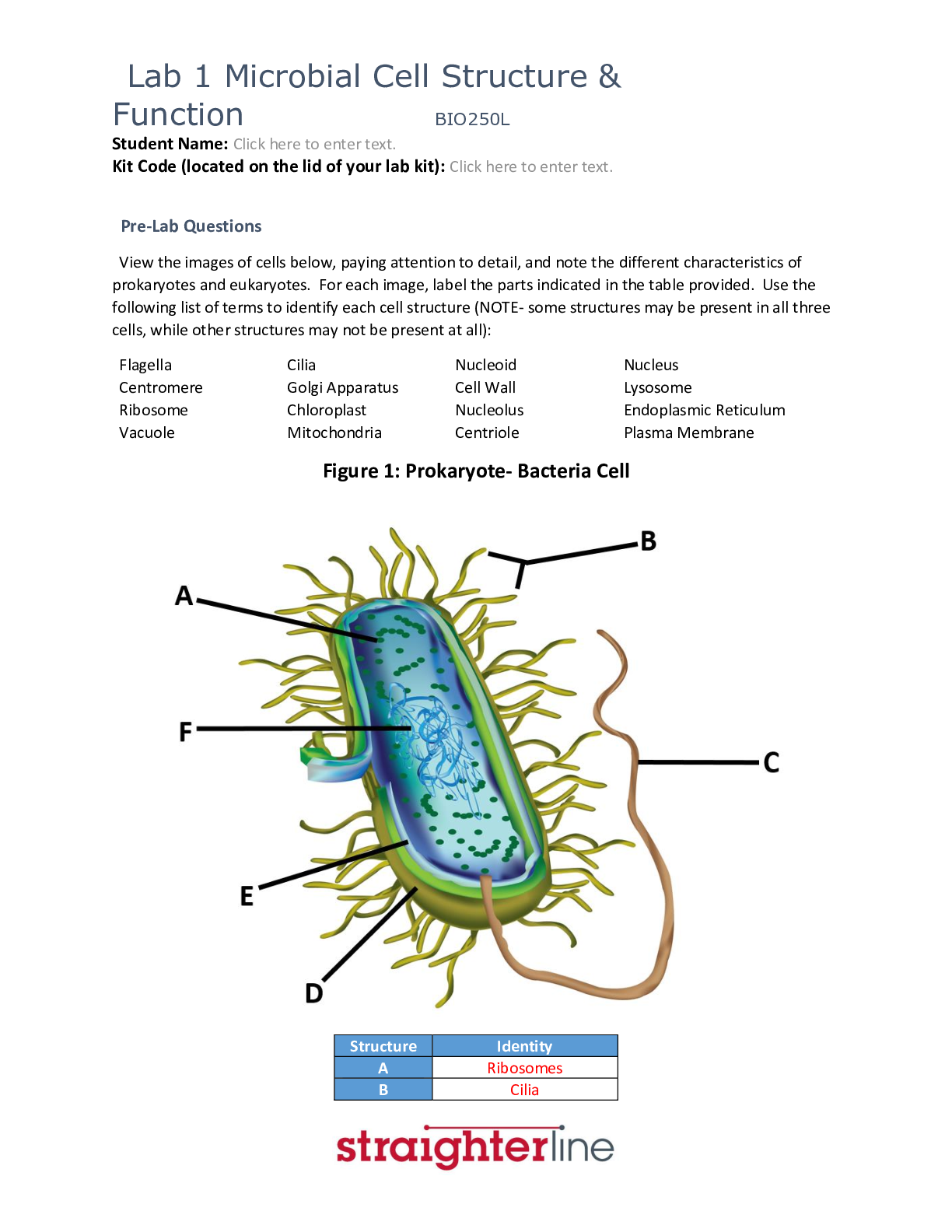
Chapter 2 Microbial Cell Structure and Function ,100% CORRECT
Document Content and Description Below
1) An organism of the genus Staphylococcus is ________, while an organism of the genus Spirochaeta is ________. A) spherical / rod shaped B) rod shaped / coiled C) spherical / coiled D) coiled / s... pherical 2) Bacteria with type IV pili A) possess tubular or stalk-like extensions of their cells. B) likely exhibit twitching motility. C) have capsules that promote dehydration. D) live in aquatic environments. Bloom's Taxonomy: Comprehension Chapter Section: 2.13 3) The terms "run" and "tumble" are generally associated with A) eukaryotic cells. B) nutrient transport. C) chemotaxis. D) clustering of certain rod-shaped bacteria. Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge Chapter Section: 2.17 4) The morphology of a cell influences its A) motility. B) metabolism. C) surface-to-volume ratio. D) motility and surface-to-volume ratio. Bloom's Taxonomy: Comprehension Chapter Section: 2.5 5) Compared to Eukaryotes, Bacteria and Archaea have ________ surface-to-volume ratios, causing ________ nutrient exchange and growth rates. A) lower / lower B) lower / higher C) higher / lower D) higher / higher Bloom's Taxonomy: Application Chapter Section: 2.6 6) The cytoplasmic membrane could best be described as A) an impermeable barrier. B) a passive conduit for intracellular transport. C) a highly selective permeability barrier. D) a rigid structure that protects the cell. Bloom's Taxonomy: Comprehension Chapter Section: 2.9 7) The use of the Gram stain in microbiology is important because it differentiates A) Bacteria from Archaea. B) prokaryotic from eukaryotic cells. C) bacterial cells with different types of cell walls. D) archaeal cells with different types of metabolism. Bloom's Taxonomy: Comprehension Chapter Section: 2.7 8) Some archaea have unique phospholipids in their cytoplasmic membrane that A) form a monolayer due to the presence of diglycerol tetraethers. B) form a bilayer due to the presence of sterols. C) form a stable ring structure due to the presence of crenarchaeol. D) form a bilayer due to the presence of phosphatidylethanolamine. Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge Chapter Section: 2.7 9) Carrier-mediated transport is necessary when A) diffusion will not allow adequate amounts of a substance to enter the cell. B) movement into the cell is against a concentration gradient. C) the level of nutrients in nature is very low. D) nutrient concentration is very low in the environment, is higher inside of the cell, or diffusion is not possible. Bloom's Taxonomy: Comprehension Chapter Section: 2.6 10) Nutrient transport requires energy because the nutrients must be transported into the cell against a concentration gradient. The energy required for nutrient transport is supplied by A) ATP. B) the proton motive force. C) phosphoenol pyruvate. D) ATP, the proton motive force, or phosphoenol pyruvate. Bloom's Taxonomy: Comprehension Chapter Section: 2.9 11) You have discovered a new microorganism, but you want to know if it is a eukaryote or a prokaryote. To investigate this question you prepare a slide with a simple stain and view it with a light microscope with a 40X objective lens and 10X ocular lens. You also prepare a control slide using Saccharomyces cerevisiae (a unicellular eukaryote). You can see the cells on your control slide, but you don't see cells when you look at your unknown microorganism. What can you conclude from this experiment? A) The experiment failed to visualize the organism because the stain killed it. B) Your new unknown microorganism is probably a virus. C) The cells of the new unknown microorganism may be too small to see with the objective and ocular lenses you used. D) The new unknown microorganism is probably an archaeon. 12) Bacteria stain as gram-positive or gram-negative because of differences in the cell A) wall. B) cytoplasm. C) nucleus. D) chromosome. 13) You are given an electron micrograph of a bacterial cell. In the micrograph you can clearly see three thin layers of different densities surrounding the cell. Based on the micrograph, you can infer that this cell is ________ and would appear ________ after application of the Gram stain procedure. A) gram-positive / purple B) gram-negative / pink C) gram-positive / pink D) gram-negative / purple 14) In gram-positive Bacteria, the cell walls are composed mainly of thick ________ layers. A) protein B) poly-β-hydroxybutryic acid (PHB) C) lipopolysaccharides (LPS) D) peptidoglycan 15) You have discovered a new coccoid-shaped microorganism with no nucleus, a rigid cell wall, and a diameter of 2 µm. Chemical tests reveal that its cell wall does NOT contain peptidoglycan. The new microorganism is A) most likely a bacterium. B) most likely a eukaryote. C) most likely an archaeon. D) either a bacterium or an archaeon. 16) The lipopolysaccharide (LPS) layer is found ONLY in the cell walls of A) gram-positive Bacteria. B) gram-negative Bacteria. C) Archaea. D) Eukarya. 17) An endotoxin is A) the toxic portion of the LPS. B) a toxin produced within archaeal cells. C) a toxin known for its primary attack on the epidermis of mammals. D) a toxin produced in the periplasm of most bacteria. 18) Hydrolytic enzymes function in the A) initial degradation of nutrients. B) transport of substrates within the cell. C) chemotactic response, particularly in gram-negative Bacteria. D) regeneration of the periplasm. 19) Using phase contrast microscopy on a wet mount of live cells, you observe motile bacilli moving rapidly and randomly through the field of view, changing directions after a brief tumble and taking off in a different direction. These cells are exhibiting ________ motility. A) twitching B) swimming C) gliding D) twitching or gliding 20) Which of the following statements is FALSE? A) A flagellar protein subunit is flagellin. B) In flagellar motion, the basal body acts as a motor. C) Flagellar rotation generates ATP. D) The hook is the wider region at the base of the flagellum. 21) Which of the following statements is TRUE? A) Fimbriae are generally shorter and more numerous than flagella. B) Fimbriae enable cells to stick to surfaces. C) Pili serve as receptors and facilitate genetic exchange between prokaryotic cells. D) Fibriae are usually shorter than flagella and enable cells to adhere to surfaces, whereas pili are involved in genetic exchange. 22) Cellular inclusions in prokaryotic cells serve to A) store energy rich compounds. B) protect DNA. C) position cells in the appropriate environment for survival. D) store energy rich compounds and position cells in the appropriate environment for survival. 23) A major function of prokaryotic gas vesicles is to A) confer buoyancy on cells by decreasing their density. B) serve as a reservoir for oxygen and carbon dioxide. C) keep the cell's organelles separated during flagellar motion. D) store oxygen for aerobic growth when oxygen becomes depleted in the environment. 24) The membrane of a gas vesicle is composed of A) various phospholipids. B) proteins. C) carbohydrates. D) both glycoproteins and phospholipids. 25) What is the biological function of endospores? A) They are bacterial reproductive structures. B) They enable organisms to endure extremes of temperature, drying, and nutrient depletion. C) They transport toxins. D) Endospores can serve as reproductive structures, enable survival in harsh environments, and transport toxins. 26) The lipids in the cytoplasmic membrane of Bacteria and ________ contain ester linkages, while the cytoplasmic membrane of ________ contain ether linkages. A) Archaea / Eukarya B) Archaea / fungi C) Eukarya / prokaryotes D) Eukarya / Archaea 27) Aquaporins are A) water transport proteins. B) molecules that prevent water from crossing a membrane. C) enzymes involved in the generation of water within cells. D) cations bound to water molecules. 28) Electron microscopy has greater ________ than light microscopy, because the wavelengths of visible light are much larger than the wavelengths of electrons. A) contrast B) magnification C) resolution D) penetration 29) The prokaryotic transport system that involves a substrate-binding protein, a membrane-integrated transporter, and an ATP-hydrolyzing protein is A) the ABC transport system. B) group translocation. C) symport. D) simple transport. 30) ________ are charged molecules that are partially responsible for the ________ charge of the gram-positive bacterial cell surface. A) Diaminopimelic acids / positive B) Teichoic acids / negative C) Phospholipids / negative D) Peptide interbridges / neutral 31) Although the inner leaflet of the gram-negative outer membrane is composed mainly of phospholipids, the outer leaflet of the outer membrane contains A) pseudopeptidoglycans. B) lipoteichoic acids. C) poly-β-hydroxybutyric acids (PHB). D) lipopolysaccharides (LPS). 32) One of the many types of proteins found in the cytoplasmic membrane is involved in the chemotactic response and is called a A) hydrolytic enzyme. B) chemoreceptor. C) binding protein. D) porin. 33) When does endospore formation commence? A) when bacterial growth ceases due to limitation of an essential nutrient B) when the bacterium is undergoing binary fission C) when bacteria are dividing exponentially D) following bacterial death 34) Which is/are a function(s) of the cytoplasmic membrane in prokaryotes? A) It functions as a permeability barrier. B) It is an anchor for many proteins involved in bioenergetic reactions and transport. C) It is a major site of energy conservation. D) It serves as a permeability barrier, a docking station for proteins involved in bioenergetics reactions and transport, and a site for energy conservation. 35) All eukaryotes contain A) a membrane-enclosed nucleus. B) mitochondria. C) hydrogenosomes. D) a nucleus, mitochondria, and hydrogenosomes. 36) Mitochondria and hydrogenosomes are similar in that they both A) are the site of energy production in eukaryotic cells. B) evolved via endosymbiosis of bacterial cells. C) are the site of aerobic respiration. D) evolved via endosymbiosis and are sites for aerobic respiration and energy production. 37) Membrane-enclosed organelles, such as nuclei, lysosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, and chloroplasts, A) form specialized compartments within eukaryotic cells for specific functions to occur. B) increase the structural complexity of eukaryotic cells. C) help large eukaryotic cells overcome the limitations of diffusion imposed by their large cell size. D) increase structural complexity, help eukaryotes overcome diffusion limitation due to their size, and form specialized environments for specific functions to occur. 38) The Golgi complex functions to A) modify and secrete proteins to the external environment. B) sort proteins used within the cell. C) both modify and sort proteins into those destined for secretion and those that function in membrane structures. D) synthesize proteins. 39) The membrane-enclosed compartments that contain digestive enzymes in eukaryotic cells are called A) cristae. B) mitosomes. C) lysosomes. D) stromas. 40) Where within a eukaryotic cell is ribosomal RNA (rRNA) synthesized? A) cytoplasm B) lysosome C) mitochondrion D) nucleolus 41) The energy source derived from the charge separation across the cytoplasmic membrane is referred to as A) the proton motive force. B) carbohydrate charging. C) adenosine triphosphate. D) the voltage source. 42) Based on the table of attributes given below, which of the following statements are FALSE about the two organisms? Characteristic Bacterium A Bacterium B Endospore formation yes no Capsule no yes Type IV pili yes no Flagella no no Morphology bacillus bacillus A) Bacterium A is more resistant to heat and ultraviolet light. B) Bacterium B likely forms a slime layer better than Bacterium A. C) Bacterium B is likely to exhibit motility. D) Both bacteria may attach to surfaces. 43) Small acid-soluble proteins (SASPs) protect DNA from ultraviolet light and are found in high numbers within A) gram-positive Bacteria. B) endospores. C) inclusion bodies. D) gram-negative Bacteria. 44) The peptide interbridge crosslinking between peptidoglycan layers is found ONLY in the cell walls of A) Archaea. B) Eukarya. C) gram-positive Bacteria. D) gram-negative Bacteria. 45) Type IV pili are involved in A) attachment of cells to surfaces. B) twitching motility. C) pathogenesis. D) attachment to surfaces, twitching motility, and pathogenesis. 46) Eukaryotes have ________ in their cytoplasmic membranes, which serve to strengthen and stabilize the membrane and make it less flexible. Many bacteria have similar molecules, known as ________, in their cytoplasmic membranes that have a similar role. A) ether bonds / ester bonds B) lipids / phospholipids C) sterols / hopanoids D) phospholipids / lipopolysaccharides 47) The rigid layer that is present in the cell walls of Bacteria that is primarily responsible for the strength of the wall is known as A) pseudomurein. B) S-layer. C) cellulose. D) peptidoglycan. 48) Some of the intestinal symptoms elicited by pathogens such as Salmonella, Shigella, and Escherichia are due to the presence of A) pseudomurein. B) S-layers. C) lipopolysaccharides. D) peptidoglycan. 49) Which of the following types of microscopy can be used with live cells? A) phase-contrast microscopy B) transmission electron microscopy C) bright-field microscopy D) scanning electron microscopy 50) Which of the following types of microscopy could be used to visualize the layers of the cell membrane and the cell wall? A) phase-contrast microscopy B) transmission electron microscopy C) bright-field microscopy D) confocal microscopy 51) Using bright-field microscopy to look at a slide prepared with a basic dye you observe cells under 400X magnification with a clear inner compartment within the cell. The cell is most likely a(n) A) prokaryote. B) bacterium. C) archaeon. D) eukaryote. True/False Questions 1) In general, most cell inclusions function as energy reserves or as a reservoir of structural building blocks. 2) Smaller prokaryotic cells generally grow faster than larger ones due to a higher surface-area-to-volume ratio. 3) In general, lipids in archaeal cytoplasmic membranes lack true fatty acids. 4) Some membrane proteins are involved in bioenergetic reactions, while others are involved in membrane transport. 5) Both hydrophilic and charged molecules readily diffuse through the cytoplasmic membrane. 6) ATP-binding cassette transport systems have high substrate affinity and thus help microorganisms survive in low nutrient environments. 7) Teichoic acids are commonly found in gram-negative cell walls. 8) Despite the invariance of the peptidoglycan backbone's structure, there are more than 100 different types of peptidoglycan. 9) Lysozyme is an enzyme that can ultimately lyse and kill eukaryotic cells by breaking β-1,4-glycosidic bonds in peptidoglycan. 10) Porins are channels in the outer membranes of gram-positive Bacteria. 11) A bacterial cell is interpreted as gram-positive when it forms purple insoluble crystal violet-iodine complexes within the cell during the Gram stain. 12) In general, swimming is performed with flagella, whereas gliding uses other cellular components such as pili. 13) Chemotaxis is a sensory response affecting the rotational direction of the flagellar motor. 14) Photoreceptors are analogous to chemoreceptors in that they are both proteinaceous sensors. 15) Pathogenic bacteria that contain S-layers are protected against host defense mechanisms. 16) Poly-β-hydroxybutyric acid (PHB) is a carbon- and energy-storing polymer. 17) Mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own DNA and ribosomes, which supports the endosymbiosis hypothesis. 18) Macromolecules resulting from lysosomal digestion are used in cellular biosynthesis and energy generation. 19) Electron microscopes have less resolving power than light microscopes. Essay Questions 1) Why is energy required for nutrient transport? Give an example of a system that transports nutrients and describe what source of energy is used to move the nutrients into the cell. 2) Describe the makeup of the phospholipid bilayer. Include molecular orientation and proteins as well. 3) Compare and contrast the chemical composition and structure of the cytoplasmic membranes found in Bacteria and Archaea. What is the advantage of the archaeal membranes in relationship to the types of environments many archaea inhabit? 4) Explain the differences between uniporters, symporters, and antiporters. 5) You are studying swimming motility in a pathogenic bacillus. You create mutations in random genes and then test which mutations effect swimming motility by looking at the mutant cells under the microscope. One of the mutant bacteria can not swim anymore, but still rotates around in a one spot when you watch them. Using electron microscopy you discover that some parts of the flagella are still present in the cell wall, but no long flagella are visible. Which gene do you think is mutated (i.e., missing) and which motility-related parts are still present in this mutant? 6) Describe the mechanisms by which certain prokaryotes glide. What are the ecological advantages of gliding motility? 7) What is the function of an endospore and how is an endospore formed? 8) What type of microscope would you use to visualize the internal structures of a chloroplast? Support your conclusion with evidence based on the size of the structures you want to see and the resolution and magnification power of different types of microscopes. 9) You have discovered a new bacterial strain that causes urinary tract infections. Closely related bacterial species cannot cause infections. You compare the strains and find that your new strain has structures composed of protein external to its cell wall. What structures might your new strain have that the other strains do not? Why? 10) Construct a chart to show at least five major differences between the cytoplasmic membrane and cell wall of bacteria and archaea. What are the implications of these differences? 11) Explain why prokaryotes tend to survive and adapt more rapidly to extreme and dynamic environmental conditions than eukaryotes. 12) Compare and contrast the location and activities of periplasm-binding proteins of ABC transport systems in gram-negative and gram-positive Bacteria. 13) Elaborate on why discovering endospores was important to microbiology. 14) Predict what would happen to a motile bacterium undergoing chemotaxis if the Mot proteins suddenly ceased to function. 15) Explain why a eukaryotic cell needs membrane-enclosed lysosomes and peroxisomes. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 36 pages
.png)
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jan 03, 2021
Number of pages
36
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jan 03, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
25