*NURSING > CASE STUDY > CCHT Practice Questions (CCHT Practice Tests & Exam Review for the CCHT Exam) Part 1 (unanswered) (All)
CCHT Practice Questions (CCHT Practice Tests & Exam Review for the CCHT Exam) Part 1 (unanswered)
Document Content and Description Below
CCHT Practice Questions Part 1 1. Which of the following terms indicate a solution that has the same concentration of solutes as blood? a. Atonic b. Isotonic c. Hypotonic d. Hypertonic 2. A pa... tient’s potassium level has been running high between dialysis treatments, so the patient has been working with the renal dietician to restrict potassium in the diet. Which of the fruits should the patient avoid? a. Bananas b. Apples c. Strawberries d. Grapes 3. During osmosis, which of the following movements takes place? a. Solutes move from an area of higher concentration to lower. b. Solutes move from an area of lower concentration to higher. c. Fluid moves from an area of higher concentration to lower. d. Fluid moves from an area of lower concentration to higher. 4. A patient’s granddaughter calls the dialysis center and asks for a progress report on her father, who is a patient in the center. The technician should a. provide the report. b. tell the daughter to ask her father. c. ask the supervisor what to do. d. state that patient information cannot be divulged. 5. If a hematoma forms at the access site where a needle infiltrated, the usual intervention is to apply a. cold compresses. b. hot compresses. c. manual pressure only. d. compression bandage. 6. Which of the following actions by a patient increases the risk of blood clots in a venous access? a. Holding a handbag in the handle on the access side b. Wearing a top with very tight-fitting long sleeves c. Exercising the arm with the access d. Using the access arm to carry out activities of daily living. 7. A patient is very anxious during initial hemodialysis treatment and requires extra attention. When the treatment is completed, the patient offers a $20 tip. The technician should Page 1 a. accept the tip. b. share the tip with other staff. c. politely decline the tip. d. donate the money to the dialysis center. 8. Which of the following statements by a hemodialysis patient suggests that the patient needs more education? a. “Avocados are high in potassium.” b. “I eat small frequent meals to control nausea.” c. “I need to limit my salt intake.” d. “I should stay on a low protein diet.” 9. The inner part of the kidney is the a. medulla. b. calyx. c. pelvis. d. glomerulus. 10. A nephron is comprise of a glomerulus and a a. pyramid. b. calyx. c. papilla. d. tubule. 11. How much urine does a patient with healthy kidneys usually excrete in 24 hours? a. 200 to 500 mL b. 500 to 1000 mL c. 1000 to 2000 mL d. 2000 to 3000 mL 12. When removing soiled gloves, the first glove removed should be a. thrown into the trash. b. grasped in the opposite gloved hand. c. placed in a hazardous waste container. d. placed into a plastic bag for disposal. 13. Which of the following hormone is produced by the kidneys? a. Erythropoietin b. Cortisol c. Aldosterone d. Parathyroid hormone 14. At which stage of chronic kidney disease should a patient begin dialysis? a. 3 b. 4 c. 5 d. 7 15. Which of the following is a genetic disorder that can lead to kidney failure? Page 2 a. Pyelonephritis b. Glomerulonephritis c. Glomerulosclerosis d. Polycystic kidney disease 16. Which of the following complaints by a patient may be an indication of uremia? a. Maculopapular rash b. Itching c. Decreased urination during the night d. Increased libido 17. A patient with a right-sided radiocephalic AV fistula (above the wrist) needs to have blood tests in the lab for a number of different lab tests. The blood should be drawn from the a. AV fistula. b. right hand. c. left antecubital (inner elbow). d. left hand. 18. When setting up hemodialysis equipment, the four things that need to be checked are (1) dialysate, (2) extracorporeal circuit, (3) dialyzer, and (4) a. machine alarms. b. portable digital alarms. c. normal saline. d. Needles. 19. Generally, the optimal dialysate flow rate for hemodialysis should be a. equal to the blood flow rate. b. 1.5 to 2 times the blood flow rate. c. 2 to 2.5 times the blood flow rate. d. 2.5 to 3 times the blood flow rate. 20. A patient is receiving hemodialysis with a dialyzer with an ultrafiltration coefficient (KUF) of 10 and a transmembrane pressure (TMP) of 100 mm Hg. How much fluid should the patient lose per hour of treatment? a. 100 mL b. 500 mL c. 1000 mL d. 1500 mL 21. If a patient has a dialyzer clearance rate of 250 mL/min with 4-hour treatment, the total volume of blood cleared is a. 6 L. b. 60 L. c. 6000 mL. d. 600 L. 22. Under what circumstance can needles be reused for hemodialysis? Page 3 a. After washing and microwaving b. After washing and soaking in alcohol c. After washing and dry-heat sterilization d. Under no circumstances 23. If an emergency (such as a tornado) occurs and patients need to be evacuated, which group of patients should be disconnected from dialysis machines first? a. Patients able to ambulate independently b. Patients furthest from the exit c. Patients who can ambulate with assistance d. Patients who are unable to ambulate 24. For patients on hemodialysis, a 1 kg (2.2 lb.) increase in weight in 24 hours is approximately equivalent to fluid retention of a. 0.5 L b. 1.0 L c. 1.5 L d. 2. 0 L 25. A patient has been advised to avoid foods high in phosphorus. Foods that the patient should be advised to limit include a. dairy products. b. vegetables. c. fruits. d. grains. 26. A patient is scheduled for a serum creatinine test and asks the technician about preparation the day before the test. The patient should be advised to a. avoid excessive exercise. b. avoid food and fluids for 12 hours. c. drink 3 to 4 glasses of water. d. avoid fluids for 6 hours. 27. Which of the following ethnic groups is most at risk for development of kidney failure? a. Caucasians b. Hispanic Americans c. Asians d. African Americans 28. A patient has buttonhole tracts for access. After the access is cleaned and prepped for treatment, what is the next step? a. Insert sharp needles into the tracts. b. Insert blunt needles into the tracts. c. Use a scab picker/aseptic tweezers to remove the scabs. d. Use the treatment needle to remove the scabs. 29. With buttonhole tracts, the technician should apply pressure as the needles are Page 4 removed and than for a. 1 to 2 minutes. b. 5 to 10 minutes. c. 10 to 20 minutes. d. 20 to 30 minutes. 30. If a buttonhole access frequently has long clots that are very difficult to remove, the most likely reason is a. subclinical infection. b. use of improper needle. c. failure to use 2-finger hold for needle removal. d. failure to adequately remove previous clot before cannulation. 31. A patient who had an AV fistula in the forearm developed an aneurysm and has had to have a new AV fistula created in the upper arm. The patient has a temporary catheter in place for dialysis until the fistula has matured. Which of the following exercises may help strengthen the AV fistula? a. Ball squeeze b. Thumb-fingertip touch c. Grasp/Squeeze clothespin d. Bicep curl 32. With buttonhole access sites, what should the technician do to prevent “hubbing”? a. Leave 1/16th to 1/8th inch of the needle exposed. b. Insert the needle just to the hub. c. Use a sharp needle to remove scabs. d. Use a long catheter so the hub is not close to the site. 33. What is the most important factor in preventing exsanguination from dialysis line separation? a. Functioning venous alarm b. Access site visibility c. Use of HemaClip d. Patient education 34. If a patient states that she has been skipping lunch because she is too tired to eat after dialysis, the best solution is to a. encourage diet supplements. b. advise the patient of the importance of eating. c. advise the patient to eat a very large breakfast. d. report this to the nurse and renal dietitian. 35. If a patient exhibits signs and symptoms of hemolysis during dialysis, the immediate action should be to a. slower the blow flow rate to less than 4000 mL/min. b. administer normal saline. c. stop the blood pump and clamp the blood lines. Page 5 d. monitor electrolytes. 36. The amount of dialysis that a hemodialysis patient is prescribed based on the removal of a. urea. b. creatinine. c. potassium. d. albumin. 37. Maturation of a prosthetic arteriovenous graft usually takes a. 1 to 2 weeks. b. 3 to 6 weeks. c. 1 to 2 months. d. 2 to 4 months. 38. The purpose of the negative germicide test is to ensure that a. the surface of the equipment has been adequately disinfected. b. the surface of the equipment has been rinsed of disinfectant. c. the reprocessed dialyzer contains germicide. d. the reprocessed dialyzer is free of germicides. 39. If a patient develops angina (chest pain) radiating to the neck, jaw, and left arm and the patient's blood pressure drops during treatment, the technician should notify the nurse and a. increase blood flow rate and ultrafiltration rate. b. advise patient to take deep breaths and relax. c. decrease blood flow rate and ultrafiltration rate. d. stop dialysis and clamp all line. 40. The technician is reinforcing a patient's training regarding management of fluid intake. The patient, who still urinates, has a base line of 1000 mL intake per day. If the patient urinates 500 mL in a 24-hour period, how much fluid is the patient allowed the following day? a. 1500 mL b. 1400 mL c. 1250 mL d. 1000 mL 41. The greatest risk of bacteremia (infection in the blood) is associated with which type of vascular access? a. Primary arteriovenous fistula b. Arteriovenous graft (biologic) c. Dialysis Catheter d. Arteriovenous graft (synthetic) 42. The external surface of the hemodialysis machine should be cleaned and disinfected at least a. every 8 hours. Page 6 b. every 24 hours. c. after every patient. d. after every 2 patients. 43. When checking the water temperature in the water system, the technician records the temperature at 78°F (25.5° C). In order for the reverse osmosis (RO) equipment that is part of the water treatment system to work properly, the water temperature must be maintained at a. 74°F to 76°F (23°C to 24.4°C). b. 77°F to 82°F (25°C to 28°C). c. 83°F to 86°F (28.3°C to 30°C). d. 87°F to 90°F (30.5°C to 32.2°C). 44. When testing the total chlorine levels in the water system, the water system, the water sample should be taken from the a. first carbon tank. b. second carbon tank. c. either carbon tank. d. reverse osmosis tank. 45. When considering the chain of infection, the three most common reservoirs of interest include humans, environment and a. vectors. b. water. c. air. d. animals. 46. A solution is a mixture of a. solute and solvent. b. solute and chemical. c. water and electrolytes. d. fluid and particles. 47. When reinforcing education about weight gain, a patient should be advised that the usual goal for interdialytic gain is less than a. 0.5 kg/d. b. 1.0 kg/d. c. 1.5 kg/d. d. 2.0 kg/d. 48. If a high-pressure alarm for arterial pressure (pre-pump) should during hemodialysis, this could indicate a. vasoconstriction. b. drop in speed of blood pump. c. kink in arterial bloodline. d. infiltration of arterial needle. 49. If a low-pressure alarm for venous pressure sounds during hemodialysis, this could Page 7 indicate a. infiltration of the venous needle. b. clotting in the access. c. poorly functioning central catheter. d. clotted dialyzer. 50. According to KDOQI guidelines, when administering hemodialysis to a patient, a facemask should be worn a. for all access connections. b. if the nurse has a cough. c. if the patient has a cough. d. to discontinue the hemodialysis. 51. The most common complication associated with poor needle site rotation in a graft is a. hematoma. b. infection. c. thrombosis. d. pseudoaneurysm. 52. In hemodialysis, ultrafiltration refers to extraction of a. electrolytes. b. proteins. c. fluid. d. wastes/toxins. 53. The patient has developed a small aneurysm and asks the technician to cannulate the aneurysm for the hemodialysis treatment because another patient told this patient that it would be less painful that cannulation of the fistula. The best response is to a. agree to cannulate the aneurysm. b. tell the patient that there is no reduced pain if cannulating the aneurysm. c. advise the patient that cannulating an aneurysm may result in rupture. d. tell the patient that the other patient was wrong. 54. A patient experiences a cardiac arrest with no pulse or respirations during hemodialysis. After the technician calls for help, the next action should be to a. stop dialysis, return blood, and flush access lines with normal saline. b. stop dialysis and clamp all lines without returning blood. c. continue dialysis without change during resuscitation. d. stop dialysis, return blood, and remove access needles. 55. When auscultating a patient's AV fistula to listen for the bruit, if the technician notes that the bruit is very high pitched, this may indicate a. normal functioning. b. collateral circulation. c. stenosis. Page 8 d. inadequate anastomosis. 56. When using the buttonhole technique for vascular access for hemodialysis, the needles are placed in a. the same sites in a graft. b. rotating sites in a graft. c. rotating sites in a fistula. d. the same sites in a fistula. 57. When inserting a needle for hemodialysis, which of the following increases of infiltration? a. Rotating the needle 180 degrees b. Flushing the needle with NS after insertion c. Leveling the needle to the surface of the skin to advance d. Using a wet needle for insertion 58. The legal document that assigns a healthcare proxy to make decisions in the event that a person is unable to do is called a. an advanced directive. b. a living will. c. durable power of attorney. d. DNR. 59. Carbon filters in the water system are necessary to remove a. organic materials and inorganic residue. b. electrolytes and endotoxins. c. microbial contamination. d. chlorine, chloramine, and organic materials. 60. Backwashing to free residue from sediment filters in water system should be done at least a. every 8 hours. b. once daily. c. every 4 hours. d. once weekly. 61. With the formula for urea kinetic modeling (UKM), the K in Kt/V formula stands for a. duration of minutes. b. mL of fluid in patient’s body. c. urea clearance (mL/min) plus residual urinary output. d. urea clearance (mL/min). 62. When inserting needles into a graft for hemodialysis, the needle tips should be at least how far apart? a. 1.0 inch b. 1.5 inches c. 2.0 inches d. 2.5 inches Page 9 63. If a patient is undergoing hemodialysis and the technician notes that a bloodline has separated and blood has pooled beneath the access site, the first intervention should be to a. clamp both sides of separated lines. b. stop the blood pump. c. reconnect the separated line. d. apply pressure at the outflow vein. 64. If a dialyzer is to be reprocessed in 3 hours, the dialyzer must be a. heated at body temperature (37°C). b. frozen. c. maintained at room temperature. d. refrigerated. 65. During hemodialysis, the technician would expect a patient's temperature to rise by about a. 0.5°C. b. 1.0°C. c. 1.5°C. d. 2.0°C. 66. Approximately what percentage of the total blood volume circulates in the veins? a. 40% to 50% b. 50% to 60% c. 65% to 80% d. 80% to 90% 67. Patients should be advised to avoid eating during hemodialysis because indigestion of food may result in a. hypotension. b. hypertension. c. nausea and vomiting. d. shivering and chills. 68. Prior to using a reprocessed dialyzer, a recirculating rinse with NS should be completed with recirculating flow rate through the blood dialysate compartment of at least a. 200 mL/min for BFR and DFR. b. 200 mL/min for BFR and 500 mL/min for DFR. c. 500 mL/min for BFR and 200 mL/min for DFR. d. 500 mL/min for BFR and DFR. 69. If a hemodialysis patient tests positive for hepatitis C virus (HCV), which of the following interventions does the KDIGO guidelines recommend when providing hemodialysis treatments? a. Isolation of HCV-infected patients b. Adherence to strict infection-control procedures Page 10 c. Use of dedicated dialysis machines for HCV-infected patients d. Discarding of all dialyzers rather than reusing them 70. When documenting observations about a patient, which of the following is the most appropriate description? a. “Patient is nervous and upset.” b. “Patient appears to be in a good mood today.” c. “Patient is sighing and rubbing hands together.” d. “Patient is uncooperative and belligerent.” 71. Which of the following is the most common cause of hypotension developing during hemodialysis? a. Eating/drinking during treatment b. Removing excessive volume of fluid c. Anemia d. Dialyzer Reaction 72. Which of the following interventions is most likely to decrease hypotension that occurs during hemodialysis? a. Using a different type of dialyzer b. Increasing sodium intake c. Increasing the ultrafiltration rate d. Decreasing the ultrafiltration rate 73. If an air detector alarm sounds during hemodialysis, the technician should initially a. stop the blood pump and clamp the patient’s venous line. b. check the lines for signs of air or foam. c. stop the blood pump and clamp the patient’s arterial line. d. stop the blood pump and check the lines for air or foam. 74. If outflow stenosis of an AV fistula occurs, the thrill usually a. is absent. b. remain continuous. c. is lower pitched and discontinuous. d. is loud and higher pitched and then discontinuous. 75. When reviewing a patient's food diary, the technician advise that which of the following protein sources of low biological value? a. Eggs b. Tofu c. Dried beans d. Fish 76. Which of the following vitamins may be removed by hemodialysis? a. Vitamin A b. Vitamin B c. Vitamin D d. Vitamin K Page 11 77. The renal nutritionist has advised the patient to have a dietin fiber, but the patient is unsure which foods to choose. Which of the following foods per serving is highest in insoluble fiber? a. Apple b. Kidney beans c. Oatmeal d. Broccoli 78. The primary purification process of the dialysis water system is a. deionization. b. filtering with activated carbon. c. reverse osmosis. d. addition of water softener. 79. If the dialysis center uses HemaClips on dialysis tubing to prevent disconnection, what other precautions should be utilized? a. None b. Visible access sites/line connections and documentation of integrity every 30 minutes c. Visible access sites/line connections and documentation of integrity at the initiation and termination of treatment d. Visible access sites/line connections and monitoring by patient 80. If during hemodialysis, blood is evident in the used dialysate, this probably indicates a. incorrect pressure gradient. b. patient hemorrhaging. c. incorrect dialysate formula. d. tear in the membrane. 81. If a patient asks a question to which the technician does not know the answer, an appropriate response is a. “I don’t know.” b. “I’m guessing...” c. “I’ll find out for you.” d. “You should ask the nurse.” 82. During routine hemodialysis, a patient’s blood pressure should be monitored every a. 15 to 30 minutes. b. 30 to 60 minutes. c. 60 to 90 minutes. d. before and after treatment. 83. If a patient develops painful muscle cramps in the hands, feet, and abdomen shortly after hemodialysis begins, the most likely intervention is a. saline bolus and/or decreased ultrafiltration rate. b. increased ultrafiltration rate. c. discontinuation of dialysis. Page 12 d. administration of medications. 84. If hemodialysis patient’s temperature per tympanic membrane thermometer is 37°C, in order to reduce incidence of intradialytic (during dialysis) hypotension, the temperature of the dialysate solution should ideally be set at a. 37.5°C. b. 36.5°C. c. 38°C. d. 39°C. 85. Foam in the venous bloodline of a dialyzer may indicate a. normal finding. b. sepsis. c. too rapid blood flow rate. d. air embolism. 86. Prior to initiating hemodialysis, the pH of the dialysate must be verified. The pH of dialysate usually ranges from a. 6.5 to 6.8. b. 6.8 to 7.0. c. 7.0 to 7.4. d. 7.4 to 7.6. 87. The number one cause of kidney failure in the United States is a. polycystic kidney disease. b. diabetes mellitus, type 1. c. diabetes mellitus, type 2. d. cardiovascular disease. 88. The use of topical anesthetics, such as EMLA< to reduce discomfort during cannulation is contraindicated with a. AV fistulas. b. AV grafts. c. all hemodialysis patients. d. buttonhole sites. 89. When determining if a new AV fistula is maturing, the three factors to assess by palpation are the a. thrill, vessel growth, and vessel firmness. b. pulse, sensitivity, and vessel growth. c. incision, pulse, and vessel growth. d. Incision, vessel growth, and pulse. 90. A patient who has been very alert and shown no sign of cognitive impairment seems confused during dialysis and repeatedly asks the same question. The best initial response is to a. administer the Confusion Assessment Method. b. observe the patient for further symptoms. Page 13 c. ask the patient if he has changed medications. d. notify the nurse. 91. Which of the following antiseptics used for skin prep for a fistula site has the broadest spectrum antibacterial activity? a. Povidone iodine b. 70% isopropyl alcohol c. 2% chlorhexidine gluconate d. Hydrogen peroxide 92. While a patient is undergoing hemodialysis, chloramine testing of the water system should be conducted every a. hour b. 2 hours. c. 4 hours. d. 5 hours. 93. If a patient is to undergo heparin-free dialysis, the optimal blood flow rate is a. 150 to 200 mL/min. b. 200 to 300 mL/min. c. 300 to 400 mL/min. d. 400 to 450 mL/min. 94. Before cannulating an AV fistula for a hemodialysis treatment, the technician examines the patient’s access arm and finds that the access arm appears arm appears slightly edematous, and the skin is pale. On further examination, the technician notes that there are small purple veins evident on the chest wall near where the arm meets the body. The technician should suspect a. infection. b. aneurysm. c. steal syndrome. d. stenosis. 95. In order to increase survival rates, the ultrafiltration rate for hemodialysis patients should be maintained at less than a. 9 mL/kg/m. b. 12 mL/kg/m. c. 16 mL/kg/m. d. 20 mL/kg/m. 96. As part of fistula assessment before cannulation, the technician evaluates thrill and then applies occlusion by placing a finger across the body of the fistula. While the fistula is occluded, the technician palpates and feels both a thrill and a pulse. This probably signifies a(n) a. accessory pathway (collateral circulation). b. stenosis. c. aneurysm. Page 14 d. normal finding. 97. How much additional protein should a patient on hemodialysis ingest every day in comparison to a healthy person? a. 10% b. 25% c. 50% d. 75% 98. Weight gain between hemodialysis treatments should not exceed a. 1% of dry weight. b. 5% of dry weight. c. 8% of dry weight. d. 10% of dry weight. 99. The technician has calculated the target weight loss for a patient’s hemodialysis session, but the patient insists that the technician has made an error and that the target is 1 kg too high. The technician should a. recalculate the target weight loss. b. ignore the patient. c. reassure the patient that the target is correct. d. advise the patient that 1 kg is inconsequential. 100. The most important reason for placing hemodialysis needles in antegrade position (in direction of blood flow) is because a. it is easier to place the needles. b. it is less painful for the patients. c. it causes less scarring. d. it decreases the chance of infection. 101. When preparing dialysate with a 45x concentrate, if the proportioning ration contains 1.0 part acid and 1.72 parts bicarbonate, how many parts of water are needed? a. 2.28 b. 4.28 c. 42.28 d. 45.00 102. If conductivity monitoring stops dialysate from flowing to the dialyzer but instead sends it to the drain (bypass), this means that a. the dialysis machine is malfunctioning. b. the conductivity monitor detected the wrong dialysate. c. the conductivity monitor is malfunctioning. d. a bloodline has become disconnected. 103. When using a portable digital dialysate meter, such as the D6 (Myron L Meters), to verify that inline meters are accurate regarding conductivity and pH, the technician must Page 15 a. obtain an unused dialysate sample. b. be within 10 meters of inline monitors. c. obtain a used dialysate sample. d. attach the meter to the arterial line. 104. The target ultrafiltration goal set for the patient is based on the patient’s a. a blood urea nitrogen (BUN) level. b. serum sodium level. c. pre-dialysis weight. d. dry weight. 105. A patient is to receive a bolus of unfractionated heparin (25 IU/kg) at the onset of dialysis and 800 U at one-hour intervals during treatment, which is scheduled from 1 to 5 PM. The first dose is given at 1 pm and the last dose at a. 3 PM. b. 4 PM. c. 4:30 PM. d. 5 PM. 106. When checking the pump occlusion for the blood pump, the technician notes that the rollers appear to loose. This may result in a. cracking of the blood pump segment of tubing. b. decreased blood flow rate under that prescribed. c. increased blood flow rate over that prescribed. d. Kinking of the blood pump segment of tubing. 107. In the hemodialysis machine, a separate air detector is usually placed a. between the arterial pressure drip changer and the dialyzer. b. before the blood pump on the arterial bloodline. c. after the blood pump on the arterial bloodline. d. between the venous pressure gauge and the venous access. 108. At the completion of a dialysis treatment, it’s important to rinse back as much blood as possible in order to a. facilitate cleaning. b. prevent clotting in the dialyzer. c. reduce the severity of anemia. d. allow reuse of the dialyzer. 109. If a power outage occurs and backup power fails, before using the hand crank to return the patient’s blood, the technician must a. remove the venous line for the air detector. b. loosen the blood pump rollers. c. flush the system with normal saline. d. administer a bolus of heparin. 110. If a patient’s blood pressure is 142/88 before dialysis and 108/72 at the completion of dialysis, the most likely intervention is Page 16 a. no intervention needed as this a normal drop in blood pressure. b. infusion of normal saline to increase blood pressure. c. deep breathing and resting in supine position for 10 minutes. d. Intravenous medication, such as dopamine. 111. Prior to opening a sterile package, the technician spills sterile normal saline on the package. The technician should a. discard the package. b. immediately open the package and remove contents. c. dry the package and use if NS has not permeated the wrapping. d. dry the package and use as intended. 112. When washing the hands, the hands should be wet and soap applied and then the hands rubbed together for at least a. 5 seconds. b. 10 seconds. c. 15 seconds. d. 20 seconds. 113. How long can hepatitis B virus live on surface if they are not properly disinfected? a. 24 hours b. 48 hours c. 3 days d. 7 days 114. In the event that a fire occurs in a dialysis center, the RACE method of response includes a. rescue, activate alarm, contain/confine fire, and extinguish/evacuate. b. run, ask for help, contain/confine fire, and extinguish/evacuate. c. rescue, ask for help, clear the area, and extinguish/evacuate. d. run, activate alarm, clear the area, and extinguish/evacuate. 115. If the technician needs to move boxes of supplies from the floor to elevated shelves, the technician should a. bend over at the waist and hold the box while standing upright. b. bend down at the knees and keep the back straight while lifting. c. pull the boxes near the shelves and stack before moving them to the shelves. d. bend over at the waist and pull the boxes near the shelves and then lift. 116. For documentation in the medical record, which of the following includes a correct abbreviation, symbol, or acronym? a. Takes furosemide Q.D. b. Has treatment Q.O.D. c. 250 cc NS d. 0.5 kg 117. For a hemodialysis cannulation with a blood flow rate of fewer than 300 Page 17 mL/min, which of the following needle gauge sizes is usually recommended? a. 14 b. 15 c. 16 d. 17 118. If the nephrologist has ordered a pre-dialytic and post-dialytic BUN (blood urea nitrogen) for a patient with an AV fistula, the pre-dialytic blood sample should be obtained from the a. arterial needle. b. venous needle. c. hand on the opposite needle. d. separate needle puncture of AV fistula. 119. The primary focus of the Life Safety Code is on a. fire prevention. b. construction. c. egress (escape) facilities. d. protection of people. 120. The dialysis prescription is for a 3-hour treatment with 1.5 kg to be removed. During treatment, 250 mL is used as saline prime and 200 mL as saline rinseback. The patient ingests 150 mL of fluid that contains oral protein supplement. The ultrafiltration rate to be removed per hour is a. 200 mL. b. 600 mL. c. 700 mL. d. 800 mL. 121. If the ultrafiltration rate to be removed per hour is 600 mL and the dialyzer KUF is 40, what is the transmembrane pressure (TMP)? a. 15 mm Hg b. 24 mm Hg c. 1.5 mm Hg d. 240 mm Hg 122. If using a combination chlorhexidine gluconate and alcohol skin prep (such as ChloraPrep) before cannulation, how much skin contact time is required? a. 15 seconds b. 30 seconds c. 60 seconds d. 3 minutes. 123. Which of the following preventive measures is usually the best approach for patients who routinely experience hypotension during dialysis because of volumerelated problems associated with large weight gain between treatments? a. Increasing the patient’s dry weight Page 18 b. Extending weekly dialysis time c. Increasing restriction of fluid intake d. Increasing restriction of sodium intake 124. If a patient undergoing hemodialysis and in the care of the technician has a persistent cough, standard precautions require that the a. technician wear a mask. b. patient and the technician wear masks. c. patient be moved to an isolation room. d. patient wear a mask. 125. What color is arterial blood tubing for hemodialysis most often color-coded? a. Red b. Blue c. Green d. Yellow 126. During hemodialysis, how much blood is usually outside of a patient’s body at one time? a. 50 to 100 mL b. 100 to 250 mL c. 250 to 400 mL d. 400 to 500 mL 127. During the first week of treatment with a new AV fistula, the initial needle size and blood flow rate are usually a. 14-gauge needle and blood flow of 200 to 250 mL/min. b. 16-gauge needle and blood flow of 250 to 300 mL/min. c. 17-gauge needle and blood flow of 200 to 250 mL/min. d. 17-gauge needle and blood flow of 300 to 350 mL/min. 128. With an AV fistula, cannulation should usually be done at an angle of a. 15° to 25°. b. 25° to 35°. c. 45°. d. 45° to 60°. 129. A hemodialysis system includes blood volume monitoring to assess changes in the patient’s hematocrit. If the hematocrit increases rapidly, this means a. blood volume is decreasing. b. blood volume is increasing. c. adequate dialysis is occurring. d. incorrect dialysate is being used. 130. A patient has a newly created AV fistula. When assessing the fistula, the technician raises the patient’s involved arm above the head. In this position, the fistula should a. collapse. Page 19 b. distend. c. remain unchanged. d. throb. 131. During cannulation, a tourniquet should be used a. never, as a tourniquet is contraindicated. b. before placing needles to assess the AV fistula. c. while placing needles if the AV fistula is small. d. while placing needles in all AV fistulas. 132. The difference between buttonhole needle and a standard needle for hemodialysis is that the buttonhole needle has a a. there is no difference. b. longer beveled tip. c. sharp tip. d. blunt tip. 133. If a hemodialysis patient has an extreme fear of needles and the physician prescribes EMLA cream to prevent pain, the cream must be applied a. 60 minutes prior to treatment. b. 20 minutes prior to treatment. c. 10 minutes prior to treatment. d. immediately prior to treatment. 134. Following formation of an AV fistula and beginning of hemodialysis, the technician notes that the plan patient's nailbed and skin on the hand below the fistula are cyanotic during hemodialysis, and the patient complains of pain in the hand. This is likely an indication of a. steal syndrome. b. stenosis. c. aneurysm. d. infection. 135. After a hemodialysis needle is removed at the end of treatment, the correct procedure is to apply pressure to a. both access sites using a compression bandage. b. both access site using one finger over each site. c. each access site with two fingers for up to 5 minutes. d. each access site with two fingers for up to 20 minutes. 136. A patient who wants to learn self-cannulation may do so if a. the patient receives appropriate training. b. the staff and physician agree. c. the center has completed an application to allow self-cannulation. d. the center has a certificate allowing self-cannulation. 137. Thrombosis is a newly-created access may be caused by a. steal syndrome. Page 20 b. infiltration. c. low blood pressure. d. high blood pressure. 138. If a patient has a HeRo (Hemodialysis Reliable Outflow) graft, the cannulation site is generally in the a. proximal upper arm (below the axilla). b. distal upper arm (above the elbow). c. proximal lower arm (below the elbow). d. distal lower arm (above the wrist). 139. If effluent (used dialysate) spills onto the floor, the technician should a. wipe up the spill as soon as possible with paper towels. b. cover the spill with absorbent material to contain it in one area. c. notify staff trained in hazardous waste removal. d. spray the spill with disinfectant and then mop up. 140. A patient is receiving hemodialysis with 17-gauge needles, but his blood flow rate has been increased to 450 mL/min. The patient complains of symptoms consistent with hemolysis (breakdown of red blood cells): sudden onset of chest tightness, back pain, dyspnea, reddening of skin color, and blood in the venous line soaring port-wine in color. What is the likely cause of the complication? a. Needle too large for blood flow rate b. Needle too small for blood flow rate c. Dialysate with incorrect glucose level d. Underlying blood disease 141. When handing off a patient to another staff person, the technician should always a. refer to notes to ensure complete information. b. refer the new staff person to computer documentation. c. plan at least 5 minutes for the hand-off procedure. d. follow the hand-off protocol established by the institution. 142. The technician should ensure when exposing the opening of a central catheter to air (such as when removing the cap or a syringe) that the a. clamp is closed. b. clamp is open. c. opening faces downward. d. opening faces upward. 143. The hemodialysis center has instituted a “zero lift” policy. The primary purpose of such a policy is to a. promote patient independence. b. prevent injuries. c. reduce liability. d. reduce staffing. Page 21 144. If the dialysis center has an extra hemodialysis machine that has not been used in the previous 2 weeks, how frequently does this make need to be disinfected? a. Every 24 hours b. Every 48 hours c. Once weekly d. Once monthly if not in use 145. Five minutes after a patient begins a hemodialysis treatment, the patient has difficulty breathing and rapidly develops generalized hives, itching, and swelling about the eyes. After asking the nurse, the next action should be to a. administer oxygen. b. decrease the blood flow rate. c. decrease the ultrafiltration rate. d. stop dialysis and clamp all lines. 146. A patient routinely experiences hypotensive episodes near the end of a session and experiences malaise (tiredness), muscle cramps, and dizziness after dialysis. What is the most likely cause? a. The dry weight is set too low. b. The dry weight is set too high. c. The patient is having an allergic reaction to dialysate. d. The patient is exhibiting signs of hypokalemia. 147. An adolescent patient had required frequent hospitalizations because of nonadherence to the treatment plan. The best approach to take patient is to a. point out how the patient has caused the hospitalizations. b. ask the patient how the staff can help the patient manage better. c. suggest that the patient needs to act more mature manner. d. suggest the patient may benefit from psychological counseling. 148. When the first carbon tank (the worker) in the water system is exhausted, the next step is to a. remove the first tank and replace it with a new one in the same position. b. remove both the first and second tanks and replace them with new tanks. c. switch the positions of the first tank and second tank. d. remove the first tank, move the second tank to first position, and add a new tank in second position. 149. Following dialysis, the patient's blood pressure in semi-reclining position is 128/86. The technician takes a series of 4 blood pressures over 3 minutes after the patient stands. At which blood pressure should the technician alert the nurse that the patient is exhibiting orthostatic hypotension? a. 120/78 b. 118/80 c. 108/74 d. 100/70 Page 22 150. The technician is able to feel no pulse or thrill along the patient's outflow vein and can detect no bruit. The technician should suspect a. steal syndrome. b. infiltration. c. infection. d. thrombosis. Page 23 [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 23 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Recommended For You
Business Law> CASE STUDY > COLLECTRO HUMAN RESOURCES ANALYSIS (All)

COLLECTRO HUMAN RESOURCES ANALYSIS
This assignment is designed to assess learning outcomes: 1. Critically evaluate the key issues involved in managing and developing people across cultural boundaries in the context of globalization,...
By Augustine , Uploaded: Oct 28, 2020
$10
Financial Accounting> CASE STUDY > SUSTAINABILITY ACCOUNTING AT OFFICEWORKS (All)

SUSTAINABILITY ACCOUNTING AT OFFICEWORKS
The Chief Executive Officer (CEO) of Officeworks has noticed an emerging and increasing trend of discussion about sustainability from businesses and some of Officeworks’s competitors are adopting va...
By Augustine , Uploaded: Oct 29, 2020
$10
Business> CASE STUDY > Analytics Mindset TechWear CASE ANALYSIS (All)
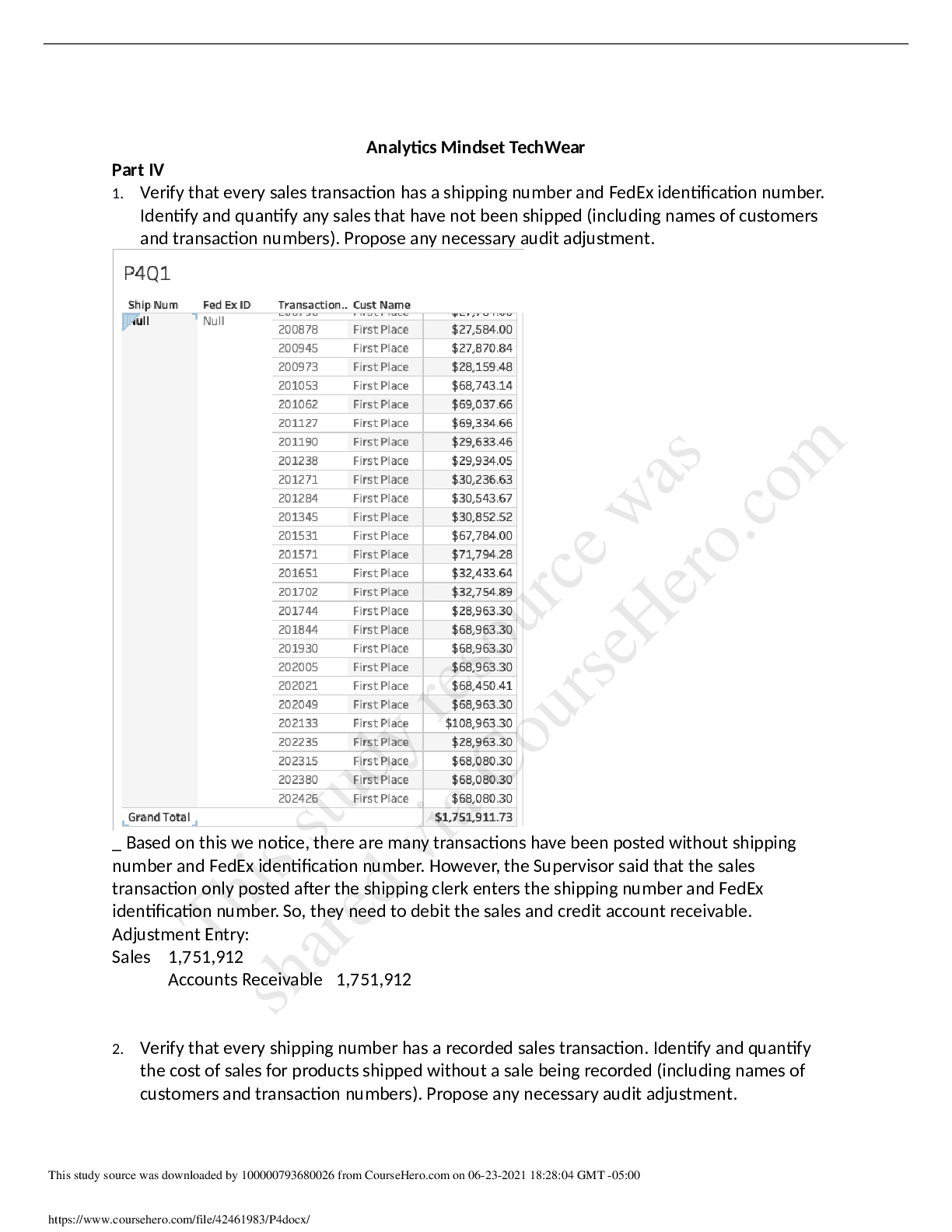
Analytics Mindset TechWear CASE ANALYSIS
Analytics Mindset TechWear Part IV 1. Verify that every sales transaction has a shipping number and FedEx identification number. Identify and quantify any sales that have not been shipped (includin...
By Cheryshev , Uploaded: Jun 24, 2021
$9.5
*NURSING> CASE STUDY > Sara Daniels Hyperbilirubinemia Unfolding Reasoning_Case Study (All)

Sara Daniels Hyperbilirubinemia Unfolding Reasoning_Case Study
Hyperbilirubinemia UNFOLDING Reasoning Sarah Daniels, newborn infant Primary Concept Elimination Interrelated Concepts (In order of emphasis) • Clinical Judgment • Patient Education • Communic...
By Martin Freeman , Uploaded: Feb 28, 2021
$6
*NURSING> CASE STUDY > Edward Carter; Pain Shadow Health Results and Focused Exam. (All)
Edward Carter; Pain Shadow Health Results and Focused Exam.
Focused Exam: Pain Results | Completed shadow health. Gerontologic Nursing - August '19, NRSE 4560 Edward Carter is a 65 year old African American male who has been admitted to the hospital with bac...
By Expert1 , Uploaded: Jul 05, 2020
$7
*NURSING> CASE STUDY > Parkinsons Disease Clinical Reasoning Case Study/ Parkinson's Disease UNFOLDING Reasoning. Key Components: 1. Develop Critical Thinking, Clinical Reasoning and Develop Clinical Judgment. (All)

Parkinsons Disease Clinical Reasoning Case Study/ Parkinson's Disease UNFOLDING Reasoning. Key Components: 1. Develop Critical Thinking, Clinical Reasoning and Develop Clinical Judgment.
Case Study Scenario: Lillian “Lilly” Jones is a 76-year-old female with a history of hypertension, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and Parkinson’s disease. Ms. Jones was hospitalized three mo...
By SuperSolutions© , Uploaded: Mar 09, 2021
$13
*NURSING> CASE STUDY > Appendicitis; R.O A 12-year-old girl who lives with her family on a farm in a rural community. Case Study 124. (All)

Appendicitis; R.O A 12-year-old girl who lives with her family on a farm in a rural community. Case Study 124.
Part 2 PediatriC, Maternity, and WoMen’s HealtH Cases CAse sTudy 124 Case Study 124 Appendicitis difficulty: Advanced setting: Hospital index Words: appendicitis, assessment, developmental care, dif...
By CoursesExams , Uploaded: Feb 18, 2021
$10
*NURSING> CASE STUDY > Mandy Gray is a two-month-old infant born with a large ventricular septal defect (VSD) that was diagnosed by her pediatrician during her two-week infant check-up. (ANSWERED) (All)

Mandy Gray is a two-month-old infant born with a large ventricular septal defect (VSD) that was diagnosed by her pediatrician during her two-week infant check-up. (ANSWERED)
History of Present Problem: Mandy Gray is a two-month-old infant born with a large ventricular septal defect (VSD) that was diagnosed by her pediatrician during her two-week infant check-up. The par...
By CoursesExams , Uploaded: Feb 16, 2021
$14
*NURSING> CASE STUDY > MGT 435 Week 1 Discussion 1 | LATEST GUIDE (All)

MGT 435 Week 1 Discussion 1 | LATEST GUIDE
MGT 435 Week 1 Discussion Question 1, Examples of Organizational Change (Two Responses) View the Social Media Revolution video. We have all watched organizations around us change in response to techn...
By Byde , Uploaded: Jan 29, 2021
$9
*NURSING> CASE STUDY > NR 533 Business Plan Assignment Week 7, Financial Management in Healthcare Organizations-Chamberlain College of Nursing (All)

NR 533 Business Plan Assignment Week 7, Financial Management in Healthcare Organizations-Chamberlain College of Nursing
Purpose The purpose of this assignment is to develop a business plan for a quality improvement project, program, or service related to an area of student interest within the selected healthcare organi...
By Rixx Dennis , Uploaded: Feb 13, 2021
$9.5
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jun 23, 2022
Number of pages
23
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jun 23, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
116






