must be an equal decrease in another asset. d. All of these answers are possible. LO7 BT: C Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 125. If services are rendered for credit, then a. assets will decrease. b. liabilities will increase. c. stockholders' equity will increase. d. liabilities will decrease. LO7 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 126. If expenses are paid in cash, then a. assets will increase. b. liabilities will decrease. c. stockholders' equity will increase. d. assets will decrease. LO7 BT: C Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 127. If a corporation distributes cash to its stockholders, then a. there has been a violation of accounting principles. b. stockholders' equity will increase. c. stockholders' equity will decrease. d. there will be a new liability showing the stockholders owes money to the business. LO7 BT: C Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 128. If supplies that have been purchased are used in the course of business, then a. a liability will increase. b. an asset will increase. c. stockholders' equity will decrease. d. stockholders' equity will increase. LO7 BT: C Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 129. As of December 31, 2015, Calexico Company has assets of $42,000 and stockholders' equity of $20,000. What are the liabilities for Calexico Company as of December 31, 2015? a. $22,000. b. $20,000. c. $42,000. d. $62,000. LO7 BT: AN Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting Solution: $42,000 $20,000 $22,000 130. Which of the following events is not a business transaction? a. Issuance of stock in exchange for cash. b. Hired employees. c. Incurred utility expenses for the month. d. Earned revenue for services provided. LO7 BT: C Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 131. Net income results when a. Assets > Liabilities. b. Revenues = Expenses. c. Revenues > Expenses. d. Revenues < Expenses. LO8 BT: C Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 132. Retained earnings at the end of the period is equal to a. retained earnings at the beginning of the period plus net income minus liabilities. b. retained earnings at the beginning of the period plus net income minus dividends. c. net income. d. assets plus liabilities. LO8 BT: C Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 133. A balance sheet shows a. revenues, liabilities, and stockholders' equity. b. expenses, dividends, and stockholders' equity. c. revenues, expenses, and dividends. d. assets, liabilities, and stockholders' equity. LO8 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 134. An income statement a. summarizes the changes in retained earnings for a specific period of time. b. reports the changes in assets, liabilities, and stockholders' equity over a period of time. c. reports the assets, liabilities, and stockholders' equity at a specific date. d. presents the revenues and expenses for a specific period of time. LO8 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 135. If the retained earnings account increases from the beginning of the year to the end of the year, then a. net income is less than dividends. b. a net loss is less than dividends. c. the company must have sold stock. d. net income is greater than dividends. LO8 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 136. Mofro’s Computer Repair Shop started the year with total assets of $300,000 and total liabilities of $200,000. During the year, the business recorded $500,000 in computer repair revenues, $300,000 in expenses, and Mofro paid dividends of $50,000. Stockholders' equity at the end of the year was a. $200,000. b. $100,000. c. $250,000. d. $300,000. LO8 BT: AP Difficulty: Medium TOT: 1.5 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting Solution: ($300,000 $200,000) ($500,000 $300,000) $50,000 $250,000 137. Mofro’s Computer Repair Shop started the year with total assets of $300,000 and total liabilities of $200,000. During the year, the business recorded $500,000 in computer repair revenues, $300,000 in expenses, and Mofro paid dividends of $50,000. The net income reported by Mofro's Computer Repair Shop for the year was a. $100,000. b. $150,000. c. $200,000. d. $250,000. LO8 BT: AP Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting Solution: $500,000 $300,000 $200,000 138. Mofro’s Computer Repair Shop started the year with total assets of $300,000 and total liabilities of $200,000. During the year, the business recorded $500,000 in computer repair revenues, $300,000 in expenses, and Mofro paid dividends of $50,000. Mofro's stockholders' equity changed by what amount from the beginning of the year to the end of the year? a. $100,000. b. $150,000. c. $200,000. d. $250,000. LO8 BT: AP Difficulty: Medium TOT: 1.5 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting Solution: ($300,000 $200,000) ($500,000 $300,000) $50,000 $250,000; $250,000 $100,000 $150,000 139. The balance sheet is frequently referred to as a. an operating statement. b. the statement of financial position. c. the statement of cash flows. d. the statement of retained earnings. LO8 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 140. The primary purpose of the statement of cash flows is to report a. a company's investing transactions. b. a company's financing transactions. c. information about cash receipts and cash payments of a company. d. the net increase or decrease in cash. LO8 BT: C Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 141. All of the financial statements are for a period of time except the a. income statement. b. retained earnings statement. c. balance sheet. d. statement of cash flows. LO8 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 142. The ending retained earnings amount is shown on a. the balance sheet only. b. the retained earnings statement only. c. both the income statement and the retained earnings statement. d. both the balance sheet and the retained earnings statement. LO8 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 143. Black Keys Company began the year with stockholders' equity of $280,000. During the year, the company recorded revenues of $375,000, expenses of $285,000, and paid dividends of $30,000. What was Black Keys’ stockholders' equity at the end of the year? a. $280,000. b. $340,000. c. $370,000. d. $400,000. LO8 BT: AP Difficulty: Medium TOT: 1.5 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting Solution: $280,000 ($375,000 $285,000) $30,000 $340,000 144. Kennedy Company issued stock to Ed Kennedy in exchange for his investment of $75,000 cash in the business. The company recorded revenues of $555,000, expenses of $420,000, and had paid dividends of $30,000. What was Kennedy's net income for the year? a. $105,000. b. $135,000. c. $165,000. d. $180,000. LO8 BT: AP Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting Solution: $555,000 $420,000 $135,000 145. Centro-matic Company began the year with stockholders' equity of $30,000. During the year, Centro-matic issued additional shares of stock in exchange for cash of $42,000, recorded expenses of $120,000, and paid dividends of $8,000. If Centro-matic’s ending stockholders' equity was $112,000, what was the company’s revenue for the year? a. $160,000. b. $168,000. c. $202,000. d. $210,000. LO8 BT: AP Difficulty: Medium TOT: 2.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting Solution: $30,000 $42,000 (X $120,000) $8,000 $112,000; X $168,000 146. Barsuk Company began the year with stockholders' equity of $108,000. During the year, Barsuk issued stock for $147,000, recorded expenses of $420,000, and paid dividends of $28,000. If Barsuk’s ending stockholders' equity was $290,000, what was the company’s revenue for the year? a. $455,000. b. $483,000. c. $602,000. d. $630,000. LO8 BT: AP Difficulty: Medium TOT: 2.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting Solution: $108,000 $147,000 (X $420,000) $28,000 $290,000; X $483,000 147. Fat Possum’s Service Shop started the year with total assets of $330,000 and total liabilities of $240,000. During the year, the business recorded $630,000 in revenues, $420,000 in expenses, and paid dividends of $60,000. Stockholders' equity at the end of the year was a. $90,000. b. $240,000. c. $300,000. d. $360,000. LO8 BT: AP Difficulty: Medium TOT: 1.5 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting Solution: ($330,000 $240,000) ($630,000 $420,000) $60,000 $240,000 148. Fat Possum’s Service Shop started the year with total assets of $330,000 and total liabilities of $2400,000. During the year, the business recorded $630,000 in revenues, $420,000 in expenses, and paid dividends of $60,000. The net income reported by Fat Possum’s Service Shop for the year was a. $150,000. b. $210,000. c. $240,000. d. $270,000. LO8 BT: AP Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting Solution: $630,000 $420,000 $210,000 149. Misra Company compiled the following financial information as of December 31, 2015: Revenues $340,000 Retained earnings (1/1/15) 60,000 Equipment 80,000 Expenses 250,000 Cash 90,000 Dividends 20,000 Supplies 10,000 Accounts payable 40,000 Accounts receivable 70,000 Common stock 80,000 Misra’s assets on December 31, 2015 are a. $180,000. b. $250,000. c. $360,000. d $490,000. LO8 BT: AP Difficulty: Medium TOT: 1.5 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting Solution: $80,000 $90,000 $10,000 $70,000 $250,000 150. Misra Company compiled the following financial information as of December 31, 2015: Revenues $340,000 Retained earnings (1/1/15) 60,000 Equipment 80,000 Expenses 250,000 Cash 90,000 Dividends 20,000 Supplies 10,000 Accounts payable 40,000 Accounts receivable 70,000 Common stock 80,000 Misra’s stockholders' equity on December 31, 2015 is a. $90,000. b. $140,000. c. $210,000. d. $250,000. LO8 BT: AP Difficulty: Medium TOT: 1.5 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting Solution: $140,000 ($340,000 $250,000) $20,000 $210,000 151. Teamboo Company’s stockholders' equity at the beginning of August 2015 was $750,000. During the month, the company earned net income of $175,000 and paid dividends of $75,000. At the end of August 2015, what is the amount of stockholders' equity? a. $675,000 b. $750,000 c. $825,000 d. $850,000 LO8 BT: AP Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting Solution: $750,000 $175,000 $75,000 $850,000 152. On January 1, 2015, Cat Power Company reported stockholders' equity of $705,000. During the year, the company paid dividends of $30,000. At December 31, 2015, the amount of stockholders' equity was $825,000. What amount of net income or net loss would the company report for 2015? a. Net loss of $30,000 b. Net income of $90,000 c. Net income of $120,000 d. Net income of $150,000 LO8 BT: AP Difficulty: Medium TOT: 1.5 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting Solution: $705,000 X $30,000 $825,000; X $150,000 153. Stahl Consulting started the year with total assets of $60,000 and total liabilities of $15,000. During the year, the business recorded $48,000 in catering revenues and $30,000 in expenses. Stahl issued stock of $9,000 and paid dividends of $15,000 during the year. The stockholders' equity at the end of the year was a. $33,000. b. $54,000. c. $57,000. d. $63,000. LO8 BT: AP Difficulty: Medium TOT: 1.5 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting Solution: ($60,000 $15,000) ($48,000 $30,000) $9,000 $15,000 $57,000 154. Stahl Consulting started the year with total assets of $60,000 and total liabilities of $15,000. During the year, the business recorded $48,000 in catering revenues and $30,000 in expenses. Stahl issued stock of $9,000 and paid dividends of $15,000 during the year. The net income reported by Stahl Consulting for the year was: a. $3,000. b. $12,000. c. $18,000. d. $27,000. LO8 BT: AP Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting Solution: $48,000 $30,000 $18,000 155. Stahl Consulting started the year with total assets of $60,000 and total liabilities of $15,000. During the year, the business recorded $48,000 in catering revenues and $30,000 in expenses. Stahl issued stock of $9,000 and paid dividends of $15,000 during the year. Stockholders' equity changed by what amount from the beginning of the year to the end of the year? a. $3,000. b. $9,000. c. $12,000. d. $45,000. LO8 BT: AP Difficulty: Medium TOT: 1.5 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting Solution: ($60,000 $15,000) ($48,000 $30,000) $9,000 $15,000 $57,000; $57,000 $45,000 $12,000 156. During the year 2015, Dilego Company earned revenues of $90,000, had expenses of $56,000, purchased assets with a cost of $10,000 and paid dividends of $6,000. Net income for the year is a. $18,000. b. $24,000. c. $28,000. d. $34,000. LO8 BT: AN Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting Solution: $90,000 $56,000 $34,000 157. At October 1, Arcade Fire Enterprises reported stockholders' equity of $70,000. During October, no stock was issued and the company earned net income of $18,000. If stockholders' equity at October 31 totals $78,000, what amount of dividends were paid during the month? a. $0 b. $8,000 c. $10,000 d. $26,000 LO8 BT: AN Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting Solution: $70,000 $18,000 X $78,000; X $10,000 158. At October 1, Arcade Fire Enterprises reported stockholders' equity of $72,000. During October, no stock was issued and the company posted a net loss of $8,000. If stockholders' equity at October 31 totals $64,000, what amount of dividends were paid during the month? a. $0 b. $4,000 c. $8,000 d. $16,000 LO8 BT: AN Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting Solution: $72,000 $8,000 X $64,000; X $0 159. At October 1, Arcade Fire Enterprises reported stockholders' equity of $70,000. During October, common stock of $4,000 was issued and the company earned net income of $14,000. If stockholders' equity at October 31 totals $80,000, what amount of dividends were paid during the month? a. $0 b. $4,000 c. $8,000 d. $10,000 LO8 BT: AN Difficulty: Medium TOT: 1.5 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting Solution: $70,000 $4,000 $14,000 X $80,000; X $8,000 160. At October 1, Arcade Fire Enterprises reported stockholders' equity of $70,000. During October, common stock of $10,000 was issued and the company posted a net loss of $4,000. If stockholders' equity at October 31 totals $70,000, what amount of dividends were paid during the month? a. $0 b. $4,000 c. $6,000 d. $10,000 LO8 BT: AN Difficulty: Medium TOT: 1.5 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting Solution: $70,000 $10,000 $4,000 X $70,000; X $6,000 a161. All of the following are services offered by public accountants except a. budgeting. b. auditing. c. tax planning. d. consulting. LO9 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting a162. Which list below best describes the major services performed by public accountants? a. Bookkeeping, mergers, budgets. b. Employee training, auditing, bookkeeping. c. Auditing, taxation, management consulting. d. Cost accounting, production scheduling, recruiting. LO9 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting a163. Preparing tax returns and engaging in tax planning is performed by a. public accountants only. b. private accountants only. c. both public and private accountants. d. IRS accountants only. LO9 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting a164. A private accountant can perform many activities in a business organization but would not work in a. budgeting. b. accounting information systems. c. external auditing. d. tax accounting. LO9 BT: C Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 165. Which of the following is not part of the accounting process? a. Recording b. Identifying c. Financial decision making d. Communicating LO1 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 166. The first part of the accounting process is a. communicating. b. identifying. c. processing. d. recording. LO1 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 167. Keeping a systematic, chronological diary of events that are measured in dollars and cents is called a. communicating. b. identifying. c. processing. d. recording. LO1 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 168. Auditing is a. the examination of financial statements by a CPA in order to express an opinion on their fairness. b. a part of accounting that involves only recording of economic events. c. an area of accounting that involves such activities as cost accounting, budgeting, and accounting information systems. d. conducted by the Securities and Exchange Commission to ensure that registered financial statements are presented fairly. LO2 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 169. Internal users of accounting information include all of the following except a. company officers. b. investors. c. marketing managers. d. production supervisors. LO2 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 170. The organization(s) primarily responsible for establishing generally accepted accounting principles is(are) the FASB SEC a. no no b. yes no c. no yes d. yes yes S04 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 171. The primary accounting standard-setting body in the United States is the a. Financial Accounting Standards Board. b. International Accounting Standards Board. c. Internal Revenue Service. d. Securities and Exchange Commission. LO5 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 172. A proprietorship is a business a. owned by one person. b. owned by two or more persons. c. organized as a separate legal entity under state corporation law. d. owned by a governmental agency. LO5 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 173. A net loss will result during a time period when a. assets exceed liabilities. b. assets exceed stockholders' equity. c. expenses exceed revenues. d. revenues exceed expenses. LO6 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 174. Bright Eyes Downtown Diner received a bill of $600 from the Jronand Wine Advertising Agency. The owner, A. A. Bondy, is postponing payment of the bill until a later date. The effect on specific items in the basic accounting equation is a. a decrease in Cash and an increase in Accounts Payable. b. a decrease in Cash and an increase in Retained Earnings. c. an increase in Accounts Payable and a decrease in Retained Earnings. d. a decrease in Accounts Payable and an increase in Retained Earnings. LO7 BT: C Difficulty: Medium TOT: 1.5 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 175. Matador Company purchases $1,300 of equipment from Danger Mouse Inc. for cash. The effect on the components of the basic accounting equation of Matador Company is a. an increase in assets and liabilities. b. a decrease in assets and liabilities. c. no change in total assets. d. an increase in assets and a decrease in liabilities. LO7 BT: C Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 176. Druganaut Company buys a $21,000 van on credit. The transaction will affect the a. income statement only. b. balance sheet only. c. income statement and retained earnings statement only. d. income statement, retained earnings statement, and balance sheet. LO8 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 177. The financial statement that summarizes the financial position of a company is the a. income statement. b. balance sheet. c. operating statement. d. retained earnings statement. LO8 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 178. Which of the following is not a reason one set of international accounting standards are needed? a. multinational corporations. b. mergers and acquisitions. c. information technology. d. all of these answer choices are correct. IFRS. LO10 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 179. Which of the following is not a reason one set of international accounting standards are needed? a. multinational corporations. b. financial markets. c. information technology. d. all of the above are reasons one set of international accounting standards are needed. IFRS. LO10 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 180. International standards are referred to as a. IFRS. b. GAAP. c. IASB. d. FASB. IFRS. LO10 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 181. U.S. standards are referred to as a. IFRS. b. GAAP. c. IASB. d. FASB. IFRS LO10 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 182. International standards are developed by the a. IFRS. b. GAAP. c. IASB. d. FASB. IFRS. LO10 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 183. U.S. standards are developed by the a. IFRS. b. GAAP. c. IASB. d. FASB. IFRS. LO10 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 184. The United States and the international standard-setting environment are primarily driven by meeting the needs of a. investors and creditors. b. tax authorities. c. central government planners. d. academic researchers. IFRS. LO10 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 185. The internal control standards applicable to Sarbanes-Oxley apply to a. all U.S. and international companies. b. U.S. and international companies listed on U.S. exchanges. c. International companies listed on U.S. exchanges. d. U.S. companies listed on U.S. exchanges. IFRS. LO10 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 186. The concern about international companies adopting SOX-type standards centers on a. cost-benefit analysis. b. ethics issues. c. the governing authorities. d. comparability. IFRS. LO10 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 187. Financial accounting ethics violations are a. not a problem in the U.S. or internationally. b. much more common in the U.S. than internationally. c. much more common internationally than in the U.S. d. a major problem both in the U.S. and internationally. IFRS. LO10 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 188. IFRS, compared to GAAP, tends to be more a. detailed. b. rules-based. c. principles-based. d. full of disclosure requirements. IFRS. LO10 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 189. GAAP, compared to IFRS, tends to be more a. simple in accounting requirements. b. rules-based. c. principles-based. d. simple in disclosure requirements. IFRS. LO10 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 190. Proprietorships, partnerships, and corporations a. are the three most common forms of business organizations in the U.S. b. are the three most common forms of business organizations internationally. c. are used in different proportions in different countries. d. all of these answers are correct. IFRS. LO10 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting 191. The conceptual framework that underlies IFRS a. is very similar to that used to develop GAAP. b. does not define assets or liabilities. c. does not define equity. d. does not define income or expenses. IFRS. LO10 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 1.0 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting BRIEF EXERCISES BE 192 Match the following external users of financial accounting information with the type of decision that user will make with the information. a. Creditor b. Investor c. Regulatory Agency d Internal Revenue Service _______ (1) Is the company operating within prescribed guidelines? _______ (2) Is the company complying with tax laws? _______ (3) Is the company able to pay its debts? _______ (4) Is the company a good investment? BE 193 Match the following terms and definitions. a. Accounts receivable c. Accounts payable b. Creditor d. Note payable _______ (1) Amounts due from customers _______ (2) Amounts owed to suppliers for goods and services purchased _______ (3) Amounts owed to bank _______ (4) Party to whom money is owed LO6 BT: K Difficulty: Easy TOT: 3 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting BE 194 Indicate which of these items is an asset (A), liability (L) or stockholders’ equity (SE) account. _______ (1) Supplies _______ (2) Dividends _______ (3) Buildings _______ (4) Notes Payable _______ (5) Salaries and Wages Payable BE 195 Use the accounting equation to answer the following questions. 1. Picaresque Sails Co. has total assets of $140,000 and total liabilities of $45,000. What is stockholders' equity? 2. The Natenal Fun Center has total assets of $225,000 and stockholders' equity of $100,000. What are total liabilities? 3. Okkervil River Restaurant has total liabilities of $50,000 and stockholders' equity of $100,000. What are total assets? BE 196 Determine the missing items. Assets = Liabilities + Stockholders' Equity $85,000 $52,000 (a) (b) $28,000 $34,000 $84,000 (c) $50,000 BE 197 Classify each of these items as an asset (A), liability (L), or stockholders' equity (SE). _____ 1. Accounts receivable _____ 2. Accounts payable _____ 3. Common stock _____ 4. Supplies _____ 5. Utilities expense _____ 6. Cash _____ 7. Notes payable _____ 8. Equipment BE 198 Identify the impact on the accounting equation of each of the following transactions. 1. Purchase office supplies on account. 2. Paid secretary weekly salary. 3. Purchased office furniture for cash. 4. Received monthly utility bill to be paid at later time. BE 199 Balance sheet amounts as of December 31, 2015 for Matt Pond's Tutoring Service are listed below. Prepare a balance sheet in good form. Accounts Payable $ 400 Accounts Receivable 1,000 Cash 300 Common Stock ? BE 200 Identify whether the following items would be reported on the income statement (IS) or balance sheet (BS). 1. Cash 2. Service Revenue 3. Notes Payable 4. Interest Expense 5. Accounts Receivable BE 201 Use the following information to calculate for the year ended December 31, 2015 (a) net income, (b) ending retained earnings, and (c) total assets. Supplies $ 3,000 Revenues $25,000 Operating expenses 12,000 Cash 15,000 Accounts payable 9,000 Dividends 1,000 Accounts receivable 3,000 Notes payable 1,000 Beginning retained earnings 5,000 Equipment 6,000 BE 202 Listed below in alphabetical order are the balance sheet items of Madjack Company at December 31, 2015. Prepare a balance sheet and include a complete heading. Accounts payable $ 21,000 Accounts receivable 15,000 Buildings 91,000 Cash 6,000 Common stock 108,000 Equipment 17,000 EXERCISES Ex. 203 Below is a list of important abbreviations widely used in business. For each abbreviation give the full designation. 1. CPA 2. IRS 3. FBI 4. FASB 5. GAAP 6. SEC Ex. 204 Determine the missing amount for each of the following. Assets = Liabilities + Stockholders' Equity 1. (a) $55,000 $95,000 2. $125,000 (b) $85,000 3. $160,000 $65,000 (c) Ex. 205 For the items listed below, fill in the appropriate code letter to indicate whether the item is an asset, liability, or stockholders' equity item. Code Asset A Liability L Stockholders' Equity SE 1. Rent Expense 6. Cash 2. Equipment 7. Accounts Receivable 3. Accounts Payable 8. Dividends 4. Common Stock 9. Service Revenue 5. Insurance Expense 10. Notes Payable Ex. 206 At the beginning of the year, Shaolin Company had total assets of $520,000 and total liabilities of $210,000. Answer the following questions viewing each situation as being independent of the others. (1) If total assets increased $200,000 during the year, and total liabilities decreased $75,000, what is the amount of stockholders' equity at the end of the year? (2) During the year, total liabilities increased $230,000 and stockholders' equity decreased $90,000. What is the amount of total assets at the end of the year? (3) If total assets decreased $40,000 and stockholders' equity increased $130,000 during the year, what is the amount of total liabilities at the end of the year? Ex. 207 Magnolia Electric Car Cleaning has the following accounts: Equipment Notes Payable Accounts Payable Common Stock Cash Dividends Supplies Accounts Receivable Identify which items are (1) Assets (2) Liabilities (3) Stockholders Equity Ex. 208 On June 1, 2015, Secretly Canadian Company prepared a balance sheet that shows the following: Assets (no cash) $100,000 Liabilities 45,000 Stockholders' Equity 55,000 Ex. 208 (cont.) Shortly thereafter, all of the assets were sold for cash. How would the balance sheet appear immediately after the sale of the assets for cash for each of the following cases? Cash Received for Balances Immediately After Sale the Assets Assets – Liabilities = Stockholders' Equity Cash A $110,000 $________ $________ $________ Cash B 100,000 ________ ________ ________ Cash C 90,000 ________ ________ ________ Ex. 209 At the beginning of 2015, Hold Steady Company had total assets of $520,000 and total liabilities of $250,000. Answer each of the following questions. 1. If total assets increased $60,000 and stockholders' equity decreased $90,000 during the year, determine the amount of total liabilities at the end of the year. 2. During the year, total liabilities decreased $75,000 and stockholders' equity increased $50,000. Compute the amount of total assets at the end of the year. 3. If total assets decreased $100,000 and total liabilities increased $55,000 during the year, determine the amount of stockholders' equity at the end of the year. Ex. 210 Compute the missing amount in each category of the accounting equation. Assets Liabilities Stockholders' Equity (a) $319,000 $ ? $143,000 (b) $223,000 $ 79,000 $ ? (c) $ ? $233,000 $325,000 Ex. 211 From the following list of selected accounts taken from the records of Ward Homeopathic Center, identify those that would appear on the balance sheet. a. Common Stock f. Accounts Payable b. Service Revenue g. Cash c. Land h. Rent Expense d. Salaries and Wages Expense i. Supplies e. Notes Payable j. Utilities Expense Ex. 212 Selected transactions for Mountain Goats Tree Service are listed below. 1. Sold common stock for cash to start business. 2. Paid for monthly advertising. 3. Purchased supplies on account. 4. Billed customers for services performed. 5. Paid cash dividends. 6. Received cash from customers billed in (4). 7. Incurred utilities expense on account. 8. Purchased additional supplies for cash. 9. Received cash from customers when service was performed. Instructions List the numbers of the above transactions and describe the effect of each transaction on assets, liabilities, and stockholders' equity. For example, the first answer is: (1) Increase in assets and increase in stockholders' equity. LO6, 7 BT: C Difficulty: Easy TOT: 3 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting Ex. 213 Wilco Legal Eagles Company entered into the following transactions during March 2015. 1. Purchased office equipment for $23,000 from Business Equipment, Inc. on account. 2. Paid $3,000 cash for March rent on office furniture. 3. Received $15,000 cash from customers for legal work billed in February. 4. Provided legal services to Amy Construction Company for $3,500 cash. 5. Paid Northern States Power Co. $2,700 cash for electric usage in March. 6. Stockholders' invested an additional $32,000 in the business. 7. Paid Business Equipment, Inc. for the office equipment purchased in (1) above. 8. Incurred advertising expense for March of $1,900 on account. Instructions Indicate with the appropriate letter whether each of the transactions above results in: (a) an increase in assets and a decrease in assets. (b) an increase in assets and an increase in stockholders' equity. (c) an increase in assets and an increase in liabilities. (d) a decrease in assets and a decrease in stockholders' equity. (e) a decrease in assets and a decrease in liabilities. (f) an increase in liabilities and a decrease in stockholders' equity. (g) an increase in stockholders' equity and a decrease in liabilities. Ex. 214 Two items are omitted from each of the following summaries of balance sheet and income statement data for two proprietorships for the year 2015, Holly Enterprises and Cat Stevens. Holly Enterprises Cat Stevens Beginning of year: Total assets $ 98,000 $129,000 Total liabilities 60,000 (c) Total stockholders' equity (a) 85,000 End of year: Total assets 160,000 180,000 Total liabilities 100,000 50,000 Total stockholders' equity 60,000 130,000 Changes during year in stockholders' equity: Additional investment (b) 25,000 Dividends 25,000 (d) Total revenues 215,000 100,000 Total expenses 185,000 65,000 Instructions Determine the missing amounts. Ex. 215 An analysis of the transactions made by White Stripes & Co., a law firm, for the month of July is shown below. Each increase and decrease in stockholders' equity is explained. Assets = Liab + Stockholders' Equity Retained Earnings Cash + Accounts Receivable + Supplies + Equipment = Accounts Payable + Com Stock + Rev. -Exp -Div. 1. +$15,000 +$15,000 2. - 2,000 +$5,000 +$3,000 3. - 750 +$750 4. + 2,500 +$6,600 +$9,100 Rev. 5. - 1,500 - 1,500 6. - 2,500 -$2,500 Div. 7. - 750 -$750 Rent. 8. + 550 -550 9. - 3,500 -$4,500 Sal. 10. + 500 + 500 -500 Util. Instructions (a) Determine how much stockholders' equity increased for the month. (b) Compute the amount of net income for the month. Ex. 216 The Constantine Company had the following assets and liabilities on the dates indicated. December 31 Total Assets Total Liabilities 2014 $480,000 $250,000 2015 $460,000 $220,000 2016 $590,000 $300,000 Constantine began business on January 1, 2014, with an investment of $100,000. Instructions From an analysis of the change in stockholders' equity during the year, compute the net income (or loss) for: (a) 2014, assuming Constantine’s dividends were $45,000 for the year. (b) 2015, assuming Constantine made an additional investment of $50,000 and paid no dividends in 2015. (c) 2016, assuming Constantine made an additional investment of $15,000 and paid dividends of $40,000 in 2016. Ex. 217 For each of the following, indicate whether the transaction affects revenue (R), expense (E), dividends (D), common stock (CS), or no effect on stockholders' equity (NOE). 1. Made an investment to start the business. 2. Billed customers for services performed. 3. Purchased equipment on account. 4. Paid monthly rent. 5. Paid dividends. Ex. 218 Presented below is a balance sheet for Jim Henson Yard Service at December 31, 2015. JIM HENSON YARD SERVICE Balance Sheet December 31, 2015 Assets Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity Cash $13,000 Liabilities Accounts receivable 6,000 Accounts payable $ 8,000 Supplies 9,000 Notes payable 15,000 Equipment 11,000 Stockholders' equity Common stock 16,000 Total assets $39,000 Total liabilities & stockholders' equity $39,000 The following additional data are available for the year which began on January 1: All expenses (excluding supplies expense) total $6,000. Supplies on January 1, were $11,000 and $7,000 of supplies were purchased during the year. Net income for the year was $8,000 and dividends paid were $9,000. Instructions Determine the following: (Show all computations.) 1. Supplies used during the year. 2. Total expenses for the year. 3. Service revenues for the year. 4. Stockholders' equity on January 1. Ex. 219 Analyze the transactions of a business organized as a corporation described below and indicate their effect on the basic accounting equation. Use a plus sign (+) to indicate an increase and a minus sign (–) to indicate a decrease. Assets = Liabilities + Stockholders' Equity 1. Received cash for services provided. 2. Purchased office equipment on credit. 3. Paid employees' salaries. 4. Received cash from customer in payment on account. 5. Paid telephone bill for the month. 6. Paid for office equipment purchased in transaction 2. 7. Purchased office supplies on credit. 8. Paid dividends. 9. Obtained a loan from the bank. 10. Billed customers for services rendered. 9. Obtained a loan from the bank. + + 10. Billed customers for services rendered. + + Ex. 220 For each of the following, indicate whether the transaction increased (+), decreased (-), or had no effect (NE) on assets, liabilities, and stockholders' equity using the following format. Assets = Liabilities + Stockholders' Equity 1. Issued stock in exchange for cash. 2. Billed customers for services performed. 3. Purchased equipment on account. 4. Paid dividends. 5. Paid for equipment purchased in 3. above. Ex. 221 Neko Case decides to open a cleaning and laundry service near the local college campus that will operate as a corporation. Analyze the following transactions for the month of June in terms of their effect on the basic accounting equation. Record each transaction by increasing (+) or decreasing (–) the dollar amount of each item affected. Indicate the new balance of each item after a transaction is recorded. It is not necessary to identify the cause of changes in stockholders' equity. Transactions (1) Issued stock in exchange for $20,000 cash on June 1. (2) Purchased equipment for $5,000 paying $3,000 in cash and the remainder due in 30 days. (3) Purchased supplies for $1,200 cash. (4) Received a bill from College News for $300 for advertising in the campus newspaper. (5) Cash receipts from customers for cleaning and laundry amounted to $2,400. (6) Paid salaries of $600 to student workers. (7) Billed the Lion Soccer Team $450 for cleaning and laundry services. (8) Paid $300 to College News for advertising that was previously billed in Transaction 4. (9) Paid dividends of $1,200. (10) Incurred utility expenses for month on account, $500. Trans- Accounts Accounts Common Retained action Cash + Receivable + Supplies + Equipment = Payable + Stock + Earnings (1) —————————————————————————————————————————— Balance (2) —————————————————————————————————————————— Balance (3) —————————————————————————————————————————— Balance (4) —————————————————————————————————————————— Balance (5) —————————————————————————————————————————— Balance (6) —————————————————————————————————————————— Balance (7) —————————————————————————————————————————— Balance (8) —————————————————————————————————————————— Ex. 221 (cont.) Balance (9) —————————————————————————————————————————— Balance (10) —————————————————————————————————————————— Totals Ex. 222 For each of the following, describe a transaction that will have the stated effect on the elements of the accounting equation. (a) Increase one asset and decrease another asset. (b) Increase an asset and increase a liability. (c) Decrease an asset and decrease a liability. (d) Increase an asset and increase stockholders' equity. (e) Increase one asset, decrease one asset, and increase a liability. Ex. 223 The following transactions represent part of the activities of Bloc Party Company for the first month of its existence. Indicate the effect of each transaction upon the total assets of the business by one of the following phrases: increased total assets, decreased total assets, or no change in total assets. (a) Issued stock in exchange for cash. (b) Purchased a computer for cash. (c) Purchased office equipment with money borrowed from the bank. (d) Paid the first month's utility bill. (e) Collected an accounts receivable. (f) Paid dividends. Ex. 224 Selected transactions for Parton Company are listed below. List the number of the transaction and then describe the effect of each transaction on assets, liabilities, and stockholders' equity. Sample: Issued common stock in exchange for cash investment. The answer would be—Increase in assets and increase in stockholders' equity. 1. Paid monthly utility bill. 2. Purchased new display case for cash. 3. Paid cash for repair work on security system. 4. Billed customers for services performed. 5. Received cash from customers billed in 4. 6. Paid dividends. 7. Incurred advertising expenses on account. 8. Paid monthly rent. 9. Received cash from customers when service was rendered. Ex. 225 A service company shows five transactions summarized below. The effect of each transaction on the accounting equation is shown, and also the new balance of each item in the equation. For each transaction (a) to (e) write an explanation of the nature of the transaction. Accounts Equip- Accounts Stockholders' Cash + Rec. + ment + Land + Building = Payable + Equity —————————————————————————————————————————— $5,000 $6,500 $10,000 $7,500 $50,000 $3,000 $76,000 a) –2,000 –2,000 3,000 6,500 10,000 7,500 50,000 1,000 76,000 b) +1,000 – 1,000 4,000 5,500 10,000 7,500 50,000 1,000 76,000 Ex. 225 (cont.) c) + 5,000 +5,000 4,000 5,500 15,000 7,500 50,000 6,000 76,000 d) +2,500 + 2,500 6,500 5,500 15,000 7,500 50,000 6,000 78,500 e) +3,000 + 3,000 $6,500 $8,500 $15,000 $7,500 $50,000 $6,000 $81,500 Ex. 226 There are ten transactions listed below. Match the transactions that have the identical effect on the accounting equation. You should end up with 5 matches. a. Receive cash from customers on account. b. Issued stock in exchange for cash. c. Pay cash to reduce an accounts payable. d. Purchase supplies for cash. e. Pay cash to reduce a notes payable. f. Purchase supplies on account. g. Additional investment by a stockholder. h. Purchase equipment with a note payable. i. Pay utilities with cash. j. Pay dividends. Ex. 227 An analysis of the transactions made by Cookie Mountain Legal, a law firm, for the month of July is shown below. Each increase and decrease in stockholders' equity is explained. Assets = Liab + Stockholders' Equity Retained Earnings Cash + Accounts Receivable + Supplies + Equipment = Accounts Payable + Com Stock + Rev. -Exp -Div. 1. +$15,000 +$15,000 2. - 2,000 +$5,000 +$3,000 3. - 750 +$750 4. + 2,500 +$6,600 +$9,100 Rev. 5. - 1,500 - 1,500 6. - 2,500 -$2,500 Div. 7. - 750 -$750 Rent. 8. + 550 -550 9. - 4,500 -$4,500 Sal. 10. + 500 -500 Util. Instructions (a) Prepare an income statement for the month ending July 31, 2015. (b) Prepare a retained earnings statement for the month ending July 31, 2015. Ex. 228 An analysis of the transactions made by Cookie Mountain Legal, a law firm, for the month of July is shown below. Each increase and decrease in retained earnings is explained. Assets = Liab + Stockholders' Equity Retained Earnings Cash + Accounts Receivable + Supplies + Equipment = Accounts Payable + Com Stock + Rev. -Exp -Div. 1. +$15,000 +$15,000 2. - 2,000 +$5,000 +$3,000 3. - 750 +$750 4. + 2,500 +$6,600 +$9,100 Rev. 5. - 1,500 - 1,500 6. - 2,500 -$2,500 Div. 7. - 750 -$750 Rent. 8. + 550 -550 9. - 4,500 -$4,500 Sal. 10. + 500 -500 Util. Instructions Prepare a balance sheet at July 31, 2015. Ex. 229 The following information relates to Bonnie Billy Co. for the year 2015. Retained earnings, January 1, 2015 $ 67,000 Advertising expense $6,500 Dividends 6,000 Rent expense 9,500 Service revenue 65,500 Utilities expense 1,400 Salaries and wages expense 29,000 Instructions After analyzing the data, prepare an income statement and a retained earnings statement for the year ending December 31, 2015 Ex. 230 Van Occupanther is the bookkeeper for Roscoe Company. Van has been trying to get the balance sheet of Roscoe Company to balance. Roscoe’s balance sheet is as follows. ROSCOE COMPANY Balance Sheet December 31, 2015 Assets Liabilities Cash $9,400 Accounts payable $25,000 Supplies 7,100 Accounts receivable (19,500) Equipment 45,000 Common stock 40,000 Dividends 9,200 Retained earnings 25,200 Total assets $70,700 Total liabilities and stockholders' equity $70,700 Instructions Prepare a correct balance sheet. Ex. 231 Presented below is information related to Anthony Scalici Company. Retained earnings, January 1, 2015 $ 21,000 Service revenue—2015 320,000 Total expenses—2015 213,000 Assets, January 1, 2015 85,000 Liabilities, January 1, 2015 64,000 Assets, December 31, 2015 165,000 Liabilities, December 31, 2015 90,000 Dividends—2015 ? Instructions Prepare the 2015 retained earnings statement for Anthony Scalici Company. Ex. 232 Prepare an income statement, a retained earnings statement, and a balance sheet for the accupuncture practice of Golda Bear, from the items listed below for the month of September, 2015. Retained earnings, September 1 $17,000 Common stock 30,000 Accounts payable 7,000 Equipment 35,000 Service revenue 28,000 Dividends 6,000 Supplies expense 4,500 Cash 3,000 Utilities expense 700 Supplies 4,800 Salaries and wages expense 9,000 Accounts receivable 14,000 Rent expense 5,000 GOLDA BEAR, ACCUPUNCTURIST Income Statement For the Month Ended September 30, 2015 —————————————————————————————————————————— Revenues $ Expenses $ $ Total expenses $ Net income $ GOLDA BEAR, ACCUPUNCTURIST Retained Earnings Statement For the Month Ended September 30, 2015 —————————————————————————————————————————— Retained Earnings, September 1 $ Add: $ Less: $ Ex. 232 (cont.) GOLDA BEAR, ACCUPUNCTURIST Balance Sheet September 30, 2015 —————————————————————————————————————————— Assets $ Total assets $ Liabilities and Stockholder' Equity Liabilities $ Stockholders' Equity $ Total liabilities and stockholders' equity $ —————————————————————————————————————————— Assets Cash $ 3,000 Accounts receivable 14,000 Supplies 4,800 Equipment 35,000 Total assets $56,800 Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity Liabilities Accounts payable $ 7,000 Stockholders' Equity Common stock $30,000 Retained earnings 19,800 49,800 Total liabilities and stockholders' equity $56,800 LO8 BT: AP Difficulty: Hard TOT: 15 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting Ex. 233 Indicate whether the following items would appear on the balance sheet (BS), income statement (IS), or retained earnings statement (RE). 1. Advertising expense 2. Accounts receivable 3. Dividends 4. Rent revenue 5. Salaries and wages payable 6. Supplies Ex. 234 Listed below in alphabetical order are the balance sheet items of Rock Plaza Company at December 31, 2015. Prepare a balance sheet and include a complete heading. Accounts Payable $ 24,000 Accounts Receivable 15,000 Buildings 51,000 Cash 7,000 Common Stock 102,000 Land 42,000 Equipment 11,000 LO8 BT: AP Difficulty: Medium TOT: 5 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting Ex. 235 One item is omitted in each of the following summaries of balance sheet and income statement data for three different sole corporations, X, Y, and Z. Determine the amounts of the missing items, identifying each corporation by letter. Corporation X Y Z Beginning of the Year: Assets $390,000 $150,000 $219,000 Liabilities 250,000 105,000 168,000 End of the Year: Assets 450,000 175,000 195,000 Liabilities 280,000 95,000 169,000 During the Year: Issued additional shares of stock ? 79,000 80,000 Dividends 90,000 83,000 ? Revenue 195,000 ? 187,000 Expenses 170,000 113,000 175,000 Ex. 236 Indicate in the space provided by each item whether it would appear on the Income Statement (IS), Balance Sheet (BS), or Retained Earnings Statement (RE): a. Service Revenue g. Accounts Receivable b. Utilities Expense h. Retained Earnings (ending) c. Cash i. Equipment d. Accounts Payable j. Advertising Expense e. Office Supplies k. Dividends f. Salaries Expense l. Notes Payable Ex. 237 Maria Queen was reviewing her business activities at the end of the year (2015) and decided to prepare a Retained Earnings Statement. At the beginning of the year her assets were $700,000 and her liabilities were $210,000. At the end of the year the assets had grown to $930,000 but liabilities had also increased to $340,000. Common Stock was $200,000 in both years. The net income for the year was $220,000. The company paid dividends of $120,000 during the year. Prepare a Retained Earnings statement in good form. LO8 BT: AP Difficulty: Medium TOT: 5 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting Ex. 238 At September 1, the balance sheet accounts for Stanley’s Restaurant were as follows: Accounts Payable $ 3,800 Land $33,000 Accounts Receivable 9,600 Common Stock ? Buildings 68,000 Notes Payable 48,000 Cash 10,000 Supplies 6,600 Equipment 18,700 The following transactions occurred during the next two days: The company issued additional shares of stock for $22,000 cash in the business. The accounts payable were paid in full. (No payment was made on the notes payable.) Instructions Prepare a balance sheet at September 1, 2015. Ex. 239 Presented below are balance sheet items for Black Angel Company at December 31, 2015. Accounts payable $35,000 Accounts receivable 36,000 Cash 17,000 Equipment 77,000 Common stock 45,000 Notes payable 50,000 Compute each of the following: 1. Total assets. 2. Total liabilities. COMPLETION STATEMENTS 240. Accounting is an information system that identifies, _____________, and _____________ the economic events of an organization. 241. The mere recording of economic events is called ______________, and is just one part of the _______________ process. 242. The three major services rendered by a certified public accountant are ______________, ________________, and management ________________. 243. Accountants who are employees of business enterprises are referred to as ________________ accountants. 244. A common set of standards that provides guidelines to accountants and indicates how to report economic events is called _________________. 245. The ________________ principle states that assets should be recorded at the value exchanged at the time the asset is acquired. 246. The _________________ assumption requires that the activities of an entity be kept separate from the activities of its owner. 247. The residual claim on total assets of a business is known as ________________ and is equal to total assets minus total liabilities. 248. Dividends ________________ stockholders' equity but are not expenses. 249. The ________________ reports the assets, liabilities, and stockholders' equity of a business enterprise at a specific date. MATCHING 250. Match the items below by entering the appropriate code letter in the space provided. A. CPA F. Corporation B. Budgeting G. Assets C. SEC H. Equities D. Proprietorship I. Expenses E. Economic Entity Assumption J. Transaction 1. Activities of an entity must be kept separate from its owner’s activities. 2. Consumed assets or services. 3. Ownership is limited to one person. 4. Offers expert accounting service to the general public. 5. Creditor and ownership claims against the assets of the business. 6. A separate legal entity under state laws. 7. Government agency that can mandate accounting rules. 8. Quantifying goals and objectives. 9. Future economic benefits. 10. Economic events recorded by accountants. SHORT-ANSWER ESSAY QUESTIONS *S-A E 251 The accounting profession provides many career opportunities for individuals. Identify the major fields that exist in accounting and comment on the major functions performed by individuals in each of these areas. S-A E 252 The framework used to record and summarize the economic activities of a business enterprise is referred to as the accounting equation. State the basic accounting equation and define its major components. How are business transactions and financial statements related to the accounting equation? S-A E 253 Your friend, Angela, made this comment: My major is biology and I plan to research for cures for major illnesses. Thus, I have no need to study accounting. What is your response to Angela? S-A E 254 The information needs of a specific user of financial accounting information depends upon the kinds of decisions that user makes. Identify the major users of accounting information and discuss what questions financial accounting information answers for each group of users. S-A E 255 (Ethics) Joanna Newsom owns and operates Joanna's Burgers, a small fast food store, located at the edge of City College campus in Newton, Ohio. After several very profitable years, Joanna's Burgers began to have problems. Most of the problems were related to Joanna's expansion of the eating area in the restaurant without corresponding increases in the food preparation area. Joanna does not have the cash or financial backing to expand further. She has therefore decided to sell her business. Vivian Girls is interested in purchasing the business. However, she is located in another city and is unfamiliar with Newton. She has asked Joanna why she is selling Joanna's Burgers. Joanna replies that her elderly mother requires extra care, and that her brother needs help in his manufacturing business. Both are true, but neither is her primary reason for selling. Joanna reasons that Vivian should not have asked her anyway, since profitable businesses don't come up for sale. Required: 1. Identify the stakeholders in this situation. 2. Did Joanna act ethically in not revealing fully her reasons for selling the business? Why or why not? S-A E 256 (Communication) Rachel Bells Havens is a friend of yours from high school. She decided to become a beautician after leaving high school, rather than to attend college. She recently opened her own shop, and has contracted her services to a local hospital. She is paid a monthly fee for her services, and receives a small gratuity from each of the patients. She has just received her first set of financial statements from her accountant. She is quite upset. The statements show a cash balance of $3,600 at the end of the month, but a net income of only $500. She has written you a letter, asking you whether such a situation is possible, or whether she should find another accountant. Required: Write a short letter to your friend. Use proper form. Answer her question completely, but briefly. CHALLENGE EXERCISES CE 1 The total assets and liabilities of Company at January 1 and December 31, 2015 are presented below. January 1 December 31 Assets $95,000 $140,000 Liabilities 30,000 36,000 Instructions: 1. Assume dividends of $10,800 were paid and no additional stock was issued during the year. Revenues were $110,000. Compute (a) net income, and (b) expenses. 2. Assume additional stock was issued for $4,800 and no dividends were paid during the year. Expenses were $42,000. Compute (a) net income, and (b) revenues. 3. Assume additional stock was issued for $62,000 and dividends of $15,600 were paid during the year. Compute net income. 4. Assume additional stock was issued for $6,000 and net income was $51,000. Compute dividends paid. Solution CE 1 1. a. January 1 stockholders' equity = $95,000 $30,000 = $65,000. December 31 stockholders' equity = $140,000 $36,000 = $104,000. The change in stockholders' equity = $104,000 $65,000 = $39,000. $39,000 = Net income + investments by owners dividends. $39,000 = NI + $0 $10,800. NI = $49,800. b. Revenues expenses = net income. $110,000 expenses = $49,800. Expenses = $60,200. 2. a. January 1 stockholders' equity = $95,000 $30,000 = $65,000. December 31 stockholders' equity = $140,000 $36,000 = $104,000. The change in stockholders' equity = $104,000 $65,000 = $39,000. $39,000 = Net income + investments by owners dividends. $39,000 = NI + $4,800 $0. NI = $34,200. b. Revenues expenses = net income. Revenues $42,000 = $34,200. Revenues = $76,200. 3. a. January 1 stockholders' equity = $95,000 $30,000 = $65,000. December 31 stockholders' equity = $140,000 $36,000 = $104,000. The change in stockholders' equity = $104,000 $65,000 = $39,000. $39,000 = Net income + investments by owners dividends. $39,000 = NI + $62,000 $15,600. NI = $7,400. (a net loss). Solution CE 1 (cont.) 4. a. January 1 stockholders' equity = $95,000 $30,000 = $65,000. December 31 stockholders' equity = $140,000 $36,000 = $104,000. The change in stockholders' equity = $104,000 $65,000 = $39,000. $39,000 = Net income + investments by owners dividends. $39,000 = $51,000 + $6,000 dividends. Dividends = $18,000. LO6 BT: AP Difficulty: Hard TOT: 15 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting CE 2 Windsor Service had the following financial information at the end of 2015. 1/1/15 2015 12/31/15 Accounts payable $19,000 Accounts Receivable 25,000 Advertising Expense $1,000 Cash 16,000 Common Stock 15,000 Dividends 9,000 Equipment 38,000 Notes Payable 20,000 Rent Expense 3,500 Retained Earnings $6,000 Salaries and Wages Expense 20,000 Service Revenue 55,000 Utilities Expense 2,500 Instructions: Prepare a 2015 income statement, 2015 retained earnings statement, and a 12/31/15 balance sheet for Windsor Service. Solution CE 2 Windsor Service Income Statement 2015 Revenue Service revenue $55,000 Expenses Salaries and wages expenses $20,000 Rent expense 3,500 Utilities expense 2,500 Advertising expense 1,000 27,000 Net income $28,000 Solution CE 2 (cont.) Windsor Service Retained Earnings Statement 2015 Retained earnings, 1/1/15 $ 6,000 Add: net income 28,000 34,000 Less: dividends 9,000 Retained earnings, 12/31/15 $25,000 Windsor Service Balance Sheet 2015 Assets Cash $16,000 Accounts receivable 25,000 Equipment 38,000 Total assets $79,000 Liabilities Accounts payable $19,000 Notes payable 20,000 Total liabilities $39,000 Stockholders' Equity Common stock $15,000 Retained earnings 25,000 40,000 Total liabilities and stockholders' equity $79,000 LO8 BT: AP Difficulty: Hard TOT: 15 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting CE 3 This information is for Downing Company for the year ended December 31, 2015. Cash received from revenues from customers $930,000 Cash received for issuance of common stock 420,000 Cash paid for new equipment 150,000 Cash dividends paid 30,000 Cash paid for expenses 640,000 Cash balance 1/1/15 50,000 Instructions Prepare the 2015 statement of cash flows for Downing Company. Solution CE 3 DOWNING COMPANY Statement of Cash Flows For the Year Ended December 31, 2015 —————————————————————————————————————————— Cash flows from operating activities Cash receipts from customers $930,000 Cash payments for expenses (640,000) Net cash provided by operating activities 290,000 Cash flows from investing activities Purchase of equipment (150,000) Cash flows from financing activities Sale of common stock $420,000 Payment of cash dividends (30,000) 390,000 Net increase in cash 530,000 Cash at the beginning of the period 50,000 Cash at the end of the period $580,000 LO8 BT: AP Difficulty: Hard TOT: 15 min. AACSB: Reflective Thinking AICPA BB: Critical Thinking AICPA FN: Reporting [Show More]
Last updated: 11 months ago
Preview 1 out of 79 pages
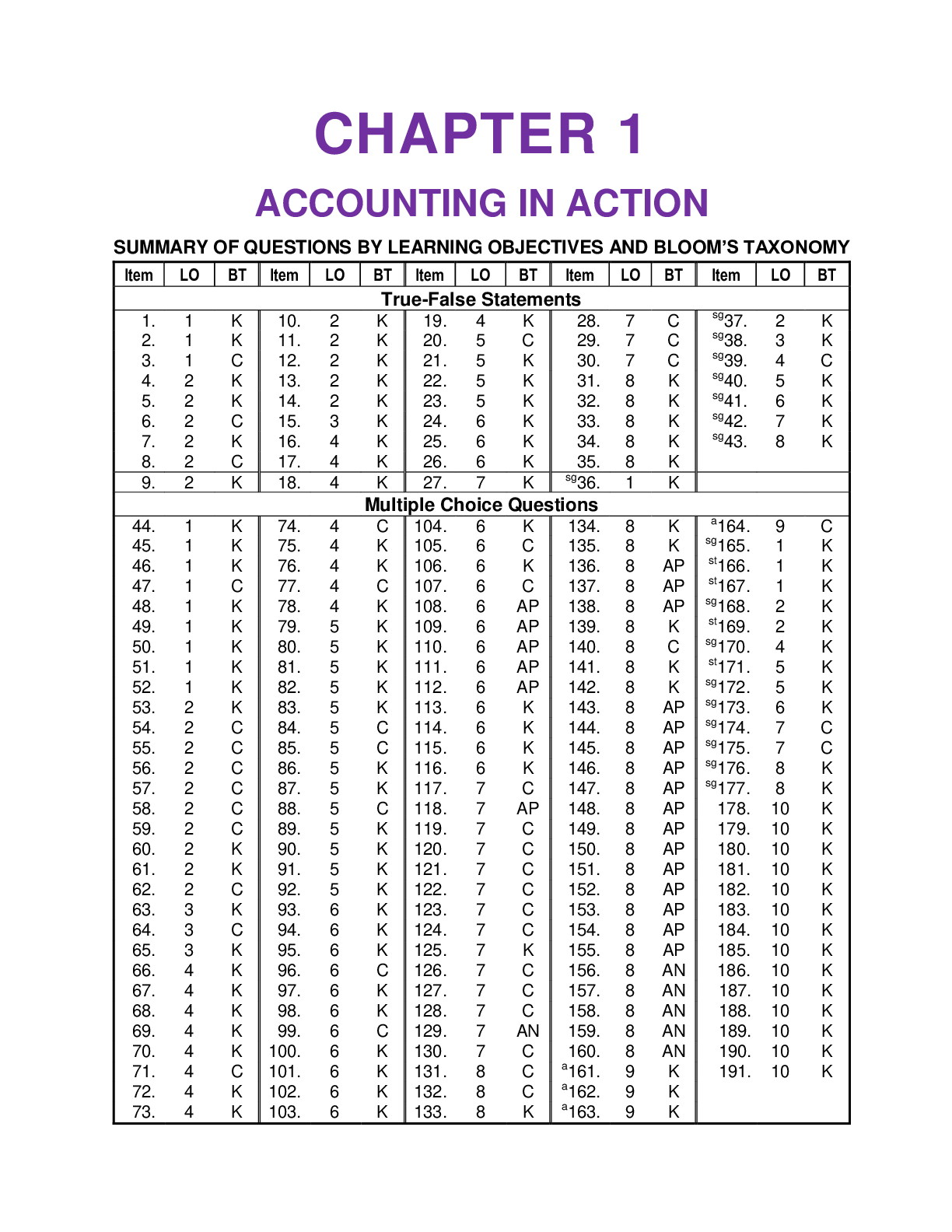
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jan 19, 2021
Number of pages
79
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jan 19, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
150












 TB.png)





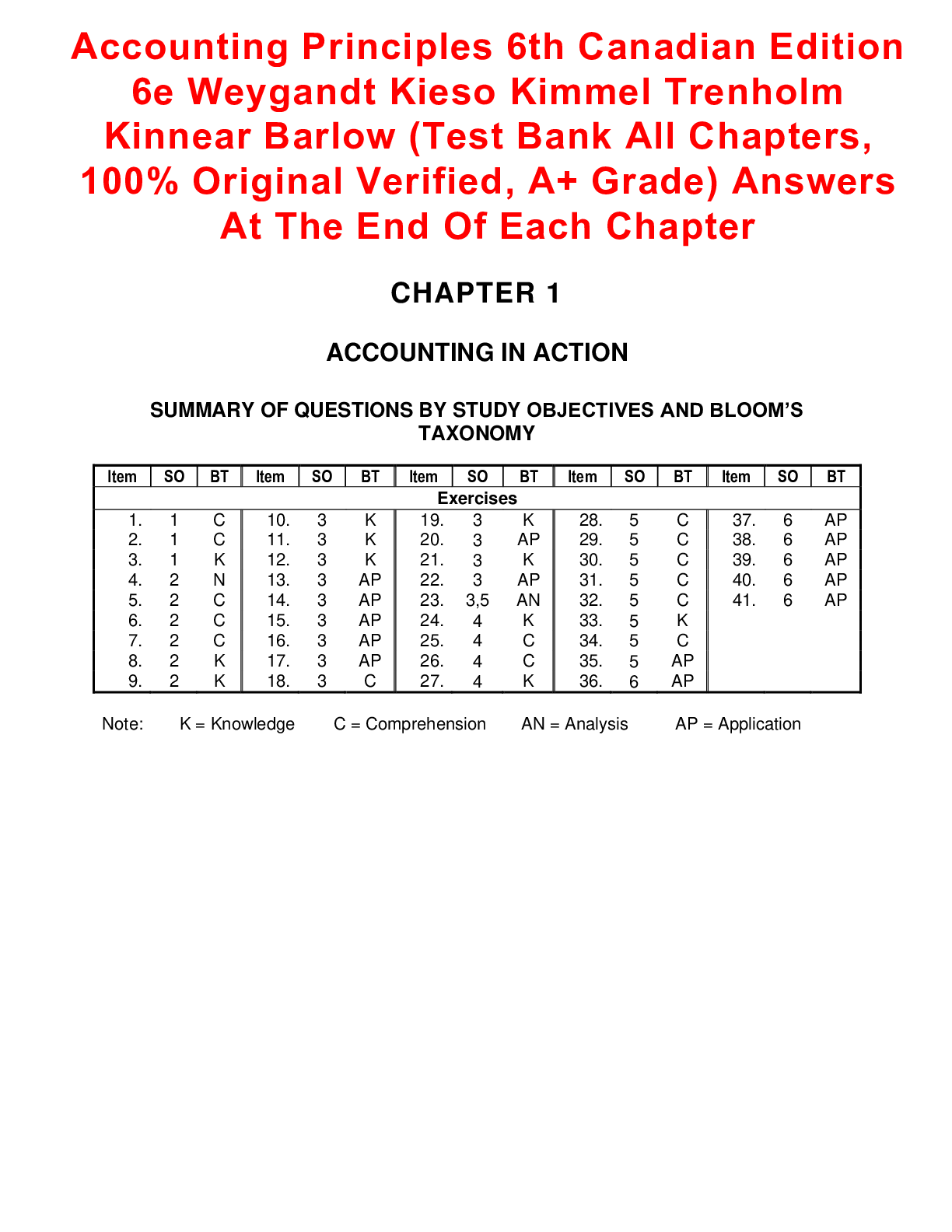

















.png)


