*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > NURS 301- Health Assessment Exam Review 2; Multiple Choice Test Bank Chapter 5 to Chapter 29, with E (All)
NURS 301- Health Assessment Exam Review 2; Multiple Choice Test Bank Chapter 5 to Chapter 29, with Explanations,MSCs, A+ Guide - Nevada State College
Document Content and Description Below
NURS 301-P Health Assessment Exam Review 2 Chapter 5 Mental Status Exam • Define the behaviors that are considered in an assessment of a person’s mental status • Describe relevant dev... elopmental care related to the mental status examination • State the purpose of a mental status assessment • Complete a Mini-Mental state examination MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. During an examination, the nurse can assess mental status by which activity? a. Examining the patient’s electroencephalogram b. Observing the patient as he or she performs an intelligence quotient (IQ) test c. Observing the patient and inferring health or dysfunction d. Examining the patient’s response to a specific set of questions 2. The nurse is assessing the mental status of a child. Which statement about children and mental status is true? a. All aspects of mental status in children are interdependent. b. Children are highly labile and unstable until the age of 2 years. c. Children’s mental status is largely a function of their parents’ level of functioning until the age of 7 years. d. A child’s mental status is impossible to assess until the child develops the ability to concentrate. 3. The nurse is assessing a 75-year-old man. As the nurse begins the mental status portion of the assessment, the nurse expects that this patient: a. Will have no decrease in any of his abilities, including response time. b. Will have difficulty on tests of remote memory because this ability typically decreases with age. c. May take a little longer to respond, but his general knowledge and abilities should not have declined. d. Will exhibit had a decrease in his response time because of the loss of language and a decrease in general knowledge. 4. When assessing aging adults, the nurse knows that one of the first things that should be assessed before making judgments about their mental status is: a. Presence of phobias b. General intelligence c. Presence of irrational thinking patterns d. Sensory-perceptive abilities Yeah I know bro, I just get sick and tired of the same promises 5. The nurse is preparing to conduct a mental status examination. Which statement is true regarding the mental status examination? a. A patient’s family is the best resource for information about the patient’s coping skills. b. Gathering mental status information during the health history interview is usually sufficient. c. Integrating the mental status examination into the health history interview takes an enormous amount of extra time. d. To get a good idea of the patient’s level of functioning, performing a complete mental status examination is usually necessary. 6. A woman brings her husband to the clinic for an examination. She is particularly worried because after a recent fall, he seems to have lost a great deal of his memory of recent events. Which statement reflects the nurse’s best course of action? a. Perform a complete mental status examination. b. Refer him to a psychometrician. c. Plan to integrate the mental status examination into the history and physical examination. d. Reassure his wife that memory loss after a physical shock is normal and will soon subside. 7. The nurse is conducting a patient interview. Which statement made by the patient should the nurse more fully explore during the interview? a. “I sleep like a baby.” b. “I have no health problems.” c. “I never did too good in school.” d. “I am not currently taking any medications.” 8. A patient is admitted to the unit after an automobile accident. The nurse begins the mental status examination and finds that the patient has dysarthric speech and is lethargic. The nurse’s best approach regarding this examination is to: a. Plan to defer the rest of the mental status examination. b. Skip the language portion of the examination, and proceed onto assessing mood and affect. c. Conduct an in-depth speech evaluation, and defer the mental status examination to another time. d. Proceed with the examination, and assess the patient for suicidal thoughts because dysarthria is often accompanied by severe depression. 9. A 19-year-old woman comes to the clinic at the insistence of her brother. She is wearing black combat boots and a black lace nightgown over the top of her other clothes. Her hair is dyed pink with black streaks throughout. She has several pierced holes in her nares and ears and is wearing an earring through her eyebrow and heavy black makeup. The nurse concludes that: a. She probably does not have any problems. b. She is only trying to shock people and that her dress should be ignored. c. She has a manic syndrome because of her abnormal dress and grooming. d. More information should be gathered to decide whether her dress is appropriate. 10. A patient has been in the intensive care unit for 10 days. He has just been moved to the medical-surgical unit, and the admitting nurse is planning to perform a mental status examination. During the tests of cognitive function, the nurse would expect that he: a. May display some disruption in thought content. b. Will state, “I am so relieved to be out of intensive care.” c. Will be oriented to place and person, but the patient may not be certain of the date. d. May show evidence of some clouding of his level of consciousness. 11. During a mental status examination, the nurse wants to assess a patient’s affect. The nurse should ask the patient which question? a. “How do you feel today?” b. “Would you please repeat the following words?” c. “Have these medications had any effect on your pain?” d. “Has this pain affected your ability to get dressed by yourself?” 12. The nurse is planning to assess new memory with a patient. The best way for the nurse to do this would be to: a. Administer the FACT test. b. Ask him to describe his first job. c. Give him the Four Unrelated Words Test. d. Ask him to describe what television show he was watching before coming to the clinic. 13. A 45-year-old woman is at the clinic for a mental status assessment. In giving her the Four Unrelated Words Test, the nurse would be concerned if she could not ____ four unrelated words ____. a. Invent; within 5 minutes b. Invent; within 30 seconds c. Recall; after a 30-minute delay d. Recall; after a 60-minute delay 14. During a mental status assessment, which question by the nurse would best assess a person’s judgment? a. “Do you feel that you are being watched, followed, or controlled?” b. “Tell me what you plan to do once you are discharged from the hospital.” c. “What does the statement, ‘People in glass houses shouldn’t throw stones,’ mean to you?” d. “What would you do if you found a stamped, addressed envelope lying on the sidewalk?” 15. Which of these individuals would the nurse consider at highest risk for a suicide attempt? a. Man who jokes about death b. Woman who, during a past episode of major depression, attempted suicide c. Adolescent who just broke up with her boyfriend and states that she would like to kill herself d. Older adult man who tells the nurse that he is going to “join his wife in heaven” tomorrow and plans to use a gun 16. The nurse is performing a mental status assessment on a 5-year-old girl. Her parents are undergoing a bitter divorce and are worried about the effect it is having on their daughter. Which action or statement might lead the nurse to be concerned about the girl’s mental status? a. She clings to her mother whenever the nurse is in the room. b. She appears angry and will not make eye contact with the nurse. c. Her mother states that she has begun to ride a tricycle around their yard. d. Her mother states that her daughter prefers to play with toddlers instead of kids her own age while in daycare. 17. The nurse is assessing orientation in a 79-year-old patient. Which of these responses would lead the nurse to conclude that this patient is oriented? a. “I know my name is John. I couldn’t tell you where I am. I think it is 2010, though.” b. “I know my name is John, but to tell you the truth, I get kind of confused about the date.” c. “I know my name is John; I guess I’m at the hospital in Spokane. No, I don’t know the date.” d. “I know my name is John. I am at the hospital in Spokane. I couldn’t tell you what date it is, but I know that it is February of a new year—2010.” 18. The nurse is performing the Denver II screening test on a 12-month-old infant during a routine well-child visit. The nurse should tell the infant’s parents that the Denver II: a. Tests three areas of development: cognitive, physical, and psychological b. Will indicate whether the child has a speech disorder so that treatment can begin. c. Is a screening instrument designed to detect children who are slow in development. d. Is a test to determine intellectual ability and may indicate whether problems will develop later in school. 19. A patient drifts off to sleep when she is not being stimulated. The nurse can easily arouse her by calling her name, but the patient remains drowsy during the conversation. The best description of this patient’s level of consciousness would be: a. Lethargic b. Obtunded c. Stuporous d. Semialert 20. A patient has had a cerebrovascular accident (stroke). He is trying very hard to communicate. He seems driven to speak and says, “I buy obie get spirding and take my train.” What is the best description of this patient’s problem? a. Global aphasia b. Broca’s aphasia c. Echolalia d. Wernicke’s aphasia 21. A patient repeatedly seems to have difficulty coming up with a word. He says, “I was on my way to work, and when I got there, the thing that you step into that goes up in the air was so full that I decided to take the stairs.” The nurse will note on his chart that he is using or experiencing: a. Blocking b. Neologism c. Circumlocution d. Circumstantiality 22. During an examination, the nurse notes that a patient is exhibiting flight of ideas. Which statement by the patient is an example of flight of ideas? a. “My stomach hurts. Hurts, spurts, burts.” b. “Kiss, wood, reading, ducks, onto, maybe.” c. “Take this pill? The pill is red. I see red. Red velvet is soft, soft as a baby’s bottom.” d. “I wash my hands, wash them, wash them. I usually go to the sink and wash my hands.” 23. A patient describes feeling an unreasonable, irrational fear of snakes. His fear is so persistent that he can no longer comfortably look at even pictures of snakes and has made an effort to identify all the places he might encounter a snake and avoids them. The nurse recognizes that he: a. Has a snake phobia. b. Is a hypochondriac; snakes are usually harmless. c. Has an obsession with snakes. d. Has a delusion that snakes are harmful, which must stem from an early traumatic incident involving snakes. 24. A patient has been diagnosed with schizophrenia. During a recent interview, he shows the nurse a picture of a man holding a decapitated head. He describes this picture as horrifying but then laughs loudly at the content. This behavior is a display of: a. Confusion b. Ambivalence c. Depersonalization d. Inappropriate affect 25. During reporting, the nurse hears that a patient is experiencing hallucinations. Which is an example of a hallucination? a. Man believes that his dead wife is talking to him. b. Woman hears the doorbell ring and goes to answer it, but no one is there. c. Child sees a man standing in his closet. When the lights are turned on, it is only a dry cleaning bag. d. Man believes that the dog has curled up on the bed, but when he gets closer he sees that it is a blanket. 26. A 20-year-old construction worker has been brought into the emergency department with heat stroke. He has delirium as a result of a fluid and electrolyte imbalance. For the mental status examination, the nurse should first assess the patient’s: a. Affect and mood b. Memory and affect c. Language abilities d. Level of consciousness and cognitive abilities 27. A patient states, “I feel so sad all of the time. I can’t feel happy even doing things I used to like to do.” He also states that he is tired, sleeps poorly, and has no energy. To differentiate between a dysthymic disorder and a major depressive disorder, the nurse should ask which question? a. “Have you had any weight changes?” b. “Are you having any thoughts of suicide?” c. “How long have you been feeling this way?” d. “Are you having feelings of worthlessness?” 28. A 26-year-old woman was robbed and beaten a month ago. She is returning to the clinic today for a follow-up assessment. The nurse will want to ask her which one of these questions? a. “How are things going with the trial?” b. “How are things going with your job?” c. “Tell me about your recent engagement!” d. “Are you having any disturbing dreams?” 29. The nurse is performing a mental status examination. Which statement is true regarding the assessment of mental status? a. Mental status assessment diagnoses specific psychiatric disorders. b. Mental disorders occur in response to everyday life stressors. c. Mental status functioning is inferred through the assessment of an individual’s behaviors. d. Mental status can be directly assessed, similar to other systems of the body (e.g., heart sounds, breath sounds). 30. A 23-year-old patient in the clinic appears anxious. Her speech is rapid, and she is fidgety and in constant motion. Which of these questions or statements would be most appropriate for the nurse to use in this situation to assess attention span? a. “How do you usually feel? Is this normal behavior for you?” b. “I am going to say four words. In a few minutes, I will ask you to recall them.” c. “Describe the meaning of the phrase, ‘Looking through rose-colored glasses.’” d. “Pick up the pencil in your left hand, move it to your right hand, and place it on the table.” 31. The nurse is planning health teaching for a 65-year-old woman who has had a cerebrovascular accident (stroke) and has aphasia. Which of these questions is most important to use when assessing mental status in this patient? a. “Please count backward from 100 by seven.” b. “I will name three items and ask you to repeat them in a few minutes.” c. “Please point to articles in the room and parts of the body as I name them.” d. “What would you do if you found a stamped, addressed envelope on the sidewalk?” 32. A 30-year-old female patient is describing feelings of hopelessness and depression. She has attempted self-mutilation and has a history of suicide attempts. She describes difficulty sleeping at night and has lost 10 pounds in the past month. Which of these statements or questions is the nurse’s best response in this situation? a. “Do you have a weapon?” b. “How do other people treat you?” c. “Are you feeling so hopeless that you feel like hurting yourself now?” d. “People often feel hopeless, but the feelings resolve within a few weeks.” 33. The nurse is providing instructions to newly hired graduates for the mini–mental state examination (MMSE). Which statement best describes this examination? a. Scores below 30 indicate cognitive impairment. b. The MMSE is a good tool to evaluate mood and thought processes. c. This examination is a good tool to detect delirium and dementia and to differentiate these from psychiatric mental illness. d. The MMSE is useful tool for an initial evaluation of mental status. Additional tools are needed to evaluate cognition changes over time. 34. The nurse discovers speech problems in a patient during an assessment. The patient has spontaneous speech, but it is mostly absent or is reduced to a few stereotypical words or sounds. This finding reflects which type of aphasia? a. Global b. Broca’s c. Dysphonic d. Wernicke’s 35. A patient repeats, “I feel hot. Hot, cot, rot, tot, got. I’m a spot.” The nurse documents this as an illustration of: a. Blocking b. Clanging c. Echolalia d. Neologism 36. During an interview, the nurse notes that the patient gets up several times to wash her hands even though they are not dirty. This behavior is an example of: a. Social phobia b. Compulsive disorder c. Generalized anxiety disorder d. Posttraumatic stress disorder 37. The nurse is administering a Mini-Cog test to an older adult woman. When asked to draw a clock showing the time of 10:45, the patient drew a clock with the numbers out of order and with an incorrect time. This result indicates which finding? a. Cognitive impairment b. Amnesia c. Delirium d. Attention-deficit disorder 38. During morning rounds, the nurse asks a patient, “How are you today?” The patient responds, “You today, you today, you today!” and mumbles the words. This speech pattern is an example of: a. Echolalia b. Clanging c. Word salad d. Perseveration MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1. The nurse is assessing a patient who is admitted with possible delirium. Which of these are manifestations of delirium? Select all that apply. a. Develops over a short period. b. Person is experiencing apraxia. c. Person is exhibiting memory impairment or deficits. d. Occurs as a result of a medical condition, such as systemic infection. e. Person is experiencing agnosia. Chapter 11- Nutritional Assessment • Purposes and components of a nutritional assessment • Important subjective data for the nutritional assessment • Cultural considerations, developmental competencies • Nutritional needs/variations based on developmental stage • Factors affecting nutritional intake • Anthropometric measures: body mass index, waist to hip ration, skinfold thickness MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The nurse recognizes which of these persons is at greatest risk for undernutrition? a. 5-month-old infant b. 50-year-old woman c. 20-year-old college student d. 30-year-old hospital administrator 2. When assessing a patient’s nutritional status, the nurse recalls that the best definition of optimal nutritional status is sufficient nutrients that: a. Are in excess of daily body requirements. b. Provide for the minimum body needs. c. Provide for daily body requirements but do not support increased metabolic demands. d. Provide for daily body requirements and support increased metabolic demands. 3. The nurse is providing nutrition information to the mother of a 1-year-old child. Which of these statements represents accurate information for this age group? a. Maintaining adequate fat and caloric intake is important for a child in this age group. b. The recommended dietary allowances for an infant are the same as for an adolescent. c. The baby’s growth is minimal at this age; therefore, caloric requirements are decreased. d. The baby should be placed on skim milk to decrease the risk of coronary artery disease when he or she grows older. 4. A pregnant woman is interested in breastfeeding her baby and asks several questions about the topic. Which information is appropriate for the nurse to share with her? a. Breastfeeding is best when also supplemented with bottle feedings. b. Babies who are breastfed often require supplemental vitamins. c. Breastfeeding is recommended for infants for the first 2 years of life. d. Breast milk provides the nutrients necessary for growth, as well as natural immunity. 5. A mother and her 13-year-old daughter express their concern related to the daughter’s recent weight gain and her increase in appetite. Which of these statements represents information the nurse should discuss with them? a. Dieting and exercising are necessary at this age. b. Snacks should be high in protein, iron, and calcium. c. Teenagers who have a weight problem should not be allowed to snack. d. A low-calorie diet is important to prevent the accumulation of fat. 6. The nurse is assessing a 30-year-old unemployed immigrant from an underdeveloped country who has been in the United States for 1 month. Which of these problems related to his nutritional status might the nurse expect to find? a. Obesity b. Hypotension c. Osteomalacia (softening of the bones) d. Coronary artery disease 7. For the first time, the nurse is seeing a patient who has no history of nutrition-related problems. The initial nutritional screening should include which activity? a. Calorie count of nutrients b. Anthropometric measures c. Complete physical examination d. Measurement of weight and weight history 8. A patient is asked to indicate on a form how many times he eats a specific food. This method describes which of these tools for obtaining dietary information? a. Food diary b. Calorie count c. 24-hour recall d. Food-frequency questionnaire 9. The nurse is providing care for a 68-year-old woman who is complaining of constipation. What concern exists regarding her nutritional status? a. Absorption of nutrients may be impaired. b. Constipation may represent a food allergy. c. The patient may need emergency surgery to correct the problem. d. Gastrointestinal problems will increase her caloric demand. 10. During a nutritional assessment, why is it important for the nurse to ask a patient what medications he or she is taking? a. Certain drugs can affect the metabolism of nutrients. b. The nurse needs to assess the patient for allergic reactions. c. Medications need to be documented in the record for the physician’s review. d. Medications can affect one’s memory and ability to identify food eaten in the last 24 hours. 11. A patient tells the nurse that his food simply does not have any taste anymore. The nurse’s best response would be: a. “That must be really frustrating.” b. “When did you first notice this change?” c. “My food doesn’t always have a lot of taste either.” d. “Sometimes that happens, but your taste will come back.” 12. The nurse is performing a nutritional assessment on a 15-year-old girl who tells the nurse that she is “so fat.” Assessment reveals that she is 5 feet 4 inches and weighs 110 pounds. The nurse’s appropriate response would be: a. “How much do you think you should weigh?” b. “Don’t worry about it; you’re not that overweight.” c. “The best thing for you would be to go on a diet.” d. “I used to always think I was fat when I was your age.” 13. The nurse is discussing appropriate foods with the mother of a 3-year-old child. Which of these foods are recommended? a. Foods that the child will eat, no matter what they are b. Foods easy to hold such as hot dogs, nuts, and grapes c. Any foods, as long as the rest of the family is also eating them d. Finger foods and nutritious snacks that cannot cause choking 14. The nurse is reviewing the nutritional assessment of an 82-year-old patient. Which of these factors will most likely affect the nutritional status of an older adult? a. Increase in taste and smell b. Living alone on a fixed income c. Change in cardiovascular status d. Increase in gastrointestinal motility and absorption 15. When considering a nutritional assessment, the nurse is aware that the most common anthropometric measurements include: a. Height and weight. b. Leg circumference. c. Skinfold thickness of the biceps. d. Hip and waist measurements. 16. If a 29-year-old woman weighs 156 pounds, and the nurse determines her ideal body weight to be 120 pounds, then how would the nurse classify the woman’s weight? a. Obese b. Mildly overweight c. Suffering from malnutrition d. Within appropriate range of ideal weight 17. How should the nurse perform a triceps skinfold assessment? a. After pinching the skin and fat, the calipers are vertically applied to the fat fold. b. The skin and fat on the front of the patient’s arm are gently pinched, and then the calipers are applied. c. After applying the calipers, the nurse waits 3 seconds before taking a reading. After repeating the procedure three times, an average is recorded. d. The patient is instructed to stand with his or her back to the examiner and arms folded across the chest. The skin on the forearm is pinched. 18. In teaching a patient how to determine total body fat at home, the nurse includes instructions to obtain measurements of: a. Height and weight. b. Frame size and weight. c. Waist and hip circumferences. d. Mid-upper arm circumference and arm span. 19. The nurse is evaluating patients for obesity-related diseases by calculating the waist-to-hip ratios. Which one of these patients would be at increased risk? a. 29-year-old woman whose waist measures 33 inches and hips measure 36 inches b. 32-year-old man whose waist measures 34 inches and hips measure 36 inches c. 38-year-old man whose waist measures 35 inches and hips measure 38 inches d. 46-year-old woman whose waist measures 30 inches and hips measure 38 inches 20. A 50-year-old woman with elevated total cholesterol and triglyceride levels is visiting the clinic to find out about her laboratory results. What would be important for the nurse to include in patient teaching in relation to these tests? a. The risks of undernutrition should be included. b. Offer methods to reduce the stress in her life. c. Provide information regarding a diet low in saturated fat. d. This condition is hereditary; she can do nothing to change the levels. 21. In performing an assessment on a 49-year-old woman who has imbalanced nutrition as a result of dysphagia, which data would the nurse expect to find? a. Increase in hair growth b. Inadequate nutrient food intake c. Weight 10% to 20% over ideal d. Sore, inflamed buccal cavity 22. A 21-year-old woman has been on a low-protein liquid diet for the past 2 months. She has had adequate intake of calories and appears well nourished. After further assessment, what would the nurse expect to find? a. Poor skin turgor b. Decreased serum albumin c. Increased lymphocyte count d. Triceps skinfold less than standard 23. The nurse is performing a nutritional assessment on an 80-year-old patient. The nurse knows that physiologic changes can directly affect the nutritional status of the older adult and include: a. Slowed gastrointestinal motility. b. Hyperstimulation of the salivary glands. c. Increased sensitivity to spicy and aromatic foods. d. Decreased gastrointestinal absorption causing esophageal reflux. 24. Which of these interventions is most appropriate when the nurse is planning nutritional interventions for a healthy, active 74-year-old woman? a. Decreasing the amount of carbohydrates to prevent lean muscle catabolism b. Increasing the amount of soy and tofu in her diet to promote bone growth and reverse osteoporosis c. Decreasing the number of calories she is eating because of the decrease in energy requirements from the loss of lean body mass d. Increasing the number of calories she is eating because of the increased energy needs of the older adult 25. A 16-year-old girl is being seen at the clinic for gastrointestinal complaints and weight loss. The nurse determines that many of her complaints may be related to erratic eating patterns, eating predominantly fast foods, and high caffeine intake. In this situation, which is most appropriate when collecting current dietary intake information? a. Scheduling a time for direct observation of the adolescent during meals b. Asking the patient for a 24-hour diet recall, and assuming it to be reflective of a typical day for her c. Having the patient complete a food diary for 3 days, including 2 weekdays and 1 weekend day d. Using the food frequency questionnaire to identify the amount of intake of specific foods 26. The nurse is preparing to measure fat and lean body mass and bone mineral density. Which tool is appropriate? a. Measuring tape b. Skinfold calipers c. Bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) d. Dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) 27. Which of these conditions is due to an inadequate intake of both protein and calories? a. Obesity b. Bulimia c. Marasmus d. Kwashiorkor 28. During an assessment of a patient who has been homeless for several years, the nurse notices that his tongue is magenta in color, which is an indication of a deficiency in what mineral and/or vitamin? a. Iron b. Riboflavin c. Vitamin D and calcium d. Vitamin C 29. A 50-year-old patient has been brought to the emergency department after a housemate found that the patient could not get out of bed alone. He has lived in a group home for years but for several months has not participated in the activities and has stayed in his room. The nurse assesses for signs of undernutrition, and an x-ray study reveals that he has osteomalacia, which is a deficiency of: a. Iron. b. Riboflavin. c. Vitamin D and calcium. d. Vitamin C. 30. An older adult patient in a nursing home has been receiving tube feedings for several months. During an oral examination, the nurse notes that patient’s gums are swollen, ulcerated, and bleeding in some areas. The nurse suspects that the patient has what condition? a. Rickets b. Vitamin A deficiency c. Linoleic-acid deficiency d. Vitamin C deficiency 31. The nurse is assessing the body weight as a percentage of ideal body weight on an adolescent patient who was admitted for suspected anorexia nervosa. The patient’s usual weight was 125 pounds, but today she weighs 98 pounds. The nurse calculates the patient’s ideal body weight and concludes that the patient is: a. Experiencing mild malnutrition. b. Experiencing moderate malnutrition. c. Experiencing severe malnutrition. d. Still within expected parameters with her current weight. MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1. The nurse is assessing a patient who is obese for signs of metabolic syndrome. This condition is diagnosed when three or more certain risk factors are present. Which of these assessment findings are risk factors for metabolic syndrome? Select all that apply. a. Fasting plasma glucose level less than 100 mg/dL b. Fasting plasma glucose level greater than or equal to 110 mg/dL c. Blood pressure reading of 140/90 mm Hg d. Blood pressure reading of 110/80 mm Hg e. Triglyceride level of 120 mg/dL SHORT ANSWER 1. A patient has been unable to eat solid food for 2 weeks and is in the clinic today complaining of weakness, tiredness, and hair loss. The patient states that her usual weight is 175 pounds, but today she weighs 161 pounds. What is her recent weight change percentage? To calculate recent weight change percentage, use this formula: Usual weight – current weight 100 usual weight Chapter 19 Heart & Neck Vessels • Heart sounds – Normal heart sounds and where sounds are heard best on precordium • Cardiac risk factors – Risk factors for CAD (Subjective data – Personal habits) • Assessment of neck vessels • Assessment findings of a patient with congestive heart failure • Findings on palpation of the precordium • Assessing heart rate and rhythm (normal variations) • Developmental competency • Timing of murmurs and what type of valvular defects according to timing (systolic or diastolic) – See Table • Grading murmurs MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The sac that surrounds and protects the heart is called the: a. Pericardium. b. Myocardium. c. Endocardium. d. Pleural space. 2. The direction of blood flow through the heart is best described by which of these? a. Vena cava right atrium right ventricle lungs pulmonary artery left atrium left ventricle b. Right atrium right ventricle pulmonary artery lungs pulmonary vein left atrium left ventricle c. Aorta right atrium right ventricle lungs pulmonary vein left atrium left ventricle vena cava d. Right atrium right ventricle pulmonary vein lungs pulmonary artery left atrium left ventricle 3. The nurse is reviewing the anatomy and physiologic functioning of the heart. Which statement best describes what is meant by atrial kick? a. The atria contract during systole and attempt to push against closed valves. b. Contraction of the atria at the beginning of diastole can be felt as a palpitation. c. Atrial kick is the pressure exerted against the atria as the ventricles contract during systole. d. The atria contract toward the end of diastole and push the remaining blood into the ventricles. 4. When listening to heart sounds, the nurse knows the valve closures that can be heard best at the base of the heart are: a. Mitral and tricuspid. b. Tricuspid and aortic. c. Aortic and pulmonic. d. Mitral and pulmonic. 5. Which of these statements describes the closure of the valves in a normal cardiac cycle? a. The aortic valve closes slightly before the tricuspid valve. b. The pulmonic valve closes slightly before the aortic valve. c. The tricuspid valve closes slightly later than the mitral valve. d. Both the tricuspid and pulmonic valves close at the same time. 6. The component of the conduction system referred to as the pacemaker of the heart is the: a. Atrioventricular (AV) node. b. Sinoatrial (SA) node. c. Bundle of His. d. Bundle branches. 7. The electrical stimulus of the cardiac cycle follows which sequence? a. AV node SA node bundle of His b. Bundle of His AV node SA node c. SA node AV node bundle of His bundle branches d. AV node SA node bundle of His bundle branches 8. The findings from an assessment of a 70-year-old patient with swelling in his ankles include jugular venous pulsations 5 cm above the sternal angle when the head of his bed is elevated 45 degrees. The nurse knows that this finding indicates: a. Decreased fluid volume. b. Increased cardiac output. c. Narrowing of jugular veins. d. Elevated pressure related to heart failure. 9. When assessing a newborn infant who is 5 minutes old, the nurse knows which of these statements to be true? a. The left ventricle is larger and weighs more than the right ventricle. b. The circulation of a newborn is identical to that of an adult. c. Blood can flow into the left side of the heart through an opening in the atrial septum. d. The foramen ovale closes just minutes before birth, and the ductus arteriosus closes immediately after. 10. A 25-year-old woman in her fifth month of pregnancy has a blood pressure of 100/70 mm Hg. In reviewing her previous examination, the nurse notes that her blood pressure in her second month was 124/80 mm Hg. In evaluating this change, what does the nurse know to be true? a. This decline in blood pressure is the result of peripheral vasodilatation and is an expected change. b. Because of increased cardiac output, the blood pressure should be higher at this time. c. This change in blood pressure is not an expected finding because it means a decrease in cardiac output. d. This decline in blood pressure means a decrease in circulating blood volume, which is dangerous for the fetus. 11. In assessing a 70-year-old man, the nurse finds the following: blood pressure 140/100 mm Hg; heart rate 104 beats per minute and slightly irregular; and the split S2 heart sound. Which of these findings can be explained by expected hemodynamic changes related to age? a. Increase in resting heart rate b. Increase in systolic blood pressure c. Decrease in diastolic blood pressure d. Increase in diastolic blood pressure 12. A 45-year-old man is in the clinic for a routine physical examination. During the recording of his health history, the patient states that he has been having difficulty sleeping. “I’ll be sleeping great, and then I wake up and feel like I can’t get my breath.” The nurse’s best response to this would be: a. “When was your last electrocardiogram?” b. “It’s probably because it’s been so hot at night.” c. “Do you have any history of problems with your heart?” d. “Have you had a recent sinus infection or upper respiratory infection?” 13. In assessing a patient’s major risk factors for heart disease, which would the nurse want to include when taking a history? a. Family history, hypertension, stress, and age b. Personality type, high cholesterol, diabetes, and smoking c. Smoking, hypertension, obesity, diabetes, and high cholesterol d. Alcohol consumption, obesity, diabetes, stress, and high cholesterol 14. The mother of a 3-month-old infant states that her baby has not been gaining weight. With further questioning, the nurse finds that the infant falls asleep after nursing and wakes up after a short time, hungry again. What other information would the nurse want to have? a. Infant’s sleeping position b. Sibling history of eating disorders c. Amount of background noise when eating d. Presence of dyspnea or diaphoresis when sucking 15. In assessing the carotid arteries of an older patient with cardiovascular disease, the nurse would: a. Palpate the artery in the upper one third of the neck. b. Listen with the bell of the stethoscope to assess for bruits. c. Simultaneously palpate both arteries to compare amplitude. d. Instruct the patient to take slow deep breaths during auscultation. 16. During an assessment of a 68-year-old man with a recent onset of right-sided weakness, the nurse hears a blowing, swishing sound with the bell of the stethoscope over the left carotid artery. This finding would indicate: a. Valvular disorder. b. Blood flow turbulence. c. Fluid volume overload. d. Ventricular hypertrophy. 17. During an inspection of the precordium of an adult patient, the nurse notices the chest moving in a forceful manner along the sternal border. This finding most likely suggests a(n): a. Normal heart. b. Systolic murmur. c. Enlargement of the left ventricle. d. Enlargement of the right ventricle. 18. During an assessment of a healthy adult, where would the nurse expect to palpate the apical impulse? a. Third left intercostal space at the midclavicular line b. Fourth left intercostal space at the sternal border c. Fourth left intercostal space at the anterior axillary line d. Fifth left intercostal space at the midclavicular line The apical impulse should occupy only one intercostal space, the fourth or fifth, and it should be at or medial to the midclavicular line. DIF: Cognitive Level: Remembering (Knowledge) REF: p. 479 MSC: Client Needs: Safe and Effective Care Environment: Management of Care 19. The nurse is examining a patient who has possible cardiac enlargement. Which statement about percussion of the heart is true? a. Percussion is a useful tool for outlining the heart’s borders. b. Percussion is easier in patients who are obese. c. Studies show that percussed cardiac borders do not correlate well with the true cardiac border. d. Only expert health care providers should attempt percussion of the heart. 20. The nurse is preparing to auscultate for heart sounds. Which technique is correct? a. Listening to the sounds at the aortic, tricuspid, pulmonic, and mitral areas b. Listening by inching the stethoscope in a rough Z pattern, from the base of the heart across and down, then over to the apex c. Listening to the sounds only at the site where the apical pulse is felt to be the strongest d. Listening for all possible sounds at a time at each specified area 21. While counting the apical pulse on a 16-year-old patient, the nurse notices an irregular rhythm. His rate speeds up on inspiration and slows on expiration. What would be the nurse’s response? a. Talk with the patient about his intake of caffeine. b. Perform an electrocardiogram after the examination. c. No further response is needed because sinus arrhythmia can occur normally. d. Refer the patient to a cardiologist for further testing. 22. When listening to heart sounds, the nurse knows that the S1: a. Is louder than the S2 at the base of the heart. b. Indicates the beginning of diastole. c. Coincides with the carotid artery pulse. d. Is caused by the closure of the semilunar valves. 23. During the cardiac auscultation, the nurse hears a sound immediately occurring after the S2 at the second left intercostal space. To further assess this sound, what should the nurse do? a. Have the patient turn to the left side while the nurse listens with the bell of the stethoscope. b. Ask the patient to hold his or her breath while the nurse listens again. c. No further assessment is needed because the nurse knows this sound is an S3. d. Watch the patient’s respirations while listening for the effect on the sound. 24. Which of these findings would the nurse expect to notice during a cardiac assessment on a 4-year-old child? a. S3 when sitting up b. Persistent tachycardia above 150 beats per minute c. Murmur at the second left intercostal space when supine d. Palpable apical impulse in the fifth left intercostal space lateral to midclavicular line 25. While auscultating heart sounds on a 7-year-old child for a routine physical examination, the nurse hears an S3, a soft murmur at the left midsternal border, and a venous hum when the child is standing. What would be a correct interpretation of these findings? a. S3 is indicative of heart disease in children. b. These findings can all be normal in a child. c. These findings are indicative of congenital problems. d. The venous hum most likely indicates an aneurysm. 26. During the precordial assessment on an patient who is 8 months pregnant, the nurse palpates the apical impulse at the fourth left intercostal space lateral to the midclavicular line. This finding would indicate: a. Right ventricular hypertrophy. b. Increased volume and size of the heart as a result of pregnancy. c. Displacement of the heart from elevation of the diaphragm. d. Increased blood flow through the internal mammary artery. 27. In assessing for an S4 heart sound with a stethoscope, the nurse would listen with the: a. Bell of the stethoscope at the base with the patient leaning forward. b. Bell of the stethoscope at the apex with the patient in the left lateral position. c. Diaphragm of the stethoscope in the aortic area with the patient sitting. d. Diaphragm of the stethoscope in the pulmonic area with the patient supine. 28. A 70-year-old patient with a history of hypertension has a blood pressure of 180/100 mm Hg and a heart rate of 90 beats per minute. The nurse hears an extra heart sound at the apex immediately before the S1. The sound is heard only with the bell of the stethoscope while the patient is in the left lateral position. With these findings and the patient’s history, the nurse knows that this extra heart sound is most likely a(n): a. Split S1. b. Atrial gallop. c. Diastolic murmur. d. Summation sound. 29. The nurse is performing a cardiac assessment on a 65-year-old patient 3 days after her myocardial infarction (MI). Heart sounds are normal when she is supine, but when she is sitting and leaning forward, the nurse hears a high-pitched, scratchy sound with the diaphragm of the stethoscope at the apex. It disappears on inspiration. The nurse suspects: a. Increased cardiac output. b. Another MI. c. Inflammation of the precordium. d. Ventricular hypertrophy resulting from muscle damage. 30. The mother of a 10-month-old infant tells the nurse that she has noticed that her son becomes blue when he is crying and that the frequency of this is increasing. He is also not crawling yet. During the examination the nurse palpates a thrill at the left lower sternal border and auscultates a loud systolic murmur in the same area. What would be the most likely cause of these findings? a. Tetralogy of Fallot b. Atrial septal defect c. Patent ductus arteriosus d. Ventricular septal defect 31. A 30-year-old woman with a history of mitral valve problems states that she has been “very tired.” She has started waking up at night and feels like her “heart is pounding.” During the assessment, the nurse palpates a thrill and lift at the fifth left intercostal space midclavicular line. In the same area, the nurse also auscultates a blowing, swishing sound right after the S1. These findings would be most consistent with: a. Heart failure. b. Aortic stenosis. c. Pulmonary edema. d. Mitral regurgitation. 32. During a cardiac assessment on a 38-year-old patient in the hospital for “chest pain,” the nurse finds the following: jugular vein pulsations 4 cm above the sternal angle when the patient is elevated at 45 degrees, blood pressure 98/60 mm Hg, heart rate 130 beats per minute, ankle edema, difficulty breathing when supine, and an S3 on auscultation. Which of these conditions best explains the cause of these findings? a. Fluid overload b. Atrial septal defect c. MI d. Heart failure 33. The nurse knows that normal splitting of the S2 is associated with: a. Expiration. b. Inspiration. c. Exercise state. d. Low resting heart rate. 34. During a cardiovascular assessment, the nurse knows that a thrill is: a. Vibration that is palpable. b. Palpated in the right epigastric area. c. Associated with ventricular hypertrophy. d. Murmur auscultated at the third intercostal space. 35. During a cardiovascular assessment, the nurse knows that an S4 heart sound is: a. Heard at the onset of atrial diastole. b. Usually a normal finding in the older adult. c. Heard at the end of ventricular diastole. d. Heard best over the second left intercostal space with the individual sitting upright. 36. During an assessment, the nurse notes that the patient’s apical impulse is laterally displaced and is palpable over a wide area. This finding indicates: a. Systemic hypertension. b. Pulmonic hypertension. c. Pressure overload, as in aortic stenosis. d. Volume overload, as in heart failure. 37. When the nurse is auscultating the carotid artery for bruits, which of these statements reflects the correct technique? a. While listening with the bell of the stethoscope, the patient is asked to take a deep breath and hold it. b. While auscultating one side with the bell of the stethoscope, the carotid artery is palpated on the other side to check pulsations. c. While lightly applying the bell of the stethoscope over the carotid artery and listening, the patient is asked to take a breath, exhale, and briefly hold it. d. While firmly placing the bell of the stethoscope over the carotid artery and listening, the patient is asked to take a breath, exhale, and briefly hold it. 38. The nurse is preparing for a class on risk factors for hypertension and reviews recent statistics. Which racial group has the highest prevalence of hypertension in the world? a. Blacks b. Whites c. American Indians d. Hispanics 39. The nurse is assessing a patient with possible cardiomyopathy and assesses the hepatojugular reflux. If heart failure is present, then the nurse should recognize which finding while pushing on the right upper quadrant of the patient’s abdomen, just below the rib cage? a. The jugular veins will rise for a few seconds and then recede back to the previous level if the heart is properly working. b. The jugular veins will remain elevated as long as pressure on the abdomen is maintained. c. An impulse will be visible at the fourth or fifth intercostal space at or inside the midclavicular line. d. The jugular veins will not be detected during this maneuver. DIF: Cognitive Level: Analyzing (Analysis) REF: p. 478 MSC: Client Needs: Safe and Effective Care Environment: Management of Care 40. The nurse is assessing the apical pulse of a 3-month-old infant and finds that the heart rate is 135 beats per minute. The nurse interprets this result as: a. Normal for this age. b. Lower than expected. c. Higher than expected, probably as a result of crying. d. Higher than expected, reflecting persistent tachycardia. MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1. The nurse is presenting a class on risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Which of these are considered modifiable risk factors for MI? Select all that apply. a. Ethnicity b. Abnormal lipids c. Smoking d. Gender e. Hypertension f. Diabetes g. Family history SHORT ANSWER 1. The nurse is assessing a patient’s pulses and notices a difference between the patient’s apical pulse and radial pulse. The apical pulse was 118 beats per minute, and the radial pulse was 105 beats per minute. What is the pulse deficit? Chapter 20 Peripheral Vascular System • Review venous flow • Palpation of pulses (upper and lower extremities) • Assessing the arms and hands • Inspection and palpation of legs • Peripheral vascular disease MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which statement is true regarding the arterial system? a. Arteries are large-diameter vessels. b. The arterial system is a high-pressure system. c. The walls of arteries are thinner than those of the veins. d. Arteries can greatly expand to accommodate a large blood volume increase. 2. The nurse is reviewing the blood supply to the arm. The major artery supplying the arm is the _____ artery. a. Ulnar b. Radial c. Brachial d. Deep palmar 3. The nurse is preparing to assess the dorsalis pedis artery. Where is the correct location for palpation? a. Behind the knee b. Over the lateral malleolus c. In the groove behind the medial malleolus d. Lateral to the extensor tendon of the great toe 4. A 65-year-old patient is experiencing pain in his left calf when he exercises that disappears after resting for a few minutes. The nurse recognizes that this description is most consistent with _______ the left leg. a. Venous obstruction of b. Claudication due to venous abnormalities in c. Ischemia caused by a partial blockage of an artery supplying d. Ischemia caused by the complete blockage of an artery supplying 5. The nurse is reviewing venous blood flow patterns. Which of these statements best describes the mechanism(s) by which venous blood returns to the heart? a. Intraluminal valves ensure unidirectional flow toward the heart. b. Contracting skeletal muscles milk blood distally toward the veins. c. High-pressure system of the heart helps facilitate venous return. d. Increased thoracic pressure and decreased abdominal pressure facilitate venous return to the heart. 6. Which vein(s) is(are) responsible for most of the venous return in the arm? a. Deep b. Ulnar c. Subclavian d. Superficial 7. A 70-year-old patient is scheduled for open-heart surgery. The surgeon plans to use the great saphenous vein for the coronary bypass grafts. The patient asks, “What happens to my circulation when this vein is removed?” The nurse should reply: a. “Venous insufficiency is a common problem after this type of surgery.” b. “Oh, you have lots of veins—you won’t even notice that it has been removed.” c. “You will probably experience decreased circulation after the vein is removed.” d. “This vein can be removed without harming your circulation because the deeper veins in your leg are in good condition.” 8. The nurse is reviewing the risk factors for venous disease. Which of these situations best describes a person at highest risk for the development of venous disease? a. Woman in her second month of pregnancy b. Person who has been on bed rest for 4 days c. Person with a 30-year, 1 pack per day smoking habit d. Older adult taking anticoagulant medication 9. The nurse is teaching a review class on the lymphatic system. A participant shows correct understanding of the material with which statement? a. “Lymph flow is propelled by the contraction of the heart.” b. “The flow of lymph is slow, compared with that of the blood.” c. “One of the functions of the lymph is to absorb lipids from the biliary tract.” d. “Lymph vessels have no valves; therefore, lymph fluid flows freely from the tissue spaces into the bloodstream.” 10. When performing an assessment of a patient, the nurse notices the presence of an enlarged right epitrochlear lymph node. What should the nurse do next? a. Assess the patient’s abdomen, and notice any tenderness. b. Carefully assess the cervical lymph nodes, and check for any enlargement. c. Ask additional health history questions regarding any recent ear infections or sore throats. d. Examine the patient’s lower arm and hand, and check for the presence of infection or lesions. 11. A 35-year-old man is seen in the clinic for an infection in his left foot. Which of these findings should the nurse expect to see during an assessment of this patient? a. Hard and fixed cervical nodes b. Enlarged and tender inguinal nodes c. Bilateral enlargement of the popliteal nodes d. Pelletlike nodes in the supraclavicular region 12. The nurse is examining the lymphatic system of a healthy 3-year-old child. Which finding should the nurse expect? a. Excessive swelling of the lymph nodes b. Presence of palpable lymph nodes c. No palpable nodes because of the immature immune system of a child d. Fewer numbers and a smaller size of lymph nodes compared with those of an adult 13. During an assessment of an older adult, the nurse should expect to notice which finding as a normal physiologic change associated with the aging process? a. Hormonal changes causing vasodilation and a resulting drop in blood pressure b. Progressive atrophy of the intramuscular calf veins, causing venous insufficiency c. Peripheral blood vessels growing more rigid with age, producing a rise in systolic blood pressure d. Narrowing of the inferior vena cava, causing low blood flow and increases in venous pressure resulting in varicosities 14. A 67-year-old patient states that he recently began to have pain in his left calf when climbing the 10 stairs to his apartment. This pain is relieved by sitting for approximately 2 minutes; then he is able to resume his activities. The nurse interprets that this patient is most likely experiencing: a. Claudication. b. Sore muscles. c. Muscle cramps. d. Venous insufficiency. 15. A patient complains of leg pain that wakes him at night. He states that he “has been having problems” with his legs. He has pain in his legs when they are elevated that disappears when he dangles them. He recently noticed “a sore” on the inner aspect of the right ankle. On the basis of this health history information, the nurse interprets that the patient is most likely experiencing: a. Pain related to lymphatic abnormalities. b. Problems related to arterial insufficiency. c. Problems related to venous insufficiency. d. Pain related to musculoskeletal abnormalities. 16. During an assessment, the nurse uses the profile sign to detect: a. Pitting edema. b. Early clubbing. c. Symmetry of the fingers. d. Insufficient capillary refill. 17. The nurse is performing an assessment on an adult. The adult’s vital signs are normal, and capillary refill time is 5 seconds. What should the nurse do next? a. Ask the patient about a history of frostbite. b. Suspect that the patient has venous insufficiency. c. Consider this a delayed capillary refill time, and investigate further. d. Consider this a normal capillary refill time that requires no further assessment. 18. When assessing a patient, the nurse notes that the left femoral pulse as diminished, 1+/4+. What should the nurse do next? a. Document the finding. b. Auscultate the site for a bruit. c. Check for calf pain. d. Check capillary refill in the toes. 19. When performing a peripheral vascular assessment on a patient, the nurse is unable to palpate the ulnar pulses. The patient’s skin is warm and capillary refill time is normal. Next, the nurse should: a. Check for the presence of claudication. b. Refer the individual for further evaluation. c. Consider this finding as normal, and proceed with the peripheral vascular evaluation. d. Ask the patient if he or she has experienced any unusual cramping or tingling in the arm. 20. The nurse is assessing the pulses of a patient who has been admitted for untreated hyperthyroidism. The nurse should expect to find a(n) _______ pulse. a. Normal b. Absent c. Bounding d. Weak, thready 21. The nurse is preparing to perform a modified Allen test. Which is an appropriate reason for this test? a. To measure the rate of lymphatic drainage b. To evaluate the adequacy of capillary patency before venous blood draws c. To evaluate the adequacy of collateral circulation before cannulating the radial artery d. To evaluate the venous refill rate that occurs after the ulnar and radial arteries are temporarily occluded 22. A patient has been diagnosed with venous stasis. Which of these findings would the nurse most likely observe? a. Unilateral cool foot b. Thin, shiny, atrophic skin c. Pallor of the toes and cyanosis of the nail beds d. Brownish discoloration to the skin of the lower leg 23. The nurse is attempting to assess the femoral pulse in a patient who is obese. Which of these actions would be most appropriate? a. The patient is asked to assume a prone position. b. The patient is asked to bend his or her knees to the side in a froglike position. c. The nurse firmly presses against the bone with the patient in a semi-Fowler position. d. The nurse listens with a stethoscope for pulsations; palpating the pulse in an obese person is extremely difficult. 24. When auscultating over a patient’s femoral arteries, the nurse notices the presence of a bruit on the left side. The nurse knows that bruits: a. Are often associated with venous disease. b. Occur in the presence of lymphadenopathy. c. In the femoral arteries are caused by hypermetabolic states. d. Occur with turbulent blood flow, indicating partial occlusion. 25. How should the nurse document mild, slight pitting edema the ankles of a pregnant patient? a. 1+/0-4+ b. 3+/0-4+ c. 4+/0-4+ d. Brawny edema 26. A patient has hard, nonpitting edema of the left lower leg and ankle. The right leg has no edema. Based on these findings, the nurse recalls that: a. Nonpitting, hard edema occurs with lymphatic obstruction. b. Alterations in arterial function will cause edema. c. Phlebitis of a superficial vein will cause bilateral edema. d. Long-standing arterial obstruction will cause pitting edema. 27. When assessing a patient’s pulse, the nurse notes that the amplitude is weaker during inspiration and stronger during expiration. When the nurse measures the blood pressure, the reading decreases 20 mm Hg during inspiration and increases with expiration. This patient is experiencing pulsus: a. Alternans. b. Bisferiens. c. Bigeminus. d. Paradoxus. 28. During an assessment, the nurse has elevated a patient’s legs 12 inches off the table and has had him wag his feet to drain off venous blood. After helping him sit up and dangle his legs over the side of the table, the nurse should expect that a normal finding at this point would be: a. Significant elevational pallor. b. Venous filling within 15 seconds. c. No change in the coloration of the skin. d. Color returning to the feet within 20 seconds of assuming a sitting position. 29. During a visit to the clinic, a woman in her seventh month of pregnancy complains that her legs feel “heavy in the calf” and that she often has foot cramps at night. The nurse notices that the patient has dilated, tortuous veins apparent in her lower legs. Which condition is reflected by these findings? a. Deep-vein thrombophlebitis b. Varicose veins c. Lymphedema d. Raynaud phenomenon 30. During an assessment, the nurse notices that a patient’s left arm is swollen from the shoulder down to the fingers, with nonpitting brawny edema. The right arm is normal. The patient had a left-sided mastectomy 1 year ago. The nurse suspects which problem? a. Venous stasis b. Lymphedema c. Arteriosclerosis d. Deep-vein thrombosis 31. The nurse is preparing to assess the ankle-brachial index (ABI) of a patient. Which statement about the ABI is true? a. Normal ABI indices are from 0.5 to 1.0. b. Normal ankle pressure is slightly lower than the brachial pressure. c. The ABI is a reliable measurement of peripheral vascular disease in individuals with diabetes. d. An ABI of 0.9 to 0.7 indicates the presence of peripheral vascular disease and mild claudication. 32. The nurse is performing a well-child checkup on a 5-year-old boy. He has no current condition that would lead the nurse to suspect an illness. His health history is unremarkable, and he received immunizations 1 week ago. Which of these findings should be considered normal in this patient? a. Enlarged, warm, and tender nodes b. Lymphadenopathy of the cervical nodes c. Palpable firm, small, shotty, mobile, and nontender lymph nodes d. Firm, rubbery, and large nodes, somewhat fixed to the underlying tissue 33. When using a Doppler ultrasonic stethoscope, the nurse recognizes venous flow when which sound is heard? a. Low humming sound b. Regular “lub, dub” pattern c. Swishing, whooshing sound d. Steady, even, flowing sound 34. The nurse is describing a weak, thready pulse on the documentation flow sheet. Which statement is correct? a. “Is easily palpable; pounds under the fingertips.” b. “Has greater than normal force, then suddenly collapses.” c. “Is hard to palpate, may fade in and out, and is easily obliterated by pressure.” d. “Rhythm is regular, but force varies with alternating beats of large and small amplitude.” 35. During an assessment, a patient tells the nurse that her fingers often change color when she goes out in cold weather. She describes these episodes as her fingers first turning white, then blue, then red with a burning, throbbing pain. The nurse suspects that she is experiencing: a. Lymphedema. b. Raynaud disease. c. Deep-vein thrombosis. d. Chronic arterial insufficiency. 36. During a routine office visit, a patient takes off his shoes and shows the nurse “this awful sore that won’t heal.” On inspection, the nurse notes a 3-cm round ulcer on the left great toe, with a pale ischemic base, well-defined edges, and no drainage. The nurse should assess for other signs and symptoms of: a. Varicosities. b. Venous stasis ulcer. c. Arterial ischemic ulcer. d. Deep-vein thrombophlebitis. 37. The nurse is reviewing an assessment of a patient’s peripheral pulses and notices that the documentation states that the radial pulses are “2+.” The nurse recognizes that this reading indicates what type of pulse? a. Bounding b. Normal c. Weak d. Absent MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1. A patient is recovering from several hours of orthopedic surgery. During an assessment of the patient’s lower legs, the nurse will monitor for signs of acute venous symptoms. Signs of acute venous symptoms include which of the following? Select all that apply. a. Intense, sharp pain, with the deep muscle tender to the touch b. Aching, tired pain, with a feeling of fullness c. Pain that is worse at the end of the day d. Sudden onset e. Warm, red, and swollen calf f. Pain that is relieved with elevation of the leg 2. A patient has been admitted with chronic arterial symptoms. During the assessment, the nurse should expect which findings? Select all that apply. a. Patient has a history of diabetes and cigarette smoking. b. Skin of the patient is pale and cool. c. His ankles have two small, weeping ulcers. d. Patient works long hours sitting at a computer desk. e. He states that the pain gets worse when walking. f. Patient states that the pain is worse at the end of the day. Chapter 21 - Abdomen • Normal percussion tones of the abdomen and liver • Internal anatomy of the abdomen • Inspection of abdomen contour and abnormalities • Subjective data needed for abdominal assessment • Auscultation of bowel sounds and vascular sounds • Appropriate techniques for palpating the abdomen • Developmental Competence – The Aging Adult MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The nurse is percussing the seventh right intercostal space at the midclavicular line over the liver. Which sound should the nurse expect to hear? a. Dullness b. Tympany c. Resonance d. Hyperresonance 2. Which structure is located in the left lower quadrant of the abdomen? a. Liver b. Duodenum c. Gallbladder d. Sigmoid colon 3. A patient is having difficulty swallowing medications and food. The nurse would document that this patient has: a. Aphasia. b. Dysphasia. c. Dysphagia. d. Anorexia. MSC: Client Needs: Safe and Effective Care Environment: Management of Care 4. The nurse suspects that a patient has a distended bladder. How should the nurse assess for this condition? a. Percuss and palpate in the lumbar region. b. Inspect and palpate in the epigastric region. c. Auscultate and percuss in the inguinal region. d. Percuss and palpate the midline area above the suprapubic bone. 5. The nurse is aware that one change that may occur in the gastrointestinal system of an aging adult is: a. Increased salivation. b. Increased liver size. c. Increased esophageal emptying. d. Decreased gastric acid secretion. 6. A 22-year-old man comes to the clinic for an examination after falling off his motorcycle and landing on his left side on the handle bars. The nurse suspects that he may have injured his spleen. Which of these statements is true regarding assessment of the spleen in this situation? a. The spleen can be enlarged as a result of trauma. b. The spleen is normally felt on routine palpation. c. If an enlarged spleen is noted, then the nurse should thoroughly palpate to determine its size. d. An enlarged spleen should not be palpated because it can easily rupture. 7. A patient’s abdomen is bulging and stretched in appearance. The nurse should describe this finding as: a. Obese. b. Herniated. c. Scaphoid. d. Protuberant. 8. The nurse is describing a scaphoid abdomen. To the horizontal plane, a scaphoid contour of the abdomen depicts a ______ profile. a. Flat b. Convex c. Bulging d. Concave 9. While examining a patient, the nurse observes abdominal pulsations between the xiphoid process and umbilicus. The nurse would suspect that these are: a. Pulsations of the renal arteries. b. Pulsations of the inferior vena cava. c. Normal abdominal aortic pulsations. d. Increased peristalsis from a bowel obstruction. 10. A patient has hypoactive bowel sounds. The nurse knows that a potential cause of hypoactive bowel sounds is: a. Diarrhea. b. Peritonitis. c. Laxative use. d. Gastroenteritis. 11. The nurse is watching a new graduate nurse perform auscultation of a patient’s abdomen. Which statement by the new graduate shows a correct understanding of the reason auscultation precedes percussion and palpation of the abdomen? a. “We need to determine the areas of tenderness before using percussion and palpation.” b. “Auscultation prevents distortion of bowel sounds that might occur after percussion and palpation.” c. “Auscultation allows the patient more time to relax and therefore be more comfortable with the physical examination.” d. “Auscultation prevents distortion of vascular sounds, such as bruits and hums, that might occur after percussion and palpation.” 12. The nurse is listening to bowel sounds. Which of these statements is true of bowel sounds? Bowel sounds: a. Are usually loud, high-pitched, rushing, and tinkling sounds. b. Are usually high-pitched, gurgling, and irregular sounds. c. Sound like two pieces of leather being rubbed together. d. Originate from the movement of air and fluid through the large intestine. 13. The physician comments that a patient has abdominal borborygmi. The nurse knows that this term refers to: a. Loud continual hum. b. Peritoneal friction rub. c. Hypoactive bowel sounds. d. Hyperactive bowel sounds. 14. During an abdominal assessment, the nurse would consider which of these findings as normal? a. Presence of a bruit in the femoral area b. Tympanic percussion note in the umbilical region c. Palpable spleen between the ninth and eleventh ribs in the left midaxillary line d. Dull percussion note in the left upper quadrant at the midclavicular line 15. The nurse is assessing the abdomen of a pregnant woman who is complaining of having “acid indigestion” all the time. The nurse knows that esophageal reflux during pregnancy can cause: a. Diarrhea. b. Pyrosis. c. Dysphagia. d. Constipation. 16. The nurse is performing percussion during an abdominal assessment. Percussion notes heard during the abdominal assessment may include: a. Flatness, resonance, and dullness. b. Resonance, dullness, and tympany. c. Tympany, hyperresonance, and dullness. d. Resonance, hyperresonance, and flatness. 17. An older patient has been diagnosed with pernicious anemia. The nurse knows that this condition could be related to: a. Increased gastric acid secretion. b. Decreased gastric acid secretion. c. Delayed gastrointestinal emptying time. d. Increased gastrointestinal emptying time. 18. A patient is complaining of a sharp pain along the costovertebral angles. The nurse is aware that this symptom is most often indicative of: a. Ovary infection. b. Liver enlargement. c. Kidney inflammation. d. Spleen enlargement. 19. A nurse notices that a patient has ascites, which indicates the presence of: a. Fluid. b. Feces. c. Flatus. d. Fibroid tumors. 20. The nurse knows that during an abdominal assessment, deep palpation is used to determine: a. Bowel motility. b. Enlarged organs. c. Superficial tenderness. d. Overall impression of skin surface and superficial musculature. 21. The nurse notices that a patient has had a black, tarry stool and recalls that a possible cause would be: a. Gallbladder disease. b. Overuse of laxatives. c. Gastrointestinal bleeding. d. Localized bleeding around the anus. 22. During an abdominal assessment, the nurse elicits tenderness on light palpation in the right lower quadrant. The nurse interprets that this finding could indicate a disorder of which of these structures? a. Spleen b. Sigmoid c. Appendix d. Gallbladder 23. The nurse is assessing the abdomen of an older adult. Which statement regarding the older adult and abdominal assessment is true? a. Abdominal tone is increased. b. Abdominal musculature is thinner. c. Abdominal rigidity with an acute abdominal condition is more common. d. The older adult with an acute abdominal condition complains more about pain than the younger person. 24. During an assessment of a newborn infant, the nurse recalls that pyloric stenosis would be exhibited by: a. Projectile vomiting. b. Hypoactive bowel activity. c. Palpable olive-sized mass in the right lower quadrant. d. Pronounced peristaltic waves crossing from right to left. 25. The nurse is reviewing the assessment of an aortic aneurysm. Which of these statements is true regarding an aortic aneurysm? a. A bruit is absent. b. Femoral pulses are increased. c. A pulsating mass is usually present. d. Most are located below the umbilicus. 26. During an abdominal assessment, the nurse is unable to hear bowel sounds in a patient’s abdomen. Before reporting this finding as silent bowel sounds, the nurse should listen for at least: a. 1 minute. b. 5 minutes. c. 10 minutes. d. 2 minutes in each quadrant. 27. A patient is suspected of having inflammation of the gallbladder, or cholecystitis. The nurse should conduct which of these techniques to assess for this condition? a. Obturator test b. Test for Murphy sign c. Assess for rebound tenderness d. Iliopsoas muscle test 28. Just before going home, a new mother asks the nurse about the infant’s umbilical cord. Which of these statements is correct? a. “It should fall off in 10 to 14 days.” b. “It will soften before it falls off.” c. “It contains two veins and one artery.” d. “Skin will cover the area within 1 week.” 29. Which of these percussion findings would the nurse expect to find in a patient with a large amount of ascites? a. Dullness across the abdomen b. Flatness in the right upper quadrant c. Hyperresonance in the left upper quadrant d. Tympany in the right and left lower quadrants 30. A 40-year-old man states that his physician told him that he has a hernia. He asks the nurse to explain what a hernia is. Which response by the nurse is appropriate? a. “No need to worry. Most men your age develop hernias.” b. “A hernia is a loop of bowel protruding through a weak spot in the abdominal muscles.” c. “A hernia is the result of prenatal growth abnormalities that are just now causing problems.” d. “I’ll have to have your physician explain this to you.” 31. A 45-year-old man is in the clinic for a physical examination. During the abdominal assessment, the nurse percusses the abdomen and notices an area of dullness above the right costal margin of approximately 11 cm. The nurse should: a. Document the presence of hepatomegaly. b. Ask additional health history questions regarding his alcohol intake. c. Describe this dullness as indicative of an enlarged liver, and refer him to a physician. d. Consider this finding as normal, and proceed with the examination. 32. When palpating the abdomen of a 20-year-old patient, the nurse notices the presence of tenderness in the left upper quadrant with deep palpation. Which of these structures is most likely to be involved? a. Spleen b. Sigmoid colon c. Appendix d. Gallbladder 33. The nurse is reviewing statistics for lactose intolerance. In the United States, the incidence of lactose intolerance is higher in adults of which ethnic group? a. Blacks b. Hispanics c. Whites d. Asians 34. The nurse is assessing a patient for possible peptic ulcer disease. Which condition or history often causes this problem? a. Hypertension b. Streptococcal infections c. Recurrent constipation with frequent laxative use d. Frequent use of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs 35. During reporting, the student nurse hears that a patient has hepatomegaly and recognizes that this term refers to: a. Enlarged liver. b. Enlarged spleen. c. Distended bowel. d. Excessive diarrhea. 36. During an assessment, the nurse notices that a patient’s umbilicus is enlarged and everted. It is positioned midline with no change in skin color. The nurse recognizes that the patient may have which condition? a. Intra-abdominal bleeding b. Constipation c. Umbilical hernia d. Abdominal tumor 37. During an abdominal assessment, the nurse tests for a fluid wave. A positive fluid wave test occurs with: a. Splenomegaly. b. Distended bladder. c. Constipation. d. Ascites. 38. The nurse is preparing to examine a patient who has been complaining of right lower quadrant pain. Which technique is correct during the assessment? The nurse should: a. Examine the tender area first. b. Examine the tender area last. c. Avoid palpating the tender area. d. Palpate the tender area first, and then auscultate for bowel sounds. 39. During a health history, the patient tells the nurse, “I have pain all the time in my stomach. It’s worse 2 hours after I eat, but it gets better if I eat again!” Based on these symptoms, the nurse suspects that the patient has which condition? a. Appendicitis b. Gastric ulcer c. Duodenal ulcer d. Cholecystitis MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1. The nurse suspects that a patient has appendicitis. Which of these procedures are appropriate for use when assessing for appendicitis or a perforated appendix? Select all that apply. a. Test for the Murphy sign b. Test for the Blumberg sign c. Test for shifting dullness d. Perform the iliopsoas muscle test e. Test for fluid wave Chapter 25 – Anus, Rectum & Prostate • Comprehension of the examination techniques • Functions of the systems • Normal & Abnormal Findings MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which statement concerning the anal canal is true? The anal canal: a. Is approximately 2 cm long in the adult. b. Slants backward toward the sacrum. c. Contains hair and sebaceous glands. d. Is the outlet for the gastrointestinal tract. 2. Which statement concerning the sphincters is correct? a. The internal sphincter is under voluntary control. b. The external sphincter is under voluntary control. c. Both sphincters remain slightly relaxed at all times. d. The internal sphincter surrounds the external sphincter. 3. The nurse is performing an examination of the anus and rectum. Which of these statements is correct and important to remember during this examination? a. The rectum is approximately 8 cm long. b. The anorectal junction cannot be palpated. c. Above the anal canal, the rectum turns anteriorly. d. No sensory nerves are in the anal canal or rectum. 4. The structure that secretes a thin, milky alkaline fluid to enhance the viability of sperm is the: a. Cowper gland. b. Prostate gland. c. Median sulcus. d. Bulbourethral gland. 5. A 46-year-old man requires an assessment of his sigmoid colon. Which instrument or technique is most appropriate for this examination? a. Proctoscope b. Ultrasound c. Colonoscope d. Rectal examination with an examining finger 6. The nurse is caring for a newborn infant. Thirty hours after birth, the infant passes a dark green meconium stool. The nurse recognizes this is important because the: a. Stool indicates anal patency. b. Dark green color indicates occult blood in the stool. c. Meconium stool can be reflective of distress in the newborn. d. Newborn should have passed the first stool within 12 hours after birth. 7. During the assessment of an 18-month-old infant, the mother expresses concern to the nurse about the infant’s inability to toilet train. What would be the nurse’s best response? a. “Some children are just more difficult to train, so I wouldn’t worry about it yet.” b. “Have you considered reading any of the books on toilet training? They can be very helpful.” c. “This could mean that there is a problem in your baby’s development. We’ll watch her closely for the next few months.” d. “The nerves that will allow your baby to have control over the passing of stools are not developed until at least 18 to 24 months of age.” 8. A 60-year-old man has just been told that he has benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH). He has a friend who just died from cancer of the prostate. He is concerned this will happen to him. How should the nurse respond? a. “The swelling in your prostate is only temporary and will go away.” b. “We will treat you with chemotherapy so we can control the cancer.” c. “It would be very unusual for a man your age to have cancer of the prostate.” d. “The enlargement of your prostate is caused by hormonal changes, and not cancer.” 9. A 30-year-old woman is visiting the clinic because of “pain in my bottom when I have a bowel movement.” The nurse should assess for which problem? a. Pinworms b. Hemorrhoids c. Colon cancer d. Fecal incontinence 10. A patient who is visiting the clinic complains of having “stomach pains for 2 weeks” and describes his stools as being “soft and black” for approximately the last 10 days. He denies taking any medications. The nurse is aware that these symptoms are mostly indicative of: a. Excessive fat caused by malabsorption. b. Increased iron intake, resulting from a change in diet. c. Occult blood, resulting from gastrointestinal bleeding. d. Absent bile pigment from liver problems. 11. After completing an assessment of a 60-year-old man with a family history of colon cancer, the nurse discusses with him early detection measures for colon cancer. The nurse should mention the need for a(n): a. Annual proctoscopy. b. Colonoscopy every 10 years. c. Fecal test for blood every 6 months. d. DREs every 2 years. 12. The mother of a 5-year-old girl tells the nurse that she has noticed her daughter “scratching at her bottom a lot the last few days.” During the assessment, the nurse finds redness and raised skin in the anal area. This finding most likely indicates: a. Pinworms. b. Chickenpox. c. Constipation. d. Bacterial infection. 13. The nurse is examining only the rectal area of a woman and should place the woman in what position? a. Lithotomy b. Prone c. Left lateral decubitus d. Bending over the table while standing 14. While performing an assessment of the perianal area of a patient, the nurse notices that the pigmentation of anus is darker than the surrounding skin, the anal opening is closed, and a skin sac that is shiny and blue is noted. The patient mentioned that he has had pain with bowel movements and has occasionally noted some spots of blood. What would this assessment and history most likely indicate? a. Anal fistula b. Pilonidal cyst c. Rectal prolapse d. Thrombosed hemorrhoid 15. The nurse is preparing to palpate the rectum and should use which of these techniques? The nurse should: a. Flex the finger, and slowly insert it toward the umbilicus. b. First instruct the patient that this procedure will be painful. c. Insert an extended index finger at a right angle to the anus. d. Place the finger directly into the anus to overcome the tight sphincter. 16. While performing a rectal examination, the nurse notices a firm, irregularly shaped mass. What should the nurse do next? a. Continue with the examination, and document the finding in the chart. b. Instruct the patient to return for a repeat assessment in 1 month. c. Tell the patient that a mass was felt, but it is nothing to worry about. d. Report the finding, and refer the patient to a specialist for further examination. 17. During an assessment of the newborn, the nurse expects to see which finding when the anal area is slightly stroked? a. Jerking of the legs b. Flexion of the knees c. Quick contraction of the sphincter d. Relaxation of the external sphincter 18. A 13-year-old girl is visiting the clinic for a sports physical examination. The nurse should remember to include which of these tests in the examination? a. Testing for occult blood b. Valsalva maneuver c. Internal palpation of the anus d. Inspection of the perianal area 19. During an assessment of a 20-year-old man, the nurse finds a small palpable lesion with a tuft of hair located directly over the coccyx. The nurse knows that this lesion would most likely be a: a. Rectal polyp. b. Pruritus ani. c. Carcinoma. d. Pilonidal cyst. 20. During an examination, the nurse asks the patient to perform the Valsalva maneuver and notices that the patient has a moist, red, doughnut-shaped protrusion from the anus. The nurse knows that this finding is consistent with a: a. Rectal polyp. b. Hemorrhoid. c. Rectal fissure. d. Rectal prolapse. 21. A 70-year-old man is visiting the clinic for difficulty in passing urine. In the health history, he indicates that he has to urinate frequently, especially at night. He has burning when he urinates and has noticed pain in his back. Considering this history, what might the nurse expect to find during the physical assessment? a. Asymmetric, hard, and fixed prostate gland b. Occult blood and perianal pain to palpation c. Symmetrically enlarged, soft prostate gland d. Soft nodule protruding from the rectal mucosa 22. A 40-year-old black man is in the office for his annual physical examination. Which statement regarding the PSA blood test is true, according to the American Cancer Society? The PSA: a. Should be performed with this visit. b. Should be performed at age 45 years. c. Should be performed at age 50 years. d. Is only necessary if a family history of prostate cancer exists. 23. A 62-year-old man is experiencing fever, chills, malaise, urinary frequency, and urgency. He also reports urethral discharge and a dull aching pain in the perineal and rectal area. These symptoms are most consistent with which condition? a. Prostatitis b. Polyps c. Carcinoma of the prostate d. BPH 24. During a discussion for a men’s health group, the nurse relates that the group with the highest incidence of prostate cancer is: a. Asian Americans. b. Blacks. c. American Indians. d. Hispanics. 25. Which characteristic of the prostate gland would the nurse recognize as an abnormal finding while palpating the prostate gland through the rectum? a. Palpable central groove b. Tenderness to palpation c. Heart shaped d. Elastic and rubbery consistency 26. The nurse notices that a patient has had a pale, yellow, greasy stool, or steatorrhea, and recalls that this is caused by: a. Occult bleeding. b. Absent bile pigment. c. Increased fat content. d. Ingestion of bismuth preparations. 27. During a health history of a patient who complains of chronic constipation, the patient asks the nurse about high-fiber foods. The nurse relates that an example of a high-fiber food would be: a. Broccoli. b. Hamburger. c. Iceberg lettuce. d. Yogurt. 28. While assessing a patient who is hospitalized and bedridden, the nurse notices that the patient has been incontinent of stool. The stool is loose and gray-tan in color. The nurse recognizes that this finding indicates which of the following? a. Occult blood b. Inflammation c. Absent bile pigment d. Ingestion of iron preparations 29. During a digital examination of the rectum, the nurse notices that the patient has hard feces in the rectum. The patient complains of feeling “full,” has a distended abdomen, and states that she has not had a bowel movement “for several days.” The nurse suspects which condition? a. Rectal polyp b. Fecal impaction c. Rectal abscess d. Rectal prolapse 30. During the taking of a health history, the patient states, “It really hurts back there, and sometimes it itches, too. I have even seen blood on the tissue when I have a bowel movement. Is there something there?” The nurse should expect to see which of these upon examination of the anus? a. Rectal prolapse b. Internal hemorrhoid c. External hemorrhoid that has resolved d. External hemorrhoid that is thrombosed MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1. The nurse is performing a digital examination of a patient’s prostate gland and notices that a normal prostate gland includes which of the following characteristics? Select all that apply. a. 1 cm protrusion into the rectum b. Heart-shaped with a palpable central groove c. Flat shape with no palpable groove d. Boggy with a soft consistency e. Smooth surface, elastic, and rubbery consistency f. Fixed mobility Chapter 27/29 – Shift Assessment • Prioritize • Safety • Communication required • Frequency of hospital assessment • SBAR Framework Chapter 27: The Complete Health Assessment: Adult Jarvis: Physical Examination & Health Assessment, 7th Edition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. An 85-year-old man has come in for a physical examination, and the nurse notices that he uses a cane. When documenting general appearance, the nurse should document this information under the section that covers: a. Posture. b. Mobility. c. Mood and affect. d. Physical deformity. 2. The nurse is performing a vision examination. Which of these charts is most widely used for vision examinations? a. Snellen b. Shetllen c. Smoollen d. Schwellon 3. After the health history has been obtained and before beginning the physical examination, the nurse should first ask the patient to: a. Empty the bladder. b. Completely disrobe. c. Lie on the examination table. d. Walk around the room. 4. During a complete health assessment, how would the nurse test the patient’s hearing? a. Observing how the patient participates in normal conversation b. Using the whispered voice test c. Using the Weber and Rinne tests d. Testing with an audiometer 5. A patient states, “Whenever I open my mouth real wide, I feel this popping sensation in front of my ears.” To further examine this, the nurse would: a. Place the stethoscope over the temporomandibular joint, and listen for bruits. b. Place the hands over his ears, and ask him to open his mouth “really wide.” c. Place one hand on his forehead and the other on his jaw, and ask him to try to open his mouth. d. Place a finger on his temporomandibular joint, and ask him to open and close his mouth. 6. The nurse has just completed an examination of a patient’s extraocular muscles. When documenting the findings, the nurse should document the assessment of which cranial nerves? a. II, III, and VI b. II, IV, and V c. III, IV, and V d. III, IV, and VI 7. A patient’s uvula raises midline when she says “ahh,” and she has a positive gag reflex. The nurse has just tested which cranial nerves? a. IX and X b. IX and XII c. X and XII d. XI and XII 8. During an examination, the nurse notices that a patient is unable to stick out his tongue. Which cranial nerve is involved with the successful performance of this action? a. I b. V c. XI d. XII 9. A patient is unable to shrug her shoulders against the nurse’s resistant hands. What cranial nerve is involved with successful shoulder shrugging? a. VII b. IX c. XI d. XII 10. During an examination, a patient has just successfully completed the finger-to-nose and the rapid-alternating-movements tests and is able to run each heel down the opposite shin. The nurse will conclude that the patient’s __________ function is intact. a. Occipital b. Cerebral c. Temporal d. Cerebellar 11. When the nurse performs the confrontation test, the nurse has assessed: a. Extraocular eye muscles (EOMs). b. Pupils (pupils equal, round, reactive to light, and accommodation [PERRLA]). c. Near vision. d. Visual fields. 12. Which statement is true regarding the complete physical assessment? a. The male genitalia should be examined in the supine position. b. The patient should be in the sitting position for examination of the head and neck. c. The vital signs, height, and weight should be obtained at the end of the examination. d. To promote consistency between patients, the examiner should not vary the order of the assessment. 13. Which of these is included in an assessment of general appearance? a. Height b. Weight c. Skin color d. Vital signs 14. The nurse should wear gloves for which of these examinations? a. Measuring vital signs b. Palpation of the sinuses c. Palpation of the mouth and tongue d. Inspection of the eye with an ophthalmoscope 15. The nurse should use which location for eliciting deep tendon reflexes? a. Achilles b. Femoral c. Scapular d. Abdominal 16. During an inspection of a patient’s face, the nurse notices that the facial features are symmetric. This finding indicates which cranial nerve is intact? a. VII b. IX c. XI d. XII 17. During inspection of the posterior chest, the nurse should assess for: a. Symmetric expansion. b. Symmetry of shoulders and muscles. c. Tactile fremitus. d. Diaphragmatic excursion. 18. During an examination, the patient tells the nurse that she sometimes feels as if objects are spinning around her. The nurse would document that she occasionally experiences: a. Vertigo. b. Tinnitus. c. Syncope. d. Dizziness. 19. A patient tells the nurse, “Sometimes I wake up at night and I have real trouble breathing. I have to sit up in bed to get a good breath.” When documenting this information, the nurse would note: a. Orthopnea. b. Acute emphysema. c. Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea. d. Acute shortness of breath episode. 20. During the examination of a patient, the nurse notices that the patient has several small, flat macules on the posterior portion of her thorax. These macules are less than 1 cm wide. Another name for these macules is: a. Warts. b. Bullae. c. Freckles. d. Papules. 21. During an examination, the nurse notices that a patient’s legs turn white when they are raised above the patient’s head. The nurse should suspect: a. Lymphedema. b. Raynaud disease. c. Chronic arterial insufficiency. d. Chronic venous insufficiency. 22. The nurse documents that a patient has coarse, thickened skin and brown discoloration over the lower legs. Pulses are present. This finding is probably the result of: a. Lymphedema. b. Raynaud disease. c. Chronic arterial insufficiency. d. Chronic venous insufficiency. MSC: Client Needs: Safe and Effective Care Environment: Management of Care 23. The nurse notices that a patient has ulcerations on the tips of the toes and on the lateral aspect of the ankles. This finding indicates: a. Lymphedema. b. Raynaud disease. c. Arterial insufficiency. d. Venous insufficiency. 24. The nurse has just recorded a positive iliopsoas test on a patient who has abdominal pain. This test is used to confirm a(n): a. Inflamed liver. b. Perforated spleen. c. Perforated appendix. d. Enlarged gallbladder. 25. The nurse will measure a patient’s near vision with which tool? a. Snellen eye chart with letters b. Snellen “E” chart c. Jaeger card d. Ophthalmoscope 26. If the nurse records the results to the Hirschberg test, the nurse has: a. Tested the patellar reflex. b. Assessed for appendicitis. c. Tested the corneal light reflex. d. Assessed for thrombophlebitis. 27. During the examination of a patient’s mouth, the nurse observes a nodular bony ridge down the middle of the hard palate. The nurse would chart this finding as: a. Cheilosis. b. Leukoplakia. c. Ankyloglossia. d. Torus palatinus. 28. During examination, the nurse finds that a patient is unable to distinguish objects placed in his hand. The nurse would document: a. Stereognosis. b. Astereognosis. c. Graphesthesia. d. Agraphesthesia. 29. After the examination of an infant, the nurse documents opisthotonos. The nurse recognizes that this finding often occurs with: a. Cerebral palsy. b. Meningeal irritation. c. Lower motor neuron lesion. d. Upper motor neuron lesion. 30. After assessing a female patient, the nurse notices flesh-colored, soft, pointed, moist, papules in a cauliflower-like patch around her introitus. This finding is most likely: a. Urethral caruncle. b. Syphilitic chancre. c. Herpes simplex virus. d. Human papillomavirus. 31. While recording in a patient’s medical record, the nurse notices that a patient’s Hematest results are positive. This finding means that there is(are): a. Crystals in his urine. b. Parasites in his stool. c. Occult blood in his stool. d. Bacteria in his sputum. 32. While examining a 48-year-old patient’s eyes, the nurse notices that he had to move the handheld vision screener farther away from his face. The nurse would suspect: a. Myopia. b. Omniopia. c. Hyperopia. d. Presbyopia. Chapter 29: Bedside Assessment of the Hospitalized Patient Jarvis: Physical Examination & Health Assessment, 7th Edition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. At the beginning of rounds when entering the room, what should the nurse do first? a. Check the intravenous (IV) infusion site for swelling or redness. b. Check the infusion pump settings for accuracy. c. Make eye contact with the patient, and introduce him or herself as the patient’s nurse. d. Offer the patient something to drink. 2. During an assessment, the nurse is unable to palpate pulses in the left lower leg. What should the nurse do next? a. Document that the pulses are nonpalpable. b. Reassess the pulses in 1 hour. c. Ask the patient turn to the side, and then palpate for the pulses again. d. Use a Doppler device to assess the pulses. 3. During a morning assessment, the nurse notices that a patient’s urine output is below the expected amount. What should the nurse do next? a. Obtain an order for a Foley catheter. b. Obtain an order for a straight catheter. c. Perform a bladder scan test. d. Refer the patient to an urologist. 4. What should the nurse assess before entering the patient’s room on morning rounds? a. Posted conditions, such as isolation precautions b. Patient’s input and output chart from the previous shift c. Patient’s general appearance d. Presence of any visitors in the room 5. The nurse has administered a pain medication to a patient by an IV infusion. The nurse should reassess the patient’s response to the pain medication within _____ minutes. a. 5 b. 15 c. 30 d. 60 6. During an assessment of a hospitalized patient, the nurse pinches a fold of skin under the clavicle or on the forearm to test the: a. Mobility and turgor. b. Patient’s response to pain. c. Percentage of the patient’s fat-to-muscle ratio. d. Presence of edema. 7. When assessing the neurologic system of a hospitalized patient during morning rounds, the nurse should include which of these during the assessment? a. Blood pressure b. Patient’s rating of pain on a scale of 1 to 10 c. Patient’s ability to communicate d. Patient’s personal hygiene level 8. When assessing a patient’s general appearance, the nurse should include which question? a. Is the patient’s muscle strength equal in both arms? b. Is ptosis or facial droop present? c. Does the patient appropriately respond to questions? d. Are the pupils equal in reaction and size? 9. When assessing a patient in the hospital setting, the nurse knows which statement to be true? a. The patient will need a brief assessment at least every 4 hours. b. The patient will need a consistent, specialized examination every 8 hours that focuses on certain parameters. c. The patient will need a complete head-to-toe physical examination every 24 hours. d. Most patients require a minimal examination each shift unless they are in critical condition. 10. The nurse is giving report to the next shift and is using the situation, background, assessment, recommendation (SBAR) framework for communication. Which of these statements reflects the Background portion of the report? a. “I’m worried that his gastrointestinal bleeding is getting worse.” b. “We need an order for oxygen.” c. “My name is Ms. Smith, and I’m giving the report on Mrs. X in room 1104.” d. “He is 4 days postoperative, and his incision is open to air.” MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1. The nurse is assessing the IV infusion at the beginning of the shift. Which factors should be included in the assessment of the infusion? Select all that apply. a. Proper IV solution is infusing, according to the physician’s orders. b. The IV solution is infusing at the proper rate, according to physician’s orders. c. The infusion is proper, according to the nurse’s assessment of the patient’s needs. d. Capillary refill in the fingers is checked and noted. e. The IV site date is noted. f. Whether the patient is sufficiently voiding is noted. 2. The nurse is completing an assessment on a patient who was just admitted from the emergency department. Which assessment findings would require immediate attention? Select all that apply. a. Temperature: 38.6° C b. Systolic blood pressure: 150 mm Hg c. Respiratory rate: 22 breaths per minute d. Heart rate: 130 beats per minute e. Oxygen saturation: 95% f. Sudden restlessness [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 92 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jan 29, 2020
Number of pages
92
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jan 29, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
267




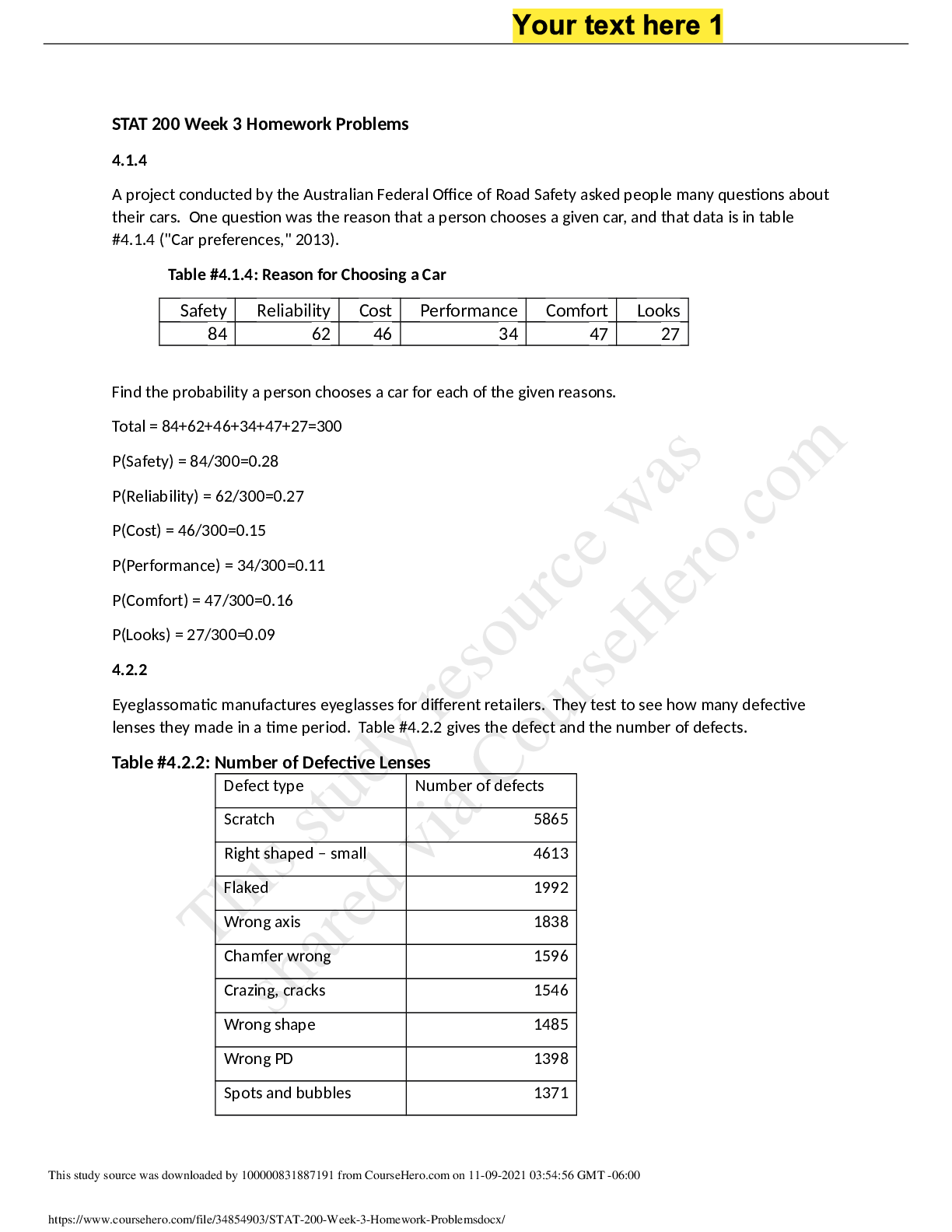





.png)

.png)


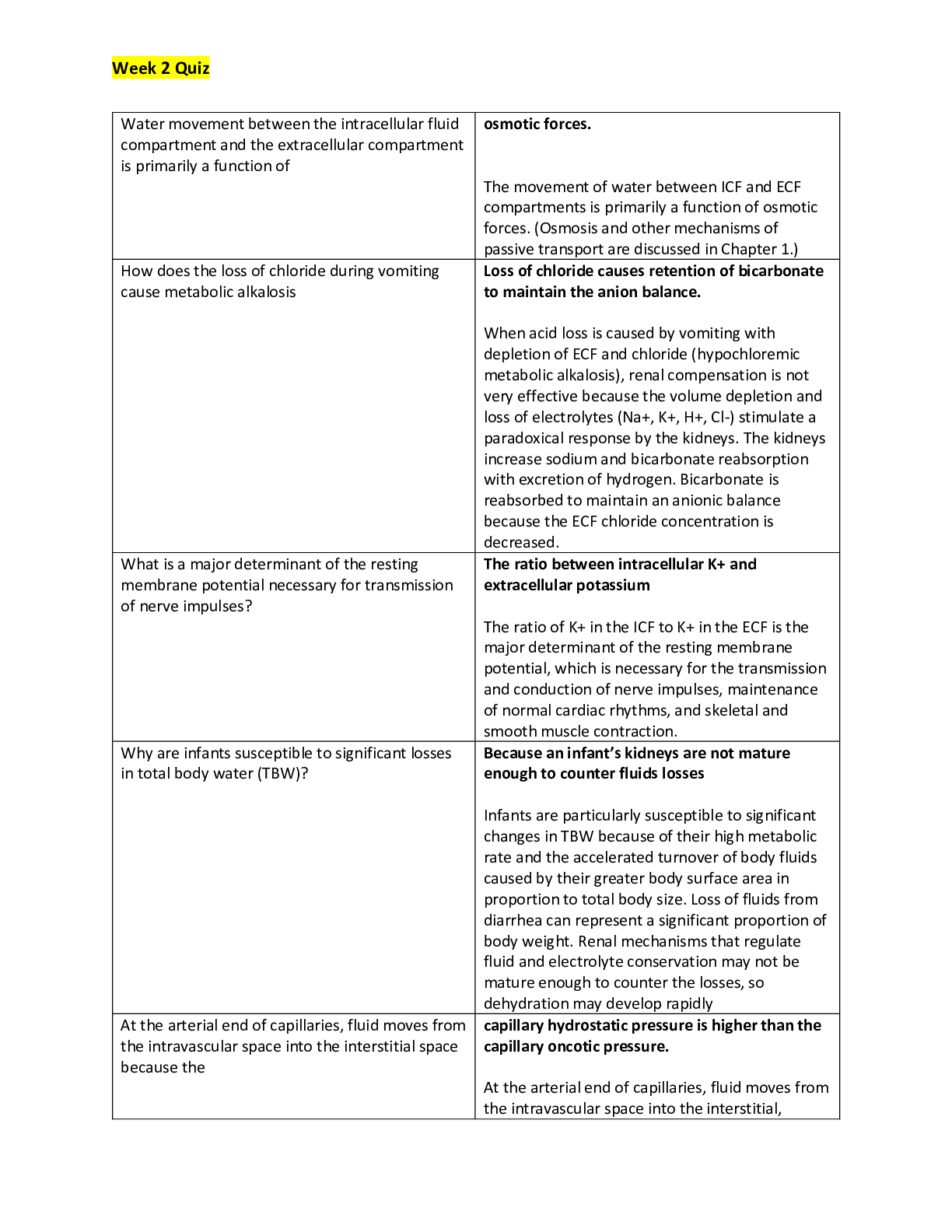






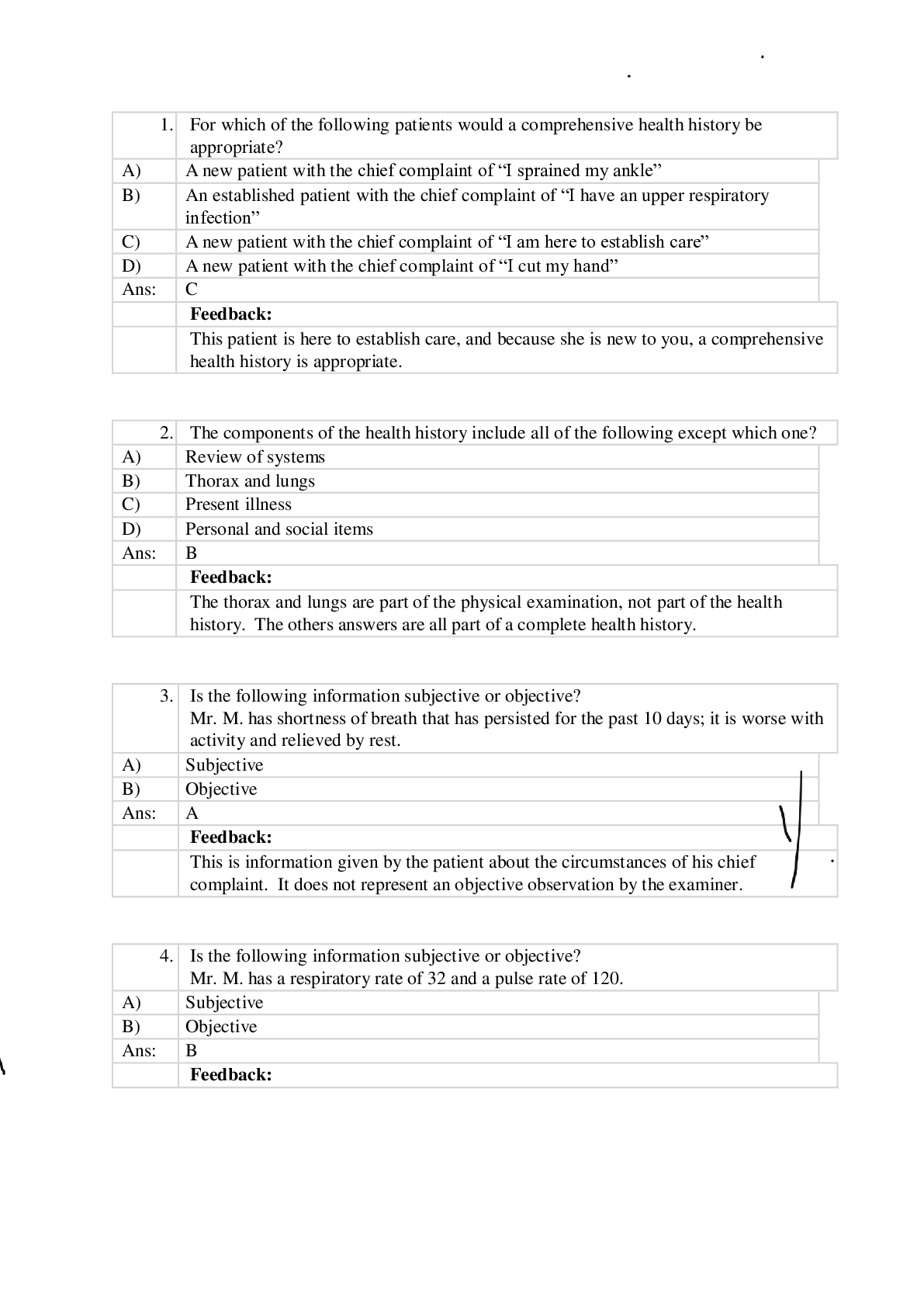
.png)



, Latest Questions and Answers with Explanations, All Correct Study Guide, Download to Score A.png)




.png)
.png)


